JP7159143B2 - absorbent article - Google Patents
absorbent article Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7159143B2 JP7159143B2 JP2019176972A JP2019176972A JP7159143B2 JP 7159143 B2 JP7159143 B2 JP 7159143B2 JP 2019176972 A JP2019176972 A JP 2019176972A JP 2019176972 A JP2019176972 A JP 2019176972A JP 7159143 B2 JP7159143 B2 JP 7159143B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- sheet
- polymer particles
- superabsorbent polymer
- nonwoven fabric
- absorbent
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/53—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/53—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium
- A61F13/534—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having an inhomogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/53—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium
- A61F13/534—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having an inhomogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad
- A61F13/535—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having an inhomogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad inhomogeneous in the plane of the pad, e.g. core absorbent layers being of different sizes
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/53—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium
- A61F13/534—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having an inhomogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad
- A61F13/537—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having an inhomogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad characterised by a layer facilitating or inhibiting flow in one direction or plane, e.g. a wicking layer
- A61F13/53708—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having an inhomogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad characterised by a layer facilitating or inhibiting flow in one direction or plane, e.g. a wicking layer the layer having a promotional function on liquid propagation in at least one direction
- A61F13/53713—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having an inhomogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad characterised by a layer facilitating or inhibiting flow in one direction or plane, e.g. a wicking layer the layer having a promotional function on liquid propagation in at least one direction the layer having a promotional function on liquid propagation in the vertical direction
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/15203—Properties of the article, e.g. stiffness or absorbency
- A61F2013/15284—Properties of the article, e.g. stiffness or absorbency characterized by quantifiable properties
- A61F2013/15463—Absorbency
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/53—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium
- A61F2013/530481—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having superabsorbent materials, i.e. highly absorbent polymer gel materials
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/53—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium
- A61F2013/530481—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having superabsorbent materials, i.e. highly absorbent polymer gel materials
- A61F2013/530708—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having superabsorbent materials, i.e. highly absorbent polymer gel materials characterized by the absorbency properties
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Absorbent Articles And Supports Therefor (AREA)
- Solid-Sorbent Or Filter-Aiding Compositions (AREA)
Description
本発明は、吸収性能を改善した吸収性物品に関するものである。 The present invention relates to absorbent articles with improved absorbent performance.
吸収性物品は、吸収体と、吸収体の表側を覆う液透過性トップシートと、吸収体の裏側を覆う液不透過性シートとを備えており、尿や経血等の排泄液はトップシートを透過して吸収体により吸収され保持されるようになっている。吸収体としては、粉砕パルプ等の親水性短繊維に高吸収性ポリマー粒子(SAP)を混合し綿状に積繊したものが広く採用されているが、十分な吸収可能量を確保しつつ、さらなる薄型化、軽量化、ローコスト化等の要請にこたえるものとして、液透過性を有する上シート及び下シートの接合部により周りを囲まれ、かつ上シート及び下シートが接合されていない多数のセル(小室)と、このセル内に含まれた高吸収性ポリマー粒子を含む粉粒体とを有する吸収シート(以下、セル吸収シートともいう)が各種提案されている(例えば下記特許文献1~6参照)。
The absorbent article includes an absorbent body, a liquid-permeable top sheet covering the front side of the absorbent body, and a liquid-impermeable sheet covering the back side of the absorbent body. and is absorbed and held by the absorber. As the absorber, a cotton-like fiber obtained by mixing superabsorbent polymer particles (SAP) with hydrophilic short fibers such as pulverized pulp is widely used. In order to meet the demands for further thinning, weight reduction, and cost reduction, a large number of cells surrounded by a liquid-permeable joint between an upper sheet and a lower sheet and in which the upper sheet and the lower sheet are not joined are provided. Various proposals have been made for an absorbent sheet (hereinafter also referred to as a cell absorbent sheet) having (small chambers) and granules containing superabsorbent polymer particles contained in the cells (for example,
しかしながら、セル吸収シートは、吸収性能が高吸収性ポリマー粒子に依存するものであるため、吸収量としては尿等の非粘性液の大量吸収に向いている反面、吸収速度が遅いため、セル吸収シートを透過した非粘性液が液不透過性シート上を移動し、吸収体の周囲から肌側に染み出して、肌に付着したり、漏れたりするおそれがあった。 However, since the absorption performance of the cell-absorbing sheet depends on the superabsorbent polymer particles, it is suitable for absorbing large amounts of non-viscous liquids such as urine. The non-viscous liquid that permeates the sheet moves on the liquid-impermeable sheet, seeps out from the periphery of the absorbent body to the skin side, and may adhere to the skin or leak.
そこで、本発明の主たる課題は、セル吸収シートの周囲への液移動を抑制することにある。 Therefore, the main object of the present invention is to suppress liquid migration to the periphery of the cell absorbent sheet.
上記課題を解決した吸収性物品は以下のとおりである。
<第1の態様>
吸収体と、この吸収体の表側に配置された液透過性トップシートと、吸収体の裏側に配置された液不透過性シートとを備え、
前記吸収体は、液透過性を有する上シート及び下シートと、上シート及び下シートの接合部により周りを囲まれた、上シート及び下シートが非接合の部分であるセルと、このセル内に収容された高吸収性ポリマー粒子を含む粉粒体とを有するセル吸収シートを含み、
前記下シートは、クレム吸水度が50mm以上、荷重下保水量が0.1g以上、かつ無荷重下保水量が0.5g以上の高吸水不織布である、
ことを特徴とする、吸収性物品。
The absorbent article that solves the above problems is as follows.
<First Aspect>
An absorbent body, a liquid-permeable top sheet arranged on the front side of the absorbent body, and a liquid-impermeable sheet arranged on the back side of the absorbent body,
The absorbent body includes a liquid-permeable upper sheet and a lower sheet, a cell surrounded by a joint portion of the upper sheet and the lower sheet, and a portion in which the upper sheet and the lower sheet are not joined, and a cell absorbent sheet having a granular material containing superabsorbent polymer particles housed in
The lower sheet is a highly absorbent nonwoven fabric having a Klemm water absorbency of 50 mm or more, a water retention capacity under load of 0.1 g or more, and a water retention capacity under no load of 0.5 g or more.
An absorbent article characterized by:
(作用効果)
本吸収性物品では、セル吸収シートに供給された非粘性液は、セル吸収シート内の高吸収性ポリマー粒子により吸収されるとともに、高吸収性ポリマー粒子により吸収されずに下シートに到達した非粘性液は下シートに吸収され、下シート内に保水され、拡散された後、セル吸収シート内の高吸収性ポリマー粒子により吸い上げることができる。よって、セル吸収シートを透過した非粘性液が液不透過性シート上を移動し、セル吸収シートの周囲から肌側に染み出して、肌に付着したり、漏れたりするおそれを低減することができる。
(Effect)
In the present absorbent article, the non-viscous liquid supplied to the cell-absorbent sheet is absorbed by the superabsorbent polymer particles in the cell-absorbent sheet, and the non-viscous liquid reaches the lower sheet without being absorbed by the superabsorbent polymer particles. The viscous liquid can be absorbed by the lower sheet, retained in the lower sheet, diffused, and then wicked up by the superabsorbent polymer particles in the cell absorbent sheet. Therefore, the non-viscous liquid that permeates the cell-absorbing sheet moves on the liquid-impermeable sheet, seeps out from the periphery of the cell-absorbing sheet to the skin side, and adheres to the skin or leaks. can.
<第2の態様>
前記下シートをなす前記高吸水不織布は、パルプ繊維又はレーヨン繊維を50%以上含む、目付け25~50g/m2の湿式不織布である、
第1の態様の吸収性物品。
<Second Aspect>
The superabsorbent nonwoven fabric forming the lower sheet is a wet-laid nonwoven fabric containing 50% or more of pulp fiber or rayon fiber and having a basis weight of 25 to 50 g/m 2 ,
The absorbent article of the first aspect.
(作用効果)
このような湿式不織布を用いると、微小な繊維間隙による毛細管現象により、非粘性液を迅速に吸収・拡散することができるため好ましい。また、このような湿式不織布はクレム吸水度が高いだけでなく、非常に薄く、柔軟であるため、セル吸収シート全体としての柔軟性の低下及び厚みの増加を抑えることができる。
(Effect)
The use of such a wet-laid nonwoven fabric is preferable because it can quickly absorb and diffuse a non-viscous liquid due to capillary action caused by minute interstices between fibers. In addition, such a wet-laid nonwoven fabric not only has a high Kremm water absorbency, but is also very thin and flexible, so that the decrease in flexibility and increase in thickness of the cell absorbent sheet as a whole can be suppressed.
<第3の態様>
前記湿式不織布は、合成樹脂の長繊維を含む支持層と、最も表側に位置し、パルプ繊維のみからなるパルプ層とを有するものである、
第2の態様の吸収性物品。
<Third Aspect>
The wet-laid nonwoven fabric has a support layer containing synthetic resin long fibers and a pulp layer located on the outermost side and made only of pulp fibers.
The absorbent article of the second aspect.
(作用効果)
このような湿式不織布は、パルプ層により下シートの上側の保水性を高くしつつ、支持層の存在により強度を高くすることができるため好ましい。
(Effect)
Such a wet-laid nonwoven fabric is preferable because it can increase the strength due to the existence of the support layer while increasing the water retentivity of the upper side of the lower sheet due to the pulp layer.
<第4の態様>
前記吸収体は、前記セル吸収シート上に、上補助層を有しており、
前記上補助層は、表面が前記吸収体の最上面に露出する、クレム吸水度が100mm以上の高吸水不織布と、この高吸水不織布の裏面に隣接する高吸収性ポリマー粒子とを有するものである、
第1~3のいずれか1つの態様の吸収性物品。
<Fourth Aspect>
The absorbent body has an upper auxiliary layer on the cell absorbent sheet,
The upper auxiliary layer has a superabsorbent nonwoven fabric whose surface is exposed on the uppermost surface of the absorber and has a Krem water absorbency of 100 mm or more, and superabsorbent polymer particles adjacent to the back surface of the superabsorbent nonwoven fabric. ,
The absorbent article according to any one of the first to third aspects.
(作用効果)
吸収対象が泥状便や水様便、軟便における液分のような粘性液の場合、吸収速度が遅いと、おむつ表面にある程度長く残存するため、吸収性物品の表面上を流れて移動し、周囲から漏れやすくなる。この点、セル吸収シートは、吸収性能が高吸収性ポリマー粒子に依存するものであるため、吸収速度が遅く、粘性液の吸収には不向きである。これを解決するために、本態様の吸収性物品では、吸収体の最上面に粘性液の吸収に特化した上補助層を設けたものである。すなわち、この上補助層は、表面が吸収体の最上面に露出する、クレム吸水度が100mm以上の高吸水不織布と、この高吸水不織布の裏面に隣接する第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子とを有するため、粘性液であっても、高吸水不織布が迅速に吸収及び拡散しつつ、その裏面に隣接する高吸収性ポリマー粒子に受渡し、その高吸収性ポリマー粒子により吸収保持することができる。
(Effect)
When the absorption target is muddy stool, watery stool, or viscous liquid such as liquid in soft stool, if the absorption rate is slow, the viscous liquid remains on the surface of the diaper for a certain length of time. It leaks easily from the surroundings. In this respect, since the absorption performance of the cell absorption sheet depends on the superabsorbent polymer particles, the absorption rate is slow and it is not suitable for absorption of viscous liquids. In order to solve this problem, in the absorbent article of this aspect, an upper auxiliary layer specialized for absorbing viscous liquid is provided on the uppermost surface of the absorbent body. That is, the upper auxiliary layer has a superabsorbent nonwoven fabric having a Klemm water absorbency of 100 mm or more, the surface of which is exposed on the uppermost surface of the absorbent body, and the first superabsorbent polymer particles adjacent to the back surface of the superabsorbent nonwoven fabric. Therefore, even a viscous liquid can be rapidly absorbed and diffused by the superabsorbent nonwoven fabric, delivered to the superabsorbent polymer particles adjacent to the back surface thereof, and absorbed and retained by the superabsorbent polymer particles.
<第5の態様>
前記上シートの各セルに位置する部分が上側に押し出されて、前記上シートの上面及び下面に一対の凹部及び凸部が形成されている、
第1~4のいずれか1つの態様の吸収性物品。
<Fifth Aspect>
a portion of the upper sheet positioned in each cell is pushed upward to form a pair of concave and convex portions on the upper surface and the lower surface of the upper sheet;
The absorbent article according to any one of the first to fourth aspects.
(作用効果)
セル吸収シートでは、内部の高吸収性ポリマー粒子が吸収膨張したときの容積を確保するため、上シート及び下シートの少なくとも一方は、各セルに位置する部分が厚み方向の外側に押し出された凹部を有していると好ましい。ここで上シートに凹部を有すると、上シートの表面積が大きくなり、セル吸収シート内の高吸収性ポリマー粒子に対してより広範囲に液を供給することができるため好ましい。
(Effect)
In the cell-absorbent sheet, at least one of the upper sheet and the lower sheet has recesses in which the portions located in the respective cells are pushed outward in the thickness direction in order to secure the volume when the superabsorbent polymer particles inside are expanded by absorption. It is preferable to have Here, if the upper sheet has recesses, the surface area of the upper sheet is increased, and the liquid can be supplied to the superabsorbent polymer particles in the cell absorbent sheet over a wider range, which is preferable.
<第6の態様>
前記下シートの各セルに位置する部分が下側に押し出されて、前記下シートの上面及び下面に一対の凹部及び凸部が形成されている、
第1~5のいずれか1つの態様の吸収性物品。
<Sixth Aspect>
A pair of concave and convex portions are formed on the upper surface and the lower surface of the lower sheet by pushing out the portion of the lower sheet located in each cell.
The absorbent article according to any one of the first to fifth aspects.
(作用効果)
セル吸収シートでは、内部の高吸収性ポリマー粒子が吸収膨張したときの容積を確保するため、上シート及び下シートの少なくとも一方は、各セルに位置する部分が厚み方向の外側に押し出された凹部を有していると好ましい。ここで、下シートに凹部を有すると、下シートの表面積が大きくなり、下シートに賦形加工を施さずに平坦とする場合と比較して下シートの保水量が多くなるため好ましい。
(Effect)
In the cell-absorbent sheet, at least one of the upper sheet and the lower sheet has recesses in which the portions located in the respective cells are pushed outward in the thickness direction in order to secure the volume when the superabsorbent polymer particles inside are expanded by absorption. It is preferable to have Here, if the bottom sheet has recesses, the surface area of the bottom sheet is increased, and the water retention capacity of the bottom sheet is increased compared to the case where the bottom sheet is flat without being shaped, which is preferable.
本発明によれば、セル吸収シートの周囲への液移動を抑制できる、等の利点がもたらされる。 ADVANTAGE OF THE INVENTION According to this invention, the advantage of being able to suppress a liquid movement to the circumference|surroundings of a cell absorption sheet is brought about.
以下、吸収性物品の一例として、テープタイプ使い捨ておむつについて添付図面を参照しつつ説明する。図1~図6はテープタイプ使い捨ておむつの一例を示しており、図中の符号Xはファスニングテープを除いたおむつの全幅を示しており、符号Lはおむつの全長を示している。なお、厚み方向に隣接する各構成部材は、以下に述べる固定又は接合部分以外も、必要に応じて公知のおむつと同様に固定又は接合される。断面図における点模様部分は、この固定又は接合手段としてのホットメルト接着剤等の接着剤を示している。ホットメルト接着剤は、スロット塗布、連続線状又は点線状のビード塗布、スパイラル状、Z状、波状等のスプレー塗布、又はパターンコート(凸版方式でのホットメルト接着剤の転写)等、公知の手法により塗布することができる。これに代えて又はこれとともに、弾性部材の固定部分では、ホットメルト接着剤を弾性部材の外周面に塗布し、弾性部材を隣接部材に固定することができる。ホットメルト接着剤としては、例えばEVA系、粘着ゴム系(エラストマー系)、オレフィン系、ポリエステル・ポリアミド系などの種類のものが存在するが、特に限定無く使用できる。各構成部材を接合する固定又は接合手段としてはヒートシールや超音波シール等の素材溶着による手段を用いることもできる。厚み方向の液の透過性が要求される部分では、厚み方向に隣接する構成部材は間欠的なパターンで固定又は接合される。例えば、ホットメルト接着剤によりこのような間欠的な固定又は接合を行う場合、スパイラル状、Z状、波状等の間欠パターン塗布を好適に用いることができ、一つのノズルによる塗布幅以上の範囲に塗布する場合には、幅方向に間隔を空けて又は空けずにスパイラル状、Z状、波状等の間欠パターン塗布を行うことができる。 A tape-type disposable diaper will be described below as an example of an absorbent article with reference to the accompanying drawings. 1 to 6 show an example of a tape-type disposable diaper, where X in the figures indicates the total width of the diaper excluding the fastening tape, and L indicates the total length of the diaper. In addition, each structural member adjacent to each other in the thickness direction is fixed or joined in the same manner as a known diaper as necessary, except for the fixed or joined portions described below. A dotted pattern portion in the cross-sectional view indicates an adhesive such as a hot-melt adhesive as the fixing or joining means. The hot-melt adhesive can be applied by slot coating, continuous-line or dotted-line bead coating, spiral-shaped, Z-shaped, wavy-shaped spray coating, or pattern coating (transfer of hot-melt adhesive by letterpress method). can be applied by any method. Alternatively or additionally, at the fixing portion of the elastic member, a hot melt adhesive can be applied to the outer peripheral surface of the elastic member to fix the elastic member to the adjacent member. Hot-melt adhesives include, for example, EVA-based, adhesive rubber-based (elastomer-based), olefin-based, and polyester-polyamide-based adhesives, and can be used without particular limitation. As a fixing or joining means for joining each constituent member, a material welding means such as heat sealing or ultrasonic sealing can be used. In portions where liquid permeability in the thickness direction is required, adjacent components in the thickness direction are fixed or joined in an intermittent pattern. For example, when such intermittent fixing or bonding is performed with a hot-melt adhesive, intermittent pattern coating such as spiral, Z-shaped, and wavy patterns can be preferably used, and the range of coating width by one nozzle or more can be preferably used. In the case of coating, intermittent pattern coating such as spiral, Z-shape, wave-like, etc. can be performed with or without spacing in the width direction.
このテープタイプ使い捨ておむつは、液透過性を有するトップシートと、裏側に位置する液不透過性シートとの間に吸収体70が介在された基本構造を有している。また、このテープタイプ使い捨ておむつは、吸収体70の前側及び後側にそれぞれ延出する部分であって、かつ吸収体70を有しない部分であるエンドフラップEFを有するとともに、吸収体70の側縁よりも側方に延出する一対のサイドフラップSFを有している。サイドフラップSFの両側縁は、脚周りに沿うように括れた形状となっているが、直線状となっていてもよい。背側部分BにおけるサイドフラップSFにはファスニングテープ13がそれぞれ設けられており、おむつの装着に際しては、背側部分BのサイドフラップSFを腹側部分FのサイドフラップSFの外側に重ねた状態で、ファスニングテープ13を腹側部分F外面の適所に係止する。
This tape-type disposable diaper has a basic structure in which an
また、このテープタイプ使い捨ておむつでは、ファスニングテープ13以外の外面全体が外装不織布12により形成されている。特に、吸収体70を含む領域においては、外装不織布12の内面側に液不透過性シート11がホットメルト接着剤等の接着剤により固定され、さらにこの液不透過性シート11の内面側に吸収体70、中間シート40、及びトップシート30がこの順に積層されている。トップシート30及び液不透過性シート11は図示例では長方形であり、吸収体70よりも前後方向LD及び幅方向WDにおいて若干大きい寸法を有しており、トップシート30における吸収体70の側縁よりはみ出る周縁部と、液不透過性シート11における吸収体70の側縁よりはみ出る周縁部とがホットメルト接着剤などにより接合されている。また液不透過性シート11は、トップシート30よりも若干幅広に形成されている。
Moreover, in this tape-type disposable diaper, the entire outer surface other than the
さらに、この吸収性本体部10の両側には、装着者の肌側に立ち上がる起き上がりギャザー60が設けられており、この起き上がりギャザー60を形成するギャザーシート62が、トップシート30の両側部上から各サイドフラップSFの内面までの範囲に固着されている。
Furthermore, on both sides of the absorbent
以下、各部の詳細について順に説明する。なお、以下の説明における不織布としては、部位や目的に応じて公知の不織布を適宜使用することができる。不織布の構成繊維としては、例えばポリエチレン又はポリプロピレン等のオレフィン系、ポリエステル系、ポリアミド系等の合成繊維(単成分繊維の他、芯鞘等の複合繊維も含む)の他、レーヨンやキュプラ等の再生繊維、綿等の天然繊維等、特に限定なく選択することができ、これらを混合して用いることもできる。不織布の柔軟性を高めるために、構成繊維を捲縮繊維とするのは好ましい。また、不織布の構成繊維は、親水性繊維(親水化剤により親水性となった繊維を含む)であっても、疎水性繊維若しくは撥水性繊維(撥水剤により撥水性となった繊維を含む)であってもよい。また、不織布は一般に繊維の長さや、シート形成方法、繊維結合方法、積層構造により、短繊維不織布、長繊維不織布、スパンボンド不織布、メルトブローン不織布、スパンレース不織布、サーマルボンド(エアスルー)不織布、ニードルパンチ不織布、ポイントボンド不織布、積層不織布(スパンボンド層間にメルトブローン層を挟んだSMS不織布、SMMS不織布等)等に分類されるが、これらのどの不織布も用いることができる。 The details of each part will be described in order below. In addition, as the nonwoven fabric in the following description, a known nonwoven fabric can be appropriately used depending on the site and purpose. Constituent fibers of non-woven fabrics include, for example, synthetic fibers such as olefin-based, polyester-based, and polyamide-based fibers such as polyethylene or polypropylene (including composite fibers such as core-sheath fibers in addition to single-component fibers), as well as recycled rayon and cupra. Fibers, natural fibers such as cotton, etc., can be selected without particular limitation, and these can also be mixed and used. In order to increase the softness of the nonwoven fabric, it is preferable to use crimped fibers as the constituent fibers. In addition, even if the constituent fibers of the nonwoven fabric are hydrophilic fibers (including fibers made hydrophilic by a hydrophilic agent), they are hydrophobic fibers or water-repellent fibers (including fibers made water-repellent by a water-repellent agent). ). In addition, nonwoven fabrics are generally classified into short fiber nonwoven fabrics, long fiber nonwoven fabrics, spunbond nonwoven fabrics, meltblown nonwoven fabrics, spunlace nonwoven fabrics, thermal bonded (air-through) nonwoven fabrics, and needle punched nonwoven fabrics, depending on the fiber length, sheet forming method, fiber bonding method, and laminate structure. Nonwoven fabrics are classified into nonwoven fabrics, point-bonded nonwoven fabrics, laminated nonwoven fabrics (such as SMS nonwoven fabrics and SMMS nonwoven fabrics in which a meltblown layer is sandwiched between spunbond layers), and any of these nonwoven fabrics can be used.
(外装不織布)
外装不織布12は製品外面を構成するものであり、製品外面を布のような外観及び肌触りとするためのものである。外装不織布の繊維目付けは10~50g/m2、特に15~30g/m2のものが望ましい。外装不織布12は省略することもでき、その場合には液不透過性シート11を外装不織布12と同形状として、製品外面を構成することができる。
(exterior non-woven fabric)
The
(液不透過性シート)
液不透過性シート11の素材は、特に限定されるものではないが、例えば、ポリエチレンやポリプロピレン等のオレフィン系樹脂や、ポリエチレンシート等に不織布を積層したラミネート不織布、防水フィルムを介在させて実質的に液不透過性を確保した不織布(この場合は、防水フィルムと不織布とで液不透過性シートが構成される。)などを例示することができる。もちろん、この他にも、近年、ムレ防止の観点から好まれて使用されている液不透過性かつ透湿性を有する素材も例示することができる。この液不透過性かつ透湿性を有する素材のシートとしては、例えば、ポリエチレンやポリプロピレン等のオレフィン系樹脂中に無機充填剤を混練して、シートを成形した後、一軸又は二軸方向に延伸して得られた微多孔性シートを例示することができる。さらに、マイクロデニール繊維を用いた不織布、熱や圧力をかけることで繊維の空隙を小さくすることによる防漏性強化、高吸水性樹脂又は疎水性樹脂や撥水剤の塗工といった方法により、防水フィルムを用いずに液不透過性としたシートも、液不透過性シート11として用いることができる。
(liquid-impermeable sheet)
The material of the liquid-
(トップシート)
トップシート30は、液を透過する性質を有するものであり、例えば、有孔又は無孔の不織布や、多孔性プラスチックシートなどを例示することができる。トップシート30の両側部は、吸収体70の裏側に折り返しても良く、また図示例のように、折り返さずに吸収体70の側縁より側方にはみ出させても良い。
(top sheet)
The
トップシート30は、裏側の部材に対する位置ずれを防止する等の目的で、ヒートシール、超音波シールのような素材溶着による接合手段や、ホットメルト接着剤により裏側に隣接する部材に固定することが望ましい。図示例では、トップシート30はその裏面に塗布されたホットメルト接着剤により中間シート40の表面及び包装シート45のうち吸収体70の表側に位置する部分の表面に固定されている。
The
(中間シート)
中間シート40は、トップシート30を透過した排泄液を吸収体70側へ速やかに移動させるため、及び逆戻りを防ぐために、トップシート30の裏面に接合されているものである。中間シート40及びトップシート30間の接合は、ホットメルト接着剤を用いる他、ヒートエンボスや超音波溶着を用いることもできる。
(intermediate sheet)
The
中間シート40としては、不織布を用いる他、多数の透過孔を有する樹脂フィルムを用いることもできる。不織布としては、トップシート30と同様の素材を用いることができるが、トップシート30より親水性が高いものや、繊維密度が高いものが、トップシート30から中間シート40への液の移動特性に優れるため好ましい。例えば、中間シート40としては、エアスルー不織布を好適に用いることができる。エアスルー不織布には芯鞘構造の複合繊維を用いるのが好ましく、この場合芯に用いる樹脂はポリプロピレン(PP)でも良いが剛性の高いポリエステル(PET)が好ましい。目付けは17~80g/m2が好ましく、25~60g/m2がより好ましい。不織布の原料繊維の太さは2.0~10dtexであるのが好ましい。不織布を嵩高にするために、原料繊維の全部又は一部の混合繊維として、芯が中央にない偏芯の繊維や中空の繊維、偏芯且つ中空の繊維を用いるのも好ましい。
As the
図示例の中間シート40は、吸収体70の幅より短く中央に配置されているが、全幅にわたって設けてもよい。中間シート40の前後方向LDの寸法は、おむつの全長と同一でもよいし、吸収体70の寸法と同一でもよいし、液を受け入れる領域を中心にした短い長さ範囲内であってもよい。
The
(起き上がりギャザー)
トップシート30上における排泄物の横方向移動を阻止し、横漏れを防止するために、幅方向WDにおける製品の両側の内面から突出(起立)する起き上がりギャザー60を設けるのは好ましい。
(Getting up gathers)
In order to prevent lateral movement of excrement on the
この起き上がりギャザー60は、ギャザーシート62と、このギャザーシート62に前後方向LDに沿って伸長状態で固定された細長状のギャザー弾性部材63とにより構成されている。このギャザーシート62としては撥水性不織布を用いることができ、また弾性部材63としては糸ゴム等を用いることができる。弾性部材は、図1及び図3に示すように各複数本設ける他、各1本設けることができる。
The riser gathers 60 are composed of a gather
ギャザーシート62の内面は、トップシート30の側部上に幅方向WDの固着始端を有し、この固着始端から幅方向WDの外側の部分は、液不透過性シート11の側部及び当該部分に位置する外装不織布12の側部にホットメルト接着剤などにより固着されている。
The inner surface of the gather
脚周りにおいては、起き上がりギャザー60の固着始端より幅方向WDの内側は、製品前後方向LDの両端部ではトップシート30上に固定されているものの、その間の部分は非固定の自由部分であり、この自由部分が弾性部材63の収縮力により起立するようになる。おむつの、装着時には、おむつが舟形に体に装着されるので、そして弾性部材63の収縮力が作用するので、弾性部材63の収縮力により起き上がりギャザー60が起立して脚周りに密着する。その結果、脚周りからのいわゆる横漏れが防止される。
Around the leg, the inner side in the width direction WD from the fixing start end of the rising gather 60 is fixed on the
図示例と異なり、ギャザーシート62の幅方向WDの内側の部分における前後方向LDの両端部を、幅方向WDの外側の部分から内側に延在する基端側部分と、この基端側部分の幅方向WDの中央側の端縁から身体側に折り返され、幅方向WDの外側に延在する先端側部分とを有する二つ折り状態で固定し、その間の部分を非固定の自由部分とすることもできる。
Unlike the illustrated example, both ends in the front-rear direction LD of the inner portion of the gather
(平面ギャザー)
各サイドフラップSFには、図1~図3に示すように、ギャザーシート62の固着部分のうち固着始端近傍の幅方向WDの外側において、ギャザーシート62と液不透過性シート11との間に、糸ゴム等の細長状の弾性部材からなる脚周り弾性部材64が前後方向LDに沿って伸長された状態で固定されており、これにより各サイドフラップSFの脚周り部分が平面ギャザーとして構成されている。脚周り弾性部材64はサイドフラップSFにおける液不透過性シート11と外装不織布12との間に配置することもできる。脚周り弾性部材64は、図示例のように各側で複数本設ける他、各側に1本のみ設けることもできる。
(flat gather)
Each side flap SF has, as shown in FIGS. A leg
(ファスニングテープ)
図1、図2及び図6に示されるように、ファスニングテープ13は、おむつの側部に固定されたテープ取付部13C、及びこのテープ取付部13Cから突出するテープ本体部13Bをなすシート基材と、このシート基材におけるテープ本体部13Bの幅方向WDの中間部に設けられた、腹側に対する係止部13Aとを有し、この係止部13Aより先端側が摘み部とされたものである。ファスニングテープ13のテープ取付部13Cは、サイドフラップSFにおける内側層をなすギャザーシート62及び外側層をなす外装不織布12間に挟まれ、かつホットメルト接着剤によりそれらのシートに接着されている。また、係止部13Aはシート基材に接着剤により固定されている。
(fastening tape)
As shown in FIGS. 1, 2 and 6, the
係止部13Aとしては、メカニカルファスナー(面ファスナー)のフック材(雄材)が好適である。フック材は、その外面側に多数の係合突起を有する。係合突起の形状としては、レ字状、J字状、マッシュルーム状、T字状、ダブルJ字状(J字状のものを背合わせに結合した形状のもの)等が存在するが、いずれの形状であっても良い。もちろん、ファスニングテープ13の係止部として粘着材層を設けることもできる。
A hook member (male member) of a mechanical fastener (surface fastener) is suitable for the locking
また、テープ取付部13Cからテープ本体部13Bまでを形成するシート基材としては、スパンボンド不織布、エアスルー不織布、スパンレース不織布等の各種不織布の他、プラスチックフィルム、ポリラミ不織布、紙やこれらの複合素材を用いることができる。
The sheet base material forming the
(ターゲットシート)
腹側部分Fにおけるファスニングテープ13の係止箇所には、係止を容易にするためのターゲット有するターゲットシート12Tを設けるのが好ましい。ターゲットシート12Tは、係止部13Aがフック材の場合、フック材の係合突起が絡まるようなループ糸がプラスチックフィルムや不織布からなるシート基材の表面に多数設けられたものを用いることができ、また粘着材層の場合には粘着性に富むような表面が平滑なプラスチックフィルムからなるシート基材の表面に剥離処理を施したものを用いることができる。また、腹側部分Fにおけるファスニングテープ13の係止箇所が不織布からなる場合、例えば図示例の外装不織布12が不織布からなる場合であって、ファスニングテープ13の係止部13Aがフック材の場合には、ターゲットシート12Tを省略し、フック材を外装不織布12の不織布に絡ませて係止することもできる。この場合、ターゲットシート12Tを外装不織布12と液不透過性シート11との間に設けてもよい。
(target sheet)
It is preferable to provide a
(吸収体)
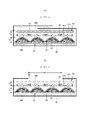
吸収体70は、図1、図3、図5、図15及び図16に示すように、排泄物の液分を吸収保持する部分であり、最上部に設けられた上補助層71と、その裏側に設けられた主吸収層72とを有している。後述するように、主吸収層72上に、上補助層71を有していると好ましいが、上補助層71は省略することも可能である。図16は、図15の吸収体70の層構造を分離して分かりやすく示したものである。吸収体70は、その表裏少なくとも一方側の部材に対してホットメルト接着剤等の接着剤50hを介して接着することができる。
(Absorber)
1, 3, 5, 15, and 16, the
(上補助層)
上補助層71は、表面が吸収体70の最上面に露出する、クレム吸水度が100mm以上の高吸水不織布42を有するものである。この高吸水不織布42は、粘性液であっても迅速に吸収及び拡散することができる。よって、吸収体70による粘性液の吸収性を顕著に向上させることができる。高吸水不織布42は、クレム吸水度が130mm以上であると、特に好ましい。また、高吸水不織布42のクレム吸水度の上限は特に限定されるものではないが、180mm程度が好ましく、160mmであると特に好ましい。
(Upper auxiliary layer)
The upper
上補助層71の高吸水不織布42の荷重下保水量は0gより大きく0.15g以下であると好ましく、0gより大きく0.12g以下であると特に好ましい。上補助層71の高吸水不織布42の無荷重下保水量は0gより大きく0.7g以下であると好ましく、0gより大きく0.3g以下であると特に好ましい。
The water retention capacity under load of the highly absorbent
高吸水不織布42は、素材及び製法により限定されるものではないが、パルプ繊維又はレーヨン繊維を50%以上含む、目付け25~50g/m2の湿式不織布(特に湿式スパンレース不織布)であると好ましい。パルプ繊維又はレーヨン繊維以外の繊維は、ポリエチレン又はポリプロピレン等のオレフィン系、ポリエステル系、ポリアミド系等の合成繊維(単成分繊維の他、芯鞘等の複合繊維も含む)を用いることができる。このような湿式不織布を用いると、微小な繊維間隙による毛細管現象により、粘性液を迅速に吸収・拡散することができるため好ましい。特に、このような湿式不織布はクレム吸水度が高いだけでなく、非常に薄く、柔軟であるため、吸収体70全体としての柔軟性の低下及び厚みの増加を抑えることができる。高吸水不織布42の厚みは限定されるものではないが、上記目付けの場合、0.13~0.48mm程度であることが好ましい。
Although the superabsorbent
また、高吸水不織布42としては、図18に示すように、合成樹脂の長繊維を含む支持層42bと、最も表側に位置し、パルプ繊維のみからなるパルプ層42aとを有する二層、又は三層以上の不織布が特に好適である。このような高吸水不織布42は、パルプ層42aによりクレム吸水度を高くしつつ、支持層42bの存在により強度を高くすることができるため、吸収体70の最上部に設けた場合に耐久性に優れるようになる。
As shown in FIG. 18, the superabsorbent
上補助層71は、高吸水不織布42の裏面に隣接する第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43を有すると、図17(a)に矢印で示すように、高吸水不織布42により吸収及び拡散した粘性液Nを、徐々に高吸水不織布42の裏側に隣接する高吸収性ポリマー粒子で吸収保持することができる。これにより、粘性液Nの吸収性を顕著に向上させることができる。特に、上補助層71の高吸水不織布42が前述の湿式不織布であると、裏面に隣接する第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43への粘性液Nの受渡しが円滑となるため好ましい。
When the upper
上補助層71の高吸水不織布42の寸法、配置は適宜定めることができる。例えば図示例のように、高吸水不織布42は主吸収層72の表面の全体を覆うように配置されていてもよいし、主吸収層72の表面の一部、例えば前端部、後端部、中央部又はこれらのうちの複数個所のみを覆うように配置されていてもよい。また、高吸水不織布42は、主吸収層72の周縁からはみ出す部分を有していてもよいし、高吸水不織布42の周縁の一部又は全部が主吸収層72の周縁よりも中央側に離間していてもよい。通常の場合、上補助層71の高吸水不織布42は、主吸収層72の面積の90%以上を覆っていると望ましい。
The dimensions and arrangement of the highly absorbent
第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43を有する領域の寸法、配置は適宜定めることができる。例えば図示例のように、第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43は、高吸水不織布42と主吸収層72とが重なる領域の全体に配置されていてもよいし、高吸水不織布42と主吸収層72とが重なる領域の一部、例えば前端部、後端部、中央部又はこれらのうちの複数個所のみに配置されていてもよい。通常の場合、第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43を有する領域は、主吸収層72の面積の83%以上を占めていると望ましい。
The dimensions and arrangement of the region having the first
第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43は、高吸水不織布42に固定されていなくてもよいが、固定されているとより好ましい。第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43は、例えば高吸水不織布42の裏面に間欠パターンで塗布されたホットメルト接着剤等の接着剤42hにより高吸水不織布42に接着することができる。
The first
第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43は、主吸収層72の表面に接するだけで固定しなくてもよいが、固定してもよい。例えば、主吸収層72の表面にホットメルト接着剤等の接着剤43hを間欠パターンで塗布した後、その塗布部分の上に第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43を散布し、さらにその上に接着剤42hを介して又は介さずに高吸水不織布42を配置することができる。
The first
第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43の目付けは適宜定めることができるが、泥状便や水様便、軟便における液分のように一度に必要とされる吸収量が少ない粘性液を想定すると、50~150g/m2であると好ましく、50~100g/m2であると特に好ましい。第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43の目付けが50g/m2未満では、少量の粘性液であっても十分な吸収が困難となるおそれがある。また、第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43の目付けが150g/m2を超えると、尿などの多量の非粘性液を吸収するとき、第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43が十分に吸収し、膨張した後にゲルブロッキングが生じ、主吸収層72に対する非粘性液の供給が阻害されるおそれが高くなる。これに対して、上記範囲内であると、第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43が十分に吸収し、膨張した後でも、ゲルブロッキングが生じない部分が残り、主吸収層72に対する非粘性液の供給が確保されるため好ましい。
The basis weight of the first
(主吸収層)
主吸収層72は、図示例のように、液透過性を有する上シート51及び下シート52の接合部54により周りを囲まれ、かつ上シート51及び下シート52が接合されていない多数のセル55(小室)と、このセル55内に含まれた第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53を含む粉粒体とを有するセル吸収シート50を用いることができる。セル吸収シート50の吸収性能は、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53に依存するものであるため、必然的に吸収速度が遅く、粘性液Nの吸収性が低いものとなる。よって、前述の上補助層71は、このようなセル吸収シート50を主吸収層72とする場合に特に意義を有するものである。
(main absorption layer)
As shown in the figure, the main
セル吸収シート50ついてさらに詳しく説明する。図7及び図15に拡大して示すように、このセル吸収シート50は、上シート51と、その裏側に配された下シート52と、上シート51及び下シート52の接合部54により周りを囲まれ、かつ上シート51及び下シート52が非接合の部分であるセル(小室)55と、このセル55内に含まれた、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53とを有する。セル55は接合部54の分の間隔を空けて多数配列される。このように、接合部54により周囲全体を囲まれた多数のセル55に第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53を分配保持させることにより、セル吸収シート50における第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の偏在を防止できる。
The cell
製造時の第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の配置を容易にするため、及び吸収膨張後の容積確保のために、セル55における上シート51及び下シート52の少なくとも一方が、展開状態でセル55の外側に窪む凹部50cとなっていると好ましいが、凹部50cを有せず、単に上シート51及び下シート52の間に第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53が挟まっているだけでもよい。
At least one of the
凹部50cは、対象シートにエンボス加工等の賦形加工を施すことにより形成できるものである。また、このエンボス加工により、対象シートにおける各セル55に位置する部分には、外側に膨らむ凸部50pが形成されることとなる。つまり、エンボス加工により上シート51に凹部50cを形成すると、上シート51における各セル55に位置する部分が上側に押し出されて、上側に膨らむ凸部50pが形成される。凹部50cの深さ50dは特に限定されないが、1.0~7.0mm、特に1.0~5.0mm程度とすることが好ましい。
The
ここで、尿等の非粘性液Uを吸収する場合、上補助層71の第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43が一様に設けられていると、第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43が優先的に吸収膨張して、膨張した第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43が密着して難液透過性の層を形成するゲルブロッキングが発生しやすくなり、主吸収層72に非粘性液Uが供給されにくくなるおそれがある。つまり、上補助層71が主吸収層72による吸収を阻害するおそれがある。これに対して、図15に示すように、上シート51における各セル55に位置する部分が、上側に膨らむ凸部50pとなっており、第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43は、主吸収層72の上シート51の上面に固定されており、上シート51の上面における第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43の付着量は、凸部50pの頂部から隣接する凸部50pの間に位置する谷部の底部に向かうにつれて多くなっていると、図17(a)に示すように上シート51の上面に固定された第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43を粘性液Nの吸収に有効に利用できるものでありながら、同じ第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子の使用量で比べた場合、図17(b)に示すように非粘性液Uの吸収に際して第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43が十分に吸収膨張した後においても、第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43の付着量が少ない部分ほどゲルブロッキングが生じにくくなり、主吸収層72に対する非粘性液Uの供給が阻害されにくくなる。また、上シート51の凸部50pを利用することで、上シート51の上面における第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43の付着量に規則的な変化をつける(付着量の多い部分と少ない部分とを交互に設ける)ことが容易となる。すなわち、前述のように、主吸収層72の表面にホットメルト接着剤を間欠パターンで塗布した後、その塗布部分の上に第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43を散布すると、その散布が均一であっても、重力により谷部の底部に向かって第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43が転げ落ちやすいために、自然に、第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43の付着量は、凸部50pの頂部から隣接する凸部50pの間に位置する谷部の底部に向かうにつれて多くなるのである。よって、このような第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43の不均一付着構造は、一見すると複雑な構造でありながら製造は比較的に容易である。なお、この場合においても、第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43の目付けは、前述の範囲内であると好ましいことはいうまでもない。
Here, when non-viscous liquid U such as urine is absorbed, if the first
上シート51の上面における第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43の付着量は、凸部50pの頂部から隣接する凸部50pの間に位置する谷部の底部に向かうにつれて多くなっている限り、凸部50pの頂部を含む一部には第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43が付着しておらず、それ以外の部分にのみ第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43が付着していてもよいし、図示例のように凸部50pの頂部及びそれ以外の部分を含むほぼ全体に第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43が付着しているとともに、その付着量が谷部の底部に向かって連続的(または段階的でもよい)に増加していてもよい。
The adhesion amount of the first
凸部50pの寸法は適宜定めることができるが、このような観点から、上シート51の凸部50pの前後方向LDの寸法55Lは6~30mmであり、上シート51の凸部50pの幅方向WDの寸法55Wは7~50mmであり、接合部54の幅54Wは1.0~1.8mmであり、上シート51の谷部の深さ50d(凸部50pの高さ)は1.0~7.0mmであると好ましい。
Although the dimension of the
上シート51に凹部50cを設けると、上シート51の上面に凸部50pが形成され、上補助層71の高吸水不織布42と密着しにくくなり(隙間が生じやすくなり)、高吸水不織布42から第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43への粘性液Nの受渡しが阻害されるおそれもある。したがって、この観点からは、図13(c)に示すように、上シート51には凹部50cを形成せずに(つまり賦形加工が施されていない平坦な上面を有し)、下シート52における各セル55を構成する部分に凹部50cを形成するのも好ましい。これにより、下シート52の凹部50cにより第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の膨張容積を確保しつつ、上シート51の上面及びそこに配置された第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43が上補助層71の高吸水不織布42と密着しやすくなり、高吸水不織布42から第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43への粘性液Nの受渡しが阻害されにくいものとなる。
When the
他方、図7(b)及び図13(a)等に示すように、上シート51及び下シート52の間には、不織布からなる中シート80が介在されていると好ましいが、図14(b)に示すように中シート80を設けなくてもよい。中シート80を設ける場合、接合部54では上シート51、中シート80及び下シート52の三層が接合される。また、中シート80は、接合部54では厚み方向に圧縮されるとともに、セル55内に位置する部分では凹部50c内まで膨らんでいる(換言すると繊維密度が接合部から遠ざかるほど低下する)と好ましい。これにより、製品の包装状態で加わる圧力や装着時に加わる圧力により凹部50cが(したがって凸部も)潰れにくく、また潰れたとしても、中シート80の弾力性により少なくとも中シート80が入り込んでいた部分又はそれに近い容積まで形状復元が促進される。そして、排泄液の吸収時には、高吸収性ポリマーが繊維間隙を拡大し、その間に入り込みながら、あるいは中シート80を容易に圧縮しながら、あるいはその両方により膨張することができるため、中シート80の存在は第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の膨張を阻害しにくい。さらに、凹部50c内に広がる中シート80の繊維が個々の第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53への通液路を確保するため、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53が膨張を開始した後も拡散性の低下が抑制され、ゲルブロッキングが生じにくい。したがって、これらの相乗作用により、本セル吸収シート50を備えた使い捨ておむつの吸収速度(特に吸収初期)が改善される。
On the other hand, as shown in FIGS. 7(b) and 13(a), etc., it is preferable that a
上シート51は、トップシート30と同様に液透過性素材であれば特に限定されるものではない。上シート51は吸収速度に対して影響するものであるため、親水性繊維、特に綿・パルプ等の天然繊維を原料とする乾式不織布、中でもパルプ70重量%以上(100重量%未満の場合における残量は適宜の合成繊維とすることができる)のエアレイドパルプ不織布は上シート51に特に好適なものの一つである。不織布の繊維結合法は特に限定されないが、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の離脱を防止するため、スパンボンド法、メルトブローン法、ニ一ドルパンチ法のように繊維密度が高くなる結合法が好ましい。また、不織布の繊度、目付け及び厚みはそれぞれ2.0~7.0dtex程度、18~50g/m2程度、0.10~0.60mm程度であると好ましい。多孔性プラスチックシートを用いる場合、その開孔径は、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の脱落を防止するため、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の外形より小さくするのが好ましい。また、上シート51の素材が疎水性の場合には、親水剤を含有させることもできる。
As with the
下シート52は、クレム吸水度が50mm以上、荷重下保水量が0.1g以上、かつ無荷重下保水量が0.5g以上の高吸水不織布であると好ましい。図17(b)に示すように、セル吸収シート50に供給された尿等の非粘性液Uは、セル吸収シート50内の第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53により吸収されるとともに、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53により吸収されずに下シート52に到達した非粘性液Uは下シート52に吸収され、下シート52内に保水され、拡散された後、セル吸収シート50内の第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53により吸い上げることができる。ここで、セル吸収シート50は第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53を有しない接合部54が、セル吸収シート50の周囲に向かって連続的に延びており、セル吸収シート50の裏面に凸部50pがある場合にはセル吸収シート50の裏面と対向面との間の隙間もセル吸収シート50の周囲に向かって連続的に延びている。このため、セル吸収シート50の保水性が低いと、セル吸収シート50を透過した非粘性液Uが液不透過性シート11上を移動し、吸収体70の周囲から肌側に染み出して、肌に付着したり、漏れたりするおそれがある。
The
下シート52をなす高吸水不織布のクレム吸水度は70mm以上であると、特に好ましい。また、下シート52をなす高吸水不織布のクレム吸水度の上限は特に限定されるものではないが、150mm程度が好ましく、100mmであると特に好ましい。下シート52をなす高吸水不織布の荷重下保水量は0.13g以上であると、特に好ましい。また、下シート52をなす高吸水不織布の荷重下保水量の上限は特に限定されるものではないが、0.30g程度が好ましく、0.26gであると特に好ましい。下シート52をなす高吸水不織布の無荷重下保水量は0.70g以上であると、特に好ましい。また、下シート52をなす高吸水不織布の荷重下保水量の上限は特に限定されるものではないが、1.40g程度が好ましく、1.20gであると特に好ましい。
It is particularly preferable that the Klemm water absorbency of the highly absorbent nonwoven fabric forming the
下シート52をなす高吸水不織布は、素材及び製法により限定されるものではなく、上補助層71と同様の高吸水不織布42を好適に用いることができる。上シート51及び下シート52の接合部54を溶着により形成する場合には、下シート52をなす高吸水不織布はポリエチレン繊維やポリエチレン成分を含む複合繊維等の熱融着繊維が好適である。特に、下シート52は尿などの非粘性液Uの一時的貯留が目的であるため、上補助層71の高吸水不織布42よりも保水量が多いものが好ましい。例えば、下シート52をなす高吸水不織布は、荷重下保水量が上補助層71の高吸水不織布42の2~4倍のものが好ましい。より具体的には、下シート52をなす高吸水不織布の目付けは、上補助層71の高吸水不織布42の目付けの1.2~1.8倍とするか、下シート52をなす高吸水不織布として、上補助層71と同等の高吸水不織布を複数枚重ねて配置することができる。
The superabsorbent nonwoven fabric forming the
上シート51に凹部50cを有すると、上シート51の表面積が大きくなり、セル吸収シート50内の高吸収性ポリマー粒子に対してより広範囲に液を供給することができるため好ましい。一方、下シート52に凹部50cを有すると、下シート52の表面積が大きくなり、下シート52に賦形加工を施さずに平坦とする場合と比較して下シート52の保水量が多くなるため好ましい。
If the
中シート80としては不織布であれば特に限定されないが、不織布の構成繊維の繊度は1.6~7.0dtex程度が好ましく、5.6~6.6dtexであるとより好ましい。また、中シート80の不織布の空隙率は80~98%であると好ましく、90~95%であるとより好ましい。中シート80の繊度及び空隙率がこの範囲であると、中シート80の弾力性を可能な限り確保しつつ、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53が排泄液の吸収前及び排泄液の吸収時に中シート80の繊維間隙に容易に入り込むことが可能なものとなる。よって、吸収時には凹部50c内に広がる中シート80の繊維が個々の第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53への通液路を確保するため、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53が膨張を開始した後も拡散性の低下が抑制され、ゲルブロッキングが生じにくいものとなる。中シート80の厚みは、凹部50cの深さ50dや凹部50c内への入り込みの程度等を考慮して適宜定めればよいが、厚みが凹部50cの深さ50dの10%~90%であると好ましく、70%~90%であるとより好ましい。中シート80の目付けも同様の理由で適宜定めればよいが、上記厚み範囲では25~40g/m2程度とすることが好ましい。中シート80の不織布の空隙率を高く(繊維間隙を広く)するためには、構成繊維を捲縮繊維とすることが好ましい。また、中シート80の不織布の構成繊維が親水性繊維(親水化剤により親水性となった繊維を含む)であると保水性が高くなり、疎水性繊維であると拡散性が向上する。不織布の繊維結合法は特に限定されないが、空隙率を高く(繊維間隙を広く)しつつ、十分に繊維を結合して弾力性を確保するため、熱風加熱により繊維を結合したエアスルー不織布が中シート80には好ましい。
The
中シート80における凹部50cと対向する面は凹部50c内に入り込んでいる限り、図13(a)(c)及び図14(a)(c)にそれぞれ示すように、凹部50cの内面に接していると好ましいが、図13(b)に示すように離間していてもよい。中シート80における凹部50cと対向する面と凹部50cの内面とを離間させる場合、その離間距離80sは適宜定めることができるが凹部50cの深さ50dの30%以下とすることが好ましい。このように、セル55内に隙間が生じる場合、製品状態で凸部50p(凹部50c)はその隙間に応じて潰れていてもよい。
As long as the surface of the
中シート80は、図13(a)~(c)及び図14(a)にそれぞれ示すように、セル55内及び接合部54の両方において、上シート51及び下シート52の少なくとも一方に対してホットメルト接着剤80hにより接着されていてもよいし、図14(c)に示すように、上シート51及び下シート52の両方に接着されていなくてもよい。
As shown in FIGS. 13(a)-(c) and 14(a), the
第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53はそのほぼ全部(例えば95%以上)を上シート51、下シート52及び中シート80に対して非固定とし、自由に移動可能とすることが好ましい。しかし、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の一部又はほぼ全部(例えば95%以上)を、上シート51、下シート52及び中シート80の少なくとも一つに接着又は粘着させることもできる。図14(b)は第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の一部をホットメルト接着剤等の接着剤53hにより下シート52に接着した例を示している。また、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53はある程度塊状化していても良い。特に、セル55内で第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53が自由に移動可能である場合、セル55内に中空部分を有すると、使用時に第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53がセル55内で移動することにより、音がしたり、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53がセル55内で偏在することによる吸収阻害が発生するおそれがある。よって、これを解決するために、前述のように中シート80における凹部50cと対向する面を凹部50cの内面に接触させる、つまり換言すると凹部50cを含むセル55内のほぼ全体にわたり高空隙率の中シート80の繊維を充満させるのは一つの好ましい形態である。これにより、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53は中シート80の繊維により捕捉されるか、又は上シート51若しくは下シート52に押し付けられるか、又はその両方となるため、自由な移動が起こりにくくなる。よって、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の膨張阻害を防止しつつも、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の移動による音の発生や、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53がセル55内で偏在することによる吸収阻害を防止することができる。
It is preferable that substantially all (for example, 95% or more) of the second
図13(a)(b)、図14(c)にそれぞれ示す例のように、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53が中シート80の上面上に最も多く存在しており、そこから下側に向かって減少していると、使用者がおむつの外面を手で触ったときに中シート80の介在により第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53のじゃりじゃりとした触感(違和感)が手に伝わりにくくなるため好ましい。特に、中シート80が空隙率の高いかさ高な不織布の場合、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53は排泄液の吸収前及び排泄液の吸収時に中シート80の繊維間隙に入り込むことが可能であるため、吸収速度がより一層向上する。すなわち、吸収初期においては、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53が多く分布する中シート80上面での吸収が進行するが、その速度には限りがある。よって、この吸収初期には、排泄液は、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53が少ない中シート80内にも多く入り込み、中シート80内の第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53により吸収されるか、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53により吸収されるまで一時的に貯留されるか、又は周囲のセル55に拡散する。周囲に拡散した排泄液は、そこに存在する中シート80内の第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53により吸収されるか、その上方に多く存在する第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53によって吸い上げられることとなる。そして、各第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53が排泄液を吸収していく過程で、高吸収性ポリマーが繊維間隙を拡大し、その間に入り込みながら、あるいは中シート80を圧縮しながら膨張することとなる。このような吸収メカニズムにより、排泄液は速やかにセル吸収シート50の広範囲に拡散し、かつセル吸収シート50の内部に受け入れられた状態となるため、吸収速度の向上はもちろん、逆戻り防止性にも優れたものとなる。また、このような吸収メカニズムを良好に発揮させるためには、凹部50cは、少なくとも上シート51における各セル55を構成する部分に形成されていると好ましい。
As in the examples shown in FIGS. 13(a), (b), and 14(c), the second
セル55内における第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の分布の程度は適宜定めることができるが、通常の場合、中シート80の上面上に存在する第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の重量割合は全量の50%以上であると好ましく、中シート80内に保持された(つまり下シート52上でない)高吸収性ポリマーの重量割合は全量の45%以上であると好ましい。
The degree of distribution of the second
もちろん、セル55内における第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の分布はこれに限定されるものではない。したがって、下シート52をなす高吸水不織布からの吸い上げ性を重視するのであれば、図13(c)に示すように第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53が下シート52の上面上に最も多く存在しており、そこから上側に向かって減少している分布とするのも好ましい。また、図14(a)に示すように、中シート80の上面上及び下シート52の上面上に存在する第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の量が、それらの間の部分よりも多い分布となっていてもよい。さらに、図示しないが、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53が中シート80の厚み方向中間に最も多く存在しており、そこから上側及び下側に向かって減少している分布とすることもできる。この形態は、中シート80を二層の不織布とし、層間に第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53を挟むことにより形成することができる。
Of course, the distribution of the second
第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の目付けは適宜定めることができる。本例の吸収体70では、上補助層71に第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43を含有するため、主吸収層72における第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の目付けを少なく抑えることができるものの、上補助層71だけで尿のような比較的に多量の排泄液の吸収を賄うことは適切ではない。したがって一概には言えないが、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の目付けは、第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43の目付けよりも多くすることが好ましく、例えば150~250g/m2とすることができる。一般に、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の目付けが150g/m2未満では吸収量を確保し難く、250g/m2を超えると使用者が製品の外面を手で触ったときに第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53のじゃりじゃりとした触感(違和感)が手に伝わりやすくなる。
The basis weight of the second
セル55の平面形状は適宜定めることができ、図8等に示すように、六角形、菱形、正方形、長方形、円形、楕円形等とすることができるが、より密な配置とするために多角形とすることが望ましく、図示例のように隙間なく配列することが望ましい。セル55は、同一形状及び同一寸法の物を配列する他、図示しないが形状及び寸法の少なくとも一方が異なる複数種のセル55を組み合わせて配列することもできる。
The planar shape of the
セル55(つまり第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の集合部も同様)の平面配列は適宜定めることができるが、規則的に繰り返される平面配列が好ましく、図12(a)に示すような斜方格子状や、図12(b)に示すような六角格子状(これらは千鳥状ともいわれる)、図12(c)に示すような正方格子状、図12(d)に示すような矩形格子状、図12(e)に示すような平行体格子(図示のように、多数の平行な斜め方向の列の群が互いに交差するように2群設けられる形態)状等(これらが伸縮方向に対して90度未満の角度で傾斜したものを含む)のように規則的に繰り返されるものの他、セル55の群(群単位の配列は規則的でも不規則でも良く、模様や文字状等でも良い)が規則的に繰り返されるものとすることもできる。
The planar arrangement of the cells 55 (that is, the assembly of the second
各セル55の寸法は適宜定めることができ、例えば前後方向LDの寸法55L(凸部50pの前後方向LDの寸法に等しい)は6~30mm程度とすることができ、また幅方向WDの寸法55W(凸部50pの幅方向WDの寸法に等しい)は7~50mm程度とすることができる。各セル55の面積は31~1650mm2程度とすることができる。
The dimension of each
上シート51及び下シート52を接合する接合部54は、超音波溶着やヒートシールのように上シート51及び下シート52の溶着により接合されていることが望ましいが、ホットメルト接着剤を介して接合されていても良い。
The joint 54 for joining the
上シート51及び下シート52の接合部54は、各セル55を取り囲むように配置され、隣接するセル間の境界となる限り、図示例のように点線状(各セル55を取り囲む方向に断続的)に形成する他、連続線状に形成することもできる。接合部54を断続的に形成する場合、セル55を取り囲む方向における接合部54の間には、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53が存在しないか又は存在するとしてもセル55内よりも少ないことが好ましい。特に、接合部が点線状(断続的)に設けられていると、中シートの繊維群が隣り合う接合部の間を通り多数のセル間にわたり延びることとなる。よって、隣り合う接合部の間には液拡散通路が形成されるため、セル間にわたる液拡散性の向上により、吸収速度の向上が図られる。
The
図10にも示すように、接合部54は、隣接するセル55内の第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の膨張力により剥離可能な弱接合部54bであっても、また、隣接するセル55内の第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の膨張力により基本的に剥離しない強接合部54aであってもよい。個々のセル55容積以上の第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の膨張にも対応するためには、接合部54の一部又は全部は弱接合部54bであることが好ましい。弱接合部54bを有することにより、弱接合部54bを挟んで隣接するセル55同士は、当該セル55内の第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の吸収膨張圧により剥離して合体して一つの大きなセル55となることが可能となる。
As shown also in FIG. It may also be a strong joint 54a that basically does not separate due to the expansion force of the second
一方、強接合部54aはその両側のセル55が吸収膨張しても基本的に剥離しない部分であるため、それが特定の方向に続くことにより拡散性を向上させたり、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53のゲル化物の流動を防止したり、表面側の接触面積を低減したりする等の効果を有する。よって、これを弱接合部と組み合わせることにより、後述するように様々な特徴を有するセル吸収シート50を構築することができる。なお、幅方向WDの最も外側に位置する接合部54は、これが剥離するとセル吸収シート50の側方に第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53又はそのゲル化物が漏れ出るおそれがあるため強接合部54aとすることが望ましい。同様の観点から、上シート51及び下シート52はセル55形成領域よりも幅方向WDの外側にある程度延在させ、この延在部分に補強のために縁部接合部54cを施しておくのが好ましい。
On the other hand, the
接合強度の差異は、接合部54の面積を変化させることにより形成するのが簡単でよいが、これに限定されず、例えば接合部54をホットメルト接着剤により形成する場合にはホットメルト接着剤の種類を部位により異ならしめるといった手法を採用することもできる。特に、上シート51及び下シート52を溶着することにより接合部54を形成する場合、弱接合部54bは、接合部54を点線状にして点間隔54Dを広くすることのみでも形成できるが、接合部54は隣接するセル55同士の境界となる部分であるため、点間隔54Dが広くなりすぎると隣接するセル55同士の境界に隙間が多くなり、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53が移動しやすくなる。よって、接合部54の幅54Wの広狭と、点間隔54Dの広狭とを組み合わせて点線状の弱接合部54bを形成すると、その弱接合部54b部分は隙間が少ない割には剥離しやすいものとなる。
The difference in bonding strength can be easily formed by changing the area of the
上シート51及び下シート52を接合する接合部54の寸法は適宜定めることができ、例えば幅(セル55を取り囲む方向と直交する方向の寸法であり、セル55の間隔に等しい)54Wは1.0~1.8mm程度とすることができる。また、点線状(セル55を取り囲む方向に断続的)に接合部54を形成する場合、セル55を取り囲む方向における接合部54の寸法54Lは0.6~1.5mm程度、点間隔54Dは0.8~3.0mm程度とすることが好ましい。特に、強接合部54aの場合には、幅54Wは1.3~1.8mm程度、接合部54の寸法54Lは1.0~1.5mm程度、点間隔54Dは0.8~2.0mm程度とすることが好ましい。また、弱接合部54bの場合には、幅54Wは1.0~1.3mm程度、接合部54の寸法54Lは0.6~1.0mm程度、点間隔54Dは1.5~3.0mm程度とすることが好ましい。
The size of the joining
弱接合部54bを剥離可能とするために、弱接合部54bに隣接するセル55の容積よりも当該セル55内の第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の飽和吸収時の体積が十分に大きくなるように、各セル55内に配置される第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の種類及び量を定めることができる。また、強接合部54aを基本的に剥離しないものとするために、弱接合部54bの剥離により合体可能なセル55の合体後の容積よりも、当該合体可能なセル55に含まれる第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の飽和吸収時の体積が小さくなるように、各セル55内に配置される第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の種類及び量を定めることができる。
In order to make the weak joint 54b detachable, the volume of the second
接合部54を連続線状に形成する場合における接合部54の幅、並びに接合部54を点線状に形成する場合における幅54Wは、セル55を取り囲む方向に一定とする他、変化させることもできる。また、接合部54を点線状に形成する場合における各接合部54の形状は適宜定めることができ、すべて同一とする他、部位に応じて異なる形状とすることもできる。特に各セル55の形状を多角形とする場合には、各辺の中間位置及び各頂点位置の少なくとも一方には接合部54を設けるのが好ましい。また、強接合部54aの場合は各頂点位置にも設けることが好ましいが、弱接合部54bの場合は各頂点位置には設けない方が弱接合部54bが剥離しやすくなり、セル55の合体が円滑に進行するため好ましい。
The width of the joint 54 when the joint 54 is formed in the shape of a continuous line and the
図8及び図11に示すように、セル吸収シート50の幅方向WDの中間の領域に、強接合部54aが前後方向LDに続く縦強接合線58、及びその両脇に隣接する低膨張セル55sからなる拡散性向上部57が設けられていると好ましい。この拡散性向上部57の低膨張セル55sは、拡散性向上部57の両脇に隣接するセル55よりも第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の単位面積当たりの内包量が少なく、かつ当該拡散性向上部57の両脇に隣接するセル55との間の接合部54が弱接合部54bとなっているものである。この場合、図10に示すように、排泄液の吸収当初、拡散性向上部57とその周囲部分との膨張量の差により、拡散性向上部57を底部とする幅の広い溝が形成され、その溝により液拡散が促進される。この状態は、拡散性向上部57の周囲のセル55における第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の膨張力により、拡散性向上部57の低膨張セル55sとその両脇のセル55との間の弱接合部54bが外れるまで続き、当該弱接合部54bが外れた後も強接合部54aは外れないため、溝の幅は狭くなるものの強接合部54aを底部とする溝が残り拡散性は維持される。つまり、多量の排泄液の拡散が重要となる吸収初期には溝の幅が広く、その後は、ゲルブロッキング等の問題が生じないように拡散性向上部57の低膨張セル55sも周囲のセル55と合体するものの、強接合部54aにより溝が残り、拡散性向上作用が維持される。
As shown in FIGS. 8 and 11, in the middle region of the cell
低膨張セル55sにおける第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の内包量は、重量比で隣接するセル55の1/3以下であることが好ましく、全く内包しないと特に好ましい。
The amount of the second
なお、図8及び図11では、強接合部54a及び相対的に接合強度が高い弱接合部54eが太い点線で表現され、他の弱接合部54b,54fは細い点線で表現されており、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53を含有するセル55(つまり低膨張セル55s及び後述の空セル56を除くセル55)には図11では斜線模様が付されている。
8 and 11, the strong joint 54a and the weak joint 54e with relatively high joint strength are represented by thick dotted lines, and the other
拡散性向上部57は、図8に示すように、セル吸収シート50の全長にわたり設けられていてもよく、図11に示すように、前後方向LDの中間部分(特に股間部を含み、その前後両側にわたる範囲)にのみ設けられていてもよい。また、拡散性向上部57は、図8及び図11に示すように、幅方向WD中央の一か所に設ける他、図示しないが、幅方向WDに間隔を空けて複数か所に設けることもできる。
The
セル吸収シート50の前後方向LD全体にわたりセル55同士が合体可能であると、吸収時に膨張した第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53のゲル化物が、合体したセル55内を前後方向LDに大きく移動可能となり、当該ゲル化物が股間部等の低所に集合して装着感を悪化させるおそれがある。よって、図8に示すように、強接合部54aが幅方向WD又は斜め方向に連続的又は断続的に続く部分である横強接合線59が、前後方向LDに間隔を空けて複数設けられているのは好ましい形態である。これにより、吸収時に基本的に剥離しない強接合部54aによって第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53のゲル化物の前後方向LD移動を阻止することができ、セル吸収シート50の形状の崩れを防止することができる。もちろん、図11に示すように、このような横強接合線59を有しない形態とすることもできる。
If the
特に、図8に示す形態のように、強接合部54aがセル吸収シート50全長にわたって前後方向LDに続く部分である縦強接合線58が、幅方向WDの最も外側に位置するセル55の側縁に沿って幅方向WDの両側にそれぞれ設けられるとともに、これらの幅方向WDの中間にも設けられており、かつ横強接合線59が、幅方向WDに隣り合う縦強接合線58間にわたるように幅方向WD又は斜め方向に続く部分であると、強接合部54aにより囲まれる最拡大区画55G以上にはセル55が合体しないため、吸収時に膨張した第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53のゲル化物は最拡大区画55G外には移動せず、吸収時におけるセル吸収シート50の形状崩れを効果的に防止できる。また、強接合部54aが前後方向LDに続く部分である縦強接合線58により縦方向の液拡散性が向上し、強接合部54aが幅方向WD又は斜め方向に続く部分である横強接合線59により横方向の液拡散性が向上する。例えば図8に示す形態において、符号Zの位置に尿が排泄されたと仮定すると、そこを中心に図9に示すように尿が周囲に拡散しつつ、その尿を各位置の第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53が吸収していく。このとき、図9及び図10に示すように、内部の第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の膨張圧が高まったセル55については、その周囲の弱接合部54bが膨張圧に抗しきれずに剥離し、隣接するセル55と合体する。この合体は、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の吸収膨張が弱接合部54bを剥離しうる限り続き、周囲に強接合部54aを有するセル55まで進行可能となる。
In particular, as in the embodiment shown in FIG. 8, the longitudinal
最拡大区画55Gの大きさや形状、配置(つまり強接合部54aの配置)は適宜定めることができるが、最拡大区画55Gを小さくし過ぎると強接合部54aを設ける意義がなくなり、またセル55数が多くても細長く形成したときにはセル55の合体後の形状が膨らみにくい形状となる。
The size, shape, and arrangement of the
図8~図10に示す形態では、縦強接合線58が、セル吸収シート50の幅方向WD中央部及び両側部にそれぞれ設けられており、横強接合線59は、前記中央の縦強接合線58及び両側部の縦強接合線58の間のそれぞれで、左右に繰り返し折れ曲がりつつ前後方向に延びるジグザグ状をなしている。この結果、中央の縦強接合線58の位置に頂点を有するほぼ三角形状の最拡大区画55Gと、両側部の縦強接合線58の位置に頂点を有するほぼ三角形状の最拡大区画55Gとが、前後方向に交互に繰り返し形成されている。横強接合線59がこのようにジグザグ状に形成されていると、少ない横強接合線59の本数で効率的に横方向の液拡散を促進でき、かつ最拡大区画55Gは膨らみやすいほぼ三角形となり、セル55合体数に対するセル容積増加量にも優れるため好ましい。
In the embodiment shown in FIGS. 8 to 10, longitudinal
低膨張セル55sを設けずに縦強接合線58のみとすることもできる。この場合、排泄液の吸収時に強接合部54aは外れないため、強接合部54aを底部とする溝が残ることによる拡散性の向上は図られる。
Only the longitudinal strong
他方、図8等に示すように、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の単位面積当たりの内包量が他のセルよりも少ない空セル56を設けることもできる。図11では、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53を含有するセル55(つまり低膨張セル55s及び後述の空セル56を除くセル55)には斜線模様が付されている。このうち、図8における斜線模様を付した領域は、製造時の第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の散布領域53Aを想定しているため、周縁のセル55には斜線模様のない部分があるが、セル55内で第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53が移動可能である場合には製品ではセル55内における第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の存在位置が固定されるものではなく、他の図のものと同様にセル55内の全体に第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53が分布しうるものである。空セル56における第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の内包量は、重量比で他のセルの1/2以下であることが好ましく、全く内包しないと特に好ましい。例えば、セル吸収シート50の前端及び後端は、製造の際に個々のセル吸収シート50へ切断することにより形成されるため、この位置に第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53を含有すると切断装置の刃の寿命が短くなるおそれがある。よって、少なくともセル吸収シート50の前後端が通過する位置のセル55は空セル56であることが望ましい。また、セル吸収シート50の前後方向LDの中間における両側部のセル55を空セル56とすることにより、当該部分は吸収後も膨張が少ないものとなり、したがって吸収後においてもセル吸収シート50が脚周りにフィットする形状となる。
On the other hand, as shown in FIG. 8 and the like,
上記例は、セル55内に第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53のみ内包させているが、第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53とともに消臭剤粒子等、高吸収性ポリマー粒子以外の粉粒体を内包させることもできる。
In the above example, only the second
(高吸収性ポリマー粒子)
第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43及び第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53としては、この種の吸収性物品に使用されるものをそのまま使用できる。第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43及び第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の粒径は特に限定されないが、例えば、500μm超の粒子の割合が30重量%以下で、500μm以下かつ180μm超の粒子の割合が60重量%以上で、106μm超かつ180μm以下の粒子の割合が10重量%以下で、かつ106μm以下の粒子の割合が10重量%以下であると好ましい。なお、これらの粒径の測定は、以下のように行う。すなわち、500μm、180μm、106μmの標準ふるい(JIS Z8801-1:2006)、及び受皿を上からこの順に並べて配置し、最上段の500μmのふるいに、高吸収性ポリマー粒子の試料を10g投入し、ふるい分け(5分間の振とう)を行った後、各ふるい上に残る粒子の重量を計測する。このふるい分けの結果、500μm、180μm、106μmの各ふるい上に残った試料、及び受皿上に残った試料の投入量に対する重量割合を、それぞれ500μm超の粒子の割合、500μm以下かつ180μm超の粒子の割合、106μm超かつ180μm以下の粒子の割合、106μm以下の粒子の割合とする。
(superabsorbent polymer particles)
As the first
第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43及び第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53としては、特に限定無く用いることができるが、吸水量が40g/g以上のものが好適である。また、第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43及び第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53は破砕法により製造されたものであると、ゲルブロッキングが生じにくいため好ましい。第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43及び第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53としては、でんぷん系、セルロース系や合成ポリマー系などのものがあり、でんぷん-アクリル酸(塩)グラフト共重合体、でんぷん-アクリロニトリル共重合体のケン化物、ナトリウムカルボキシメチルセルロースの架橋物やアクリル酸(塩)重合体などのものを用いることができる。第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43及び第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53の形状としては、通常用いられる粉粒体状のものが好適であるが、他の形状のものも用いることができる。
Although the first
第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43及び第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53としては、吸水速度が70秒以下、特に40秒以下のものが好適に用いられる。吸水速度が遅すぎると、吸収体70内に供給された液が吸収体70外に戻り出てしまういわゆる逆戻りを発生しやすくなる。
As the first
また、第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子43及び第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子53としては、ゲル強度が1000Pa以上のものが好適に用いられる。これにより、液吸収後のべとつき感を効果的に抑制できる。
As the first
(包装シート)
図3及び図16(a)に示すように、吸収体70は包装シート45により包装することができる。この場合、一枚の包装シート45を吸収体70の表裏面及び両側面を取り囲むように筒状に巻き付ける他、2枚の包装シート45で表裏両側から挟むようにして包装することができる。包装シート45としては、ティッシュペーパ、特にクレープ紙、不織布、ポリラミ不織布、小孔が開いたシート等を用いることができる。ただし、高吸収性ポリマー粒子53が抜け出ないシートであるのが望ましい。包装シート45に不織布を使用する場合、親水性のSMS不織布(SMS、SSMMS等)が特に好適であり、その材質はポリプロピレン、ポリエチレン/ポリプロピレン複合材などを使用できる。包装シート45に用いる不織布の目付けは、5~40g/m2、特に10~30g/m2のものが望ましい。
(packaging sheet)
As shown in FIGS. 3 and 16(a), the
図16(b)に示すように、吸収体70の裏面から、吸収体70の幅方向WD両側を経て吸収体70の上面の両側部まで包装シート45を巻付け、吸収体70の上面の幅方向WD中間部に包装シート45により覆われていない領域45Sを設けるとともに、この領域45Sの全体を含むように、上補助層71が設けられていると好ましい。吸収体70は、製造時、使用前、又は吸収後の高吸収性ポリマー粒子の漏出を防止するために、包装シート45で被覆することが一般的であるが、前述の上補助層71を有する吸収体70の場合、上補助層71が速やかに粘性液Nに接触することが望ましい。したがって、図16(b)に示すように、包装シート45の被覆範囲を制限し、上補助層71は吸収体70の上面に露出させることが望ましい。このような構造としても、吸収体70における包装シート45により覆われていない部分は、上補助層71の高吸水不織布42で覆われており、上補助層71はクレム吸水度が高い(つまり緻密な)高吸水不織布42を基本とするから、吸収体70全体を包装シート45で覆うものとほぼ同様の、高吸収性ポリマー粒子の漏出防止効果を発揮するものとなる。
As shown in FIG. 16(b), the
<明細書中の用語の説明>
明細書中で以下の用語が使用される場合、明細書中に特に記載がない限り、以下の意味を有するものである。
<Description of terms in the specification>
When the following terms are used in the specification, they shall have the following meanings, unless stated otherwise in the specification.
「MD方向」及び「CD方向」とは、製造設備における流れ方向(MD方向)及びこれと直交する横方向(CD方向)を意味し、いずれか一方が製品の前後方向となるものであり、他方が製品の幅方向となるものである。不織布のMD方向は、不織布の繊維配向の方向である。繊維配向とは、不織布の繊維が沿う方向であり、例えば、TAPPI標準法T481の零距離引張強さによる繊維配向性試験法に準じた測定方法や、前後方向及び幅方向の引張強度比から繊維配向方向を決定する簡易的測定方法により判別することができる。 "MD direction" and "CD direction" mean the flow direction (MD direction) and the transverse direction (CD direction) perpendicular to this in the manufacturing equipment, one of which is the front-back direction of the product, The other is the width direction of the product. The MD direction of a nonwoven fabric is the direction of fiber orientation of the nonwoven fabric. The fiber orientation is the direction along which the fibers of the nonwoven fabric are aligned. It can be determined by a simple measurement method for determining the orientation direction.
・「前後方向」とは図中に符号LDで示す方向(縦方向)を意味し、「幅方向」とは図中にWDで示す方向(左右方向)を意味し、前後方向と幅方向とは直交するものである。 ・"Front-back direction" means the direction (longitudinal direction) indicated by symbol LD in the figure, and "width direction" means the direction (left-right direction) indicated by WD in the figure. are orthogonal.
・「表側」とは着用した際に着用者の肌に近い方を意味し、「裏側」とは着用した際に着用者の肌から遠い方を意味する。 - The "front side" means the side closer to the wearer's skin when worn, and the "back side" means the side farther from the wearer's skin when worn.
・「表面」とは部材の、着用した際に着用者の肌に近い方の面を意味し、「裏面」とは着用した際に着用者の肌から遠い方の面を意味する。 - "Front" means the side of the member that is closer to the wearer's skin when worn, and "back" means the side that is farther from the wearer's skin when worn.
「展開状態」とは、収縮や弛み無く平坦に展開した状態を意味する。 The "deployed state" means a flat unfolded state without contraction or slack.
「伸長率」は、自然長を100%としたときの値を意味する。例えば、伸長率が200%とは、伸長倍率が2倍であることと同義である。 "Elongation rate" means a value when the natural length is taken as 100%. For example, an elongation rate of 200% is synonymous with an elongation ratio of 2 times.
「人工尿」は、尿素:2wt%、塩化ナトリウム:0.8wt%、塩化カルシウム二水和物:0.03wt%、硫酸マグネシウム七水和物:0.08wt%、及びイオン交換水:97.09wt%を混合したものであり、特に記載の無い限り、温度37度で使用される。 "Artificial urine" contains urea: 2 wt%, sodium chloride: 0.8 wt%, calcium chloride dihydrate: 0.03 wt%, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate: 0.08 wt%, and deionized water: 97 wt%. 09 wt% and used at a temperature of 37°C unless otherwise specified.
「ゲル強度」は次のようにして測定されるものである。人工尿49.0gに、高吸収性ポリマーを1.0g加え、スターラーで攪拌させる。生成したゲルを40℃×60%RHの恒温恒湿槽内に3時間放置したあと常温にもどし、カードメーター(I.techno Engineering社製:Curdmeter-MAX ME-500)でゲル強度を測定する。 "Gel strength" is measured as follows. 1.0 g of superabsorbent polymer is added to 49.0 g of artificial urine and stirred with a stirrer. The resulting gel is left in a constant temperature and humidity bath at 40° C. and 60% RH for 3 hours, then returned to room temperature, and the gel strength is measured with a card meter (Curdmeter-MAX ME-500 manufactured by I. techno Engineering).
「目付け」は次のようにして測定されるものである。試料又は試験片を予備乾燥した後、標準状態(試験場所は、温度23±1℃、相対湿度50±2%)の試験室又は装置内に放置し、恒量になった状態にする。予備乾燥は、試料又は試験片を温度100℃の環境で恒量にすることをいう。なお、公定水分率が0.0%の繊維については、予備乾燥を行わなくてもよい。恒量になった状態の試験片から、試料採取用の型板(100mm×100mm)を使用し、100mm×100mmの寸法の試料を切り取る。試料の重量を測定し、100倍して1平米あたりの重さを算出し、目付けとする。
"Matsuke" is measured as follows. After pre-drying the sample or test piece, it is left in a test room or apparatus under standard conditions (test location: temperature 23±1° C.,
「厚み」は、自動厚み測定器(KES-G5 ハンディー圧縮試験機)を用い、荷重:0.098N/cm2、及び加圧面積:2cm2の条件下で自動測定する。 "Thickness" is automatically measured using an automatic thickness gauge (KES-G5 handy compression tester) under the conditions of a load of 0.098 N/cm 2 and a pressurized area of 2 cm 2 .
「空隙率」とは、以下の方法により計測するものである。すなわち、中シートにおける接合部以外の部分を矩形に切取り、試料とする。試料の長さ、幅、厚み、重量を測定する。不織布の原料密度を用いて、試料と同じ体積で空隙率が0%の場合の仮想重量を算出する。試料重量及び仮想重量を以下の式に代入し、空隙率を求める。
空隙率 = 〔 (仮想重量 - 試料重量) / 仮想重量 〕 × 100
"Porosity" is measured by the following method. That is, a portion of the middle sheet other than the joint portion is cut into a rectangular shape and used as a sample. Measure the length, width, thickness and weight of the sample. Using the raw material density of the nonwoven fabric, calculate the virtual weight when the volume is the same as the sample and the porosity is 0%. Substitute the sample weight and virtual weight into the following formula to obtain the porosity.
Porosity = [(virtual weight - sample weight) / virtual weight] x 100
「吸水量」は、JIS K7223-1996「高吸水性樹脂の吸水量試験方法」によって測定する。 "Water absorption" is measured according to JIS K7223-1996 "Testing method for water absorption of superabsorbent resin".
「吸水速度」は、2gの高吸収性ポリマー及び50gの生理食塩水を使用して、JIS K7224‐1996「高吸水性樹脂の吸水速度試験法」を行ったときの「終点までの時間」とする。 "Water absorption rate" is defined as "Time to end point" when JIS K7224-1996 "Test method for water absorption rate of superabsorbent polymer" is performed using 2g of superabsorbent polymer and 50g of physiological saline. do.
「クレム吸水度」は、JIS P 8141:2004に規定される「紙及び板紙-吸水度試験方法-クレム法」により測定されるクレム吸水度を意味する。 "Klemm water absorbency" means the Klemm water absorbency measured by "Paper and paperboard-Water absorbency test method-Klemm method" defined in JIS P 8141:2004.
「保水量」は、以下の方法により測定されるものを意味する。MD方向10cm×CD方向10cm(面積100cm2)の試験片を用意し、吸収前重量を測定する。次に、試験片を人工尿に5秒間浸漬した後、いずれか1つの角部を親指と人差し指で軽く摘んで(可能な限り水を絞り出さないように軽く摘まむ)対向する角部が下に向くように吊し上げ、30秒間放置し、しずくを落とす。その後、「荷重下保水量」を測定する場合、ろ紙(縦150mm×横150mm)を8枚重ねて敷いた上に試験片を載せ、その試験片の上面全体に荷重が加わるように縦100mm×横100mmの底面を有する四角柱状の錘(重量3kg)を載せ、5分経過した時点で錘を取り除き、試験片の吸収後重量を測定する。「無荷重下保水量」を測定する場合、ろ紙を8枚重ねて敷いた上に試験片を載せ、その上に何も載せずに、5分経過した時点で試験片の吸収後重量を測定する。これらの測定結果に基づき、吸収後重量と吸収前重量との差を面積10cm2あたりに換算した値を「荷重下保水量」及び「無荷重下保水量」とする。 "Water retention capacity" means what is measured by the following method. A test piece of 10 cm in the MD direction×10 cm in the CD direction (area 100 cm 2 ) is prepared, and the weight before absorption is measured. Next, after immersing the test piece in artificial urine for 5 seconds, any one corner is lightly pinched with the thumb and index finger (lightly pinched so as not to squeeze out water as much as possible), and the opposite corner is down. and leave it for 30 seconds to remove the drops. After that, when measuring the "water retention capacity under load", place the test piece on top of 8 sheets of filter paper (150 mm long x 150 mm wide) and place the test piece so that the entire upper surface of the test piece is loaded. A square column-shaped weight (weight: 3 kg) having a bottom surface with a width of 100 mm is placed on the test piece. When measuring the "water retention capacity under no load", place the test piece on 8 layers of filter paper and measure the weight of the test piece after absorption after 5 minutes without placing anything on it. do. Based on these measurement results, the difference between the post-absorption weight and the pre-absorption weight is converted into a value per 10 cm 2 of area, which is defined as the "water retention capacity under load" and the "water retention capacity under no load."
各部の寸法は、特に記載がない限り、自然長状態ではなく展開状態における寸法を意味する。 Unless otherwise specified, the dimension of each part means the dimension in the unfolded state, not in the natural length state.
試験や測定における環境条件についての記載がない場合、その試験や測定は、標準状態(試験場所は、温度23±1℃、相対湿度50±2%)の試験室又は装置内で行うものとする。 Unless otherwise specified, the test or measurement shall be conducted in a laboratory or equipment under standard conditions (temperature of 23±1°C, relative humidity of 50±2%). .
本発明は、上記例のようなテープタイプ使い捨ておむつの他、パンツタイプ使い捨ておむつ、パッドタイプ使い捨ておむつ、生理用ナプキン等の吸収性物品全般に利用できるものである。 INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY The present invention can be used not only for tape-type disposable diapers as described above, but also for general absorbent articles such as underpants-type disposable diapers, pad-type disposable diapers, and sanitary napkins.
LD…前後方向、N…粘性液、U…非粘性液、WD…幅方向、11…液不透過性シート、12…外装不織布、12T…ターゲットシート、13…ファスニングテープ、13A…係止部、13B…テープ本体部、13C…テープ取付部、30…トップシート、40…中間シート、42…高吸水不織布、42a…パルプ層、42b…支持層、43…第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子、45…包装シート、50…セル吸収シート、50c…凹部、50d…深さ、50p…凸部、51…上シート、52…下シート、53…第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子、54…接合部、54a…強接合部、54b…弱接合部、54c…縁部接合部、55…セル、55G…最拡大区画、55s…低膨張セル、56…空セル、57…拡散性向上部、58…縦強接合線、59…横強接合線、60…起き上がりギャザー、62…ギャザーシート、70…吸収体、71…上補助層、72…主吸収層、80…中シート。
LD... Front-back direction, N... Viscous liquid, U... Non-viscous liquid, WD... Width direction, 11... Liquid-impermeable sheet, 12... Exterior nonwoven fabric, 12T... Target sheet, 13... Fastening tape, 13A... Locking part, 13B...
Claims (6)
前記吸収体は、最上部に設けられた上補助層と、この上補助層の裏側に設けられた主吸収層とを有しており、
前記上補助層は、表面が前記吸収体の最上面に露出する、クレム吸水度が130~180mmの高吸水不織布と、この高吸水不織布の裏面に隣接する第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子とを有するものであり、
前記主吸収層は、液透過性を有する上シート及び下シートと、上シート及び下シートの接合部により周りを囲まれた、上シート及び下シートが非接合の部分であるセルと、このセル内に収容された第2高吸収性ポリマー粒子を含む粉粒体とを有するセル吸収シートであり、
前記セル吸収シートには、前記セルが間隔を空けて配列されており、
前記上シートにおける各セルに位置する部分が、それぞれ上側に膨らむ凸部となっているとともに、隣接する前記凸部の間が谷部となっており、
前記高吸水不織布は前記上シートに対して固定されるとともに、前記高吸水不織布における前記上シートの谷部に位置する部分が前記上シートの谷部に沿って落ち込んでおり、
前記下シートは、クレム吸水度が50~100mm、荷重下保水量が0.1g以上、かつ無荷重下保水量が0.5g以上の高吸水不織布である、
ことを特徴とする、吸収性物品。 An absorbent body, a liquid-permeable top sheet arranged on the front side of the absorbent body, and a liquid-impermeable sheet arranged on the back side of the absorbent body,
The absorbent body has an upper auxiliary layer provided on the top and a main absorbent layer provided on the back side of the upper auxiliary layer,
The upper auxiliary layer has a superabsorbent nonwoven fabric having a Klemm water absorbency of 130 to 180 mm, the surface of which is exposed on the uppermost surface of the absorbent body, and first superabsorbent polymer particles adjacent to the back surface of the superabsorbent nonwoven fabric. is a
The main absorbent layer includes a liquid-permeable upper sheet and a lower sheet, cells surrounded by a joined portion of the upper sheet and the lower sheet, and a portion where the upper sheet and the lower sheet are not joined, and the cells. a granular material containing second superabsorbent polymer particles housed therein;
The cells are arranged at intervals on the cell absorption sheet,
A portion of the upper sheet located in each cell forms a convex portion that swells upward, and a valley portion is formed between the adjacent convex portions,
The highly absorbent nonwoven fabric is fixed to the upper sheet, and a portion of the highly absorbent nonwoven fabric located in the valley of the upper sheet is depressed along the valley of the upper sheet,
The lower sheet is a highly absorbent nonwoven fabric having a Klemm water absorbency of 50 to 100 mm, a water retention capacity under load of 0.1 g or more, and a water retention capacity under no load of 0.5 g or more.
An absorbent article characterized by:
請求項1記載の吸収性物品。 The superabsorbent nonwoven fabric forming the lower sheet is a wet-laid nonwoven fabric containing 50% or more of pulp fiber or rayon fiber and having a basis weight of 25 to 50 g/m 2 ,
The absorbent article according to claim 1.
請求項2記載の吸収性物品。 The wet-laid nonwoven fabric has a support layer containing synthetic resin long fibers and a pulp layer located on the outermost side and made only of pulp fibers.
The absorbent article according to claim 2.
前記上シートの上面における前記第1高吸収性ポリマー粒子の付着量は、前記凸部の頂部から隣接する前記凸部の間に位置する谷部の底部に向かうにつれて多くなっている、
請求項1~3のいずれか1項に記載の吸収性物品。 The first superabsorbent polymer particles are fixed to the upper surface of the upper sheet of the main absorbent layer,
The adhesion amount of the first superabsorbent polymer particles on the upper surface of the upper sheet increases from the top of the projections toward the bottom of the valleys located between the adjacent projections.
The absorbent article according to any one of claims 1-3.
請求項4記載の吸収性物品。 A portion of the upper sheet located in each cell is pushed upward to form concave portions and convex portions on the upper surface and the lower surface of the upper sheet.
The absorbent article according to claim 4.
請求項1~5のいずれか1項に記載の吸収性物品。 A portion of the lower sheet located in each cell is pushed downward to form concave portions and convex portions on the upper surface and the lower surface of the lower sheet.
The absorbent article according to any one of claims 1-5.
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019176972A JP7159143B2 (en) | 2019-09-27 | 2019-09-27 | absorbent article |
| PCT/JP2020/035219 WO2021060132A1 (en) | 2019-09-27 | 2020-09-17 | Absorbent article |
| CN202080055918.XA CN114206287B (en) | 2019-09-27 | 2020-09-17 | Absorbent article |
| TW109132729A TWI838582B (en) | 2019-09-27 | 2020-09-22 | Absorbent articles |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019176972A JP7159143B2 (en) | 2019-09-27 | 2019-09-27 | absorbent article |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2021052899A JP2021052899A (en) | 2021-04-08 |
| JP2021052899A5 JP2021052899A5 (en) | 2021-05-27 |
| JP7159143B2 true JP7159143B2 (en) | 2022-10-24 |
Family
ID=75166947
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019176972A Active JP7159143B2 (en) | 2019-09-27 | 2019-09-27 | absorbent article |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7159143B2 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN114206287B (en) |
| TW (1) | TWI838582B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2021060132A1 (en) |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015226582A (en) | 2014-05-30 | 2015-12-17 | 日本製紙クレシア株式会社 | Absorbent article |
| JP2018166557A (en) | 2017-03-29 | 2018-11-01 | 大王製紙株式会社 | Absorbent article |
| JP2019063127A (en) | 2017-09-29 | 2019-04-25 | 大王製紙株式会社 | Absorbent article |
| JP2019216856A (en) | 2018-06-15 | 2019-12-26 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | Absorber for absorbent article |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH09562A (en) * | 1995-06-16 | 1997-01-07 | New Oji Paper Co Ltd | Absorptive article |
| US20020095127A1 (en) * | 2000-12-28 | 2002-07-18 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Controlled delamination of laminate structures having enclosed discrete regions of a material |
| US20050107759A1 (en) * | 2002-01-17 | 2005-05-19 | Andrew Waksmundzki | Absorbent article with three-dimensional extrudate forming sap containment wells |
| JP2011062227A (en) * | 2009-09-15 | 2011-03-31 | Kochi Prefecture | Absorptive article |
| IN2014DN03302A (en) * | 2011-11-21 | 2015-06-26 | Procter & Gamble | |
| CN104470479B (en) * | 2012-07-13 | 2017-03-08 | 株式会社瑞光 | The manufacture device of absorbent commodity |
| JP5683742B1 (en) * | 2014-06-30 | 2015-03-11 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | Absorbent article and wearing article comprising the absorbent article |
| JP6219435B2 (en) * | 2016-03-30 | 2017-10-25 | 大王製紙株式会社 | Absorber manufacturing method and absorber manufacturing apparatus |
| JP6379248B1 (en) * | 2017-03-21 | 2018-08-22 | 大王製紙株式会社 | Absorber |
| JP6458102B1 (en) * | 2017-08-30 | 2019-01-23 | 大王製紙株式会社 | Absorbent articles |
-
2019
- 2019-09-27 JP JP2019176972A patent/JP7159143B2/en active Active
-
2020
- 2020-09-17 CN CN202080055918.XA patent/CN114206287B/en active Active
- 2020-09-17 WO PCT/JP2020/035219 patent/WO2021060132A1/en active Application Filing
- 2020-09-22 TW TW109132729A patent/TWI838582B/en active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015226582A (en) | 2014-05-30 | 2015-12-17 | 日本製紙クレシア株式会社 | Absorbent article |
| JP2018166557A (en) | 2017-03-29 | 2018-11-01 | 大王製紙株式会社 | Absorbent article |
| JP2019063127A (en) | 2017-09-29 | 2019-04-25 | 大王製紙株式会社 | Absorbent article |
| JP2019216856A (en) | 2018-06-15 | 2019-12-26 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | Absorber for absorbent article |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN114206287B (en) | 2023-03-14 |
| CN114206287A (en) | 2022-03-18 |
| JP2021052899A (en) | 2021-04-08 |
| TW202128105A (en) | 2021-08-01 |
| TWI838582B (en) | 2024-04-11 |
| WO2021060132A1 (en) | 2021-04-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7159144B2 (en) | absorbent article | |
| JP7159143B2 (en) | absorbent article | |
| JP7153002B2 (en) | absorbent article | |
| JP7291053B2 (en) | absorbent article | |
| JP6942771B2 (en) | Absorbent article | |
| WO2021193002A1 (en) | Absorbent article | |
| WO2021060130A1 (en) | Absorbent article | |
| JP7499661B2 (en) | Absorbent articles | |
| JP2021153716A5 (en) | ||
| JP2022049273A5 (en) | ||
| JP2021052897A5 (en) | ||
| JP2021052901A5 (en) | ||
| JP2021052898A5 (en) |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20210401 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20210401 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20220325 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20220506 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20220617 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20220824 |
|
| C60 | Trial request (containing other claim documents, opposition documents) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: C60 Effective date: 20220824 |
|
| A911 | Transfer to examiner for re-examination before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date: 20220902 |
|
| C21 | Notice of transfer of a case for reconsideration by examiners before appeal proceedings |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: C21 Effective date: 20220909 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20220930 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20221012 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 7159143 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |