JP5155311B2 - Ultrasonic transmitting / receiving transducer housed in header of implantable medical device - Google Patents
Ultrasonic transmitting / receiving transducer housed in header of implantable medical device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5155311B2 JP5155311B2 JP2009521020A JP2009521020A JP5155311B2 JP 5155311 B2 JP5155311 B2 JP 5155311B2 JP 2009521020 A JP2009521020 A JP 2009521020A JP 2009521020 A JP2009521020 A JP 2009521020A JP 5155311 B2 JP5155311 B2 JP 5155311B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- medical device
- implantable medical
- ultrasonic transducer
- disposed
- header
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 24
- 229920002981 polyvinylidene fluoride Polymers 0.000 claims description 17
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 claims description 13
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 238000002604 ultrasonography Methods 0.000 claims description 12
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000004806 packaging method and process Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 210000002216 heart Anatomy 0.000 description 17
- 210000005241 right ventricle Anatomy 0.000 description 11
- 229910052451 lead zirconate titanate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 9
- 210000005240 left ventricle Anatomy 0.000 description 8
- 230000000747 cardiac effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 210000001147 pulmonary artery Anatomy 0.000 description 6
- 206010019280 Heart failures Diseases 0.000 description 5
- 230000017531 blood circulation Effects 0.000 description 5
- 210000000709 aorta Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 210000005245 right atrium Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- 238000002560 therapeutic procedure Methods 0.000 description 4
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 206010003119 arrhythmia Diseases 0.000 description 3
- 239000000560 biocompatible material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 210000005246 left atrium Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 230000007774 longterm Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 description 3
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004593 Epoxy Substances 0.000 description 2
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N Glucose Natural products OC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 208000037656 Respiratory Sounds Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000008827 biological function Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000009125 cardiac resynchronization therapy Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000035487 diastolic blood pressure Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000008103 glucose Substances 0.000 description 2
- NOESYZHRGYRDHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N insulin Chemical compound N1C(=O)C(NC(=O)C(CCC(N)=O)NC(=O)C(CCC(O)=O)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(NC(=O)CN)C(C)CC)CSSCC(C(NC(CO)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)NC(CC=2C=CC(O)=CC=2)C(=O)NC(CCC(N)=O)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)NC(CCC(O)=O)C(=O)NC(CC(N)=O)C(=O)NC(CC=2C=CC(O)=CC=2)C(=O)NC(CSSCC(NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC=2C=CC(O)=CC=2)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CCC(O)=O)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC=2NC=NC=2)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)CNC2=O)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(CCC(O)=O)C(=O)NC(CCCNC(N)=N)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(CC=3C=CC=CC=3)C(=O)NC(CC=3C=CC=CC=3)C(=O)NC(CC=3C=CC(O)=CC=3)C(=O)NC(C(C)O)C(=O)N3C(CCC3)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(C)C(O)=O)C(=O)NC(CC(N)=O)C(O)=O)=O)NC(=O)C(C(C)CC)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)C1CSSCC2NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(NC(=O)C(CCC(N)=O)NC(=O)C(CC(N)=O)NC(=O)C(NC(=O)C(N)CC=1C=CC=CC=1)C(C)C)CC1=CN=CN1 NOESYZHRGYRDHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WABPQHHGFIMREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N lead(0) Chemical compound [Pb] WABPQHHGFIMREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000000737 periodic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002792 vascular Effects 0.000 description 2
- 102000004877 Insulin Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090001061 Insulin Proteins 0.000 description 1
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 208000001871 Tachycardia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000007792 addition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003321 amplification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000202 analgesic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000001765 aortic valve Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000036772 blood pressure Effects 0.000 description 1
- 208000006218 bradycardia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000036471 bradycardia Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001647 drug administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012377 drug delivery Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000001174 endocardium Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002513 implantation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940125396 insulin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000001678 irradiating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001788 irregular Effects 0.000 description 1
- HFGPZNIAWCZYJU-UHFFFAOYSA-N lead zirconate titanate Chemical compound [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Ti+4].[Zr+4].[Pb+2] HFGPZNIAWCZYJU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000007726 management method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000004115 mitral valve Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000004165 myocardium Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000003199 nucleic acid amplification method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001902 propagating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000003102 pulmonary valve Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000638 stimulation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000035488 systolic blood pressure Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006794 tachycardia Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001225 therapeutic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000000591 tricuspid valve Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000005166 vasculature Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000003462 vein Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N1/00—Electrotherapy; Circuits therefor
- A61N1/18—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes
- A61N1/32—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes alternating or intermittent currents
- A61N1/36—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes alternating or intermittent currents for stimulation
- A61N1/372—Arrangements in connection with the implantation of stimulators
- A61N1/37211—Means for communicating with stimulators
- A61N1/37217—Means for communicating with stimulators characterised by the communication link, e.g. acoustic or tactile
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Acoustics & Sound (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Electrotherapy Devices (AREA)
Description
本発明は、植え込み型医療機器と組み合わせて使用されることにより、無線通信を、植え込み型医療機器と、体内に埋め込まれるリモートセンサか、または他の植え込み型医療機器との間で行なうトランスデューサに関するものである。本発明は更に詳細には、植え込み型医療機器のヘッダ内に配置されるトランスデューサに関するものである。 The present invention relates to a transducer that, when used in combination with an implantable medical device, performs wireless communication between the implantable medical device and a remote sensor implanted in the body or other implantable medical device. It is. More particularly, the present invention relates to a transducer disposed within a header of an implantable medical device.
本出願は、2006年7月21日出願の仮出願第60/820,062号の優先権を主張するものであり、2005年8月26日出願の米国特許出願第11/212,176号の一部継続出願であり、これらの出願の両方を本明細書において参照することにより、これらの出願の内容全体が本明細書に組み込まれる。
This application claims the priority of
植え込み型医療機器は多くの場合、種々の症状を治療するために使用される。植え込み型医療機器の例として、薬剤投与器具、鎮痛装置、及び心臓不整脈を治療する器具を挙げることができる。心臓不整脈を治療するために使用される植え込み型医療機器の一例が心臓ペースメーカであり、心臓ペースメーカは普通、患者の体内に埋め込まれることにより除脈(すなわち、異常に遅い心臓の拍動)を治療する。ペースメーカはパルス発生器及び複数のリード線を含み、これらのリード線は、パルス発生器と心臓との間の電気接続を形成する。植え込み型除細動器(ICD)を使用して頻脈(すなわち、異常に速い心臓の拍動)を治療する。ICDもパルス発生器及び複数のリード線を含み、これらのリード線は、電気エネルギーを心臓に供給する。パルス発生器は通常、バッテリ及び電気回路を収容するハウジングと、そしてリード線をパルス発生器に接続するヘッダと、を含む。 Implantable medical devices are often used to treat various conditions. Examples of implantable medical devices include drug administration devices, analgesic devices, and devices for treating cardiac arrhythmias. An example of an implantable medical device used to treat cardiac arrhythmias is a cardiac pacemaker, which typically treats a bradycardia (ie, an abnormally slow heart beat) by being implanted in the patient's body. To do. The pacemaker includes a pulse generator and a plurality of leads that form an electrical connection between the pulse generator and the heart. An implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) is used to treat tachycardia (ie, abnormally fast heart beats). The ICD also includes a pulse generator and a plurality of leads that supply electrical energy to the heart. A pulse generator typically includes a housing that houses a battery and electrical circuitry, and a header that connects leads to the pulse generator.
植え込み型医療機器は、心不全の治療にも有用である。心臓再同期療法(CRT)(普通、両室ペーシングとも表記される)は、心不全に対する新しい治療法であり、この治療法では、右心室及び左心室の両方を刺激して血流効率及び心拍出量を上げる。心不全及び心臓不整脈の治療は、長期植え込み型センサ(chronically implanted sensor)を使用することにより向上させることができる。例えば、圧力センサを脈管系内に配置することができれば有用である、というのは、拡張期圧が心不全患者における代償不全進展への有意な予測因子となり得るからである。圧力センサは、ペーシング治療または除細動治療の一部として使用することもできる。植え込み型医療機器と長期植え込み型センサとの間で通信することによって、センサデータを臨床医がダウンロードすることができる、またはセンサデータを使用して、植え込み型医療機器で行なう治療を変更することができる。従って、長期植え込み型センサとの通信を行なうトランスデューサを含む植え込み型医療機器が必要になる。 Implantable medical devices are also useful for the treatment of heart failure. Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), commonly referred to as biventricular pacing, is a new treatment for heart failure that stimulates both the right and left ventricles to improve blood flow efficiency and heart rate. Increase the amount. The treatment of heart failure and cardiac arrhythmias can be improved by using chronically implanted sensors. For example, it would be useful if a pressure sensor could be placed in the vasculature because diastolic pressure could be a significant predictor of decompensation progression in heart failure patients. The pressure sensor can also be used as part of a pacing therapy or a defibrillation therapy. By communicating between the implantable medical device and the long-term implantable sensor, the sensor data can be downloaded by the clinician or the sensor data can be used to change the treatment performed on the implantable medical device. it can. Accordingly, there is a need for an implantable medical device that includes a transducer that communicates with a long-term implantable sensor.
1つの実施形態による本発明は、体内組織に埋め込まれるように適合された植え込み型医療機器である。植え込み型医療機器は、ハウジングと、そしてハウジングに接続されるヘッダとを備える。キャビティはヘッダ内に配置される。超音波を伝搬周波数で送信するように適合された超音波トランスデューサはキャビティ内に配置され、そして結合表面は超音波トランスデューサと体内組織との間に配置され、かつ体内組織と音響結合する。 The present invention according to one embodiment is an implantable medical device adapted to be implanted in a body tissue. The implantable medical device includes a housing and a header connected to the housing. The cavity is disposed in the header. An ultrasound transducer adapted to transmit ultrasound at a propagation frequency is disposed within the cavity, and a coupling surface is disposed between the ultrasound transducer and the body tissue and is acoustically coupled to the body tissue.
別の実施形態によれば、本発明は体内組織に埋め込まれる植え込み型医療機器である。植え込み型医療機器はハウジングと、そしてハウジングに接続されるヘッダと、を備える。キャビティはヘッダ内に配置され、そして超音波信号を送信する手段はキャビティ内に配置される。結合表面は超音波信号を送信する手段と体内組織との間に配置され、かつ体内組織と音響結合する。 According to another embodiment, the present invention is an implantable medical device implanted in a body tissue. The implantable medical device includes a housing and a header connected to the housing. The cavity is located in the header and the means for transmitting the ultrasonic signal is located in the cavity. The coupling surface is disposed between the means for transmitting the ultrasonic signal and the body tissue and is acoustically coupled to the body tissue.
更に別の実施形態による本発明は、体内組織に埋め込まれる植え込み型医療機器である。植え込み型医療機器はハウジングと、ハウジングに接続されるヘッダと、そしてハウジングに接続されるタブと、を備える。キャビティはタブ内に配置され、そして超音波を伝搬周波数で送信するように適合された超音波トランスデューサはキャビティ内に配置される。結合表面は超音波トランスデューサと体内組織との間に配置され、かつ体内組織と音響結合する。 The invention according to yet another embodiment is an implantable medical device that is implanted in a body tissue. The implantable medical device includes a housing, a header connected to the housing, and a tab connected to the housing. A cavity is disposed in the tub, and an ultrasound transducer adapted to transmit ultrasound at a propagation frequency is disposed in the cavity. The coupling surface is disposed between the ultrasonic transducer and the body tissue and is acoustically coupled to the body tissue.
複数の実施形態が開示されるが、本発明の更に別の実施形態が存在することは、この技術分野の当業者には、以下の詳細な記載から明らかであり、以下の詳細な記載では、本発明の例示としての実施形態が示され、そして記載される。従って、図面及び詳細な記述は本質的に例示として捉えられるべきであり、本発明を制限するものとして捉えられるべきではない。 While multiple embodiments are disclosed, it will be apparent to those skilled in the art from the following detailed description that further embodiments of the present invention exist, and in the following detailed description, Illustrative embodiments of the invention are shown and described. Accordingly, the drawings and detailed description are to be regarded as illustrative in nature and not as restrictive on the present invention.
本発明は種々の変形物及び代替形態に変更することができるが、特定の実施形態が例示として図面に示されており、そして以下に詳細に記載される。しかしながら、本発明を、記載される特定の実施形態に制限しようと意図するのではない。そうではなく、本発明は、全ての変形物、等価物、及び代替物を、添付の請求項に規定される本発明の技術的範囲に含まれるものとして包含するものである。 While the invention is susceptible to various modifications and alternative forms, specific embodiments have been shown by way of example in the drawings and are described in detail below. However, it is not intended that the invention be limited to the specific embodiments described. On the contrary, the invention is intended to cover all modifications, equivalents, and alternatives as falling within the scope of the invention as defined by the appended claims.
図1は、植え込み型医療機器(IMD)10の透視図である。IMD10はパルス発生器12と、そして心臓リード線14と、を含む。リード線14は、電気信号を心臓16とパルス発生器12との間で伝送するように機能する。リード線14の近位端18はパルス発生器12に接続され、そして遠位端20は心臓16に接続される。リード線14は、リード近位端18からリード遠位端20に延びるリード線本体17を含む。
FIG. 1 is a perspective view of an implantable medical device (IMD) 10. The IMD 10 includes a
心臓16は、右心房22と、右心室24と、そして肺動脈26と、を含む。三尖弁28は右心房22と右心室24との間に位置し、かつ右心房22から右心室24への血流を制御する。肺動脈弁30は右心室24と肺動脈26との間に位置し、かつ右心室24から肺動脈26への血流を制御する。心臓16は更に、左心房32と、左心室34と、そして大動脈36と、を含む。僧帽弁38は左心房32と左心室34との間に位置し、かつ左心房32から左心室34への血流を制御する。大動脈弁40は左心室34と大動脈36との間に位置し、かつ左心室34から大動脈36への血流を制御する。図示の実施形態では、IMD10は一つのリード線14を含むが、他の実施形態では、IMD10は複数のリード線14を含む。例えば、IMD10は、電気信号をパルス発生器12と左心室34との間で伝送するように適合された第1リード線14と、そして電気信号をパルス発生器12と右心室24との間で伝送するように適合された第2リード線14とを含む。
The
図1に示す実施形態では、螺旋電極42が右心室24の心内膜43を貫通し、そして心臓16の心筋44に埋め込まれる。上記のように配置される場合、電極42を使用することにより、心臓16の電気的活動を検出する、または刺激パルスを右心室24に印加することができる。他の実施形態では、本発明の心臓リード線14は、この技術分野では公知の如く、心臓16の他のいずれかの部分に埋め込むこともできる。例えば、リード線14は、右心房22、右心室24、肺動脈26、左心室34に、または冠状静脈に埋め込むことができる。1つの実施形態では、IMD10は複数の電極42を含み、これらの電極は、電気的活動を検出し、そして/または治療を心臓16の左側及び右側に、または心臓16の両側に行なうように配置される。1つの実施形態では、リード線14は心外膜リード線とすることができ、この場合、電極42が心外膜45を貫通する。図1に示すIMD10は心臓ペースメーカであるが、他の実施形態では、IMD10は体内埋め込みに適する他のいずれかの医療器具を含むことができる。
In the embodiment shown in FIG. 1, a spiral electrode 42 penetrates the endocardium 43 of the
図1に示すように、遠隔操作用器具46は肺動脈26内に配置される。別の構成として、器具46は右心室24内、大動脈36内に配置することができる、または心臓16内または脈管系内の、或いは心臓16または脈管系の近傍の他のいずれかの位置に配置することができる。器具46は圧力センサを備えることができる、または別の構成として、ボリュームセンサを備えることができ、或いは最高血圧または最低血圧のような他のいずれかの心臓パラメータを検出するか、或いは血圧勾配のような心臓パラメータの微分を計算することができる。他の実施形態では、器具46は、所望の生物学的パラメータを検出するために適合する体内のいずれの位置にも配置することができる。例えば、器具46を使用して、グルコース濃度のような他の生物学的機能を検出するか、またはモニタリングすることができる。図1に示す器具46は、肺動脈26内の圧力を検出するために使用されるリモート圧力センサとすることができる。検出された圧力を利用して、心不全患者の代償不全を予測する、またはペーシング治療または除細動治療を最適化することができる。圧力を測定するために適合されたリモート圧力センサ46の一例が、Wolinskyらによる米国特許第6,764,446号に開示されている。
As shown in FIG. 1, the
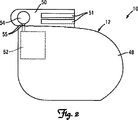
図2は、図1のパルス発生器12の1つの実施形態の正面図を示している。図2に示すように、パルス発生器12はハウジング48と、そしてヘッダ50と、を含む。ハウジング48は制御回路52を含む。ヘッダ50は、リード線14またはリード線群14との接続を行なうコネクタ51を含む。超音波トランスデューサ54はヘッダ50内に配置され、ヘッダ50は制御回路52に電気フィードスルー55を介して接続される。1つの実施形態では、超音波トランスデューサ54は、約20キロヘルツ超の周波数の超音波信号を送信し、そして受信する。別の実施形態では、超音波トランスデューサ54は、約40キロヘルツの周波数の超音波信号を送信し、そして受信する。図2に示す超音波トランスデューサ54は円形形状を有するが、別の構成として、方形、矩形、三角形、または不規則形状のような他のいずれかの形状を有することができる。超音波トランスデューサ54はいずれかの圧電材料を含むことができる。1つの実施形態では、超音波トランスデューサ54は、二フッ化ポリビニリデン(PVDF)材料を含むことができる。PVDF材料により構成される一つの超音波トランスデューサが、Todaらによる米国特許出願公開公報第2002/0036446号に開示されており、この特許文献をここで参照することにより、当該文献の内容全体が本明細書に組み込まれる。別の実施形態では、超音波トランスデューサ54はジルコン酸チタン酸鉛(PZT)材料を含むことができる。PZT材料により構成される一つの超音波トランスデューサが、Todaによる米国特許出願公開公報第2002/0027400号に開示されており、この特許文献をここで参照することにより、当該文献の内容全体が本明細書に組み込まれる。別の構成として、超音波トランスデューサ54は、容量型超微細加工超音波トランスデューサ(cMUT)またはこの技術分野で公知の他のいずれかのトランスデューサを含むことができる。
FIG. 2 shows a front view of one embodiment of the
植え込み型医療機器10の1つの実施形態の断面図を図3に示す。図3に示す実施形態では、超音波トランスデューサ54は、PVDFトランスデューサを含む。キャビティ56がヘッダ50内に配置される。セラミック基板またはシリコン基板58がキャビティ56の後壁60から屹立して配置される。基板58は開口62を含み、そしてPVDF材料64が開口62の上に配置され、かつ開口62を覆う。PVDF材料64は基板58にエポキシまたは医用接着剤を使用して接着させることができる。1つの実施形態では、PVDF材料64は、2つのPVDF材料層を有するバイモルフ構造を構成することができる。キャビティ56には水、油、超音波ジェル、超音波を伝達するように適合された他のいずれかの媒質または材料を充填することができる。1つの実施形態では、キャビティ56には、超音波を伝達するように適合されたいずれかの生体適合材料を充填することができる。
A cross-sectional view of one embodiment of the implantable
結合表面66がキャビティ56の上に配置され、かつキャビティ56を覆う。1つの実施形態では、結合表面66は、超音波圧力をキャビティ56の媒質と体内組織との間で伝搬させる性質を持ついずれかの表面を含む。1つの実施形態では、結合表面66は、薄いチタンダイヤフラムを含むことができる。他の実施形態では、結合表面66は、超音波圧力をキャビティ56の媒質と体内組織との間で伝搬させる機能を実現する寸法を有するいずれかの生体適合材料を含む。超音波トランスデューサにおける使用に適合されたPVDF材料の一例は、米国ペンシルバニア州19403ノーリスタウンの950 Forge Avenueを所在地とするMeasurement Specialties, Inc.から入手することができる。
A binding
図4は、図2の植え込み型医療機器の別の実施形態を示している。この実施形態では、超音波トランスデューサ54はPZT材料68を含む。キャビティ56がヘッダ50内に配置され、そして結合表面66によって覆われる。PZT材料68は結合表面66に接続される。PZT材料68は結合表面66にエポキシまたはいずれかの医用接着剤を使用して接着させることができる。キャビティ56には空気、窒素、または他のいずれかのガスを充填することができる。別の構成として、キャビティ56は真空とすることができる。図4に示す実施形態では、結合表面66は、超音波伝搬周波数で共振する共振表面を含む。1つの実施形態では、この周波数は20キロヘルツ超である。別の実施形態では、この周波数は約40キロヘルツである。
FIG. 4 shows another embodiment of the implantable medical device of FIG. In this embodiment,
超音波トランスデューサ54の別の構造を図5に示す。この実施形態では、超音波トランスデューサ54は包装体70の内部に配置される。包装体70はヘッダ内50に配置されるキャビティ56内に挿入することができる。包装体70はチタンまたは他のいずれかの適切な材料を含むことができる。結合表面66は包装体70を覆って配置される。包装体70の内部の超音波トランスデューサ54構造は、図3及び4に関して議論した構造を含むことができる、またはこの技術分野で公知の他のいずれかの超音波トランスデューサ構造を含むことができる。包装体70は円筒形状を図5では有するが、超音波トランスデューサ54の形状に丁度合うように適合されたいずれかの形状を有することができる。
Another structure of the
図6は、本発明の植え込み型医療機器10の別の実施形態を示している。この実施形態では、複数の超音波トランスデューサ54がヘッダ50内に配置される。超音波トランスデューサ54は、図3、図4に関して、または図3及び4のいずれかの組み合わせに関して議論した超音波トランスデューサを含むことができる。複数の超音波トランスデューサ54は、cMUTトランスデューサまたはこの技術分野で公知の他の種類の超音波トランスデューサを含むこともできる。超音波トランスデューサ54はヘッダ50の複数の表面に配置することができる。6個の円形超音波トランスデューサ54を図6に示しているが、どのような個数のいずれかの形状のトランスデューサも使用することができる。必要に応じて、超音波トランスデューサ54は包装体70を含むことができる。このような構成によって、超音波トランスデューサ54は並列に作動することができるので、共振特性及び増幅特性が向上する。
FIG. 6 shows another embodiment of the implantable
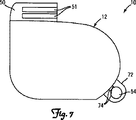
図7は、植え込み型医療機器10の更に別の実施形態の正面図を示している。この実施形態では、超音波トランスデューサ54はタブ72内に配置され、タブ72はハウジング48に取り付けられ、かつ制御回路にフィードスルー74を介して接続される。タブ72はヘッダ50内に使用される材料と同じ材料を含むことができる。1つの実施形態では、タブ72はTecothane(テコタン)を含む。別の構成として、タブ72は、チタンのようないずれかの生体適合材料を含むことができ、そしてハウジング48に溶接によって接合する、またはハウジング48に取り付けることができる。タブ72は、複数の超音波トランスデューサ54を含むことができる。IMD10は複数のタブ72を含むことができる。超音波トランスデューサ54は、ヘッダ50内に、タブまたはタブ群72内に、或いはヘッダ50内、かつタブまたはタブ群72内に配置することができる。超音波トランスデューサ54は、PZTトランスデューサ、PVDFトランスデューサ、cMUTトランスデューサのいずれかの組み合わせ、またはこの技術分野で公知の他のいずれかのトランスデューサを含むことができる。
FIG. 7 shows a front view of yet another embodiment of the implantable
図8は、植え込み型医療機器10を模式的に示している。図示のように、パルス発生器12はハウジング48と、そしてヘッダ50と、を含む。ハウジング48は、制御回路52と、メモリ80と、バッテリ82と、受信機84と、そして送信機86と、を含む。超音波トランスデューサ54はヘッダ50内に配置され、かつ送信機86及び受信機84に電気的に接続される。送信機86、受信機84、及びメモリ80は制御回路52に接続される。制御回路52にはバッテリ82から電源が供給される。
FIG. 8 schematically shows the implantable
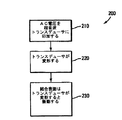
図9は、図1の植え込み型医療機器10を使用して超音波信号を送信する例示としての方法200を示すフローチャートである。制御回路52は送信機86に指示して伝搬周波数のAC電圧を超音波トランスデューサ54に印加させる(ブロック210)。この電圧によって超音波トランスデューサ54が伝搬周波数で周期的に変形する(ブロック220)。この周期的な変形によって、結合表面66が伝搬周波数で振動するので、超音波信号が組織を伝搬周波数で通過する(ブロック230)。1つの実施形態では、超音波トランスデューサ54はPVDF材料64を含み、そして結合表面66はダイヤフラムを含み、ダイヤフラムの往復動によって超音波がPVDF材料64から外部組織に伝搬する。別の実施形態では、超音波トランスデューサ54はPZT材料58を含み、そして結合表面66は、伝搬周波数で共振する共振表面を含む。
FIG. 9 is a flowchart illustrating an
図10は、図1の植え込み型医療機器を使用して超音波信号を受信する例示としての方法300を示すフローチャートである。超音波信号を結合表面66に照射することにより、結合表面が伝搬周波数で振動する(ブロック310)。1つの実施形態では、超音波トランスデューサ54はPVDF材料64を含み、そして結合表面66はダイヤフラムを含み、ダイヤフラムの往復動によって超音波が外部組織からPVDF材料64に伝搬する。別の実施形態では、超音波トランスデューサ54はPZT材料58を含み、そして結合表面66は、伝搬周波数で共振する共振表面を含む。結合表面66が振動することによって、超音波トランスデューサ54が周期的に変形する(ブロック320)。この周期的な変形によって、電圧変化または電流変化が超音波トランスデューサ54に伝搬周波数で発生し、この変化が受信機84によって検出され、そして制御回路52によって処理される(ブロック330)。図9及び10に示す態様で、超音波トランスデューサ54を使用することにより、信号を植え込み型医療機器10からリモートセンサ46に送信し、そして信号をリモートセンサ46から受信することができる。
FIG. 10 is a flowchart illustrating an
本発明を、ペースメーカ及び除細動器のような植え込み型医療機器に関して説明してきたが、本発明は、インスリンポンプ、神経刺激装置、薬剤投与システム、疼痛管理システム、心拍センサまたは肺音センサのような他のいずれかの植え込み型医療機器に、或いは他のいずれかの埋め込み可能な医療器具における使用に適合させることができる。遠隔操作用器具46は、治療を行なうように適合された、または生物学的機能をモニタリングするように適合された、圧力センサ、グルコース濃度モニタ、肺音センサ、ボリュームセンサ、衛星を介してデータ伝送を行なうペーシング器具、または他のいずれかの遠隔操作型検出器または治療用器具のようないずれかの種類の長期埋め込み型機器またはリモートセンサを含むことができ、そして所望の生物学的パラメータを検出する、または治療を行なうために適合する体内のあらゆる部位に配置することができる。複数の遠隔操作用器具46は体内のどこにでも、そして互いに、かつIMD10と無線通信するように埋め込むことができる。
Although the present invention has been described with respect to implantable medical devices such as pacemakers and defibrillators, the present invention can be applied to insulin pumps, neurostimulators, drug delivery systems, pain management systems, heart rate sensors or lung sound sensors. It can be adapted for use in any other implantable medical device or in any other implantable medical device.
種々の変更及び追加を、議論した例示としての実施形態に対して、本発明の技術範囲から逸脱しない限り行なうことができる。例えば、上に説明した実施形態は特定の特徴に関して記載されているが、本発明の技術範囲には、複数の特徴の異なる組み合わせを有する実施形態、及び記載の特徴の全てを含む訳ではない実施形態が含まれる。従って、本発明の技術範囲は、このような代替物、変形物、及び変更物の全てを、請求項の全ての等価物を含む請求項の範囲に含まれるものとして包含するものである。 Various changes and additions can be made to the exemplary embodiments discussed without departing from the scope of the present invention. For example, although the embodiments described above have been described with respect to particular features, the scope of the invention includes embodiments having different combinations of features and implementations that do not include all of the described features. Includes form. Accordingly, the scope of the invention includes all such alternatives, modifications, and variations as if they fall within the scope of the claims, including all equivalents of the claims.
Claims (9)
ハウジングと、前記ハウジングに接続されるヘッダと、
前記ヘッダ内に配置されるキャビティと、
前記キャビティ内に配置され、ダイヤフラムを含む結合表面を形成する壁を有する包装体と、
前記包装体内に配置され、かつ超音波を伝搬周波数で送信するように適合される超音波トランスデューサであって、二フッ化ポリビニリデン(PVDF)材料を含む前記超音波トランスデューサと、
前記トランスデューサを前記伝搬周波数で駆動して前記トランスデューサから受信した信号を処理することによりリモートデバイスと通信するように構成された制御回路とを備え、
前記ダイヤフラムは、前記超音波トランスデューサと体内組織との間に配置され、前記ダイヤフラムは、20キロヘルツを超える共振周波数を有し、前記ダイヤフラムは、体内組織と音響結合される、植え込み型医療機器。An implantable medical device that is implanted in a body tissue,
A housing and a header connected to the housing;
A cavity disposed in the header;
A package having a wall disposed within the cavity and forming a binding surface comprising a diaphragm;
Wherein arranged in the packaging body, and an ultrasonic transducer adapted to transmit ultrasound propagation frequencies, said ultrasonic transducer comprising a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) material,
A control circuit configured to communicate with a remote device by driving the transducer at the propagation frequency and processing a signal received from the transducer;
The diaphragm, the disposed between the ultrasonic transducer and the body tissue, the diaphragm has a resonant frequency of greater than 20 kilohertz, said diaphragm body tissues and Ru are acoustically coupled, planting Ekomi medical device .
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US82006206P | 2006-07-21 | 2006-07-21 | |
| US60/820,062 | 2006-07-21 | ||
| PCT/US2007/073989 WO2008011570A1 (en) | 2006-07-21 | 2007-07-20 | Acoustic communication transducer in implantable medical device header |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009544365A JP2009544365A (en) | 2009-12-17 |
| JP2009544365A5 JP2009544365A5 (en) | 2010-07-22 |
| JP5155311B2 true JP5155311B2 (en) | 2013-03-06 |
Family
ID=38786994
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009521020A Expired - Fee Related JP5155311B2 (en) | 2006-07-21 | 2007-07-20 | Ultrasonic transmitting / receiving transducer housed in header of implantable medical device |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2043738A1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP5155311B2 (en) |
| AU (1) | AU2007275231B2 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2008011570A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20030036746A1 (en) | 2001-08-16 | 2003-02-20 | Avi Penner | Devices for intrabody delivery of molecules and systems and methods utilizing same |
| JP5121011B2 (en) | 2004-11-24 | 2013-01-16 | レモン メディカル テクノロジーズ リミテッド | Implantable medical device incorporating an acoustic transducer |
| US7742815B2 (en) | 2005-09-09 | 2010-06-22 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Using implanted sensors for feedback control of implanted medical devices |
| US7955268B2 (en) | 2006-07-21 | 2011-06-07 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Multiple sensor deployment |
| EP2043740A2 (en) | 2006-07-21 | 2009-04-08 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Ultrasonic transducer for a metallic cavity implanted medical device |
| EP2162185B1 (en) | 2007-06-14 | 2015-07-01 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Multi-element acoustic recharging system |
| US8725260B2 (en) | 2008-02-11 | 2014-05-13 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc | Methods of monitoring hemodynamic status for rhythm discrimination within the heart |
| US8369960B2 (en) * | 2008-02-12 | 2013-02-05 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Systems and methods for controlling wireless signal transfers between ultrasound-enabled medical devices |
| DE102008024857A1 (en) * | 2008-05-23 | 2009-11-26 | Biotronik Crm Patent Ag | Wireless feedthrough for medical implants |
| JP5465252B2 (en) | 2008-10-10 | 2014-04-09 | カーディアック ペースメイカーズ, インコーポレイテッド | System and method for determining cardiac output using pulmonary artery pressure measurements |
| EP3191233B1 (en) * | 2014-09-11 | 2022-11-23 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Wide band through-body ultrasonic communication system |
| US11678897B2 (en) | 2021-01-07 | 2023-06-20 | Medtronic, Inc. | Surgical system and methods |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3831809A1 (en) * | 1988-09-19 | 1990-03-22 | Funke Hermann | DEVICE DETERMINED AT LEAST PARTLY IN THE LIVING BODY |
| US6307302B1 (en) | 1999-07-23 | 2001-10-23 | Measurement Specialities, Inc. | Ultrasonic transducer having impedance matching layer |
| US6321428B1 (en) | 2000-03-28 | 2001-11-27 | Measurement Specialties, Inc. | Method of making a piezoelectric transducer having protuberances for transmitting acoustic energy |
| US6654638B1 (en) * | 2000-04-06 | 2003-11-25 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Ultrasonically activated electrodes |
| US6628989B1 (en) * | 2000-10-16 | 2003-09-30 | Remon Medical Technologies, Ltd. | Acoustic switch and apparatus and methods for using acoustic switches within a body |
| US7273457B2 (en) * | 2000-10-16 | 2007-09-25 | Remon Medical Technologies, Ltd. | Barometric pressure correction based on remote sources of information |
| US6764446B2 (en) | 2000-10-16 | 2004-07-20 | Remon Medical Technologies Ltd | Implantable pressure sensors and methods for making and using them |
| US7610092B2 (en) * | 2004-12-21 | 2009-10-27 | Ebr Systems, Inc. | Leadless tissue stimulation systems and methods |
| US7489967B2 (en) * | 2004-07-09 | 2009-02-10 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Method and apparatus of acoustic communication for implantable medical device |
| JP5121011B2 (en) * | 2004-11-24 | 2013-01-16 | レモン メディカル テクノロジーズ リミテッド | Implantable medical device incorporating an acoustic transducer |
-
2007
- 2007-07-20 EP EP07799739A patent/EP2043738A1/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2007-07-20 JP JP2009521020A patent/JP5155311B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2007-07-20 AU AU2007275231A patent/AU2007275231B2/en not_active Ceased
- 2007-07-20 WO PCT/US2007/073989 patent/WO2008011570A1/en active Application Filing
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2043738A1 (en) | 2009-04-08 |
| AU2007275231A1 (en) | 2008-01-24 |
| AU2007275231B2 (en) | 2010-09-02 |
| JP2009544365A (en) | 2009-12-17 |
| WO2008011570A1 (en) | 2008-01-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5155311B2 (en) | Ultrasonic transmitting / receiving transducer housed in header of implantable medical device | |
| US7570998B2 (en) | Acoustic communication transducer in implantable medical device header | |
| US9095284B2 (en) | Distance measurement using implantable acoustic transducers | |
| US7615012B2 (en) | Broadband acoustic sensor for an implantable medical device | |
| US8548592B2 (en) | Ultrasonic transducer for a metallic cavity implanted medical device | |
| US7912548B2 (en) | Resonant structures for implantable devices | |
| US9731141B2 (en) | Multi-element acoustic recharging system | |
| JP4931809B2 (en) | Acoustic communication system for implantable medical devices | |
| US7558631B2 (en) | Leadless tissue stimulation systems and methods | |
| US7914452B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for controlling cardiac therapy using ultrasound transducer | |
| WO2007027940A2 (en) | Methods and systems for heart failure prevention and treatments using ultrasound and leadless implantable devices | |
| US8784310B2 (en) | Vascular pressure sensor with electrocardiogram electrodes | |
| US8825161B1 (en) | Acoustic transducer for an implantable medical device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100604 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100604 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20120302 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120508 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120808 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20121113 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20121206 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20151214 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5155311 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |