JP6296769B2 - Object detection device - Google Patents
Object detection device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6296769B2 JP6296769B2 JP2013248523A JP2013248523A JP6296769B2 JP 6296769 B2 JP6296769 B2 JP 6296769B2 JP 2013248523 A JP2013248523 A JP 2013248523A JP 2013248523 A JP2013248523 A JP 2013248523A JP 6296769 B2 JP6296769 B2 JP 6296769B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- human body
- distribution
- image
- window
- suitability
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 title claims description 167
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 claims description 118
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 claims description 29
- 239000013598 vector Substances 0.000 claims description 18
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 24
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 16
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 15
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 10
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 9
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000015654 memory Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000006978 adaptation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000010801 machine learning Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012706 support-vector machine Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000012935 Averaging Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000037237 body shape Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004590 computer program Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010606 normalization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Description
本発明は、画像から物体を検出する物体検出装置に関する。 The present invention relates to an object detection apparatus that detects an object from an image.
従来、写真もしくはビデオの画像検索や防犯用の画像センサなど様々な目的のために、画像から人体、車両等の対象物体を検出する物体検出装置が研究されている。特に近年では機械学習した識別器を用いた物体検出装置が多く研究されている。例えば、学習識別器は、人体が写っている多数の学習用画像と人体が写っていない多数の学習用画像のそれぞれから抽出した特徴量を用い、特徴量空間において人体の特徴量空間とそれ以外の空間とを分ける識別境界を機械学習することによって生成される。この識別器は、人体の有無を判定したい画像から抽出した特徴量が入力されると、その特徴量が特徴量空間において識別境界のどちら側に位置するかによりその画像に人体が写っているか否かを判定する。 2. Description of the Related Art Conventionally, an object detection device that detects a target object such as a human body or a vehicle from an image has been studied for various purposes such as a photo or video image search or an image sensor for crime prevention. In recent years, many researches have been made on object detection devices using machine-learned classifiers. For example, the learning classifier uses feature quantities extracted from each of a large number of learning images in which a human body is photographed and a large number of learning images in which a human body is not photographed. It is generated by machine learning of an identification boundary that divides the space. When a feature value extracted from an image for which the presence / absence of a human body is to be determined is input to this classifier, whether or not the human body is reflected in the image depends on which side of the feature boundary the feature value is located in the feature space. Determine whether.
例えば、特許文献1には、入力画像に現れる対象物を検知する対象物検知装置が提案されている。この対象物検知装置は、学習用画像(標本画像)を複数のセルごとに区分けしている。そして、各セルに対象物の部分の存否を識別する部分識別器と、全ての部分識別器が出力したセル識別指標値から対象物の存否を識別可能な全体識別器とを有する。 For example, Patent Document 1 proposes an object detection device that detects an object appearing in an input image. In this object detection device, a learning image (specimen image) is divided into a plurality of cells. Each cell includes a partial discriminator that identifies the presence / absence of a portion of the object, and an overall discriminator that can identify the presence / absence of the object from cell identification index values output by all the partial discriminators.
特許文献1に記載された対象物検知装置は、セル毎の識別結果を全体識別器にて利用し対象物を検知するので、対象物の一部が他の物体により隠蔽されているような場合でも、対象物を精度良く検知することができる。しかしながら、セルの位置によっては、入力画像に表れる対象物の特徴的な部位(例えば対象物が人物である場合の頭部等)が一つのセルに収まらず、複数のセルにまたがってしまうため、その部位の特徴を学習した部分識別器での識別精度が低下し、対象物を検知することができない場合があった。また、セルを大きくし、部位が一つのセルに収まるようにすると、部位の特徴がセル全体に占める割合が減少し、部分識別器の学習数にもよるが部分識別器の識別精度が低下してしまい、対象物の存否を識別する全体識別器の性能も低下することとなる。 Since the object detection device described in Patent Document 1 uses the identification result for each cell to detect the object using the overall classifier, a part of the object is hidden by another object However, the object can be detected with high accuracy. However, depending on the position of the cell, the characteristic part of the target object appearing in the input image (for example, the head when the target object is a person) does not fit in one cell, and spans multiple cells. In some cases, the identification accuracy of the partial classifier that learned the feature of the part is lowered, and the object cannot be detected. In addition, if the cell is enlarged so that the part fits in one cell, the proportion of the part features in the whole cell decreases, and the classification accuracy of the partial classifier decreases depending on the number of learning of the partial classifier. As a result, the performance of the overall discriminator for identifying the presence / absence of the target object also deteriorates.
本発明の目的は、画像内において対象物体の特徴的な部位が表れる位置が変動する場合でも、その部位の特徴を利用して対象物体を精度良く検出することができる物体検出装置を提供することにある。 An object of the present invention is to provide an object detection device capable of accurately detecting a target object using the characteristics of the part even when the position where the characteristic part of the target object appears in the image fluctuates. It is in.
かかる課題を解決するため本発明は、対象物体を構成する一または複数の部位の画像特徴である部位特徴を用いて、検出対象画像に対象物体像が存在するか否かを識別する物体検出装置であって、検出対象画像における複数の位置に所定サイズの部位窓を設定し、当該部位窓内に対して前記部位特徴に適合する程度である部位適合度を算出する部位適合度算出部と、部位適合度の分布を生成する分布生成部と、部位適合度の分布を特徴量として前記対象物体の存否を識別する分布識別部とを少なくとも含む物体検出装置を提供する。
これにより本発明は、検出対象画像内に対象物体を構成する部位特徴が分布している状況を特徴量として対象物体の存否を識別するので、一つの部位適合度、例えば部位適合度のピーク値を用いた識別よりも対象物体の識別精度が向上する。
In order to solve such a problem, the present invention provides an object detection device for identifying whether or not a target object image exists in a detection target image using a part feature that is an image feature of one or a plurality of parts constituting the target object. A part suitability calculator that sets a part window of a predetermined size at a plurality of positions in the detection target image and calculates a part suitability that is suitable for the part feature within the part window; Provided is an object detection device including at least a distribution generation unit that generates a distribution of part suitability and a distribution identification unit that identifies the presence or absence of the target object using the distribution of part suitability as a feature amount.
Thus, the present invention identifies the presence / absence of the target object using the situation in which the part features constituting the target object are distributed in the detection target image as a feature quantity, so that one part suitability, for example, the peak value of the part suitability The identification accuracy of the target object is improved as compared with the identification using.
部位適合度算出部は、部位ごとに部位窓を設定する探索範囲を定めることが好適である。これにより、検出対象画像中における対象物体の各部位が所在する可能性のある位置が予め分かっている場合、その部位が所在する可能性のある範囲を探索範囲に設定できるので、部位適合度の分布の精度を更に向上させることができる。 The part suitability calculation unit preferably determines a search range in which a part window is set for each part. Thereby, when the position where each part of the target object in the detection target image is likely to be located is known in advance, the range where the part may be located can be set as the search range. The accuracy of distribution can be further improved.
部位適合度算出部は、部位窓のサイズを予め定めた変化量の範囲にて変化させることが好適である。これにより、検出対象画像中における対象物体像の大きさ等に変動があった場合でも、部位窓のサイズを変化させてその変動に対応できるので、部位適合度の分布精度を更に向上させることができる。 It is preferable that the part suitability calculation unit changes the size of the part window within a predetermined change amount range. As a result, even if there is a change in the size of the target object image in the detection target image, the size of the part window can be changed to cope with the change, so that the distribution accuracy of the part suitability can be further improved. it can.
分布生成部は、部位窓ごとに設定された前記検出対象画像における各部位の所在する基準位置から同一の投票位置までの投票ベクトルを用いて、部位適合度を算出した部位窓の位置から投票して前記部位適合度分布を生成することが好適である。これにより、一部の部位における部位適合度がオクルージョンなどに起因して精度良く算出できなくとも、他の部位による部位適合度が投票されているので、全体の状況を表す部位適合度分布への影響が軽減され、対象物体の識別精度が向上する。 The distribution generation unit uses the voting vector from the reference position where each part is located in the detection target image set for each part window to the same voting position, to vote from the part window position where the part suitability is calculated. It is preferable to generate the site suitability distribution. As a result, even if the site suitability at some sites cannot be calculated accurately due to occlusion, etc., the site suitability by other sites has been voted. The influence is reduced, and the identification accuracy of the target object is improved.
分布生成部は、検出対象画像を複数領域に分割し、当該分割領域ごとに適合度分布を生成することも好適である。これにより、検出対象画像における部位毎のおおよその位置が分かっている際に、部位の配置を重視した適合度分布を用いることができる。 It is also preferable that the distribution generation unit divides the detection target image into a plurality of regions and generates a fitness distribution for each of the divided regions. Thereby, when the approximate position for each part in the detection target image is known, it is possible to use a fitness distribution that places importance on the arrangement of the part.
本発明に係る物体検出装置は、画像内において対象物体の特徴的な部位が表れる位置が変動する場合でも、その部位の特徴を利用して対象物体を精度良く検出することができるという効果を奏する。 The object detection device according to the present invention has an effect that the target object can be accurately detected by using the feature of the part even when the position where the characteristic part of the target object appears in the image fluctuates. .
以下、本発明の物体検出装置を人体検出装置に適応した形態について図を参照しつつ説明する。
なお、物体検出装置の対象物体は、人体に限定されることなく、車両、かばん、扉など、画像中に表れる物体であれば良い。また、本実施形態では、人体検出装置が、頭部、右肩、左肩、胴体、右脚、左脚等の全ての部位適合度の分布を用いて人体を検出する例について説明する。本実施の形態では、6つの部位適合度を用いているが、これに限らず、一つの部位適合度の分布を用いて人体を検出しても良い。または、部位を詳細に分けて多数の部分を用いてもよい。
Hereinafter, an embodiment in which the object detection device of the present invention is applied to a human body detection device will be described with reference to the drawings.
The target object of the object detection device is not limited to a human body, and may be any object that appears in an image, such as a vehicle, a bag, or a door. Further, in the present embodiment, an example will be described in which the human body detection device detects a human body using distributions of all part suitability such as a head, a right shoulder, a left shoulder, a trunk, a right leg, and a left leg. In the present embodiment, six site suitability levels are used. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and a human body may be detected using one site suitability distribution. Or you may divide a site | part into details and may use many parts.
図1は、本実施形態による人体検出システム100の概略構成を示す図である。人体検出システム100は、人体検出装置1及び撮像装置2を有する。
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a schematic configuration of a human
撮像装置2は、所定の撮影領域を撮影するカメラであり、例えば、2次元に配列され、受光した光量に応じた電気信号を出力する光電変換素子(例えば、CCDセンサ、C−MOSなど)と、その光電変換素子上に監視領域の像を結像するための結像光学系を有する。撮像装置2は、人体検出装置1と接続され、撮影した撮影画像を人体検出装置1へ出力する。
The
人体検出装置1は、CPU(Central Processing Unit)、MPU(Micro Processing Unit)、周辺回路、端子、各種メモリなどから構成され、撮像装置2が撮影した撮影画像から、検出対象である人体を検出し、撮影画像から人体を抽出した画像を出力する。人体検出装置1は、画像取得部10、出力部20、記憶部30及び画像処理部40を有する。以下、人体検出装置1の各部について詳細に説明する。
The human body detection device 1 includes a central processing unit (CPU), a micro processing unit (MPU), peripheral circuits, terminals, various memories, and the like, and detects a human body that is a detection target from a captured image captured by the
画像取得部10は、撮像装置2と接続され、撮像装置2から撮影画像を取得し、画像処理部40に出力するインタフェース及びその制御回路である。なお、本実施形態では、画像取得部10は、撮像装置2から撮影画像を取得して画像処理部40へ出力するが、ハードディスク等の媒体から画像を取得して画像処理部40へ出力してもよい。以下では、画像取得部10が取得して画像処理部40へ出力する画像を入力画像と称する。
The
出力部20は、外部装置(不図示)と接続するインタフェース及びその制御回路である。出力部20は、画像処理部40から、入力画像に人体が含まれるか否かの判定結果を含む結果信号を受け取ると、接続されている外部装置が受信可能な形式の信号に変換して出力する。判定結果が入力画像に人体が含まれていることを示す場合、結果信号には、入力画像から抽出された人体を含む画像がさらに含まれる。
なお、結果信号には、入力画像から抽出された人体を含む画像の代りに、入力画像と、入力画像において人体が写っている領域の座標情報及び大きさを示す情報が含まれてもよい。これにより、例えば、出力部20に接続する外部装置を物体追跡装置とすることにより、撮影領域内に存在する人体を追跡しながら監視することができる。
また、出力部20は、一般公衆回線、携帯電話回線などの通信回線を介して各情報を監視センタ装置などの外部装置へ出力してもよい。
The
Note that the result signal may include, instead of the image including the human body extracted from the input image, the input image and information indicating the coordinate information and the size of the region in which the human body is shown in the input image. Accordingly, for example, by using an external device connected to the
The
記憶部30は、ROM(Read Only Memory)、RAM(Random Access Memory)等の半導体メモリ、あるいは磁気記録媒体及びそのアクセス装置若しくは光記録媒体及びそのアクセス装置などを有する。記憶部30は、人体検出装置1を制御するためのコンピュータプログラム及び各種データを記憶し、画像処理部40との間でこれらの情報を入出力する。各種データは、部位窓設定情報31、部位学習データ32、及び分布学習データ33を少なくとも含んでいる。
部位学習データ32は、部位の識別に有用な一つ以上の特徴量である部位特徴量を算出するための情報、部位特徴量についての特徴量空間において部位が写っている画像について算出された部位特徴量が分布する空間とそれ以外の空間とを分ける識別境界、部位特徴量が識別境界のどちら側に位置するかと、部位特徴量と識別境界の間の距離とを求めるための情報等を含む。部位学習データ32は、部位が写っている複数の学習用部位画像及び部位が写っていない複数の学習用非部位画像から事前学習により決定される。部位学習データ32は、後述する特徴量算出手段43及び部位適合度算出手段44において部位適合度を算出する際に用いられる。
分布学習データ33は、後述する部位適合度分布についての特徴量空間において、人体が写っている画像について算出された部位適合度分布が分布する空間とそれ以外の空間とを分ける識別境界、部位適合度分布が識別境界のどちら側に位置するかと、部位適合度分布と識別境界の間の距離とを求めるための情報等である。分布学習データ33は、複数の学習用人体画像から生成された部位適合度分布と、複数の学習用非人体画像から生成された部位適合度分布から事前学習により決定される。分布学習データ33は、後述する人体分布識別器46及び人体検出手段47において入力画像に人体が含まれるか否かを判定する際に用いられる。
なお、部位窓設定情報31については、後述する。
The
The
The
The part
画像処理部40は、メモリ、その周辺回路及びそのマイクロプロセッサなどのいわゆるコンピュータにより構成され、画像取得部10から取得した入力画像に対して記憶部30を参照しながら人体を検出し、結果信号を出力部20に出力する。画像処理部40は、検出窓設定手段41、部位窓設定手段42、特徴量算出手段43、部位適合度算出手段44、部位適合度分布生成手段45、人体分布識別器46及び人体検出手段47を有する。画像処理部40の各手段は、マイクロプロセッサ上で動作するソフトウェアにより実現される機能モジュールである。なお、画像処理部40の各手段は、独立した集積回路、ファームウェア、マイクロプロセッサなどで構成されてもよい。
以下、画像処理部40の各手段について詳細に説明する。
The
Hereinafter, each unit of the
検出窓設定手段41は、撮像装置2の解像度や設置条件、人体の標準的な身長(例えば170cm)から想定される、入力画像中での検出したい人体の大きさを考慮したサイズの検出窓を、入力画像の全体を順次走査するように設定する。以下、検出窓設定手段41が入力画像中の各走査位置にて設定した検出窓内の画像を検出対象画像と称する。
The detection window setting means 41 is a detection window having a size in consideration of the size of the human body to be detected in the input image, which is assumed from the resolution and installation conditions of the
検出窓設定手段41は、検出対象画像のサイズを正規化してスケールを合わせた検出対象画像を生成する。本実施の形態では、横60画素、縦120画素に正規化している。そして、後述するように部位窓設定手段42は、部位窓設定情報31に基づいて、人体の頭部、右肩、左肩、胴体、右脚、左脚の各部位ごとに所定位置、所定サイズの部位窓を検出対象画像に順次設定し、部位窓画像を出力する。
The detection
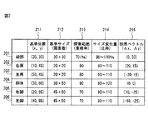
ここで、部位窓設定情報31について、図2を参照して説明する。部位窓設定情報31には、検出対象画像における人体の頭部201、右肩202、左肩203、胴体204、右脚205、左脚206の各部位を検出するための情報として、基準位置211、基準サイズ212、探索範囲213、サイズ変化量214および投票ベクトル215が含まれる。なお、図2に記載の値は、検出対象画像のサイズを横60画素、縦120画素に正規化したときの部位窓設定情報31を例示したものである。
Here, the part
基準位置211は、経験的に定めた各部位の重心位置を部位窓の重心位置とし、検出対象画像の左上を原点(0、0)として表した座標値である。図2に示す通り、頭部(30、30)、右肩(10、45)、左肩(50、45)、胴体(30、60)、右脚(20、85)、左脚(40、85)が記憶されている。なお、本実施の形態では、部位の重心位置を経験的に定めたが、部位学習データ32の事前学習に用いた複数の学習用人物画像における各部位画像の外接矩形の重心の平均位置等を用いても良い。なお、事前学習に用いた人物画像は検出対象画像と同様に正規化してスケールを合わせてある。
The
基準サイズ212は、経験的に定めた各部位の外接矩形を部位窓とし、その縦横の画素数で表している。本実施の形態では、図2に示す通り、頭部30×30、右肩20×20、左肩20×20、胴体30×50、右脚45×50、左脚45×50が記憶されている。なお、本実施の形態では、基準サイズ212を経験的に定めたが、部位学習データ32の事前学習に用いた複数の学習用部位画像における各部位の外接矩形の縦横長の平均等を用いても良い。
The
探索範囲213は、各部位の位置が変動し基準位置から外れる可能性がある範囲であって、その範囲を部位窓にて走査探索するために設定する。具体的には、各部位の基準位置211に基準サイズ212の部位窓を設定した場合に、この部位窓に同じ基準サイズ212の部位窓が重なる割合で表現する。重なりの割合が大きいほど、基準位置211に近い範囲までしか設定されない。重なりの割合が小さいほど、基準位置211から遠い範囲まで設定される。基準位置211から大きく変動し得る部位については小さな値、基準位置211から小さくしか変動し得ない部位については大きな値を設定する。本実施の形態では、図2に示す通り、頭部70%、右肩80%、左肩80%、胴体90%、右脚70%、左脚70%が記憶されている。すなわち、胴体が最も変動が小さく、頭部及び左右脚が最も変動が大きいものとして設定している。これらの値は、実験的かつ経験的に定められる。なお、本実施の形態では、探索範囲213を経験的に定めたが、部位学習データ32の事前学習に用いた複数の学習用部位画像における各部位の外接矩形の基準位置からの外れ量の平均等を用いても良い。
The
サイズ変化量214は、基準サイズ211の部位窓のみでなく、人物によって異なる体型や撮影時によって異なる環境の変動に対応するための部位窓のサイズを変化させる量であって、部位窓を基準サイズ212から拡大または縮小する比率として表している。本実施の形態では、図2に示す通り、頭部90〜110%、右肩90〜110%、左肩90〜110%、胴体80〜120%、右脚90〜110%、左脚90〜110%が記憶されている。なお、部位窓を変化させる刻み幅は、1%ごとに設定される。これらの値は、実験的かつ経験的に定められる。なお、本実施の形態では、サイズ変化量214を経験的に定めたが、部位学習データ32の事前学習に用いた複数の学習用部位画像における各部位の外接矩形のサイズの変化範囲から算出しても良い。また、刻み幅は、計算負荷に応じて設計的に定められる。
The
投票ベクトル215は、各部位窓の基準位置211を始点とし、人体の中心付近に所在する胴体部の重心位置を終点としたベクトルであって、後述する部位適合度分布を生成する際に用いる。
The
ここで、図3を参照して、部位窓設定手段42が検出対象画像に部位窓を設定する様子を説明する。図3は、検出対象画像に理想的な状況にて人体が撮影された場合の検出対象画像と部位窓との位置関係を模式的に示した図である。 Here, with reference to FIG. 3, a state in which the part window setting means 42 sets a part window in the detection target image will be described. FIG. 3 is a diagram schematically showing the positional relationship between the detection target image and the part window when the human body is photographed in an ideal situation for the detection target image.
図3(a)は、基準サイズの部位窓301〜306を基準位置に配置した場合を示している。図3(a)では、各部位窓301〜306の基準位置を黒丸(●)で、投票ベクトルを矢印で示している。学習した結果に合致した人体が撮影されていると、同図に示すように、各部位窓301〜306の投票ベクトルが胴体の重心位置に集中する。
FIG. 3A shows a case where the reference
図3(b)は、頭部を例に、部位窓の探索範囲と投票ベクトルを示している。図3(b)では、部位窓設定情報の探索範囲の外縁を点線311で、各部位窓の重心位置を黒丸(●)で示し、それぞれの投票ベクトルにしたがって投票した投票位置が示されている。同図のように、投票位置は、図2に示す部位窓設定情報の探索範囲に応じて分散している。したがって、人体の姿勢変動や撮影環境の違いなどにより頭部の位置ずれ等が生じても、探索範囲内に頭部が存在すれば、その頭部の示す特徴を捉えることができる。本実施の形態では、右肩、左肩、胴体、右脚、左脚の各部位についても、探索範囲に部位窓を順次設定し、部位適合度を投票して部位適合度分布を作成する。かかる部位適合度分布は、各部位の投票ベクトルの終点を一致させることにより、一部の部位適合度が低い値となっても、各部位を持つ人体全体としての有効な特徴となる。ちなみに、頭部を検出するのが目的であれば、頭部適合度の分布のみを用いれば良い。
FIG. 3B shows a part window search range and a voting vector using the head as an example. In FIG. 3B, the outer edge of the search range of the part window setting information is indicated by a dotted
図3(c)は、図2に示す部位窓設定情報における頭部のサイズ変化量に応じて、位置を基準位置に固定したままで、部位窓のサイズが変化している様子を示している。位置が固定なので、投票位置は胴体の重心位置のまま変化しないが、部位窓のサイズの変化に起因して後述する部位適合度が変化する。これは、撮影された人体固有の頭の大きさや撮影角度等による変動に対応するものである。 FIG. 3C shows a state in which the size of the part window is changed while the position is fixed at the reference position in accordance with the size change amount of the head in the part window setting information shown in FIG. . Since the position is fixed, the voting position remains the same as the position of the center of gravity of the trunk, but the degree of matching of the part described later changes due to the change in the size of the part window. This corresponds to fluctuations due to the size of the head that is photographed and the photographing angle.
部位窓設定手段42は、図3(a)、(b)、(c)に示すように、各部位窓の位置・サイズを変化させつつ、検出対象画像に部位窓を順次設定する。
As shown in FIGS. 3A, 3B, and 3C, the part
特徴量算出手段43は、検出対象画像における、部位窓設定手段42により設定された各部位窓画像から部位特徴量を算出する。本実施形態では、特徴量算出手段43は、部位特徴量としてHOG(Histograms of Oriented Gradients)特徴量を用いる。HOG特徴量は、各部位窓画像において複数のブロックを設定し、さらに各ブロックを分割した複数のセルごとに、各勾配方向の勾配強度の総和を度数としたヒストグラムを正規化して算出される。
The feature
各部位の適合度算出手段は、部位特徴量が入力されると、その部位特徴量が算出された部位窓に各部位が含まれている可能性を表す部位適合度を出力する。すなわち、部位適合度算出手段44は、頭部の適合度を算出する頭部適合度算出手段441、右肩の適合度を算出する右肩適合度算出手段442、左肩の適合度を算出する左肩適合度算出手段443、胴体の適合度を算出する胴体適合度算出手段444、右脚の適合度を算出する右脚適合度算出手段445及び左脚の適合度を算出する左脚適合度算出手段446を有する。 When the part feature amount is inputted, the part degree-of-compatibility calculation means outputs a part suitability degree indicating the possibility that each part is included in the part window in which the part feature amount is calculated. That is, the part suitability calculation means 44 includes a head suitability calculation means 441 that calculates the fit degree of the head, a right shoulder suitability calculation means 442 that calculates the fit degree of the right shoulder, and a left shoulder that calculates the fit degree of the left shoulder. The fitness calculation means 443, the body fitness calculation means 444 for calculating the body fitness, the right leg fitness calculation means 445 for calculating the right leg fitness, and the left leg fitness calculation means for calculating the left leg fitness. 446.
なお、本実施形態では、特徴量算出手段43及び部位適合度算出手段44を、部位学習データ32を用いるリアルアダブースト識別器により実現している。リアルアダブースト識別器の詳細については、例えば、R.E.Schapire and Y.Singer, Improved boosting algorithms using confidence-rated predictions, Machine Learning, 37, pp.297-336, 1999に開示されている。
ここで、特許請求の範囲にて用いている「部位適合度算出部」は、本実施の形態における「部位窓設定手段42」、「特徴量算出手段43」及び「部位適合度算出手段44」にて実現されていることを付言しておく。
In the present embodiment, the feature amount calculation means 43 and the part suitability calculation means 44 are realized by a real Adaboost discriminator using the
Here, the “part conformity degree calculation unit” used in the claims is “part part window setting means 42”, “feature amount calculation means 43” and “part conformity degree calculation means 44” in the present embodiment. It is added that it is realized in.
部位適合度分布生成手段45は、部位窓設定手段42により設定された各部位窓について算出された部位適合度を各部位の投票ベクトルにしたがって投票し、投票値(投票された部位適合度の総和)の分布を部位適合度分布として作成する。 The part suitability distribution generation means 45 votes the part suitability calculated for each part window set by the part window setting means 42 according to the vote vector of each part, and the voting value (the sum of the voted part suitability). ) Is created as a site fitness distribution.
ここで、投票について、図3を参照して説明する。まず、部位適合度分布生成手段45は、図3(b)に示すように、頭部について探索範囲内に設定された各部位窓から算出された部位適合度を図2に示す投票ベクトル215にしたがって投票する。同様に、部位適合度分布生成手段45は、右肩、左肩、胴体、右脚、左脚の各部位についても各部位窓から算出された部位適合度を図2に示す投票ベクトル215にしたがって投票する。
さらに、部位適合度分布生成手段45は、図3(c)に示すように、図2の基準サイズ212を頭部のサイズ変化量214に応じて変化させた各部位窓から算出された部位適合度を投票ベクトル215にしたがって投票する。同様に、部位適合度分布生成手段45は、右肩、左肩、胴体、右脚、左脚の各部位についても図2の基準サイズ212をサイズ変化量214に応じて変化させた各部位窓から算出された部位適合度を投票ベクトルにしたがって投票する。
Here, voting will be described with reference to FIG. First, as shown in FIG. 3 (b), the site suitability distribution generation means 45 sets the site suitability calculated from each site window set in the search range for the head to a
Further, as shown in FIG. 3C, the site suitability
次に、部位適合度を投票した結果である部位適合度分布について、図4を参照して説明する。図4は、人体が写っている検出対象画像又は人体以外の物体が写っている検出対象画像について生成される部位適合度分布を模式的に示した図である。図4には、検出対象画像の水平方向及び垂直方向をそれぞれx軸及びy軸とし、検出対象画像の各画素に対応する位置における投票値をz軸とした部位適合度分布が示される。 Next, the site fitness distribution, which is the result of voting the site suitability, will be described with reference to FIG. FIG. 4 is a diagram schematically showing a site fitness distribution generated for a detection target image showing a human body or a detection target image showing an object other than a human body. FIG. 4 shows a site fitness distribution in which the horizontal direction and the vertical direction of the detection target image are the x-axis and the y-axis, respectively, and the voting value at the position corresponding to each pixel of the detection target image is the z-axis.
図4(a)は、理想的な状況で人体が写っている検出対象画像400から生成された部位適合度分布401を示している。同図に示すように、部位適合度分布401では、胴体の重心位置402において投票値が最も高くなり、胴体の重心位置402から離れるにつれて投票値が低くなる。
FIG. 4A shows a
図4(b)は、頭を傾けている人体が写っている検出対象画像410から生成された部位適合度分布411を示している。同図に示すように、部位適合度分布411では、胴体の重心位置412における投票値は図4(a)の胴体の重心位置402における投票値と比較して低くなり、代わりに、重心位置412からずれた位置413、414における投票値が高くなっている。
FIG. 4B shows a
図4(c)は、人体が写っておらず、代わりにハンガーに掛けられた上着が写っている検出対象画像420から生成された部位適合度分布421を示している。同図に示すように、検出対象画像420には人体の右肩、左肩及び胴体に類似するものが写っているが、頭部、右脚及び左脚に類似するものは写っていないため、部位適合度分布421の投票値のピークは極めて低くなっている。
FIG. 4C shows a
図4(d)は、人体が写っておらず、代わりに木が写っている検出対象画像430から生成された部位適合度分布431を示している。同図に示すように、検出対象画像430に写っている木の枝は人体の頭部、右肩、左肩及び胴体に類似しているため、分布431にはわずかに高くなっている箇所がいくつか存在するが、部位適合度分布431は全体にわたって極めて低くなっている。
FIG. 4D shows a
このように、検出対象画像に人体が写っている場合、人体の姿勢が多少ずれていても、基準位置からずれた位置に部位が写っているため、分布内のどこかで投票値が高くなる。一方、検出対象画像に人体が写っていない場合、人体の全ての部位にそれぞれ類似する物が想定する位置に検出されず、投票値の分布は全体にわたって低くなる。 In this way, when the human body is shown in the detection target image, even if the posture of the human body is slightly deviated, the part is shown at a position deviated from the reference position, so the vote value increases somewhere in the distribution. . On the other hand, when the human body is not shown in the detection target image, objects similar to all parts of the human body are not detected at the assumed positions, and the distribution of vote values becomes low throughout.
部位適合度分布生成手段45は、後述する人体分布識別器46にて処理するために、検出対象画像(60画素×120画素)の各画素に対応する位置における投票値をその位置の順に一列に並べた7200次元ベクトルを部位適合度分布として生成している。
The part fitness
人体分布識別器46は、部位適合度分布が特徴量として入力されると、記憶部30に記憶している分布学習データ33を用いて検出対象画像に人体像が存在するか否かを識別した結果を出力する。人体分布識別器46は、分布学習データ33を用いるサポートベクタマシンを用いて実現している。
The human
ここで、人体分布識別器46における人体像の存否を識別するための原理について、図5を参照して説明する。図5は、7200次元ベクトルの部位適合度分布のうち簡単化のため2次元の特徴量空間を模式的に示した図である。なお実際には7200次元の特徴量空間である。図5では、サポートベクタマシンにて学習した各部位適合度分布を×で示している。グループ501は、人体が写っている学習画像から生成された部位適合度分布のグループであり、グループ502は、人体以外の物体が写っている学習画像から生成された部位適合度分布のグループである。グループ501には、図4(a)の理想的な状況で人体が写っている検出対象画像400から生成された部位適合度分布503と、図4(b)の頭を傾けている人体が写っている検出対象画像410から生成された部位適合度分布504が特徴量空間にプロットされている。グループ502には、図4(c)のハンガーに掛けられた上着が写っている検出対象画像420から生成された部位適合度分布505と、図4(d)の木が撮影された検出対象画像430から生成された部位適合度分布506が特徴量空間にプロットされている。識別境界507は、グループ501とグループ502とを分けるように学習により定められ、分布学習データ33として記憶されている。人体分布識別器46は、入力された検出対象画像の部位適合度分布が識別境界507のどちら側に位置するかにより、人体像を含むか否かを識別する。
Here, the principle for identifying the presence or absence of a human body image in the human
また、人体分布識別器46は、入力された部位適合度分布と識別境界の間の距離に基づいて、部位適合度分布が人体を含む検出対象画像から生成された可能性を表す分布適合度を出力する。分布適合度は、後述するように、人体が含まれると判定された検出対象画像が複数ある場合に、人体検出手段47において、出力する人体画像を決定する際に用いられる。
このように、部位適合度分布は、複数の部位についての部位適合度を7200次元の特徴量空間に投票した結果なので、7200の特徴を加味した人体識別が可能となる。
Further, the human
As described above, the site suitability distribution is a result of voting the site suitability for a plurality of sites to a 7200-dimensional feature amount space, so that human body identification can be made taking into account the 7200 features.
人体検出手段47は、人体分布識別器46にて検出対象画像に人体が含まれると判定した場合、その検出対象画像の入力画像における位置及び大きさと、分布適合度とを関連付けて記憶部30に記憶する。
When it is determined by the human
なお、人体検出手段47は、人体が含まれると判定した所定数(例えば2)以上の検出対象画像が相互に所定サイズ(例えば50%)以上重なっている場合に限り、その検出対象画像に人体が含まれると判定してもよい。入力画像に人体が含まれる場合、複数の検出対象画像において人体が含まれると判定される可能性が高いため、これにより、検出精度を向上させることが可能となる。 Note that the human body detection means 47 only detects a human body on the detection target image when a predetermined number (for example, 2) or more of the detection target images determined to include a human body overlap each other by a predetermined size (for example, 50%). May be determined to be included. When a human body is included in the input image, there is a high possibility that it is determined that a human body is included in a plurality of detection target images. Thus, detection accuracy can be improved.
また、人体検出手段47は、人体が含まれると判定した検出対象画像が複数ある場合、記憶部30から各検出対象画像の位置及び大きさを読み出し、各検出対象画像が相互に所定サイズ以上重なっているか否かを判定する。人体検出手段47は、各検出対象画像が相互に所定サイズ以上重なっている場合、各検出対象画像には同一の人体が含まれると判定する。
その場合、人体検出手段47は、記憶部30から各検出対象画像に関連付けて記憶された分布適合度を読み出し、各検出対象画像の中で分布適合度が最も大きい検出対象画像を出力する人体画像に決定する。
なお、部位適合度分布生成手段45が、各検出対象画像について算出された部位適合度の総和をその検出対象画像と関連付けて記憶部30に記憶しておく。そして、人体検出手段47は、記憶部30から各検出対象画像に関連付けて記憶された部位適合度の総和を読み出し、各検出対象画像の中で部位適合度の総和が最も大きい検出対象画像を出力する人体画像に決定してもよい。
または、人体検出手段47は、Mean Shift法を用いて、出力する検出対象画像を決定してもよい。その場合、人体検出手段47は、入力画像における水平方向をX軸とし、垂直方向をY軸とし、検出対象画像の大きさをZ軸とする三次元空間を設定する。人体検出手段47は、三次元空間内の、各検出対象画像の中心位置及び大きさに対応する点をプロットする。そして、人体検出手段47は、プロットした点の密度が極大となる点をMean Shift法により探索し、極大となる点に対応する検出対象画像を出力する人体画像に決定する。
In addition, when there are a plurality of detection target images determined to include a human body, the human body detection unit 47 reads the position and size of each detection target image from the
In that case, the human body detection unit 47 reads out the distribution fitness stored in association with each detection target image from the
The part suitability
Or the human body detection means 47 may determine the detection target image to output using the Mean Shift method. In this case, the human body detection unit 47 sets a three-dimensional space in which the horizontal direction in the input image is the X axis, the vertical direction is the Y axis, and the size of the detection target image is the Z axis. The human body detection unit 47 plots points corresponding to the center position and size of each detection target image in the three-dimensional space. Then, the human body detection means 47 searches for a point at which the density of the plotted points becomes maximum by means of the Mean Shift method, and determines a human body image to output a detection target image corresponding to the maximum point.
人体検出手段47は、人体が含まれると判定した検出対象画像が一つ以上あるか否かにより、入力画像に人体が含まれるか否かを判定し、その判定結果と、人体が含まれると判定した検出対象画像が一つ以上ある場合には人体画像に関する情報とを含む結果信号を出力部20に送る。
The human body detection means 47 determines whether or not a human body is included in the input image depending on whether or not there are one or more detection target images determined to include the human body, and the determination result and the human body are included. When there are one or more determined detection target images, a result signal including information on the human body image is sent to the
以下、図6を参照して、人体検出装置1の全体の動作フローを説明する。
ステップS101では、人体検出装置1の画像取得部10が、撮像装置2にて撮影した画像を入力画像として取得し、画像処理部40に出力する。
ステップS102では、画像取得部10から取得した入力画像に対して、検出窓設定手段41が検出窓を設定し、入力画像中の検出窓内画像を検出対象画像として取得し、部位窓設定手段42に出力する。なお、検出窓の設定は、後述するステップS109にて入力画像全体を順次走査し終わるまで実行される。
Hereinafter, the overall operation flow of the human body detection device 1 will be described with reference to FIG.
In step S <b> 101, the
In step S102, the detection
ステップS103〜ステップS105の処理は、記憶部30に記憶された部位窓設定情報31および部位学習データ32を参照して処理する。
ステップS103では、検出対象画像に対して、部位窓設定手段42が部位窓を設定し、その部位窓画像を特徴量算出手段43に出力する。具体的には、先ず、頭部201について、基準サイズ212の「30×30」の矩形窓の重心位置が基準位置211の「(30,30)」になる位置へ部位窓を設定し、検出対象画像中の設定した部位窓内の部位窓画像を特徴量算出手段に出力する。
The processes in steps S103 to S105 are performed with reference to the part
In step S <b> 103, the part
ステップS104では、先ず部位窓画像について特徴量算出手段43がHOG特徴である部位特徴量を算出する。そして、部位適合度算出手段がこの部位特徴量と、記憶部30に記憶している部位学習データを参照し、部位適合度を算出して部位適合度分布生成手段45に出力する。ここでは、頭部201の場合であるので、頭部について学習した部位学習データを用いて、部位特徴量との適合している程度を頭部適合度算出手段441が算出する。なお、頭部でなく、右肩であれば右肩適合度算出手段442、左肩であれば左肩適合度算出手段443、胴体であれば胴体適合度算出手段444、右脚であれば右脚適合度算出手段445、左脚であれば左脚適合度算出手段446がそれぞれ選択されて部位適合度を算出する。
In step S104, first, the feature
ステップS105では、部位適合度分布生成手段45が投票ベクトル215を参照し、部位適合度を投票する。ここでは頭部201の場合であるので(0,30)に部位適合度を投票する。部位適合度分布生成手段45は、投票された部位適合度をその位置の投票値に順次加算する。その後、図2に示す頭部201、右肩202、左肩203、胴体204、右脚205、左脚206の順に投票が全て行われていなければ、ステップS103に戻り次の部位窓を設定する。他方、全ての部位窓に対する処理が終了していれば、部位適合度分布を人体分布識別器46に出力し、ステップS106に進む。
ステップS106では、部位適合度分布を特徴量として記憶部30に記憶している分布学習データ33を用いて、人体分布識別器46にて分布適合度を算出するとともに人体の存否を判定する。そして、人体が存在しているとの判定であれば(S107−Yes)、処理した検出窓の位置、サイズおよび分布適合度を一時記憶する。他方、人体が存在していないとの判定であれば(S107−No)、そのまま、ステップS109に進み、入力画像全体に検出窓を設定したか判定する。検出窓の設定が終了していなければ(S109−No)、ステップS102に戻り、同様の処理を実行する。他方検出窓の設定が終了していれば(S109−Yes)、ステップS110の処理に進む。
ステップS110では、人体検出手段47がステップS108にて一時記憶している検出窓が存在するか否かにより、入力画像に人体が存在しているか否か判定する。
人体検出手段47は、入力画像に人体が含まれると判定した場合(ステップS111−Yes)、人体が含まれる検出対象画像を出力する人体画像に特定する(ステップS112)。一方、人体検出手段47は、入力画像に人体が含まれないと判定した場合(ステップS111−No)、出力する人体画像を特定する処理は行わず、処理をステップS113へ移行する。次に、人体検出手段47は、結果信号および入力画像に人体が含まれると判定した場合には人体画像を出力部20に送り(ステップS113)、一連のステップを終了し、次の入力画像を取得する。
In step S105, the site suitability
In step S106, using the
In step S110, it is determined whether or not a human body exists in the input image based on whether or not the detection window temporarily stored in step S108 by the human body detection unit 47 exists.
When it is determined that the human body is included in the input image (step S111-Yes), the human body detection unit 47 identifies the human body image to be output as the detection target image including the human body (step S112). On the other hand, if the human body detection unit 47 determines that the human body is not included in the input image (No in step S111), the process of specifying the human body image to be output is not performed, and the process proceeds to step S113. Next, when it is determined that the human body is included in the result signal and the input image, the human body detection unit 47 sends the human body image to the output unit 20 (step S113), ends a series of steps, and then displays the next input image. get.
なお、例えば、入力画像に人体がちょうど収まるように撮像装置2が設置されるような場合、画像処理部40は、入力画像中に検出窓を設定する必要がないため、入力画像を検出対象画像として用いてもよい。その場合、画像処理部40から検出窓設定手段41が省略され、図5のフローチャートにおいて、ステップS102及びS109の処理が省略される。
For example, when the
以上、本発明の好適な実施形態について説明してきたが、本発明はこれらの実施形態に限定されるものではない。例えば、本実施形態では、人体検出装置が複数の部位についての部位適合度の分布を用いて人体を検出する例について説明したが、一つの部位についての部位適合度の分布を用いて人体を検出してもよい。一つの部位についての部位適合度の分布を用いて人体を検出する場合、検出対象画像内にその部位が写っていないと人体を検出することができないが、検出対象画像内にその部位が写っていれば人体を検出することができる。 The preferred embodiments of the present invention have been described above, but the present invention is not limited to these embodiments. For example, in the present embodiment, an example has been described in which the human body detection device detects a human body using a distribution of part suitability for a plurality of parts. However, a human body is detected using a distribution of part suitability for one part. May be. When a human body is detected using the distribution of part suitability for one part, the human body cannot be detected unless the part is shown in the detection target image, but the part is shown in the detection target image. If so, the human body can be detected.
また、部位適合度分布生成手段は、複数の部位について一つの部位適合度分布を生成するのではなく、各部位ごとに別個に部位適合度分布を生成してもよい。その場合、画像処理部は、各部位ごとに対応する分布識別器を有し、人体検出手段は、各部位ごとに、その部位についての部位適合度分布を対応する分布識別器に入力したときに出力される識別情報により検出対象画像に人体が含まれるか否かを判定する。人体検出手段は、例えば、出力される識別情報の総和が判定閾値以上であるか否かにより検出対象画像に人体が含まれるか否かを判定する。この場合、人体検出装置は、部位ごとの分布識別器をそれぞれ事前学習しておく必要があるが、各部位について、他の部位が写っていない場合でもその影響を受けずに部位適合度分布を生成することができ、一方、その部位が写っていない場合でも他の部位についての識別情報から人体を検出することができる。 Further, the site fitness distribution generation unit may generate a site fitness distribution separately for each site instead of generating one site fitness distribution for a plurality of sites. In that case, the image processing unit has a distribution discriminator corresponding to each part, and the human body detecting means inputs the part suitability distribution for the part for each part to the corresponding distribution discriminator. It is determined whether or not a human body is included in the detection target image based on the output identification information. For example, the human body detection means determines whether or not a human body is included in the detection target image based on whether or not the sum of the output identification information is equal to or greater than a determination threshold. In this case, the human body detection device needs to learn the distribution classifier for each part in advance, but for each part, even if no other part is shown, the part fitness distribution is not affected by the influence. On the other hand, even when the part is not shown, the human body can be detected from the identification information about the other part.
また、本実施形態では、部位窓設定手段がサイズの異なる部位窓を設定する例について説明したが、基準サイズの部位窓のみを設定してもよい。その場合、人体固有の部位の大きさ、撮影角度等による変動に対応できない可能性があるが、理想的な環境における標準的な人体については検出することができる。 In the present embodiment, the example in which the part window setting unit sets the part windows having different sizes has been described. However, only the part window having the reference size may be set. In that case, it may not be possible to cope with fluctuations due to the size of the part specific to the human body, the imaging angle, etc., but a standard human body in an ideal environment can be detected.
また、本実施形態では、識別器により部位適合度を算出する例について説明したが、パターンマッチングにより部位適合度を算出してもよい。その場合、部位が写っている複数の画像に平均化処理等を実施した画像のパターンを予め生成して記憶部に記憶しておく。部位適合度算出手段は、各部位窓と、記憶部に記憶しておいた画像のパターンの類似の程度を求め、求めた類似の程度を部位適合度とする。類似の程度は、例えば、部位窓と、画像のパターンを部位窓と同じサイズに拡大/縮小した画像との正規化相互相関値とすることができる。 Further, in the present embodiment, the example in which the part suitability is calculated by the classifier has been described, but the part suitability may be calculated by pattern matching. In that case, a pattern of an image in which an averaging process or the like is performed on a plurality of images showing a part is generated in advance and stored in the storage unit. The part suitability calculating means obtains the degree of similarity between each part window and the image pattern stored in the storage unit, and uses the obtained degree of similarity as the part suitability. The degree of similarity can be, for example, a normalized cross-correlation value between a part window and an image obtained by enlarging / reducing an image pattern to the same size as the part window.
図7は、グループ毎に部位適合度分布を生成する処理を説明するための模式図である。
図7(a)〜(d)には、同一の検出対象画像700が示されているものとする。部位窓設定手段により設定された各部位窓は、その中心位置が、検出対象画像700の右上領域702、左上領域712、右下領域722、左下領域732のうちの何れに存在するかにより、4つのグループに分類される。部位適合度分布生成手段は、分類したグループごとに、そのグループに含まれる部位窓から算出された部位適合度から部位適合度分布701、711、721、731をそれぞれ生成する。一方、画像処理部は、分類したグループごとに対応する分布識別器を有し、人体検出手段は、各グループごとの分布識別器から出力された識別情報により検出対象画像に人体が含まれるか否かを判定する。人体検出手段は、例えば、出力される識別情報の総和が判定閾値以上であるか否かにより検出対象画像に人体が含まれるか否かを判定する。この場合、人体検出装置は、他のグループの影響を受けずに、部位適合度分布を生成することができるので、一部のグループにて適切に部位適合度分布を生成できなかったとしても、精度良く人体を検出することができる。
さらに、この場合、部位窓の設定を探索範囲に限定せず、検出対象画像全体に設定しても、人体を精度良く検出することができる。
FIG. 7 is a schematic diagram for explaining processing for generating a site suitability distribution for each group.
7A to 7D show the same
Further, in this case, the human body can be detected with high accuracy even if the setting of the part window is not limited to the search range and is set for the entire detection target image.
また、部位適合度算出手段は、検出窓ごとに個別に部位適合度を算出するのではなく、入力画像内に設定された全ての部位窓に対して部位適合度を算出し、算出した部位適合度を記憶部に記憶しておいてもよい。その場合、部位適合度算出手段は、図6のステップS104において、記憶部から対応する部位適合度を読み出すことにより部位適合度を取得する。これにより、各検出窓において重複する部位窓について重複して部位適合度を算出することがなくなり、処理負荷を低減することが可能となる。 Also, the site suitability calculation means does not calculate the site suitability for each detection window, but calculates the site suitability for all the site windows set in the input image, and calculates the calculated site suitability. The degree may be stored in the storage unit. In that case, the part suitability calculation means acquires the part suitability by reading the corresponding part suitability from the storage unit in step S104 of FIG. As a result, it is not necessary to calculate the part suitability for overlapping part windows in each detection window, and the processing load can be reduced.
以上のように、当業者は、本発明の範囲内で、実施される形態に合わせて様々な変更を行うことができる。 As described above, those skilled in the art can make various modifications in accordance with the embodiment to be implemented within the scope of the present invention.
1 人体検出装置
2 撮像装置
10 画像取得部
20 出力部
30 記憶部
40 画像処理部
41 検出窓設定手段
42 部位窓設定手段
43 特徴量算出手段
44 部位適合度算出手段
45 部位適合度分布生成手段
46 人体分布識別器
47 人体検出手段
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1 Human
Claims (5)
前記部位毎に、前記検出対象画像に設定される部位窓の位置と投票位置との位置関係を記憶する記憶部と、
前記部位毎に前記検出対象画像における複数の位置に所定サイズの前記部位窓を設定し、当該部位窓内に対して前記部位特徴に適合する程度である部位適合度を算出する部位適合度算出部と、
前記部位毎に設定された各部位窓に対する部位適合度を、当該部位の前記位置関係に応じた投票位置に投票し、各投票位置に投票された前記部位適合度の総和値の分布を生成する分布生成部と、
前記各投票位置における前記総和値を要素とする特徴量を用いて前記対象物体の存否を識別する分布識別部と、
を少なくとも含むことを特徴とした物体検出装置。 An object detection device for identifying whether or not a target object image exists in a detection target image using a part feature that is an image feature of one or more parts constituting the target object,
A storage unit that stores the positional relationship between the position of the part window set in the detection target image and the voting position for each part;
Setting the site window of a predetermined size into a plurality of positions in the detection target image for each of the sites, site fitness calculating unit for calculating a site fit is approximately conforms to the characteristic portions relative to the portion within the window When,
The part suitability for each part window set for each part is voted to a voting position corresponding to the positional relationship of the part, and a distribution of the total value of the part suitability voted for each voting position is generated. A distribution generator;
A distribution identifying unit that identifies the presence / absence of the target object using a feature amount having the total value at each voting position as an element ;
An object detection apparatus characterized by including at least.
前記投票位置は、前記各部位窓の前記基準位置に対して同一位置に位置するように設定される、請求項1〜請求項3の何れか1項に記載の物体検出装置。 The storage unit stores a reference position of each part window for each of the one or a plurality of parts and, as the positional relationship, a voting vector from the position of the part window set in the detection target image to the voting position. Remember,
4. The object detection device according to claim 1 , wherein the voting position is set to be located at the same position with respect to the reference position of each part window . 5.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013248523A JP6296769B2 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2013-11-29 | Object detection device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013248523A JP6296769B2 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2013-11-29 | Object detection device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2015106307A JP2015106307A (en) | 2015-06-08 |
| JP2015106307A5 JP2015106307A5 (en) | 2016-09-23 |
| JP6296769B2 true JP6296769B2 (en) | 2018-03-20 |
Family
ID=53436359
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013248523A Active JP6296769B2 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2013-11-29 | Object detection device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6296769B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2021204189A1 (en) * | 2020-04-08 | 2021-10-14 | 华为技术有限公司 | Driveability adjustment method and device |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6656987B2 (en) | 2016-03-30 | 2020-03-04 | 株式会社エクォス・リサーチ | Image recognition device, mobile device, and image recognition program |
| CN109461495B (en) | 2018-11-01 | 2023-04-14 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Medical image recognition method, model training method and server |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5787642B2 (en) * | 2011-06-28 | 2015-09-30 | キヤノン株式会社 | Object holding device, method for controlling object holding device, and program |
-
2013
- 2013-11-29 JP JP2013248523A patent/JP6296769B2/en active Active
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2021204189A1 (en) * | 2020-04-08 | 2021-10-14 | 华为技术有限公司 | Driveability adjustment method and device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2015106307A (en) | 2015-06-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7130368B2 (en) | Information processing device and information processing system | |
| CN102375974B (en) | Information processing apparatus and information processing method | |
| US6961466B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for object recognition | |
| JP4479478B2 (en) | Pattern recognition method and apparatus | |
| US20100296706A1 (en) | Image recognition apparatus for identifying facial expression or individual, and method for the same | |
| US9245206B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus and image processing method | |
| CN110348270B (en) | Image object identification method and image object identification system | |
| US8995714B2 (en) | Information creation device for estimating object position and information creation method and program for estimating object position | |
| JP6071002B2 (en) | Reliability acquisition device, reliability acquisition method, and reliability acquisition program | |
| JP5290227B2 (en) | Object detection device and learning device thereof | |
| CN113508420A (en) | Object tracking device and object tracking method | |
| JP6095817B1 (en) | Object detection device | |
| CN111191644B (en) | Identity recognition method, system and device | |
| JP5279517B2 (en) | Object detection apparatus and object detection method | |
| JP2011113313A (en) | Attitude estimation device | |
| JPWO2014010203A1 (en) | Fall detection device, fall detection method, fall detection camera, and computer program | |
| JP6296769B2 (en) | Object detection device | |
| JP2018120283A (en) | Information processing device, information processing method and program | |
| JP7255173B2 (en) | Human detection device and human detection method | |
| JP7188067B2 (en) | Human detection device and human detection method | |
| CN113646803A (en) | Human detection device and human detection method | |
| JP2021071769A (en) | Object tracking device and object tracking method | |
| JP2012068948A (en) | Face attribute estimating apparatus and method therefor | |
| JP6253397B2 (en) | Object detection device | |
| JP5791361B2 (en) | PATTERN IDENTIFICATION DEVICE, PATTERN IDENTIFICATION METHOD, AND PROGRAM |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20160803 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20160803 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20170703 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20170718 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20170908 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20180123 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20180220 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6296769 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |