JP5374415B2 - GPS reception clock - Google Patents
GPS reception clock Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5374415B2 JP5374415B2 JP2010041984A JP2010041984A JP5374415B2 JP 5374415 B2 JP5374415 B2 JP 5374415B2 JP 2010041984 A JP2010041984 A JP 2010041984A JP 2010041984 A JP2010041984 A JP 2010041984A JP 5374415 B2 JP5374415 B2 JP 5374415B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- leap
- information
- state
- time
- reception
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Electric Clocks (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明はGPS受信時計に係り、特に不定期に更新されるうるう秒情報を保持するGPS受信装置に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a GPS receiving clock, and more particularly to a GPS receiving apparatus that holds leap second information that is updated irregularly.
GPSは衛星32基を使い、全世界どこでも現在位置及び時刻が得られる情報源として、ナビゲーションシステムや時計等に利用されている。GPS衛星にはそれぞれ原子時計が搭載されており、極めて精度の高い時刻情報を提供している。GPSの時刻情報は、TOW(TIME OF WEEK)、週番号、及びうるう秒情報等からなり、これらを演算して正確な時間を得ることが可能である。一方、GPS受信機は近年、小型化、省電力化が進み、腕時計型GPS受信時計も実用性の高いサイズにまで小型化が進んでいる状況である。 GPS uses 32 satellites and is used in navigation systems, clocks, etc. as an information source from which the current position and time can be obtained anywhere in the world. Each GPS satellite is equipped with an atomic clock, which provides time information with extremely high accuracy. GPS time information includes TOW (TIME OF WEEK), week number, leap second information, and the like, and these can be calculated to obtain accurate time. On the other hand, in recent years, GPS receivers have been reduced in size and power saving, and wristwatch-type GPS reception watches are also being reduced in size to a practical size.
使用者に時刻情報を正確に提供するには、うるう秒情報は欠かすことの出来ない情報であるが、TOWが6秒周期、週番号が30秒周期で送信されるのに対し、うるう秒情報は12.5分周期であるため、うるう秒情報を得るのに最長12.5分かかってしまう。省電力化が進んでいるとは言え、電池駆動の場合は12分超の連続受信は早期に電圧低下となってしまう。その回避としてうるう秒情報の送信タイミングに合わせて受信を開始する技術が開示されている(特許文献1参照)。 Leap second information is indispensable for providing time information accurately to the user, while TOW is transmitted in a cycle of 6 seconds and a week number is transmitted in a cycle of 30 seconds. Since it has a period of 12.5 minutes, it takes a maximum of 12.5 minutes to obtain leap second information. Even though power saving is progressing, in the case of battery driving, continuous reception for more than 12 minutes causes an early voltage drop. As a technique for avoiding this, a technique for starting reception in accordance with the transmission timing of leap second information is disclosed (see Patent Document 1).
腕時計においては、電池駆動の宿命から電源の容量が限られており、使用し続けることによって電池容量が減少し、腕時計を継続使用できない状態となる。
1次電池の場合は電池容量の枯渇により機器が停止する。機器によっては、電池容量を(電圧測定などにより)事前に予測し、停止させるものもある。
ソーラーセル(太陽電池)などの発電源と2次電池からなる充電系電源を使用した場合も、電池容量を(電圧測定などにより)事前に予測し、停止させるのが普通である。
このような停止状態では、時刻データを含む腕時計に蓄えられたデータは消失してしまう。これは、腕時計型GPS受信時計に当てはめた場合も同様である。
In a wristwatch, the capacity of a power source is limited due to the fate of battery driving, and the battery capacity decreases with continued use, and the wristwatch cannot be used continuously.
In the case of a primary battery, the device stops due to the battery capacity being depleted. Some devices predict battery capacity in advance (by voltage measurement, etc.) and stop it.
Even when a power source such as a solar cell (solar battery) and a charging system power source comprising a secondary battery are used, the battery capacity is generally predicted in advance (by voltage measurement or the like) and stopped.
In such a stopped state, the data stored in the wristwatch including the time data is lost. This is the same when applied to a wristwatch type GPS reception clock.
上記停止状態から、腕時計を再使用する場合、1次電池なら電池交換、充電系電源なら再充電により電源容量を回復させ、腕時計を使用可能な状態に復帰させる。
しかしながら、上述の如く、復帰時点では時刻データは失われているので、何らかの形で時刻データを再設定する必要がある。腕時計型GPS受信時計の場合は、GPS情報を受信することで時刻を設定することが可能である。
しかし、この場合でも以下のような問題を有している。
When the wristwatch is reused from the stopped state, the power source capacity is recovered by battery replacement for the primary battery and recharging for the charging system power source, and the wristwatch is returned to a usable state.
However, as described above, since the time data is lost at the time of return, it is necessary to reset the time data in some form. In the case of a wristwatch type GPS receiving clock, the time can be set by receiving GPS information.
However, even in this case, there are the following problems.
(1)GPS情報から正確な時刻情報を得るためには、うるう秒情報を含めた時刻情報を受信しなければならない。GPS情報のフォーマットが、TOWとうるう秒を合わせて初めて意味を成す時刻情報となる構成となっているからである。
ところが、特許文献1記載の技術を用いても、うるう秒を含めた正確な時間を提供できるまで最長で12.5分かかってしまう。
そのため受信時間が長くなってしまうため、消費電流が大きく、充電系電源を使用した場合、電源容量は急速に低下し、再び停止してしまう可能性がある。
また、受信時間が長く時計が動作を開始しないので、ユーザーに不信感を与えてしまう。
(1) In order to obtain accurate time information from GPS information, time information including leap second information must be received. This is because the format of GPS information is time information that makes sense only when TOW and leap seconds are combined.
However, even if the technique described in Patent Document 1 is used, it takes 12.5 minutes at the longest to provide an accurate time including leap seconds.
For this reason, since the reception time becomes long, the current consumption is large, and when a charging system power supply is used, the power supply capacity may rapidly decrease and stop again.
In addition, since the reception time is long and the clock does not start operation, the user is distrusted.
(2)うるう秒情報は6月末日および12月末日の年2回のタイミングに、うるう秒調整があるときだけ更新される変更頻度の低い情報であり、受信頻度も極めて低くてよい情報である。しかし、停止からの復帰後は、当然カレンダー情報も無い為、必ず受信する必要が有り、結果的に(1)で説明したうるう秒の受信を行う必要がある。 (2) Leap second information is information that is updated only when there is a leap second adjustment at the timing of the end of June and the end of December, and is a low change frequency information that may be received at a very low frequency. . However, since there is no calendar information after returning from the stop, it is necessary to receive it without fail, and as a result, it is necessary to receive the leap second described in (1).
本発明は、受信不可能状態から受信可能状態に移行するとき、長時間受信状態にしなくても、正確な時間もしくは正確な時間に極めて近い時間をすぐに得ることができるGPS時計を提供することを目的としている。 An object of the present invention is to provide a GPS clock that can immediately obtain an accurate time or a time very close to an accurate time without going into the reception state for a long time when shifting from the reception-incapable state to the reception-enabled state. It is an object.
本発明のGPS受信時計は、少なくとも時刻に関する衛星情報を受信する受信手段1と、該受信手段で受信した情報を処理する処理手段2と、時刻を計時する計時手段3と、前記処理手段の復調信号を元に時刻情報を生成し、前記計時手段に設定する時刻情報生成手段(6)と、各種データを記憶する不揮発性記憶手段9と、各種制御を実施する制御手段6とを有し、前記制御手段は、前記GPS受信時計の受信可能状態と受信不可能状態とを判別し、第1の所定条件により、受信不可能状態に移行し、第2の所定条件により、受信不可能状態から受信可能状態へ復帰し、受信不可能状態への移行時に、うるう秒情報を前記不揮発性記憶手段に記憶し、受信不可能状態から受信可能状態への復帰時に、うるう秒情報を前記不揮発性記憶手段から読み出すことを特徴とする。 The GPS reception clock according to the present invention includes at least receiving means 1 for receiving satellite information relating to time, processing means 2 for processing information received by the receiving means, timing means 3 for measuring time, and demodulation of the processing means. A time information generating means (6) for generating time information based on the signal and setting the time measuring means; a non-volatile storage means 9 for storing various data; and a control means 6 for performing various controls. The control means discriminates between a receivable state and a receivable state of the GPS reception clock, shifts to a receivable state according to a first predetermined condition, and changes from a receivable state to a second predetermined condition. When returning to the receivable state and shifting to the unreceivable state, the leap second information is stored in the nonvolatile storage means, and when returning from the unreceivable state to the receivable state, the leap second information is stored in the non-volatile storage. Means Characterized in that the read.
本発明では、受信可能状態中に得られた最新のうるう秒情報を不揮発性記憶手段に記憶しておくことで、受信不可能状態から受信可能状態に復帰した際に、うるう秒を加味した時刻を提供することができる。 In the present invention, the latest leap second information obtained in the receivable state is stored in the non-volatile storage means, so that the leap second is taken into account when returning from the unreceivable state to the receivable state. Can be provided.
本発明において、前記制御手段は、受信不可能状態から受信可能状態への復帰後の最初の受信時にうるう秒情報を取得せず、前記不揮発性記憶手段から読み出したうるう秒情報を使用して時刻情報を生成するように制御することを特徴とする。 In the present invention, the control means does not acquire leap second information at the time of first reception after returning from the unreceivable state to the receivable state, and uses the leap second information read from the non-volatile storage means to Control is performed to generate information.
本発明では、受信不可能状態から受信可能状態への復帰の際に、12.5分毎に送信されるうるう秒情報以外の時刻(TOW)・カレンダ情報(週番号)を受信し、うるう秒は不揮発性記憶手段に記憶された情報を使うことで、受信可能状態移行後において短時間のうちに正確な時刻・カレンダを提供することができる。 In the present invention, when returning from the unreceivable state to the receivable state, time (TOW) / calendar information (week number) other than leap second information transmitted every 12.5 minutes is received, and leap second. By using the information stored in the non-volatile storage means, it is possible to provide an accurate time and calendar within a short time after the transition to the receivable state.
本発明において、前記制御手段は受信不可能状態から受信可能状態への復帰後の最初の受信時に、さらに、第3の所定条件を満たした場合にうるう秒情報を受信し、うるう秒情報取得に成功した場合に、取得したうるう秒情報により時刻情報を生成するように制御することを特徴とする。 In the present invention, the control means receives leap second information when the third predetermined condition is satisfied at the time of the first reception after returning from the unreceivable state to the receivable state, and acquires leap second information. When successful, it is controlled to generate time information based on the acquired leap second information.
本発明では、充分な電源電圧がある場合にうるう秒情報を受信することで、動作禁止期間が長期間に渡って継続されたような場合に、記憶していたうるう秒情報が最新情報と違っている状況においても正確な時刻を提供することができる。 In the present invention, when the operation prohibition period is continued for a long time by receiving leap second information when there is a sufficient power supply voltage, the stored leap second information is different from the latest information. It is possible to provide an accurate time even in a certain situation.
本発明において、電源を供給する電源部を有し、前記第1、第2、第3の所定条件は該電源部の電源電圧が所定値に達したことであることを特徴とする。
In the present invention, a power supply unit that supplies power is provided, and the first, second, and third predetermined conditions are that a power supply voltage of the power supply unit reaches a predetermined value.
本発明では、前記第1、第2、第3の所定条件としてそれぞれ第1の電圧(V1)、第2の電圧(V2)、第3の電圧(V3)であり、V1<V2<V3の関係である場合、受信不可能状態に移行する電圧V1より高い電圧V2で受信可能状態に移行することで、受信可能状態復帰直後にすぐに電圧V1以下とならないよう配慮している。またうるう秒情報を受信する電圧は、電圧V2よりさらに高い電圧V3以上とすることで最大12.5分の受信を要するうるう秒情報の受信中に電圧V1以下となって受信不可能状態に移行し、GPS受信時計が再び使用できない状態とならないようにしている。 In the present invention, the first, second, and third predetermined conditions are the first voltage (V1), the second voltage (V2), and the third voltage (V3), respectively, and V1 <V2 <V3. In the case of the relationship, consideration is given so that the voltage V1 does not become immediately below the voltage V1 immediately after the return to the receivable state by shifting to the receivable state at the voltage V2 higher than the voltage V1 that shifts to the receivable state. In addition, the voltage for receiving leap second information is set to a voltage V3 higher than the voltage V2, so that it becomes lower than the voltage V1 during the reception of the leap second information requiring a maximum of 12.5 minutes and shifts to the unreceivable state. However, the GPS reception clock is prevented from being used again.
本発明において、前記電源部が充電可能な蓄電手段と該蓄電手段に充電する発電手段を有し、前記第1、第2の所定条件は該発電手段の発電状態を示す値であることを特徴とする。 In the present invention, the power supply unit has a chargeable storage means and a power generation means for charging the power storage means, and the first and second predetermined conditions are values indicating a power generation state of the power generation means. And
本発明では、例えば発電手段が太陽電池で、第1の所定条件として低発電状態が数日継続している状態、第2の所定条件として第1の所定条件より高い発電状態である場合、第1の所定条件では暗所に保管されている可能性が高いと判断し受信禁止状態に移行し、その後第2の所定条件となると受信禁止状態を解除する。このような構成とすることで暗所保管、つまり屋内など衛星が見えない場所で受信ができない環境では受信を禁止することで無駄な消費電力を抑える効果が得られる。 In the present invention, for example, when the power generation means is a solar cell and the low power generation state continues for several days as the first predetermined condition, and the power generation state is higher than the first predetermined condition as the second predetermined condition, If it is determined that there is a high possibility of being stored in a dark place under the first predetermined condition, the state shifts to the reception prohibited state, and then the reception prohibited state is canceled when the second predetermined condition is reached. With such a configuration, an effect of suppressing wasteful power consumption can be obtained by prohibiting reception in an environment where reception is not possible in a dark place, that is, indoors where a satellite cannot be seen.
本発明において、前記第1、第2の所定条件は前記発電手段の発電電圧であり、前記第32の所定条件に対応する電圧の絶対値は、前記第1の所定条件に対応する電圧の絶対値より高いか同一であることを特徴とする。 In the present invention, the first and second predetermined conditions are generated voltages of the power generation means, and the absolute value of the voltage corresponding to the thirty-second predetermined condition is the absolute value of the voltage corresponding to the first predetermined condition. It is characterized by being higher than or equal to the value.
本発明では、例えば発電手段が太陽電池で、第1の所定条件として低発電状態での電圧(V4)、第2の所定条件として第1の所定条件より高い発電状態での電圧(V5)でV4≦V5の関係である場合、発電電圧がV4以下となると受信禁止状態に移行し、その後発電電圧がV5となると受信禁止状態を解除する。これにより、復帰条件にヒステリシスを設け、復帰動作を確実にすることが出来る。 In the present invention, for example, the power generation means is a solar cell, the first predetermined condition is a voltage (V4) in a low power generation state, and the second predetermined condition is a voltage (V5) in a power generation state higher than the first predetermined condition. In the case of the relationship of V4 ≦ V5, when the generated voltage becomes V4 or less, the state is shifted to the reception prohibited state, and when the generated voltage becomes V5 thereafter, the reception prohibited state is cancelled. Thereby, hysteresis is provided in the return condition, and the return operation can be ensured.
本発明において、前記第2の所定条件以上の発電電圧の検出により受信可能状態への復帰した場合の最初の受信時は、時刻情報のみ取得することを特徴とする。 In the present invention, only time information is acquired at the time of the first reception when returning to a receivable state upon detection of a generated voltage that is equal to or higher than the second predetermined condition.
完全に時計を停止する停止状態と比較し、節電(パワーセーブ)状態では計時は継続するので、計時時刻の狂いは大きくない。
本発明では、このことを利用し、受信対象をTOWのみとすることで、長期の非発電状態継続により電圧低下(停止となる電圧よりは高い)となっていても、長時間受信する状態にならないことから停止状態にならず、受信禁止状態解除後も通常使用を提供することができる。
Compared with the stop state in which the clock is completely stopped, the timekeeping continues in the power saving state, so that the timekeeping time is not significantly different.
In the present invention, this is utilized, and only the TOW is received, so that even if the voltage is lowered (higher than the voltage at which it is stopped) due to the long-term non-power generation state, the signal is received for a long time. Therefore, normal use can be provided even after the reception prohibited state is released.
本発明において、うるう秒情報として、現在のうるう秒、うるう秒の更新週、うるう秒の更新日、更新後のうるう秒を記憶し、受信時に週番号を受信し、週番号の受信に成功した場合に受信した週番号から得られた更新タイミングと、記憶していたうるう秒情報の更新タイミングを比較し、更新タイミング前ならば現在のうるう秒にて、更新タイミング後ならば更新後のうるう秒にて、時刻情報を生成することを特徴とする。 In the present invention, as the leap second information, the current leap second, leap second update week, leap second update date, and leap second after update are stored, the week number is received at the time of reception, and the week number is successfully received. The update timing obtained from the received week number is compared with the update timing of the stored leap second information. If it is before the update timing, it is the current leap second, and after the update timing, the leap second after the update. And generating time information.
本発明では、受信不可能状態から受信可能状態に移行したときにカレンダ情報を受信することで、不揮発性記憶手段に記憶していたうるう秒情報の更新タイミングが過ぎたかどうかを判断することができ、適切なタイミングでのうるう秒補正が可能となる。 In the present invention, it is possible to determine whether or not the update timing of the leap second information stored in the non-volatile storage means has passed by receiving the calendar information when shifting from the unreceivable state to the receivable state. Leap second correction at an appropriate timing becomes possible.
本発明において、生産時に、前記不揮発性記憶手段にうるう秒のデフォルトデータが記憶され、使用開始から最初のうるう秒受信成功までは、該デフォルトデータを使用して時刻情報が作成されることを特徴とする。 In the present invention, at the time of production, default data of leap seconds is stored in the non-volatile storage means, and time information is created using the default data from the start of use until the first successful leap second reception. And
本発明では、時計の組立が完了している在庫品に対して、保管中にうるう秒情報の更新がある場合でも、最終出荷時にうるう秒情報を非接触通信手段等により更新し不揮発性記憶手段に記憶させることで、出荷時においてはいつでも最新のうるう秒情報となっているため、正確な時刻を提供することができる。 In the present invention, even when there is an update of leap second information during storage for a stock item in which the timepiece has been assembled, the leap second information is updated by non-contact communication means or the like at the time of final shipment. By storing the information, the latest leap second information is always available at the time of shipment, so that an accurate time can be provided.
本発明によれば、受信可能状態から受信不可能状態に移行するときは、うるう秒情報を保持・記憶しておき、受信不可能状態から受信可能状態に移行するときは、保持・記憶していたうるう秒情報を読み出すことで、受信可能状態移行後にうるう秒情報を得るために長時間受信状態にしなくても、読み出したうるう秒情報をもとに正確な時間、もしくは正確な時間に極めて近い時間をすぐに提供できるものである。 According to the present invention, leap second information is held and stored when shifting from the receivable state to the unreceivable state, and held and stored when shifting from the unreceivable state to the receivable state. By reading out the leap second information, it is possible to obtain the leap second information after shifting to the receivable state, so even if it is not in the reception state for a long time, it is based on the read leap second information, or it is very close to the accurate time. It can provide time immediately.
以下に、添付図面を用いてこの発明にかかるGPS受信時計の好適な実施の形態を詳細に説明する。 Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of a GPS reception timepiece according to the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
[第1の実施の形態:基本実施形態]
<回路構成>
まず、図1に基づいて本発明の一実施例としてのGPS受信時計100の回路構成の概略を説明する。図1は、本発明の第1の実施の形態にかかるGPS受信時計100のブロック図である。
1は、GPS衛星から50bpsで送信されるGPS信号を受信し、復調した結果を出力するGPS受信手段である。2はGPS受信手段1の出力を受けてデータ処理を行うデータ処理手段である。3は時刻の計時を行う計時手段、4は計時手段の出力に基づいて表示を制御する表示駆動手段、5は時刻を表示する表示手段である。
[First Embodiment: Basic Embodiment]
<Circuit configuration>
First, an outline of a circuit configuration of a
Reference numeral 1 denotes GPS receiving means for receiving a GPS signal transmitted from a GPS satellite at 50 bps and outputting a demodulated result. Reference numeral 2 denotes data processing means for receiving data from the GPS receiving means 1 and performing data processing. 3 is a time measuring means for measuring time, 4 is a display driving means for controlling display based on the output of the time measuring means, and 5 is a display means for displaying time.
6はGPS受信手段1に対する受信開始命令の出力、データ処理手段2から得られる情報の演算処理、計時手段3に対する時刻情報の出力、表示駆動手段4に対する駆動命令、後述する電圧検出手段7への検出開始命令、不揮発性メモリ制御手段8に対する不揮発性
メモリアクセス命令、などGPS受信時計100内の制御全般を行う制御手段である。
6 is an output of a reception start command to the GPS receiving means 1, an arithmetic processing of information obtained from the data processing means 2, an output of time information to the time measuring means 3, a drive command to the display drive means 4, Control means for performing overall control within the
7は電源部12の電圧を検出する電圧検出手段、8は制御手段6の命令を受けて後述の不揮発性メモリの消去、書込み、読み出しを行う不揮発性メモリ制御手段、9は各種データを記憶する不揮発性メモリ、10は制御手段など時計内動作の制御シーケンスを記憶するROM(リードオンリーメモリ)、11はRAM(ランダムアクセスメモリ)、12はGPS受信時計に電源を供給する電源部である。
なお、本発明の説明上関係のない回路構成、例えば発振器などは図示していないが、GPS受信時計100に必要な構成は含まれているものとする。
Reference numeral 7 denotes voltage detection means for detecting the voltage of the
It should be noted that a circuit configuration that is not relevant to the description of the present invention, such as an oscillator, is not shown, but a configuration necessary for the
<動作概要>
続いて、図1に基づいてGPS受信時計の概略動作を説明する。
制御手段6は、スイッチ(図示しない)などの外部入力、もしくは計時手段3で計時されるGPS受信時計内部時刻が所定時刻となると、GPS受信手段1に受信開始の命令を出力し、表示手段5に受信開始の表示となるよう(例えばデジタルで受信マークを点灯)、表示駆動手段4に命令を出力する。
GPS受信手段1は受信状態となり、衛星の捕捉、位相同期など復調に必要な処理を行う。復調された信号はデータ処理手段2に入力され、GPS受信時計に必要な情報、本実施例では時刻に関係するデータについて正確に受信できているかどうか判断し、受信できていれば制御手段6にデータを出力する。
制御手段6はデータ処理手段2から出力される時刻データをもとに年、月、日、時、分、秒を算出し計時手段3に出力するとともに、GPS受信手段1に受信終了命令を出力する。計時手段3の時刻情報を元に、表示駆動手段4は表示手段5に対し時刻情報の更新を実施する。受信開始からある規定時間以内に衛星の補足が出来ない場合や外部入力により受信中止となった場合は、制御手段は計時手段3への時刻更新は行わず、受信終了命令をGPS受信手段1に出力する。
<Overview of operation>
Next, a schematic operation of the GPS reception clock will be described with reference to FIG.
The control means 6 outputs a command to start reception to the GPS receiving means 1 when the external time input from a switch (not shown) or the internal time of the GPS reception clock timed by the time measuring means 3 reaches a predetermined time, and the display means 5 A command is output to the display driving means 4 so that the reception start display is displayed (for example, the reception mark is turned on digitally).
The GPS receiving means 1 enters a receiving state, and performs processing necessary for demodulation such as satellite acquisition and phase synchronization. The demodulated signal is input to the data processing means 2, and it is determined whether or not the information necessary for the GPS reception clock, that is, the data related to the time in this embodiment can be received correctly. Output data.
The control means 6 calculates the year, month, day, hour, minute, and second based on the time data output from the data processing means 2 and outputs it to the time measuring means 3 and outputs a reception end command to the GPS receiving means 1 To do. Based on the time information of the time measuring means 3, the display driving means 4 updates the time information to the display means 5. If the satellite cannot be captured within a specified time from the start of reception or if reception is stopped due to external input, the control means does not update the time to the time measuring means 3 and sends a reception end command to the GPS receiving means 1. Output.
GPS受信時計100は、使用経過とともに電源部12の電圧が低下していく。電圧低下するとGPS受信時計100は正常制御できなくなるため、制御手段6は、ある規定電圧以下となると時計を停止する処理を実行する。
図5は時計の動作状況を表す状態遷移図であり、電圧が低下すると動作可能状態200から動作禁止状態300に移行する。以下に詳細動作について説明する。
In the
FIG. 5 is a state transition diagram showing the operation state of the watch. When the voltage decreases, the operation state 200 is shifted to the operation inhibition state 300. Detailed operation will be described below.
電圧検出手段7が電源部12の電圧を検出し、ある規定電圧以下、例えば第1の所定電圧以下となるとその情報を制御手段6に出力する。
制御手段6は電圧低下の情報を受けて、表示駆動手段4に表示停止の命令を出力するとともに、不揮発性メモリ制御手段8に時計内部の情報を不揮発性メモリ9に記憶するよう命令を出す。その命令により、不揮発性メモリ制御手段8は、うるう秒情報を始めとする時計内部の必要情報を不揮発性メモリ9に記憶する。
うるう秒情報以外では、ユーザが設定したアラーム、タイムゾーン、サマータイムなどの情報、指針式表示時計の場合は停止している指針位置、などの情報が不揮発性メモリ9に記憶される。時刻やカレンダーは、GPS受信時計100の停止中も時々刻々と変化し記憶しても意味を成さないため、時刻情報やカレンダー情報は記憶しない。
書込みが終了すると、GPS受信時計100は電圧が復帰するまで、動作禁止状態300を継続し、受信手段1による受信動作や計時手段3による計時は行われない。動作禁止状態300は、受信不可能状態とも言える。
The voltage detection means 7 detects the voltage of the
The control means 6 receives the information about the voltage drop and outputs a display stop command to the display drive means 4 and also issues a command to the nonvolatile memory control means 8 to store the information inside the watch in the nonvolatile memory 9. In response to the command, the nonvolatile memory control means 8 stores necessary information inside the timepiece including the leap second information in the nonvolatile memory 9.
In addition to the leap second information, information such as an alarm, time zone, daylight saving time, and the like set by the user and information such as a stopped hand position in the case of a pointer type display clock are stored in the nonvolatile memory 9. Since the time and calendar change every moment even when the
When the writing is completed, the
停止後、電池交換もしくは充電式電源の場合は充電が行われ電圧が第2の所定電圧以上に復帰すると、GPS受信時計100はパワーオンリセットがかかり、動作禁止状態300を解除する。図5では、電圧が復帰し動作禁止状態300から動作可能状態200に移
行したときである。
停止解除後、電圧検出手段7が電圧検出を行い、時計動作を再開できる電圧があると制御手段6が判断すると、制御手段6は不揮発性メモリ9から記憶したデータの読み出し命令を不揮発性メモリ制御手段8に対して出力する。読み出し後、受信を開始し、TOW、週番号、うるう秒情報などの受信を行う。動作可能状態200は受信可能状態である。
なお、第1の所定電圧と第2の所定電圧は同一でも異なっても良いが、異ならせる場合は、システムの安全性を考慮し、第2の所定電圧が第1の所定電圧より高く設定される。
After the stop, in the case of battery replacement or a rechargeable power source, when charging is performed and the voltage returns to the second predetermined voltage or higher, the
After the suspension is released, when the voltage detecting means 7 detects the voltage and the control means 6 determines that there is a voltage at which the clock operation can be resumed, the control means 6 sends a read command of the data stored in the nonvolatile memory 9 to the nonvolatile memory control. Output to means 8. After reading, reception is started, and TOW, week number, leap second information, etc. are received. The operable state 200 is a receivable state.
Note that the first predetermined voltage and the second predetermined voltage may be the same or different. However, if they are different, the second predetermined voltage is set higher than the first predetermined voltage in consideration of system safety. The
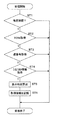
<基本受信動作>
続いて受信処理動作を図2のフローチャートに基づいて説明する。なお、GPSの送信フォーマットについては特許文献1などに記載があり、よく知られたものであるので、ここでは省略する。
<Basic reception operation>
Next, the reception processing operation will be described based on the flowchart of FIG. Note that the GPS transmission format is described in Patent Document 1 and the like and is well known, and is omitted here.
外部スイッチによる手動受信、もしくはGPS受信時計内で計時している時刻がある規定した時刻に達した場合、制御回路6は受信開始命令をGPS受信手段1に出力する。
受信開始後、衛星の補足ができているかデータ処理手段2が判断し(ST1)、捕捉、復調が出来ていると判断すると(ST1:Y)、情報の取得を開始し(ST2)、捕捉が出来ないと判断すると受信を終了する(ST1:N)。
When the time manually received by the external switch or the time measured in the GPS reception clock reaches a specified time, the control circuit 6 outputs a reception start command to the GPS receiving means 1.
After the start of reception, the data processing means 2 determines whether or not the satellite is supplemented (ST1), and if it is determined that acquisition and demodulation are possible (ST1: Y), acquisition of information is started (ST2), and acquisition is performed. If it is determined that it cannot be performed, the reception ends (ST1: N).
ST2にて情報の取得を開始すると、まず送信データとの同期を取るためTLM(TELEMETORY)情報の検出を行い、検出ができるとTOWの抽出を行う。
時刻情報が抽出できると(ST2:Y)、週番号情報の検出に移行する(ST3)。
TLM情報が検出できない、またはTOWがノイズなどにより時刻情報として抽出できない場合は(ST2:N)、受信を終了する。
When acquisition of information is started in ST2, first, TLM (TELEMETRY) information is detected in order to synchronize with transmission data, and if detection is possible, TOW is extracted.
When the time information can be extracted (ST2: Y), the process proceeds to detection of week number information (ST3).
If TLM information cannot be detected or TOW cannot be extracted as time information due to noise or the like (ST2: N), reception ends.
以下同様に、週番号情報が正常に抽出できた場合は(ST3:Y)、うるう秒情報の取得に移行し(ST4)、出来ない場合は(ST3:Y)受信を終了する。
うるう秒情報が正常に抽出できた場合(ST4:Y)、制御手段6は表示時刻の算出を行い(ST5)、受信した情報をRAM10に保持し(ST6)、計時手段3に対して算出時刻による更新を実施し、表示駆動手段4は表示手段5に更新時刻を表示させる。
うるう秒情報が抽出できなかった場合は(ST4:N)、受信を終了する。
Similarly, when the week number information can be normally extracted (ST3: Y), the process proceeds to acquisition of leap second information (ST4). When the week number information cannot be obtained (ST3: Y), the reception is terminated.
When the leap second information has been successfully extracted (ST4: Y), the control means 6 calculates the display time (ST5), holds the received information in the RAM 10 (ST6), and calculates the time to the time measuring means 3 The display drive unit 4 causes the display unit 5 to display the update time.
If the leap second information could not be extracted (ST4: N), the reception is terminated.
図2ではTOW、週番号(WN)、うるう秒情報(LS)が抽出できないと受信成功しない処理としているが、上記いずれかが受信できても受信成功終了するようにしても良い。
例えば、TOWのみ受信が成功した場合には、前回受信した週番号とうるう秒情報を用いて表示時刻を更新するようにしても良い。
In FIG. 2, the process is such that reception is not successful unless TOW, week number (WN), and leap second information (LS) cannot be extracted.
For example, when only the TOW is successfully received, the display time may be updated using the previously received week number and leap second information.
<電圧低下時(停止)処理>
次に電圧低下時における処理について、図3のフローチャートに基づいて説明する。
GPS受信時計100は規定電圧以下かどうかを定期的に検出し(ST11)、規定電圧(第1の所定電圧)以上ならば(ST11:N)正常動作できる電圧と判断し、動作を継続する。規定電圧(第1の所定電圧)以下となった場合は(ST11:Y)機能停止の処理に移行し、制御手段6は、不揮発性メモリ9に受信したうるう秒情報を記憶させるために、不揮発性メモリ制御手段8に不揮発性メモリ9の消去を実行させ、消去終了後うるう秒情報の書込みを実行させる(ST12)。
書込みが終了すると、制御手段6は、表示駆動手段4に表示駆動停止命令を出力し、表示手段5の表示を停止させ、さらに時計全体を停止状態にする(ST13)。
停止状態になると電圧が復帰するまではGPS受信時計100は動作を再開しない。
<Voltage drop (stop) process>
Next, processing at the time of voltage drop will be described based on the flowchart of FIG.
The
When the writing is completed, the control means 6 outputs a display drive stop command to the display drive means 4, stops the display on the display means 5, and puts the entire timepiece into a stop state (ST13).
In the stop state, the
<電圧復帰時(復帰)処理>
続いて電圧復帰時における処理について、図4のフローチャートに基づいて説明する。
停止状態中に、電池交換、または充電式電源の場合は充電が行われ、GPS受信時計100の動作可能電圧(第2の所定電圧)まで電源部12が回復した場合、パワーオンリセットが実行されGPS受信時計100は動作を開始する。
このとき規定電圧(第2の所定電圧)以上かどうか判断するため、制御手段6は動作が充分可能な電圧かどうか電圧検出手段7に電圧検出の命令を出力する(ST21)。規定電圧以下であれば(ST21:N)規定電圧以上となるまで電圧検出を続けるか、もしくは、図示しないが、再度停止すべき電圧低下と判断されれば、そのまま停止状態に移行する。
<Voltage recovery (recovery) processing>
Next, processing at the time of voltage recovery will be described based on the flowchart of FIG.
In the stop state, when the battery is replaced or in the case of a rechargeable power source, charging is performed, and when the
At this time, in order to determine whether the voltage is equal to or higher than the specified voltage (second predetermined voltage), the control means 6 outputs a voltage detection command to the voltage detection means 7 as to whether the voltage is sufficiently operable (ST21). If the voltage is less than the specified voltage (ST21: N), the voltage detection is continued until the voltage becomes equal to or higher than the specified voltage.
規定電圧(第2の所定電圧)以上ある場合(ST21:Y)、制御手段6は不揮発性メモリ制御手段8に対し、不揮発性メモリ9からうるう秒情報を読み出すよう命令を出し、読み出されたうるう秒情報をRAM11に格納する(ST22)。
手動受信開始動作、もしくは、電圧復帰時に自動で受信させる仕様の場合、制御手段6は受信開始命令をGPS受信手段1に命令を出力し(ST23)、データ処理手段2は受信データの検出を開始する。
When the voltage is equal to or higher than the specified voltage (second predetermined voltage) (ST21: Y), the control means 6 instructs the nonvolatile memory control means 8 to read the leap second information from the nonvolatile memory 9, and the readout is performed. Leap second information is stored in the RAM 11 (ST22).
In the case of a specification for manual reception start operation or automatic reception upon voltage recovery, the control means 6 outputs a reception start command to the GPS reception means 1 (ST23), and the data processing means 2 starts detection of received data To do.
まずTOWが抽出できたかどうか判断し(ST24)、抽出できなければ(ST24:N)受信を終了し、時刻及びカレンダーにデフォルトデータを設定して(ST31)時計の動作を開始する(ST30)。このときデフォルトデータは、例えば2009年1月1日午前12時00分00秒とする。
抽出できた場合は(ST24:Y)、次に週番号の抽出を開始する(ST25)。
週番号の抽出が出来ない場合(ST25:N)受信を終了しカレンダーはデフォルトデータ(例えば、2009年1月1日)に設定して(ST27)、週番号の抽出ができた場合は抽出した情報からカレンダーを算出する(ST26)。続いて受信により取得したTOWと、不揮発性メモリ9から読み出たうるう秒情報から現在時刻を計算し(ST28)、受信した時刻情報を保持して(ST29)、時刻情報のみ修正して計時手段3に出力し、表示駆動手段4を介し表示手段5に修正時刻を表示させる(ST30)。
First, it is determined whether or not the TOW can be extracted (ST24). If it cannot be extracted (ST24: N), reception is terminated, default data is set in the time and calendar (ST31), and the clock operation is started (ST30). At this time, the default data is, for example, 12:00 am on January 1, 2009.
If extraction is successful (ST24: Y), extraction of week numbers is started (ST25).
When the week number cannot be extracted (ST25: N), the reception is terminated and the calendar is set to default data (for example, January 1, 2009) (ST27), and the week number is extracted when extracted. A calendar is calculated from the information (ST26). Subsequently, the present time is calculated from the TOW acquired by reception and the leap second information read from the nonvolatile memory 9 (ST28), the received time information is held (ST29), and only the time information is corrected to measure time. 3 and the correction time is displayed on the display means 5 via the display driving means 4 (ST30).
<第1実施例の効果>
以上説明したように本実施形態によれば、電圧が低下し停止した状態から規定電圧値以上に復帰したときに少なくとも時刻については正確もしくは極めて正確な時間に近い時刻を短時間で提供できる効果が得られる。
<Effect of the first embodiment>
As described above, according to the present embodiment, there is an effect that it is possible to provide a time close to an accurate or extremely accurate time in a short time, at least for a time when the voltage drops and stops from a stopped state. can get.
<第1実施例の変形例>
本実施形態ではTOW、週番号を受信する例として記載してきた。
しかし、週番号を取得するには最大約30秒必要であるため、復帰後の電源状態によっては大きな負荷となる場合もあり、また、ユーザーが長く待たされていると感じる可能性もある。
そこで、電源復帰後さらに短時間で正確な時刻を表示させたい場合には、週番号の受信は行わず、TOWと記憶していたうるう秒情報を使用するのが望ましい。
この場合、受信開始後、数秒で正確な時刻を表示することが可能である。
なお、週番号受信の実施・不実施は次に示す実施例2と同様、電源電圧により制御しても良い。
<Modification of the first embodiment>
This embodiment has been described as an example of receiving TOW and week numbers.
However, since it takes about 30 seconds at the maximum to acquire the week number, there may be a heavy load depending on the power state after the return, and the user may feel that the user has been waiting for a long time.
Therefore, when it is desired to display the accurate time in a shorter time after the power is restored, it is desirable to use the leap second information stored as TOW without receiving the week number.
In this case, it is possible to display an accurate time within a few seconds after the start of reception.
Note that the execution / non-execution of week number reception may be controlled by the power supply voltage as in the second embodiment.
[第2の実施の形態:復帰時にうるう秒も受信]
図6を用いて本発明にかかる第2の実施の形態を説明する。本実施例の形態では、第1の実施の形態と同様に、GPS受信時計100を用い、第1の実施の形態と同様の構成の説明を省略し、異なる部分を主として説明する。
[Second Embodiment: Receive Leap Second at Return]
A second embodiment according to the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. In the present embodiment, as in the first embodiment, the
第2の実施の形態では、復帰後の最初の受信時にうるう秒を取得し、より正確な時刻情報を得ることを想定した実施例である。
図6のステップ番号は、図4のステップ番号と同一のものの処理については図6でも同一であるため、説明を省略する。また電源部12は充電系電源として説明する。
In the second embodiment, a leap second is acquired at the time of the first reception after return, and it is assumed that more accurate time information is obtained.
6 are the same as those in FIG. 6 for the same processing as the step number in FIG. The
ST28までは、図4と同じであるので説明は省略する。
TOW、週番号の抽出処理が終了し、記憶していたうるう秒情報を用いて時刻、カレンダーの算出が終了(ST28)すると、再び電圧検出手段7による電源部12の電圧検出が実行される(ST40)。ST40の電圧検出の実行は以下の理由による。
Steps up to ST28 are the same as in FIG.
When the TOW and week number extraction processing is completed and the calculation of time and calendar is completed using the stored leap second information (ST28), voltage detection of the
ST21における停止状態からの復帰の場合は、TOWや週番号のみの短時間の受信実行を想定した電池容量(第2の所定電圧)で復帰させている。これにより、必要以上の充電が不要なため、ユーザは早期に時計の使用が可能となる。
それに対し、上述の如く、うるう秒の受信には最長12.5分の受信時間が必要とされるため電源部12への負担も大きくなり、停止からの復帰許可レベルでは必ずしも十分ではない可能性が高い。
従って、ST40では、ST21での規定電圧より高い第3の所定電圧での判定が実施される。規定電圧以下と判断された場合(ST40:N)は、規定電圧以上となるまで待機する。
なお、所定時間以上待機しても規定電圧(第3の所定電圧)以下の場合は、ST29に移行する。
In the case of the return from the stopped state in ST21, the battery capacity (second predetermined voltage) is assumed assuming that the TOW and the week number alone are executed for a short time. As a result, unnecessary charging is unnecessary, and the user can use the watch at an early stage.
On the other hand, as described above, reception of leap seconds requires a reception time of up to 12.5 minutes, which increases the burden on the
Therefore, in ST40, the determination at the third predetermined voltage higher than the specified voltage in ST21 is performed. When it is determined that the voltage is equal to or lower than the specified voltage (ST40: N), the process waits until the voltage becomes equal to or higher than the specified voltage.
If the voltage is not more than the specified voltage (third predetermined voltage) even after waiting for a predetermined time, the process proceeds to ST29.
規定電圧以上の電圧を検出した場合(ST40:Y)は、次に、うるう秒情報の抽出を開始する(ST42)。うるう秒の抽出が出来ない場合(ST42:N)は受信を終了し、ST28で算出した時刻及びカレンダー(さらにST40、ST41、ST42に要した経過時間も加算)を計時手段3に出力し、抽出したTOW、週番号をRAM11に格納し(ST29)、表示駆動手段4を介し表示手段5に時刻、カレンダーを表示させ時計動作を開始する(ST30)。 When a voltage equal to or higher than the specified voltage is detected (ST40: Y), extraction of leap second information is started (ST42). If the leap second cannot be extracted (ST42: N), the reception is terminated, and the time and calendar calculated in ST28 (and the elapsed time required for ST40, ST41, ST42 are also added) are output to the time measuring means 3 and extracted. The stored TOW and week number are stored in the RAM 11 (ST29), the time and calendar are displayed on the display means 5 via the display driving means 4, and the clock operation is started (ST30).
うるう秒の抽出が出来た場合(ST42:Y)、抽出したTOW、週番号、うるう秒情報から表示時刻を計算し(ST43)、抽出した情報をRAM11に記憶し(ST29)、修正された時刻及びカレンダーを計時手段3に出力、表示駆動手段4を介し表示手段5に時刻及びカレンダーを表示させ、時計動作を開始する(ST30)。 When the leap second can be extracted (ST42: Y), the display time is calculated from the extracted TOW, week number, and leap second information (ST43), the extracted information is stored in the RAM 11 (ST29), and the corrected time is corrected. Then, the calendar is output to the time measuring means 3, the time and calendar are displayed on the display means 5 via the display driving means 4, and the clock operation is started (ST30).
<第2実施例の効果>
本実施例に拠れば、復帰受信時において、電源電圧(=電池容量)に余裕があればうるう秒も受信するようにしたので、復帰時により正確な時刻の生成が可能となる。
また、うるう秒情報受信の許可電源電圧(第3の所定電圧)を、TOWや週番号のみを受信する場合の電圧(第2の所定電圧)より高く設定することで、TOWや週番号のみの受信を許可する復帰を早期に実現できる。
<Effect of the second embodiment>
According to this embodiment, when the return is received, the leap second is also received if there is a margin in the power supply voltage (= battery capacity), so that more accurate time can be generated at the time of return.
Also, by setting the permitted power supply voltage (third predetermined voltage) for receiving leap second information higher than the voltage (second predetermined voltage) when receiving only the TOW and week number, only the TOW and week number are received. Return to permit reception can be realized at an early stage.
<第2実施例の変形例>
本実施例ではうるう秒受信可能な状態になるまで電圧検出を継続し、時計動作を行わないようになっているが、これに限らず、TOW、週番号の抽出ができた時点で記憶していたうるう秒情報を使って時計動作を開始し、時計動作中にうるう秒受信に必要な電圧になった時点でうるう秒情報の受信を行うようにしても良い。
<Modification of Second Embodiment>
In this embodiment, the voltage detection is continued until the leap second reception is possible, and the clock operation is not performed. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and the TOW and the week number are stored when they are extracted. The clock operation may be started using the leap second information, and the leap second information may be received when the voltage necessary for the leap second reception is reached during the clock operation.
[第3の実施の形態:節電状態での挙動]
本発明に係る第3の実施の形態を、図面を用いて説明する。また第1の実施の形態と
同様の構成の説明を省略し、異なる部分を主として説明する。
第3の実施形態は、発電手段による充電系電源を有し、発電の有無により、節電(パワーセーブ)状態に移行するGPS受信時計における実施形態である。
[Third embodiment: behavior in a power saving state]
A third embodiment according to the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. Also, the description of the same configuration as that of the first embodiment is omitted, and different portions will be mainly described.
The third embodiment is an embodiment of a GPS reception timepiece that has a charging system power supply by power generation means and shifts to a power saving state depending on the presence or absence of power generation.
充電系電源の蓄電手段(2次電池)は1次電池に比べその容量が小さいものが多く、寿命を延ばすためには節電機能が必要である。また、非発電状態はユーザーが使用していない場合が多く、そのような場合に通常と同じように動作させることは無駄も多い。
そこで、所定期間以上非発電を連続的に検出した場合に、機能を制限する節電(パワーセーブ)状態への移行機能は充電系電源には有用であり、GPS受信時計においても同様である。
受信機能付電子時計では、節電(パワーセーブ)状態では、内部時計の計時は継続し、時刻表示手段や受信手段を停止することで、節電を図ることが多い。
GPS受信時計においても同様の制御が有効である。
The power storage means (secondary battery) of the charging system power supply often has a smaller capacity than the primary battery, and a power saving function is required to extend the life. Further, the non-power generation state is often not used by the user, and in such a case, it is wasteful to operate as usual.
Therefore, the function of shifting to a power saving state that restricts the function when non-power generation is continuously detected for a predetermined period or longer is useful for the charging system power supply, and the same applies to the GPS reception clock.
In an electronic timepiece with a reception function, in the power saving state, the internal clock keeps counting, and the time display means and the reception means are often stopped to save power.
The same control is effective for the GPS reception clock.
外部入力(図示しない)による受信禁止命令、もしくは制御手段6が電源部12を構成する発電手段(図示しない)を定期的に検出してある期間以上非発電状態が続いた場合、制御手段6はパワーセーブ機能を動作させる。
パワーセーブ状態では、GPS受信手段1に対する受信開始命令の出力禁止、表示駆動手段4に対する表示手段5の停止(運針停止、LCD表示消灯など)を実行する。また、受信したうるう秒情報はRAM11に保持しつつ、制御手段6は不揮発性メモリ制御手段8に対し、不揮発性メモリ9にうるう秒情報などを記憶するよう命令を出力する。
図5は動作状況を表しており、ある期間以上非発電(第1所定電圧以下の発電電圧)状態のが続くと動作可能状態から動作禁止状態に移行する。
なお、動作可能状態が受信可能状態、動作禁止状態(パワーセーブ)状態が受信不可能状態であることは、第1実施形態と同じである。
When a non-power generation state continues for a period when a reception prohibition command by an external input (not shown) or a power generation means (not shown) constituting the
In the power saving state, output of a reception start command to the GPS receiving means 1 is prohibited, and the display means 5 is stopped (display of the needle is stopped, LCD display is turned off, etc.) for the display driving means 4. Further, while the received leap second information is held in the RAM 11, the control unit 6 outputs a command to the nonvolatile memory control unit 8 to store the leap second information in the nonvolatile memory 9.
FIG. 5 shows an operation state. When a non-power generation (power generation voltage equal to or lower than the first predetermined voltage) state continues for a certain period or longer, the operation state shifts to the operation prohibition state.
It is to be noted that the operable state is the receivable state and the operation prohibited state (power save) state is the unreceivable state, as in the first embodiment.
制御手段6は、パワーセーブ解除のための外部入力(図示しない)、もしくは発電手段(図示しない)の発電(第2所定電圧以上の発電電圧)を検出すると、パワーセーブ機能を解除する。パワーセーブ機能が解除されると、表示駆動手段4に表示復帰の命令を出力し表示手段5を表示状態にさせる。さらに表示復帰前、復帰中もしくは復帰後いずれかのタイミングに受信を行う。
図5は動作状況を表しており、パワーセーブ解除のための外部入力、もしくは発電を検出すると動作禁止状態300から動作可能状態200に移行する。
When the control means 6 detects an external input (not shown) for canceling the power save, or a power generation means (not shown) generating power (a power generation voltage equal to or higher than the second predetermined voltage), the control means 6 cancels the power saving function. When the power saving function is canceled, a display return command is output to the display driving means 4 to cause the display means 5 to be in a display state. Furthermore, reception is performed at any timing before, during or after the return of display.
FIG. 5 shows an operation state. When an external input for canceling power save or power generation is detected, the operation prohibition state 300 shifts to the operation enable state 200.
パワーセーブ機能中も計時は継続しているため、精度にもよるがカレンダーのズレはなく、時刻のみがずれている可能性が高い。また、パワーセーブ解除後はすぐにGPS受信時計を使用したいときでもあるため、受信は短時間で終わることが望ましい。
よってパワーセーブ解除後の受信はTOWのみ受信することとし、週番号、うるう秒情報は受信しない。具体的には、制御手段6はデータ処理手段2に対し、TOWのデータのみ抽出対象とするよう命令を出す。受信成功後、受信したTOWと記憶していたうるう秒情報から現在時刻を算出して、計時手段3の時刻情報を更新し、表示駆動手段4を介し表示手段5に表示させる。
Since the timekeeping continues even during the power save function, there is no deviation of the calendar, depending on the accuracy, and there is a high possibility that only the time is shifted. Further, since it is sometimes necessary to use the GPS reception clock immediately after canceling the power save, it is desirable that the reception should be completed in a short time.
Therefore, only TOW is received after canceling the power save, and the week number and leap second information are not received. Specifically, the control unit 6 issues a command to the data processing unit 2 so that only TOW data is extracted. After successful reception, the current time is calculated from the received TOW and the stored leap second information, the time information of the time measuring means 3 is updated, and displayed on the display means 5 via the display driving means 4.
<第3実施例の効果>
以上、説明したように本実施形態によれば、TOWのみ受信しうるう秒は記憶していたうるう秒情報を使用することで、パワーセーブ解除直後でも正確な時刻もしくは極めて正確な時間に近い時刻を提供できる効果が得られる。
<Effect of the third embodiment>
As described above, according to the present embodiment, the leap second that can be received only by TOW is used by using the stored leap second information, so that an accurate time or a time close to an extremely accurate time can be obtained even immediately after canceling the power save. The effect which can be provided is acquired.
また、抽出対象をTOWのみとすることで、長期のパワーセーブ継続により電圧低下(停止となる電圧よりは高い)となっていても、長時間受信する状態にならないことから
停止状態にならず、パワーセーブ解除後も通常の状態で使用できる効果が得られる。
In addition, by selecting only TOW as the extraction target, even if the voltage drops (higher than the voltage at which it stops) due to long-term power saving, it will not be in a state of receiving for a long time, so it will not stop. An effect that can be used in a normal state even after canceling the power save is obtained.
<第3実施例の変形例>
また、本実施形態ではTOWのみ抽出としているが、これに限らず、停止している期間が短期間であればTLMのみ抽出して時刻修正したり、カレンダーがずれる可能性がある程の長期間であれば1分未満で抽出可能な週番号まで受信するようにしても良い。
<Modification of the third embodiment>
In the present embodiment, only TOW is extracted. However, the present invention is not limited to this. If the stopped period is short, only TLM is extracted to correct the time, or the calendar may shift. If so, it may be received up to a week number that can be extracted in less than one minute.
[第4の実施の形態;生産時におけるうるう秒のデフォルトデータ書き込み]
以上3つの実施形態においては、受信不可能状態への移行時にうるう秒情報を不揮発性メモリに書き込む実施例を記載してきた。
ところで、出荷後の在庫状態や店頭での陳列時はGPS電波の受信環境は必ずしも良くない場合が多い。このような場合、比較的受信時間の短いTOWや週番号はまだしも受信時間の長いうるう秒情報を取得することは必ずしも好ましくない。
しかしながら、時刻情報はTOWにうるう秒の情報を加算しないと正確な情報となり得ない。
そこで、GPS受信時計100では出荷時にうるう秒情報のデフォルトデータを不揮発性メモリ9に書き込んでおき、うるう秒受信に成功するまではこのデフォルトデータを使用して時刻情報を作成し、表示することが好ましい。
これにより、比較的精度の高い時刻情報を出荷直後から提供することが可能となる。
[Fourth Embodiment; Leap Second Default Data Writing in Production]
In the above three embodiments, an example has been described in which leap second information is written in the nonvolatile memory at the time of transition to the unreceivable state.
By the way, there are many cases where the GPS radio wave reception environment is not always good at the time of stocking after shipment or display at a store. In such a case, it is not always preferable to acquire leap second information with a long reception time for TOW and week numbers with a relatively short reception time.
However, the time information cannot be accurate unless the leap second information is added to the TOW.
Therefore, the
This makes it possible to provide time information with relatively high accuracy immediately after shipment.
このデフォルトデータの書き込みは、GPS受信時計100の生産時に時計外部から検査・調整用の端子などを使用して書き込まれる。書き込み方法は接触式でも良いが、非接触方式の方が、完成時計状態での書き込みも行えて便利である。
非接触書き込み方式は各種存在するが、例えば、表示駆動手段4としてステップモータを使用している場合、このモータを介しての通信を用いると部品の追加が無いので、より好ましい。
The default data is written by using an inspection / adjustment terminal or the like from the outside of the watch when the
There are various types of non-contact writing methods. For example, when a step motor is used as the display driving unit 4, it is more preferable to use communication via the motor because no components are added.
図7のフローチャートを用いて、生産・出荷から最初の受信までの概略を説明する。
図7は、本発明の第4の形態にかかるGPS受信時計の、生産・出荷から最初の受信までの動作を示すフローチャートである。
時計完成(ST100)後、例えばモータコイルを用いての非接触通信により、うるう秒情報のデフォルトデータを不揮発性メモリ9に書き込む(ST101)。デフォルトデータとしては、生産時における最新のうるう秒情報が書き込まれる。
An outline from production / shipment to the first reception will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG.
FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing operations from production / shipment to the first reception of the GPS reception timepiece according to the fourth embodiment of the present invention.
After completion of the watch (ST100), default data of leap second information is written in the nonvolatile memory 9 by non-contact communication using, for example, a motor coil (ST101). As default data, the latest leap second information at the time of production is written.
完成時計を起動するためのシステムリセット(ST102)後、不揮発性メモリ9のうるう秒(LS)が読み出され、RAM11に書き込まれる(ST103)。
その後TOWと週番号のみの受信が行われる(ST104)。うるう秒を受信しないのは、出荷時の工程を短縮することも考慮してのことでもある。
受信失敗したら(ST105:N)、デフォルトの時刻・カレンダー情報が書き込まれる(ST107)。
受信成功したら(ST105:Y)、受信した時刻情報にデフォルトのうるう秒情報を加えた時間を作成し表示する。
After a system reset (ST102) for starting the completed clock, the leap second (LS) of the nonvolatile memory 9 is read and written to the RAM 11 (ST103).
Thereafter, only the TOW and week number are received (ST104). The reason for not receiving the leap second is to consider shortening the shipping process.
If reception fails (ST105: N), default time / calendar information is written (ST107).
If reception is successful (ST105: Y), a time obtained by adding default leap second information to the received time information is created and displayed.
その後、GPS受信時計は、実使用状態にてうるう秒の受信を行う。うるう秒の受信の受信に成功したら、デフォルトデータに代わって受信したうるう秒情報を時計内(例えば、RAM11)に記憶する。以降は、受信したうるう秒情報により時刻情報データが作成される。また、受信不可能状態への移行時も、受信したうるう秒情報が不揮発性メモリ9に記憶される。 Thereafter, the GPS reception clock receives leap seconds in the actual use state. When the reception of the leap second is successful, the received leap second information is stored in the clock (for example, the RAM 11) instead of the default data. Thereafter, time information data is created from the received leap second information. Also, the received leap second information is stored in the nonvolatile memory 9 when the state is shifted to the reception disabled state.
<第4実施例の効果>
以上説明したように、出荷時にうるう秒情報のデフォルトデータを不揮発性メモリ9に書き込むことで、在庫時や店頭陳列時などの受信が困難な環境においても、正確な時刻情報の作成・表示が可能となる。
<Effect of the fourth embodiment>
As described above, the default data of leap second information at the time of shipment is written in the non-volatile memory 9, so that accurate time information can be created and displayed even in an environment where reception is difficult such as in stock or store display. It becomes.
[第5の実施の形態:うるう秒更新週記憶の場合]
第5の実施の形態は、第1〜第4の実施形態において、記憶しているうるう秒情報によりその補正方法を変更する実施形態である。
GPS送信信号のうるう秒情報には、現在のうるう秒、うるう秒の更新週、うるう秒の更新日、更新後のうるう秒が含まれている。
停止時や生産時に記憶するうるう秒情報としては、上記4種類の情報の一部でも全てでもよいのであるが、本実施例では全てを記憶しているものとする。
[Fifth embodiment: Leap second update week storage]
The fifth embodiment is an embodiment in which the correction method is changed according to the stored leap second information in the first to fourth embodiments.
The leap second information of the GPS transmission signal includes the current leap second, the leap second update week, the leap second update date, and the leap second after the update.
As the leap second information stored at the time of stoppage or production, some or all of the above four types of information may be stored, but in the present embodiment, all are stored.
図8に示すフローチャートにより動作を説明する。
まず、電圧復帰時の受信で週番号の受信に成功しているかどうかを判断し(ST200)、失敗していたなら(ST200:N)うるう秒の更新時期が判断できないので、電圧低下時に記憶していた現在のうるう秒を使用し、時刻を生成する(ST204)。
The operation will be described with reference to the flowchart shown in FIG.
First, it is determined whether or not the week number has been successfully received when receiving the voltage (ST200). If it has failed (ST200: N), the leap second update time cannot be determined. Using the current leap second, the time is generated (ST204).
週番号の受信に成功していたなら(ST200:Y)記憶している更新週ならびに更新日と比較する(ST201)。更新タイミングを過ぎている場合は(ST202:Y)、更新後のうるう秒を用いて時刻を生成し(ST203)、更新タイミング前ならば現在のうるう秒を使用し、時刻を生成する(ST204)。
このような構成にすることで、記憶していた現在のうるう秒よりも正確な時刻を提供できる。
If the week number has been successfully received (ST200: Y), the stored update week and update date are compared (ST201). If the update timing has passed (ST202: Y), the time is generated using the updated leap second (ST203), and if it is before the update timing, the current leap second is used to generate the time (ST204). .
With this configuration, it is possible to provide a time that is more accurate than the current leap second that has been stored.
[その他の変形例]
以上、第1から第4の実施の形態について述べてきたが、それぞれの実施の形態に対し以下のような変形例をとっても構わない。
[Other variations]
Although the first to fourth embodiments have been described above, the following modifications may be made to the respective embodiments.
(1)本実施例ではTOW、週番号、うるう秒情報を抽出対象としてるが、これら以外に、受信データの信頼性確保のためにサブルレームID、パリティなども抽出対象としてもよく、逆に抽出対象を減らしても良い。 (1) In this embodiment, TOW, week number, and leap second information are targeted for extraction, but in addition to these, the sub-frame ID, parity, etc. may be extracted for ensuring the reliability of received data. The target may be reduced.
(2)第5の実施形態では、現在のうるう秒、うるう秒の更新週、うるう秒の更新日、更新後のうるう秒の全てのうるう秒情報を記憶したが、第5の実施形態を採用しないのならば、一部のうるう秒情報のみを記憶するようにしても良い。
これにより、不揮発性メモリ9の容量を削減することが可能となる。
(2) In the fifth embodiment, the current leap second, leap second update week, leap second update date, and all leap second information after the leap second are stored. However, the fifth embodiment is adopted. If not, only some leap second information may be stored.
As a result, the capacity of the nonvolatile memory 9 can be reduced.
(3)また、本実施例では表示の詳細には触れていないが、表示は指針式、LCD、LEDなど表示を構成できる手段のいずれか、または複数の組み合わせでも構わない。 (3) Although details of the display are not touched in the present embodiment, the display may be any one of means capable of constituting a display such as a pointer type, LCD, LED, or a combination of a plurality of means.
(4)また、本発明の構成はランダムロジックでもCPUを有するマイクロプロセッサでも良く、またその両方を組み合わせた構成でも良い。 (4) The configuration of the present invention may be a random logic, a microprocessor having a CPU, or a combination of both.
(5)また、本実施例では不揮発性メモリ9に書き込む情報をうるう秒情報としているが、これに限らず、受信により得られる測位情報や、タイムゾーン設定、アラーム時刻、サマータイム設定など時計に関する情報を記憶しても構わない。特にタイムゾーンは、時計停止時および電圧復帰時に同じゾーンにいる場合は、再度ゾーン設定する必要がないため有効である。 (5) In the present embodiment, the information to be written in the nonvolatile memory 9 is leap second information. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and positioning information obtained by reception, information on the clock such as time zone setting, alarm time, daylight saving time setting, etc. May be stored. In particular, the time zone is effective because it is not necessary to set the zone again when the time zone is in the same zone when the clock is stopped and when the voltage is restored.
(6)また、本実施例では動作可能状態から動作禁止状態に移行する電圧、及び動作禁止
状態から動作可能状態に移行する電圧を同一としているがこれに限らず、異なる電圧としても構わない。
(6) In the present embodiment, the voltage for shifting from the operable state to the disabled state and the voltage for shifting from the disabled state to the operable state are the same. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and different voltages may be used.
(7)また本実施例では電圧により動作可能状態と動作禁止状態の2状態としているがこれに限らず、動作可能状態の中でもさらに電圧により状態を二分し動作可能状態と動作禁止状態の中間状態を作り、機能制限するが時計動作をさせるなどの状態があってもよい。 (7) Further, in this embodiment, the two states of the operation enable state and the operation prohibition state are set according to the voltage. However, the present invention is not limited to this. There may be a state where the function is limited but the function is restricted but the clock is operated.
(8)また、電源部12としては1次電池でも2次電池でも良く、さらに2次電池の場合の発電手段としては太陽電池、自動巻き、熱発電、またはこれら以外のいずれかまたは複数の組み合わせでも構わない。
(8) The
(9)また、本実施例では受信動作後、時計動作を開始しているがこれに限らず、時計動作を開始後にTOW、週番号、うるう秒情報などを順次受信して更新するようにすれば、ユーザは電圧復帰後から時刻表示までの間待たされるストレスも無い。 (9) In this embodiment, the clock operation is started after the reception operation. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and TOW, week number, leap second information, etc. are sequentially received and updated after the clock operation is started. For example, there is no stress that the user waits until the time is displayed after the voltage is restored.
1 GPS受信手段
6 制御手段
7 電圧検出手段
8 不揮発性メモリ制御手段
9 不揮発性メモリ
12 電源部
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1 GPS receiving means 6 Control means 7 Voltage detection means 8 Non-volatile memory control means 9
Claims (10)
該受信手段で受信した情報を処理する処理手段と、
時刻を計時する計時手段と、
前記処理手段の復調信号を元に時刻情報を生成し、前記計時手段に設定する時刻情報生成手段と、
各種データを記憶する不揮発性記憶手段と、
各種制御を実施する制御手段と、
を有するGPS受信時計において、
前記制御手段は、前記GPS受信時計の受信手段の受信可能状態と受信不可能状態とを判別し、
第1の所定条件により、受信不可能状態に移行し、
第2の所定条件により、受信不可能状態から受信可能状態へ復帰し、
受信不可能状態への移行後に、うるう秒情報を前記不揮発性記憶手段に記憶し、
受信不可能状態から受信可能状態への復帰時に、うるう秒情報を前記不揮発性記憶手段から読み出す
ことを特徴とするGPS受信時計。 Receiving means for receiving satellite information about at least time;
Processing means for processing the information received by the receiving means;
A time measuring means for measuring time;
Time information generating means for generating time information based on the demodulated signal of the processing means and setting the time measuring means;
Non-volatile storage means for storing various data;
Control means for performing various controls;
In a GPS reception watch having
The control means discriminates a reception enabled state and a reception disabled state of the receiving means of the GPS reception clock,
Due to the first predetermined condition, it shifts to a reception impossible state,
Due to the second predetermined condition, it returns from the unreceivable state to the receivable state,
After the transition to the unreceivable state, the leap second information is stored in the nonvolatile storage means,
A GPS reception timepiece which reads leap second information from the non-volatile storage means when returning from a non-receivable state to a receivable state.
受信不可能状態から受信可能状態への復帰後の最初の受信時にうるう秒情報を取得せず、前記不揮発性記憶手段から読み出したうるう秒情報を使用して時刻情報を生成するように制御する
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載のGPS受信時計。 The control means includes
Control to generate time information using the leap second information read from the non-volatile storage means without acquiring the leap second information at the first reception after returning from the unreceivable state to the receivable state. The GPS reception timepiece according to claim 1.
前記第1、第2の所定条件は該電源部の電源電圧が所定値に達したことである
ことを特徴とする請求項1ないし2のいずれか1つに記載のGPS受信時計。 Having a power supply for supplying power,
It said first, second predetermined condition GPS receiver clock according to any one of claims 1 to 2, wherein the power supply voltage of the power supply unit is to reach a predetermined value.
さらに、第3の所定条件を満たした場合にうるう秒情報を受信し、
うるう秒情報取得に成功した場合に、取得したうるう秒情報により時刻情報を生成するように制御する
ことを特徴とする請求項1ないし3のいずれか1つに記載のGPS受信時計。 The control means, at the time of the first reception after returning from the unreceivable state to the receivable state,
Furthermore, the leap second information is received when the third predetermined condition is satisfied,
If successful leap second information acquisition, GPS receiver clock according to control any one of claims 1 to 3, characterized in that to generate the time information by the acquired leap second information.
前記第3の所定条件に対応する電源電圧の絶対値は、前記第2の所定条件に対応する電圧の絶対値より高いことを特徴とする請求項4に記載のGPS受信時計。 The third predetermined condition is that the power supply voltage of the power supply unit has reached a predetermined value,
5. The GPS receiving timepiece according to claim 4, wherein an absolute value of a power supply voltage corresponding to the third predetermined condition is higher than an absolute value of a voltage corresponding to the second predetermined condition.
前記第1、第2の所定条件は該発電手段の発電状態を示す値である
ことを特徴とする請求項1ないし5のいずれか1つに記載のGPS受信時計。 The power supply unit has a chargeable power storage means and a power generation means for charging the power storage means,
6. The GPS reception timepiece according to claim 1, wherein the first and second predetermined conditions are values indicating a power generation state of the power generation means.
前記第2の所定条件に対応する電圧の絶対値は、
前記第1の所定条件に対応する電圧の絶対値より高いか同一である
ことを特徴とする請求項6に記載のGPS受信時計。 The first and second predetermined conditions are power generation voltages of the power generation means,
The absolute value of the voltage corresponding to the second predetermined condition is
The GPS reception timepiece according to claim 6, wherein the GPS reception timepiece is higher than or equal to an absolute value of a voltage corresponding to the first predetermined condition.
ことを特徴とする請求項6ないし7のいずれか1つに記載のGPS受信時計。 8. Only time information is acquired at the time of the first reception when returning to a receivable state upon detection of a generated voltage that is equal to or higher than the second predetermined condition. 9. GPS reception clock.
受信時に週番号を受信し、
週番号の受信に成功した場合に受信した週番号から得られた更新タイミングと、
記憶していたうるう秒情報の更新タイミングを比較し、
更新タイミング前ならば現在のうるう秒にて、
更新タイミング後ならば更新後のうるう秒にて、時刻情報を生成する
ことを特徴とする請求項1ないし8のいずれか1つに記載のGPS受信時計。 As the leap second information, the current leap second, leap second update week, leap second update date, leap second after update are stored,
Receive the week number when receiving,
Update timing obtained from the received week number when the week number is successfully received,
Compare the update timing of the stored leap second information,
If the current leap second before the update timing,
The GPS reception clock according to any one of claims 1 to 8, wherein time information is generated in a leap second after the update timing.
使用開始から最初のうるう秒受信成功までは、該デフォルトデータを使用して時刻情報が作成される
ことを特徴とする請求項1ないし9のいずれか1つに記載のGPS受信時計。 During production, default data of leap seconds is stored in the nonvolatile storage means,
10. The GPS reception clock according to claim 1, wherein time information is created using the default data from the start of use until the first successful leap second reception.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010041984A JP5374415B2 (en) | 2010-02-26 | 2010-02-26 | GPS reception clock |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010041984A JP5374415B2 (en) | 2010-02-26 | 2010-02-26 | GPS reception clock |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2011179856A JP2011179856A (en) | 2011-09-15 |
| JP2011179856A5 JP2011179856A5 (en) | 2013-01-10 |
| JP5374415B2 true JP5374415B2 (en) | 2013-12-25 |
Family
ID=44691530
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010041984A Active JP5374415B2 (en) | 2010-02-26 | 2010-02-26 | GPS reception clock |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5374415B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5802637B2 (en) * | 2012-09-21 | 2015-10-28 | 株式会社東芝 | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and program |
| JP6364924B2 (en) * | 2014-04-24 | 2018-08-01 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Electronic device and control method of electronic device |
| JP7225835B2 (en) | 2019-01-24 | 2023-02-21 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Electronic clock, satellite signal receiving device, and control method for satellite signal receiving device |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4032069B2 (en) * | 1995-12-06 | 2008-01-16 | シチズンホールディングス株式会社 | Clock with radio wave correction function |
| JP4294966B2 (en) * | 2002-02-18 | 2009-07-15 | シチズンホールディングス株式会社 | Electronic timepiece, secondary battery storage state display method, secondary battery storage state display program, and information processing terminal device |
| JP2004294206A (en) * | 2003-03-26 | 2004-10-21 | Fuji Photo Optical Co Ltd | Date display device and camera equipped with the same |
| JP5294621B2 (en) * | 2007-12-28 | 2013-09-18 | シチズン時計株式会社 | Electronics |
| JP2009229359A (en) * | 2008-03-25 | 2009-10-08 | Citizen Watch Co Ltd | Electronic hardware |
-
2010
- 2010-02-26 JP JP2010041984A patent/JP5374415B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2011179856A (en) | 2011-09-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5463630B2 (en) | Time correction device, time measuring device with time correction device, and time correction method | |
| JP6552665B2 (en) | Radio clock | |
| EP2693276B1 (en) | Radiowave-controlled wristwatch | |
| JP5428167B2 (en) | Time correction device, time measuring device with time correction device, and time correction method | |
| JP5310426B2 (en) | Electronic clock and time correction method of electronic clock | |
| JP5374912B2 (en) | Time correction device, time measuring device with time correction device, and time correction method | |
| KR20030078737A (en) | Electronic device and reception control method of electronic device | |
| JP6508103B2 (en) | Radio wave clock, leap second correction information acquisition method, and program | |
| JP6679844B2 (en) | Radio clock, date and time information acquisition method and program | |
| JP5374415B2 (en) | GPS reception clock | |
| JP4803230B2 (en) | Electronic clock | |
| JP2023112161A (en) | Satellite radio wave receiver, electronic timepiece, positioning control method and program | |
| JP5386422B2 (en) | Radio wave watch | |
| JP6009444B2 (en) | Radio wave watch | |
| JP5323758B2 (en) | GPS reception clock | |
| JP2016121877A (en) | Electronic apparatus | |
| JP6485148B2 (en) | Radio clock | |
| JP6278766B2 (en) | Electronic clock | |
| JP6961446B2 (en) | Radio clock | |
| JP2005227038A (en) | Measuring instrument | |
| JP2009229359A (en) | Electronic hardware | |
| JP6493574B2 (en) | Radio wave receiver, radio wave clock, signal acquisition method and program | |
| JP2018151267A (en) | Radio correction watch | |
| JP4458163B2 (en) | Reception device and reception control method | |
| JP6687141B2 (en) | Radio clock |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20121120 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20121120 |
|
| RD07 | Notification of extinguishment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7427 Effective date: 20130528 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20130612 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130625 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130716 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130903 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130920 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5374415 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313115 |
|
| S533 | Written request for registration of change of name |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313533 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |