JP4469518B2 - Content usage control device, content usage control method, and content usage control program - Google Patents
Content usage control device, content usage control method, and content usage control program Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4469518B2 JP4469518B2 JP2001197224A JP2001197224A JP4469518B2 JP 4469518 B2 JP4469518 B2 JP 4469518B2 JP 2001197224 A JP2001197224 A JP 2001197224A JP 2001197224 A JP2001197224 A JP 2001197224A JP 4469518 B2 JP4469518 B2 JP 4469518B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- control module
- content
- license
- module
- control
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、映画、音楽、映像等のコンテンツの利用を制御するコンテンツ利用制御装置、コンテンツ利用制御方法およびコンテンツ利用制御プログラムに関するものであり、特に、コンテンツ利用の柔軟性を高め、課金管理を容易にするコンテンツ利用制御装置、コンテンツ利用制御方法およびコンテンツ利用制御プログラムに関するものである。
【0002】
近時においては、マルチメディア化の波を受けて、ディジタル化された映画、音楽等のコンテンツのインターネット配信がスタートしたことから、コンテンツ利用に関するユーザの関心が高まっている。このニーズを受けて、コンテンツ利用の際の柔軟性が高いコンテンツ利用制御の手段、方法が切望されている。
【0003】
【従来の技術】
従来より、映画、音楽等のコンテンツ(著作物)に関しては、著作者の許諾を得なければ、営利目的で販売、譲渡することができない。ここでいうコンテンツとは、単一の記録媒体に記録可能なビット列の集合としての構造をもつディジタルコンテンツをいい、文章テキスト、静止画、動画、プログラムソフトウェア等をいう。
【0004】
この種のコンテンツは、インターネット上のダウンロードサイトや、記録媒体により利用者に提供される。この場合、著作権保護を目的としてライセンス(利用許諾情報)を用いたコンテンツの利用に関する制御(以下、コンテンツ利用制御という)が行われる。このコンテンツ利用制御は、正当な許諾を受けた利用者のみがコンテンツを利用できるようにするためのものである。
【0005】
また、コンテンツを利用するためのコンテンツ利用制御装置では、当該ライセンスおよびコンテンツを利用するための、固有の利用環境が設定されている。この利用環境では、当該コンテンツ利用制御装置を識別するための装置識別情報が設定されている。従って、コンテンツ利用制御装置では、装置識別情報、当該ライセンスを用いて、コンテンツを復号することにより、コンテンツ利用制御が行われる。また、従来では、有料でコンテンツを利用する際に、利用者に対して課金されるが、この課金に関する管理は、コンテンツ提供者側で管理されている。
【0006】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
ところで、前述したように、従来のコンテンツ利用制御装置では、装置側の利用環境に対応するように個別的に作成されたコンテンツおよびライセンスが提供される。従って、従来では、コンテンツおよびライセンスがコンテンツ利用制御装置の利用環境に大きく依存していることから、利用者側で柔軟にコンテンツ利用ができず、しかも個別的にコンテンツおよびライセンスを作成しなければならず無駄が多くコンテンツ提供者側の負担が大きいという問題があった。
【0007】
また、従来では、ライセンスに課金情報を持たせることができないため、コンテンツ利用の課金に関する管理をコンテンツ提供者側で行っており、課金管理が非常に面倒であるという問題もあった。
【0008】
本発明は、上記に鑑みてなされたもので、コンテンツ利用の柔軟性を高めることができ、コンテンツ利用に関する課金管理を容易に行うことができるコンテンツ利用制御装置、コンテンツ利用制御方法およびコンテンツ利用制御プログラムを提供することを目的とする。
【0009】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上記目的を達成するために、本発明は、コンテンツ提供権限者からコンテンツ利用者に対して提供されるコンテンツの利用制御を行うコンテンツ利用制御装置において、コンテンツと第1の制御モジュールとからなる制御モジュール付きコンテンツ、および前記コンテンツの利用許諾情報からなるライセンスと第2の制御モジュールとからなる制御モジュール付きライセンスを入力する入力手段と、複数の制御モジュール付きコンテンツおよび複数の制御モジュール付きライセンスを格納するデータベースをとさらに備え、前記制御モジュール付きコンテンツは、自コンテンツに関連のある制御モジュール付きライセンスを前記データベースから検索し、検索された制御モジュール付きライセンスを起動させ、前記制御モジュール付きライセンスは、前記制御モジュール付きコンテンツによって起動された場合に、自ライセンスに関連のある制御モジュール付きコンテンツを前記データベースから検索し、検索されたコンテンツを起動させる。そして、制御モジュール付きライセンスによって起動された制御モジュール付きコンテンツは、自コンテンツに関連のある制御モジュール付きライセンスを検索し、検索された制御モジュール付きライセンスを起動させ、制御モジュール付きコンテンツによって起動された制御モジュール付きライセンスは、自ライセンスに関連のある制御モジュール付きコンテンツを検索し、検索された制御モジュール付きコンテンツを起動させることを特徴とする。
【0010】
この発明によれば、第1の制御モジュールと第2の制御モジュールとの相互連携により、コンテンツ利用に関する制御を行うようにしたので、従来のようにコンテンツを利用する装置側の環境に依存することなく、柔軟にコンテンツ利用を行うことができる。
【0011】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、図面を参照して本発明にかかるコンテンツ利用制御装置、コンテンツ利用制御方法およびコンテンツ利用制御プログラムの一実施の形態について詳細に説明する。
【0012】
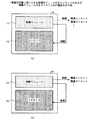
はじめに、本発明にかかる一実施の形態で用いられる各種制御モジュール付きコンテンツおよび制御モジュール付きライセンスの構成について図1〜図4を参照して説明する。図1(a)および(b)には、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ10および制御モジュール付きライセンス20が図示されている。これらの制御モジュール付きコンテンツ10および制御モジュール付きライセンス20は、記録媒体、インターネット等を介してコンテンツ提供者から利用者へ提供される。
【0013】
図1(a)に示した制御モジュール付きコンテンツ10は、制御モジュール11およびコンテンツ12から構成されている。この制御モジュール11は、コンテンツ12、制御モジュール21(図1(b)参照)、外部のモジュール(図示略)を動的に制御するものである。また、制御モジュール11は、ソースコード形式のファイルである。従って、制御モジュール11を起動させるためには、制御モジュール11を実行形式のファイル(exeファイル)にコンパイルする必要がある。コンテンツ12は、音楽、映像、音声等の情報である。
【0014】
図1(b)に示した制御モジュール付きライセンス20は、制御モジュール21およびライセンス22から構成されている。制御モジュール21は、ライセンス22、制御モジュール11(図1(a)参照)、外部のモジュールを動的に制御するものである。また、制御モジュール21は、ソースコード形式のファイルである。従って、制御モジュール21を起動させるためには、制御モジュール21を実行形式のファイル(exeファイル)にコンパイルする必要がある。ライセンス22は、コンテンツ12の利用許諾情報である。従って、利用者は、コンテンツ12とライセンス22の双方を入手しなければ、コンテンツ12を利用(再生)することができないようになっている。
【0015】
図2(a)および(b)には、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ30および制御モジュール付きライセンス40が図示されている。これらの制御モジュール付きコンテンツ30および制御モジュール付きライセンス40は、記録媒体、インターネット等を介してコンテンツ提供者から利用者へ提供される。
【0016】
図2(a)に示した制御モジュール付きコンテンツ30は、制御モジュール31およびコンテンツ32から構成されている。この制御モジュール31は、コンテンツ32、制御モジュール41(図2(b)参照)、外部のモジュール(図示略)を動的に制御するものである。また、制御モジュール31は、実行形式のファイル(exeファイル)であり、実行命令により起動される。従って、制御モジュール31は、コンパイルする必要がない。コンテンツ32は、音楽、映像、音声等の情報である。
【0017】
図2(b)に示した制御モジュール付きライセンス40は、制御モジュール41およびライセンス42から構成されている。制御モジュール41は、ライセンス42、制御モジュール31(図2(a)参照)、外部のモジュールを動的に制御するものである。また、制御モジュール41は、実行形式のファイル(exeファイル)であり、実行命令により起動される。従って、制御モジュール41は、コンパイルする必要がない。ライセンス42は、コンテンツ32の利用許諾情報である。従って、利用者は、コンテンツ32とライセンス42の双方を入手しなければ、コンテンツ32を利用(再生)することができないようになっている。
【0018】
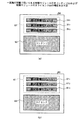
図3(a)および(b)には、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ50および制御モジュール付きライセンス60が図示されている。これらの制御モジュール付きコンテンツ50および制御モジュール付きライセンス60は、記録媒体、インターネット等を介してコンテンツ提供者から利用者へ提供される。
【0019】
図3(a)に示した制御モジュール付きコンテンツ50は、制御モジュール51およびコンテンツ52から構成されている。この制御モジュール51は、三種類の第1の制御モジュール511 〜第3の制御モジュール513 から構成されており、コンテンツ52、制御モジュール61(図3(b)参照)、外部のモジュール(図示略)を動的に制御するものである。これらの第1の制御モジュール511 〜第3の制御モジュール513 は、後述する第1の制御モジュール611 〜第3の制御モジュール613 との組み合わせ(例えば、第1の制御モジュール511 と第2の制御モジュール612 )に応じた複数種類の制御を実現するためのものである。コンテンツ52は、音楽、映像、音声等の情報である。
【0020】
図3(b)に示した制御モジュール付きライセンス60は、制御モジュール61およびライセンス62から構成されている。制御モジュール61は、三種類の第1の制御モジュール611 〜第3の制御モジュール613 から構成されており、ライセンス62、制御モジュール51(図3(a)参照)、外部のモジュールを動的に制御するものである。
【0021】
これらの第1の制御モジュール611 〜第3の制御モジュール613 は、第1の制御モジュール511 〜第3の制御モジュール513 との組み合わせ(例えば、第1の制御モジュール511 と第2の制御モジュール612 )に応じた複数種類の制御を実現するためのものである。ライセンス62は、コンテンツ52の利用許諾情報である。従って、利用者は、コンテンツ52とライセンス62の双方を入手しなければ、コンテンツ52を利用(再生)することができないようになっている。
【0022】
図4(a)には、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集/ライセンス集70の構成が図示されている。この制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集/ライセンス集70は、図4(b)に示したように、階層構造をなす複数のコンテンツ(コンテンツ集)およびこれらの複数のコンテンツに対応する複数のライセンス(ライセンス集)ならびに複数のコンテンツおよびライセンスに対応する複数の制御モジュールから構成されている。この制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集/ライセンス集70は、一つのファイルとして格納されている。また、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集/ライセンス集70は、記録媒体、インターネット等を介してコンテンツ提供者から利用者へ提供される。
【0023】
具体的には、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集/ライセンス集70は、制御モジュール71、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集80および制御モジュール付きライセンス集120から構成されている。図4(b)に示したように、制御モジュール71は、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集/ライセンス集70から制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集80と制御モジュール付きライセンス集120とを取り出す際の制御を行う。
【0024】
制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集80は、制御モジュール81、ビューアコンテンツ90、制御モジュール付き映画コンテンツ100および制御モジュール付き音楽コンテンツ110から構成されている。この制御モジュール81は、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集80からビューアコンテンツ90、制御モジュール付き映画コンテンツ100および制御モジュール付き音楽コンテンツ110を取り出す際の制御を行う。
【0025】
ビューアコンテンツ90は、ビューアからなるコンテンツであり、後述するビューア/音楽ライセンス132により利用可能とされる。制御モジュール付き映画コンテンツ100は、制御モジュール101、映像コンテンツ102および音声コンテンツ103から構成されている。制御モジュール101は、映像コンテンツ102、音声コンテンツ103や、後述する制御モジュール141、外部のモジュール(図示略)を動的に制御するものである。
【0026】
映像コンテンツ102は、映画を構成する映像からなるコンテンツである。この映像コンテンツ102は、後述する映像ライセンス143により利用可能とされる。音声コンテンツ103は、映画を構成する音声からなるコンテンツである。音声コンテンツ103は、後述する音声ライセンス142により利用可能とされる。制御モジュール付き音楽コンテンツ110は、制御モジュール111および音楽コンテンツ112から構成されている。
【0027】
制御モジュール111は、音楽コンテンツ112や後述する制御モジュール131、外部のモジュール(図示略)を動的に制御するものである。音楽コンテンツ112は、音楽からなるコンテンツである。この音楽コンテンツ112は、後述するビューア/音楽ライセンス132により利用可能とされる。
【0028】
一方、制御モジュール付きライセンス集120は、制御モジュール121、制御モジュール付きライセンス130および制御モジュール付きライセンス140から構成されている。制御モジュール121は、制御モジュール付きライセンス集120から制御モジュール付きライセンス130および制御モジュール付きライセンス140を取り出す際の制御を行う。
【0029】
制御モジュール付きライセンス130は、制御モジュール131およびビューア/音楽ライセンス132から構成されている。制御モジュール131は、ビューア/音楽ライセンス132や、上述した制御モジュール81、制御モジュール111、外部のモジュール(図示略)を動的に制御するものである。ビューア/音楽ライセンス132は、音楽コンテンツ112およびビューアコンテンツ90の利用許諾情報である。
【0030】
制御モジュール付きライセンス140は、制御モジュール141、音声ライセンス142および映像ライセンス143から構成されている。制御モジュール141は、音声ライセンス142、映像ライセンス143、制御モジュール101や、外部のモジュール(図示略)を動的に制御するものである。音声ライセンス142は、音声コンテンツ103の利用許諾情報である。映像ライセンス143は、映像コンテンツ102の利用許諾情報である。
【0031】
ここで、図4に示した制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集/ライセンス集70においては、所望の制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集および制御モジュール付きライセンス集が取り出され、これらが利用/配布される。例えば、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集/ライセンス集70から制御モジュール付き映画コンテンツ100およびこれに対応する制御モジュール付きライセンス140が取り出された場合、図5に示したように、制御モジュール付き映画コンテンツ100の制御モジュール101(図4参照)および制御モジュール141(図4参照)は、相互連携により、音声ライセンス142および映像ライセンス143を用いて、映像コンテンツ102および音声コンテンツ103を利用する。
【0032】
ここで、前述した制御モジュール付きライセンスおよび制御モジュール付きコンテンツ(図1〜図4参照)によりコンテンツを利用するための構成例について図6〜図11を参照して説明する。図6〜図11は、本発明にかかる一実施の形態の構成例1〜6を示すブロック図である。
【0033】
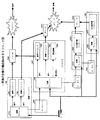
まず、図6を参照して一実施の形態の構成例1について詳述する。この図において、CPU(Central Processing Unit)300は、制御モジュール付きライセンス210および制御モジュール付きコンテンツ200に基づいて、暗号化ライセンス212を復号することでコンテンツ復号鍵330を生成し、このコンテンツ復号鍵330を用いて暗号化コンテンツ202が復号されたコンテンツ(例えば、コンピュータプログラム)を実行する。
【0034】
制御モジュール付きコンテンツ200は、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ10(図1(a)参照)に対応するものであり、記録媒体やインターネット(図示略)を介してCPU300に入力される。この制御モジュール付きコンテンツ200は、制御モジュール201および暗号化コンテンツ202から構成されている。制御モジュール201は、制御モジュール11(図1(a)参照)と同様の機能を備えている。暗号化コンテンツ202は、暗号化されたコンテンツ(例えば、コンピュータプログラム)である。
【0035】
制御モジュール付きライセンス210は、制御モジュール付きライセンス20(図1(b)参照)に対応するものであり、記録媒体やインターネットを介してCPU300に入力される。この制御モジュール付きライセンス210は、制御モジュール211および暗号化ライセンス212から構成されている。制御モジュール211は、制御モジュール21(図1(b)参照)と同様の機能を備えている。暗号化ライセンス212は、暗号化コンテンツ202を復号するためのコンテンツ復号鍵330が暗号化されたものである。
【0036】
CPU300において、常駐モジュール310(「特許請求の範囲」の第3の制御モジュールに対応)は、制御モジュール211および制御モジュール201が正規のものであるか否かを認証する機能を備えている。CPU個別鍵320は、当該CPU300に予め割り当てられており、暗号化ライセンス212を復号する際に用いられる鍵である。コンテンツ復号鍵330は、CPU個別鍵320を用いて暗号化ライセンス212が復号された鍵であり、暗号化コンテンツ202を復号する際に用いられる。コンテンツ復号部340は、コンテンツ復号鍵330を用いて、暗号化コンテンツ202を復号する。実行部350は、暗号化コンテンツ202が復号されたコンテンツを実行する。
【0037】
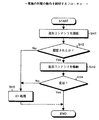
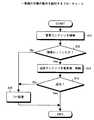
つぎに、図12に示したフローチャートを参照しつつ、図6に示した構成例1の動作について説明する。同図に示したステップSA1〜ステップSA7は、モジュールMA(図6の常駐モジュール310に対応)の認証動作の工程を表し、ステップSB1〜ステップSB7は、モジュールMB(図6の制御モジュール211および制御モジュール201に対応)の認証動作の工程を表す。図6に示したCPU300に制御モジュール付きコンテンツ200および制御モジュール付きライセンス210が入力されると、常駐モジュール310(図12:モジュールMA )と、制御モジュール201および制御モジュール211(図12:モジュールMB )との間で認証動作が行われる。
【0038】
すなわち、図12に示したステップSA1では、常駐モジュール310(モジュールMA )は、乱数RA を生成する。ステップSA2では、常駐モジュール310は、乱数RA を秘密鍵HA で暗号化し、制御モジュール201(モジュールMB )に送る。この暗号化された乱数RA を受け取ると、ステップSB1では、制御モジュール201は、暗号化された乱数RA を公開鍵KA で復号し、乱数RA を取り出す。ステップSB2では、制御モジュール201は、乱数RB を生成する。
【0039】
ステップSB3では、制御モジュール201は、上記乱数RA および乱数RB を秘密鍵HB で暗号化し、常駐モジュール310に送る。この暗号化された乱数RA および乱数RB を受け取ると、ステップSA3では、常駐モジュール310は、暗号化された乱数RA および乱数RB を公開鍵KB で復号し、乱数RA および乱数RB を取り出す。ステップSA4では、常駐モジュール310は、制御モジュール201に送った乱数RA(ステップSA1で生成)と、受け取った乱数RA(ステップSA3で復号)とが同じものであるか否かを判断する。
【0040】
このステップSA4の判断結果が「No」である場合、常駐モジュール310は、制御モジュール201が正規のものではなく、認証されなかったものとして、ステップSA7でエラー処理を実行する。この場合、ステップSA4の判断結果が「Yes」、すなわち認証されたものとすると、ステップSA5では、常駐モジュール310は、乱数RB を秘密鍵HA で暗号化し、これを制御モジュール201に送る。ステップSA6では、常駐モジュール310は、乱数RA と乱数RB との排他的論理和をセッション鍵とする。
【0041】
そして、暗号化された乱数RB を受け取ると、ステップSB4では、制御モジュール201は、暗号化された乱数RB を公開鍵KA で復号し、乱数RB を取り出す。ステップSB5では、制御モジュール201は、常駐モジュール310に送った乱数RB(ステップSB2で生成)と、受け取った乱数RB(ステップSB4で復号)とが同じものであるか否かを判断する。
【0042】
このステップSB5の判断結果が「No」である場合、制御モジュール201は、常駐モジュール310が正規のものではなく、認証されなかったものとしてステップSB7でエラー処理を実行する。この場合、ステップSB5の判断結果が「Yes」、すなわち常駐モジュール310と制御モジュール201との間で相互認証されたものとすると、ステップSB6では、制御モジュール201は、乱数RA と乱数RB との排他的論理和をセッション鍵とする。
【0043】
一方、常駐モジュール310と制御モジュール211との間でも、上述した常駐モジュール310と制御モジュール201との間の認証動作と同様にして、認証動作が行われる。この場合、常駐モジュール310と制御モジュール211との間で相互認証されたものとする。
【0044】
つぎに、図6に示した常駐モジュール310は、CPU個別鍵320を用いて、暗号化ライセンス212を復号し、コンテンツ復号鍵330を生成し、これをコンテンツ復号部340へ送る。これにより、コンテンツ復号部340は、暗号化コンテンツ202をコンテンツ復号鍵330を用いて復号し、復号結果(コンテンツ)を実行部350へ送る。実行部350では、上記コンテンツ(例えば、コンピュータプログラム)が実行される。
【0045】
つぎに、図7を参照して一実施の形態の構成例2について詳述する。この図において、図6の各部に対応する部分には同一の符号を付ける。同図では、図6に示したCPU300に代えてデコーダ400が設けられている。デコーダ400は、制御モジュール付きライセンス210および制御モジュール付きコンテンツ200に基づいて、暗号化ライセンス212を復号することでコンテンツ復号鍵430を生成し、このコンテンツ復号鍵430を用いて暗号化コンテンツ202が復号されたコンテンツをデコードする。
【0046】
デコーダ400において、常駐モジュール410は、常駐モジュール310(図6参照)と同様の機能(認証機能等)を備えている。デコーダ個別鍵420は、当該デコーダ400に予め割り当てられており、暗号化ライセンス212を復号する際に用いられる鍵である。コンテンツ復号鍵430は、デコーダ個別鍵420を用いて暗号化ライセンス212が復号された鍵であり、暗号化コンテンツ202を復号する際に用いられる。コンテンツ復号部440は、コンテンツ復号鍵430を用いて、暗号化コンテンツ202を復号する。デコード部450は、暗号化コンテンツ202が復号されたコンテンツをデコードする。
【0047】
つぎに、図12に示したフローチャートを参照しつつ、図7に示した構成例2の動作について説明する。同図に示したステップSA1〜ステップSA7は、モジュールMA(図7の常駐モジュール410に対応)の認証動作の工程を表し、ステップSB1〜ステップSB7は、モジュールMB(図7の制御モジュール211および制御モジュール201に対応)の認証動作の工程を表す。図7に示したデコーダ400に制御モジュール付きコンテンツ200および制御モジュール付きライセンス210が入力されると、常駐モジュール410(図12:モジュールMA )と、制御モジュール201および制御モジュール211(図12:モジュールMB )との間で認証動作が行われる。
【0048】
すなわち、図12に示したステップSA1では、常駐モジュール410(モジュールMA )は、乱数RA を生成する。ステップSA2では、常駐モジュール410は、乱数RA を秘密鍵HA で暗号化し、制御モジュール201(モジュールMB )に送る。この暗号化された乱数RA を受け取ると、ステップSB1では、制御モジュール201は、暗号化された乱数RA を公開鍵KA で復号し、乱数RA を取り出す。ステップSB2では、制御モジュール201は、乱数RB を生成する。
【0049】
ステップSB3では、制御モジュール201は、上記乱数RA および乱数RB を秘密鍵HB で暗号化し、常駐モジュール410に送る。この暗号化された乱数RA および乱数RB を受け取ると、ステップSA3では、常駐モジュール410は、暗号化された乱数RA および乱数RB を公開鍵KB で復号し、乱数RA および乱数RB を取り出す。ステップSA4では、常駐モジュール410は、制御モジュール201に送った乱数RA(ステップSA1で生成)と、受け取った乱数RA(ステップSA3で復号)とが同じものであるか否かを判断する。
【0050】
このステップSA4の判断結果が「No」である場合、常駐モジュール410は、制御モジュール201が正規のものではなく、認証されなかったものとして、ステップSA7でエラー処理を実行する。この場合、ステップSA4の判断結果が「Yes」、すなわち認証されたものとすると、ステップSA5では、常駐モジュール410は、乱数RB を秘密鍵HA で暗号化し、これを制御モジュール201に送る。ステップSA6では、常駐モジュール410は、乱数RA と乱数RB との排他的論理和をセッション鍵とする。
【0051】
そして、暗号化された乱数RB を受け取ると、ステップSB4では、制御モジュール201は、暗号化された乱数RB を公開鍵KA で復号し、乱数RB を取り出す。ステップSB5では、制御モジュール201は、常駐モジュール410に送った乱数RB(ステップSB2で生成)と、受け取った乱数RB(ステップSB4で復号)とが同じものであるか否かを判断する。
【0052】
このステップSB5の判断結果が「No」である場合、制御モジュール201は、常駐モジュール410が正規のものではなく、認証されなかったものとしてステップSB7でエラー処理を実行する。この場合、ステップSB5の判断結果が「Yes」、すなわち常駐モジュール410と制御モジュール201との間で相互認証されたものとすると、ステップSB6では、制御モジュール201は、乱数RA と乱数RB との排他的論理和をセッション鍵とする。
【0053】
一方、常駐モジュール410と制御モジュール211との間でも、上述した常駐モジュール410と制御モジュール201との間の認証動作と同様にして、認証動作が行われる。この場合、常駐モジュール410と制御モジュール211との間で相互認証されたものとする。
【0054】
つぎに、図7に示した常駐モジュール410は、デコーダ個別鍵420を用いて、暗号化ライセンス212を復号し、コンテンツ復号鍵430を生成し、これをコンテンツ復号部440へ送る。これにより、コンテンツ復号部440は、暗号化コンテンツ202をコンテンツ復号鍵430を用いて復号し、復号結果(コンテンツ)をデコード部450へ送る。デコード部450では、上記コンテンツがデコードされる。
【0055】
つぎに、図8を参照して一実施の形態の構成例3について詳述する。この図において、記録媒体500は、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ510および個別鍵520を記録してなり、光ディスク、フロッピーディスク等である。制御モジュール付きコンテンツ510は、制御モジュール511および暗号化コンテンツ512から構成されている。制御モジュール511は、制御モジュール11(図1(a)参照)と同様の機能を備えており、後述する常駐モジュール640との間で認証処理等を実行する。暗号化コンテンツ512は、鍵Kcおよび鍵Kc’により二重に暗号化されている。個別鍵520は、暗号化された暗号化コンテンツ512を復号するための鍵である。
【0056】
記憶装置600は、記録媒体500から制御モジュール付きコンテンツ510、個別鍵520を読み出す機能と、暗号化コンテンツ512を復号する機能とを備えている。復号部610は、個別鍵520を用いて、暗号化コンテンツ512を復号し、暗号化コンテンツ512aを生成する。常駐モジュール640は、制御モジュール511が正規のものであるか否かを認証する機能等を備えている。個別鍵630は、当該記憶装置600に予め割り当てられており、暗号化コンテンツ512aを復号する際に用いられる鍵である。復号部620は、個別鍵630を用いて、暗号化コンテンツ512aを復号し、復号済コンテンツ512bを生成する。
【0057】
つぎに、図19に示したフローチャートを参照しつつ、図8に示した構成例3の動作について説明する。同図に示したステップSJ1〜ステップSJ6は、常駐モジュール640の動作を表し、ステップSK1〜ステップSK4は、制御モジュール511の動作を表す。図8に示した記憶装置600に記録媒体500がセットされると、ステップSJ1では、常駐モジュール640は、制御モジュール511から個別鍵520を受け取り、これを復号部610に渡すことにより、復号処理を実行する。すなわち、復号処理では、復号部610は、個別鍵520を用いて、暗号化コンテンツ512を復号し、暗号化コンテンツ512aを生成する。
【0058】
ステップSJ2では、常駐モジュール640は、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ510が制御モジュールを備えるコンテンツであるか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSJ6でエラー処理を実行する。この場合、ステップSJ2の判断結果を「Yes」とし、ステップSJ3では、常駐モジュール640は、制御モジュール511との間で認証処理を実行する。これに平行して、ステップSK1では、制御モジュール511は、常駐モジュール640との間で認証処理を実行する。この認証処理では、図12を参照して説明した動作を経て相互認証が行われる。
【0059】
この認証処理が終了すると、ステップSJ4では、常駐モジュール640は、認証されたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSJ6でエラー処理を実行する。一方、ステップSK2では、制御モジュール511は、認証されたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSK4でエラー処理を実行する。この場合、相互認証されたものとすると、常駐モジュール640は、ステップSJ4の判断結果を「Yes」とし、制御モジュール511は、ステップSK2の判断結果を「Yes」とする。
【0060】
ステップSJ5では、常駐モジュール640は、制御モジュール511を起動する。これにより、ステップSK3では、制御モジュール511は、自身に記述された制御の内容に従って処理を実行する。具体的には、制御モジュール511は、個別鍵630を復号部620に渡す。これにより、復号部620は、暗号化コンテンツ512aを復号し、復号済コンテンツ512bを生成する。この復号済コンテンツ512bは、図示しないデコーダで再生される。
【0061】
つぎに、図9を参照して一実施の形態の構成例4について詳述する。この図において、映画コンテンツ700は、制御モジュール710、音声コンテンツ720および映像コンテンツ730から構成されている。制御モジュール710は、音声コンテンツ720および映像コンテンツ730を発行する機能や、データベース800を検索する機能を備えている。音声コンテンツ720は、映画を構成する音楽に関するコンテンツであり、暗号化されている。映像コンテンツ730は、映画を構成する映像に関するコンテンツであり、暗号化されている。
【0062】
データベース800は、複数の制御モジュール付きライセンスを格納している。同図に示した例では、データベース800には、制御モジュール付きライセンスとしてライセンス900が格納されている。ライセンス900は、映画コンテンツ700の利用許諾情報であり、制御モジュール910、音声ライセンス920、映像ライセンス930および課金情報940から構成されている。制御モジュール910は、音声ライセンス920、映像ライセンス930を発行する機能、課金情報940を書き換える機能、データベース1000を検索する機能を備えている。
【0063】
音声ライセンス920は、上述した音声コンテンツ720の利用許諾情報(コンテンツ復号鍵)である。映像ライセンス930は、上述した映像コンテンツ730の利用許諾情報(コンテンツ復号鍵)である。課金情報940は、音声コンテンツ720、映像コンテンツ730、後述する日本語字幕コンテンツ1220の利用に係る課金情報である。
【0064】
データベース1000は、複数の制御モジュール付きライセンスを格納している。同図に示した例では、データベース1000には、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1200が格納されている。制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1200は、制御モジュール1210および日本語字幕コンテンツ1220から構成されており、映画コンテンツ700を再生する際の日本語字幕の情報を提供する。制御モジュール1210は、日本語字幕コンテンツ1220を発行する機能や、データベース1300を検索する機能を備えている。日本語字幕コンテンツ1220は、映画の日本語字幕の情報であり、暗号化されている。
【0065】
データベース1300は、複数の制御モジュール付きライセンスを格納している。同図に示した例では、制御モジュール付きライセンス1400が格納されている。制御モジュール付きライセンス1400は、制御モジュール1410および日本語字幕ライセンス1420から構成されており、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1200の利用許諾情報である。制御モジュール1410は、日本語字幕ライセンス1420を発行する機能を備える。日本語字幕ライセンス1420は、日本語字幕コンテンツ1220の利用許諾情報(コンテンツ復号鍵)である。
【0066】
デコーダ1500は、音声ライセンス920を用いて音声コンテンツ720をデコード(復号)する。デコードされた音声コンテンツ720は、スピーカを介して、映画の音声として出力される。デコーダ1510は、映像ライセンス930を用いて映像コンテンツ730をデコード(復号)する。デコーダ1520は、日本語字幕ライセンス1420を用いて日本語字幕コンテンツ1220をデコード(復号)する。デコーダ1510およびデコーダ1520のそれぞれの出力は、ビューアにより合成され、日本語字幕を含む映画の映像とされる。
【0067】
つぎに、図14に示したフローチャートを参照しつつ、図9に示した構成例4の動作について説明する。同図に示したステップSD1〜ステップSD8は、図9に示した制御モジュール710、制御モジュール1210の動作を表し、ステップSE1〜ステップSE4は、制御モジュール910および制御モジュール1410の動作を表す。
【0068】
同図に示したステップSD1では、制御モジュール710は、映画コンテンツ700に対応するライセンス側の制御モジュールについて、データベース800を検索する。ステップSD2では、制御モジュール710は、検索ヒット数がいくつであるかを判断する。検索ヒット数が0である場合、制御モジュール710は、ステップSD8でエラー処理を実行する。また、検索ヒット数が2である場合、制御モジュール710は、ステップSD3で二つのライセンス(制御モジュール)のうちいずれか一方を選択する。
【0069】
この場合、検索ヒット数が1であり、制御モジュール910(ライセンス900)がヒットしたものとする。従って、ステップSD4では、制御モジュール710は、制御モジュール910との間で認証処理を実行する。この認証処理では、図12を参照して説明した動作を経て相互認証が行われる。また、ステップSE1でも、制御モジュール910は、制御モジュール710との間で認証処理を実行する。
【0070】
この認証処理が終了すると、ステップSD5では、制御モジュール710は、認証されたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSD8でエラー処理を実行する。一方、ステップSE2では、制御モジュール910は、認証されたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSE4でエラー処理を実行する。
【0071】
この場合、相互認証されたものとすると、制御モジュール710は、ステップSD5の判断結果を「Yes」とし、制御モジュール910は、ステップSE2の判断結果を「Yes」とする。ステップSD6では、制御モジュール710は、制御モジュール910を起動する。これにより、ステップSE3では、制御モジュール910は、復号鍵として音声ライセンス920および映像ライセンス930を取り出す。
【0072】
つぎに、制御モジュール910は、図13に示したフローチャートに従って、課金情報940を書き換える処理を実行する。すなわち、ステップSC1では、制御モジュール910は、課金情報940を復号する。ステップSC2では、制御モジュール910は、課金計算を実行する。
【0073】
すなわち、制御モジュール910は、復号された課金情報940から得られる残高から、映画に関するコンテンツ(音声コンテンツ720、映像コンテンツ730等)を1回利用する際の利用料金を減算し、減算結果を新たな残高とする。ステップSC3では、上記残高が、残高しきい値以上であるか否かを判断する。この判断結果が「No」である場合、制御モジュール910は、料金不足により、当該映画に関するコンテンツの利用ができないものとし、ステップSC7でエラー処理を実行する。
【0074】
この場合、ステップSC3の判断結果が「Yes」であるものとすると、ステップSC4では、制御モジュール910は、課金情報(残高)を暗号化し、これを課金情報940として格納する。ステップSC5では、制御モジュール710は、格納が成功したか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSC7でエラー処理を実行する。この場合、ステップSC5の判断結果が「Yes」であるものとすると、制御モジュール910は、音声ライセンス920をデコーダ1500に対して発行するとともに、映像ライセンス930をデコーダ1510に対して発行する。
【0075】
これに並行して、図14に示したステップSD7では、制御モジュール710は、暗号化された音声コンテンツ720および映像コンテンツ730を取り出し、音声コンテンツ720をデコーダ1500に対して発行するとともに、映像コンテンツ730をデコーダ1510に対して発行する。これにより、デコーダ1500により、音声コンテンツ720が音声ライセンス920を用いてデコードされ、スピーカーから映画の音声が出力される。また、デコーダ1510により、映像コンテンツ730が映像ライセンス930を用いてデコードされ、映画の映像が出力される。
【0076】
つぎに、制御モジュール910は、図15に示したフローチャートに従って、データベース1000から、映画に関連する制御モジュール付きコンテンツを検索する処理を実行する。すなわち、ステップSF1では、制御モジュール910は、データベース1000から、映画に関連する制御モジュール付きコンテンツを検索する。ステップSF2では、制御モジュール910は、検索ヒットしたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSF6でエラー処理を実行する。
【0077】
この場合、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1200が検索ヒットしたものとすると、制御モジュール910は、ステップSF2の判断結果を「Yes」とする。ステップSF3では、制御モジュール910は、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1200をデータベース1000から取り出す。ステップSF4では、制御モジュール910は、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1200の制御モジュール1210を起動する。ステップSF5では、制御モジュール910は、上記起動が成功したか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「Yes」である場合、正常終了する。一方、ステップSF6の判断結果が「No」である場合、制御モジュール910は、ステップSF6でエラー処理を実行する。
【0078】
また、制御モジュール1210が起動されると、図14に示したフローチャートに従って処理が実行される。すなわち、ステップSD1では、制御モジュール1210は、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1200に対応するライセンス側の制御モジュールについて、データベース1300を検索する。ステップSD2では、制御モジュール1210は、検索ヒット数がいくつであるかを判断する。検索ヒット数が0である場合、制御モジュール1210は、ステップSD8でエラー処理を実行する。また、検索ヒット数が2である場合、制御モジュール1210は、ステップSD3で二つのライセンス(制御モジュール)のうちいずれか一方を選択する。
【0079】
この場合、検索ヒット数が1であり、制御モジュール1410(制御モジュール付きライセンス1400)がヒットしたものとする。従って、ステップSD4では、制御モジュール1210は、制御モジュール1410との間で認証処理を実行する。この認証処理では、図12を参照して説明した動作を経て相互認証が行われる。また、ステップSE1でも、制御モジュール1410は、制御モジュール1210との間で認証処理を実行する。
【0080】
この認証処理が終了すると、ステップSD5では、制御モジュール1210は、認証されたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSD8でエラー処理を実行する。一方、ステップSE2では、制御モジュール1410は、認証されたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSE4でエラー処理を実行する。この場合、相互認証されたものとすると、制御モジュール1210は、ステップSD5の判断結果を「Yes」とし、制御モジュール1410は、ステップSE2の判断結果を「Yes」とする。
【0081】
ステップSD6では、制御モジュール1210は、制御モジュール1410を起動する。これにより、ステップSE3では、制御モジュール1410は、復号鍵として日本語字幕ライセンス1420を取り出し、これをデコーダ1520に渡す。これに並行して、ステップSD7では、制御モジュール1210は、日本語字幕コンテンツ1220を取り出し、これをデコーダ1520に対して発行する。これにより、デコーダ1520により、日本語字幕コンテンツ1220が日本語字幕ライセンス1420を用いてデコードされ、映画の日本語字幕の情報が出力される。
【0082】
また、上述した制御モジュール910は、データベース1000におけるコンテンツ(この場合、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ)に関して、消去、追加および変更を行う機能を備える。以下では、図16〜図18に示したフローチャートを参照して、消去、追加および変更のそれぞれの処理について説明する。消去処理において、図16に示したステップSG1では、制御モジュール910は、データベース1000から消去すべきコンテンツを検索する。ステップSG2では、制御モジュール910は、検索ヒットしたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSG5でエラー処理を実行する。
【0083】
ステップSG2の判断結果が「Yes」である場合、ステップSG3では、制御モジュール910は、データベース1000から当該コンテンツを消去する。ステップSG4では、制御モジュール910は、消去が成功したか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSG5でエラー処理を実行する。ステップSG4の判断結果が「Yes」である場合、制御モジュール910は、正常終了する。
【0084】
また、追加処理において、図17に示したステップSH1では、制御モジュール910は、図12で説明した手順に従って、データベース1000に追加すべきコンテンツ(制御モジュール付きコンテンツ)を認証する。ステップSH2では、制御モジュール910は、認証されたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSH5でエラー処理を実行する。
【0085】
ステップSH2の判断結果が「Yes」である場合、ステップSH3では、制御モジュール910は、コンテンツ(制御モジュール付きコンテンツ)をデータベース1000に格納する。ステップSH4では、制御モジュール910は、格納が成功したか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSH5でエラー処理を実行する。ステップSH4の判断結果が「Yes」である場合、制御モジュール910は、正常終了する。
【0086】
また、変更処理において、図18に示したステップSI1では、制御モジュール910は、データベース1000から、変更すべきコンテンツ(制御モジュール付きコンテンツ)を検索する。ステップSI2では、制御モジュール910は、検索ヒットしたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSI5でエラー処理を実行する。
【0087】
ステップSI2の判断結果が「Yes」である場合、ステップSI3では、制御モジュール910は、当該コンテンツ(制御モジュール付きコンテンツ)を変更後、これをデータベース1000に格納する。ステップSI4では、制御モジュール910は、格納が成功したか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSI5でエラー処理を実行する。ステップSI4の判断結果が「Yes」である場合、制御モジュール910は、正常終了する。なお、上述した消去、変更、追加の処理は、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ内の制御モジュール、前述した常駐モジュールによっても実行可能である。
【0088】
つぎに、図10を参照して一実施の形態の構成例5について詳述する。この図において、送信側システム1600は、コンテンツ1603と制御モジュール1604とを合成する機能と、合成された制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1605を受信側システム1650へ送信する機能とを備えている。送信側システム1600において、常駐モジュール1601は、外部プログラムとしての送信プログラム1602および受信プログラム1652を認証する機能と、送信プログラム1602の実行を制御する機能とを備えている。
【0089】
送信プログラム1602は、図示しないCPUにより実行され、コンテンツ1603と制御モジュール1604とを合成する機能と、合成された制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1605をセッション鍵(図12参照)で暗号化する機能と、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1605を送信する機能を実現する。受信側システム1650は、送信側システム1600からの制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1605を受信する機能と、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1605に基づいて処理を実行する機能とを備えている。
【0090】
受信側システム1650において、常駐モジュール1651は、常駐モジュール1601を認証する機能と、外部プログラムとしての受信プログラム1652の実行を制御する機能とを備えている。受信プログラム1652は、図示しないCPUにより実行され、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1605を受信する機能と、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1605をセッション鍵(図12参照)で復号する機能と、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1653を認証する機能と、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1653に基づいて処理を実行する機能とを備えている。
【0091】
なお、構成例5では、送信プログラム1602および受信プログラム1652がCPUで実行されることにより、各種機能が実現されるが、以下では、説明を簡単にするために、送信プログラム1602および受信プログラム1652が各種機能を実現するものとして説明する。
【0092】
つぎに、図20に示したフローチャートを参照しつつ、図10に示した構成例5の動作について説明する。同図に示したステップSL1〜ステップSL5は、常駐モジュール1601および常駐モジュール1651の動作を表す。はじめに、常駐モジュール1601および常駐モジュール1651は、図12で説明した認証処理を実行する。この場合、図12に示したモジュールMA は、常駐モジュール1601に対応しており、モジュールMB は、常駐モジュール1651に対応している。
【0093】
そして、常駐モジュール1601と常駐モジュール1651との間の相互認証処理が正常終了すると、図20に示したステップSL1では、常駐モジュール1601は、送信プログラム1602との間で図12で説明した認証処理を実行する。この場合、図12に示したモジュールMA は、常駐モジュール1601に対応しており、モジュールMB は、送信プログラム1602に対応している。ステップSL2では、常駐モジュール1601は、認証されたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSL5でエラー処理を実行する。
【0094】
この場合、ステップSL2の判断結果が「Yes」であるものとすると、ステップSL3では、常駐モジュール1601は、外部プログラムとしての送信プログラム1602に制御を要求する。具体的には、常駐モジュール1601は、送信プログラム1602に対して送信要求を出す。ステップSL4では、常駐モジュール1601は、上記送信要求が送信プログラム1602に正常に受け取られたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSL5でエラー処理を実行する。この場合、ステップSL4の判断結果が「Yes」であるものとし、常駐モジュール1601は、正常終了する。
【0095】
また、常駐モジュール1601からの送信要求が出されると、送信プログラム1602は、コンテンツ1603と制御モジュール1604とを合成し、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1605を生成する。つぎに、送信プログラム1602は、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1605をセッション鍵(図12参照)で暗号化した後、これを受信側システム1650へ送信する。
【0096】
一方、図20に示したステップSL1では、常駐モジュール1651は、受信プログラム1652との間で図12で説明した認証処理を実行する。この場合、図12に示したモジュールMA は、常駐モジュール1651に対応しており、モジュールMB は、受信プログラム1652に対応している。ステップSL2では、常駐モジュール1651は、認証されたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSL5でエラー処理を実行する。
【0097】
この場合、ステップSL2の判断結果が「Yes」であるものとすると、ステップSL3では、常駐モジュール1651は、外部プログラムとしての受信プログラム1652に制御を要求する。具体的には、常駐モジュール1651は、受信プログラム1652に対して受信要求を出す。ステップSL4では、常駐モジュール1651は、上記受信要求が受信プログラム1652に正常に受け取られたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSL5でエラー処理を実行する。この場合、ステップSL4の判断結果が「Yes」であるものとし、常駐モジュール1651は、正常終了する。
【0098】
また、常駐モジュール1651からの受信要求が出されると、受信プログラム1652は、暗号化された制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1605を受信した後セッション鍵(図12参照)を用いて復号する。つぎに、受信プログラム1652は、復号された制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1653内の制御モジュール1604との間で図12で説明した認証処理を実行する。この場合、図12に示したモジュールMA は、受信プログラム1652に対応しており、モジュールMBは、制御モジュール1604に対応している。そして、認証処理が正常終了すると、受信プログラム1652は、前述した各種制御モジュールと同様の処理を実行するように、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1653内の制御モジュール1604を起動する。
【0099】
つぎに、図11を参照して一実施の形態の構成例6について詳述する。この図において、システム1700は、コンテンツ1705、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703および制御モジュール付きライセンス1702を認証・制御・処理する機能や、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703をシステム1750へ送信する機能を備えている。制御モジュール付きライセンス1702は、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703の利用許諾情報であり、図1(b)に示した制御モジュール付きライセンス20と同様にして、制御モジュールおよびライセンスから構成されている。
【0100】
制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703は、図1(a)に示した制御モジュール付きコンテンツ10と同様にして、制御モジュールおよびコンテンツから構成されている。常駐モジュール1701は、制御モジュール付きライセンス1702および制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703を認証・処理・制御する機能や、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703をシステム1750へ送信する機能を備えている。
【0101】
さらに、常駐モジュール1701は、常駐モジュール1704を認証・制御する機能や、コンテンツ1705を処理・制御する機能も備えている。常駐モジュール1704は、常駐モジュール1701の認証・制御を行う機能や、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703やコンテンツ1705を制御する機能を備えている。
【0102】
一方、システム1750において、常駐モジュール1751は、制御モジュール付きライセンス1702を認証・処理・制御する機能、常駐モジュール1701を認証する機能、システム1700からの制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703を受信する機能等を備えている。ここで、システム1700内の制御モジュール付きライセンス1702と、システム1750内の制御モジュール付きライセンス1702とは、いずれも制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703の利用許諾情報である。
【0103】
つぎに、図21に示したフローチャートを参照しつつ、図11に示した構成例6の動作について説明する。同図において、システムSYA 、制御モジュールCMA 、常駐モジュールJMA 、システムSYB および常駐モジュールJMB は、図11に示したシステム1700、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703内の制御モジュール(図示略)、常駐モジュール1701、システム1750および常駐モジュール1751に対応している。
【0104】
ステップSM1では、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703内の制御モジュールは、常駐モジュール1701に対して図12で説明した認証処理を実行する。同時に、ステップSN1では、常駐モジュール1701は、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703内の制御モジュールに対して図12で説明した認証処理を実行する。この場合、図12に示したモジュールMA は、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703内の制御モジュールに対応しており、モジュールMB は、常駐モジュール1701に対応している。
【0105】
そして、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703内の制御モジュールと常駐モジュール1701との間の相互認証処理が正常終了すると、ステップSM2では、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703内の制御モジュールは、認証されたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSM5でエラー処理を実行する。同時に、ステップSN2では、常駐モジュール1701は、認証されたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSN8でエラー処理を実行する。
【0106】
この場合、ステップSM2およびステップSN2の両判断結果が「Yes」であるものとする。ステップSM3では、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703内の制御モジュールは、常駐モジュール1701に対して、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703をシステム1750へ送信する処理を要求する。ステップSM4では、上記要求が常駐モジュール1701に正常に受け取られたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSM5でエラー処理を実行する。この場合、ステップSM4の判断結果が「Yes」であるものとすると、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703内の制御モジュールは、正常終了する。
【0107】
また、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703内の制御モジュールからの要求(ステップSM3)を受け取ると、ステップSN3では、常駐モジュール1701は、システム1750の常駐モジュール1751に対して図12で説明した認証処理を実行する。同時に、ステップSO1では、常駐モジュール1751は、常駐モジュール1701に対して図12で説明した認証処理を実行する。この場合、図12に示したモジュールMA は、常駐モジュール1701に対応しており、モジュールMB は、常駐モジュール1751に対応している。
【0108】
そして、常駐モジュール1701と常駐モジュール1751との間の相互認証処理が正常終了すると、ステップSN4では、常駐モジュール1701は、認証されたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSN8でエラー処理を実行する。同時に、ステップSO2では、常駐モジュール1751は、認証されたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSO8でエラー処理を実行する。
【0109】
この場合、ステップSN4およびステップSO2の両判断結果が「Yes」であるものとする。ステップSN5では、常駐モジュール1701は、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703をセッション鍵(図12参照)を用いて暗号化し、これをシステム1750へ送信するとともに、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703内の制御モジュールに従って処理を実行するようにシステム1750へ要求を出す。
【0110】
ステップSN6では、常駐モジュール1701は、ステップSN5の一連の処理が正常に行われたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSN8でエラー処理を実行する。この場合、ステップSN6の判断結果が「Yes」であるものとすると、ステップSN7では、常駐モジュール1701は、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703内の制御モジュールに対して送信完了通知を出し、正常終了する。
【0111】
一方、ステップSO3では、常駐モジュール1751は、暗号化された制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703を受信した後、セッション鍵(図12参照)を用いて復号する。ステップSO4では、ステップSO3の処理が正常に行われたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSO8でエラー処理を実行する。この場合、ステップSO4の判断結果が「Yes」であるものとすると、ステップSO5では、常駐モジュール1751は、常駐モジュール1701に対して、受信完了通知を出す。
【0112】
ステップSO6では、常駐モジュール1751は、受信した制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1703の制御モジュール(図示略)と制御モジュール付きライセンス1702の制御モジュールとの間で認証処理を行い、前述した動作と同様にして、コンテンツを利用するための一連の処理を実行する。ステップSO7では、常駐モジュール1751は、一連の処理が正常に行われたか否かを判断し、この判断結果が「No」である場合、ステップSO8でエラー処理を実行する。この場合、ステップSO7の判断結果が「Yes」であるものとすると、常駐モジュール1751は、正常終了する。
【0113】
以上説明したように、一実施の形態によれば、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ側の制御モジュールと、制御モジュール付きライセンス側の制御モジュールとの相互連携により、コンテンツ利用に関する制御を行うようにしたので、従来のようにコンテンツを利用する装置側の環境に依存することなく、柔軟にコンテンツ利用を行うことができる。
【0114】
また、一実施の形態によれば、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ側の制御モジュール、常駐モジュール、制御モジュール付きライセンス側の制御モジュールの相互間で認証し、この認証結果に従って、コンテンツ利用に関する制御を行うようにしたので、セキュリティを高めることができ、不正利用を防止することができる。
【0115】
また、一実施の形態によれば、図10に示したようにコンテンツ1603と制御モジュール1604とを合成し制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1605を生成した後、これを受信側システム1650へ送信するようにしたので、受信側システム1650でも装置側の環境に依存することなく、柔軟にコンテンツ利用を行うことができる。
【0116】
また、一実施の形態によれば、図10に示したように、常駐モジュール1601と常駐モジュール1651との間で相互認証を行った結果に基づいて、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1605を送信するようにしたので、セキュリティを高めることができ、悪意の第三者へ誤送信することを防止できる。
【0117】
また、一実施の形態によれば、図9に示したように、制御モジュール710、910および1210に、関連性が高い制御モジュール付きライセンスおよび制御モジュール付きコンテンツをデータベース800、1000および1300から検索する検索機能を持たせ、検索されたものとの相互連携によりコンテンツ利用に関する制御を行うようにしたので、装置側の複雑な制御を必要とすることなく、容易に複数のコンテンツを利用することができる。
【0118】
また、一実施の形態によれば、図16〜図18を参照して説明したように、制御モジュール910にデータベース1000の更新処理を行わせるようにしたので、装置側のデータベース管理に関する負担を低減させることができる。
【0119】
また、一実施の形態によれば、図3を参照して説明したように、第1の制御モジュール511 〜第3の制御モジュール513 と第1の制御モジュール611 〜第3の制御モジュール613 との組み合わせに対応する、コンテンツ利用に関する複数の制御を行うようにしたので、従来のようにコンテンツを利用する装置側の環境に依存することなく、さらに柔軟にコンテンツ利用を行うことができる。
【0120】
また、一実施の形態によれば、図13を参照して説明したように、制御モジュール910により、当該コンテンツの利用に際して課金情報940を更新するようにしたので、従来のようにコンテンツ提供権限者側で課金管理する場合に比して、コンテンツ提供の管理負担を低減させることができる。
【0121】
また、一実施の形態によれば、図4を参照して説明したように、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集/ライセンス集70を用い、コンテンツ利用に関する制御を階層的に行うようにしたので、効率良く複数のコンテンツを利用することができる。
【0122】
以上本発明にかかる一実施の形態について図面を参照して詳述してきたが、具体的な構成例はこの一実施の形態に限られるものではなく、本発明の要旨を逸脱しない範囲の設計変更等があっても本発明に含まれる。以下では、図22〜図26を参照して一実施の形態の変形例1〜8について説明する。
【0123】
前述した一実施の形態では、図1(a)に示した制御モジュール11によりコンテンツ12を制御する例について説明したが、外部の制御モジュールにより制御を行うようにしてもよい。この場合を一実施の形態の変形例1として説明する。図22は、一実施の形態の変形例1を説明する図である。この図において、仮制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1800は、仮制御モジュール1810およびコンテンツ1820から構成されている。
【0124】
この仮制御モジュール1810は、外部からの実行要求を受けた場合に、外部の真制御モジュール1830に対して制御要求を出す。従って、仮制御モジュール1810は、コンテンツ1820を直接制御できない。真制御モジュール1830は、図1(a)に示した制御モジュール11に対応するものであり、仮制御モジュール1810からの制御要求に応じて、制御モジュール11と同様の制御を実行する。
【0125】
また、一実施の形態では、図1(a)に示した制御モジュール付きコンテンツ10内の制御モジュール11およびコンテンツ12を、CPU、制御モジュール、常駐モジュール等(以下、単にCPU等という)により、新たな制御モジュールおよびコンテンツに更新できるようにしてもよい。以下では、この場合を一実施の形態の変形例2として説明する。図23(a)は、一実施の形態の変形例2を説明する図である。
【0126】
この図において、旧制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1900Aは、更新前のものであり、旧制御モジュール1910Aおよび旧コンテンツ1920Aから構成されている。この状態でCPU等により、更新処理が行われると、旧制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1900Aは、新制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1900Bに更新される。この新制御モジュール付きコンテンツ1900Bは、更新後の新制御モジュール1910B(旧制御モジュール1910Aに対応)と、更新後の新コンテンツ1920B(旧コンテンツ1920Aに対応)とから構成されている。
【0127】
また、図23(a)に示した一実施の形態の変形例2では、制御モジュールおよびコンテンツの全ての部分を更新する例について説明したが、コンテンツの一部分を更新するようにしてもよい。この場合を一実施の形態の変形例3として説明する。図23(b)は、一実施の形態の変形例3を説明する図である。
【0128】
この図において、旧制御モジュール付きコンテンツ2000Aは、更新前のものであり、旧制御モジュール2010Aおよび旧コンテンツ2020Aから構成されている。旧コンテンツ2020Aには、変更可能な旧部分コンテンツ2030Aが含まれている。この状態でCPU等により、旧制御モジュール2010Aおよび旧部分コンテンツ2030Aに対する更新処理が行われると、旧制御モジュール付きコンテンツ2000Aは、新制御モジュール付きコンテンツ2000Bに更新される。
【0129】
この新制御モジュール付きコンテンツ2000Bは、更新後の新制御モジュール2010B(旧制御モジュール2010Aに対応)と、更新後の新コンテンツ2020B(旧コンテンツ2020Aに対応)とから構成されている。新コンテンツ2020Bにおいて更新された部分は、新部分コンテンツ2030Bである。
【0130】
また、図23(a)に示した一実施の形態の変形例2では、制御モジュールおよびコンテンツの全ての部分を更新する例について説明したが、制御モジュールのみを更新するようにしてもよい。この場合を一実施の形態の変形例4として説明する。図24(a)は、一実施の形態の変形例4を説明する図である。
【0131】
この図において、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ2100Aは、更新前のものであり、コンテンツ2110Aおよび旧制御モジュール2120Aから構成されている。この状態でCPU等により、旧制御モジュール2120Aに対する更新処理が行われると、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ2100Aは、新制御モジュール付きコンテンツ2100Bに更新される。この新制御モジュール付きコンテンツ2100Bは、更新されない制御モジュール付きコンテンツ2100Aと、更新後の新制御モジュール2120B(旧制御モジュール2120Aに対応)とから構成されている。
【0132】
また、図23(a)に示した一実施の形態の変形例2では、制御モジュールおよびコンテンツの全ての部分を更新する例について説明したが、制御モジュールの一部分を更新するようにしてもよい。この場合を一実施の形態の変形例5として説明する。図24(b)は、一実施の形態の変形例5を説明する図である。
【0133】
この図において、旧制御モジュール付きコンテンツ2200Aは、更新前のものであり、コンテンツ2210Aおよび旧制御モジュール2220Aから構成されている。旧制御モジュール2220Aには、更新できない制御モジュール不変部2230Aと、更新可能な旧制御モジュール可変部2240Aが含まれている。この状態でCPU等により、旧制御モジュール可変部2240Aに対する更新処理が行われると、旧制御モジュール付きコンテンツ2200Aは、新制御モジュール付きコンテンツ2200Bに更新される。
【0134】
この新制御モジュール付きコンテンツ2200Bは、更新されないコンテンツ2210Aと、更新後の新制御モジュール2220B(旧制御モジュール2220Aに対応)とから構成されている。新制御モジュール2220Bは、制御モジュール不変部2230Aおよび新制御モジュール可変部2240Bから構成されている。新制御モジュール2220Bにおいて更新された部分は、新制御モジュール可変部2240Bである。
【0135】
また、一実施の形態では、常駐モジュールを、CPU、制御モジュール、常駐モジュール等(以下、単にCPU等という)により、新たな常駐モジュールに更新できるようにしてもよい。以下では、この場合を一実施の形態の変形例6として説明する。図25(a)は、一実施の形態の変形例6を説明する図である。旧常駐モジュール2300Aは、更新前のものである。この状態でCPU等により、更新処理が行われると、旧常駐モジュール2300Aは、新常駐モジュール2300Bに更新される。なお、上述した変形例1〜5では、制御モジュール付きコンテンツに代えて、制御モジュール付きライセンスに対しても更新できるようにしてもよい。
【0136】
また、一実施の形態の変形例6では、常駐モジュールの全ての部分を更新する例について説明したが、一部分を更新するようにしてもよい。以下では、この場合を実施の形態7として説明する。図25(b)は、一実施の形態の変形例7を説明する図である。
【0137】
この図において、旧常駐モジュール2400Aは、更新されない常駐モジュール不変部2410Aと、更新可能な旧常駐モジュール可変部2420Aとから構成されている。この状態でCPU等により、旧常駐モジュール可変部2420Aに対する更新処理が行われると、旧常駐モジュール2400Aは、新常駐モジュール2400Bに更新される。この新常駐モジュール2400Bは、更新されない常駐モジュール不変部2410Aと、更新後の新常駐モジュール可変部2420Bとから構成されている。
【0138】
また、一実施の形態では、変形例8として、前述したコンテンツ利用制御を実現するためのコンテンツ利用制御プログラムを図26に示したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体2600に記録して、この記録媒体2600に記録されたコンテンツ利用制御プログラムを同図に示したコンピュータ2500に読み込ませ、実行することによりコンテンツ利用制御を行うようにしてもよい。
【0139】
図26に示したコンピュータ2500は、上記コンテンツ利用制御プログラムを実行するCPU2501と、キーボード、マウス等の入力装置2502と、各種データを記憶するROM(Read Only Memory)2503と、演算パラメータ等を記憶するRAM(Random Access Memory)2504と、記録媒体2600からコンテンツ利用制御プログラムを読み取る読取装置2505と、ディスプレイ、プリンタ等の出力装置2506と、装置各部を接続するバスBUとから構成されている。
【0140】
CPU2501は、読取装置2505を経由して記録媒体2600に記録されているコンテンツ利用制御プログラムを読み込んだ後、コンテンツ利用制御プログラムを実行することにより、前述したコンテンツ利用制御を行う。なお、記録媒体2600には、光ディスク、フロッピーディスク、ハードディスク等の可搬型の記録媒体が含まれることはもとより、ネットワークのようにデータを一時的に記録保持するような伝送媒体も含まれる。
【0141】
また、前述した一実施の形態では、制御モジュールのファイル形式として「ソースコード形式」、「実行形式」の例について説明したが、これらに限られることなく、JAVA SCRIPTやPERL等のスクリプト言語で記述されたファイル形式を用いてもよい。
【0142】
なお、前述した一実施の形態では、複数の構成例、動作例、制御モジュール、常駐モジュールについて説明したが、これらを必要に応じて組み合わせた場合も本発明に含まれる。
【0143】
(付記1)コンテンツ提供権限者からコンテンツ利用者に対して提供されるコンテンツの利用制御を行うコンテンツ利用制御装置において、
コンテンツと第1の制御モジュールとからなる制御モジュール付きコンテンツ、および前記コンテンツの利用許諾情報からなるライセンスと第2の制御モジュールとからなる制御モジュール付きライセンスを入力する入力手段を備え、
前記第1の制御モジュールと前記第2の制御モジュールとは、相互連携によりコンテンツ利用に関する制御を行うこと、
を特徴とするコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記2)前記第1の制御モジュールおよび前記第2の制御モジュールを認証し、前記第1の制御モジュールおよび前記第2の制御モジュールとの相互連携によりコンテンツ利用に関する制御を行う第3の制御モジュールを備えたことを特徴とする付記1に記載のコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記3)前記第3の制御モジュールの制御に従って、コンテンツと第1の制御モジュールとを合成し前記制御モジュール付きコンテンツを生成した後、該制御モジュール付きコンテンツを外部装置へ送信する送信手段を備えたことを特徴とする付記2に記載のコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記4)前記第3の制御モジュールは、前記外部装置との間で相互認証を行った結果に基づいて、前記送信手段を制御することを特徴とする付記3に記載のコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記5)前記送信手段と前記外部装置との間では、前記制御モジュール付きコンテンツに関して暗号化通信が行われ、前記送信手段は、所定の暗号鍵を用いて前記制御モジュール付きコンテンツを暗号化したものを送信することを特徴とする付記3または4に記載のコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記6)前記第3の制御モジュールの制御に従って、外部装置から送信された制御モジュール付きコンテンツを受信した後、該制御モジュール付きコンテンツの利用に関する制御を実行させる受信手段を備えたことを特徴とする付記2に記載のコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記7)前記第3の制御モジュールは、前記外部装置との間で相互認証を行った結果に基づいて、前記受信手段を制御することを特徴とする付記6に記載のコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記8)前記外部装置と前記受信手段との間では、前記制御モジュール付きコンテンツに関して暗号化通信が行われ、前記受信手段は、所定の復号鍵を用いて暗号化された制御モジュール付きコンテンツを復号することを特徴とする付記6または7に記載のコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記9)前記第1の制御モジュールおよび前記第2の制御モジュールは、少なくとも、相互認証し、認証された場合にライセンスに基づいてコンテンツを利用することを特徴とする付記1〜8のいずれか一つに記載のコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記10)複数の制御モジュール付きコンテンツおよび複数の制御モジュール付きライセンスを格納するデータベースを備え、
前記第1の制御モジュールは、前記データベースから当該コンテンツに関連のある制御モジュール付きライセンスを検索し、検索された当該制御モジュール付きライセンスの制御モジュールと相互連携し、当該コンテンツの利用に関する制御を行い、前記第2の制御モジュールは、前記データベースから当該ライセンスに関連のある制御モジュール付きコンテンツを検索し、検索された当該制御モジュール付きコンテンツの制御モジュールと相互連携し、当該コンテンツの利用に関する制御を行うことを特徴とする付記1または2に記載のコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記11)前記第2の制御モジュールは、前記データベース内の制御モジュール付きコンテンツの消去、追加、変更に関する更新処理を実行することを特徴とする付記10に記載のコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記12)前記第1の制御モジュールは、複数の第1のサブ制御モジュールからなり、前記第2の制御モジュールは、複数の第2のサブ制御モジュールからなり、前記複数の第1のサブ制御モジュールと前記複数の第2のサブ制御モジュールとは、組み合わせに対応する、コンテンツ利用に関する複数の制御を行うことを特徴とする付記1に記載のコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記13)前記制御モジュール付きライセンスは、当該コンテンツ利用に関する課金情報を含み、前記第2の制御モジュールは、当該コンテンツの利用に際して前記課金情報を更新することを特徴とする付記1〜12のいずれか一つに記載のコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記14)コンテンツ提供権限者からコンテンツ利用者に対して提供されるコンテンツの利用制御を行うコンテンツ利用制御装置において、
階層構造をなす複数のコンテンツと該複数のコンテンツにそれぞれ対応する複数の第1の制御モジュールとからなる制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集、および前記複数のコンテンツの利用許諾情報にそれぞれ対応し階層構造をなす複数のライセンスと前記複数のライセンスにそれぞれ対応する複数の第2の制御モジュールとからなる制御モジュール付きライセンス集を入力する入力手段を備え、
前記制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集および前記制御モジュール付きライセンス集は、少なくとも一つのファイルに格納されており、
前記第1の制御モジュールと前記第2の制御モジュールとは、相互連携によりコンテンツ利用に関する制御を階層的に行うこと、
を特徴とするコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記15)前記制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集および前記制御モジュール付きライセンス集からは、所望のコンテンツ、該コンテンツに対応する第1の制御モジュール、所望のライセンス、該ライセンスに対応する第2の制御モジュールが取り出し可能とされており、これらのコンテンツ、第1の制御モジュール、ライセンスおよび第2の制御モジュールは、制御モジュール付きコンテンツおよび制御モジュール付きライセンスとして利用/配布されることを特徴とする付記14に記載のコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記16)前記第1の制御モジュールと同一の機能を備える真制御モジュールを備え、前記制御モジュール付きコンテンツは、前記第1の制御モジュールに代えて、前記真制御モジュールへ制御要求を出す仮制御モジュールを備えていることを特徴とする付記1〜15のいずれか一つに記載のコンテンツ利用制御装置。(付記17)前記コンテンツおよび前記第1の制御モジュールを更新する更新手段を備えたことを特徴とする付記1〜15のいずれか一つに記載のコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記18)前記コンテンツの一部分を更新する更新手段を備えたことを特徴とする付記1〜15のいずれか一つに記載のコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記19)前記第1の制御モジュールを更新する更新手段を備えたことを特徴とする付記1〜15のいずれか一つに記載のコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記20)前記第1の制御モジュールの一部分を更新する更新手段を備えたことを特徴とする付記1〜15のいずれか一つに記載のコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記21)前記第3の制御モジュールを更新する更新手段を備えたことを特徴とする付記2に記載のコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記22)前記第3の制御モジュールの一部を更新する更新手段を備えたことを特徴とする付記2に記載のコンテンツ利用制御装置。
(付記23)コンテンツ提供権限者からコンテンツ利用者に対して提供されるコンテンツの利用制御を行うコンテンツ利用制御方法において、
コンテンツと第1の制御モジュールとからなる制御モジュール付きコンテンツ、および前記コンテンツの利用許諾情報からなるライセンスと第2の制御モジュールとからなる制御モジュール付きライセンスを入力する入力工程を含み、
前記第1の制御モジュールと前記第2の制御モジュールとは、相互連携によりコンテンツ利用に関する制御を行うこと、
を特徴とするコンテンツ利用制御方法。
(付記24)前記第1の制御モジュールおよび前記第2の制御モジュールを認証し、前記第1の制御モジュールおよび前記第2の制御モジュールとの相互連携によりコンテンツ利用に関する制御を行う第3の制御モジュール工程を含むことを特徴とする付記23に記載のコンテンツ利用制御方法。
(付記25)前記第3の制御モジュール工程における制御に従って、コンテンツと第1の制御モジュールとを合成し前記制御モジュール付きコンテンツを生成した後、該制御モジュール付きコンテンツを外部装置へ送信する送信工程を含むことを特徴とする付記24に記載のコンテンツ利用制御方法。
(付記26)前記第3の制御モジュール工程の制御に従って、外部装置から送信された制御モジュール付きコンテンツを受信した後、該制御モジュール付きコンテンツの利用に関する制御を実行させる受信工程を備えたことを特徴とする付記24に記載のコンテンツ利用制御方法。
(付記27)複数の制御モジュール付きコンテンツおよび複数の制御モジュール付きライセンスをデータベースに格納させる格納工程を含み、
前記第1の制御モジュールは、前記データベースから当該コンテンツに関連のある制御モジュール付きライセンスを検索し、検索された当該制御モジュール付きライセンスの制御モジュールと相互連携し、当該コンテンツの利用に関する制御を行い、前記第2の制御モジュールは、前記データベースから当該ライセンスに関連のある制御モジュール付きコンテンツを検索し、検索された当該制御モジュール付きコンテンツの制御モジュールと相互連携し、当該コンテンツの利用に関する制御を行うことを特徴とする付記23または24に記載のコンテンツ利用制御方法。
(付記28)前記制御モジュール付きライセンスは、当該コンテンツ利用に関する課金情報を含み、前記第2の制御モジュールは、当該コンテンツの利用に際して前記課金情報を更新することを特徴とする付記23〜27のいずれか一つに記載のコンテンツ利用制御方法。
(付記29)コンテンツ提供権限者からコンテンツ利用者に対して提供されるコンテンツの利用制御を行うコンテンツ利用制御方法において、
階層構造をなす複数のコンテンツと該複数のコンテンツにそれぞれ対応する複数の第1の制御モジュールとからなる制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集、および前記複数のコンテンツの利用許諾情報にそれぞれ対応し階層構造をなす複数のライセンスと前記複数のライセンスにそれぞれ対応する複数の第2の制御モジュールとからなる制御モジュール付きライセンス集を入力する入力工程を備え、
前記制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集および前記制御モジュール付きライセンス集は、少なくとも一つのファイルに格納されており、
前記第1の制御モジュールと前記第2の制御モジュールとは、相互連携によりコンテンツ利用に関する制御を階層的に行うこと、
を特徴とするコンテンツ利用制御方法。
(付記30)前記制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集および前記制御モジュール付きライセンス集からは、所望のコンテンツ、該コンテンツに対応する第1の制御モジュール、所望のライセンス、該ライセンスに対応する第2の制御モジュールが取り出し可能とされており、これらのコンテンツ、第1の制御モジュール、ライセンスおよび第2の制御モジュールは、制御モジュール付きコンテンツおよび制御モジュール付きライセンスとして利用/配布されることを特徴とする付記29に記載のコンテンツ利用制御方法。
(付記31)前記付記23〜30のいずれか一つに記載のコンテンツ利用制御方法をコンピュータに実行させるためのコンテンツ利用制御プログラム。
(付記32)前記付記23〜30のいずれか一つに記載のコンテンツ利用制御方法をコンピュータに実行させるためのコンテンツ利用制御プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体。
【0144】
【発明の効果】
以上説明したように、本発明によれば、第1の制御モジュールと第2の制御モジュールとの相互連携により、コンテンツ利用に関する制御を行うようにしたので、従来のようにコンテンツを利用する装置側の環境に依存することなく、柔軟にコンテンツ利用を行うことができるという効果を奏する。
【0145】
また、本発明によれば、第1の制御モジュールおよび前記第2の制御モジュールを認証し、この認証結果に従って、第1の制御モジュールおよび第2の制御モジュールとの相互連携によりコンテンツ利用に関する制御を行うようにしたので、セキュリティを高めることができ、不正利用を防止することができるという効果を奏する。
【0146】
また、本発明によれば、コンテンツと第1の制御モジュールとを合成し制御モジュール付きコンテンツを生成した後、これを外部装置へ送信するようにしたので、外部装置でも装置側の環境に依存することなく、柔軟にコンテンツ利用を行うことができるという効果を奏する。
【0147】
また、本発明によれば、外部装置との間で相互認証を行った結果に基づいて、制御モジュール付きコンテンツを送信するようにしたので、セキュリティを高めることができ、悪意の第三者へ誤送信することを防止できるという効果を奏する。
【0148】
また、本発明によれば、外部装置から送信された制御モジュール付きコンテンツを受信した後、該制御モジュール付きコンテンツの利用に関する制御を行うようにしたので、外部装置でも装置側の環境に依存することなく、柔軟にコンテンツ利用を行うことができるという効果を奏する。
【0149】
また、本発明によれば、外部装置との間で相互認証を行った結果に基づいて、制御モジュール付きコンテンツを受信するようにしたので、セキュリティを高めることができ、意図しない制御モジュール付きコンテンツを誤受信することを防止できるという効果を奏する。
【0150】
また、本発明によれば、第1の制御モジュールと第2の制御モジュールとの間で相互認証し、認証された場合にライセンスに基づいてコンテンツを利用するようにしたので、極めて高いセキュリティを確保することができるという効果を奏する。
【0151】
また、本発明によれば、第1の制御モジュールおよび第2の制御モジュールに、当該コンテンツおよび当該ライセンスに関連のある制御モジュール付きライセンスおよび制御モジュール付きコンテンツをデータベースから検索する検索機能を持たせ、検索されたものとの相互連携によりコンテンツ利用に関する制御を行うようにしたので、装置側の複雑な制御を必要とすることなく、容易に複数のコンテンツを利用することができるという効果を奏する。
【0152】
また、本発明によれば、第2の制御モジュールにデータベースの更新処理を行わせるようにしたので、装置側のデータベース管理に関する負担を低減させることができるという効果を奏する。
【0153】
また、本発明によれば、複数の第1のサブ制御モジュールと複数の第2のサブ制御モジュールとの組み合わせに対応する、コンテンツ利用に関する複数の制御を行うようにしたので、従来のようにコンテンツを利用する装置側の環境に依存することなく、さらに柔軟にコンテンツ利用を行うことができるという効果を奏する。
【0154】
また、本発明によれば、第2の制御モジュールにより、当該コンテンツの利用に際して課金情報を更新するようにしたので、従来のようにコンテンツ提供権限者側で課金管理する場合に比して、コンテンツ提供の管理負担を低減させることができるという効果を奏する。
【0155】
また、本発明によれば、制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集、および制御モジュール付きライセンス集を用い、第1の制御モジュールと第2の制御モジュールとが相互連携によりコンテンツ利用に関する制御を階層的に行うようにしたので、効率良く複数のコンテンツを利用することができるという効果を奏する。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】 本発明にかかる一実施の形態で用いられる制御モジュール付きコンテンツ10および制御モジュール付きライセンス20の構成を示す図である。
【図2】 同一実施の形態で用いられる制御モジュール付きコンテンツ30および制御モジュール付きライセンス40の構成を示す図である。
【図3】 同一実施の形態で用いられる制御モジュール付きコンテンツ50および制御モジュール付きライセンス60の構成を示す図である。
【図4】 同一実施の形態で用いられる制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集/ライセンス集70の構成を示す図である。
【図5】 同一実施の形態の動作を説明する図である。
【図6】 同一実施の形態の構成例1を示すブロック図である。
【図7】 同一実施の形態の構成例2を示すブロック図である。
【図8】 同一実施の形態の構成例3を示すブロック図である。
【図9】 同一実施の形態の構成例4を示すブロック図である。
【図10】 同一実施の形態の構成例5を示すブロック図である。
【図11】 同一実施の形態の構成例6を示すブロック図である。
【図12】 同一実施の形態の動作を説明するフローチャートである。
【図13】 同一実施の形態の動作を説明するフローチャートである。
【図14】 同一実施の形態の動作を説明するフローチャートである。
【図15】 同一実施の形態の動作を説明するフローチャートである。
【図16】 同一実施の形態の動作を説明するフローチャートである。
【図17】 同一実施の形態の動作を説明するフローチャートである。
【図18】 同一実施の形態の動作を説明するフローチャートである。
【図19】 同一実施の形態の動作を説明するフローチャートである。
【図20】 同一実施の形態の動作を説明するフローチャートである。
【図21】 同一実施の形態の動作を説明するフローチャートである。
【図22】 同一実施の形態の変形例1を説明する図である。
【図23】 同一実施の形態の変形例2および3を説明する図である。
【図24】 同一実施の形態の変形例4および5を説明する図である。
【図25】 同一実施の形態の変形例6および7を説明する図である。
【図26】 同一実施の形態の変形例8示すブロック図である。
【符号の説明】
10 制御モジュール付きコンテンツ
11 制御モジュール
12 コンテンツ
20 制御モジュール付きライセンス
21 制御モジュール
22 ライセンス
70 制御モジュール付きコンテンツ集/ライセンス集
300 CPU
310 常駐モジュール
400 デコーダ
410 常駐モジュール
800 データベース
1000 データベース
1300 データベース
1600 送信側システム
1601 常駐モジュール
1602 送信プログラム
1650 受信側システム
1651 常駐モジュール
1652 受信プログラム
1700 システム
1701 常駐モジュール
1704 常駐モジュール
1750 システム
1751 常駐モジュール
2500 コンピュータ
2501 CPU
2600 記録媒体[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a content use control device, a content use control method, and a content use control program for controlling the use of content such as movies, music, and videos. To In particular, a content usage control device, a content usage control method, and a content usage control program that increase the flexibility of content usage and facilitate billing management. To It is related.
[0002]
Recently, in response to the wave of multimedia, Internet distribution of content such as digitized movies and music has started, and the interest of users regarding content use is increasing. In response to this need, a means and method for content usage control with high flexibility in content usage is desired.
[0003]
[Prior art]
Conventionally, contents (works) such as movies and music cannot be sold or transferred for commercial purposes without the permission of the author. The content here refers to digital content having a structure as a set of bit strings that can be recorded on a single recording medium, and refers to text, still images, moving images, program software, and the like.
[0004]
This type of content is provided to the user via a download site on the Internet or a recording medium. In this case, control related to the use of content using a license (use permission information) for the purpose of copyright protection (hereinafter referred to as content use control) is performed. This content usage control is intended to allow only authorized users to use the content.
[0005]
In the content usage control apparatus for using content, a unique usage environment for using the license and the content is set. In this usage environment, device identification information for identifying the content usage control device is set. Therefore, in the content usage control device, content usage control is performed by decrypting the content using the device identification information and the license. In addition, conventionally, when content is used for a fee, the user is charged, but management related to this charge is managed by the content provider.
[0006]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
By the way, as described above, in the conventional content use control apparatus, contents and licenses individually created so as to correspond to the use environment on the apparatus side are provided. Therefore, in the past, content and licenses are highly dependent on the usage environment of the content usage control device, so the user cannot flexibly use the content and must individually create the content and license. There was a problem that there was a lot of waste and a heavy burden on the content provider side.
[0007]
Conventionally, since it is not possible to give charging information to the license, the content provider manages the usage of the content, and there is a problem that the charging management is very troublesome.
[0008]
The present invention has been made in view of the above. A content usage control apparatus, a content usage control method, and a content usage control program that can increase the flexibility of content usage and can easily perform charge management related to content usage. The The purpose is to provide.
[0009]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides a control module comprising a content and a first control module in a content usage control apparatus for controlling the usage of content provided from a content providing authority to a content user. Input means for inputting a licensed content, a license consisting of usage permission information of the content and a license with a second control module, a database storing a plurality of content with a control module and a plurality of licenses with a control module The content with a control module further searches the database for a license with a control module related to the content, activates the searched license with a control module, and Scan, when invoked by the content with the control module, search for content with the control module that is associated to its own license from the database, activating the searched content . Then, the content with control module activated by the license with control module searches for the license with control module related to the own content, activates the searched license with control module, and the control activated by the content with control module. The license with module searches the content with the control module related to the self-license and starts the searched content with the control module. It is characterized by that.
[0010]
According to the present invention, since the control related to the use of the content is performed by the mutual cooperation between the first control module and the second control module, it depends on the environment of the device side that uses the content as in the prior art. Content can be used flexibly.
[0011]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, a content usage control apparatus, a content usage control method, and a content usage control program according to the present invention with reference to the drawings Of An embodiment will be described in detail.
[0012]
First, the configuration of various control module-attached contents and control module-attached licenses used in an embodiment according to the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 1A and 1B show a
[0013]
The
[0014]
The license with
[0015]
2A and 2B show a
[0016]
The
[0017]
The license with
[0018]
3A and 3B show a
[0019]
The
[0020]
The license with
[0021]
These
[0022]
FIG. 4A shows the configuration of a content collection /
[0023]
Specifically, the content collection / license collection with
[0024]
The
[0025]
The
[0026]
The
[0027]
The
[0028]
On the other hand, the
[0029]
The license with
[0030]
The license with
[0031]
Here, in the content collection / license collection with
[0032]
Here, a configuration example for using content by the above-described license with a control module and content with a control module (see FIGS. 1 to 4) will be described with reference to FIGS. FIGS. 6-11 is a block diagram which shows the structural examples 1-6 of one Embodiment concerning this invention.
[0033]
First, with reference to FIG. 6, the structural example 1 of one Embodiment is explained in full detail. In this figure, a CPU (Central Processing Unit) 300 generates a
[0034]
The content with
[0035]
The license with
[0036]
In the
[0037]
Next, the operation of the configuration example 1 shown in FIG. 6 will be described with reference to the flowchart shown in FIG. Step SA1 to step SA7 shown in FIG. A This represents an authentication operation process (corresponding to the
[0038]
That is, in step SA1 shown in FIG. 12, the resident module 310 (module M A ) Is a random number R A Is generated. In step SA2, the
[0039]
In step SB3, the
[0040]
If the determination result in step SA4 is “No”, the
[0041]
And the encrypted random number R B In step SB4, the
[0042]
If the determination result in step SB5 is “No”, the
[0043]
On the other hand, an authentication operation is performed between the
[0044]
Next, the
[0045]
Next, a configuration example 2 of one embodiment will be described in detail with reference to FIG. In this figure, parts corresponding to those in FIG. In the figure, a
[0046]
In the
[0047]
Next, the operation of the configuration example 2 shown in FIG. 7 will be described with reference to the flowchart shown in FIG. Step SA1 to step SA7 shown in FIG. A This represents the authentication operation process (corresponding to the
[0048]
That is, in step SA1 shown in FIG. 12, the resident module 410 (module M A ) Is a random number R A Is generated. In step SA2, the
[0049]
In step SB3, the
[0050]
If the determination result in step SA4 is “No”, the
[0051]
And the encrypted random number R B In step SB4, the
[0052]
When the determination result in step SB5 is “No”, the
[0053]
On the other hand, an authentication operation is performed between the
[0054]
Next, the
[0055]
Next, configuration example 3 of one embodiment will be described in detail with reference to FIG. In this figure, a
[0056]
The storage device 600 has a function of reading the content with
[0057]
Next, the operation of the configuration example 3 shown in FIG. 8 will be described with reference to the flowchart shown in FIG. Steps SJ1 to SJ6 shown in the figure represent the operation of the
[0058]
In step SJ2, the
[0059]
When this authentication process is completed, in step SJ4, the
[0060]
In step SJ5, the
[0061]
Next, a configuration example 4 of one embodiment will be described in detail with reference to FIG. In this figure,
[0062]
The
[0063]
The audio license 920 is use permission information (content decryption key) of the
[0064]
The
[0065]
The
[0066]
The
[0067]
Next, the operation of the configuration example 4 shown in FIG. 9 will be described with reference to the flowchart shown in FIG. Step SD1 to step SD8 shown in the figure represent operations of the
[0068]
In step SD1 shown in the figure, the
[0069]
In this case, it is assumed that the number of search hits is 1 and the control module 910 (license 900) has been hit. Therefore, in step SD4, the
[0070]
When this authentication process is completed, in step SD5, the
[0071]
In this case, assuming that mutual authentication has been performed, the
[0072]
Next, the
[0073]
That is, the
[0074]
In this case, assuming that the determination result in step SC3 is “Yes”, in step SC4, the
[0075]
In parallel with this, in step SD7 shown in FIG. 14, the
[0076]
Next, the
[0077]
In this case, assuming that the content with a
[0078]
When the
[0079]
In this case, it is assumed that the number of search hits is 1, and the control module 1410 (
[0080]
When this authentication process ends, in step SD5, the
[0081]
In step SD6, the
[0082]
Further, the
[0083]
When the determination result in step SG2 is “Yes”, in step SG3, the
[0084]
Further, in the addition process, in step SH1 shown in FIG. 17, the
[0085]
If the determination result in step SH2 is “Yes”, in step SH3, the
[0086]
In the change process, in step SI1 shown in FIG. 18, the
[0087]
When the determination result in step SI2 is “Yes”, in step SI3, the
[0088]
Next, a configuration example 5 of one embodiment will be described in detail with reference to FIG. In this figure, the
[0089]
The
[0090]
In the
[0091]
In the configuration example 5, various functions are realized by the
[0092]
Next, the operation of the configuration example 5 shown in FIG. 10 will be described with reference to the flowchart shown in FIG. Step SL1 to step SL5 shown in the figure represent the operations of the
[0093]
When the mutual authentication process between the
[0094]
In this case, assuming that the determination result in step SL2 is “Yes”, in step SL3, the
[0095]
When a transmission request is issued from the
[0096]
On the other hand, in step SL1 shown in FIG. 20, the resident module 1651 executes the authentication process described with reference to FIG. In this case, the module M shown in FIG. A Corresponds to the resident module 1651 and the module M B Corresponds to the reception program 1652. In step SL2, the resident module 1651 determines whether or not it has been authenticated. If the determination result is “No”, error processing is executed in step SL5.
[0097]
In this case, assuming that the determination result in step SL2 is “Yes”, in step SL3, the resident module 1651 requests control from the reception program 1652 as an external program. Specifically, the resident module 1651 issues a reception request to the reception program 1652. In step SL4, the resident module 1651 determines whether or not the reception request has been normally received by the reception program 1652. If the determination result is “No”, error processing is executed in step SL5. In this case, it is assumed that the determination result in step SL4 is “Yes”, and the resident module 1651 ends normally.
[0098]
When a reception request is issued from the resident module 1651, the reception program 1652 receives the
[0099]
Next, a configuration example 6 of one embodiment will be described in detail with reference to FIG. In this figure, a
[0100]
The
[0101]
Further, the
[0102]
On the other hand, in the
[0103]
Next, the operation of the configuration example 6 shown in FIG. 11 will be described with reference to the flowchart shown in FIG. In the figure, the system SY A , Control module CM A Resident module JM A , System SY B And resident module JM B Corresponds to the
[0104]
In step SM1, the control module in the control module-attached
[0105]
When the mutual authentication process between the control module in the content with
[0106]
In this case, it is assumed that the determination results of both step SM2 and step SN2 are “Yes”. In step SM3, the control module in the content with
[0107]
Also, when a request (step SM3) is received from the control module in the
[0108]
When the mutual authentication process between the
[0109]
In this case, it is assumed that the determination results of both step SN4 and step SO2 are “Yes”. In step SN5, the
[0110]
In step SN6, the
[0111]
On the other hand, in step SO3, the
[0112]
In step SO6, the
[0113]
As described above, according to one embodiment, since the control on the content side with the control module and the control module on the license side with the control module are performed in cooperation with each other, the content usage control is performed. Thus, the content can be used flexibly without depending on the environment of the device side that uses the content.
[0114]
Further, according to one embodiment, authentication is performed between the control module on the content side with the control module, the resident module, and the control module on the license side with the control module, and control regarding content use is performed according to the authentication result. As a result, security can be improved and unauthorized use can be prevented.
[0115]
Further, according to one embodiment, as shown in FIG. 10, the
[0116]
Further, according to the embodiment, as shown in FIG. 10, the
[0117]
Further, according to one embodiment, as shown in FIG. 9, the
[0118]
In addition, according to the embodiment, as described with reference to FIGS. 16 to 18, the
[0119]
Also, according to one embodiment, as described with reference to FIG. 3, the first control module 51 1 -
[0120]
Also, according to the embodiment, as described with reference to FIG. 13, the charging
[0121]
In addition, according to the embodiment, as described with reference to FIG. 4, the content collection / license collection with
[0122]
Although one embodiment of the present invention has been described in detail with reference to the drawings, a specific configuration example is not limited to this one embodiment, and the design can be changed without departing from the gist of the present invention. And the like are included in the present invention. Below, with reference to FIGS. 22-26, the modifications 1-8 of one Embodiment are demonstrated.
[0123]
In the above-described embodiment, the example in which the
[0124]
The
[0125]
In one embodiment, the
[0126]
In this figure, the old control module-added content 1900A is the one before update, and is composed of the
[0127]
In the second modification of the embodiment shown in FIG. 23A, an example in which the control module and all parts of the content are updated has been described. However, a part of the content may be updated. This case will be described as a third modification of the embodiment. FIG. 23B is a diagram for explaining the third modification of the embodiment.
[0128]
In this figure, the old control module-added content 2000A is the one before update, and is composed of the
[0129]
The new control module-added content 2000B includes an updated
[0130]
In the second modification of the embodiment shown in FIG. 23A, the example in which the control module and all parts of the content are updated has been described. However, only the control module may be updated. This case will be described as a fourth modification of the embodiment. FIG. 24A is a diagram illustrating a fourth modification of the embodiment.
[0131]
In this figure, the content 2100A with a control module is the one before update, and is composed of a
[0132]
In the second modification of the embodiment shown in FIG. 23A, an example in which the control module and all parts of the content are updated has been described. However, a part of the control module may be updated. This case will be described as a fifth modification of the embodiment. FIG. 24B is a diagram for explaining a fifth modification of the embodiment.
[0133]
In this figure, the content 2200A with the old control module is the one before update, and is composed of the
[0134]
This content 2200B with a new control module is composed of
[0135]
In one embodiment, the resident module may be updated to a new resident module by a CPU, a control module, a resident module, etc. (hereinafter simply referred to as a CPU). Hereinafter, this case will be described as a sixth modification of the embodiment. FIG. 25A is a diagram illustrating a sixth modification of the embodiment. The old resident module 2300A is the one before update. When update processing is performed by the CPU or the like in this state, the old resident module 2300A is updated to the new resident module 2300B. In the first to fifth modifications, the license with control module may be updated instead of the content with control module.
[0136]
Moreover, although the modification 6 of one embodiment demonstrated the example which updates all the parts of a resident module, you may make it update a part. Hereinafter, this case will be described as a seventh embodiment. FIG. 25B is a diagram for explaining a
[0137]
In this figure, the old resident module 2400A includes a resident module
[0138]
In one embodiment, as a modified example 8, a content usage control program for realizing the above-described content usage control is recorded on a computer-
[0139]
A
[0140]
The
[0141]
In the embodiment described above, examples of “source code format” and “execution format” have been described as the file format of the control module. However, the present invention is not limited to these, and is described in a script language such as JAVA SCRIPT or PERL. The file format specified may be used.
[0142]
In the above-described embodiment, a plurality of configuration examples, operation examples, control modules, and resident modules are described. However, the present invention also includes a combination of these as necessary.
[0143]
(Supplementary Note 1) In a content usage control apparatus that performs usage control of content provided from a content providing authority to content users,
Input means for inputting a content with a control module consisting of a content and a first control module, and a license with a control module consisting of a license consisting of use permission information of the content and a second control module;
The first control module and the second control module perform control related to content use by mutual cooperation;
A content use control device characterized by the above.
(Additional remark 2) The 3rd control module which authenticates the 1st control module and the 2nd control module, and controls content use by mutual cooperation with the 1st control module and the 2nd control module The content use control device according to
(Additional remark 3) It has a transmission means which synthesize | combines a content and a 1st control module according to control of the said 3rd control module, produces | generates the said content with a control module, and transmits this content with a control module to an external device The content use control apparatus according to Supplementary Note 2, wherein the content use control apparatus is described above.
(Supplementary note 4) The content usage control apparatus according to supplementary note 3, wherein the third control module controls the transmission unit based on a result of mutual authentication with the external device.
(Supplementary Note 5) Encrypted communication is performed on the content with the control module between the transmission unit and the external device, and the transmission unit encrypts the content with the control module using a predetermined encryption key. The content use control device according to appendix 3 or 4, wherein the content is transmitted.
(Additional remark 6) It has the receiving means which performs the control regarding utilization of the content with a control module after receiving the content with a control module transmitted from the external device according to control of the said 3rd control module, It is characterized by the above-mentioned. The content usage control apparatus according to Supplementary Note 2.
(Supplementary note 7) The content usage control apparatus according to supplementary note 6, wherein the third control module controls the reception unit based on a result of mutual authentication with the external device.
(Supplementary Note 8) Encrypted communication is performed between the external device and the receiving unit with respect to the content with the control module, and the receiving unit stores the content with the control module encrypted using a predetermined decryption key. 8. The content use control device according to
(Supplementary note 9) Any one of
(Supplementary Note 10) A database for storing a plurality of contents with control modules and a plurality of licenses with control modules is provided,
The first control module searches the database for a license with a control module that is related to the content, interoperates with the searched control module for the license with the control module, and controls the use of the content, The second control module searches the content with a control module related to the license from the database, and performs mutual control with respect to the use of the content in cooperation with the searched control module of the content with the control module. The content use control device according to
(Supplementary note 11) The content usage control apparatus according to
(Supplementary Note 12) The first control module includes a plurality of first sub-control modules, the second control module includes a plurality of second sub-control modules, and the plurality of first sub-control modules. The content usage control apparatus according to
(Supplementary note 13) Any one of
(Supplementary Note 14) In a content usage control apparatus that performs usage control of content provided from a content providing authority to content users,
A collection of contents with a control module comprising a plurality of contents having a hierarchical structure and a plurality of first control modules respectively corresponding to the plurality of contents, and a plurality of layers having a hierarchical structure corresponding to use permission information of the plurality of contents, respectively. And an input means for inputting a license collection with a control module consisting of a plurality of licenses and a plurality of second control modules respectively corresponding to the plurality of licenses,
The content collection with the control module and the license collection with the control module are stored in at least one file,
The first control module and the second control module perform hierarchical control of content usage through mutual cooperation;
A content use control device characterized by the above.
(Supplementary Note 15) From the content collection with the control module and the license collection with the control module, there are a desired content, a first control module corresponding to the content, a desired license, and a second control module corresponding to the license. Item 14. The supplementary note 14, wherein the content, the first control module, the license, and the second control module are used / distributed as a content with a control module and a license with a control module. Content usage control device.
(Supplementary Note 16) A temporary control including a true control module having the same function as that of the first control module, and the content with the control module is a temporary control that issues a control request to the true control module instead of the first control module. The content use control device according to any one of
(Supplementary note 18) The content use control apparatus according to any one of
(Supplementary note 19) The content use control apparatus according to any one of
(Additional remark 20) The content utilization control apparatus as described in any one of additional remarks 1-15 provided with the update means which updates a part of said 1st control module.
(Supplementary note 21) The content use control apparatus according to supplementary note 2, further comprising update means for updating the third control module.
(Supplementary note 22) The content use control apparatus according to supplementary note 2, further comprising an update unit that updates a part of the third control module.
(Supplementary Note 23) In a content usage control method for performing usage control of content provided from a content providing authority to a content user,
Including an input step of inputting a content with a control module composed of a content and a first control module, and a license with a control module composed of a license composed of usage permission information of the content and a second control module;
The first control module and the second control module perform control related to content use by mutual cooperation;
Content usage control method characterized by the above.
(Supplementary Note 24) A third control module that authenticates the first control module and the second control module and performs control related to content use through mutual cooperation with the first control module and the second control module The content use control method according to attachment 23, further comprising a step.
(Supplementary Note 25) According to the control in the third control module step, the content and the first control module are combined to generate the control module-attached content, and then the control module-attached content is transmitted to an external device. The content use control method according to Supplementary Note 24, comprising:
(Supplementary note 26) A reception step of performing control related to use of the content with the control module after receiving the content with the control module transmitted from the external device according to the control of the third control module step is provided. The content usage control method according to attachment 24.
(Supplementary note 27) including a storage step of storing a plurality of contents with a control module and a plurality of licenses with a control module in a database,
The first control module searches the database for a license with a control module that is related to the content, interoperates with the searched control module for the license with the control module, and controls the use of the content, The second control module searches the content with a control module related to the license from the database, and performs mutual control with respect to the use of the content in cooperation with the searched control module of the content with the control module. Item 25. The content use control method according to Item 23 or 24, wherein
(Supplementary note 28) Any of Supplementary notes 23 to 27, wherein the license with a control module includes billing information related to the use of the content, and the second control module updates the billing information when the content is used. The content usage control method according to
(Supplementary Note 29) In a content usage control method for performing usage control of content provided from a content providing authority to content users,
A collection of contents with a control module comprising a plurality of contents having a hierarchical structure and a plurality of first control modules respectively corresponding to the plurality of contents, and a plurality of layers having a hierarchical structure corresponding to use permission information of the plurality of contents, respectively. And an input step of inputting a license collection with a control module comprising a plurality of licenses and a plurality of second control modules respectively corresponding to the plurality of licenses,
The content collection with the control module and the license collection with the control module are stored in at least one file,
The first control module and the second control module perform hierarchical control of content usage through mutual cooperation;
Content usage control method characterized by the above.
(Additional remark 30) From the content collection with the control module and the license collection with the control module, there is a desired content, a first control module corresponding to the content, a desired license, and a second control module corresponding to the license. Item 29. The supplementary note 29, wherein the content, the first control module, the license, and the second control module are used / distributed as a content with a control module and a license with a control module. Content usage control method.
(Additional remark 31) The content utilization control program for making a computer perform the content utilization control method as described in any one of the said additional remarks 23-30.
(Supplementary Note 32) A computer-readable recording medium on which a content usage control program for causing a computer to execute the content usage control method according to any one of Supplementary Notes 23 to 30 is recorded.
[0144]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, since the control relating to the use of the content is performed by the mutual cooperation between the first control module and the second control module, the device side that uses the content as in the prior art. The content can be used flexibly without depending on the environment.
[0145]
In addition, according to the present invention, the first control module and the second control module are authenticated, and according to the authentication result, control related to content use is performed by mutual cooperation with the first control module and the second control module. Since this is done, it is possible to increase security and to prevent unauthorized use.
[0146]
In addition, according to the present invention, the content and the first control module are combined to generate the content with the control module and then transmitted to the external device. Therefore, the external device also depends on the environment on the device side. Without using it, the content can be used flexibly.
[0147]
In addition, according to the present invention, since the content with the control module is transmitted based on the result of mutual authentication with the external device, the security can be improved, and an error can be made to a malicious third party. There is an effect that transmission can be prevented.
[0148]
Further, according to the present invention, after receiving the content with the control module transmitted from the external device, the control regarding the use of the content with the control module is performed, so that the external device also depends on the environment on the device side. The content can be used flexibly.
[0149]
In addition, according to the present invention, since the content with the control module is received based on the result of mutual authentication with the external device, the security can be improved, and the content with the unintended control module can be obtained. There is an effect that it is possible to prevent erroneous reception.
[0150]
In addition, according to the present invention, since mutual authentication is performed between the first control module and the second control module, and content is used based on the license when authenticated, extremely high security is ensured. There is an effect that can be done.
[0151]
Further, according to the present invention, the first control module and the second control module are provided with a search function for searching the database for the license with the control module and the content with the control module related to the content and the license, Since the control related to the use of content is performed by mutual cooperation with the searched one, there is an effect that a plurality of contents can be easily used without requiring complicated control on the device side.
[0152]
In addition, according to the present invention, since the second control module performs database update processing, it is possible to reduce the burden on the apparatus-side database management.
[0153]
In addition, according to the present invention, since a plurality of controls related to content use corresponding to a combination of a plurality of first sub-control modules and a plurality of second sub-control modules are performed, content can be provided as in the past. There is an effect that the content can be used more flexibly without depending on the environment of the device side that uses.
[0154]
Also, according to the present invention, the billing information is updated when the content is used by the second control module, so that the content can be compared with the case where billing management is performed on the content providing authority side as in the past. There is an effect that the management burden of provision can be reduced.
[0155]
In addition, according to the present invention, the content collection with a control module and the license collection with a control module are used so that the first control module and the second control module perform hierarchical control of content usage through mutual cooperation. Therefore, there is an effect that a plurality of contents can be used efficiently.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a configuration of a content with
FIG. 2 is a diagram showing a configuration of a content with
FIG. 3 is a diagram showing a configuration of a content with
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing a configuration of a content collection / license collection with a
FIG. 5 is a diagram for explaining the operation of the same embodiment;
FIG. 6 is a block diagram showing a configuration example 1 of the same embodiment.
FIG. 7 is a block diagram showing a configuration example 2 of the same embodiment.
FIG. 8 is a block diagram showing a configuration example 3 of the same embodiment.
FIG. 9 is a block diagram showing a configuration example 4 of the same embodiment.
FIG. 10 is a block diagram showing a configuration example 5 of the same embodiment.
FIG. 11 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration example 6 of the same embodiment;
FIG. 12 is a flowchart for explaining the operation of the same embodiment;
FIG. 13 is a flowchart for explaining the operation of the same embodiment;
FIG. 14 is a flowchart for explaining the operation of the same embodiment;
FIG. 15 is a flowchart for explaining the operation of the same embodiment;
FIG. 16 is a flowchart for explaining the operation of the same embodiment;
FIG. 17 is a flowchart for explaining the operation of the same embodiment;
FIG. 18 is a flowchart for explaining the operation of the same embodiment;
FIG. 19 is a flowchart for explaining the operation of the same embodiment;
FIG. 20 is a flowchart for explaining the operation of the same embodiment;
FIG. 21 is a flowchart for explaining the operation of the same embodiment;
FIG. 22 is a diagram illustrating a first modification of the same embodiment.
FIG. 23 is a diagram for explaining modifications 2 and 3 of the same embodiment.
FIG. 24 is a diagram for explaining modifications 4 and 5 of the same embodiment.
FIG. 25 is a diagram for explaining
FIG. 26 is a block diagram showing a modification 8 of the same embodiment.
[Explanation of symbols]
10 Content with control module
11 Control module
12 content
20 License with control module
21 Control module
22 licenses
70 Content collection / license collection with control module
300 CPU
310 Resident module
400 decoder
410 Resident module
800 database
1000 databases
1300 database
1600 Sender system
1601 Resident module
1602 Transmission program
1650 Receiver system
1651 Resident Module
1652 Reception program
1700 system
1701 Resident module
1704 Resident module
1750 system
1751 Resident Module
2500 computer
2501 CPU
2600 recording medium
Claims (5)
コンテンツと第1の制御モジュールとからなる制御モジュール付きコンテンツ、および前記コンテンツの利用許諾情報からなるライセンスと第2の制御モジュールとからなる制御モジュール付きライセンスを入力する入力手段と、
複数の制御モジュール付きコンテンツおよび複数の制御モジュール付きライセンスを格納するデータベースをとさらに備え、
前記制御モジュール付きコンテンツは、自コンテンツに関連のある制御モジュール付きライセンスを前記データベースから検索し、検索された制御モジュール付きライセンスを起動させ、
前記制御モジュール付きライセンスは、前記制御モジュール付きコンテンツによって起動された場合に、自ライセンスに関連のある制御モジュール付きコンテンツを前記データベースから検索し、検索されたコンテンツを起動させ、
前記制御モジュール付きライセンスによって起動された制御モジュール付きコンテンツは、自コンテンツに関連のある制御モジュール付きライセンスを検索し、検索された制御モジュール付きライセンスを起動させ、
前記制御モジュール付きコンテンツによって起動された制御モジュール付きライセンスは、自ライセンスに関連のある制御モジュール付きコンテンツを検索し、検索された制御モジュール付きコンテンツを起動させること
を特徴とするコンテンツ利用制御装置。In a content usage control apparatus that performs usage control of content provided from a content providing authority to content users,
An input means for inputting a content with a control module composed of a content and a first control module, and a license with a control module composed of a license composed of use permission information of the content and a second control module;
A database for storing content with a plurality of control modules and a license with a plurality of control modules;
The content with a control module searches the database for a license with a control module related to the content, and activates the searched license with a control module,
When the license with the control module is activated by the content with the control module, the content with the control module related to the own license is searched from the database, and the searched content is activated .
The content with a control module activated by the license with a control module searches for a license with a control module related to the content, and activates the searched license with a control module,
The content usage control apparatus, wherein the license with a control module activated by the content with a control module searches the content with a control module related to the own license and activates the retrieved content with the control module .
コンテンツと第1の制御モジュールとからなる制御モジュール付きコンテンツ、および前記コンテンツの利用許諾情報からなるライセンスと第2の制御モジュールとからなる制御モジュール付きライセンスを入力する入力工程を含み、
前記制御モジュール付きコンテンツは、自コンテンツに関連のある制御モジュール付きライセンスを検索し、検索された制御モジュール付きライセンスを起動させ、
前記制御モジュール付きライセンスは、前記制御モジュール付きコンテンツによって起動された場合に、自ライセンスに関連のある制御モジュール付きコンテンツを検索し、検索されたコンテンツを起動させること
を特徴とするコンテンツ利用制御方法。In a content usage control apparatus that performs usage control of content provided from a content providing authority to content users,
Including an input step of inputting a content with a control module composed of a content and a first control module, and a license with a control module composed of a license composed of usage permission information of the content and a second control module;
The content with a control module searches for a license with a control module that is related to the content, activates the searched license with a control module,
When the license with a control module is activated by the content with the control module, the content with the control module related to the own license is searched, and the searched content is activated.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001197224A JP4469518B2 (en) | 2000-07-06 | 2001-06-28 | Content usage control device, content usage control method, and content usage control program |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000205755 | 2000-07-06 | ||
| JP2000-205755 | 2000-07-06 | ||
| JP2001197224A JP4469518B2 (en) | 2000-07-06 | 2001-06-28 | Content usage control device, content usage control method, and content usage control program |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2002109255A JP2002109255A (en) | 2002-04-12 |
| JP2002109255A5 JP2002109255A5 (en) | 2006-09-28 |
| JP4469518B2 true JP4469518B2 (en) | 2010-05-26 |
Family
ID=26595548
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001197224A Expired - Fee Related JP4469518B2 (en) | 2000-07-06 | 2001-06-28 | Content usage control device, content usage control method, and content usage control program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4469518B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4489022B2 (en) | 2003-10-16 | 2010-06-23 | シャープ株式会社 | Content usage control apparatus and content usage control method |
| JP2005167914A (en) * | 2003-12-05 | 2005-06-23 | Sony Corp | Content distribution system, content distribution method, content processing apparatus and method, content providing apparatus and method, recording medium, and program |
| CN1774926B (en) * | 2003-12-05 | 2012-07-18 | 索尼株式会社 | Content distribution system and distribution method, and content processing device and processing method |
| EP1585044A1 (en) | 2004-04-06 | 2005-10-12 | Thomson Licensing | Device and method for multimedia data retrieval |
| JP4594753B2 (en) * | 2005-01-24 | 2010-12-08 | 日本放送協会 | Content usage license transmission device, content usage license transmission program, and content usage license reception program |
| JP4969821B2 (en) * | 2005-09-15 | 2012-07-04 | Kddi株式会社 | Program and content decryption method |
| JP5378119B2 (en) * | 2009-09-01 | 2013-12-25 | 富士通エフ・アイ・ピー株式会社 | Wrapping file update system and wrapping file update method |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3688356B2 (en) * | 1995-08-31 | 2005-08-24 | 富士通株式会社 | Licensee notification system |
| JP3666708B2 (en) * | 1997-03-04 | 2005-06-29 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | Server environment migration method and server network |
| JP3792896B2 (en) * | 1997-05-13 | 2006-07-05 | 株式会社東芝 | Information reproducing apparatus and information reproducing method |
| JPH11203124A (en) * | 1998-01-20 | 1999-07-30 | Oki Electric Ind Co Ltd | Software driving method |
| JPH11213010A (en) * | 1998-01-29 | 1999-08-06 | Planet Computer:Kk | Distribution system for digital contents |
| JP2000113048A (en) * | 1998-10-01 | 2000-04-21 | Hitachi Ltd | Contents receiver group and ic card to be used for the same |
| JP2000113066A (en) * | 1998-10-09 | 2000-04-21 | Fujitsu Ltd | Method and system for managing distribution of digital contents |
-
2001
- 2001-06-28 JP JP2001197224A patent/JP4469518B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2002109255A (en) | 2002-04-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8280818B2 (en) | License source component, license destination component, and method thereof | |
| JP4622087B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and program storage medium | |
| US20060059105A1 (en) | Move component, program, and move method | |
| JP4760101B2 (en) | Content providing system, content reproducing apparatus, program, and content reproducing method | |
| US20060069652A1 (en) | Copy component, program and method thereof | |
| US20050076208A1 (en) | Data terminal capable of transferring ciphered content data and license acquired by software | |
| WO2002075550A1 (en) | Data recorder restoring original data allowed to exist only uniquely | |
| WO2002056535A1 (en) | Apparatus and method for recording/reproducing information | |
| KR101478337B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for providing encrypted key based on DRM type of host device | |
| JP4561146B2 (en) | Content distribution system, encryption apparatus, encryption method, information processing program, and storage medium | |
| WO2005117332A1 (en) | Storing medium converting method, program and device | |
| EP1348178A1 (en) | Distribution device, terminal device, and program and method for use therein | |
| KR20060017774A (en) | Information server, information device, information processing system, information processing method, and information processing program | |
| CN101192261A (en) | Method and apparatus for generating proxy-signature on right object and issuing proxy signature certificate | |
| JP2003308252A (en) | Apparatus and method for information processing, recording medium, and program | |
| US20060059101A1 (en) | Reproduction component, program and method thereof | |
| KR20090000624A (en) | Method for mutual authenticating with host device and system thereof | |
| KR100871199B1 (en) | Information recording/reproducing apparatus and method | |
| KR20080007278A (en) | Information processing device and method, and providing medium | |
| US20060059104A1 (en) | Rent component, program, and rent component method | |
| US20060059103A1 (en) | Return component, program, and return component method | |
| JP2003158514A (en) | Digital work protection system, recording medium apparatus, transmission apparatus, and playback apparatus | |
| JP4469518B2 (en) | Content usage control device, content usage control method, and content usage control program | |
| CN1637851B (en) | Music apparatus with selective decryption of usable component in loaded composite content | |
| US7477742B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for controlling contents utilization, and a computer product |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20060815 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20060815 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20090107 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20090127 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090330 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20090623 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090824 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20090929 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20091130 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20100223 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20100301 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130305 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130305 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140305 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |