JP7063344B2 - Decorative sheet and decorative resin molded product - Google Patents
Decorative sheet and decorative resin molded product Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7063344B2 JP7063344B2 JP2020018607A JP2020018607A JP7063344B2 JP 7063344 B2 JP7063344 B2 JP 7063344B2 JP 2020018607 A JP2020018607 A JP 2020018607A JP 2020018607 A JP2020018607 A JP 2020018607A JP 7063344 B2 JP7063344 B2 JP 7063344B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- resin
- layer
- laminated
- decorative sheet
- acrylic
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Description
本発明は、加飾樹脂成形品の表面に高い平滑性を付与することができる加飾シートに関する。さらに、本発明は、当該加飾シートを利用した加飾樹脂成形品に関する。 The present invention relates to a decorative sheet capable of imparting high smoothness to the surface of a decorative resin molded product. Further, the present invention relates to a decorative resin molded product using the decorative sheet.
従来、車両内外装部品、建材内装材、家電筐体等には、樹脂成形品の表面に加飾シートを積層させた加飾樹脂成形品が使用されている。このような加飾樹脂成形品の製造においては、予め意匠が付与された加飾シートを、射出成形によって樹脂と一体化させる成形法などが用いられている。係る成形法の代表的な例としては、加飾シートを真空成形型により予め立体形状に成形しておき、当該加飾シートを射出成形型に挿入し、流動状態の樹脂を型内に射出することにより樹脂と加飾シートとを一体化するインサート成形法や、射出成形の際に金型内に挿入された加飾シートを、キャビティ内に射出注入された溶融樹脂と一体化させる射出成形同時加飾法が挙げられる。また、射出成形による成形法以外には、真空圧着法のように予め成形された成形体上に加熱や加圧を伴いながら貼着される加飾方法においても加飾シートが用いられている。 Conventionally, decorative resin molded products in which a decorative sheet is laminated on the surface of a resin molded product have been used for vehicle interior / exterior parts, building material interior materials, home appliance housings, and the like. In the production of such a decorative resin molded product, a molding method or the like is used in which a decorative sheet having a pre-designed design is integrated with the resin by injection molding. As a typical example of such a molding method, a decorative sheet is molded into a three-dimensional shape in advance by a vacuum molding mold, the decorative sheet is inserted into an injection molding mold, and a fluid resin is injected into the mold. By doing so, the insert molding method that integrates the resin and the decorative sheet, and the injection molding that integrates the decorative sheet inserted in the mold during injection molding with the molten resin injected into the cavity at the same time. The decoration method can be mentioned. In addition to the molding method by injection molding, a decorative sheet is also used in a decorative method such as a vacuum crimping method in which a preformed molded body is attached while being heated or pressurized.
近年、消費者の多様な志向に伴って、明度の高い意匠や、光沢のある意匠を有する加飾樹脂成形品へのニーズが高まっている。例えば、特許文献1では、パール顔料と、バインダー樹脂として塩化ビニル-酢酸ビニル共重合体とを含むインキ組成物を用いて形成されたパールインキ層により、光沢のある意匠を表出する技術が提案されている。ところが、金属顔料、パール顔料などの顔料を含む層に光が当たると、バインダー樹脂が劣化し、加飾シートの耐候性が低下する場合がある。
In recent years, with the diverse orientations of consumers, there is an increasing need for decorative resin molded products having high-brightness designs and glossy designs. For example,
本発明者は、上記のような顔料を用いた加飾シートにおいて、耐候性に優れたアクリル系樹脂をバインダー樹脂として用いて絵柄層を形成することを検討した。その結果、耐候性は高められるものの、加飾樹脂成形品に成形された後において、加飾樹脂成形品の表面の平滑性が低下することが明らかとなった。この原因について、本発明者が詳細に検討したところ、加飾樹脂成形品の表面において、絵柄層が位置している領域と、絵柄層が位置していない領域とによって凹凸形状が形成されていることが明らかとなった。特に、このような問題は、絵柄層を転写用基材の上に形成した転写用シートを用いて、基材の上に絵柄層を転写して製造される加飾シートにおいて、顕著であった。
このような状況下、本発明は、加飾樹脂成形品の表面に高い平滑性を付与することができる加飾シート、及び当該加飾シートを利用した加飾樹脂成形品を提供することを主な目的とする。
The present inventor has studied to form a pattern layer by using an acrylic resin having excellent weather resistance as a binder resin in a decorative sheet using a pigment as described above. As a result, it was clarified that although the weather resistance was improved, the smoothness of the surface of the decorative resin molded product was lowered after being molded into the decorative resin molded product. As a result of a detailed examination by the present inventor of this cause, an uneven shape is formed on the surface of the decorative resin molded product by a region where the pattern layer is located and a region where the pattern layer is not located. It became clear. In particular, such a problem was remarkable in a decorative sheet manufactured by transferring a pattern layer onto a substrate by using a transfer sheet in which the pattern layer was formed on the transfer substrate. ..
Under such circumstances, the present invention mainly provides a decorative sheet capable of imparting high smoothness to the surface of a decorative resin molded product, and a decorative resin molded product using the decorative sheet. Purpose.
本発明者は、上記のような課題を解決すべく鋭意検討を行った。その結果、少なくとも、顔料を含む絵柄層と、ベタ層とが積層された積層体からなる加飾シートであって、当該積層体において、絵柄層が部分的に積層されており、絵柄層に含まれるバインダー樹脂が、アクリル系樹脂を80質量%以上含み、ベタ層に含まれるバインダー樹脂が、アクリル系樹脂を80質量%以上含むことにより、加飾樹脂成形品の表面に高い平滑性を付与することができることを見出した。本発明は、このような知見に基づいて、さらに検討を重ねることにより完成された発明である。 The present inventor has made diligent studies to solve the above problems. As a result, at least, it is a decorative sheet composed of a laminated body in which a pattern layer containing a pigment and a solid layer are laminated, and the pattern layer is partially laminated in the laminated body and is included in the pattern layer. The binder resin contains 80% by mass or more of the acrylic resin, and the binder resin contained in the solid layer contains 80% by mass or more of the acrylic resin, thereby imparting high smoothness to the surface of the decorative resin molded product. I found that I could do it. The present invention is an invention completed by further studies based on such findings.
すなわち、本発明は、下記に掲げる態様の発明を提供する。
項1. 少なくとも、顔料を含む絵柄層と、ベタ層とが積層された積層体からなる加飾シートであって、
前記積層体において、前記絵柄層は、部分的に積層されており、
前記絵柄層に含まれるバインダー樹脂が、アクリル系樹脂を80質量%以上含み、
前記ベタ層に含まれるバインダー樹脂が、アクリル系樹脂を80質量%以上含む、加飾シート。
項2. 前記顔料が、金属顔料、パール顔料、及び酸化チタン顔料からなる群から選択された少なくとも1種である、項1に記載の加飾シート。
項3. 塩素系樹脂を30質量%以上含むバインダー樹脂とを含む樹脂層がさらに積層されている、項1または2に記載の加飾シート。
項4. 前記樹脂層が、有機顔料及び無機顔料の少なくとも一方の顔料を含む、項3に記載の加飾シート。
項5. 前記絵柄層及び前記ベタ層が、基材層の上に積層されている、項1~4のいずれかに記載の加飾シート。
項6. 最表面に表面保護層をさらに備える、項1~5のいずれかに記載の加飾シート。項7. 前記表面保護層の厚みが、30μm以下である、項6に記載の加飾シート。
項8. 転写用基材の上に、アクリル樹脂を80質量%以上含むバインダー樹脂及び顔料を含む絵柄層を部分的に積層する工程と、アクリル樹脂を80質量%以上含むバインダー樹脂を含むベタ層を積層する工程とを行い、転写シートを作製する、転写シート作製工程と、
前記転写シートに積層された前記絵柄層及びベタ層を基材上に転写する転写工程と、
を備える、加飾シートの製造方法。
項9.前記転写工程の後、さらに表面保護層を積層する工程を備える、項8に記載の加飾シートの製造方法。
項10. 少なくとも、成形樹脂層の上に、顔料を含む絵柄層と、ベタ層とが積層された積層体からなる加飾樹脂成形品であって、
前記積層体において、前記絵柄層は、部分的に積層されており、
前記絵柄層に含まれるバインダー樹脂が、アクリル系樹脂を80質量%以上含み、
前記ベタ層に含まれるバインダー樹脂が、アクリル系樹脂を80質量%以上含む、加飾樹脂成形品。
That is, the present invention provides the inventions of the following aspects.
In the laminated body, the pattern layer is partially laminated, and is
The binder resin contained in the pattern layer contains 80% by mass or more of an acrylic resin, and contains 80% by mass or more.
A decorative sheet in which the binder resin contained in the solid layer contains 80% by mass or more of an acrylic resin.
Item 4.
Item 6.
Item 8. A step of partially laminating a binder resin containing 80% by mass or more of acrylic resin and a pattern layer containing a pigment on a transfer substrate, and a solid layer containing a binder resin containing 80% by mass or more of acrylic resin are laminated. The transfer sheet preparation process, in which the transfer sheet is produced by performing the steps,
A transfer step of transferring the pattern layer and the solid layer laminated on the transfer sheet onto a substrate,
A method of manufacturing a decorative sheet.
Item 10. At least, it is a decorative resin molded product composed of a laminated body in which a pattern layer containing a pigment and a solid layer are laminated on a molding resin layer.
In the laminated body, the pattern layer is partially laminated, and is
The binder resin contained in the pattern layer contains 80% by mass or more of an acrylic resin, and contains 80% by mass or more.
A decorative resin molded product in which the binder resin contained in the solid layer contains 80% by mass or more of an acrylic resin.
本発明によれば、加飾樹脂成形品の表面に高い平滑性を付与し得る加飾シートを提供することができる。さらに、本発明によれば、表面が高い平滑性を有する加飾樹脂成形品を提供することができる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to provide a decorative sheet capable of imparting high smoothness to the surface of a decorative resin molded product. Further, according to the present invention, it is possible to provide a decorative resin molded product having a high surface smoothness.
1.加飾シート
本発明の加飾シートは、少なくとも、顔料を含む絵柄層と、ベタ層とが積層された積層体からなる加飾シートであって、当該積層体において、絵柄層が部分的に積層されており、絵柄層に含まれるバインダー樹脂が、アクリル系樹脂を80質量%以上含み、ベタ層に含まれるバインダー樹脂が、アクリル系樹脂を80質量%以上含むことを特徴とする。本発明の加飾シートは、このような構成を有することにより、加飾樹脂成形品の表面に高い平滑性を付与することができる。以下、本発明の加飾シートについて詳述する。
1. 1. Decorative sheet The decorative sheet of the present invention is a decorative sheet composed of a laminated body in which at least a pattern layer containing a pigment and a solid layer are laminated, and the pattern layer is partially laminated in the laminated body. The binder resin contained in the pattern layer contains 80% by mass or more of acrylic resin, and the binder resin contained in the solid layer contains 80% by mass or more of acrylic resin. By having such a structure, the decorative sheet of the present invention can impart high smoothness to the surface of the decorative resin molded product. Hereinafter, the decorative sheet of the present invention will be described in detail.
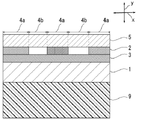
加飾シートの積層構造
本発明の加飾シートは、少なくとも、絵柄層2と、ベタ層3とが積層された積層体からなる。本発明の加飾シートは、加飾シートの保形性を高めることなどを目的として、必要に応じて、基材層1を有していてもよい。また、後述の通り、絵柄層2及びベタ層3とは異なるバインダー樹脂組成を有する樹脂層4を有していてもよい。また、本発明の加飾シートは、加飾シートの表面を保護することなどを目的として、必要に応じて、最外層として表面保護層5を設けてもよい。また、表面保護層5と、これに隣接する層との密着性を高めることなどを目的として、必要に応じて、表面保護層5の下にプライマー層6を設けてもよい。また、加飾シートと成形樹脂層9との密着性を高めることなどを目的として、必要に応じて、接着層8を有していてもよい。
Laminated structure of decorative sheet The decorative sheet of the present invention is composed of at least a laminated body in which a
図1または図2に示されるように、絵柄層2は、本発明の加飾シートを構成する積層体において、水平方向x(積層方向yとは垂直な方向)に部分的に積層されている。また、ベタ層3は、本発明の加飾シートを構成する積層体において、水平方向xの全面に積層されている。
As shown in FIG. 1 or 2, the
絵柄層2、ベタ層3、及び樹脂層4は、それぞれ、複数積層されてもよい。また、絵柄層2、ベタ層3、及び樹脂層4の積層順は、特に制限されないが、加飾樹脂成形品の表面の平滑性をより一層高める観点からは、ベタ層3が絵柄層2よりも最外層側(視認される側)に積層されていることが好ましい。
A plurality of the
樹脂層4は、水平方向xの少なくとも一部分に積層されていればよい。すなわち、樹脂層4は、水平方向xに部分的に積層されていてもよいし、全面に積層されていてもよい。例えば、図3おいては、水平方向xに部分的に形成された絵柄層2が1層、全面に形成されたベタ層3が1層、部分的に形成された樹脂層41、42が2層積層されている。
The resin layer 4 may be laminated on at least a part of the horizontal direction x. That is, the resin layer 4 may be partially laminated in the horizontal direction x, or may be laminated on the entire surface. For example, in FIG. 3, the
なお、図1~5は、加飾シート及び加飾樹脂成形品の積層構造を示すため模式図であり、描画の都合により、絵柄層2、樹脂層4が積層された層と同一平面に、これらの何れの層も形成されていない空間が存在するかのように描写されているが、実際の加飾シートにおいては、このような箇所は実質的に存在せず、順に積層される層によって埋められている。 In addition, FIGS. It is described as if there is a space in which none of these layers are formed, but in an actual decorative sheet, such a place does not substantially exist, and the layers stacked in order do not exist. It is buried.
本発明の加飾シートの積層構造として、絵柄層/ベタ層がこの順に積層された積層構造;基材層/絵柄層/ベタ層がこの順に積層された積層構造;基材層/ベタ層/絵柄層がこの順に積層された積層構造;基材層/絵柄層/ベタ層/表面保護層がこの順に積層された積層構造;基材層/ベタ層/絵柄層/表面保護層がこの順に積層された積層構造;基材層/ベタ層/絵柄層/樹脂層/表面保護層がこの順に積層された積層構造;基材層/ベタ層/絵柄層/樹脂層/プライマー層/表面保護層がこの順に積層された積層構造などが挙げられる。なお、当該積層構造の例示において、絵柄層、ベタ層、樹脂層と記載したものは、それぞれ、複数の絵柄層、複数のベタ層、複数の樹脂層であってもよい。図1に、本発明における加飾シートの積層構造の一態様として、基材層/ベタ層/絵柄層/表面保護層がこの順に積層された加飾シートの一例の略図的断面図を示す。図2に、本発明における加飾シートの積層構造の一態様として、基材層/絵柄層/ベタ層/表面保護層がこの順に積層された加飾シートの一例の略図的断面図を示す。図3に、本発明における加飾シートの積層構造の一態様として、基材層/ベタ層/絵柄層/樹脂層/樹脂層/プライマー層/表面保護層がこの順に積層された加飾シートの一例の略図的断面図を示す。 As the laminated structure of the decorative sheet of the present invention, a laminated structure in which a pattern layer / a solid layer is laminated in this order; a laminated structure in which a base material layer / a pattern layer / a solid layer are laminated in this order; a base material layer / a solid layer / Laminated structure in which the pattern layers are laminated in this order; Laminated structure in which the base material layer / pattern layer / solid layer / surface protection layer are laminated in this order; the base material layer / solid layer / pattern layer / surface protection layer are laminated in this order. Laminated structure; Substrate layer / Solid layer / Picture layer / Resin layer / Surface protection layer are laminated in this order; Base material layer / Solid layer / Picture layer / Resin layer / Primer layer / Surface protection layer Examples thereof include a laminated structure in which the layers are laminated in this order. In the example of the laminated structure, the ones described as the pattern layer, the solid layer, and the resin layer may be a plurality of pattern layers, a plurality of solid layers, and a plurality of resin layers, respectively. FIG. 1 shows a schematic cross-sectional view of an example of a decorative sheet in which a base material layer / solid layer / pattern layer / surface protection layer are laminated in this order as one aspect of the laminated structure of the decorative sheet in the present invention. FIG. 2 shows a schematic cross-sectional view of an example of a decorative sheet in which a base material layer / a pattern layer / a solid layer / a surface protection layer are laminated in this order as one aspect of the laminated structure of the decorative sheet in the present invention. FIG. 3 shows, as one aspect of the laminated structure of the decorative sheet in the present invention, the decorative sheet in which the base material layer / solid layer / pattern layer / resin layer / resin layer / primer layer / surface protection layer are laminated in this order. A schematic cross-sectional view of an example is shown.
加飾シートを形成する各層の組成Composition of each layer forming the decorative sheet
[絵柄層2]
本発明の加飾シートにおいては、顔料を含む絵柄層2が、積層体の水平方向xにおいて部分的に積層されており、かつ、絵柄層2に含まれるバインダー樹脂が、アクリル系樹脂を80質量%以上含む。本発明においては、このようなバインダー樹脂を用いた絵柄層2が部分的に積層されて絵柄が形成されているにも拘わらず、後述するベタ層3が積層されていることにより、加飾樹脂成形品の表面に高い平滑性を付与することが可能となっている。
[Picture layer 2]
In the decorative sheet of the present invention, the
具体的には、本発明者が検討を重ねたところ、図5に示されるように、加飾シートが積層された加飾樹脂成形品の表面においては、アクリル系樹脂を80質量%以上含むバインダー樹脂を含む絵柄層2が位置する領域5a(加飾樹脂成形品の表面の領域であって、積層体の積層方向yにおいて絵柄層2が位置する領域に対応する領域)は、加飾樹脂成形品の製造過程の熱と圧力によっても平坦性が維持されることが明らかとなった。一方、加飾シートに本発明におけるベタ層3が形成されていない場合には、絵柄層2が位置していない領域5bは、加飾樹脂成形品の製造過程の熱と圧力によって、加飾シートにおける平坦性が維持されず凸状に突出することが明らかとなった。このため、本発明のベタ層3を有しない加飾樹脂成形品の表面においては、絵柄層2が位置する領域5aと位置しない領域5bとによって、凹凸形状が形成されることになる。これに対して、後述の通り、本発明の加飾シートにおいては、アクリル系樹脂を80質量%以上含むバインダー樹脂を含むベタ層3が積層されているため、このような凹凸形状が形成されることを効果的に抑制することができ、加飾樹脂成形品の表面に高い平滑性を付与することができる。
Specifically, as a result of repeated studies by the present inventor, as shown in FIG. 5, a binder containing 80% by mass or more of acrylic resin on the surface of the decorative resin molded product on which the decorative sheet is laminated. The region 5a (the region on the surface of the decorative resin molded product and corresponding to the region in which the
絵柄層2は、顔料及びバインダー樹脂に加えて、必要に応じて、染料、体質顔料、溶剤、安定剤、可塑剤、触媒、硬化剤等を適宜混合したインキ組成物を用いて形成することができる。絵柄層2の形成過程において、溶剤は揮発するため、絵柄層2は、顔料、バインダー樹脂などの固形分により形成される。絵柄層2は、実質的に顔料及びバインダー樹脂のみにより形成されていてもよい。
The
絵柄層2において、バインダー樹脂に含まれるアクリル系樹脂の割合としては、80質量%以上であれば特に制限されないが、好ましくは80~100質量%程度、より好ましくは90~100質量%程度が挙げられる。絵柄層2を形成するバインダー樹脂におけるアクリル系樹脂の割合は、100質量%としてもよい。すなわち、バインダー樹脂は、実質的にアクリル系樹脂のみにより構成されていてもよい。アクリル系樹脂は、1種類単独で使用してもよいし、2種類以上を組み合わせて使用してもよい。
The proportion of the acrylic resin contained in the binder resin in the
アクリル系樹脂の具体例としては、好ましくはアクリル樹脂、アクリルポリオール樹脂などが挙げられる。アクリル樹脂としては、少なくとも(メタ)アクリル酸エステルモノマーを構成単位とするアクリル樹脂が好ましい。具体的には、(メタ)アクリル酸エステルモノマーの単独重合体、2種以上の異なる(メタ)アクリル酸エステルモノマーの共重合体、(メタ)アクリル酸エステルモノマーと他のモノマーとの共重合体などが挙げられる。アクリル樹脂は、1種類単独で使用してもよいし、2種類以上を組み合わせて使用してもよい。なお、本明細書において、「(メタ)アクリル」は、「アクリルまたはメタクリル」を意味し、他の類似するものも同様の意である。 Specific examples of the acrylic resin include acrylic resin, acrylic polyol resin and the like. As the acrylic resin, at least an acrylic resin containing a (meth) acrylic acid ester monomer as a constituent unit is preferable. Specifically, a homopolymer of a (meth) acrylic acid ester monomer, a copolymer of two or more different (meth) acrylic acid ester monomers, and a copolymer of a (meth) acrylic acid ester monomer and another monomer. And so on. One type of acrylic resin may be used alone, or two or more types may be used in combination. In addition, in this specification, "(meth) acrylic" means "acrylic or methacrylic", and other similar ones have the same meaning.
(メタ)アクリル酸エステルモノマーとしては、例えば、(メタ)アクリル酸メチル、(メタ)アクリル酸エチル、(メタ)アクリル酸プロピル、(メタ)アクリル酸シクロヘキシル、(メタ)アクリル酸ノルマルブチル、(メタ)アクリル酸イソブチル、(メタ)アクリル酸セカンダリーブチル、(メタ)アクリル酸ターシャリーブチル、(メタ)アクリル酸イソボニル、2-メチル-2-アダマンチル(メタ)アクリレート、2-エチル-2-アダマンチル(メタ)アクリレートなどが好ましく挙げられ、これらのうち(メタ)アクリル酸メチルがより好ましい。2種以上の異なる(メタ)アクリル酸エステルモノマーの共重合体としては、上記例示されたものから選ばれる2種以上の(メタ)アクリル酸エステルの共重合体が例示され、これらの共重合体はランダム共重合体であってもブロック共重合体であってもよい。 Examples of the (meth) acrylic acid ester monomer include methyl (meth) acrylate, ethyl (meth) acrylate, propyl (meth) acrylate, cyclohexyl (meth) acrylate, normal butyl (meth) acrylate, and (meth). ) Isobutyl acrylate, secondary butyl (meth) acrylate, tertiary butyl (meth) acrylate, isobonyl (meth) acrylate, 2-methyl-2-adamantyl (meth) acrylate, 2-ethyl-2-adamantyl (meth) ) Acrylate and the like are preferable, and among these, methyl (meth) acrylate is more preferable. Examples of the copolymer of two or more different (meth) acrylic acid ester monomers include copolymers of two or more (meth) acrylic acid esters selected from the above-exemplified ones, and these copolymers are exemplified. May be a random copolymer or a block copolymer.
(メタ)アクリル酸エステルモノマーと共重合体を形成する他のモノマーとしては、(メタ)アクリル酸エステルと共重合可能なものであれば特に限定されないが、本発明では、(メタ)アクリル酸、スチレン、(無水)マレイン酸、フマル酸、ジビニルベンゼン、ビニルビフェニル、ビニルナフタレン、ジフェニルエチレン、酢酸ビニル、塩化ビニル、フッ化ビニル、ビニルアルコール、アクリロニトリル、アクリルアミド、ブタジエン、イソプレン、イソブテン、1-ブテン、2-ブテン、N-ビニル-2-ピロリドン、ジシクロペンタジエン、エチリデンノルボルネン、ノルボルネン類などの脂環式オレフィンモノマー、ビニルカプロラクタム、シトラコン酸無水物、N-フェニルマレイミドなどのマレイミド類、ビニルエーテル類などが好ましく挙げられ、特にスチレン及び(無水)マレイン酸が共重合成分として好適である。すなわち、(メタ)アクリル酸エステルとスチレン又は(無水)マレイン酸の二元共重合体、(メタ)アクリル酸エステルとスチレン及び(無水)マレイン酸の三元共重合体が好適である。なお、(メタ)アクリル酸エステルと他のモノマーとの共重合体はランダム共重合体であってもブロック共重合体であってもよい。 The other monomer that forms a copolymer with the (meth) acrylic acid ester monomer is not particularly limited as long as it can be copolymerized with the (meth) acrylic acid ester, but in the present invention, the (meth) acrylic acid, Styrene, (maleic) maleic anhydride, fumaric acid, divinylbenzene, vinylbiphenyl, vinylnaphthalene, diphenylethylene, vinyl acetate, vinyl chloride, vinyl fluoride, vinyl alcohol, acrylonitrile, acrylamide, butadiene, isoprene, isobutene, 1-butene, Alicyclic olefin monomers such as 2-butene, N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone, dicyclopentadiene, etilidennorbornene, norbornenes, vinylcaprolactam, citraconic anhydride, maleimides such as N-phenylmaleimide, vinyl ethers, etc. Preferred are mentioned, and styrene and (maleic anhydride) maleic anhydride are particularly suitable as the copolymerization component. That is, a binary copolymer of (meth) acrylic acid ester and styrene or (maleic anhydride) maleic acid, and a ternary copolymer of (meth) acrylic acid ester and styrene and (maleic anhydride) maleic anhydride are suitable. The copolymer of the (meth) acrylic acid ester and the other monomer may be a random copolymer or a block copolymer.
また、アクリルポリオール樹脂としては、特に制限されないが、例えば、メチル(メタ)アクリレート、エチル(メタ)アクリレート、ブチル(メタ)アクリレート、2-エチルヘキシル(メタ)アクリレート、オクチル(メタ)アクリレートなどの(メタ)アクリル酸アルキルエステルと、2-ヒドロキシエチル(メタ)アクリレート、2-ヒドロキシブチル(メタ)アクリレート、2-ヒドロキシ-3-フェノキシプロピル(メタ)アクリレート等の分子中に水酸基を有する(メタ)アクリル酸エステルとを共重合させて得られるものが挙げられる。 The acrylic polyol resin is not particularly limited, and is, for example, (meth) such as methyl (meth) acrylate, ethyl (meth) acrylate, butyl (meth) acrylate, 2-ethylhexyl (meth) acrylate, and octyl (meth) acrylate. ) Acrylic acid alkyl ester and (meth) acrylic acid having a hydroxyl group in molecules such as 2-hydroxyethyl (meth) acrylate, 2-hydroxybutyl (meth) acrylate, and 2-hydroxy-3-phenoxypropyl (meth) acrylate. Examples thereof include those obtained by copolymerizing with an ester.
当該アクリル系樹脂の重量平均分子量としては、特に制限されないが、好ましくは30000~200000程度、より好ましくは70000~150000程度が挙げられる。なお、本明細書におけるアクリル系樹脂の重量平均分子量は、ゲルパーミエーションクロマトグラフィー法により、ポリスチレンを標準物質として測定した値である。 The weight average molecular weight of the acrylic resin is not particularly limited, but is preferably about 30,000 to 200,000, and more preferably about 70,000 to 150,000. The weight average molecular weight of the acrylic resin in the present specification is a value measured by a gel permeation chromatography method using polystyrene as a standard substance.
絵柄層2において、バインダー樹脂に含まれ得るアクリル系樹脂以外の他のバインダー樹脂としては、特に制限されないが、好ましくは塩素系樹脂、ポリウレタン、ポリエステル、ポリアミド、ブチラール樹脂、ポリスチレン、ニトロセルロース樹脂、酢酸セルロース樹脂等が挙げられ、好ましくは塩素系樹脂が挙げられる。好ましい塩素系樹脂としては、後述の樹脂層4で例示したものが挙げられる。これらの他のバインダー樹脂は、1種単独で使用してもよく、また2種以上を組み合わせて使用してもよい。
In the
絵柄層2は、加飾シートに装飾性を付与することなどを目的として、顔料を含む。顔料としては、特に制限されないが、好ましくは金属顔料、パール顔料、酸化チタン顔料などが挙げられる。本発明では、絵柄層2に含まれるバインダー樹脂がアクリル系樹脂を80質量%以上含むことにより、上記のような顔料を用いた場合でも耐候性が良好となる。また、絵柄層2に含まれる顔料としては、後述するベタ層3で例示した有機顔料、無機顔料なども挙げられる。顔料は、1種類単独で使用してもよいし、2種類以上を組み合わせて使用してもよい。
The
金属顔料としては、特に制限されないが、例えば、アルミニウム粉、真鍮粉、ステンレス鋼粉、錫粉、亜鉛粉、ブロンズ粉、ニッケル粉、銅粉、金粉、銀粉等や、これらの混合粉、これらの金属の合金粉などからなる顔料が挙げられる。 The metal pigment is not particularly limited, and is, for example, aluminum powder, brass powder, stainless steel powder, tin powder, zinc powder, bronze powder, nickel powder, copper powder, gold powder, silver powder, etc., a mixed powder thereof, and the like. Examples thereof include pigments made of metal alloy powder and the like.
パール顔料としては、例えば、表面部分に金属酸化物を含む粒子が挙げられる。このようなパール顔料としては、例えば、雲母等の鱗片状粒子の表面が金属酸化物で被覆された顔料が挙げられる。パール顔料に含まれる金属酸化物としては、加飾シートに光輝性の意匠を付与できるものであれば、特に制限されないが、例えば、チタン、鉄、ジルコニウム、ケイ素、アルミニウム、セリウムなどの金属の酸化物が挙げられる。金属酸化物としては、1種類単独で含んでいてもよいし、2種類以上を含んでいてよい。パール顔料の具体例としては、好ましくは二酸化チタン被覆雲母、酸化鉄被覆雲母、二酸化チタンと酸化鉄で被覆した雲母などが挙げられる。 Examples of the pearl pigment include particles containing a metal oxide on the surface portion. Examples of such pearl pigments include pigments in which the surface of scaly particles such as mica is coated with a metal oxide. The metal oxide contained in the pearl pigment is not particularly limited as long as it can impart a brilliant design to the decorative sheet, but for example, oxidation of metals such as titanium, iron, zirconium, silicon, aluminum, and cerium. Things can be mentioned. As the metal oxide, one type may be contained alone, or two or more types may be contained. Specific examples of the pearl pigment include titanium dioxide-coated mica, iron oxide-coated mica, and titanium dioxide-iron oxide-coated mica.
顔料の平均粒子径としては、特に制限されないが、通常1~500μm程度、好ましくは5~100μm程度が挙げられる。なお、本発明において、顔料の平均粒子径は、レーザー回折散乱法によって測定した体積基準粒度分布のメジアン径を意味する。 The average particle size of the pigment is not particularly limited, but is usually about 1 to 500 μm, preferably about 5 to 100 μm. In the present invention, the average particle size of the pigment means the median size of the volume-based particle size distribution measured by the laser diffraction / scattering method.
本発明の加飾シートにおいて、絵柄層2、後述のベタ層3、及び後述の樹脂層4によって加飾シートに表現される模様については、特に制限されないが、例えば、木目模様、大理石模様(例えばトラバーチン大理石模様)等の岩石の表面を模した石目模様、布目や布状の模様を模した布地模様、タイル貼模様、煉瓦積模様等が挙げられ、これらを複合した寄木、パッチワーク等の模様であってもよい。これらの模様は、通常の黄色、赤色、青色、及び黒色のプロセスカラーによる多色印刷によって形成されるが、模様を構成する個々の色の版を用意して行う特色による多色印刷等によっても形成することができる。
In the decorative sheet of the present invention, the pattern expressed on the decorative sheet by the
絵柄層2の厚みとしては、特に制限されないが、好ましくは1.0~5.0μm程度、より好ましくは1.5~3.0μm程度、さらに好ましくは2.0~3.0μm程度が挙げられる。なお、上述の通り、絵柄層2は複数積層されていてもよく、絵柄層2が複数積層される場合は、絵柄層2の合計厚みが、この範囲にあることが好ましい。
The thickness of the
絵柄層2は、例えば、インキ組成物を用いて印刷することにより、後述の基材層1、ベタ層3、必要に応じて形成される樹脂層4などの上に部分的に形成される。なお、絵柄層2は、後述のように、ベタ層3、必要に応じて形成される樹脂層4と共に転写用基材7の上に積層した後、当該転写用基材7を用いて基材層1の上などに転写して加飾シートに積層することが好ましい。絵柄層2は、積層体の水平方向xに部分的に印刷することにより形成することができる。絵柄層2を形成するための印刷方法については、特に制限されないが、例えば、グラビア印刷、オフセット印刷、シルクスクリーン印刷、転写シートからの転写による印刷、インクジェット印刷等が挙げられる。
The
[ベタ層3]
本発明の加飾シートにおいては、上記の絵柄層2と共に、ベタ層3が積層されており、ベタ層3に含まれるバインダー樹脂は、アクリル系樹脂を80質量%以上含む。上述の通り、本発明の加飾シートにおいては、バインダー樹脂にアクリル系樹脂を80質量%以上含むベタ層3が積層体の前面に積層されているため、上記の絵柄層2が部分的に積層されているにも拘わらず、加飾樹脂成形品の表面に高い平滑性を付与することができる。
[Solid layer 3]
In the decorative sheet of the present invention, the
ベタ層3は、バインダー樹脂に加えて、必要に応じて、顔料、染料、体質顔料、溶剤、安定剤、可塑剤、触媒、硬化剤等を適宜混合したインキ組成物を用いて形成することができる。ベタ層3の形成過程において、溶剤は揮発するため、ベタ層3は、バインダー樹脂などの固形分により形成される。ベタ層3は、実質的にバインダー樹脂のみにより形成されていてもよい。
The
ベタ層3において、バインダー樹脂に含まれるアクリル系樹脂の割合としては、80質量%以上であれば特に制限されないが、好ましくは80~100質量%程度、より好ましくは90~100質量%程度が挙げられる。ベタ層3を形成するバインダー樹脂におけるアクリル系樹脂の割合は、100質量%としてもよい。すなわち、バインダー樹脂は、実質的にアクリル系樹脂のみにより構成されていてもよい。アクリル系樹脂は、1種類単独で使用してもよいし、2種類以上を組み合わせて使用してもよい。
The proportion of the acrylic resin contained in the binder resin in the
アクリル系樹脂の具体例としては、特に制限されず、上記の絵柄層2で例示したものが挙げられる。
Specific examples of the acrylic resin are not particularly limited, and examples thereof include those exemplified in the above-mentioned
また、ベタ層3において、バインダー樹脂に含まれ得るアクリル系樹脂以外の他のバインダー樹脂としては、特に制限されず、上記の絵柄層2と同様とすることができる。
Further, in the
ベタ層3は、加飾シートに装飾性や隠蔽性を付与することなどを目的として、必要に応じて、顔料を含んでいてもよい。顔料としては、特に制限されないが、好ましくは無機顔料及び有機顔料が挙げられる。顔料は1種類単独で使用してもよいし、2種類以上を組み合わせて使用してもよい。無機顔料としては、特に制限されないが、例えば、カーボンブラック(墨)、鉄黒、チタン白、アンチモン白、黄鉛、チタン黄、弁柄、カドミウム赤、群青、コバルトブルー等が挙げられる。また有機顔料としては、キナクリドンレッド、イソインドリノンイエロー、フタロシアニンブルー等が挙げられる。
The
有機顔料及び無機顔料の平均粒子径としては、特に制限されないが、それぞれ、通常1~500μm程度、好ましくは5~100μm程度が挙げられる。なお、本発明において、有紀顔料及び無機顔料の平均粒子径は、それぞれ、レーザー回折散乱法によって測定した体積基準粒度分布のメジアン径を意味する。なお、ベタ層3には、絵柄層2例示した金属顔料、パール顔料、酸化チタン顔料などを含んでいてもよい。
The average particle size of the organic pigment and the inorganic pigment is not particularly limited, but is usually about 1 to 500 μm, preferably about 5 to 100 μm, respectively. In the present invention, the average particle size of the Yuki pigment and the inorganic pigment means the median diameter of the volume-based particle size distribution measured by the laser diffraction / scattering method, respectively. The
ベタ層3の厚みとしては、特に制限されないが、好ましくは0.5μm以上、より好ましくは1.0~5.0μm程度、さらに好ましくは1.0~3.0μm程度が挙げられる。絵柄層2がこのような厚みを有することにより、加飾樹脂成形品の表面に高い平滑性をより効果的に付与することが可能となる。なお、上述の通り、ベタ層3は複数積層されていてもよく、ベタ層3が複数積層される場合は、ベタ層3の合計厚みが、この範囲にあることが好ましい。
The thickness of the
ベタ層3は、例えば、インキ組成物を用いて印刷することにより、後述の基材層1、絵柄層2、必要に応じて形成される樹脂層4などの上に部分的に形成される。なお、ベタ層3は、後述のように、絵柄層2、必要に応じて形成される樹脂層4と共に転写用基材7の上に積層した後、当該転写用基材7を用いて基材層1の上などに転写して加飾シートに積層することが好ましい。ベタ層3は、積層体の水平方向xの全面に印刷することにより形成することができる。ベタ層3を形成するための印刷方法については、特に制限されないが、例えば、グラビア印刷、オフセット印刷、シルクスクリーン印刷、転写シートからの転写による印刷、インクジェット印刷等が挙げられる。
The
[樹脂層4]
本発明の加飾シートにおいては、上記の絵柄層2及びベタ層3と共に、必要に応じて、樹脂層4が積層されていてもよい。樹脂層4は、絵柄層2及びベタ層3とは異なるバインダー樹脂組成を有するインキ組成物により形成される層である。すなわち、樹脂層4に含まれるバインダー樹脂は、アクリル系樹脂の含有量が80質量%未満である。第3樹脂層は、バインダー樹脂を構成する樹脂の組成が異なること以外は、上記の絵柄層2またはベタ層3と同様とすることができる。また、樹脂層4は部分的に設けられていてもよく、全面に設けられてベタ層を形成してもよい。
[Resin layer 4]
In the decorative sheet of the present invention, the resin layer 4 may be laminated together with the above-mentioned
樹脂層4に含まれるバインダー樹脂としては、アクリル系樹脂の含有量が80質量%未満であれば特に制限されない。樹脂層4に含まれるバインダー樹脂としては、好ましくは塩素系樹脂の含有量が30質量%以上、より好ましくは40~100質量%程度、さらに好ましくは50~100質量%程度が挙げられる。樹脂層4に含まれるバインダー樹脂における塩素系樹脂の含有量を上記の範囲とすることで、樹脂層4を印刷により形成する際の印刷適正を良好とすることができる。このため、後述のように樹脂層4が着色剤を含有して装飾層を形成する場合において、本発明の加飾シートの意匠性を良好にすることができるため、特に好適である。樹脂層4を形成するバインダー樹脂における塩素系樹脂の割合は、100質量%としてもよい。すなわち、バインダー樹脂は、実質的に塩素系樹脂のみにより構成されていてもよい。塩素系樹脂は、1種類単独で使用してもよいし、2種類以上を組み合わせて使用してもよい。 The binder resin contained in the resin layer 4 is not particularly limited as long as the content of the acrylic resin is less than 80% by mass. The binder resin contained in the resin layer 4 preferably has a chlorine-based resin content of 30% by mass or more, more preferably about 40 to 100% by mass, and further preferably about 50 to 100% by mass. By setting the content of the chlorine-based resin in the binder resin contained in the resin layer 4 within the above range, the printability when the resin layer 4 is formed by printing can be improved. Therefore, when the resin layer 4 contains a colorant to form a decorative layer as described later, the decorative sheet of the present invention can be particularly suitable in terms of design. The proportion of the chlorine-based resin in the binder resin forming the resin layer 4 may be 100% by mass. That is, the binder resin may be substantially composed of only chlorine-based resin. One type of chlorine-based resin may be used alone, or two or more types may be used in combination.
塩素系樹脂の具体例としては、ポリ塩化ビニル、塩素化ポリエチレン、ポリ塩化ビニリデン、エチレン-塩化ビニル共重合体、塩化ビニル-酢酸ビニル共重合体、塩化ビニル-酢酸ビニル-(メタ)アクリル共重合体などのポリ塩化ビニル系樹脂、ポリ塩化プロピレン、塩素化ポリプロピレンなどが挙げられるが、特に好ましくはポリ塩化ビニル、エチレン-塩化ビニル共重合体、塩化ビニル-酢酸ビニル共重合体等の塩化ビニル系樹脂が挙げられる。 Specific examples of the chlorine-based resin include polyvinyl chloride, chlorinated polyethylene, polyvinylidene chloride, ethylene-vinyl chloride copolymer, vinyl chloride-vinyl acetate copolymer, vinyl chloride-vinyl acetate- (meth) acrylic copolymer weight. Examples thereof include polyvinyl chloride-based resins such as coalesced products, polyvinyl chloride, chlorinated polypropylene, etc., but particularly preferably polyvinyl chloride-based resins such as polyvinyl chloride, ethylene-vinyl chloride copolymer, and vinyl chloride-vinyl acetate copolymer. Resin is mentioned.
当該塩素系樹脂の重量平均分子量としては、特に制限されないが、好ましくは50000~200000程度、より好ましくは50000~100000程度が挙げられる。なお、本明細書における塩素系樹脂の重量平均分子量は、ゲルパーミエーションクロマトグラフィー法により、ポリスチレンを標準物質として測定した値である。 The weight average molecular weight of the chlorine-based resin is not particularly limited, but is preferably about 50,000 to 200,000, and more preferably about 50,000 to 100,000. The weight average molecular weight of the chlorine-based resin in the present specification is a value measured by a gel permeation chromatography method using polystyrene as a standard substance.
樹脂層4において、バインダー樹脂に含まれ得る塩素系樹脂以外の他のバインダー樹脂としては、特に制限されないが、好ましくはアクリル系樹脂、ポリウレタン、ポリエステル、ポリアミド、ブチラール樹脂、ポリスチレン、ニトロセルロース樹脂、酢酸セルロース樹脂等が挙げられ、好ましくはアクリル系樹脂が挙げられる。好ましいアクリル系樹脂としては、上記の絵柄層2で例示したものが挙げられる。これらの他のバインダー樹脂は、1種単独で使用してもよく、また2種以上を組み合わせて使用してもよい。
In the resin layer 4, the binder resin other than the chlorine-based resin that can be contained in the binder resin is not particularly limited, but is preferably acrylic resin, polyurethane, polyester, polyamide, butyral resin, polystyrene, nitrocellulose resin, acetic acid. Examples thereof include cellulose resins, and preferably acrylic resins. Preferred acrylic resins include those exemplified in the above-mentioned
樹脂層4は、加飾シートに装飾性を付与することなどを目的として、必要に応じて、着色剤を含んでいてもよい。すなわち、樹脂層4が装飾層を形成していてもよい。着色剤としては、特に制限されず、絵柄層2またはベタ層3で例示した顔料が挙げられる。また、絵柄層2、ベタ層3、及び樹脂層4の少なくとも1層によって、加飾シートに表現される模様については、上述の通りである。
The resin layer 4 may contain a colorant, if necessary, for the purpose of imparting decorativeness to the decorative sheet. That is, the resin layer 4 may form a decorative layer. The colorant is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include the pigments exemplified in the
樹脂層4の厚みとしては、特に制限されないが、好ましくは1~7μm程度、より好ましくは2~5μm程度、さらに好ましくは3~4μm程度が挙げられる。なお、上述の通り、樹脂層4は複数積層されていてもよく、樹脂層4が複数積層される場合は、樹脂層4の合計厚みが、この範囲にあることが好ましい。 The thickness of the resin layer 4 is not particularly limited, but is preferably about 1 to 7 μm, more preferably about 2 to 5 μm, and further preferably about 3 to 4 μm. As described above, a plurality of resin layers 4 may be laminated, and when a plurality of resin layers 4 are laminated, the total thickness of the resin layers 4 is preferably in this range.
樹脂層4は、例えば、インキ組成物を用いて印刷することにより、後述の基材層1、絵
柄層2、ベタ層3などの上に形成される。なお、樹脂層4は、後述のように、絵柄層2、ベタ層3と共に転写用基材7の上に積層した後、当該転写用基材7を用いて基材層1の上などに転写して加飾シートに積層することが好ましい。樹脂層4は、積層体の水平方向xの少なくとも一部分に印刷すればよい。すなわち、樹脂層4は、水平方向xに部分的に印刷してもよいし、全面に印刷してもよい。樹脂層4を複数層印刷する場合には、部分的に印刷した層と、全面に印刷した層とを組み合わせてもよい。樹脂層4を形成するための印刷方法については、特に制限されないが、例えば、グラビア印刷、オフセット印刷、シルクスクリーン印刷、転写シートからの転写による印刷、インクジェット印刷等が挙げられる。
The resin layer 4 is formed on the
[基材層1]
基材層1は、本発明の加飾シートにおいて支持体としての役割を果たすことを目的として、必要に応じて設けられる層である。基材層1は、樹脂シート(樹脂フィルム)により形成されている。基材層1に使用される樹脂成分については、特に制限されず、三次元成形性や成形樹脂層との相性等に応じて適宜選定すればよいが、好ましくは、熱可塑性樹脂が挙げられる。熱可塑性樹脂としては、具体的には、アクリロニトリル-ブタジエン-スチレン樹脂(以下「ABS樹脂」と表記することもある);アクリロニトリル-スチレン-アクリル酸エステル樹脂;アクリル樹脂;ポリプロピレン、ポリエチレン等のポリオレフィン系樹脂;ポリカーボネート樹脂;塩化ビニル系樹脂;ポリエチレンテレフタラート(PET)樹脂等が挙げられる。これらの中でも、ABS樹脂が三次元成形性の観点から好ましい。基材層1を形成する樹脂成分としては、1種類のみを用いてもよいし、2種類以上を混合して用いてもよい。また、基材層1は、これら樹脂の単層シートで形成されていてもよく、また同種又は異種樹脂による複層シートで形成されていてもよい。
[Base material layer 1]
The
基材層1は、隣接する層との密着性を向上させるために、必要に応じて、片面又は両面に酸化法や凹凸化法等の物理的又は化学的表面処理が施されていてもよい。基材層1の表面処理として行われる酸化法としては、例えば、コロナ放電処理、プラズマ処理、クロム酸化処理、火炎処理、熱風処理、オゾン紫外線処理法等が挙げられる。また、基材層1の表面処理として行われる凹凸化法としては、例えばサンドブラスト法、溶剤処理法等が挙げられる。これらの表面処理は、基材層1を構成する樹脂成分の種類に応じて適宜選択されるが、効果及び操作性等の観点から、好ましくはコロナ放電処理法が挙げられる。
The
また、基材層1には、着色剤などを配合した着色、色彩を整えるための塗装、デザイン性を付与するための模様の形成などがなされていてもよい。
Further, the
基材層1の厚みは、特に制限されず、加飾シートの用途等に応じて適宜設定されるが、通常50~800μm程度、好ましくは100~600μm程度、さらに好ましくは200~500μm程度が挙げられる。基材層1の厚みが上記範囲内であると、加飾シートに対してより一層優れた三次元成形性、意匠性などを備えさせることができる。
The thickness of the
[表面保護層5]
表面保護層5は、加飾シートの耐薬品性、耐傷付き性などを高めるために、加飾樹脂成形品の最表面に位置するようにして、必要に応じて設けられる層である。本発明において、表面保護層5を形成する樹脂としては、特に制限されず、熱硬化性樹脂、熱可塑性樹脂、電離放射線硬化性樹脂などが挙げられる。これらの中でも、加飾樹脂成形品の表面の平滑性をより効果的に高め、さらに、耐傷付き性を高め、優れた表面特性を付与する観点からは、電離放射線硬化性樹脂が好ましいが、表面保護層5を形成する樹脂は、加飾シートの用途に応じて適宜選択することができる。また、表面保護層5は、樹脂フィルムにより形成してもよい。樹脂フィルムとしては、後述の熱可塑性樹脂または熱硬化性樹脂により形成された樹脂フィルムフィルムが挙げられる。表面保護層5は、例えば電離放射線硬化性樹脂または樹脂フィルムの1層により形成されていてもよいし、これらの2層以上により形成されていてもよい。
[Surface protection layer 5]
The surface
熱硬化性樹脂としては、特に制限されず、例えば、エポキシ樹脂、フェノール樹脂、ユリア樹脂、不飽和ポリエステル樹脂、メラミン樹脂、アルキド樹脂、ポリイミド樹脂、シリコーン樹脂、水酸基官能性アクリル樹脂、カルボキシル官能性アクリル樹脂、アミド官能性共重合体、ウレタン樹脂などが挙げられる。また、熱可塑性樹脂としては、特に制限されず、ポリメチル(メタ)アクリレート、ポリエチル(メタ)アクリレートなどのアクリル樹脂;ポリプロピレン、ポリエチレン等のポリオレフィン系樹脂;ポリカーボネート樹脂;塩化ビニル系樹脂;ポリエチレンテレフタレート(PET)、ポリブチレンテレフタレート(PBT)、ポリエチレンナフタレート(PEN)などのポリエステル樹脂;アクリロニトリル-ブタジエン-スチレン樹脂(ABS樹脂);アクリロニトリル-スチレン-アクリル酸エステル樹脂;などが挙げられる。 The thermosetting resin is not particularly limited, and for example, epoxy resin, phenol resin, urea resin, unsaturated polyester resin, melamine resin, alkyd resin, polyimide resin, silicone resin, hydroxyl group functional acrylic resin, and carboxyl functional acrylic. Examples thereof include resins, amide functional copolymers, and urethane resins. The thermoplastic resin is not particularly limited, and acrylic resins such as polymethyl (meth) acrylate and polyethyl (meth) acrylate; polyolefin resins such as polypropylene and polyethylene; polycarbonate resins; vinyl chloride resins; polyethylene terephthalates (PET). ), Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) and other polyester resins; acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene resin (ABS resin); acrylonitrile-styrene-acrylic acid ester resin; and the like.
(電離放射線硬化性樹脂)
表面保護層5の形成に使用される電離放射線硬化性樹脂とは、電離放射線を照射することにより、架橋、硬化する樹脂であり、具体的には、分子中に重合性不飽和結合又はエポキシ基を有する、プレポリマー、オリゴマー、及びモノマーなどのうち少なくとも1種を適宜混合したものが挙げられる。ここで電離放射線とは、電磁波又は荷電粒子線のうち、分子を重合あるいは架橋しうるエネルギー量子を有するものを意味し、通常紫外線(UV)又は電子線(EB)が用いられるが、その他、X線、γ線等の電磁波、α線、イオン線等の荷電粒子線も含むものである。電離放射線硬化性樹脂の中でも、電子線硬化性樹脂は、無溶剤化が可能であり、光重合用開始剤を必要とせず、安定な硬化特性が得られるため、表面保護層5の形成において好適に使用される。
(Ionizing radiation curable resin)
The ionizing radiation curable resin used for forming the surface
電離放射線硬化性樹脂として使用される上記モノマーとしては、分子中にラジカル重合性不飽和基を持つ(メタ)アクリレートモノマーが好適であり、中でも多官能性(メタ)アクリレートモノマーが好ましい。多官能性(メタ)アクリレートモノマーとしては、分子内に重合性不飽和結合を2個以上(2官能以上)、好ましくは3個以上(3官能以上)有する(メタ)アクリレートモノマーであればよい。多官能性(メタ)アクリレートとして、具体的には、エチレングリコールジ(メタ)アクリレート、プロピレングリコールジ(メタ)アクリレート、1,4-ブタンジオールジ(メタ)アクリレート、1,6-ヘキサンジオールジ(メタ)アクリレート、ネオペンチルグリコールジ(メタ)アクリレート、ポリエチレングリコールジ(メタ)アクリレート、ヒドロキシピバリン酸ネオペンチルグリコールジ(メタ)アクリレート、ジシクロペンタニルジ(メタ)アクリレート、カプロラクトン変性ジシクロペンテニルジ(メタ)アクリレート、エチレンオキシド変性リン酸ジ(メタ)アクリレート、アリル化シクロヘキシルジ(メタ)アクリレート、イソシアヌレートジ(メタ)アクリレート、トリメチロールプロパントリ(メタ)アクリレート、エチレンオキシド変性トリメチロールプロパントリ(メタ)アクリレート、ジペンタエリスリトールトリ(メタ)アクリレート、プロピオン酸変性ジペンタエリスリトールトリ(メタ)アクリレート、ペンタエリスリトールトリ(メタ)アクリレート、プロピレンオキシド変性トリメチロールプロパントリ(メタ)アクリレート、トリス(アクリロキシエチル)イソシアヌレート、プロピオン酸変性ジペンタエリスリトールペンタ(メタ)アクリレート、ジペンタエリスリトールヘキサ(メタ)アクリレート、エチレンオキシド変性ジペンタエリスリトールヘキサ(メタ)アクリレート、カプロラクトン変性ジペンタエリスリトールヘキサ(メタ)アクリレート等が挙げられる。これらのモノマーは、1種単独で使用してもよく、また2種以上を組み合わせて使用してもよい。 As the above-mentioned monomer used as the ionizing radiation curable resin, a (meth) acrylate monomer having a radically polymerizable unsaturated group in the molecule is preferable, and a polyfunctional (meth) acrylate monomer is particularly preferable. The polyfunctional (meth) acrylate monomer may be a (meth) acrylate monomer having two or more (bifunctional or more), preferably three or more (trifunctional or more) polymerizable unsaturated bonds in the molecule. Specific examples of the polyfunctional (meth) acrylate include ethylene glycol di (meth) acrylate, propylene glycol di (meth) acrylate, 1,4-butanediol di (meth) acrylate, and 1,6-hexanediol di (). Meta) acrylate, neopentyl glycol di (meth) acrylate, polyethylene glycol di (meth) acrylate, hydroxypivalate neopentyl glycol di (meth) acrylate, dicyclopentanyldi (meth) acrylate, caprolactone-modified dicyclopentenyldi (meth) Meta) acrylate, ethylene oxide-modified di (meth) acrylate, allylated cyclohexyl di (meth) acrylate, isocyanurate di (meth) acrylate, trimethylol propanetri (meth) acrylate, ethylene oxide-modified trimethylol propanetri (meth) acrylate , Dipentaerythritol tri (meth) acrylate, propionic acid-modified dipentaerythritol tri (meth) acrylate, pentaerythritol tri (meth) acrylate, propylene oxide-modified trimethylol propanetri (meth) acrylate, tris (acryloxyethyl) isocyanurate , Propionic acid-modified dipentaerythritol penta (meth) acrylate, dipentaerythritol hexa (meth) acrylate, ethylene oxide-modified dipentaerythritol hexa (meth) acrylate, caprolactone-modified dipentaerythritol hexa (meth) acrylate and the like. These monomers may be used alone or in combination of two or more.
また、電離放射線硬化性樹脂として使用される上記オリゴマーとしては、分子中にラジカル重合性不飽和基を持つ(メタ)アクリレートオリゴマーが好適であり、中でも分子内に重合性不飽和結合を2個以上(2官能以上)有する多官能性(メタ)アクリレートオリゴマーが好ましい。多官能性(メタ)アクリレートオリゴマーとしては、例えば、ポリカーボネート(メタ)アクリレート、アクリルシリコーン(メタ)アクリレート、ウレタン(メタ)アクリレート、エポキシ(メタ)アクリレート、ポリエステル(メタ)アクリレート、ポリエーテル(メタ)アクリレート、ポリブタジエン(メタ)アクリレート、シリコーン(メタ)アクリレート、分子中にカチオン重合性官能基を有するオリゴマー(例えば、ノボラック型エポキシ樹脂、ビスフェノール型エポキシ樹脂、脂肪族ビニルエーテル、芳香族ビニルエーテル等)等が挙げられる。ここで、ポリカーボネート(メタ)アクリレートは、ポリマー主鎖にカーボネート結合を有し、かつ末端または側鎖に(メタ)アクリレート基を有するものであれば特に制限されず、例えば、ポリカーボネートポリオールを(メタ)アクリル酸でエステル化することにより得ることができる。ポリカーボネート(メタ)アクリレートは、例えば、ポリカーボネート骨格を有するウレタン(メタ)アクリレートなどであってもよい。ポリカーボネート骨格を有するウレタン(メタ)アクリレートは、例えば、ポリカーボネートポリオールと、多価イソシアネート化合物と、ヒドロキシ(メタ)アクリレートとを反応させることにより得られる。アクリルシリコーン(メタ)アクリレートは、シリコーンマクロモノマーを(メタ)アクリレートモノマーとラジカル共重合させることにより得ることができる。ウレタン(メタ)アクリレートは、例えば、ポリエーテルポリオールやポリエステルポリオールとポリイソシアネート化合物の反応によって得られるポリウレタンオリゴマーを、(メタ)アクリル酸でエステル化することにより得ることができる。エポキシ(メタ)アクリレートは、例えば、比較的低分子量のビスフェノール型エポキシ樹脂やノボラック型エポキシ樹脂のオキシラン環に、(メタ)アクリル酸を反応しエステル化することにより得ることができる。また、このエポキシ(メタ)アクリレートを部分的に二塩基性カルボン酸無水物で変性したカルボキシル変性型のエポキシ(メタ)アクリレートも用いることができる。ポリエステル(メタ)アクリレートは、例えば多価カルボン酸と多価アルコールの縮合によって得られる両末端に水酸基を有するポリエステルオリゴマーの水酸基を(メタ)アクリル酸でエステル化することにより、或いは多価カルボン酸にアルキレンオキシドを付加して得られるオリゴマーの末端の水酸基を(メタ)アクリル酸でエステル化することにより得ることができる。ポリエーテル(メタ)アクリレートは、ポリエーテルポリオールの水酸基を(メタ)アクリル酸でエステル化することにより得ることができる。ポリブタジエン(メタ)アクリレートは、ポリブタジエンオリゴマーの側鎖に(メタ)アクリル酸を付加することにより得ることができる。シリコーン(メタ)アクリレートは、主鎖にポリシロキサン結合をもつシリコーンの末端又は側鎖に(メタ)(メタ)アクリル酸を付加することにより得ることができる。これらの中でも、多官能性(メタ)アクリレートオリゴマーとしては、ポリカーボネート(メタ)アクリレート、ウレタン(メタ)アクリレートなどが特に好ましい。これらのオリゴマーは、1種単独で使用してもよく、また2種以上を組み合わせて使用してもよい。 Further, as the above-mentioned oligomer used as an ionizing radiation curable resin, a (meth) acrylate oligomer having a radically polymerizable unsaturated group in the molecule is suitable, and among them, two or more polymerizable unsaturated bonds in the molecule. A polyfunctional (meth) acrylate oligomer having (bifunctional or higher) is preferable. Examples of the polyfunctional (meth) acrylate oligomer include polycarbonate (meth) acrylate, acrylic silicone (meth) acrylate, urethane (meth) acrylate, epoxy (meth) acrylate, polyester (meth) acrylate, and polyether (meth) acrylate. , Polybutadiene (meth) acrylate, silicone (meth) acrylate, oligomers having a cationically polymerizable functional group in the molecule (for example, novolak type epoxy resin, bisphenol type epoxy resin, aliphatic vinyl ether, aromatic vinyl ether, etc.) and the like. .. Here, the polycarbonate (meth) acrylate is not particularly limited as long as it has a carbonate bond in the polymer main chain and has a (meth) acrylate group in the terminal or side chain, and for example, a polycarbonate polyol (meth) is used. It can be obtained by esterification with acrylic acid. The polycarbonate (meth) acrylate may be, for example, urethane (meth) acrylate having a polycarbonate skeleton. Urethane (meth) acrylate having a polycarbonate skeleton can be obtained, for example, by reacting a polycarbonate polyol with a polyhydric isocyanate compound and a hydroxy (meth) acrylate. Acrylic silicone (meth) acrylate can be obtained by radically copolymerizing a silicone macromonomer with a (meth) acrylate monomer. Urethane (meth) acrylate can be obtained, for example, by esterifying a polyurethane oligomer obtained by reacting a polyether polyol or a polyester polyol with a polyisocyanate compound with (meth) acrylic acid. Epoxy (meth) acrylate can be obtained, for example, by reacting (meth) acrylic acid with an oxylan ring of a relatively low molecular weight bisphenol type epoxy resin or a novolak type epoxy resin to esterify it. Further, a carboxyl-modified epoxy (meth) acrylate obtained by partially modifying this epoxy (meth) acrylate with a dibasic carboxylic acid anhydride can also be used. The polyester (meth) acrylate can be obtained, for example, by esterifying the hydroxyl group of a polyester oligomer having hydroxyl groups at both ends obtained by condensation of a polyvalent carboxylic acid and a polyhydric alcohol with (meth) acrylic acid, or to a polyvalent carboxylic acid. It can be obtained by esterifying the hydroxyl group at the end of the oligomer obtained by adding an alkylene oxide with (meth) acrylic acid. The polyether (meth) acrylate can be obtained by esterifying the hydroxyl group of the polyether polyol with (meth) acrylic acid. Polybutadiene (meth) acrylate can be obtained by adding (meth) acrylic acid to the side chain of the polybutadiene oligomer. The silicone (meth) acrylate can be obtained by adding (meth) (meth) acrylic acid to the terminal or side chain of a silicone having a polysiloxane bond in the main chain. Among these, as the polyfunctional (meth) acrylate oligomer, polycarbonate (meth) acrylate, urethane (meth) acrylate and the like are particularly preferable. These oligomers may be used alone or in combination of two or more.
上記した電離放射線硬化性樹脂の中でも、優れた三次元成形性を得る観点からは、ポリカーボネート(メタ)アクリレートを用いることが好ましい。また、三次元成形性と耐傷付き性を両立する観点からは、ポリカーボネート(メタ)アクリレートとウレタン(メタ)アクリレートを組み合わせて使用することがより好ましい。 Among the above-mentioned ionizing radiation curable resins, it is preferable to use polycarbonate (meth) acrylate from the viewpoint of obtaining excellent three-dimensional moldability. Further, from the viewpoint of achieving both three-dimensional moldability and scratch resistance, it is more preferable to use a combination of polycarbonate (meth) acrylate and urethane (meth) acrylate.
(他の添加成分)
表面保護層5を形成する電離放射線硬化性樹脂組成物には、表面保護層5に備えさせる所望の物性に応じて、上記の無機粒子及び有機粒子の他、各種添加剤を配合することができる。この添加剤としては、例えば紫外線吸収剤や光安定剤等の耐候性改善剤、耐摩耗性向上剤、重合禁止剤、架橋剤、赤外線吸収剤、帯電防止剤、接着性向上剤、レベリング剤、チクソ性付与剤、カップリング剤、可塑剤、消泡剤、充填剤、溶剤、着色剤、マット剤等が挙げられる。これらの添加剤は、常用されるものから適宜選択して用いることができ、例えばマット剤としてはシリカ粒子や水酸化アルミニウム粒子等が挙げられる。また、紫外線吸収剤や光安定剤として、分子内に(メタ)アクリロイル基等の重合性基を有する反応性の紫外線吸収剤や光安定剤を用いることもできる。
(Other additive ingredients)
In addition to the above-mentioned inorganic particles and organic particles, various additives can be added to the ionizing radiation curable resin composition forming the surface
(表面保護層5の厚み)
表面保護層5の厚みについては、特に制限されないが、好ましくは30μm以下、より好ましくは5~20μm程度、より好ましくは7~15μm程度が挙げられる。本発明者らの知見によれば、絵柄層2のバインダー樹脂としてアクリル系樹脂を用いることにより加飾樹脂成形品の平滑性が損なわれるという課題は、表面保護層5の厚みが例えば30μm以下のように薄い場合に生じやすいが、本発明の加飾シートはベタ層3を備えることにより、表面保護層5の厚みを上記のような範囲とした場合であっても、加飾樹脂成形品の表面を平滑にすることができる。さらに、このような範囲の厚みを満たすと、耐傷付き性、耐候性等の表面保護層としての十分な物性が得られると共に、表面保護層5を電離放射線硬化性樹脂を用いて形成する場合には電離放射線を均一に照射することが可能であるため、均一に硬化することが可能となり、経済的にも有利になる。また、表面保護層5の硬化後の厚みが前記範囲を充足することによって、加飾シートの三次元成形性が一層向上するため自動車内装用途等の複雑な三次元形状に対して高い追従性を得ることができる。このように、本発明の加飾シートは表面保護層5の厚みを従来のものより厚くしても、十分に高い三次元成形性が得られることから、特に表面保護層5に高い膜厚を要求される部材、例えば車両外装部品等の加飾シートとしても有用である。なお、表面保護層5を電離放射線硬化性樹脂などの硬化性樹脂を用いて形成する場合、上記の厚みは硬化後の厚みを示す。
(Thickness of surface protective layer 5)
The thickness of the surface
(電離放射線硬化性樹脂を用いる場合の表面保護層5の形成)
表面保護層5の形成は、例えば、電離放射線硬化性樹脂を含む電離放射線硬化性樹脂組成物を調製し、これを塗布し、架橋硬化することにより行われる。なお、電離放射線硬化性樹脂組成物の粘度は、後述の塗布方式により、表面保護層5の下に位置する絵柄層2、ベタ層3、樹脂層4、プライマー層6などの層の表面に未硬化樹脂層を形成し得る粘度であればよい。
(Formation of surface
The surface
本発明においては、調製された塗布液を、前記厚みとなるように、表面保護層5の下に位置する層の上に、グラビアコート、バーコート、ロールコート、リバースロールコート、コンマコート等の公知の方式、好ましくはグラビアコートにより塗布し、未硬化樹脂層を形成させる。
In the present invention, the prepared coating liquid is applied onto a layer located under the surface
このようにして形成された未硬化樹脂層に、電子線、紫外線等の電離放射線を照射して該未硬化樹脂層を硬化させて表面保護層5を形成する。ここで、電離放射線として電子線を用いる場合、その加速電圧については、用いる樹脂や層の厚みに応じて適宜選定し得るが、通常加速電圧70~300kV程度が挙げられる。
The uncured resin layer thus formed is irradiated with ionizing radiation such as an electron beam and ultraviolet rays to cure the uncured resin layer to form the surface
なお、電子線の照射において、加速電圧が高いほど透過能力が増加するため、表面保護層5の下に電子線照射によって劣化しやすい樹脂を使用する場合には、電子線の透過深さと表面保護層5の厚みが実質的に等しくなるように、加速電圧を選定する。これにより、表面保護層5の下に位置する層への余分の電子線の照射を抑制することができ、過剰電子線による各層の劣化を最小限にとどめることができる。
In electron beam irradiation, the higher the acceleration voltage, the higher the transmission capacity. Therefore, when a resin that is easily deteriorated by electron beam irradiation is used under the
また、照射線量は、表面保護層5の架橋密度が飽和する量が好ましく、通常5~300kGy(0.5~30Mrad)、好ましくは10~50kGy(1~5Mrad)の範囲で選定される。
The irradiation dose is preferably an amount at which the crosslink density of the surface
更に、電子線源としては、特に制限はなく、例えばコックロフトワルトン型、バンデグラフト型、共振変圧器型、絶縁コア変圧器型、直線型、ダイナミトロン型、高周波型等の各種電子線加速器を用いることができる。 Further, the electron beam source is not particularly limited, and various electron beam accelerators such as a cockloft Walton type, a van de Graaff type, a resonance transformer type, an insulated core transformer type, a linear type, a dynamitron type, and a high frequency type can be used. Can be used.
電離放射線として紫外線を用いる場合には、波長190~380nmの紫外線を含む光線を放射すればよい。紫外線源としては、特に制限されないが、例えば、高圧水銀燈、低圧水銀燈、メタルハライドランプ、カーボンアーク燈、紫外線発光ダイオード(LED-UV)等が挙げられる。 When ultraviolet rays are used as ionizing radiation, light rays including ultraviolet rays having a wavelength of 190 to 380 nm may be emitted. The ultraviolet source is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include a high-pressure mercury lamp, a low-pressure mercury lamp, a metal halide lamp, a carbon arc lamp, and an ultraviolet light emitting diode (LED-UV).
かくして形成された表面保護層5には、各種の添加剤を添加することにより、ハードコート機能、防曇コート機能、防汚コート機能、防眩コート機能、反射防止コート機能、紫外線遮蔽コート機能、赤外線遮蔽コート機能等の機能を付与する処理を行ってもよい。
By adding various additives to the surface
なお、表面保護層5を樹脂フィルムにより形成する場合には、表面保護層5の下に位置する層の上に樹脂フィルムを積層すればよい。なお、樹脂フィルムとしては、上記した他の添加剤を含む樹脂フィルムや、サンドブラスト加工等の表面加工を施された樹脂フィルムを用いることもできる。
When the surface
[プライマー層6]
プライマー層6は、表面保護層5とその下に位置する絵柄層2、ベタ層3、樹脂層4などの層との密着性を高めることなどを目的として、必要に応じて含まれる層である。プライマー層6は、樹脂により形成することができる。
[Primer layer 6]
The primer layer 6 is a layer included as necessary for the purpose of enhancing the adhesion between the surface
プライマー層6を形成する樹脂としては、特に制限されないが、例えば、ウレタン樹脂、アクリル樹脂、(メタ)アクリル-ウレタン共重合体樹脂、ポリエステル樹脂、ブチラール樹脂等が挙げられる。これらの樹脂の中でも、好ましくは、ウレタン樹脂、アクリル樹脂、及び(メタ)アクリル-ウレタン共重合体樹脂が挙げられる。これらの樹脂は、1種単独で使用してもよく、また2種以上を組み合わせて使用してもよい。 The resin forming the primer layer 6 is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include a urethane resin, an acrylic resin, a (meth) acrylic-urethane copolymer resin, a polyester resin, and a butyral resin. Among these resins, urethane resin, acrylic resin, and (meth) acrylic-urethane copolymer resin are preferable. These resins may be used alone or in combination of two or more.
上記ウレタン樹脂としては、ポリオール(多価アルコール)を主剤とし、イソシアネートを架橋剤(硬化剤)とするポリウレタンを使用できる。ポリオールとしては、分子中に2個以上の水酸基を有する化合物であればよく、具体的には、ポリエステルポリオール、ポリエチレングリコール、ポリプロピレングリコール、アクリルポリオール、ポリエーテルポリオール等が挙げられる。上記イソシアネートとしては、具体的には、分子中に2個以上のイソシアネート基を有する多価イソシアネート;4,4-ジフェニルメタンジイソシアネート等の芳香族イソシアネート;ヘキサメチレンジイソシアネート、イソホロンジイソシアネート、水素添加トリレンジイソシアネート、水素添加ジフェニルメタンジイソシアネート等の脂肪族(又は脂環族)イソシアネートが挙げられる。 As the urethane resin, polyurethane having a polyol (polyhydric alcohol) as a main component and an isocyanate as a cross-linking agent (curing agent) can be used. The polyol may be a compound having two or more hydroxyl groups in the molecule, and specific examples thereof include polyester polyols, polyethylene glycols, polypropylene glycols, acrylic polyols, and polyether polyols. Specific examples of the isocyanate include polyvalent isocyanates having two or more isocyanate groups in the molecule; aromatic isocyanates such as 4,4-diphenylmethane diisocyanate; hexamethylene diisocyanates, isophorone diisocyanates, and hydrogenated tolylene diisocyanates. Examples thereof include aliphatic (or alicyclic group) isocyanates such as hydrogenated diphenylmethane diisocyanate.
上記ウレタン樹脂の中でも、架橋後の密着性の向上等の観点から、好ましくは、ポリオールとしてアクリルポリオール、又はポリエステルポリオールと、架橋材としてヘキサメチレンジイソシアネート、4,4-ジフェニルメタンジイソシアネートとから組み合わせ;さらに好ましくは、アクリルポリオールとヘキサメチレンジイソシアネートとを組み合わせが挙げられる。 Among the above urethane resins, from the viewpoint of improving adhesion after cross-linking, a combination of an acrylic polyol or a polyester polyol as a polyol and a hexamethylene diisocyanate or a 4,4-diphenylmethane diisocyanate as a cross-linking material is preferable; more preferably. Is a combination of an acrylic polyol and a hexamethylene diisocyanate.
上記アクリル樹脂としては、特に制限されないが、例えば、(メタ)アクリル酸エステルの単独重合体、2種以上の異なる(メタ)アクリル酸エステルモノマーの共重合体、又は(メタ)アクリル酸エステルと他のモノマーとの共重合体が挙げられる。(メタ)アクリル樹脂として、より具体的には、ポリ(メタ)アクリル酸メチル、ポリ(メタ)アクリル酸エチル、ポリ(メタ)アクリル酸プロピル、ポリ(メタ)アクリル酸ブチル、(メタ
)アクリル酸メチル-(メタ)アクリル酸ブチル共重合体、(メタ)アクリル酸エチル-(メタ)アクリル酸ブチル共重合体、エチレン-(メタ)アクリル酸メチル共重合体、スチレン-(メタ)アクリル酸メチル共重合体等の(メタ)アクリル酸エステル等が挙げられる。これらのアクリル樹脂は、1種単独で使用してもよく、また2種以上を組み合わせて使用してもよい。
The acrylic resin is not particularly limited, and is, for example, a homopolymer of a (meth) acrylic acid ester, a copolymer of two or more different (meth) acrylic acid ester monomers, or a (meth) acrylic acid ester and others. Examples thereof include a copolymer with the monomer of. More specifically, the (meth) acrylic resin includes methyl poly (meth) acrylate, ethyl poly (meth) acrylate, propyl poly (meth) acrylate, butyl poly (meth) acrylate, and (meth) acrylic acid. Methyl- (meth) butyl acrylate copolymer, ethyl (meth) acrylate- (meth) butyl acrylate copolymer, ethylene- (meth) methyl acrylate copolymer, styrene-methyl acrylate- (meth) acrylate Examples thereof include (meth) acrylic acid esters such as polymers. These acrylic resins may be used alone or in combination of two or more.
(メタ)アクリル-ウレタン共重合体樹脂としては、特に制限されないが、例えば、アクリル-ウレタン(ポリエステルウレタン)ブロック共重合系樹脂が挙げられる。また、硬化剤としては、前述する各種イソシアネートが用いられる。アクリル-ウレタン(ポリエステルウレタン)ブロック共重合系樹脂におけるアクリルとウレタン比の比率については、特に制限されないが、例えば、アクリル/ウレタン比(質量比)として、9/1~1/9、好ましくは8/2~2/8が挙げられる。 The (meth) acrylic-urethane copolymer resin is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include an acrylic-urethane (polyester urethane) block copolymer resin. Further, as the curing agent, the above-mentioned various isocyanates are used. The ratio of acrylic to urethane in the acrylic-urethane (polyester urethane) block copolymer resin is not particularly limited, but for example, the acrylic / urethane ratio (mass ratio) is 9/1 to 1/9, preferably 8. / 2 to 2/8 can be mentioned.
プライマー層6の厚みについては、特に制限されないが、例えば0.1~10μm程度、好ましくは1~10μm程度が挙げられる。プライマー層6がこのような厚みを充足することにより、加飾シートの耐候性をより高めると共に、表面保護層5の割れ、破断、白化等を有効に抑制することができる。
The thickness of the primer layer 6 is not particularly limited, but may be, for example, about 0.1 to 10 μm, preferably about 1 to 10 μm. By satisfying such a thickness of the primer layer 6, the weather resistance of the decorative sheet can be further enhanced, and cracking, breaking, whitening and the like of the surface
プライマー層6は、プライマー層6を形成する樹脂を用いて、グラビアコート、グラビアリバースコート、グラビアオフセットコート、スピンナーコート、ロールコート、リバースロールコート、キスコート、ホイラーコート、ディップコート、シルクスクリーンによるベタコート、ワイヤーバーコート、フローコート、コンマコート、かけ流しコート、刷毛塗り、スプレーコート等の通常の塗布方法や転写コーティング法により形成される。ここで、転写コーティング法とは、薄いシート(フィルム基材)にプライマー層や接着層の塗膜を形成し、その後に加飾シート中の対象となる層表面に被覆する方法である。 The primer layer 6 is a gravure coat, a gravure reverse coat, a gravure offset coat, a spinner coat, a roll coat, a reverse roll coat, a kiss coat, a wheeler coat, a dip coat, and a solid coat with a silk screen, using the resin forming the primer layer 6. It is formed by a usual coating method such as wire bar coat, flow coat, comma coat, flow coat, brush coat, spray coat, or transfer coating method. Here, the transfer coating method is a method in which a coating film of a primer layer or an adhesive layer is formed on a thin sheet (film base material), and then the surface of the target layer in the decorative sheet is coated.
[接着層8]
接着層8は、加飾シートと成形樹脂層9との密着性や接着性を向上させることなどを目的として、基材層1の裏面に必要に応じて設けられる層である。接着層8を形成する樹脂としては、加飾シートと成形樹脂層9との密着性や接着性を向上させることができるものであれば、特に制限されず、例えば、熱可塑性樹脂または熱硬化性樹脂が用いられる。熱可塑性樹脂としては、例えば、アクリル樹脂、アクリル変性ポリオレフィン樹脂、塩素化ポリオレフィン樹脂、塩化ビニル-酢酸ビニル共重合体、熱可塑性ウレタン樹脂、熱可塑性ポリエステル樹脂、ポリアミド樹脂、ゴム系樹脂などが挙げられる。熱可塑性樹脂は、1種類単独で使用してもよいし、2種類以上を組み合わせて使用してもよい。また、熱硬化性樹脂としては、例えば、ウレタン樹脂、エポキシ樹脂等挙げられる。熱硬化性樹脂は、1種類単独で使用してもよいし、2種類以上を組み合わせて使用してもよい。
[Adhesive layer 8]
The adhesive layer 8 is a layer provided on the back surface of the
接着層8は必ずしも必要な層ではないが、本発明の加飾シートを、後述する真空圧着法など、予め用意された樹脂成形体上へ貼着による加飾方法に適用することを想定した場合は、設けられていることが好ましい。真空圧着法に用いる場合、上記した各種の樹脂のうち、加圧又は加熱により接着性を発現する樹脂として慣用のものを使用して接着層8を形成することが好ましい。 Although the adhesive layer 8 is not necessarily a necessary layer, it is assumed that the decorative sheet of the present invention is applied to a decorative method by sticking on a resin molded body prepared in advance, such as a vacuum crimping method described later. Is preferably provided. When used in the vacuum crimping method, it is preferable to form the adhesive layer 8 by using a conventional resin that develops adhesiveness by pressurization or heating among the various resins described above.
接着層8の厚みは、特に制限されないが、例えば、0.1~30μm程度、好ましくは0.5~20μm程度、さらに好ましくは1~8μm程度が挙げられる。 The thickness of the adhesive layer 8 is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include about 0.1 to 30 μm, preferably about 0.5 to 20 μm, and more preferably about 1 to 8 μm.
加飾シートの製造方法
本発明の加飾シートは、例えば次の工程を備える方法により製造することができる。
転写シート作製工程:転写用基材の上に、アクリル樹脂を80質量%以上含むバインダー樹脂及び顔料を含む絵柄層を部分的に積層する工程と、アクリル樹脂を80質量%以上含むバインダー樹脂を含むベタ層を積層する工程とを行い、転写シートを作製する。
転写工程:転写シートに積層された前記絵柄層及びベタ層を基材上に転写する。
Method for Manufacturing Decorative Sheet The decorative sheet of the present invention can be manufactured, for example, by a method including the following steps.
Transfer sheet preparation step: A step of partially laminating a binder resin containing 80% by mass or more of acrylic resin and a pattern layer containing a pigment on a transfer substrate, and a binder resin containing 80% by mass or more of acrylic resin are included. A transfer sheet is produced by performing the steps of laminating the solid layer.
Transfer step: The pattern layer and the solid layer laminated on the transfer sheet are transferred onto the substrate.
(転写シート作製工程)
図4に示されるように、本発明の加飾シートの製造方法においては、まず、転写シート作製工程を行う。転写シート作製工程においては、転写用基材7の上に、絵柄層2を部分的に積層する工程と、ベタ層3を積層する工程とを行う。また、転写シート作製工程においては、必要に応じて、樹脂層4を積層する工程を行う。絵柄層2、ベタ層3、及び樹脂層4の積層は、上述の通り、印刷などにより行うことができる。転写シート作製工程においては、所望の加飾シートの積層構造となるようにして、転写用基材7の上に絵柄層2、ベタ層3、必要に応じて樹脂層4を積層する。また、プライマー層6を備える加飾シートを製造する場合、転写シート作製工程において、絵柄層2などの形成に先立って転写用基材7の上にプライマー層6を形成してもよく、後述の転写工程後、表面保護層形成工程においてプライマー層6を形成してもよい。
(Transfer sheet manufacturing process)
As shown in FIG. 4, in the method for manufacturing a decorative sheet of the present invention, first, a transfer sheet manufacturing step is performed. In the transfer sheet manufacturing step, a step of partially laminating the
[転写用基材7]
本発明において、転写用基材7は、絵柄層2、ベタ層3、必要に応じて設けられる樹脂層4やプライマー層6を基材層1の上に積層するために用いられる。本発明で用いられる転写用基材7は、代表的には熱可塑性樹脂からなる樹脂シートが使用される。該熱可塑性樹脂としては、ポリエステル樹脂;アクリル樹脂;ポリプロピレン、ポリエチレン等のポリオレフィン樹脂;ポリカーボネート樹脂;アクリロニトリル-ブタジエン-スチレン樹脂(ABS樹脂);塩化ビニル樹脂等が挙げられる。
[Transfer substrate 7]
In the present invention, the
転写用基材7としては、絵柄層2、ベタ層3、必要に応じて設けられる樹脂層4の剥離性などの観点から、これらの中でもポリエステルシートを用いることがこのましい。ポリエステルシートを構成するポリエステル樹脂とは、多価カルボン酸と、多価アルコールとから重縮合によって得られるエステル基を含むポリマーを示し、ポリエチレンテレフタレート(PET)、ポリブチレンテレフタレート(PBT)、ポリエチレンナフタレート(PEN)などを好ましく挙げることができ、ポリエチレンテレフタレート(PET)が特に好ましい。
As the
転写用基材7の厚みは、通常10~150μmであり、10~125μmが好ましく、10~80μmがより好ましい。また、転写用基材7としては、これら樹脂の単層シート、あるいは同種又は異種樹脂による複層シートを用いることができる。
The thickness of the
[離型層]
離型層は、転写用基材7と絵柄層2、ベタ層3、必要に応じて設けられる樹脂層4やプライマー層6との剥離性を高めることなどを目的として、必要に応じて、転写用基材7の絵柄層2、ベタ層3、必要に応じて設けられる樹脂層4やプライマー層6が積層される側の表面に設けられる。離型層は、全面を被覆(全面ベタ状)しているベタ離型層であってもよいし、一部に設けられるものであってもよい。通常は、剥離性を考慮して、ベタ離型層が好ましい。
[Release layer]
The release layer is transferred as necessary for the purpose of enhancing the releasability between the
離型層は、シリコーン系樹脂、フッ素系樹脂、アクリル系樹脂(例えば、アクリル-メラミン系樹脂が含まれる。)、ポリエステル系樹脂、ポリオレフィン系樹脂、ポリスチレン系樹脂、ポリウレタン系樹脂、セルロース系樹脂、塩化ビニル-酢酸ビニル系共重合体樹脂、硝化綿などの熱可塑性樹脂、該熱可塑性樹脂を形成するモノマーの共重合体、あるいはこれらの樹脂を(メタ)アクリル酸やウレタンで変性したものを、単独で又は複数を混合した樹脂組成物を用いて形成することができる。なかでも、アクリル系樹脂、ポリエ
ステル系樹脂、ポリオレフィン系樹脂、ポリスチレン系樹脂、これらの樹脂を形成するモノマーの共重合体、及びこれらをウレタン変性したものが好ましく、より具体的には、アクリル-メラミン系樹脂単独、アクリル-メラミン系樹脂含有組成物、ポリエステル系樹脂とエチレン及びアクリル酸の共重合体をウレタン変性したものとを混合した樹脂組成物、アクリル系樹脂とスチレン及びアクリルとの共重合体のエマルションとを混合した樹脂組成物などが挙げられる。これらの内、アクリル-メラミン系樹脂単独又はアクリル-メラミン系樹脂を50質量%以上含有組成物で離型層を構成することが特に好ましい。
The release layer includes a silicone resin, a fluororesin, an acrylic resin (for example, an acrylic-melamine resin is included), a polyester resin, a polyolefin resin, a polystyrene resin, a polyurethane resin, and a cellulose resin. Vinyl chloride-vinyl acetate copolymer resin, thermoplastic resin such as vitrified cotton, copolymer of the monomer forming the thermoplastic resin, or these resins modified with (meth) acrylic acid or urethane. It can be formed by using a resin composition alone or by mixing a plurality of them. Among them, acrylic resins, polyester resins, polyolefin resins, polystyrene resins, copolymers of monomers forming these resins, and urethane-modified products thereof are preferable, and more specifically, acrylic-melamine. A resin composition alone, an acrylic-melamine resin-containing composition, a resin composition obtained by mixing a polyester resin with a urethane-modified copolymer of ethylene and acrylic acid, and a copolymer of an acrylic resin and styrene and acrylic. Examples thereof include a resin composition mixed with the above emulsion. Of these, it is particularly preferable to form the release layer with a composition containing acrylic-melamine resin alone or acrylic-melamine resin in an amount of 50% by mass or more.
離型層の厚みは、通常、0.01~5μm程度であり、好ましくは、0.05~3μm程度である。 The thickness of the release layer is usually about 0.01 to 5 μm, preferably about 0.05 to 3 μm.
(転写工程)
次に、図3に示されるように、転写工程を行う。転写工程においては、転写シートに積層された絵柄層2、ベタ層3、必要に応じて設けられる樹脂層4やプライマー層6を基材上に転写する。すなわち、転写シートの転写用基材7とは反対側を、基材層1の表面上に積層する。このとき、基材層1の表面を溶融させて、転写シートの転写用基材7とは反対側を基材層1の表面上に積層することにより、転写シートを基材層1の上に熱融着させることができる。次に、得られた積層体の表面に位置する転写用基材7を剥離することにより、基材層1の上に絵柄層2、ベタ層3、必要に応じて設けられる樹脂層4やプライマー層6が転写された加飾シートが得られる。
(Transfer process)
Next, a transfer step is performed as shown in FIG. In the transfer step, the
(表面保護層形成工程)
本発明の加飾シートに表面保護層5を設ける場合、上記の転写工程の後、表面保護層5を積層する表面保護層形成工程を行ってもよい。表面保護層5の積層は、上記のようにして行うことができる。また、表面保護層5とその下に位置する層との密着性を高めることなどを目的として、表面保護層5を積層する前に、必要に応じて、プライマー層6を積層してもよい。表面保護層5は、プライマー層6と同様、絵柄層2、ベタ層3などを形成する前に転写用基材1に設けてもよい。
(Surface protective layer forming process)
When the surface
2.加飾樹脂成形品
本発明の加飾樹脂成形品は、本発明の加飾シートに成形樹脂を一体化させることにより成形されてなるものである。即ち、本発明の加飾樹脂成形品は、少なくとも、成形樹脂層の上に、絵柄層と、ベタ層とが積層された積層体からなり、当該積層体において、絵柄層が部分的に積層されており、絵柄層に含まれるバインダー樹脂が、アクリル系樹脂を80質量%以上含み、ベタ層に含まれるバインダー樹脂が、アクリル系樹脂を80質量%以上含むことを特徴とする。本発明の加飾樹脂成形品では、必要に応じて、加飾シートに上述の基材層1、樹脂層4、表面保護層5、プライマー層6、接着層8などの少なくとも1層がさらに設けられていてもよい。
2. 2. Decorative Resin Molded Product The decorative resin molded product of the present invention is formed by integrating a molding resin into the decorative sheet of the present invention. That is, the decorative resin molded product of the present invention is composed of a laminated body in which a pattern layer and a solid layer are laminated on at least the molded resin layer, and the pattern layer is partially laminated in the laminated body. The binder resin contained in the pattern layer contains 80% by mass or more of the acrylic resin, and the binder resin contained in the solid layer contains 80% by mass or more of the acrylic resin. In the decorative resin molded product of the present invention, at least one layer such as the above-mentioned
本発明の加飾樹脂成形品は、例えば、本発明の加飾シートを用いて、インサート成形法、射出成形同時加飾法、ブロー成形法、ガスインジェクション成形法等の各種射出成形法により作製される。これらの射出成形法の中でも、好ましくはインサート成形法及び射出成形同時加飾法が挙げられる。また、本発明の加飾樹脂成形品は、真空圧着法等の、予め用意された立体的な樹脂成形体(成形樹脂層)上に、本発明の加飾シートを貼着する加飾方法によっても作製することができる。 The decorative resin molded product of the present invention is produced by various injection molding methods such as an insert molding method, an injection molding simultaneous decoration method, a blow molding method, and a gas injection molding method, for example, using the decorative sheet of the present invention. To. Among these injection molding methods, an insert molding method and an injection molding simultaneous decoration method are preferably mentioned. Further, the decorative resin molded product of the present invention is prepared by a decorative method such as a vacuum crimping method in which a decorative sheet of the present invention is attached onto a three-dimensional resin molded body (molded resin layer) prepared in advance. Can also be produced.
インサート成形法では、まず、真空成形工程において、本発明の加飾シートを真空成形型により予め成形品表面形状に真空成形(オフライン予備成形)し、次いで必要に応じて余分な部分をトリミングして成形シートを得る。この成形シートを射出成形型に挿入し、射出成形型を型締めし、流動状態の樹脂を型内に射出し、固化させて、射出成形と同時に
樹脂成形物の外表面に加飾シートを一体化させることにより、加飾樹脂成形品が製造される。
In the insert molding method, first, in the vacuum forming step, the decorative sheet of the present invention is vacuum-formed (offline pre-molding) into the surface shape of the molded product in advance by a vacuum forming mold, and then the excess portion is trimmed if necessary. Obtain a molded sheet. This molding sheet is inserted into an injection molding mold, the injection molding mold is molded, the fluid resin is injected into the mold and solidified, and the decorative sheet is integrated on the outer surface of the resin molded product at the same time as the injection molding. By making it a decorative resin molded product, a decorative resin molded product is manufactured.
より具体的には、下記の工程を含むインサート成形法によって、本発明の加飾樹脂成形品が製造される。
本発明の加飾シートを真空成形型により予め立体形状に成形する真空成形工程、
真空成形された加飾シートの余分な部分をトリミングして成形シートを得るトリミング工程、及び
成形シートを射出成形型に挿入し、射出成形型を閉じ、流動状態の樹脂を射出成形型内に射出して樹脂と成形シートを一体化する一体化工程。
More specifically, the decorative resin molded product of the present invention is manufactured by an insert molding method including the following steps.
A vacuum forming step of forming the decorative sheet of the present invention into a three-dimensional shape in advance using a vacuum forming mold.
The trimming process to obtain a molded sheet by trimming the excess part of the vacuum-formed decorative sheet, and the molding sheet is inserted into the injection molding mold, the injection molding mold is closed, and the fluid resin is injected into the injection molding mold. An integration process that integrates the resin and the molded sheet.
インサート成形法における真空成形工程では、加飾シートを加熱して成形してもよい。この時の加熱温度は、特に限定されず、加飾シートを構成する樹脂の種類や、加飾シートの厚みなどによって適宜選択すればよいが、通常120~200℃程度とすることができる。また、一体化工程において、流動状態の樹脂の温度は、特に限定されないが、通常180~320℃程度とすることができる。 In the vacuum forming step in the insert molding method, the decorative sheet may be heated and molded. The heating temperature at this time is not particularly limited, and may be appropriately selected depending on the type of resin constituting the decorative sheet, the thickness of the decorative sheet, and the like, but is usually about 120 to 200 ° C. Further, in the integration step, the temperature of the resin in the flowing state is not particularly limited, but can usually be about 180 to 320 ° C.
また、射出成形同時加飾法では、本発明の加飾シートを射出成形の吸引孔が設けられた真空成形型との兼用雌型に配置し、この雌型で予備成形(インライン予備成形)を行った後、射出成形型を型締めして、流動状態の樹脂を型内に射出充填し、固化させて、射出成形と同時に樹脂成形物の外表面に本発明の加飾シートを一体化させることにより、加飾樹脂成形品が製造される。 Further, in the injection molding simultaneous decoration method, the decoration sheet of the present invention is placed in a female mold that also serves as a vacuum molding mold provided with a suction hole for injection molding, and pre-molding (in-line pre-molding) is performed with this female mold. After that, the injection molding mold is molded, the fluid resin is injection-filled in the mold and solidified, and at the same time as the injection molding, the decorative sheet of the present invention is integrated on the outer surface of the resin molded product. As a result, a decorative resin molded product is manufactured.
より具体的には、下記の工程を含む射出成形同時加飾法によって、本発明の加飾樹脂成形品が製造される。
本発明の加飾シートを、所定形状の成形面を有する可動金型の当該成形面に対し、加飾シートの表面が対面するように設置した後、当該加飾シートを加熱、軟化させると共に、可動金型側から真空吸引して、軟化した加飾シートを当該可動金型の成形面に沿って密着させることにより、加飾シートを予備成形する予備成形工程、
成形面に沿って密着された加飾シートを有する可動金型と固定金型とを型締めした後、両金型で形成されるキャビティ内に、流動状態の樹脂を射出、充填して固化させることにより樹脂成形体を形成し、樹脂成形体と加飾シートを積層一体化させる一体化工程、及び
可動金型を固定金型から離間させて、加飾シート全層が積層されてなる樹脂成形体を取り出す取出工程。
More specifically, the decorative resin molded product of the present invention is produced by an injection molding simultaneous decoration method including the following steps.
After installing the decorative sheet of the present invention so that the surface of the decorative sheet faces the molded surface of the movable mold having a molded surface of a predetermined shape, the decorative sheet is heated and softened, and at the same time, the decorative sheet is heated and softened. Pre-molding step of pre-molding a decorative sheet by vacuum suctioning from the movable mold side and bringing the softened decorative sheet into close contact with the molding surface of the movable mold.
After the movable mold having the decorative sheet adhered along the molding surface and the fixed mold are molded, a fluid resin is injected, filled and solidified in the cavity formed by both molds. As a result, a resin molded body is formed, and an integration step of laminating and integrating the resin molded body and the decorative sheet, and resin molding in which all layers of the decorative sheet are laminated by separating the movable mold from the fixed mold. Extraction process to take out the body.
射出成形同時加飾法の予備成形工程において、加飾シートの加熱温度は、特に限定されず、加飾シートを構成する樹脂の種類や、加飾シートの厚みなどによって適宜選択すればよいが、通常70~130℃程度とすることができる。また、射出成形工程において、流動状態の樹脂の温度は、特に限定されないが、通常180~320℃程度とすることができる。 In the preforming process of the injection molding simultaneous decoration method, the heating temperature of the decorative sheet is not particularly limited, and may be appropriately selected depending on the type of resin constituting the decorative sheet, the thickness of the decorative sheet, and the like. Usually, it can be about 70 to 130 ° C. Further, in the injection molding step, the temperature of the resin in the fluid state is not particularly limited, but can usually be about 180 to 320 ° C.
真空圧着法では、まず、上側に位置する第1真空室及び下側に位置する第2真空室からなる真空圧着機内に、本発明の加飾シート及び樹脂成形体を、加飾シートが第1真空室側、樹脂成形体が第2真空室側となるように真空圧着機内に設置し、2つの真空室を真空状態とする。樹脂成形体は、第2真空室側に備えられた、上下に昇降可能な昇降台上に設置される。次いで、第1の真空室を加圧すると共に、昇降台を用いて成形体を加飾シートに押し当て、2つの真空室間の圧力差を利用して、加飾シートを延伸しながら樹脂成形体の表面に貼着する。最後に2つの真空室を大気圧に開放し、必要に応じて加飾シートの余分な部分をトリミングすることにより、本発明の加飾樹脂成形品を得ることができる。 In the vacuum crimping method, first, the decorative sheet and the resin molded body of the present invention are placed in a vacuum crimping machine consisting of a first vacuum chamber located on the upper side and a second vacuum chamber located on the lower side. The resin molded body is installed in the vacuum crimping machine so that the vacuum chamber side and the resin molded body are on the second vacuum chamber side, and the two vacuum chambers are put into a vacuum state. The resin molded body is installed on an elevating table that can be raised and lowered up and down, which is provided on the second vacuum chamber side. Next, while pressurizing the first vacuum chamber, the molded body is pressed against the decorative sheet using an elevating table, and the resin molded body is stretched while stretching the decorative sheet by utilizing the pressure difference between the two vacuum chambers. Stick on the surface of. Finally, the decorative resin molded product of the present invention can be obtained by opening the two vacuum chambers to atmospheric pressure and trimming the excess portion of the decorative sheet as needed.
真空圧着法においては、上記の成形体を加飾シートに押し当てる工程の前に、加飾シートを軟化させて成形性を高めるため、加飾シートを加熱する工程を備えることが好ましい。当該工程を備える真空圧着法は、特に真空加熱圧着法と呼ばれることがある。当該工程における加熱温度は、加飾シートを構成する樹脂の種類や、加飾シートの厚みなどによって適宜選択すればよいが、通常60~200℃程度とすることができる。 In the vacuum crimping method, it is preferable to include a step of heating the decorative sheet in order to soften the decorative sheet and improve the moldability before the step of pressing the molded body against the decorative sheet. The vacuum crimping method including this step may be particularly called a vacuum heating crimping method. The heating temperature in the step may be appropriately selected depending on the type of resin constituting the decorative sheet, the thickness of the decorative sheet, and the like, but is usually about 60 to 200 ° C.
本発明の加飾樹脂成形品において、成形樹脂層は、用途に応じた樹脂を選択して形成すればよい。成形樹脂層を形成する成形樹脂としては、熱可塑性樹脂であってもよく、また熱硬化性樹脂であってもよい。 In the decorative resin molded product of the present invention, the molded resin layer may be formed by selecting a resin according to the intended use. The molding resin forming the molding resin layer may be a thermoplastic resin or a thermosetting resin.
熱可塑性樹脂としては、例えば、ポリエチレン、ポリプロピレン等のポリオレフィン系樹脂、ABS樹脂、スチレン樹脂、ポリカーボネート樹脂、アクリル樹脂、塩化ビニル系樹脂等が挙げられる。これらの熱可塑性樹脂は、1種単独で使用してもよく、また2種以上を組み合わせて使用してもよい。 Examples of the thermoplastic resin include polyolefin resins such as polyethylene and polypropylene, ABS resins, styrene resins, polycarbonate resins, acrylic resins, vinyl chloride resins and the like. These thermoplastic resins may be used alone or in combination of two or more.
また、熱硬化性樹脂としては、例えば、ウレタン樹脂、エポキシ樹脂等が挙げられる。これらの熱硬化性樹脂は、1種単独で使用してもよく、また2種以上を組み合わせて使用してもよい。 Examples of the thermosetting resin include urethane resin and epoxy resin. These thermosetting resins may be used alone or in combination of two or more.
上述の通り、本発明の加飾樹脂成形品は、高い平滑性を有するため、例えば、自動車等の車両の内装材又は外装材;窓枠、扉枠等の建具;壁、床、天井等の建築物の内装材;テレビ受像機、空調機等の家電製品の筐体;容器等として利用することができる。 As described above, since the decorative resin molded product of the present invention has high smoothness, for example, interior or exterior materials of vehicles such as automobiles; fittings such as window frames and door frames; walls, floors, ceilings, etc. It can be used as an interior material for buildings; housings for home appliances such as television receivers and air conditioners; and containers.
以下に、実施例及び比較例を示して本発明を詳細に説明する。ただし、本発明は、実施例に限定されない。 Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail with reference to Examples and Comparative Examples. However, the present invention is not limited to the examples.
(加飾シートの作製)
<実施例1>
下記の手順により、加飾シートを作製した。
1.転写シート作製工程
転写用基材としてのポリエチレンテレフタレート(PET)フィルム(厚み25μm)の表面上に、アクリルウレタン樹脂からなるプライマー層を形成した。プライマー層の厚みは約1μmとした。次に、塩化ビニル-酢酸ビニル共重合体50質量%及びアクリル樹脂50質量%の混合樹脂をバインダー樹脂としたインキ組成物を4回部分的に印刷して、樹脂層を4層形成した。各樹脂層の厚みは約1.0μmとした。次に、アクリル樹脂からなるバインダー樹脂とパール顔料を含むインキ組成物を厚み約2.0μmとなるように部分的に印刷して、絵柄層を形成した。次に、アクリル樹脂からなるバインダー樹脂とパール顔料を含むインキ組成物を厚み約1.5μmとなるように全面に印刷して、ベタ層を形成した。ベタ層の表面に、塩化ビニル-酢酸ビニル共重合体50質量%及びアクリル樹脂50質量%の混合樹脂からなるバインダー樹脂を用いたインキ組成物を2回全面に印刷して、樹脂層を2層形成した。このとき、各樹脂層の厚みは約1.5μmとした。以上のようにして、転写用基材/部分的に形成された樹脂層(4層)/部分的に形成された絵柄層/全面に形成されたベタ層/全面に形成された樹脂層(2層)が順に積層された転写シートを作製した。
(Making a decorative sheet)
<Example 1>
A decorative sheet was prepared by the following procedure.
1. 1. Transfer sheet manufacturing process
A primer layer made of acrylic urethane resin was formed on the surface of a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film (thickness 25 μm) as a transfer substrate. The thickness of the primer layer was about 1 μm. Next, an ink composition using a mixed resin of 50% by mass of a vinyl chloride-vinyl acetate copolymer and 50% by mass of an acrylic resin as a binder resin was partially printed four times to form four resin layers. The thickness of each resin layer was about 1.0 μm. Next, an ink composition containing a binder resin made of an acrylic resin and a pearl pigment was partially printed so as to have a thickness of about 2.0 μm to form a pattern layer. Next, an ink composition containing a binder resin made of an acrylic resin and a pearl pigment was printed on the entire surface so as to have a thickness of about 1.5 μm to form a solid layer. An ink composition using a binder resin composed of a mixed resin of 50% by mass of a vinyl chloride-vinyl acetate copolymer and 50% by mass of an acrylic resin was printed twice on the entire surface of the solid layer, and the resin layer was printed on the entire surface twice. Formed. At this time, the thickness of each resin layer was set to about 1.5 μm. As described above, a transfer substrate / a partially formed resin layer (4 layers) / a partially formed pattern layer / a solid layer formed on the entire surface / a resin layer formed on the entire surface (2). A transfer sheet in which layers) were laminated in order was produced.
2.転写工程
基材層としてのABSフィルム(厚み400μm)の一方側の面を約170℃に加熱して溶融させた。この溶融面に対して、上記で得られた転写シートを転写用基材とは反対側から積層して熱融着させ、その後、室温(25℃)まで冷却した。次に、得られた積層体から転写用基材を剥離して、基材の上に絵柄層、ベタ層、及び樹脂層を転写した。
2. 2. One side of the ABS film (thickness 400 μm) as the transfer step substrate layer was heated to about 170 ° C. and melted. The transfer sheet obtained above was laminated on this molten surface from the side opposite to the transfer substrate and heat-fused, and then cooled to room temperature (25 ° C.). Next, the transfer substrate was peeled off from the obtained laminate, and the pattern layer, the solid layer, and the resin layer were transferred onto the substrate.
3.表面保護層形成工程
転写工程で得られた積層体の表面に位置する樹脂層の表面に、2官能ポリカーボネートアクリレート(重量平均分子量10,000)80質量部及び6官能ウレタンアクリレート(重量平均分子量6,000)20質量部を含む電子線硬化性樹脂を、硬化後の厚みが10μmとなるようにバーコートにより塗工し、未硬化の電子線硬化性樹脂からなる表面保護層を形成した。次に、未硬化の表面保護層に対して、加速電圧195kV、照射線量50kGy(5Mrad)の電子線を照射して、電子線硬化性樹脂を硬化させて、表面保護層を形成した。以上の手順により加飾シートを得た。
3. 3. Surface protective layer forming step On the surface of the resin layer located on the surface of the laminate obtained in the transfer step, 80 parts by mass of bifunctional polycarbonate acrylate (weight average molecular weight 10,000) and hexafunctional urethane acrylate (weight average molecular weight 6,) 000) An electron beam curable resin containing 20 parts by mass was coated with a bar coat so that the thickness after curing was 10 μm to form a surface protective layer made of an uncured electron beam curable resin. Next, the uncured surface protective layer was irradiated with an electron beam having an acceleration voltage of 195 kV and an irradiation dose of 50 kGy (5Mrad) to cure the electron beam curable resin to form a surface protective layer. A decorative sheet was obtained by the above procedure.
<実施例2>
上記の転写シート作製工程において、ベタ層を形成した後、絵柄層を形成したこと以外は、実施例1と同様にして、加飾シートを得た。
<Example 2>
A decorative sheet was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that a solid layer was formed and then a pattern layer was formed in the above transfer sheet manufacturing step.
<実施例3>
ベタ層を形成するインキ組成物にパール顔料を配合しなかったこと以外は、実施例2と同様にして、加飾シートを得た。
<Example 3>
A decorative sheet was obtained in the same manner as in Example 2 except that the pearl pigment was not blended in the ink composition forming the solid layer.
<比較例1>
ベタ層を形成しなかったこと以外は、実施例1と同様にして、加飾シートを得た。
<Comparative Example 1>
A decorative sheet was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the solid layer was not formed.
(加飾樹脂成形品の作製)
上記で得られた各加飾シートを、それぞれを真空成形機(布施真空社製「VPF-T1」)に配し、ヒーターにて表面温度が170℃になるまで加熱し、真空成形を行った。真空成形品を取り出し、トリミングした後、射出成形を行った。成形用樹脂としては、ポリカーボネートとABS樹脂の混合物(商品名:サイコロイIP1000BK GEプラスチック製)を用いた。
(Manufacturing of decorative resin molded products)
Each of the decorative sheets obtained above was placed in a vacuum forming machine (“VPF-T1” manufactured by Fuse Vacuum Co., Ltd.) and heated with a heater until the surface temperature reached 170 ° C. to perform vacuum forming. .. The vacuum formed product was taken out, trimmed, and then injection molded. As the molding resin, a mixture of polycarbonate and ABS resin (trade name: Psycholoy IP1000BK GE plastic) was used.
(平滑性の評価)
実施例1~3及び比較例1の加飾シートから得られた上記の加飾樹脂成形品の表面に斜光を照射して、表面を目視で観察した際の平滑性を以下の基準により評価した。結果を表1に示す。
◎:絵柄層によって形成された絵柄に同調した凹凸形状が全く観察されず、鏡面性が高い。
○:絵柄層によって形成された絵柄に同調した凹凸形状が観察されない。
△:絵柄層によって形成された絵柄に同調した凹凸形状が若干観察されるが、観察する角度を変えると観察されなくなる。
×:絵柄層によって形成された絵柄に同調した凹凸形状が、いずれの角度からも観察される。
(Evaluation of smoothness)
The surface of the decorative resin molded product obtained from the decorative sheets of Examples 1 to 3 and Comparative Example 1 was irradiated with oblique light, and the smoothness when the surface was visually observed was evaluated according to the following criteria. .. The results are shown in Table 1.
⊚: The uneven shape synchronized with the pattern formed by the pattern layer is not observed at all, and the mirror surface is high.
◯: The uneven shape synchronized with the pattern formed by the pattern layer is not observed.
Δ: The uneven shape synchronized with the pattern formed by the pattern layer is slightly observed, but it is not observed when the observation angle is changed.
X: The uneven shape synchronized with the pattern formed by the pattern layer is observed from any angle.
1…基材層
2…絵柄層
3…ベタ層
4…樹脂層
41…樹脂層
42…樹脂層
5…表面保護層
6…プライマー層
7…転写用基材
8…接着層
9…成形樹脂層
1 ...
Claims (6)
前記積層体において、前記絵柄層は、部分的に積層されており、
前記絵柄層に含まれるバインダー樹脂が、アクリル系樹脂を80質量%以上含み、前記アクリル系樹脂は、アクリル樹脂及びアクリルポリオール樹脂の少なくとも一方であり、
前記顔料がパール顔料であり、
前記ベタ層に含まれるバインダー樹脂が、アクリル系樹脂を80質量%以上含み、前記アクリル系樹脂は、アクリル樹脂及びアクリルポリオール樹脂の少なくとも一方であり、
前記表面保護層の厚みは30μm以下である、三次元成形用加飾シート。 At least, a surface protective layer located on the outermost surface, a pattern layer containing a pigment (excluding those containing a compound having at least two or more acryloyl groups in one molecule), a solid layer, and a base material layer are formed. It is a decorative sheet composed of laminated bodies laminated in this order.
In the laminated body, the pattern layer is partially laminated, and is
The binder resin contained in the pattern layer contains 80% by mass or more of an acrylic resin, and the acrylic resin is at least one of an acrylic resin and an acrylic polyol resin.
The pigment is a pearl pigment,
The binder resin contained in the solid layer contains 80% by mass or more of the acrylic resin, and the acrylic resin is at least one of the acrylic resin and the acrylic polyol resin.
A decorative sheet for three-dimensional molding, wherein the surface protective layer has a thickness of 30 μm or less.
前記転写シートに積層された前記絵柄層及びベタ層を基材上に転写する転写工程と、
前記転写工程の後、さらに厚みが30μm以下の最表面に位置する表面保護層を積層する工程を備え、
前記顔料がパール顔料である、三次元成形用加飾シートの製造方法。 A step of partially laminating a binder resin containing 80% by mass or more of acrylic resin and a pattern layer containing a pigment on a transfer substrate, and a solid layer containing a binder resin containing 80% by mass or more of acrylic resin are laminated. The transfer sheet preparation process, in which the transfer sheet is produced by performing the steps,
A transfer step of transferring the pattern layer and the solid layer laminated on the transfer sheet onto a substrate,
After the transfer step, a step of laminating a surface protective layer located on the outermost surface having a thickness of 30 μm or less is provided.
A method for manufacturing a decorative sheet for three-dimensional molding, wherein the pigment is a pearl pigment.
前記積層体において、前記絵柄層は、部分的に積層されており、
前記絵柄層に含まれるバインダー樹脂が、アクリル系樹脂を80質量%以上含み、前記アクリル系樹脂は、アクリル樹脂及びアクリルポリオール樹脂の少なくとも一方であり、
前記顔料がパール顔料であり、
前記ベタ層に含まれるバインダー樹脂が、アクリル系樹脂を80質量%以上含み、前記アクリル系樹脂は、アクリル樹脂及びアクリルポリオール樹脂の少なくとも一方であり、
前記表面保護層の厚みは30μm以下である、三次元加飾樹脂成形品。
At least, on the molding resin layer, a surface protective layer located on the outermost surface, a pattern layer containing a pigment (excluding a cured product containing a compound having at least two or more acryloyl groups in one molecule). It is a three-dimensional decorative resin molded product composed of a laminated body in which a solid layer and a base material layer are laminated in this order.
In the laminated body, the pattern layer is partially laminated, and is
The binder resin contained in the pattern layer contains 80% by mass or more of an acrylic resin, and the acrylic resin is at least one of an acrylic resin and an acrylic polyol resin.
The pigment is a pearl pigment,
The binder resin contained in the solid layer contains 80% by mass or more of the acrylic resin, and the acrylic resin is at least one of the acrylic resin and the acrylic polyol resin.
A three-dimensional decorative resin molded product having a surface protective layer having a thickness of 30 μm or less.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020018607A JP7063344B2 (en) | 2020-02-06 | 2020-02-06 | Decorative sheet and decorative resin molded product |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020018607A JP7063344B2 (en) | 2020-02-06 | 2020-02-06 | Decorative sheet and decorative resin molded product |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018011797A Division JP6658774B2 (en) | 2018-01-26 | 2018-01-26 | Decorative sheet and decorative resin molding |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2020073350A JP2020073350A (en) | 2020-05-14 |
| JP2020073350A5 JP2020073350A5 (en) | 2020-11-19 |
| JP7063344B2 true JP7063344B2 (en) | 2022-05-09 |
Family
ID=70609920
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020018607A Active JP7063344B2 (en) | 2020-02-06 | 2020-02-06 | Decorative sheet and decorative resin molded product |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7063344B2 (en) |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007245647A (en) | 2006-03-17 | 2007-09-27 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | Decoration sheet for insert molding |
| JP2012213927A (en) | 2011-03-31 | 2012-11-08 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | Decorative sheet for three-dimensional molding, method for producing the decorative sheet, decorative resin molding, and method for producing the decorative resin molding |
| JP2012218301A (en) | 2011-04-08 | 2012-11-12 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | Decorative sheet, and decorative resin molded article using the same |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3226644B2 (en) * | 1992-12-28 | 2001-11-05 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | Transfer sheet made of vinyl chloride resin molding for exterior material |
| JP3289201B2 (en) * | 1993-07-26 | 2002-06-04 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | Transfer foil for vinyl chloride resin base material |
| JPH09300397A (en) * | 1996-05-15 | 1997-11-25 | Nissha Printing Co Ltd | Acrylic insert film and manufacture of grain pattern molded product |
| JPH1058631A (en) * | 1996-08-20 | 1998-03-03 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | Decorative sheet |
-
2020
- 2020-02-06 JP JP2020018607A patent/JP7063344B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007245647A (en) | 2006-03-17 | 2007-09-27 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | Decoration sheet for insert molding |
| JP2012213927A (en) | 2011-03-31 | 2012-11-08 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | Decorative sheet for three-dimensional molding, method for producing the decorative sheet, decorative resin molding, and method for producing the decorative resin molding |
| JP2012218301A (en) | 2011-04-08 | 2012-11-12 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | Decorative sheet, and decorative resin molded article using the same |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2020073350A (en) | 2020-05-14 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2015046568A1 (en) | Decorative sheet, decorative resin molded article, and manufacturing method for decorative resin molded article | |
| JP6957853B2 (en) | Decorative sheet | |
| JP6965919B2 (en) | Decorative sheets, decorative resin molded products, and methods for manufacturing these | |
| JP6409265B2 (en) | Decorative sheet and decorative resin molded product | |
| JP6687154B2 (en) | Decorative sheet and decorative resin molded product | |
| JP6756136B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of decorative sheet and decorative resin molded product | |
| JP5663928B2 (en) | Decorative sheet manufacturing method, decorative sheet and decorative resin molded product using the same | |
| JP2020163865A (en) | Decorative sheet and decorative resin molding | |
| JP6728569B2 (en) | Transfer sheet and decorative resin molded product using the same | |
| JP6503628B2 (en) | Decorative sheet and decorative resin molded article | |
| JP2018058216A (en) | Decorative sheet | |
| JP7172365B2 (en) | Decorative sheet, decorative resin molded product, and method for producing the same | |
| JP6331546B2 (en) | Decorative sheet manufacturing method | |
| JP6809317B2 (en) | Decorative sheet and decorative resin molded product | |
| JP2017177729A (en) | Decorative sheet and manufacturing method of decorative resin molding | |
| JP6379580B2 (en) | Decorative sheet and decorative resin molded product | |
| WO2015046549A1 (en) | Decorative sheet and decorative resin molded article | |
| JP7063344B2 (en) | Decorative sheet and decorative resin molded product | |
| JP6467840B2 (en) | Laminated sheet and decorative resin molded product | |
| JP6484978B2 (en) | Decorative sheet and decorative resin molded product | |
| JP6331576B2 (en) | Decorative sheet and decorative resin molded product | |
| JP7215045B2 (en) | Laminates and decorative articles | |
| JP7013746B2 (en) | Decorative sheet and decorative resin molded product | |
| JP6658774B2 (en) | Decorative sheet and decorative resin molding | |
| JP6972527B2 (en) | Decorative sheets, decorative resin molded products, and methods for manufacturing these |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20200206 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20201012 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20210330 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20210527 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20210727 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20220104 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20220301 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20220322 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20220404 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 7063344 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |