JP6169962B2 - Positioning terminal, mobile phone search system, mobile phone search method, program, and server - Google Patents
Positioning terminal, mobile phone search system, mobile phone search method, program, and server Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6169962B2 JP6169962B2 JP2013257243A JP2013257243A JP6169962B2 JP 6169962 B2 JP6169962 B2 JP 6169962B2 JP 2013257243 A JP2013257243 A JP 2013257243A JP 2013257243 A JP2013257243 A JP 2013257243A JP 6169962 B2 JP6169962 B2 JP 6169962B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- mobile
- terminal
- positioning terminal
- positioning
- mobile phone
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Description
本発明は、携帯電話の位置を特定する測位端末、携帯電話探索システム、携帯電話探索方法、プログラムおよびサーバに関する。 The present invention, measuring position terminal that identifies the location of the mobile phone, cellular phone search system, a mobile phone searching method, a program, and a server.
地震等の災害発生時には、災害が発生したエリア内の被災状況の把握と被災者の救助活動を迅速に行うことが重要である。被災者の早期の救助には、個々の被災者の位置情報を迅速かつ正確に収集することが必要であるが、被災者は倒壊した瓦礫の下や、火災を発生した建物の中にいることが少なくない。 When a disaster such as an earthquake occurs, it is important to quickly grasp the situation of the disaster in the area where the disaster occurred and rescue the victim. Early rescue of victims requires the collection of individual victims' location information quickly and accurately, but the victims must be under collapsed rubble or in a building that has fired. There are many.
近年では携帯電話が広く普及しており、第3世代(3G)以降の携帯電話にはGPS(Global Positioning System)モジュールが標準搭載されている。GPSを用いることで位置情報が全地球で数m〜10mの精度で得られるため、被災者の携帯電話がGPSで取得した位置情報を何らかの手段で収集することにより、捜索に役立てることができる。ただし先に述べたとおり、被災者はGPS衛星の信号が受信できない瓦礫の下や建物の中にいることが少なくなく、そのような場合にはGPSでは被災者の位置を特定できないという問題がある。 In recent years, cellular phones have become widespread, and GPS (Global Positioning System) modules are standardly installed in third-generation (3G) and later cellular phones. By using GPS, position information can be obtained with an accuracy of several meters to 10 meters all over the earth. Therefore, by collecting the position information acquired by the victim's mobile phone using GPS by some means, it can be used for searching. However, as mentioned earlier, victims are often under rubble or buildings where GPS satellite signals cannot be received. In such cases, there is a problem that the location of the victim cannot be determined by GPS. .
このような問題に対しては、GPS衛星の信号が受信可能な屋外にGPSを用いた測位を行う機器を設け、そのような機器がGPSを用いて自己の絶対位置を求め、さらに瓦礫や建物の壁を透過可能な電波を用いて被災者の自己に対する相対位置を求めることで、絶対位置と相対位置から被災者の絶対位置を求めることが考えられる。 For such a problem, a device that performs positioning using GPS is provided outdoors where GPS satellite signals can be received, such a device uses GPS to determine its absolute position, and further, rubble and buildings It is conceivable to obtain the absolute position of the victim from the absolute position and the relative position by obtaining the relative position of the victim with the self using radio waves that can pass through the wall.
これに関連する技術として、例えば、特許文献1では、地下に設置した工事対象物の管理を目的として、準天頂衛星とGPS衛星の信号を用いて自己位置を求めると同時に、超音波の地中レーダ等を用いた自己に対する対象物の位置を求めることで、対象物の絶対位置を求めることを特徴とした埋設物探索装置を提案している。
As a technology related to this, for example, in
非特許文献1には、日本全国でセンチメータ級あるいはサブメートル級の高精度測位を可能にする誤差補正情報を日本全国に一律に配信する準天頂衛星が記載されている。
Non-Patent
非特許文献2には、アレイ・アンテナによる到来波の方向推定について記載されている。
Non-Patent
しかしながら、特許文献1のような技術による探索は、どのあたりに埋設物が設置されているかの事前情報に基づいており、また地中レーダ等の有効な距離は数mである。実際の被災現場ではまず被災者がどこにいるかは事前に分からない上、被災の規模が大きい場合には、事前情報なしで闇雲に捜索を行っても被災者の迅速な発見には繋がらないという問題がある。
However, the search by the technique as in
地中レーダの代わりに生体センサを用いても被災者の直接的な位置情報が得られないため、被災者との距離が遠い場合や、生体センサで検出できないほど被災者が衰弱している場合など、被災者生体センサ等の反応値が低い場合には、被災者の存在を見落としてしまう。 Even if a living body sensor is used instead of a ground penetrating radar, the location information of the victim cannot be obtained, so the distance from the victim is too far away, or the victim is so weak that it cannot be detected by the living body sensor. If the response value of the victim biosensor is low, the presence of the victim is overlooked.
また地中レーダの代わりに、被災者が保有している携帯電話が基地局探索のために定期的に発している電波を用い、捜索装置に対する被災者の携帯電話の相対位置を求めることが考えられるが、電波の発信には一定の時間間隔があり、闇雲な捜索では被災者の携帯電話の位置特定に長時間を要してしまう。 In addition, instead of using ground penetrating radar, it is possible to determine the relative position of the victim's mobile phone with respect to the search device using radio waves periodically emitted by the mobile phone held by the victim to search for base stations. However, there is a certain time interval for the transmission of radio waves, and it takes a long time to locate the victim's mobile phone in a dark cloud search.
さらに災害により地上インフラが破壊されて基地局と繋がらないような場合には、一般に携帯電話の電池の消耗が激しい上、近年のスマートフォン等では多機能化のため電池が1日程度しか持たない。被災した時点で電池がフル充電されているとは限らず、被災者の携帯電話の電池が切れる前に被災者の位置を特定できるような、高効率な捜索システムが必須である。 Furthermore, when the ground infrastructure is destroyed due to a disaster and is not connected to the base station, the battery of the mobile phone is generally consumed heavily, and recent smartphones or the like have a battery of only about a day for multifunctional purposes. The battery is not always fully charged at the time of the disaster, and a highly efficient search system that can identify the location of the victim before the victim's mobile phone battery runs out is essential.
特許文献1のような技術では、広く普及していて被災者が保有していると考えられる携帯電話の機能を、捜索活動に生かし切れないという問題がある。
In the technique such as
本発明は、地震等の災害が発生した場合に、基地局等の地上インフラが利用できないような場合においても、GPS信号の届かない建物内や瓦礫の下にいる被災者の位置情報を、被災者が保有する携帯電話の機能を活用して、迅速かつ正確に収集することを可能にすることを目的とする。 In the case where an earthquake or other disaster occurs, even if the ground infrastructure such as a base station cannot be used, the location information of the victims in the building or under the rubble where GPS signals do not reach The purpose is to make it possible to collect information quickly and accurately by utilizing the functions of the mobile phone held by the user.
上記目的を達成するため、本発明に係る測位端末は、複数の測位衛星と通信可能であり移動可能な測位端末である。測位端末は、測距信号受信部、端末位置算出部、携帯電波受信部、携帯ID判別部、携帯幾何情報算出部、基本情報生成部、携帯位置算出部、端末移動計画部および端末誘導部を備える。測距信号受信部は、測位衛星から測距信号を受信し、測距信号から、測位衛星に対する擬似距離観測量、搬送波位相観測量、および、航法メッセージを取得する。端末位置算出部は、擬似距離観測量、搬送波位相観測量および航法メッセージを用いて測位端末の位置、速度、および、時計誤差を算出する。携帯電波受信部は、携帯電話が発する携帯電波を受信する。携帯ID判別部は、携帯電波受信部が受信した携帯電波から、携帯電話を識別する携帯IDを取得する。携帯幾何情報算出部は、端末位置算出部が算出した測位端末の時計誤差と携帯電波受信部が受信した携帯電波とから、測位端末に対する携帯電話の携帯電話距離または携帯電話方向を算出する。基本情報生成部は、端末位置算出部が算出した測位端末の位置と携帯ID判別部が取得した携帯IDと携帯幾何情報算出部が算出した携帯電話距離または携帯電話方向とを含む基本情報を生成する。携帯位置算出部は、基本情報のうち、携帯IDが同じ2つ以上の基本情報から、携帯IDに該当する携帯電話の位置を算出し、携帯IDと算出した携帯電話の位置とを含む携帯位置情報を生成する。端末移動計画部は、基本情報と携帯位置情報との、いずれかまたは両方を用いて、次に携帯電波を受信する地点を算出し、算出した次に携帯電波を受信する地点を目的地として、測位端末の位置の最新値から測位端末を誘導する移動計画データを生成する。端末誘導部は、端末移動計画部が生成した移動計画データを出力する。端末移動計画部は、携帯IDが同じ2つの基本情報が得られて3つめの地点を求める場合、測位端末の位置、携帯電話距離の差を一定とする双曲線の漸近線および携帯電波の発信時間間隔で測位端末が移動可能な距離から次に携帯電波を受信する地点を求める。端末移動計画部は、携帯IDが異なる2つ以上の基本情報または携帯位置情報がある場合、携帯IDが同じである基本情報が少ない携帯IDの基本情報または携帯位置情報を用いて、次に携帯電波を受信する地点を算出し、算出した次に携帯電波を受信する地点を目的地として、測位端末の位置の最新値から測位端末を誘導する移動計画データを生成する。 In order to achieve the above object, a positioning terminal according to the present invention is a positioning terminal that can communicate with a plurality of positioning satellites and is movable. A positioning terminal includes a ranging signal receiving unit, a terminal position calculating unit, a portable radio wave receiving unit, a portable ID determining unit, a portable geometric information calculating unit, a basic information generating unit, a portable position calculating unit, a terminal movement planning unit, and a terminal guiding unit. Prepare. The ranging signal receiving unit receives a ranging signal from the positioning satellite, and acquires a pseudorange observation amount, a carrier phase observation amount, and a navigation message for the positioning satellite from the ranging signal. The terminal position calculation unit calculates the position, speed, and clock error of the positioning terminal using the pseudorange observation amount, the carrier phase observation amount, and the navigation message. The portable radio wave receiving unit receives a portable radio wave emitted from the mobile phone. The mobile ID discriminating unit acquires a mobile ID for identifying the mobile phone from the mobile radio wave received by the mobile radio wave receiving unit. The mobile geometric information calculation unit calculates the mobile phone distance or mobile phone direction of the mobile phone relative to the positioning terminal from the clock error of the positioning terminal calculated by the terminal position calculation unit and the mobile radio wave received by the mobile radio wave reception unit. The basic information generation unit generates basic information including the position of the positioning terminal calculated by the terminal position calculation unit, the mobile ID acquired by the mobile ID determination unit, and the mobile phone distance or mobile phone direction calculated by the mobile geometric information calculation unit. To do. The mobile position calculation unit calculates the position of the mobile phone corresponding to the mobile ID from two or more pieces of basic information having the same mobile ID among the basic information, and includes the mobile ID and the calculated mobile phone position. Generate information. The terminal movement planning unit uses one or both of the basic information and the mobile location information to calculate the next point to receive the mobile radio wave, The movement plan data for guiding the positioning terminal from the latest value of the position of the positioning terminal is generated. The terminal guiding unit outputs the movement plan data generated by the terminal movement planning unit. When two basic information with the same mobile ID is obtained and the third point is obtained, the terminal movement planning unit determines the position of the positioning terminal, the hyperbolic asymptote with a constant difference in mobile phone distance, and the transmission time of the mobile radio wave Next, a point at which the portable radio wave is received is obtained from the distance that the positioning terminal can move at intervals. When there are two or more basic information or mobile location information with different mobile IDs, the terminal movement planning unit uses the basic information or mobile location information of the mobile ID with the same basic mobile ID and the next mobile information. A location for receiving the radio wave is calculated, and movement plan data for guiding the positioning terminal from the latest value of the position of the positioning terminal is generated using the calculated location for receiving the mobile radio wave as the destination.
本発明によれば、被災者の早期の位置特定を可能とする、次に携帯電波を受信する最良の計測点を定める移動計画データを出力することで、地震等の災害が発生した場合に、基地局等の地上インフラが利用できないような場合においても、GPS信号の届かない建物内や瓦礫の下にいる被災者の位置情報を、被災者が保有する携帯電話の機能を活用して、迅速かつ正確に収集することが可能になる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to specify the location of the victim early, and by outputting the movement plan data for determining the best measurement point for receiving the next portable radio wave, when a disaster such as an earthquake occurs, Even when the ground infrastructure such as a base station cannot be used, the location information of the victim in the building where the GPS signal does not reach or under the debris can be quickly obtained by using the mobile phone function held by the victim. And it becomes possible to collect accurately.
以下に、本発明を実施するための形態について図面を参照して詳細に説明する。なお、図中同一または相当する部分には同じ符号を付す。 EMBODIMENT OF THE INVENTION Below, the form for implementing this invention is demonstrated in detail with reference to drawings. In addition, the same code | symbol is attached | subjected to the part which is the same or it corresponds in a figure.
(実施の形態1)
図1は、本発明の実施の形態1に係る救難救助支援システムの構成例を示すブロック図である。実施の形態1の救難救助支援システム100は、測位端末1、測位端末1を搭載した移動車両2、準天頂衛星等の多機能測位衛星3およびGPS衛星等の測位衛星4で構成される。本実施の形態では、携帯電話5は、被災地域において動けない被災者が所持していることを想定しているため、携帯電話5は移動しない。測位端末1は携帯電話5が発する携帯電波を受信する。測位衛星4は、例えばGPS衛星であり、測位端末1は測位衛星4の測距信号を受信する。
(Embodiment 1)
FIG. 1 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration example of a rescue and rescue support system according to
測位端末1および移動車両2は、代表して1台記載したが、これに限らず2台以上であってもよい。多機能測位衛星3も、代表して1基記載したが、これに限らず2基以上であってもよい。測位衛星4は、実際には4基以上である。また、測位端末1は移動可能であれば、移動車両2に搭載されていなくてもよい。
Although one
多機能測位衛星3は、例えば非特許文献1に示すような準天頂衛星であり、誤差補正情報を日本全国に一律に配信する。誤差補正情報とは、日本全国の電子基準点網で取得したGPS観測データを処理して得られる測位衛星4の測距信号の誤差を補正する情報であって、管制局を介して多機能測位衛星3に伝送され、日本全国でセンチメータ級あるいはサブメートル級の高精度測位を可能にする。測位端末1は多機能測位衛星3から誤差補正情報を受信する。
The
図2は、実施の形態1に係る測位端末の構成例を示すブロック図である。測位端末1は、測距信号受信部11、誤差補正情報受信部12、端末位置算出部13、携帯電波受信部14、携帯ID判別部15、携帯幾何情報算出部16、基本情報生成部17、記憶部18、携帯位置算出部19、端末移動計画部20および端末誘導部21を備える。
FIG. 2 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration example of the positioning terminal according to the first embodiment. The
測距信号受信部11は、測位衛星4が発信する測距信号を受信し、測位衛星4に対する擬似距離観測量、搬送波位相観測量、および、航法メッセージを取得する。測距信号は複数の測位衛星4から同時に受信し、その受信時刻を記憶する。
The ranging
なお擬似距離とは、衛星から発信された信号が受信機に到達するまでの伝播時間を、信号の搬送波に乗せられた測位用符号列(C/Aコード、P2コードなど)の観測値と、受信機の時計を衛星の時計と同じ基準時刻に同期して生成した同じ測位用符号列の値と、の位相差から計算し、光速を掛けることで求めた衛星―受信機間の距離である。受信機の時計および衛星の時計の基準時刻に対する同期には誤差があり、求めた距離には時計のずれによる誤差が含まれているため、“擬似”距離と呼ばれる。 Note that the pseudorange refers to the propagation time until the signal transmitted from the satellite reaches the receiver, the observation value of the positioning code string (C / A code, P2 code, etc.) carried on the carrier of the signal, This is the distance between the satellite and the receiver calculated by multiplying the speed of light by calculating the phase difference between the value of the same positioning code string generated by synchronizing the receiver clock with the same reference time as the satellite clock. . Since there is an error in the synchronization of the receiver clock and the satellite clock with the reference time, and the obtained distance includes an error due to clock deviation, it is called a “pseudo” distance.
また搬送波位相とは、上記の測位用符号列の観測時に追尾した搬送波の位相と、受信機の時計を衛星の時計と同じ基準時刻に同期して生成した同じ搬送波信号との位相差である。位相差には2π×N(Nは波数で整数値)のあいまいさ(アンビギュイティ)があり、搬送波位相のみからは一意的に衛星―受信機間の距離を求めることはできないが、搬送波位相は擬似距離よりも距離観測分解能が高く低ノイズであるため、波数Nを正しく決定することができれば、擬似距離観測量よりも高精度な距離観測量として利用することができる。 The carrier phase is a phase difference between the phase of the carrier tracked when the positioning code string is observed and the same carrier signal generated by synchronizing the receiver clock with the same reference time as the satellite clock. The phase difference has an ambiguity of 2π × N (N is an integer value of wave number), and the distance between the satellite and the receiver cannot be determined uniquely from the carrier phase alone, but the carrier phase Since the distance observation resolution is higher than the pseudorange and has low noise, if the wave number N can be determined correctly, it can be used as a distance observation quantity with higher accuracy than the pseudorange observation quantity.
また航法メッセージとは、測位端末1の位置算出に必要な、測距信号を発信したGPS衛星等の測位衛星4の位置や時計誤差を計算するために必要なパラメータを含むメッセージである。
The navigation message is a message including parameters necessary for calculating the position of a
誤差補正情報受信部12は、多機能測位衛星3から誤差補正情報を受信し、測距信号受信部11が取得した各測位衛星4に対する擬似距離観測量、搬送波位相観測量に含まれる誤差を補正するための擬似距離補正量、搬送波位相補正量を算出する。
The error correction
各測位衛星4に対する観測量の補正量は、例えば誤差補正情報に衛星時計誤差Clk[m](mは単位メートルを指す)、軌道誤差Orb[m]、対流圏遅延Trop[m]、電離層遅延Ion[m]、および、C/Aコード、P2コード、L1波搬送波位相、L2波搬送波位相のシグナル間バイアスBias(C/A、P2、L1、L2)[m]が含まれている場合、次式により擬似距離補正量と搬送波位相補正量を求めることができる。ただし、次式においては、誤差補正情報に含まれる衛星時計誤差Clk[m]は、航法メッセージに含まれる衛星時計誤差で観測値を補正後、さらに補正誤差分を補正するために使用することを仮定している。
The amount of observation correction for each
C/Aコードの擬似距離補正量=−Clk+Orb+Trop+(120/154)Ion+C/A_Bias
P2コードの擬似距離補正量=−Clk+Orb+Trop+(154/120)Ion+P2_Bias
L1波の搬送波位相補正量=−Clk+Orb+Trop−(120/154)Ion+L1_Bias
L2波の搬送波位相補正量=−Clk+Orb+Trop−(154/120)Ion+L2_Bias
C / A code pseudo distance correction amount = −Clk + Orb + Trop + (120/154) Ion + C / A_Bias
P2 code pseudo distance correction amount = −Clk + Orb + Trop + (154/120) Ion + P2_Bias
L1 wave carrier phase correction amount = −Clk + Orb + Trop− (120/154) Ion + L1_Bias
Carrier phase correction amount of L2 wave = −Clk + Orb + Trop− (154/120) Ion + L2_Bias
その他、誤差補正情報の提供者が推奨あるいは仕様にて規定する手法があれば、それらに従い計算するとよい。 In addition, if there is a method recommended by the provider of error correction information or specified in the specification, it is good to calculate according to them.
端末位置算出部13は、測距信号受信部11が取得した4基以上の測位衛星4に対する擬似距離観測量や搬送波位相観測量を、誤差補正情報受信部12が算出した測位衛星4に対する擬似距離補正量や搬送波位相補正量と、航法メッセージに含まれる衛星時計誤差で補正し、測位衛星4に対する補正済擬似距離観測量PRや補正済搬送波位相観測量CPを以下のように算出する。
The terminal
補正済擬似距離観測量PR=擬似距離観測量+航法メッセージに含まれる衛星時計誤差+擬似距離補正量
補正済搬送波位相観測量CP=擬似距離観測量+航法メッセージに含まれる衛星時計誤差+搬送波位相補正量
Corrected pseudorange observation amount PR = Pseudorange observation amount + satellite clock error included in navigation message + Pseudorange correction amount Corrected carrier phase observation amount CP = Pseudorange observation amount + satellite clock error included in navigation message + carrier phase Correction amount
続いて、端末位置算出部13は、補正済擬似距離観測量PRや補正済搬送波位相観測量CPを用い、測位端末1の位置(以下、測位端末位置という)、速度、および、時計誤差(以下、測位端末時計誤差という)を推定する。例えば4基以上の測位衛星4に対する補正済擬似距離観測量のみを用いて、数1に示すカルマンフィルタにより、測位端末1の位置、速度、および、時計誤差を推定する。位置をX={x,y,z}、速度をV={vx,vy,vz}、時計誤差をδTとする。
Subsequently, the terminal
位置、速度を表す座標系としては、例えばGPSで汎用的に用いられるWGS84地球固定座標系を用いる。時刻t−1における位置の推定値Xt−1|t−1、速度の推定値Vt−1|t−1、時計誤差の推定値δTt−1|t−1、および、共分散行列Pt−1|t−1から、時刻tにおける位置Xt|t−1、速度Vt|t−1、時計誤差δTt|t−1および共分散行列Pt|t−1を予測する。Qはプロセスノイズ行列である。Δtは時刻tと時刻t−1の間隔(秒)である。 As a coordinate system representing the position and velocity, for example, a WGS84 fixed earth coordinate system that is used for GPS in general is used. The estimated position value Xt-1 | t-1, the estimated speed value Vt-1 | t-1, the estimated clock error value δTt-1 | t-1, and the covariance matrix Pt-1 From | t−1, a position Xt | t−1 at a time t, a velocity Vt | t−1, a clock error δTt | t−1, and a covariance matrix Pt | t−1 are predicted. Q is a process noise matrix. Δt is an interval (seconds) between time t and time t−1.
状態量ベクトルをZ={X,V,δt}とし、数2に示す観測残差eを用いて、時刻tにおける位置、速度、時計誤差の推定値と共分散を求め、位置を測位端末位置、時計誤差を測位端末時計誤差とする。
The state quantity vector is set to Z = {X, V, δt}, and the estimated value and covariance of the position, speed, and clock error at time t are obtained using the observation residual e shown in
数2において、hは観測モデルであり、航法メッセージに含まれるパラメータから算出した各測位衛星4の位置Xsat1,Xsat2,…および、位置と時計誤差の推定値から計算する。hは測位に利用する測位衛星数と同じ行数を持つ行ベクトルである。または▽Zhは、hの状態量ベクトルZに関する微分を示す。Rは観測ノイズ行列である。航法暦に含まれるパラメータから測位衛星の位置を算出する手法は、各測位衛星を運用する機関が提供する仕様書に記載されている手順に従うとよい。
In Equation 2, h is an observation model, which is calculated from the positions X sat1 , X sat2 ,... Of the
一般に補正済擬似距離観測量のみを用いた測位では、サブメートル級(水平0.5〜1m)の精度で位置Xが得られ、10ns以下の精度で時計誤差δTが得られる。 In general, in positioning using only the corrected pseudorange observation amount, the position X is obtained with submeter class (horizontal 0.5 to 1 m) accuracy, and the clock error δT is obtained with accuracy of 10 ns or less.
また、5基以上の測位衛星4に対する補正済擬似距離観測量と補正済搬送波位相観測量の両方を用い、位置、速度、時計誤差、各衛星の搬送波位相のアンビギュイティを状態変数としたカルマンフィルタと、LAMBDA(The Least Squares Ambiguity Decorrelation Adjustment)等のアンビギュイティを整数化する手法を組み合わせた測位を行うことが挙げられる。一般に補正済擬似距離観測量と補正済搬送波位相観測量の両方を用い、アンビギュイティを整数化する測位ではセンチメートル級(水平6cm以下)の精度で位置Xが得られ、1ns以下の精度で時計誤差δTが得られる。
In addition, the Kalman filter using both the corrected pseudorange observation amount and the corrected carrier phase observation amount for five or
前述の手法で推定した時計誤差δTの値にはアンテナケーブルや電子系統による遅延も含まれているため、それらを事前に測定して補正することが望ましい。現在の電子技術によれば10n以下の精度で測定可能で、その範囲では安定(温度等による変動は10n以下)と考えられるため、補正済擬似距離観測量のみを用いた場合で10〜20ns、補正済擬似距離観測量と補正済搬送波位相観測量の両方を用いた場合で10ns以下の精度で測位端末1の測位端末時計誤差が得られると言える。
Since the value of the clock error δT estimated by the above-described method includes a delay due to the antenna cable and the electronic system, it is desirable to measure and correct them in advance. According to the current electronic technology, it can be measured with an accuracy of 10n or less, and it is considered that the range is stable (variation due to temperature etc. is 10n or less). Therefore, when using only the corrected pseudorange observation amount, 10 to 20ns, When both the corrected pseudorange observation amount and the corrected carrier phase observation amount are used, it can be said that the positioning terminal clock error of the
端末位置算出部13の処理は繰り返し行い、常に測位端末位置と測位端末時計誤差の値を更新する。その更新周期は例えば1秒である。
The processing of the terminal
携帯電波受信部14は、携帯電話5が発する携帯電波を受信する。例えば、携帯電波受信部14は、携帯電話5が基地局等との通信や基地局の探索等を目的として定期的に発する携帯電波を受信する。
The mobile
携帯ID判別部15は、携帯電波受信部14が受信した携帯電波を解析し、電波を復調して得られる携帯電話5の端末固有の番号であるIMEI(International Mobile Equipment Identity)等により、携帯電話5の携帯IDを取得する。
The mobile
携帯幾何情報算出部16は、端末位置算出部13が算出した測位端末時計誤差と携帯電波受信部14が受信した携帯電波から、測位端末1に対する携帯電話5の携帯電話距離または携帯電話方向を算出する。携帯電話距離を算出する場合は、携帯電波受信部14で携帯電波を受信した時刻Treceiveを記憶しておき、端末位置算出部13が算出した測位端末時計誤差でTreceiveを補正した時刻と、携帯電波を復調して得られる、携帯電話5が携帯電波を発信した時刻Ttrance[秒]から、次式により携帯電話距離を算出する。
The mobile geometric
携帯電話距離[m]=C×{(Treceive−δT)−Ttrans} Mobile phone distance [m] = C × {(T receive −δT) −T trans }
Cは光速で例えば299792458[m/秒]を用いる。携帯電波が約1GHzであり、一般的なCPUの処理速度が数GHzであることから、瓦礫内でマルチパスの影響を受けても、時刻Treceiveは数nsの精度で求められる。ただし携帯電話5の時計は、測位端末1のようにGPS衛星等の測距信号を用いた時計誤差の補正を行っていない。そのためTtransにバイアスが含まれ、上式で得られる携帯電話距離は実際の距離と大きく異なることが考えられる。携帯電話距離が負の値になる場合も考えられる。この影響は、携帯位置算出部16の説明に示すように、携帯IDが同じ4つ以上の携帯電話5に対する携帯電話距離を用いて携帯電話5の時計誤差δTmobileを推定することで、取り除かれる。
For C, the speed of light is, for example, 29792458 [m / sec]. Since the portable radio wave is about 1 GHz and the processing speed of a general CPU is several GHz, the time T receive can be obtained with an accuracy of several ns even if it is affected by multipath in the rubble. However, the clock of the
携帯電話方向を算出する場合は、例えば、非特許文献2に示すような技術を用いる。携帯電波受信部14は、アレイ・アンテナを備え、アレイ・アンテナ用いて指向性ビームによる空間捜査を行うビーム・フォーマ法等を用いて、携帯電話方向を算出する。携帯電話方向は、測位端末1の位置において東方向をx軸、北方向をy軸、高さ方向をz軸とした局所水平座標系における方位角AZ[度]と仰角EL[度]等で表現する。
When calculating the mobile phone direction, for example, a technique as shown in
基本情報生成部17は、端末位置算出部13が算出した測位端末位置と携帯ID判別部15が得た携帯IDと携帯幾何情報算出部16が算出した携帯電話距離または携帯電話方向を含む1単位の基本情報を生成する。例えば測位端末位置のx,y,zのそれぞれを16ビットの浮動小数点で表わし、携帯IDを32ビットの2進数で表わし、携帯電話距離または携帯電話方向の方位角と仰角をそれぞれ16ビットの浮動小数点で表わす場合、1単位の基本情報は、それぞれ96ビット(16×3+32+16)と112ビット(16×3+32+16×2)の情報となる。
The basic
記憶部18は、基本情報生成部17が生成した基本情報を所定のメモリに保存する。メモリは、複数単位の基本情報を保存することができるよう、ハードディスクやフラッシュメモリ等を利用する。
The
携帯位置算出部19は、記憶部18に保存されている複数の基本情報のうち、基本情報に含まれる携帯IDが同じ2つ以上の基本情報から、携帯IDに該当する携帯電話5の位置(以下、携帯電話位置という)を算出する。基本情報に含まれる携帯電話距離を用いる場合、携帯電話距離には携帯電話5の時計誤差の影響が含まれているため、3次元の携帯電話位置に加えて携帯電話5の時計誤差も同時に算出するため、携帯IDが同じ4つ以上の基本情報を使用する。
The mobile
携帯電話距離を用いる場合、例えば数4に示すニュートン法により、3次元の携帯電話位置Xmobile={xmobile,Ymobile,Zmobile}と携帯電話5の時刻誤差δTmobileを算出する。状態変数をZmobile={Xmobile,δTmobile}とおき、Zmobileが収束するまでニュートン法による更新を繰り返す。δTmobileを推定パラメータとすることで携帯電話5の時計誤差の影響を取り除くことができ、測位端末時計誤差δTおよびTreceiveの精度に応じた携帯電話位置が得られる。
When the mobile phone distance is used, for example, a three-dimensional mobile phone position X mobile = {x mobile , Y mobile , Z mobile } and a time error δT mobile of the
端末位置算出部13で補正済擬似距離観測量と補正済搬送波位相観測量の両方を用いた場合、測位端末時計誤差δTおよびTreceiveの誤差は合わせて10ns程度であることから、距離換算で3mとなり、携帯電話位置としては3〜5mの精度が期待される。この精度は後述する端末移動計画部20の説明で示すとおり、異なる地点からの幾何情報に基づく位置算出を適切に繰り返すことにより、さらに向上(1m程度まで)させることができる。
When both the corrected pseudorange observation amount and the corrected carrier phase observation amount are used in the terminal
収束の目安としては、携帯電話5を保有する被災者の位置の特定が可能となるよう、例えばニュートン法の反復前後の位置の差のノルムが1m以下となることを条件とする。
As an indication of convergence, for example, the norm of the position difference before and after the iteration of the Newton method is 1 m or less so that the position of the victim holding the
Fは携帯電話距離、状態変数、測位端末位置で表わされる関数であり、使用する基本情報の数と同じ数の行を持つ行ベクトルである。▽zF、Fの状態量ベクトルZに関する微分を示す。 F is a function represented by a mobile phone distance, a state variable, and a positioning terminal position, and is a row vector having the same number of rows as the number of basic information to be used. Z z Denotes the derivative with respect to the state quantity vector Z of F and F.
Riは、使用する基本情報のうちi番目の基本情報に含まれる携帯電話距離、xi,yi,ziは、使用する基本情報のうちi番目の基本情報に含まれる測位端末位置である(i=1,2,3,4…)。携帯電話距離の長さに応じて各基本情報に重みを付け、重み付きのニュートン法を用いてもよい。 R i is the mobile phone distance included in the i-th basic information of the basic information to be used, and x i , y i , and z i are the positioning terminal positions included in the i-th basic information of the basic information to be used. Yes (i = 1, 2, 3, 4 ...). Each basic information may be weighted according to the length of the mobile phone distance, and the weighted Newton method may be used.
基本情報に含まれる携帯電話方向を用いる場合は、携帯IDが同じ2つ以上の基本情報を使用する。携帯電話方向を用いる場合、例えば数6に示すニュートン法により、3次元の携帯電話位置Xmobile={xmobile,ymobile,zmobile}を算出する。状態変数をZmobile=Xmobileとおき、Zmobileが収束するまでニュートン法による更新を繰り返す。収束の目安としては、携帯電話5を保有する被災者の位置の特定が可能となるよう、例えばニュートン法の反復前後の位置の差のノルムが1m以下となることを条件とする。
When the mobile phone direction included in the basic information is used, two or more pieces of basic information having the same mobile ID are used. When the mobile phone direction is used, for example, a three-dimensional mobile phone position X mobile = {x mobile , y mobile , z mobile } is calculated by the Newton method shown in Equation 6. The state variable is set as Z mobile = X mobile , and the update by Newton's method is repeated until Z mobile converges. As an indication of convergence, for example, the norm of the position difference before and after the iteration of the Newton method is 1 m or less so that the position of the victim holding the
Fは携帯幾何情報算出部16が算出した携帯電話方向をWGS84等の地球固定座標系に変換した携帯電話方向、状態変数、測位端末位置で表わされる関数であり、使用する基本情報の数と同じ数の行を持つ行ベクトルである。
F is a function represented by the mobile phone direction, state variable, and positioning terminal position obtained by converting the mobile phone direction calculated by the mobile geometric
携帯電話方向を、測位端末1の位置における局所水平座標系で表わした場合は、ELi ECEFとAZi ECEFは使用する基本情報のうちi番目の基本情報に含まれる携帯電話方向の仰角(EL)と方位角(AZ)を、局所水平座標系から地球固定座標から見た方向に変換した方向の仰角と方位角となる(i=1,2,…)。 xi,yi,ziは、使用する基本情報のうちi番目の基本情報に含まれる測位端末位置である(i=1,2,…)。携帯電話方向に応じて、また携帯幾何情報算出部16で同時に携帯電話距離も得られる場合には携帯電話距離の長さに応じて、各基本情報に重みを付け、重み付きのニュートン法を用いてもよい。
When the mobile phone direction is represented by the local horizontal coordinate system at the position of the
携帯位置算出部19は、携帯IDと算出した携帯電話位置とを含む、1単位の携帯位置情報を生成する。
The mobile
記憶部18は、携帯位置算出部19が生成した携帯位置情報を所定のメモリに保存する。メモリは、複数単位の携帯位置情報を保存することができるよう、ハードディスクやフラッシュメモリ等を利用する。
The
端末移動計画部20は、記憶部18に保存されている基本情報と、携帯位置情報との、いずれかまたは両方を用いて、次に携帯電波を受信する地点を算出する。端末移動計画部20は、算出した次に携帯電波を受信する地点を目的地として、測位端末位置の最新値から測位端末1を誘導する移動計画データを生成する。
The terminal
まず、基本情報のみを用い、基本情報として携帯IDが同じ携帯電話5の携帯電話距離を用いる場合の、計画指針の例を示す。記憶部18に保存されている基本情報が1つである場合、携帯電話5の位置(以下、携帯電話位置という)は、基本情報に含まれる測位端末位置を中心とした、半径が携帯電話距離の球面上となる。ただし前述の通りTtransに含まれるバイアスのため、携帯電話距離が実際の距離と大きく異なる場合があり、基本情報1つのみでは有意な情報を与えない。そのため基本情報として携帯電話距離を用いる場合は、基本情報が1つのみの場合には、次の携帯電波受信の機会までにできるだけ遠くまで測位端末1を移動させる移動計画データを生成することが考えられる。
First, an example of a plan guideline when only the basic information is used and the mobile phone distance of the
図3は、実施の形態1に係る双曲面の一例を示す図である。2つの基本情報が得られれば、Ttransに依らず2つの地点に対する携帯電話距離の差分が計算可能となり、携帯電話位置APはその差分が一定の面上となる。図3に示すように、2つの基本情報にそれぞれ含まれる測位端末位置P1およびP2に対する距離の差分が一定の面は、双曲面Hをなす。実際には差分に誤差が含まれていることから、より正確には、携帯電話位置APは双曲面Hに対し誤差分だけの厚みを考慮した層の中となる。従ってその層の厚みの影響を低減するために、次に携帯電波を受信する3地点目としては、すでに存在する双曲面Hに対して新たに生成される双曲面ができるだけ垂直に交差するような地点を選択することが望ましい。 FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating an example of a hyperboloid according to the first embodiment. If two pieces of basic information are obtained, the difference between the mobile phone distances to the two points can be calculated regardless of T trans , and the mobile phone position AP is on the surface where the difference is constant. As shown in FIG. 3, a surface having a constant distance difference with respect to the positioning terminal positions P1 and P2 included in the two basic information forms a hyperboloid H. Actually, since the difference includes an error, the mobile phone position AP is more accurately in the layer considering the thickness corresponding to the error with respect to the hyperboloid H. Therefore, in order to reduce the influence of the thickness of the layer, the next generation of the hyperboloid H with respect to the existing hyperboloid H intersects as perpendicularly as possible at the third point for receiving the portable radio wave. It is desirable to select a point.
ここで通常は被災地域の水平方向の距離スケールに対して垂直方向のスケールが小さいと考えられることから、垂直方向を無視し、経度と緯度をx軸y軸とした局所的な水平面に双曲面を投影して得られる双曲線を考える。 Here, since the vertical scale is usually smaller than the horizontal distance scale of the affected area, the vertical direction is ignored, and the hyperboloid is formed on a local horizontal plane with the longitude and latitude as the x-axis and y-axis. Consider the hyperbola obtained by projecting.
図4は、実施の形態1に係る計画手法の一例を示す図である。3地点目の選択の指針の1つとしては、その水平面での2地点のうち、携帯電話位置APに近い方の地点から、双曲線の漸近線に平行な直線(図中、一点鎖線)を2本引き、そのいずれかの線上の点を選択することが挙げられる(図中、候補点PAまたはPB)。候補点PAおよびPBは、例えば、漸近線に平行な直線上の、次の携帯電波受信の機会までに移動できる地点とする。 FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating an example of a planning method according to the first embodiment. One of the guidelines for selecting the third point is that a straight line parallel to the asymptote of the hyperbola from the point closest to the mobile phone position AP out of the two points on the horizontal plane (the one-dot chain line in the figure) is 2 The main pulling and selecting a point on one of the lines (candidate points PA or PB in the figure). Candidate points PA and PB are, for example, points on a straight line parallel to an asymptote that can be moved to the next mobile radio wave reception opportunity.
図4に候補点PAを選んだ場合の双曲面HAおよび候補点PBを選んだ場合の双曲面HBを示す。いずれの候補点を選択した場合も2つの双曲線(従って双曲面も)間の高い垂直度が得られる。特に実際の携帯位置に近い側の直線上の点(候補点PA)を選択した場合は、携帯電話位置APによっては、ほぼ直角に交わる2つの双曲面HおよびHAが得られる。 FIG. 4 shows the hyperboloid HA when the candidate point PA is selected and the hyperboloid HB when the candidate point PB is selected. Regardless of which candidate point is selected, a high degree of perpendicularity between the two hyperbolas (and thus also the hyperboloid) is obtained. In particular, when a point on the straight line (candidate point PA) on the side closer to the actual mobile position is selected, two hyperboloids H and HA intersecting at almost right angles are obtained depending on the mobile phone position AP.
3地点からの携帯電話距離を算出すると、携帯電話位置APは、2つの双曲面の交線に対し距離の誤差分を考慮した厚みのある層の中まで絞り込まれる。4地点目から携帯電話距離を得ることにより、携帯電話位置APの推定値は一点に決まり、携帯電話位置APはその一点に対し誤差分を考慮した領域内に絞り込まれる。 When the mobile phone distance from the three points is calculated, the mobile phone position AP is narrowed down to a thick layer in consideration of the distance error with respect to the intersection of the two hyperboloids. By obtaining the mobile phone distance from the fourth point, the estimated value of the mobile phone position AP is determined as one point, and the mobile phone position AP is narrowed down to an area in consideration of the error with respect to the one point.
ここでその領域の大きさをできるだけ小さくする(すなわち測位精度をできるだけ高める)ような、4地点目の場所を選択する。4地点目の選択の指針の1つとしては、例えば衛星測位で用いる指標であるPDOP(Position Dilution Of Precision)を用いる。PDOPは衛星測位において測位を行う受信機に対する測位衛星4の幾何学的配置の悪さを示す指標であり、値が小さいほどよい。被災者の携帯電話5を受信機、測位端末1を測位衛星に見立てると、携帯電話位置をXmobile={xmobile,ymobile,zmobile}、携帯電話位置の算出に用いる測位端末1の位置をX1, X2, X3, X4(Xi= xi, yi, zi)とすると、携帯電話位置の算出におけるPDOPは次式で表わされる。
Here, the location of the fourth point is selected so that the size of the region is as small as possible (that is, the positioning accuracy is increased as much as possible). For example, PDOP (Position Dilution Of Precision), which is an index used in satellite positioning, is used as one of selection guidelines for the fourth point. PDOP is an index indicating the poor geometric arrangement of the
一方、携帯電話位置Xmobileは得られていないため、3地点目の選択時と同様に経度と緯度をx軸y軸とした局所的な水平面を考え、その水平面と2つの双曲面の交線との交点を携帯電話位置の概略位置とし、X1, X2, X3はすでに携帯電話距離算出を行った3地点目の座標値(基本情報に測位端末位置として保存されている値)とし、PDOPを最小とする座標値X4=(x4, y4, z4)を求め、これを4地点目とし、次に携帯電波を受信する地点として定める。 On the other hand, since the mobile phone position X mobile has not been obtained, a local horizontal plane with longitude and latitude as the x-axis and y-axis is considered as in the selection of the third point, and the intersection of the horizontal plane and the two hyperboloids Is the approximate position of the mobile phone position, and X 1 , X 2 , and X 3 are the coordinate values of the third point where the mobile phone distance calculation has already been performed (value stored as the positioning terminal position in the basic information) , The coordinate value X 4 = (x 4 , y 4 , z 4 ) that minimizes the PDOP is obtained, which is set as the fourth point, and then determined as the point where the portable radio wave is received.
PDOPの代わりに、水平方向の精度を優先する場合にはHDOP(Horizontal Dilution Of Precision)を、垂直方向の精度を優先する場合にはVDOP(Vertical Dilution Of Precision)を指標として用いることも考えられる。ただし、端末移動計画部20は、測位端末1が移動できる範囲に応じて、異なる指標の選択や、地点算出結果に応じた次に携帯電波を受信する地点の決定を行う。
Instead of PDOP, HDOP (Horizontal Dilution Of Precision) may be used as an index when priority is given to accuracy in the horizontal direction, and VDOP (Vertical Dilution Of Precision) may be used as an index when priority is given to accuracy in the vertical direction. However, the terminal
PDOPは、記憶部18に保存されている携帯位置情報に基づく移動計画の指標にも使用することができる。すなわちすでに4つ以上の携帯電話距離から携帯電話位置の算出が完了している携帯電話5について、追加で携帯電話距離の観測を行うことで位置精度の向上を行う。4つ以上の携帯電話距離から携帯電話位置の算出が完了した直後の携帯電話位置は、必ずしも幾何学的に良好な地点から計測した携帯電話距離に基づいてはおらず、最良の精度が得られていない。そこで4つ以上の携帯電話距離から得られた携帯電話位置をXmobileとし、5地点目からの観測を考慮したPDOPを最小化するX5=(x5, y5, z5)を求め、これを5地点目とし、次に携帯電波を受信する地点として定める。この場合、行ベクトルFは次式で表わされる。
The PDOP can also be used as an index for a movement plan based on portable location information stored in the
さらに一般には、位置計測は、計測を複数回繰り返すことにより、精度が向上できることが知られている。個々の携帯電話5について、携帯電話距離に基づく携帯位置計測において、4つの基本情報を1セットとして携帯電話位置を求め、さらに追加で4つの別の基本情報を得てそれらを1セットとして携帯電話位置を求めることが考えられる。この場合、2セットの基本情報から得られた携帯電話位置を、例えばそれらのPDOPの逆数で重みづけを行って平均化することにより、単一のセットで求めた場合よりも位置精度を向上することができる。例えば、単一のセットでは3〜5mであった位置精度が2〜3セットの繰り返しにより1m程度までに向上することが期待できる。
More generally, it is known that the position measurement can be improved in accuracy by repeating the measurement a plurality of times. For each
すなわち実施の形態1における救難救助支援システムでは、実際には複数の携帯電話5からの携帯電波を受信し、それらから次々に基本情報を生成し、個々の携帯電話5の位置を算出していく。携帯電話5が複数存在する場合には、端末移動計画部20で次に携帯電波を受信する地点を算出する際、例えば個々の携帯電話位置Xmobileから計算したPDOPの重み付き和を最小化することにより、重みに応じて位置算出精度の低い携帯電話5の精度を優先して向上させたい場合や、全ての携帯電話5の位置精度を均一に向上させたい場合に対応することができる。
That is, in the rescue and rescue support system according to the first embodiment, mobile radio waves from a plurality of
また基本情報が不足している携帯電話5を優先(例えば前述の双曲面が1つしかない携帯電話)させたい場合にも対応することができる。計測を繰り返すことで、すでに位置が定まった携帯電話についても、位置精度を向上することができ、その目的に応じて、様々な重み付けによる移動計画データを生成することが可能である。
In addition, it is possible to deal with a case where priority is given to the
端末誘導部21は、端末移動計画部20から受け取った移動計画データを表示装置等29に出力して、測位端末1を誘導する。
The
例えば、次に携帯電波を受信する地点と最新の測位端末位置と携帯位置情報とを表示する移動計画データを表示装置に表示させることで、移動車両2の運転者は、表示装置に表示された移動計画データに従って、移動車両2を移動させればよいので、捜索効率の向上が期待できる。あるいは、次に携帯電波を受信する地点と、最新の測位端末位置とを含む移動計画データを移動車両2の駆動制御装置に出力し、移動計画データに従って、移動車両2を自動で移動させてもよい。
For example, the driver of the moving
移動計画データは、表示を見易くするため、例えばWGS84等の地球固定座標系に対して求めた3次元の測位端末位置から、測位端末位置を原点とした東方向をx軸、北方向をy軸、高さ方向をz軸とした局所水平座標系における次に携帯電波を受信する地点および携帯電話位置を表示してもよいし、例えばWGS84等の地球固定座標系に対して求めた3次元の測位端末位置と携帯電話位置をそれぞれ緯度、経度、高度に変換して表示してもよい。 In order to make the movement plan data easy to see, for example, from the three-dimensional positioning terminal position obtained with respect to the earth fixed coordinate system such as WGS84, the east direction with the positioning terminal position as the origin is the x axis, and the north direction is the y axis. In addition, it is possible to display the next mobile radio wave reception point and mobile phone position in the local horizontal coordinate system with the height direction as the z-axis, or, for example, the three-dimensional obtained for the earth fixed coordinate system such as WGS84. The positioning terminal position and the mobile phone position may be converted into the latitude, longitude, and altitude, respectively, and displayed.
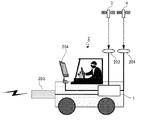
図5は、実施の形態1に係る移動車両の一例を示す図である。移動車両2は、測位端末1を搭載し、測位衛星4が発信する測距信号を受信する測距信号受信アンテナ201と、多機能測位衛星3から誤差補正情報を受信する誤差補正情報受信アンテナ202と、携帯電話5が発する携帯電波を受信する携帯電波受信アンテナ203と、携帯位置情報を表示する表示モニタ204とを備える。表示モニタ204は、測位端末1が備えてもよい。測距信号受信アンテナ201、誤差補正情報受信アンテナ202、携帯電波受信アンテナ203および表示モニタ204と、測位端末1とは接続されている。
FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating an example of the moving vehicle according to the first embodiment. The moving
測距信号受信アンテナ201は、受信した測距信号を測距信号受信部11に送る。誤差補正情報受信アンテナ202は、受信した誤差補正情報を誤差補正情報受信部12に送る。携帯電波受信アンテナ203は、受信した携帯電波を携帯電波受信部14に送る。端末誘導部21は、移動計画データを表示モニタ204に出力して、表示させる。
The ranging
また、移動車両2の形態としては、車両の他、ヘリコプタ等の飛行体でもよいし、リモートコントロール可能な車両や飛行体であってもよい。測位端末1は、コンパクトで持ち運び可能な機器として、人間が持ち歩いて使用してもよい。
In addition to the vehicle, the moving
図6は、実施の形態1に係る表示画面の一例を示す図である。図6の表示画面は、表示モニタ204に局所水平座標系における現在地点241と次に携帯電波を受信する地点242と携帯電話位置243を含む移動計画データを表示した例である。図6の例では、矢印は進行方向を示している。
FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating an example of a display screen according to the first embodiment. The display screen of FIG. 6 is an example in which movement plan data including the
携帯電話位置243は、記憶部18に保存された全て携帯IDに対応する携帯電話位置をすべて表示してもよいし、測位端末1からの距離が一定以下の携帯電話位置を表示してもよい。また携帯電話5を所持する被災者を救助できた場合には、その被災者が所持する携帯電話位置243の表示を手動で消す等の機能を追加してもよい。
The
高精度な測位端末位置と、携帯位置算出部19が算出した携帯電話位置から、移動しながらでも現在地に対する、被災者が所持する携帯電話5の位置がリアルタイムに、直感的な表示によって把握することができ、被災者の迅速な救助を可能になる。
From the highly accurate positioning terminal position and the mobile phone position calculated by the mobile
図7は、実施の形態1に係る端末位置算出処理の動作の一例を示すフローチャートである。図7に示す端末位置算出処理は、例えば測位端末1に電源が投入されると開始する。
FIG. 7 is a flowchart illustrating an example of the operation of the terminal position calculation process according to the first embodiment. The terminal position calculation process shown in FIG. 7 is started when the
測位端末1の測距信号受信部11は、測位衛星4が発信する測距信号を受信しない場合(ステップS11;NO)、ステップS11を繰り返し、測距信号の受信を待機する。測距信号を受信した場合(ステップS11;YES)、測距信号受信部11は、測距信号から、測位衛星4に対する擬似距離観測量、搬送波位相観測量、および、航法メッセージを取得する(ステップS12)。また、測距信号は複数のGPS衛星等の測位衛星4から同時に受信し、測距信号受信部11は、その受信時刻を記録する(ステップS13)。
When the ranging
誤差補正情報受信部12は、多機能測位衛星3から誤差補正情報を受信しない場合(ステップS14;NO)、ステップS14を繰り返し、誤差補正情報の受信を待機する。誤差補正情報を受信した場合(ステップS14;YES)、誤差補正情報受信部12は、誤差補正情報から、測距信号受信部11が取得した各測位衛星4に対する擬似距離観測量や搬送波位相観測量に含まれる誤差を補正するための擬似距離補正量や搬送波位相補正量を算出する(ステップS15)。
When the error correction
端末位置算出部13は、測距信号受信部11が取得した4基以上の測位衛星4に対する擬似距離観測量や搬送波位相観測量を、誤差補正情報受信部12が算出した測位衛星に対する擬似距離補正量や搬送波位相補正量と、航法メッセージに含まれる衛星時計誤差で補正し、測位衛星に対する補正済擬似距離観測量PRや補正済搬送波位相観測量CPを算出する(ステップS16)。
The terminal
次に、端末位置算出部13は、補正済擬似距離観測量PRや補正済搬送波位相観測量CPを用い、測位端末1の位置、速度、および、時計誤差を算出する(ステップS17)。
Next, the terminal
電源がOFFになっていなければ(ステップS18;NO)、処理はステップS11に戻り、ステップS11〜ステップS18を繰り返す。電源がOFFになると(ステップS18;YES)、処理を終了する。 If the power is not turned off (step S18; NO), the process returns to step S11, and steps S11 to S18 are repeated. When the power is turned off (step S18; YES), the process is terminated.
図8は、実施の形態1に係る携帯位置算出処理の動作の一例を示すフローチャートである。図8に示す携帯位置算出処理は、例えば測位端末1に電源が投入されると開始する。
FIG. 8 is a flowchart showing an example of the operation of the portable position calculation process according to the first embodiment. The portable position calculation process shown in FIG. 8 is started when the
測位端末1の携帯電波受信部14は、携帯電話5が発する携帯電波を受信しない場合(ステップS21;NO)、ステップS21を繰り返し、携帯電波の受信を待機する。携帯電波を受信した場合(ステップS21;YES)、携帯ID判別部15は、携帯電波受信部14が受信した携帯電波を解析し、携帯電話5の携帯IDを取得する(ステップS22)。
When the mobile
携帯幾何情報算出部16は、端末位置算出処理で端末位置算出部13が算出した測位端末時計誤差と携帯電波受信部14が受信した携帯電波から、測位端末1に対する携帯電話5の携帯電話距離または携帯電話方向を算出する(ステップS23)。
The mobile geometric
基本情報生成部17は、端末位置算出処理で端末位置算出部13が算出した測位端末位置と携帯ID判別部15が得た携帯IDと携帯幾何情報算出部16が算出した携帯電話距離または携帯電話方向とを含む1単位の基本情報を生成する(ステップS24)。記憶部18は、基本情報生成部17が生成した基本情報を所定のメモリに保存する(ステップS25)。
The basic
携帯位置算出部19は、記憶部18に保存されている複数の基本情報のうち、基本情報に含まれる携帯IDが同じ2つ以上の基本情報から、携帯IDに該当する携帯電話位置を算出する(ステップS26)。携帯位置算出部19は、携帯IDと算出した携帯電話位置とを含む、1単位の携帯位置情報を生成する(ステップS27)。記憶部18は、携帯位置算出部19が生成した携帯電話位置を所定のメモリに保存する(ステップS28)。
The mobile
電源がOFFになっていなければ(ステップS29;NO)、処理はステップS21に戻り、ステップS21〜ステップS29を繰り返す。電源がOFFになると(ステップS29;YES)、処理を終了する。 If the power is not turned off (step S29; NO), the process returns to step S21 and repeats steps S21 to S29. When the power is turned off (step S29; YES), the process is terminated.
図9は、実施の形態1に係る端末誘導処理の動作の一例を示すフローチャートである。図9に示す端末誘導処理は、例えば測位端末1に電源が投入されると開始する。
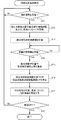
FIG. 9 is a flowchart showing an example of operation of terminal guidance processing according to the first embodiment. The terminal guidance process shown in FIG. 9 starts when the
端末移動計画部20は、携帯位置算出処理で記憶部18に保存された基本情報と、携帯位置情報との、いずれかまたは両方を用いて、次に携帯電波を受信する地点を算出する(ステップS31)。
The terminal
端末移動計画部20は、算出した次に携帯電波を受信する地点を目的地として、測位端末位置の最新値から測位端末1を誘導する移動計画データを生成する(ステップS32)。端末誘導部21は、移動計画データを表示装置等29に出力して、測位端末1を誘導する(ステップS33)。
The terminal
電源がOFFになっていなければ(ステップS34;NO)、処理はステップS31に戻り、ステップS31〜ステップS34を繰り返す。電源がOFFになると(ステップS34;YES)、処理を終了する。 If the power is not turned off (step S34; NO), the process returns to step S31, and steps S31 to S34 are repeated. When the power is turned off (step S34; YES), the process is terminated.
以上説明したように実施の形態1の救難救助支援システム100によれば、被災者の早期の位置特定を可能とする次に携帯電波を受信する最良の計測点を定める移動計画データを出力することで、捜索者が闇雲に被災地域を探索することなく、定期的に発信される携帯電波を有効に用い、短時間で被災者の位置を絞り込む得ることができる。被災者の衰弱、二次災害の可能性、被災者の携帯電話5の電池切れによる通信手段の喪失の可能性等、一刻を争う被災現場において、被災者の早期の救助が実現できる。
As described above, according to the rescue /
また、携帯電話5の電波を利用して被災者との距離を計測することで、GPS信号の届かない建物内や瓦礫の下にいる被災者の位置情報が取得できる。また準天頂衛星等の多機能測位衛星3が配信する誤差補正情報を利用することにより、被災者の探索に用いる測位端末位置と測位端末時計誤差がリアルタイム(誤差補正情報の受信開始から1分以内)に高精度(位置:センチメートル級、時計:10ns)に得られるため、携帯電話の電波を利用して得られる距離の精度(3m程度)に応じた、被災者の位置特定に必要な精度の位置情報が得られる。さらに構成要素には地上インフラが含まれず、測位端末1の他は、地上で発生した災害の影響を受けない宇宙インフラである準天頂衛星等の多機能測位衛星3のみを含むため、本発明は周辺の地上インフラの被災状況によらず利用可能である。
Further, by measuring the distance from the victim using the radio wave of the
以上より、地震等の災害発生した場合に、基地局等の周辺の地上インフラが利用できないような場合においても、GPS信号の届かない建物内や瓦礫の下にいる被災者の位置情報を、被災者が保有する携帯電話5の機能を活用して迅速かつ正確に収集することが可能になる。
Based on the above, in the event of a disaster such as an earthquake, even if the ground infrastructure around the base station etc. cannot be used, the location information of the victims in the building or under the rubble where GPS signals do not reach It is possible to collect quickly and accurately by utilizing the functions of the
例えば、この測位端末1を自家用車等に搭載することにより、災害発生時に地上インフラに頼ることなく、GPSと準天頂衛星等の多機能測位衛星3のみを利用して被災者を捜索するシステムが構築できる。またヘリコプタに搭載することにより、空中からの高効率な捜索が可能である。測位端末1を持って被災地域を歩き回ることで、被災者の位置情報を収集することも可能である。
For example, by installing this
(実施の形態2)
図10は、本発明の実施の形態2に係る測位端末の構成例を示すブロック図である。実施の形態2の救難救助支援システム200は、実施の形態1の救難救助支援システム100と同様の構成であるが、測位端末1の構成が異なる。また、救難救助支援システム200における測位端末1は2台以上であり、他の測位端末1と通信可能である。
(Embodiment 2)
FIG. 10 is a block diagram showing a configuration example of a positioning terminal according to
実施の形態2の測位端末1は、実施の形態1の測位端末1の構成に加え、他の測位端末1と通信可能な通信部22を備える。
The
通信部22は、記憶部18に保存されている基本情報を、無線等を用いて他の測位端末1に送信する。通信部22は、他の測位端末1から基本情報を受信すると、記憶部18に保存する。同様に、通信部22は、記憶部18に保存されている携帯位置情報を、無線等を用いて他の測位端末1に送信する。通信部22は、他の測位端末1から携帯位置情報を受信すると、記憶部18に保存する。
The
携帯位置算出部19は、記憶部18に保存されている、自身の測位端末1の基本情報および他の測位端末1から取得した基本情報に基づいて、携帯電話位置を算出する。
The mobile
端末移動計画部20は、記憶部18に保存されている、自身の測位端末1の基本情報および他の測位端末1から取得した基本情報と、自身の測位端末1が算出した携帯位置情報および他の測位端末1から取得した携帯位置情報と、のいずれかまたは両方を用いて、次に携帯電波を受信する地点を算出する。
The terminal
実施の形態2のその他の構成は、実施の形態1と同様である。 Other configurations of the second embodiment are the same as those of the first embodiment.
実施の形態2の救難救助支援システム200によれば、複数の測位端末1を利用することにより、幾何学的に異なる方向から携帯電話距離または携帯電話方向を計測するために個々の測位端末1が移動しなければならない距離が短くて済み、災害発生により路面状況が悪い場合でも一定の探索効率が確保できる。さらに幾何学的に異なる複数の方向から、携帯電話5が同時刻に発した携帯電波を受信して基本情報を生成できることにより、携帯電話5の時刻誤差の変動の影響が無視でき、携帯電話の時刻誤差の変動が早い場合にも、精度が低下することなく携帯電話位置を算出することができる。
According to the rescue and
(実施の形態3)
図11は、本発明の実施の形態3に係る測位端末の構成例を示すブロック図である。実施の形態3の救難救助支援システム300は、実施の形態2の救難救助支援システム200と同様の構成であるが、測位端末1の記憶部18は、自身の測位端末1を識別する端末IDを記憶している。
(Embodiment 3)
FIG. 11 is a block diagram showing a configuration example of a positioning terminal according to
通信部22は、記憶部18に保存されている基本情報および携帯位置情報に加えて、記憶部18が記憶している端末IDと、端末位置算出部13が算出した測位端末位置の最新値とを対応付けた最新位置情報を、無線等を用いて他の測位端末1に送信する。通信部22は、他の測位端末1から最新位置情報を受信すると、端末移動計画部20に送る。
In addition to the basic information and portable position information stored in the
端末移動計画部20は、記憶部18に保存されている自身の測位端末1の基本情報および他の測位端末1から取得した基本情報と、自身の測位端末1が算出した携帯位置情報および他の測位端末1から取得した携帯位置情報と、のいずれかまたは両方を用いて、自身の測位端末1と他の測位端末1のそれぞれについて次に携帯電波を受信する地点を算出する。
The terminal
端末移動計画部20は、実施の形態1や実施の形態2の場合と異なり、単一の測位端末1ではなく、複数台の測位端末1を同時に考慮して移動計画データを生成する。一例として、複数の携帯電話5に対する重み付きのPDOPに基づいて次に携帯電波を受信する位置を算出する場合を示す。
Unlike the cases of the first and second embodiments, the terminal
測位端末1の台数をM、携帯電話5の台数をKとする。測位端末1i(i=1…M)が次に携帯電波を受信する位置をXi={xi,yi,zi}とし、個々の携帯電話5k(k=1…K)について概略位置をXmobile_k、その携帯電話位置を算出するために既に収集した1セットの基本情報に含まれる基本情報の個数をnkとすると、Z={X1,X2,…XM}を変数として、以下に示す評価関数Jを最小化する。
Let M be the number of
(j=1…nk)は携帯電話5kの位置算出を行う1セットの基本情報に含まれる測位端末位置を示す。Wkは重みである。 (J = 1... Nk) indicates a positioning terminal position included in one set of basic information for calculating the position of the mobile phone 5k. W k is a weight.
また他の一例として、一部の測位端末1は基本情報が不足している携帯電話5(例えば前述の双曲面が1つしかない携帯電話)を優先し、残りの測位端末1はすでに概略位置が求められている携帯電話5の位置精度を向上することを優先する、という組み合わせも可能である。
As another example, some of the
端末移動計画部20は、各測位端末1について、算出した次に携帯電波を受信する地点を目的地として、測位端末位置の最新値から測位端末1を誘導する、端末IDごとの移動計画データを生成する。
The terminal
通信部22はさらに、端末移動計画部20が生成した端末IDごとの移動計画データをで他の測位端末1に送信してもよい。この場合、通信部22は、他の測位端末1から端末IDごとの移動計画データを受信し、端末誘導部21に送る。
The
端末誘導部21は、端末移動計画部20または通信部22から受け取った端末IDごとの移動計画データのうち記憶部18に記憶している自身の測位端末1の端末IDの移動計画データを表示装置等29に出力する。これによれば、自身の測位端末1で、移動計画データを生成できなかった場合などに、他の測位端末1で生成された移動計画データを利用できる。
The
実施の形態3のその他の構成は、実施の形態2と同様である。 Other configurations of the third embodiment are the same as those of the second embodiment.
以上説明したように実施の形態3の救難救助支援システム300によれば、システム全体で取得した基本情報や携帯位置情報、および複数台の測位端末1の位置情報を同時に考慮して移動計画データを生成するため、各測位端末1で個別に移動計画データを生成する場合と比較して、より良い移動計画データが得られ、短時間の捜索でより高精度な被災者の位置算出が期待できる。
As described above, according to the rescue /
(実施の形態4)
図12は、本発明の実施の形態4に係る測位端末の構成例を示すブロック図である。実施の形態4の救難救助支援システム400は、実施の形態3の救難救助支援システム300のすべての測位端末1の端末移動計画部20の機能を別途設けたサーバ6が備える構成である。救難救助支援システム400の測位端末1は、端末移動計画部20を備えない。
(Embodiment 4)
FIG. 12 is a block diagram showing a configuration example of a positioning terminal according to
測位端末1の通信部22は、記憶部18に保存されている基本情報および携帯位置情報に加えて、記憶部18が記憶している端末IDと、端末位置算出部13が算出した測位端末位置の最新値とを対応付けた最新位置情報とを、無線等を用いてサーバ6に送信する。
The
サーバ6は、通信部61と記憶部62と端末移動計画部63を備える。通信部61は、測位端末1から基本情報、携帯位置情報および最新位置情報を受信する。記憶部62は、通信部61が受信した、すべての測位端末1の基本情報、携帯位置情報および最新位置情報を所定のメモリに保存する。メモリは、複数単位の基本情報および携帯位置情報を保存することができるよう、ハードディスクやフラッシュメモリ等を利用する。
The server 6 includes a communication unit 61, a storage unit 62, and a terminal
端末移動計画部63は、記憶部62に保存されている基本情報と携帯位置情報と、のいずれかまたは両方を用いて、それぞれの測位端末1について次に携帯電波を受信する地点を算出する。端末移動計画部63は、各測位端末1について、算出した次に携帯電波を受信する地点を目的地として、測位端末位置の最新値から測位端末1を誘導する、端末IDごとの移動計画データを生成する。
The terminal
通信部61は、端末移動計画部63が生成した移動計画データを該当する端末IDの測位端末1に送信する。
The communication unit 61 transmits the movement plan data generated by the terminal
測位端末1の通信部22は、サーバ6から移動計画データを受信し、端末誘導部21に送る。端末誘導部21は、受け取った移動計画データを表示装置等29に出力して、測位端末1を誘導する。
The
以上説明したように実施の形態4の救難救助支援システム400によれば、次に携帯電波を受信する地点を算出し、移動計画データの生成する処理をサーバ6で行うことにより、移動型高精度測位端末よりも高いスペックの計算環境が期待でき、より計算負荷の高い数学的に優れたアルゴリズムが適用できる。これにより、測位端末1で移動計画データを生成する場合よりも、アルゴリズムに応じて良い移動計画データが得られ、短時間の捜索でより高精度な被災者の位置算出が期待できる。
As described above, according to the rescue /
(実施の形態5)
図13は、本発明の実施の形態5に係る測位端末の構成例を示すブロック図である。実施の形態5の救難救助支援システム500は、実施の形態1の救難救助支援システム100の構成に加え、センタ7を備える。また、救難救助支援システム500における測位端末1は2台以上である。
(Embodiment 5)
FIG. 13 is a block diagram showing a configuration example of a positioning terminal according to
救難救助支援システム500の測位端末1は、実施の形態1の測位端末1の構成に加え、多機能測位衛星3に情報を伝送可能な携帯位置情報送信部23を備える。また、記憶部18は、自身の測位端末1を識別する端末IDを記憶している。
The
携帯位置情報送信部23は、記憶部18が保存している携帯位置情報を多機能測位衛星3に伝送する。多機能測位衛星3への携帯位置情報の伝送には、多機能測位衛星3の双方向通信機能を利用する。例えば3次元の携帯位置情報をそれぞれ16ビットの浮動小数点、携帯IDを32ビットの2進数で表わす場合、多機能測位衛星3に伝送される1つの携帯位置情報の情報量は80ビット(16×3+32)となる。伝送方法は、準天頂衛星等の多機能測位衛星3が指定する所定のメッセージフォーマットや仕様に従うものとする。多機能測位衛星3は、測位端末1から受信した携帯位置情報をセンタ7に伝送する。
The portable position
センタ7は、携帯位置情報受信部71と携帯位置情報記憶部72とを備える。携帯位置情報受信部71は、多機能測位衛星3から携帯位置情報を受信する。携帯位置情報記憶部72は、携帯位置情報受信部71が受信した携帯位置情報を所定のメモリに保存する。メモリは、複数単位の携帯位置情報を保存することができるよう、ハードディスクやフラッシュメモリ等を利用する。
The center 7 includes a portable position information receiving unit 71 and a portable position
以上説明したように実施の形態5の救難救助支援システム500によれば、多機能測位衛星3の双方向通信機能を利用して被災地域における多数の被災者の携帯電話5の位置情報を集約することができるため、多数の被災者の位置を一括して把握することができ、迅速な救助を行うための救難救助計画を立てることができる。また被災者の携帯電話5の位置情報の集約に、宇宙インフラである多機能測位衛星3の双方向通信機能を利用するため、災害の発生により基地局等の地上インフラが使用不可となった場合にも、継続的に被災者の位置情報を収集することができる。
As described above, according to the rescue and
上記の説明では、実施の形態5は実施の形態1と組み合わせたが、他の実施の形態と組み合わせてもよい。
In the above description,
図14は、本発明の実施の形態に係る処理装置のハードウェア構成の一例を示すブロック図である。測位端末1は、図14に示すように、制御部31、主記憶部32、外部記憶部33、操作部34、表示部35、入出力部36および送受信部37を備える。主記憶部32、外部記憶部33、操作部34、表示部35、入出力部36および送受信部37はいずれも内部バス30を介して制御部31に接続されている。
FIG. 14 is a block diagram showing an example of a hardware configuration of the processing apparatus according to the embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 14, the
制御部31はCPU(Central Processing Unit)などから構成され、外部記憶部33に記憶されている制御プログラム39に従って、測位端末1の端末位置算出部13、携帯ID判別部15、携帯幾何情報算出部16、基本情報生成部17、携帯位置算出部19、端末移動計画部20および端末誘導部21の各処理を実行する。
The
主記憶部32はRAM(Random-Access Memory)などから構成され、外部記憶部33に記憶されている制御プログラム39をロードし、制御部31の作業領域として用いられる。
The
外部記憶部33は、フラッシュメモリ、ハードディスク、DVD−RAM、DVD−RWなどの不揮発性メモリから構成され、測位端末1の処理を制御部31に行わせるためのプログラムをあらかじめ記憶し、また、制御部31の指示に従って、このプログラムが記憶するデータを制御部31に供給し、制御部31から供給されたデータを記憶する。記憶部18は外部記憶部33に構成される。
The
操作部34はキーボードおよびマウスなどのポインティングデバイスなどと、キーボードおよびポインティングデバイスなどを内部バス30に接続するインタフェース装置から構成されている。ユーザが測位端末1に情報を入力する場合は、操作部34を介して、入力された情報が制御部31に供給される。
The
表示部35は、CRTまたはLCDなどから構成されている。ユーザが測位端末1に情報を入力する場合は、操作画面を表示する。測位端末1が表示モニタ204を備える場合には、表示部35は表示モニタ204として機能する。
The
入出力部36は、シリアルインタフェースまたはパラレルインタフェースから構成されている。入出力部36は測距信号受信アンテナ201、誤差補正情報受信アンテナ202、携帯電波受信アンテナ203および表示モニタ204と接続する。入出力部36は、測距信号受信部11、誤差補正情報受信部12、携帯電波受信部14、端末誘導部21、および、携帯位置情報送信部23として機能する。
The input /
送受信部37は、ネットワークに接続する網終端装置または無線通信装置、およびそれらと接続するシリアルインタフェースまたはLAN(Local Area Network)インタフェースから構成されている。測位端末1の通信部22として機能する。
The transmission /
図2、図10、図11、図12および図13に示す測位端末1の測距信号受信部11、誤差補正情報受信部12、端末位置算出部13、携帯電波受信部14、携帯ID判別部15、携帯幾何情報算出部16、基本情報生成部17、記憶部18、携帯位置算出部19、端末移動計画部20、端末誘導部21、通信部22および携帯位置情報送信部23の処理は、制御プログラム39が、制御部31、主記憶部32、外部記憶部33、操作部34、表示部35、入出力部36および送受信部37などを資源として用いて処理することによって実行する。
2, 10, 11, 12, and 13, ranging
その他、前記のハードウェア構成やフローチャートは一例であり、任意に変更および修正が可能である。 In addition, the hardware configuration and the flowchart described above are merely examples, and can be arbitrarily changed and modified.
制御部31、主記憶部32、外部記憶部33、操作部34、表示部35、入出力部36、送受信部37、内部バス30などから構成される測位端末1の処理を行う中心となる部分は、専用のシステムによらず、通常のコンピュータシステムを用いて実現可能である。例えば、前記の動作を実行するためのコンピュータプログラムを、コンピュータが読み取り可能な記録媒体(フレキシブルディスク、CD−ROM、DVD−ROMなど)に格納して配布し、当該コンピュータプログラムをコンピュータにインストールすることにより、前記の処理を実行する測位端末1を構成してもよい。また、インターネットなどの通信ネットワーク上のサーバ装置が有する記憶装置に当該コンピュータプログラムを格納しておき、通常のコンピュータシステムがダウンロードなどすることで測位端末1を構成してもよい。
A central part that performs processing of the
また、測位端末1の機能を、OS(オペレーティングシステム)とアプリケーションプログラムの分担、またはOSとアプリケーションプログラムとの協働により実現する場合などには、アプリケーションプログラム部分のみを記録媒体や記憶装置に格納してもよい。
Further, when the functions of the
また、搬送波にコンピュータプログラムを重畳し、通信ネットワークを介して提供することも可能である。例えば、通信ネットワーク上の掲示板(BBS,Bulletin Board System)にコンピュータプログラムを掲示し、ネットワークを介してコンピュータプログラムを提供してもよい。そして、このコンピュータプログラムを起動し、OSの制御下で、他のアプリケーションプログラムと同様に実行することにより、測位端末1の処理を実行できるように構成してもよい。
It is also possible to superimpose a computer program on a carrier wave and provide it via a communication network. For example, a computer program may be posted on a bulletin board (BBS, Bulletin Board System) on a communication network, and the computer program may be provided via the network. And you may comprise so that the process of the
1 測位端末、2 移動車両、3 多機能測位衛星、4 測位衛星、5 携帯電話、6 サーバ、7 センタ、11 測距信号受信部、12 誤差補正情報受信部、13 端末位置算出部、14 携帯電波受信部、15 携帯ID判別部、16 携帯幾何情報算出部、17 基本情報生成部、18 記憶部、19 携帯位置算出部、20 端末移動計画部、21 端末誘導部、22 通信部、23 携帯位置情報送信部、29 表示装置等、30 内部バス、31 制御部、32 主記憶部、33 外部記憶部、34 操作部、35 表示部、36 入出力部、37 送受信部、39 制御プログラム、61 通信部、62 記憶部、63 端末移動計画部、71 携帯位置情報受信部、72 携帯位置情報記憶部、100,200,300,400,500 救難救助支援システム、201 測距信号受信アンテナ、202 誤差補正情報受信アンテナ、203 携帯電波受信アンテナ、204 表示モニタ、241 現在地点、242 次に携帯電波を受信する地点、243 携帯電話位置、AP 携帯電話位置、H,HA,HB 双曲面、P1,P2 測位端末位置、PA,PB 候補点。 1 positioning terminal, 2 moving vehicle, 3 multifunctional positioning satellite, 4 positioning satellite, 5 mobile phone, 6 server, 7 center, 11 ranging signal receiving unit, 12 error correction information receiving unit, 13 terminal position calculating unit, 14 carrying Radio wave reception unit, 15 mobile ID discrimination unit, 16 mobile geometric information calculation unit, 17 basic information generation unit, 18 storage unit, 19 mobile location calculation unit, 20 terminal movement planning unit, 21 terminal guidance unit, 22 communication unit, 23 mobile phone Position information transmission unit, 29 display device, etc. 30 internal bus, 31 control unit, 32 main storage unit, 33 external storage unit, 34 operation unit, 35 display unit, 36 input / output unit, 37 transmission / reception unit, 39 control program, 61 Communication unit, 62 storage unit, 63 terminal movement planning unit, 71 mobile location information receiving unit, 72 mobile location information storage unit, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 rescue rescue Support system, 201 Ranging signal receiving antenna, 202 Error correction information receiving antenna, 203 Mobile radio wave receiving antenna, 204 Display monitor, 241 Current location, 242 Next location to receive mobile radio wave, 243 Mobile phone location, AP mobile phone location , H, HA, HB hyperboloid, P1, P2 positioning terminal position, PA, PB candidate points.
Claims (14)
前記測位端末は、
前記測位衛星から測距信号を受信し、前記測距信号から、前記測位衛星に対する擬似距離観測量、搬送波位相観測量、および、航法メッセージを取得する測距信号受信部と、
前記擬似距離観測量、前記搬送波位相観測量および前記航法メッセージを用いて前記測位端末の位置、速度、および、時計誤差を算出する端末位置算出部と、
携帯電話が発する携帯電波を受信する携帯電波受信部と、
前記携帯電波受信部が受信した携帯電波から、前記携帯電話を識別する携帯IDを取得する携帯ID判別部と、
前記端末位置算出部が算出した前記測位端末の時計誤差と前記携帯電波受信部が受信した携帯電波とから、前記測位端末に対する前記携帯電話の携帯電話距離または携帯電話方向を算出する携帯幾何情報算出部と、
前記端末位置算出部が算出した前記測位端末の位置と前記携帯ID判別部が取得した前記携帯IDと前記携帯幾何情報算出部が算出した前記携帯電話距離または前記携帯電話方向とを含む基本情報を生成する基本情報生成部と、
前記基本情報のうち、前記携帯IDが同じ2つ以上の前記基本情報から、前記携帯IDに該当する前記携帯電話の位置を算出し、前記携帯IDと算出した前記携帯電話の位置とを含む携帯位置情報を生成する携帯位置算出部と、
前記基本情報と前記携帯位置情報との、いずれかまたは両方を用いて、次に携帯電波を受信する地点を算出し、算出した次に携帯電波を受信する地点を目的地として、前記測位端末の位置の最新値から前記測位端末を誘導する移動計画データを生成する端末移動計画部と、
前記移動計画データを出力する端末誘導部と、
を備え、
前記端末移動計画部は、前記携帯IDが同じ2つの前記基本情報が得られて3つめの地点を求める場合、前記測位端末の位置、前記携帯電話距離の差を一定とする双曲線の漸近線および携帯電波の発信時間間隔で前記測位端末が移動可能な距離から次に携帯電波を受信する地点を求め、
前記端末移動計画部は、前記携帯IDが異なる2つ以上の前記基本情報または前記携帯位置情報がある場合、前記携帯IDが同じである前記基本情報が少ない前記携帯IDの前記基本情報または前記携帯位置情報を用いて、次に携帯電波を受信する地点を算出し、算出した次に携帯電波を受信する地点を目的地として、前記測位端末の位置の最新値から前記測位端末を誘導する移動計画データを生成する、
測位端末。 A positioning terminal that can communicate with multiple positioning satellites and is movable.
The positioning terminal is
A ranging signal receiving unit that receives a ranging signal from the positioning satellite, and obtains a pseudorange observation amount, a carrier phase observation amount, and a navigation message for the positioning satellite from the ranging signal;
A terminal position calculation unit that calculates the position, speed, and clock error of the positioning terminal using the pseudorange observation amount, the carrier phase observation amount, and the navigation message;
A mobile radio wave receiver for receiving mobile radio waves emitted by a mobile phone;
A mobile ID discriminating unit for acquiring a mobile ID for identifying the mobile phone from the mobile radio wave received by the mobile radio wave receiving unit;
Mobile geometric information calculation for calculating a mobile phone distance or a mobile phone direction of the mobile phone relative to the positioning terminal from a clock error of the positioning terminal calculated by the terminal position calculation unit and a mobile radio wave received by the mobile radio wave reception unit And
Basic information including the position of the positioning terminal calculated by the terminal position calculation unit, the mobile ID acquired by the mobile ID determination unit, and the mobile phone distance or the mobile phone direction calculated by the mobile geometric information calculation unit. A basic information generation unit to generate;
Of the basic information, the position of the mobile phone corresponding to the mobile ID is calculated from two or more pieces of the basic information having the same mobile ID, and the mobile including the mobile ID and the calculated position of the mobile phone A portable position calculation unit for generating position information;
Using either or both of the basic information and the mobile location information, the next location for receiving mobile radio waves is calculated, and the next location for receiving mobile radio waves is calculated as the destination. A terminal movement planning unit for generating movement planning data for guiding the positioning terminal from the latest value of the position;
A terminal guidance unit for outputting the movement plan data;
With
The terminal movement planning unit, when two basic information with the same mobile ID is obtained and a third point is obtained, a hyperbolic asymptotic line with a constant difference between the position of the positioning terminal and the mobile phone distance; Find the next point to receive mobile radio waves from the distance that the positioning terminal can move at the mobile radio wave transmission time interval ,
When there are two or more pieces of the basic information or the mobile location information having different mobile IDs, the terminal movement planning unit has the basic information with the same mobile ID and the basic information of the mobile ID or the mobile Using the location information, the next location for receiving the mobile radio wave is calculated, and the next location for receiving the mobile radio wave is calculated as a destination, and the movement plan for guiding the positioning terminal from the latest value of the location of the positioning terminal Generate data,
Positioning terminal.
前記携帯幾何情報算出部は、前記携帯電波受信部が出力した前記方向毎受信強度から、前記携帯電話方向を算出する請求項1または2に記載の測位端末。 The portable radio wave receiving unit is equipped with a directional antenna such as an array antenna showing a high received radio wave intensity with respect to the direction of the source of the portable radio wave, and outputs the reception intensity for each direction when the portable radio wave is received from the mobile phone. And
It said portable geometric information calculation unit, wherein the said direction each reception strength portable radio receiver has an output, the positioning terminal according to claim 1 or 2 calculates the mobile phone direction.
前記携帯位置算出部は、前記自身の測位端末の前記基本情報および前記他の測位端末から取得した前記基本情報に基づいて、携帯電話位置を算出し、
前記端末移動計画部は、前記自身の測位端末の前記基本情報および前記他の測位端末から取得した前記基本情報と、前記自身の測位端末が算出した前記携帯位置情報および前記他の測位端末から取得した前記携帯位置情報と、のいずれかまたは両方を用いて、次に携帯電波を受信する地点を算出し、算出した次に携帯電波を受信する地点を目的地として、前記測位端末の位置の最新値から前記測位端末を誘導する移動計画データを生成する請求項1から3のいずれか1項に記載の測位端末。 A communication unit that transmits the basic information of the positioning terminal and the mobile location information to another positioning terminal, and receives and stores the basic information and the mobile location information of the other positioning terminal;
The mobile position calculation unit calculates a mobile phone position based on the basic information of the positioning terminal of itself and the basic information acquired from the other positioning terminal,
The terminal movement planning unit acquires the basic information acquired from the positioning terminal and the basic information acquired from the other positioning terminal, the portable position information calculated by the positioning terminal and the other positioning terminal. Using the mobile location information, or both, the next location for receiving the mobile radio wave is calculated, and the next location for receiving the next mobile radio wave is calculated as the destination and the latest location of the positioning terminal is calculated. The positioning terminal of any one of Claim 1 to 3 which produces | generates the movement plan data which guides the said positioning terminal from a value.
前記端末移動計画部は、前記自身の測位端末の前記基本情報および前記他の測位端末から取得した前記基本情報と、前記自身の測位端末が算出した前記携帯位置情報および前記他の測位端末から取得した前記携帯位置情報と、のいずれかまたは両方を用いて、前記自身の測位端末と前記他の測位端末のそれぞれについて次に携帯電波を受信する地点を算出し、前記端末IDごとの前記移動計画データを生成し、
前記端末誘導部は、前記端末IDごとの移動計画データのうち、前記自身の測位端末の前記端末IDの前記移動計画データを出力する請求項4に記載の測位端末。 The communication unit transmits the latest position information that associates the terminal ID and the latest value of the position of the positioning terminal to the other positioning terminal, receives the latest position information from the other positioning terminal,
The terminal movement planning unit acquires the basic information acquired from the positioning terminal and the basic information acquired from the other positioning terminal, the portable position information calculated by the positioning terminal and the other positioning terminal. Using the mobile location information, or both of the mobile location information, the next location for receiving mobile radio waves is calculated for each of the own positioning terminal and the other positioning terminal, and the movement plan for each terminal ID is calculated. Generate data,
The positioning terminal according to claim 4 , wherein the terminal guiding unit outputs the movement plan data of the terminal ID of the own positioning terminal among movement plan data for each terminal ID.
前記端末誘導部は、前記端末移動計画部が生成した前記端末IDごとの前記移動計画データ、または、前記他の測位端末から受信した前記端末IDごとの前記移動計画データのうち、前記自身の測位端末の前記端末IDの前記移動計画データを出力する請求項5に記載の測位端末。 The communication unit transmits the movement plan data for each terminal ID generated by the terminal movement planning unit to the other positioning terminal, and receives the movement plan data for each terminal ID from the other positioning terminal. ,
The terminal guidance unit includes the positioning information of the movement planning data for each terminal ID generated by the terminal movement planning unit or the movement planning data for each terminal ID received from the other positioning terminal. The positioning terminal according to claim 5 , wherein the movement plan data of the terminal ID of the terminal is output.
前記測位端末は、
前記測位衛星から測距信号を受信し、前記測距信号から、前記測位衛星に対する擬似距離観測量、搬送波位相観測量、および、航法メッセージを取得する測距信号受信部と、
前記擬似距離観測量、前記搬送波位相観測量および前記航法メッセージを用いて前記測位端末の位置、速度、および、時計誤差を算出する端末位置算出部と、
携帯電話が発する携帯電波を受信する携帯電波受信部と、
前記携帯電波受信部が受信した携帯電波から、前記携帯電話を識別する携帯IDを取得する携帯ID判別部と、
前記端末位置算出部が算出した前記測位端末の時計誤差と前記携帯電波受信部が受信した携帯電波とから、前記測位端末に対する前記携帯電話の携帯電話距離または携帯電話方向を算出する携帯幾何情報算出部と、
前記端末位置算出部が算出した前記測位端末の位置と前記携帯ID判別部が取得した前記携帯IDと前記携帯幾何情報算出部が算出した前記携帯電話距離または前記携帯電話方向とを含む基本情報を生成する基本情報生成部と、
前記基本情報のうち、前記携帯IDが同じ2つ以上の前記基本情報から、前記携帯IDに該当する前記携帯電話の位置を算出し、前記携帯IDと算出した前記携帯電話の位置とを含む携帯位置情報を生成する携帯位置算出部と、
前記基本情報および前記携帯位置情報と、前記測位端末を識別する端末IDおよび前記測位端末の位置の最新値を対応付けた最新位置情報とを前記サーバに送信する第1送信部と、
前記サーバから、前記測位端末を誘導する移動計画データを受信する第1受信部と、
前記移動計画データを出力する端末誘導部と、
を備え、
前記サーバは、
前記測位端末から前記基本情報および前記携帯位置情報と、前記最新位置情報とを受信する第2受信部と、
前記第2受信部が受信した、前記基本情報と前記携帯位置情報と、のいずれかまたは両方を用いて、前記測位端末について次に携帯電波を受信する地点を算出し、算出した次に携帯電波を受信する地点を目的地として、前記最新位置情報が示す前記測位端末の位置の最新値から前記測位端末を誘導する、前記端末IDごとの前記移動計画データを生成する端末移動計画部と、
前記移動計画データを該当する前記端末IDの前記測位端末に送信する第2送信部と、
を備え、
前記端末移動計画部は、前記携帯IDが同じ2つの前記基本情報が得られて3つめの地点を求める場合、前記測位端末の位置、前記携帯電話距離の差を一定とする双曲線の漸近線および携帯電波の発信時間間隔で前記測位端末が移動可能な距離から次に携帯電波を受信する地点を求め、
前記端末移動計画部は、前記携帯IDが異なる2つ以上の前記基本情報または前記携帯位置情報がある場合、前記携帯IDが同じである前記基本情報が少ない前記携帯IDの前記基本情報または前記携帯位置情報を用いて、次に携帯電波を受信する地点を算出し、算出した次に携帯電波を受信する地点を目的地として、前記測位端末の位置の最新値から前記測位端末を誘導する移動計画データを生成する、
携帯電話探索システム。 A mobile phone search system comprising a positioning terminal and a server that can communicate with and move with a plurality of positioning satellites,
The positioning terminal is
A ranging signal receiving unit that receives a ranging signal from the positioning satellite, and obtains a pseudorange observation amount, a carrier phase observation amount, and a navigation message for the positioning satellite from the ranging signal;
A terminal position calculation unit that calculates the position, speed, and clock error of the positioning terminal using the pseudorange observation amount, the carrier phase observation amount, and the navigation message;
A mobile radio wave receiver for receiving mobile radio waves emitted by a mobile phone;
A mobile ID discriminating unit for acquiring a mobile ID for identifying the mobile phone from the mobile radio wave received by the mobile radio wave receiving unit;
Mobile geometric information calculation for calculating a mobile phone distance or a mobile phone direction of the mobile phone relative to the positioning terminal from a clock error of the positioning terminal calculated by the terminal position calculation unit and a mobile radio wave received by the mobile radio wave reception unit And
Basic information including the position of the positioning terminal calculated by the terminal position calculation unit, the mobile ID acquired by the mobile ID determination unit, and the mobile phone distance or the mobile phone direction calculated by the mobile geometric information calculation unit. A basic information generation unit to generate;
Of the basic information, the position of the mobile phone corresponding to the mobile ID is calculated from two or more pieces of the basic information having the same mobile ID, and the mobile including the mobile ID and the calculated position of the mobile phone A portable position calculation unit for generating position information;
A first transmitter that transmits the basic information and the portable position information, a terminal ID for identifying the positioning terminal, and the latest position information that associates the latest value of the position of the positioning terminal to the server;
A first receiving unit for receiving movement plan data for guiding the positioning terminal from the server;
A terminal guidance unit for outputting the movement plan data;
With
The server
A second receiving unit that receives the basic information and the mobile location information and the latest location information from the positioning terminal;
Using the basic information and / or the mobile location information received by the second receiving unit, a location for receiving the next mobile radio wave is calculated for the positioning terminal, and then the mobile radio wave is calculated. A terminal movement planning unit that generates the movement plan data for each terminal ID, which guides the positioning terminal from the latest value of the position of the positioning terminal indicated by the latest position information, with the point of receiving the destination as a destination,
A second transmitter for transmitting the movement plan data to the positioning terminal of the corresponding terminal ID;
With
The terminal movement planning unit, when two basic information with the same mobile ID is obtained and a third point is obtained, a hyperbolic asymptotic line with a constant difference between the position of the positioning terminal and the mobile phone distance; Find the next point to receive mobile radio waves from the distance that the positioning terminal can move at the mobile radio wave transmission time interval ,
When there are two or more pieces of the basic information or the mobile location information having different mobile IDs, the terminal movement planning unit has the basic information with the same mobile ID and the basic information of the mobile ID or the mobile Using the location information, the next location for receiving the mobile radio wave is calculated, and the next location for receiving the mobile radio wave is calculated as a destination, and the movement plan for guiding the positioning terminal from the latest value of the location of the positioning terminal Generate data,
Mobile phone search system.
携帯電話を識別する携帯IDおよび前記携帯電話の位置を含む携帯位置情報を集約管理するセンタと、
請求項1から9のいずれか1項に記載の測位端末と、
を備え、
前記測位端末は、
前記携帯位置情報を前記多機能測位衛星に伝送する携帯位置情報送信部をさらに備え、
前記多機能測位衛星は、前記測位端末との双方向の通信機能を保有し、前記測位端末から前記携帯位置情報を受信して前記センタに伝送し、
前記センタは、
前記多機能測位衛星から前記携帯位置情報を受信する携帯位置情報受信部と、
前記携帯位置情報受信部が受信した前記携帯位置情報を保存する携帯位置情報記憶部と、
を備える携帯電話探索システム。 Multi-function positioning satellite,
A center for centrally managing mobile location information including a mobile ID for identifying a mobile phone and the location of the mobile phone;
The positioning terminal according to any one of claims 1 to 9 ,
With
The positioning terminal is
A portable position information transmitter for transmitting the portable position information to the multifunctional positioning satellite;
The multi-function positioning satellite has a bidirectional communication function with the positioning terminal, receives the portable position information from the positioning terminal and transmits it to the center,
The center is
A portable position information receiving unit for receiving the portable position information from the multi-function positioning satellite;
A portable position information storage unit for storing the portable position information received by the portable position information receiving unit;
A mobile phone search system comprising:
前記測位衛星から測距信号を受信し、前記測距信号から、前記測位衛星に対する擬似距離観測量、搬送波位相観測量、および、航法メッセージを取得する測距信号受信ステップと、
前記擬似距離観測量、前記搬送波位相観測量および前記航法メッセージを用いて前記測位端末の位置、速度、および、時計誤差を算出する端末位置算出ステップと、
携帯電話が発する携帯電波を受信する携帯電波受信ステップと、
前記携帯電波受信ステップで受信した携帯電波から、前記携帯電話を識別する携帯IDを取得する携帯ID判別ステップと、
前記端末位置算出ステップで算出した前記測位端末の時計誤差と前記携帯電波受信ステップで受信した携帯電波とから、前記測位端末に対する前記携帯電話の携帯電話距離または携帯電話方向を算出する携帯幾何情報算出ステップと、
前記端末位置算出ステップで算出した前記測位端末の位置と前記携帯ID判別ステップで取得した前記携帯IDと前記携帯幾何情報算出ステップで算出した前記携帯電話距離または前記携帯電話方向とを含む基本情報を生成する基本情報生成ステップと、
前記基本情報のうち、前記携帯IDが同じ2つ以上の前記基本情報から、前記携帯IDに該当する前記携帯電話の位置を算出し、前記携帯IDと算出した前記携帯電話の位置とを含む携帯位置情報を生成する携帯位置算出ステップと、
前記基本情報と前記携帯位置情報との、いずれかまたは両方を用いて、次に携帯電波を受信する地点を算出し、算出した次に携帯電波を受信する地点を目的地として、前記測位端末の位置の最新値から前記測位端末を誘導する移動計画データを生成する端末移動計画ステップと、
前記移動計画データを出力する端末誘導ステップと、
を備え、
前記端末移動計画ステップでは、前記携帯IDが同じ2つの前記基本情報が得られて3つめの地点を求める場合、前記測位端末の位置、前記携帯電話距離の差を一定とする双曲線の漸近線および携帯電波の発信時間間隔で前記測位端末が移動可能な距離から次に携帯電波を受信する地点を求め、
前記端末移動計画ステップでは、前記携帯IDが異なる2つ以上の前記基本情報または前記携帯位置情報がある場合、前記携帯IDが同じである前記基本情報が少ない前記携帯IDの前記基本情報または前記携帯位置情報を用いて、次に携帯電波を受信する地点を算出し、算出した次に携帯電波を受信する地点を目的地として、前記測位端末の位置の最新値から前記測位端末を誘導する移動計画データを生成する、
携帯電話探索方法。 A mobile phone search method executed by a mobile positioning terminal that can communicate with a plurality of positioning satellites,
A ranging signal receiving step for receiving a ranging signal from the positioning satellite, and obtaining a pseudorange observation amount, a carrier phase observation amount, and a navigation message for the positioning satellite from the ranging signal;
A terminal position calculating step of calculating a position, speed, and clock error of the positioning terminal using the pseudorange observable, the carrier phase observable, and the navigation message;
A portable radio wave receiving step for receiving a portable radio wave emitted by a mobile phone;
A mobile ID determination step for acquiring a mobile ID for identifying the mobile phone from the mobile radio wave received in the mobile radio wave reception step;
Mobile geometric information calculation for calculating the mobile phone distance or the mobile phone direction of the mobile phone relative to the positioning terminal from the clock error of the positioning terminal calculated in the terminal position calculating step and the mobile radio wave received in the mobile radio wave receiving step. Steps,
Basic information including the position of the positioning terminal calculated in the terminal position calculating step, the mobile ID acquired in the mobile ID determining step, and the mobile phone distance or the mobile phone direction calculated in the mobile geometric information calculating step. A basic information generation step to generate;
Of the basic information, the position of the mobile phone corresponding to the mobile ID is calculated from two or more pieces of the basic information having the same mobile ID, and the mobile including the mobile ID and the calculated position of the mobile phone A portable position calculating step for generating position information;
Using either or both of the basic information and the mobile location information, the next location for receiving mobile radio waves is calculated, and the next location for receiving mobile radio waves is calculated as the destination. A terminal movement plan step for generating movement plan data for guiding the positioning terminal from the latest value of the position;
A terminal guidance step for outputting the movement plan data;
With
In the terminal movement planning step, when two basic information having the same mobile ID is obtained and a third point is obtained, a hyperbolic asymptotic line with a constant difference between the position of the positioning terminal and the mobile phone distance, and Find the next point to receive mobile radio waves from the distance that the positioning terminal can move at the mobile radio wave transmission time interval ,
In the terminal movement planning step, when there are two or more pieces of the basic information or the mobile location information having different mobile IDs, the basic information of the mobile ID or the mobile phone having the same basic mobile ID is small. Using the location information, the next location for receiving the mobile radio wave is calculated, and the next location for receiving the mobile radio wave is calculated as a destination, and the movement plan for guiding the positioning terminal from the latest value of the location of the positioning terminal Generate data,
Mobile phone search method.
前記測位衛星から測距信号を受信し、前記測距信号から、前記測位衛星に対する擬似距離観測量、搬送波位相観測量、および、航法メッセージを取得する測距信号受信部、
前記擬似距離観測量、前記搬送波位相観測量および前記航法メッセージを用いて前記コンピュータの位置、速度、および、時計誤差を算出する端末位置算出部、
携帯電話が発する携帯電波を受信する携帯電波受信部、
前記携帯電波受信部が受信した携帯電波から、前記携帯電話を識別する携帯IDを取得する携帯ID判別部、
前記端末位置算出部が算出した前記コンピュータの時計誤差と前記携帯電波受信部が受信した携帯電波とから、前記コンピュータに対する前記携帯電話の携帯電話距離または携帯電話方向を算出する携帯幾何情報算出部、
前記端末位置算出部が算出した前記コンピュータの位置と前記携帯ID判別部が取得した前記携帯IDと前記携帯幾何情報算出部が算出した前記携帯電話距離または前記携帯電話方向とを含む基本情報を生成する基本情報生成部、
前記基本情報のうち、前記携帯IDが同じ2つ以上の前記基本情報から、前記携帯IDに該当する前記携帯電話の位置を算出し、前記携帯IDと算出した前記携帯電話の位置とを含む携帯位置情報を生成する携帯位置算出部、
前記基本情報と前記携帯位置情報との、いずれかまたは両方を用いて、前記携帯IDが同じ2つの前記基本情報が得られて3つめの地点を求める場合、前記コンピュータの位置、前記携帯電話距離の差を一定とする双曲線の漸近線および携帯電波の発信時間間隔で前記コンピュータが移動可能な距離から次に携帯電波を受信する地点を算出し、前記携帯IDが異なる2つ以上の前記基本情報または前記携帯位置情報がある場合、前記携帯IDが同じである前記基本情報が少ない前記携帯IDの前記基本情報または前記携帯位置情報を用いて、次に携帯電波を受信する地点を算出し、算出した次に携帯電波を受信する地点を目的地として、前記コンピュータの位置の最新値から前記コンピュータを誘導する移動計画データを生成する端末移動計画部、および、
前記移動計画データを出力する端末誘導部、
として機能させるプログラム。 A mobile computer that can communicate with multiple positioning satellites
A ranging signal receiving unit that receives a ranging signal from the positioning satellite and obtains a pseudorange observation amount, a carrier phase observation amount, and a navigation message for the positioning satellite from the ranging signal;
A terminal position calculation unit that calculates the position, speed, and clock error of the computer using the pseudorange observation, the carrier phase observation, and the navigation message;
A mobile radio wave receiver for receiving mobile radio waves emitted by mobile phones,
A mobile ID discriminating unit for acquiring a mobile ID for identifying the mobile phone from the mobile radio wave received by the mobile radio wave receiving unit;
A mobile geometric information calculation unit for calculating a mobile phone distance or a mobile phone direction of the mobile phone relative to the computer from a clock error of the computer calculated by the terminal position calculation unit and a mobile radio wave received by the mobile radio wave reception unit;
Basic information including the computer position calculated by the terminal position calculation unit, the mobile ID acquired by the mobile ID determination unit, and the mobile phone distance or the mobile phone direction calculated by the mobile geometric information calculation unit is generated. A basic information generator,
Of the basic information, the position of the mobile phone corresponding to the mobile ID is calculated from two or more pieces of the basic information having the same mobile ID, and the mobile including the mobile ID and the calculated position of the mobile phone A portable position calculation unit for generating position information;
When the basic information and the mobile location information are used to obtain a third point by obtaining the two basic information having the same mobile ID, the location of the computer, the mobile phone distance A point at which the computer receives the next mobile radio wave from a hyperbolic asymptote and a mobile radio wave transmission time interval with a constant difference between the two, and two or more pieces of the basic information having different mobile IDs Alternatively, when the mobile location information is present, the mobile information is calculated using the basic information or the mobile location information of the mobile ID having the same mobile ID and the basic information being less, Then, a terminal mobile meter that generates movement plan data for guiding the computer from the latest value of the position of the computer, with a point where a portable radio wave is received next as a destination Parts, and,
A terminal guidance unit for outputting the movement plan data;
Program to function as.
前記測位端末から、前記測位端末の位置、携帯電話を識別する携帯IDおよび前記測位端末に対する前記携帯電話の携帯電話距離または携帯電話方向を含む基本情報、前記携帯IDおよび前記携帯電話の位置を含む携帯位置情報、ならびに、前記基本情報および前記携帯位置情報と前記測位端末を識別する端末IDおよび前記測位端末の位置の最新値とを対応付けた最新位置情報、を受信する受信部と、
前記受信部が受信した、前記測位端末の基本情報および前記携帯位置情報のいずれかまたは両方を用いて、前記測位端末について次の携帯電波を受信する地点を算出し、算出した次に携帯電波を受信する地点を目的地として、前記最新位置情報が示す前記測位端末の位置の最新値から前記測位端末を誘導する、前記端末IDごとの前記移動計画データを生成する端末移動計画部と、
前記移動計画データを該当する前記端末IDの前記測位端末に送信する送信部とを備え、
前記端末移動計画部は、前記携帯IDが同じ2つの前記基本情報が得られて3つめの地点を求める場合、前記測位端末の位置、前記携帯電話距離の差を一定とする双曲線の漸近線および携帯電波の発信時間間隔で前記測位端末が移動可能な距離から次に携帯電波を受信する地点を求め、
前記端末移動計画部は、前記携帯IDが異なる2つ以上の前記基本情報または前記携帯位置情報がある場合、前記携帯IDが同じである前記基本情報が少ない前記携帯IDの前記基本情報または前記携帯位置情報を用いて、次に携帯電波を受信する地点を算出し、算出した次に携帯電波を受信する地点を目的地として、前記測位端末の位置の最新値から前記測位端末を誘導する移動計画データを生成する、
サーバ。 A server that communicates with a plurality of positioning satellites and with a movable positioning terminal,
From the positioning terminal, including the position of the positioning terminal, a mobile ID for identifying a mobile phone, and basic information including the mobile phone distance or mobile phone direction of the mobile phone relative to the positioning terminal, the mobile ID and the location of the mobile phone A receiver that receives portable position information, and the latest position information that associates the basic information and the portable position information with a terminal ID that identifies the positioning terminal and the latest value of the position of the positioning terminal;
Using either or both of the basic information of the positioning terminal and the mobile location information received by the receiving unit, the location for receiving the next mobile radio wave is calculated for the positioning terminal, and then the mobile radio wave is calculated. A terminal movement planning unit that generates the movement plan data for each terminal ID, with the receiving point as a destination, guiding the positioning terminal from the latest value of the position of the positioning terminal indicated by the latest position information;
A transmission unit for transmitting the movement plan data to the positioning terminal corresponding to the terminal ID,
The terminal movement planning unit, when two basic information with the same mobile ID is obtained and a third point is obtained, a hyperbolic asymptotic line with a constant difference between the position of the positioning terminal and the mobile phone distance; Find the next point to receive mobile radio waves from the distance that the positioning terminal can move at the mobile radio wave transmission time interval ,
When there are two or more pieces of the basic information or the mobile location information having different mobile IDs, the terminal movement planning unit has the basic information with the same mobile ID and the basic information of the mobile ID or the mobile Using the location information, the next location for receiving the mobile radio wave is calculated, and the next location for receiving the mobile radio wave is calculated as a destination, and the movement plan for guiding the positioning terminal from the latest value of the location of the positioning terminal Generate data,
server.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013257243A JP6169962B2 (en) | 2013-12-12 | 2013-12-12 | Positioning terminal, mobile phone search system, mobile phone search method, program, and server |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013257243A JP6169962B2 (en) | 2013-12-12 | 2013-12-12 | Positioning terminal, mobile phone search system, mobile phone search method, program, and server |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017127339A Division JP6440777B2 (en) | 2017-06-29 | 2017-06-29 | Positioning terminal, mobile phone search system, mobile phone search method, program, and server |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2015114899A JP2015114899A (en) | 2015-06-22 |
| JP2015114899A5 JP2015114899A5 (en) | 2016-01-14 |
| JP6169962B2 true JP6169962B2 (en) | 2017-07-26 |
Family
ID=53528630
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013257243A Active JP6169962B2 (en) | 2013-12-12 | 2013-12-12 | Positioning terminal, mobile phone search system, mobile phone search method, program, and server |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6169962B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3457162A4 (en) * | 2016-05-11 | 2020-04-22 | Alps Alpine Co., Ltd. | Position measurement device |
| CN105957338A (en) * | 2016-06-07 | 2016-09-21 | 北京智驾互联信息服务有限公司 | Vehicle rescue method and system |
| CN109917425A (en) * | 2019-01-11 | 2019-06-21 | 丰疆智慧农业股份有限公司 | The system and method for detecting distance between intelligent agricultural machinery and remote terminal |
| CN113808423B (en) * | 2021-09-18 | 2022-10-11 | 公安部道路交通安全研究中心 | Emergency rescue channel scheduling decision system based on high-precision map |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3595093B2 (en) * | 1997-01-30 | 2004-12-02 | 株式会社東芝 | GPS satellite location system |
| JP2001330657A (en) * | 2000-05-19 | 2001-11-30 | Futoshi Uenishi | System for grasping position of phs or portable telephone |
| JP2004309364A (en) * | 2003-04-09 | 2004-11-04 | Hitachi Ltd | Positioning system |
| JP3872045B2 (en) * | 2003-08-07 | 2007-01-24 | 埼玉日本電気株式会社 | A portable wireless terminal equipped with an arrival direction estimation function |
| US7616155B2 (en) * | 2006-12-27 | 2009-11-10 | Bull Jeffrey F | Portable, iterative geolocation of RF emitters |
| JP2011043955A (en) * | 2009-08-20 | 2011-03-03 | Hitachi Ltd | Device for supporting rescue of person in distress, support system, and support method |
| JP2011112387A (en) * | 2009-11-24 | 2011-06-09 | Navitime Japan Co Ltd | Navigation system, route search server, terminal, method of navigation, and navigation device |
| JP2013101013A (en) * | 2011-11-08 | 2013-05-23 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Position orientation device, on-vehicle unit, position orientation method, position orientation program, driving support method, driving support program, road accounting method, road accounting program, position orientation system, driving support system and road accounting system |
-
2013
- 2013-12-12 JP JP2013257243A patent/JP6169962B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2015114899A (en) | 2015-06-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN106255065B (en) | Indoor and outdoor seamless positioning system and method for smart phone | |
| US7953327B2 (en) | Commissioning tool, commissioning system and method of commissioning a number of wireless nodes | |
| Zwirello et al. | Sensor data fusion in UWB-supported inertial navigation systems for indoor navigation | |
| US10564287B2 (en) | Positional measurement system, positional measurement method, and mobile robot | |
| JP2011047922A (en) | Method and device for using gnss satellite trajectory extension information | |
| JP2018189639A (en) | Method, program, and computer system for determining positions of beacons | |
| JP6169962B2 (en) | Positioning terminal, mobile phone search system, mobile phone search method, program, and server | |
| JP2018040785A (en) | Position measurement system, position measurement method and mobile robot | |
| JP6440777B2 (en) | Positioning terminal, mobile phone search system, mobile phone search method, program, and server | |
| JP5691517B2 (en) | POSITION ESTIMATION PROGRAM, POSITION ESTIMATION DEVICE, AND POSITION ESTIMATION METHOD | |
| KR20190094684A (en) | System for measuring position | |
| US9588228B2 (en) | Method of positioning and electronic apparatus using the same | |
| Zwirello et al. | Study on UWB/INS integration techniques | |
| Yang et al. | Resilient smartphone positioning using native sensors and PPP augmentation | |
| CN111765905A (en) | Method for calibrating array elements of unmanned aerial vehicle in air | |
| JP2017122581A (en) | Positioning location verification processing system | |
| US11255665B2 (en) | Systems and methods for determining where to place atmospheric sensors used to estimate an altitude of a mobile device in an environment | |
| US20130176169A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for mobile navigation using smart phone | |
| RU137394U1 (en) | DEVICE FOR PROCESSING INFORMATION OF NETWORK DISTANCED IN THE SPACE OF PELENGATION POST | |
| JP2017009561A (en) | Measuring device, measuring method and measuring program | |
| EP2569958B1 (en) | Method, computer program and apparatus for determining an object in sight | |
| KR101058098B1 (en) | A terminal and a system for measuring its own location according to the location information of another terminal and the reliability of the location information and a method for measuring the location | |
| JP4341720B1 (en) | Surveying system using GPS mobile phone | |
| JP4237581B2 (en) | Positioning device | |
| CN104833995A (en) | Passive area geographic information acquiring system based on Android platform and method thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20151120 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20151120 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20160822 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20160830 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20161028 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20170117 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20170302 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20170530 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20170629 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6169962 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |