JP5063756B2 - COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, BASE STATION DEVICE, AND COMMUNICATION CONTROL METHOD - Google Patents
COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, BASE STATION DEVICE, AND COMMUNICATION CONTROL METHOD Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5063756B2 JP5063756B2 JP2010180535A JP2010180535A JP5063756B2 JP 5063756 B2 JP5063756 B2 JP 5063756B2 JP 2010180535 A JP2010180535 A JP 2010180535A JP 2010180535 A JP2010180535 A JP 2010180535A JP 5063756 B2 JP5063756 B2 JP 5063756B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- base station
- station
- synchronization
- base stations
- base
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Synchronisation In Digital Transmission Systems (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Description
本発明は、多数の基地局を有し、基地局が同期した送信タイミング及び受信タイミングで移動局と通信をする通信システム、基地局装置及び通信制御方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a communication system, a base station apparatus, and a communication control method that have a large number of base stations and communicate with a mobile station at transmission timings and reception timings synchronized with the base stations.
携帯無線機等の移動通信システムでは、無線基地局と移動局との間に電波による通信回線を設定し、無線により音声、データ等を送受して通信を行うものであり、周波数利用効率の観点からTDMA方式やCDMA(符号分割多重接続)方式によるデジタル方式の携帯電話システムが広く用いられている。このTDMA方式の基地局及び移動局は、自局に割り当てられた受信スロットを受信し、自局に割り当てられた送信スロットにて送信をして、間欠的に送受信を繰り返すように動作している。また、CDMA方式の基地局及び移動局は、自局に割り当てられた拡散符号で変調したデジタル信号を送受信している。これらの、デジタル方式の移動通信システムにおいては、基地局と移動局とが同期して、同じタイミングで送受信しなければならない。 In a mobile communication system such as a portable wireless device, a communication line using radio waves is set between a wireless base station and a mobile station, and communication is performed by transmitting and receiving voice, data, etc. wirelessly. Since then, digital cellular phone systems based on TDMA and CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) have been widely used. The base station and mobile station of this TDMA system operate so as to receive a reception slot assigned to the own station, transmit in the transmission slot assigned to the own station, and repeat transmission / reception intermittently. . In addition, CDMA base stations and mobile stations transmit and receive digital signals modulated by spreading codes assigned to the CDMA system. In these digital mobile communication systems, base stations and mobile stations must synchronize and transmit and receive at the same timing.
TDMA方式において、基地局と移動局との同期をとるために、基地局からの信号を受信した移動局は、基地局からの信号に含まれる同期信号(同期ワード)に基づいて自局の送受信フレームの同期をとって、移動局からの送信を開始する。また、基地局と移動局間の距離等により生じるフレームタイミングのズレを吸収するために、各受信スロットの最初には送信スロットが侵入しても受信に影響が生じないガードタイムが設けられている。 In the TDMA scheme, in order to synchronize the base station and the mobile station, the mobile station that has received the signal from the base station transmits / receives its own station based on the synchronization signal (synchronization word) included in the signal from the base station. Synchronize the frames and start transmission from the mobile station. In addition, in order to absorb the frame timing shift caused by the distance between the base station and the mobile station, a guard time is provided at the beginning of each reception slot so that reception is not affected even if a transmission slot enters. .
このような移動通信システムでは、移動局の移動に伴い接続先の基地局を切り換えて通信を継続している。よって、各基地局の送信タイミング及び受信タイミングが一致していなくてはならない。基地局間で送信タイミング及び受信タイミングにズレが生じていると、送信スロットと受信スロットとが干渉して、正常な受信ができなくなる。 In such a mobile communication system, communication is continued by switching the base station of the connection destination as the mobile station moves. Therefore, the transmission timing and the reception timing of each base station must match. If there is a difference in transmission timing and reception timing between base stations, the transmission slot and the reception slot interfere with each other and normal reception cannot be performed.
特に、時分割双方向伝送を行うTDMA−TDD方式では、同一周波数に基地局への上りの信号と、移動局への下りの信号とが混在しているので、送受信タイミングのズレにより、上りの信号と下りの信号とが衝突してしまう。 In particular, in the TDMA-TDD system that performs time-division bidirectional transmission, an uplink signal to the base station and a downlink signal to the mobile station are mixed at the same frequency. The signal and the downstream signal collide.
具体的には、TDMA−TDD方式を採用するPHS方式(PersonalHandyphone System)では、図8に示すように、1TDD/TDMAフレーム中に4つの受信スロットと4つの送信スロットとが配置されており、5ミリ秒周期で送受信スロットが繰り返されている。このとき、基地局1と基地局2との送受信タイミング(フレームタイミング)がズレていると、基地局間で送信スロットと、受信スロットとが干渉してしまう。すなわち、移動局が基地局1への上りの信号を送信している間に(RX4)、基地局2が移動局への下りの信号を送信してしまい(TX1)、上りの信号(RX4)と下りの信号(TX1)とが衝突してしまう。移動局より基地局の方が送信出力が大きい場合が多く、基地局1では受信スロットRX4での上りの信号が受信できない。
Specifically, in the PHS system (Personal Handyphone System) that employs the TDMA-TDD system, as shown in FIG. 8, four reception slots and four transmission slots are arranged in one TDD / TDMA frame. The transmission / reception slots are repeated with a millisecond cycle. At this time, if the transmission / reception timing (frame timing) between the
移動通信システムにおける基地局間のフレームタイミングの同期には様々な方法が提案されている。例えば、各基地局が周囲の基地局のうち最も電界強度の強い基地局に合わせて、自律的に同期を確立する方法がある。しかし、この方法では、同期の無限連鎖により基準局のフレームタイミングから大きくずれる基地局が発生してしまう。また、同期の基準となる基地局が複数存在して、複数の同期群が形成され、同期群間でフレームタイミングにズレがあることから、同期群間で干渉が発生してしまう。 Various methods have been proposed for synchronizing frame timing between base stations in a mobile communication system. For example, there is a method in which each base station autonomously establishes synchronization in accordance with a base station having the strongest electric field strength among surrounding base stations. However, in this method, a base station is generated that deviates greatly from the frame timing of the reference station due to an infinite chain of synchronization. In addition, since there are a plurality of base stations serving as a reference for synchronization, a plurality of synchronization groups are formed, and frame timing is shifted between the synchronization groups, so that interference occurs between the synchronization groups.
また、各基地局は有線回線で接続されているので、この有線で基準信号を配信して同期を確立する方法もある。しかし、ISDN等の標準的なインターフェースでは基準信号の配信ができず、基準信号を配信するために特別なインターフェースが必要となることから、大規模な公衆ネットワークには適さない。また、複数の交換機にまたがって基地局間の同期をとることは、交換機による伝送遅延の影響を考慮すると困難である。 In addition, since each base station is connected by a wired line, there is a method of establishing synchronization by distributing a reference signal via this wired line. However, since a standard interface such as ISDN cannot distribute a reference signal, and a special interface is required to distribute the reference signal, it is not suitable for a large-scale public network. In addition, it is difficult to synchronize base stations across a plurality of exchanges in consideration of the effect of transmission delay caused by the exchanges.
また、各基地局は、通信ネットワークを統括的に制御するセンター設備により制御されているので、このセンター設備からの指示によりフレームタイミングを修正する方法もある。しかし、この方法では、運用者によるセンター設備からの指示が必要であり運用コストが発生する。また、基地局の増設時に再度同期指示をしなければならない等、複雑な処理が必要になる。 Further, since each base station is controlled by a center facility that comprehensively controls the communication network, there is a method of correcting the frame timing according to an instruction from the center facility. However, this method requires an instruction from the center facility by the operator, resulting in an operation cost. In addition, complicated processing is required, for example, the synchronization instruction must be given again when adding base stations.
本発明は、複数の基地局間の送信タイミング及び受信タイミングの同期を、簡易かつ確実に自律的に確立する通信システムを提供することにある。 An object of the present invention is to provide a communication system that establishes synchronization of transmission timings and reception timings between a plurality of base stations in a simple and reliable manner.
第1の発明は、複数の基地局と、前記複数の基地局を制御できるネットワーク側の制御と、を含む通信システムにおいて、前記基地局は、自局を示す識別情報と自局の同期の階層レベルを示す情報とを含む基地局情報を前記制御装置に送信する手段を有する、ことを特徴とする。
The first invention is a communication system including a plurality of base stations, and a control of the network side can control a plurality of base stations, the base station identification information and synchronization hierarchy of its own station indicating the own station and means for transmitting the base station information including the information indicating the level to the control device, characterized in that.
基地局は、当該基地局が初期化された場合に、前記基地局情報を前記他の基地局装置へ通知してもよい。
The base station may notify the other base station apparatus of the base station information when the base station is initialized.
第2の発明は、複数の基地局と、前記複数の基地局を制御できるネットワーク側の制御装置と、を含む通信システムにおける前記基地局であって、自局を示す識別情報と自局の同期の階層レベルを示す情報とを含む基地局情報を前記制御装置に送信する手段を有する、ことを特徴とする。
2nd invention is the said base station in the communication system containing a some base station and the network side control apparatus which can control these some base stations, Comprising: The identification information which shows a self station, and the synchronization of a self station And means for transmitting base station information including information indicating the hierarchical level to the control device .
第3の発明は、複数の基地局と、前記複数の基地局を制御できるネットワーク側の制御装置と、を含む通信システムにおける通信制御方法において、前記基地局が、自局を示す識別情報と自局の同期の階層レベルを示す情報とを含む基地局情報を前記制御装置に送信するステップを含む、ことを特徴とする。
A third invention is a communication control method in a communication system including a plurality of base stations and a network-side control device capable of controlling the plurality of base stations, wherein the base station includes identification information indicating its own station and its own information. Transmitting base station information including information indicating a hierarchical level of station synchronization to the control device .
また、その他の第1の移動通信システムは、複数の基地局を有し、移動局が一又は二以上の前記基地局と選択的に回線を接続して、所定のタイミングで送受信をして通信を行う移動通信システムにおいて、前記複数の基地局は、GPS受信機を有する基地局と、GPS受信機を有さない基地局とで構成され、前記GPS受信機を有する基地局は、前記GPS受信機により受信したGPS衛星からの信号に基づき、自局の送信タイミング及び受信タイミングを決定し、前記GPS受信機を有さない基地局は、前記GPS受信機を有する基地局を中心に階層的に同期をして、送信タイミング及び受信タイミングを決定する。これにより、GPS受信機を有する基地局とGPS受信機を有さない基地局とが配置されており、GPS受信機を有さない基地局は、GPS受信機を有する基地局を中心に階層的に同期をして、送信タイミング及び受信タイミングを決定するので、高い精度で送信タイミング及び受信タイミングの同期をすることができる。 In addition, the other first mobile communication system has a plurality of base stations, and the mobile station selectively connects to one or two or more of the base stations and performs transmission / reception at a predetermined timing. In the mobile communication system, the plurality of base stations are composed of a base station having a GPS receiver and a base station having no GPS receiver, and the base station having the GPS receiver Based on the signal from the GPS satellite received by the machine, the transmission timing and reception timing of its own station are determined, and the base station not having the GPS receiver is hierarchically centered on the base station having the GPS receiver. Synchronize to determine transmission timing and reception timing. As a result, a base station having a GPS receiver and a base station not having a GPS receiver are arranged, and the base station having no GPS receiver is hierarchically structured around the base station having a GPS receiver. Since the transmission timing and the reception timing are determined in synchronization with each other, the transmission timing and the reception timing can be synchronized with high accuracy.
その他の第2の移動通信システムは、複数の基地局を有し、移動局が一又は二以上の前記基地局と選択的に回線を接続して、所定のタイミングで送受信をして通信を行う移動通信システムにおいて、前記基地局のうち、高精度な送信タイミング及び受信タイミングを生成する基地局を基準局として階層の上位に設定して、他の基地局は、より上位の階層の基地局を選択して送信タイミング及び受信タイミングを決定し、自局の階層を前記選択した基地局より下位に設定することにより、前記基準局を中心に階層的に同期をする。これにより、高精度な送信タイミング及び受信タイミングを生成する基地局を基準局として階層の上位に設定して、他の基地局は自局より上位の階層の基地局を選択して送信タイミング及び受信タイミングを決定し、基準局を中心に階層的に同期をするので、各基地局が自律的に最適な同期相手の基地局を選択することから、運用者による同期制御の操作が必要なく、運用コストを低減することができる。 The other second mobile communication system has a plurality of base stations, and the mobile station selectively connects to one or two or more of the base stations and performs communication by transmitting and receiving at a predetermined timing. In a mobile communication system, a base station that generates high-accuracy transmission timing and reception timing among the base stations is set as a reference station at a higher level, and other base stations select a higher-level base station. Then, the transmission timing and the reception timing are determined, and the hierarchy of the own station is set lower than the selected base station, so that synchronization is hierarchically centered on the reference station. As a result, a base station that generates high-accuracy transmission timing and reception timing is set as a reference station at a higher level in the hierarchy, and other base stations select a base station in a higher hierarchy than its own station to transmit and receive timing. Since each base station autonomously selects the optimal synchronization partner base station, there is no need for an operator to perform synchronization control and the operation cost is reduced. Can be reduced.
その他の第3の移動通信システムは、前記基地局が送信する信号には、自局の階層内の地位を示す同期制御符号を含み、他の前記基地局は前記同期制御符号により、自局より上位の階層の基地局を選択することを特徴とする。これにより、基地局が送信する信号には、自局の階層内の地位を示す同期制御符号を含み、他の基地局は同期制御符号により、自局より上位の階層の基地局を選択するので、簡易な構成で自律的な同期の階層を形成することができる。 In the other third mobile communication system, the signal transmitted by the base station includes a synchronization control code indicating the position in the hierarchy of the own station, and the other base station receives the synchronization control code from the own station. It is characterized by selecting a base station in a higher hierarchy. As a result, the signal transmitted by the base station includes a synchronization control code indicating the status in the hierarchy of the own station, and other base stations select a base station in a higher hierarchy than the own station by the synchronization control code. It is possible to form an autonomous synchronization hierarchy with a simple configuration.
その他の第4の移動通信システムは、前記基地局は、同じ階層の基地局のうち、信号強度が強い基地局を選択して、送信タイミング及び受信タイミングを決定することを特徴とする。これにより、同じ階層の他の基地局のうち、信号強度が強い基地局を選択して、送信タイミング及び受信タイミングを決定するので、確実に同期をすることができる。 The other fourth mobile communication system is characterized in that the base station selects a base station having a strong signal strength among base stations of the same layer and determines a transmission timing and a reception timing. As a result, a base station having a strong signal strength is selected from other base stations in the same hierarchy, and the transmission timing and the reception timing are determined. Therefore, synchronization can be reliably performed.
その他の第5の移動通信システムは、TDD方式で通信をするものであって、前記基地局は送信タイミング及び受信タイミングとしてフレームタイミングを決定することを特徴とする。これにより、基地局は、他の基地局に基づいてフレームタイミング決定するので、送信スロットと受信スロットとが衝突することがない。 The other fifth mobile communication system performs communication by the TDD method, and the base station determines frame timing as transmission timing and reception timing. As a result, the base station determines the frame timing based on other base stations, so that the transmission slot and the reception slot do not collide.
その他の第6の移動通信システムは、前記基地局を統括的に制御するセンター設備を有し、前記基地局は、他の基地局に同期をすると、自局の階層内の地位をセンター設備に通知することを特徴とする。これにより、他の基地局に同期をすると、自局の階層内の地位を基地局を統括的に制御するセンター設備に通知するので、センター設備で各基地局の同期階層内の地位を把握することができる。 The other sixth mobile communication system has a center facility for overall control of the base station. When the base station synchronizes with another base station, the position in the hierarchy of the own station becomes the center facility. It is characterized by notifying. As a result, when synchronizing with other base stations, the status in the own station's hierarchy is notified to the center equipment that controls the base station in an integrated manner, so the center equipment grasps the position in the synchronization hierarchy of each base station. be able to.
その他の第7の移動通信システムは、前記基地局を統括的に制御するセンター設備を有し、前記基地局は、他の基地局に同期せずに自局の送信タイミング及び受信タイミングを決定すると、センター設備に通知をすることを特徴とする。これにより、他の基地局に同期せずに自局の送信タイミング及び受信タイミングを決定すると、基地局を統括的に制御するセンター設備に通知をするので、センター設備で異常となった基地局を把握することができる。 The other seventh mobile communication system has a center facility for overall control of the base station, and the base station determines its transmission timing and reception timing without synchronizing with other base stations. The center facility is notified. As a result, when the transmission timing and reception timing of its own station are determined without synchronizing with other base stations, it notifies the center equipment that controls the base station in an integrated manner. I can grasp it.
本発明によれば、複数の基地局間の同期を、簡易かつ確実に自律的に確立することができる。 ADVANTAGE OF THE INVENTION According to this invention, the synchronization between several base stations can be established autonomously simply and reliably.
次に、本発明の実施の形態について図面を参照して説明する。 Next, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
図1は、本発明が適用されるPHSシステム全体の構成図である。 FIG. 1 is a configuration diagram of an entire PHS system to which the present invention is applied.
PHSシステムの移動局であるPHS端末機(PS)1は、基地局装置(CS)2との間で無線による回線を設定し、音声、データによる通信を行う。このPHS方式では、多元接続方式(マルチ・チャネル・アクセス方式)を使用しているので、端末機1と基地局装置2とは、制御チャネルにおいて通話チャネルを設定するために必要な情報のやりとり(ネゴシエーション)をし、通話チャネルを設定して、通話チャネルにおいて通信を始める。
A PHS terminal (PS) 1, which is a mobile station of the PHS system, establishes a wireless line with the base station apparatus (CS) 2 and performs voice and data communication. Since this PHS method uses a multiple access method (multi-channel access method), the
基地局装置2は加入者交換機3に接続されており、さらに加入者交換機3は中継交換機4を介してISDN網5に接続されている。また、基地局装置2は交換機3、4を介してセンター設備6に接続されており、センター設備6は基地局装置2の起動、停止、設定変更等を統括して制御している。
The
図2は、本発明の実施の形態の基地局装置2のブロック図である。
FIG. 2 is a block diagram of the
基地局装置2は交換機3を介して加入者電話網(ISDN網)5に接続されている。交換機3から基地局装置2に入力された信号はインターフェース部11にてレベル変換され、符号化・復号化部12によって符号化され、ベースバンド部13、無線部14で変調、逓倍、増幅等の処理がされて高周波信号となり、アンテナ15からPHS端末機1に対する下りの信号として送信される。
The
一方、アンテナ15で受信されたPHS端末機1からの上りの信号は、無線部14にて周波数変換等の処理がされ、ベースバンド部13に送られ検波(復調)等のベースバンド処理がされる。符号化・復号化部12はベースバンド処理がされた信号を復号化しアナログ信号に変換する。復号化された信号は、インターフェース部11にて、交換機3に入力可能なレベルに変換され、交換機3に送られる。
On the other hand, the upstream signal received from the
CPU17は基地局装置2の各部を制御する。クロック部16はクロック信号を発生し、CPU17はこのクロック信号に基づいて無線部14に送受信切替タイミングを指示する。記憶部18にはCPU17が基地局装置2を制御する制御プログラムや、CPU17が動作するために必要なデータが記憶されている。これらのクロック部16、CPU17、記憶部18等により基地局装置2の制御部が構成されている。
The
さらに、一部の基地局装置2は、GPS受信機19を備えており、GPS受信アンテナ20を介してGPS衛星からの信号を受信して、クロック抽出部21においてGPS衛星からの信号から時間情報を抽出する。GPS衛星は原子時計を備えており正確な時間情報を送信している。GPS受信部を備えた基地局装置2では、抽出された時間情報に従ってフレーム同期のタイミング信号を生成するので、極めて正確(±1マイクロ秒程度)で、狂いのないタイミング信号を生成することができる。
Further, some of the
このGPS受信機19、クロック抽出部21、GPS受信アンテナ20は、GPSユニットを構成しており、基地局装置2から着脱可能に構成されている。このため、GPS非搭載局をGPS搭載局に容易に変更することができる。
The GPS receiver 19, the clock extraction unit 21, and the GPS reception antenna 20 constitute a GPS unit and are configured to be detachable from the
図3は、本発明の実施の形態の識別符号(CSID)の構成図である。 FIG. 3 is a configuration diagram of an identification code (CSID) according to the embodiment of the present invention.
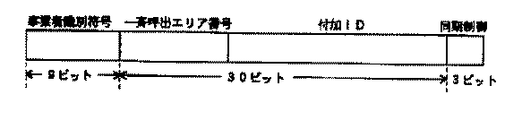
基地局装置2は、制御チャネルにおいて、自装置の識別符号(CSID)を一定の時間間隔(100ミリ秒間隔)で送信している。このCSIDには9ビットの事業者識別符号、一斉呼び出しエリア番号、付加IDの他に、3ビットの同期制御符号が含まれている。
この同期制御符号は、各基地局の同期レベルの階層における地位を表し、他の基地局からみて同期相手となる基地局であるかを規定している。
The
This synchronization control code represents the position of each base station in the hierarchy of the synchronization level, and defines whether it is a base station that is a synchronization partner as viewed from other base stations.
図4は、本発明の実施の形態の同期制御符号の内容を示す図表である。 FIG. 4 is a table showing the contents of the synchronization control code according to the embodiment of the present invention.
同期制御符号は3ビットの信号からなり、本実施の形態では5段階の同期レベルが設定されている。GPS受信機19を備えた基地局(GPS搭載局)は、最も高い同期レベル(同期レベル1)に設定され、”100”の同期制御符号で表される。
「同期レベル2」は、同期レベル1の基地局(GPS搭載局)からの信号に基づいて自局のフレームタイミングの同期をした局であり、他の基地局から基準とされる優先度が同期レベル1の基地局の次に高く、”101”の同期制御符号で表される。
「同期レベル3」は、同期レベル2の基地局からの信号に基づいて自局のフレームタイミングの同期をした局であり、他の基地局から基準とされる優先度が同期レベル1、2の基地局の次に高く、”110”の同期制御符号で表される。
「同期レベル4」は、同期レベル3の基地局からの信号に基づいて自局のフレームタイミングの同期をした局であり、他の基地局から基準とされる優先度が最も低く、”111”の同期制御符号で表される。
「非同期局」は、GPS受信機19も搭載していなく、他の基地局に同期をしていない基地局の同期レベルであり、”000”の同期制御符号で表される。また、同期レベル4の基地局からの信号に基づいてフレームタイミングの同期をした基地局も、「非同期局」の同期レベルに設定される。
The synchronization control code is composed of a 3-bit signal, and in this embodiment, five levels of synchronization are set. The base station (GPS station) provided with the GPS receiver 19 is set to the highest synchronization level (synchronization level 1) and is represented by a synchronization control code of “100”.
“
“
“
The “asynchronous station” is a synchronization level of a base station that is not equipped with the GPS receiver 19 and is not synchronized with other base stations, and is represented by a synchronization control code of “000”. A base station that has synchronized frame timing based on a signal from a base station at
この同期レベルは、「同期レベル1」がフレームタイミングの精度が最も高いので、他局から見て同期の基準とする優先順位が最も高い。また、「同期レベル4」がフレームタイミングの精度が最も低いので、他局から見て同期の基準とする優先順位が最も低い。また、「非同期局」は同期レベル4の下位に設けられており、非同期局のフレームタイミングの誤差は大きいと推定されるので、他の基地局から同期の基準にされることはない。
This synchronization level has the highest priority as a reference for synchronization as viewed from other stations because “
本実施の形態では同期制御符号を3ビットで表現しているが、同期制御符号のビット数を増加して、より多階層の同期レベルを設定してもよい。この場合、同期の際に遅延により同期がずれて、回線が接続できなくならない程度の階層とすることが望ましい。 In the present embodiment, the synchronization control code is represented by 3 bits, but the number of bits of the synchronization control code may be increased to set a higher-level synchronization level. In this case, it is desirable to set the hierarchy so that the synchronization is lost due to the delay and the line cannot be connected.
図5は、本発明の実施の形態の基地局装置2の電源投入時の動作を示すフローチャートである。
FIG. 5 is a flowchart showing an operation at power-on of the
新たに運用を開始する又はリセット信号等により再起動される基地局装置2は、電源が投入されると諸定数が初期化され、各回路(ベースバンド部13、無線部14等)が初期化される(S101)。制御部のCPU17は、基地局装置2にGPS受信機19が備わっているかを検出して(S102)、GPS受信機19が搭載されていたならば、GPS衛星からの信号からクロック信号を抽出して、この時間情報に自局のフレームタイミングを同期させる(S103)。その後、自局の同期レベルを”1”に設定して(S104)、制御チャネルでの送信を開始する(S109)。この制御チャネルで送信される識別符号(CSID)に含まれる同期制御符号により、自局がGPS搭載局であることを他の基地局に対して通知する。
When the
一方、基地局装置2にGPS受信機19が搭載されていなければ(S102)、制御チャネルを受信して、周囲の基地局からのCSIDを受信する(S105)。このCSIDには同期制御符号が含まれている。周囲の基地局からの識別符号(CSID)を受信した基地局装置2は、同期相手を選択する(S106)。このステップS105〜S106の動作は図6にて後に詳細に説明する。
On the other hand, if the GPS receiver 19 is not mounted on the base station apparatus 2 (S102), the control channel is received and CSIDs from surrounding base stations are received (S105). This CSID includes a synchronization control code. Receiving the identification code (CSID) from the surrounding base station, the
そして、相手局の同期信号(同期ワード)に同期させて、自局の同期クロックを生成して、自局のフレームタイミングを相手局のフレームタイミングに同期させる(S107)。 Then, in synchronization with the synchronization signal (synchronization word) of the partner station, a synchronization clock of the station is generated, and the frame timing of the station is synchronized with the frame timing of the partner station (S107).
その後、フレーム同期の基準となった相手局の同期レベルに1を加えて、自局の同期レベルを基準とした基地局の同期レベルの下位に設定する(S108)。そして、制御チャネルでのCSIDの送信を開始して(S109)、自局の同期レベルを他の基地局に対して通知する。 Thereafter, 1 is added to the synchronization level of the partner station that is the reference for frame synchronization, and it is set at a lower level of the synchronization level of the base station based on the synchronization level of the local station (S108). Then, transmission of the CSID on the control channel is started (S109), and the synchronization level of the own station is notified to other base stations.
また、自局の同期レベルが決定した旨を有線回線でセンター設備6に通知する(S110)。このとき、本実施の形態のように同期後に無条件にセンター設備6に通知するのではなく、非同期局となった場合にのみセンター設備6に通知するように構成してもよい。
このように構成すると、センター設備6では異常が生じた基地局のみを把握することができる。
Also, the center facility 6 is notified by a wired line that the synchronization level of the own station has been determined (S110). At this time, instead of notifying the center facility 6 unconditionally after synchronization as in the present embodiment, the center facility 6 may be notified only when the station becomes an asynchronous station.
With this configuration, the center facility 6 can grasp only the base station in which an abnormality has occurred.
図6は、本発明の実施の形態の基地局で自局のフレームタイミングを同期する相手の基地局を選択する動作の詳細を示すフローチャートであり、図5における、ステップS105〜S106の周囲の基地局の受信から同期相手局の選択までの動作の詳細を示す。 FIG. 6 is a flowchart showing details of an operation of selecting a partner base station that synchronizes the frame timing of the own station in the base station according to the embodiment of the present invention. The bases around steps S105 to S106 in FIG. Details of the operation from the reception of the station to the selection of the synchronization partner station are shown.
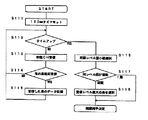
基地局の制御部のCPU17は、制御チャネルを受信するための時間として、100ミリ秒のタイマをセットして、100ミリ秒の計時を開始する(S111)。その後、タイマがタイムアップして100ミリ秒が経過するまでの間(S112)、制御チャネルを連続的に受信する(S113)。PHS方式では、各基地局は制御チャネルにおいて、100ミリ秒間隔でCSIDを送信しているので、100ミリ秒連続して制御チャネルを受信すれば、自局が受信可能な全ての基地局からのCSIDを受信することができる。
The
基地局装置2は、100ミリ秒の間で、いずれかのタイムスロットで、他の基地局が受信できたなら(S114)、受信した基地局のCSID、同期制御符号、受信電界強度(RSSI、ビットエラーレート等)を記憶する(S115)。一方、他の基地局が受信できなかったら(S114)、タイマがタイムアップして所定の時間(100ミリ秒)が経過するまで、制御チャネルの受信を継続して(S112〜S115)、他の近くの基地局を捜索する。
If the
制御チャネルの所定時間(100ミリ秒)の連続受信が終了したら、受信した周辺の基地局から同期相手の基地局を選択する。制御部のCPU17は、記憶部18に記憶された近隣の基地局のデータから、最も同期レベルが小さい(階層が高く、同期の優先度が高い)基地局を選択する(S116)。このとき同じ同期レベルの基地局が複数受信できていたら(S117)、同じ同期レベルを有する基地局のうち、受信レベルが最大の基地局を選択する(S118)。
When continuous reception of the control channel for a predetermined time (100 milliseconds) is completed, a synchronization partner base station is selected from the received base stations. The
図7は、本発明の実施の形態により同期した基地局の階層を示す図である。 FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating a hierarchy of base stations synchronized according to an embodiment of the present invention.
図に丸印(黒丸、白丸)で示したものが、配置された基地局である。また、図の中心に黒い丸印で示した基地局(CS1)がGPS搭載局であり、図示した基地局の同期群の中心となっている基準局である。 The base stations shown in the figure are indicated by circles (black circles, white circles). A base station (CS1) indicated by a black circle at the center of the figure is a GPS-equipped station, and is a reference station that is the center of a synchronous group of the illustrated base stations.
CS1はGPS搭載局であり同期レベルは1である。CS2、CS3はCS1のフレームタイミングに同期して自局のフレームタイミング生成しており、CS2、CS3の同期レベルはCS1の同期レベルより1ランク低い”2”に設定される。また、CS4はCS3のフレームタイミングに同期し、CS5はCS2のフレームタイミングに同期して自局のフレームタイミング生成しているので、CS4、CS5の同期レベルはCS2、CS3の同期レベルより1ランク低い”3”に設定される。 CS1 is a GPS-equipped station and the synchronization level is 1. CS2 and CS3 generate their own frame timing in synchronization with the CS1 frame timing, and the synchronization level of CS2 and CS3 is set to “2” which is one rank lower than the synchronization level of CS1. Since CS4 synchronizes with the frame timing of CS3 and CS5 generates the frame timing of its own station in synchronization with the frame timing of CS2, the synchronization level of CS4 and CS5 is one rank lower than the synchronization level of CS2 and CS3. Set to “3”.
このとき、CS5は、CS2とCS4との双方の基地局を受信できるが、CS2の方が同期レベルが高位なので(CS2は同期レベル2、CS4は同期レベル3)、より高位の基地局であるCS2を選択して、CS2のフレームタイミングに同期して自局のフレーム同期クロック信号を生成する。また、CS4は同一の同期レベルを有するCS2とCS3とを受信しても、CS2よりCS3の方が近い距離にあり、受信電界強度が強いので、CS4はCS3を選択して、CS3のフレームタイミングに同期する。
At this time, CS5 can receive both CS2 and CS4 base stations, but CS2 has a higher synchronization level (CS2 is
このGPS搭載局は周囲の基地局の次数が低位に(同期レベルが大きく)なって、周囲に同期の基準となる基地局が存在しなくならないように、適宜設置される。
このため、センター設備6では基地局の同期レベルを監視しており、GPS局を多く配置しなくてもよいので、システムに柔軟性があり、安価にシステムを構成することができる。
This GPS-equipped station is appropriately installed so that the order of surrounding base stations is low (the synchronization level is large), and base stations serving as a reference for synchronization do not exist around.
For this reason, the center facility 6 monitors the synchronization level of the base stations, and it is not necessary to arrange many GPS stations. Therefore, the system is flexible and can be configured at low cost.
なお、このように複数の基地局を階層化すると、広域に基地局が配置された場合には複数の同期群が形成されるが、基準となる基地局がGPS衛星からの時間情報を基準としているので、同期群間の誤差が小さく、異なる同期群が接する場所でもガードタイムを超えるフレームタイミングのズレが生じることはない。 In addition, when a plurality of base stations are hierarchized in this way, a plurality of synchronization groups are formed when base stations are arranged in a wide area, but the base station serving as a reference is based on time information from GPS satellites. Therefore, the error between the synchronization groups is small, and a frame timing shift exceeding the guard time does not occur even in a place where different synchronization groups are in contact.
非同期局は、定期的に制御チャネルを受信して、周囲に同期相手となる基地局が設置されたら、図5と同様な手順により、同期相手となる基地局に同期するように構成することもできる。また、現在の同期相手より高次の基地局からのCSIDが受信できたら、再度同期をし直すこともできる。 Asynchronous stations can be configured to receive control channels periodically and to synchronize with the base station to be synchronized by the same procedure as in FIG. it can. In addition, if a CSID from a higher-order base station than the current synchronization partner can be received, the synchronization can be performed again.
このように、GPS受信機を有さない基地局は、GPS受信機を有するGPS搭載局を中心として、GPS搭載局を基準局として階層の上位に設定して、他の基地局は、各基地局が送信する同期制御符号により、自局より上位の階層の基地局を選択してフレームタイミングを決定して、GPS搭載局を中心に、各基地局が自律的に階層を形成して同期をするので、高い精度(基準局同士が±1μ秒程度)で送受信タイミングの同期をすることができる。また、運用者による同期制御の操作が必要なく、運用コストを低減することができる。 In this way, base stations that do not have GPS receivers are centered on GPS-equipped stations that have GPS receivers, and GPS-equipped stations are set at the top of the hierarchy with reference stations, and other base stations The base station of the higher hierarchy than the own station is selected by the synchronization control code transmitted by the mobile station, the frame timing is determined, and each base station autonomously forms a hierarchy and synchronizes with the GPS-equipped station as the center. Therefore, it is possible to synchronize transmission / reception timing with high accuracy (reference stations are about ± 1 μsec). In addition, there is no need for an operation of synchronization control by the operator, and the operation cost can be reduced.
さらに、GPS搭載局が分散して設置されているので、一つのGPS搭載局が故障しても、このGPS搭載局に同期していた基地局は他の周辺の局に同期すればよいことから、移動通信システムの運用が停止することがなく、故障に対する耐性が強い。 Furthermore, because GPS-equipped stations are distributed and installed, even if one GPS-equipped station breaks down, the base station synchronized with this GPS-equipped station only needs to be synchronized with other peripheral stations. The operation of the mobile communication system does not stop, and the resistance to failure is strong.
さらに、同じ階層の他の基地局のうち信号強度が強い基地局を選択して、フレームタイミングを同期するので、確実に同期をすることができる。 Furthermore, since the frame timing is synchronized by selecting a base station having a strong signal strength among other base stations in the same hierarchy, the synchronization can be surely performed.
さらに、他の基地局に同期をして、自局の同期レベルが決定すると、自局の同期レベルが決定した旨を有線回線でセンター設備に通知するので、センター設備で各基地局の同期階層内の地位を把握することができる。 In addition, when the synchronization level of the own station is determined by synchronizing with other base stations, the center facility is notified by a wired line that the synchronization level of the own station has been determined. It is possible to grasp the status within.
1:PHS端末機(PS)、2:基地局装置(CS)、3:加入者交換機、4:中継交換機、5:ISDN網、6:センター設備、11:インターフェース部、12:符号化・復号化部(CODEC)、13:ベースバンド部(B/B)、14:無線部(TRX)、15:アンテナ、16:クロック部(CLK)、17:CPU、18:記憶部(RAM/ROM)、19:GPS受信機、20:GPSアンテナ、21:クロック抽出部。 1: PHS terminal (PS), 2: Base station apparatus (CS), 3: Subscriber exchange, 4: Relay exchange, 5: ISDN network, 6: Center equipment, 11: Interface unit, 12: Encoding / decoding Conversion unit (CODEC), 13: baseband unit (B / B), 14: radio unit (TRX), 15: antenna, 16: clock unit (CLK), 17: CPU, 18: storage unit (RAM / ROM) , 19: GPS receiver, 20: GPS antenna, 21: Clock extraction unit.
Claims (3)
前記基地局は、自局を示す識別情報と自局の同期の階層レベルを示す情報とを含む基地局情報を前記制御装置に送信する手段を有する、ことを特徴とする通信システム。 In a communication system including a plurality of base stations and a network-side control device capable of controlling the plurality of base stations ,
The base station, a communication system, characterized by have a means for transmitting the base station information including the information indicating the synchronization hierarchy level identification information and the own station indicating the own station to the controller.
自局を示す識別情報と自局の同期の階層レベルを示す情報とを含む基地局情報を前記制御装置に送信する手段を有する、ことを特徴とする基地局。A base station comprising means for transmitting base station information including identification information indicating the own station and information indicating a hierarchical level of synchronization of the own station to the control device.
前記基地局が、自局を示す識別情報と自局の同期の階層レベルを示す情報とを含む基地局情報を前記制御装置に送信するステップを含む、ことを特徴とする通信制御方法。The communication control method comprising the step of the base station transmitting base station information including identification information indicating the own station and information indicating a hierarchy level of synchronization of the own station to the control device.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010180535A JP5063756B2 (en) | 2010-08-11 | 2010-08-11 | COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, BASE STATION DEVICE, AND COMMUNICATION CONTROL METHOD |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010180535A JP5063756B2 (en) | 2010-08-11 | 2010-08-11 | COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, BASE STATION DEVICE, AND COMMUNICATION CONTROL METHOD |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000359341A Division JP4627870B2 (en) | 2000-11-27 | 2000-11-27 | Mobile communication system and base station apparatus |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2011010349A JP2011010349A (en) | 2011-01-13 |
| JP2011010349A5 JP2011010349A5 (en) | 2011-10-06 |
| JP5063756B2 true JP5063756B2 (en) | 2012-10-31 |
Family
ID=43566374
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010180535A Expired - Fee Related JP5063756B2 (en) | 2010-08-11 | 2010-08-11 | COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, BASE STATION DEVICE, AND COMMUNICATION CONTROL METHOD |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5063756B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5869431B2 (en) * | 2012-05-30 | 2016-02-24 | 京セラ株式会社 | COMMUNICATION DEVICE, RADIO COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, AND COMMUNICATION CONTROL METHOD |
| JP2014017600A (en) * | 2012-07-06 | 2014-01-30 | Kyocera Corp | Communication device, radio communication system, and communication control method |
| US9276689B2 (en) * | 2012-09-25 | 2016-03-01 | Rad Data Communications Ltd. | Pluggable packet master clock |
| JP6081889B2 (en) * | 2013-09-09 | 2017-02-15 | 京セラ株式会社 | Wireless communication system |
| JP6458942B2 (en) * | 2015-03-09 | 2019-01-30 | サクサ株式会社 | Telephone system, cordless telephone device and host device |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2997856B2 (en) * | 1992-02-18 | 2000-01-11 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | Time division wireless communication system |
| JPH07283772A (en) * | 1992-10-07 | 1995-10-27 | Nippon Steel Corp | Method for establishing syncyronization between radio base stations and mobile communication systeem using the same |
| JP3406745B2 (en) * | 1995-09-28 | 2003-05-12 | 株式会社東芝 | Frame synchronization between base stations for mobile communication systems |
| JPH1084567A (en) * | 1996-09-06 | 1998-03-31 | Japan Radio Co Ltd | Channel changeover control system between base stations |
| JPH10190562A (en) * | 1996-12-26 | 1998-07-21 | Toshiba Corp | Inter-base station frame synchronizing system of mobile communication system and base station device adapting the same |
-
2010
- 2010-08-11 JP JP2010180535A patent/JP5063756B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2011010349A (en) | 2011-01-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4514938B2 (en) | Mobile communication system and base station apparatus | |
| JP4627870B2 (en) | Mobile communication system and base station apparatus | |
| EP1091611B1 (en) | Location system for a cellular telecommunications network | |
| JP5063756B2 (en) | COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, BASE STATION DEVICE, AND COMMUNICATION CONTROL METHOD | |
| EP1509059A1 (en) | Wireless communication system enhanced call recovery | |
| CN109565641B (en) | System and method for beacon interval adaptation | |
| JPH10190562A (en) | Inter-base station frame synchronizing system of mobile communication system and base station device adapting the same | |
| US6614770B1 (en) | Mobile station apparatus and base station apparatus | |
| EP2587881A1 (en) | Wireless communication device, wireless communication system, wireless communication method, and base station | |
| KR20150128493A (en) | Method and apparatus of synchronization in a device to device communication system | |
| JPH08289359A (en) | Frame synchronizing system between base stations in mobile communication system and base station equipment adopting this synchronizing system | |
| JP3313573B2 (en) | Spread code synchronization establishment method in mobile communication system, mobile station apparatus and base station apparatus | |
| CN101511115A (en) | Method and a device for determiming if a handover has to be excuted for a terminal | |
| CN1330109C (en) | Method for synchronising base stations in radio communication system | |
| JP2957140B2 (en) | Intermittent reception method for incoming signal in mobile communication, base station device and mobile device | |
| US7428224B2 (en) | Radio base station system, and method and program for controlling transmission of synchronous burst | |
| JP2008109550A (en) | Radio communication terminal, and base station selection method | |
| CN107431960A (en) | Method, mobile communications network, base station entity, program and the computer program product synchronous for the radio net of the mobile communications network with the local clock functive that local timing reference is provided for each base station entity | |
| JP2000050351A (en) | Mobile communication device and method for establishing synchronization in mobile communication | |
| US8385904B2 (en) | Space time coding where space diversity derives from use of multiple base stations | |
| JP5803566B2 (en) | Wireless communication system, mobile station, base station, and communication control method | |
| JP2018019235A (en) | Base station, communication system, and synchronization signal transmission device | |
| KR101781639B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for non-calibrating auto frequency correction in portable terminal | |
| US8102816B2 (en) | Methods and devices for determining if a handover has to be executed for a terminal | |
| JP2009171228A (en) | Reference signal generator, base station system, and signal transmission method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110805 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20120423 |
|
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date: 20120424 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120508 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120615 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A975 | Report on accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971005 Effective date: 20120704 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20120710 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20120807 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5063756 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20150817 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |