JP5367785B2 - Vibration isolator for blower fan and blower fan structure including the same - Google Patents
Vibration isolator for blower fan and blower fan structure including the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5367785B2 JP5367785B2 JP2011186692A JP2011186692A JP5367785B2 JP 5367785 B2 JP5367785 B2 JP 5367785B2 JP 2011186692 A JP2011186692 A JP 2011186692A JP 2011186692 A JP2011186692 A JP 2011186692A JP 5367785 B2 JP5367785 B2 JP 5367785B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- outer cylinder
- vibration isolator
- blower fan
- vibration
- diameter side
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims description 52
- 229920005992 thermoplastic resin Polymers 0.000 claims description 14
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 20
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 19
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 19
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 description 16
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 8
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000012916 structural analysis Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000009423 ventilation Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000001746 injection moulding Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000007689 inspection Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000013011 mating Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 4
- 210000003746 feather Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 230000002452 interceptive effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229920002725 thermoplastic elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000001771 impaired effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000644 propagated effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000008719 thickening Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000009466 transformation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910000838 Al alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007664 blowing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004512 die casting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005489 elastic deformation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920001971 elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000000806 elastomer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000704 physical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013040 rubber vulcanization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007493 shaping process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006641 stabilisation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011105 stabilization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920003051 synthetic elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920003002 synthetic resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000000057 synthetic resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000005061 synthetic rubber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012795 verification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004636 vulcanized rubber Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Structures Of Non-Positive Displacement Pumps (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、いわゆる、エアコン(エアコンディショナー)等の空調装置やエレクトロニクス機器等に装備される送風用ファンの防振具及びそれを備える送風用ファン構造体に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a vibration isolator for a blower fan installed in an air conditioner such as a so-called air conditioner (air conditioner), an electronic device, and the like, and a blower fan structure including the same.
送風用ファン構造体としては、モータからの電磁振動が送風用ファン全体に伝播されることの防止や、製造上の工数の削減及び材料費の低減による低コスト化、軽量化、リサイクル性の向上等を目的として、図14に示すように、熱可塑性樹脂からなる外筒51と内筒52とを、熱可塑性エラストマーからなる弾性部材53で連結したオール樹脂製の防振具50をインサート部品として用い、これに送風用ファンを射出成形してなるものが知られている。(例えば、特許文献1参照。)
As a blower fan structure, it is possible to prevent electromagnetic vibration from the motor from being propagated throughout the blower fan, reduce manufacturing man-hours, reduce material costs, reduce weight, and improve recyclability. For example, as shown in FIG. 14, an all-
更に詳細には、同図に示すように、防振具50を可動型D1にインサートした後、この可動型D1を固定型D2方向に移動させて型締めし、可動型D1と固定型D2との相互間に形成されたキャビティC4内にゲートGを通して熱可塑性樹脂を矢印mに示すように射出することにより、防振具50を備える送風用ファン構造体が形成される。
More specifically, as shown in the figure, after the
しかしながら、送風用ファン構造体の形成にあたり、防振具50の外筒51(特に、周壁51a)には、同図矢印で示すように、高い充填圧(200〜400kg/cm2)と、高い温度(200〜300°C)とが加わることになる。この場合、可動型D1内で防振具50の外筒51に変形、傾き、芯ずれ等を生じると、可動型D1から取り出した送風用ファン構造体にも、内筒52の偏心等に伴うアンバランスが生じ、振動や異音を発生する虞がある。
However, in forming the blower fan structure, the outer cylinder 51 (particularly the
これを解決する手段としては、外筒51の剛性を高めるべく、外筒51の肉厚を厚くすることが考えられるが、樹脂使用量が増えることで、材料コストの面で改善の余地を残す。
As a means for solving this, it is conceivable to increase the thickness of the
一方、外筒51の成形にあたり、使用される樹脂を選択して充填温度や充填圧に起因した外筒51への影響を抑えることも考えられるが、この場合、曲げ強度や引張り強度等の強度、曲げ弾性率等の剛性、熱変形温度等の耐熱性などに代表される諸物性を含めて樹脂を選択する必要があることから、材料コスト面で改善の余地を残す。
On the other hand, when molding the
加えて、外筒51を厚肉化すれば、金型内での冷却に時間を要するため、1個当たりの成形サイクルが長くなることで、作業能率が悪くなると共に、これに起因する製造コストとの面で改善の余地を残す。
In addition, if the
また、単一の部品を厚肉に射出成形しようとすると、その厚さが厚くなればなる程、冷却時に各部位で生じる樹脂収縮が大きくなるため、外筒51に反りやヒケを生じさせる虞があり、品質面で改善の余地を残す。
In addition, when attempting to injection-mold a single part thickly, the thicker the thickness, the greater the resin shrinkage that occurs at each part during cooling, which may cause warping and sink marks on the
また、こうした問題に配慮して、好適な製造条件を定めても、製造条件のバラツキ等により、歩留りが悪化することが予想されることから、その分、検査項目も増やす必要があり、製造管理に費やす費用に改善の余地を残す。 Considering these problems, even if suitable manufacturing conditions are determined, the yield is expected to deteriorate due to variations in manufacturing conditions, etc., so it is necessary to increase the number of inspection items accordingly, manufacturing management. Leave room for improvement in the cost of spending.
これに対し、従来の防振具50は、外筒51における一方の軸方向端部にフランジ51bを設けることで、結果的に外筒51全体の剛性を高めているが、フランジ51bが大径化すれば、材料コスト面で改善の余地を残す。
In contrast, the
また、外筒51にフランジ51bを設ける場合、単位の金型当たりの成形個数が減少するので、多数個取りを目的とした成形には不利であり、改善の余地を残す。
Further, when the
また、外筒51に高温の高い圧力が加わるという問題は、送風用ファン構造体の成形時のみに起きるのではなく、外筒51と内筒52とを弾性部材53で連結するとき、例えば、弾性部材53を合成ゴムで加硫成形するときや、弾性部材53をエラストマーで射出成形するときにおいても起こり得る問題である。
In addition, the problem that high temperature and high pressure is applied to the
即ち、従来の技術では、防振具の外筒に高温高圧が加わることで起きる様々な問題を解消するにあたり、コストの上昇、作業能率の悪化や製品品質のバラツキを生じ、また、これらを抑制するにあたっては、製造管理が煩雑でこの管理にも限界があり、更に、従来の技術では、多数個取りを目的とした成形には不利であるところから、本発明の目的とするところは、こうした課題を解決した送風用ファンの防振具及び、それを備えた送風用ファン構造体を提供することにある。 In other words, in the conventional technology, in solving various problems caused by high temperature and high pressure applied to the outer cylinder of the vibration isolator, cost increases, work efficiency deteriorates and product quality varies, and these are suppressed. In doing so, manufacturing management is complicated and there is a limit to this management, and further, the conventional technique is disadvantageous for molding for the purpose of obtaining a large number of pieces. An object of the present invention is to provide a blower fan vibration isolator and a blower fan structure including the same.
本発明である送風用ファンの防振具は、送風用ファンを保持するための外筒を有しその内側に弾性部材を介して内筒が連結される送風用ファンの防振具であって、前記外筒における外周面の全周に亘って段差を形成して送風用ファンの保持領域を設けたことを特徴とするものである。 The blower vibration isolator of the present invention is a blower fan vibration isolator having an outer cylinder for holding the blower fan and having an inner cylinder connected to the inner cylinder via an elastic member. Further, a holding area for the blower fan is provided by forming a step over the entire circumference of the outer peripheral surface of the outer cylinder.
本発明にあっては、前記段差が、外筒の軸方向に対して直交する面としてなることが好ましい。 In this invention, it is preferable that the said level | step difference becomes a surface orthogonal to the axial direction of an outer cylinder.
加えて、この場合、外筒の端部のうちの少なくとも一方は、弾性部材よりも突出した突出部位としてなることが好ましい。 In addition, in this case, it is preferable that at least one of the end portions of the outer cylinder is a protruding portion that protrudes more than the elastic member.
また、本発明である他の送風用ファンの防振具は、送風用ファンを保持するための外筒を有しその内側に弾性部材を介して内筒が連結される送風用ファンの防振具であって、前記外筒の端部のうちの少なくとも一方が、前記弾性部材よりも突出した突出部位としてなることを特徴とするものである。 Further, another vibration isolator for a blower fan according to the present invention has an outer cylinder for holding the blower fan and has an outer cylinder connected to the inner cylinder via an elastic member inside thereof. It is a tool, Comprising: At least one of the edge parts of the said outer cylinder becomes a protrusion part which protruded rather than the said elastic member, It is characterized by the above-mentioned.
本発明はいずれも、前記突出部位の内周面が、その端面に向かうに従って拡径する傾斜面としてなることが好ましい。 In any of the present invention, it is preferable that the inner peripheral surface of the projecting portion is an inclined surface that increases in diameter toward the end surface.
また、本発明である送風用ファン構造体は、上記の防振具と、この防振具の外筒における前記保持領域に保持される送風用ファンとを有することを特徴とするものである。 A blower fan structure according to the present invention includes the vibration isolator described above and a blower fan held in the holding region of the outer cylinder of the vibration isolator.
なお、本発明によれば、防振具の外筒が熱可塑性樹脂等の合成樹脂からなる場合に特に有効であるが、防振具の外筒がアルミ合金等の金属からなる場合にも適用できる。 The present invention is particularly effective when the outer cylinder of the vibration isolator is made of a synthetic resin such as a thermoplastic resin, but is also applicable when the outer cylinder of the vibration isolator is made of a metal such as an aluminum alloy. it can.
本発明である送風用ファンの防振具は、防振具の外筒における外周面の全周に亘って段差を形成して送風用ファンの保持領域を設けたことで、当該外筒に送風用ファンを成形するにあたり、この成形に用いられる領域として、例えば、この段差の大径側の領域を用いれば、成形領域の面積が小さく済む。即ち、本発明である防振具によれば、外筒の外周面全体に送風用ファンを成形した従来の場合に比べて、成形時に樹脂圧を受ける面積(受圧面積)が小さく済むことから、外筒が樹脂圧を受けることによって受ける力も小さく済む。 The vibration isolator for the blower fan according to the present invention is configured to form a step over the entire circumference of the outer peripheral surface of the outer cylinder of the vibration isolator to provide a holding area for the blower fan. In forming the fan for use, for example, if the region on the large diameter side of the step is used as the region used for the forming, the area of the forming region can be reduced. That is, according to the vibration isolator of the present invention, compared to the conventional case where the blower fan is formed on the entire outer peripheral surface of the outer cylinder, the area that receives the resin pressure during molding (pressure receiving area) can be reduced. The force received by the outer cylinder receiving the resin pressure can be reduced.
従って、本発明である防振具によれば、外筒を厚肉化し、又は、外筒にフランジを設けることなく、外筒に高温・高圧が加わることで生じる変形を抑えることができる。 Therefore, according to the vibration isolator which is this invention, the deformation | transformation which arises when high temperature and a high pressure are added to an outer cylinder can be suppressed, without thickening an outer cylinder or providing a flange in an outer cylinder.
また、本発明である上記防振具を用いて、防振具と送風用ファンとを有する送風用ファン構造体を一体に成形した場合、防振具における外筒の変形が抑えられたことで、防振具が変形し、又は、偏心することによって防振機能が損なわれるようなことがない。従って、本発明である送風用ファン構造体によれば、外筒を厚肉化し、又は、外筒にフランジを設けることなく、防振機能を維持することができる。 Further, when the blower fan structure having the vibration isolator and the blower fan is integrally formed using the above vibration isolator according to the present invention, deformation of the outer cylinder in the vibration isolator is suppressed. The anti-vibration function is not impaired by deformation or eccentricity of the anti-vibration tool. Therefore, according to the blower fan structure of the present invention, the vibration isolation function can be maintained without increasing the thickness of the outer cylinder or providing a flange on the outer cylinder.
ところで、外筒の外周面に段差が存在しなくとも、成形型に段差を形成し、この段差の大径側と外筒の外周面との間にキャビティを形成すれば、外筒の外周面の一部だけを送風用ファンの保持領域とすることも可能である。 By the way, even if there is no step on the outer peripheral surface of the outer cylinder, if the step is formed in the mold and a cavity is formed between the large diameter side of the step and the outer peripheral surface of the outer cylinder, the outer peripheral surface of the outer cylinder It is also possible to make only a part of the area a holding area for the blower fan.
しかしながら、この場合、段差の大径側と外筒の外周面との間にキャビティを形成し、このキャビティ内の樹脂が段差の小径側と外筒の外周面との間に流入しないようにするためには、外筒を密着させた状態又は極微小なクリアランスを持った状態でインサートできるように寸法調整をしなければならない。 However, in this case, a cavity is formed between the large diameter side of the step and the outer peripheral surface of the outer cylinder so that the resin in the cavity does not flow between the small diameter side of the step and the outer peripheral surface of the outer cylinder. For this purpose, the dimensions must be adjusted so that the insert can be inserted with the outer cylinder in close contact or with a very small clearance.
ところが、こうした寸法調整は、成形型や外筒の寸法精度を考慮すれば、実際上は非常に困難である。しかも、このように寸法調整しても、スムースなインサートが実現できないため、作業能率が悪い。 However, such dimensional adjustment is actually very difficult in consideration of the dimensional accuracy of the mold and the outer cylinder. Moreover, even if the dimensions are adjusted in this way, a smooth insert cannot be realized, so that the work efficiency is poor.
加えて、成形型に段差を形成し、外筒の外周面の一部だけを送風用ファンの保持領域とする場合、防振具外筒が調心されていない状態で成形型にインサートすれば、インサート時には調心されているものの、送風用ファン構造体として取り出したときには調心されていない状態に戻ってしまい、振動や騒音等を発生する場合がある。 In addition, if a step is formed in the mold and only a part of the outer peripheral surface of the outer cylinder is used as a holding area for the blower fan, the vibration isolator outer cylinder is inserted into the mold without being aligned. Although it is aligned at the time of insertion, it may return to an unaligned state when taken out as a blower fan structure, and vibration or noise may occur.
これに対し、本発明である防振具は、外筒の外周面に段差が形成されていることから、成形型に大径側と小径側に区画する段差を形成し、この段差に、外筒の段差を接触させるだけで、成形型に形成した段差の大径側と外筒の保持領域との間にキャビティを形成し、このキャビティ内の樹脂が、成形型に形成した段差の小径側と、外筒の保持領域以外の領域との間に流入しないようにシールすることができる。 On the other hand, the vibration isolator according to the present invention has a step formed on the outer peripheral surface of the outer cylinder. Therefore, a step is formed in the molding die that is divided into a large diameter side and a small diameter side. By simply contacting the step of the cylinder, a cavity is formed between the large diameter side of the step formed in the mold and the holding area of the outer cylinder, and the resin in this cavity is the small diameter side of the step formed in the mold And a region other than the holding region of the outer cylinder can be sealed so as not to flow.
即ち、本発明である防振具のように、外筒の外周面に段差を形成すれば、外筒を成形型にインサートするにあたり、この成形型に形成した段差の小径側にクリアランスを持った状態でもインサートできるから、外筒を密着させた状態又は極微小なクリアランスを持った状態でインサートする必要がなく、作業能率も向上する。そして、このことは、結果的に、本発明である送風用ファン構造体においても同様である。 That is, when a step is formed on the outer peripheral surface of the outer cylinder as in the case of the vibration isolator according to the present invention, a clearance is provided on the small diameter side of the step formed on the molding die when the outer cylinder is inserted into the molding die. Since it can be inserted even in a state, it is not necessary to insert in a state where the outer cylinder is in close contact or with a very small clearance, and the work efficiency is improved. As a result, this also applies to the blower fan structure of the present invention.
また、本発明である防振具によれば、外筒に段差が形成されているため、例えば、段差の大径側を送風用ファンの保持領域とすれば、当該防振具の内筒に対し外筒が偏心を伴っていたり、外筒自体が変形等により真円が維持できていない状態のまま、当該防振具を成形型内に収納しても、当該段差により形成される防振具の小径側領域は、成形型に対してクリアランスを持った状態でインサートできる。即ち、本発明である防振具は、成形型と干渉することなく収納できる。このため、本発明である防振具が予め偏心等を伴っていても、送風用ファンを成形するにあたっては、防振具の精度に左右されることなく調心されることから、プロペラファン構造体として成形型から取り出しても、回転精度が悪化して振動や騒音等を発生することがない。 Further, according to the vibration isolator of the present invention, since the outer cylinder has a step, for example, if the large diameter side of the step is a holding area for the blower fan, the inner cylinder of the vibration isolator is On the other hand, even if the vibration isolator is housed in the mold while the outer cylinder is eccentric or is not maintained in a perfect circle due to deformation or the like, the vibration isolation is formed by the step. The small diameter region of the tool can be inserted with a clearance from the mold. That is, the vibration isolator according to the present invention can be stored without interfering with the mold. For this reason, even if the vibration isolator according to the present invention is preliminarily accompanied by eccentricity or the like, the propeller fan structure is used because the air blower fan is aligned without being affected by the accuracy of the vibration isolator. Even if it is taken out from the mold as a body, the rotational accuracy is not deteriorated and vibrations and noises are not generated.
また、本発明によれば、以下に例示するような各種の問題も併せて改善することができる。 Moreover, according to the present invention, various problems exemplified below can be improved together.
まず、本発明である防振具によれば、外筒を厚肉化し、又は、外筒にフランジを設ける必要がないので、材料コストの改善、作業能率の改善及び、これに伴う製造コストの改善を実現することができる。また、このことは、結果的に、本発明である送風用ファン構造体においても同様である。 First, according to the vibration isolator of the present invention, it is not necessary to thicken the outer cylinder or provide a flange on the outer cylinder. Therefore, the material cost is improved, the work efficiency is improved, and the manufacturing cost associated therewith is reduced. Improvements can be realized. In addition, as a result, the same applies to the blower fan structure according to the present invention.
また、本発明である防振具によれば、外筒の厚肉化に伴い外筒に生じる外筒の反りやヒケが抑制されるため品質の安定化が図れる。これは、防振具に送風用ファンを成形するにあたり、防振具の外筒に生じる反りやヒケの影響を当該送風用ファンに波及させないことから、結果的に、本発明である送風用ファン構造体の品質も安定化する。 Moreover, according to the vibration isolator which is this invention, since the curvature and sink of the outer cylinder which arise in an outer cylinder with the thickening of an outer cylinder are suppressed, quality stabilization can be aimed at. This is because, in forming the blower fan in the vibration isolator, the influence of warpage and sink marks generated in the outer cylinder of the vibration isolator is not propagated to the blower fan. The quality of the structure is also stabilized.
また、本発明である防振具によれば、外筒を厚肉化したり、外筒にフランジを設けた場合に比べ、その歩留りが製造条件のバラツキ等で悪化しない。しかも、外筒を厚肉化し、又は、外筒にフランジを設ける必要がないことから、外筒を肉厚化したことに伴う検査や、フランジを設けたことに伴う検査等が不要となるため、製造管理が容易なものとなる。そして、こうした防振具を用いて送風用ファン構造体を成形すれば、結果的に、その歩留りも製造条件のバラツキ等で悪化せず、検査項目も削減できるから製造管理も容易なものとなる。 Moreover, according to the vibration isolator which is this invention, the yield does not deteriorate by the variation in manufacturing conditions etc. compared with the case where an outer cylinder is thickened or a flange is provided in an outer cylinder. Moreover, since it is not necessary to increase the thickness of the outer cylinder or to provide a flange on the outer cylinder, the inspection associated with increasing the thickness of the outer cylinder, the inspection associated with providing the flange, etc. are not required. Manufacturing management becomes easy. If a blower fan structure is formed using such a vibration isolator, as a result, the yield is not deteriorated due to variations in manufacturing conditions, and inspection items can be reduced, thereby facilitating manufacturing management. .
加えて、外筒を厚肉化し、又は、外筒にフランジを設ける必要がないことは、防振具の小型化に繋がることから、単位の金型当たりの成形個数が増大し、多数個取りを目的とした成形には有効である。 In addition, increasing the thickness of the outer cylinder or eliminating the need to provide a flange on the outer cylinder leads to a reduction in the size of the vibration isolator. It is effective for forming for the purpose.
更に、本発明である防振具において、外筒の端部のうちの少なくとも一方を、前記弾性部材よりも突出した突出部位とすれば、この突出部位を、成形型に対する位置決め用及び保持用の部位として利用できるため、外筒に対して高温・高圧が加わることで生じる変形を、より効果的に抑えることができる。このため、こうした防振具を用いて成形した送風用ファン構造体は、その防振機能がより良い状態に維持される。 Furthermore, in the vibration isolator according to the present invention, if at least one of the end portions of the outer cylinder is a protruding portion protruding from the elastic member, the protruding portion is used for positioning and holding with respect to the mold. Since it can utilize as a site | part, the deformation | transformation which arises when high temperature and a high pressure are added with respect to an outer cylinder can be suppressed more effectively. For this reason, the fan structure for ventilation shape | molded using such a vibration isolator is maintained in the state where the vibration proof function is better.
加えて、本発明である防振具において、上記突出部位の内周面が、その端面に向かうに従って拡径する傾斜面としてなれば、インサート部品として成形型にインサートし、型締めする際に、当該突出部位の内周面が案内面として機能することで、成形型とのスムースな嵌合が可能となる。このため、成形型内に取り付けられた外筒に高温・高圧が加わることに伴う当該外筒の変形の抑止にも同様に効果的である。このため、こうした防振具を用いて成形した送風用ファン構造体も、その防振機能がより良い状態に維持される。 In addition, in the vibration isolator according to the present invention, if the inner peripheral surface of the projecting portion is an inclined surface that expands in diameter toward the end surface, when inserted into a mold as an insert part and clamped, Since the inner peripheral surface of the projecting portion functions as a guide surface, smooth fitting with the molding die is possible. For this reason, it is similarly effective in suppressing the deformation of the outer cylinder accompanying the application of high temperature and high pressure to the outer cylinder attached in the mold. For this reason, the fan structure for air blow molded using such a vibration isolator also maintains its vibration isolating function in a better state.
なお、外筒の端部のうちの少なくとも一方を、前記弾性部材よりも突出させることにより突出部位とする構成は、外筒における外周面の全周に亘って段差を形成する構成とは、独立した構成とすることもできる。 Note that the configuration in which at least one of the end portions of the outer cylinder is projected from the elastic member is independent of the configuration in which a step is formed over the entire outer peripheral surface of the outer cylinder. It can also be set as the structure which carried out.
また、本発明に係る段差は、外筒の軸方向に沿って傾斜する面としてなるものや、外筒の軸方向に対して直交する面としてなるもの等、その形状は様々に選択できるが、本発明に係る段差が、外筒の軸方向に対して直交する面としてなれば、型締めした時に段差に作用する型締め圧が当該段差に効率的に伝わることにより、キャビティが形成される領域とキャビティが形成されない領域との間を効率的にシールすることができる。 Further, the step according to the present invention can be selected in various shapes, such as a surface inclined along the axial direction of the outer cylinder, a surface orthogonal to the axial direction of the outer cylinder, If the step according to the present invention is a surface perpendicular to the axial direction of the outer cylinder, a region in which a cavity is formed by efficiently transmitting a mold clamping pressure acting on the step when the mold is clamped to the step. And an area where no cavity is formed can be effectively sealed.
このため、本発明である防振具において、外筒の段差が外筒の軸方向に対して直交する面としてなれば、外筒の保持領域だけに送風用ファンを確実に成形することができる。このため、こうした防振具を用いて成形した送風用ファン構造体は、その防振機能がより良い状態に維持される。 For this reason, in the vibration isolator according to the present invention, if the step of the outer cylinder is a surface orthogonal to the axial direction of the outer cylinder, the blower fan can be reliably formed only in the holding area of the outer cylinder. . For this reason, the fan structure for ventilation shape | molded using such a vibration isolator is maintained in the state where the vibration proof function is better.
以下、図面を参照して、本発明の形態を詳細に説明する。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
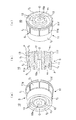
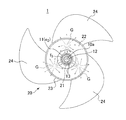
図1(a)〜(c)はそれぞれ、本発明である防振具の一形態である防振具10をその一方の端面から示す斜視図、防振具10の断面図及び防振具10をその他方の端面から示す斜視図である。
1 (a) to 1 (c) are perspective views showing a
符号11は、熱可塑性樹脂を用いて射出成形してなる外筒である。外筒11は、図示のように、その外周面の全周に亘って段差Sが形成されている。
段差Sは、図1(b)に示すように、軸O方向に対して直交する垂直な面(以下、「段差面」という)f1としてなり、外筒11の外周面を、外径の大きい大径側領域面f2と、大径側領域面f2よりも外径の小さい小径側領域面f3とに区画する。
As shown in FIG. 1B, the step S is a vertical surface (hereinafter referred to as “step surface”) f1 orthogonal to the direction of the axis O, and the outer peripheral surface of the
大径側領域面f2は、その全周に亘って外向きに突出する環状凸部11fを一体に備え、この環状凸部11fと段差Sとの相互間には、軸Oに沿って伸びる複数の溝11gが形成されている。
The large-diameter region surface f2 is integrally provided with an annular
符号12は、熱可塑性樹脂を用いて射出成形してなる内筒である。内筒12は、弾性部材13を介して外筒11の内側に連結され、その内側に、モータ等に繋がる回転シャフトが接続される嵌合孔10aを有する。
弾性部材13は、外筒11と内筒12とを同一の成形用金型にインサートし、熱可塑性エラストマーや加硫ゴム等を主原料として成形される。
The
なお、本形態に係る外筒11では、外筒11の内周面f4は、外筒11の一方の端面(以下、便宜上、「大径側端面」という)e1から他方の端面(以下、便宜上、「小径側端面」という)e2に軸Oに沿って向かうに従って縮径するように傾斜し、更に、小径側端面e2付近には、軸Oに向かって突出する環状の突出部11pが一体に形成されているが、外筒11の内周面形状は、これに限ることなく、例えば、大径側領域面f2の肉厚と、小径側領域面f3の肉厚とが同一の肉厚となるようにしてもよい。
In the
また、外筒11は、図1(b)に示すように、その大径側及び小径側に位置する端部がそれぞれ、弾性部材13よりも突出した突出部位Pとしてなる。本形態に係る突出部位Pは、弾性部材13の端面における最外周側縁部を軸O周りに環状に切り欠くことで形成される。
Further, as shown in FIG. 1 (b), the
また、大径側に位置する突出部位Pの内周面f5は、同図に示すように、その大径側端面e1に向かうに従って拡径する傾斜面としてなる。同様に、小径側に位置する突出部位Pの内周面f5も、同図に示すように、その小径側端面e2に向かうに従って拡径する傾斜面としてなる。 Further, as shown in the figure, the inner peripheral surface f5 of the projecting portion P located on the large-diameter side is an inclined surface that increases in diameter toward the large-diameter end surface e1. Similarly, the inner peripheral surface f5 of the protruding portion P located on the small diameter side is also an inclined surface that increases in diameter toward the small diameter side end surface e2, as shown in FIG.
図2(a),(b)はそれぞれ、図1の防振具10を用いてプロペラファン(軸流ファン)20を一体に成形した本発明の一形態であるプロペラファン構造体1を防振具外筒11の大径側端面e1から示す斜視図と、防振具外筒11の小径側端面e2から示す斜視図である。
FIGS. 2 (a) and 2 (b) respectively show the vibration isolation of the
プロペラファン20は、防振具外筒11の大径側領域面f2に固定保持される内筒部(以下、「ハブ」という。)21と、このハブ21に隔壁22を介して一体に繋がる外筒部23と、この外筒部23の周りに当該外筒部23と一体に繋がる複数の羽根24とを有する。
The
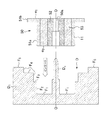
ここで、図3,4はそれぞれ、プロペラファン構造体1を成形するにあたり、防振具10を可動型D1に取り付ける直前の状態を拡大して示す要部断面図と、その後、可動型D1と固定型D2とを型締めした状態を拡大して示す要部断面図である。
Here, FIGS. 3 and 4 are enlarged cross-sectional views showing a main part immediately before the
符号D1は、可動型である。可動型D1には、防振具10を保持するための凹部Dが形成されている。凹部Dは、防振具外筒11の小径側端面e2が突き当る最深面F1と、防振具外筒11の小径側領域面f3を取り囲む第一内周面F2と、この第一内周面F2と段差面F3を介して繋がり第一内周面F2よりも大径の第二内周面F4とで形作られ、最深面F1には、防振具10の嵌合孔10aが貫通するシャフト部Dsが一体に形成されている。
Reference sign D1 is a movable type. The movable die D1 has a recess D for holding the
また、段差面F3は、軸O方向に対して直交する面としてなり、図4に示すように、可動型D1と固定型D2とを型締めした状態で、防振具外筒11の段差面f1と面接触する。更に、第二内周面F4は、同図に示すように、防振具外筒11の大径側領域面f2と共にキャビティC4の一部を形成し、このキャビティが、プロペラファン20のハブ21の一部を形成するためのキャビティとなる。
Further, the step surface F3 is a surface orthogonal to the direction of the axis O, and as shown in FIG. 4, the step surface of the vibration isolator
符号D2は、固定型である。固定型D2は、図4に示すように、可動型D1との型締め状態において、その合せ面F6が可動型D1の合せ面F5と共にキャビティC4の残部を形成し、このキャビティが、ハブ21の残部及び隔壁22を形成するためのキャビティとなる。
Reference sign D2 is a fixed type. As shown in FIG. 4, the fixed die D <b> 2, in the clamping state with the movable die D <b> 1, forms a remaining portion of the cavity C <b> 4 together with the mating surface F <b> 5 of the movable die D <b> 1. It becomes a cavity for forming the remaining part and the
加えて、固定型D2の合せ面F6には、図4に示すように、可動型D1との型締め状態において、防振具突出部位Pの内周面f5と面接触する突条Drが一体に形成されている。 In addition, the mating surface F6 of the fixed die D2 is integrally provided with a protrusion Dr that is in surface contact with the inner peripheral surface f5 of the vibration isolator projecting portion P in the clamping state with the movable die D1, as shown in FIG. Is formed.
なお、図3及び図4では省略しているが、可動型D1と固定型D2の間には、ハブ21及び隔壁22を成形するためのキャビティC4だけでなく、外筒部23及び羽根24を成形するためのキャビティも形成される。
Although omitted in FIGS. 3 and 4, not only the cavity C4 for forming the
即ち、防振具10を用いてプロペラファン構造体1を成形するにあたっては、先ず図3に示すように、可動型D1の凹部Dに、シャフト部Dsに沿って防振具10をインサートし、次いで、可動型D1を固定型D2に移動させて型締めする。
That is, in forming the
このとき、可動型D1にインサートされた防振具10は、固定型D2の突条Drを案内にして位置決め及び保持される。可動型D1と固定型D2との型締め後は、固定型D2のゲートGから熱可塑性樹脂が圧送され、この熱可塑性樹脂が、可動型D1と固定型D2との間に形成されたキャビティ内に充填される。
At this time, the
このとき、可動型D1の段差面F3と防振具外筒11の段差面f1とは、可動型D1と固定型D2との型締めによって面接触しているので、熱可塑性樹脂は、防振具外筒11の大径側領域面f2側に存在する空間(キャビティC4)のみに充填される。
At this time, the step surface F3 of the movable mold D1 and the step surface f1 of the vibration isolator
要するに、本発明に従う防振具10によれば、防振具外筒11における外周面の全周に亘って段差Sを形成し、この段差Sの大径側領域面f2をプロペラファン20の保持領域としたことで、防振具外筒11にプロペラファン20を成形するにあたり、この成形に用いられる領域の面積が小さく済む。即ち、本形態の防振具10によれば、防振具外筒11の外周面全体にプロペラファン20を成形した従来の場合に比べて、受圧面積が小さく済むことから、防振具外筒11が樹脂圧を受けることによって受ける力も小さく済む。
In short, according to the
従って、本形態の防振具10によれば、防振具外筒11を厚肉化し、又は、防振具外筒11にフランジを設けることなく、防振具外筒11に高温・高圧が加わることで生じる変形を抑えることができる。
Therefore, according to the
また、この防振具10を用いて、プロペラファン構造体1を成形した場合、防振具外筒11の変形が抑えられたことで、防振具10が変形し、又は、偏心することによって防振機能が損なわれるようなことがない。従って、プロペラファン構造体1によれば、防振具外筒11を厚肉化し、又は、防振具外筒11にフランジを設けることなく、防振機能を維持することができる。
Further, when the
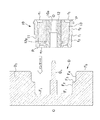
これに対し、従来の防振具50を用いて防振具外筒51の一部だけを、プロペラファン20の保持領域とすることは可能であり、図5,6はそれぞれ、従来の防振具外筒51の一部だけにハブ21を成形するにあたり、防振具50を可動型D1に取り付ける直前の状態を拡大して示す要部断面図と、その後、可動型D1と固定型D2とを型締めした状態を拡大して示す要部断面図である。
On the other hand, it is possible to use only a part of the vibration isolator
この場合、防振具外筒51における周壁51aの外周面と、可動型D1の第一内周面F2との関係は、樹脂が流入しないように接触又は近接させる必要があり、その相互間のクリアランスは、高い充填圧を伴う樹脂の流れ(図6の矢印m)を阻止するために、約0.1mm以下の精度に保つ必要がある。
In this case, the relationship between the outer peripheral surface of the
しかしながら、防振具51の外径精度は、その製造段階での寸法誤差を予め最小限に抑えるように管理・製造されるが、こうした製造段階での管理・製造には限界がある。例えば、寸法誤差には、外筒51や内筒52の製造工程(切削加工、ダイカスト成形、絞り加工、樹脂射出成形等)で発生するもの、更には、外筒51と内筒52とを連結する弾性部材53の製造工程(ゴム加硫成形や熱可塑性エラストマーによる射出成形等)時に発生するものがあり、それぞれ寸法誤差が累積される。
However, the outer diameter accuracy of the
即ち、本発明に係る防振具のように、その構造が外筒、弾性部材及び内筒からなる積層構造の場合には、同芯度や真円度等の精度において、製造上回避し難い寸法誤差を保有し、具体的には、量産時における製造能力の影響により、外筒の外径が軸心に対して0.3mm程度の偏心を伴うことがある。 That is, when the structure is a laminated structure composed of an outer cylinder, an elastic member, and an inner cylinder, as in the case of the vibration isolator according to the present invention, it is difficult to avoid in manufacturing with accuracy such as concentricity and roundness. In particular, due to the influence of manufacturing capacity during mass production, the outer diameter of the outer cylinder may be eccentric by about 0.3 mm with respect to the shaft center.
こうした場合、図5,6に示すように、防振具30をインサートしようとすると、防振具外筒51の外周面51aと、可動型D1の内面(第一内周面F2)とが干渉して、外筒51が軸O方向に押圧されながらインサートされ、更に防振具外筒51が僅かでも変形していると、スムースなインサートに支障をきたし、作業能率が低下する。
In such a case, as shown in FIGS. 5 and 6, when the
しかも、可動型D1に段差F3を形成し、従来の防振具外筒51の外周面の一部だけをプロペラファン20の保持領域とする場合、防振具50がインサートできても、防振具外筒51の調心は、弾性部材53の弾性変形に伴う一時的なものに過ぎない。このため、プロペラファン20の成形が完了して成形型D1,D2から取り出されると、防振具外筒51は、弾性部材53の復元力により、精度が悪いインサート前の状態に戻ってしまう。
Moreover, when the step F3 is formed in the movable die D1 and only a part of the outer peripheral surface of the conventional vibration isolator
このため、こうして得られたプロペラファン構造体は、防振具外筒51の影響を確実に受け、回転精度(振れ、バランス)が悪化することで、例えば、空調機器としての運転時に、振動や騒音等を発生する場合がある。
For this reason, the propeller fan structure thus obtained is reliably influenced by the vibration isolator
これに対し、本形態の防振具10は、防振具外筒11の外周面に段差Sが形成されていることから、可動型D1に大径側と小径側に区画する段差面F3を形成し、この段差面F3に、防振具外筒11の段差面f1を接触させるだけで、可動型D1に形成した第二内周面F4と防振具外筒11の保持領域面f2との間にキャビティを形成し、このキャビティ内の樹脂が、可動型D1に形成した第一内周面F2と、防振具外筒11の小径側領域面f3との間に流入しないようにシールすることができる。
On the other hand, since the
即ち、本形態の防振具によれば、図4に示すように、可動型D1の第一内周面F2と、防振具外筒11の小径側領域面f3との相互間にクリアランス(例えば、0.5mm程度)Cを設けることができる。
That is, according to the vibration isolator of this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 4, a clearance (between the first inner peripheral surface F2 of the movable die D1 and the small-diameter side region surface f3 of the vibration isolator
このように、可動型D1の第一内周面F2と、防振具外筒11の小径側領域面f3との間にクリアランスCを設ければ、防振具10が偏芯を伴っていても、可動型D1と干渉することなく、防振具10を可動型D1内に収納できるから、作業能率も向上する。
Thus, if the clearance C is provided between the first inner peripheral surface F2 of the movable die D1 and the small-diameter side region surface f3 of the vibration isolator
また、本形態の防振具10によれば、外筒11に段差Sが形成されているため、例えば、段差の大径側を送風用ファンの保持領域とすれば、防振具10の内筒13に対し外筒11が偏心していたり、外筒11自体が変形等により真円が維持できていない状態のまま、防振具10を可動型D1内に収納しても、当該段差Sにより形成される小径側領域面f3は、可動型D1に対してクリアランスCを持った状態でインサートできる。即ち、本発明である防振具10は、可動型D1と干渉することなく収納できる。このため、本発明である防振具10が予め偏心等を伴っていても、プロペラファン20を成形するにあたっては、防振具10の精度に左右されることなくプロペラファン20は調心されることから、プロペラファン構造体1として成形型D1,D2から取り出しても、回転精度が悪化して振動や騒音等を発生することがない。
Further, according to the
従って、防振具10を用いて成形されたプロペラファン構造体1の回転精度は、防振具10が含有する精度の良否に左右されることなく、品質の安定したものとなる。
Therefore, the rotational accuracy of the
更に、本形態の防振具10では、防振具外筒11の大径側端部を弾性部材13よりも突出した突出部位Pとしたことで、この突出部位Pを、固定型D2に対する位置決め用及び保持用の部位として利用できるため、防振具外筒11に対して高温・高圧が加わることで生じる変形を、より効果的に抑えることができる。このため、防振具10を用いて成形したプロペラファン構造体1は、その防振機能がより良い状態に維持される。
Furthermore, in the
なお、本形態の場合、外筒11の小径側領域面f3には熱可塑性樹脂が充填されないため、可動型D1に突条Drを設けていないが、可動型D1に突条Drを設ければ、小径側端部に設けた突出部位Pを、可動型D1に対して固定するための位置決め用及び保持用の部位として利用できる。これは、小径側領域面f3をプロペラファン20の保持領域として使用した場合に有効である。
In the case of this embodiment, the small diameter side region surface f3 of the
即ち、本発明に係る突出部位Pは、小径側端部及び大径側端部のうちの少なくとも、一方に形成すればよい。また、突出部位Pは、外筒51に段差Sを形成する構成とは、独立した構成とすることもできる。
That is, the protruding portion P according to the present invention may be formed in at least one of the small diameter side end and the large diameter side end. Further, the protruding portion P can be configured independently of the configuration in which the step S is formed in the
加えて、防振具10では、突出部位Pの内周面f5が、その端面e1に向かうに従って拡径する傾斜面としてなるから、インサート部品として可動型D1にインサートし、型締めする際に、当該突出部位Pの内周面f5が案内面として機能することで、固定型D2に取り付ける際の当該固定型D2との干渉が可能な限り小さく抑えられ、固定型D2とのスムースな嵌合が可能となる。このため、成形型D1,D2内に取り付けられた防振具外筒11に高温・高圧が加わることに伴う防振具外筒11の変形の抑止にも同様に効果的である。このため、こうした防振具10を用いて成形したプロペラファン構造体1も、その防振機能がより良い状態に維持される。
In addition, in the
なお、本発明によれば、可動型D1に突条Drを設けた場合も、小径側端部に設けた突出部位Pの内周面f5を、同様に傾斜面としても、防振具外筒11を可動型D1にインサートして当該可動型D1に取り付ける際の当該可動型D1との干渉が可能な限り小さく抑えられ、可動型D1とのスムースな嵌合が可能となる。また、こうした構成によれば、小径側領域面f3をプロペラファン20の保持領域として使用した場合にも、成形型D1,D2内に取り付けられた防振具外筒11に高温・高圧が加わることに伴う防振具外筒11の変形の抑止に効果的であり、この場合のプロペラファン構造体1も、その防振機能がより良い状態に維持される。
According to the present invention, even when the protrusion D is provided on the movable die D1, the inner peripheral surface f5 of the protruding portion P provided at the small-diameter side end portion is similarly inclined, so that the vibration isolator outer cylinder When 11 is inserted into the movable mold D1 and attached to the movable mold D1, the interference with the movable mold D1 is suppressed as much as possible, and a smooth fitting with the movable mold D1 becomes possible. In addition, according to such a configuration, even when the small-diameter side region surface f3 is used as a holding region of the
ところで、本発明に係る段差Sは、防振具外筒11の軸O方向に沿って傾斜する面としてなるものや、防振具外筒11の軸O方向に対して直交する面としてなるもの等、その形状は様々に選択できるが、本形態に係る段差Sの段差面f1は、防振具外筒11の軸O方向に対して直交する面としてなるから、型締めした時に段差Sの段差面f1に作用する型締め圧が当該段差面f1に効率的に伝わることにより、キャビティが形成される大径側領域面f2とキャビティが形成されない小径側領域面f3との間を効率的にシールすることができる。
Incidentally, the step S according to the present invention is a surface that is inclined along the axis O direction of the vibration isolator
このため、本形態の防振具10では、防振具外筒11の段差面f1が防振具外筒11の軸O方向に対して直交する面としてなるから、防振具外筒11の保持領域だけにプロペラファン20のハブ21を確実に成形することができる。このため、防振具10を用いて成形したプロペラファン構造体1は、その防振機能がより良い状態に維持される。
For this reason, in the
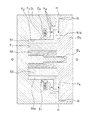
ところで、送風用ファンの成形にあたっては、生産効率や品質の安定化を図るため、固定型D2に形成されたゲートGの位置選定が重要である。例えば、図7に示すプロペラファン20では、ハブ21と共に各羽根24の先端に至るまで樹脂をバランスよく供給するため、ゲートGの位置をハブ21と羽根24との間の好適な位置に設定する。
By the way, in forming the blower fan, it is important to select the position of the gate G formed on the fixed mold D2 in order to stabilize production efficiency and quality. For example, in the
しかしながら、ゲートGからの流動方向は、同図の矢印に示すように、ゲートGを中心にして放射状に広がるため、防振具外筒11の外周面に加わる充填圧も防振具外筒11の外周面に対して均一ではなく、熱可塑性樹脂の流動方向に従ってそれぞれ、若干異なる。
However, since the flow direction from the gate G spreads radially around the gate G as shown by the arrow in the figure, the filling pressure applied to the outer peripheral surface of the vibration isolator
しかも、ゲートGからの熱可塑性樹脂は、その温度が、例えば、200〜300C°と比較的高温で、しかも、その圧力も、約200〜400kg/cm2と高いため、防振具外筒11が変形してしまう場合がある。 Moreover, the temperature of the thermoplastic resin from the gate G is relatively high, for example, 200 to 300 C °, and the pressure is as high as about 200 to 400 kg / cm 2. It may be deformed.
更に、図8(a)〜(c)はそれぞれ、防振具をプロペラファン用の金型にインサートして熱可塑性樹脂を射出成形する際に、防振具の外筒が受ける圧力に対し外筒の変形する度合いを、それぞれ外筒の形態別に構造解析(応力変形解析)を行った事例である。 Further, FIGS. 8 (a) to 8 (c) show the external force against the pressure received by the outer cylinder of the vibration isolator when the vibration isolator is inserted into the propeller fan mold and the thermoplastic resin is injection molded. This is an example in which the degree of deformation of the cylinder is subjected to structural analysis (stress deformation analysis) for each form of the outer cylinder.
例えば、図8(a)の構造解析図に示す従来例1は、防振具外筒がストレートの円筒形であり、その一方の外筒端部側にハブを成形すると、同図に示すように、それと反対側端部(端面e2側)も大きく変形する。これに対し、図8(b)の構造解析図に示す従来例2は、防振具外筒にフランジ51bを設けた従来の防振具50であり、そのフランジ51b側にハブを成形すれば、それと反対側端部(端面e2側)での変形は小さく抑えられるものの、同図に示すように、その変位量は依然大きい。
For example, in Conventional Example 1 shown in the structural analysis diagram of FIG. 8 (a), the vibration isolator outer cylinder is a straight cylinder, and when a hub is formed on one end of the outer cylinder, as shown in FIG. In addition, the opposite end (end face e2 side) is also greatly deformed. On the other hand, the conventional example 2 shown in the structural analysis diagram of FIG. 8 (b) is a
一方、本発明に従う防振具外筒11は、図8(c)の構造解析図に示すように、その大径側領域面f2にハブを成形しても、同図に示すように、小径側領域面f3ではほとんど変形を生じない。
On the other hand, as shown in the structural analysis diagram of FIG. 8 (c), the vibration isolator
図9(a),(b)はそれぞれ、本発明に係るプロペラファン構造体1の変形例を示す要部斜視図である。
FIGS. 9 (a) and 9 (b) are perspective views showing a main part of a modified example of the
図9(a)に示す形態は、隔壁22と一体に成形した複数のフィン25がハブ21と外筒部23との間を放射状に連結するものである。この場合、プロペラファン20に対する防振具10の取り付け強度を更に増加させることができる。
In the form shown in FIG. 9 (a), a plurality of
図9(b)に示す形態は、防振具外筒11の大径側領域面f2の一部をハブ21で保持する一方、大径側領域面f2の残部をフィン25で保持するものである。この場合、プロペラファン構造体1の成形にあたり、大径側領域面f2に加わる樹脂圧を更に軽減させることができる。また、樹脂圧の軽減に併せて、防振具外筒11の薄肉化を図ることもできる。
In the form shown in FIG. 9 (b), a part of the large-diameter region surface f2 of the vibration isolator
更に、本形態の場合、同図に示すように、フィン25は防振具外筒11の大径側領域面f2に形成した溝11gに嵌合する構成となっている。この場合、フィン25による保持が強固なものとなる。加えて、本形態では、フィン25の先端を「あり」とし、溝11gを「あり」の嵌合する「あり溝」とすることで、又は、これと逆の構成とすることで、フィン25による保持を更に強固なものとしているが、溝11gは単なる溝であってもよい。
Further, in the case of this embodiment, as shown in the figure, the
また、本形態では、ハブ21とフィン25との組み合わせで、防振具外筒11を保持しているが、フィン25のみで保持してもよい。更に、大径側領域面f2に溝11gを形成することなく、大径側領域面f2に直接フィン25を接合させてもよい。
Further, in this embodiment, the vibration isolator
図10(a),(b)はそれぞれ、防振具10を他の送風用ファンである遠心ファンと組み合わせた構造体をその空気の流入する側から示す斜視図である。
FIGS. 10 (a) and 10 (b) are perspective views showing a structure in which the
図10(a)に示す遠心ファンは、所謂、ターボファン30であり、防振具外筒11の大径側領域面f2を保持するハブ31を有する支持板32と、この支持板32と軸線方向に間隔を空けて配置されるシュラウド33とを有し、その間が複数の羽根34により連結されている。また、図10(b)に示す遠心ファンは、所謂、シロッコファン40であり、防振具外筒11の大径側領域面f2を保持するハブ41を有するディスク部材42と、このディスク部材42に対してその軸線周りに複数の羽根43がリング部材44で規制しつつ連結されることで成っている。
The centrifugal fan shown in FIG. 10 (a) is a so-called
上述したところは、本発明の好適な形態であるが、当業者によれば、特許請求の範囲内で種々の変更を加えることができる。例えば、外筒の全長に対する段差の配置比率は、送風用ファンに要求される性能や使用状況に応じて適宜変更することができ、また、送風用ファンの形状や羽根の枚数等も適宜変更することができる。また、本発明によれば、上述した各形態の部材やその形態、又は、その周辺構造等は用途に応じてそれぞれ組み合わせて使用することができる。 The above is the preferred embodiment of the present invention, but various modifications can be made within the scope of the claims by those skilled in the art. For example, the arrangement ratio of the step with respect to the entire length of the outer cylinder can be changed as appropriate according to the performance and usage conditions required for the blower fan, and the shape of the blower fan, the number of blades, and the like can be changed as appropriate. be able to. Moreover, according to this invention, the member of each form mentioned above, its form, its peripheral structure, etc. can be used in combination according to a use, respectively.
送風用ファン構造体の防振具には、例えば、図11に示すように、モータMに繋がるモータ軸Msからの回転トルク、ファンの重量(自重)、回転により生じる遠心力及び、これに実用上の熱履歴等が加わるため、本発明のように、送風用ファンの保持領域を削減したことで、従来の防振具10及びその保持方法を変更した場合、新たな実用上の問題(負荷、熱履歴等による変形に伴い発生する振動、騒音等)が伴わないこと、即ち、少なくとも、従来の性能を維持していることを確認する必要がある。
For example, as shown in FIG. 11, the vibration isolator of the fan structure for blower includes rotational torque from the motor shaft Ms connected to the motor M, weight of the fan (self-weight), centrifugal force generated by the rotation, and practical use for this. Since the heat history etc. are added, if the
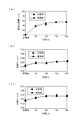
そこで、本願発明者は、本発明である送風用ファン構造体に関する性能を評価すべく、本発明に従う防振具10を備えるプロペラファン構造体を実施例とする一方、従来の防振具50を備えたプロペラファン構造体を比較例とし、各々を同一条件で運転させることで、図12に示す試験データを得た。
Therefore, in order to evaluate the performance of the blower fan structure according to the present invention, the present inventor uses a propeller fan structure including the
なお、両者の比較は、モータとして同一性能のものを用い、温度80°Cの環境下で、モータ回転数を1000rpmに統一し、2分間回転後2分間停止を繰り返して200時間運転させることで行った。 In addition, the comparison of both uses the same performance as the motor, unifies the motor rotation speed to 1000rpm in the environment of the temperature of 80 ° C, repeats the stop for 2 minutes after the rotation for 2 minutes, and operates for 200 hours. went.
また、図12(a)の「偏重心距離(μm)」とは、軸Oに対するプロペラファン構造体1の試験前後(試験前と200時間運転後)のアンバランス量の変化分を重心の移動距離に置き換えて表現したものであり、更に、同図(b)の「面振れ(mm)」及び同図(c)の「芯振れ(mm)」はそれぞれ、図11の矢印で示した位置におけるプロペラファン外筒部23の外周面にて同じく試験前後(試験前と200時間運転後)に発生する変位量を表したものである。なお、これらは、プロペラファン構造体の性能を左右する重要な要素である。
In addition, “Eccentric center of gravity distance (μm)” in FIG. 12 (a) is the change in the center of gravity of the change in the unbalance amount before and after the test of the
図12(a)〜(c)に示す各実験データから明らかなように、実施例は、各評価項目において、比較例に対して同等以上の性能を維持しており、運転に伴い応力や熱履歴を受けても、実用上プロペラファン構造体として支障をきたすことのないレベルであることが確認された。 As is clear from the respective experimental data shown in FIGS. 12 (a) to (c), the examples maintain the same or better performance than the comparative examples in each evaluation item, and the stress and heat are increased with the operation. Even if it received the history, it was confirmed that it was a level that would not cause any trouble as a propeller fan structure in practice.
更に、図13(a),(b)はそれぞれ、比較例と実施例とを既存のエアコン室外機に装着し、その運転時に広域の周波数帯(0〜5KHz間の周波数帯)において発生する音圧レベル(dB)を比較検証した実験データである。 Further, FIGS. 13 (a) and 13 (b) show the sound generated in a wide frequency band (frequency band between 0 to 5 KHz) during operation when the comparative example and the example are mounted on an existing air conditioner outdoor unit, respectively. It is the experimental data which compared and verified the pressure level (dB).
この検証では、DCブラシレスモータを備えたエアコン室外機に各プロペラファン構造体を取り付けて回転数1000rpmで運転し、「JIS C 9612」に準拠してエアコン室外機の前方1mの位置で測定を行った。 In this verification, each propeller fan structure is attached to an air conditioner outdoor unit equipped with a DC brushless motor and operated at a rotational speed of 1000 rpm, and measurement is performed at a position 1 m ahead of the air conditioner outdoor unit in accordance with “JIS C 9612”. It was.
図13(a),(b)を比較すれば明らかなように、比較例に対して実施例は、広域の周波数帯において、特に突出した音圧レベルの上昇もないことが確認された。また、騒音値についても、比較例の騒音値が40.9dB(A)であるのに対し、実施例の騒音値が39.1dB(A)であり、比較例に対して同等以下の騒音値であることが確認された。 As is clear from a comparison of FIGS. 13 (a) and 13 (b), it was confirmed that the embodiment did not have a particularly prominent increase in sound pressure level in a wide frequency band compared to the comparative example. Also, the noise value of the comparative example is 40.9 dB (A), whereas the noise value of the example is 39.1 dB (A), which is equal to or lower than that of the comparative example. It was confirmed.
本発明である防振具は、軸流ファンや遠心ファンに限らず、斜流ファンや横流れファン(クロスフローファン)等の送風用ファンにも適用することで、送風用ファン構造体とすることができる。 The vibration isolator according to the present invention is not limited to an axial flow fan or a centrifugal fan, but is also applied to a blower fan such as a mixed flow fan or a cross flow fan (cross flow fan) to form a blower fan structure. Can do.
プロペラファン構造体(送風用ファン構造体)
10 防振具(本発明防振具)
10a シャフト嵌合孔
11 外筒
11f 環状凸部
11g 溝
11p 突出部
11r リブ
12 内筒
13 弾性部材
20 プロペラファン(本発明に係る送風用ファン)
21 ハブ
22 隔壁
23 プロペラファン外筒部
24 羽根
25 フィン
30 ターボファン(本発明に係る送風用ファン)
31 ハブ
32 支持板
33 シュラウド
34 羽根
40 シロッコファン(本発明に係る送風用ファン)
41 ハブ
42 ディスク部材
43 羽根
50 防振具(従来防振具)
51 外筒
51a 周壁
51b フランジ
52 内筒
53 弾性部材
D 可動型側凹部
D1 可動型
D2 固定型
e1 大径側軸方向端面
e2 小径側軸方向端面
f1 外筒外周の段差面
f2 外筒外周の大径側領域面
f3 外筒外周の小径側領域面
f4 外筒内周面
f5 筒状部内周面
F1 段差面
F2 凹部第一内周面
F3 凹部段差面
F4 凹部第二内周面
F5 可動型側合せ面
F6 固定型側合せ面
P 突出部位
S 段差
O 軸(軸心)
M モータ
Ms モータ軸
Propeller fan structure (fan structure for ventilation)
10 Anti-vibration device (Invention anti-vibration device)
10a Shaft fitting hole
11 outer cylinder
11f Annular projection
11g groove
11p protrusion
11r rib
12 inner cylinder
13 Elastic member
20 Propeller fan (fan for ventilation according to the present invention)
21 Hub
22 Bulkhead
23 Propeller fan outer cylinder
24 feathers
25 fins
30 Turbo fan (fan for blowing according to the present invention)
31 Hub
32 Support plate
33 Shroud
34 feathers
40 Sirocco fan (fan for ventilation according to the present invention)
41 Hub
42 Disc members
43 feathers
50 Vibration isolator (conventional vibration isolator)
51 outer cylinder
51a Perimeter wall
51b flange
52 inner cylinder
53 Elastic member D Movable mold side recess
D1 Movable type
D2 fixed type
e1 Large-diameter axial end face
e2 Small diameter side axial end face
f1 Stepped surface around the outer cylinder
f2 Large-diameter area on the outer periphery of the outer cylinder
f3 Small-diameter area on the outer periphery of the outer cylinder
f4 Inner peripheral surface of outer cylinder
f5 Inner circumferential surface of cylindrical part
F1 Step surface
F2 Concave first inner peripheral surface
F3 Recessed step surface
F4 Concave second inner peripheral surface
F5 Movable side mating surface
F6 Fixed mold side mating surface P Projection part S Step difference O Axis (axial center)
M motor
Ms Motor shaft
Claims (2)
前記外筒における外周面の全周に亘って段差を形成して、該段差で分けられた小径側の領域面及び大径側の領域面のうち大径側の領域面を送風用ファンの保持領域とし、
前記外筒の端部のうちの少なくとも一方が、前記弾性部材よりも突出した突出部位としてなることを特徴とする、送風用ファンの防振具。 A vibration isolator as an insert product in which an outer cylinder and an inner cylinder made of a thermoplastic resin are connected by an elastic member, and a blower fan vibration isolator in which a blower fan is injection-molded in the outer cylinder.
A step is formed over the entire circumference of the outer peripheral surface of the outer cylinder, and the large-diameter region surface among the small-diameter region surface and the large-diameter region surface divided by the step is held by the blower fan. Area and
At least one of the end portions of the outer cylinder is a protruding portion that protrudes beyond the elastic member.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011186692A JP5367785B2 (en) | 2011-08-30 | 2011-08-30 | Vibration isolator for blower fan and blower fan structure including the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011186692A JP5367785B2 (en) | 2011-08-30 | 2011-08-30 | Vibration isolator for blower fan and blower fan structure including the same |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007156541A Division JP5142596B2 (en) | 2007-06-13 | 2007-06-13 | Vibration isolator for blower fan and blower fan structure including the same |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2011236917A JP2011236917A (en) | 2011-11-24 |
| JP2011236917A5 JP2011236917A5 (en) | 2012-01-12 |
| JP5367785B2 true JP5367785B2 (en) | 2013-12-11 |
Family
ID=45325134
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011186692A Active JP5367785B2 (en) | 2011-08-30 | 2011-08-30 | Vibration isolator for blower fan and blower fan structure including the same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5367785B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6175285B2 (en) * | 2013-06-07 | 2017-08-02 | 日清紡メカトロニクス株式会社 | Anti-vibration device for blower fan and blower fan structure |
| US11852156B1 (en) * | 2022-11-11 | 2023-12-26 | Air International (Us) Inc. | HVAC blower wheel insert |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0185497U (en) * | 1987-11-27 | 1989-06-06 | ||
| JPH0921399A (en) * | 1995-07-04 | 1997-01-21 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | Blower |
| JPH09228993A (en) * | 1996-02-26 | 1997-09-02 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | Propeller fan |
| JPH09268998A (en) * | 1996-04-01 | 1997-10-14 | Hitachi Ltd | Cylindrical impeller |
| JP2000110780A (en) * | 1998-10-08 | 2000-04-18 | Daikin Ind Ltd | Impeller of fan |
| JP2003056492A (en) * | 2001-06-07 | 2003-02-26 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Impeller for blower and method of manufacturing the impeller |
| JP4907018B2 (en) * | 2001-09-03 | 2012-03-28 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Blower and air conditioner |
| JP2003269381A (en) * | 2002-03-13 | 2003-09-25 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Air blower and fan support mechanism and air conditioner |
| JP2003343488A (en) * | 2002-05-28 | 2003-12-03 | Daikin Ind Ltd | Impeller for air blower |
| JP2005299524A (en) * | 2004-04-13 | 2005-10-27 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Impeller for blower and method of manufacturing the same |
| JP5142596B2 (en) * | 2007-06-13 | 2013-02-13 | 日清紡メカトロニクス株式会社 | Vibration isolator for blower fan and blower fan structure including the same |
-
2011
- 2011-08-30 JP JP2011186692A patent/JP5367785B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2011236917A (en) | 2011-11-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US20180156233A1 (en) | Blower and vacuum cleaner | |
| JP4747754B2 (en) | motor | |
| JP5142596B2 (en) | Vibration isolator for blower fan and blower fan structure including the same | |
| JP5840151B2 (en) | Rotating electric machine | |
| US20110318200A1 (en) | Blower fan and method of manufacturing the same | |
| US20180258947A1 (en) | Axial fan | |
| JP5367785B2 (en) | Vibration isolator for blower fan and blower fan structure including the same | |
| US8310116B2 (en) | Brushless motor and manufacturing method thereof | |
| US20190376530A1 (en) | Motor support for motor vehicle blower | |
| KR20180037993A (en) | Axial flow fan | |
| JP2012092810A (en) | Method of producing rotation fan | |
| JP6175285B2 (en) | Anti-vibration device for blower fan and blower fan structure | |
| JP2014015851A (en) | Vibration control boss for fan, and method of manufacturing rotary fan | |
| KR101528877B1 (en) | Hub assembly for fan | |
| JP2011190705A (en) | Supercharger and method of manufacturing supercharger | |
| US20210148376A1 (en) | Impeller and blower | |
| CN108880036B (en) | Rotor iron core assembly, rotor and motor | |
| JP2023032785A (en) | impeller cup and fan | |
| CN211790987U (en) | Rotor core and rotor with same | |
| JP4159493B2 (en) | Motor rotor, motor, air conditioner, refrigerator and ventilation fan | |
| KR102582901B1 (en) | axial fan assembly | |
| JPWO2021171435A5 (en) | ||
| JP2009091962A (en) | Centrifugal fan | |
| JP6083918B1 (en) | Manufacturing method of molded products with vibration damping function | |
| JPWO2020039774A1 (en) | Blower |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A625 | Written request for application examination (by other person) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A625 Effective date: 20110922 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110929 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20120627 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130107 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130307 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130910 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130911 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5367785 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |