JP6690289B2 - Telescopic shaft - Google Patents
Telescopic shaft Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6690289B2 JP6690289B2 JP2016030257A JP2016030257A JP6690289B2 JP 6690289 B2 JP6690289 B2 JP 6690289B2 JP 2016030257 A JP2016030257 A JP 2016030257A JP 2016030257 A JP2016030257 A JP 2016030257A JP 6690289 B2 JP6690289 B2 JP 6690289B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- shaft
- peripheral surface
- spline
- diameter
- axial
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Shafts, Cranks, Connecting Bars, And Related Bearings (AREA)
Description
この発明に係る伸縮自在シャフトは、例えば自動車の操舵装置を構成する中間シャフトとして使用される。 The expandable shaft according to the present invention is used as, for example, an intermediate shaft that constitutes a steering device of an automobile.
自動車のステアリング装置として従来から、図7に記載する様な構造のものが知られている。このステアリング装置は、ステアリングホイール1が、ステアリングシャフト2の後端部に固定されている。又、これと共に、このステアリングシャフト2の前端部が、1対の自在継手3a、3b及び中間シャフト4を介して、ステアリングギヤユニット5を構成する入力軸6の基端部に接続されている。更に、前記ステアリングギヤユニット5に内蔵されてラックアンドピニオン機構により左右1対のタイロッド7、7を押し引きして、左右1対の操舵輪に、前記ステアリングホイール1の操作量に応じた舵角を付与する様に構成されている。
2. Description of the Related Art Conventionally, a vehicle steering device having a structure as shown in FIG. 7 has been known. In this steering device, a steering wheel 1 is fixed to a rear end portion of a steering shaft 2. Along with this, the front end portion of the steering shaft 2 is connected to the base end portion of the
この様なステアリング装置に組み込まれる前記中間シャフト4は、例えば、走行時に自動車から入力される振動が、前記ステアリングホイール1に伝わる事を防止する(吸収する)為、或いは、前記中間シャフト4を、全長を縮めた状態で車体に組み込む為に、伸縮式のものが使用されている。 The intermediate shaft 4 incorporated in such a steering device is, for example, for preventing (absorbing) the vibration input from the automobile during traveling from being transmitted to the steering wheel 1, or A telescopic type is used to install it in the vehicle body with the entire length shortened.
図8は、特許文献1に記載された伸縮式の中間シャフト4の構造を示している。この中間シャフト4は、軸方向一端部(前端部であって、図8の左端部。組み付け状態でアウタチューブ10側の端部)の外周面に雄スプライン部8が形成されたインナシャフト9と、内周面にこの雄スプライン部8とスプライン係合可能な雌スプライン部12が形成された円管状のアウタチューブ10とから成る。そして、前記雄スプライン部8と前記雌スプライン部12とをスプライン係合する事で、前記インナシャフト9と前記アウタチューブ10とを、伸縮自在に組み合わせている。
FIG. 8 shows the structure of the telescopic intermediate shaft 4 described in Patent Document 1. The intermediate shaft 4 includes an inner shaft 9 in which a male spline portion 8 is formed on the outer peripheral surface of one end portion in the axial direction (the front end portion, that is, the left end portion in FIG. 8; the end portion on the
又、図8に示す構造の場合、前記インナシャフト9を、後側(前後方向とは、車体の前後方向を言う。本明細書及び特許請求の範囲全体で同じ。)に配置すると共に、前記アウタチューブ10を前側に配置している。又、前記インナシャフト9の軸方向他端部には、前記両自在継手3a、3bのうちの後側に配置された自在継手3aを構成する第一のヨーク11が外嵌固定(圧入)されている。一方、前記アウタチューブ10の軸方向一端部には、前記両自在継手3a、3bのうちの前側に配置された自在継手3bを構成する第二のヨーク13が外嵌固定(圧入)されている。
尚、前記インナシャフト9と前記第一のヨーク11との結合、或いは、前記アウタチューブ10と前記第二のヨーク13との結合は、溶接により行う事もできる。又、後述する実施の形態の構造の様に、インナシャフトを前側に、アウタチューブを後側に配置する構造を採用する事もできる。
Further, in the case of the structure shown in FIG. 8, the inner shaft 9 is arranged on the rear side (the front-rear direction means the front-rear direction of the vehicle body, which is the same throughout the present specification and claims), and The
The inner shaft 9 and the first yoke 11 or the
上述の様な構成を有する中間シャフト4の様に、前記インナシャフト9と前記アウタチューブ10とをトルク伝達可能、且つ、軸方向の伸縮(摺動)可能に組み合わせた伸縮軸は、回転方向のがたつきが小さく、且つ、伸縮時の摺動抵抗が小さい事が要求される。この為に、従来から、前記インナシャフト9の雄スプライン部8の外周面に、ポリアミド樹脂等の摩擦係数が低い合成樹脂製のコーティング層を設けると共に、前記雄スプライン部8と前記雌スプライン部12とを締め代を持たせた状態で係合させる事が行われている。但し、この様な構造の場合、前記インナシャフト9のうち、前記コーティング層を設けた部分の径方向に関する剛性が高いと、前記締め代に対する摺動抵抗(摺動荷重)の変動が敏感になってしまい、前記アウタチューブ10に対する前記インナシャフト9の摺動を、安定させる事が難しくなる可能性がある。この様な問題は、前記がたつきを十分に抑える為に前記締め代を大きくするほど顕著になる。
Like the intermediate shaft 4 having the above-mentioned configuration, the expansion shaft that combines the inner shaft 9 and the
又、図9は、特許文献2に記載された中間シャフト4aの構造を示している。この中間シャフト4aの場合、アウタチューブ10aのうちの雌スプライン部12が形成された部分を、軸方向他方側に形成されたアウタ側薄肉部14と、このアウタ側薄肉部14の軸方向一方側に隣接した位置に形成され、外径寸法及び径方向に関する厚さ寸法が前記アウタ側薄肉部14よりも大きいアウタ側厚肉部15とより構成している。この様にして、前記雌スプライン部12が形成された部分のうちの前記アウタ側薄肉部14が形成された部分の径方向に関する剛性を低くしている。尚、このアウタ側厚肉部15の軸方向他端部の外周面は、軸方向他方側に向かうほど外径寸法が小さくなる部分円錐面状に形成されている。
Further, FIG. 9 shows the structure of the
以上の様な構成を有する特許文献2に記載された発明によれば、前記アウタチューブ10aとインナシャフト9aとの摺動抵抗(摺動荷重)の変動が敏感になる事を防止して、前記アウタチューブ10aと前記インナシャフト9aとの摺動を、安定させる事が可能である。但し、特許文献2に記載された発明の場合、使用時に於ける、前記アウタチューブ10aと前記インナシャフト9aとの伸縮ストロークの範囲内で、前記雌スプライン部12のうちの前記アウタ側厚肉部15の内周面に形成された部分が、前記インナシャフト9aの雄スプライン部8とスプライン係合しない状態(図9に示す状態)が存在する。この状態でトルク伝達を行うと、前記アウタ側薄肉部14と前記アウタ側厚肉部15との境界部分17に応力集中が発生し易くなる可能性がある。
According to the invention described in Patent Document 2 having the above-mentioned configuration, it is possible to prevent the fluctuation of the sliding resistance (sliding load) between the
本発明は、上述の様な事情に鑑みて、インナシャフトの雄スプライン部とアウタチューブの雌スプライン部との係合部の回転方向のがたつきを小さく抑えられる構造を採用した場合にも、前記インナシャフトと前記アウタチューブとを安定して摺動させる事ができ、更に、アウタチューブのアウタ側薄肉部とアウタ側厚肉部との境界部分に応力集中が発生し難い構造を実現するものである。 In view of the circumstances as described above, the present invention also adopts a structure in which rattling in the rotational direction of the engaging portion between the male spline portion of the inner shaft and the female spline portion of the outer tube is suppressed to be small, A structure in which the inner shaft and the outer tube can be slid stably, and further, stress concentration is less likely to occur at the boundary portion between the outer thin portion and the outer thick portion of the outer tube. Is.
本発明の対象となる伸縮自在シャフトは、インナシャフトと、アウタチューブと、コーティング層とを備えている。
このうちのインナシャフトは、中空状に構成されており、軸方向一端部の外周面に雄スプライン部が形成されている。
前記アウタチューブは、内周面に雌スプライン部が形成されている。
前記コーティング層は、前記雄スプライン部の外周面を覆う状態で設けられている。
そして、前記雄スプライン部と前記雌スプライン部とを、前記コーティング層を介してスプライン係合させる事により、前記インナシャフトと前記アウタチューブとがトルク伝達可能、且つ、全長を伸縮可能な状態に組み合わされている。
The expandable shaft that is the subject of the present invention includes an inner shaft, an outer tube, and a coating layer.
The inner shaft has a hollow shape, and a male spline portion is formed on the outer peripheral surface of one end portion in the axial direction.
The outer tube has a female spline portion formed on its inner peripheral surface.
The coating layer is provided so as to cover the outer peripheral surface of the male spline portion.
Then, the male spline portion and the female spline portion are spline-engaged with each other via the coating layer, whereby the inner shaft and the outer tube are combined so that torque can be transmitted and the entire length can be expanded and contracted. Has been done.
特に、本発明の伸縮自在シャフトは、前記アウタチューブのうち、内周面に前記雌スプライン部が形成された部分が、軸方向他端部に形成されたアウタ側薄肉部と、該アウタ側薄肉部の軸方向一方側に隣接した位置に形成された、前記アウタ側薄肉部の外径寸法よりも大きい外径寸法を有する、アウタ側厚肉部とにより構成されている。
又、前記インナシャフトのうち、外周面に前記雄スプラインが形成された部分が、軸方向一端部に形成されたインナ側薄肉部と、該インナ側薄肉部の軸方向他方側に隣接した位置に形成された、前記インナ側薄肉部の内径寸法よりも小さい内径寸法を有する、インナ側厚肉部とにより構成されている。
又、前記インナ側厚肉部の軸方向他端部の内周面には、前記インナ側厚肉部の軸方向中間部の内周面よりも全周に亙り径方向内方に張り出した内向張出部が形成されている。
そして、使用時に於ける前記インナシャフトと前記アウタチューブとの伸縮ストロークの範囲で、前記雌スプライン部のうち、前記アウタ側厚肉部の軸方向他端部の内周面に形成された部分と、前記雄スプライン部とが、常にスプライン係合する様に構成しており、且つ、前記雄スプライン部のうち、前記インナ側厚肉部の外周面に形成された部分と、前記雌スプライン部とが、常にスプライン係合する様に構成している。
Particularly, in the expandable shaft of the present invention, in the outer tube, a portion where the female spline portion is formed on the inner peripheral surface is an outer thin portion formed at the other end in the axial direction, and the outer thin wall. And an outer thick-walled portion having an outer diameter dimension larger than an outer diameter dimension of the outer thin-walled portion formed adjacent to one axial side of the portion .
Further, in the inner shaft, a portion where the male spline is formed on the outer peripheral surface is located at a position adjacent to the inner thin portion formed at one axial end and the other axial side of the inner thin portion. The formed inner-side thick portion has an inner diameter smaller than that of the formed inner-side thin portion.
In addition, the inner peripheral surface of the other axial end of the inner thick portion has an inward direction that extends radially inward over the entire circumference of the inner peripheral surface of the axial middle portion of the inner thick portion. An overhang is formed.
Then, within a range of expansion and contraction stroke of the inner shaft and the outer tube during use, a portion of the female spline portion formed on the inner peripheral surface of the other axial end of the outer thick portion. , The male spline portion is configured to always engage with the spline , and, of the male spline portion, a portion formed on the outer peripheral surface of the inner side thick portion, and the female spline portion. However, the spline is always engaged .
上述した様な構成を有する本発明の伸縮自在シャフトの場合、インナシャフトの雄スプライン部の外周面を覆う状態でコーティング層を設けている。又、これと共に、アウタチューブのうち、雌スプライン部に相当する部分の軸方向他端部にアウタ側薄肉部を形成している。この為、前記アウタチューブの雌スプライン部が形成された部分のうちのこのアウタ側薄肉部が形成された部分の径方向に関する剛性を、同じくアウタ側厚肉部が形成された部分の径方向に関する剛性より低くする事ができる。従って、前記インナシャフトの雄スプライン部と前記アウタチューブの雌スプライン部との係合部の回転方向のがたつきを防止する為に、この係合部に締め代を持たせた場合でも、この締め代に対する摺動抵抗(摺動荷重)の変動を鈍感にでき、前記インナシャフトと前記アウタチューブとの摺動を安定させる事ができる。 In the case of the expandable shaft of the present invention having the above-mentioned configuration, the coating layer is provided in a state of covering the outer peripheral surface of the male spline portion of the inner shaft. Along with this, an outer thin portion is formed at the other axial end of a portion of the outer tube corresponding to the female spline portion. Therefore, the radial rigidity of a portion of the outer tube where the female spline portion is formed and the outer thin portion thereof is related to the radial direction of the portion where the outer thick portion is formed. It can be made lower than the rigidity. Therefore, in order to prevent rattling of the engaging portion between the male spline portion of the inner shaft and the female spline portion of the outer tube in the rotational direction, even if a tightening margin is provided to this engaging portion, Fluctuations in sliding resistance (sliding load) with respect to the tightening allowance can be made insensitive, and sliding between the inner shaft and the outer tube can be stabilized.
又、本発明の場合、使用時に於ける、前記インナシャフトと前記アウタチューブとの伸縮ストロークの範囲で、前記雌スプライン部のうち、前記アウタ側厚肉部の軸方向他端部の内周面に形成された部分と、前記雄スプライン部とが、常にスプライン係合する様に構成している。この為、前記インナシャフトと前記アウタチューブとの間のトルク伝達を、前記雌スプライン部のうちの前記アウタ側厚肉部の軸方向他端部に相当する部分と、前記雄スプライン部のうちの当該部分とスプライン係合する部分とで行う事ができる。この結果、この雌スプライン部のうち、前記アウタ側薄肉部と前記アウタ側厚肉部との境界部分に応力集中が発生する事を防止できる。 Also, in the case of the present invention, the inner peripheral surface of the other axial end of the outer thick portion of the female spline portion is within a range of expansion / contraction stroke of the inner shaft and the outer tube during use. The portion formed in and the male spline portion are always configured to be in spline engagement. Therefore, torque transmission between the inner shaft and the outer tube is performed by a portion of the female spline portion corresponding to the other axial end of the outer thick portion and a male spline portion. This can be done with the part and the part that engages with the spline. As a result, it is possible to prevent stress concentration from occurring at the boundary portion between the outer-side thin portion and the outer-side thick portion of the female spline portion.
[参考例]
本発明の参考例に就いて、図1〜3を参照しつつ説明する。尚、本参考例は、本発明を、ステアリング装置を構成する中間シャフトに適用したものである。但し、本発明は、この様な中間シャフト以外にも、各種用途で使用される伸縮自在シャフトの構造に適用する事ができる。又、本参考例の中間シャフト4bを組み込んだステアリング装置の構造は、図7に示したステアリング装置と同様の構造を有している。但し、本参考例の中間シャフト4bは、図7に示したステアリング装置の構造に限らず、従来から知られている各種構造のステアリング装置に組み込む事ができる。以下、ステアリング装置の構造を簡単に説明した後、本参考例の中間シャフト4bの構造に就いて説明する。
[ Reference example ]
A reference example of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. In this reference example, the present invention is applied to an intermediate shaft that constitutes a steering device. However, the present invention can be applied to structures of expandable shafts used for various purposes other than such intermediate shafts. Further, the structure of the steering device incorporating the
本参考例の中間シャフト4bを組み込んだステアリング装置は、ステアリングホイール1(図7参照)が、ステアリングシャフト2の後端部に固定されている。又、これと共に、このステアリングシャフト2の前端部が、1対の自在継手3c、3d及び前記中間シャフト4bを介して、ステアリングギヤユニット5を構成する入力軸6の基端部に接続されている。更に、このステアリングギヤユニット5に内蔵したラックアンドピニオン機構により左右1対のタイロッド7、7を押し引きして、左右1対の操舵輪に、前記ステアリングホイール1の操作量に応じた舵角を付与する様に構成されている。
In the steering device incorporating the
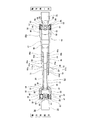
前記中間シャフト4bは、特許請求の範囲に記載したインナシャフトの1例に相当するインナシャフト9bの軸方向一端部(図1の右端部であって、組み付け状態に於いて、アウタチューブ10b側となる端部)と、同じくアウタチューブの1例に相当するアウタチューブ10bの軸方向他端部(図1の左端部であって、組み付け状態に於いて、前記インナシャフト9b側となる端部)とをスプライン係合させる事により、トルク伝達可能、且つ全長を伸縮可能に組み合わせている。以下、前記中間シャフト4bの具体的な構造に就いて説明する。
The
前記インナシャフト9bは、中空状であって、軸方向一方側(図1〜3の右側)から順に、スプライン形成部18と、インナ側連続部19と、小径軸部20と、インナ側ヨーク部21とを備えている。
このうちのスプライン形成部18は、前記インナシャフト9bのうちの軸方向中間部から軸方向一端寄り部分にかけての部分に設けられている。この様なスプライン形成部18の外周面には、円周方向に関して交互に形成された軸方向に長い、複数ずつの凹部22、22と凸部23、23とから成る雄スプライン部8bが、全長に亙り形成されている。
The
Of these, the
又、前記スプライン形成部18の内周面は、内径が軸方向の全長に亙り変化しない円筒面状である。又、前記スプライン形成部18の径方向に関する厚さ寸法は、軸方向一端部に形成された面取り部に相当する部分を除いて、軸方向の全長に亙り一定である。
The inner peripheral surface of the
前記インナ側連続部19は、前記インナシャフト9bのうちの前記スプライン形成部18の軸方向他方側に隣接した部分に形成されている。この様なインナ側連続部19の外周面には、円周方向に関して交互に形成された、複数ずつの凹部24、24と、前記インナシャフト9bの中心軸を含む仮想平面に関する断面形状が直角三角形状の凸部25、25とから成る不完全スプライン部26が形成されている。この様な不完全スプライン部26を構成する各凸部25、25の外周面は、軸方向他方に向かうほど外径寸法が小さくなる方向に傾斜している。又、前記不完全スプライン部26の各凸部25、25の外周面の軸方向一端縁は、前記雄スプライン部8bを構成する各凸部23、23の外周面の軸方向他端縁に連続している。一方、前記不完全スプライン部26の各凸部23、23の外周面の軸方向他端縁は、前記小径軸部20の外周面の軸方向一端縁に連続している。尚、本参考例の場合、前記雄スプライン部8bの凹部22、22の外接円の直径と、前記不完全スプライン部26の凹部24、24の外接円の直径とが等しい。
The inner-side
又、前記インナ側連続部19の内周面は、内径が軸方向の全長に亙り変化しない円筒面状である。この様なインナ側連続部19の内周面の軸方向一端縁は、前記スプライン形成部18の内周面の軸方向他端縁に連続している。一方、前記インナ側連続部19の内周面の軸方向他端縁は、前記小径軸部20の内周面の軸方向一端縁に連続している。
The inner peripheral surface of the inner-side
前記小径軸部20は、前記インナシャフト9bのうち、前記インナ側連続部19の軸方向他方側に隣接した位置から、軸方向他端部にかけての部分に設けられている。この様な小径軸部20は、インナ側大径部27と、インナ側小径部28と、インナ側段部29と、外向鍔部(かしめ部)30とを有している。
The small-
このうちのインナ側大径部27は、前記小径軸部20のうちの軸方向一端部から軸方向他端寄り部分にかけての部分に形成されている。この様なインナ側大径部27の外周面は、外径が軸方向の全長に亙り変化しない円筒面状である。又、このインナ側大径部27の内周面の内径は、軸方向の全長に亙り一定である。
The inner-side large-
前記インナ側小径部28は、前記小径軸部20のうちの軸方向他端寄り部分に形成されている。この様なインナ側小径部28の外周面には、円周方向に凹部と凸部とを交互に配置して成る凹凸部である雄セレーション31が形成されている。この雄セレーション31を構成する凸部の外接円の直径寸法は、前記インナ側大径部27の外径寸法よりも小さい。
The inner-side small-
前記インナ側段部29は、前記インナ側大径部27の外周面の軸方向他端縁と、前記インナ側小径部28の外周面の軸方向一端縁とを連続した状態で形成されている。この様なインナ側段部29は、前記インナシャフト9bの中心軸に直交する仮想平面上に存在している。
The inner
前記外向鍔部30は、前記小径軸部20のうちの軸方向他端部に、全周に亙り前記インナ側小径部28の外周面よりも径方向外方に突出した状態で形成されている。この様な外向鍔部30は、この外向鍔部30を形成する前の状態のインナシャフト9bの軸方向他端部を、例えば、ローリングかしめにより全周に亙りかしめ拡げる事により形成する。
The
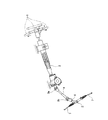
前記インナ側ヨーク部21は、前記小径軸部20の軸方向他端部に結合固定されている。尚、本参考例の場合、前記インナ側ヨーク部21と、十字軸32と、前記入力軸6の基端部に支持固定されたヨーク33とにより、前記両自在継手3c、3dのうちの、前側(図1の左側)に配置された自在継手3dを構成している。
The
この様なインナ側ヨーク部21は、筒状の基部34と、この基部34の外周面のうち、この基部34の中心軸に関して反対となる2箇所位置から軸方向他方側に延出した状態で設けられた1対の腕部35、35とから成る。
このうちの基部34は、中央部に中心孔36が形成されている。この中心孔36の内周面には、円周方向に凹部と凸部とを交互に配置して成る凹凸部である雌セレーション37が形成されている。この様な基部34は、前記中心孔36の内側に前記インナ側小径部28を挿通すると共に、前記雌セレーション37と前記雄セレーション31とをセレーション係合させた状態で、前記インナ側段部29と前記外向鍔部30との間で挟持されている。
Such inner
A
又、前記両腕部35、35のうち、軸方向に関して前記基部34と反対側端部寄り部分には、互いの中心軸が同軸となる状態で1対の円孔38、38が形成されている。
又、図1に示す組み立て状態に於いて、前記1対の腕部35、35の1対の円孔38、38のそれぞれの内側には、それぞれ有底円筒状の軸受カップ39、39が内嵌固定されている。これと共に、これら両軸受カップ39、39の内側に、それぞれ複数本のニードル40、40を介して、前記十字軸32を構成する4本の軸部41、41のうちの1対の軸部41、41の端部が回動自在に支持されている。
Further, a pair of
Also, in the assembled state shown in FIG. 1, inside the pair of
尚、前記十字軸32を構成する4本の軸部41、41のうち、前記インナ側ヨーク部21の両円孔38、38内に支持された軸部41、41以外の1対の軸部41(一方の軸部41は図示省略)の端部は、前記ヨーク33を構成する1対の腕部43(一方の腕部43は図示省略)に形成された円孔(図示省略)の内側に、軸受カップ(図示省略)及びニードル(図示省略)を介して回動自在に支持されている。
Of the four
又、前記インナシャフト9bを構成する雄スプライン部8bの外周面には、滑りやすい(摩擦係数の低い)合成樹脂製のコーティング層44が設けられている。具体的には、本参考例の場合、このコーティング層44は、前記インナシャフト9bの外周面のうち、前記スプライン形成部18の軸方向一端縁から前記小径軸部20の軸方向一端寄り部分(前記インナ側連続部19の軸方向他端縁よりも軸方向他方側に位置する部分であって、図1に直線Xで示す位置)にかけての部分に設けられている。
Further, a
前記アウタチューブ10bは、軸方向他方側から順に、小径筒部45と、アウタ側連続部46と、大径筒部47と、アウタ側ヨーク部48とを備えている。
このうちの小径筒部45は段付円筒状であり、前記アウタチューブ10bのうちの軸方向他端部から軸方向中間部にかけての部分に設けられている。具体的には、前記小径筒部45は、軸方向一方側半部に設けられたアウタ側大径部49と、軸方向他方側半部に設けられ、外径寸法がこのアウタ側大径部49の外径寸法よりも小さいアウタ側小径部50とから成る。又、このアウタ側大径部49の外周面の軸方向他端縁と、このアウタ側小径部50の外周面の軸方向一端縁とは、アウタ側段部51により連続されている。又、前記小径筒部45の内周面には、全長に亙り前記雌スプライン部52が形成されている。又、前記小径筒部45のうちの前記アウタ側小径部50に相当する部分をアウタ側薄肉部53としている。一方、この小径筒部45のうちの前記アウタ側大径部49に相当する部分をアウタ側厚肉部54としている。このアウタ側厚肉部54の径方向に関する厚さ寸法は、前記アウタ側薄肉部53の径方向に関する厚さ寸法よりも大きい。尚、本参考例の場合、前記アウタ側厚肉部54の外周面の軸方向他端部を、外径寸法が変化しない円筒面状としているが、軸方向他方側に向かうほど外径寸法が小さくなる部分円錐面状に形成する事もできる。
The
The small-
前記アウタ側連続部46は、外径寸法及び内径寸法が軸方向一方側(図1の右側)に向かうほど大きくなる部分円錐筒状であり、軸方向他端縁が、前記小径筒部45の軸方向一端縁に連続している。
前記大径筒部47は円筒状であり、軸方向他端縁が、前記アウタ側連続部46の軸方向一端縁に連続している。この様な大径筒部47の内径寸法及び外径寸法は、前記小径筒部45の内径寸法及び外径寸法よりも大きい。
The outer-side
The large-diameter
前記アウタ側ヨーク部48は、前記自在継手3cを構成するものであり、前記大径筒部47の軸方向一端縁のうちで、この大径筒部47に関する直径方向反対側となる2箇所位置から軸方向一方側に延出する状態で設けられた1対の腕部55、55から成る。この様な両腕部55、55の軸方向一端寄り部分には、互いの中心軸が同軸となる状態で1対の円孔56、56が形成されている。尚、図1に示す組み立て状態に於いて、これら1対の円孔56、56の内側には、それぞれ有底円筒状の軸受カップ57、57が内嵌固定されている。これと共に、これら各軸受カップ57、57の内側に、それぞれ複数本のニードル58、58を介して、十字軸59を構成する4本の軸部60、60のうちの1対の軸部60、60の端部が回動自在に支持されている。
The
尚、前記十字軸59を構成する4本の軸部60、60のうち、前記アウタ側ヨーク部48の両円孔56、56内に支持された軸部60、60以外の1対の軸部60(一方の軸部60は図示省略)の端部は、前記ステアリングシャフト2の前端部に支持固定されたヨーク61を構成する1対の腕部62(片方の腕部62は図示省略)に形成された円孔(図示省略)の内側に、軸受カップ及びニードル(図示省略)を介して回動自在に支持されている。
本参考例の場合、前記アウタ側ヨーク部48を、前記アウタチューブ10bに一体に設ける構造を採用しているが、アウタチューブとヨーク部とを別体に設けて溶接或は嵌合等により結合固定する構造を採用する事もできる。
Of the four
In the case of the present reference example, the outer
以上の様な構成を有する前記インナシャフト9bと前記アウタチューブ10bとは、前記雄スプライン部8bと、前記雌スプライン部52とを、前記コーティング層44を介してスプライン係合させる事により、トルクの伝達を可能、且つ、全長を伸縮可能な状態に組み合わされている。この様に組み付けられた状態で、前記雄スプライン部8bと前記雌スプライン部52との係合部には、所定量の締め代が設けられている。
With the
又、本参考例の場合、使用時に於ける、前記インナシャフト9bと前記アウタチューブ10bとの伸縮ストロークの範囲内で、前記アウタチューブ10bの雌スプライン部52のうちの前記アウタ側厚肉部54に相当する部分の軸方向他端部が、常に、前記雄スプライン部8bとスプライン係合する様に規制している。具体的には、前記伸縮ストロークの範囲内に於いて、前記インナシャフト9bと前記アウタチューブ10bとの径方向に重畳する部分が最も短い状態{図2(A)に示す状態であって、前記中間シャフト4bの全長が最も長い状態}で、前記アウタチューブ10bの雌スプライン部52のうちの前記アウタ側厚肉部54の軸方向他半部に相当する部分が、前記雄スプライン部8bとスプライン係合している。一方、前記伸縮ストロークの範囲内に於いて、前記インナシャフト9bと前記アウタチューブ10bとの径方向に重畳する部分が最も長い状態{図2(B)に示す状態であって、前記中間シャフト4bの全長が最も短い状態}では、前記アウタチューブ10bの雌スプライン部52のうちの前記アウタ側厚肉部54に相当する部分が全長に亙り、前記雄スプライン部8bとスプライン係合している。
Further, in the case of the present reference example, the outer
以上の様な構成を有する本参考例の中間シャフト4bによれば、前記インナシャフト9bの雄スプライン部8bと、前記アウタチューブ10bの雌スプライン部52との係合部の回転方向のがたつきを小さく抑えられる構造を採用した場合にも、前記インナシャフト9bと前記アウタチューブ10bとの摺動抵抗を小さく抑える事ができる。
即ち、本参考例の場合、前記インナシャフト9bの雄スプライン部8bの外周面を覆う状態でコーティング層44を設けている。又、これと共に、前記アウタチューブ10bのうち、前記雌スプライン部52に相当する部分の軸方向他端部から軸方向中間部にかけての部分に前記アウタ側薄肉部53を形成している。この為、前記アウタチューブ10bの雌スプライン部52が形成された部分のうちの前記アウタ側薄肉部53が形成された部分の径方向に関する剛性を、前記アウタ側厚肉部54が形成された部分の径方向に関する剛性より低くする事ができる。従って、前記インナシャフト9bの雄スプライン部8bと前記アウタチューブ10bの雌スプライン部52との係合部の回転方向のがたつきを防止する為に、この係合部に締め代を持たせた場合でも、この締め代に対する摺動抵抗(摺動荷重)の変動を鈍感にでき、前記インナシャフト9bと前記アウタチューブ10bとの摺動を安定させる事ができる。
According to the
That is, in the case of this reference example, the
又、上述の様に前記雌スプライン部52の径方向の剛性を適度に小さくする事ができる為、この雌スプライン部52と前記雄スプライン部8bとの係合部の回転方向のがたつきを防止する為に、この係合部に締め代を持たせた構造を採用した場合でも、この締め代に対する摺動抵抗(摺動荷重)を小さくする事ができる。又、この摺動抵抗(摺動荷重)の変動が鈍感になり、前記インナシャフト9bと前記アウタチューブ10bとの摺動を安定させる事ができる。更に、前記インナシャフト9b或いはこのアウタチューブ10bの誤差を許容できる範囲(寸法公差)を大きく確保した場合でも、この寸法公差の影響で、前記摺動抵抗が徒に大きくなる事を防止できる。従って、前記インナシャフト9b及び前記アウタチューブ10bの、製造コストの低減を図れる。
Further, as described above, since the radial rigidity of the
更に、本参考例の場合、使用時に於ける、前記インナシャフト9bと前記アウタチューブ10bとの伸縮ストロークの範囲で、このアウタチューブ10bの雌スプライン部52のうち、前記アウタ側厚肉部54の軸方向他端部の内周面に形成された部分と、前記インナシャフト9bの雄スプライン部8bとを、常にスプライン係合させている。この為、このインナシャフト9bと前記アウタチューブ10bとの間のトルク伝達を、前記アウタチューブ10bのうちの前記アウタ側厚肉部54に相当する部分と、前記インナシャフト9bのうちの当該部分とスプライン係合する部分とで行う事ができる。この様な本参考例の場合、トルクを伝達する部分に対して、前記アウタ側薄肉部53と前記アウタ側厚肉部54との境界部分17a(前記アウタ側段部51の径方向内端縁)が、軸方向一方側に位置する事がない。即ち、本参考例の場合、前記アウタチューブ10bから前記インナシャフト9bに伝達されるトルクの多くは、前記境界部分17aよりも軸方向一方側(前記アウタチューブ10b側)を通って伝達される。この結果、前記境界部分17aに、応力集中が発生する事を防止できる。
Further, in the case of the present reference example, the outer
[実施の形態の第1例]
本発明の実施の形態の第1例に就いて、図4、5を参照しつつ説明する。本例の中間シャフト4cは、インナシャフト9cを構成するスプライン形成部18aの内周面の形状を、前述した参考例の構造と異ならせている。尚、アウタチューブ10bの構造は、前述した参考例と同様である。
[ First Example of Embodiment]
A first example of the embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. In the
本例の場合、前記インナシャフト9cを構成するスプライン形成部18aの内周面のうち、軸方向一端部から軸方向中間部にかけての部分には、大径孔部63が形成されている。この様な大径孔部63の内径寸法は、軸方向の全長に亙り一定である。
又、前記スプライン形成部18aの内周面のうち、軸方向中間部から軸方向他端寄り部分にかけての部分には、内径寸法が、前記大径孔部63の内径寸法よりも小さい中径孔部64が形成されている。この中径孔部64の内径は、軸方向の全長に亙り一定である。
又、前記スプライン形成部18aの内周面の軸方向他端部(前記中径孔部64よりも軸方向他方側に位置する部分)には、内径寸法が、この中径孔部64の内径寸法よりも小さい小径孔部68が形成されている。
In the case of this example, a large-
Further, in the portion of the inner peripheral surface of the
At the other end of the inner peripheral surface of the
又、前記大径孔部63の軸方向他端縁と前記中径孔部64の軸方向一端縁とは、第一の連続段部65により連続している。
又、前記中径孔部64の軸方向他端縁と、前記小径孔部68の軸方向一端縁とは、第二の連続段部70により連続している。本例の場合、前記第一の連続段部65及び前記第二の連続段部70は、径方向外方に向かうほど軸方向一方に向かう方向に傾斜した状態で形成されている。尚、前記第一の連続段部65又は前記第二の連続段部70を、前記インナシャフト9cの中心軸に直交する仮想平面上に設ける事もできる。又、前記第一の連続段部65及び前記第二の連続段部70を、部分球面状に形成する事もできる。別の言い方をすれば、具体的には、前記第一の連続段部65及び前記第二の連続段部70の、前記インナシャフト9bの中心軸を含む仮想平面に関する断面形状を、円弧状とする。この様な構成を採用する場合には、前記第一の連続段部65及び前記第二の連続段部70の前記仮想平面に関する断面形状の曲率半径Rを、0.2mm以上(好ましくは、0.5mm以上)とする。この様な構成を採用すれば、前記第一の連続段部65及び前記第二の連続段部70に、応力集中が発生する事を防止できる。
Further, the other axial end of the large
Further, the other axial end of the medium
又、前記スプライン形成部18aのうち、前記大径孔部63に相当する部分をインナ側薄肉部66としている。一方、前記スプライン形成部18aのうち、前記中径孔部64に相当する部分を、径方向に関する厚さ寸法が、前記インナ側薄肉部66の径方向に関する厚さ寸法よりも大きいインナ側厚肉部67としている。本例の場合、このインナ側厚肉部67(前記スプライン形成部18a)の軸方向他端部の内周面に、このインナ側厚肉部67の軸方向中間部の内周面よりも全周に亙り径方向内方に張り出した内向張出部71が形成されている。この様にして前記インナ側厚肉部67のうちのこの内向張出部71が形成された部分の径方向の厚さ寸法を、このインナ側厚肉部67のうちの他の部分(この内向張出部71が形成されていない部分)の径方向厚さ寸法よりも大きくしている。
Further, a portion of the
又、前記インナ側薄肉部66の、前記インナシャフト9bの中心軸に直交する仮想平面に関する断面積は、前記インナ側厚肉部67のこの仮想平面に関する断面積よりも小さい。
又、本例の場合、前記インナ側薄肉部66の軸方向他端縁は、前記スプライン形成部18a(雄スプライン部8b)の軸方向に関する長さ寸法をL18とした場合に、このスプライン形成部18a(前記雄スプライン部8b)の軸方向一端縁から、(0.6〜0.9)・L18となる位置に配置する。
The cross-sectional area of the inner
Further, in the case of this example, the other end in the axial direction of the inner side
又、前記インナ側厚肉部67のうちの前記内向張出部71が形成された部分の前記仮想平面に関する断面積は、前記インナ側厚肉部67のうちの他の部分(この内向張出部71が形成されていない部分)の前記仮想平面に関する断面積よりも大きい。
In addition, the cross-sectional area of the portion of the inner side
又、本例の場合も、前記インナシャフト9cを構成するインナ側連続部19aは、前記インナシャフト9cのうちの前記スプライン形成部18aの軸方向他方側に隣接した部分に形成されている。この様なインナ側連続部19aの外周面には、円周方向に関して交互に形成された、複数ずつの凹部24、24(図3参照)と、前記インナシャフト9cの中心軸を含む仮想平面に関する断面形状が直角三角形状の凸部25、25(図3参照)とから成る不完全スプライン部26が形成されている。この様な不完全スプライン部26の構造は、前述した参考例と同様である。
Also in the case of this example, the inner-side
又、本例の場合、前記インナ側連続部19aの内周面は、軸方向に関して内径寸法が変化しない円筒面状に形成されている。この様なインナ側連続部19aの内周面の内径寸法は、前記小径孔部68の内径寸法と等しい。又、このインナ側連続部19aの内周面の軸方向一端縁は、この第二の連続段部70の軸方向他端縁に連続している。一方、前記インナ側連続部19aの内周面の軸方向他端縁は、前記小径軸部20の内周面の軸方向一端縁に連続している。
Further, in the case of this example, the inner peripheral surface of the inner-side
前記小径軸部20は、前記インナシャフト9cのうち、前記インナ側連続部19aの軸方向他方側に隣接した位置から、軸方向他端部にかけての部分に設けられている。この様な小径軸部20は、インナ側大径部27と、インナ側小径部28と、インナ側段部29と、外向鍔部(かしめ部)30とを有している。
The small-
又、本例の場合、前記インナ側大径部27の内周面は、内径寸法が軸方向の全長に亙り一定であり、この内径寸法は、前記インナ側連続部19aの内周面及び前記小径孔部68の内径寸法と等しい。この様なインナ側大径部27の内周面の軸方向一端縁は、前記インナ側連続部19aの内周面の軸方向他端縁に連続している。又、本例の場合、前記インナ側大径部27の、前記インナシャフト9cの中心軸に直交する仮想平面に関する断面積を、前記インナ側厚肉部67のうちの前記内向張出部71が形成されていない部分の前記仮想平面に関する断面積と実質的に(製造上不可避な寸法公差を除いて)等しくしている。又、前記インナ側大径部27の前記仮想平面に関する断面積を、前記インナ側厚肉部67のうちの前記内向張出部71が形成された部分の前記仮想平面に関する断面積よりも小さくしている。
Further, in the case of this example, the inner peripheral surface of the inner-side large-
又、本例の場合も、前記外向鍔部30は、前記小径軸部20のうちの軸方向他端部に、全周に亙り前記インナ側小径部28の外周面よりも径方向外方に突出した状態で形成されている。この様な外向鍔部30は、図5に示す状態の前記インナシャフト9c(この外向鍔部30を形成する前の状態のインナシャフト9c)の軸方向他端部を、例えば、ローリングかしめにより全周に亙りかしめ拡げる事により形成する。尚、図5に示す状態(この外向鍔部30を形成する前の状態)の前記インナシャフト9bの軸方向他端部には、当外部分の軸方向一方側に隣接した部分よりも径方向の肉厚が薄い第二のインナ側薄肉部69が形成されている。この様にして、前記外向鍔部30を形成する前の状態のインナシャフト9bの軸方向他端部の剛性を低くして、前記外向鍔部30を形成し易くしている。その他の前記小径軸部20の具体的な構造は、前述した参考例と同様である。
Also in the case of this example, the
以下、前記インナシャフト9cの製造方法に就いて簡単に説明する。
先ず、第1工程に於いて、炭素鋼(例えば、S10C〜S45C)等の鉄系合金、或いは、アルミニウム系合金、マグネシウム合金等の軽合金から成る、中空円管状の素材(図示省略)の軸方向一端部から軸方向中間部にかけての部分(前記スプライン形成部18aに相当する部分)を、当該部分を拡径して第一中間素材とする。尚、この様に拡径する作業は、例えば、前記素材の軸方向一端部から軸方向中間部にかけての部分の内側に、マンドレルを挿入し、このマンドレルにより前記素材の内周面を扱く様にして行う。この様な拡径作業の際には、前記素材のうち、拡径される部分の外径側に、円筒面状の内周面を有する外型を配置して行う事もできる。
Hereinafter, a method for manufacturing the
First, in the first step, a shaft of a hollow circular tubular material (not shown) made of an iron alloy such as carbon steel (for example, S10C to S45C) or a light alloy such as an aluminum alloy or a magnesium alloy. The part from the one end in the direction to the intermediate part in the axial direction (the part corresponding to the
次いで、第2工程に於いて、前記第一中間素材のうちの拡径された部分の外周面に切削加工を施す事により、当該部分の外径寸法を転造下径(プレス下径)に加工する。この様にして第二中間素材を得る。 Next, in the second step, the outer peripheral surface of the expanded portion of the first intermediate material is subjected to cutting to change the outer diameter of the portion to the rolled lower diameter (press lower diameter). To process. In this way, the second intermediate material is obtained.
次いで、第3工程に於いて、前記第二中間素材のうちの転造下径(プレス下径)に加工された部分に、転造又はプレス成形を施す事により円周方向に凹部と凸部とを交互に配置して成る凹凸部である前記雄スプライン部8bを形成する。この様にして第三中間素材を得る。尚、上述の様にして前記雄スプライン部8bを形成する際には、前記第二中間素材のうちの転造下径(プレス下径)に加工された部分の内径側に、サポート軸を挿入した状態で行う。又、上述の工程では、前記雄スプライン部8bと共に、前記不完全スプライン部26も形成される。
Then, in the third step, the portion of the second intermediate material that has been processed into the rolling lower diameter (press lower diameter) is subjected to rolling or press molding to form concave and convex portions in the circumferential direction. The
次いで、第4工程に於いて、前記第三中間素材の外周面の軸方向他端部に、例えば、切削加工、転造加工、又はプレス成型を施す事により、前記インナ側小径部28(雄セレーション31)と、前記インナ側段部29とを形成する。この様にして第四中間素材を得る。
Next, in the fourth step, the inner side small diameter portion 28 (male) is formed by, for example, performing cutting, rolling, or press molding on the other axial end of the outer peripheral surface of the third intermediate material. The serration 31) and the inner
次いで、第5工程に於いて、前記第四中間素材のうちの、軸方向一端部から軸方向中間部(前記インナ側連続部19aに相当する部分よりも軸方向他方側に位置する部分)に、例えば、流動浸漬法、静電塗装法等により粗コーティング層を形成する。そして、この粗コーティング層に、シェービング加工を施す事により前記コーティング層44を形成する。この様にして第五中間素材を得る。
Next, in the fifth step, from the one axial end portion of the fourth intermediate material to the axial intermediate portion (the portion located on the other axial side of the portion corresponding to the inner side
次いで、第6工程に於いて、この第五中間素材のうちの前記雄スプライン部8bに相当する部分の内周面の軸方向一端部から軸方向中間部にかけての部分に切削加工を施す事により、前記大径孔部63(前記インナ側薄肉部66)を形成する。一方、前記第五中間素材のうちの前記雄スプライン部8bに相当する部分の内周面の軸方向中間部から軸方向他端寄り部分にかけての部分は、そのまま前記中径孔部64とする。
Next, in a sixth step, by cutting the portion of the inner peripheral surface of the portion corresponding to the
最後に、第7工程に於いて、前記第六中間素材(図4に示す、前記ヨーク33が固定される前の状態のインナシャフト9c)の軸方向他端部に前記インナ側ヨーク部21を固定して、前記インナシャフト9cとする。尚、前記第六中間素材にこのインナ側ヨーク部21を結合固定する作業は、この第六中間素材の軸方向他端部を全周に亙り、ローリングかしめによりかしめ拡げる事により行う。
尚、上述の各工程は、矛盾が生じない範囲で、適宜入れ替えて実施する事が可能である。
Finally, in the seventh step, the
It should be noted that the above steps can be appropriately replaced with each other as long as no contradiction occurs.
以上の様な構成を有するインナシャフト9cは、前記雄スプライン部8bを全長に亙り、アウタチューブ10bの雌スプライン部52に、コーティング層44を介してスプライン係合させる事により、前記アウタチューブ10bに組み付けられている。この様に組み付けられた状態で、前記雄スプライン部8bとこのアウタチューブ10bの雌スプライン部52との係合部には、所定量の締め代が設けられている。この様にして、前記インナシャフト9bと前記アウタチューブ10bとは、トルクの伝達を可能、且つ、全長を伸縮可能な状態に組み合わされている。
The
又、本例の場合、使用時に於ける、前記インナシャフト9cと前記アウタチューブ10bとの伸縮ストロークの範囲内で、前記雄スプライン部8bのうちの前記インナ側厚肉部67(前記中径孔部64)に相当する部分を、常に、前記雌スプライン部52とスプライン係合する様に規制している。
又、本例の場合も、使用時に於ける、前記インナシャフト9cと前記アウタチューブ10bとの伸縮ストロークの範囲内で、前記アウタチューブ10bの雌スプライン部52のうちのアウタ側厚肉部54の軸方向他端部に相当する部分と、前記雄スプライン部8bとが、常にスプライン係合する様に規制している。要するに、前記インナシャフト9cと前記アウタチューブ10bとの径方向に重畳する部分が最も短い状態から同じく長い状態にかけて、前記雄スプライン部8bのうちのインナ側厚肉部67に相当する部分と、前記雌スプライン部52のうちのアウタ側厚肉部54の軸方向他端部に相当する部分とがスプライン係合する様にしている。
Further, in the case of this example, the inner side thick portion 67 (the medium diameter hole) of the
Also in the case of this example, the outer
以上の様な構成を有する本例の中間シャフト4cの場合、前記インナシャフト9cのうち、前記雄スプライン部8bが形成された部分の内周面に、軸方向一方側から順に前記インナ側薄肉部66と前記インナ側厚肉部67とを設けている。この為、前記雄スプライン部8bが形成された部分のうちの前記インナ側薄肉部66が形成された部分の径方向の剛性を、同じくインナ側厚肉部67が形成された部分と比べて適度に小さくできる。従って、前記雄スプライン部8bと前記雌スプライン部52との係合部の回転方向のがたつきを防止する為に、この係合部に締め代を持たせた場合でも、この締め代に対する摺動抵抗(摺動荷重)の変動を鈍感にでき、前記インナシャフト9cの、前記アウタチューブ10bに対する摺動を安定させる事ができる。
In the case of the
又、本例の場合、使用時に於ける、前記インナシャフト9cと前記アウタチューブ10bとの伸縮ストロークの範囲内で、前記雄スプライン部8bのうちの前記インナ側厚肉部67に相当する部分を、常に、前記雌スプライン部52とスプライン係合する様に規制している。この為、前記インナシャフト9cと前記アウタチューブ10bとの間のトルク伝達を、このインナシャフト9cの雄スプライン部8bが形成された部分のうち、径方向に関する剛性が比較的高い前記インナ側厚肉部67に相当する部分で行う事ができる。この結果、摺動性を向上しつつ、前記インナシャフト9bの耐久性の向上も図れる。
Further, in the case of this example, a portion of the
又、本例の場合、前記第二の連続段部70を前記インナ側連続部19aの外周面よりも軸方向一方側に位置させる事により、前記インナ側厚肉部67(前記スプライン形成部18a)の軸方向他端部の内周面に、このインナ側厚肉部67の軸方向中間部の内周面よりも全周に亙り径方向内方に張り出した内向張出部71を形成している。この様にして、前記インナ側連続部19aの径方向に関する厚さ寸法を大きく確保する事により、このインナ側連続部19aと前記小径軸部20との境界部分の様に、応力が集中し易い部分の剛性を確保して、前記インナシャフト9cの耐久性の向上を図れる。
Further, in the case of the present example, by arranging the second continuous stepped
[実施の形態の第2例]
本発明の実施の形態の第2例に就いて、図6を参照しつつ説明する。
本例の中間シャフト4dを構成するアウタチューブ10cは、小径筒部45aと、アウタ側連続部46と、大径筒部47と、アウタ側ヨーク部48とを備えている。
このうちの小径筒部45aは段付円筒状であり、前記アウタチューブ10cのうちの、軸方向他端部から軸方向中間部にかけての部分に設けられている。具体的には、前記小径筒部45aは、軸方向一端部から軸方向他端寄り部分にかけての部分に設けられたアウタ側大径部49aと、軸方向他端部に設けられ、外径寸法がこのアウタ側大径部49aの外径寸法よりも小さいアウタ側小径部50aとから成る。又、このアウタ側大径部49aの外周面の軸方向他端縁とこのアウタ側小径部50aの外周面の軸方向一端縁とは、アウタ側段部51aにより連続されている。即ち、本例の場合、このアウタ側段部51aの軸方向に関する位置を、前述した実施の形態の第1例のアウタ側段部51よりも軸方向他方側に位置させている。又、前記小径筒部45aの内周面には、全長に亙り雌スプライン部52が形成されている。尚、前記アウタ側連続部46、前記大径筒部47、及び前記アウタ側ヨーク部48の構造は、前述した実施の形態の第1例及び参考例の場合と同様である。
[ Second Example of Embodiment]
A second example of the embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG.
The
The small-diameter
又、本例の場合、インナシャフト9dを構成するスプライン形成部18bの内周面に形成された、大径孔部63aの軸方向他端縁と、中径孔部64aの軸方向一端縁とを連続する第一の連続段部65aの軸方向位置を、前述した実施の形態の第1例の場合よりも軸方向一方側に位置させている。又、前記スプライン形成部18bのうち、前記大径孔部63aに相当する部分をインナ側薄肉部66aとしている。一方、前記スプライン形成部18bのうち、前記中径孔部64aに相当する部分を、径方向に関する厚さ寸法が、前記インナ側薄肉部66aの径方向に関する厚さ寸法よりも大きいインナ側厚肉部67aとしている。別の言い方をすれば、本例の場合、前記インナ側薄肉部66a(前記大径孔部63a)の軸方向に関する長さ寸法を、前述した実施の形態の第1例の場合よりも短くすると共に、前記インナ側厚肉部67a(前記中径孔部64a)の軸方向に関する長さ寸法を、前述した実施の形態の第1例の場合よりも長くしている。
Further, in the case of the present example, the other axial end of the large
以上の様な構成を有する本例の場合も、前記インナシャフト9dの雄スプライン部8bと、前記アウタチューブ10cの雌スプライン部52とを、コーティング層44を介してスプライン係合させる事により、前記インナシャフト9dと前記アウタチューブ10cとを、トルクの伝達を可能、且つ、全長を伸縮可能な状態に組み合わせている。尚、この様に組み付けられた状態で、前記雄スプライン部8bと前記雌スプライン部52との係合部には、所定量の締め代が設けられている。
Also in the case of the present example having the above-mentioned configuration, the
又、本例の場合、使用時に於ける、前記インナシャフト9dと前記アウタチューブ10cとの伸縮ストロークの範囲内で、このアウタチューブ10cの雌スプライン部52のうちの前記アウタ側厚肉部54の軸方向他端部の内周面に形成された部分と、前記インナシャフト9dの雄スプライン部8bのうちのインナ側厚肉部67aの軸方向一端部に相当する部分とが、常にスプライン係合する様に規制している。その他の構造、及び作用・効果は前述した実施の形態の第1例及び参考例と同様である。
Further, in the case of this example, the outer
前述した実施の形態の各例及び参考例では、本発明を、ステアリング装置を構成する中間シャフトを構成するインナシャフトに適用した例に就いて説明した。但し、本発明は、この様なインナシャフト以外にも、各種用途で使用される伸縮自在シャフトの構造に適用する事ができる。
又、前述した実施の形態の第1例で説明した伸縮自在シャフト用インナシャフトの製造方法を構成する各工程は、矛盾が生じない範囲で、順番を入れ替える事が可能である。又、これら各工程は、可能な範囲で同時に行う事もできる。
In each of the above-described embodiments and reference examples , the present invention is described as an example in which the present invention is applied to an inner shaft that constitutes an intermediate shaft that constitutes a steering device. However, the present invention can be applied to structures of expandable shafts used for various purposes other than such an inner shaft.
In addition, the steps of the method of manufacturing the inner shaft for a retractable shaft described in the first example of the above-described embodiment can be interchanged in order so long as no contradiction occurs. Further, each of these steps can be performed simultaneously within a possible range.
1 ステアリングホイール
2 ステアリングシャフト
3a、3b、3c、3d 自在継手
4、4a、4b、4c、4d 中間シャフト
5 ステアリングギヤユニット
6 入力軸
7 タイロッド
8、8a、8b 雄スプライン部
9、9a、9b、9c、9d インナシャフト
10、10a、10b、10c アウタチューブ
11 第一のヨーク
12 雌スプライン部
13 第二のヨーク
14 アウタ側薄肉部
15 アウタ側厚肉部
17、17a 境界部分
18、18a、18b スプライン形成部
19、19a インナ側連続部
20 小径軸部
21 インナ側ヨーク部
22 凹部
23 凸部
24 凹部
25 凸部
26 不完全スプライン部
27 インナ側大径部
28 インナ側小径部
29、29a インナ側段部
30 外向鍔部
31 雄セレーション
32 十字軸
33 ヨーク
34 基部
35 腕部
36 中心孔
37 雌セレーション
38 円孔
39 軸受カップ
40 ニードル
41 軸部
43 腕部
44 コーティング層
45、45a 小径筒部
46 アウタ側連続部
47 大径筒部
48 アウタ側ヨーク部
49、49a アウタ側大径部
50、50a アウタ側小径部
51、51a アウタ側段部
52 雌スプライン部
53 アウタ側薄肉部
54 アウタ側厚肉部
55 腕部
56 円孔
57 軸受カップ
58 ニードル
59 十字軸
60 軸部
61 ヨーク
62 腕部
63、63a 大径孔部
64、64a 中径孔部
65、65a 第一の連続段部
66、66a インナ側薄肉部
67、67a インナ側厚肉部
68 小径孔部
69 第二のインナ側薄肉部
70 第二の連続段部
71 内向張出部
1 Steering Wheel 2
8, 8a, 8b
10, 10a, 10b, 10c Outer tube 11
37
Claims (1)
内周面に雌スプライン部が形成されたアウタチューブと、
前記雄スプライン部の外周面を覆う状態で設けられたコーティング層とを備えており、
前記雄スプライン部と前記雌スプライン部とを、前記コーティング層を介してスプライン係合させる事により、前記インナシャフトと前記アウタチューブとがトルク伝達可能、且つ、全長を伸縮可能な状態に組み合わされている伸縮自在シャフトであって、
前記アウタチューブのうち、内周面に前記雌スプライン部が形成された部分が、軸方向他端部に形成されたアウタ側薄肉部と、該アウタ側薄肉部の軸方向一方側に隣接した位置に形成された、前記アウタ側薄肉部の外径寸法よりも大きい外径寸法を有する、アウタ側厚肉部とにより構成されており、
前記インナシャフトのうち、外周面に前記雄スプラインが形成された部分が、軸方向一端部に形成されたインナ側薄肉部と、該インナ側薄肉部の軸方向他方側に隣接した位置に形成された、前記インナ側薄肉部の内径寸法よりも小さい内径寸法を有する、インナ側厚肉部とにより構成されており、
前記インナ側厚肉部の軸方向他端部の内周面には、前記インナ側厚肉部の軸方向中間部の内周面よりも全周に亙り径方向内方に張り出した内向張出部が形成されており、
使用時に於ける前記インナシャフトと前記アウタチューブとの伸縮ストロークの範囲で、前記雌スプライン部のうち、前記アウタ側厚肉部の軸方向他端部の内周面に形成された部分と、前記雄スプライン部とが、常にスプライン係合しており、且つ、前記雄スプライン部のうち、前記インナ側厚肉部の外周面に形成された部分と、前記雌スプライン部とが、常にスプライン係合している、
伸縮自在シャフト。 A hollow inner shaft having a male spline portion formed on the outer peripheral surface of one end in the axial direction,
An outer tube having a female spline portion formed on the inner peripheral surface,
A coating layer provided so as to cover the outer peripheral surface of the male spline portion,
By engaging the male spline portion and the female spline portion with a spline through the coating layer, the inner shaft and the outer tube are combined so that torque can be transmitted and the entire length can be expanded and contracted. It is a retractable shaft,
A portion of the outer tube where the female spline portion is formed on the inner peripheral surface is adjacent to the outer thin portion formed at the other axial end and one axial side of the outer thin portion. to the formed, has a larger outer diameter than the outer diameter of the outer side thin portion is constituted by the outer-side thick portion,
A portion of the inner shaft where the male spline is formed on the outer peripheral surface is formed at a position adjacent to the inner thin portion formed at one axial end and the other axial side of the inner thin portion. Also, having an inner diameter dimension smaller than the inner diameter dimension of the inner side thin portion, is composed of an inner thick portion,
On the inner peripheral surface of the other axial end of the inner thick portion, an inward protrusion protruding radially inward over the entire circumference of the inner peripheral surface of the axial middle portion of the inner thick portion. Part is formed,
Within the range of expansion and contraction stroke of the inner shaft and the outer tube during use, a portion of the female spline portion formed on the inner peripheral surface of the other axial end of the outer thick portion, and The male spline portion is always in spline engagement , and the portion of the male spline portion formed on the outer peripheral surface of the inner-side thick portion and the female spline portion are always in spline engagement. Is doing
Telescopic shaft.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016030257A JP6690289B2 (en) | 2016-02-19 | 2016-02-19 | Telescopic shaft |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016030257A JP6690289B2 (en) | 2016-02-19 | 2016-02-19 | Telescopic shaft |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2017145946A JP2017145946A (en) | 2017-08-24 |
| JP2017145946A5 JP2017145946A5 (en) | 2019-03-28 |
| JP6690289B2 true JP6690289B2 (en) | 2020-04-28 |
Family
ID=59682933
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016030257A Active JP6690289B2 (en) | 2016-02-19 | 2016-02-19 | Telescopic shaft |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6690289B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109093327A (en) * | 2018-07-13 | 2018-12-28 | 安徽金诚汽车装饰设计开发有限公司 | A kind of production method of instrument desk of passenger car tubing string collapsing structure |
-
2016
- 2016-02-19 JP JP2016030257A patent/JP6690289B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2017145946A (en) | 2017-08-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6354761B2 (en) | Torque transmission shaft with universal joint yoke | |
| JP6597010B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing telescopic shaft | |
| JP6481797B2 (en) | Telescopic shaft | |
| JP6760507B2 (en) | Shaft coupling structure and telescopic shaft | |
| US7488257B1 (en) | Multiple-tube propeller shaft assembly | |
| JP6690289B2 (en) | Telescopic shaft | |
| JP6512129B2 (en) | Telescopic shaft | |
| JP6699198B2 (en) | Telescopic shaft | |
| JP7342631B2 (en) | Outer tube with hole cover | |
| JP2017172613A (en) | Telescopic shaft | |
| JP6798122B2 (en) | Telescopic shaft | |
| JP6746988B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of telescopic shaft | |
| CN110953256B (en) | Telescopic shaft with stopper | |
| JP6601004B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing telescopic shaft | |
| JP2017166542A (en) | Telescopic shaft | |
| JP2017106565A (en) | Telescopic shaft | |
| JP6897184B2 (en) | Outer tube and its manufacturing method | |
| JP2017003055A5 (en) | ||
| JP2017161031A (en) | Telescopic shaft | |
| JP7359056B2 (en) | Telescopic shaft with stopper | |
| JP2017106566A (en) | Manufacturing method of male shaft for telescopic shaft | |
| JP7254566B2 (en) | Joint member manufacturing method and joint member used for constant velocity joint | |
| JP2017161032A (en) | Telescopic shaft | |
| JP7234686B2 (en) | Outer shaft and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP6528541B2 (en) | Telescopic shaft and method of manufacturing the same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20190212 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20190212 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20191128 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20191203 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20200131 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20200310 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20200323 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6690289 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |