JP6237318B2 - 管理装置、業務負荷分散管理方法および業務負荷分散管理プログラム - Google Patents
管理装置、業務負荷分散管理方法および業務負荷分散管理プログラム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6237318B2 JP6237318B2 JP2014029801A JP2014029801A JP6237318B2 JP 6237318 B2 JP6237318 B2 JP 6237318B2 JP 2014029801 A JP2014029801 A JP 2014029801A JP 2014029801 A JP2014029801 A JP 2014029801A JP 6237318 B2 JP6237318 B2 JP 6237318B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- virtual machine
- load
- private
- virtual
- cloud
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/44—Arrangements for executing specific programs
- G06F9/455—Emulation; Interpretation; Software simulation, e.g. virtualisation or emulation of application or operating system execution engines
- G06F9/45533—Hypervisors; Virtual machine monitors
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/46—Multiprogramming arrangements
- G06F9/50—Allocation of resources, e.g. of the central processing unit [CPU]
- G06F9/5005—Allocation of resources, e.g. of the central processing unit [CPU] to service a request
- G06F9/5027—Allocation of resources, e.g. of the central processing unit [CPU] to service a request the resource being a machine, e.g. CPUs, Servers, Terminals
- G06F9/505—Allocation of resources, e.g. of the central processing unit [CPU] to service a request the resource being a machine, e.g. CPUs, Servers, Terminals considering the load
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/46—Multiprogramming arrangements
- G06F9/50—Allocation of resources, e.g. of the central processing unit [CPU]
- G06F9/5061—Partitioning or combining of resources
- G06F9/5077—Logical partitioning of resources; Management or configuration of virtualized resources
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/46—Multiprogramming arrangements
- G06F9/50—Allocation of resources, e.g. of the central processing unit [CPU]
- G06F9/5083—Techniques for rebalancing the load in a distributed system
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/46—Multiprogramming arrangements
- G06F9/50—Allocation of resources, e.g. of the central processing unit [CPU]
- G06F9/5083—Techniques for rebalancing the load in a distributed system
- G06F9/5088—Techniques for rebalancing the load in a distributed system involving task migration
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/44—Arrangements for executing specific programs
- G06F9/455—Emulation; Interpretation; Software simulation, e.g. virtualisation or emulation of application or operating system execution engines
- G06F9/45533—Hypervisors; Virtual machine monitors
- G06F9/45558—Hypervisor-specific management and integration aspects
- G06F2009/45583—Memory management, e.g. access or allocation
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer And Data Communications (AREA)
- Debugging And Monitoring (AREA)
Description
[第1の実施の形態]
図1は、第1の実施の形態の管理装置の例を示す図である。
図2は、第2の実施の形態の情報処理システムを示す図である。
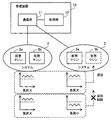
第2の実施の形態の情報処理システムは、企業が所有するプライベートクラウド4のシステムとサービス提供者が所有するパブリッククラウド5のシステムとを含み、ハイブリッドクラウドを実現する。企業内のユーザのネットワーク21には、クライアント33,34が属する。プライベートクラウド4のネットワーク22には、プライベート管理サーバ31、業務サーバ35,36および管理サーバ100が属する。パブリッククラウド5のネットワーク23には、パブリック管理サーバ32および業務サーバ37,38が属する。ネットワーク21はネットワーク22と接続され、ネットワーク22はインターネットなどの広域ネットワークを介してネットワーク23と接続されている。
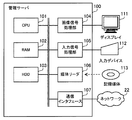
管理サーバ100は、CPU101、RAM102、HDD103、画像信号処理部104、入力信号処理部105、媒体リーダ106および通信インタフェース107を有する。CPU101は、第1の実施の形態の制御部12の一例である。通信インタフェース107は、第1の実施の形態の通信部11の一例である。
第2の実施の形態では、1つの業務として、3階層アーキテクチャのWebシステムを用いたWebサービスの提供を考える。3階層アーキテクチャのWebシステムは、サーバアプリケーションとして、Webサーバとアプリケーションサーバ(APサーバ)とデータベースサーバ(DBサーバ)とを含む。Webサーバは、クライアントコンピュータが送信したHTTP(Hypertext Transfer Protocol)リクエストを受信し、HTTPリクエストに対するHTTPレスポンスを返信する。APサーバは、Webサーバが受信したHTTPリクエストに応じた業務ロジックを実行し、業務ロジックの実行結果をWebサーバに提供する。DBサーバは、APサーバの業務ロジックにおいて使用され得るデータを管理し、APサーバからの要求に応じてデータの検索や更新を行う。
図5は、サーバアプリケーションの起動・停止の例を示す第1の図である。
ここでは、ロードバランサ50、Webサーバ51aおよびAPサーバ51bがプライベートクラウド4で実行されているとする。また、このWebサービスの業務に関して、プライベートクラウド4に配置されている仮想マシンの数は上限に達していないとする。
管理サーバ100は、Webサーバ51a,52aおよびAPサーバ51b,52bの実行に用いる仮想マシンの負荷が依然として高いことを検出する。例えば、管理サーバ100は、4つの仮想マシンのCPU使用率の平均が閾値以上であることを検出する。ここでは、このWebサービスの業務に関して、プライベートクラウド4に配置されている仮想マシンの数が上限に達しているとする。すると、管理サーバ100は、パブリック管理サーバ32に仮想マシンの配置を指示する。パブリック管理サーバ32は、パブリッククラウド5に、Webサーバ53aを実行する仮想マシンとAPサーバ53bを実行する仮想マシンとを起動させる。また、管理サーバ100は、Webサーバ53aにもHTTPリクエストが振り分けられるようにロードバランサ50を設定する。
管理サーバ100は、このWebサービスの業務に対して依然としてリソースが不足している(仮想マシンが不足している)と判断したとする。すると、管理サーバ100は、パブリック管理サーバ32に仮想マシンの追加を指示する。パブリック管理サーバ32は、パブリッククラウド5に、Webサーバ54aを実行する仮想マシンとAPサーバ54bを実行する仮想マシンとを起動させる。また、管理サーバ100は、Webサーバ54aにもHTTPリクエストが振り分けられるようにロードバランサ50を設定する。
ここでは、プライベートクラウド4のシステムはCPU61〜64(CPU#1〜#4)を備え、パブリッククラウド5のシステムはCPU65,66(CPU#11,#12)を含む多数のCPUを備えているとする。説明を簡単にするため、全てのCPUの演算速度は同じであるとし、1つのCPUの処理時間100%を100リソースと定義する。CPU61の100リソースは、業務Aに用いる1つの仮想マシンに割り当てられている。CPU63の50リソースとCPU64の50リソースは業務Bに割り当てられ、CPU63の50リソースとCPU64の50リソースは業務Cに割り当てられている。また、仮想マシンのCPU使用率が60%以上になったとき、当該仮想マシンの負荷が高いと判断するものとする。また、業務Aについてプライベートクラウド4に配置可能な仮想マシンの上限数を2とする。
業務Aに用いる仮想マシンそれぞれのCPU使用率が60%に上昇したとする。このとき、プライベートクラウド4に配置された仮想マシンの数は上限に達している。そこで、例えば、パブリック管理サーバ32は、業務Aに用いる仮想マシンをパブリッククラウド5に配置し、配置した仮想マシンにCPU65の100リソースを割り当てる。これにより、業務Aに用いる3個の仮想マシンそれぞれのCPU使用率が40%に低下する。
プライベートクラウド4に対し、業務Dのユーザおよび業務Eのユーザから仮想マシンの起動が要求されたとする。このとき、プライベートクラウド4のシステムは未割当のCPUリソースをもっていない。そこで、例えば、プライベート管理サーバ31は、複数の業務の間の公平性の観点から、未使用のCPUリソースが多い仮想マシンに対する割当を削減する。ここでは、業務Aの1番目の仮想マシンへの割当をCPU61の60リソースに削減し、2番目の仮想マシンへの割当をCPU62の60リソースに削減する。
管理サーバ100は、Webサーバ51a,52aおよびAPサーバ51b,52bの実行に用いる仮想マシンの負荷が高い一方、Webサーバ53aおよびAPサーバ53bの実行に用いる仮想マシンの負荷が低いことを検出する。例えば、管理サーバ100は、プライベートクラウド4に配置された4つの仮想マシンのCPU使用率の平均が閾値以上であり、かつ、パブリッククラウド5に配置された2つの仮想マシンのCPU使用率の平均が閾値未満であることを検出する。この場合、管理サーバ100は、仮想マシンを増やしてもプライベートクラウド4の負荷が下がらないと判断する。
管理サーバ100は、Webサーバ51aおよびAPサーバ51bの実行に用いる仮想マシンの負荷が高い一方、Webサーバ53a,54aおよびAPサーバ53b,54bの実行に用いる仮想マシンの負荷が低いことを検出する。例えば、管理サーバ100は、プライベートクラウド4に配置された2つの仮想マシンのCPU使用率の平均が閾値以上であり、かつ、パブリッククラウド5に配置された4つの仮想マシンのCPU使用率の平均が閾値未満であることを検出する。この場合、管理サーバ100は、仮想マシンを増やしてもプライベートクラウド4の負荷が下がらないと判断する。
管理サーバ100は、Webサーバ51aおよびAPサーバ51bの実行に用いる仮想マシンの負荷が低くなったことを検出する。例えば、管理サーバ100は、プライベートクラウド4に配置された2つの仮想マシンのCPU使用率の平均が閾値未満に低下したことを検出する。すると、管理サーバ100は、図11の場合と逆に、プライベートクラウド4からパブリッククラウド5へ仮想マシンを移動させる。
ここでは、図10で説明したように、プライベートクラウド4に対し、業務Dのユーザおよび業務Eのユーザから仮想マシンの起動が要求されたとする。そして、業務Aの1番目の仮想マシンへの割当がCPU61の60リソースに削減され、2番目の仮想マシンへの割当がCPU62の60リソースに削減されたとする。
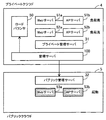
図15は、管理サーバのソフトウェア構成例を示すブロック図である。
管理サーバ100は、パラメータ設定部121、制御情報記憶部122、負荷情報取得部123、配置判定部124、起動・停止指示部125およびロードバランサ設定部126を有する。制御情報記憶部122は、例えば、RAM102またはHDD103に確保した記憶領域として実装できる。パラメータ設定部121、負荷情報取得部123、配置判定部124、起動・停止指示部125およびロードバランサ設定部126は、例えば、CPU101が実行するプログラムのモジュールとして実装できる。
仮想マシン数テーブル131は、業務毎に用意されて制御情報記憶部122に記憶される。図16は、1つの業務に対応する仮想マシン数テーブル131の例を示している。仮想マシン数テーブル131には、5個のパラメータ(private_min,private_limit,private_vms,public_limit,public_vms)のパラメータ名とその値とが対応付けて登録される。
負荷判定テーブル132は、業務毎に用意されて制御情報記憶部122に記憶される。図17は、1つの業務に対応する負荷判定テーブル132の例を示している。負荷判定テーブル132には、2個のパラメータ(private_loadTh,public_loadTh)のパラメータ名とその値とが対応付けて登録される。
仮想マシン配置テーブル133は、業務毎に用意されて制御情報記憶部122に記憶される。図18は、1つの業務に対応する仮想マシン配置テーブル133の例を示している。仮想マシン配置テーブル133は、仮想マシン名および配置ゾーンの項目を含む。
図19は、仮想マシン配置の判断基準の例を示す図である。
ここで、移動中フラグ=YES(=1)は、パブリッククラウド5に仮想マシンを追加することが制限され、プライベートクラウド4からパブリッククラウド5へ移動された仮想マシンがあることを示している。移動中フラグ=NO(=0)は、プライベートクラウド4からパブリッククラウド5へ移動された仮想マシンがないこと(移動した仮想マシンの全てをプライベートクラウド4に戻した場合を含む)を示している。
(2)プライベート負荷が高く、プライベートクラウド4の仮想マシン数が上限であり、移動中フラグ=NOであり、パブリッククラウド5の仮想マシン数がゼロの場合、パブリッククラウド5に仮想マシンが追加される。
(7)プライベート負荷が高く、移動中フラグ=YESであり、パブリック負荷が高い場合、パブリッククラウド5へ仮想マシンが追加される。
(10)プライベート負荷が低く、プライベートクラウド4の仮想マシン数が下限ではなく、移動中フラグ=NOであり、パブリッククラウド5の仮想マシン数がゼロである場合、プライベートクラウド4から仮想マシンを削減する。
仮想マシン配置制御は、例えば、複数の業務それぞれについて定期的に実行される。
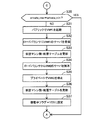
(S10)負荷情報取得部123は、プライベート管理サーバ31からプライベートクラウド4の各仮想マシンの負荷(例えば、CPU使用率)を示す負荷情報を取得する。仮想マシンの負荷は、瞬間的な値でもよいし直近の所定時間の平均値でもよい。負荷情報取得部123は、取得した負荷情報に基づいて、一の業務に用いる複数の仮想マシンの負荷の平均(例えば、平均CPU使用率)をプライベート負荷として算出する。
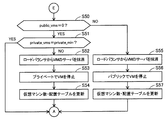
(S20)配置判定部124は、仮想マシン数テーブル131に登録されたパブリッククラウド5の配置数(public_vms)を読み出し、public_vmsがゼロであるか判断する。条件を満たす場合はステップS24に処理が進み、条件を満たさない場合(public_vmsが1以上の場合)はステップS21に処理が進む。
(S30)配置判定部124は、仮想マシン数テーブル131から、プライベートクラウド4の配置数(private_vms)とプライベートクラウド4の下限数(private_min)を読み出す。そして、配置判定部124は、private_vmsがprivate_minと一致するか判断する。条件を満たす場合は仮想マシンの配置に変化なく処理が終了し、条件を満たさない場合はステップS31に処理が進む。
(S40)配置判定部124は、移動中フラグ=YES(または、値「1」)であるか判断する。移動中フラグ=YESの場合はステップS41に処理が進み、移動中フラグ=NOの場合はステップS50に処理が進む。
(S50)配置判定部124は、仮想マシン数テーブル131に登録されたパブリッククラウド5の配置数(public_vms)を読み出し、public_vmsがゼロであるか判断する。条件を満たす場合はステップS51に処理が進み、条件を満たさない場合(public_vmsが1以上の場合)はステップS55に処理が進む。
11 通信部
12 制御部
2,3 システム
2a,2b,3a,3b 仮想マシン
Claims (5)
- 第1のシステムに配置された1または2以上の第1の仮想マシンの負荷を示す情報を取得し、また、第2のシステムに1または2以上の第2の仮想マシンが配置されているとき、前記第2の仮想マシンの負荷を示す情報を取得する通信部と、
前記第1の仮想マシンの負荷が第1の負荷条件を満たす場合、前記第2のシステムに前記第2の仮想マシンを配置して、ある業務の処理を前記第1の仮想マシンと前記第2の仮想マシンとに分散させ、
前記第2の仮想マシンの配置後、前記第1の仮想マシンの負荷が前記第1の負荷条件を満たし、前記第2の仮想マシンの負荷が第2の負荷条件を満たす場合、前記第2のシステムに他の第2の仮想マシンを追加することを許容し、
前記第2の仮想マシンの配置後、前記第1の仮想マシンの負荷が前記第1の負荷条件を満たし、前記第2の仮想マシンの負荷が前記第2の負荷条件を満たさない場合、前記第2のシステムに前記他の第2の仮想マシンを追加することを制限する、制御部と、
を有する管理装置。 - 前記制御部は、前記第1の仮想マシンの負荷が前記第1の負荷条件を満たし、前記第2の仮想マシンの負荷が前記第2の負荷条件を満たさない場合、前記第1の仮想マシンの少なくとも一部を前記第2のシステムに移動させる、請求項1記載の管理装置。
- 前記制御部は、一部の第1の仮想マシンの移動後に、前記第1のシステムに配置された他の一部の第1の仮想マシンの負荷が前記第1の負荷条件を満たさなくなった場合、前記一部の第1の仮想マシンまたは前記第2の仮想マシンの少なくとも一部を前記第1のシステムに移動させる、請求項2記載の管理装置。
- コンピュータが実行する業務負荷分散管理方法であって、
第1のシステムに配置された1または2以上の第1の仮想マシンの負荷が第1の負荷条件を満たす場合、第2のシステムに1または2以上の第2の仮想マシンを配置して、ある業務の処理を前記第1の仮想マシンと前記第2の仮想マシンとに分散させ、
前記第2の仮想マシンの配置後、前記第1の仮想マシンの負荷が前記第1の負荷条件を満たし、前記第2の仮想マシンの負荷が第2の負荷条件を満たす場合、前記第2のシステムに他の第2の仮想マシンを追加することを許容し、
前記第2の仮想マシンの配置後、前記第1の仮想マシンの負荷が前記第1の負荷条件を満たし、前記第2の仮想マシンの負荷が前記第2の負荷条件を満たさない場合、前記第2のシステムに前記他の第2の仮想マシンを追加することを制限する、
業務負荷分散管理方法。 - コンピュータに、
第1のシステムに配置された1または2以上の第1の仮想マシンの負荷が第1の負荷条件を満たす場合、第2のシステムに1または2以上の第2の仮想マシンを配置して、ある業務の処理を前記第1の仮想マシンと前記第2の仮想マシンとに分散させ、
前記第2の仮想マシンの配置後、前記第1の仮想マシンの負荷が前記第1の負荷条件を満たし、前記第2の仮想マシンの負荷が第2の負荷条件を満たす場合、前記第2のシステムに他の第2の仮想マシンを追加することを許容し、
前記第2の仮想マシンの配置後、前記第1の仮想マシンの負荷が前記第1の負荷条件を満たし、前記第2の仮想マシンの負荷が前記第2の負荷条件を満たさない場合、前記第2のシステムに前記他の第2の仮想マシンを追加することを制限する、
処理を実行させる業務負荷分散管理プログラム。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014029801A JP6237318B2 (ja) | 2014-02-19 | 2014-02-19 | 管理装置、業務負荷分散管理方法および業務負荷分散管理プログラム |
| US14/603,841 US9588789B2 (en) | 2014-02-19 | 2015-01-23 | Management apparatus and workload distribution management method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014029801A JP6237318B2 (ja) | 2014-02-19 | 2014-02-19 | 管理装置、業務負荷分散管理方法および業務負荷分散管理プログラム |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2015153402A JP2015153402A (ja) | 2015-08-24 |
| JP6237318B2 true JP6237318B2 (ja) | 2017-11-29 |
Family
ID=53798202
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014029801A Expired - Fee Related JP6237318B2 (ja) | 2014-02-19 | 2014-02-19 | 管理装置、業務負荷分散管理方法および業務負荷分散管理プログラム |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9588789B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6237318B2 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (28)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10291472B2 (en) | 2015-07-29 | 2019-05-14 | AppFormix, Inc. | Assessment of operational states of a computing environment |
| US10581687B2 (en) * | 2013-09-26 | 2020-03-03 | Appformix Inc. | Real-time cloud-infrastructure policy implementation and management |
| JP6097235B2 (ja) * | 2014-02-19 | 2017-03-15 | 西日本電信電話株式会社 | 負荷分散システム、負荷分散装置及び負荷分散方法 |
| EP2988214A1 (en) * | 2014-08-20 | 2016-02-24 | Alcatel Lucent | Method for balancing a load, a system, an elasticity manager and a computer program product |
| US10171313B2 (en) * | 2015-01-23 | 2019-01-01 | International Business Machines Corporation | Managing workload to meet execution criterion in a hybrid cloud environment |
| US10216744B2 (en) * | 2015-05-01 | 2019-02-26 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Data migration to a cloud computing system |
| US10310883B2 (en) * | 2015-07-06 | 2019-06-04 | Purdue Research Foundation | Integrated configuration engine for interference mitigation in cloud computing |
| EP3179699B1 (en) * | 2015-12-11 | 2020-05-27 | Alcatel Lucent | A controller for a cloud based service in a telecommunications network, and a method of providing a cloud based service |
| CN106933673B (zh) * | 2015-12-30 | 2020-11-27 | 阿里巴巴集团控股有限公司 | 调整组件逻辑线程数量的方法及装置 |
| US10432707B2 (en) | 2016-03-02 | 2019-10-01 | International Business Machines Corporation | Optimization of integration flows in cloud environments |
| US10360187B1 (en) * | 2016-03-05 | 2019-07-23 | Virtuozzo International Gmbh | Hybrid storage for virtual machines and containers |
| JP6872117B2 (ja) * | 2017-01-26 | 2021-05-19 | 富士フイルムビジネスイノベーション株式会社 | 情報処理装置及びプログラム |
| US20180260262A1 (en) * | 2017-03-07 | 2018-09-13 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Availability management interfaces in a distributed computing system |
| US10868742B2 (en) | 2017-03-29 | 2020-12-15 | Juniper Networks, Inc. | Multi-cluster dashboard for distributed virtualization infrastructure element monitoring and policy control |
| US11323327B1 (en) | 2017-04-19 | 2022-05-03 | Juniper Networks, Inc. | Virtualization infrastructure element monitoring and policy control in a cloud environment using profiles |
| US10904323B2 (en) * | 2017-06-08 | 2021-01-26 | F5 Networks, Inc. | Methods for server load balancing in a cloud environment using dynamic cloud pricing and devices thereof |
| US10579488B2 (en) * | 2017-07-31 | 2020-03-03 | Vmare, Inc. | Auto-calculation of recovery plans for disaster recovery solutions |
| CN107689925B (zh) | 2017-09-28 | 2020-01-14 | 平安科技(深圳)有限公司 | 基于云监控的负载均衡优化方法及装置 |
| US20190250959A1 (en) * | 2018-02-14 | 2019-08-15 | Red Hat, Inc. | Computing resource balancing among different computing zones |
| EP3561671A1 (en) * | 2018-04-27 | 2019-10-30 | Nokia Solutions and Networks Oy | Allocating workload |
| US10761875B1 (en) * | 2018-12-13 | 2020-09-01 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Large scale compute instance launching |
| CN114090223A (zh) * | 2020-08-24 | 2022-02-25 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | 访存请求调度方法、装置、设备以及存储介质 |
| KR102418251B1 (ko) * | 2020-11-24 | 2022-07-07 | 주식회사 이노그리드 | 장애 대비를 위한 멀티클라우드 서비스 시스템 및 방법 |
| KR102418250B1 (ko) * | 2020-11-24 | 2022-07-07 | 주식회사 이노그리드 | 효율적인 자원 활용을 위한 멀티클라우드 서비스 시스템 및 방법 |
| US12197957B2 (en) | 2021-05-11 | 2025-01-14 | Jpmorgan Chase Bank, N.A. | Method and system for hosting platform in public cloud computing environment |
| JP2023009934A (ja) * | 2021-07-08 | 2023-01-20 | 富士通株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及び情報処理プログラム |
| US12273409B2 (en) * | 2022-05-04 | 2025-04-08 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Method and system of managing resources in a cloud computing environment |
| US11971791B2 (en) * | 2022-08-12 | 2024-04-30 | Capital One Services, Llc | Automated regional failover |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20110078303A1 (en) * | 2009-09-30 | 2011-03-31 | Alcatel-Lucent Usa Inc. | Dynamic load balancing and scaling of allocated cloud resources in an enterprise network |
| US8631403B2 (en) * | 2010-01-04 | 2014-01-14 | Vmware, Inc. | Method and system for managing tasks by dynamically scaling centralized virtual center in virtual infrastructure |
| US20120173709A1 (en) * | 2011-01-05 | 2012-07-05 | Li Li | Seamless scaling of enterprise applications |
| JP5675471B2 (ja) | 2011-04-05 | 2015-02-25 | 株式会社日立製作所 | データセンタシステム管理方法、データセンタシステム、及び管理装置 |
| WO2013158139A1 (en) * | 2012-04-16 | 2013-10-24 | Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. | Virtual computing resource orchestration |
| US9164808B2 (en) * | 2012-07-20 | 2015-10-20 | Verizon Patent And Licensing Inc. | Virtual container for network systems |
| US8978035B2 (en) * | 2012-09-06 | 2015-03-10 | Red Hat, Inc. | Scaling of application resources in a multi-tenant platform-as-a-service environment in a cloud computing system |
| EP2895945B1 (en) * | 2012-09-12 | 2019-11-06 | Greeneden U.S. Holdings II, LLC | System and method for dynamic configuration of contact centers via templates |
| US10642800B2 (en) * | 2013-10-25 | 2020-05-05 | Vmware, Inc. | Multi-tenant distributed computing and database |
-
2014
- 2014-02-19 JP JP2014029801A patent/JP6237318B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2015
- 2015-01-23 US US14/603,841 patent/US9588789B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US9588789B2 (en) | 2017-03-07 |
| US20150234670A1 (en) | 2015-08-20 |
| JP2015153402A (ja) | 2015-08-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6237318B2 (ja) | 管理装置、業務負荷分散管理方法および業務負荷分散管理プログラム | |
| US11106508B2 (en) | Elastic multi-tenant container architecture | |
| JP6199514B2 (ja) | ファブリック分散リソースのスケジューリング | |
| CN103635882B (zh) | 控制网络利用 | |
| US9405572B2 (en) | Optimized resource allocation and management in a virtualized computing environment | |
| JP6102949B2 (ja) | 仮想計算機管理プログラム,仮想計算機管理方法及び仮想計算機システム | |
| US11126467B2 (en) | Proactive load-balancing using retroactive work refusal | |
| US20140245298A1 (en) | Adaptive Task Scheduling of Hadoop in a Virtualized Environment | |
| JP2016103179A (ja) | 計算機リソースの割り当て方法及び計算機システム | |
| JP2015007942A (ja) | プログラム、仮想マシン管理方法および情報処理装置 | |
| WO2012056596A1 (ja) | 計算機システム及び処理制御方法 | |
| US9690608B2 (en) | Method and system for managing hosts that run virtual machines within a cluster | |
| JP2017107274A (ja) | 仮想マシン増設方法、情報処理装置および仮想マシン増設システム | |
| US10320892B2 (en) | Rolling capacity upgrade control | |
| US10802884B2 (en) | Efficient provisioning of an infrastructure based on different factors | |
| US10484262B2 (en) | Dynamic cloning of application infrastructures | |
| US20200036782A1 (en) | Service location management in computing systems | |
| KR20200080458A (ko) | 클라우드 멀티-클러스터 장치 | |
| US20220237024A1 (en) | Diagonal autoscaling of serverless computing processes for reduced downtime | |
| JP2016526723A (ja) | 複数のコンピューティングシステムへのクライアントアクセスの管理 | |
| JP7176633B2 (ja) | 仮想化基盤制御装置、仮想化基盤制御方法および仮想化基盤制御プログラム | |
| JP2009181249A (ja) | 仮想マシンサーバ装置、仮想マシンシステム及びそれらに用いる仮想マシン分散方法並びにそのプログラム | |
| US10587529B1 (en) | Dynamic selection of router groups to manage computing instances | |
| CN103257899A (zh) | 计算机系统 | |
| JP6595952B2 (ja) | リソース割り当てシステム、および、リソース割り当て方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20161102 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20170817 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20171003 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20171016 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6237318 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |