JP6758069B2 - Autonomous flying robot - Google Patents
Autonomous flying robot Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6758069B2 JP6758069B2 JP2016072711A JP2016072711A JP6758069B2 JP 6758069 B2 JP6758069 B2 JP 6758069B2 JP 2016072711 A JP2016072711 A JP 2016072711A JP 2016072711 A JP2016072711 A JP 2016072711A JP 6758069 B2 JP6758069 B2 JP 6758069B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- flight
- vibration state
- autonomous
- value
- speed
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- RZVHIXYEVGDQDX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9,10-anthraquinone Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(=O)C3=CC=CC=C3C(=O)C2=C1 RZVHIXYEVGDQDX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 17
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 50
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 49
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 13
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 11
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 10
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 9
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 8
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000005856 abnormality Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000036544 posture Effects 0.000 description 2
- 241000132092 Aster Species 0.000 description 1
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010191 image analysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002040 relaxant effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Control Of Position, Course, Altitude, Or Attitude Of Moving Bodies (AREA)
Description
本発明は、移動空間内を自律的に飛行する自律飛行ロボットに関する。 The present invention relates to an autonomous flying robot that autonomously flies in a moving space.
従来、現在位置から所定の移動目標位置に至る移動経路を算出し、当該移動経路に沿うよう自律的に飛行可能な自律飛行ロボットが提案されている。例えば、特許文献1には、賊等の移動物体から所定の離間距離だけ離れた位置に移動目標位置を設定し、現在位置から当該移動目標位置に至る移動経路を生成し、当該移動経路に沿うよう飛行制御される自律飛行ロボットが開示されている。
Conventionally, an autonomous flight robot capable of calculating a movement path from a current position to a predetermined movement target position and autonomously flying along the movement path has been proposed. For example, in
しかしながら、上記従来技術では、姿勢制御等に用いる各種センサの異常や、突風などの外乱の影響などを受けて稀に飛行制御ができなくなる場合があった。例えば、自律飛行ロボットが同じ位置にホバリングすることを意図して飛行制御をしていても、ホバリング位置を中心として左右に移動するといった意図とは異なる振動移動を行うことがあった。このような自律的な飛行制御が機能しない振動状態が発生すると、飛行が許可されたエリアから大きく外れて飛行したり、建物等へ接触したりといったような危険な事態に発展しうることになる。 However, in the above-mentioned conventional technique, flight control may not be possible in rare cases due to an abnormality of various sensors used for attitude control or the like or the influence of a disturbance such as a gust. For example, even if the autonomous flight robot controls the flight with the intention of hovering to the same position, it may perform vibration movement different from the intention of moving left and right around the hovering position. If such a vibration state in which autonomous flight control does not work occurs, it may develop into a dangerous situation such as flying far outside the permitted area or coming into contact with a building or the like. ..
そこで、本発明は、振動状態が発生したか否かを判定し、振動状態となったときに速度が最小となるタイミングで飛行停止させることにより、迅速に振動状態を解消して安全を確保することを目的とする。 Therefore, the present invention quickly eliminates the vibration state and secures safety by determining whether or not the vibration state has occurred and stopping the flight at the timing when the speed becomes the minimum when the vibration state occurs. The purpose is.
本発明の1つの態様は、移動空間内を自律飛行する自律飛行ロボットであって、前記自律飛行ロボットの飛行状態を計測した計測値から飛行速度を推定する速度推定手段と、現在時刻から所定時間前までの過去期間における前記飛行速度の変化履歴に基づいて該飛行速度が符号反転を繰り返している振動状態を検出する振動状態検出手段と、前記振動状態検出手段にて前記振動状態を検出したとき、前記飛行速度が最小となるタイミングで飛行停止させる飛行制御手段と、を有することを特徴とする自律飛行ロボットである。 One aspect of the present invention is an autonomous flight robot that autonomously flies in a moving space, a speed estimation means that estimates a flight speed from a measured value obtained by measuring the flight state of the autonomous flight robot, and a predetermined time from the current time. When the vibration state detecting means for detecting the vibration state in which the flight speed repeats code reversal based on the change history of the flight speed in the past period up to the previous time and the vibration state being detected by the vibration state detecting means. The autonomous flight robot is characterized by having a flight control means for stopping the flight at the timing when the flight speed becomes the minimum.
ここで、前記振動状態検出手段は、前記過去期間における前記飛行速度の符号が所定の回数閾値以上変化しているとき、前記振動状態と判定することが好適である。 Here, it is preferable that the vibration state detecting means determines the vibration state when the code of the flight speed in the past period has changed by a predetermined number of times or more.
また、前記振動状態検出手段は、現在時刻の直近における前記飛行速度の振幅値が大きいほど長い前記過去期間を設定することが好適である。 Further, it is preferable that the vibration state detecting means set the past period, which is longer as the amplitude value of the flight speed in the immediate vicinity of the current time is larger.
また、前記振動状態検出手段は、前記過去期間において前記飛行速度の符号が前記所定回数以上変化し、該振幅値が時間の経過と共に減少傾向であるとき、現在時刻から所定の判定時間の経過後における前記振幅値が所定の振幅閾値よりも大きいならば前記振動状態であると判定することが好適である。 Further, when the vibration state detection means changes the code of the flight speed more than the predetermined number of times in the past period and the amplitude value tends to decrease with the passage of time, after the lapse of a predetermined determination time from the current time. If the amplitude value in the above is larger than a predetermined amplitude threshold value, it is preferable to determine that the vibration state is present.
また、前記飛行空間内に存在する障害物の位置を示す障害物情報を記憶し、前記自律飛行ロボットの自己位置を推定する自己位置推定部を更に備え、前記飛行制御部は、前記障害物情報を用いて前記自己位置の下方に障害物が存在しないとき前記飛行停止を実行することが好適である。 Further, an obstacle information indicating the position of an obstacle existing in the flight space is stored, and a self-position estimation unit for estimating the self-position of the autonomous flight robot is further provided, and the flight control unit is provided with the obstacle information. It is preferable to perform the flight stop when there are no obstacles below the self-position using.
また、前記飛行空間内に移動目標位置を設定し、自己位置から当該移動目標位置に至る飛行経路を求める経路探索手段を更に有し、前記飛行制御手段は、前記飛行経路に沿って飛行するよう制御し、振動状態検出手段は、前記移動目標位置の変化が大きいとき前記回数閾値を大きい値に変更し、前記移動目標位置の変化が小さいとき前記回数閾値を小さい値に変更することが好適である。
Further, the flight control means further includes a route search means for setting a movement target position in the flight space and obtaining a flight path from the self position to the movement target position, and the flight control means flies along the flight path. It is preferable that the control and vibration state detecting means changes the number-of-times threshold value to a large value when the change in the movement target position is large, and changes the number-time threshold value to a small value when the change in the movement target position is small. is there.
本発明によれば、振動状態となったときに速度が最小となるタイミングで飛行停止することにより、迅速に振動状態を解消して安全を確保することができる。 According to the present invention, by stopping the flight at the timing when the speed becomes the minimum when the vibration state is reached, the vibration state can be quickly eliminated and safety can be ensured.
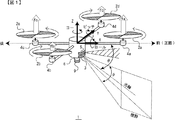
本発明の実施の形態における自律飛行ロボット1は、図1の概観図に示すように、クアッドロータ型の小型無人ヘリコプタである。なお、本発明の適用範囲は、クアッドロータ型の小型無人ヘリコプタに限定されるものではなく、シングルロータ型の小型無人ヘリコプタについても同様に適用することができる。
The
自律飛行ロボット1は、図2のシステム構成図に示すように、外部の警備センタ100や管理装置102と通信し、移動空間内に存在する所定の移動物体を目標対象物Mとして追跡し、当該目標対象物Mに対して所定の機能を発揮するように構成されている。目標対象物Mとなる移動物体は、例えば、監視領域内に侵入した人物(賊等)である。本実施の形態では、所定の機能として、目標対象物Mを撮像する機能を例に説明するが、特に限定されるものではなく、目標対象物Mに対して音を発したり、発光による警告を行ったりする等の機能であってもよい。
As shown in the system configuration diagram of FIG. 2, the
警備センタ100と管理装置102とはインターネット等の情報通信網110を介して情報伝達可能に接続される。また、自律飛行ロボット1と管理装置102は、無線通信等によって情報伝達可能に接続される。警備センタ100は、管理装置102を介して自律飛行ロボット1と通信を行い、自律飛行ロボット1によって撮像された目標対象物Mの撮像画像を受信する。警備センタ100は、撮像画像に対して画像処理を行い、警備センタ100にて異常監視している管理者等(図示しない)に警告を発するような機能を備えていてもよい。また、管理装置102から目標対象物Mの位置(座標)に関する情報を受信し、当該目標対象物Mと自律飛行ロボット1によって撮像された撮像画像とを関連付けて管理するというような機能を備えてもよい。
The
管理装置102は、地面や壁面等に設置された固定型の移動物体検出センサ104(104a,104b・・・)を備え、各目標対象物Mの位置を検知する。移動物体検出センサ104は、例えば、レーザセンサとすることができる。レーザセンサは、一定の角度サンプル間隔の角度毎にレーザを二次元的にスキャンすることによって、地面(又は床面)から一定の高さの水平面における検知範囲内に存在する物体(障害物)との距離情報を極座標値として取得する。レーザセンサは、放射状にレーザ光である探査信号を走査し、物体に反射して戻ってきた探査信号を受信して、送信と受信の時間差から物体までの距離を算出し、レーザセンサの設置位置の座標及び探査信号を送信した方向と算出した距離から当該物体の位置の極座標値を求め、当該極座標値から3次元の直交座標値(Xt,Yt,Zt)を求める。管理装置102は、移動物体検出センサ104によって求められた目標対象物Mの位置を自律飛行ロボット1へ送信する。自律飛行ロボット1は、目標対象物Mの位置を受信すると、その位置に基づいて自らの移動経路を算出し、当該移動経路に沿って移動する。なお、管理装置102は、レーザセンサの検知範囲が重複する領域に存在する目標対象物Mの同一性を検証することで複数のレーザセンサの検知範囲に渡る目標対象物Mの追跡を行う。すなわち、レーザセンサ104aの検知範囲に存在する目標対象物Mがレーザセンサ104bの検知範囲に移動したとしても、管理装置102は、当該目標対象物Mが同一の物体であると判定することができる。
The
以下、図1の概観図及び図3の機能ブロック図を参照して、自律飛行ロボット1の構成及び機能について説明する。
Hereinafter, the configuration and function of the
自律飛行ロボット1は、図1に示すように、4枚のロータ(プロペラ)2(2a〜2d)を一平面上に有する。各ロータ2は、バッテリ(二次電池:図示しない)により駆動されるモータ4(4a〜4d)を用いて回転させられる。一般的に、シングルロータ型のヘリコプタでは、メインロータによって発生する反トルクをテールロータが生み出すモーメントで相殺することによって方位角を保っている。一方、自律飛行ロボット1のようなクアッドロータ型のヘリコプタでは、前後・左右で異なる方向に回転するロータ2を用いることで反トルクの相殺を行っている。そして、各ロータ2の回転数(fa〜fd)を制御することにより、様々な機体の移動や姿勢の調節を行うことができる。例えば、機体をヨー方向に回転させたいときは、前後のロータ2a、2cと左右ロータ2d、2bの回転数に差を与えればよい。
As shown in FIG. 1, the
撮像部3は、例えばレンズなどの光学系および所定画素数(例えば640×480画素からなる解像度)のCCDやCMOSなどの2次元アレイ素子を有する二次元イメージセンサで構成され、移動空間の撮像画像を所定の時間間隔で取得するいわゆるカラーカメラである。本実施の形態では、撮像部3は、その光軸が自律飛行ロボット1の正面方向を撮像するよう筐体部分に設置され、かつ、水平面(XY平面)から予め定めた俯角θにより斜め下方の空間を視野角φ(画角)において撮像するよう設置されている。取得した撮像画像は後述する制御部7に出力され、制御部7により記憶部8に記憶されたり、後述する通信部9を介して管理装置102に送信されたりする。
The image pickup unit 3 is composed of, for example, an optical system such as a lens and a two-dimensional image sensor having a two-dimensional array element such as a CCD or CMOS having a predetermined number of pixels (for example, a resolution of 640 × 480 pixels), and is an image captured in a moving space. Is a so-called color camera that acquires images at predetermined time intervals. In the present embodiment, the imaging unit 3 is installed in the housing portion so that its optical axis images the front direction of the
距離検出センサ5は、自律飛行ロボット1の周囲に存在する障害物と自律飛行ロボット1との間の距離を検出し、センサ検出範囲内に存在する障害物の相対的な位置を取得するセンサである。本実施の形態では、距離検出センサ5としてマイクロ波センサを備える。マイクロ波センサは、空間にマイクロ波を放出し、その反射波を検知することによって、自律飛行ロボット1の周囲にある物体を探知し、その物体までの距離を求める。距離検出センサ5は、例えば、自律飛行ロボット1の前方に向けて設け、目標対象物Mまでの距離を測定するために用いることができる。また、距離検出センサ5は、例えば、自律飛行ロボット1の下部に下向きに設け、地面との距離(高度)を測定するために用いることもできる。また、距離検出センサ5は、例えば、撮像部3の光軸方向に向けて設け、撮像部3の撮像対象物である目標対象物Mまでの距離を測定するために用いることができる。
The
位置検出センサ6は、自律飛行ロボット1の現在位置を取得するためのセンサである。位置検出センサ6は、例えば、GNSS(Global Navigation Satellite System)等の航法衛星から送信される電波(航法信号)を受信する。位置検出センサ6は、複数の航法衛星から送信される航法信号を受信して制御部7へ入力する。なお、位置検出センサ6は、レーザスキャナ、ジャイロセンサ、電子コンパス、気圧センサ等の他のセンサを用いて既知の技術により自己位置を得るための情報を取得するものとしてもよい。
The position detection sensor 6 is a sensor for acquiring the current position of the
通信部9は管理装置102との間で、例えば無線LANや携帯電話回線等により無線通信するための通信モジュールである。本実施の形態では、撮像部3によって取得した撮像画像を通信部9により管理装置102に送信し、当該撮像画像を管理装置102から警備センタ100に送信することにより、警備員等が遠隔から侵入者を監視することを可能にする。また、通信部9は、管理装置102から目標対象物Mの位置(座標:Xt,Yt,Zt)を受信することにより、後述するような移動経路の設定を可能にする。
The communication unit 9 is a communication module for wireless communication with the
記憶部8は、ROM(Read Only Memory)、RAM(Random Access Memory)、HDD(Hard Disk Drive)等の情報記憶装置である。記憶部8は、各種プログラムや各種データを記憶し、制御部7との間でこれらの情報を入出力する。各種データには、目標対象物位置81、変化履歴情報82、ボクセル情報83、各種パラメータ84等の制御部7の各処理に用いられる情報、各センサ等の出力値及び撮像画像等が含まれる。
The
目標対象物位置81は、管理装置102から受信した目標対象物Mの位置情報(座標:Xt,Yt,Zt)である。本実施の形態では、目標対象物位置81を目標対象物Mの足元位置、すなわち目標対象物Mが地面(床面)に接している位置とする。制御部7は、通信部9を介して目標対象物Mの位置を受信すると目標対象物位置81として記憶部8に記憶させる。なお、管理装置102は、目標対象物Mの位置(座標:Xt,Yt,Zt)の時間変化に基づいて目標対象物Mの姿勢(例えば、目標対象物Mの正面方向を示した情報)を推定し、目標対象物位置81として記憶してもよい。
The
変化履歴情報82は、自律飛行ロボット1の飛行速度と当該飛行速度が推定された時刻とを対応付けた飛行速度の過去から現在までの変化履歴を表す情報である。本実施の形態では、後述する速度推定手段72にて飛行速度を推定する度に、当該飛行速度と推定時刻とを対応付けて変化履歴情報82として記憶部8に記憶されるものとする。
The
ボクセル情報83は、移動空間をボクセル空間として複数のボクセルに分割して移動空間の障害物の構造等を表した情報であり、予め管理者等によって設定され記憶部8に記憶され、また、後述するように位置推定手段71にて更新される情報である。本実施の形態では、移動空間を所定の大きさ(例えば15cm×15cm×15cm)のボクセルに等分割し、各ボクセルの識別子であるボクセルIDと、移動空間におけるボクセルの位置(三次元座標)と、ボクセル属性と、ボクセルコスト値とを対応付けてボクセル情報83として記憶する。飛行禁止エリアに相当するボクセルは、そのボクセル属性を「占有ボクセル」と定義して、自律飛行ロボット1が移動できない空間とする。なお飛行禁止エリアには、例えば建造物等の障害物に相当するエリア、飛行が許可された敷地外のエリア、飛行が許可された高度よりも高いエリアなどが挙げられる。そして、占有ボクセルの近くに存在する空間に位置するボクセルのボクセル属性を「近接ボクセル」、それ以外の自由に飛行可能なエリアに位置するボクセルのボクセル属性を「自由ボクセル」と定義する。
The
各ボクセルには、後述する経路探索手段73にて移動経路を生成する際に利用できるよう、占有度を示すボクセルコスト値が関連付けて登録される。ボクセルコスト値は、占有ボクセルにおいて最大値Cmaxをとり、占有ボクセルからの距離が大きくなるほど小さな値となるように設定される。例えば、あるボクセル(評価ボクセル)のボクセルコスト値は、ボクセルコスト値=Cmax × exp{−λ×R}の計算式により算出することが好適である。ここでλは実験によって求めたパラメータとし、Rは評価ボクセルに最も近い占有ボクセルからの距離とする。そして、予め定めた閾値以上のボクセルコスト値を有するボクセルを「近接ボクセル」とする。また、ボクセルコスト値が当該閾値よりも小さいボクセルを「自由ボクセル」とし、自由ボクセルとみなされたボクセルのボクセルコスト値を0と設定する。 A voxel cost value indicating the degree of occupancy is associatedly registered with each voxel so that it can be used when a movement route is generated by the route search means 73 described later. The voxel cost value takes the maximum value C max in the occupied voxel, and is set so as to become smaller as the distance from the occupied voxel increases. For example, the voxel cost value of a certain voxel (evaluation voxel) is preferably calculated by the formula of voxel cost value = C max × exp {−λ × R}. Here, λ is a parameter obtained by experiment, and R is the distance from the occupied voxel closest to the evaluation voxel. Then, a voxel having a voxel cost value equal to or higher than a predetermined threshold value is referred to as a "proximity voxel". Further, a voxel whose voxel cost value is smaller than the threshold value is set as a "free voxel", and a voxel cost value of a voxel regarded as a free voxel is set to 0.
また、記憶部8には、各種パラメータ84として離間距離等も記憶される。離間距離は、目標対象物Mに追従飛行するにあたって、自律飛行ロボット1と目標対象物Mとの水平面における維持すべき相対距離である。離間距離は、自律飛行ロボット1の管理者等によって予め設定される。自律飛行ロボット1を用いて所定の目標対象物Mを監視する場合、目標対象物Mに近づき、より詳細な撮像画像を取得できる必要がある。しかし、侵入者などの敵対する目標対象物Mから攻撃を受けないようにするためには一定距離以上離間する必要がある。そのため、本実施の形態の自律飛行ロボット1は、目標対象物Mの詳細な撮像画像を取得でき、かつ、当該目標対象物Mから攻撃を受け難い距離に離間距離を予め、当該離間距離を保ちつつ追従飛行するように制御される。離間距離は、例えば3mと設定される。離間距離の他にも、後述する回数閾値や振幅閾値などの振動状態を判定するための条件や式なども、各種パラメータ84として記憶部8に記憶される。
Further, the
制御部7は、CPU等を備えたコンピュータで構成され、位置推定処理、速度推定処理、経路探索処理、振動状態検出処理、経路追従制御、飛行停止制御等を行う一連の処理として、位置推定手段71、速度推定手段72、経路探索手段73、移動制御手段74、振動状態検出手段75を含んでいる。
The
位置推定手段71は、位置検出センサ6の出力に基づいて、移動空間における自律飛行ロボット1の現在位置である自己位置を推定する位置推定処理を行う。
The position estimation means 71 performs a position estimation process for estimating the self-position, which is the current position of the
具体的には、位置検出センサ6から得られた複数の航法衛星からの信号に基づいて周知技術によって推定した緯度・経度と、距離検出センサ5から得られた高度とから自己位置の座標(Xs,Ys,Zs)を計算する。さらに、電子コンパスやジャイロセンサなどの位置検出センサ6からの出力を受けて自己位置として姿勢YAWを求める。なお、自己位置の推定方法はこれに限定されるものではなく、他の方法を用いて自律飛行ロボット1の現在位置を推定してもよい。
Specifically, the coordinates of the self-position (X) from the latitude / longitude estimated by a well-known technique based on the signals from a plurality of navigation satellites obtained from the position detection sensor 6 and the altitude obtained from the
位置推定手段71は、推定された自己位置(座標:Xs,Ys,Zs及び姿勢YAW)と管理装置102から受信した目標対象物Mの位置(座標:Xt,Yt,Zt)を経路探索手段73へ出力する。また、位置推定手段71は、推定された自己位置を速度推定手段72及び移動制御手段74へ出力する。 The position estimating means 71 receives the estimated self-position (coordinates: X s , Y s , Z s and attitude YAW) and the position of the target object M received from the management device 102 (coordinates: X t , Y t , Z t). ) Is output to the route search means 73. Further, the position estimation means 71 outputs the estimated self-position to the speed estimation means 72 and the movement control means 74.
なお、位置推定手段71は、目標対象物Mの位置に基づいてボクセル情報83を更新する処理を行う。具体的には、記憶部8のボクセル情報83に基づいたボクセル空間に目標対象物Mの位置を重心として予め定めた目標対象物Mの大きさと略同じ大きさの円柱モデル(例えば、監視対象の目標対象物Mを侵入者であるとしたとき、底面の半径0.3m、高さ1.7mの円柱モデル)を配置し、当該円柱モデルと干渉するボクセルを占有ボクセルとして設定することによりボクセル情報83を更新する。後述するように、自律飛行ロボット1は、占有ボクセルには移動しないように飛行制御されるが、上記のように目標対象物Mの位置に基づいてボクセル情報83を更新することにより、自律飛行ロボット1と目標対象物Mとの接触を回避することができる。
The position estimation means 71 performs a process of updating the
速度推定手段72は、後述する移動制御手段74における移動制御で利用するため、自律飛行ロボット1の現在の飛行速度(vx,vy,vz,vyaw)を推定する速度推定処理を行う。本実施の形態では、位置推定手段71にて推定した自己位置(座標:Xs,Ys,Zs及び姿勢YAW)の時間変化から飛行速度を求める。この際、測定誤差等の影響を考慮して拡張カルマンフィルタを利用して飛行速度を推定することが好適である。また、推定した飛行速度は、大きさだけでなく速度の向きを考慮したベクトル値であり、向きに応じた正と負の符号を有している。例えば、北方向及び東方向への飛行速度を正とし、反対に南方向及び西方向への飛行速度を負として設定する。なお、本実施の形態では、自己位置の時間変化から飛行速度を求めているが、これに限らず、GNSSにおけるドップラー効果を利用した速度推定方法を用いてもよい。速度推定手段72は、飛行速度を推定すると、推定時刻と対応付けて変化履歴情報82として記憶部8に逐次記憶する。また、速度推定手段72は、推定した飛行速度を移動制御手段74へ出力する。
Since the speed estimation means 72 is used for movement control in the movement control means 74, which will be described later, the speed estimation means 72 performs a speed estimation process for estimating the current flight speed (v x , v y , v z , v yaw ) of the
経路探索手段73は、位置推定手段71で推定された自己位置と、記憶部8に記憶された移動物体位置81及び各種情報とを用いて、自己位置から所定の移動目標位置に至る移動経路を算出する経路探索処理を行う。
The route search means 73 uses the self-position estimated by the position estimation means 71, the moving
経路探索処理では、まず、目標対象物位置81から離間距離だけ離れた位置に移動候補位置を設定する処理を行う。すなわち、目標対象物位置81から離間距離だけ離れた周囲の領域に複数の移動候補位置を設定する。本実施の形態では、移動候補位置を、目標対象物位置81を中心として、予め設定された離間距離を半径とした円状の位置で、かつ、管理者等により予め定められた飛行高度(例えば3m)の領域に、それぞれ等間隔になるように設定する。
In the route search process, first, a process of setting a movement candidate position at a position separated from the
次に、経路探索処理では、設定した移動候補位置の其々を評価し、最も高い評価値となる移動候補位置を移動目標位置として設定する処理を行う。この際、まず、自律飛行ロボット1が障害物に接触することを防止するため、ボクセル情報83を参照して占有ボクセル又は近接ボクセルに含まれる位置には移動目標位置を設定しないよう、最低の評価値となるようにする。また、自律飛行ロボット1の自己位置から各移動候補位置までの距離が小さいほど評価値が高くなるようにする。更に、前回設定した移動目標位置から移動候補位置までの距離が小さいほど評価値が高くなるようにする。
Next, in the route search process, each of the set movement candidate positions is evaluated, and the movement candidate position having the highest evaluation value is set as the movement target position. At this time, first, in order to prevent the
次に、経路探索処理では、位置推定手段71で推定された自己位置と、設定した移動目標位置とを用いて自律飛行ロボット1の移動経路を算出する移動経路生成処理を行う。具体的には、移動経路生成処理では、まず、記憶部8からボクセル情報82を読出し、分割した移動可能な空間である自由ボクセル及び近接ボクセルの各ボクセルの中心をノードとし、当該ノードに隣接するノード間を連結した線分をエッジとしてグラフ構造を生成する。この際、エッジの重みとして、隣接するノード間の距離に基づいて求められる距離コストが設定されているものとする。このようにボクセル情報82に基づいて全ての移動可能なボクセルについてグラフ構造を生成した後、自律飛行ロボット1が存在しているボクセルのノードから移動目標位置が存在しているボクセルのノードまでの移動経路を生成する。移動経路の生成方法については、さまざまな経路生成方法が適用可能であるが、本実施の形態ではA*(エースター)経路探索法を用いて移動経路を探索する。この際、ボクセル情報82として記憶されたボクセルコストと距離コストとを、A*経路探索法における移動コストとして利用する。経路探索手段73で生成された生成された移動経路のデータは、経由点(x,y,z)の集合データであり、この情報は記憶部8に一時的に記憶される。
Next, in the route search process, a movement route generation process for calculating the movement route of the
振動状態検出手段75は、速度推定手段72にて推定した飛行速度の過去の変化履歴を示した変化履歴情報82を用いて、現在の飛行状態が自律的な飛行制御が機能しない振動状態であるか否かを検出する振動状態検出処理を行う。振動状態検出処理では、現在時刻から所定時間前までの過去期間において飛行速度が符号反転を繰り返しているか否かに基づいて振動状態を検出する。以下、本実施の形態の自律飛行ロボット1に係る振動状態検出手段75が実行する振動状態検出処理の流れの一例について、図4を参照しながら詳細に説明する。なお、振動状態検出処理は、予め設定されたタイミング(例えば5秒毎)に実施されるものとする。
The vibration state detecting means 75 uses the
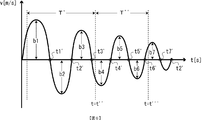
振動状態検出処理では、まず、振動状態であるか否かを判定するための期間である過去期間を設定する(ST1)。本実施の形態では、変化履歴情報82を参照して現在の直近における飛行速度の振幅値が大きいほど、長い過去期間を設定する。図5と図6は、飛行速度の変化をグラフによって表した図であり、図5は飛行速度の振幅値が増加傾向にある変化を示した図であり、図6は飛行速度の振幅値が減少傾向にある変化を示した図である。図5において、現在時刻がt’であるとき、振動状態検出手段75は、変化履歴情報82を参照して現在時刻から所定時間だけ過去の過去期間における飛行速度の変化履歴を読み出し、直近の飛行速度の振幅値a3を求める。そして、例えば、直近の飛行速度の振幅値a3に基づいて、過去期間の長さTを、T=α×a3+T0の計算式により算出することが好適である。ここでαは実験によって求めたパラメータとし、T0は基準となる過去期間の長さとして実験によって設定した期間長とする。図6では、現在時刻がt’’であるとき、直近の飛行速度の振幅値はb3であり、時刻t’の直近の振幅値a3よりも大きい振幅値であるため(b3>a3)、過去期間の長さT’は、過去期間の長さTよりも長い期間長(T’>T)に設定していることを表している。
In the vibration state detection process, first, a past period, which is a period for determining whether or not the vibration state is present, is set (ST1). In the present embodiment, the larger the amplitude value of the current latest flight speed with reference to the
次に、振動状態検出処理では、変化履歴情報82を参照し、現在時刻からST1にて設定した過去期間における飛行速度の符号の変化回数を計数し、当該符号の変化回数が予め設定した回数閾値以上であるか否かを判定する(ST2)。本実施の形態では、回数閾値を3回として以下を説明する。図5において、現在時刻がt’であるとき、振動状態検出手段75は、変化履歴情報82から過去期間Tにおける飛行速度の変化履歴を読み出す。そして、過去期間Tにおける飛行速度の符号の変化回数を計数する。図5では、過去期間Tの間に、飛行速度の符号が変化しているのはt1、t2、t3の3回であり、回数閾値以上であるため(ST2−Yes)、処理をST3へ進める。図6の場合も同様に、過去期間T’の間に、飛行速度の符号が変化しているのはt1’、t2’、t3’の3回であり、回数閾値以上であるため(ST2−Yes)、処理をST3へ進める。一方、飛行速度の符号の変化回数が回数閾値以上でないとき(ST2−No)、現在は振動状態ではないと判定して振動状態検出処理を終了する。
Next, in the vibration state detection process, the
次に、振動状態検出処理では、ST2にて求めた振幅の平均値を求め、当該平均値が予め設定した振幅閾値以上であるか否かを判定する(ST3)。振幅閾値Th1としたとき、図5の例では、振幅の平均値AをA=(a1+a2+a3)/3により求め、求めた平均値AがTh1以上であるか否かを判定する。求めた平均値が予め設定した振幅閾値Th1以上であるとき(ST3−Yes)、処理をST4へ進める。一方、平均値が予め設定した振幅閾値以上でないとき(ST3−No)、現在は振動状態ではないと判定して振動状態検出処理を終了する。このように、過去期間における振幅値を閾値判定することにより、通常時の飛行制御においても生じうる速度が小さい振動移動を異常状態である振動状態として誤判定されないようにすることができる。なお、本実施の形態では、ST3にて、ST2にて求めた振幅の平均値Aと振幅閾値Th1との比較により上記判定を行っているが、これに限らず、ST2にて求めた振幅値が全て振幅閾値Th1以上であるか否かに基づいて上記判定を行ってもよい。 Next, in the vibration state detection process, the average value of the amplitudes obtained in ST2 is obtained, and it is determined whether or not the average value is equal to or higher than the preset amplitude threshold value (ST3). When the amplitude threshold is Th1, in the example of FIG. 5, the average value A of the amplitude is obtained by A = (a1 + a2 + a3) / 3, and it is determined whether or not the obtained average value A is Th1 or more. When the obtained average value is equal to or higher than the preset amplitude threshold Th1 (ST3-Yes), the process proceeds to ST4. On the other hand, when the average value is not equal to or higher than the preset amplitude threshold value (ST3-No), it is determined that the vibration state is not present and the vibration state detection process is terminated. In this way, by determining the amplitude value in the past period as a threshold value, it is possible to prevent erroneous determination of vibrational movement, which can occur even in normal flight control, as an abnormal vibration state. In the present embodiment, the above determination is made by comparing the average value A of the amplitudes obtained in ST2 with the amplitude threshold Th1 in ST3, but the above determination is not limited to this, and the amplitude value obtained in ST2 is not limited to this. The above determination may be made based on whether or not all of the above are equal to or higher than the amplitude threshold Th1.
次に、振動状態検出処理では、過去期間における振幅値の変化が減少傾向にあるか否かを判定する(ST4)。図5の例では、過去期間Tにおける振幅値の変化は、a1、a2、a3と時間が進むにつれて大きくなっており、減少傾向ではないと判定されて(ST4−No)、処理をST7に進める。一方、図6の例では、過去期間T’における振幅値の変化は、b1、b2、b3と時間が進むにつれて小さくなっており、減少傾向であると判定されて(ST4−Yes)、処理をST5に進める。 Next, in the vibration state detection process, it is determined whether or not the change in the amplitude value in the past period tends to decrease (ST4). In the example of FIG. 5, the change in the amplitude value in the past period T increases as time advances to a1, a2, and a3, and it is determined that there is no decreasing tendency (ST4-No), and the process proceeds to ST7. .. On the other hand, in the example of FIG. 6, the change in the amplitude value in the past period T'becomes small as time progresses to b1, b2, and b3, and it is determined that the amplitude is decreasing (ST4-Yes). Proceed to ST5.
ST4にて振幅値の変化が減少傾向であると判定されると(ST4−Yes)、振動状態検出処理では、予め設定した判定時間だけ処理を待機させる(ST5)。そして、判定時間が経過した直後の振幅値が振幅閾値Th1以上となっているか否かを判定する(ST6)。図6の例では、判定時間T’’が経過した時刻t’’’の直後の振幅値b6と振幅閾値Th1とを比較する。判定時間が経過した直後の振幅値が振幅閾値Th1以上となっていないとき(ST6−No)、現在は振動状態ではないと判定して振動状態検出処理を終了する。一方、判定時間が経過した時刻の直後の振幅値が振幅閾値Th1以上となっているとき(ST6−Yes)、処理をST7に進める。なお、本実施の形態では、ST6にて、判定時間が経過した直後の振幅値が振幅閾値Th1以上となっているか否かを判定しているが、これに限らず、判定時間内の振幅値の平均値が振幅閾値Th1以上となっているか否かに基づいて上記判定を行ってもよい。また、本実施の形態では、判定時間を予め設定した値としているが、これに限らず、所定回数(例えば3回)以上の振幅値が求められるまでの時間を判定時間としてもよい。例えば、図6の例では、現在時刻t=t’’から3回目の振幅値であるb6が求まるまでの時間を判定時間とし、当該b6と振幅閾値Th1とを比較して、上記判定を行ってもよい。 When it is determined in ST4 that the change in the amplitude value tends to decrease (ST4-Yes), the vibration state detection process waits for a predetermined determination time (ST5). Then, it is determined whether or not the amplitude value immediately after the determination time has elapsed is equal to or greater than the amplitude threshold Th1 (ST6). In the example of FIG. 6, the amplitude value b6 immediately after the time t ″ ″ when the determination time T ″ has elapsed is compared with the amplitude threshold value Th1. When the amplitude value immediately after the determination time has elapsed is not equal to or higher than the amplitude threshold Th1 (ST6-No), it is determined that the vibration state is not present and the vibration state detection process is terminated. On the other hand, when the amplitude value immediately after the time when the determination time has elapsed is equal to or higher than the amplitude threshold Th1 (ST6-Yes), the process proceeds to ST7. In the present embodiment, in ST6, it is determined whether or not the amplitude value immediately after the determination time has elapsed is equal to or higher than the amplitude threshold Th1. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and the amplitude value within the determination time is determined. The above determination may be made based on whether or not the average value of is equal to or higher than the amplitude threshold Th1. Further, in the present embodiment, the determination time is set to a preset value, but the determination time is not limited to this, and the time until an amplitude value of a predetermined number of times (for example, 3 times) or more is obtained may be used as the determination time. For example, in the example of FIG. 6, the time from the current time t = t'' to the determination of the third amplitude value b6 is set as the determination time, and the b6 is compared with the amplitude threshold Th1 to perform the above determination. You may.
振動状態検出処理では、過去期間における振幅値の変化が減少傾向にないと判定されたとき(ST4−No)、又は、判定時間の経過後の振幅値が振幅閾値Th1以上となっているとき(ST6−Yes)、現在の飛行状態が自律的な飛行制御が機能しない振動状態であると判定する(ST7)。そして、振動状態であると判定すると、振動状態検出手段75は、振動状態である旨を示す情報を移動制御手段74に出力すると共に、変化履歴情報82に基づいて飛行速度(絶対値)が最小となるタイミング(すなわち、現在を基準として飛行速度が最小となる時間長)を求め、当該タイミングを表すタイミング値を移動制御手段74に出力する。例えば、現在の飛行速度がちょうどゼロであるとき、移動制御手段74にタイミング値として“0”を出力する。また、変化履歴情報82を参照して、飛行速度の変化の振幅値と周期(振動周波数)とに基づいて飛行速度(絶対値)が最小(例えば、飛行速度がゼロ)となる未来時刻を推測し、現在時刻から当該未来時刻までの時間長をタイミング値として出力する(例えば、“0.5秒後”など)。移動制御手段74にタイミング値を出力すると振動状態検出処理を終了する。
In the vibration state detection process, when it is determined that the change in the amplitude value in the past period does not tend to decrease (ST4-No), or when the amplitude value after the elapse of the determination time is equal to or greater than the amplitude threshold Th1 (). ST6-Yes), it is determined that the current flight state is a vibration state in which autonomous flight control does not work (ST7). When it is determined that the vehicle is in a vibration state, the vibration state detecting means 75 outputs information indicating that the vibration state is in the movement control means 74, and the flight speed (absolute value) is the minimum based on the
移動制御手段74(本発明における飛行制御手段)は、経路探索手段73にて算出された移動経路と位置推定手段71にて推定された自己位置と速度推定手段72で推定された飛行速度とを用いて、自律飛行ロボット1が経路探索手段73で算出された移動経路に沿って飛行するように経路追従制御を行う。具体的には、移動経路、自己位置及び飛行速度を用いて各時刻での飛行制御値である制御指令値を求め、当該制御指令値に基づいてモータ4を制御し、ロータ2の回転数を制御する。また、移動制御手段74は、振動状態検出手段75にて振動状態であると判定されたとき、振動状態検出手段75から受けたタイミング値に基づいてモータ4を制御し、飛行停止するようロータ2の回転数を制御する飛行停止制御を行う。
The movement control means 74 (flight control means in the present invention) combines the movement path calculated by the route search means 73, the self-position estimated by the position estimation means 71, and the flight speed estimated by the speed estimation means 72. By using this, the
経路追従制御では、まず、各時刻での自律飛行ロボット1が目標とすべき直近の位置(以下、「ローカル目標」と呼ぶ)を算出する処理を行う。図7はローカル目標の算出を説明する図である。ローカル目標の算出にあたり、移動制御手段74は、経路探索手段73で生成された移動経路を記憶部8から読出し、自律飛行ロボット1が現在時刻で目指している経由点Wp1と前回通過済みである経由点Wp0との2点間を繋げた直線Wを求める。そして、移動制御手段74は、求めた直線Wと自律飛行ロボット1の自己位置を中心とした球Sとの交点Lp’、Lpを算出し、目指している経由点Wp1に近い交点Lpをローカル目標として求める。このように、各時刻においてローカル目標を目指して自律飛行ロボット1が移動するよう飛行制御することで、常にローカル目標も移動経路上を移動目標位置Poに向かって移動していき、自律飛行ロボット1は移動経路に沿って飛行していくことになる。
In the route tracking control, first, a process of calculating the nearest position (hereinafter, referred to as “local target”) to be targeted by the
次に、経路追従制御では、算出したローカル目標に向かって飛行するようX、Y、Z、ヨー角の各方向毎に制御指令値ux,uy,uz,uψを算出する処理を行う。この際、現在の自己位置とローカル目標の位置との差異が小さくなるような制御指令値を求める。具体的には、XYZ軸方向の制御指令値u=(ux,uy,uz)は、位置推定手段71で求められた自己位置r=(Xs,Ys,Zs)と速度推定手段72で推定した速度v=(vx,vy,vz)とを利用し、PID制御により求める。XYZ軸方向の各制御指令値をu=(ux,uy,uz)、ローカル目標をr’=(x,y,z)としたとき、制御指令値は、u=Kp(r’−r)+Kd・v+Ki・eの式で算出される。ここで、Kp、Kd、KiはそれぞれPID制御のゲインのことであり、e=(ex,ey,ez)は誤差の積分値である。一方、ヨー角方向の制御指令値uψは、ψ'を目標角度、ψを位置推定手段71にて推定した自律飛行ロボット1の姿勢(角度)、vyawを速度推定手段72で推定した角速度とすると、uψ=Kp(ψ’−ψ)+Kd・vyawの式のようなPD制御により求める。なお、本実施の形態では、目標角度ψ'を目標対象物Mの方向、すなわち、目標対象物Mの位置の方向を向く角度とした。
Next, in the route tracking control, the process of calculating the control command values u x , u y , u z , u ψ for each direction of the X, Y, Z, and yaw angles so as to fly toward the calculated local target is performed. Do. At this time, a control command value is obtained so that the difference between the current self position and the local target position becomes small. Speed Specifically, the control command value XYZ axis u = (u x, u y , u z) , the self-position r = obtained by the position estimation means 71 (X s, Y s, Z s) and It is obtained by PID control using the velocity v = (v x , v y , v z ) estimated by the estimation means 72. Each control command value of the XYZ-axis direction u = (u x, u y , u z), the local target r '= (x, y, z) when the control command value is, u = Kp (r' -R) + Kd · v + Ki · e is calculated. Here, Kp, Kd, Ki is that the gain of the PID control, respectively, e = (e x, e y, e z) is the integral value of the error. On the other hand, for the control command value u ψ in the yaw angle direction, ψ'is the target angle, ψ is the attitude (angle) of the
飛行停止制御では、振動状態検出手段75から受けたタイミング値に基づいてモータ4の回転を停止させ、ロータ2の回転を停止させる。すなわち、現在時刻を基準としてタイミング値に応じた期間が経過した後にモータ4の回転を停止させる。なお、本実施の形態では、振動状態検出手段75から受けたタイミング値に基づいてモータ4の回転を急停止させることにより飛行停止(緊急着陸)させているが、これに限らず、タイミング値に基づいてモータ4の回転速度を徐々に低下させることによって飛行停止させてもよい。
In the flight stop control, the rotation of the motor 4 is stopped based on the timing value received from the vibration state detecting means 75, and the rotation of the
このように、本実施の形態における自律飛行ロボット1は、振動状態検出手段75にて所定の過去期間における飛行速度の変化履歴に基づいて、当該飛行速度の符号反転を繰り返していることから振動状態を検出し、振動状態検出手段75にて振動状態であると検出したとき、移動制御手段74は、飛行速度が最小となるタイミングで飛行停止(緊急着陸)させる。したがって、本実施の形態における自律飛行ロボット1は、現在の飛行状態が自律的な飛行制御が機能しない振動状態であるとき、飛行速度が最小となるタイミングで飛行停止させることができ、迅速かつ安全に緊急着陸させることが可能となる。すなわち、飛行速度が最小であるため、着陸(落下)時の慣性移動を最小にすることができ、落下距離を最小にできることから周囲の物体への衝突の可能性を少なくすることができる。また、着陸(落下)時における運動エネルギーを最小にできるため、衝突時における周囲の物体や自律飛行ロボット1自体に対する被害を最小にすることができる。
As described above, since the
また、本実施の形態における自律飛行ロボット1は、振動状態検出手段75にて、所定の過去期間において飛行速度の符号が回数閾値以上変化しているときに振動状態と判定する。このように、飛行速度の変化によって振動状態を検知することにより、簡易かつ確実に振動状態を検出することができる。
Further, the
また、本実施の形態における自律飛行ロボット1は、振動状態検出手段75にて、現在時刻から直近(直前)の振幅値が大きいほど長い期間となるよう過去期間を設定し、当該過去期間における飛行速度の変化に基づいて振動状態であるか否かを判定する。すなわち、自律飛行ロボット1が振動状態となっているとき、直前の振幅値が大きいほど、振動の周期が長くなる傾向がある。そのため、直近の振幅値が大きいほど過去期間を長期間とすることにより、振動の状況に応じた適切な過去期間を設定することができ、振動の検出精度を向上させることができる。
Further, in the
また、本実施の形態における自律飛行ロボット1は、過去期間において速度の符号が回数閾値以上変化し、当該過去期間における振幅値の最大値が時間の経過と共に減少傾向であるとき、現在から所定の判定時間だけ判定を保留し、当該判定時間の経過後における振幅値が振幅閾値よりも大きいならば振動状態であると判定する。これにより、たとえ、過去期間における飛行速度の符号が回数閾値以上であったとしても、振動移動が収束傾向(振幅値が減少傾向)にある場合は振動状態とはみなさない。したがって、飛行停止制御によって着陸しなくても、飛行制御が回復するまで様子を見ることが可能となり、通常飛行へ迅速に復帰させることが可能となる。
Further, the
ところで、本発明は、上記実施の形態に限定されるものではなく、特許請求の範囲に記載した技術的思想の範囲内で、更に種々の異なる実施の形態で実施されてもよいものである。また、実施の形態に記載した効果は、これに限定されるものではない。 By the way, the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment, and may be further implemented in various different embodiments within the scope of the technical idea described in the claims. Moreover, the effect described in the embodiment is not limited to this.
上記実施の形態では、速度推定手段72は本発明における飛行状態の計測値である自己位置の時間変化から求めた飛行速度を求め、振動状態検出手段75は、当該飛行速度の過去の変化履歴を示した変化履歴情報82に基づいて、過去期間における飛行速度の符号反転の繰り返しから振動状態を検出している。しかし、これに限らず、飛行状態の計測値として、例えば、別途備えた加速度センサやジャイロセンサによる計測値を積分した値を飛行速度としてを求め、当該飛行速度が符号反転を繰り返している振動状態を検出してもよい。これにより、自律飛行ロボット1の姿勢の時間変化についても飛行速度として求めることができ、姿勢の振動状態を検出することも可能となる。
In the above embodiment, the speed estimating means 72 obtains the flight speed obtained from the time change of the self-position which is the measured value of the flight state in the present invention, and the vibration state detecting means 75 obtains the past change history of the flight speed. Based on the
また、上記実施の形態における、移動制御手段74は、振動状態検出手段75にて出力されたタイミング値に基づいて、モータ4の回転を停止させる飛行停止制御を行っている。しかし、これに限らず、ボクセル情報83(本発明における障害物情報)を参照することによって、モータ4の回転を停止させるタイミングにおいて自己位置の下方に地面以外の障害物(地面以外の占有ボクセル)が存在するか否かを判定し、障害物が存在しないときにモータ4の回転を停止させる飛行停止制御を行ってもよい。または、目標対象物位置81を参照することによって、自己位置の下方に目標対象物Mが存在しないときにモータ4の回転を停止させる飛行停止制御を行ってもよい。これにより、自律飛行ロボット1の下方に人や物体などの障害物が存在するとき、飛行停止(落下)させないため、より安全なタイミングで振動状態を解消して着陸することができる。
Further, the movement control means 74 in the above embodiment performs flight stop control for stopping the rotation of the motor 4 based on the timing value output by the vibration
また、上記実施の形態では、振動状態検出手段75は、予め設定された回数閾値及び振幅閾値を用いて振動状態を検知している。しかし、これに限らず、移動目標位置の位置変化に基づいて、これらの閾値の少なくとも一方をを変更してもよい。具体的には、移動目標位置が大きく変化しているとき、回数閾値や振幅閾値を大きい値に変更し、反対に移動目標位置の変化が小さいとき回数閾値や振幅閾値を小さい値に変更する。すなわち、移動目標位置が大きく変化している場合、振動状態らしい変化をする可能性が高くなるため、振動状態の判定条件を厳しくすることにより、振動状態の誤検出を少なくすることができる。反対に、移動目標位置の変化が小さい場合については、振動状態の判定条件を緩和することにより、振動状態の失検出を少なくすることができる。したがって、振動状態の検出精度を向上させることができる。 Further, in the above embodiment, the vibration state detecting means 75 detects the vibration state using a preset number-of-times threshold value and an amplitude threshold value. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and at least one of these threshold values may be changed based on the position change of the movement target position. Specifically, when the movement target position changes significantly, the number-of-times threshold value and the amplitude threshold value are changed to a large value, and conversely, when the change in the movement target position is small, the number-of-times threshold value and the amplitude threshold value are changed to a small value. That is, when the moving target position is significantly changed, there is a high possibility that the change is likely to occur in the vibration state. Therefore, by tightening the conditions for determining the vibration state, it is possible to reduce the false detection of the vibration state. On the contrary, when the change in the moving target position is small, the loss detection of the vibration state can be reduced by relaxing the condition for determining the vibration state. Therefore, the accuracy of detecting the vibration state can be improved.
また、上記実施の形態では、移動制御手段74は、振動状態検出手段75から振動状態である旨と、モータ4の回転を停止させるタイミング値を出力されたとき、当該タイミング値に基づいてモータ4の回転を停止させる。しかしこれに限らず、移動制御手段74は、振動状態検出手段75から振動状態である旨を出力されたとき、経路探索手段73に対して、タイミング値が示す時間における自己位置と当該自己位置の直下の着陸位置を出力し、経路探索手段73に対して当該自己位置から着陸位置に至る移動経路(着陸経路)を求めさせるようにしてもよい。 Further, in the above embodiment, when the movement control means 74 outputs the vibration state and the timing value for stopping the rotation of the motor 4 from the vibration state detecting means 75, the motor 4 is based on the timing value. Stop the rotation of. However, not limited to this, when the vibration state detecting means 75 outputs that the vibration state is in the movement control means 74, the self-position and the self-position at the time indicated by the timing value with respect to the route search means 73 The landing position immediately below may be output, and the route search means 73 may be made to obtain a movement route (landing route) from the self-position to the landing position.
また、上記実施の形態では、管理装置102に接続された移動物体検出センサ104を用いて目標対象物Mを検出している。しかしながら、これに限定されるものではなく、撮像部3で取得した撮像画像を画像解析することにより、目標対象物Mの位置を推定してもよい。例えば、撮像画像の各フレームを画像処理して目標対象物Mの画像領域を抽出する処理を行う。この際、既知の技術(特開2006−146551号公報を参照)であるオプティカルフロー法、ブースティング学習(例えば、Haar−like特徴を用いているAdaBoostベース識別器による顔検出手法)による識別器等を用いて目標対象物Mの画像領域(人物領域)を抽出する。次に、当該抽出された画像領域の位置に基づいて目標対象物Mと自律飛行ロボット1との距離を推定する。具体的には、抽出した目標対象物Mの画像領域の頭頂部の(撮像画像における)y座標位置と距離との対応表を予め飛行高度毎に作成しておき、現在の飛行高度及び目標対象物Mの頭頂部のy座標位置を当該対応表に照らし合わせて自律飛行ロボット1との距離を推定する。しかし、これに限らず、抽出した目標対象物Mの頭部の大きさから距離を算出してもよい。すなわち、頭部の大きさと距離との対応表を予め作成しておき、抽出された目標対象物Mの頭部の大きさを当該対応表に照らし合わせて自律飛行ロボット1との距離を推定してもよい。
Further, in the above embodiment, the target object M is detected by using the moving object detection sensor 104 connected to the
また、自律飛行ロボット1に撮像部3としてカラーカメラの代わりに距離画像センサを搭載して、当該距離画像センサから取得した距離画像を用いて、既知の移動物体抽出技術により目標対象物Mを抽出して、抽出した目標対象物Mと自律飛行ロボット1との距離値と自己位置とから目標対象物Mの位置を推定してもよい。また、自律飛行ロボット1にレーザスキャナを搭載し、当該レーザスキャナの出力値と自己位置とを用いて目標対象物Mの位置を推定してもよい。
Further, the
また、上記実施の形態では、制御部7において位置推定処理、速度推定処理、移動経路生成処理、経路追従制御の一連の処理を行っている。しかし、これに限らず、図示しない制御用のPCを用意し、当該PCにこれらの一連の処理を実施させてもよい。すなわち、自律飛行ロボット1は、PCによって行われた位置推定処理、速度推定処理、移動経路生成処理、経路追従制御によって得られた制御指令値を無線通信又は有線通信によりPCから受信し、当該制御指令値に基づいてモータ4の回転数を制御することにより、目的の位置に飛行するようにしてもよい。このように、外部PCを用いて上記の一連の処理を分担することにより、自律飛行ロボット1のCPU処理負荷を低減することができ、ひいてはバッテリの消耗も抑えることができる。
Further, in the above embodiment, the
1・・・自律飛行ロボット
2・・・ロータ
3・・・撮像部
4・・・モータ
5・・・距離検出センサ
6・・・位置検出センサ
7・・・制御部
8・・・記憶部
9・・・通信部
71・・・位置推定手段
72・・・速度推定手段
73・・・経路探索手段
74・・・移動制御手段
75・・・振動状態検出手段
81・・・目標対象物位置
82・・・変化履歴情報
83・・・ボクセル情報
84・・・各種パラメータ
100・・・警備センタ
102・・・管理装置
104・・・移動物体検出センサ
110・・・情報通信網
M・・・目標対象物
1 ...
Claims (6)
前記自律飛行ロボットの飛行状態を計測した計測値から飛行速度を推定する速度推定手段と、
現在時刻から所定時間前までの過去期間における前記飛行速度の変化履歴に基づいて該飛行速度が符号反転を繰り返している振動状態を検出する振動状態検出手段と、
前記振動状態検出手段にて前記振動状態を検出したとき、前記飛行速度が最小となるタイミングで飛行停止させる飛行制御手段と、
を有することを特徴とする自律飛行ロボット。
An autonomous flying robot that autonomously flies in a moving space.
A speed estimation means for estimating the flight speed from the measured values obtained by measuring the flight state of the autonomous flight robot, and
A vibration state detecting means for detecting a vibration state in which the flight speed repeats code reversal based on a history of changes in the flight speed in the past period from the current time to a predetermined time ago.
When the vibration state is detected by the vibration state detecting means, the flight control means for stopping the flight at the timing when the flight speed becomes the minimum, and the flight control means.
An autonomous flying robot characterized by having.
The autonomous flight robot according to claim 1, wherein the vibration state detecting means determines the vibration state when the code of the flight speed in the past period changes by a predetermined number of times or more.
The autonomous flight robot according to any one of claims 1 or 2, wherein the vibration state detecting means sets the past period longer as the amplitude value of the flight speed in the immediate vicinity of the current time is larger.
The vibration state detecting means has a predetermined determination time from the current time when the sign of the flight speed has changed by a predetermined number of times threshold value or more in the past period and the amplitude value of the flight speed tends to decrease with the passage of time. The autonomous flying robot according to any one of claims 1 to 3, wherein if the amplitude value after the lapse is larger than a predetermined amplitude threshold value, the vibration state is determined.
前記自律飛行ロボットの自己位置を推定する自己位置推定部を更に備え、
前記飛行制御手段は、前記障害物情報を用いて前記自己位置の下方に障害物が存在しないとき前記飛行停止を実行する請求項1〜4の何れか一項に記載の自律飛行ロボット。
The obstacle information indicating the position of the obstacle existing in the moving space is stored, and the obstacle information is stored.
Further provided with a self-position estimation unit that estimates the self-position of the autonomous flying robot,
The autonomous flight robot according to any one of claims 1 to 4, wherein the flight control means uses the obstacle information to execute the flight stop when there is no obstacle below the self-position.
前記飛行制御手段は、前記飛行経路に沿って飛行するよう制御し、
振動状態検出手段は、前記移動目標位置の変化が大きいとき前記回数閾値を大きい値に変更し、前記移動目標位置の変化が小さいとき前記回数閾値を小さい値に変更する請求項2に記載の自律飛行ロボット。 Further having a route search means for setting a movement target position in the flight space and finding a flight path from its own position to the movement target position.
The flight control means controls to fly along the flight path and controls the flight.
The autonomous state according to claim 2 , wherein the vibration state detecting means changes the number-of-times threshold value to a large value when the change in the movement target position is large, and changes the number-time threshold value to a small value when the change in the movement target position is small. Flying robot.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016072711A JP6758069B2 (en) | 2016-03-31 | 2016-03-31 | Autonomous flying robot |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016072711A JP6758069B2 (en) | 2016-03-31 | 2016-03-31 | Autonomous flying robot |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2017182691A JP2017182691A (en) | 2017-10-05 |
| JP2017182691A5 JP2017182691A5 (en) | 2019-03-28 |
| JP6758069B2 true JP6758069B2 (en) | 2020-09-23 |
Family
ID=60007506
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016072711A Active JP6758069B2 (en) | 2016-03-31 | 2016-03-31 | Autonomous flying robot |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6758069B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6923479B2 (en) | 2018-03-28 | 2021-08-18 | Kddi株式会社 | Flight equipment, flight systems, flight methods and programs |
| JP7165278B2 (en) * | 2018-03-28 | 2022-11-02 | Kddi株式会社 | Management device, management method and program |
| JP6923026B1 (en) * | 2020-02-27 | 2021-08-18 | 沖電気工業株式会社 | Aircraft and programs |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2964573B1 (en) * | 2010-09-15 | 2012-09-28 | Parrot | METHOD FOR CONTROLLING A MULTI-ROTOR ROTOR SAILING DRONE |
-
2016
- 2016-03-31 JP JP2016072711A patent/JP6758069B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2017182691A (en) | 2017-10-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6664162B2 (en) | Autonomous flying robot | |
| JP6029446B2 (en) | Autonomous flying robot | |
| JP6195450B2 (en) | Autonomous flying robot | |
| JP6599143B2 (en) | Autonomous mobile robot | |
| TWI804538B (en) | Adjustable object avoidance proximity threshold of a robotic vehicle based on presence of detected payload(s) | |
| JP6235213B2 (en) | Autonomous flying robot | |
| JP6527726B2 (en) | Autonomous mobile robot | |
| JP5990453B2 (en) | Autonomous mobile robot | |
| JP6140458B2 (en) | Autonomous mobile robot | |
| JP6014485B2 (en) | Autonomous flying robot | |
| TWI827649B (en) | Apparatuses, systems and methods for vslam scale estimation | |
| CN107087429B (en) | Aircraft control method and device | |
| JP6758068B2 (en) | Autonomous mobile robot | |
| JP6014484B2 (en) | Autonomous mobile robot | |
| JPWO2017033976A1 (en) | Aircraft control device, aircraft control method, and program | |
| JP2017182692A (en) | Autonomous Mobile Robot | |
| JP6469492B2 (en) | Autonomous mobile robot | |
| JP6530212B2 (en) | Autonomous mobile robot | |
| JP6758069B2 (en) | Autonomous flying robot | |
| JP6595284B2 (en) | Autonomous mobile robot | |
| JP2024026785A (en) | Aerial vehicle, inspection method and inspection system | |
| JP7155062B2 (en) | Surveillance system and flying robot | |
| JP7351609B2 (en) | Route searching device and program | |
| JP6664258B2 (en) | Self-location estimation device | |
| JP6905771B2 (en) | Aircraft, inspection method and inspection system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20190215 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20190215 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20200123 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20200218 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20200414 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20200825 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20200901 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6758069 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |