JP5805065B2 - Fasteners made of polymer material - Google Patents
Fasteners made of polymer material Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5805065B2 JP5805065B2 JP2012502607A JP2012502607A JP5805065B2 JP 5805065 B2 JP5805065 B2 JP 5805065B2 JP 2012502607 A JP2012502607 A JP 2012502607A JP 2012502607 A JP2012502607 A JP 2012502607A JP 5805065 B2 JP5805065 B2 JP 5805065B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- fastener
- group
- kink
- phenylene
- arylene
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000002861 polymer material Substances 0.000 title claims description 19
- 125000000732 arylene group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 83
- 229920000412 polyarylene Polymers 0.000 claims description 48
- 125000001424 substituent group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 36
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 31
- 125000005649 substituted arylene group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 27
- 125000001989 1,3-phenylene group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([*:1])=C([H])C([*:2])=C1[H] 0.000 claims description 15
- 125000001140 1,4-phenylene group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([*:2])=C([H])C([H])=C1[*:1] 0.000 claims description 12
- RWCCWEUUXYIKHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzophenone Chemical group C=1C=CC=CC=1C(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 RWCCWEUUXYIKHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 11
- 125000002030 1,2-phenylene group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([*:1])=C([*:2])C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 claims description 3
- -1 polyphenylene Polymers 0.000 description 54
- 125000001183 hydrocarbyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 30
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 22
- 229920000265 Polyparaphenylene Polymers 0.000 description 17
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 17
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 17
- 125000003118 aryl group Chemical group 0.000 description 11
- 125000001997 phenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(*)C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 11
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 11
- 239000004696 Poly ether ether ketone Substances 0.000 description 10
- 150000002576 ketones Chemical class 0.000 description 10
- 229920002530 polyetherether ketone Polymers 0.000 description 10
- 229920000049 Carbon (fiber) Polymers 0.000 description 9
- 125000004432 carbon atom Chemical group C* 0.000 description 9
- 239000004917 carbon fiber Substances 0.000 description 9
- VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N methane Chemical compound C VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 7
- 230000007797 corrosion Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000005260 corrosion Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 7
- 125000005843 halogen group Chemical group 0.000 description 6
- 239000012744 reinforcing agent Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 5
- 125000006575 electron-withdrawing group Chemical group 0.000 description 5
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 125000002877 alkyl aryl group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 125000003710 aryl alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 150000001721 carbon Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 125000001309 chloro group Chemical group Cl* 0.000 description 4
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 4
- 125000000843 phenylene group Chemical group C1(=C(C=CC=C1)*)* 0.000 description 4
- 230000002787 reinforcement Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000010079 rubber tapping Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 4
- UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Benzene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1 UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chlorine atom Chemical compound [Cl] ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylformamide Chemical compound CN(C)C=O ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 3
- 125000002947 alkylene group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 150000003863 ammonium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000000460 chlorine Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052801 chlorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000005227 gel permeation chromatography Methods 0.000 description 3
- 125000002887 hydroxy group Chemical group [H]O* 0.000 description 3
- 238000001746 injection moulding Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000000314 lubricant Substances 0.000 description 3
- 125000005650 substituted phenylene group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- OCJBOOLMMGQPQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-dichlorobenzene Chemical compound ClC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 OCJBOOLMMGQPQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- SYCQGUJFSLJURL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,5-dichloro-5-phenylcyclohexa-1,3-diene Chemical group C1=CC(Cl)=CCC1(Cl)C1=CC=CC=C1 SYCQGUJFSLJURL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Bromine atom Chemical compound [Br] WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- SECXISVLQFMRJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Methylpyrrolidone Chemical compound CN1CCCC1=O SECXISVLQFMRJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 241001417523 Plesiopidae Species 0.000 description 2
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 2
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrahydrofuran Chemical compound C1CCOC1 WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000001154 acute effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N bromine Substances BrBr GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052794 bromium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 125000002915 carbonyl group Chemical group [*:2]C([*:1])=O 0.000 description 2
- 150000001244 carboxylic acid anhydrides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920001577 copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000001125 extrusion Methods 0.000 description 2
- 210000003811 finger Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000003063 flame retardant Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003365 glass fiber Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000009477 glass transition Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 description 2
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000003754 machining Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000010128 melt processing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000005575 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 230000002829 reductive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000779 smoke Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000003381 solubilizing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 125000006850 spacer group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000001174 sulfone group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 229920001169 thermoplastic Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 210000003813 thumb Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000013585 weight reducing agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002023 wood Substances 0.000 description 2
- WIPXWWURGIFNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N (1-chlorocyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-yl)-(4-chlorophenyl)methanone;(2,5-dichlorophenyl)-phenylmethanone Chemical compound C1=CC(Cl)=CC=C1C(=O)C1(Cl)C=CC=CC1.ClC1=CC=C(Cl)C(C(=O)C=2C=CC=CC=2)=C1 WIPXWWURGIFNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZPQOPVIELGIULI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-dichlorobenzene Chemical compound ClC1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1 ZPQOPVIELGIULI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RNFJDJUURJAICM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,2,4,4,6,6-hexaphenoxy-1,3,5-triaza-2$l^{5},4$l^{5},6$l^{5}-triphosphacyclohexa-1,3,5-triene Chemical compound N=1P(OC=2C=CC=CC=2)(OC=2C=CC=CC=2)=NP(OC=2C=CC=CC=2)(OC=2C=CC=CC=2)=NP=1(OC=1C=CC=CC=1)OC1=CC=CC=C1 RNFJDJUURJAICM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GVLZQVREHWQBJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3,5-dimethyl-7-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]hepta-1,3,5-triene Chemical compound CC1=C(O2)C(C)=CC2=C1 GVLZQVREHWQBJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZCYVEMRRCGMTRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7553-56-2 Chemical compound [I] ZCYVEMRRCGMTRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LSNNMFCWUKXFEE-UHFFFAOYSA-M Bisulfite Chemical compound OS([O-])=O LSNNMFCWUKXFEE-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000004215 Carbon black (E152) Substances 0.000 description 1
- XTHFKEDIFFGKHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethoxyethane Chemical compound COCCOC XTHFKEDIFFGKHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MYMOFIZGZYHOMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dioxygen Chemical compound O=O MYMOFIZGZYHOMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorine Chemical compound FF PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000015842 Hesperis Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000012633 Iberis amara Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920000106 Liquid crystal polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004977 Liquid-crystal polymers (LCPs) Substances 0.000 description 1
- 241001417935 Platycephalidae Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000004952 Polyamide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004962 Polyamide-imide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004693 Polybenzimidazole Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002614 Polyether block amide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004695 Polyether sulfone Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004697 Polyetherimide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004642 Polyimide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004734 Polyphenylene sulfide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000491 Polyphenylsulfone Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004954 Polyphthalamide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004743 Polypropylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004793 Polystyrene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910010413 TiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000006096 absorbing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002318 adhesion promoter Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000003545 alkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000003973 alkyl amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000004983 alkyl aryl ketones Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000005248 alkyl aryloxy group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005907 alkyl ester group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000003368 amide group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000001408 amides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000003277 amino group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004103 aminoalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005001 aminoaryl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004653 anthracenylene group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000003963 antioxidant agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002216 antistatic agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000004982 aromatic amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000002102 aryl alkyloxo group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000007860 aryl ester derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000005362 aryl sulfone group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005325 aryloxy aryl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004104 aryloxy group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000000712 assembly Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000429 assembly Methods 0.000 description 1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000751 azo group Chemical group [*]N=N[*] 0.000 description 1
- 125000006267 biphenyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000006229 carbon black Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011203 carbon fibre reinforced carbon Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001732 carboxylic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000001735 carboxylic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000003636 chemical group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000003638 chemical reducing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010411 cooking Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000005690 diesters Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005553 drilling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000975 dye Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920001971 elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000010292 electrical insulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000005678 ethenylene group Chemical group [H]C([*:1])=C([H])[*:2] 0.000 description 1
- 125000001495 ethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 125000000219 ethylidene group Chemical group [H]C(=[*])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 239000000945 filler Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007667 floating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011737 fluorine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- NBVXSUQYWXRMNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N fluoromethane Chemical group FC NBVXSUQYWXRMNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000013305 food Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 125000002485 formyl group Chemical class [H]C(*)=O 0.000 description 1
- 239000003574 free electron Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010528 free radical solution polymerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004927 fusion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000001188 haloalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005067 haloformyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000012760 heat stabilizer Substances 0.000 description 1
- GNOIPBMMFNIUFM-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexamethylphosphoric triamide Chemical compound CN(C)P(=O)(N(C)C)N(C)C GNOIPBMMFNIUFM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical group [H]* 0.000 description 1
- 125000002768 hydroxyalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005027 hydroxyaryl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000001023 inorganic pigment Substances 0.000 description 1
- PNDPGZBMCMUPRI-UHFFFAOYSA-N iodine Chemical compound II PNDPGZBMCMUPRI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052740 iodine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011630 iodine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000000959 isobutyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001449 isopropyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 239000003562 lightweight material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002521 macromolecule Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002923 metal particle Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 239000006082 mold release agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000004108 n-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 125000004123 n-propyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001624 naphthyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004957 naphthylene group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 231100000252 nontoxic Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 230000003000 nontoxic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002667 nucleating agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- OCDRLZFZBHZTKQ-NMUBGGKPSA-N onetine Chemical compound C[C@@H](O)[C@@]1(O)C[C@@H](C)[C@@](C)(O)C(=O)OC\C2=C\CN(C)CC[C@@H](OC1=O)C2=O OCDRLZFZBHZTKQ-NMUBGGKPSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000012860 organic pigment Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003960 organic solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- MPQXHAGKBWFSNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxidophosphanium Chemical group [PH3]=O MPQXHAGKBWFSNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000005562 phenanthrylene group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920003023 plastic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004014 plasticizer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000110 poly(aryl ether sulfone) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920013655 poly(bisphenol-A sulfone) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001643 poly(ether ketone) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001652 poly(etherketoneketone) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002647 polyamide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002312 polyamide-imide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002480 polybenzimidazole Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004417 polycarbonate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000515 polycarbonate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 125000003367 polycyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229920000728 polyester Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920006393 polyether sulfone Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920005649 polyetherethersulfone Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001601 polyetherimide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001721 polyimide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000000379 polymerizing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920000306 polymethylpentene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000098 polyolefin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001955 polyphenylene ether Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000069 polyphenylene sulfide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920006375 polyphtalamide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001155 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002223 polystyrene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004810 polytetrafluoroethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001343 polytetrafluoroethylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002635 polyurethane Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004814 polyurethane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010248 power generation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000036316 preload Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000002924 primary amino group Chemical group [H]N([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000005548 pyrenylene group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000006578 reductive coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012783 reinforcing fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003252 repetitive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920003252 rigid-rod polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000005060 rubber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007493 shaping process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- BUUPQKDIAURBJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N sulfinic acid Chemical compound OS=O BUUPQKDIAURBJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000003375 sulfoxide group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229910052717 sulfur Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 125000004434 sulfur atom Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000454 talc Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052623 talc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 125000000999 tert-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(*)(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 238000010998 test method Methods 0.000 description 1
- YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrahydrofuran Natural products C=1C=COC=1 YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000005382 thermal cycling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004416 thermosoftening plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 231100000048 toxicity data Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 125000006837 triphenylylene group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G61/00—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming a carbon-to-carbon link in the main chain of the macromolecule
- C08G61/02—Macromolecular compounds containing only carbon atoms in the main chain of the macromolecule, e.g. polyxylylenes
- C08G61/10—Macromolecular compounds containing only carbon atoms in the main chain of the macromolecule, e.g. polyxylylenes only aromatic carbon atoms, e.g. polyphenylenes
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L65/00—Compositions of macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming a carbon-to-carbon link in the main chain; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers
- C08L65/02—Polyphenylenes
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16B—DEVICES FOR FASTENING OR SECURING CONSTRUCTIONAL ELEMENTS OR MACHINE PARTS TOGETHER, e.g. NAILS, BOLTS, CIRCLIPS, CLAMPS, CLIPS OR WEDGES; JOINTS OR JOINTING
- F16B21/00—Means for preventing relative axial movement of a pin, spigot, shaft or the like and a member surrounding it; Stud-and-socket releasable fastenings
- F16B21/10—Means for preventing relative axial movement of a pin, spigot, shaft or the like and a member surrounding it; Stud-and-socket releasable fastenings by separate parts
- F16B21/12—Means for preventing relative axial movement of a pin, spigot, shaft or the like and a member surrounding it; Stud-and-socket releasable fastenings by separate parts with locking-pins or split-pins thrust into holes
- F16B21/14—Details of locking-pins or split-pins
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16B—DEVICES FOR FASTENING OR SECURING CONSTRUCTIONAL ELEMENTS OR MACHINE PARTS TOGETHER, e.g. NAILS, BOLTS, CIRCLIPS, CLAMPS, CLIPS OR WEDGES; JOINTS OR JOINTING
- F16B33/00—Features common to bolt and nut
- F16B33/006—Non-metallic fasteners using screw-thread
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16B—DEVICES FOR FASTENING OR SECURING CONSTRUCTIONAL ELEMENTS OR MACHINE PARTS TOGETHER, e.g. NAILS, BOLTS, CIRCLIPS, CLAMPS, CLIPS OR WEDGES; JOINTS OR JOINTING
- F16B37/00—Nuts or like thread-engaging members
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16B—DEVICES FOR FASTENING OR SECURING CONSTRUCTIONAL ELEMENTS OR MACHINE PARTS TOGETHER, e.g. NAILS, BOLTS, CIRCLIPS, CLAMPS, CLIPS OR WEDGES; JOINTS OR JOINTING
- F16B5/00—Joining sheets or plates, e.g. panels, to one another or to strips or bars parallel to them
- F16B5/02—Joining sheets or plates, e.g. panels, to one another or to strips or bars parallel to them by means of fastening members using screw-thread
- F16B5/0275—Joining sheets or plates, e.g. panels, to one another or to strips or bars parallel to them by means of fastening members using screw-thread the screw-threaded element having at least two axially separated threaded portions
Description
本出願は、2009年3月30日出願の米国仮出願第61/164,599号および2009年3月30日出願の米国仮出願第61/164,601号(これらの出願の全内容がすべての目的で参照により本明細書に組み入れられるものとする)に基づく優先権の特典を請求する。 This application is filed with US Provisional Application No. 61 / 164,599, filed March 30, 2009, and US Provisional Application No. 61 / 164,601, filed March 30, 2009, all of which are incorporated herein by reference. For the purpose of claiming priority benefits based on the above.
本発明は、特定のポリアリーレン材料で作製された締結具に関する。 The present invention relates to a fastener made of a specific polyarylene material.
ナット、ネジ、クリップ、リベット、および多くの他の種類のものを含めて、多くのデザインの締結具が、とくに含まれる用途に応じて利用可能になっている。これらの共通した特徴は、これらに関連するとくに厳しい要件にある。 Many designs of fasteners are available depending on the particular application involved, including nuts, screws, clips, rivets, and many others. These common features lie in the particularly stringent requirements associated with them.
実際には、耐用期間の間、ネジ無しおよびネジ付きの締結具を含めて、いずれの締結具も、とくに、過酷な機械的条件に晒され、伸び、捩れ、および曲げを受ける。締結具はさらに、一般的には、振動、熱サイクル、および/または化学的攻撃などの種々の腐食性環境に晒され、それにより、経時的にその機械的性能が変化し、最悪の想定では、締結具が事実上「消失」することもありうる。 In practice, all fasteners, including unthreaded and threaded fasteners, are exposed to harsh mechanical conditions and undergo elongation, twisting, and bending during their lifetime. Fasteners are also typically exposed to various corrosive environments such as vibration, thermal cycling, and / or chemical attack, which changes their mechanical performance over time, with worst case assumptions. It is also possible that the fastener will effectively “disappear”.
とくに重要な一群の締結具は、そのほかの特有の問題に直面するネジ付き締結具である。ネジ付き締結具を締め付ける場合、我々は、それにエネルギーを付与し、そして解除した後、このエネルギーは、摩擦拘束によりそこに保持される。典型的には、この摩擦拘束は、締結具のネジ部にかなりの程度まで集中し、そのうえ多くの場合、このネジ部は、微細であるがゆえに締結具の最も破損しやすい部分に相当する。以上に述べた腐食性環境因子は、ネジ付き締結具にそのすべての前負荷を解放させ、事実上消失させることもありうる(「緩み」の問題)。緩みにいくらか関連するのは、ネジ付き締結具を締め付けすぎた場合に起こる他の損傷であるネジ山潰れであり、ネジ山潰れは、締結具のネジ部の変形(変化)により特徴付けられ、典型的には、性能の低下を引き起こす。 A particularly important group of fasteners are threaded fasteners that face other unique problems. When tightening a threaded fastener, we apply energy to it and after release, this energy is held there by frictional constraints. Typically, this frictional constraint is concentrated to a significant degree on the threaded portion of the fastener, and in many cases the threaded portion corresponds to the most fragile portion of the fastener due to its fineness. The corrosive environmental factors described above can cause the threaded fastener to release all of its preload and effectively disappear ("loosening" problem). Somewhat related to loosening is thread collapse, another damage that occurs when a threaded fastener is over-tightened, which is characterized by deformation (changes) in the threaded portion of the fastener, Typically, it causes performance degradation.
ネジ無しおよびネジ付きの締結具を含めて、特定の締結具は、複雑なデザインを有することもあり、適切な材料からの造形/機械加工は、厄介な問題になることもある。ネジ付き締結具の場合、微細かつ規則的なネジ部を形成することは、とくに容易でないことがわかっている。 Certain fasteners, including unthreaded and threaded fasteners, can have complex designs, and shaping / machining from the appropriate material can be a daunting problem. In the case of threaded fasteners, it has been found that it is not particularly easy to form fine and regular threaded parts.
材料の選択は、締結具にきわめて重要である。プラスチック材料は、所要のレベルの機械的性質、とくに、高い伸び強度、高い曲げ強度、および最後に忘れてはならないものとして高い捩り強度(またはトルク)を提供することができなかったので、数十年間にわたり金属が唯一の好適な選択肢であった。実際には、限定されるものではないがネジ付き締結具をはじめとする多くの締結具では、耐荷重能力は、典型的には、構成材料の剪断強度または捩り強度の関数である。 The choice of material is critical to the fastener. Since plastic materials have not been able to provide the required level of mechanical properties, in particular high elongation strength, high bending strength, and finally high torsional strength (or torque) that must not be forgotten, tens of For years, metal was the only preferred option. In practice, in many fasteners, including but not limited to threaded fasteners, the load bearing capacity is typically a function of the shear strength or torsional strength of the constituent materials.
しかしながら、金属締結具は、いくつかの欠点を呈する。金属締結具は重いが、これとは対照的に、ある用途、特定的には自走式輸送機関、より特定的には航空機では、軽量材料が要求される。金属締結具は、一般的には腐食を起こしやすく、それに加えて、異種金属を継合一体化した場合、ガルバニック腐食が起こりうる。金属締結具は電気伝導性である。金属からの複雑な形状の機械加工さらには微細かつ規則的なネジ部の形成は、厄介な問題である。 However, metal fasteners present some drawbacks. Metal fasteners are heavy, but in contrast, certain applications, particularly self-propelled transportation, and more particularly aircraft, require lightweight materials. Metal fasteners are generally prone to corrosion, and in addition, galvanic corrosion can occur when dissimilar metals are joined together. The metal fastener is electrically conductive. Machining complex shapes from metal and the formation of fine and regular threads is a troublesome problem.
炭素繊維強化ポリエーテルエーテルケトン(PEEK)などのエンジニアリング複合材料の開発により、それほど要求が厳しくない締結具用途にいくつかの実用可能な代替品が良好に提供されてきた。繊維強化材の添加は、引張り性および曲げ性を良好に増大させるが、剪断性にはほとんど効果がない。それに加えて、繊維強化材は、実用的靭性の尺度である引張り伸びを低減させる。それに加えて、繊維強化材を用いて射出成形プロセスにより締結具を製造した場合、流動方向に起因する性質変動が起こる。それに加えて、締結具がネジ付きである場合、ネジ部は、比較的薄くかつ通常の流動方向に垂直であるので、多量の繊維強化材を含有する可能性が低い。 The development of engineering composites such as carbon fiber reinforced polyetheretherketone (PEEK) has successfully provided several practical alternatives for less demanding fastener applications. The addition of fiber reinforcement increases the tensile and bendability well but has little effect on shear. In addition, fiber reinforcement reduces tensile elongation, a measure of practical toughness. In addition, when a fastener is manufactured by an injection molding process using a fiber reinforcement, property variations due to the direction of flow occur. In addition, when the fastener is threaded, the threaded portion is relatively thin and perpendicular to the normal flow direction, so it is unlikely to contain a large amount of fiber reinforcement.
剛性棒状ポリフェニレンの使用がネジ無し締結具の製造のために初めて提案された時、重要な進歩を遂げた。次に、欧州特許第2014251号明細書には、場合により置換されていてもよいポリパラフェニレン(第一世代の非キンク形剛性棒状ポリフェニレン)、たとえば、
〔式中、RおよびR’は、−C(=O)C6H5などの置換基である〕
などで作製された、医療処置のために生体の一部(たとえば頭部)の位置を固定するためのピンが記載されている。
Significant progress was made when the use of rigid rod-like polyphenylene was first proposed for the manufacture of screwless fasteners. Next, EP 20142511 includes optionally substituted polyparaphenylene (first generation non-kink rigid rod-like polyphenylene), for example,
[Wherein R and R ′ are substituents such as —C (═O) C 6 H 5 ]
A pin for fixing the position of a part of a living body (for example, the head) for medical treatment is described.
Ensingerから市販されているTECAMAX(登録商標)SRPポリフェニレンは、そのような材料であると言われている。それらの剛性分子構造の結果として、欧州特許第2014251号明細書に記載のポリパラフェニレンは、実際に、従来の複合ポリマー材料(たとえば炭素繊維強化PEEK)よりもかなり高いトルクを可能にする。強化用繊維は必要とされないので、均一材料は、機械的性質の均一性に関して顕著な利点を有する。しかしながら、第一世代の提案された剛性棒状ポリフェニレンも、事実上、次世代の低キンク形剛性棒状ポリフェニレン(PrimoSpire(登録商標)PR−120としてSOLVAY ADVANCED POLYMERS,L.L.C.によりとくに提案された)も、関連するピンを製造するうえで十分に満足すべきものではない。そのようなポリフェニレンは、特定のネジ無し締結具ではとくにそのデザイン(形状、厚さなど)の結果として、ネジ付き締結具のほとんどではネジ部の存在が不可欠である結果として、非常に要求の厳しい用途では「それほど満足すべきものでない」とみなしうる。上述の非常に要求の厳しい締結具用途では、依然として、より高い引張り伸び(実用的靭性の尺度)を提供するポリマー材料の必要性が存在する。特定のデザインでは前のものよりもさらに重大な問題となりうる他の問題は、最初の2世代のそのように提案されたポリアリーレンの固有剛性から生じる。すなわち、それらを、射出成形や押出しなどの溶融加工技術により、複雑な形状を有するかまたは非常に薄い厚さを有する物品に造形することは、当初の金属の場合と同様に依然として困難である。 TECAMAX® SRP polyphenylene, commercially available from Ensinger, is said to be such a material. As a result of their rigid molecular structure, the polyparaphenylenes described in EP 2014251 in fact allow considerably higher torque than conventional composite polymer materials (eg carbon fiber reinforced PEEK). Since reinforcing fibers are not required, uniform materials have significant advantages with respect to uniformity of mechanical properties. However, the first generation of the proposed rigid rod-like polyphenylene has also been proposed in particular by SOLVAY ADVANCED POLYMERS, L.C. However, it is not satisfactory enough to produce the relevant pins. Such polyphenylenes are very demanding as a result of their design (shape, thickness, etc.), especially in certain threadless fasteners, and as a result of the presence of threaded parts in most threaded fasteners. It can be considered “not very satisfactory” in use. In the above highly demanding fastener applications, there remains a need for polymeric materials that provide higher tensile elongation (a measure of practical toughness). Another problem that can be a more serious problem in certain designs than the previous one arises from the inherent stiffness of the first two generations of such proposed polyarylene. That is, it is still difficult to shape them into articles having complex shapes or very thin thicknesses by melt processing techniques such as injection molding or extrusion, as with the original metal.
したがって、高トルク、高い実用的靭性(高い引張り伸び)、高い伸び強度、高剛性、高い耐薬品性、軽量性をはじめとする一群の特性を呈し、かつ関連する部分が複雑な形状および/または非常に薄い部分を有する場合(たとえば、ネジ部、または小オリフィスを有する押出し機を使用しなければならない場合)を含めて、押出しや射出成形などの溶融加工技術を用いて容易に形成しうる、締結具に対して、重要なニーズが存在する。 Therefore, it exhibits a group of properties including high torque, high practical toughness (high tensile elongation), high elongation strength, high rigidity, high chemical resistance, light weight, and the related parts have complicated shapes and / or Can be easily formed using melt processing techniques such as extrusion or injection molding, including when it has very thin parts (for example, if you have to use an extruder with threads or small orifices), There is an important need for fasteners.
このニーズおよびさらに他のニーズは、反復ユニットの50wt%超が、場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基よりなる1つ以上の式で示される反復ユニット(R)である、少なくとも1種のキンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレン(P)を含むポリマー材料(M)を含む締結具(F)により満たされる。ただし、前記場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基は、その2つの末端のそれぞれにより、直接C−C結合を介して、2つの他の場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基に結合され、前記反復ユニット(R)は、
・ 反復ユニット(R)の全モル数を基準にして0〜75モル%の、少なくとも1個の一価置換基で場合により置換されていてもよい剛性棒状体形成性アリーレンユニット(Ra)と、
・ 反復ユニット(R)の全モル数を基準にして25〜100モル%の、少なくとも1個の一価置換基で場合により置換されていてもよいキンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb)と、
よりなる混合物(M)である。
This need and yet another need is for at least one kink in which more than 50 wt% of the repeating units are repeating units (R) represented by one or more formulas consisting of optionally substituted arylene groups. Filled with a fastener (F) comprising a polymeric material (M) comprising a shaped rigid rod-like polyarylene (P). Provided that the optionally substituted arylene group is bonded to two other optionally substituted arylene groups via a direct C-C bond by each of its two ends, The repeating unit (R) is
A rigid rod-forming arylene unit (Ra) optionally substituted with at least one monovalent substituent, from 0 to 75 mol%, based on the total number of moles of repeating units (R);
A kink-forming arylene unit (Rb) optionally substituted with at least one monovalent substituent, from 25 to 100 mol%, based on the total number of moles of the repeating unit (R);
It is a mixture (M) consisting of
次に、本発明の詳細な説明のために、添付の図面を参照する。
締結具(F)
締結具(F)を記述するために本明細書中で用いられる用語はすべて、当業者の熟知するところであり、それらの通常の意味で理解しなければならない。
Fastener (F)
All terms used herein to describe the fastener (F) are familiar to those skilled in the art and should be understood in their ordinary meaning.
締結具(F)は、一般的には、単一もしくは複数の部材の保持、継合、結合、集成、または平衡維持を行うようにとくに設計された機械的手段である。得られた集成体は、機構または構造の一次もしくは二次の部材として動的もしくは静的に機能しうる。目的の用途に基づいて、締結具(F)は、さまざまな度合いの組込み精度および工学的機能を満たし、計画された既定の環境条件下で適正健全な使用を確保しうる。 Fasteners (F) are generally mechanical means specifically designed to hold, join, join, assemble, or balance a single or multiple members. The resulting assembly can function dynamically or statically as a primary or secondary member of the mechanism or structure. Based on the intended application, the fastener (F) can meet varying degrees of built-in accuracy and engineering capabilities and ensure proper and sound use under planned and predetermined environmental conditions.
ポリマー材料(M)の重量は、締結具(F)の全重量を基準にして、通常は10%超、好ましくは50%超、より好ましくは90%超である。さらにより好ましくは、締結具(F)は、ポリマー材料(M)より本質的になる。最も好ましくは、締結具(F)は、ポリマー材料(M)よりなる。 The weight of the polymeric material (M) is usually more than 10%, preferably more than 50%, more preferably more than 90%, based on the total weight of the fastener (F). Even more preferably, the fastener (F) consists essentially of the polymeric material (M). Most preferably, the fastener (F) is made of a polymer material (M).
締結具(F)は、1つの部分よりなりうる。すなわち、単一部材の手段でありうる。その場合、単一部分は、ポリマー材料(M)よりなる。他の選択肢として、締結具(F)は、いくつかの部分よりなりうる。場合にもよるが、締結具(F)の一部分またはいくつかの部分は、ポリマー材料(M)よりなりうる。締結具(F)のいくつか部分がポリマー材料(M)をよりなる場合、それらのそれぞれは、まったく同一のポリマー材料(M)よりなりうる。他の選択肢として、それらの少なくとも2つは、本発明に係る異なるポリマー材料(M)よりなりうる。 The fastener (F) can consist of one part. That is, it can be a single member means. In that case, the single part consists of the polymeric material (M). As another option, the fastener (F) may consist of several parts. Depending on the case, a part or some of the fasteners (F) can be made of a polymer material (M). If several parts of the fastener (F) consist of a polymer material (M), each of them can consist of the exact same polymer material (M). As another option, at least two of them can consist of different polymeric materials (M) according to the invention.
締結具(F)は、ネジ付き締結具、すなわち、ネジ部を含有する締結具でありうる。 The fastener (F) can be a threaded fastener, ie, a fastener containing a threaded portion.
ネジ部は、典型的には、ネジ付き締結具の表面の少なくとも一部分上に存在する稜(すなわち隆起したラインもしくはストリップ)または溝またはリブである。ネジ部は、渦巻き形、螺旋形、または平行形をはじめとするさまざまな形態を有しうる。ネジ部は、とくに、特定のネジ、ボルト、およびナットの外周を取り囲むように存在しうる。 The threaded portion is typically a ridge (ie, a raised line or strip) or groove or rib present on at least a portion of the surface of the threaded fastener. The threaded portion may have various forms including a spiral shape, a spiral shape, or a parallel shape. In particular, the threaded portion may exist so as to surround the outer periphery of the specific screw, bolt, and nut.
有利には、締結具(F)に含有されるネジ部の少なくとも一部分は、ポリマー材料(M)で構成される。好ましくは、締結具(F)に含有される本質的にすべてのネジ部は、ポリマー材料(M)で構成される。より好ましくは、締結具(F)に含有されるすべてのネジ部は、ポリマー材料(M)で構成される。 Advantageously, at least a part of the thread part contained in the fastener (F) is made of a polymer material (M). Preferably, essentially all the threads contained in the fastener (F) are composed of a polymer material (M). More preferably, all the screw parts contained in the fastener (F) are made of the polymer material (M).
本発明に係るネジ付き締結具のネジ表面は、とくに本質的にすべてのそのネジ部がポリマー材料(M)で構成される場合、前記ネジ付き締結具が呈する全表面の1%超、2%超、5%超、10%超、20%超、30%超、40%超、50%超、60%超、70%超、80%超、90%超、95%超、99%超、または約100%を占めることが可能である。 The threaded surface of the threaded fastener according to the present invention is more than 1% and 2% of the total surface exhibited by the threaded fastener, especially when essentially all of the threaded portion is made of polymer material (M). More than 5%, more than 10%, more than 20%, more than 30%, more than 40%, more than 50%, more than 60%, more than 70%, more than 80%, more than 90%, more than 95%, more than 99%, Or it can occupy about 100%.
締結具(F)は、外ネジ付きでありうる。すなわち、円筒または他の立体の外面の少なくとも一部分上、たとえば、ボルト上またはネジ上などに形成されたネジ部を有しうる。本発明に係る外ネジ付き締結具のネジ表面は、とくに本質的にすべてのそのネジ部がポリマー材料(M)で構成される場合、前記外ネジ付き締結具が呈する外表面の1%超、2%超、5%超、10%超、20%超、30%超、40%超、50%超、60%超、70%超、80%超、90%超、95%超、99%超、または約100%を占めることが可能である。 The fastener (F) can be externally threaded. That is, it may have a threaded portion formed on at least a part of a cylindrical or other three-dimensional outer surface, for example, on a bolt or a screw. The thread surface of the externally threaded fastener according to the present invention is more than 1% of the external surface exhibited by the externally threaded fastener, particularly when essentially all of the threaded portion is composed of a polymer material (M). Over 2%, over 5%, over 10%, over 20%, over 30%, over 40%, over 50%, over 60%, over 70%, over 80%, over 90%, over 95%, over 99% Can account for more than or about 100%.
締結具(F)は、内ネジ付きでありうる。すなわち、円筒または他の立体の内面の少なくとも一部分上、たとえば、ナット上などに形成されたネジ部を有しうる。本発明に係る内ネジ付き締結具のネジ表面は、とくに本質的にすべてのそのネジ部がポリマー材料(M)で構成される場合、前記内ネジ付き締結具が呈する内表面の1%超、2%超、5%超、10%超、20%超、30%超、40%超、50%超、60%超、70%超、80%超、90%超、95%超、99%超、または約100%を占めることが可能である。 The fastener (F) can be internally threaded. That is, it may have a threaded portion formed on at least a part of a cylindrical or other three-dimensional inner surface, for example, on a nut. The thread surface of the internally threaded fastener according to the present invention is more than 1% of the interior surface exhibited by the internally threaded fastener, particularly when essentially all of the threaded portion is composed of a polymer material (M). Over 2%, over 5%, over 10%, over 20%, over 30%, over 40%, over 50%, over 60%, over 70%, over 80%, over 90%, over 95%, over 99% Can account for more than or about 100%.
締結具(F)は、内外両ネジ付きでありうる。すなわち、内外ネジ付きブッシングなどのように、円筒または他の立体の外面の少なくとも一部分上に形成されたネジ部と、前記円筒または他の立体の内面の少なくとも一部分上に形成されたネジ部と、を有しうる。 The fastener (F) can be provided with both internal and external screws. That is, a threaded portion formed on at least a part of a cylindrical or other three-dimensional outer surface, such as an internal / external threaded bushing, and a threaded portion formed on at least a part of the cylindrical or other three-dimensional inner surface, Can be included.
本発明は、締結具(F)がネジ付き締結具である場合にとくに(ただし、この場合だけではない)有用であり、ネジ付き締結具の本質的にすべてのネジ部がポリマー材料(M)で構成され、かつネジ付き締結具のネジ表面がその全表面の10%超、好ましくは20%超、より好ましくは50%超を占める場合に卓越した結果が得られる。 The present invention is particularly useful when the fastener (F) is a threaded fastener (but not only in this case), where essentially all threads of the threaded fastener are made of polymer material (M). Excellent results are obtained when the thread surface of the threaded fastener occupies more than 10%, preferably more than 20%, more preferably more than 50% of its total surface.
本発明に係るネジ付き締結具の一般的なタイプとしては、ボルト、ナット、ネジ、無頭止めネジ、スクリベット、ネジ付きスタッド、およびネジ付きブッシングが挙げられる。 Common types of threaded fasteners according to the present invention include bolts, nuts, screws, headless screws, scribets, threaded studs, and threaded bushings.
締結具(F)はボルトでありうる。ボルトは、典型的には、頭付き外ネジ付き締結具である。ボルトは、一般的には、集成される部分の孔に挿入してナットに嵌合するように設計され、通常、そのナットを回転させることにより締付けまたは解放が行われるように意図される。 The fastener (F) can be a bolt. The bolt is typically a headed external threaded fastener. Bolts are generally designed to be inserted into the holes in the assembled part and fit into a nut, and are usually intended to be tightened or released by rotating the nut.
本発明に係る特定のボルトは、その形状に関連して「曲げボルト」とみなされる。曲げボルトは、とくに、「U」ボルト、「J」ボルト、「L」ボルト、またはアイボルトの形状でありうる。「U」形ボルトは、典型的には、その両端にネジ部を有し、一方、他の挙げられた曲げボルトは、典型的には、一端のみにネジ部を有する。 Certain bolts according to the present invention are considered “bending bolts” in relation to their shape. The bending bolt may in particular be in the form of a “U” bolt, “J” bolt, “L” bolt or eyebolt. “U” shaped bolts typically have threads at both ends, while other listed bending bolts typically have threads at only one end.
本発明に係る他のボルトは、以下のとおりである。
・ 四角ボルト(その頭の形状が四角形であることに関連して)、
・ 六角ボルト(その頭の形状が六角形であることに関連して)、
・ 六角フランジボルト(六角ボルトに類似しているが、基材に嵌合するワッシャー様のフラット表面を含有する)、
・ 丸頭ボルト(典型的には、一端に丸形の頭を有し、それらは、とくに、短角根丸頭ボルト、リブ付き丸頭ボルト、フィン付き丸頭ボルト、ステップボルト、皿頭ボルトおよびスロット付き皿頭ボルト、平皿頭エレベーターボルト、T頭ボルト、プラウボルト、ならびに継ぎ目板ボルトとして区別される。)、
・ アイボルト(典型的には、図1に例示されたフックボルトの場合のように、フックまたはロープを受容するように設計されたループ状の頭を有する)。
Other bolts according to the present invention are as follows.
A square bolt (in relation to the shape of its head being square),
-Hex bolts (in connection with the head shape being hexagonal),
Hexagon flange bolts (similar to hexagonal bolts, but containing a washer-like flat surface that fits into the substrate),
• Round head bolts (typically with round heads at one end, especially those with short square root bolts, round head bolts with ribs, round head bolts with fins, step bolts, countersunk head bolts And slotted countersunk bolts, flat countersunk elevator bolts, T-head bolts, plow bolts, and seam plate bolts).
An eyebolt (typically having a looped head designed to receive a hook or rope, as in the case of the hook bolt illustrated in FIG. 1).
締結具(F)はナットでありうる。ナットは、典型的には、2つ以上の物体を一定の関連位置で締め付けるかまたは保持することを目的としてボルトなどの外ネジまたは雄ネジに接して使用することが意図された、内ネジまたは雌ネジを有する有孔ブロックである。 The fastener (F) can be a nut. A nut is typically an internal thread or intended for use against an external or male thread, such as a bolt, for the purpose of tightening or holding two or more objects in a fixed relative position. It is a perforated block having an internal thread.
本発明に係る特定のナットは、フランジナットである。フランジナットは、典型的には、一体化された非回転ワッシャーとして機能する幅広フランジを一端に有し、これは、通常、固定された部分全体にナットの圧力を分配することにより、その部分の損傷の可能性を低減するとともに、不均一な締結表面の結果として緩みを生じる可能性を低減する役割を担う。フランジは、一般に、ロック動作を提供するように鋸歯状である。 The specific nut according to the present invention is a flange nut. Flange nuts typically have a wide flange at one end that functions as an integrated non-rotating washer, which is usually distributed in the part by distributing the nut pressure over the fixed part. It serves to reduce the possibility of damage and reduce the possibility of loosening as a result of a non-uniform fastening surface. The flange is generally serrated to provide a locking action.
本発明に係る特定の他のナットは、カップリングナットである。カップリングナットは、典型的には、全体を通じて同一方向にではなく各側から中間部で出合うように雌ネジが切られた長ナットであり、2本のネジ付きロッドを終端間で接続するために使用可能である。 Another particular nut according to the present invention is a coupling nut. Coupling nuts are typically long nuts that are internally threaded to meet in the middle from each side, not in the same direction throughout, to connect two threaded rods between the ends Can be used.
本発明に係るさらに特定の他のナットは、摘みナットとも呼ばれる蝶ナットである。このものは、典型的には、回転時の親指および人指し指の梃子の作用のための突起のようなウィングを有するナットである。 Yet another particular nut according to the present invention is a wing nut, also called a knob nut. This is typically a nut with a wing like protrusion for the action of the thumb and index finger levers during rotation.
締結具(F)はネジでありうる。ネジは、典型的には、頭付きかつ外ネジ付きの締結具である。それは、通常、集成される部分の孔中への挿入を可能にする能力、あらかじめ形成された内ネジに嵌合するかまたはそれ自体のネジ部を形成する能力、および頭にトルクを与えることにより締付けまたは解放を行う能力を有する。 The fastener (F) can be a screw. The screw is typically a headed and externally threaded fastener. It usually has the ability to allow the assembled part to be inserted into the hole, the ability to fit into a pre-formed internal screw or form its own thread, and torque the head Has the ability to tighten or release.
本発明に係る特定のネジは、ソケットネジである。ソケットネジは、典型的には、整合する「ネジ回しの先端」を必要とする六角形、スプライン形、または特殊形の孔を頂部に有するスクリューキャップである。 The specific screw according to the present invention is a socket screw. Socket screws are typically screw caps with a hexagonal, splined, or specially shaped hole at the top that requires a matching “screwdriver tip”.
本発明に係る特定の他のネジは、タッピングネジである。タッピングネジは、種々の材料のあらかじめ形成された孔中に押し込む時にそれ自体が嵌合する内ネジを「ネジ切り」することが可能である。タッピングネジは、典型的には、高強度ワンピース片側装着ネジ付き締結具である。それはそれ自体が嵌合するネジ部を形成または切削することができるので、使用時のその緩みに対する耐性を増強する並はずれて良好なネジ嵌合が存在する。本発明に係るタッピングネジは、取外し可能であり、一般的には再使用可能である。 Another particular screw according to the present invention is a tapping screw. A tapping screw can “thread” an internal screw that fits itself when pushed into pre-formed holes of various materials. The tapping screw is typically a high strength one-piece one-side mounted screwed fastener. Since it can form or cut a threaded part that fits itself, there is an exceptionally good threaded fit that enhances its resistance to loosening in use. The tapping screw according to the present invention is removable and is generally reusable.
本発明に係るさらに他のネジは、機械ネジである。機械ネジは、典型的には、そのシャフトの全長に沿ってネジ部を有する。それはまた、皿頭状の孔に嵌入しかつネジ止め時に螺入される表面に接触するテーパー状の頂部を有するネジとみなすことが可能である。 Still another screw according to the present invention is a mechanical screw. A machine screw typically has a thread along the entire length of its shaft. It can also be regarded as a screw with a tapered top that fits into a countersunk hole and contacts the surface to be screwed in when screwed.
本発明に係るさらに他のネジは、摘みネジまたは蝶ネジ、すなわち、典型的には親指およびそれ以外の指で回転しうるように設計されるネジである。 Yet another screw according to the present invention is a thumbscrew or thumbscrew, i.e., a screw that is typically designed to rotate with the thumb and other fingers.
本発明に係るさらに他のネジは、典型的には、尖頭形のシャンク、スロット付きまたは凹陥付きの頭、および木材の場合(ただし、この場合だけではない)に本質的に使用に好適な比較的粗いピッチの尖鋭テーパー付きネジ部を有するという点で、「木ネジ」とみなされるものである。 Still other screws according to the present invention are typically suitable for use in the case of (but not exclusively) a pointed shank, slotted or recessed head, and wood. It is regarded as a “wood screw” in that it has a thread portion with a sharp taper with a relatively coarse pitch.
本発明に係るさらに他のネジは、その小さなサイズに基づいてミニチュアネジとみなされるものである。前記ミニチュアネジの中では、丸平頭、鍋頭、平頭、およびバインド頭のものがとくに挙げられうる。 Still other screws according to the present invention are considered miniature screws based on their small size. Among the miniature screws, round heads, pan heads, flat heads, and bind heads may be mentioned in particular.
少なくともネジがポリマー材料(M)を含むネジ−ワッシャー集成体(SEMS)もまた、本発明の一部を形成する。 Screw-washer assemblies (SEMS), at least where the screws comprise polymeric material (M), also form part of the present invention.
締結具(F)は、無頭止めネジでありうる。典型的には頭付きである以上に規定された本発明に係るネジとは対照的に、本無頭止めネジは、突出頭を有していない。一般的には、その頂部は、スロット付きであるかまたはソケットを備えているかのいずれかである。 The fastener (F) can be a headless set screw. In contrast to the screw according to the invention defined above which is typically headed, the headless set screw does not have a protruding head. In general, the top is either slotted or provided with a socket.
締結具(F)は、ネジ付きスタッドでありうる。ネジ付きスタッドは、典型的には、一方の尖頭形の端がコンクリートなどの材料中に押し込まれ、他方の端がネジ付きで、構造部材を取り付けるための表面上に延在する、締結手段である。 The fastener (F) can be a threaded stud. A threaded stud is typically a fastening means in which one pointed end is pushed into a material such as concrete and the other end is threaded and extends over a surface for mounting a structural member It is.
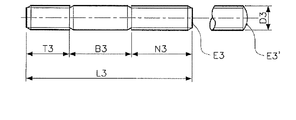
本発明に係る特定のネジ付きスタッドは、連続ネジスタッドである。すなわち、端から端までネジ付きであり、多くの場合、適用された2つのナットでフランジをボルト締めするために使用される。図2は、本発明に係る汎用連続ネジスタッドの例を示している。 The particular threaded stud according to the present invention is a continuous threaded stud. That is, it is threaded from end to end and is often used to bolt the flange with two applied nuts. FIG. 2 shows an example of a general purpose continuous thread stud according to the present invention.
本発明に係る連続ネジスタッドの先端は、一般的には、フラットであり、面取りされている。本発明に係る連続ネジスタッドは、パイプ用途にとくに使用可能であり、その際、こうした用途に必要とされるように、このものは、すべての他のスタッドとは異なる長さ測定要件を有する。すなわち、その長さは、先端を除いて第一ネジ山から第一ネジ山まで測定される。 The tip of the continuous thread stud according to the present invention is generally flat and chamfered. The continuous thread stud according to the invention is particularly usable for pipe applications, where it has different length measurement requirements than all other studs, as required for such applications. That is, its length is measured from the first thread to the first thread except for the tip.
本発明に係る特定の他のネジ付きスタッドは、植込みボルトである。典型的な植込みボルトは、一方の端に、特定の等級の嵌合に合わせてネジ切りされたタップ端と呼ばれる短いネジ部を有し(この端は、ネジ穴に螺入するのに好適である)、他方の端またはナット端は、他の等級の嵌合でネジ切りされている。タップ端は、面取りされた先端を有するが、ナット端は、面取りされた先端または丸みのある先端のいずれかを有しうる。図3は、本発明に係る植込みボルトの例を示している。 Certain other threaded studs according to the present invention are studs. A typical stud has a short thread at one end called a tap end that is threaded to fit a particular grade (this end is suitable for screwing into a threaded hole. The other end or nut end is threaded with other grades of fitting. The tap end has a chamfered tip, while the nut end can have either a chamfered tip or a rounded tip. FIG. 3 shows an example of a stud bolt according to the present invention.
本発明に係るさらに他のネジ付きスタッドは、両ネジボルトである。両ネジボルトは、典型的には、ナットを収容するために各端に実質的に等しい長さまたは等しい長さのネジ部を有し、特定の等級の嵌合に合わせてネジ切りされている。両端は、互いに独立して、面取りされた先端または丸みのある先端を有しうる。両ネジボルトは、フランジのボルト締めにまたは両端からのトーチ溶断が必要であるかもしくは望ましい他の用途に有用である。図4は、本発明に係る両ネジボルトの例を示している。 Yet another threaded stud according to the invention is a double threaded bolt. Both threaded bolts typically have thread portions of substantially equal or equal length at each end to accommodate the nut and are threaded for a particular grade of fit. Both ends can have a chamfered tip or a rounded tip independent of each other. Both screw bolts are useful for bolting flanges or other applications where torch fusing from both ends is necessary or desirable. FIG. 4 shows an example of a double screw bolt according to the present invention.
締結具(F)は、スクリベットでありうる。スクリベットは、典型的には、少なくとも部分的にネジ付きのシャンクと頭とを含むネジ付き締結具である。シャンクは、その全表面がネジ付きでありうる。本発明に係る特定のスクリベットは、前記ネジ付きシャンクと頭とよりなる。スクリベットは、一般的には、孔中に挿入される。スクリベットは、完成した機械式継ぎ手を形成するように平らなスクリベット端を変形させる印加力により2つ以上の部材を集成するのに有用である。 The fastener (F) can be a scribet. A scribet is a threaded fastener that typically includes an at least partially threaded shank and a head. The shank can be threaded on its entire surface. A specific scribet according to the present invention comprises the threaded shank and the head. The scribet is generally inserted into the hole. A scribet is useful for assembling two or more members with an applied force that deforms a flat scribet end to form a finished mechanical joint.
締結具(F)は、ネジ付きブッシングでありうる。該当するブッシングは、結合機能に加えて耐性機能を提供するように、内ネジ付きおよび/または外ネジ付きである。好ましくは、内外ネジ付きである。本発明に係る内外ネジ付きブッシングの例は、図5に示される六角ブッシングである。 The fastener (F) can be a threaded bushing. Applicable bushings are internally and / or externally threaded to provide a resistance function in addition to the coupling function. Preferably, it has internal and external screws. An example of a bushing with internal and external threads according to the present invention is a hexagonal bushing shown in FIG.
本発明の特定の実施形態では、締結具(F)は、プリベリングトルク形ネジやプリベリングトルク形ナットなどのプリベリングトルク形締結具である。プリベリングトルク形締結具は、内蔵されたプリベリングトルク特性に基づいて回転に対して摩擦抵抗性であるネジ付き締結具として定義可能であり、とくに、プリベリングトルク形ネジは、ネジの首下支承表面に対して発生する圧縮負荷やネジのシャンクに発生する引張り負荷に起因するのではなく内蔵されたプリベリングトルク特性に起因して回転に対して摩擦抵抗性である外ネジ付き締結具とみなすことが可能である。本発明に係る特定のプリベリングトルク形締結具は、そのネジ部長さ内に滑剤などのようなポリマー材料(M)以外の融合物質の挿入物が添加された、ポリマー材料(M)製の締結具である。表面仕上げ剤および滑剤に起因して存在する摩擦量に依存して、挿入物の寸法特性は、性能要件を達成するように変化させうる。 In a particular embodiment of the invention, the fastener (F) is a pre-leveling torque type fastener such as a pre-leveling torque type screw or pre-leveling torque type nut. Preveling torque type fasteners can be defined as threaded fasteners that are friction resistant to rotation based on the built-in preveling torque characteristics, and in particular, pre-torque torque type screws are located under the neck of the screw. An externally threaded fastener that is friction resistant to rotation due to the built-in preveling torque characteristics, not due to the compressive load generated on the bearing surface or the tensile load generated on the screw shank; and It can be considered. A specific pre-torque torque type fastener according to the present invention is a fastening made of a polymer material (M) in which an insert of a fusion substance other than the polymer material (M) such as a lubricant is added in the length of a screw portion. It is a tool. Depending on the amount of friction present due to the surface finish and the lubricant, the dimensional characteristics of the insert can be varied to achieve performance requirements.
締結具(F)は、ネジ無し締結具でありうる。すなわち、それはネジ部を含有しない。 The fastener (F) can be a screwless fastener. That is, it does not contain a thread.
本発明に係るネジ無し締結具の一般的なタイプとしては、ピン、保持リング、リベット、および締結ワッシャーが挙げられる。 Common types of threadless fasteners according to the present invention include pins, retaining rings, rivets, and fastening washers.
締結具(F)は、ピンでありうる。ピンは、典型的には細く、多くは直線状の、円柱形ネジ無し締結具であり、2つ以上の機械部品の位置を固定するのに好適である。 The fastener (F) can be a pin. The pin is typically a thin, often straight, cylindrical threaded fastener and is suitable for fixing the position of two or more machine parts.
本発明に係る特定のピンは、クレビスピンである。クレビスピンは、典型的には、一方の端に頭と、他方の端に、クレビスをロッドに継合するために使用される孔と、を有する締結具である。クレビスは、典型的には、ロッドの一方の端に形成されているかまたは取り付けられている孔を有するヨークであり、図6は、ヨークをロッド端に継合する本発明に係るクレビスピンの例を示している。第2のロッドの目または孔がヨークの孔にアライメントされた時、クレビスピンを挿入して両者を継合することが可能である。次に、コッターピンをクレビスピンの孔に挿入してその中に保持することが可能であるが、それにもかかわらず、締結は容易に解除可能である。この継ぎ手は、いくらかの可撓性が必要とされる引張り力を受けるロッドに使用される。 The specific pin according to the present invention is a clevis pin. A clevis pin is typically a fastener having a head at one end and a hole at the other end that is used to join the clevis to the rod. A clevis is typically a yoke having a hole formed or attached to one end of a rod, and FIG. 6 is an example of a clevis pin according to the present invention that joins the yoke to the rod end. Show. When the eye or hole of the second rod is aligned with the hole in the yoke, it is possible to insert the clevis pin and join them together. The cotter pin can then be inserted into the hole in the clevis pin and retained therein, but nevertheless the fastening can be easily released. This joint is used for rods that are subject to tensile forces that require some flexibility.
本発明に係る特定の他のピンは、コッターピン(米国用語)である。コッターピンは、典型的には、2つの部片を保持一体化する目的でスロット中に挿入可能な2つのタインを有するネジ無し締結具である。コッターピンは、伝統的には、半円形断面を有する。英国では、同一の手段を記述するために「割りピン」という用語が伝統的に用いられている。新しいコッターピン(図7A参照)は、その長さのほとんどで接触するそのフラットな内表面を有するので、典型的には、分割円柱(図7D)のようにみえる。挿入後、ピンの2つの端は、離れる方向に曲げられ、その結果、それは所定の位置にロックされる(図7B)。タインの最初の分離を容易にするために、コッターピンの一方のタインは、多くの場合、他方よりも顕著に長く、孔中への挿入を容易にするために、長いほうのタインは、多くの場合、短いほうのタインの先端にオーバーラップするようにわずかに湾曲または傾斜されている。 Another particular pin according to the present invention is a cotter pin (US term). A cotter pin is typically a screwless fastener having two tines that can be inserted into a slot for the purpose of holding and integrating the two pieces. A cotter pin traditionally has a semi-circular cross-section. In the UK, the term “divided pin” is traditionally used to describe the same means. The new cotter pin (see FIG. 7A) typically looks like a split cylinder (FIG. 7D) because it has its flat inner surface that contacts most of its length. After insertion, the two ends of the pin are bent away so that it is locked in place (FIG. 7B). To facilitate initial separation of the tines, one tine of the cotter pin is often significantly longer than the other, and the longer tine is often much longer to facilitate insertion into the hole. If it is slightly curved or inclined to overlap the tip of the shorter tine.
本発明に係るさらに他のピンは、スプリングピンである。ヒッチピンとも呼ばれる図7Cに示されるようなスプリングピン(ときには、その形状からRピンとして知られる)もまた、入手可能であり、これは永続的に曲げられた状態になるようには設計されていない。このデザインでは、ピンの一方の部分のみが、固定されるシャフトの中を通過し、他方の部分は、シャフトの外面を取り囲んで覆うように湾曲されている(図7C)。 Still another pin according to the present invention is a spring pin. A spring pin (sometimes known as an R pin because of its shape), also called a hitch pin, is also available and is not designed to be permanently bent. . In this design, only one part of the pin passes through the fixed shaft and the other part is curved to surround and cover the outer surface of the shaft (FIG. 7C).
本発明に係るさらに他のピンは、テーパーピンである。テーパーピンは、制御された直径、長さ、およびテーパーを有する無頭中実ピンであり、一般的には、クラウン状の端を有する。この自己保持ピンは、部品を継合一体化するのに有用である。標準的テーパーピンは、1/4in.〜12in.(0.6cm〜30cm)のダイヤメトラルテープを有し、穿孔された孔中に押し込まれて拡大することにより嵌合する。それは、ときには、ハブまたはカラーをシャフトに結合するために使用される。テーパーピンは、多くの場合、一方の表面の位置を他方に対して保持するために使用される。テーパーピンのデザインの例は、図8に示されている。 Still another pin according to the present invention is a tapered pin. A tapered pin is a headless solid pin having a controlled diameter, length, and taper, and generally has a crowned end. This self-holding pin is useful for splicing parts together. Standard taper pins are 1/4 in. ~ 12 in. It has a diaphragm (0.6 cm to 30 cm) and fits by being expanded by being pushed into the drilled hole. It is sometimes used to connect a hub or collar to a shaft. Tapered pins are often used to hold the position of one surface relative to the other. An example of a tapered pin design is shown in FIG.
本発明に係るさらに他のピンは、ダウエルピンである。多くの場合、ダウエルピンは、典型的には、先鋭化または変形された端を有する。それは、2つの隣接する部片の孔中に挿入してそれらを保持一体化することが可能である。それは、とくに、ホゾ継ぎ手を締結するのに有用である。ダウエルピンは、ダウエルロッドすなわち中実円柱ロッドを短い長さに切断することから取得可能である。 Still another pin according to the present invention is a dowel pin. In many cases, dowel pins typically have sharpened or deformed ends. It can be inserted into the holes of two adjacent pieces to hold them together. It is particularly useful for fastening tenon joints. Dowel pins can be obtained by cutting dowel rods or solid cylindrical rods into short lengths.
本発明に係るさらに他のピンは、平行ピンである。平行ピンは、典型的には、両端が面取りされた研削されていない直線状円柱面を有する。 Still another pin according to the present invention is a parallel pin. Parallel pins typically have an unground straight cylindrical surface that is chamfered at both ends.
本発明に係るさらに他のピンは、溝付きピンである。溝付きピンは、溝を有するピンであり、溝付きピンは、多くの場合、ピンの直径上に等間隔に配置された3つの溝を有する。 Yet another pin according to the present invention is a grooved pin. A grooved pin is a pin with a groove, and the grooved pin often has three grooves that are equally spaced on the diameter of the pin.
締結具(F)は、保持リングでありうる。保持リングは、典型的には、中空の中心および開断面を有するフラットな円形のネジ無し締結具である。保持リングは、典型的には、ショルダーを提供し、シャフト上にまたは内部溝を有する孔の内側に挿入することが可能である。 The fastener (F) can be a retaining ring. The retaining ring is typically a flat circular unthreaded fastener with a hollow center and an open cross-section. The retaining ring typically provides a shoulder and can be inserted on the shaft or inside a hole with an internal groove.
締結具(F)は、リベットでありうる。リベットは、典型的には、シャンクおよび頭を含むネジ無し締結具であり、本発明に係る特定のリベットは、前記シャンクおよび前記頭よりなる。リベットは、一般的には、孔中に挿入される。リベットシャンクは、リベットの他方の側に位置する整合頭の形状に形成可能である。リベットは、完成した機械式継ぎ手を形成するように平らなリベット端を変形する印加力により2つ以上の部材を集成するのに有用である。 The fastener (F) can be a rivet. A rivet is typically a screwless fastener including a shank and a head, and a particular rivet according to the present invention consists of the shank and the head. The rivet is generally inserted into the hole. The rivet shank can be formed in the shape of an alignment head located on the other side of the rivet. A rivet is useful for assembling two or more members with an applied force that deforms a flat rivet end to form a finished mechanical joint.
締結具(F)は、ロックワッシャーなどの締結ワッシャーでありうる。ロックワッシャーは、典型的には、圧力を加えることにより緩みを防止する目的でナットまたはネジの下側に配置されるワッシャーである。本発明に係るロックワッシャーは、有利には、圧力を加えるのに役立つ螺旋構造を有する。スプリングワッシャーは、ロックワッシャーに類似している。 The fastener (F) can be a fastening washer such as a lock washer. A lock washer is typically a washer placed under a nut or screw for the purpose of preventing loosening by applying pressure. The lock washer according to the invention advantageously has a helical structure that serves to apply pressure. Spring washers are similar to lock washers.
キンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレン(P)
本発明の目的では、アリーレン基とは、1個のベンゼン環または2個以上の近接する環炭素原子を共有することにより縮合一体化された複数個のベンゼン環で構成された1個の核よりなりかつ2つの末端を有する炭化水素二価基のことである。
Kink type rigid rod-shaped polyarylene (P)
For the purposes of the present invention, an arylene group is a single benzene ring or a single nucleus composed of a plurality of benzene rings fused together by sharing two or more adjacent ring carbon atoms. And a hydrocarbon divalent group having two ends.
アリーレン基の例としては、フェニレン、ナフチレン、アントリレン、フェナントリレン、テトラセニレン、トリフェニリレン、ピレニレン、およびペリレニレンが挙げられるが、これらに限定されるものではない。アリーレン基(とくに環炭素原子の番号付け)は、CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics,64th editionのC1−C44ページとくにC11−C12ページの推奨基準に準拠して命名した。 Examples of arylene groups include, but are not limited to, phenylene, naphthylene, anthrylene, phenanthrylene, tetrasenylene, triphenylylene, pyrenylene, and peryleneylene. Arylene groups (especially the numbering of the ring carbon atoms) were named in compliance with CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 64 th C1-C44 pages and recommended standard of country C11-C12 page of edition.
アリーレン基は、通常、特定レベルの芳香族性を呈する。このため、多くの場合、「芳香族」基として報告される。アリーレン基の芳香族性のレベルは、アリーレン基の性質に依存し、Chem.Rev.2003,103,3449−3605,”Aromaticity of Polycyclic Conjugated Hydrocarbons”に十分に説明されているように、多環式芳香族炭化水素の芳香族性のレベルは、とくに、同論文の3531ページに定義されている「ベンゼン特性の指標」Bにより定量化可能であり、一群の多数の多環式芳香族炭化水素に対するBの値が同ページの表40に報告されている。 Arylene groups usually exhibit a certain level of aromaticity. For this reason, it is often reported as an “aromatic” group. The level of aromaticity of the arylene group depends on the nature of the arylene group and is described in Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 3449-3605, “Aromaticity of Polycyclic Conjugated Hydrocarbons”, the level of aromaticity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons is specifically defined on page 3531 of the same paper. The value of B for a group of many polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons is reported in Table 40 on the same page.
アリーレン基の末端は、アリーレン基のベンゼン環に含有される炭素原子の遊離電子であり、前記炭素原子に結合された水素原子は除去されている。アリーレン基の各末端は、他の化学基と結合を形成しうる。アリーレン基の末端、より正確には前記末端により形成可能な結合は、方向および向きにより特徴付け可能であり、本発明の目的では、アリーレン基の末端の向きは、アリーレン基の核の内側から前記核の外側に向かうものとして定義される。より正確には、末端が同一の方向を有するアリーレン基に関しては、そのような末端は、同一の向きまたは反対の向きのいずれかでありうる。また、それらの末端は、互いに一直線上にありうるか、またはそうでないこともありうる(別の言い方をすると、それらは、互いに交わらないこともありうる)。 The terminal of the arylene group is a free electron of a carbon atom contained in the benzene ring of the arylene group, and a hydrogen atom bonded to the carbon atom is removed. Each end of the arylene group can form a bond with another chemical group. The end of the arylene group, more precisely the bond that can be formed by the end, can be characterized by the direction and orientation, and for the purposes of the present invention the orientation of the end of the arylene group is from the inside of the core of the arylene group. Defined as going outside the nucleus. More precisely, for arylene groups whose ends have the same direction, such ends can be either in the same orientation or in the opposite orientation. Also, their ends may be in line with each other or not (in other words, they may not cross each other).
ポリアリーレンは、反復ユニットの50wt%超が、場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基よりなる1つ以上の式で示される反復ユニット(R)である、ポリマーを意味するものとする。ただし、前記場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基は、その2つの末端のそれぞれにより、直接C−C結合を介して、2つの他の場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基に結合されている。場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基が、その2つの末端のそれぞれにより、直接C−C結合を介して、2つの他の場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基に結合されていることは、反復ユニット(R)の本質的特徴である。したがって、以下のように、すなわち、
−O−φ1−S(=O)2−、
−O−φ2−φ2’−O−、
のように、アリーレン反復ユニットが、その2つの末端の少なくとも1つにより、フェニレン反復ユニットφ1、φ2、およびφ2’などのアリーレン基以外の基に結合されている場合には、本発明の意味するところによれば、反復ユニット(R)ではない。
Polyarylene shall mean a polymer in which more than 50 wt% of the repeating units are repeating units (R) represented by one or more formulas consisting of optionally substituted arylene groups. However, the optionally substituted arylene group is bonded to the two other optionally substituted arylene groups via a direct C-C bond by each of its two ends. Yes. That an optionally substituted arylene group is bonded to each of its two ends by a direct C-C bond to two other optionally substituted arylene groups. , An essential feature of the repeating unit (R). Thus, as follows:
-O-φ 1 -S (= O ) 2 -,
-O-φ 2 -φ 2 ' -O-,
When the arylene repeating unit is bonded to a group other than an arylene group such as phenylene repeating unit φ 1 , φ 2 , and φ 2 ′ by at least one of its two ends, the present invention Is not a repeat unit (R).
反復ユニット(R)を構成するアリーレン基は、無置換型でありうる。他の選択肢として、それらは、少なくとも1個の一価置換基で置換可能である。 The arylene group constituting the repeating unit (R) may be unsubstituted. As another option, they can be substituted with at least one monovalent substituent.
一価置換基は、通常、本質的に高分子ではなく、その分子量は、好ましくは500未満、より好ましくは300未満、さらにより好ましくは200未満、最も好ましくは150未満である。 Monovalent substituents are usually not essentially macromolecules, and their molecular weight is preferably less than 500, more preferably less than 300, even more preferably less than 200, and most preferably less than 150.
一価置換基は、有利には、可溶化基である。可溶化基とは、溶液重合プロセスによるポリアリーレンの合成時に溶媒として使用可能な少なくとも1種の有機溶媒、とくに、ジメチルホルムアミド、N−メチルピロリジノン、ヘキサメチルリン酸トリアミド、ベンゼン、テトラヒドロフラン、およびジメトキシエタンの少なくとも1つに対するポリアリーレンの溶解性を増大させる基のことである。 The monovalent substituent is advantageously a solubilizing group. Solubilizing groups are at least one organic solvent that can be used as a solvent during the synthesis of polyarylene by a solution polymerization process, in particular dimethylformamide, N-methylpyrrolidinone, hexamethylphosphoric triamide, benzene, tetrahydrofuran, and dimethoxyethane. A group that increases the solubility of the polyarylene in at least one of the above.
一価置換基はまた、有利には、ポリアリーレンの可融性を増大させる基である。すなわち、それは、望ましくはポリアリーレンを熱加工に好適なものにするために、そのガラス転移温度およびその融解粘度を低下させる。 Monovalent substituents are also advantageously groups that increase the fusibility of the polyarylene. That is, it lowers its glass transition temperature and its melt viscosity, preferably in order to make the polyarylene suitable for thermal processing.
好ましくは、一価置換基は、以下のものから選択される。
・ ヒドロカルビル、たとえば、アルキル、アリール、アルキルアリール、およびアラルキルなど、
・ ハロゲノ、たとえば、−Cl、−Br、−F、および−Iなど、
・ 少なくとも1個のハロゲン原子により部分置換または完全置換されたヒドロカルビル基、たとえば、ハロゲノアルキル、ハロゲノアリール、ハロゲノアルキルアリール、およびハロゲノアラルキルなど、
・ ヒドロキシル、
・ 少なくとも1個のヒドロキシル基により置換されたヒドロカルビル基、たとえば、ヒドロキシアルキル、ヒドロキシアリール、ヒドロキシアルキルアリール、およびヒドロキシアラルキルなど、
・ ヒドロカルビルオキシ[−O−R〔式中、Rはヒドロカルビル基である〕]、たとえば、アルコキシ、アリールオキシ、アルキルアリールオキシ、およびアラルキルオキシなど、
・ アミノ(−NH2)、
・ 少なくとも1個のアミノ基により置換されたヒドロカルビル基、たとえば、アミノアルキルおよびアミノアリールなど、
・ ヒドロカルビルアミン[−NHRまたは−NR2〔式中、Rはヒドロカルビル基である〕]、たとえば、アルキルアミンおよびアリールアミンなど、
・ カルボン酸およびその金属塩またはアンモニウム塩、カルボン酸ハロゲン化物、カルボン酸無水物、
・ カルボン酸、その金属塩またはアンモニウム塩、カルボン酸ハロゲン化物、およびカルボン酸無水物の少なくとも1つにより置換されたヒドロカルビル基、たとえば、−R−C(=O)OH〔式中、Rはアルキル基またはアリール基である〕など、
・ ヒドロカルビルエステル[−C(=O)ORまたは−O−C(=O)R〔式中、Rはヒドロカルビル基である〕]、たとえば、アルキルエステル、アリールエステル、アルキルアリールエステル、およびアラルキルエステルなど、
・ アミド[−C(=O)NH2]、
・ 少なくとも1個のアミド基により置換されたヒドロカルビル基、
・ ヒドロカルビルアミドモノエステル[−C(=O)NHRまたは−NH−C(=O)−R〔式中、Rはヒドロカルビル基である〕]、たとえば、アルキルアミド、アリールアミド、アルキルアリールアミド、およびアラルキルアミドなど、ならびにヒドロカルビルアミドジエステル[−C(=O)NR2または−N−C(=O)R2〔式中、Rはヒドロカルビル基である〕]、たとえば、ジアルキルアミドおよびジアリールアミドなど、
・ スルフィン酸(−SO2H)、スルホン酸(−SO3H)、それらの金属塩またはアンモニウム塩、
・ ヒドロカルビルスルホン[−S(=O)2−R〔式中、Rはヒドロカルビル基である〕]、たとえば、アルキルスルホン、アリールスルホン、アルキルアリールスルホン、アラルキルスルホンなど、
・ アルデヒド[−C(=O)H]およびハロホルミル[−C(=O)X〔式中、Xはハロゲン原子である〕]、
・ ヒドロカルビルケトン[−C(=O)−R〔式中、Rはヒドロカルビル基である〕]、たとえば、アルキルケトン、アリールケトン、アルキルアリールケトン、およびアラルキルケトンなど、
・ ヒドロカルビルオキシヒドロカルビルケトン[−C(=O)−R1−O−R2〔式中、R1は、二価炭化水素基、たとえば、アルキレン、アリーレン、アルキルアリーレン、またはアラルキレン、好ましくはC1〜C18アルキレン、フェニレン、少なくとも1個のアルキル基により置換されたフェニレン基、または少なくとも1個のフェニル基により置換されたアルキレン基などであり、かつR2は、ヒドロカルビル基、たとえば、アルキル基、アリール基、アルキルアリール基、またはアラルキル基などである〕]、たとえば、アルキルオキシアルキルケトン、アルキルオキシアリールケトン、アルキルオキシアルキルアリールケトン、アルキルオキシアラルキルケトン、アリールオキシアルキルケトン、アリールオキシアリールケトン、アリールオキシアルキルアリールケトン、およびアリールオキシアラルキルケトンなど、
・ 少なくとも1個のヒドロカルビル基または二価炭化水素基R1を含む以上の基のいずれか(ただし、前記ヒドロカルビル基または前記R1はそれ自体、以上に列挙された一価置換基の少なくとも1つにより置換されている)、たとえば、アリールケトン−C(=O)−R〔式中、Rは、1個のヒドロキシル基により置換されたアリール基である〕、
ここで、
・ ヒドロカルビル基は、好ましくは1〜30個の炭素原子、より好ましくは1〜12個の炭素原子、さらにより好ましくは1〜6個の炭素原子を含有し、
・ アルキル基は、好ましくは1〜18個の炭素原子、より好ましくは1〜6個の炭素原子を含有し、非常に好ましくは、メチル、エチル、n−プロピル、イソプロピル、n−ブチル、イソブチル、およびtert−ブチルから選択され、
・ アリール基は、1つの末端と、1個のベンゼン環(たとえばフェニル基など)または炭素−炭素結合を介して互いに直接結合された複数個のベンゼン環(たとえばビフェニル基など)または2個以上の近接する環炭素原子を共有することにより縮合一体化された複数個のベンゼン環(たとえばナフチル基など)で構成された1つの核と、よりなる一価基として定義され、ただし、環炭素原子は、少なくとも1個の窒素原子、酸素原子、または硫黄原子により置き換えることが可能であり、好ましくは、アリール基中、環炭素原子は、置き換えられておらず、
・ アリール基は、好ましくは6〜30個の炭素原子を含有し、より好ましくはフェニル基であり、
・ アルキルアリール基中に含まれるアルキル基は、以上に述べたアルキル基の優先性を満たし、
・ アラルキル基中に含まれるアリール基は、以上に述べたアリール基の優先性を満たす。
Preferably, the monovalent substituent is selected from:
Hydrocarbyl, such as alkyl, aryl, alkylaryl, and aralkyl, etc.
Halogeno, such as -Cl, -Br, -F, and -I, etc.
Hydrocarbyl groups partially or fully substituted by at least one halogen atom, such as halogenoalkyl, halogenoaryl, halogenoalkylaryl, and halogenoaralkyl, etc.
Hydroxyl,
Hydrocarbyl groups substituted by at least one hydroxyl group, such as hydroxyalkyl, hydroxyaryl, hydroxyalkylaryl, and hydroxyaralkyl, etc.
Hydrocarbyloxy [—O—R wherein R is a hydrocarbyl group]], for example, alkoxy, aryloxy, alkylaryloxy, aralkyloxy, etc.
Amino (-NH 2),
A hydrocarbyl group substituted by at least one amino group, such as aminoalkyl and aminoaryl,
Hydrocarbylamine [—NHR or —NR 2 wherein R is a hydrocarbyl group]], such as alkylamines and arylamines, etc.
Carboxylic acids and their metal or ammonium salts, carboxylic acid halides, carboxylic acid anhydrides,
A hydrocarbyl group substituted by at least one of a carboxylic acid, its metal salt or ammonium salt, a carboxylic acid halide, and a carboxylic anhydride, eg, —R—C (═O) OH, wherein R is alkyl Group or aryl group), etc.
Hydrocarbyl esters [—C (═O) OR or —O—C (═O) R wherein R is a hydrocarbyl group]], for example, alkyl esters, aryl esters, alkylaryl esters, aralkyl esters, and the like ,
An amide [—C (═O) NH 2 ],
A hydrocarbyl group substituted by at least one amide group,
Hydrocarbyl amide monoesters [—C (═O) NHR or —NH—C (═O) —R where R is a hydrocarbyl group]], for example, alkylamides, arylamides, alkylarylamides, and Aralkylamides and the like, as well as hydrocarbylamide diesters [—C (═O) NR 2 or —N—C (═O) R 2 wherein R is a hydrocarbyl group]], for example, dialkylamides and diarylamides,
Sulfinic acid (—SO 2 H), sulfonic acid (—SO 3 H), their metal salts or ammonium salts,
Hydrocarbyl sulfone [—S (═O) 2 —R wherein R is a hydrocarbyl group]], for example, alkyl sulfone, aryl sulfone, alkylaryl sulfone, aralkyl sulfone, etc.
An aldehyde [—C (═O) H] and a haloformyl [—C (═O) X wherein X is a halogen atom]],
Hydrocarbyl ketones [—C (═O) —R wherein R is a hydrocarbyl group]], such as alkyl ketones, aryl ketones, alkyl aryl ketones, and aralkyl ketones, etc.
A hydrocarbyloxyhydrocarbyl ketone [—C (═O) —R 1 —O—R 2 wherein R 1 is a divalent hydrocarbon group such as alkylene, arylene, alkylarylene, or aralkylene, preferably C 1 -C 18 alkylene, phenylene, and the like at least one of a phenylene group substituted by an alkyl group or at least one alkylene group substituted by a phenyl group, and R 2 is a hydrocarbyl group, for example, an alkyl group, Aryl groups, alkylaryl groups, aralkyl groups, etc.]], for example, alkyloxyalkyl ketones, alkyloxyaryl ketones, alkyloxyalkylaryl ketones, alkyloxyaralkyl ketones, aryloxyalkyl ketones, aryloxy aryls Ruketone, aryloxyalkyl aryl ketone, and aryloxy aralkyl ketone,
Any one of the foregoing groups comprising at least one hydrocarbyl group or divalent hydrocarbon group R 1 , wherein said hydrocarbyl group or said R 1 itself is at least one of the monovalent substituents listed above Substituted) by, for example, aryl ketone-C (= O) -R, wherein R is an aryl group substituted by one hydroxyl group;
here,
The hydrocarbyl group preferably contains 1 to 30 carbon atoms, more preferably 1 to 12 carbon atoms, even more preferably 1 to 6 carbon atoms,
The alkyl group preferably contains 1 to 18 carbon atoms, more preferably 1 to 6 carbon atoms, very preferably methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, And tert-butyl,
An aryl group is composed of one end and one benzene ring (for example, a phenyl group) or a plurality of benzene rings (for example, a biphenyl group) directly connected to each other via a carbon-carbon bond, or two or more Defined as a monovalent group consisting of one nucleus composed of a plurality of benzene rings fused together by sharing adjacent ring carbon atoms (for example, a naphthyl group, etc.), provided that the ring carbon atom is Can be replaced by at least one nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur atom, and preferably in the aryl group, the ring carbon atom is not replaced;
The aryl group preferably contains 6 to 30 carbon atoms, more preferably a phenyl group,
・ The alkyl group contained in the alkylaryl group satisfies the above-mentioned preference of the alkyl group,
-The aryl group contained in the aralkyl group satisfies the above-mentioned priority of the aryl group.
より好ましくは、一価置換基は、ヒドロカルビルケトン[−C(=O)−R〔式中、Rはヒドロカルビル基である〕]およびヒドロカルビルオキシヒドロカルビルケトン[−C(=O)−R1−O−R2〔式中、R1は二価炭化水素基であり、かつR2はヒドロカルビル基である〕]から選択され、前記ヒドロカルビルケトンおよび前記ヒドロカルビルオキシヒドロカルビルケトンは、置換されていないか、または以上に列挙された一価置換基の少なくとも1つによりで置換されている。 More preferably, the monovalent substituent is hydrocarbyl ketone [—C (═O) —R wherein R is a hydrocarbyl group]] and hydrocarbyloxyhydrocarbyl ketone [—C (═O) —R 1 —O. -R 2 wherein R 1 is a divalent hydrocarbon group and R 2 is a hydrocarbyl group, and the hydrocarbyl ketone and the hydrocarbyloxyhydrocarbyl ketone are unsubstituted or Substitution with at least one of the monovalent substituents listed above.
さらにより好ましくは、一価置換基は、アリールケトンおよびアリールオキシアリールケトンから選択され、前記アリールケトンおよびアリールオキシアリールケトンは、置換されていないか、または以上に列挙された一価置換基の少なくとも1つにより置換されている。 Even more preferably, the monovalent substituent is selected from aryl ketones and aryloxy aryl ketones, said aryl ketone and aryloxy aryl ketone being unsubstituted or at least of the monovalent substituents listed above. Is replaced by one.
最も好ましくは、一価置換基は、(無置換型)アリールケトンであり、特定的にはフェニルケトン[−C(=O)−フェニル]である。 Most preferably, the monovalent substituent is an (unsubstituted) aryl ketone, specifically phenyl ketone [—C (═O) -phenyl].
反復ユニット(R)の場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基の核は、好ましくは多くとも3個、より好ましくは多くとも2個、さらにより好ましくは多くとも1個のベンゼン環で構成される。その場合、反復ユニット(R)の場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基の核が1個のベンゼン環で構成されるとき、反復ユニット(R)は、場合により置換されていてもよいフェニレン基よりなる1つ以上の式で示され、ただし、前記場合により置換されていてもよいフェニレン基は、その2つの末端のそれぞれにより、直接C−C結合を介して、2つの他の場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基に結合される。 The nucleus of the optionally substituted arylene group in the repeating unit (R) is preferably composed of at most 3, more preferably at most 2 and even more preferably at most 1 benzene ring. . In that case, when the nucleus of the arylene group which may be optionally substituted in the case of the repeating unit (R) is composed of one benzene ring, the repeating unit (R) may be an optionally substituted phenylene group. Wherein the optionally substituted phenylene group is substituted by each of its two ends by two other optionally substituted via a direct C—C bond. To an arylene group which may be substituted.
以上に説明したように、反復ユニット(R)の場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基は、その2つの末端のそれぞれにより、直接C−C結合を介して、2つの他の場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基に結合される。好ましくは、それは、その2つの末端のそれぞれにより、直接C−C結合を介して、2つの他の場合により置換されていてもよいフェニレン基に結合される。 As explained above, the arylene group which may optionally be substituted in the repeating unit (R) is substituted by two other cases via a direct C—C bond with each of its two ends. To an arylene group which may be present. Preferably it is linked by two of its two ends to two other optionally substituted phenylene groups via a direct C-C bond.
同様に以上に説明したように、反復ユニット(R)の場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基の両方の末端は、とくに、方向および向きにより特徴付け可能である。 Similarly, as explained above, both ends of the arylene group which may optionally be substituted in the repeating unit (R) can be characterized in particular by direction and orientation.
反復ユニット(R)の第1の集合は、場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基で構成され、その末端は、
・ 同一の方向を有し、
・ 反対の向きであり、かつ
・ 互いに一直線上にある
[これ以降で、剛性棒状体形成性アリーレンユニット](Ra)。
The first set of repeating units (R) is composed of an optionally substituted arylene group, the ends of which are
Have the same direction,
-Opposite orientations; and-in line with each other [from now on, rigid rod-forming arylene units] (Ra).
そのような場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基の例としては、以下のもの、および以上に定義された少なくとも1個の一価置換基により、特定的にはフェニルケトン基により置換されたこれらの基のいずれかが挙げられるが、これらに限定されるものではない。
Examples of optionally substituted arylene groups include the following, and those substituted with at least one monovalent substituent as defined above, specifically with a phenyl ketone group: Any of these groups may be mentioned, but the invention is not limited to these.
場合により置換されていてもよいp−フェニレンは、剛性棒状体形成性アリーレンユニット(Ra)として有利である。 The optionally substituted p-phenylene is advantageous as a rigid rod-forming arylene unit (Ra).
剛性棒状体形成性アリーレンユニット(Ra)は、ポリアリーレン中に含有される場合、卓越した剛性を呈する直線状ポリマー鎖を生じる。このため、そのようなポリアリーレンは、一般に「剛性棒状ポリマー」として参照される。 Rigid rod-forming arylene units (Ra), when contained in polyarylene, produce linear polymer chains that exhibit excellent stiffness. For this reason, such polyarylenes are generally referred to as “rigid rod polymers”.
反復ユニット(R)の第2の集合は、場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基で構成され、その末端は、
・ いずれも異なる方向を有して、互いに0〜180°の角度(前記角度は鋭角または鈍角でありうる)を形成するか、
・ または同一の方向および同一の向きを有するか、
・ または同一の方向を有し、かつ反対の向きであり、かつ互いに交わらない(すなわち、互いに一直線上にない)
[包括的にこれ以降ではキンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb)として参照される]。
The second set of repeating units (R) is composed of optionally substituted arylene groups, the ends of which are
Either have different directions to form an angle of 0 to 180 ° with each other (the angle can be acute or obtuse);
Or have the same direction and the same direction,
Or they have the same direction and are in opposite directions and do not cross each other (ie are not in line with each other)
[Generally referred to hereinafter as the kink-forming arylene unit (Rb)].
この場合、キンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb)の第1の部分集合は、場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基で構成され、その末端は、異なる方向を有して、互いに鋭角を形成する[キンク形成性アリーレンユニット](Rb−1)。末端が互いに異なる方向を有する場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基の例としては、以下のもの、および以上に定義された少なくとも1個の一価置換基により、特定的にはフェニルケトン基により置換されたこれらの基のいずれかが挙げられるが、これらに限定されるものではない。
In this case, the first subset of kink-forming arylene units (Rb) is composed of optionally substituted arylene groups whose ends have different directions and form acute angles with each other [ Kink-forming arylene unit] (Rb-1). Examples of optionally substituted arylene groups in which the ends have different directions from each other include the following, and at least one monovalent substituent as defined above, specifically a phenyl ketone group. Although any of these substituted groups is mentioned, it is not limited to these.
キンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb)の第2の部分集合は、場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基で構成され、その末端は、異なる方向を有し、互いに鈍角を形成する[キンク形成性ユニット](Rb−2)。末端が互いに異なる方向を有する場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基の例としては、以下のもの、および以上に定義された少なくとも1個の一価置換基により、特定的にはフェニルケトン基により置換されたこれらの基のいずれかが挙げられるが、これらに限定されるものではない。
The second subset of kink-forming arylene units (Rb) is made up of optionally substituted arylene groups, the ends of which have different directions and form obtuse angles with each other [kink-forming units ] (Rb-2). Examples of optionally substituted arylene groups in which the ends have different directions from each other include the following, and at least one monovalent substituent as defined above, specifically a phenyl ketone group. Although any of these substituted groups is mentioned, it is not limited to these.
キンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb)の第3の部分集合は、場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基で構成され、その末端は、同一の方向および同一の向きを有する[キンク形成性アリーレンユニット](Rb−3)。末端が同一の方向および同一の向きである場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基の例としては、以下のもの、および以上に定義された少なくとも1個の一価置換基により、特定的にはフェニルケトン基により置換されたこれらの基のいずれかが挙げられるが、これらに限定されるものではない。
The third subset of the kink-forming arylene unit (Rb) is composed of an optionally substituted arylene group, and the terminal has the same direction and the same direction [kink-forming arylene unit] (Rb-3). Examples of arylene groups which may be optionally substituted if the ends are in the same direction and in the same direction are, in particular, by the following and at least one monovalent substituent as defined above: Any of these groups substituted by a phenylketone group can be mentioned, but not limited thereto.
キンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb)の第4の部分集合は、場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基で構成され、その末端は、同一の方向を有し、かつ反対の向きであり、かつ互いに交わらない[キンク形成性アリーレンユニット](Rb−4)。そのような場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基の例としては、以下のもの、および以上に定義された少なくとも1個の一価置換基により、特定的にはフェニルケトン基により置換されたこれらの基のいずれかが挙げられるが、これらに限定されるものではない。
好ましくは、キンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb)は、キンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb−1)、キンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb−2)、およびキンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb−4)から選択される。より好ましくは、キンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb)は、キンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb−1)およびキンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb−2)から選択される。さらにより好ましくは、キンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb)は、キンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb−1)から選択される。そのうえさらにより好ましくは、キンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb)は、場合により置換されていてもよいm−フェニレンである。
The fourth subset of kink-forming arylene units (Rb) is composed of optionally substituted arylene groups, the ends of which are in the same direction and in opposite directions, and [Kink-forming arylene unit] (Rb-4) not intersected. Examples of optionally substituted arylene groups include the following, and those substituted with at least one monovalent substituent as defined above, specifically with a phenyl ketone group: Any of these groups may be mentioned, but the invention is not limited to these.
Preferably, the kink-forming arylene unit (Rb) is selected from the kink-forming arylene unit (Rb-1), the kink-forming arylene unit (Rb-2), and the kink-forming arylene unit (Rb-4). . More preferably, the kink-forming arylene unit (Rb) is selected from a kink-forming arylene unit (Rb-1) and a kink-forming arylene unit (Rb-2). Even more preferably, the kink-forming arylene unit (Rb) is selected from the kink-forming arylene unit (Rb-1). Even more preferably, the kink-forming arylene unit (Rb) is an optionally substituted m-phenylene.
キンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb)は、ポリアリーレン中に含有される場合、多かれ少なかれキンク形ポリマー鎖を生じ、直線状ポリマー鎖よりも高い溶解性および可融性を呈する。このため、そのようなポリアリーレンは、一般に「キンク形ポリマー」として参照される。 The kink-forming arylene unit (Rb), when contained in polyarylene, produces more or less kink-shaped polymer chains and exhibits higher solubility and fusibility than linear polymer chains. For this reason, such polyarylenes are generally referred to as “kink-type polymers”.
キンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレン(P)の反復ユニット(R)は、特定のタイプのものでなければならない。すなわち、
・ 反復ユニット(R)の全モル数を基準にして0〜75モル%の、少なくとも1個の一価置換基で場合により置換されていてもよい剛性棒状体形成性アリーレンユニット(Ra)と、
・ 反復ユニット(R)の全モル数を基準にして25〜100モル%の、少なくとも1個の一価置換基により場合により置換されていてもよいし置換されていなくてもよいキンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb)と、
よりなる混合物(M)でなければならない。
反復ユニット(R)は、好ましくは、
・ 反復ユニット(R)の全モル数を基準にして0〜75モル%の、場合により置換されていてもよいp−フェニレンから選択される剛性棒状体形成性アリーレンユニット(Ra)と、
・ 反復ユニット(R)の全モル数を基準にして25〜100モル%の、(i)場合により置換されていてもよいm−フェニレンおよび(ii)場合により置換されていてもよいm−フェニレンと場合により置換されていてもよいo−フェニレンとの混合物から選択されるキンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb)と、
よりなる混合物(M)である。
The repeating unit (R) of the kink-shaped rigid rod-like polyarylene (P) must be of a specific type. That is,
A rigid rod-forming arylene unit (Ra) optionally substituted with at least one monovalent substituent, from 0 to 75 mol%, based on the total number of moles of repeating units (R);
A kink-forming arylene which may be optionally substituted by at least one monovalent substituent, in an amount of 25 to 100 mol%, based on the total number of moles of repeating units (R) A unit (Rb);
It must be a mixture (M).
The repeating unit (R) is preferably
A rigid rod-forming arylene unit (Ra) selected from 0-75 mol%, optionally substituted p-phenylene, based on the total number of moles of repeating units (R);
25 to 100 mol%, based on the total number of moles of repeating units (R), (i) optionally substituted m-phenylene and (ii) optionally substituted m-phenylene And a kink-forming arylene unit (Rb) selected from a mixture of optionally substituted o-phenylene,
It is a mixture (M) consisting of
好ましくは、混合物(M)中の全部ではないにしても本質的にすべての剛性棒状体形成性アリーレンユニット(Ra)は、少なくとも1個の置換基により置換されたp−フェニレンユニットである。より好ましくは、混合物(M)中の全部ではないにしても本質的にすべての剛性棒状体形成性アリーレンユニット(Ra)は、ヒドロカルビルケトン[−C(=O)−R〔式中、Rはヒドロカルビル基である〕]およびヒドロカルビルオキシヒドロカルビルケトン[−C(=O)−R1−O−R2〔式中、R1は二価炭化水素基であり、かつR2はヒドロカルビル基である〕]から選択される少なくとも1個の一価置換基により置換されたp−フェニレンである。ただし、前記ヒドロカルビルケトンおよび前記ヒドロカルビルオキシヒドロカルビルケトンはそれ自体、置換されていないか、または以上に列挙されたような少なくとも1個の一価置換基により置換されている。さらにより好ましくは、混合物(M)中の全部ではないにしても本質的にすべての剛性棒状体形成性アリーレンユニット(Ra)は、アリールケトンおよびアリールオキシアリールケトンから選択される少なくとも1個の一価置換基により置換されたp−フェニレンである。ただし、前記アリールケトンおよび前記アリールオキシアリールケトンは、置換されていないか、または以上に列挙されたような少なくとも1個の一価置換基により置換されている。最も好ましくは、混合物(M)中の全部ではないにしても本質的にすべての剛性棒状体形成性アリーレンユニット(Ra)は、アリールケトン基により、特定的にはフェニルケトン基により置換されたp−フェニレンである。 Preferably, essentially, if not all, of the rigid rod-forming arylene units (Ra) in the mixture (M) are p-phenylene units substituted with at least one substituent. More preferably, essentially all if not all rigid rod-forming arylene units (Ra) in mixture (M) are hydrocarbyl ketone [—C (═O) —R, where R is Is a hydrocarbyl group]] and hydrocarbyloxyhydrocarbyl ketone [—C (═O) —R 1 —O—R 2 wherein R 1 is a divalent hydrocarbon group and R 2 is a hydrocarbyl group] P-phenylene substituted with at least one monovalent substituent selected from However, the hydrocarbyl ketone and the hydrocarbyloxyhydrocarbyl ketone are themselves unsubstituted or substituted with at least one monovalent substituent as listed above. Even more preferably, essentially all if not all rigid rod-forming arylene units (Ra) in mixture (M) are at least one selected from aryl ketones and aryloxy aryl ketones. P-phenylene substituted by a valent substituent. However, the aryl ketone and the aryloxy aryl ketone are unsubstituted or substituted with at least one monovalent substituent as listed above. Most preferably essentially all if not all rigid rod-forming arylene units (Ra) in the mixture (M) are substituted by arylketone groups, in particular by phenylketone groups. -Phenylene.
混合物(M)中の全部ではないにしても本質的にすべてのキンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb)は、少なくとも1個の置換基により場合により置換されていてもよいm−フェニレンユニットである。より好ましくは、混合物(M)中の全部ではないにしても本質的にすべてのキンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb)は、ヒドロカルビルケトン[−C(=O)−R〔式中、Rはヒドロカルビル基である〕]およびヒドロカルビルオキシヒドロカルビルケトン[−C(=O)−R1−O−R2〔式中、R1は二価炭化水素基であり、かつR2はヒドロカルビル基である〕]から選択される少なくとも1個の一価置換基により場合により置換されていてもよいm−フェニレンユニットである。ただし、前記ヒドロカルビルケトンおよび前記ヒドロカルビルオキシヒドロカルビルケトンはそれ自体、置換されていないか、または以上に列挙されたような少なくとも1個の一価置換基により置換されている。さらにより好ましくは、混合物(M)中の全部ではないにしても本質的にすべてのキンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb)は、無置換型m−フェニレンユニットである。 Essentially all if not all kink-forming arylene units (Rb) in the mixture (M) are m-phenylene units optionally substituted by at least one substituent. More preferably, essentially all if not all kink-forming arylene units (Rb) in the mixture (M) are hydrocarbyl ketone [—C (═O) —R, wherein R is a hydrocarbyl group. ]] And hydrocarbyloxyhydrocarbyl ketone [—C (═O) —R 1 —O—R 2 wherein R 1 is a divalent hydrocarbon group and R 2 is a hydrocarbyl group]]. M-phenylene units optionally substituted by at least one selected monovalent substituent. However, the hydrocarbyl ketone and the hydrocarbyloxyhydrocarbyl ketone are themselves unsubstituted or substituted with at least one monovalent substituent as listed above. Even more preferably essentially all if not all kink-forming arylene units (Rb) in the mixture (M) are unsubstituted m-phenylene units.
混合物(M)中、キンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb)のモル数は、反復ユニット(R)の全モル数を基準にして、好ましくは少なくとも25%、より好ましくは少なくとも30%、さらにより好ましくは少なくとも35%、さらにより好ましくは少なくとも40%、最も好ましくは少なくとも45%である。一方、混合物(M)中、キンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb)のモル数は、反復ユニット(R)の全モル数を基準にして、好ましくは多くとも90%、より好ましくは多くとも75%、さらにより好ましくは多くとも65%、最も好ましくは、多くとも55%である。 In the mixture (M), the number of moles of kink-forming arylene units (Rb) is preferably at least 25%, more preferably at least 30%, even more preferably based on the total number of moles of repeating units (R). At least 35%, even more preferably at least 40%, most preferably at least 45%. On the other hand, the number of moles of the kink-forming arylene unit (Rb) in the mixture (M) is preferably at most 90%, more preferably at most 75%, based on the total number of moles of the repeating unit (R). Even more preferably at most 65%, most preferably at most 55%.
反復ユニット(R)が、約50:50のモル比で、フェニルケトン基により置換されたp−フェニレンユニットと無置換型m−フェニレンユニットとよりなる混合物である場合、良好な結果が得られた。 Good results have been obtained when the repeating unit (R) is a mixture of p-phenylene units substituted with phenylketone groups and unsubstituted m-phenylene units in a molar ratio of about 50:50. .
キンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレン(P)はさらに、反復ユニット(R)とは異なる反復ユニット(R*)を含みうる。 The kink-shaped rigid rod-shaped polyarylene (P) may further include a repeating unit (R * ) different from the repeating unit (R).
反復ユニット(R*)は、その末端のそれぞれでアリーレン基に結合された少なくとも1個の強力な二価電子求引性基を含有していてもよいし含有していなくてもよい。そのような強力な二価電子求引性基を含まない反復ユニット(R*)の例としては、が挙げられるが、これらに限定されるものではない。
The repeating unit (R * ) may or may not contain at least one strong divalent electron withdrawing group bonded to the arylene group at each of its ends. Examples of repeating units (R * ) that do not contain such strong divalent electron withdrawing groups include, but are not limited to:
反復ユニット(R*)は、好ましくは、その末端のそれぞれでアリーレン基とくにp−フェニレン基に結合された少なくとも1個の強力な二価電子求引性基を含有する。二価電子求引性基は、好ましくは、スルホン基[−S(=O)2−]、カルボニル基[−C(=O)−]、ビニレン基[−CH=CH−]、スルホキシド基[−S(=O)−]、アゾ基[−N=N−]、−C(CF3)2−のような飽和フルオロカーボン基、有機ホスフィンオキシド基[−P(=O)(=Rh)−〔式中、Rhはヒドロカルビル基である〕]、およびエチリデン基[−C(=CA2)−〔式中、Aは水素またはハロゲンでありうる〕]。より好ましくは、二価電子求引性基は、スルホン基およびカルボニル基から選択される。さらにより好ましくは、反復ユニット(R*)は、以下のものから選択される。
(i) 式
で示される反復ユニット
(ii) 式
で示される反復ユニット
〔式中、Qは、
{ここで、nは1〜6の整数であり、かつn’は2〜6の整数である}
から選択される基であり、Qは、好ましくは、
から選択される〕
(iii) 式
で示される反復ユニット
(iv) 式
で示される反復ユニット
The repeating unit (R * ) preferably contains at least one strong divalent electron withdrawing group bonded to an arylene group, in particular a p-phenylene group, at each of its ends. The divalent electron withdrawing group is preferably a sulfone group [—S (═O) 2 —], a carbonyl group [—C (═O) —], a vinylene group [—CH═CH—], a sulfoxide group [ —S (═O) —], azo group [—N═N—], saturated fluorocarbon group such as —C (CF 3 ) 2 —, organic phosphine oxide group [—P (═O) (═R h ) - wherein, R h is a hydrocarbyl group]], and ethylidene group [-C (= CA 2) - in the formulas, a may be hydrogen or halogen]. More preferably, the divalent electron withdrawing group is selected from a sulfone group and a carbonyl group. Even more preferably, the repeating unit (R * ) is selected from:
(I) Formula
Iteration unit represented by (ii)
(Where Q is
{Where n is an integer from 1 to 6 and n ′ is an integer from 2 to 6}
Q is preferably a group selected from
Selected from)
(Iii) Formula
Repeat unit (iv) expressed by
Iteration unit indicated by
ポリアリーレン中の反復ユニットの好ましくは75wt%超、より好ましくは90wt%超は、反復ユニット(R)である。さらにより好ましくは、ポリアリーレン中の全部ではないにしても本質的にすべての反復ユニットは、反復ユニット(R)である。 Preferably more than 75 wt%, more preferably more than 90 wt% of the repeat units in the polyarylene are repeat units (R). Even more preferably, essentially all, if not all, repeat units in the polyarylene are repeat units (R).
ポリアリーレンがキンク形剛性棒状ポリフェニレンであり、その中の全部ではないにしても本質的にすべての反復ユニットが、10:90〜70:30、好ましくは25:75〜65:35、より好ましくは35:65〜60:40、さらにより好ましくは45:55〜55:45、最も好ましくは約50:50のモル比p−フェニレン:m−フェニレンで、フェニルケトン基により置換されたp−フェニレンと無置換型m−フェニレンとの混合物よりなる場合、優れた結果が得られた。そのようなキンク形剛性棒状ポリフェニレンは、PrimoSpire(登録商標)PR−250ポリフェニレンとしてSolvay Advanced Polymers,L.L.C.から市販されている。 The polyarylene is a kink-shaped rigid rod-like polyphenylene in which essentially all if not all repeating units are 10:90 to 70:30, preferably 25:75 to 65:35, more preferably P-phenylene substituted with a phenyl ketone group in a molar ratio p-phenylene: m-phenylene of 35: 65-60: 40, even more preferably 45: 55-55: 45, most preferably about 50:50 In the case of a mixture with unsubstituted m-phenylene, excellent results were obtained. Such a kink-shaped rigid rod-like polyphenylene is disclosed in Solvay Advanced Polymers, L. as PrimoSpire® PR-250 polyphenylene. L. C. Commercially available.
キンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレン(P)は、通常は1000超、好ましくは5000超、より好ましくは約10000超、さらにより好ましくは15000超の数平均分子量を有する。一方、キンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレンの数平均分子量は、通常は100000未満、好ましくは70000未満である。特定の実施形態では、キンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレンの数平均分子量は、35000超である。他の実施形態では、多くとも35000であり、この実施形態では、多くの場合は多くとも25000、ときには多くとも20000である。一般的なポリアリーレンの数平均分子量、とくにキンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレン(P)のものは、有利には、(1)ポリスチレン校正標準を用いてゲル浸透クロマトグラフィー(GPC)によりポリアリーレンの「相対」数平均分子量を測定し、次に、(2)そのように測定された「相対」数平均分子量を2で割り算することにより決定される。ポリアリーレンの専門家である当業者であれば、GPCにより測定されるその「相対」数平均分子量が一般に2倍にずれていることはわかっているので、それに従って処理される。以上に挙げた分子量の下限および上限のいずれについても、この補正係数が考慮されている。 The kink-shaped rigid rod-like polyarylene (P) usually has a number average molecular weight of greater than 1000, preferably greater than 5000, more preferably greater than about 10,000, and even more preferably greater than 15,000. On the other hand, the number average molecular weight of the kink-shaped rigid rod-shaped polyarylene is usually less than 100,000, preferably less than 70000. In certain embodiments, the number average molecular weight of the kink-shaped rigid rod-shaped polyarylene is greater than 35000. In other embodiments, it is at most 35000, and in this embodiment it is often at most 25000 and sometimes at most 20000. The number average molecular weight of common polyarylenes, in particular those of kink-shaped rigid rod-like polyarylenes (P), are advantageously (1) “relative” of polyarylenes by gel permeation chromatography (GPC) using polystyrene calibration standards. The number average molecular weight is measured, and then (2) the “relative” number average molecular weight so measured is divided by two. Those skilled in the art who are specialists in polyarylene know that their “relative” number average molecular weight, as measured by GPC, generally deviates by a factor of two and are treated accordingly. This correction factor is taken into consideration for both the lower limit and the upper limit of the molecular weight mentioned above.
それは、アモルファスでありうるか(すなわち、融点を有していない)、または半結晶性でありうる(すなわち、融点を有する)。それは、好ましくはアモルファスである。 It can be amorphous (ie, has no melting point) or semi-crystalline (ie, has a melting point). It is preferably amorphous.
それは、有利には50℃超、好ましくは120℃超、より好ましくは150℃超のガラス転移温度を有する。 It advantageously has a glass transition temperature above 50 ° C, preferably above 120 ° C, more preferably above 150 ° C.
キンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレン(P)は、一般的には非分岐状である。特定的には、それは、一般に、反復分岐状ユニット
〔式中、Aryは多価アリーレンであり、かつxは、2を超える結合数x≧1を表す〕
を本質的に含まないかまたはまったく含まない。
The kink-shaped rigid rod-like polyarylene (P) is generally unbranched. In particular, it is generally a repetitive branching unit
[In the formula, Ary is a polyvalent arylene, and x represents the number of bonds x ≧ 1 exceeding 2.]
Is essentially free of or not at all.
キンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレン(P)は、任意の方法により調製可能である。そのようなキンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレンを調製するための当技術分野で周知の方法は、(i)場合により置換されていてもよい剛性棒状体形成性アリーレン基(その2つの末端で、塩素、臭素、およびヨウ素などの1個のハロゲン原子に結合されている)よりなる少なくとも1種のジハロアリーレン分子化合物を、(ii)場合により置換されていてもよいキンク形成性アリーレン基(その2つの末端のそれぞれで、塩素、臭素、ヨウ素、およびフッ素などの1個のハロゲン原子に結合されている)よりなる少なくとも1種のジハロアリーレン分子化合物と、好ましくは還元的カップリングにより、重合することを含む。ジハロアリーレン分子化合物からハロゲン原子が脱離すると、それぞれ、場合により置換されていてもよい剛性ロッド形成性アリーレン基および場合により置換されていてもよいキンク形成性アリーレン基が得られる。 The kink-shaped rigid rod-like polyarylene (P) can be prepared by any method. Methods well known in the art for preparing such kink-shaped rigid rod-like polyarylenes are: (i) optionally substituted rigid rod-forming arylene groups (at their two ends, chlorine, At least one dihaloarylene molecular compound consisting of bromine and one halogen atom such as iodine) (ii) an optionally substituted kink-forming arylene group (the two Polymerizing with at least one dihaloarylene molecular compound consisting of chlorine, bromine, iodine, and fluorine at each end, which is bonded to one halogen atom, such as chlorine, preferably by reductive coupling. including. When the halogen atom is eliminated from the dihaloarylene molecular compound, an optionally substituted rigid rod-forming arylene group and an optionally substituted kink-forming arylene group are obtained, respectively.
したがって、たとえば、以下のとおりである。
・ p−ジクロロベンゼン、p−ジクロロビフェニル、またはNが3〜10の整数である一般式Cl−(φ)N−Clで示されるそれらの同族体の分子から両方の塩素原子が脱離すると、それぞれ、1、2、またはN隣接のp−フェニレンユニット(剛性棒状体形成性アリーレンユニット)が形成され、したがって、p−ジクロロベンゼン、p−ジクロロビフェニル、および以上に定義された一般式Cl−(φ)N−Clで示されるそれらの同族体は、p−フェニレンユニットを形成するように重合可能である。
・ 2,5−ジクロロベンゾフェノン(p−ジクロロベンゾフェノン)は、1,4−(ベンゾイルフェニレン)ユニット(同様に剛性棒状体形成性アリーレンユニット)を形成するように重合可能である。
・ m−ジクロロベンゼンは、m−フェニレンユニット(キンク形成性アリーレンユニット)を形成するように重合可能である。
Thus, for example:
When both chlorine atoms are desorbed from p-dichlorobenzene, p-dichlorobiphenyl, or their homologous molecules represented by the general formula Cl- (φ) N —Cl, where N is an integer of 3-10, 1, 2, or N adjacent p-phenylene units (rigid rod-forming arylene units) are formed, respectively, so that p-dichlorobenzene, p-dichlorobiphenyl, and the general formula Cl- ( Those homologues represented by [phi]) N-Cl are polymerizable to form p-phenylene units.
2,5-dichlorobenzophenone (p-dichlorobenzophenone) can be polymerized to form 1,4- (benzoylphenylene) units (also rigid rod-forming arylene units).
M-Dichlorobenzene can be polymerized to form m-phenylene units (kink-forming arylene units).
本発明では、1、2、3種、さらには3種超の異なるキンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレン(P)を使用することが可能である。 In the present invention, 1, 2, 3, or even more than three different kink-shaped rigid rod-like polyarylenes (P) can be used.
場合により存在していてもよい成分
以上に記載のポリマー材料(M)はさらに、キンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレン(P)以外の1種以上のポリマーおよび/または1種以上の非高分子添加剤(総称して、場合により存在していてもよい成分と呼ばれる)を含有しうる。
The polymer material (M) described above in the components that may optionally be present may further include one or more polymers and / or one or more non-polymeric additives other than the kink-shaped rigid rod-shaped polyarylene (P) ( (Collectively referred to as components that may optionally be present).
関連する非高分子添加剤としては、とくに、繊維状強化剤、タルクやシリカなどの微粒子充填材および核剤、接着促進剤、相溶化剤、硬化剤、滑剤、金属粒子、離型剤、TiO2やカーボンブラックのような有機顔料および/または無機顔料、染料、遅炎剤、防煙剤、熱安定剤、酸化防止剤、UV吸収剤、ゴムなどの強靭化剤、可塑剤、帯電防止剤、融解粘度降下剤、およびそれらの混合物が挙げられる。 Related non-polymeric additives include, among others, fibrous reinforcing agents, particulate fillers and nucleating agents such as talc and silica, adhesion promoters, compatibilizers, curing agents, lubricants, metal particles, mold release agents, TiO 2 and organic pigments such as carbon black and / or inorganic pigments, dyes, flame retardants, smoke suppressants, heat stabilizers, antioxidants, UV absorbers, tougheners such as rubber, plasticizers, antistatic agents , Melt viscosity reducing agents, and mixtures thereof.
第1の特定の実施形態では、ポリマー材料(M)はさらに、キンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレン(P)以外の少なくとも1種のポリアリーレンを含む。キンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレン(P)以外のポリアリーレンは、好ましくは、反復ユニットの50wt%超が、場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基よりなる1つ以上の式で示される反復ユニット(R2)である、キンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレン(P2)である。ただし、前記場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基は、その2つの末端のそれぞれにより、直接C−C結合を介して、2つの他の場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基に結合されており、前記反復ユニット(R2)は、
・ 反復ユニット(R2)の全モル数を基準にして75モル%〜100モル%の、少なくとも1個の一価置換基により場合により置換されていてもよい剛性棒状体形成性アリーレンユニット(R2a)と、
・ 反復ユニット(R2)の全モル数を基準にして0〜25モル%の、少なくとも1個の一価置換基により場合により置換されていてもよいキンク形成性アリーレンユニット(R2b)と、
よりなる混合物(M2)である。
In a first particular embodiment, the polymeric material (M) further comprises at least one polyarylene other than the kink-shaped rigid rod-like polyarylene (P). The polyarylenes other than the kink-shaped rigid rod-like polyarylene (P) are preferably a repeating unit (R2) represented by one or more formulas in which more than 50 wt% of the repeating units consist of an optionally substituted arylene group. ), A kink-shaped rigid rod-shaped polyarylene (P2). However, the optionally substituted arylene group is bonded to the two other optionally substituted arylene groups via a direct C-C bond by each of its two ends. And the repeating unit (R2) is
A rigid rod-forming arylene unit (R2a) optionally substituted by at least one monovalent substituent, from 75 mol% to 100 mol%, based on the total number of moles of the repeating unit (R2) When,
-0 to 25 mol% of the kink-forming arylene unit (R2b) optionally substituted by at least one monovalent substituent, based on the total number of moles of the repeating unit (R2);
(M2).
とくに明記されていないかぎり、キンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレン(P2)は、有利には、以上に詳述されたキンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレン(P)のすべての特性を任意の優先レベルで満たす。 Unless otherwise stated, the kink-shaped rigid rod polyarylene (P2) advantageously satisfies all the properties of the kink-shaped rigid rod polyarylene (P) detailed above at any priority level.
キンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレン(P2)の反復ユニット(R2a)および(R2b)の量、混合物(M2)中のキンク形成性アリーレンユニット(R2b)のモル数は、反復ユニット(R2)の全モル数を基準にして好ましくは少なくとも1.0%、より好ましくは少なくとも5%、さらにより好ましくは少なくとも10%である。一方、混合物(M2)中、キンク形成性アリーレンユニット(R2b)のモル数は、反復ユニット(R2)の全モル数を基準にして好ましくは多くとも20%、より好ましくは多くとも18%である。ポリアリーレン(P2)がキンク形剛性棒状ポリフェニレンコポリマーであり、その中の全部ではないにしても本質的にすべての反復ユニットが、80:20〜95:5、好ましくは80:20〜90:10、さらにより好ましくは約85:15のモル比p−フェニレン:m−フェニレンで、フェニルケトン基により置換されたp−フェニレンと無置換型m−フェニレンとよりなる混合物(M2)である場合、良好な結果が得られる。そのようなキンク形剛性棒状ポリフェニレンコポリマーは、PrimoSpire(登録商標)PR−120ポリフェニレンとしてSolvay Advanced Polymers,L.L.C.から市販されている。 The amount of the repeating unit (R2a) and (R2b) of the kink-shaped rigid rod-shaped polyarylene (P2), the number of moles of the kink-forming arylene unit (R2b) in the mixture (M2) is the total number of moles of the repeating unit (R2). Is preferably at least 1.0%, more preferably at least 5%, even more preferably at least 10%. On the other hand, in the mixture (M2), the number of moles of the kink-forming arylene unit (R2b) is preferably at most 20%, more preferably at most 18%, based on the total number of moles of the repeating unit (R2). . The polyarylene (P2) is a kink-shaped rigid rod-like polyphenylene copolymer, and essentially all if not all of the repeating units are 80:20 to 95: 5, preferably 80:20 to 90:10. Even more preferably, it is a mixture (M2) of p-phenylene: m-phenylene having a molar ratio of about 85:15 and p-phenylene substituted with a phenylketone group and unsubstituted m-phenylene (M2). Results. Such a kink-shaped rigid rod-shaped polyphenylene copolymer is disclosed in Solvay Advanced Polymers, L. as PrimoSpire® PR-120 polyphenylene. L. C. Commercially available.
この第1の特定の実施形態では、ポリアリーレン(P2)の重量は、ポリマー材料(M)の全重量を基準にして、少なくとも1%、少なくとも5%、少なくとも10%、または少なくとも15%でありうる。一方、ポリアリーレン(P2)の重量は、材料の全重量を基準にして、多くとも99%、多くとも95%、多くとも75%、多くとも60%でありうる。 In this first particular embodiment, the weight of polyarylene (P2) is at least 1%, at least 5%, at least 10%, or at least 15%, based on the total weight of the polymeric material (M) sell. On the other hand, the weight of polyarylene (P2) can be at most 99%, at most 95%, at most 75%, at most 60%, based on the total weight of the material.
他の特定の実施形態では、ポリマー材料(M)はさらに、ポリアミド(たとえばポリフタルアミドなど)、ポリエーテルブロックアミド、ポリイミド、ポリエーテルイミド、ポリアミドイミド、ポリアリールエーテルスルホン(たとえば、ポリフェニルスルホン、ビスフェノールAポリスルホン、ポリエーテルスルホン、ポリエーテルエーテルスルホン、など、ポリエーテルスルホンイミド、ならびにそれらのコポリマーおよび混合物)、ポリエーテルケトン、ポリエーテルエーテルケトン、ポリエーテルケトンケトン、ポリアリーレンエーテル[たとえば、ポリフェニレンエーテルおよびポリ(2,6−ジメチル−1,4−フェニレンエーテル)など]、ポリフェニレンスルフィド、ポリベンゾイミダゾール、ポリカーボネート、ポリエステル、ポリウレタン、ポリオレフィン、ポリ(メチルペンテン)、ポリテトラフルオロエチレン、ポリエチレン、ポリプロピレン、液晶ポリマー、ハロゲン化ポリマー、ならびにそれらのコポリマーおよび混合物よりなる群から選択される、ポリアリーレン以外の少なくとも1種の熱可塑性ポリマーを含む。 In other specific embodiments, the polymeric material (M) further comprises a polyamide (eg, polyphthalamide), a polyether block amide, a polyimide, a polyetherimide, a polyamideimide, a polyarylethersulfone (eg, polyphenylsulfone, Bisphenol A polysulfone, polyethersulfone, polyetherethersulfone, etc., polyethersulfonimide, and copolymers and mixtures thereof), polyetherketone, polyetheretherketone, polyetherketoneketone, polyarylene ether [eg, polyphenylene ether And poly (2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene ether)], polyphenylene sulfide, polybenzimidazole, polycarbonate, polyester At least one other than polyarylene selected from the group consisting of polyethylene, polyurethane, polyolefin, poly (methylpentene), polytetrafluoroethylene, polyethylene, polypropylene, liquid crystal polymer, halogenated polymer, and copolymers and mixtures thereof. Includes thermoplastic polymers.
さらに他の特定の実施形態では、ポリマー材料(M)はさらに、少なくとも1種の繊維状強化剤、特定的にはガラス繊維や炭素繊維などの無機繊維状強化剤を、通常はポリマー材料(M)の全重量を基準にして10〜50重量%の量で、含有する。 In yet another particular embodiment, the polymeric material (M) further comprises at least one fibrous reinforcing agent, in particular an inorganic fibrous reinforcing agent such as glass fiber or carbon fiber, usually a polymeric material (M ) In an amount of 10 to 50% by weight based on the total weight.
好ましい実施形態では、ポリマー材料(M)は、いかなる繊維状強化剤をも、とくにガラス繊維や炭素繊維などの無機繊維状強化剤を本質的に含まない。より好ましくは、いかなる繊維状強化剤をも含まない。 In a preferred embodiment, the polymeric material (M) is essentially free of any fibrous reinforcing agent, especially inorganic fibrous reinforcing agents such as glass fibers and carbon fibers. More preferably, it does not contain any fibrous reinforcing agent.
他の好ましい実施形態では、ポリマー材料(M)は、0〜1%の金属、より好ましくは0〜0.1%の金属を含有する。さらにより好ましくは、いかなる金属をも本質的に含まず、最も好ましくはいかなる金属をも含まない。 In other preferred embodiments, the polymeric material (M) contains 0-1% metal, more preferably 0-0.1% metal. Even more preferably, it is essentially free of any metal, most preferably free of any metal.
材料の全重量を基準にした、場合により存在していてもよい成分の重量は、ポリマー材料(M)の全重量を基準にして、有利には0〜75重量%、好ましくは0〜50wt%、より好ましくは0〜25重量%、さらにより好ましくは0〜10重量%、さらにより好ましくは0〜5重量%の範囲内である。材料が、前記場合により存在していてもよい成分を本質的に含まないかまたはまったく含まない場合、優れた結果が得られる。 The weight of components which may optionally be present, based on the total weight of the material, is advantageously 0-75% by weight, preferably 0-50% by weight, based on the total weight of the polymer material (M) More preferably, it is in the range of 0 to 25% by weight, even more preferably 0 to 10% by weight, and even more preferably 0 to 5% by weight. Excellent results are obtained when the material is essentially free or completely free of components that may be present in the foregoing cases.
締結具(F)は、そのままの状態で、またはボールロックピン、ラッチ、クリップ、クリップナット、プラグおよびスリーブ、フローティングナット締結具、アイソレーターマウント、ナットプレート、スプリットジョイント取付け具、床取付け具、クォーターターン締結具、インサート、支持ブラケット、マウントブラケットマウン、ラッチ、リリースピン、蝶番、ボルトブッシング、ケーブルタイ、チュービングハンガー、ワイヤリングクランプ、スタンドオフ、スペーサー、コンジットブラケットなどのように多くの手段の構成要素として利用可能である。 Fastener (F) can be used as it is or ball lock pin, latch, clip, clip nut, plug and sleeve, floating nut fastener, isolator mount, nut plate, split joint fixture, floor fixture, quarter turn Used as a component of many means such as fasteners, inserts, support brackets, mount bracket mounts, latches, release pins, hinges, bolt bushings, cable ties, tubing hangers, wiring clamps, standoffs, spacers, conduit brackets, etc. Is possible.
締結具(F)は、要求の厳しい用途にとくに有用である。たとえば、それは、航空機、ならびに軽量性、トルク、強度、靭性、および耐熱分解性が重要な性質となる他の自走式輸送機関の用途にとくに好適である。 The fastener (F) is particularly useful for demanding applications. For example, it is particularly suitable for aircraft and other self-propelled transportation applications where lightness, torque, strength, toughness, and thermal degradability are important properties.
したがって、本発明の他の態様は、以上に記載の少なくとも1つの締結具(F)を含む航空機に関する。 Accordingly, another aspect of the invention relates to an aircraft comprising at least one fastener (F) as described above.
締結具(F)は、とくに、航空機仕切り壁、航空機側壁、航空機床、航空機天井パネル、航空機旅客輸送ユニット、航空機嵌込みパネル、航空機照明具の側壁および天井、航空機ビデオモニター、航空機荷物入れ、航空機酸素ボックス、航空機HVACダクト系統、航空機フードトレー、航空機アームレスト、航空機座席構造体、航空機のトイレ、調理室、および配膳用手押し車の側壁、航空機操縦室計測器、航空機のワイヤーおよびケーブルのハーネスおよびクランプ、ならびに航空機の発電および配電システムに組込み可能である。 Fasteners (F) include, in particular, aircraft partitions, aircraft sidewalls, aircraft floors, aircraft ceiling panels, aircraft passenger transport units, aircraft fitting panels, aircraft lighting sidewalls and ceilings, aircraft video monitors, aircraft luggage compartments, aircraft Oxygen boxes, aircraft HVAC duct systems, aircraft food trays, aircraft armrests, aircraft seat structures, aircraft toilets, cooking rooms, and barrow sidebars, aircraft cockpit instruments, aircraft wire and cable harnesses and clamps And can be incorporated into aircraft power generation and distribution systems.
本発明の関連態様としては、以下のものが挙げられる。
・ 乗客の搭乗および/または荷物の搭載ための、以上に記載の少なくとも1つの締結具(F)を含む航空機の使用、
・ 乗客および/または荷物の輸送のための、以上に記載の少なくとも1つの締結具(F)を含む航空機の使用、
・ 前記航空機からの乗客の降機および/または荷物の搭降のための、以上に記載の少なくとも1つの締結具(F)を含む航空機の使用、
・ 航空機以外の航空輸送機関(前記航空輸送機関は、以上に記載の少なくとも1つの締結具(F)を含む)、特定的には、ヘリコプター、熱気球、グライダー、ならびに宇宙ロケットおよび宇宙シャトル、
・ 航空輸送機関以外の自走式輸送機関(前記自走式輸送機関は、以上に記載の少なくとも1つの締結具(F)を含む)、特定的には、自動車、オートバイ、トラック、またはバン、
・ 以上に記載の少なくとも1つの締結具(F)を含む自走式輸送機関、
・ 乗客および/または荷物の輸送のための、少なくとも1つの締結具(F)を含む自走式輸送機関の使用。
The following are mentioned as a related aspect of this invention.
The use of an aircraft comprising at least one fastener (F) as described above for boarding passengers and / or loading luggage;
The use of an aircraft comprising at least one fastener (F) as described above for the transport of passengers and / or luggage;
The use of an aircraft comprising at least one fastener (F) as described above for the unloading of passengers and / or the unloading of luggage from said aircraft;
Non-aircraft air transport (the air transport includes at least one fastener (F) as described above), in particular helicopters, hot air balloons, gliders, and space rockets and space shuttles,
A self-propelled transport other than an air transport (the self-propelled transport includes at least one fastener (F) as described above), in particular an automobile, motorcycle, truck or van,
A self-propelled transport comprising at least one fastener (F) as described above,
The use of a self-propelled transport including at least one fastener (F) for the transport of passengers and / or luggage;
より一般的には、締結具(F)は、耐薬品性、機械的耐性、軽量性、耐食性、および/または電気絶縁性が重要となる任意の工業用途、たとえば、半導体工業に有用であろう。したがって、本発明のさらに他の態様は、半導体用途における締結具(F)の使用に関する。 More generally, the fastener (F) will be useful in any industrial application where chemical resistance, mechanical resistance, light weight, corrosion resistance, and / or electrical insulation are important, such as the semiconductor industry. . Accordingly, yet another aspect of the present invention relates to the use of fasteners (F) in semiconductor applications.
セット1
PrimoSpire(登録商標)PR−250ポリフェニレン(SOLVAY ADVANCED POLYMERS,L.L.C.から市販されている最新の世代の高キンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレン)ならびに非強化および炭素繊維強化の両方のPEEKの所定の物理的および機械的な性質を表1に示す。以下の結果からわかるように、データシートの性質から締結具の性能を予測することは本質的に不可能である。
Set 1
PrimoSpire® PR-250 polyphenylene (the latest generation of high kink rigid rod-shaped polyarylene commercially available from SOLVAY ADVANCED POLYMERS, L.C.) and both unreinforced and carbon fiber reinforced PEEK The physical and mechanical properties of are shown in Table 1. As can be seen from the following results, it is essentially impossible to predict fastener performance from the nature of the data sheet.
締結具とくに航空宇宙用締結具に好適な材料としてPrimoSpire(登録商標)PR−250ポリフェニレンの有用性を実証するために、いくつかの試験を行った。締結具試験には、破損トルクおよび引張り強度が含まれていた。内ネジおよび外ネジの両方を評価した。 Several tests were conducted to demonstrate the usefulness of PrimoSpire® PR-250 polyphenylene as a material suitable for fasteners, particularly aerospace fasteners. Fastener tests included failure torque and tensile strength. Both inner and outer screws were evaluated.
内ネジ
内ネジを評価するために、試験材料の試験片にドリルで孔を設けた。次に、適切なタップを用いて孔をネジ切りした。鋼製機械ネジを装着し、破損トルクを測定した。この試験では、ネジ部がネジ山潰れを起こした時に破損を生じた。表2に示された試験結果は、30%炭素繊維強化PEEKよりもPrimoSpire(登録商標)PR−250のほうが明らかに優れていることを示している。また、非強化PEEKのデータは、30%の炭素繊維を添加してもトルク強度が実質的に改良されなかったことを示している。
In order to evaluate the internal thread in the screw, the hole provided by drilling the specimen of the test material. The holes were then threaded using appropriate taps. A steel machine screw was attached and the damage torque was measured. In this test, the thread part was damaged when the thread crushed. The test results shown in Table 2 show that PrimoSpire® PR-250 is clearly superior to 30% carbon fiber reinforced PEEK. The unreinforced PEEK data also shows that the torque strength was not substantially improved by the addition of 30% carbon fiber.
したがって、本発明のさらに他の態様は、反復ユニットの50wt%超が、場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基よりなる1つ以上の式で示される反復ユニット(R)である、少なくとも1種のキンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレン(P)の使用に関する。ただし、前記場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基は、その2つの末端のそれぞれにより、直接C−C結合を介して、2つの他の場合により置換されていてもよいアリーレン基に結合されており、前記反復ユニット(R)は、
・ 反復ユニット(R)の全モル数を基準にして0〜75モル%の、少なくとも1個の一価置換基で場合により置換されていてもよい剛性棒状体形成性アリーレンユニット(Ra)と、
・ 反復ユニット(R)の全モル数を基準にして25〜100モル%の、以上に記載の締結具(F)の製造に好適なポリマー材料(M)のトルクを増大させるために少なくとも1個の一価置換基により場合により置換されていてもよいキンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb)と、
よりなる混合物(M)である。
Accordingly, yet another aspect of the present invention is that at least one of the repeating units (R) represented by one or more formulas, wherein more than 50 wt% of the repeating units consist of optionally substituted arylene groups. To the use of kink-shaped rigid rod-shaped polyarylene (P). However, the optionally substituted arylene group is bonded to the two other optionally substituted arylene groups via a direct C-C bond by each of its two ends. And the repeating unit (R) is
A rigid rod-forming arylene unit (Ra) optionally substituted with at least one monovalent substituent, from 0 to 75 mol%, based on the total number of moles of repeating units (R);
At least one to increase the torque of the polymer material (M) suitable for the production of the fastener (F) as described above, based on the total number of moles of the repeating unit (R), 25-100 mol% A kink-forming arylene unit (Rb) optionally substituted by a monovalent substituent of
It is a mixture (M) consisting of
外ネジ
外ネジを試験するために、機械ネジを候補樹脂から射出成形した。0.625”(16mm)の厚さの鋼板にドリルで孔を設けた。適切なタップを用いて孔をネジ切りした。試験対象のネジを装着し、次に、ネジが破壊するまでトルクを印加した。トルク値を表3に示す。PrimoSpire(登録商標)PR−250ネジを破壊するのに必要なトルクは、30%CF PEEKネジを破壊するのに必要なトルクの約2倍である。
To test the external screw external screw, a mechanical screw was injection molded from the candidate resin. A hole was drilled in a 0.625 "(16 mm) thick steel plate. The hole was threaded using a suitable tap. The screw to be tested was attached and then torque was applied until the screw broke. Torque values are shown in Table 3. The torque required to break the PrimoSpire® PR-250 screw is approximately twice that required to break the 30% CF PEEK screw.
引張り強度試験
NASM1312−8A試験法および射出成形された10〜32個の機械ネジを用いて引張り強度データを得た。結果を表4に示す。SRPは、30%炭素繊維強化PEEKよりも高い引張り強度およびはるかに小さい標準偏差を示した。
Tensile strength data Tensile strength data was obtained using the NASM 1312-8A test method and 10-32 machined injection molded screws. The results are shown in Table 4. SRP showed higher tensile strength and much smaller standard deviation than 30% carbon fiber reinforced PEEK.
他の重要な考慮点
本実験データは、機械ネジで得たものであったが、結論は、ボルト、ナット、ワッシャー、ピン、およびスクリベットなどの多くの締結具にあてはまる。クリップナット、ナットプレート、マウント、インサート、ラッチ、蝶番、クランプ、およびスペーサーのような工学的締結具もまた、重量低減および性能向上に対する候補とみなされるべきである。PrimoSpire(登録商標)PR−250などの高キンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレンが航空機用締結具で提供しうる重量低減および高強度と同程度に重要なこととして、本質的に電気非伝導性の材料を用いることによっても、利点が得られる。PrimoSpireR PR−250および30%炭素繊維PEEKの電気的性質を表5に示す。
Other Important Considerations Although this experimental data was obtained with machine screws, the conclusions apply to many fasteners such as bolts, nuts, washers, pins, and scribets. Engineering fasteners such as clip nuts, nut plates, mounts, inserts, latches, hinges, clamps, and spacers should also be considered candidates for weight reduction and performance enhancement. As important as the weight reduction and high strength that high kink rigid rod-like polyarylenes, such as PrimoSpire® PR-250, can provide in aircraft fasteners, essentially non-electrically conductive materials Use also provides advantages. The electrical properties of PrimoSpire® PR-250 and 30% carbon fiber PEEK are shown in Table 5.
異種金属の連結を回避することによりガルバニック腐食が防止される。類似の金属を用いた場合でさえも腐食が起こりうるので、非伝導性締結具の使用は、腐食からのさらなる保護を提供する。これは、多くの場合、維持費の削減および停止時間の減少をもたらす。熱可塑性成形締結具は、決して腐食しないし、他の部材のいかなるガルバニック腐食にも関与しないであろう。PrimoSpire(登録商標)PR−250材料の引火性、発煙性、および毒性のデータを表6に示す。データから示唆されるように、材料は、本質的に遅炎性であり(添加剤を用いることなく)、ほとんど煙を発生せず、しかも非毒性であり、いずれも、航空機用途に望ましい特性である。
By avoiding dissimilar metal connections, galvanic corrosion is prevented. Because corrosion can occur even with similar metals, the use of non-conductive fasteners provides additional protection from corrosion. This often results in reduced maintenance costs and reduced downtime. The thermoplastic molded fastener will never corrode and will not participate in any galvanic corrosion of other parts. The flammability, fuming, and toxicity data for the PrimoSpire® PR-250 material is shown in Table 6. As suggested by the data, the materials are inherently flame retardant (without the use of additives), generate little smoke and are non-toxic, both of which are desirable properties for aircraft applications. is there.
セット2
例示を目的として、最新の世代の高キンク形剛性棒状ポリアリーレンPrimoSpire(登録商標)PR−250ポリフェニレン製のさまざまな締結具を示す写真を図9に示す。
Set 2
For purposes of illustration, photographs showing various fasteners made of the latest generation high kink rigid rod polyarylene PrimoSpire® PR-250 polyphenylene are shown in FIG.
参照により本明細書に組み入れられる特許、特許出願、および出版物のいずれかの開示が、用語が不明確になるほど本明細書と矛盾する場合、本明細書が優先するものとする。 In the event that any disclosure of patents, patent applications, and publications incorporated herein by reference conflicts with this specification to the extent that the term is unclear, this specification shall control.
Claims (11)
・ 前記反復ユニット(R)の全モル数を基準にして0〜75モル%の、
少なくとも1個の一価置換基により場合により置換されていてもよいp−フェニレンから選択される剛性棒状体形成性アリーレンユニット(Ra)と、
・ 前記反復ユニット(R)の全モル数を基準にして25〜100モル%の、
(i)少なくとも1個の一価置換基により場合により置換されていてもよいm−フェニレン又は(ii)m−フェニレンおよびoフェニレンが両方とも、互いに独立して、少なくとも1個の一価置換基により場合により置換されていてもよいm−フェニレンとo−フェニレンからなるキンク形成性アリーレンユニット(Rb)と、
よりなることを条件とする、締結具。 A polymeric material comprising at least one kink-shaped rigid rod-like polyarylene (P), wherein the repeating unit is a repeating unit (R) of one or more formulas consisting of optionally substituted arylene groups ( A fastener (F) consisting of M), wherein the optionally substituted arylene group is substituted by each of its two ends by two other cases via a direct C-C bond Bonded to an arylene group which may be substituted, said repeating unit (R)
-0 to 75 mol% based on the total number of moles of the repeating unit (R),
A rigid rod-forming arylene unit (Ra) selected from p-phenylene optionally substituted by at least one monovalent substituent ;
-25 to 100 mol%, based on the total number of moles of the repeating unit (R),
(I) m-phenylene optionally substituted by at least one monovalent substituent or (ii) both m-phenylene and o-phenylene, independently of one another, at least one monovalent substituent. A kink-forming arylene unit (Rb) composed of optionally substituted m-phenylene and o-phenylene ;
A fastener, subject to
Applications Claiming Priority (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US16459909P | 2009-03-30 | 2009-03-30 | |
| US16460109P | 2009-03-30 | 2009-03-30 | |
| US61/164,601 | 2009-03-30 | ||
| US61/164,599 | 2009-03-30 | ||
| PCT/EP2010/054048 WO2010112435A1 (en) | 2009-03-30 | 2010-03-26 | Fasteners made of a polymer material |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2012522195A JP2012522195A (en) | 2012-09-20 |
| JP2012522195A5 JP2012522195A5 (en) | 2013-04-18 |
| JP5805065B2 true JP5805065B2 (en) | 2015-11-04 |
Family
ID=42166784
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012502607A Active JP5805065B2 (en) | 2009-03-30 | 2010-03-26 | Fasteners made of polymer material |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9006384B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP2413984B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP5805065B2 (en) |
| WO (2) | WO2010112436A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1998056A1 (en) * | 2007-05-29 | 2008-12-03 | Sgl Carbon Ag | Composite fastener for ceramic components |
| US9006384B2 (en) | 2009-03-30 | 2015-04-14 | Solvay Specialty Polymers Usa, Llc | Fasteners made of a polymer material |
| KR101091426B1 (en) * | 2009-11-06 | 2011-12-07 | 주식회사 니프코코리아 | a Cell Case |
| US9267748B2 (en) * | 2011-09-29 | 2016-02-23 | Alan T. Thordsen | Systems and methods for releasing detachable firearm magazines |
| EP2765317A1 (en) * | 2013-02-12 | 2014-08-13 | Solvay Specialty Polymers USA, LLC. | Improved fasteners |
| EP2851387A1 (en) | 2013-09-19 | 2015-03-25 | Solvay Specialty Polymers USA, LLC. | Oil and gas recovery articles |
| EP2899233A1 (en) | 2014-01-22 | 2015-07-29 | Solvay Specialty Polymers USA, LLC. | Chemical processing articles |
| EP2899231A1 (en) | 2014-01-22 | 2015-07-29 | Solvay Specialty Polymers USA, LLC. | Aerospace articles |
| EP2899230A1 (en) | 2014-01-22 | 2015-07-29 | Solvay Specialty Polymers USA, LLC. | Automotive articles |
| EP2899232A1 (en) | 2014-01-22 | 2015-07-29 | Solvay Specialty Polymers USA, LLC. | Oil and gas recovery articles |
| US9981447B2 (en) * | 2014-03-25 | 2018-05-29 | Teijin Limited | Fiber-reinforced resin joined body having caulked part and manufacturing method thereof |
| CA2944964C (en) * | 2014-04-14 | 2022-08-09 | Short Brothers Plc | Apparatus and method for forming fiber reinforced composite structures |
| KR101617520B1 (en) * | 2014-05-30 | 2016-05-02 | 신인학 | The method of manufacturing a car seat cushion, and thus the tension Product |
| US20160101600A1 (en) | 2014-10-09 | 2016-04-14 | Baker Hughes Incorporated | Methods of forming structures for downhole applications, and related downhole structures and assemblies |
| US10337270B2 (en) * | 2015-12-16 | 2019-07-02 | Neo Products, LLC | Select fire system and method of using same |
| WO2018086873A1 (en) | 2016-11-11 | 2018-05-17 | Solvay Specialty Polymers Usa, Llc | Polyarylether ketone copolymer |
| US11708457B2 (en) | 2016-11-11 | 2023-07-25 | Solvay Specialty Polymers Usa, Llc | Polyarylether ketone copolymer |
| KR101954078B1 (en) * | 2018-05-30 | 2019-03-06 | (주)피코팩 | A manufacturing method of oral sensor using print circuit board of build-up multi layer |
| US11300281B2 (en) * | 2018-03-16 | 2022-04-12 | Luminiz Inc. | Light fixture |
| JP2020067170A (en) * | 2018-10-26 | 2020-04-30 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Cap fastening structure |
| KR20220100888A (en) | 2019-11-08 | 2022-07-18 | 솔베이 스페셜티 폴리머즈 유에스에이, 엘.엘.씨. | Blends of polyarylether ketone copolymers |
| US20210221536A1 (en) * | 2019-11-21 | 2021-07-22 | Volansi, Inc. | Drone assembly hanger |
| CN112623263A (en) * | 2020-12-23 | 2021-04-09 | 大连长丰实业总公司 | Special supporting device for aircraft canopy connecting lock |
Family Cites Families (22)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE795354A (en) | 1972-02-14 | 1973-05-29 | Long Lok Fasteners Corp | METHOD OF MANUFACTURING A FIXING ELEMENT FORMING A SELF-LOCKING SCREW WITH INSERTION PIECE AND ARTICLE THUS OBTAINED |
| US5565543A (en) | 1988-02-17 | 1996-10-15 | Maxdem Incorporated | Rigid-rod polymers |
| US5227457A (en) | 1988-02-17 | 1993-07-13 | Maxdem Incorporated | Rigid-rod polymers |
| US5654392A (en) | 1988-02-17 | 1997-08-05 | Maxdem Incorporated | Rigid-rod polymers |
| US5646231A (en) | 1988-02-17 | 1997-07-08 | Maxdem, Incorporated | Rigid-rod polymers |
| WO1993004099A1 (en) | 1991-08-19 | 1993-03-04 | Maxdem Incorporated | Macromonomers having reactive end groups |
| US5869592A (en) | 1991-08-19 | 1999-02-09 | Maxdem Incorporated | Macromonomers having reactive side groups |
| US5302067A (en) | 1992-08-11 | 1994-04-12 | Jack Rath | Prevailing torque fastener |
| US5668245A (en) | 1995-11-02 | 1997-09-16 | Maxdem Incorporated | Polymers with heterocyclic side groups |
| US5886130A (en) | 1995-11-02 | 1999-03-23 | Maxdem Incorporated | Polyphenylene co-polymers |
| JPH10281132A (en) * | 1997-03-31 | 1998-10-20 | Ntn Corp | Resin nut, manufacture thereof, and slide screw device |
| JP2000141416A (en) * | 1998-11-12 | 2000-05-23 | Nippon Petrochem Co Ltd | Resin washer, sealing member and manufacture thereof |
| US20020106259A1 (en) | 2001-02-05 | 2002-08-08 | Kaufman Stephen R. | Reinforced plastic bolt with injection molded head and mold therefor |
| JP2006342862A (en) * | 2005-06-08 | 2006-12-21 | Daiwa Kasei Ind Co Ltd | Screw member |
| EP1994093B1 (en) * | 2006-03-07 | 2011-07-27 | Solvay Advanced Polymers, L.L.C. | New polyarylene composition |
| US7575404B2 (en) | 2006-11-01 | 2009-08-18 | Sps Technologies, Llc | Nut plate fastener assembly for composite materials |
| EP2014251B1 (en) | 2007-07-10 | 2012-05-30 | BrainLAB AG | Attachment device for securing a body made of polyphenyls in position for medical purposes and attachment device for securing a silicon nitride ceramic body in position for medical purposes |
| US20090016843A1 (en) | 2007-07-13 | 2009-01-15 | Igor Komsitsky | Spacer Assemblies, Apparatus and Methods of Supporting Hardware |
| US7874779B2 (en) | 2007-07-23 | 2011-01-25 | The Monadnock Company | Fasteners, fastener components and fastener receptacles |
| PL2200672T3 (en) * | 2007-09-11 | 2012-11-30 | Solvay Specialty Polymers Usa | Improved prosthetic devices |
| US8119764B2 (en) * | 2007-09-11 | 2012-02-21 | Solvay Advanced Polymers, L.L.C. | Medical devices made of a polymer material |
| US9006384B2 (en) | 2009-03-30 | 2015-04-14 | Solvay Specialty Polymers Usa, Llc | Fasteners made of a polymer material |
-
2010
- 2010-03-26 US US13/260,812 patent/US9006384B2/en active Active
- 2010-03-26 WO PCT/EP2010/054049 patent/WO2010112436A1/en active Application Filing
- 2010-03-26 JP JP2012502607A patent/JP5805065B2/en active Active
- 2010-03-26 WO PCT/EP2010/054048 patent/WO2010112435A1/en active Application Filing
- 2010-03-26 EP EP10710589.2A patent/EP2413984B1/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2413984B1 (en) | 2017-08-23 |
| US9006384B2 (en) | 2015-04-14 |
| EP2413984A1 (en) | 2012-02-08 |
| WO2010112435A1 (en) | 2010-10-07 |
| US20120025020A1 (en) | 2012-02-02 |
| JP2012522195A (en) | 2012-09-20 |
| WO2010112436A1 (en) | 2010-10-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5805065B2 (en) | Fasteners made of polymer material | |
| RU2678043C1 (en) | Composite materials with electrically conductive and delamination resistance properties | |
| JP6549484B2 (en) | High melt flow PEAK composition | |
| US8900486B2 (en) | Conductivity of resin materials and composite materials | |
| US8474759B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for fastening components using a composite two-piece fastening system | |
| Mahajan et al. | Composite material: A review over current development and automotive application | |
| US10683415B2 (en) | PAEK/PPSU/PES compositions | |
| BRPI0721577A2 (en) | MAINTENANCE SLIDING BEARING | |
| US20160304716A1 (en) | Friction and wear resistant articles | |
| JP2015519423A (en) | Continuous fiber reinforced polyarylene sulfide | |
| US9845383B2 (en) | Fasteners | |
| DE202016106096U1 (en) | Heating paint, surface heating device and kit for producing a surface heating device | |
| BR112012029463B1 (en) | reinforced joint material | |
| WO2005092517A1 (en) | Method for preparing pre-coated, composite components and components prepared thereby | |
| BRPI0615376B1 (en) | Method of adjusting a component in a receiver | |
| US11920034B2 (en) | Polyamide composition containing flat glass fibres (B) with improved fatigue resistance | |
| EP2899231A1 (en) | Aerospace articles | |
| JPH10281132A (en) | Resin nut, manufacture thereof, and slide screw device | |
| RU202560U1 (en) | THERMOPLASTIC COMPOSITE PIPE | |
| Bal et al. | Mechanical and microstructural analysis of carbon nanotube composites pretreated at different temperatures | |
| JP7377039B2 (en) | carbon composite material | |
| JP6984388B2 (en) | Structures and interior materials | |
| Wang et al. | Nature‐mimic tough helicoidal composites with aligned short carbon fibers by 3D printing | |
| KR102423417B1 (en) | Fixed anchor to wall structure using reinforced materials | |
| Jain et al. | Comparative Study on strengthening of RC beam in flexure using CFRP & GFRP: A Review |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130304 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20130304 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20131209 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20140325 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20140609 |
|
| A602 | Written permission of extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A602 Effective date: 20140616 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140725 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20150203 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150602 |
|
| A911 | Transfer to examiner for re-examination before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date: 20150709 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20150804 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20150901 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5805065 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |