JP5082940B2 - Disaster observation system and disaster analysis program - Google Patents
Disaster observation system and disaster analysis program Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5082940B2 JP5082940B2 JP2008058609A JP2008058609A JP5082940B2 JP 5082940 B2 JP5082940 B2 JP 5082940B2 JP 2008058609 A JP2008058609 A JP 2008058609A JP 2008058609 A JP2008058609 A JP 2008058609A JP 5082940 B2 JP5082940 B2 JP 5082940B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- disaster
- pulse length
- unit
- observation
- detected
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A10/00—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE at coastal zones; at river basins
- Y02A10/40—Controlling or monitoring, e.g. of flood or hurricane; Forecasting, e.g. risk assessment or mapping
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A50/00—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE in human health protection, e.g. against extreme weather
Landscapes
- Emergency Alarm Devices (AREA)
- Alarm Systems (AREA)
Description
この発明は、災害観測システムおよび災害解析プログラムに関し、特に、災害の検知手段を多数設置した場合でも、維持管理工数の増大を招くことなく、災害の発生位置を正確に特定できる災害観測システムおよび災害解析プログラムに関する。 The present invention relates to a disaster observation system and a disaster analysis program, and in particular, even when a large number of disaster detection means are installed, a disaster observation system and a disaster that can accurately specify a disaster occurrence position without causing an increase in maintenance man-hours It relates to an analysis program.
従来、災害の発生状況を遠隔地で把握するためのシステムが知られている。例えば、潮位を観測する装置が、観測データを上空の衛星経由で遠隔の基地局へ電波で送信し、観測データを受信した基地局が、津波に関する警告の発信等を行う技術が知られている。 Conventionally, a system for grasping the occurrence of a disaster at a remote place is known. For example, a technology is known in which a device that observes tide levels transmits observation data by radio waves to a remote base station via a satellite in the sky, and the base station that receives the observation data transmits a tsunami warning or the like. .
しかしながら、上記の従来技術のように電波を用いて情報を送信することとした場合、送信された電波そのものから発信元の位置を特定することができないため、災害の発生状況を検知する装置を多数設置することが困難であるという問題があった。 However, when information is transmitted using radio waves as in the prior art described above, since the location of the transmission source cannot be specified from the transmitted radio waves themselves, there are many devices that detect the occurrence of disasters. There was a problem that it was difficult to install.
例えば、火災の発生を検知し、電波で通知する装置を多数の施設に設置した場合、その装置からの通知を消防署等が受信しても、受信した電波そのものからは、どこに設置した装置からの通知であるかを特定できないため、迅速な対処をとることができないおそれがあった。 For example, when a device that detects the occurrence of a fire and notifies by radio waves is installed in many facilities, even if a fire department etc. receives a notification from that device, the received radio wave itself is Since it is not possible to identify whether the notification is a notification, there is a possibility that a prompt action cannot be taken.
装置の識別番号と設置場所の対応を予めデータベースに登録しておき、装置が発信する情報に識別番号を含めることとすれば、通知先において通知元の装置を特定することが可能になるが、災害の発生状況を検知する装置を多数設置するほど、データベースの維持管理に要する工数が増大してしまう。 If the correspondence between the identification number of the device and the installation location is registered in the database in advance and the identification number is included in the information transmitted by the device, the notification source device can be specified at the notification destination. The more devices that detect the occurrence of a disaster, the more man-hours required for database maintenance.
この発明は、上述した従来技術による問題点を解消するためになされたものであり、災害の検知手段を多数設置した場合でも、維持管理工数の増大を招くことなく、災害の発生位置を正確に特定できる災害観測システムおよび災害解析プログラムを提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made to solve the above-described problems caused by the prior art, and even when a large number of disaster detection means are installed, the occurrence location of the disaster can be accurately determined without increasing the maintenance man-hours. The objective is to provide a disaster observation system and disaster analysis program that can be identified.
上述した課題を解決し、目的を達成するため、本願の開示する災害観測システムは、一つの態様において、災害の発生状況を観測する災害観測システムであって、災害の発生を検知し、検知した災害を示す信号を、波長の異なる2種類の光線を同時に用いて上空に送信する災害検知手段と、前記災害検知手段が送信する信号を上空で撮影する災害観測手段と、前記災害観測手段の撮影によって得られた画像データから前記2種類の光線が同時に発射されている位置を特定し、該位置から送信されている信号が表す災害の種別を判定する災害解析手段とを含む。 In order to solve the above-described problems and achieve the object, the disaster observation system disclosed in the present application is a disaster observation system that observes the occurrence of a disaster in one aspect, and detects and detects the occurrence of a disaster. Disaster detection means for transmitting a signal indicating a disaster to the sky using two types of light beams having different wavelengths simultaneously, disaster observation means for imaging a signal transmitted by the disaster detection means in the sky, and imaging of the disaster observation means And a disaster analysis unit that identifies a position at which the two types of light beams are simultaneously emitted from the image data obtained by the above and determines a type of disaster represented by a signal transmitted from the position.
この態様によれば、災害検知手段が、検知した災害に関する情報を、光線を用いて上空に送信し、これを上空から撮影した画像データに基づいて災害の発生場所を判定することとしたので、災害検知手段を多数設置した場合でも、各災害検知手段の識別番号と位置とを集中管理するといった工数を要することなく、災害の発生位置を正確に特定できる。 According to this aspect, the disaster detection means transmits information about the detected disaster to the sky using light rays, and determines the location of the disaster based on the image data taken from the sky. Even when a large number of disaster detection means are installed, it is possible to accurately specify the disaster occurrence position without requiring man-hours such as centralized management of identification numbers and positions of each disaster detection means.
また、本願の開示する災害解析プログラムは、一つの態様において、災害を検知した災害検知手段が、波長の異なる2種類の光線を同時に用いて上空に送信した信号を上空で撮影して得られた画像データに基づいて、災害の発生状況を解析する災害解析プログラムであって、前記画像データから、前記波長の異なる2種類の光線が同時に発射されている位置を検出する光源検出手順と、前記光源検出手順から送信されている信号が表す災害の種別を判定する災害種別解析手順とをコンピュータに実行させる。 Further, the disaster analysis program disclosed in the present application is obtained in one aspect by capturing, in the sky, a signal transmitted by the disaster detection means that detects the disaster using the two types of light beams having different wavelengths simultaneously. A disaster analysis program for analyzing a disaster occurrence state based on image data, the light source detection procedure for detecting a position where two types of light beams having different wavelengths are simultaneously emitted from the image data, and the light source Causing the computer to execute a disaster type analysis procedure for determining the type of disaster represented by the signal transmitted from the detection procedure.
この態様によれば、災害検知手段が光線を用いて上空に送信した検知した災害に関する情報を上空から撮影して得られた画像データに基づいて災害の発生場所を判定することとしたので、災害検知手段を多数設置した場合でも、各災害検知手段の識別番号と位置とを集中管理するといった工数を要することなく、災害の発生位置を正確に特定できる。 According to this aspect, the disaster occurrence means determines the location of the disaster based on the image data obtained by photographing the information about the detected disaster transmitted from the sky using light rays. Even when a large number of detection means are installed, the disaster occurrence position can be accurately specified without requiring man-hours such as centralized management of identification numbers and positions of the disaster detection means.
なお、上記の災害観測システムおよび災害解析プログラムの構成要素、表現または構成要素の任意の組合せを、方法、装置、システム、コンピュータプログラム、記録媒体、データ構造などに適用したものも上述した課題を解決するために有効である。 In addition, the above-mentioned problem can be solved by applying any combination of the constituent elements, expressions, or constituent elements of the disaster observation system and disaster analysis program to methods, apparatuses, systems, computer programs, recording media, data structures, and the like. It is effective to do.
本願の開示する災害観測システムおよび災害解析プログラムの一つの態様によれば、災害の検知手段を多数設置した場合でも、維持管理工数の増大を招くことなく、災害の発生位置を正確に特定できるという効果を奏する。 According to one aspect of the disaster observation system and the disaster analysis program disclosed in the present application, even when a large number of disaster detection means are installed, the occurrence location of the disaster can be accurately identified without increasing the maintenance man-hours. There is an effect.
以下に添付図面を参照して、本発明に係る災害観測システムおよび災害解析プログラムの好適な実施の形態を詳細に説明する。 Exemplary embodiments of a disaster observation system and a disaster analysis program according to the present invention will be described below in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
まず、本実施例に係る災害観測システムの全体構成について説明する。図1は、本実施例に係る災害観測システムの全体構成を示す図である。同図に示すように、本実施例に係る災害観測システムは、建物11や電柱12等に設置された複数の災害検知装置100と、後述する災害観測装置200を搭載する飛行船20と、通信衛星30と、後述する災害解析装置400が設置される災害対策センタ40とを含む。
First, the overall configuration of the disaster observation system according to the present embodiment will be described. FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating the overall configuration of the disaster observation system according to the present embodiment. As shown in the figure, the disaster observation system according to this embodiment includes a plurality of
災害検知装置100は、地上における災害の発生状況を検知し、検知結果に応じた信号を、波長の異なる2種類の光線を用いて、上空へ送信する。波長の異なる2種類の光線を用いることにより、航空障害灯等の他の光源との区別が可能になるとともに、様々な条件下においても信号の検出が容易になる。例えば、可視光線と赤外光線を用いることとすれば、日中は赤外光線により、夜間は可視光線により、信号の検出が行い易くなる。
The
飛行船20は、地震等の災害が発生した場合に、被災地へ派遣される。近年の飛行船は、性能改善により時速130km程度の速度で飛行が可能になっており、3時間以内に被災地に到着すればよいこととすれば、5機程度の飛行船で日本全国をカバーすることができる。飛行船20は、被災地に到着すると、地上数100mから数1000mの高度に長時間静止し、地上の状況を観測する。
The
飛行船20が搭載する災害観測装置200は、撮像装置を用いて、観測域1内の地形や構築物とともに、災害検知装置100が送信する信号を撮影し、画像データを生成する。災害観測装置200は、撮影した画像データを、通信衛星30を経由して、災害対策センタ40へ送信する。
The
災害対策センタ40の災害解析装置400は、送信された画像データに含まれる信号の位置と種別を解析し、解析結果に基づいて、どこでどのような災害が発生しているかを示す災害データを生成する。この災害データは、例えば、画像データ中の信号が検出された位置に、検出された信号の種別を示すシンボルを追加したものである。災害観測装置200から送信された画像データには、上空から見た地形や構築物が写っているため、シンボルを追加するだけでも、災害の発生位置と状況を容易に把握可能な災害データを得ることができ、有効な対策をとることが可能になる。
The
このように、本実施例に係る災害観測システムは、災害検知装置100が波長の異なる2種類の光線を用いて上空へ送信する信号に基づいて、災害の発生位置と状況を把握する。この方式によれば、上空から撮影された画像データ中に、災害を検知した災害検知装置100の位置が記録されるため、多数の災害検知装置100を設置しても災害の発生場所を容易に特定することができる。
As described above, the disaster observation system according to the present embodiment grasps the disaster occurrence position and the situation based on the signals transmitted from the
次に、図1に示した災害検知装置100について、詳細に説明する。なお、以下の説明においては、同一の部位については、同一の符号を付すこととする。
Next, the
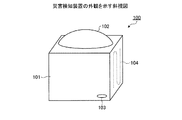
図2−1は、災害検知装置100の外観を示す斜視図である。同図に示すように、災害検知装置100の側壁および底面は、火災発生時の熱による損害を防ぐため、耐火素材101からなる。また、災害検知装置100の上面はドーム状に成形された透明な強化ガラス102からなる。強化ガラス102をドーム状に成形することにより、災害検知装置100が多少傾いた場合でも、上空へ照射される光線の屈折を最小限にすることができるとともに、落下物による遮蔽を防止することができる。
FIG. 2A is a perspective view illustrating an appearance of the
災害検知装置100の側壁の下方には水侵入口103が設けられており、水害発生時には、ここから侵入した水を災害検知装置100内部の水検知センサ111cが検知するようになっている。なお、災害検知装置100は、水侵入口103から水が浸入した場合でも、水検知センサ111c以外の回路や機構が水没しないように防水構造となっている。
A
災害検知装置100の側壁のうち、建物等と接する側壁には、微弱な電流が流れる導線104が埋め込まれる。地震等により建物に亀裂等が生じ、それにともなって導線104が断線すると、それを災害検知装置100内部の断線センサ111eが検知するようになっている。
Of the side walls of the
図2−2は、災害検知装置100の内部を示す透過図である。同図に示すように、災害検知装置100の内部には、発光部120が設けられている。なお、図2−2においては、発光部120以外の図示を省略している。
FIG. 2B is a transparent diagram illustrating the inside of the
発光部120は、強化ガラス102を介して、波長の異なる2種類の光線を上空へ向けて照射するための装置である。発光部120は、ある波長の光線を発光する光源121と、これとは異なる波長の光線を発光する光源122と、災害検知装置100が建物等の傾きにともなって傾いた場合でも光線が上空へ向けて照射されるように発光部120の向きを変更するための可動部123とを有する。
The
なお、災害検知装置100が増水を検知できるようにするには、災害検知装置100を地上1m〜2m程度の位置に設置する必要がある。この位置に災害検知装置100を設置した場合、設置対象の建物が地震等によって傾いた場合に、その建物そのものが遮蔽物となって、災害検知装置100が上空へ向けて信号を送信できなくなるおそれがある。この問題は、建物の異なる2面に災害検知装置100を設置することで解決できる。例えば、建物の東面と西面に災害検知装置100を設置して置けば、建物が西に傾いたとしても、東面に設置された災害検知装置100が上空へ向けて信号を送信できる。
In addition, in order for the
図3は、災害検知装置100の機能構成を示すブロック図である。同図に示すように、災害検知装置100は、傾きセンサ111aと、温度センサ111bと、水検知センサ111cと、停電センサ111dと、断線センサ111eと、パルス長決定部112と、パルス長記憶部113と、パルス発生部114と、姿勢制御部115と、充電池116と、発光部120とを有する。
FIG. 3 is a block diagram illustrating a functional configuration of the
傾きセンサ111aは、傾きを検知する。傾きセンサ111aにより、地震等による建物の傾きを検知することができる。温度センサ111bは、温度を検知する。温度センサ111bにより、火災による温度の上昇を検知することができる。水検知センサ111cは、水の存在を検知する。水検知センサ111cにより、増水による水位の上昇を検知することができる。停電センサ111dは、災害検知装置100への給電の停止を検知する。停電センサ111dにより、停電の発生を検知することができる。断線センサ111eは、導線104の破損を検知する。断線センサ111eにより、建物の破損を検知することができる。
The tilt sensor 111a detects the tilt. The inclination sensor 111a can detect the inclination of the building due to an earthquake or the like. The
なお、上記の各種センサは一例であり、災害検知装置100は、これらのセンサを全て備える必要はないし、また、これらとは異なるセンサを備えていてもよい。
The various sensors described above are examples, and the
パルス長決定部112は、傾きセンサ111a、温度センサ111b、水検知センサ111c、停電センサ111dおよび断線センサ111eの検出結果に基づいて、発光部120がどのような信号を送信するかを決定する。具体的には、発光部120は、何らかの長さのパルス信号を、波長の異なる2種類の光線を用いて同時に送信するように構成されており、パルス長決定部112は、傾きセンサ111a等の検出結果に基づいて、パルス長を決定する。
The pulse length determination unit 112 determines what signal the
パルス長記憶部113は、パルス長決定部112がパルス長を決定するための設定データを記憶する。図4は、パルス長記憶部113に記憶される設定データの一例を示す図である。同図に示すように、パルス長記憶部113には、各種センサにおいて所定の信号が検出された場合のパルス長が、センサ毎に定義されている。 The pulse length storage unit 113 stores setting data for the pulse length determination unit 112 to determine the pulse length. FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating an example of setting data stored in the pulse length storage unit 113. As shown in the figure, the pulse length storage unit 113 defines a pulse length for each sensor when a predetermined signal is detected by various sensors.
パルス長記憶部113に記憶されている設定データが図4に示した例の通りである場合、パルス長決定部112は、断線センサ111eによって導線104の断線が検知された場合は、パルス長を1秒と決定し、停電センサ111dによって給電停止が検出された場合は、パルス長を2秒と決定する。また、水検知センサ111cによって水位の上昇が検知された場合は、パルス長を4秒と決定し、温度センサ111bによって閾値を超える温度が検知された場合は、パルス長を8秒と決定し、傾きセンサ111aによって閾値を超える傾きが検知された場合は、パルス長を16秒と決定する。
When the setting data stored in the pulse length storage unit 113 is as shown in FIG. 4, the pulse length determination unit 112 sets the pulse length when the disconnection sensor 111e detects the disconnection of the
また、パルス長決定部112は、災害の発生を示す状況が複数のセンサによって同時に検知された場合、それぞれの検知結果に対応するパルス長を合計したものをパルス長とする。例えば、パルス長記憶部113に記憶されている設定データが図4に示した例の通りである場合、温度センサ111bによって閾値を超える温度が検知され、同時に、傾きセンサ111aによって閾値を超える傾きが検知されたならば、パルス長を、8秒と16秒の合計である24秒と決定する。図4に示した例では、パルス長が2の乗数に設定されているため、どのセンサに対応するパルス長を合計したのかが不明になることはない。
In addition, when a situation indicating the occurrence of a disaster is detected simultaneously by a plurality of sensors, the pulse length determination unit 112 sets the pulse length corresponding to each detection result as the pulse length. For example, when the setting data stored in the pulse length storage unit 113 is as in the example shown in FIG. 4, a temperature exceeding the threshold is detected by the
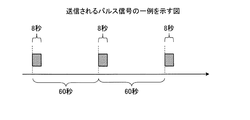
図5−1は、発光部120が送信するパルス信号の一例を示す図である。同図に示すように、発光部120は、パルス長決定部112によって決定された長さのパルス信号を定期的に送信する。同図に示す例では、発光部120は60秒毎にパルス信号を送信している。この60秒という値は、図4に示した設定データの例において、全てのセンサの検知結果を反映させた場合のパルス長が31秒であるため、それよりも大きくなるように決定されている。図5−1の例は、温度センサ111bによって閾値を超える温度が継続的に検知されている場合の例であり、8秒のパルス長の信号が送信されている。
FIG. 5A is a diagram illustrating an example of a pulse signal transmitted by the
図5−2は、複数の状況が検出された場合のパルス信号の一例を示す図である。同図に示す例は、温度センサ111bによって閾値を超える温度が継続的に検知され、同時に、傾きセンサ111aによって閾値を超える傾きが継続的に検知されている場合の例であり、8秒と16秒の合計である24秒のパルス長の信号が送信されている。
FIG. 5-2 is a diagram illustrating an example of a pulse signal when a plurality of situations are detected. The example shown in the figure is an example in the case where the temperature exceeding the threshold is continuously detected by the
なお、上記の説明では、センサの種別毎に1つのパルス長を設定することとしたが、センサの検出値の大きさに応じてパルス長を設定することとしてもよい。例えば、温度センサ111bによって検知された温度が40〜60℃の場合と、60℃以上の場合とでパルス長が異なるように設定してもよい。
In the above description, one pulse length is set for each sensor type, but the pulse length may be set according to the magnitude of the detection value of the sensor. For example, the pulse length may be set differently when the temperature detected by the
図3に戻って、パルス発生部114は、パルス長決定部112によって決定されたパルス長のパルス信号を発生させて発光部120へ供給する。姿勢制御部115は、発光部120から照射される光線が上空へ向かうように発光部120の可動部123を制御する。充電池116は、外部からの給電が停止した場合に、各部へ電力を供給する。発光部120は、パルス発生部114から供給されるパルス信号に従って、光源121と光源122から異なる波長の2種類の光線(例えば、可視光線と赤外光線)を同時に照射する。
Returning to FIG. 3, the
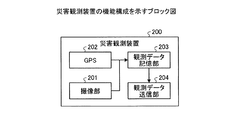
次に、飛行船20に搭載される災害観測装置200について、詳細に説明する。図6は、災害観測装置200の機能構成を示すブロック図である。同図に示すように、災害観測装置200は、撮像部201と、GPS(Global Positioning System)202と、観測データ記憶部203と、観測データ送信部204とを有する。
Next, the
撮像部201は、撮像素子等を用いて、観測域1内の地形や構築物とともに、災害検知装置100が送信する信号を撮影し、画像データを生成する。なお、撮像部201が、光源121が発信する信号と、光源122が発信する信号とを異なる画像データに記録するように構成してもよいし、同一の画像データ中に波長の異なる両者の信号を記録するように構成してもよい。
The
GPS202は、災害観測装置200の現在位置を取得する。観測データ記憶部203は、撮像部201によって生成された画像データと、GPS202によって取得された現在位置と、現在時刻とを関連付けて観測データとして記憶する。観測データ送信部204は、観測データ記憶部203に記憶された観測データを、通信衛星30を経由して、災害対策センタ40へ送信する。
The
次に、災害対策センタ40に設置される災害解析装置400について、詳細に説明する。図7は、災害解析装置400の機能構成を示すブロック図である。同図に示すように、災害解析装置400は、観測データ取得部401と、制御部410と、各種データを記憶する記憶部420とを有する。観測データ取得部401は、災害観測装置200から通信衛星30経由で送信された観測データを取得し、記憶部420に観測データ421として記憶させる。
Next, the
制御部410は、災害解析装置400を全体制御する制御部であり、観測データ補正部411と、光源検出部412と、災害種別解析部413と、災害情報生成部414とを有する。
The
観測データ補正部411は、観測データ取得部401において取得され、記憶部420に記憶された観測データ421に含まれる画像データの補正を行う。飛行船20は、上空に静止している場合でも、気流の影響により揺れたり流されたりしてしまう。この影響により、災害観測装置200が撮影する各画像データは、それぞれ僅かにずれている。観測データ補正部411は、このずれを補正し、いずれの画像データにおいても同一の対象物が同一の画素に位置するようにする。なお、この補正は、例えば、ビデオカメラ等で利用されている手ぶれ補正技術を応用して実現することができる。また、この補正を災害観測装置200において行うこともできる。
The observation data correction unit 411 corrects image data included in the
光源検出部412は、観測データ補正部411によって補正された画像データから、災害観測装置200に対応する光源を検出する。具体的には、光源検出部412は、災害観測装置200が発する2種類の波長の光が同一または近隣の画素から検出された場合に、その画素の位置を、災害観測装置200に対応する光源として検出する。なお、2種類の波長の光は、それぞれ、時間帯や気象条件等によって検出され易さが異なる。そこで、光源検出部412は、画像データ中に2種類の波長の光の一方を検出すると、もう一方の波長の光が検出され易いように判定レベルを一時的に変更して、同一および近隣の画素を調べる。このようにすることで、一方の光源を検出しにくい条件下でも、もう一方の光源を手掛かりにして、2種類の波長の光源を精度よく検出することができる。
The light
災害種別解析部413は、光源検出部412によって検出された光源が、どの種別の災害の発生を示しているのかを解析する。具体的には、災害種別解析部413は、光源検出部412によって検出された光源毎に、発光がどれだけの時間継続しているかを確認し、その継続時間を、記憶部420に記憶されているパルス長データ422と照合して、災害の種別を判定する。パルス長データ422の内容は、図4に示した設定データと同様のものである。パルス長データ422の内容が、図4に示した設定データと同一である場合、災害種別解析部413は、発光の継続時間が8秒であれば、その光源の位置で災害検知装置100が火災の発生を検知していると判断し、発光の継続時間が24秒であれば、その光源の位置で災害検知装置100が火災の発生と建物等の傾きを検知していると判断する。
The disaster
災害情報生成部414は、災害種別解析部413の解析結果に基づいて、どの場所でどのような災害が発生しているかを示す災害データ423を生成し、これを記憶部420に記憶させる。災害データ423の一例を図8に示す。同図に示すデータは、災害観測装置200から送信された画像データ中の、光源検出部412によって検出された光源の位置に、災害種別解析部413によって判定された災害の種別に対応するシンボルを付加したものである。画像データには、地上の地形や構造物も写っているため、このように、画像データ中の光源の位置に種別の災害に対応するシンボルを付加するだけでも、どこでどのような災害が発生しているかを具体的に示すことができ、迅速かつ適切な対策を立案するのに有用なデータが得られる。
The disaster
なお、観測データ421に含まれる災害観測装置200の位置情報を利用して、光源検出部412によって検出された光源の位置を緯度経度や住所に変換し、この緯度経度や住所と、災害種別解析部413によって判定された災害の種別とを対応付けて記録したものを災害データ423とすることもできる。
In addition, the position information of the
次に、本実施例に係る災害観測システムの動作について説明する。図9は、本実施例に係る災害観測システムの動作を示すフローチャートである。同図に示すように、災害検知装置100においては、パルス長決定部112が、傾きセンサ111a等の各種センサの出力を確認し(ステップS101)、パルス長記憶部113を参照してパルス長を決定する(ステップS102)。そして、姿勢制御部115が、発光部120の向きを補正し(ステップS103)、発光部120の光源121と光源122が、パルス長決定部112によって決定されたパルス長で、それぞれの波長の光線を上空へ向けて同時に照射する(ステップS104)。災害検知装置100は、このステップS101〜S104を繰り返し実行する。
Next, the operation of the disaster observation system according to the present embodiment will be described. FIG. 9 is a flowchart showing the operation of the disaster observation system according to the present embodiment. As shown in the figure, in the
また、飛行船20が被災地の上空に到着すると、災害観測装置200においては、撮像部201が地上を撮影し(ステップS201)、GPS202が現在位置を取得し(ステップS202)、観測データ記憶部203が画像データと、現在位置と、現在時刻とを関連付けて観測データとして記憶する(ステップS203)。そして、前回の送信から所定時間経過したならば(ステップS204肯定)、観測データ送信部204が、未送信の観測データを通信衛星30経由で災害対策センタ40へ送信する(ステップS205)。災害観測装置200は、災害の観測処理を実行中は、このステップS201〜S205を繰り返し実行する。
When the
また、災害対策センタ40の災害解析装置400においては、観測データ取得部401が、災害観測装置200から送信された観測データを取得して(ステップS301)、記憶部420に観測データ421として記憶させる(ステップS302)。そして、観測データ補正部411が、観測データを補正し(ステップS303)、光源検出部412が光源を検出し(ステップS304)、災害種別解析部413が光源の位置において発生している災害の種別を解析する(ステップS305)。そして、災害情報生成部414が、災害データ423を生成し(ステップS306)、記憶部420に記憶させる(ステップS307)。災害解析装置400は、災害の解析処理を実行中は、このステップS301〜S307を繰り返し実行する。
Further, in the
なお、上記の災害検知装置100、災害観測装置200および災害解析装置400の構成は、本発明の要旨を逸脱しない範囲で種々に変更することができる。例えば、災害解析装置400の制御部410の機能をソフトウェアとして実装し、これをコンピュータで実行することにより、災害解析装置400と同等の機能を実現することもできる。以下に、制御部410の機能をソフトウェアとして実装した災害解析プログラム1071を実行するコンピュータの一例を示す。
Note that the configurations of the
図10は、災害解析プログラム1071を実行するコンピュータ1000を示す機能ブロック図である。このコンピュータ1000は、各種演算処理を実行するCPU(Central Processing Unit)1010と、ユーザからのデータの入力を受け付ける入力装置1020と、各種情報を表示するモニタ1030と、記録媒体からプログラム等を読み取る媒体読取り装置1040と、ネットワークを介して他のコンピュータとの間でデータの授受を行うネットワークインターフェース装置1050と、各種情報を一時記憶するRAM(Random Access Memory)1060と、ハードディスク装置1070とをバス1080で接続して構成される。
FIG. 10 is a functional block diagram showing a
そして、ハードディスク装置1070には、図7に示した制御部410と同様の機能を有する災害解析プログラム1071と、図7に示した記憶部420に記憶される各種データに対応する災害解析用データ1072とが記憶される。なお、災害解析用データ1072を、適宜分散させ、ネットワークを介して接続された他のコンピュータに記憶させておくこともできる。
The hard disk device 1070 includes a
そして、CPU1010が災害解析プログラム1071をハードディスク装置1070から読み出してRAM1060に展開することにより、災害解析プログラム1071は、災害解析プロセス1061として機能するようになる。そして、災害解析プロセス1061は、災害解析用データ1072から読み出した情報等を適宜RAM1060上の自身に割り当てられた領域に展開し、この展開したデータ等に基づいて各種データ処理を実行する。
Then, the CPU 1010 reads out the
なお、上記の災害解析プログラム1071は、必ずしもハードディスク装置1070に格納されている必要はなく、CD−ROM等の記憶媒体に記憶されたこのプログラムを、コンピュータ1000が読み出して実行するようにしてもよい。また、公衆回線、インターネット、LAN(Local Area Network)、WAN(Wide Area Network)等を介してコンピュータ1000に接続される他のコンピュータ(またはサーバ)等にこのプログラムを記憶させておき、コンピュータ1000がこれらからプログラムを読み出して実行するようにしてもよい。
The
上述してきたように、本実施例では、災害検知装置100が、検知した災害に関する情報を、光線を用いて上空に送信し、これを災害観測装置200が上空から撮影した画像データに基づいて、災害解析装置400が、災害の発生場所を判定することとしたので、災災害検知装置100を多数設置した場合でも、各災害検知装置100の識別番号と位置とを集中管理するといった工数を要することなく、災害の発生位置を正確に特定できる。
As described above, in the present embodiment, the
以上の各実施例を含む実施形態に関し、さらに以下の付記を開示する。 The following supplementary notes are further disclosed with respect to the embodiments including the above examples.
(付記1)災害の発生状況を観測する災害観測システムであって、
災害の発生を検知し、検知した災害を示す信号を、波長の異なる2種類の光線を同時に用いて上空に送信する災害検知手段と、
前記災害検知手段が送信する信号を上空で撮影する災害観測手段と、
前記災害観測手段の撮影によって得られた画像データから前記2種類の光線が同時に発射されている位置を特定し、該位置から送信されている信号が表す災害の種別を判定する災害解析手段と
を含むことを特徴とする災害観測システム。
(Appendix 1) A disaster observation system for observing the occurrence of disasters,
Disaster detection means for detecting the occurrence of a disaster and transmitting a signal indicating the detected disaster to the sky using two types of light beams having different wavelengths simultaneously;
Disaster observation means for photographing the signal transmitted by the disaster detection means in the sky;
Disaster analysis means for identifying a position at which the two types of light beams are simultaneously emitted from image data obtained by photographing of the disaster observation means, and determining a disaster type represented by a signal transmitted from the position; Disaster observation system characterized by including.
(付記2)前記災害検知手段は、
前記2種類の光線を照射する発光部と、
前記2種類の光線が上空へ向かって照射されるように前記発光部の向きを制御する姿勢制御部と
を備えることを特徴とする付記1に記載の災害観測システム。
(Appendix 2) The disaster detection means
A light emitting unit that emits the two types of light rays;
The disaster observation system according to claim 1, further comprising: an attitude control unit that controls an orientation of the light emitting unit so that the two types of light beams are emitted toward the sky.
(付記3)前記災害検知手段は、
検知され得る災害の種別毎にパルス長を記憶するパルス長記憶部と、
検知された災害の種別に応じて、前記パルス長記憶部に記憶された情報に基づいてパルス長を決定するパルス長決定部と、
前記パルス長決定部で決定されたパルス長の光線を照射する発光部と
を備えることを特徴とする付記1に記載の災害観測システム。
(Appendix 3) The disaster detection means
A pulse length storage unit that stores a pulse length for each type of disaster that can be detected;
A pulse length determination unit that determines a pulse length based on information stored in the pulse length storage unit according to the type of disaster detected,
The disaster observation system according to appendix 1, further comprising: a light emitting unit that emits a light beam having a pulse length determined by the pulse length determining unit.
(付記4)前記パルス長決定部は、種別の異なる複数の災害が同時に検知された場合に、それぞれの災害の種別に対応するパルス長を前記パルス長記憶部から取得し、取得されたパルス長を合計したものを、前記複数の災害に対応するパルス長として決定することを特徴とする付記3に記載の災害観測システム。 (Supplementary Note 4) When a plurality of disasters of different types are detected at the same time, the pulse length determination unit acquires a pulse length corresponding to each disaster type from the pulse length storage unit, and the acquired pulse length The disaster observation system according to appendix 3, wherein a sum of the two is determined as a pulse length corresponding to the plurality of disasters.
(付記5)前記パルス長記憶部は、検知され得る災害の種別毎のパルス長として、2の乗数が設定されていることを特徴とする付記4に記載の災害観測システム。 (Supplementary note 5) The disaster observation system according to supplementary note 4, wherein the pulse length storage unit sets a multiplier of 2 as a pulse length for each type of disaster that can be detected.
(付記6)前記災害検知手段は、可視光線と赤外光線の2種類の光線を同時に用いて上空に信号を送信することを特徴とする付記1〜5のいずれか1つに記載の災害観測システム。 (Additional remark 6) The said disaster detection means transmits a signal to the sky using two types of light rays, visible light and infrared rays simultaneously, The disaster observation as described in any one of Additional remark 1-5 characterized by the above-mentioned. system.
(付記7)災害を検知した災害検知手段が、波長の異なる2種類の光線を同時に用いて上空に送信した信号を上空で撮影して得られた画像データに基づいて、災害の発生状況を解析する災害解析プログラムであって、
前記画像データから、前記波長の異なる2種類の光線が同時に発射されている位置を検出する光源検出手順と、
前記光源検出手順から送信されている信号が表す災害の種別を判定する災害種別解析手順と
をコンピュータに実行させることを特徴とする災害解析プログラム。
(Supplementary note 7) The disaster detection means that detected the disaster analyzes the occurrence of the disaster based on the image data obtained by photographing the signal transmitted in the sky using two types of light beams with different wavelengths simultaneously A disaster analysis program that
From the image data, a light source detection procedure for detecting a position where two types of light beams having different wavelengths are simultaneously emitted;
A disaster analysis program for causing a computer to execute a disaster type analysis procedure for determining a disaster type represented by a signal transmitted from the light source detection procedure.
(付記8)前記光源検出手順によって検出された位置に前記災害種別解析手順によって判定された災害の種別に対応するシンボルを付加した前記画像データを解析結果として出力する災害情報生成手順をさらにコンピュータに実行させることを特徴とする付記7に記載の災害解析プログラム。 (Supplementary Note 8) A disaster information generation procedure for outputting, as an analysis result, the image data in which the symbol corresponding to the disaster type determined by the disaster type analysis procedure is added to the position detected by the light source detection procedure is further added to the computer The disaster analysis program according to appendix 7, which is executed.
(付記9)災害を検知した災害検知手段が、波長の異なる2種類の光線を同時に用いて上空に送信した信号を上空で撮影して得られた画像データに基づいて、災害の発生状況を解析する災害解析装置であって、
前記画像データから、前記波長の異なる2種類の光線が同時に発射されている位置を検出する光源検出手段と、
前記光源検出手段から送信されている信号が表す災害の種別を判定する災害種別解析手段と
を備えることを特徴とする災害解析装置。
(Supplementary note 9) The disaster detection means that has detected a disaster analyzes the occurrence of a disaster based on image data obtained by photographing the signal transmitted to the sky using two types of light beams having different wavelengths simultaneously. A disaster analysis device that
From the image data, a light source detection means for detecting a position where two types of light beams having different wavelengths are simultaneously emitted,
A disaster analysis apparatus comprising: a disaster type analysis unit that determines a type of disaster represented by a signal transmitted from the light source detection unit.
(付記10)前記光源検出手段によって検出された位置に前記災害種別解析手段によって判定された災害の種別に対応するシンボルを付加した前記画像データを解析結果として出力する災害情報生成手段をさらに備えることを特徴とする付記9に記載の災害解析装置。 (Additional remark 10) It is further provided with the disaster information generation means which outputs the said image data which added the symbol corresponding to the classification of the disaster determined by the said disaster classification analysis means to the position detected by the said light source detection means as an analysis result The disaster analysis apparatus according to appendix 9, characterized by:
1 観測域
11 建物
12 電柱
100 災害検知装置
101 耐火素材
102 強化ガラス
103 水侵入口
104 導線
111a 傾きセンサ
111b 温度センサ
111c 水検知センサ
111d 停電センサ
111e 断線センサ
112 パルス長決定部
113 パルス長記憶部
114 パルス発生部
115 姿勢制御部
116 充電池
120 発光部
121、122 光源
123 可動部
20 飛行船
200 災害観測装置
201 撮像部
202 GPS
203 観測データ記憶部
204 観測データ送信部
30 通信衛星
40 災害対策センタ
400 災害解析装置
401 観測データ取得部
410 制御部
411 観測データ補正部
412 光源検出部
413 災害種別解析部
414 災害情報生成部
420 記憶部
421 観測データ
422 パルス長データ
423 災害データ
1000 コンピュータ
1010 CPU
1020 入力装置
1030 モニタ
1040 媒体読取り装置
1050 ネットワークインターフェース装置
1060 RAM
1061 災害解析プロセス
1070 ハードディスク装置
1071 災害解析プログラム
1072 災害解析用データ
1080 バス
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1
DESCRIPTION OF
1020
1061 Disaster analysis process 1070
Claims (5)
災害の発生を検知し、災害の種別毎にパルス長を記憶したパルス長記憶部を参照して、
検知された災害の種別に対応するパルス長を決定し、決定されたパルス長の信号を、波長
の異なる2種類の光線を同時に用いて上空に送信する災害検知手段と、
前記災害検知手段が送信する信号を上空で撮影する災害観測手段と、
前記災害観測手段の撮影によって得られた画像データから前記2種類の波長に基づき、
前記光線が同時に発射されている位置を特定し、該位置から送信されている信号のパルス
長に基づき、災害の種別を判定する災害解析手段と
を含むことを特徴とする災害観測システム。 A disaster observation system for observing the occurrence of disasters,
Detect the occurrence of disaster, refer to the pulse length storage unit that stored the pulse length for each disaster type,
A disaster detection means for determining a pulse length corresponding to a detected disaster type, and transmitting a signal having the determined pulse length to the sky using two types of light beams having different wavelengths simultaneously ;
Disaster observation means for photographing the signal transmitted by the disaster detection means in the sky;
Based on the two types of wavelengths from the image data obtained by photographing by the disaster observation means,
A disaster observation system comprising: disaster analysis means for identifying a position where the light beams are simultaneously emitted and determining a disaster type based on a pulse length of a signal transmitted from the position.
前記光線を照射する発光部と、
前記光線が上空へ向かって照射されるように前記発光部の向きを制御する姿勢制御部と
を備えることを特徴とする請求項1に記載の災害観測システム。 The disaster detection means includes
A light emitting unit for irradiating the light beam;
The disaster observation system according to claim 1, further comprising: an attitude control unit that controls an orientation of the light emitting unit so that the light beam is irradiated toward the sky.
検知された災害の種別に応じて、前記パルス長記憶部に記憶された情報に基づいてパル
ス長を決定するパルス長決定部と、
前記パルス長決定部で決定されたパルス長の光線を照射する発光部と
を備えることを特徴とする請求項1に記載の災害観測システム。 The disaster detection means includes
A pulse length determination unit that determines a pulse length based on information stored in the pulse length storage unit according to the type of disaster detected,
The disaster observation system according to claim 1, further comprising: a light emitting unit that emits a light beam having a pulse length determined by the pulse length determination unit.
の災害の種別に対応するパルス長を前記パルス長記憶部から取得し、取得されたパルス長
を合計したものを、前記複数の災害に対応するパルス長として決定することを特徴とする
請求項3に記載の災害観測システム。 The pulse length determination unit acquires a pulse length corresponding to each disaster type from the pulse length storage unit when a plurality of disasters of different types are detected at the same time, and totals the acquired pulse lengths The disaster observation system according to claim 3, wherein the pulse length corresponding to the plurality of disasters is determined.
災害を検知した災害検知手段が、災害の種別毎にパルス長を記憶したパルス長記憶部を
参照して、検知された災害の種別に対応するパルス長を決定し、決定されたパルス長の信
号を、波長の異なる2種類の光線を同時に用いて上空に送信し、送信された信号を上空で
撮影して得られた画像データを取得し、
前記画像データから、前記2種類の波長に基づき、前記光線が同時に発射されている位
置を特定し、
特定された前記位置から送信されている信号のパルス長に基づき、災害の種別を判定す
る
各処理を実行させることを特徴とする災害解析プログラム。 To computer of disaster observation system to observe the occurrence situation of disaster,
The disaster detection means that detects the disaster refers to the pulse length storage unit that stores the pulse length for each disaster type, determines the pulse length corresponding to the detected disaster type, and the signal of the determined pulse length Is transmitted to the sky using two types of light beams having different wavelengths simultaneously, and the image data obtained by photographing the transmitted signal in the sky is acquired,
From the image data, based on the two types of wavelengths, identify the position where the light beam is simultaneously emitted,
A disaster analysis program characterized by causing each process to determine a disaster type based on a pulse length of a signal transmitted from the identified position.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008058609A JP5082940B2 (en) | 2008-03-07 | 2008-03-07 | Disaster observation system and disaster analysis program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008058609A JP5082940B2 (en) | 2008-03-07 | 2008-03-07 | Disaster observation system and disaster analysis program |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009217399A JP2009217399A (en) | 2009-09-24 |
| JP2009217399A5 JP2009217399A5 (en) | 2010-11-11 |
| JP5082940B2 true JP5082940B2 (en) | 2012-11-28 |
Family
ID=41189205
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008058609A Active JP5082940B2 (en) | 2008-03-07 | 2008-03-07 | Disaster observation system and disaster analysis program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5082940B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6073094B2 (en) * | 2012-09-07 | 2017-02-01 | 綜合警備保障株式会社 | Security system and security method |
| JP5809174B2 (en) * | 2013-01-09 | 2015-11-10 | 株式会社Nttファシリティーズ | Building safety verification system, building safety verification method and program |
| JP6499832B2 (en) * | 2014-07-08 | 2019-04-10 | 株式会社Nttファシリティーズ | Structure safety verification system, structure safety verification method and program |
| JP5799183B2 (en) * | 2015-01-22 | 2015-10-21 | 株式会社Nttファシリティーズ | Building safety verification system, building safety verification method and program |
| JP6028119B1 (en) * | 2016-05-09 | 2016-11-16 | 有限会社 ジオテック | Building health management apparatus and building health management method using the building health management apparatus |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001060288A (en) * | 1999-08-20 | 2001-03-06 | Matsushita Electric Works Ltd | Fire sensor and tester for fire sensor |
| JP2001148077A (en) * | 1999-11-19 | 2001-05-29 | Fujitsu General Ltd | Intruder detecting device |
| JP2007156793A (en) * | 2005-12-05 | 2007-06-21 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Disaster management apparatus and disaster management method |
| JP4505647B2 (en) * | 2006-03-16 | 2010-07-21 | 国立大学法人 筑波大学 | Ground condition observation method and ground condition observation system |
-
2008
- 2008-03-07 JP JP2008058609A patent/JP5082940B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2009217399A (en) | 2009-09-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101911756B1 (en) | The system for real-time remote monitoring buoys on the sea | |
| JP5082940B2 (en) | Disaster observation system and disaster analysis program | |
| US10271016B2 (en) | Integrated monitoring CCTV, abnormality detection apparatus, and method for operating the apparatus | |
| JP2019052954A (en) | Inspection system, inspection method, server device, and program | |
| US10706696B1 (en) | Security system with distributed sensor units and autonomous camera vehicle | |
| KR20170101519A (en) | Apparatus and method for disaster monitoring using unmanned aerial vehicle | |
| US20200273309A1 (en) | Smoke detection method with visual depth | |
| JP2006331150A (en) | Disaster prevention system | |
| US20160155097A1 (en) | Reports of repairable objects and events | |
| JPWO2019235415A1 (en) | Disaster situation judgment system and disaster judgment flight system | |
| CN112862821A (en) | Water leakage detection method and device based on image processing, computing equipment and medium | |
| US20170184740A1 (en) | Detecting earthquakes through a network of geographically distributed sensors | |
| US20230401941A1 (en) | Monitoring system, monitoring apparatus, monitoring method, and computer readable medium | |
| KR102480079B1 (en) | Monitoring system for odor spread prediction | |
| KR101634336B1 (en) | Damage control system of warship and a method thereof | |
| JP7505597B2 (en) | Information processing device, information processing method, and program | |
| Xie et al. | On‐line physical security monitoring of power substations | |
| US10096175B2 (en) | Structural damage detection | |
| JP2020028179A (en) | Abnormality monitoring system, abnormality monitoring device, and program | |
| JP7327355B2 (en) | Map update device and map update method | |
| Ko et al. | Intelligent wireless sensor network for wildfire detection | |
| KR20220077332A (en) | IoT and drone-based port management methods, devices, and platforms | |
| Rasheed et al. | Rapidly Deployable Video Analysis Sensor units for wide area surveillance | |
| KR102518056B1 (en) | A method for monitoring and cause analysis of safety accident of manless charging or refueling facility | |
| JP6046784B1 (en) | Information recording device for buildings |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100924 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100924 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20120229 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120306 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120507 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120529 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120719 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20120807 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20120820 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5082940 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20150914 Year of fee payment: 3 |