JP5302463B2 - Adaptive streaming for digital content distribution - Google Patents
Adaptive streaming for digital content distribution Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5302463B2 JP5302463B2 JP2012521846A JP2012521846A JP5302463B2 JP 5302463 B2 JP5302463 B2 JP 5302463B2 JP 2012521846 A JP2012521846 A JP 2012521846A JP 2012521846 A JP2012521846 A JP 2012521846A JP 5302463 B2 JP5302463 B2 JP 5302463B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- buffer
- digital content
- content
- unit
- playback
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000003044 adaptive effect Effects 0.000 title description 2
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 109
- 239000000872 buffer Substances 0.000 claims description 177
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 19
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 12
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 11
- 230000003139 buffering effect Effects 0.000 description 9
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 8
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000002776 aggregation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004220 aggregation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000010348 incorporation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003993 interaction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000005236 sound signal Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000005055 memory storage Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009877 rendering Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/40—Client devices specifically adapted for the reception of or interaction with content, e.g. set-top-box [STB]; Operations thereof
- H04N21/43—Processing of content or additional data, e.g. demultiplexing additional data from a digital video stream; Elementary client operations, e.g. monitoring of home network or synchronising decoder's clock; Client middleware
- H04N21/44—Processing of video elementary streams, e.g. splicing a video clip retrieved from local storage with an incoming video stream or rendering scenes according to encoded video stream scene graphs
- H04N21/44004—Processing of video elementary streams, e.g. splicing a video clip retrieved from local storage with an incoming video stream or rendering scenes according to encoded video stream scene graphs involving video buffer management, e.g. video decoder buffer or video display buffer
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/40—Client devices specifically adapted for the reception of or interaction with content, e.g. set-top-box [STB]; Operations thereof
- H04N21/43—Processing of content or additional data, e.g. demultiplexing additional data from a digital video stream; Elementary client operations, e.g. monitoring of home network or synchronising decoder's clock; Client middleware
- H04N21/442—Monitoring of processes or resources, e.g. detecting the failure of a recording device, monitoring the downstream bandwidth, the number of times a movie has been viewed, the storage space available from the internal hard disk
- H04N21/44209—Monitoring of downstream path of the transmission network originating from a server, e.g. bandwidth variations of a wireless network
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/60—Network structure or processes for video distribution between server and client or between remote clients; Control signalling between clients, server and network components; Transmission of management data between server and client, e.g. sending from server to client commands for recording incoming content stream; Communication details between server and client
- H04N21/61—Network physical structure; Signal processing
- H04N21/6156—Network physical structure; Signal processing specially adapted to the upstream path of the transmission network
- H04N21/6175—Network physical structure; Signal processing specially adapted to the upstream path of the transmission network involving transmission via Internet
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/60—Network structure or processes for video distribution between server and client or between remote clients; Control signalling between clients, server and network components; Transmission of management data between server and client, e.g. sending from server to client commands for recording incoming content stream; Communication details between server and client
- H04N21/63—Control signaling related to video distribution between client, server and network components; Network processes for video distribution between server and clients or between remote clients, e.g. transmitting basic layer and enhancement layers over different transmission paths, setting up a peer-to-peer communication via Internet between remote STB's; Communication protocols; Addressing
- H04N21/637—Control signals issued by the client directed to the server or network components
- H04N21/6373—Control signals issued by the client directed to the server or network components for rate control, e.g. request to the server to modify its transmission rate
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Two-Way Televisions, Distribution Of Moving Picture Or The Like (AREA)
- Information Transfer Between Computers (AREA)
- Signal Processing For Digital Recording And Reproducing (AREA)
Abstract
Description
[0001]本出願は、参照により本明細書に組み込まれている2009年7月24日出願の米国特許出願第12/509,365号の利益を主張する。 [0001] This application claims the benefit of US patent application Ser. No. 12 / 509,365, filed Jul. 24, 2009, which is incorporated herein by reference.
[0002]本発明の実施形態は、一般にデジタルメディアに関し、より詳細には、デジタルコンテンツの配布のための適応型ストリーミング(adaptive streaming)に関する。 [0002] Embodiments of the present invention generally relate to digital media, and more particularly to adaptive streaming for distribution of digital content.
[0003]デジタルコンテンツ配布システムは、従来、コンテンツサーバ、コンテンツプレーヤ、及びコンテンツサーバをコンテンツプレーヤに接続する通信ネットワークを含む。コンテンツサーバは、コンテンツサーバからコンテンツプレーヤにダウンロードすることができるデジタルコンテンツファイルを格納するように構成される。各デジタルコンテンツファイルは、例えば、ユーザに親しまれている「風と共に去りぬ」など、特定の識別タイトルに対応する。デジタルコンテンツファイルは、通常、再生年代順に従って編成された一連のコンテンツデータを含んでおり、音声データ、ビデオデータ、又はその組み合わせを備え得る。 [0003] Digital content distribution systems conventionally include a content server, a content player, and a communication network that connects the content server to the content player. The content server is configured to store digital content files that can be downloaded from the content server to the content player. Each digital content file corresponds to a specific identification title such as “Gone with the wind” familiar to the user. A digital content file typically includes a series of content data organized according to playback chronological order and may comprise audio data, video data, or a combination thereof.
[0004]コンテンツプレーヤは、再生するためのタイトルを選択するユーザ要求に応答して、デジタルコンテンツファイルをダウンロードし、再生するように構成される。デジタルコンテンツファイルを再生するプロセスは、音声データ及びビデオデータを、スピーカサブシステム及びビデオサブシステムを有するディスプレイシステムを駆動することができる音声信号及びビデオ信号にデコードし、レンダリングすることを含む。再生は通常、当分野で「ストリーミング」として知られている技術を伴い、それによって、コンテンツサーバは、デジタルコンテンツファイルをコンテンツプレーヤに順次送信し、デジタルコンテンツファイルを備えるコンテンツデータが受信される間に、コンテンツプレーヤがデジタルコンテンツファイルを再生する。通信ネットワーク内での可変の待ち時間及び帯域幅を考慮に入れるために、コンテンツバッファは、コンテンツデータが実際に再生される前に、入って来るコンテンツデータを待ち行列に入れる。使用可能な帯域幅をより低減させるネットワーク輻輳の間、コンテンツデータはコンテンツバッファにあまり追加されず、ある再生ビットレートでの再生をサポートするために、コンテンツデータが待ち行列から取り出されるにつれて、コンテンツバッファは空になり得る。しかし、ネットワーク帯域幅が高い間、コンテンツバッファが再度概ねいっぱいになるまで、コンテンツバッファは補充され、追加のバッファ時間が追加される。実用的なシステムにおいて、コンテンツバッファは、数秒から1分以上にわたるタイムスパンに対応するコンテンツデータを待ち行列に入れることができる。 [0004] A content player is configured to download and play a digital content file in response to a user request to select a title for playback. The process of playing the digital content file includes decoding and rendering the audio and video data into audio and video signals that can drive a display system having a speaker subsystem and a video subsystem. Playback typically involves a technique known in the art as “streaming”, whereby the content server sequentially sends the digital content file to the content player, while content data comprising the digital content file is received. The content player plays the digital content file. In order to take into account variable latency and bandwidth within the communication network, the content buffer queues incoming content data before the content data is actually played. During network congestion that further reduces available bandwidth, content data is not added to the content buffer much, and as content data is dequeued to support playback at a certain playback bit rate, the content buffer Can be empty. However, while the network bandwidth is high, the content buffer is replenished and additional buffer time is added until the content buffer is almost full again. In practical systems, the content buffer can queue content data corresponding to time spans ranging from a few seconds to over a minute.
[0005]コンテンツサーバに格納された各デジタルコンテンツファイルは、通常、特定の再生ビットレートのためにコード化されている。再生を開始する前に、コンテンツプレーヤは、コンテンツサーバから使用可能な帯域幅を測定することができ、測定された使用可能な帯域幅によってサポートすることができるビットレートを有するデジタルコンテンツファイルを選択することができる。再生品質を最大にするために、従来、最高ビットレートが測定された帯域幅を超えないデジタルコンテンツファイルが選択される。通信ネットワークがビットレート要件を満たしながら選択されたデジタルコンテンツファイルをダウンロードするのに十分な帯域幅を提供することができる範囲で、再生は申し分なく進行する。しかし、実際には、通信ネットワークにおいて使用可能な帯域幅は、通信ネットワークに接続された異なるデバイスが独立したタスクを実行するにつれて絶えず変化している。通信ネットワークにおいて使用可能な帯域幅がかなり長い期間の間再生ビットレート要件を満たすのに必要なレベルを下回る場合、コンテンツバッファは、完全に空になり、その結果、当分野でバッファアンダーランとして知られている状態になる。バッファアンダーランが生じる場合、再生は、きわめて信頼できなくなり、又はまったく停止し、全体的な再生品質をかなり低減させる可能性がある。従来の通信ネットワーク上でのトラフィックが予測不可能な傾向にあるので、輻輳及び帯域幅の低減がよく起こり、従来のストリーミング再生システムに負の影響を与える。 [0005] Each digital content file stored in a content server is typically encoded for a specific playback bit rate. Before starting playback, the content player can measure the available bandwidth from the content server and select a digital content file having a bit rate that can be supported by the measured available bandwidth. be able to. In order to maximize playback quality, digital content files are conventionally selected where the highest bit rate does not exceed the measured bandwidth. Playback proceeds satisfactorily to the extent that the communication network can provide sufficient bandwidth to download the selected digital content file while meeting the bit rate requirements. In practice, however, the bandwidth available in a communication network is constantly changing as different devices connected to the communication network perform independent tasks. If the bandwidth available in the communication network falls below the level required to meet the playback bit rate requirement for a fairly long period of time, the content buffer is completely emptied, and as a result is known in the art as a buffer underrun. It will be in the state. If a buffer underrun occurs, playback may become very unreliable or stop at all and significantly reduce the overall playback quality. Since traffic on conventional communication networks tends to be unpredictable, congestion and bandwidth reduction often occur and negatively impact conventional streaming playback systems.
[0006]ストリーミング再生システムにおけるバッファアンダーランの可能性を低減するための1つの技術は、再生のために控えめに低いビットレートを選択することである。しかし、この際、より高品質の経験が可能であった場合でも、ユーザは、結局低品質の再生経験で終わる。バッファアンダーランの可能性を低減するための別の技術は、再生を開始する前に全体的なデジタルコンテンツファイルの比較的大きい部分をプリバッファリングすることである。しかし、この技術は必然的に、再生が始まり得る前に、ユーザが比較的長い時間待つ必要があり、したがって、全体的な再生経験を低下させる。 [0006] One technique for reducing the possibility of buffer underrun in streaming playback systems is to select a conservatively low bit rate for playback. However, even if a higher quality experience is possible at this time, the user ends up with a lower quality playback experience. Another technique for reducing the possibility of buffer underrun is to pre-buffer a relatively large portion of the overall digital content file before starting playback. However, this technique inevitably requires the user to wait a relatively long time before playback can begin, thus reducing the overall playback experience.
[0007]上記が示すように、当分野では、従来の手法より高品質の再生経験を提供するコンテンツプレーヤにデジタルコンテンツファイルをダウンロードするための手法が必要である。 [0007] As indicated above, there is a need in the art for a technique for downloading digital content files to a content player that provides a higher quality playback experience than conventional techniques.
[0008]本発明の一実施形態は、コンテンツサーバからコンテンツプレーヤにデジタルコンテンツのファイルを適応的にダウンロードするための方法を記載する。この方法は、コンテンツプレーヤ内のコンテンツバッファに、ファイル内に含まれる第1のコード化済みシーケンスから少なくとも1単位のデジタルコンテンツをダウンロードするステップであり、ファイルが複数のコード化済みシーケンスを含み、各コード化済みシーケンスが、再生のためにコンテンツバッファに格納されたデジタルコンテンツにアクセスすることができる異なるビットレートに対応し、第1のコード化済みシーケンスが、再生のためにコンテンツバッファに格納されたデジタルコンテンツにアクセスすることができる最低のビットレートに対応する、ステップと、デジタルコンテンツのファイルの中の1単位又は複数単位のデジタルコンテンツを、依然として再生のためにダウンロードし、バッファに入れなければならないことを決定するステップと、次の単位のデジタルコンテンツをダウンロードするための複数のコード化済みシーケンスに含まれる次のコード化済みシーケンスを決定するステップと、次の単位のデジタルコンテンツを、再生のために、次のコード化済みシーケンスからコンテンツバッファにダウンロードするステップとを含む。 [0008] One embodiment of the present invention describes a method for adaptively downloading a file of digital content from a content server to a content player. The method is the step of downloading at least one unit of digital content from a first encoded sequence contained in a file to a content buffer in a content player, wherein the file includes a plurality of encoded sequences, The encoded sequence corresponds to different bit rates that can access the digital content stored in the content buffer for playback, and the first encoded sequence is stored in the content buffer for playback Steps corresponding to the lowest bit rate at which digital content can be accessed and one or more units of digital content in the digital content file must still be downloaded and buffered for playback Determining the next encoded sequence included in the plurality of encoded sequences for downloading the next unit of digital content, and reproducing the next unit of digital content for playback. To download to the content buffer from the next encoded sequence.
[0009]開示された方法の1つの利点は、再生ビットレート及び使用可能なダウンロード帯域幅に基づく可能なバッファアンダーランが追跡され、バッファアンダーラン状態を回避しながら、複数単位のデジタルコンテンツが可能な限り最高の画質でダウンロードされることである。 [0009] One advantage of the disclosed method is that possible buffer underruns based on playback bit rate and available download bandwidth are tracked, allowing multiple units of digital content while avoiding buffer underrun conditions It will be downloaded with the best possible image quality.
[0010]他の実施形態は、それだけには限定されないが、処理ユニットが開示された方法の1つ又は複数の態様を実施することができる命令を含むコンピュータ可読媒体、及び開示された方法の1つ又は複数の態様を実施するように構成されたシステムを含む。 [0010] Other embodiments include, but are not limited to, computer readable media including instructions that allow a processing unit to perform one or more aspects of the disclosed method, and one of the disclosed methods. Or a system configured to implement a plurality of aspects.
[0011]本発明の上記の特徴を詳しく理解することができるように、実施形態を参照して上記で簡単に要約した本発明のより特定の説明を行い、その一部が添付の図面に図示される。しかし、添付の図面は本発明の代表的な実施形態のみを示しており、したがって、本発明は、他の等しく有効な実施形態を認めることができるため、その範囲を制限するものと見なされないことに留意されたい。 [0011] In order that the above features of the present invention may be more fully understood, a more particular description of the invention briefly summarized above will be made by reference to embodiments that are illustrated in part in the accompanying drawings. Is done. However, the accompanying drawings show only typical embodiments of the invention, and therefore the invention is not to be considered as limiting its scope, as other equally valid embodiments can be recognized. Please note that.
[0024]以下の説明では、本発明をより完全に理解できるように、多数の特定の詳細について記載する。しかし、本発明をこれらの特定の詳細のうちの1つ又は複数なしに実施することができることは、当業者にとって明らかである。他の例では、本発明をわかりにくくすることを避けるために、周知の特徴については記載していない。 [0024] In the following description, numerous specific details are set forth in order to provide a more thorough understanding of the present invention. However, it will be apparent to one skilled in the art that the present invention may be practiced without one or more of these specific details. In other instances, well-known features are not described in order to avoid obscuring the present invention.
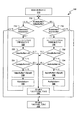
[0025]図1は、本発明の1つ又は複数の態様を実施するように構成されたコンテンツ配布システム100を示す。示すように、コンテンツ配布システム100は、それだけには限定されないが、コンテンツプレーヤ110、1つ又は複数のコンテンツサーバ130、及び通信ネットワーク150を含む。コンテンツ配布システム100は、コンテンツディレクトリサーバ120も含み得る。一実施形態において、1つ又は複数のコンテンツサーバ130は、コンテンツ配布ネットワーク(CDN)140を備える。
[0025] FIG. 1 illustrates a
[0026]通信ネットワーク150は、コンテンツプレーヤ110と1つ又は複数のコンテンツサーバ130との間のデータ通信を容易にするように構成された、ルータやスイッチなど複数のネットワーク通信システムを含む。周知のインターネット通信ネットワークを配置する際に実施される技術を含めて、通信システム150を構築するための技術的に実行可能な多くの技術があることを当業者であれば認識されよう。
[0026]
[0027]コンテンツディレクトリサーバ120は、タイトルルックアップ要求152を受信し、ファイル位置データ154を生成するように構成されたコンピュータシステムを備える。タイトルルックアップ要求152は、それだけには限定されないが、ユーザによって要求される動画又は歌の名前を含む。コンテンツディレクトリサーバ120は、特定の再生ビットレートでコード化される所与のタイトルのビデオストリームを、関連するコンテンツサーバ130内にあるデジタルコンテンツファイル132にマップするデータベース(図示せず)に対する問い合わせを行う。ファイル位置データ154は、それだけには限定されないが、デジタルコンテンツファイル132をコンテンツプレーヤ110に提供するように構成されたコンテンツサーバ130への参照を含む。
[0027] The
[0028]コンテンツサーバ130は、コンテンツプレーヤ110からのデジタルコンテンツファイル132についてのダウンロード要求に応えるように構成されたコンピュータシステムである。デジタルコンテンツファイルは、コンピュータシステムからアクセス可能な大容量記憶システムに存在し得る。大容量記憶システムは、それだけには限定されないが、直接接続されたストレージ、ネットワーク接続されたファイルストレージ、又はネットワーク接続されたブロックレベルストレージを含み得る。デジタルコンテンツファイル132は、任意の技術的に実行可能な技術を使用して、フォーマットされ、大容量記憶システムに格納され得る。デジタルコンテンツファイル132をコンテンツサーバ130からコンテンツプレーヤ110にダウンロードするために、データ転送プロトコル、例えば周知のハイパーテキストトランスファプロトコル(HTTP)を使用することができる。
[0028] The
[0029]各タイトル(動画、歌、又は他の形のデジタルメディア)は、1つ又は複数のデジタルコンテンツファイル132に関連付けられる。各デジタルコンテンツファイル132は、それだけには限定されないが、シーケンスヘッダインデックス114、音声データ、及びコード化済みシーケンスを備える。コード化済みシーケンスは、特定の再生ビットレートにコード化された完全なバージョンのビデオデータ対応のタイトルを備える。例えば、所与のタイトルは、デジタルコンテンツファイル132−1、デジタルコンテンツファイル132−2、及びデジタルコンテンツファイル132−3と関連付けられ得る。デジタルコンテンツファイル132−1は、シーケンスヘッダインデックス114−1、及び約250キロビット/秒(Kbps)の平均再生ビットレートにコード化されたコード化済みシーケンスを備え得る。デジタルコンテンツファイル132−2は、シーケンスヘッダインデックス114−2、及び約1000Kbpsの平均再生ビットレートにコード化されたコード化済みシーケンスを備え得る。同様に、デジタルコンテンツファイル132−3は、シーケンスヘッダインデックス114−3、及び約1500Kbpsの平均再生ビットレートにコード化されたコード化済みシーケンスを備え得る。1500Kbpsのコード化済みシーケンスは、より高品質の再生を可能にし、したがって、250Kbpsのコード化済みシーケンスに対して、再生にはより望ましい。 [0029] Each title (video, song, or other form of digital media) is associated with one or more digital content files 132. Each digital content file 132 includes, but is not limited to, a sequence header index 114, audio data, and a coded sequence. The encoded sequence comprises a title corresponding to a complete version of video data encoded to a specific playback bit rate. For example, a given title may be associated with digital content file 132-1, digital content file 132-2, and digital content file 132-3. Digital content file 132-1 may comprise a sequence header index 114-1 and a coded sequence encoded to an average playback bit rate of approximately 250 kilobits per second (Kbps). Digital content file 132-2 may comprise a sequence header index 114-2 and a coded sequence encoded to an average playback bit rate of approximately 1000 Kbps. Similarly, the digital content file 132-3 may comprise a sequence header index 114-3 and a coded sequence encoded to an average playback bit rate of about 1500 Kbps. The 1500 Kbps coded sequence allows for higher quality playback and is therefore more desirable for playback than the 250 Kbps coded sequence.
[0030]デジタルコンテンツファイル132内のコード化済みシーケンスは、固定スパンの再生時間を表す複数単位のビデオデータとして編成される。全再生時間は、それぞれ1つの再生時間の固定スパンに対応する一連のタイムスロットに編成される。所与のタイムスロットの間に、1単位のビデオデータが、デジタルコンテンツファイル132と関連した再生ビットレートについて、デジタルコンテンツファイル132内で表される。可変ビットレートのコード化が使用され得るため、再生時間の固定スパンに直接対応するにもかかわらず、各単位のビデオデータはサイズが可変とすることができる。上記の例について、1500Kbpsの再生ビットレートにコード化されるコード化済みシーケンスを備えるデジタルコンテンツファイル132−1内の各タイムスロットは、1500Kbpsでコード化される1単位のビデオデータを含む。一実施形態において、複数単位の音声データは、タイムスロットごとに固定ビットレートでコード化され、デジタルコンテンツファイル132に格納される。 [0030] The encoded sequence in the digital content file 132 is organized as multiple units of video data representing fixed span playback times. The total playback time is organized into a series of time slots, each corresponding to a fixed span of one playback time. During a given time slot, a unit of video data is represented in the digital content file 132 for the playback bit rate associated with the digital content file 132. Since variable bit rate coding can be used, each unit of video data can be variable in size, even though it directly corresponds to a fixed span of playback time. For the above example, each time slot in the digital content file 132-1 with a coded sequence encoded at a playback bit rate of 1500 Kbps contains one unit of video data encoded at 1500 Kbps. In one embodiment, multiple units of audio data are encoded at a fixed bit rate for each time slot and stored in the digital content file 132.
[0031]複数単位のビデオデータ及び複数単位の音声データは、各タイムスロットの最初に開始する、時間同期の再生を提供するように構成される。音声再生又はビデオ再生のいずれかが不足することを回避するために、音声バッファ244及びビデオバッファ246が相当する期間の再生時間をそれぞれ格納することを保証するために、複数単位の音声データ及び複数単位のビデオデータは、一般に交互のパターンでダウンロードされる。
[0031] The plurality of units of video data and the plurality of units of audio data are configured to provide time-synchronized playback starting at the beginning of each time slot. In order to avoid the shortage of either audio playback or video playback, in order to ensure that the
[0032]各コード化済みシーケンスは、上記に定義した通り、デジタルコンテンツ「ストリーム」を備えることを当業者であれば容易に理解されよう。さらに、特定のコード化済みシーケンスをコンテンツサーバ130からコンテンツプレーヤ110にダウンロードするプロセスは、特定の再生ビットレートで再生のためにコンテンツプレーヤ110にデジタルコンテンツを「ストリームすること」を備える。
[0032] One skilled in the art will readily appreciate that each encoded sequence comprises a digital content "stream" as defined above. Further, the process of downloading a specific encoded sequence from the
[0033]コンテンツプレーヤ110は、コンピュータシステム、セットトップボックス、携帯電話などのモバイルデバイス、又はネットワーク接続を有し、それぞれビデオフレームを提示し、音響出力を生成するための表示装置及びスピーカ装置に結合される、又は表示装置及びスピーカ装置を含む他の任意の技術的に実行可能なコンピューティングプラットフォームを備え得る。後でより詳細に説明するように、コンテンツプレーヤ110は、選択されたビットレートについて、1単位のビデオデータをダウンロードし、通信ネットワーク150内の主だった帯域幅状態に基づいて、選択されたビットレートを、その後ダウンロードされる複数単位のビデオデータに適応させるように構成される。
[0033] The
[0034]通信ネットワーク150内で使用可能な帯域幅が制限されるようになるにつれて、コンテンツプレーヤは、その後のタイムスロットに対応してまだダウンロードされていない複数単位のビデオデータのために、より低いビットレートのコード化を選択することができる。使用可能な帯域幅が増加するにつれて、より高いビットレートのコード化を選択することができる。
[0034] As the available bandwidth in
[0035]上記の説明において、1つのコンテンツプレーヤ110及び1つのCDN140を含むコンテンツ配布システム100が示されているが、図1のアーキテクチャは単に本発明の実施形態例を企図するにすぎないことを当業者であれば理解されよう。他の実施形態は、任意の数のコンテンツプレーヤ110及び/又はCDN140を含むことができる。したがって、図1は、決して本発明の範囲を制限するものではない。
[0035] In the above description, a
[0036]図2は、本発明の一実施形態による図1のコンテンツプレーヤ110のより詳細な図である。示すように、コンテンツプレーヤ110は、それだけには限定されないが、中央演算処理装置(CPU)210と、グラフィックサブシステム212と、入出力(I/O)デバイスインターフェース214と、ネットワークインターフェース218と、相互接続220と、メモリサブシステム230とを含む。コンテンツプレーヤ110は、大容量記憶装置216も含み得る。
[0036] FIG. 2 is a more detailed view of the
[0037]CPU210は、メモリサブシステム230に格納されたプログラミング命令を取り出し、実行するように構成される。同様に、CPU210は、メモリサブシステム230にアプリケーションデータを格納し、メモリサブシステム230にあるアプリケーションデータを取り出すように構成される。相互接続220は、CPU210、グラフィックサブシステム212、I/Oデバイスインターフェース214、大容量記憶装置216、ネットワークインターフェース218、及びメモリサブシステム230の間の例えばプログラミング命令及びアプリケーションデータなどデータの送信を容易にするように構成される。
[0037] The
[0038]グラフィックサブシステム212は、ビデオデータの複数のフレームを生成し、ビデオデータの複数のフレームを表示装置250に送信するように構成される。一実施形態において、グラフィックサブシステム212は、CPU210とともに、集積回路に統合される。表示装置250は、表示する画像を生成するための任意の技術的に実行可能な手段を備え得る。例えば、表示装置250は、液晶式ディスプレイ(LCD)技術、陰極線技術、及び発光ダイオード(LED)ディスプレイ技術(有機又は無機)を使用して製造することができる。入出力(I/O)デバイスインターフェース214は、相互接続220を介してユーザI/O装置252から入力データを受信し、入力データをCPU210に送信するように構成される。例えば、ユーザI/O装置252は、1つ又は複数のボタン、キーボード、及びマウス又は他のポインティングデバイスを備え得る。I/Oデバイスインターフェース214は、電気音声出力信号を生成するように構成された音声出力ユニットも含む。ユーザI/O装置252は、電気音声出力信号に応答して音響出力を生成するように構成されたスピーカを含む。代替の実施形態では、表示装置250は、スピーカを含み得る。テレビは、ビデオフレームを表示し、音響出力を生成することができる、当分野で知られているデバイスの一例である。例えばハードディスクドライブ又はフラッシュメモリ記憶ドライブなど、大容量記憶装置216は、不揮発性データを格納するように構成される。ネットワークインターフェース218は、通信ネットワーク150を介してデータのパケットを送信及び受信するように構成される。一実施形態において、ネットワークインターフェース218は、周知のイーサネット標準を使用して通信するように構成される。ネットワークインターフェース218は、相互接続220を介してCPU210に結合される。
[0038] The graphics subsystem 212 is configured to generate multiple frames of video data and send the multiple frames of video data to the
[0039]メモリサブシステム230は、オペレーティングシステム232、ユーザインターフェース234、及び再生アプリケーション236を備えるデータ及びプログラミング命令を含む。オペレーティングシステム232は、例えばネットワークインターフェース218、大容量記憶装置216、I/Oデバイスインターフェース214、及びグラフィックサブシステム212を含むハードウェアデバイスの管理など、システム管理機能を実行する。また、オペレーティングシステム232は、ユーザインターフェース234及び再生アプリケーション236のプロセス及びメモリ管理モデルを提供する。ユーザインターフェース234は、コンテンツプレーヤ110とのユーザ対話のために、例えばウィンドウ及びオブジェクトメタファなど、特定の構造を提供する。当業者であれば、当分野で周知の、及びコンテンツプレーヤ110への組み込みに適している様々なオペレーティングシステム及びユーザインターフェースを認識されよう。
[0039] The memory subsystem 230 includes data and programming instructions comprising an
[0040]再生アプリケーション236は、ネットワークインターフェース218を介してコンテンツサーバ130からデジタルコンテンツファイル132を取り出し、グラフィックサブシステム212を介してデジタルコンテンツファイル132を再生するように構成される。グラフィックサブシステム212は、レンダリングされたビデオ信号を表示装置250に送信するように構成される。通常の動作において、再生アプリケーション236は、特定のタイトルを再生する旨のユーザからの要求を受信する。次いで、再生アプリケーション236は、要求されたタイトルと関連したデジタルコンテンツファイル132の位置を突き止め、要求されたタイトルと関連した各デジタルコンテンツファイル132は、異なる再生ビットレートにコード化されたコード化済みシーケンスを含む。一実施形態において、再生アプリケーション236は、タイトルルックアップ要求152をコンテンツディレクトリサーバ120に対して掲示することによって、デジタルコンテンツファイル132の位置を突き止める。コンテンツディレクトリサーバ120は、タイトルルックアップ要求152に、要求されたタイトルと関連した各デジタルコンテンツファイル132のファイル位置データ154で答える。各ファイル位置データ154は、要求されたデジタルコンテンツファイル132が存在する、関連するコンテンツサーバ130への参照を含む。タイトルルックアップ要求152は、要求されたタイトルの名前、又はタイトルに関する他の識別情報を含み得る。再生アプリケーション236が要求されたタイトルと関連したデジタルコンテンツファイル132の位置を突き止めた後、再生アプリケーション236は、コンテンツサーバ130から要求されたタイトルと関連した各デジタルコンテンツファイル132と関連したシーケンスヘッダインデックス114をダウンロードする。図4Aでより詳細に記載する、デジタルコンテンツファイル132と関連したシーケンスヘッダインデックス114は、デジタルコンテンツファイル132に含まれるコード化済みシーケンスに関連した情報を含む。
[0040] The playback application 236 is configured to retrieve the digital content file 132 from the
[0041]一実施形態において、再生アプリケーション236は、再生のための起動時間を最小化するために最低の再生ビットレートにコード化されたコード化済みシーケンスを備える要求されたタイトルと関連したデジタルコンテンツファイル132をダウンロードし始める。単に説明上、デジタルコンテンツファイル132−1は、要求されたタイトルと関連付けられ、最低の再生ビットレートにコード化されたコード化済みシーケンスを備える。要求されたデジタルコンテンツファイル132−1は、先入れ先出しキューとして働くように構成されるコンテンツバッファ112にダウンロードされる。一実施形態において、ダウンロードされたデータの各単位は、1単位のビデオデータ、又は1単位の音声データを備える。要求されたデジタルコンテンツファイル132−1と関連した複数単位のビデオデータがコンテンツプレーヤ110にダウンロードされるにつれて、複数単位のビデオデータはコンテンツバッファ112に押し込まれる。同様に、要求されたデジタルコンテンツファイル132−1と関連した複数単位の音声データがコンテンツプレーヤ110にダウンロードされるにつれて、複数単位の音声データはコンテンツバッファ112に押し込まれる。一実施形態において、複数単位のビデオデータは、コンテンツバッファ112内のビデオバッファ246に格納され、複数単位の音声データは、この場合もコンテンツバッファ112内の音声バッファ224に格納される。
[0041] In one embodiment, the playback application 236 provides digital content associated with the requested title with a coded sequence encoded at the lowest playback bit rate to minimize start-up time for playback. Start downloading file 132. For illustrative purposes only, the digital content file 132-1 comprises a coded sequence that is associated with the requested title and coded to the lowest playback bit rate. The requested digital content file 132-1 is downloaded to the
[0042]ビデオデコーダ248は、複数単位のビデオデータをビデオバッファ246から読み出し、期間において再生時間の固定スパンに対応する一連のビデオフレームにレンダリングする。ビデオバッファ246から1単位のビデオデータを読み出すことは、ビデオバッファ246(及びコンテンツバッファ112から)の待ち行列から1単位のビデオデータを効果的に取り出す。ビデオフレームのシーケンスは、グラフィックサブシステム212によって処理され、表示装置250に送信される。
[0042] The
[0043]オーディオデコーダ242は、複数単位の音声データを音声バッファ244から読み出し、通常、ビデオフレームのシーケンスに時間的に同期して、一連の音声サンプルにレンダリングする。一実施形態において、音声サンプルのシーケンスはI/Oデバイスインターフェース214に送信され、I/Oデバイスインターフェース214は音声サンプルのシーケンスを電気音声信号に変換する。電気音声信号は、ユーザI/O装置252内のスピーカに送信され、ユーザI/O装置252は、その送信に応答して、音響出力を生成する。
[0043] The audio decoder 242 reads multiple units of audio data from the
[0044]再生が開始されると、再生アプリケーション236は、最低の使用可能なビットレートにコード化される複数単位のビデオデータを要求し、それによって、ユーザによって認められる開始時刻が最小化される。しかし、通信ネットワーク150内の帯域幅状態が許容するなら、再生アプリケーション236は、より高いビットレートにコード化される複数単位のビデオデータを要求することができ、それによって、再生アプリケーション236によって最終的に達成される最高レベルの再生品質に相応した起動の遅延をもたらすことなく、時間にわたって再生品質を向上させる。通信ネットワーク150内の帯域幅状態が再生中に悪化する場合、再生アプリケーション236は、より低いビットレートにコード化される次の複数単位のビデオデータを要求することができる。一実施形態において、再生アプリケーション236は、最近ダウンロードされた1単位又は複数単位のビデオデータにわたって計算される帯域幅の評価に基づいて、どのコード化されたビットレートが1単位のビデオデータの順次の各ダウンロードに使用されるべきかを決定する。
[0044] When playback is initiated, playback application 236 requests multiple units of video data that are encoded to the lowest available bit rate, thereby minimizing the start time allowed by the user. . However, if the bandwidth conditions within the
[0045]図3は、本発明の一実施形態による図1のコンテンツサーバ130のより詳細な図である。コンテンツサーバ130は、それだけには限定されないが、中央演算処理装置(CPU)310と、ネットワークインターフェース318と、相互接続320と、メモリサブシステム330と、大容量記憶装置316とを含む。コンテンツサーバ130は、I/Oデバイスインターフェース314も含み得る。
[0045] FIG. 3 is a more detailed view of the
[0046]CPU310は、メモリサブシステム330に格納されたプログラミング命令を取り出し、実行するように構成される。同様に、CPU310は、メモリサブシステム330にあるアプリケーションデータを格納し、取り出すように構成される。相互接続320は、CPU310、I/Oデバイスインターフェース314、大容量記憶装置316、ネットワークインターフェース318、及びメモリサブシステム330の間の例えばプログラミング命令及びアプリケーションデータなどデータの送信を容易にするように構成される。
[0046] The
[0047]大容量記憶装置316は、デジタルコンテンツファイル132−1〜132−Nを格納する。デジタルコンテンツファイル132は、任意の技術的に実行可能なファイルシステムを使用して任意の技術的に実行可能なメディアに格納され得る。例えば、大容量記憶装置316は、従来のファイルシステムを組み込む独立ディスク冗長アレイ(RAID)システムを備え得る。
[0047] The
[0048]メモリサブシステム330は、オペレーティングシステム332、ユーザインターフェース334、及びファイルダウンロードアプリケーション336を備えるデータ及びプログラミング命令を含む。オペレーティングシステム332は、例えばネットワークインターフェース318、大容量記憶装置316、及びI/Oデバイスインターフェース314を含むハードウェアデバイスの管理など、システム管理機能を実行する。また、オペレーティングシステム332は、ユーザインターフェース334及びファイルダウンロードアプリケーション336のプロセス及びメモリ管理モデルを提供する。ユーザインターフェース334は、コンテンツサーバ130とのユーザ対話のために、例えばウィンドウ及びオブジェクトメタファ又はコマンドラインインターフェースなど、特定の構造を提供する。ユーザは、ユーザインターフェース334を使用して、コンテンツサーバの機能を管理することができる。一実施形態において、ユーザインターフェース334は、コンテンツサーバ130の動作を管理するための管理ウェブページを提示する。当業者であれば、当分野で周知の、及びコンテンツプレーヤ130への組み込みに適している様々なオペレーティングシステム及びユーザインターフェースを認識されよう。
[0048] The
[0049]ファイルダウンロードアプリケーション336は、ファイルダウンロード操作又は操作の組を介して、デジタルコンテンツファイル132−1〜132−Nのコンテンツプレーヤ110への転送を容易にするように構成される。ダウンロードされたデジタルコンテンツファイル132は、ネットワークインターフェース318によって、通信ネットワーク150を介してコンテンツプレーヤ110に送信される。一実施形態において、各デジタルコンテンツファイル132のファイルコンテンツは、任意の順序(当分野で「ランダムアクセス」として知られている)でアクセスされ得る。本明細書において上述したように、各デジタルコンテンツファイル132は、シーケンスヘッダインデックス114、及びコード化済みシーケンスを含む。コード化済みシーケンスは、特定のビットレートにコード化されたフルバージョンの所与の動画又は歌を備え、コード化済みシーケンスと関連したビデオデータは、複数単位のビデオデータに分割される。各単位のビデオデータは、特定のスパンの再生時間に対応し、ビデオデータの単位に格納されたビデオデータのサイズ及び解像度を指定するシーケンスヘッダを含むフレームで開始する。
[0049] The file download application 336 is configured to facilitate the transfer of the digital content files 132-1 to 132-N to the
[0050]図4Aは、本発明の一実施形態による図1のシーケンスヘッダインデックス114のより詳細な図である。シーケンスヘッダインデックス114は、ビデオビットレートプロフィール452を含み、任意の技術的に実行可能なやり方で埋めることができるデータ構造である。
[0050] FIG. 4A is a more detailed view of the sequence header index 114 of FIG. 1 according to one embodiment of the invention. The sequence header index 114 is a data structure that includes a video
[0051]デジタルコンテンツファイル132に含まれるシーケンスヘッダインデックス114は、デジタルコンテンツファイル132にも含まれるコード化済みシーケンスに関連した情報を指定する。ビデオビットレートプロフィール452は、コード化済みシーケンスの複数単位のビデオデータと関連した異なるシーケンスヘッダの位置及びタイムスタンプオフセットを指定する対応する1組のエントリ464を含む。通常、コード化済みシーケンスにおけるシーケンスヘッダは、(例えば3秒など)コード化済みシーケンス内で予測可能なタイムスタンプオフセットに位置する。所与のエントリ464は、ビデオビットレートプロフィール452と関連したコード化済みシーケンスの1単位のビデオデータ内に含まれる特定のシーケンスヘッダのタイムスタンプオフセット及び位置を示す。例えば、エントリ464−1は、コード化済みシーケンスの第1の単位のビデオデータと関連したシーケンスヘッダのタイムスタンプオフセット及び位置を示す。エントリ464−2は、同じコード化済みシーケンスの第2の単位のビデオデータと関連したシーケンスヘッダのタイムスタンプオフセット及び位置を示す。重要なことに、エントリ464の組に含まれるタイムスタンプオフセットに基づいて、エントリ464−Kと関連した現在の再生位置から再生の完了までの所与のコード化済みシーケンスを備えるバイトがいくつあるかを特徴付ける総バイト数を、計算することができる。
[0051] The sequence header index 114 included in the digital content file 132 specifies information associated with the encoded sequence that is also included in the digital content file 132. The video
[0052]拡張されたシーケンスと関連した音声データも、デジタルコンテンツファイル132に格納される。一実施形態において、音声データは、固定ビットレートのコード化を有する。代替実施形態において、音声データに可変ビットレートコード化技術が適用され、シーケンスヘッダインデックス114に音声ビットレートプロフィール472が含まれる。音声ビットレートプロフィール472は、それぞれの再生時間に音声データのそれぞれの単位ごとにタイムスタンプオフセット及びシーケンスヘッダ位置を格納するように構成されるエントリ484を含む。
[0052] Audio data associated with the extended sequence is also stored in the digital content file 132. In one embodiment, the audio data has a constant bit rate encoding. In an alternative embodiment, variable bit rate coding techniques are applied to the audio data and the sequence header index 114 includes the audio
[0053]図4Bは、本発明の一実施形態による、ある評価ポイント444で、2つの異なるビットレート410、412において実行されるバッファ予測アルゴリズムの結果を示すグラフ401である。正の縦軸に沿って示されるバッファ時間430は、図1のコンテンツバッファ112内にどれくらい有効な再生時間が格納されるかを示す。負の縦軸に沿って示されるバッファアンダーラン時間434は、バッファアンダーラン420中の同等の時間の不足を示す。評価ポイント444で、図2の再生アプリケーション236は、現在使用可能な帯域幅が与えられると、再生が現在の再生ビットレート410で完了することができるかどうかを推定する。推定されたバッファ時間430が再生の完了の前に任意の再生時440に現在のビットレート410についてのバッファアンダーラン420を示す場合、現在のビットレートを維持することは実行不可能であるが、より低いビットレート412は実行可能であり得る。より低いビットレートは、現在使用可能な帯域幅が与えられると、再生をうまく完了することができるより低いビットレートを見つけるためにテストされる。一実施形態において、再生アプリケーション236は、再生の間、例えば3秒ごとなど周期的に、再生が、評価ポイント444で表される現在の再生ビットレートで完了することができるかどうかを推定する。
[0053] FIG. 4B is a
[0054]示すように、バッファ時間430は、ビットレート410については、将来のある時点でバッファアンダーランがあること、ビットレート412については、バッファアンダーランがないことを推定する。こうしたシナリオでは、現在使用可能な帯域幅が与えられると、ビットレート410で再生を完了することは、実行不可能であり、一方、現在使用可能な帯域幅が与えられると、ビットレート412で再生を完了することは、実行可能であるように思える。
[0054] As shown,
[0055]特定のコード化済みシーケンスの実行可能性を予測するとき、再生アプリケーション236は、単一のコード化済みシーケンス、及びしたがって、単一の再生ビットレート、又は「集計されたコード化済みシーケンス(aggregate encoded sequence)」を、図5〜図7においてより詳細に記載される予測アルゴリズムへの入力として使用することを選択することができる。集計されたコード化済みシーケンスは、1つ又は複数のコード化済みシーケンスの組み合わせ、及び再生のために将来使用され得る1つ又は複数のコード化済みシーケンスについての対応する再生ビットレートを表す。例えば、再生アプリケーション236が高ビットレートのコード化済みシーケンスを再生している場合、再生アプリケーション236は、ダウンロードが一定の閾値期間の間続くことができる場合、(今のところ)コード化済みシーケンスが実行可能であると予測することができる。 [0055] When predicting the feasibility of a particular coded sequence, the playback application 236 may use a single coded sequence, and thus a single playback bit rate, or "aggregated coded sequence". (Aggregate encoded sequence) "can be chosen to be used as an input to the prediction algorithm described in more detail in FIGS. The aggregated coded sequence represents a combination of one or more coded sequences and a corresponding playback bit rate for the one or more coded sequences that may be used for playback in the future. For example, if the playback application 236 is playing a high bit rate coded sequence, the playback application 236 may (for now) have a coded sequence if the download can continue for a certain threshold period. It can be predicted that it is feasible.
[0056]閾値期間の後、再生アプリケーション236は、追加の期間の間、現在のコード化済みシーケンスをバッファリングし続けることができ、その後低ビットレートのコード化済みシーケンスに切り替えることができる。このことは、現在のコード化済みシーケンスの一部を、より低いビットレートのコード化済みシーケンスと関連した時間の後の部分と集計し、結果として得られた集計されたコード化済みシーケンス、すなわち、2つのコード化済みシーケンスの集計の実行可能性を予測することによって達成される。再生アプリケーション236は、予想された切替の方向に応じて、予測計算において2つ以上のコード化済みシーケンスについての全期間の情報を分析することを選択することもできる。例えば、再生アプリケーション236が将来の再生のためにより高いビットレートのコード化済みシーケンスを評価する予定である場合、再生アプリケーション236は、より高いビットレートで実行可能性を確実にするためにより高いビットレートの全コード化済みシーケンスを評価することができる。しかし、再生アプリケーション236は、現在のコード化済みシーケンスである高ビットレートのコード化済みシーケンスを評価している場合、代わりに、より低いビットレートのコード化済みシーケンスへの切替を遅らせるために、現在のコード化済みシーケンスとより低いビットレートのコード化済みシーケンスとの集計における実行可能性を予測することができる。 [0056] After the threshold period, playback application 236 may continue to buffer the current coded sequence for an additional period of time, and then switch to a low bit rate coded sequence. This aggregates a portion of the current coded sequence with the later portion of time associated with the lower bit rate coded sequence, and the resulting aggregated coded sequence, i.e. This is accomplished by predicting the feasibility of aggregation of two coded sequences. The playback application 236 may also choose to analyze full-time information about two or more coded sequences in the prediction calculation, depending on the expected direction of switching. For example, if the playback application 236 intends to evaluate a higher bit rate coded sequence for future playback, the playback application 236 may use a higher bit rate to ensure feasibility at a higher bit rate. The entire encoded sequence of can be evaluated. However, if the playback application 236 is evaluating a high bit rate coded sequence that is the current coded sequence, instead, to delay switching to the lower bit rate coded sequence, The feasibility in the aggregation of the current coded sequence and the lower bit rate coded sequence can be predicted.
[0057]図4Cは、本発明の一実施形態による、デジタルコンテンツファイル132と関連したデジタルコンテンツ494のバッファリング及び再生のデータフローを示す。図1のコンテンツサーバ130は、複数単位の音声データ及び複数単位のビデオデータを備える、デジタルコンテンツファイル132のコンテンツデータ494をバッファリングプロセス490に提供する。バッファリングプロセス490は、コンテンツプレーヤ110内で実行されるスレッドとして実施することができる。バッファリングプロセス490は、コンテンツデータ494をダウンロードし、コンテンツバッファ112に書き込むように構成される。バッファリングプロセス490は、コンテンツバッファ112内の音声バッファ244に複数単位の音声データを書き込み、これもまたコンテンツバッファ112内のビデオバッファ246に複数単位のビデオデータを書き込む。一実施形態において、コンテンツバッファ112は、先入れ先出し方式(FIFO)キューとして構築される。再生プロセス492は、これもまたコンテンツプレーヤ110内で実行され、再生のために、コンテンツバッファ112の待ち行列から複数単位の音声データ及び複数単位のビデオデータを取り出す。コンテンツデータ494の連続的な再生を維持するために、コンテンツバッファ112は、再生プロセス492がコンテンツバッファ112において読み出しを実行する必要があるとき、使用可能な少なくとも1単位の音声データ及び1単位のビデオデータを常に有しているものとする。コンテンツバッファ112が空であり、再生プロセス492が読み出しの実行を必要とするとき、図4Bに示すように、バッファアンダーランが生じる。
[0057] FIG. 4C illustrates a data flow for buffering and playback of digital content 494 associated with digital content file 132, according to one embodiment of the invention. The
[0058]図5は、本発明の一実施形態による、再生のためにコンテンツデータをコンテンツバッファ112に適応的にバッファリングするための方法ステップ500のフロー図である。方法ステップは図1、図2、及び図3のシステムとの関係で記載されているが、方法ステップを任意の順序で実行するように構成される任意のシステムは本発明の範囲内に含まれることを当業者であれば理解されよう。
[0058] FIG. 5 is a flow diagram of method steps 500 for adaptively buffering content data in
[0059]方法は、ステップ510で開始し、図2の再生アプリケーション236は、デジタルコンテンツファイル132の再生を開始する旨の要求を受信する。ステップ512において、再生アプリケーション236は、図1のコンテンツバッファ112に、最低の使用可能なビットレートでデジタルコンテンツファイル132の1単位又は複数単位のビデオデータをプリバッファリングする。再生アプリケーション236は、コンテンツバッファ112に、対応する1単位又は複数単位の音声データもプリバッファリングする。プリバッファリングは、再生を開始する前に一定量のビデオデータ及び音声データをダウンロードすることを含む。ステップ514において、再生アプリケーション236は、再生を始める。これ以降、新しいデータをコンテンツバッファ112に入れるために方法ステップ500が実行される間に、コンテンツバッファ112からデータをレンダリングし、表示するために再生スレッドが実行される。一実施形態において、再生スレッドは、再生アプリケーション236の一部として実行される。
[0059] The method begins at step 510, where the playback application 236 of FIG. 2 receives a request to start playback of the digital content file 132. In
[0060]ステップ520において、再生アプリケーション236は、ユーザシーク要求が受信されたかどうかを決定する。ステップ520で、ユーザシーク要求が受信された場合、方法はプリバッファリングのためにステップ512に戻る。しかし、ステップ520で、ユーザシーク要求が受信されていない場合、方法はステップ522に進む。ステップ522で、再生アプリケーション236は、音声バッファ244(AudioBuff)内に残っている再生時間がビデオバッファ246(VideoBuff)内に残っている再生時間未満であるかどうかを決定する。音声バッファ244内に残っている再生時間がビデオバッファ246内に残っている再生時間以上であるとき、より多くの単位のビデオデータが再生アプリケーション236によって再生のために必要とされる。音声バッファ244内に残っている再生時間がビデオバッファ246内に残っている再生時間未満であるとき、より多くの単位の音声データが再生アプリケーション236によって再生のために必要とされる。こうしたやり方で、再生アプリケーション236は、デジタルコンテンツファイル132の複数単位のビデオデータ及び複数単位の音声データのダウンロードのバランスをとる。
[0060] In
[0061]ステップ522で、音声バッファ244内に残っている再生時間がビデオバッファ246内に残っている再生時間以上である場合、方法はステップ530に進む。ステップ530で、再生アプリケーション236は、現在再生しているビデオデータの単位についての一連のタイムスロットに対応するビデオインデックス(VideoIndex)が、現在再生されているデジタルコンテンツファイル132のビデオデータ(VideoUnits)の単位の合計数未満かどうかを決定する。デジタルコンテンツファイル132のビデオデータの単位の合計数を、デジタルコンテンツファイル132と関連したシーケンスヘッダインデックス114から取り出すことができる。
[0061] If, at
[0062]ステップ530で、ビデオインデックスがデジタルコンテンツファイル132のビデオデータの単位の合計数未満である場合、すなわち、デジタルコンテンツファイル132のビデオデータのすべての単位が再生されたわけではない場合、方法はステップ540に進む。ステップ540で、再生アプリケーション236は、図6でより詳細に説明したように、バッファアンダーラン予測に基づいて、次の複数単位のビデオデータをバッファリングするための次のコード化済みシーケンスを決定する。次のコード化済みシーケンスは、より高いビットレートのコード化済みシーケンス、より低いビットレートのコード化済みシーケンス、又は現在のコード化済みシーケンスと同じコード化済みシーケンスでもよい。ステップ542で、再生アプリケーション236は、決定された次のコード化済みシーケンスに基づいて、1単位のビデオデータをダウンロードし、コンテンツバッファ112内のビデオバッファ246にその単位のビデオデータをバッファリングする。
[0062] At
[0063]ステップ530に戻って、ビデオインデックスが現在再生されているデジタルコンテンツファイル132のビデオデータの単位の合計数以上であると再生アプリケーション236が決定した場合、再生アプリケーション236はビデオデータの単位をそれ以上必要とせず、方法はステップ590で終了する。
[0063] Returning to step 530, if the playback application 236 determines that the video index is greater than or equal to the total number of video data units of the digital content file 132 currently being played, the playback application 236 determines the unit of video data. No more is required and the method ends at
[0064]ステップ522に戻って、音声バッファ244内に残っている時間がビデオバッファ246内に残っている時間未満であると再生アプリケーション236が決定した場合、再生アプリケーション236は再生のためにより多くの単位の音声データを必要し、方法はステップ550に進む。ステップ550で、再生アプリケーション236は、現在再生している音声データの単位についての一連のタイムスロットに対応する音声インデックス(AudioIndex)が、現在再生されているデジタルコンテンツファイル132の音声データ(AudioUnits)の単位の合計数未満かどうかを決定する。
[0064] Returning to step 522, if the playback application 236 determines that the time remaining in the
[0065]ステップ550で、音声インデックスが現在再生されているデジタルコンテンツファイル132の音声データの単位の合計数未満であると再生アプリケーション236が決定した場合、再生アプリケーション236は別の単位の音声データを必要し、方法はステップ552に進む。ステップ552で、再生アプリケーション236は、1単位の音声データをダウンロードし、コンテンツバッファ112内の音声バッファ244にその単位の音声データをバッファリングする。
[0065] If, in
[0066]しかし、ステップ550で、音声インデックスが現在再生されているデジタルコンテンツファイル132の音声データの単位の合計数以上であると再生アプリケーション236が決定した場合、再生アプリケーション236は音声データの単位をそれ以上必要とせず、方法はステップ590で終了する。
[0066] However, if the playback application 236 determines in
[0067]図6は、本発明の一実施形態による、再生のためにバッファリングすべき次のコード化済みシーケンスを決定するための方法ステップ600のフロー図である。方法ステップは図1、図2、及び図3のシステムとの関係で記載されているが、方法ステップを任意の順序で実行するように構成される任意のシステムは本発明の範囲内に含まれることを当業者であれば理解されよう。この場合もまた、方法ステップ600は、図5のステップ540をより詳細に記載し、一実施形態において、再生アプリケーション236によって実行される。
[0067] FIG. 6 is a flow diagram of method steps 600 for determining the next coded sequence to be buffered for playback, according to one embodiment of the invention. Although the method steps are described in the context of the systems of FIGS. 1, 2, and 3, any system configured to perform the method steps in any order is within the scope of the present invention. Those skilled in the art will appreciate that. Again,
[0068]方法は、ステップ610で開始し、再生アプリケーション236は、バッファアンダーランなしに完了まで現在のコード化済みシーケンスを再生する実行可能性を予測する。図4B及び図7Aとの関連で記載されている技術など、任意の技術的に実行可能な技術を使用して実行可能性の決定を実施することができることを当業者であれば理解されよう。
[0068] The method begins at
[0069]ステップ620で、現在のビットレートに対応する現在のコード化済みシーケンスが実行可能でないと再生アプリケーション236が決定すると、方法はステップ630に進む。ステップ630で、再生アプリケーション236が最低のビットレートのコード化済みシーケンスではないコード化済みシーケンスを現在再生している場合、方法はステップ632に進み、再生アプリケーション236は、現在のビットレートより低いビットレートに対応するコード化済みシーケンスをコード化済みシーケンス候補として選択する。ステップ634で、再生アプリケーション236はコード化済みシーケンス候補を再生する実行可能性を予測し、この場合もまた、このステップは、図7Aにより詳細に記載されている。ステップ640で、コード化済みシーケンス候補が実行可能であると再生アプリケーション236が決定した場合、方法はステップ690で終了し、コード化済みシーケンス候補は、次のコード化済みシーケンスとして戻される。
[0069] If, at
[0070]ステップ630に戻って、再生アプリケーション236が最低のビットレートに対応するコード化済みシーケンスを表すコード化済みシーケンスを現在再生している場合、方法はステップ690で終了し、現在の(最低の)コード化済みシーケンスが次のコード化済みシーケンスとして戻される。 [0070] Returning to step 630, if the playback application 236 is currently playing a coded sequence representing the coded sequence corresponding to the lowest bit rate, the method ends at step 690 and the current (lowest The encoded sequence is returned as the next encoded sequence.
[0071]ステップ620に戻って、現在のコード化済みシーケンスが実行可能であると再生アプリケーション236が決定した場合、方法はステップ650に進む。ステップ650で、再生アプリケーション236が最高のビットレートのコード化済みシーケンスではないコード化済みシーケンスを現在再生している場合、方法はステップ652に進む。ステップ652で、再生アプリケーション236は、現在のビットレートより高いビットレートに対応するコード化済みシーケンスの実行可能性を予測する。この場合もまた、実行可能性を予測することは、図7Aにより詳細に記載されている。
[0071] Returning to step 620, if the playback application 236 determines that the current coded sequence is executable, the method proceeds to step 650. If, at
[0072]ステップ660で、より高いビットレートに対応するコード化済みシーケンスが実行可能であると再生アプリケーション236が決定した場合、方法はステップ662に進む。ステップ662で、再生アプリケーション236は、より高いビットレートのコード化済みシーケンスが次のコード化済みシーケンスとして戻されるように選択する。しかし、ステップ660で、より高いビットレートに対応するコード化済みシーケンスが実行可能でないと再生アプリケーション236が決定した場合、方法はステップ690で終了し、現在のコード化済みシーケンスが次のコード化済みシーケンスとして戻される。
[0072] If, at
[0073]ステップ650に戻って、再生アプリケーション236が最高のビットレートに対応するコード化済みシーケンスを表すコード化済みシーケンスを現在再生している場合、方法はステップ690で終了し、現在の(最高の)コード化済みシーケンスが次のコード化済みシーケンスとして戻される。 [0073] Returning to step 650, if the playback application 236 is currently playing a coded sequence that represents the coded sequence corresponding to the highest bit rate, the method ends at step 690 and the current (highest The encoded sequence is returned as the next encoded sequence.
[0074]図7Aは、本発明の一実施形態による、現在のビットレートで再生を完了する実行可能性を予測するための方法ステップ700のフロー図である。方法ステップは図1、図2、及び図3のシステムとの関係で記載されているが、方法ステップを任意の順序で実行するように構成される任意のシステムは本発明の範囲内に含まれることを当業者であれば理解されよう。この場合もまた、方法ステップ700は、図6のステップ610、634、及び652をより詳細に記載し、一実施形態において、再生アプリケーション236によって実行される。
[0074] FIG. 7A is a flow diagram of
[0075]方法は、ステップ710で開始し、再生アプリケーション236は、AudioIndex、VideoIndex、AudioBuffer、及びVideoBufferを含む1組の変数を初期化する。AudioIndexは、特定のタイムスロットに対応する1単位の音声データを選択するために使用されるインデックスを表す。VideoIndexは、特定のタイムスロットに対応する1単位のビデオデータを選択するために使用されるインデックスを表す。AudioBufferは、音声バッファ244に現在格納されているバッファに入れられた再生時間量を表す。VideoBufferは、ビデオバッファ246に現在格納されているバッファに入れられた再生時間量を表す。AudioIndexは、現在の音声のコード化済みシーケンスの現在の再生状態を表す現在のAudioIndexに初期化される。VideoIndexは、現在のビデオのコード化済みシーケンスの現在の再生状態を表す現在のVideoIndexに初期化される。AudioBufferは、現在のAudioBuffer再生値に初期化される。VideoBufferは、現在のVideoBuffer再生値に初期化される。
[0075] The method begins at
[0076]ステップ712で、AudioBufferがVideoBuffer以上であると再生アプリケーション236が決定した場合、音声バッファより少ない再生時間がビデオバッファで使用可能であり、方法はステップ714に進んで、別の単位のビデオデータをダウンロードする影響を推定し始める。ステップ714で、VideoIndexが現在のコード化済みシーケンスのビデオデータの単位の合計数を表すVideoUnits未満であると再生アプリケーション236が決定した場合、再生アプリケーション236は、別の単位のビデオデータをダウンロードする必要があり、方法はステップ720に進む。ステップ720で、コンテンツバッファ112の現在の状態、及び主だった帯域幅の可用性が与えられると、別の単位のビデオデータがコンテンツサーバ130からダウンロードされる場合、再生アプリケーション236は、コンテンツバッファ112の結果として得られた状態を推定する。利点値も期間として計算、測定され、これは、1単位のビデオデータのダウンロードが実行される場合、ビデオバッファ246に追加することができる。利点値は、追加の単位のビデオデータをダウンロードすることと関連した追加の再生時間を表す。ステップ720は、図7Cにより詳細に記載されている。
[0076] If, in
[0077]ステップ722で、VideoBufferがゼロ以上である場合、ビデオバッファ246におけるバッファアンダーランは、現在予想されておらず、方法はステップ724に進む。ステップ724で、AudioBufferがゼロ以上である場合、音声バッファ244におけるバッファアンダーランは、現在予想されておらず、方法はステップ726に進む。ステップ726で、利点値は、1単位のビデオデータのダウンロードを考慮に入れるために、VideoBuffer変数に追加される。ステップ728で、VideoIndexは、ビデオデータの単位のダウンロードを考慮に入れるために増分される。次のダウンロードは、VideoIndexの増分された値に対応する1単位のビデオデータについてのものである。
[0077] If VideoBuffer is greater than or equal to zero at
[0078]ステップ724に戻って、AudioBufferがゼロ以下であると再生アプリケーション236が決定した場合、音声バッファ244におけるバッファアンダーランが予想され、方法はステップ740で終了し、戻り値は「実行不可能」である。
[0078] Returning to step 724, if the playback application 236 determines that the AudioBuffer is less than or equal to zero, a buffer underrun in the
[0079]ステップ722に戻って、VideoBufferがゼロ以下であると再生アプリケーション236が決定した場合、ビデオバッファ246におけるバッファアンダーランが予想され、方法はステップ740で終了し、戻り値は「実行不可能」である。
[0079] Returning to step 722, if the playback application 236 determines that VideoBuffer is less than or equal to zero, a buffer underrun in the
[0080]ステップ714に戻って、VideoIndexが現在のコード化済みシーケンスのビデオデータの単位の合計数を表すVideoUnits以上であると再生アプリケーション236が決定した場合、再生アプリケーション236は、別の単位のビデオデータをダウンロードする必要はなく、バッファアンダーランは検出されていない。この時点で、ビデオ及び音声のコード化済みシーケンスのダウンロードを、バッファアンダーランなしで実行することができるとアプリケーション236が決定しており、方法はステップ742で終了し、戻り値は「実行可能」である。
[0080] Returning to step 714, if the playback application 236 determines that the VideoIndex is greater than or equal to VideoUnits, which represents the total number of units of video data in the current coded sequence, the playback application 236 determines that another unit of video There is no need to download data and no buffer underrun has been detected. At this point, the application 236 has determined that the download of the video and audio encoded sequence can be performed without a buffer underrun, the method ends in
[0081]ステップ712に戻って、AudioBufferがVideoBuffer未満であると再生アプリケーション236が決定した場合、ビデオバッファより少ない再生時間が音声バッファで使用可能であり、方法はステップ716に進んで、別の単位の音声データをダウンロードする影響を推定し始める。ステップ716で、AudioIndexが現在のコード化済みシーケンスの音声データの単位の合計数を表すAudioUnits未満であると再生アプリケーション236が決定した場合、再生アプリケーション236は、別の単位の音声データをダウンロードする必要があり、方法はステップ730に進む。ステップ730で、コンテンツバッファ112の現在の状態、及び主だった帯域幅の可用性が与えられると、別の単位の音声データがコンテンツサーバ130からダウンロードされる場合、再生アプリケーション236は、コンテンツバッファ112の結果として得られた状態を推定する。利点値も期間として計算、測定され、これは、1単位の音声データのダウンロードが実行される場合、音声バッファ244に追加することができる。ステップ730は、図7Dにより詳細に記載されている。
[0081] Returning to step 712, if the playback application 236 determines that the AudioBuffer is less than the VideoBuffer, less playback time is available in the audio buffer than the video buffer, and the method proceeds to step 716 and proceeds to another unit. Start estimating the impact of downloading audio data. If at
[0082]ステップ732で、VideoBufferがゼロ以上である場合、ビデオバッファ246におけるバッファアンダーランは、現在予想されておらず、方法はステップ734に進む。ステップ734で、AudioBufferがゼロ以上である場合、音声バッファ244におけるバッファアンダーランは、現在予想されておらず、方法はステップ736に進む。ステップ736で、利点値は、1単位の音声データのダウンロードを考慮に入れるために、AudioBuffer変数に追加される。ステップ738で、AudioIndexは、音声データの単位のダウンロードを考慮に入れるために増分される。次のダウンロードは、AudioIndexの増分された値に対応する1単位の音声データについてのものである。
[0082] If the VideoBuffer is greater than or equal to zero at
[0083]ステップ734に戻って、AudioBufferがゼロ以下であると再生アプリケーション236が決定した場合、音声バッファ244におけるバッファアンダーランが予想され、方法はステップ740で終了し、戻り値は「実行不可能」である。
[0083] Returning to step 734, if the playback application 236 determines that the AudioBuffer is less than or equal to zero, a buffer underrun in the
[0084]ステップ732に戻って、VideoBufferがゼロ以下であると再生アプリケーション236が決定した場合、ビデオバッファ246におけるバッファアンダーランが予想され、方法はステップ740で終了し、戻り値は「実行不可能」である。
[0084] Returning to step 732, if the playback application 236 determines that the VideoBuffer is less than or equal to zero, a buffer underrun in the
[0085]ステップ716に戻って、AudioIndexが現在のコード化済みシーケンスの音声データの単位の合計数を表すAudioUnits以上であると再生アプリケーション236が決定した場合、再生アプリケーション236は、別の単位の音声データをダウンロードする必要はなく、バッファアンダーランは検出されていない。この時点で、ビデオ及び音声のコード化済みシーケンスのダウンロードを、バッファアンダーランなしで実行することができるとアプリケーション236が決定しており、方法はステップ742で終了し、戻り値は「実行可能」である。
[0085] Returning to step 716, if the playback application 236 determines that the AudioIndex is greater than or equal to AudioUnits, which represents the total number of units of audio data in the current coded sequence, the playback application 236 determines that another unit of audio There is no need to download data and no buffer underrun has been detected. At this point, the application 236 has determined that the download of the video and audio encoded sequence can be performed without a buffer underrun, the method ends in
[0086]図7Bは、本発明の一実施形態による、図7Aにおける変数を初期化するステップ710を実行するための方法ステップ701のフロー図である。方法ステップは図1、図2、及び図3のシステムとの関係で記載されているが、方法ステップを任意の順序で実行するように構成される任意のシステムは本発明の範囲内に含まれることを当業者であれば理解されよう。この場合もまた、方法ステップ701は、図7Aのステップ710をより詳細に記載し、一実施形態において、再生アプリケーション236によって実行される。
[0086] FIG. 7B is a flow diagram of
[0087]方法は、ステップ750で開始し、AudioIndexは、現在の音声のコード化済みシーケンスの現在の再生状態を表す現在のAudioIndexに初期化される。ステップ752で、VideoIndexは、現在のビデオのコード化済みシーケンスの現在の再生状態を表す現在のVideoIndexに初期化される。ステップ754で、AudioBufferは、現在のAudioBuffer再生値に初期化される。方法は、ステップ756で終了し、VideoBufferは、現在のVideoBuffer再生値に初期化される。
[0087] The method begins at
[0088]図7Cは、本発明の一実施形態による、図7Aにおけるコンテンツバッファ112の状態を推定するステップを実行するための方法ステップ702のフロー図である。方法ステップは図1、図2、及び図3のシステムとの関係で記載されているが、方法ステップを任意の順序で実行するように構成される任意のシステムは本発明の範囲内に含まれることを当業者であれば理解されよう。この場合もまた、方法ステップ702は、図7Aのステップ720をより詳細に記載し、一実施形態において、再生アプリケーション236によって実行される。
[0088] FIG. 7C is a flow diagram of
[0089]方法は、ステップ760で開始し、再生アプリケーション236は、次の1単位のビデオデータのダウンロード時間を推定する。異なる再生ビットレートにコード化されたコード化済みシーケンスと関連しており、要求されたタイトルと関連した異なるデジタルコンテンツファイル132に含まれるビデオビットレートプロフィール452は、次の単位のビデオデータのサイズを調べるために、VideoIndexを使用してインデックスが付けられる。次の単位のビデオデータのサイズは、現在の帯域幅の可用性と直接連動して、推定ダウンロード時間を決定する。ステップ762で、再生アプリケーション236は、VideoBufferの現在の値からダウンロード時間を減算することによって、VideoBufferの値を計算する。この新しい値は、ダウンロード時間中のビデオバッファ246からのデータの推定された再生消費を表す。同様に、ステップ764で、再生アプリケーション236は、AudioBufferの現在の値からダウンロード時間を減算することによって、AudioBufferの値を計算する。
[0089] The method begins at
[0090]図7Dは、本発明の一実施形態による、図7Aにおけるコンテンツバッファ112の状態を推定するステップを実行するための方法ステップ703のフロー図である。方法ステップは図1、図2、及び図3のシステムとの関係で記載されているが、方法ステップを任意の順序で実行するように構成される任意のシステムは本発明の範囲内に含まれることを当業者であれば理解されよう。この場合もまた、方法ステップ703は、図7Aのステップ730をより詳細に記載し、一実施形態において、再生アプリケーション236によって実行される。
[0090] FIG. 7D is a flow diagram of
[0091]方法は、ステップ770で開始し、再生アプリケーション236は、次の1単位の音声データのダウンロード時間を推定する。次の単位の音声データのサイズは、現在の帯域幅の可用性と直接連動して、推定ダウンロード時間を決定する。ステップ772で、再生アプリケーション236は、VideoBufferの現在の値からダウンロード時間を減算することによって、VideoBufferの値を計算する。この新しい値は、ダウンロード時間中のビデオバッファ246からのデータの推定された再生消費を表す。同様に、ステップ774で、再生アプリケーション236は、AudioBufferの現在の値からダウンロード時間を減算することによって、AudioBufferの値を計算する。
[0091] The method begins at
[0092]本発明の一実施形態は、コンテンツプレーヤ110内のコンピュータ可読記憶媒体に格納されるプログラム製品として実装することができる。この実施形態では、コンテンツプレーヤ110は、セットトップボックスなどの組み込みコンピュータプラットフォームを備える。本発明の代替実施形態は、インターネットウェブサイト内に組み込まれた実行可能命令など、コンピュータシステム内のメモリにダウンロードされるプログラム製品として実装することができる。この実施形態では、コンテンツプレーヤ110は、コンピュータシステムを備える。
[0092] One embodiment of the present invention may be implemented as a program product stored on a computer-readable storage medium in
[0093]要するに、コンテンツプレーヤ110上でデジタルコンテンツファイルを再生するための技術が開示される。この技術は、現在使用可能な帯域幅が与えられると、特定のデジタルコンテンツファイルを特定のビットレートでうまく再生することができるかどうかを推定するステップと、主だった帯域幅状態を考慮に入れるためにビットレートを適応させるステップとを伴う。実行可能性を推定するステップは、実質的に、再生の完了に間に合うように、現在の再生位置からビデオ及び音声データの残りの単位のダウンロードをシミュレーションすることを伴う。実行可能性は、周期的に再評価され、必要に応じて、ビットレートは実行可能なビットレートまで下げられる。しかし、実行可能である場合、表示品質を増加させるために、ビットレートが増加する。
[0093] In short, techniques for playing digital content files on the
[0094]開示された技術の1つの利点は、再生ビットレート及び使用可能なダウンロード帯域幅に基づく可能なバッファアンダーランが追跡され、バッファアンダーラン状態を回避しながら、複数単位のデジタルコンテンツが可能な限り最高の画質でダウンロードされることである。さらに、再生の始まりと関連した遅延時間は、比較的低いビットレートで再生を開始し、可能な場合はいつでも、より高い再生ビットレートに適応させることによって減らされる。 [0094] One advantage of the disclosed technique is that possible buffer underruns based on playback bit rate and available download bandwidth are tracked, allowing multiple units of digital content while avoiding buffer underrun conditions It will be downloaded with the best possible image quality. Further, the delay time associated with the beginning of playback is reduced by starting playback at a relatively low bit rate and adapting to a higher playback bit rate whenever possible.
[0095]上記は本発明の実施形態を対象とするが、本発明の他の及びさらなる実施形態は、その基本的な範囲を逸脱しない範囲で考案され得る。例えば、本発明の態様は、ハードウェア若しくはソフトウェア、又はハードウェアとソフトウェアとの組み合わせに実装することができる。本発明の一実施形態を、コンピュータシステム用のプログラム製品として実装することができる。プログラム製品のプログラム(複数可)は、(本明細書に記載した方法を含む)実施形態の機能を定義し、様々なコンピュータ可読記憶媒体上に含めることができる。コンピュータ可読記憶媒体例には、それだけには限定されないが、(i)情報が永久に格納される書き込み不可の記憶媒体(例えば、CD−ROMドライブによって読み込み可能なCD−ROMディスク、フラッシュメモリ、ROMチップ、又は任意のタイプの固体不揮発性半導体メモリなど、コンピュータ内の読み取り専用記憶装置)、及び(ii)変更可能な情報が格納される書き込み可能な記憶媒体(例えば、ディスケットドライブ又はハードディスクドライブ内のフロッピーディスク、又は任意のタイプの固体ランダムアクセス半導体メモリ)を含む。本発明の機能を指示するコンピュータ可読命令を含むとき、こうしたコンピュータ可読記憶媒体は本発明の実施形態である。 [0095] While the above is directed to embodiments of the invention, other and further embodiments of the invention may be devised without departing from the basic scope thereof. For example, aspects of the invention can be implemented in hardware or software, or a combination of hardware and software. One embodiment of the present invention can be implemented as a program product for a computer system. The program product (s) define the functionality of the embodiments (including the methods described herein) and can be included on various computer-readable storage media. Examples of computer readable storage media include, but are not limited to: (i) a non-writable storage medium in which information is permanently stored (eg, a CD-ROM disk readable by a CD-ROM drive, flash memory, ROM chip) Or any type of solid state non-volatile semiconductor memory, such as a read-only storage device in a computer), and (ii) a writable storage medium in which changeable information is stored (eg, a floppy in a diskette drive or hard disk drive) Disk, or any type of solid state random access semiconductor memory). Such computer readable storage media are embodiments of the present invention when including computer readable instructions that direct the functionality of the present invention.
[0096]上記を鑑み、本発明の範囲は、以下の特許請求の範囲によって決定される。 [0096] In view of the above, the scope of the present invention is determined by the following claims.
Claims (15)
デジタルコンテンツのファイルの中の1単位又は複数単位のデジタルコンテンツを、依然として再生のためにダウンロードし、バッファに入れなければならないことを決定するステップと、
第1の単位のデジタルコンテンツのサイズ、及び使用可能なダウンロード帯域幅に基づいて、前記第1の単位のデジタルコンテンツと関連したダウンロード時間を推定するステップであり、前記第1の単位のデジタルコンテンツの前記サイズが、前記第1の単位のデジタルコンテンツがダウンロードされるデジタルコンテンツの前記ファイルに含まれる第1のコード化済みシーケンスによって決まる、ステップと、
前記推定されたダウンロード時間に基づいて、前記コンテンツバッファに格納された前記デジタルコンテンツのすべてを再生することと関連した時間を計算するステップと、
前記計算された時間が、バッファアンダーランが生じることを示すゼロ以下であるかどうかを決定するステップと、
バッファアンダーランが生じない場合、前記第1のコード化済みシーケンスから前記第1の単位のデジタルコンテンツをダウンロードすることが実行可能であることを示すステップ、又は
バッファアンダーランが生じる場合、前記第1のコード化済みシーケンスから前記第1の単位のデジタルコンテンツをダウンロードすることが実行不可能であることを示すステップと
を含む方法。 A method for determining whether digital content downloaded from a content server to a content buffer can be accessed from the content buffer for playback at a predetermined bit rate without causing a buffer underrun. And
Determining that one or more units of digital content in the digital content file must still be downloaded and buffered for playback;
Estimating a download time associated with the digital content of the first unit based on a size of the digital content of the first unit and an available download bandwidth, The size is determined by a first encoded sequence included in the file of digital content from which the first unit of digital content is downloaded;
Calculating a time associated with playing all of the digital content stored in the content buffer based on the estimated download time;
Determining whether the calculated time is less than or equal to zero indicating that a buffer underrun occurs;
A step indicating that downloading the first unit of digital content from the first encoded sequence is feasible if no buffer underrun occurs, or if a buffer underrun occurs, the first Indicating that it is not feasible to download the first unit of digital content from the encoded sequence of:
前記ビデオデータと関連した前記推定されたダウンロード時間に基づいて、前記コンテンツバッファ内のビデオバッファに格納されたすべてのビデオデータを再生することと関連した時間を計算するステップと、
前記ビデオデータと関連した前記推定されたダウンロード時間に基づいて、前記コンテンツバッファ内の音声バッファに格納されたすべての音声データを再生することと関連した時間を計算するステップと
を含む請求項4に記載の方法。 Calculating the time associated with playing all of the digital content stored in the content buffer;
Calculating a time associated with playing all video data stored in a video buffer in the content buffer based on the estimated download time associated with the video data;
And calculating a time associated with playing all audio data stored in an audio buffer in the content buffer based on the estimated download time associated with the video data. The method described.
前記ビデオバッファ内に格納されたすべてのビデオデータを再生することと関連した前記計算された時間が、ビデオバッファアンダーランが生じることを示すゼロ以下であるかどうかを決定するステップと、
前記音声バッファ内に格納されたすべての音声データを再生することと関連した前記計算された時間が、音声バッファアンダーランが生じることを示すゼロ以下であるかどうかを決定するステップと
を含む請求項5に記載の方法。 The step of determining whether the calculated time is less than or equal to zero indicating that a buffer underrun occurs;
Determining whether the calculated time associated with playing all video data stored in the video buffer is less than or equal to zero indicating that a video buffer underrun occurs;
Determining whether the calculated time associated with playing all audio data stored in the audio buffer is less than or equal to zero indicating that an audio buffer underrun occurs. 5. The method according to 5.
ビデオバッファアンダーランも音声バッファアンダーランも生じない場合、前記第1のコード化済みシーケンスから前記ビデオデータをダウンロードすることが実行可能であることを示すステップ、又は
ビデオバッファアンダーラン又は音声バッファアンダーランのいずれかが生じる場合、前記第1のコード化済みシーケンスから前記ビデオデータをダウンロードすることが実行不可能であることを示すステップ
を含む請求項6に記載の方法。 Said step of indicating
If neither video buffer underrun nor audio buffer underrun occurs, a step indicating that downloading the video data from the first encoded sequence is feasible, or video buffer underrun or audio buffer underrun 7. The method of claim 6, comprising: indicating that downloading of the video data from the first encoded sequence is not feasible if any of the following occurs:
前記1単位の音声データと関連した前記推定されたダウンロード時間に基づいて、前記コンテンツバッファ内に格納されたすべての音声データを再生することと関連した時間を計算するステップと、
前記1単位の音声データと関連した前記推定されたダウンロード時間に基づいて、前記コンテンツバッファ内に格納されたすべてのビデオデータを再生することと関連した時間を計算するステップと、
前記コンテンツバッファ内に格納された前記音声データのすべてを再生することと関連した前記計算された時間が、バッファアンダーランが生じることを示すゼロ以下であるかどうかを決定するステップと、
前記コンテンツバッファ内に格納された前記ビデオデータのすべてを再生することと関連した前記計算された時間が、バッファアンダーランが生じることを示すゼロ以下であるかどうかを決定するステップと、
バッファアンダーランが生じない場合、前記1単位の音声データをダウンロードすることが実行可能であることを示すステップ、又は
バッファアンダーランが生じる場合、前記1単位の音声データをダウンロードすることが実行不可能であることを示すステップと
をさらに含むことを特徴とする請求項4に記載の方法。 Estimating a download time associated with the unit of audio data based on the size of the unit of audio data and the available download bandwidth;
Calculating a time associated with playing all audio data stored in the content buffer based on the estimated download time associated with the unit of audio data;
Calculating a time associated with playing all video data stored in the content buffer based on the estimated download time associated with the unit of audio data;
Determining whether the calculated time associated with playing all of the audio data stored in the content buffer is less than or equal to zero indicating that a buffer underrun occurs;
Determining whether the calculated time associated with playing all of the video data stored in the content buffer is less than or equal to zero indicating that a buffer underrun occurs;
If the buffer underrun does not occur, the step indicating that the one unit of audio data can be downloaded; or if the buffer underrun occurs, the unit of audio data cannot be downloaded. The method of claim 4, further comprising the step of indicating:
デジタルコンテンツのファイルの中の1単位又は複数単位のデジタルコンテンツを、依然として再生のためにダウンロードし、バッファに入れなければならないことを決定するステップと、
第1の単位のデジタルコンテンツのサイズ、及び使用可能なダウンロード帯域幅に基づいて、前記第1の単位のデジタルコンテンツと関連したダウンロード時間を推定するステップであり、前記第1の単位のデジタルコンテンツの前記サイズが、前記第1の単位のデジタルコンテンツがダウンロードされるデジタルコンテンツの前記ファイルに含まれる第1のコード化済みシーケンスによって決まる、ステップと、
前記推定されたダウンロード時間に基づいて、前記コンテンツバッファに格納された前記デジタルコンテンツのすべてを再生することと関連した時間を計算するステップと、
前記計算された時間が、バッファアンダーランが生じることを示すゼロ以下であるかどうかを決定するステップと、
バッファアンダーランが生じない場合、前記第1のコード化済みシーケンスから前記第1の単位のデジタルコンテンツをダウンロードすることが実行可能であることを示すステップ、又は
バッファアンダーランが生じる場合、前記第1のコード化済みシーケンスから前記第1の単位のデジタルコンテンツをダウンロードすることが実行不可能であることを示すステップと
を実行することによって、コンテンツサーバからコンテンツバッファにダウンロードされたデジタルコンテンツに、バッファアンダーランを引き起こすことなく、所定のビットレートで、再生のために前記コンテンツバッファからアクセスすることができるかどうかを前記処理ユニットに決定させる命令を格納するコンピュータ可読媒体。 When executed by the processing unit,
Determining that one or more units of digital content in the digital content file must still be downloaded and buffered for playback;
Estimating a download time associated with the digital content of the first unit based on a size of the digital content of the first unit and an available download bandwidth, The size is determined by a first encoded sequence included in the file of digital content from which the first unit of digital content is downloaded;
Calculating a time associated with playing all of the digital content stored in the content buffer based on the estimated download time;
Determining whether the calculated time is less than or equal to zero indicating that a buffer underrun occurs;
A step indicating that downloading the first unit of digital content from the first encoded sequence is feasible if no buffer underrun occurs, or if a buffer underrun occurs, the first The digital content downloaded from the content server to the content buffer is buffered by performing a step indicating that downloading the first unit of digital content from the encoded sequence of A computer readable medium storing instructions that cause the processing unit to determine whether it can be accessed from the content buffer for playback at a predetermined bit rate without causing a run.
ダウンロードされたデジタルコンテンツを格納するための前記コンテンツバッファを含むメモリと、
デジタルコンテンツのファイルの中の1単位又は複数単位のデジタルコンテンツを、依然として再生のためにダウンロードし、バッファに入れなければならないことを決定し、
第1の単位のデジタルコンテンツのサイズ、及び使用可能なダウンロード帯域幅に基づいて、前記第1の単位のデジタルコンテンツと関連したダウンロード時間を推定し、前記第1の単位のデジタルコンテンツの前記サイズが、前記第1の単位のデジタルコンテンツがダウンロードされるデジタルコンテンツの前記ファイルに含まれる第1のコード化済みシーケンスによって決まり、
前記推定されたダウンロード時間に基づいて、前記コンテンツバッファに格納された前記デジタルコンテンツのすべてを再生することと関連した時間を計算し、
前記計算された時間が、バッファアンダーランが生じることを示すゼロ以下であるかどうかを決定し、
バッファアンダーランが生じない場合、前記第1のコード化済みシーケンスから前記第1の単位のデジタルコンテンツをダウンロードすることが実行可能であることを示す、又は
バッファアンダーランが生じる場合、前記第1のコード化済みシーケンスから前記第1の単位のデジタルコンテンツをダウンロードすることが実行不可能であることを示す
ように構成された、前記メモリに結合された処理ユニットと
を備えるコンテンツプレーヤデバイス。 Configured to determine whether digital content downloaded from a content server to a content buffer can be accessed from the content buffer for playback at a predetermined bit rate without causing a buffer underrun A content player device,
A memory including the content buffer for storing downloaded digital content;
Determining that one or more units of digital content in the digital content file must still be downloaded and buffered for playback;
Based on the size of the first unit of digital content and the available download bandwidth, the download time associated with the first unit of digital content is estimated, and the size of the first unit of digital content is The first unit of digital content is determined by a first encoded sequence included in the file of digital content to be downloaded;
Calculating the time associated with playing all of the digital content stored in the content buffer based on the estimated download time;
Determining whether the calculated time is less than or equal to zero indicating that a buffer underrun occurs;
If no buffer underrun occurs, it indicates that it is feasible to download the first unit of digital content from the first encoded sequence, or if a buffer underrun occurs, the first A content player device comprising: a processing unit coupled to the memory configured to indicate that downloading of the first unit of digital content from an encoded sequence is not feasible.
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US12/509,365 US8631455B2 (en) | 2009-07-24 | 2009-07-24 | Adaptive streaming for digital content distribution |
| US12/509,365 | 2009-07-24 | ||
| PCT/US2010/043114 WO2011011724A1 (en) | 2009-07-24 | 2010-07-23 | Adaptive streaming for digital content distribution |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013128908A Division JP5652971B2 (en) | 2009-07-24 | 2013-06-19 | Adaptive streaming for digital content distribution |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013500635A JP2013500635A (en) | 2013-01-07 |
| JP5302463B2 true JP5302463B2 (en) | 2013-10-02 |
Family
ID=43498420
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012521846A Active JP5302463B2 (en) | 2009-07-24 | 2010-07-23 | Adaptive streaming for digital content distribution |
| JP2013128908A Active JP5652971B2 (en) | 2009-07-24 | 2013-06-19 | Adaptive streaming for digital content distribution |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013128908A Active JP5652971B2 (en) | 2009-07-24 | 2013-06-19 | Adaptive streaming for digital content distribution |
Country Status (11)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US8631455B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP2457167B1 (en) |
| JP (2) | JP5302463B2 (en) |
| BR (1) | BR112012002182B1 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2768964C (en) |
| CL (1) | CL2012000194A1 (en) |
| CO (1) | CO6491092A2 (en) |
| DK (1) | DK2457167T3 (en) |
| IN (1) | IN2012DN00717A (en) |
| MX (1) | MX2012001100A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2011011724A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (26)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2010025686A1 (en) * | 2008-09-05 | 2010-03-11 | The Chinese University Of Hong Kong | Methods and devices for live streaming using pre-indexed file formats |
| US9060187B2 (en) | 2008-12-22 | 2015-06-16 | Netflix, Inc. | Bit rate stream switching |
| US9014545B2 (en) * | 2009-07-24 | 2015-04-21 | Netflix, Inc. | Adaptive streaming for digital content distribution |
| US8914835B2 (en) * | 2009-10-28 | 2014-12-16 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Streaming encoded video data |
| US9872057B1 (en) * | 2009-11-30 | 2018-01-16 | The Directv Group, Inc. | Method and system for accessing content in another format in a communications system |
| US9237178B2 (en) * | 2010-02-03 | 2016-01-12 | Futurewei Technologies, Inc. | Combined binary string for signaling byte range of media fragments in adaptive streaming |
| US8504713B2 (en) * | 2010-05-28 | 2013-08-06 | Allot Communications Ltd. | Adaptive progressive download |
| US9037742B2 (en) | 2011-11-15 | 2015-05-19 | International Business Machines Corporation | Optimizing streaming of a group of videos |
| US9166864B1 (en) * | 2012-01-18 | 2015-10-20 | Google Inc. | Adaptive streaming for legacy media frameworks |
| CN103425504A (en) * | 2012-05-18 | 2013-12-04 | 阿里巴巴集团控股有限公司 | Method and device for loading video files |
| JP6142488B2 (en) * | 2012-09-13 | 2017-06-07 | 株式会社Jvcケンウッド | Content playback apparatus, content playback method, and content playback program |
| TWI507022B (en) * | 2012-12-05 | 2015-11-01 | Ind Tech Res Inst | Buffer output method for multimedia stream and multimedia stream buffer module |
| US9654528B1 (en) | 2013-03-11 | 2017-05-16 | Google Inc. | Dynamic bitrate selection for streaming media |
| US10433014B2 (en) | 2014-10-28 | 2019-10-01 | Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development Lp | Media content download time |
| CN107534798A (en) * | 2015-04-22 | 2018-01-02 | Lg 电子株式会社 | Broadcast singal sends equipment, broadcasting signal receiving, broadcast singal sending method and broadcast signal received method |
| WO2017063189A1 (en) * | 2015-10-16 | 2017-04-20 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Deadline signaling for streaming of media data |
| US10433023B1 (en) * | 2015-10-27 | 2019-10-01 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Heuristics for streaming live content |
| WO2017132434A1 (en) * | 2016-01-28 | 2017-08-03 | Arris Enterprises Llc | Variable buffer handling for adaptive bitrate streaming |
| US10091559B2 (en) * | 2016-02-09 | 2018-10-02 | Disney Enterprises, Inc. | Systems and methods for crowd sourcing media content selection |
| CN108886638A (en) * | 2016-03-28 | 2018-11-23 | 索尼公司 | Transcriber and reproducting method and file creating apparatus and document generating method |
| CN108886628A (en) * | 2016-03-28 | 2018-11-23 | 索尼公司 | File creating apparatus and document generating method |
| US10735508B2 (en) * | 2016-04-04 | 2020-08-04 | Roku, Inc. | Streaming synchronized media content to separate devices |
| US10387993B2 (en) * | 2017-09-29 | 2019-08-20 | Intel Corporation | Fault-tolerant graphics display engine |
| CN107809647A (en) * | 2017-10-24 | 2018-03-16 | 深圳市创维软件有限公司 | Code check switching method, device and the storage medium of video playback |
| EP3767962A1 (en) * | 2019-07-19 | 2021-01-20 | THEO Technologies | A media client with adaptive buffer size and the related method |
| US10958947B1 (en) * | 2020-03-12 | 2021-03-23 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Content delivery of live streams with playback-conditions-adaptive encoding |
Family Cites Families (45)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5159447A (en) * | 1991-05-23 | 1992-10-27 | At&T Bell Laboratories | Buffer control for variable bit-rate channel |
| US5414455A (en) | 1993-07-07 | 1995-05-09 | Digital Equipment Corporation | Segmented video on demand system |
| US5608732A (en) * | 1993-09-01 | 1997-03-04 | Zenith Electronics Corporation | Television distribution system having virtual memory downloading |
| KR100407085B1 (en) | 1994-12-28 | 2004-03-20 | 코닌클리케 필립스 일렉트로닉스 엔.브이. | Buffer management in variable bit-rate compression systems |
| US6721952B1 (en) | 1996-08-06 | 2004-04-13 | Roxio, Inc. | Method and system for encoding movies, panoramas and large images for on-line interactive viewing and gazing |
| US6453114B2 (en) * | 1997-02-18 | 2002-09-17 | Thomson Licensing Sa | Random picture decoding |
| JPH11331792A (en) * | 1998-05-08 | 1999-11-30 | Sony Corp | Client device and server-client system |
| US6438630B1 (en) * | 1999-10-06 | 2002-08-20 | Sun Microsystems, Inc. | Scheduling storage accesses for multiple continuous media streams |
| JP2002157825A (en) * | 2000-11-21 | 2002-05-31 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Information recording device |
| US7274661B2 (en) * | 2001-09-17 | 2007-09-25 | Altera Corporation | Flow control method for quality streaming of audio/video/media over packet networks |
| US7646816B2 (en) * | 2001-09-19 | 2010-01-12 | Microsoft Corporation | Generalized reference decoder for image or video processing |
| EP1359722A1 (en) | 2002-03-27 | 2003-11-05 | BRITISH TELECOMMUNICATIONS public limited company | Data streaming system and method |
| JP2004040526A (en) * | 2002-07-04 | 2004-02-05 | Ricoh Co Ltd | System for distributing image and system for distributing and reproducing image |
| US7263129B2 (en) * | 2002-08-29 | 2007-08-28 | Sony Corporation | Predictive encoding and data decoding control |
| JP3935419B2 (en) | 2002-11-19 | 2007-06-20 | Kddi株式会社 | Video coding bit rate selection method |
| EP1465186A1 (en) | 2003-04-02 | 2004-10-06 | Deutsche Thomson-Brandt Gmbh | Method for buffering data streams read from an optical storage medium |
| US7924921B2 (en) * | 2003-09-07 | 2011-04-12 | Microsoft Corporation | Signaling coding and display options in entry point headers |
| US8345754B2 (en) * | 2003-09-07 | 2013-01-01 | Microsoft Corporation | Signaling buffer fullness |
| US7234007B2 (en) * | 2003-09-15 | 2007-06-19 | Broadcom Corporation | Adjustable elasticity FIFO buffer have a number of storage cells equal to a frequency offset times a number of data units in a data stream |
| US7818444B2 (en) * | 2004-04-30 | 2010-10-19 | Move Networks, Inc. | Apparatus, system, and method for multi-bitrate content streaming |
| JP2005333478A (en) * | 2004-05-20 | 2005-12-02 | Mitsumi Electric Co Ltd | Streaming content reproduction method and internet connecting device using the same |
| KR20060065482A (en) | 2004-12-10 | 2006-06-14 | 마이크로소프트 코포레이션 | A system and process for controlling the coding bit rate of streaming media data |
| US7480701B2 (en) | 2004-12-15 | 2009-01-20 | Microsoft Corporation | Mixed-media service collections for multimedia platforms |
| JP4643330B2 (en) * | 2005-03-28 | 2011-03-02 | ソニー株式会社 | COMMUNICATION PROCESSING DEVICE, DATA COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, COMMUNICATION PROCESSING METHOD, AND COMPUTER PROGRAM |
| JP2006279843A (en) * | 2005-03-30 | 2006-10-12 | Nippon Telegraph & Telephone West Corp | Content distribution system and content reproduction device |
| EP1872536B1 (en) | 2005-04-11 | 2008-09-10 | Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson (publ) | Technique for controlling data packet transmissions of variable bit rate data |
| US7743183B2 (en) * | 2005-05-23 | 2010-06-22 | Microsoft Corporation | Flow control for media streaming |
| JP2007036666A (en) * | 2005-07-27 | 2007-02-08 | Onkyo Corp | Contents distribution system, client, and client program |
| JP4640860B2 (en) | 2005-12-01 | 2011-03-02 | シャープ株式会社 | Communication system and communication terminal |
| US8607287B2 (en) | 2005-12-29 | 2013-12-10 | United Video Properties, Inc. | Interactive media guidance system having multiple devices |
| JP4944484B2 (en) * | 2006-04-20 | 2012-05-30 | キヤノン株式会社 | Playback apparatus, playback method, and program |
| US20080133766A1 (en) | 2006-05-05 | 2008-06-05 | Wenjun Luo | Method and apparatus for streaming media to a plurality of adaptive client devices |
| US20080062322A1 (en) | 2006-08-28 | 2008-03-13 | Ortiva Wireless | Digital video content customization |
| US7743161B2 (en) | 2006-10-10 | 2010-06-22 | Ortiva Wireless, Inc. | Digital content buffer for adaptive streaming |
| US8745676B2 (en) * | 2006-12-19 | 2014-06-03 | General Instrument Corporation | Admitting a data file into a channel |
| CN101622846B (en) | 2007-03-01 | 2013-02-27 | 艾利森电话股份有限公司 | Bit streams combination of downloaded multimedia files |
| JP4930148B2 (en) | 2007-03-29 | 2012-05-16 | ブラザー工業株式会社 | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and information processing program |
| US7706384B2 (en) * | 2007-04-20 | 2010-04-27 | Sharp Laboratories Of America, Inc. | Packet scheduling with quality-aware frame dropping for video streaming |
| JP2008293436A (en) * | 2007-05-28 | 2008-12-04 | Victor Co Of Japan Ltd | Content reception control device and content reception control program |
| US8561116B2 (en) * | 2007-09-26 | 2013-10-15 | Charles A. Hasek | Methods and apparatus for content caching in a video network |
| ES2624910T3 (en) | 2008-06-06 | 2017-07-18 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Client side sequence switching |
| KR20100009903A (en) * | 2008-07-21 | 2010-01-29 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method and apparatus for playing of contents, portable terminal device |
| US8726310B2 (en) * | 2009-02-05 | 2014-05-13 | Purplecomm Inc. | Meta channel media system control and advertisement technology |
| EP2257073A1 (en) | 2009-05-25 | 2010-12-01 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Method and device for transmitting video data |
| US9014545B2 (en) | 2009-07-24 | 2015-04-21 | Netflix, Inc. | Adaptive streaming for digital content distribution |
-
2009
- 2009-07-24 US US12/509,365 patent/US8631455B2/en active Active
-
2010
- 2010-07-23 DK DK10802981.0T patent/DK2457167T3/en active
- 2010-07-23 CA CA2768964A patent/CA2768964C/en active Active
- 2010-07-23 EP EP10802981.0A patent/EP2457167B1/en active Active
- 2010-07-23 JP JP2012521846A patent/JP5302463B2/en active Active
- 2010-07-23 IN IN717DEN2012 patent/IN2012DN00717A/en unknown
- 2010-07-23 WO PCT/US2010/043114 patent/WO2011011724A1/en active Application Filing
- 2010-07-23 BR BR112012002182-6A patent/BR112012002182B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2010-07-23 MX MX2012001100A patent/MX2012001100A/en active IP Right Grant
-
2012
- 2012-01-24 CL CL2012000194A patent/CL2012000194A1/en unknown
- 2012-01-27 CO CO12012756A patent/CO6491092A2/en not_active Application Discontinuation
-
2013
- 2013-06-19 JP JP2013128908A patent/JP5652971B2/en active Active
-
2014
- 2014-01-10 US US14/152,705 patent/US9648385B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CO6491092A2 (en) | 2012-07-31 |
| DK2457167T3 (en) | 2021-02-08 |
| US9648385B2 (en) | 2017-05-09 |
| CL2012000194A1 (en) | 2012-08-24 |
| JP2013219819A (en) | 2013-10-24 |
| US8631455B2 (en) | 2014-01-14 |
| EP2457167A4 (en) | 2015-09-02 |
| BR112012002182B1 (en) | 2020-12-08 |
| JP2013500635A (en) | 2013-01-07 |
| IN2012DN00717A (en) | 2015-06-19 |
| WO2011011724A1 (en) | 2011-01-27 |
| US20140189771A1 (en) | 2014-07-03 |
| JP5652971B2 (en) | 2015-01-14 |
| MX2012001100A (en) | 2012-06-13 |
| CA2768964C (en) | 2015-08-25 |
| EP2457167B1 (en) | 2020-12-02 |
| BR112012002182A2 (en) | 2016-05-31 |
| US20110023076A1 (en) | 2011-01-27 |
| CA2768964A1 (en) | 2011-01-27 |
| EP2457167A1 (en) | 2012-05-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5302463B2 (en) | Adaptive streaming for digital content distribution | |
| US9769505B2 (en) | Adaptive streaming for digital content distribution | |
| US9781183B2 (en) | Accelerated playback of streaming media | |
| US8997160B2 (en) | Variable bit video streams for adaptive streaming | |
| US8689267B2 (en) | Variable bit video streams for adaptive streaming | |
| US20170034233A1 (en) | Pre-Buffering Audio Streams | |
| AU2012207151A1 (en) | Variable bit video streams for adaptive streaming |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20130515 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130521 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130620 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5302463 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |