JP6699646B2 - Vehicle display control device - Google Patents
Vehicle display control device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6699646B2 JP6699646B2 JP2017243498A JP2017243498A JP6699646B2 JP 6699646 B2 JP6699646 B2 JP 6699646B2 JP 2017243498 A JP2017243498 A JP 2017243498A JP 2017243498 A JP2017243498 A JP 2017243498A JP 6699646 B2 JP6699646 B2 JP 6699646B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- vehicle
- display
- virtual image
- lane
- display control
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 claims description 30
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 claims description 15
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 claims description 13
- 230000000007 visual effect Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 35
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 32
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 30
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 30
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 25
- 230000033228 biological regulation Effects 0.000 description 23
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 15
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 description 14
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 13
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000012790 confirmation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000004088 simulation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 241000283070 Equus zebra Species 0.000 description 2
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004907 flux Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 210000001747 pupil Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000003190 augmentative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009194 climbing Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002485 combustion reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001276 controlling effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009977 dual effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000003128 head Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012876 topography Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W50/00—Details of control systems for road vehicle drive control not related to the control of a particular sub-unit, e.g. process diagnostic or vehicle driver interfaces
- B60W50/08—Interaction between the driver and the control system
- B60W50/14—Means for informing the driver, warning the driver or prompting a driver intervention
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60K—ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PROPULSION UNITS OR OF TRANSMISSIONS IN VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PLURAL DIVERSE PRIME-MOVERS IN VEHICLES; AUXILIARY DRIVES FOR VEHICLES; INSTRUMENTATION OR DASHBOARDS FOR VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENTS IN CONNECTION WITH COOLING, AIR INTAKE, GAS EXHAUST OR FUEL SUPPLY OF PROPULSION UNITS IN VEHICLES
- B60K35/00—Instruments specially adapted for vehicles; Arrangement of instruments in or on vehicles
- B60K35/20—Output arrangements, i.e. from vehicle to user, associated with vehicle functions or specially adapted therefor
- B60K35/21—Output arrangements, i.e. from vehicle to user, associated with vehicle functions or specially adapted therefor using visual output, e.g. blinking lights or matrix displays
- B60K35/23—Head-up displays [HUD]
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60K—ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PROPULSION UNITS OR OF TRANSMISSIONS IN VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PLURAL DIVERSE PRIME-MOVERS IN VEHICLES; AUXILIARY DRIVES FOR VEHICLES; INSTRUMENTATION OR DASHBOARDS FOR VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENTS IN CONNECTION WITH COOLING, AIR INTAKE, GAS EXHAUST OR FUEL SUPPLY OF PROPULSION UNITS IN VEHICLES
- B60K35/00—Instruments specially adapted for vehicles; Arrangement of instruments in or on vehicles
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60K—ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PROPULSION UNITS OR OF TRANSMISSIONS IN VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PLURAL DIVERSE PRIME-MOVERS IN VEHICLES; AUXILIARY DRIVES FOR VEHICLES; INSTRUMENTATION OR DASHBOARDS FOR VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENTS IN CONNECTION WITH COOLING, AIR INTAKE, GAS EXHAUST OR FUEL SUPPLY OF PROPULSION UNITS IN VEHICLES
- B60K35/00—Instruments specially adapted for vehicles; Arrangement of instruments in or on vehicles
- B60K35/20—Output arrangements, i.e. from vehicle to user, associated with vehicle functions or specially adapted therefor
- B60K35/28—Output arrangements, i.e. from vehicle to user, associated with vehicle functions or specially adapted therefor characterised by the type of the output information, e.g. video entertainment or vehicle dynamics information; characterised by the purpose of the output information, e.g. for attracting the attention of the driver
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60K—ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PROPULSION UNITS OR OF TRANSMISSIONS IN VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PLURAL DIVERSE PRIME-MOVERS IN VEHICLES; AUXILIARY DRIVES FOR VEHICLES; INSTRUMENTATION OR DASHBOARDS FOR VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENTS IN CONNECTION WITH COOLING, AIR INTAKE, GAS EXHAUST OR FUEL SUPPLY OF PROPULSION UNITS IN VEHICLES
- B60K35/00—Instruments specially adapted for vehicles; Arrangement of instruments in or on vehicles
- B60K35/20—Output arrangements, i.e. from vehicle to user, associated with vehicle functions or specially adapted therefor
- B60K35/29—Instruments characterised by the way in which information is handled, e.g. showing information on plural displays or prioritising information according to driving conditions
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60K—ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PROPULSION UNITS OR OF TRANSMISSIONS IN VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PLURAL DIVERSE PRIME-MOVERS IN VEHICLES; AUXILIARY DRIVES FOR VEHICLES; INSTRUMENTATION OR DASHBOARDS FOR VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENTS IN CONNECTION WITH COOLING, AIR INTAKE, GAS EXHAUST OR FUEL SUPPLY OF PROPULSION UNITS IN VEHICLES
- B60K35/00—Instruments specially adapted for vehicles; Arrangement of instruments in or on vehicles
- B60K35/80—Arrangements for controlling instruments
- B60K35/81—Arrangements for controlling instruments for controlling displays
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W40/00—Estimation or calculation of non-directly measurable driving parameters for road vehicle drive control systems not related to the control of a particular sub unit, e.g. by using mathematical models
- B60W40/02—Estimation or calculation of non-directly measurable driving parameters for road vehicle drive control systems not related to the control of a particular sub unit, e.g. by using mathematical models related to ambient conditions
- B60W40/06—Road conditions
- B60W40/072—Curvature of the road
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60K—ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PROPULSION UNITS OR OF TRANSMISSIONS IN VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PLURAL DIVERSE PRIME-MOVERS IN VEHICLES; AUXILIARY DRIVES FOR VEHICLES; INSTRUMENTATION OR DASHBOARDS FOR VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENTS IN CONNECTION WITH COOLING, AIR INTAKE, GAS EXHAUST OR FUEL SUPPLY OF PROPULSION UNITS IN VEHICLES
- B60K2360/00—Indexing scheme associated with groups B60K35/00 or B60K37/00 relating to details of instruments or dashboards
- B60K2360/16—Type of output information
- B60K2360/177—Augmented reality
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60K—ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PROPULSION UNITS OR OF TRANSMISSIONS IN VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PLURAL DIVERSE PRIME-MOVERS IN VEHICLES; AUXILIARY DRIVES FOR VEHICLES; INSTRUMENTATION OR DASHBOARDS FOR VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENTS IN CONNECTION WITH COOLING, AIR INTAKE, GAS EXHAUST OR FUEL SUPPLY OF PROPULSION UNITS IN VEHICLES
- B60K2360/00—Indexing scheme associated with groups B60K35/00 or B60K37/00 relating to details of instruments or dashboards
- B60K2360/16—Type of output information
- B60K2360/178—Warnings
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60K—ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PROPULSION UNITS OR OF TRANSMISSIONS IN VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PLURAL DIVERSE PRIME-MOVERS IN VEHICLES; AUXILIARY DRIVES FOR VEHICLES; INSTRUMENTATION OR DASHBOARDS FOR VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENTS IN CONNECTION WITH COOLING, AIR INTAKE, GAS EXHAUST OR FUEL SUPPLY OF PROPULSION UNITS IN VEHICLES
- B60K2360/00—Indexing scheme associated with groups B60K35/00 or B60K37/00 relating to details of instruments or dashboards
- B60K2360/18—Information management
- B60K2360/186—Displaying information according to relevancy
- B60K2360/1868—Displaying information according to relevancy according to driving situations
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60K—ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PROPULSION UNITS OR OF TRANSMISSIONS IN VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PLURAL DIVERSE PRIME-MOVERS IN VEHICLES; AUXILIARY DRIVES FOR VEHICLES; INSTRUMENTATION OR DASHBOARDS FOR VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENTS IN CONNECTION WITH COOLING, AIR INTAKE, GAS EXHAUST OR FUEL SUPPLY OF PROPULSION UNITS IN VEHICLES
- B60K2360/00—Indexing scheme associated with groups B60K35/00 or B60K37/00 relating to details of instruments or dashboards
- B60K2360/20—Optical features of instruments
- B60K2360/33—Illumination features
- B60K2360/334—Projection means
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60K—ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PROPULSION UNITS OR OF TRANSMISSIONS IN VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PLURAL DIVERSE PRIME-MOVERS IN VEHICLES; AUXILIARY DRIVES FOR VEHICLES; INSTRUMENTATION OR DASHBOARDS FOR VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENTS IN CONNECTION WITH COOLING, AIR INTAKE, GAS EXHAUST OR FUEL SUPPLY OF PROPULSION UNITS IN VEHICLES
- B60K35/00—Instruments specially adapted for vehicles; Arrangement of instruments in or on vehicles
- B60K35/20—Output arrangements, i.e. from vehicle to user, associated with vehicle functions or specially adapted therefor
- B60K35/21—Output arrangements, i.e. from vehicle to user, associated with vehicle functions or specially adapted therefor using visual output, e.g. blinking lights or matrix displays
- B60K35/23—Head-up displays [HUD]
- B60K35/235—Head-up displays [HUD] with means for detecting the driver's gaze direction or eye points
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W50/00—Details of control systems for road vehicle drive control not related to the control of a particular sub-unit, e.g. process diagnostic or vehicle driver interfaces
- B60W50/08—Interaction between the driver and the control system
- B60W50/14—Means for informing the driver, warning the driver or prompting a driver intervention
- B60W2050/146—Display means
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W2552/00—Input parameters relating to infrastructure
- B60W2552/30—Road curve radius
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Transportation (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Instrument Panels (AREA)
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
Description
本開示は、車両用表示制御装置に関するものである。 The present disclosure relates to a vehicle display control device.
従来、特許文献1に開示されるような、フロントガラス等の投影部材へ画像を投影することによって車両の前景に虚像を重畳表示させるヘッドアップディスプレイ(以下、HUD)が知られている。HUDによって、自車が走行予定の車線の形状に沿った虚像を前景中のその車線に重畳表示させることで、自車の走行予定の車線をドライバに認識させ、ドライバを支援する技術が知られている。また、特許文献2に開示されるような、HUDによって、自車の走行路の道路標識の情報を示す虚像を車両の前景に重畳表示させ、ドライバを支援する技術も知られている。
BACKGROUND ART Conventionally, as disclosed in
しかしながら、自車が走行予定の車線の形状に沿った虚像(以下、進路虚像)を前景中のその車線に重畳表示させる場合、画像を投影可能な範囲に制約があることにより、進路虚像の表示が違和感の大きなものとなり、ドライバに煩わしさを感じさせてしまう場合がある。詳しくは、カーブ中には、自車が走行予定の車線のうち自車から遠位側が、運転席から左右に外れて湾曲して見える状況が生じる。このような状況において、画像を投影可能な範囲が運転席前方に限られていた場合、進路虚像を前景に重畳表示させようとしても、運転席前方から左右に外れた部分の進路虚像の表示が大きく欠けた進路虚像が表示されてしまう場合がある。このような進路虚像が大きく欠けた表示がドライバの目にとまると、ドライバに煩わしさを感じさせてしまう場合がある。カーブ中以外にも勾配の変化時にも、同様の問題が生じる場合がある。 However, when a virtual image along the shape of the lane that the vehicle is going to travel (hereinafter, virtual route image) is displayed on the lane in the foreground in a superimposed manner, there is a limit to the range in which the image can be projected. May become uncomfortable and may make the driver feel annoyed. Specifically, during the curve, a situation occurs in which the distant side from the own vehicle in the lane in which the own vehicle is scheduled to travel appears to be curved to the left and right from the driver's seat. In such a situation, when the range in which the image can be projected is limited to the front of the driver's seat, even if an attempt is made to superimpose the virtual virtual image of the route on the foreground, the virtual virtual image of the part deviated from the front of the driver's seat to the left and right is displayed. There may be a case in which a large virtual image of the path is displayed. If such a display in which the virtual course image is largely cut off is noticeable to the driver, the driver may feel annoyed. Similar problems may occur not only during the curve but also when the slope changes.
また、勾配の変化時には、進路虚像を重畳表示させる領域が、画像を投影可能な範囲内におさまっている場合であっても、進路虚像の表示が違和感の大きなものとなり、ドライバに煩わしさを感じさせてしまう場合がある。詳しくは、自車の進路前方に勾配が減少する区間が存在する場合に、勾配が減少する度合いによっては、下り勾配の路面にドライバから視認できない死角が生じる。このような状況において、ドライバの死角にあたる路面の形状にまで沿った進路虚像を前景に重畳表示させると、ドライバに視認される路面の形状と大きく異なった表示となるので、ドライバに煩わしさを感じさせてしまう場合がある。 In addition, when the gradient changes, even if the area in which the route virtual image is superimposed and displayed is within the range in which the image can be projected, the display of the route virtual image becomes uncomfortable and the driver feels annoyed. There is a case to let you. Specifically, when there is a section where the gradient decreases in front of the route of the host vehicle, a blind spot that cannot be visually recognized by the driver occurs on the road surface having a downward gradient depending on the degree of the gradient decrease. In such a situation, if a virtual road image along the shape of the road surface, which is the blind spot of the driver, is displayed on the foreground in a superimposed manner, the display will be significantly different from the shape of the road surface as seen by the driver, which makes the driver feel annoyed. There is a case to let you.
他にも、自車の走行路の道路標識の情報を示す虚像を車両の前景に重畳表示させる場合に、道路標識が自車の前方に現れるごとにこの道路標示を示す虚像がドライバの目にとまると、ドライバに煩わしさを感じさせてしまう場合がある。 In addition, when a virtual image showing the information of the road sign of the own vehicle's road is superimposed on the foreground of the vehicle, a virtual image showing this road sign is displayed to the driver's eyes every time the road sign appears in front of the own vehicle. When stopped, the driver may feel annoyed.
この開示のひとつの目的は、車両の前景に虚像を重畳表示させることでドライバの支援を行いつつも、虚像を重畳表示させることによるドライバの煩わしさを低減させることを可能にする車両用表示制御装置を提供することにある。 One object of this disclosure is to provide a vehicle display control that can reduce the inconvenience of a driver by displaying a virtual image in a superimposed manner while supporting the driver by displaying a virtual image in the foreground of the vehicle. To provide a device.
上記目的は独立請求項に記載の特徴の組み合わせにより達成され、また、下位請求項は、開示の更なる有利な具体例を規定する。特許請求の範囲に記載した括弧内の符号は、一つの態様として後述する実施形態に記載の具体的手段との対応関係を示すものであって、本開示の技術的範囲を限定するものではない。 The above objective is achieved by a combination of features described in independent claims, and the subclaims define further advantageous embodiments of the disclosure. The reference numerals in parentheses in the claims indicate the correspondence with the specific means described in the embodiments described below as one aspect, and do not limit the technical scope of the present disclosure. ..
上記目的を達成するために、本開示の車両用表示制御装置は、車両で用いられ、投影部材へ画像を投影することによって車両の前景に虚像を重畳表示させるヘッドアップディスプレイ(220)による表示を制御する車両用表示制御装置であって、自車の走行路の道路構造である自車状況を判定する状況判定部(203,203c)と、虚像の重畳表示の対象に対する虚像の重畳表示の制限の有無を、状況判定部で判定した自車状況に応じて切り替える表示制御部(204,204c,204d)とを備え、状況判定部で判定する自車状況は、自車の走行路の曲率及び勾配変化の少なくともいずれかであって、表示制御部は、状況判定部で判定した自車の走行路の曲率及び勾配変化の少なくともいずれかに応じて、虚像の重畳表示の対象となる、自車が走行予定の車線に対して、前景中へのその車線の形状に沿った虚像の重畳表示を制限する。 To achieve the above object, a car dual display control device of the present disclosure is used in a vehicle, the display by the head-up display (220) to superimpose the virtual image to the foreground of the vehicle by projecting an image to the projection member A display control device for a vehicle that controls, a situation determination unit (203, 203c) that determines a vehicle state, which is a road structure of a traveling path of the vehicle, and a limitation on a virtual image superimposed display with respect to a virtual image superimposed display target. And a display control unit (204, 204c, 204d) that switches the presence/absence of the vehicle according to the vehicle status determined by the status determination section. The display control unit, which is at least one of the gradient changes, is a target of the virtual image superimposed display according to at least one of the curvature and the gradient change of the traveling path of the own vehicle determined by the situation determination unit. respect lane but driving schedule, that limits the superimposed display of the virtual image along with the shape of the lane into the foreground.
これによれば、自車の走行路の道路構造である自車状況に応じて、前景への虚像の重畳表示の対象となる同一の対象に対する虚像の重畳表示の制限の有無を切り替えることが可能になる。よって、自車の走行路の道路構造によってドライバに煩わしさを与えるおそれがある状況で対象に対する虚像の重畳表示を制限することが可能になる。従って、ドライバにとって虚像の重畳表示の必要性がより少ないと考えられる状況の場合に、対象に対する虚像の重畳表示を制限することが可能になる。その結果、車両の前景に虚像を重畳表示させることでドライバの支援を行いつつも、虚像を重畳表示させることによるドライバの煩わしさを低減させることが可能になる。 According to this, it is possible to switch the presence/absence of the restriction of the virtual image superimposition display for the same target, which is the target of the virtual image superimposition display on the foreground, depending on the vehicle structure that is the road structure of the traveling path of the own vehicle. become. Therefore, it is possible to limit the superimposed display of the virtual image on the target in a situation where the driver may be annoyed by the road structure of the traveling path of the vehicle. Therefore, in a situation where it is considered that the driver does not need to display the virtual image in a superimposed manner, it is possible to limit the superimposed display of the virtual image on the target. As a result, it is possible to reduce the inconvenience of the driver caused by displaying the virtual image in a superimposed manner while supporting the driver by displaying the virtual image in the foreground of the vehicle.
図面を参照しながら、開示のための複数の実施形態及び変形例を説明する。なお、説明の便宜上、複数の実施形態及び変形例の間において、それまでの説明に用いた図に示した部分と同一の機能を有する部分については、同一の符号を付し、その説明を省略する場合がある。同一の符号を付した部分については、他の実施形態及び変形例における説明を参照することができる。 A plurality of embodiments and modifications for disclosure will be described with reference to the drawings. Note that, for convenience of description, between a plurality of embodiments and modified examples, parts having the same functions as those shown in the figures used in the above description are designated by the same reference numerals, and description thereof will be omitted. There is a case. For the portions denoted by the same reference numerals, the description in other embodiments and modifications can be referred to.
(実施形態1)
<車両システム1の概略構成>
以下、本実施形態について図面を用いて説明する。図1に示す車両システム1は、自動車といった車両で用いられるものであり、HMI(Human Machine Interface)システム2、ADAS(Advanced Driver Assistance Systems)ロケータ3、周辺監視センサ4、車両制御ECU5、自動運転ECU6、及びウィンカースイッチ7を含んでいる。HMIシステム2、ADASロケータ3、周辺監視センサ4、車両制御ECU5、自動運転ECU6、及びウィンカースイッチ7は、例えば車内LANに接続されているものとする。以下では、車両システム1を用いる車両を自車と呼ぶ。
(Embodiment 1)
<Schematic configuration of
Hereinafter, the present embodiment will be described with reference to the drawings. A
ADASロケータ3は、GNSS(Global Navigation Satellite System)受信機30、慣性センサ31、及び地図データを格納した地図データベース(以下、地図DB)32を備えている。GNSS受信機30は、複数の人工衛星からの測位信号を受信する。慣性センサ31は、例えば3軸ジャイロセンサ及び3軸加速度センサを備える。地図DB32は、不揮発性メモリであって、リンクデータ、セグメントデータ、ノードデータ、道路形状等の地図データを格納している。
The
リンクデータは、リンクを特定するリンクID、リンクの長さを示すリンク長、リンク方位、リンク旅行時間、リンクの始端と終端とのノード座標、及び道路属性等の各データから構成される。セグメントデータは、リンクを形状点で分割したセグメントごとのデータであって、セグメントを特定するセグメントID、セグメントの長さを表すセグメント長、セグメントの曲率、セグメントの両端の形状点ID等から構成される。ノードデータは、地図上のノード毎に固有の番号を付したノードID、ノード座標、ノード名称、ノード種別、ノードに接続するリンクのリンクIDが記述される接続リンクID、交差点種別等の各データから構成される。道路形状のデータには、縦断勾配,曲率等のデータを含むものとする。また、地図データとして、地形,道路標識を含む構造物,道路標示等のデータも含む三次元地図データも用いる構成としてもよい。なお、地図データは、自車に搭載された車載通信モジュールを用いて自車の外部から取得する構成としてもよい。 The link data is composed of each data such as a link ID for identifying the link, a link length indicating the length of the link, a link azimuth, a link travel time, node coordinates of the start and end of the link, and road attributes. The segment data is data for each segment obtained by dividing a link by a shape point, and is composed of a segment ID that identifies the segment, a segment length that represents the length of the segment, a curvature of the segment, shape point IDs at both ends of the segment, and the like. It The node data is each data such as a node ID given a unique number for each node on the map, a node coordinate, a node name, a node type, a connection link ID in which a link ID of a link connecting to the node is described, an intersection type, etc. Composed of. The road shape data includes data such as vertical gradient and curvature. Further, as the map data, it is also possible to use three-dimensional map data including data such as topography, structures including road signs, and road markings. Note that the map data may be acquired from the outside of the own vehicle by using an in-vehicle communication module mounted on the own vehicle.
ADASロケータ3は、GNSS受信機30で受信する測位信号と、慣性センサ31の計測結果とを組み合わせることにより、ADASロケータ3を搭載した自車の車両位置を逐次測位する。なお、車両位置の測位には、自車に搭載された車輪速センサから逐次出力されるパルス信号から求めた走行距離を用いる構成としてもよい。そして、測位した車両位置を車内LANへ出力する。また、ADASロケータ3は、地図DB32から地図データを読み出し、車内LANへ出力することも行う。
The
周辺監視センサ4は、自車周辺の静止物体,移動体を検出したり、規制標示,指示標示,走行区画線等の道路標示を検出したりする。周辺監視センサ4としては、自車の前方の所定範囲を撮像範囲とする前方カメラ40を用いる構成とすればよい。例えば前方カメラ40は、自車のルームミラー11(図2参照)に設ける構成とすればよい。前方カメラ40は、自車のインストルメントパネル12(図2参照)の上面に設ける等してもよい。周辺監視センサ4としては、自車の前方以外を撮像するカメラを用いたり、ミリ波レーダ,ソナー,LIDAR(Light Detection and Ranging/Laser Imaging Detect ion and Ranging)等を用いたりする構成としてもよい。
The
車両制御ECU5は、自車の加減速制御及び/又は操舵制御を行う電子制御装置である。車両制御ECU5としては、操舵制御を行う操舵ECU、加減速制御を行うパワーユニット制御ECU及びブレーキECU等がある。車両制御ECU5は、自車に搭載されたアクセルポジションセンサ、ブレーキ踏力センサ、舵角センサ、車輪速センサ等の各センサから出力される検出信号を取得し、電子制御スロットル、ブレーキアクチュエータ、EPS(Electric Power Steering)モータ等の各走行制御デバイスへ制御信号を出力する。また、車両制御ECU5は、上述の各センサの検出信号を車内LANへ出力可能である。
The
自動運転ECU6は、車両制御ECU5を制御することにより、ドライバによる運転操作の代行を行う自動運転機能を実行する。自動運転ECU6は、ADASロケータ3から取得した自車の車両位置及び地図データ,周辺監視センサ4での検出結果から、自車の走行環境を認識する。一例としては、周辺監視センサ4での検出結果から、自車周辺の物体の形状及び移動状態を認識したり、自車周辺の標示の形状を認識したりする。そして、自車の車両位置及び地図データと組み合わせることで、実際の走行環境を三次元で再現した仮想空間を生成する。
By controlling the
また、自動運転ECU6は、認識した走行環境に基づき、自動運転機能によって自車を自動走行させるための走行計画を生成する。走行計画としては、長中期の走行計画と、短期の走行計画とが生成される。長中期の走行計画では、設定された目的地に自車を向かわせるための経路が規定される。短期の走行計画では、生成した自車の周囲の仮想空間を用いて、長中期の走行計画に従った走行を実現するための予定走行軌跡が規定される。具体的に、車線追従及び車線変更のための操舵、速度調整のための加減速、並びに衝突回避のための急制動等の実行が、短期の走行計画に基づいて決定される。
Further, the
ウィンカースイッチ7は、自車のウィンカーレバーに対する点灯操作を検出するためのスイッチである。ウィンカースイッチ7は、ウィンカーレバーの操作に応じた右左折時のウィンカ信号を車内LANへ出力する。
The
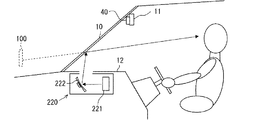
HMIシステム2は、HCU(Human Machine Interface Control Unit)20、操作デバイス21、及び表示装置22を備えており、自車のドライバからの入力操作を受け付けたり、自車のドライバに向けて情報を提示したりする。操作デバイス21は、自車のドライバが操作するスイッチ群である。操作デバイス21は、各種の設定を行うために用いられる。例えば、操作デバイス21としては、自車のステアリングのスポーク部に設けられたステアリングスイッチ等がある。表示装置22としては、ヘッドアップディスプレイ(HUD)220を用いる。ここで、図2を用いてHUD220について説明を行う。
The
図2に示すようにHUD220は、自車のインストルメントパネル12に設けられる。HUD220は、例えば液晶式又は走査式等のプロジェクタ221により、HCU20から出力される画像データに基づく表示画像を形成する。表示画像としては、例えば車速,自動運転機能の動作状態等の自車状態を示す画像がある。また、自車の予定進路を示す画像,道路標識及び道路標示といった情報源を示す画像等がある。なお、ここに挙げた以外の情報を示す画像を用いる構成としてもよい。
As shown in FIG. 2, the
HUD220は、プロジェクタ221によって形成される表示画像を、例えば凹面鏡等の光学系222を通じて、投影部材としてのフロントウインドシールド10に既定された投影領域に投影する。投影領域は、例えば運転席前方に位置するものとする。フロントウインドシールド10によって車室内側に反射された表示画像の光束は、運転席に着座するドライバによって知覚される。また、透光性ガラスにより形成されるフロントウインドシールド10を透過した、自車の前方に存在する風景としての前景からの光束も、運転席に着座するドライバによって知覚される。これにより、ドライバは、フロントウインドシールド10の前方にて結像される表示画像の虚像100を、前景の一部と重ねて視認可能となる。つまり、HUD220は、自車の前景に虚像100を重畳表示し、所謂AR(Augmented Reality)表示を実現する。
The
なお、HUD220が表示画像を投影する投影部材は、フロントウインドシールド10に限らず、透光性コンバイナであっても構わない。また、表示装置22として、HUD220の他にも、画像を表示する装置を用いる構成としてもよい。一例としては、コンビネーションメータ、CID(Center Information Display)等がある。
The projection member on which the
HCU20は、プロセッサ、揮発性メモリ、不揮発性メモリ、I/O、これらを接続するバスを備えるマイクロコンピュータを主体として構成され、HUD220と車内LANとに接続されている。HCU20は、不揮発性メモリに記憶された制御プログラムを実行することにより、HUD220による表示を制御する。このHCU20が車両用表示制御装置に相当する。なお、HUD220による表示の制御に関するHCU20の構成については以下で詳述する。
The
<HCU20の概略構成>
ここで、図3を用いてHCU20の概略構成についての説明を行う。HCU20は、HUD220による表示の制御に関して、図3に示すように、情報取得部201、対象区間判定部202、状況判定部203、及び表示制御部204を機能ブロックとして備える。なお、HCU20が実行する機能の一部又は全部を、一つ或いは複数のIC等によりハードウェア的に構成してもよい。また、HCU20が備える機能ブロックの一部又は全部は、プロセッサによるソフトウェアの実行とハードウェア部材の組み合わせによって実現されてもよい。
<Schematic configuration of
Here, the schematic configuration of the
情報取得部201は、HUD220での表示に必要な情報を取得する。一例としては、ADASロケータ3から出力される車両位置及び地図データ,車両制御ECU5から出力される各センサの検出信号,自動運転ECU6で認識した走行環境及び自動運転ECU6で生成した走行計画の情報等がある。
The
対象区間判定部202は、自車の走行路がレーンガイダンスの虚像の表示(以下、レーンガイダンス表示)を行う対象となる区間(以下、対象区間)か否かを判定する。レーンガイダンス表示とは、前景中の走行予定車線の形状に沿ってその車線内の範囲を示す表示であって、一例として対象車線の車線幅の例えば半分以上等の大半にわたる表示とする。本実施形態では、レーンガイダンス表示が、対象車線の車線幅と略一致する幅にわたる表示である場合を例に挙げて以降の説明を行う。ここで言うところの前景中の走行予定車線とは、走行計画から自車が走行する予定の車線である。また、ここで言うところの対象区間とは、リンク単位の区間であってもよいし、セグメント単位の区間であってもよいし、他の基準で区分される区間であってもよい。対象区間の一例としては、分岐前,合流前,カーブ前等の自車が旋回目前の区間、及びカーブ路といった自車が旋回を必要とする区間等が挙げられる。
The target
対象区間判定部202は、ADASロケータ3から出力される車両位置及び地図データから、自車の車両位置に相当する区間が対象区間か否かを判定すればよい。自車の車両位置に相当する区間は、例えばマップマッチング処理によって特定すればよい。なお、ADASロケータ3でマップマッチング処理まで行って自車の道路上の位置を特定する場合には、車両位置の代わりに自車の道路上の位置を用いる構成とすればよい。カーブ路の判別は、地図データでカーブ路と直線路との区別がされている場合には、これに従って判別すればよい。なお、道路形状のうちの曲率によってカーブ路を判別する等してもよい。また、対象区間判定部202は、自動運転ECU6で認識した走行環境から、自車の車両位置に相当する区間が対象区間か否かを判定してもよい。
The target
状況判定部203は、自車の走行路の曲率を判定する。自車の走行路は、自車の車両位置に相当する区間とすればよい。自車の走行路の曲率が自車状況に相当する。自車の車両位置に相当する区間は、前述したのと同様にして特定すればよい。自車の車両位置に相当する区間は、リンク単位の区間であってもよいし、セグメント単位の区間であってもよいし、他の基準で区分される区間であってもよい。状況判定部203は、自動運転ECU6で認識した走行環境から自車の走行路の曲率を判定してもよいし、ADASロケータ3から出力される車両位置及び地図データから自車の走行路の曲率を判定してもよい。
The
また、状況判定部203は、自車の走行路の曲率が閾値以上か否かを判定する。ここで言うところの閾値とは、レーンガイダンス表示がドライバに違和感を与えると推定されるほど投影領域から外れると予測される曲率の値とすればよい。この閾値は、シミュレーションによって推算したり、実験走行によって求めたりすればよい。
The
表示制御部204は、対象区間判定部202で対象区画と判定するとともに、状況判定部203で自車の走行路の曲率が閾値未満と判定した場合には、前景中の走行予定車線の形状に沿ってその車線内の範囲を示すレーンガイダンス表示をHUD220に行わせる。走行予定車線については、自動運転ECU6で生成した走行計画から特定すればよい。前景中の走行予定車線とレーンガイダンス表示との位置及び形状合わせは、自動運転ECU6で認識した走行環境,前方カメラ40のカメラパラメータ等を用いて行う構成とすればよい。走行予定車線の形状に沿ったレーンガイダンス表示の描画は、三次スプライン曲線,多項式等で走行予定車線の形状を近似することで行う構成とすればよい。
When the target
一方、表示制御部204は、対象区間判定部202で対象区画と判定した場合であっても、状況判定部203で自車の走行路の曲率が閾値以上と判定した場合には、レーンガイダンス表示をHUD220に行わせない。これは、自車が旋回する場合に、走行路の曲率の大きさによっては、以下に示す問題が生じるためである。詳しくは、図4に示すように、自車が旋回する場合に、走行路の曲率の大きさによっては、自車の走行予定車線(図4のLa参照)のうち自車から遠位側が、運転席前方の投影領域(図4のPa参照)から左右に外れてしまう状況が生じる。そして、図4に示すように、レーンガイダンス表示(図4のGu参照)が欠けてしまう状況が生じる。これにより、レーンガイダンス表示が示す意図がドライバに認識しにくくなって、ドライバがレーンガイダンス表示から受ける違和感が大きくなり、ドライバに煩わしさを感じさせてしまう場合が生じる。これに対して、本実施形態では、自車の走行路の曲率が閾値以上と判定した場合に、レーンガイダンス表示を行わせないことで、このような煩わしさを低減することを可能にする。
On the other hand, the
また、表示制御部204は、対象区間判定部202で対象区画でないと判定した場合にも、レーンガイダンス表示をHUD220に行わせない。表示制御部204は、自車の自動運転中にHUD220での表示を行わせる場合には、レーンガイダンス表示を行わせる場合もレーンガイダンス表示を行わせない場合にも、自車の予定進路方向を示すアイコン(以下、進路方向アイコン)の虚像を表示させる(図3のIc参照)。進路方向アイコンは、前述したレーンガイダンスとは異なる種類の画像であって、例えば自車の予定進路の方向を指す矢印の形状をしている構成とすればよい。以下では、進路方向アイコンの虚像の表示を進路方向アイコン表示と呼ぶ。
Further, the
表示制御部204は、進路方向アイコンの虚像を、自車の予定進路方向であることをドライバが直感的に認識しやすいように、前景中の走行予定車線内に重畳して表示させることが好ましい。前景中の走行予定車線は、少なくとも一部が自車の運転席前方に位置するので、進路方向アイコンの虚像は、デフォルトとして運転席前方に位置する投影領域の車幅方向中心に重畳して表示させることで、前景中の走行予定車線内に表示させることが好ましい。
The
また、表示制御部204は、進路方向アイコンの虚像を表示させる位置を、自車が旋回する方向に、自車の走行路の曲率が大きくなるのに応じてずらすことがより好ましい。これは、進路方向アイコンの虚像の表示位置を投影領域の車幅方向中心に固定すると以下の問題が生じるためである。詳しくは、図4に示すように、自車が旋回する場合に、走行路の曲率の大きさによっては、運転席前方の投影領域(図4のPa参照)の大部分を自車の走行予定車線の隣接車線(図4のLb参照)が占めてしまう状況が生じる。そして、図4に示すように、投影領域の車幅方向中心に固定した進路方向アイコン(図4のIc参照)の虚像が、この隣接車線に重畳して表示されてしまう状況が生じる。これにより、進路方向アイコンが示す意図がドライバに認識しにくくなって、ドライバが進路方向アイコンから受ける違和感が大きくなり、ドライバに煩わしさを感じさせてしまう場合が生じる。
Further, it is more preferable that the
これに対して、本実施形態では、進路方向アイコンの虚像の表示位置を、自車が旋回する方向に、自車の走行路の曲率が大きくなるのに応じてずらすので、進路方向アイコンの虚像の表示位置が自車の走行予定車線におさまりやすくなり、このような煩わしさを低減することが可能になる。自車の走行路の曲率の大きさと、進路方向アイコンの虚像の表示位置をずらす量との対応関係は、進路方向アイコンの虚像が自車の走行予定車線におさまるように対応付けられているものとする。 On the other hand, in the present embodiment, the display position of the virtual image of the path direction icon is shifted in the direction in which the vehicle is turning in accordance with the increase in the curvature of the road on which the vehicle is traveling. The display position of is easy to fit in the lane in which the vehicle is to travel, and it is possible to reduce such annoyance. The correspondence between the magnitude of the curvature of the vehicle's running path and the amount by which the virtual image display position of the path direction icon is displaced is such that the virtual image of the path direction icon fits in the planned lane of the vehicle. And
さらに、表示制御部204は、進路方向アイコンの虚像を前景に重畳表示させる位置をずらす際に、投影領域におさまるようにずらすことが好ましい。一例として、進路方向アイコンの表示位置が、投影領域の範囲内におさまるまでは、自車が旋回する方向に、自車の走行路の曲率が大きくなるのに応じてずらす一方、投影領域を越える場合には、投影領域内外の境界部分に止める構成とすればよい。これにより、進路方向アイコンの虚像が欠けて表示される不具合を回避することが可能になる。
Furthermore, when the
<HCU20での虚像表示制御関連処理>
続いて、図5のフローチャートを用いて、HCU20でのHUD220による表示の制御に関連する処理(以下、虚像表示制御関連処理)の流れの一例について説明を行う。図5のフローチャートでは、HUD220の電源がオン且つHUD220の機能がオンになった場合に開始する構成とすればよい。HUD220の機能のオンオフは、操作デバイス21で受け付ける入力操作に応じて切り替えられる構成とすればよい。また、HUD220の電源のオンオフは、自車の内燃機関又はモータジェネレータを始動させるためのスイッチ(以下、パワースイッチ)のオンオフに応じて切り替えられる構成とすればよい。
<Process related to virtual image display control in
Next, an example of the flow of processing (hereinafter, virtual image display control-related processing) related to display control by the
まず、ステップS1では、対象区間判定部202が、自車の走行路が対象区間か否かを判定する。そして、対象区間と判定した場合(S1でYES)には、ステップS2に移る。一方、対象区間でないと判定した場合(S1でNO)には、ステップS4に移る。
First, in step S1, the target
ステップS2では、状況判定部203が、自車の走行路の曲率が閾値以上か否かを判定する。そして、曲率が閾値以上と判定した場合(S2でYES)には、ステップS4に移る。一方、曲率が閾値未満と判定した場合(S2でNO)には、ステップS3に移る。なお、状況判定部203は、曲率の代わりに曲率半径を用いる構成としてもよい。この場合には、閾値も逆数とし、閾値以下と判定した場合にS4に移る一方、閾値よりも大きいと判定した場合にS3に移る構成とすればよい。
In step S2, the
ステップS3では、表示制御部204がHUD220に、進路方向アイコン表示に加え、レーンガイダンス表示も行わせ、ステップS5に移る。一方、ステップS4では、表示制御部204がHUD220に、進路方向アイコン表示は行わせるが、レーンガイダンス表示は行わずに、ステップS5に移る。S3でもS4でも、表示制御部204は、進行方向アイコンの虚像の表示位置を、自車が旋回する方向に、自車の走行路の曲率が大きくなるのに応じてずらすことが好ましい。また、表示制御部204は、進路方向アイコンの虚像を前景に重畳表示させる位置をずらす際に、投影領域におさまるようにずらすことがより好ましい。
In step S3, the
ステップS5では、虚像表示制御関連処理の終了タイミングであった場合(S5でYES)には、虚像表示制御関連処理を終了する。一方、虚像表示制御関連処理の終了タイミングでなかった場合(S5でNO)には、S1に戻って処理を繰り返す。虚像表示制御関連処理の終了タイミングの一例としては、自車のパワースイッチがオフになった場合,HUD220の機能がオフになった場合等がある。
In step S5, if it is the end timing of the virtual image display control-related processing (YES in S5), the virtual image display control-related processing is ended. On the other hand, if it is not the end timing of the virtual image display control-related processing (NO in S5), the processing returns to S1 and is repeated. An example of the end timing of the virtual image display control-related processing is when the power switch of the vehicle is turned off, when the function of the
ここで、図6を用いて、自車の走行路の切り替わりに応じた虚像の重畳表示の遷移の一例について説明を行う。図6のAは直線路,Bがカーブ前,Cがカーブ中の虚像の重畳表示の例を示している。図6のPaが投影領域,Icが進路方向アイコン表示,Guがガイダンス表示,Ceが投影領域の車幅方向中心の領域を示している。 Here, an example of the transition of the superimposed display of the virtual image according to the switching of the traveling path of the own vehicle will be described with reference to FIG. 6A shows an example of superimposed display of virtual images in a straight road, B before curve, and C in curve. In FIG. 6, Pa indicates the projection area, Ic indicates the traveling direction icon display, Gu indicates the guidance display, and Ce indicates the center area of the projection area in the vehicle width direction.
図6に示すように、自車が直線路を走行中は、進路方向アイコン表示(図6のIc参照)とガイダンス表示(図6のGu参照)とのうちの進路方向アイコン表示のみが前景に重畳される。一方、自車がカーブ前に差し掛かると、進路方向アイコン表示に加え、ガイダンス表示も前景に重畳される。そして、自車が閾値以上の曲率のカーブを旋回中には、ガイダンス表示が中止され、進路方向アイコン表示とガイダンス表示とのうちの進路方向アイコン表示のみが前景に重畳される。また、進路方向アイコン表示は、投影領域(図6のPa参照)の車幅方向中心(図6のCe参照)から自車が旋回する方向に、自車の走行路の曲率が大きくなるのに応じてずれて行われる。 As shown in FIG. 6, when the vehicle is traveling on a straight road, only the route direction icon display of the route direction icon display (see Ic in FIG. 6) and the guidance display (see Gu in FIG. 6) is in the foreground. Are overlaid. On the other hand, when the vehicle approaches a curve, guidance display is superimposed on the foreground in addition to the route direction icon display. Then, while the vehicle is turning through a curve having a curvature equal to or greater than the threshold value, the guidance display is stopped and only the route direction icon display of the route direction icon display and the guidance display is superimposed on the foreground. Further, the route direction icon display indicates that the curvature of the traveling path of the vehicle becomes large in the direction in which the vehicle turns from the vehicle width direction center (see Ce in FIG. 6) of the projection area (see Pa in FIG. 6). It is performed according to the shift.
<実施形態1のまとめ>
実施形態1の構成によれば、ドライバは、ガイダンス表示によって、自車が自動運転中であっても、カーブ手前,合流前,分岐前,閾値未満の曲率のカーブといった対象区間において、自車のシステムがカーブ路の車線を認識できていて旋回を行うことを確認でき、システム状態に対して安心することができる。一方、自車が直進を継続することが確認できれば十分にドライバが安心できると考えられる直線路の走行中は、進路方向アイコン表示とガイダンス表示とのうちの進路方向アイコン表示のみを前景に重畳して行わせることで、情報過多によるドライバの煩わしさを低減することができる。さらに、閾値以上の曲率のカーブを旋回中には、レーンガイダンス表示を中止することで、レーンガイダンス表示が欠けてしまうことで生じるドライバの煩わしさを低減する。また、閾値以上の曲率のカーブを旋回中にも、進路方向アイコン表示を継続するので、ドライバが、自車のシステムがカーブ路において旋回を行うことは確認でき、システム状態に対して安心することができる。
<Summary of
According to the configuration of the first embodiment, the driver displays the guidance of the own vehicle in the target section such as before the curve, before the merging, before the divergence, or the curve having the curvature less than the threshold even when the own vehicle is automatically driving. It is possible to confirm that the system recognizes the lane of the curved road and makes a turn, so it is possible to feel confident about the system state. On the other hand, when driving on a straight road where it is considered that the driver can feel reassured if it can be confirmed that the vehicle continues straight ahead, only the direction icon display of the direction icon display and the guidance display is superimposed on the foreground. By doing so, the annoyance of the driver due to excessive information can be reduced. Further, by stopping the lane guidance display while turning the curve having the curvature equal to or more than the threshold value, the annoyance of the driver caused by the lack of the lane guidance display is reduced. In addition, the route direction icon is displayed even while turning a curve with a curvature equal to or greater than the threshold, so the driver can confirm that the vehicle's system is turning on a curved road, and feel reassured about the system status. You can
(変形例1)
実施形態1では、表示制御部204が、前景中の走行予定車線の形状に沿ってその車線内の範囲を示すレーンガイダンス表示について、自車の走行路の曲率が閾値以上か否かに応じて、前景への重畳表示を中止するか否かを切り替える構成を示したが、必ずしもこれに限らない。例えば、レーンガイダンス表示以外の前景中の走行予定車線の形状に沿ったガイダンス表示に適用する構成としてもよい。例えば、先行車両との車間距離を示すためのガイダンス表示であってもよい。この場合には、周辺監視センサ4で自車の先行車両を検出している場合をガイダンス表示の対象とし、自車の走行路の曲率が閾値以上か否かに応じて、前景への重畳表示を中止するか否かを切り替える構成とすればよい。また、ガイダンス表示の形状は、図3,図6で示したレーンガイダンス表示の一例のようなシート状に限らず、例えば梯子状,矢印の矢頭部分が進路上に複数並んだ形状等の他の形状であってもよい。
(Modification 1)
In the first embodiment, the
(変形例2)
実施形態1では、表示制御部204が、自動運転中にHUD220での表示を行わせる場合に、進路方向アイコン表示を常時行わせる構成を示したが、必ずしもこれに限らない。例えば、表示制御部204は、レーンガイダンス表示を行わせない場合に限って進路方向アイコン表示を行わせる構成としてもよい。なお、レーンガイダンス表示の代わりにガイダンス表示を行う変形例1についても同様である。
(Modification 2)
In the first embodiment, when the
(変形例3)
前述の実施形態及び変形例では、自車が自動運転を行う場合に適用した例を挙げて説明を行ったが、必ずしもこれに限らない。例えば、自車の手動運転時に適用する構成としてもよい。また、自車が自動運転機能を有していない構成であってもよい。この場合には、車両システム1に自動運転ECU6を含まず、走行環境の認識はHCU20等の他のECUで行う構成とすればよい。
(Modification 3)
In the above-described embodiment and modified examples, description has been given by taking an example applied to the case where the own vehicle performs automatic driving, but the present invention is not limited to this. For example, the configuration may be applied when the own vehicle is manually driven. Alternatively, the host vehicle may not have the automatic driving function. In this case, the
(変形例4)
実施形態1では、レーンガイダンス表示を行う対象区間を限定する構成を示したが、必ずしもこれに限らない。例えば、レーンガイダンス表示を行う対象区間を限定しない構成としてもよい。この場合には、HCU20に対象区間判定部202を備えない構成とすればよい。なお、レーンガイダンス表示の代わりにガイダンス表示を行う変形例1についても同様である。
(Modification 4)
In the first embodiment, the configuration in which the target section for which the lane guidance is displayed is limited is shown, but the configuration is not necessarily limited to this. For example, the target section in which the lane guidance is displayed may not be limited. In this case, the
(変形例5)
実施形態1では、表示制御部204が、自車の走行路の曲率が閾値以上か否かに応じて、前景へのレーンガイダンス表示を中止するか否かを切り替える構成を示したが、必ずしもこれに限らない。例えば、自車の走行路の勾配変化が閾値以上か否かに応じて、前景へのレーンガイダンス表示を中止するか否かを切り替える構成(以下、変形例5)としてもよい。これは、自車の勾配変化の大きさによっては、自車の走行予定車線のうち自車から遠位側が、運転席前方の投影領域から上下に外れてしまう状況が生じることでレーンガイダンス表示が欠けてしまい、ドライバに煩わしさを感じさせてしまう場合が生じるためである。
(Modification 5)
In the first embodiment, the
変形例5を採用した場合には、状況判定部203が、自車の走行路の勾配変化を判定する構成とすればよい。この場合、状況判定部203は、自動運転ECU6で認識した走行環境から自車の走行路の勾配変化を判定してもよいし、ADASロケータ3から出力される車両位置及び地図データから自車の走行路の勾配変化を判定してもよい。この自車の走行路の勾配変化が自車状況に相当する。一例として勾配変化としては、現在の車両位置に相当する区間に対する次の区間の縦断勾配の変化率を用いる等すればよい。
When the fifth modification is adopted, the
また、変形例5を採用した場合には、状況判定部203は、自車の走行路の勾配変化が閾値以上か否かを判定する。ここで言うところの閾値とは、レーンガイダンス表示がドライバに違和感を与えると推定されるほど投影領域から外れると予測される勾配変化の値とすればよい。この閾値は、シミュレーションによって推算したり、実験走行によって求めたりすればよい。なお、変形例5を採用した場合にも、実施形態1と同様に、自車の走行路の曲率が閾値以上か否かに応じて、前景への重畳表示を中止するか否かを切り替える構成としてもよい。また、レーンガイダンス表示の代わりにガイダンス表示を行う変形例1と組み合わせる構成としてもよい。
Further, when the fifth modification is adopted, the
(実施形態2)
前述の実施形態及び変形例では、自車の走行路の曲率,勾配変化といった道路構造に応じて、前景へのレーンガイダンス表示を中止するか否かを切り替える構成を示したが、必ずしもこれに限らない。例えば、自車の進路前方の、対象となる道路標識又は道路標示である対象情報源が、ドライバに確認しにくい状況か否かに応じて、その対象情報源を示す虚像を前景へ重畳表示させるか否かを切り替える構成(以下、実施形態2)としてもよい。以下、実施形態2について説明する。
(Embodiment 2)
In the above-described embodiment and modification, the configuration in which whether or not to stop the lane guidance display in the foreground is switched according to the road structure such as the curvature and gradient change of the traveling path of the vehicle has been shown, but the present invention is not limited to this. Absent. For example, depending on whether or not the target information source, which is the target road sign or road marking in front of the route of the own vehicle, is difficult for the driver to confirm, a virtual image indicating the target information source is superimposed and displayed on the foreground. It may be configured to switch whether or not to do so (hereinafter, Embodiment 2). Hereinafter, the second embodiment will be described.
実施形態2の車両システム1は、HCU20の代わりにHCU20aを含む点を除けば、実施形態1の車両システム1と同様である。HCU20aは、HUD220による表示の制御に関する構成の一部が異なる点を除けば、実施形態1のHCU20と同様である。
The
実施形態2は、自動運転中に対象情報源を示す虚像を前景へ重畳表示させる場合に適用する構成としてもよいが、以下では、手動運転中に対象情報源を示す虚像を前景へ重畳表示させる場合に適用するものとして説明を行う。よって、実施形態2では、車両システム1に自動運転ECU6を含まず、走行環境の認識はHCU20a等の他のECUで行う構成としてもよい。
The second embodiment may be applied to a case where a virtual image showing the target information source is displayed on the foreground in a superimposed manner during automatic driving. However, in the following, the virtual image showing the target information source is displayed on the foreground while being manually driven. Description will be given as applied to the case. Therefore, in the second embodiment, the
<HCU20aの概略構成>
ここで、図7を用いてHCU20aの概略構成についての説明を行う。HCU20aは、HUD220による表示の制御に関して、図7に示すように、情報取得部201、対象区間判定部202a、状況判定部203a、表示制御部204a、及び表示条件判定部205を機能ブロックとして備える。このHCU20aも車両用表示制御装置に相当する。
<Schematic configuration of
Here, the schematic configuration of the
対象区間判定部202aは、自車の走行路が、対象情報源の存在する対象区間か否かを判定する。対象情報源は、あらゆる道路標識及び道路標示から任意に設定可能である。対象情報源の一例としては、一時停止,駐車禁止,進入禁止,最高速度等の特定の交通方法を禁止したり指定したりする標識、許容される内容を伝える標識、注意を促す標識、及び案内を行う標識等がある。また、一時停止,駐車禁止,最高速度,停止禁止部分等の特定の交通方法を禁止したり指定したりする標示、及び右折専用レーンの右折矢印等の許容される内容を伝える標示等がある。ここで言うところの対象区間とは、リンク単位の区間であってもよいし、セグメント単位の区間であってもよいし、他の基準で区分される区間であってもよい。
The target
対象区間判定部202aは、ADASロケータ3から出力される車両位置及び地図データから、対象区間判定部202と同様にして、自車の車両位置に相当する区間が対象区間か否かを判定すればよい。対象情報源の存在については、三次元地図データのうちの道路標識のデータ,道路標示のデータ等を利用して判別すればよい。
If the target
状況判定部203aは、自車の進路前方の対象情報源がドライバに確認しにくい状況(以下、確認困難状況)か否かを判定する。この確認困難状況か否かが自車状況に相当する。例えば状況判定部203aは、自車の進路前方の、地図データから対象情報源が存在すると推定される位置に、周辺監視センサ4によってその対象情報源を検出できなかった場合に、確認困難状況と判定する。一方、周辺監視センサ4によってその対象情報源を検出できた場合には、確認困難状況でないと判定する。一例として、周辺監視センサ4によってその対象情報源を検出できたか否かは、自動運転ECU6で認識した走行環境中の、地図データから対象情報源が存在すると推定される位置に、その対象情報源が認識できていたか否かによって判別すればよい。
The
確認困難状況が生じる例としては、以下のような例が挙げられる。例えば、対象情報源である道路標示がかすれたり、雪等で覆われたりして認識しづらくなっている場合が挙げられる。また、対象情報源である道路標識がかすれたり、駐車車両,先行車両,地形,構造物によって隠されたりして認識しづらくなっている場合が挙げられる。 The following examples are examples of situations in which it is difficult to confirm. For example, there is a case where the road marking, which is the target information source, is faint or covered with snow or the like, which makes it difficult to recognize. In addition, there are cases in which the road sign, which is the target information source, is faint or is hidden by the parked vehicle, the preceding vehicle, the terrain, and the structure, making it difficult to recognize.
表示条件判定部205は、状況判定部203aで確認困難状況と判定した場合に、確認困難状況と判定した対象情報源を示す虚像の表示条件を満たしたか否かを判定する。表示条件の一例としては、対象情報源と自車との距離が設定値未満となること等が挙げられる。設定値は任意に設定可能な距離であって、自車が対象情報源に達するまでにその対象情報源の示す内容に対応可能と推定される距離とすればよい。他にも、対象情報源が、駐車禁止等の特定の交通方法を禁止したり指定したりする規制を示すものである場合には、その対象情報源が示す規制に従わない兆候を自車が示したことを、表示条件としてもよい。
When the
対象情報源が示す規制に従わない兆候の検出は、自車の走行状態から検出すればよい。一例としては、車両制御ECU5から出力される各センサの検出信号等をもとに、対象情報源が示す規制に従わない兆候を検出すればよい。対象情報源が駐車禁止を示す標識である場合には、車輪速センサの検出信号をもとに、自車の速度が所定速度以下となったことを規制に従わない兆候として検出してもよい。また、ハザードスイッチの信号をもとに、ハザードスイッチがオンとなったことを、規制に従わない兆候として検出してもよい。対象情報源が最高速度を示す標識,標示である場合には、車輪速センサの検出信号をもとに、自車の速度が対象情報源で規制されている最高速度を超過していることを、規制に従わない兆候として検出すればよい。
The sign of non-compliance with the regulation indicated by the target information source may be detected from the running state of the own vehicle. As an example, a sign that the target information source does not comply with the regulation may be detected based on the detection signal of each sensor output from the
表示制御部204aは、表示条件判定部205で表示条件を満たしたと判定した場合には、HUD220に、前景中へ対象情報源を示す虚像を重畳して表示させる。対象情報源を示す虚像の表示を以降では対象情報源表示と呼ぶ。一方、表示制御部204aは、表示条件判定部205で表示条件を満たしていないと判定した場合には、HUD220に対象情報源表示を行わせない。
When the display
表示制御部204aは、対象情報源表示を、確認困難状況と判定した対象情報源が前景中に存在する筈の位置(以下、対象存在位置)に重畳して行わせる構成としてもよいし、前景中のその対象情報源が存在する筈の位置以外に重畳して行わせる構成としてもよい。また、表示制御部204aは、確認困難状況の種類に応じて、対象情報源表示を、対象存在位置に重畳して行わせるか対象存在位置以外に重畳して行わせるか切り替える構成としてもよい。
The
一例として、対象情報源が存在すると推定される位置に、周辺監視センサ4で地形,構造物,駐車車両,先行車両といった障害物を検出していることで、状況判定部203aが確認困難状況と判定していた場合には、対象情報源表示を、対象存在位置以外に重畳して行わせる構成とすればよい。一方、対象情報源が存在すると推定される位置に、周辺監視センサ4で障害物を検出していないにも関わらず、状況判定部203aが確認困難状況と判定していた場合には、対象情報源表示を、対象存在位置に重畳して行わせる構成とすればよい。
As an example, the
ここで、表示制御部204aでの対象情報源表示の具体例について説明を行う。例えば、右折専用レーンにおける右折矢印といった、車線において許容される進行方向を示す標示が、かすれたり雪で覆われたりして確認困難状況と判定される場合には、この標示が前景中に本来存在する位置に対象情報源表示を重畳して行わせればよい。対象情報源表示としては、進行方向を示す標示の画像の虚像を表示させればよい。
Here, a specific example of the target information source display on the
また、図8のFに示すように、駐車禁止を示す標識(図8のNP参照)が、駐車車両(図8のPV参照)によって隠され、確認困難状況と判定される場合には、図8のGに示すように、駐車禁止を示す標識が前景中に本来存在する位置以外の位置に対象情報源表示(図8のViNP参照)を重畳して行わせればよい。対象情報源表示としては、駐車禁止を示す標識の画像の虚像(図8のViNP参照)を、駐車車両から外れた位置に表示させればよい。なお、表示制御部204aは、駐車禁止を示す標識の画像の虚像に加え、駐車禁止の領域を示す虚像(図8のNPAr参照)を、前景中の駐車禁止の領域に該当する領域に重畳表示させる構成としてもよい。一例として、駐車禁止の領域のデータを地図データに含ませることによって、地図データから駐車禁止の領域を特定可能とすればよい。駐車禁止の領域を示す虚像は、禁止を意図していることがドライバに認識しやすいように、レーンガイダンス表示とは色,模様等を異ならせることが好ましい。一例としては、ゼブラゾーンと同様の模様等にすればよい。また、駐車禁止の領域を示す虚像として、禁止を意図していることがドライバに認識しやすいように、立体物を虚像として表示させる構成としてもよい。
Further, as shown in F of FIG. 8, when the sign indicating the parking prohibition (see NP of FIG. 8) is hidden by the parked vehicle (see PV of FIG. 8) and it is determined that it is difficult to confirm, As indicated by G in FIG. 8, the target information source display (see ViNP in FIG. 8) may be superimposed on a position other than the position where the sign indicating parking prohibition originally exists in the foreground. As the target information source display, a virtual image of the image of the sign indicating parking prohibition (see ViNP in FIG. 8) may be displayed at a position outside the parked vehicle. In addition to the virtual image of the image of the sign indicating parking prohibited, the
他にも、図9のHに示すように、一時停止を示す標識(図9のSP参照)が、地形によって隠され、確認困難状況と判定される場合には、図9のIに示すように、一時停止を示す標識が前景中に本来存在する位置以外の位置に対象情報源表示(図9のViSP参照)を重畳して行わせればよい。対象情報源表示としては、一時停止を示す標識の画像の虚像(図9のViSP参照)を表示させればよい。なお、表示制御部204aは、一時停止を示す標識の画像の虚像に加え、前述のレーンガイダンス表示(図8のGu参照)を、前景中の走行予定車線に重畳表示させる構成としてもよい。一例として、走行予定車線は、自車の走行中の車線と同じ車線とすればよい。
In addition, as shown in H of FIG. 9, when the sign indicating the stop (see SP of FIG. 9) is hidden by the terrain and it is determined that it is difficult to confirm, as shown in I of FIG. In addition, the target information source display (see ViSP in FIG. 9) may be superimposed on a position other than the position where the sign indicating the temporary stop originally exists in the foreground. As the target information source display, a virtual image of the image of the sign indicating the temporary stop (see ViSP in FIG. 9) may be displayed. Note that the
<HCU20aでの虚像表示制御関連処理>
続いて、図10のフローチャートを用いて、HCU20aでの虚像表示制御関連処理の流れの一例について説明を行う。図10のフローチャートでも、図5のフローチャートと同様に、HUD220の電源がオン且つHUD220の機能がオンになった場合に開始する構成とすればよい。
<Process related to virtual image display control in
Next, an example of the flow of virtual image display control related processing in the
まず、ステップS21では、対象区間判定部202aが、自車の走行路が対象区間か否かを判定する。そして、対象区間と判定した場合(S21でYES)には、ステップS22に移る。一方、対象区間でないと判定した場合(S21でNO)には、ステップS25に移る。
First, in step S21, the target
ステップS22では、状況判定部203aが、自車の進路前方の対象情報源がドライバに確認しにくい確認困難状況か否かを判定する。そして、確認困難状況と判定した場合(S22でYES)には、ステップS23に移る。一方、確認困難状況でないと判定した場合(S22でNO)には、ステップS25に移る。
In step S22, the
ステップS23では、表示条件判定部205が、確認困難状況と判定した対象情報源を示す虚像の表示条件を満たしたか否かを判定する。そして、表示条件を満たしたと判定した場合(S23でYES)には、ステップS24に移る。一方、表示条件を満たしていないと判定した場合には、ステップS25に移る。
In step S23, the display
ステップS24では、表示制御部204aがHUD220に、前景に重畳して対象情報源表示を行わせ、ステップS25に移る。対象情報源表示は、対象情報源が存在する位置を自車が通過した場合に終了させたり、表示条件判定部205で表示条件を満たしていないと判定した場合に終了させたりすればよい。
In step S24, the
ステップS25では、虚像表示制御関連処理の終了タイミングであった場合(S25でYES)には、虚像表示制御関連処理を終了する。一方、虚像表示制御関連処理の終了タイミングでなかった場合(S25でNO)には、S21に戻って処理を繰り返す。 In step S25, if it is the end timing of the virtual image display control-related processing (YES in S25), the virtual image display control-related processing ends. On the other hand, if it is not the end timing of the virtual image display control-related processing (NO in S25), the processing returns to S21 and is repeated.
<実施形態2のまとめ>
実施形態2の構成によれば、対象情報源を示す虚像を常に表示させるのでなく、自車の進路前方の対象情報源がドライバに確認しにくい状況と判定した場合に表示させる。よって、ドライバにとって対象情報源を示す虚像の表示が有用と推定されるタイミングで対情報源を示す虚像を表示させることを可能にしつつ、対象情報源を常に表示させる場合に比べて、ドライバの煩わしさを低減させることが可能になる。
<Summary of
According to the configuration of the second embodiment, the virtual image indicating the target information source is not always displayed, but is displayed when it is determined that the driver cannot confirm the target information source ahead of the route of the own vehicle. Therefore, it is possible for the driver to display the virtual image indicating the counter information source at the timing when it is estimated that the display of the virtual image indicating the target information source is useful, while the driver is more troublesome than when the target information source is always displayed. Can be reduced.
また、対象情報源への接近も表示条件とすることで、ドライバにとって対象情報源を示す虚像の表示が有用となりにくいタイミングでの表示を抑えることが可能になる。これにより、さらにドライバの煩わしさを低減させることが可能になる。他にも、対象情報源が示す規制に従わない兆候も表示条件とすることで、その対象情報源が示す規制に従っているにも関わらずその対象情報源の虚像の表示が行われることを防ぐことが可能になる。これによっても、さらにドライバの煩わしさを低減させることが可能になる。 Further, by setting the approach to the target information source as the display condition, it is possible to suppress the display at the timing when it is difficult for the driver to display the virtual image indicating the target information source. This makes it possible to further reduce the troublesomeness of the driver. In addition, by using a sign that does not comply with the regulation indicated by the target information source as a display condition, it is possible to prevent the virtual image of the target information source from being displayed despite the regulation indicated by the target information source. Will be possible. This also makes it possible to further reduce the troublesomeness of the driver.
(変形例6)
実施形態2では、表示条件判定部205で表示条件を満たしたと判定した場合に、表示制御部204aがHUD220に、前景中へ対象情報源を示す虚像を重畳して表示させる構成を示したが、必ずしもこれに限らない。例えば、HCU20aが表示条件判定部205を備えず、状況判定部203aが、自車の進路前方の対象情報源がドライバに確認しにくい確認困難状況と判定した場合に、表示制御部204aが前景中へ対象情報源を示す虚像を重畳して表示させる構成としてもよい。
(Modification 6)
In the second embodiment, when the display
(実施形態3)
また、自車の進路前方の、対象となる道路標識又は道路標示である対象情報源のドライバによる見落としが推定される状況か否かに応じて、その対象情報源を示す虚像を前景へ重畳表示させるか否かを切り替える構成(以下、実施形態3)としてもよい。以下、実施形態3について説明する。
(Embodiment 3)
In addition, a virtual image showing the target information source is displayed on the foreground in a superimposed manner depending on whether the driver overlooks the target information source, which is the target road sign or road marking, ahead of the vehicle's path. A configuration for switching whether or not to perform (hereinafter, Embodiment 3) may be adopted. The third embodiment will be described below.
実施形態3の車両システム1は、HCU20の代わりにHCU20bを含む点を除けば、実施形態1の車両システム1と同様である。HCU20bは、HUD220による表示の制御に関する構成の一部が異なる点を除けば、実施形態1のHCU20と同様である。
The
実施形態3は、手動運転中に対象情報源を示す虚像を前景へ重畳表示させる場合に適用するものとして説明を行う。よって、実施形態2では、車両システム1に自動運転ECU6を含まず、走行環境の認識はHCU20b等の他のECUで行う構成としてもよい。
The third embodiment will be described as being applied to a case where a virtual image showing a target information source is displayed in a superimposed manner on the foreground during manual operation. Therefore, in the second embodiment, the
<HCU20bの概略構成>
ここで、図11を用いてHCU20bの概略構成についての説明を行う。HCU20bは、HUD220による表示の制御に関して、図11に示すように、情報取得部201、対象区間判定部202a、状況判定部203b、及び表示制御部204bを機能ブロックとして備える。このHCU20bも車両用表示制御装置に相当する。
<Schematic configuration of
Here, the schematic configuration of the
対象区間判定部202aは、HCU20aの対象区間判定部202aと同様にして、自車の走行路が、対象情報源の存在する対象区間か否かを判定する。対象情報源は、規制を示すあらゆる道路標識及び道路標示から任意に設定可能である。本実施形態における対象情報源の一例としては、一時停止,駐車禁止,進入禁止,最高速度等の特定の交通方法を禁止したり指定したりする標識及び標示等がある。
The target
状況判定部203bは、自車の進路前方の対象情報源のドライバによる見落としが推定される状況(以下、見落とし状況)か否かを判定する。この見落とし状況か否かが自車状況に相当する。例えば状況判定部203bは、対象情報源が示す規制に従わない兆候を自車が示した場合に、見落とし状況と判定する。一方、対象情報源が示す規制に従わない兆候を自車が示していない場合には、見落とし状況でないと判定する。
The
対象情報源が示す規制に従わない兆候の検出は、自車の走行状態から検出すればよい。一例としては、車両制御ECU5から出力される各センサの検出信号等をもとに、対象情報源が示す規制に従わない兆候を検出すればよい。対象情報源が駐車禁止を示す標識である場合には、車輪速センサの検出信号をもとに、自車の速度が所定速度以下となったことを規制に従わない兆候として検出してもよい。また、ハザードスイッチの信号をもとに、ハザードスイッチがオンとなったことを、規制に従わない兆候として検出してもよい。対象情報源が最高速度を示す標識,標示である場合には、車輪速センサの検出信号をもとに、自車の速度が対象情報源で規制されている最高速度を超過していることを、規制に従わない兆候として検出すればよい。他にも、対象情報源が進入禁止を示す標識である場合には、ウィンカースイッチ7のウィンカ信号が、その対象情報源が設けられた道路へ進入する方向への方向転換を示す信号であったことを、規制に従わない兆候として検出すればよい。
The sign of non-compliance with the regulation indicated by the target information source may be detected from the running state of the own vehicle. As an example, a sign that the target information source does not comply with the regulation may be detected based on the detection signal of each sensor output from the
また、状況判定部203bは、車両システム1に、ドライバの顔画像を撮像するカメラが含まれる場合には、以下のような構成によって見落とし状況か否かを判定してもよい。詳しくは、状況判定部203bは、顔画像からドライバの視線方向を検出し、対象情報源への視線の停留時間が設定時間に満たない場合に、この対象情報源のドライバによる見落としが推定される状況と判定すればよい。なお、顔画像からドライバの視線方向を検出するのは、HCU20b以外の例えばDSM(Driver Status Monitor)で行う構成としてもよい。
If the
表示制御部204bは、状況判定部203bが、自車の進路前方の対象情報源のドライバによる見落としが推定される見落とし状況と判定した場合には、HUD220に、前景中へ対象情報源を示す虚像を重畳して表示させる。対象情報源を示す虚像の表示を本実施形態でも対象情報源表示と呼ぶ。一方、表示制御部204bは、状況判定部203bで見落とし状況でないと判定した場合には、HUD220に対象情報源表示を行わせない。
When the
表示制御部204bは、対象情報源表示を、対象情報源が前景中に存在する位置に重畳して行わせる構成としてもよいが、見落としが推定される対象情報源への気付きをドライバに与えるために、対象情報源が前景中に存在する位置以外に重畳して行わせることが好ましい。また、表示制御部204bは、対象情報源が示す規制に自車を従わせる緊急性の高さに応じて、対象情報源の虚像を前景中へ重畳表示させる表示態様を変更することが好ましい。表示制御部204bは、場所についての規制を示す対象情報源に対しては、対象情報源までの距離が短いほど緊急性が高いものとして扱う構成とすればよい。また、表示制御部204bは、最高速度についての規制を示す対象情報源に対しては、対象情報源で規制された最高速度を超える方向への乖離度合いが大きいほど緊急性が高いものとして扱う構成とすればよい。
The
ここで、表示制御部204bでの対象情報源表示の具体例について説明を行う。例えば、状況判定部203bが、進入禁止を示す標識(図12のNT参照)のドライバによる見落としが推定される見落とし状況と判定した場合には、図12に示すように、前景中の進入禁止の道路に対象情報源表示(図12のViNT参照)を重畳して行わせればよい。対象情報源表示としては、進入禁止を示す標識の画像の虚像(図12のViNT参照)を表示させればよい。なお、表示制御部204bは、進入禁止を示す標識の画像の虚像に加え、進入禁止の領域を示す虚像(図12のNTAr参照)を、前景中の進入禁止の道路に該当する領域に重畳表示させる構成としてもよい。進入禁止の領域を示す虚像は、禁止を意図していることがドライバに認識しやすいように、レーンガイダンス表示とは色,模様等を異ならせることが好ましい。一例としては、ゼブラゾーンと同様の模様等にすればよい。また、駐車禁止の領域を示す虚像として、禁止を意図していることがドライバに認識しやすいように、立体物を虚像として表示させる構成としてもよい。
Here, a specific example of the display of the target information source on the
他にも、状況判定部203bが、最高速度を示す標識のドライバによる見落としが推定される見落とし状況と判定した場合には、前景中に、対象情報源表示として、最高速度を示す標識の画像の虚像を重畳表示させればよい。また、最高速度を示す標識の画像の虚像を重畳表示させる場合には、対象情報源が示す規制に自車を従わせる緊急性の高さに応じて、表示態様を変更すればよい。ここで、図13を用いて一例についての説明を行う。図13では、最高速度80kmの区間に進入時に、速度超過が閾値未満の速度超過「低」であった後、速度超過がない状態となり、最高速度80kmの区間から最高速度50kmの区間に移った時に速度超過が閾値以上の速度超過「高」となった場合を例に挙げて説明を行う。ここで言うところの閾値は、任意に設定可能な値である。
In addition, when the
表示制御部204bは、速度超過「低」の場合には、ドライバが最高速度を示す標識を意識して速度を抑えている可能性があるため、ドライバに煩わしさを感じさせにくいように、対象情報源表示をフェードインさせる(図13のJ参照)。続いて、表示制御部204bは、速度超過の状態から速度超過なしの状態となった場合には、表示の急激な変化がドライバの目にとまってわずらわしさを感じさせないように、対象情報源表示をフェードアウトさせる(図13のK参照)。一方、表示制御部204bは、速度超過「高」の場合には、ドライバが最高速度を示す標識を見落としている可能性が高いため、ドライバに気付かせることを優先して、対象情報源表示を点滅させる(図13のL参照)。このように、対象情報源が示す規制に自車を従わせる緊急性の高さに応じて、表示態様を変更することで、必要に応じてドライバの煩わしさを低減しつつ、運転の支援を行うことが可能になる。
When the speed is excessively “low”, the
<HCU20bでの虚像表示制御関連処理>
続いて、図14のフローチャートを用いて、HCU20bでの虚像表示制御関連処理の流れの一例について説明を行う。図14のフローチャートでも、図5のフローチャートと同様に、HUD220の電源がオン且つHUD220の機能がオンになった場合に開始する構成とすればよい。
<Process related to virtual image display control in
Next, an example of the flow of virtual image display control related processing in the
まず、ステップS41では、対象区間判定部202aが、自車の走行路が対象区間か否かを判定する。そして、対象区間と判定した場合(S41でYES)には、ステップS42に移る。一方、対象区間でないと判定した場合(S41でNO)には、ステップS44に移る。
First, in step S41, the target
ステップS42では、状況判定部203bが、自車の進路前方の対象情報源のドライバによる見落としが推定される見落とし状況か否かを判定する。そして、見落とし状況と判定した場合(S42でYES)には、ステップS43に移る。一方、見落とし状況でないと判定した場合(S42でNO)には、ステップS44に移る。
In step S42, the
ステップS43では、表示制御部204bがHUD220に、前景に重畳して対象情報源表示を行わせ、ステップS44に移る。対象情報源表示は、対象情報源表示を開始してからの経過時間が設定時間に達した場合に終了させたり、対象情報源が示す規制に従わない兆候の検出が行われなくなった場合に終了させたりすればよい。
In step S43, the
ステップS44では、虚像表示制御関連処理の終了タイミングであった場合(S44でYES)には、虚像表示制御関連処理を終了する。一方、虚像表示制御関連処理の終了タイミングでなかった場合(S44でNO)には、S41に戻って処理を繰り返す。 In step S44, if it is the end timing of the virtual image display control-related processing (YES in S44), the virtual image display control-related processing is ended. On the other hand, if it is not the end timing of the virtual image display control-related processing (NO in S44), the processing returns to S41 and is repeated.
<実施形態3のまとめ>
実施形態3の構成によれば、対象情報源を示す虚像を常に表示させるのでなく、自車の進路前方の対象情報源のドライバによる見落としが推定される状況と判定した場合に表示させる。よって、ドライバにとって対象情報源を示す虚像の表示が有用と推定されるタイミングで対情報源を示す虚像を表示させることを可能にしつつ、対象情報源を常に表示させる場合に比べて、ドライバの煩わしさを低減させることが可能になる。
<Summary of
According to the configuration of the third embodiment, the virtual image indicating the target information source is not always displayed, but is displayed when it is determined that the driver overlooks the target information source ahead of the route of the vehicle. Therefore, it is possible for the driver to display the virtual image indicating the counter information source at the timing when it is estimated that the display of the virtual image indicating the target information source is useful, while the driver is more troublesome than when the target information source is always displayed. Can be reduced.
(変形例7)
実施形態2,3では、対象情報源表示を行う対象区間を限定する構成を示したが、必ずしもこれに限らない。例えば、対象情報源表示を行う対象区間を限定しない構成としてもよい。この場合には、HCU20a,20bに対象区間判定部202aを備えない構成とすればよい。対象情報源表示を行う対象区間を限定しない構成とした場合、HCU20a,20bは、虚像表示制御関連処理において、状況判定部203a,203bでの判定を逐次行う構成とすればよい。
(Modification 7)
In the second and third embodiments, the configuration in which the target section for which the target information source is displayed is limited is shown, but the configuration is not necessarily limited to this. For example, the target section in which the target information source is displayed may not be limited. In this case, the
(変形例8)
前述の実施形態1〜3では、レーンガイダンス表示,対象情報源表示といった前景への虚像の重畳表示を制限する構成として、重畳表示を行わせないことで重畳表示を制限する構成を示したが、必ずしもこれに限らない。例えば、重畳表示の輝度を低下させることで重畳表示を制限する構成としてもよい。重畳表示の輝度を低下させることで重畳表示を制限した場合でも、重畳表示の輝度が低下することによって、この重畳表示がドライバの目にとまりにくくなるので、ドライバの煩わしさを低減することが可能になる。
(Modification 8)
In the above-described first to third embodiments, as the configuration for limiting the superimposition display of the virtual image on the foreground such as the lane guidance display and the target information source display, the superposition display is limited by not performing the superimposition display. It is not necessarily limited to this. For example, the configuration may be such that the superimposed display is restricted by reducing the brightness of the superimposed display. Even if the superimposed display is restricted by lowering the luminance of the superimposed display, the luminance of the superimposed display is reduced, and the superimposed display is less likely to be caught by the driver's eyes, so that the driver's annoyance can be reduced. become.
(実施形態4)
前述の変形例5では、自車の走行路の勾配変化が、レーンガイダンス表示がドライバに違和感を与えると推定されるほど投影領域から外れると予測される勾配変化の値以上か否かに応じて、前景への重畳表示を中止するか否かを切り替える構成を示したが、必ずしもこれに限らない。例えば、自車の走行路の勾配変化が、自車の走行路の前方の路面にドライバから視認不能な死角を生じさせると推定される勾配変化の値以上か否かに応じて、レーンガイダンス表示といった前景への重畳表示を制限するか否かを切り替える構成(以下、実施形態4)としてもよい。以下、実施形態4について説明する。
(Embodiment 4)
In
<車両システム1cの概略構成>
実施形態4の車両システム1cは、HMIシステム2の代わりにHMIシステム2cを含む点と、ナビゲーション装置8を含む点とを除けば、実施形態1の車両システム1と同様である。HMIシステム2cは、図15に示すように、HCU20c、操作デバイス21、表示装置22、及びDSM(Driver Status Monitor)23を備えている。HMIシステム2cは、HCU20の代わりにHCU20cを備える点と、DSM23を備える点とを除けば、実施形態1のHMIシステム2と同様である。
<Schematic configuration of
The
DSM23は、近赤外光源及び近赤外カメラと、これらを制御する制御ユニット等とによって構成されている。DSM23は、近赤外カメラを自車の運転席側に向けた姿勢にて、例えばインスツルメントパネルの上面に配置される。DSM23は、近赤外光源によって近赤外光を照射された運転手の頭部を、近赤外カメラによって撮影する。近赤外カメラによる撮像画像は、制御ユニットによって画像解析される。制御ユニットは、撮像画像から画像認識処理によって目を検出し、検出した目の位置をもとにアイポイントを特定する。アイポイントは、運転席に着座したドライバの目の位置であって、例えばADASロケータ3で測位する自車の車両位置を原点とする三次元空間上の座標として特定する構成とすればよい。アイポイントの座標は、予め定義されている近赤外カメラによる撮像画像中の位置と三次元空間上の位置との対応関係をもとに特定する構成とすればよい。
The
なお、DSM23は、ドライバの視線方向も検出する構成としてもよい。ドライバの視線方向の検出は、以下のようにして行う構成とすればよい。まず、制御ユニットは、撮像画像から、画像認識処理によって顔の輪郭、目、鼻、口などの部位を検出し、各部位の相対的な位置関係からドライバの顔向きを検出する。また、制御ユニットは、撮像画像から、画像認識処理によって瞳孔及び角膜反射を検出し、検出した顔向き、及び検出した瞳孔と角膜反射との位置関係から視線方向を検出する。
The
ナビゲーション装置8は、ナビ用地図DB80を備え、設定される目的地までの時間優先,距離優先等の条件を満たす経路を探索し、その探索した経路に従った経路案内を行う。ナビ用地図DB80は、不揮発性メモリであって、リンクデータ、セグメントデータ、ノードデータ、道路形状等の地図データを格納しているものとすればよい。ナビ用地図DB80を用いる場合には、例えばADASロケータ3の地図DB32には、ナビ用地図DB80に格納されるリンクデータ、セグメントデータ、ノードデータ、道路形状等のデータを格納せず、道路形状及び構造物の特徴点の点群からなる三次元地図を格納する構成とすればよい。また、自動運転ECU6での長中期の走行計画については、ナビゲーション装置8で探索した経路を用いる構成としてもよい。なお、実施形態1〜3に、このナビゲーション装置8を含む構成を適用しても構わない。
The
<HCU20cの概略構成>
続いて、図16を用いてHCU20cの概略構成についての説明を行う。HCU20cは、HUD220による表示の制御に関して、図16に示すように、情報取得部201c、状況判定部203c、表示制御部204c、及び視認範囲推定部206を機能ブロックとして備える。このHCU20cも車両用表示制御装置に相当する。HCU20cは、対象区間判定部202を備えない点と、視認範囲推定部206を備える点と、情報取得部201、状況判定部203、及び表示制御部204の代わりに情報取得部201c、状況判定部203c、及び表示制御部204cを備える点とを除けば、実施形態1のHCU20と同様である。
<Schematic configuration of
Subsequently, the schematic configuration of the
情報取得部201cは、ナビゲーション装置8から出力される地図データ及び経路の情報を取得する点を除けば、実施形態1の情報取得部201と同様である。状況判定部203cは、自車の走行路のうちの自車前方の縦断勾配の勾配変化を判定する。自車の走行路のうちの自車前方は、例えば現在の車両位置に相当する区間に対する次の区間とすればよい。区間は、リンク単位の区間であってもよいし、セグメント単位の区間であってもよいし、他の基準で区分される区間であってもよい。状況判定部203cは、自動運転ECU6で認識した走行環境から自車前方の勾配変化を判定してもよいし、ADASロケータ3,ナビゲーション装置8等から出力される車両位置及び地図データから自車前方の勾配変化を判定してもよい。
The
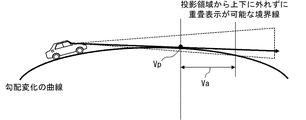
状況判定部203cは、自車前方の勾配変化として自車前方の勾配減少率が閾値以上か否かを判定する。この自車前方の勾配減少率が自車状況に相当する。なお、上り勾配の値は正の値,下り勾配の値は負の値,水平が勾配の値0であるものとする。ここで言うところの閾値とは、自車の走行路の前方の路面にドライバから視認不能な死角を生じさせると推定される勾配減少率の値とすればよい。この閾値は、シミュレーションによって推算したり、実験走行によって求めたりすればよい。勾配変化によって自車の走行路の前方の路面にドライバから視認不能な死角を生じる状況とは、例えば自車の登坂中において坂の頂上よりも先の路面が隠れてドライバから見えない状況等を指している。
The
視認範囲推定部206は、自車前方の路面のうち、自車のドライバから視認可能な路面の範囲を推定する。具体的には、DSM23から取得する自車のドライバのアイポイント、及び情報取得部201cで取得する自車の走行路の道路構造をもとに、自車のドライバから視認可能な路面の範囲を推定する。情報取得部201cで取得する自車の走行路の道路構造は、例えば三次元地図で表される道路構造とすればよい。
The visible
ここで、自車のドライバから視認可能な路面の範囲の推定方法の一例について、図17を用いて説明を行う。一例として、視認範囲推定部206は、ドライバのアイポイントの座標を、三次元地図上の位置に置き換え、三次元地図上でアイポイントの座標からドライバの視線方向へ直線を伸ばし、路面と交わる点を消失点(図17のVp)とする。ドライバの視線方向は、ドライバが正面を向いているものと仮定した視線方向を用いる構成としてもよいし、DSM23で検出した視線方向を用いる構成としてもよい。そして、自車からこの消失点までの路面を、自車のドライバから視認可能な路面の範囲と推定する。なお、消失点以降の路面については、表示画像を投影する投影領域から上下に外れない範囲(図17のVa)であっても、自車のドライバから視認可能な路面の範囲外と推定する。
Here, an example of a method of estimating the range of the road surface that can be visually recognized by the driver of the own vehicle will be described with reference to FIG. As an example, the visual recognition
表示制御部204cは、状況判定部203cで自車前方の勾配減少率が閾値未満と判定した場合には、実施形態1の表示制御部204と同様にして、前景中の走行予定車線の形状に沿ってその車線内の範囲を示すレーンガイダンス表示をHUD220に行わせる。走行予定車線については、ナビゲーション装置8で案内する経路から特定すればよい。
When the
一方、表示制御部204cは、状況判定部203cで自車前方の勾配減少率が閾値以上と判定した場合には、前景中へのレーンガイダンス表示を制限する。詳しくは、表示制御部204cは、自車前方の勾配減少率が閾値以上と判定した場合には、視認範囲推定部206で自車のドライバから視認可能な路面の範囲と推定した範囲内に、レーンガイダンス表示の範囲を制限する。図18を用いて説明すると、ドライバから視認可能と推定される路面の範囲(図18中のPr)と、ドライバから視認可能でないと推定される路面の範囲(図18中のDi)とからなるレーンガイダンス表示のうち、Prのみを重畳表示させるよう制限する。なお、表示制御部204cは、ドライバから視認可能な路面の範囲と推定した範囲外の路面については、レーンガイダンス表示が投影領域から上下に外れない場合であっても、レーンガイダンス表示を行わせない。
On the other hand, the
これは、自車の進路前方に勾配が減少する区間が存在する場合に、勾配が減少する度合いによっては、下り勾配の路面にドライバから視認できない死角が生じ、死角にあたる路面にまでレーンガイダンス表示を行わせると、ドライバがレーンガイダンス表示から受ける違和感が大きくなり、ドライバに煩わしさを感じさせてしまう場合が生じるためである。これに対して、本実施形態では、自車前方の勾配減少率が閾値以上と判定した場合に、ドライバから視認可能な路面の範囲と推定した範囲内に、レーンガイダンス表示の範囲を制限することで、このような煩わしさを低減することを可能にする。 This is because when there is a section where the slope decreases in front of the vehicle's path, a blind spot that cannot be seen by the driver occurs on the road surface with a downward slope depending on the degree to which the slope decreases, and the lane guidance display is displayed even on the road surface that is the blind spot. If this is done, the driver may feel a sense of discomfort from the lane guidance display, and the driver may feel annoyed. On the other hand, in the present embodiment, when it is determined that the gradient reduction rate in front of the vehicle is equal to or greater than the threshold value, the range of the lane guidance display is limited to the range estimated to be the range of the road surface visible to the driver. Thus, it is possible to reduce such annoyance.
なお、ここでは、消失点を求めることで自車のドライバから視認可能な路面の範囲を推定する構成を示したが、必ずしもこれに限らない。例えば、三次元地図上から路面形状を面の情報として取得し、3Dグラフィックの技術として利用されている陰面処理を用いることで、自車のドライバから視認可能な路面の範囲を推定する構成としてもよい。陰面処理を用いる場合には、アイポイントを特定の視点とし、レーンガイダンス表示の全画素のうち、例えばZ−バッファ法(Z buffer algorithm)によってアイポイントから見えない陰面を求めることで、自車のドライバから視認可能な路面の範囲を推定すればよい。 Note that, here, the configuration has been shown in which the range of the road surface that can be visually recognized by the driver of the own vehicle is estimated by obtaining the vanishing point, but the present invention is not limited to this. For example, the road surface shape may be acquired from the three-dimensional map as surface information, and the hidden surface processing used as a 3D graphic technique may be used to estimate the range of the road surface visible to the driver of the vehicle. Good. When the hidden surface processing is used, the eye point is set as a specific viewpoint, and the hidden surface that is not visible from the eye point is obtained by using the Z-buffer algorithm among all pixels of the lane guidance display. It suffices to estimate the range of the road surface that is visible to the driver.
また、表示制御部204cは、自動運転中にHUD220での表示を行わせる場合には、レーンガイダンス表示を行わせる場合もレーンガイダンス表示を行わせない場合にも、自車の予定進路方向を示す進路方向アイコンの虚像を表示させる構成としてもよい。自車の予定進路方向は、ナビゲーション装置8で案内する経路,自動運転ECU6で生成する走行計画等から特定すればよい。
Further, when the display on the
<HCU20cでの虚像表示制御関連処理>
続いて、図19のフローチャートを用いて、HCU20cでの虚像表示制御関連処理の流れの一例について説明を行う。図19のフローチャートでも、図5のフローチャートと同様に、HUD220の電源がオン且つHUD220の機能がオンになった場合に開始する構成とすればよい。
<Process related to virtual image display control in
Next, an example of the flow of virtual image display control related processing in the
まず、ステップS61では、状況判定部203cが、自車前方の勾配減少率が閾値以上か否かを判定する。そして、勾配減少率が閾値以上と判定した場合(S61でYES)には、ステップS62に移る。一方、勾配減少率が閾値未満と判定した場合(S61でNO)には、ステップS64に移る。
First, in step S61, the
ステップS62では、視認範囲推定部206が、自車のドライバのアイポイント、及び自車の走行路の道路構造をもとに、自車前方の路面のうち、自車のドライバから視認可能な路面の範囲を推定する。
In step S62, the visible
ステップS63では、表示制御部204cがHUD220に、視認範囲推定部206で自車のドライバから視認可能な路面の範囲と推定した範囲内に制限して、レーンガイダンス表示を行わせ、ステップS65に移る。一方、ステップS64では、表示制御部204cがHUD220に、上述の制限なしでレーンガイダンス表示を行わせ、ステップS65に移る。
In step S63, the
ステップS65では、虚像表示制御関連処理の終了タイミングであった場合(S65でYES)には、虚像表示制御関連処理を終了する。一方、虚像表示制御関連処理の終了タイミングでなかった場合(S65でNO)には、S61に戻って処理を繰り返す。虚像表示制御関連処理の終了タイミングの一例としては、自車のパワースイッチがオフになった場合,HUD220の機能がオフになった場合等がある。
In step S65, if it is the end timing of the virtual image display control-related processing (YES in S65), the virtual image display control-related processing is ended. On the other hand, if it is not the end timing of the virtual image display control related process (NO in S65), the process returns to S61 and is repeated. An example of the end timing of the virtual image display control-related processing is when the power switch of the vehicle is turned off, when the function of the
<実施形態4のまとめ>
実施形態4の構成によれば、自車前方の勾配減少率が閾値以上の場合には、視認範囲推定部206で自車のドライバから視認可能な路面の範囲と推定した範囲内に、レーンガイダンス表示の範囲を制限することで、死角にあたる路面にまでレーンガイダンス表示を行うことで生じるドライバの煩わしさを低減することが可能になる。
<Summary of
According to the configuration of the fourth embodiment, when the gradient reduction rate in front of the own vehicle is equal to or greater than the threshold value, the lane guidance is included in the range estimated to be the range of the road surface visible to the driver of the own vehicle by the visible
(変形例9)
実施形態4では、自車のドライバのアイポイントをDSM23によって特定する構成を示したが、必ずしもこれに限らない。例えば、他の方法によって特定する構成としてもよい。一例としては、ドライバの身長といったプロファイル別に、ドライバのアイポイントの傾向が存在することを利用し、ドライバの身長といったプロファイルからアイポイントを推定する構成としてもよい。以下では、ドライバのプロファイルとして身長を用いる場合を例に挙げて説明を行う。
(Modification 9)
In the fourth embodiment, the configuration in which the driver's eye point of the own vehicle is specified by the
HCU20cの不揮発性メモリには、身長別にアイポイントの代表値が対応付けられた対応関係を格納しておくものとする。ここで言うところの代表値としては、最頻値,平均値,中間値等を用いることができる。そして、操作デバイス21等を介してドライバから入力を受け付けていたドライバの身長をもとに、この対応関係から、ドライバの身長に応じたアイポイントを特定し、特定したアイポイントをドライバのアイポイントと推定すればよい。
It is assumed that the non-volatile memory of the
(実施形態5)
実施形態4では、自車前方の勾配減少率が閾値以上の場合に、視認範囲推定部206で自車のドライバから視認可能な路面の範囲と推定した範囲内に、レーンガイダンス表示の範囲を制限する構成を示したが、必ずしもこれに限らない。例えば、自車前方の勾配減少率が閾値以上の場合に、レーンガイダンス表示自体を行わせないことで、レーンガイダンス表示を制限する構成(以下、実施形態5)としてもよい。以下、実施形態4について説明する。
(Embodiment 5)
In the fourth embodiment, when the gradient decrease rate in front of the own vehicle is equal to or more than the threshold value, the range of lane guidance display is limited to the range estimated to be the range of the road surface visible to the driver of the own vehicle by the visible
<車両システム1dの概略構成>
実施形態5の車両システム1dは、HMIシステム2cの代わりにHMIシステム2dを含む点を除けば、実施形態4の車両システム1cと同様である。HMIシステム2dは、図20に示すように、HCU20d、操作デバイス21、及び表示装置22を備えている。HMIシステム2dは、HCU20cの代わりにHCU20dを備える点と、DSM23を備えない点とを除けば、実施形態4のHMIシステム2cと同様である。
<Schematic configuration of
The
<HCU20dの概略構成>
続いて、図21を用いてHCU20dの概略構成についての説明を行う。HCU20dは、HUD220による表示の制御に関して、図21に示すように、情報取得部201c、状況判定部203c、及び表示制御部204dを機能ブロックとして備える。このHCU20dも車両用表示制御装置に相当する。HCU20dは、視認範囲推定部206を備えない点と、表示制御部204cの代わりに表示制御部204dを備える点とを除けば、実施形態4のHCU20cと同様である。
<Schematic configuration of HCU 20d>
Subsequently, the schematic configuration of the HCU 20d will be described with reference to FIG. Regarding the display control by the
表示制御部204dは、状況判定部203cで自車前方の勾配減少率が閾値未満と判定した場合には、実施形態4の表示制御部204cと同様にして、前景中の走行予定車線の形状に沿ってその車線内の範囲を示すレーンガイダンス表示をHUD220に行わせる。
When the
一方、表示制御部204dは、状況判定部203cで自車前方の勾配減少率が閾値以上と判定した場合には、前景中へのレーンガイダンス表示を行わせない。また、表示制御部204dは、自動運転中にHUD220での表示を行わせる場合には、レーンガイダンス表示を行わせる場合もレーンガイダンス表示を行わせない場合にも、実施形態4で述べたのと同様にして、自車の予定進路方向を示す進路方向アイコンの虚像を表示させる構成とすればよい。これによれば、自車前方の勾配減少率が閾値以上であって、レーンガイダンス表示を行わせない場合にも、進路方向アイコン表示を継続するので、ドライバが、自車のシステムが予定進路方向に走行を行うことは確認でき、システム状態に対して安心することができる。
On the other hand, the
なお、進路方向アイコン表示は、手動運転中にHUD220での表示を行わせる場合にも適用する構成としても構わない。これによれば、自車前方の勾配減少率が閾値以上であって、レーンガイダンス表示を行わせない場合にも、進路方向アイコン表示を継続することで、ドライバが、自車のシステムが動作していることを確認でき、システム状態に対して安心することができる。
In addition, the course direction icon display may be applied to a case where the display on the
<実施形態5のまとめ>
実施形態5の構成によれば、自車前方の勾配減少率が閾値以上の場合には、レーンガイダンス表示自体を行わせないことで、死角にあたる路面にまでレーンガイダンス表示を行うことで生じるドライバの煩わしさを低減することが可能になる。
<Summary of
According to the configuration of the fifth embodiment, when the gradient reduction rate in front of the host vehicle is equal to or greater than the threshold value, the lane guidance display itself is not displayed, so that the lane guidance display is performed even on the road surface that is a blind spot. It is possible to reduce annoyance.
(変形例10)
実施形態4,5では、表示制御部204c,204dが、前景中の走行予定車線の形状に沿ってその車線内の範囲を示すレーンガイダンス表示について、自車前方の勾配減少率が閾値以上か否かに応じて、前景への重畳表示を制限するか否かを切り替える構成を示したが、必ずしもこれに限らない。例えば、変形例1で述べたように、レーンガイダンス表示以外の前景中の走行予定車線の形状に沿ったガイダンス表示に適用する構成としてもよい。
(Modification 10)
In the fourth and fifth embodiments, the
(変形例11)
実施形態4,5では、表示制御部204c,204dが、自動運転中にHUD220での表示を行わせる場合に、進路方向アイコン表示を常時行わせる構成を示したが、必ずしもこれに限らない。例えば、表示制御部204c,204dは、レーンガイダンス表示を行わせない場合に限って進路方向アイコン表示を行わせる構成としてもよい。なお、レーンガイダンス表示の代わりにガイダンス表示を行う変形例9についても同様である。
(Modification 11)
In the fourth and fifth embodiments, the
(変形例12)
実施形態4,5では、自車が自動運転を行う場合に適用した例を挙げて説明を行ったが、必ずしもこれに限らない。例えば、自車の手動運転時に適用する構成としてもよい。また、自車が自動運転機能を有していない構成であってもよい。この場合には、車両システム1c,1dに自動運転ECU6を含まず、走行環境の認識は他のECUで行ったり、ナビゲーション装置8で案内する経路の地図データをもとに行ったりする構成とすればよい。
(Modification 12)
Although the fourth and fifth embodiments have been described with reference to the example applied to the case where the own vehicle performs automatic driving, the present invention is not limited to this. For example, the configuration may be applied when the own vehicle is manually driven. Alternatively, the host vehicle may not have the automatic driving function. In this case, the
(変形例13)
実施形態4,5では、レーンガイダンス表示を行う対象区間を限定しない構成を示したが、必ずしもこれに限らない。例えば、レーンガイダンス表示を行う対象区間を限定する構成としてもよい。
(Modification 13)
In the fourth and fifth embodiments, the configuration in which the target section for which the lane guidance is displayed is not limited is shown, but the configuration is not necessarily limited to this. For example, the target section for which the lane guidance is displayed may be limited.
(変形例14)
実施形態5では、レーンガイダンス表示といった前景への虚像の重畳表示を制限する構成として、重畳表示を行わせないことで重畳表示を制限する構成を示したが、必ずしもこれに限らない。例えば、重畳表示の輝度を低下させることで重畳表示を制限する構成としてもよい。重畳表示の輝度を低下させることで重畳表示を制限した場合でも、重畳表示の輝度が低下することによって、この重畳表示がドライバの目にとまりにくくなるので、ドライバの煩わしさを低減することが可能になる。
(Modification 14)
In the fifth embodiment, as the configuration for limiting the superimposed display of the virtual image on the foreground such as the lane guidance display, the configuration for limiting the superimposed display by not performing the superimposed display is shown, but the configuration is not necessarily limited to this. For example, the configuration may be such that the superimposed display is restricted by reducing the brightness of the superimposed display. Even if the superimposed display is limited by lowering the luminance of the superimposed display, the luminance of the superimposed display is reduced, and the superimposed display is less likely to be caught by the driver's eyes, so that the driver's annoyance can be reduced. become.
(変形例15)
また、表示制御部204,204a,204b,204cは、HUD220に、車速及びエンジン回転数といった自車の走行状態を示す情報,自動運転機能の動作状態を示す情報,経路案内情報及び渋滞情報といったナビゲーション情報を示す虚像も表示させる構成としてもよい。
(Modification 15)
In addition, the
なお、本開示は、上述した実施形態及び変形例に限定されるものではなく、請求項に示した範囲で種々の変更が可能であり、異なる実施形態及び変形例にそれぞれ開示された技術的手段を適宜組み合わせて得られる実施形態についても本開示の技術的範囲に含まれる。 The present disclosure is not limited to the above-described embodiments and modification examples, and various modifications can be made within the scope of the claims, and the technical means disclosed in different embodiments and modification examples, respectively. Embodiments obtained by appropriately combining are also included in the technical scope of the present disclosure.
1,1c,1d 車両システム、2,2c HMIシステム、3 ADASロケータ、4 周辺監視センサ、5 車両制御ECU、6 自動運転ECU、7 ウィンカースイッチ、8 ナビゲーション装置、10 フロントウインドシールド(投影部材)、20,20a,20b,20c,20d HCU(車両用表示制御装置)、40 前方カメラ、100 虚像、201,201c 情報取得部、202,202a 対象区間判定部、203,203a,203b,203c 状況判定部、204,204a,204b,204c,204d 表示制御部、205 表示条件判定部、206 視認範囲推定部、220 HUD(ヘッドアップディスプレイ) 1, 1c, 1d vehicle system, 2, 2c HMI system, 3 ADAS locator, 4 peripheral monitoring sensor, 5 vehicle control ECU, 6 automatic driving ECU, 7 winker switch, 8 navigation device, 10 front windshield (projection member), 20, 20a, 20b, 20c, 20d HCU (vehicle display control device), 40 front camera, 100 virtual image, 201, 201c information acquisition unit, 202, 202a target section determination unit, 203, 203a, 203b, 203c situation determination unit , 204, 204a, 204b, 204c, 204d Display control unit, 205 Display condition determination unit, 206 Viewing range estimation unit, 220 HUD (head-up display)
Claims (13)
自車の走行路の道路構造である自車状況を判定する状況判定部(203,203c)と、
前記虚像の重畳表示の対象に対する前記虚像の重畳表示の制限の有無を、前記状況判定部で判定した自車状況に応じて切り替える表示制御部(204,204c,204d)とを備え、
前記状況判定部で判定する前記自車状況は、自車の走行路の曲率及び勾配変化の少なくともいずれかであって、
前記表示制御部は、前記状況判定部で判定した自車の走行路の曲率及び勾配変化の少なくともいずれかに応じて、前記虚像の重畳表示の対象となる、自車が走行予定の車線に対して、前記前景中へのその車線の形状に沿った虚像の重畳表示を制限する車両用表示制御装置。 A display control device for a vehicle, which is used in a vehicle and controls a display by a head-up display (220) for displaying a virtual image in a superimposed manner on a foreground of the vehicle by projecting an image on a projection member,
A situation determination unit (203, 203c) for determining the situation of the vehicle, which is the road structure of the traveling path of the vehicle,
A display control unit (204, 204c, 204d) that switches whether or not there is a restriction on the superimposed display of the virtual image with respect to the target of the superimposed display of the virtual image according to the own vehicle situation determined by the situation determination unit,
The own vehicle situation determined by the situation determination unit is at least one of a curvature and a gradient change of a traveling path of the own vehicle,
The display control unit is a target of the superimposed display of the virtual image according to at least one of the curvature and the gradient change of the traveling path of the own vehicle determined by the situation determining unit, with respect to the lane in which the own vehicle is scheduled to travel. Te, the lane to that vehicle display control device limits the superimposed display of the virtual image along with the shape of to the foreground in.
前記表示制御部は、前記虚像の重畳表示の対象となる、自車が走行予定の車線に対して、自車の走行路の曲率が閾値未満の場合には、前記前景中への、その車線の形状に沿った虚像のその車線内への重畳表示を制限しない一方、自車の走行路の曲率が閾値以上の場合には、その虚像のその車線内への重畳表示を制限する請求項1又は2に記載の車両用表示制御装置。 The own vehicle situation determined by the situation determination unit is at least the curvature of the traveling path of the own vehicle,
The display control unit, when the curvature of the traveling path of the own vehicle is less than a threshold with respect to the lane in which the own vehicle is to travel, which is the target of the superimposed display of the virtual image, the lane in the foreground. while not limiting the superimposed display on the lane of the virtual image along with the shape, when the curvature of the traveling path of the vehicle is equal to or larger than the threshold, claim 1 that limit its superimposed into the lane of the virtual image Or the display control device for a vehicle according to 2 .
前記表示制御部は、前記虚像の重畳表示の対象となる、自車が走行予定の車線に対して、自車の走行路の曲率が閾値未満の場合には、前記前景中への、その車線の形状に沿ったその車線内の範囲を示す虚像のその車線内への重畳表示を制限しない一方、自車の走行路の曲率が閾値以上の場合には、その虚像のその車線内への重畳表示を制限する請求項1〜3のいずれか1項に記載の車両用表示制御装置。 The own vehicle situation determined by the situation determination unit is at least the curvature of the traveling path of the own vehicle,
The display control unit, when the curvature of the traveling path of the own vehicle is less than a threshold value with respect to the lane in which the own vehicle is scheduled to travel, which is the target of the superimposed display of the virtual image, the lane in the foreground. When the curvature of the road on which the vehicle is traveling is equal to or greater than the threshold, the virtual image showing the range within the lane along the shape of the vehicle is not restricted, and the virtual image is superimposed in the lane. The vehicle display control device according to any one of claims 1 to 3, which limits display.
前記表示制御部(204c,204d)は、前記虚像の重畳表示の対象となる、自車が走行予定の車線に対して、自車前方の勾配減少率が閾値未満の場合には、前記前景中への、その車線の形状に沿った虚像のその車線内への重畳表示を制限しない一方、自車前方の勾配減少率が閾値以上の場合には、その虚像のその車線内への重畳表示を制限する請求項1〜5のいずれか1項に記載の車両用表示制御装置。 The own vehicle status determined by the status determination unit (203c) is at least a gradient in front of the own vehicle on the traveling path of the own vehicle,
The display control unit (204c, 204d), in the foreground, when the gradient decrease rate in front of the own vehicle is less than a threshold value with respect to the lane in which the own vehicle is scheduled to travel, which is a target of the superimposed display of the virtual image. If the gradient reduction rate in front of the vehicle is equal to or greater than the threshold, the virtual image along the shape of the lane is not limited to be displayed in the lane. vehicle display control device according to any one of claims 1 to 5, limited to.
前記表示制御部(204c)は、自車前方の勾配減少率が閾値以上の場合には、前記視認範囲推定部で前記ドライバから視認可能な路面の範囲と推定した範囲内に、前記前景中への、自車が走行予定の車線の形状に沿った虚像の重畳表示の範囲を制限する請求項6又は7に記載の車両用表示制御装置。 A visual range estimation unit (206) for estimating the range of the road surface visible to the driver on the road surface in front of the vehicle based on the eye structure of the driver of the vehicle and the road structure of the traveling path of the vehicle. ,
When the gradient reduction rate in front of the vehicle is equal to or greater than a threshold value, the display control unit (204c) moves into the foreground within a range estimated to be a range of the road surface visible to the driver by the visible range estimation unit. The display control device for a vehicle according to claim 6 or 7 , which limits the range of the superimposed display of the virtual image along the shape of the lane in which the vehicle is scheduled to travel.
前記表示制御部は、前記アイコンの虚像を重畳表示させる位置を、自車が旋回する方向に、自車の走行路の曲率が大きくなるのに応じてずらす請求項10に記載の車両用表示制御装置。 The own vehicle situation determined by the situation determination unit is at least the curvature of the traveling path of the own vehicle,
The display controller, a position to superimpose the virtual image of the icon, in the direction in which the vehicle is turning, the display for a vehicle according to claim 1 0 shifted in response to the curvature of the traffic lane of the subject vehicle is increased Control device.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2018/001849 WO2018147066A1 (en) | 2017-02-08 | 2018-01-23 | Display control apparatus for vehicles |
| US16/532,627 US11220274B2 (en) | 2017-02-08 | 2019-08-06 | Vehicle display control device |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017021509 | 2017-02-08 | ||
| JP2017021509 | 2017-02-08 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2018127204A JP2018127204A (en) | 2018-08-16 |
| JP2018127204A5 JP2018127204A5 (en) | 2019-05-09 |
| JP6699646B2 true JP6699646B2 (en) | 2020-05-27 |
Family
ID=63173492
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017243498A Active JP6699646B2 (en) | 2017-02-08 | 2017-12-20 | Vehicle display control device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6699646B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7193911B2 (en) * | 2017-09-28 | 2022-12-21 | 株式会社Subaru | Object information providing device for vehicle |
| JP6991948B2 (en) * | 2018-09-11 | 2022-01-13 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Display system, display control method, and program |
| CN112823101B (en) | 2018-10-23 | 2024-09-20 | 麦克赛尔株式会社 | Head-up display system |
| JP6930563B2 (en) * | 2019-01-16 | 2021-09-01 | 株式会社デンソー | Display control device and display control program |
| JP7028228B2 (en) | 2019-01-16 | 2022-03-02 | 株式会社デンソー | Display system, display control device and display control program |
| JP7234650B2 (en) * | 2019-01-23 | 2023-03-08 | 株式会社デンソー | Display control device and display control program |
| JP7365594B2 (en) * | 2019-03-27 | 2023-10-20 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | display system |
| JP6856085B2 (en) * | 2019-03-28 | 2021-04-07 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Vehicle display controls, methods and programs |
| JP7043450B2 (en) | 2019-03-28 | 2022-03-29 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Vehicle control devices, vehicle control methods, and programs |
| JP7014205B2 (en) | 2019-06-05 | 2022-02-01 | 株式会社デンソー | Display control device and display control program |
| JP7206010B2 (en) | 2019-09-19 | 2023-01-17 | 株式会社 ミックウェア | Control device |
| JP7230960B2 (en) * | 2019-09-24 | 2023-03-01 | 株式会社デンソー | display controller |
| JP7111137B2 (en) * | 2019-10-02 | 2022-08-02 | 株式会社デンソー | Display controller and display control program |
| WO2021065735A1 (en) * | 2019-10-02 | 2021-04-08 | 株式会社デンソー | Display control device and display control program |
| JP2021066197A (en) * | 2019-10-17 | 2021-04-30 | 株式会社デンソー | Display control apparatus, display control program and on-vehicle system |
| JP7543354B2 (en) | 2022-09-06 | 2024-09-02 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Vehicle display device |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4609695B2 (en) * | 2003-10-21 | 2011-01-12 | 日本精機株式会社 | Vehicle display device |
| JP4366716B2 (en) * | 2005-03-04 | 2009-11-18 | 株式会社デンソー | Vehicle information display device |
| JP2008030729A (en) * | 2006-07-05 | 2008-02-14 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | Vehicular display device |
| JP6524417B2 (en) * | 2014-02-05 | 2019-06-05 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Display device for vehicle and display method of display device for vehicle |
| JP6372402B2 (en) * | 2015-03-16 | 2018-08-15 | 株式会社デンソー | Image generation device |
| JP2016172480A (en) * | 2015-03-17 | 2016-09-29 | 株式会社デンソー | Display device for vehicle |
-
2017
- 2017-12-20 JP JP2017243498A patent/JP6699646B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2018127204A (en) | 2018-08-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6699646B2 (en) | Vehicle display control device | |
| WO2018147066A1 (en) | Display control apparatus for vehicles | |
| US11008016B2 (en) | Display system, display method, and storage medium | |
| JP6642972B2 (en) | Vehicle image display system and method | |
| JP6428713B2 (en) | Information display device | |
| JP6176478B2 (en) | Vehicle information projection system | |
| JP6459205B2 (en) | Vehicle display system | |
| WO2015151438A1 (en) | Vehicle display control device | |
| KR20200016958A (en) | Parking Assistance Method and Parking Assistance Device | |
| WO2017082067A1 (en) | Image display system for vehicle | |
| WO2018230245A1 (en) | Traveling support device, control program, and computer-readable non-transitory tangible recording medium | |
| JP6684940B2 (en) | Vehicle gaze guidance device | |
| JP2011070311A (en) | Driving support display device | |
| WO2016088312A1 (en) | Image processing device | |
| WO2020189238A1 (en) | Vehicular display control device, vehicular display control method, and vehicular display control program | |
| JP7424327B2 (en) | Vehicle display control device, vehicle display control system, and vehicle display control method | |
| JP7400242B2 (en) | Vehicle display control device and vehicle display control method | |
| US20230294517A1 (en) | Vehicle display control device, display device, and vehicle display control method | |
| JP2016071666A (en) | Visual guidance device for vehicle | |
| JP7263962B2 (en) | VEHICLE DISPLAY CONTROL DEVICE AND VEHICLE DISPLAY CONTROL METHOD | |
| WO2023171458A1 (en) | Vehicular notification control device and vehicular notification control method | |
| JP7294091B2 (en) | Display controller and display control program | |
| JP7275985B2 (en) | display controller | |
| WO2021015090A1 (en) | Control device | |
| JP2023130310A (en) | Vehicle notification control device and vehicle notification control method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20190325 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20190325 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20200331 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20200413 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 6699646 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |