JP4454099B2 - Mobile phone - Google Patents
Mobile phone Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4454099B2 JP4454099B2 JP2000128906A JP2000128906A JP4454099B2 JP 4454099 B2 JP4454099 B2 JP 4454099B2 JP 2000128906 A JP2000128906 A JP 2000128906A JP 2000128906 A JP2000128906 A JP 2000128906A JP 4454099 B2 JP4454099 B2 JP 4454099B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- call
- incoming
- mobile phone
- mode
- setting
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、携帯電話機に係わり、とくに置忘れ時の対策を備えた携帯電話機に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
携帯電話機をどこかに置忘れると、金品等の置忘れと同様に容易には探し出せず、また拾った人も所有者がわからず返すのが難しい。場合によっては拾った人がそのまま携帯電話機を使用することもあり、多大な料金を支払うことにもなる。これはとくに携帯電話機が盗難に会ったときに起こり易い。このような問題への対策をもつ携帯電話機として予め設定した暗証番号を入力したのちでなければ発呼できないようにしたものがある。しかしこれでは発呼の度に暗証番号入力を必要とし、操作がわずらわしい。
【0003】
また、特開平9−312687号に「防犯機能付き携帯電話機」が開示されている。この携帯電話機を紛失したときは、その所有者が他の電話機から紛失した携帯電話機へ発呼する。この発呼を着信した紛失携帯電話機では、誰かに拾われてもその人がオフフックして応答すれば通常の接続が行われて通話状態になるが、応答がなければ発呼の停止とともに着信動作も停止される。このような着信回数をカウントする回路を備えておき、そのカウント数が所定値を越えると携帯電話機を回線に接続し、接続したことを確認音により発呼側の所有者に伝える。所有者はこの確認音を受けると次に予め設定された暗証番号を入力して携帯電話機へ送信する。携帯電話機側ではこれを受信して、設定された暗証番号との一致を確認すると当該携帯電話機の動作モードを切替え、再びモード切替えを行ったことを確認音により、発呼側に伝える。これを確認した所有者は自分の使っている電話機をオンフックして操作を終える。ここで、この操作により切替えられる動作モードは通常の通話を行う通話モードと、発呼を不可とする受信専用の防犯モードであり、上記操作が行われる度にモードが入れ替わる。このようにしてユーザは携帯電話機の紛失、盗難などに気付いたときに、近くの電話機から上述した操作を行ってその携帯電話機を防犯モードとすることができ、不正使用による通話料金の登算を防ぐことができる。
【0004】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
上記した特開平9−312687号の技術では、動作モード切替えを行うごとに暗証番号の入力を必要とする。このためにはユーザは暗証番号を記憶しているかそれを記録したメモ等をもっていないと操作できない。ところが、紛失/盗難等に気付いたときは、なるべく早くモード切替操作をして不正使用を防止するのが好ましいが、その気付いたときに暗証番号を記憶していなくてメモも所持していないと、メモのおいてある自宅や会社へ行ってからでないと操作できない。また、モード切替のためには複数回の発呼により当該携帯電話機を回線接続するので、接続後の操作時間は通話料金がかかり、これは防犯モードを解除するときにも同じであって、端末のみの操作ではできない問題もある。さらに拾った人に持主の連絡先等を知らせる機能は考慮されていなかった。
【0005】
本発明の目的は、置き忘れモードへの移行操作が容易でかつそのために何回も回線接続を行わなくてもその操作が可能な携帯電話機を提供することにあり、また置き忘れモード移行時にプライベート情報が漏れないようにした携帯電話機を提供することにある。
【0006】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上記の目的を達成するために、本発明は、着信があったときに相手端末の発呼種別、発呼側電話番号を判定する相手端末判定手段と、着信時間及び着信回数の設定手段と、同一の相手端末からの着信が前記設定された着信時間の内に何回あったかをカウントするカウント手段と、このカウント手段のカウント値が前記設定された着信回数の値になったときに自機を発呼禁止モードとする処理手段と、前記処理手段により発呼禁止モードとされた状態では、予め設定された電話番号への発呼のみを可能とする発呼制御手段と、を備えたことを特徴とする携帯電話機を提供する。
【0007】
また、本発明は、着信があったときに相手端末の発呼種別、発呼側電話番号を判定する相手端末判定手段と、着信時間及び着信回数の設定手段と、同一の相手端末からの着信が前記設定された着信時間の内に何回あったかをカウントするカウント手段と、このカウント手段のカウント値が前記設定された着信回数の値になったときに自機を発呼禁止モードとする処理手段と、 前記処理手段により発呼禁止モードとされた状態では、自機内に登録されたメモリダイヤル情報、ツータッチダイヤル情報、あるいは自局電話番号の少なくとも1つを表示しないようにする表示制御手段と、を備えたことを特徴とする携帯電話機を提供する。
【0008】
また、本発明は、前記処理手段により発呼禁止モードとされた状態では、予め設定された置忘れメッセージを表示することを特徴とする携帯電話を提供する。
【0009】
【発明の実施の形態】
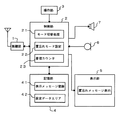
以下、本発明の実施の形態を図面を用いて説明する。図2は、本発明になる携帯電話機の概略構成を示すブロック図で、無線信号の送受を行う無線部1と、通話に伴う信号処理及び表示や鳴音等の制御を行う制御部2と、利用者が文字データを入力する操作部3と、制御部2における処理プログラムや電話帳データを記憶する記憶部4と、入力された文字データを表示する表示部5と、音声を電気信号に変換するマイク6と、電気信号を音声に変換するスピーカ7とから構成されている。
【0010】
制御部2は、モード切替処理機能21と、置忘れモード設定機能22、及び着信カウンタ23をもち、記憶部4は置忘れモード時に表示するメッセージ登録エリア41と設定データエリア42をもっている。ここで着信カウンタ23は、本携帯電話機の電源オン時にクリアされるものとする。
【0011】
置忘れモード設定機能22は、他の機能と同様な操作部3からの操作により起動され、置忘れモードとなったときに表示部に表示する置忘れメッセージの入力や置忘れモードとするための着信方式の設定や着信回数及び着信時間の設定、及び置忘れモードとなったときに発呼を禁止する方法を設定するのに利用される。図3はこの設定機能22の実行時の画面例を示しており、置忘れモード設定機能22を起動するとまず図3(a)のような画面で置忘れメッセージの入力を行う。ここで置忘れメッセージとしては例えば、1行全角6文字で3行分が利用可能とすると(この表示量も設定可能としてもよい)、1〜2行目に「下記まで連絡下さい」、3行目に連絡先(自宅等)の電話番号を入力し、これをその登録部41へ登録しておく。このような入力は電話帳等の入力と同様な機能で容易に実現できる。なお前記のメッセージ例で、「下記までご連絡下さい」は固定として予め処理系に用意しておき、電話番号のみをユーザが入力するようにしてもよい。
【0012】
置き忘れメッセージの入力が終わると、次に図3(b)の画面が表示され、置き忘れモードへ移行するときの着信のカウント方法を着信方式として設定する。ここで「通常」の方を選べば、同一の電話番号(番号通知のとき)又は同一機種(公衆、アナログ電話等)からの着信を、間に他電話や他機種からの着信があっても無視してカウントし、「連続」を選ぶと、間に他番号や他機種からの着信があるとカウントを1からやり直す着信方式となる。
【0013】
次に着信時間等の設定を行う。これは、後にモード切替処理21の説明でくわしく述べるが、ある設定時間(着信時間という)内に先に述べた着信方式で何回(着信回数という)の着信があるとモード切替を実行するかの設定である。図3(c)はその設定画面例で着信時間を5分、着信回数を5回に設定している。さらにこれが終わると図3(d)のような画面で、発呼禁止(ロック状態)の方法として「発信制限」又は「キーロック」のいずれかを選ぶ。以上の各設定結果は設定データエリア42に保存される。勿論これらはメモリダイヤル等と同様に設定変更が可能である。
【0014】
以上のような置忘れモード設定機能22による設定が行われた携帯電話機を紛失したときには、その所持者であるユーザは設定された着信時間内に設定された着信回数の発呼を他の電話機から当該携帯電話機に対して行う。図1は、このとき実行される携帯電話機の置忘れモード切替機能21の処理を示すフローチャートである。この処理は周期的に起動される受信処理の一部であって、着信があると(ステップ101でYes)、着信音を出力し、着信履歴を書き込む(ステップ102)。ここて゛携帯電話機には一般に着信履歴をとる機能が設けられていて、着信日や時刻、発呼種別(番号通知か、番号非通知か、公衆電話からか、アナログダイヤル電話機からかの区別)、番号通知のときの発信電話番号等が着信動作ごとに記録され、最新の20件分程度がつねに記録に残るようになっている。ここでオフフックがあると通常の受信動作へ移行するが(ステップ103でYes)、紛失して誰も所持していない状態であればオフフックされない。そこで着信音の鳴音に対して、オフフックがないと(ステップ103でNo)、着信カウンタの値jが0かをみる(ステップ104)。この値は置忘れモードになった直後、あるいは電源がONされた直後には0であり、その後着信が1回でもあればj≧1となっている。そしてj=0のときは着信カウンタの値jを1とし(ステップ105)、処理を終わる。
【0015】
着信カウンタの値jが0でないときは(ステップ104でNo)、システム時計から現時刻tbを取得し(ステップ106)、さらに着信履歴を参照してj回前の着信時刻taを取得する(ステップ107)。そしてtbーtaの値が置忘れモード設定機能22によりエリア42に設定された着信時間Tよりも小さいかをしらべ(ステップ108)、小さくなければステップ105で着信カウンタの値jを1にして処理を終了するが、tbーtaが着信時間Tよりも小さいときは(ステップ108でYes)、着信履歴を参照して今回着信の発呼種別が前回着信時と同じかを調べる(ステップ109)。ここで前回着信と同じ発呼種別であれば(ステップ109でYes)、その発呼種別が番号通知かを調べる(ステップ110)。これが番号通知のときは再び着信履歴を参照して今回と前回の発呼側電話番号が同じかをチェックする(ステップ111)。着信が番号通知でないか(ステップ110でNo)、番号通知であって前回と同じ電話番号からのもののときは(ステップ111でYes)、着信カウンタの値jを+1し(ステップ112)、更新後の値jが置忘れモード設定機能22により設定された着信回数jmaxに達したかを調べ(ステップ113)、着信カウンタの値jが着信回数jmax以下のときは処理を終わる。
【0016】
発呼種別が前回と異なっているとき(ステップ109でNo)、あるいは番号通知で電話番号が同じでないときは(ステップ111でNo)、エリア42に設定された着信方式を調べ(ステップ114)、“連続”が設定されているときはカウンタ値jを1にリセットし(ステップ105)、再カウントを始める。また着信方式が“通常”に設定されているときは、今回の着信は無視し、カウント値jを変更せずに次の着信を待つ。
【0017】
着信カウンタの値jが着信回数jmaxになったときは(ステップ113でYes)、同一の発呼種別の電話機から、またとくに番号通知のときは同一電話番号の電話機から着信時間T以内に着信回数jmaxに等しい回数の着信があったことを示す。これは携帯電話機を紛失していないが家へ置忘れたときなどに、たまたま着信時間T以内に着信回数jmax回の着信があると間違って置忘れモードへ移行するのをなるべく防ぐために、発呼種別及び番号通知のときの電話番号チェックを行ったことを意味する。そしてこのときは所持者からの指示があったものとして置忘れモードへ移行する。即ちまず着信カウンタの値jを0にリセットしておき(ステップ115)、着信音を最大レベルで例えば20秒間鳴音させる(ステップ116)。これにより、置忘れられた携帯電話機があることを周囲に人がいると知らせることができる。次に、置忘れモード設定機能22で設定しておいた置忘れメッセージを図4のように表示部5へ表示し(ステップ117)、次に置き忘れモード移行に伴う各種機能の停止処理を行う(ステップ118)。これは前述したように、プライベート情報が表示されないように、あるいはそのような情報を消去してそれが他人に知られないようにするためである。このために、この処理では、メモリダイヤル表示、ツータッチダイヤル発信、及び自局電話番号表示の各々を禁止する。具体的には、置き忘れモードに入ったときに、モードフラグを“禁止”を表す値としておき、上記各機能呼び出し時にモードフラグを参照してこれが、“禁止”のときはその機能をスキップするようにしておけばよい。この停止処理が終わると、やはり置忘れモード設定機能22で設定した発呼禁止の方法を調べ(ステップ119)、それに従って発信制限またはキーロックをONとし(ステップ120または121)、処理を終わる。
【0018】
但しこの発信制限もしくはキーロックの状態であっても、図4のような置き忘れメッセージ表示中に何らかのキー(例えば発呼キー)が押下された場合、置き忘れメッセージに表示された連絡先電話番号に発呼することができるようにしておく。これにより携帯電話機を紛失した場合等、拾得者が経済的負担をすることなく、携帯電話の持ち主に簡易な手法で連絡することができる。なお、置き忘れメッセージ中に電話番号を表示させなくてもよく、この場合は携帯電話の持ち主の個人情報の漏洩を防止することができる。
【0019】
以上のようにして、紛失した携帯電話機を発呼禁止の状態にしておくと、予め登録しておいた連絡先電話番号以外には発呼できなくなり、それ以外は受信だけが可能な状態となる。このようにして、図1の処理によれば、とくに暗証番号を用いなくても近くの電話機からの発呼により紛失した携帯電話機を発呼禁止状態、即ち置忘れモードとすることができ、そのための通話料金も不要である。また、発呼禁止とするための操作中に他機からの着信が想定されるようなときでも、着信方式の設定により置き忘れモードへの移行が容易になる。さらに携帯電話機に登録されたプライベート情報も保護することができる。なお、置忘れモードの解除は、機能キーを解除モードに割り当てておき、その解除モードで暗証番号入力によって行えるようにする。置忘れモードの解除は、紛失時の乱用防止のための発呼禁止への移行と比べれば緊急性はなく、暗証番号を忘れてもメモ等を参照するまで使用を待つだけのことで、解除のための暗証番号の利用は、他人に勝手に置忘れモードを解除されないために必要である。
【0020】
【発明の効果】
本発明によれば、特に暗証番号を用いなくても紛失した携帯電話機を通話料金なしで発呼禁止の置忘れモードとすることができ、不当な料金を加算されるのを防止できる。また置忘れモードとするための操作も容易となり、登録されたプライベート情報が他人に洩れるのを防ぐことができる効果がある。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の特徴とするモード切替処理のフローチャートである。
【図2】本発明の携帯電話機の概略構成を示すブロック図である。
【図3】置忘れモード設定機能22の説明図である。
【図4】置忘れメッセージの表示例である。
【符号の説明】
2 制御部
4 記憶部
5 表示部
21 モード切替処理機能
22 置忘れモード設定機能
23 着信カウンタ
41 表示メッセージ登録部
42 設定データエリア[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a mobile phone, and more particularly, to a mobile phone provided with a measure against misplacement.
[0002]
[Prior art]
If you leave your mobile phone somewhere, it will not be as easy to find as if you left your money away, and it will be difficult for the owner to pick it up and return it. In some cases, the person who picks up uses the mobile phone as it is, and pays a large fee. This is especially likely when a mobile phone encounters theft. Some portable telephones having a countermeasure against such a problem are such that a call cannot be made unless a preset password is inputted. However, this requires a password input each time a call is made, which is cumbersome to operate.
[0003]
Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 9-312687 discloses “a mobile phone with a crime prevention function”. When this mobile phone is lost, the owner calls it from another phone to the lost mobile phone. A lost mobile phone that receives this call will be connected to a normal connection if it is picked up by someone and responds with an off-hook response. Is also stopped. A circuit for counting the number of incoming calls is provided, and when the count exceeds a predetermined value, the mobile phone is connected to the line, and the connection side is notified to the calling party owner by a confirmation sound. When the owner receives this confirmation sound, the owner then inputs a preset password and transmits it to the mobile phone. When the mobile phone side receives this and confirms the coincidence with the set personal identification number, the operation mode of the mobile phone is switched, and the calling side is notified by a confirmation sound that mode switching has been performed again. The owner who confirms this ends the operation by on-hooking his / her telephone. Here, the operation mode switched by this operation is a call mode for performing a normal call and a reception-only security mode for disabling a call, and the mode is switched every time the above operation is performed. In this way, when the user becomes aware of the loss or theft of a mobile phone, the user can perform the above-described operation from a nearby phone to put the mobile phone into a security mode, and add up to the call charge due to unauthorized use. Can be prevented.
[0004]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
In the technique disclosed in Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 9-312687 described above, it is necessary to input a personal identification number every time the operation mode is switched. For this purpose, the user cannot operate unless the personal identification number is stored or a memo or the like recorded therein is recorded. However, if you notice a loss / theft, it is preferable to switch the mode as soon as possible to prevent unauthorized use. However, if you do not remember your PIN and do not have a memo , You can only operate after going to your home or office where the notes are. In addition, since the mobile phone is connected to the line by making multiple calls for mode switching, the operation time after connection is charged a call fee, and this is the same when canceling the crime prevention mode. There is also a problem that cannot be done with only the operation. Furthermore, the function of notifying the contact person of the owner of the person who picked it up was not considered.
[0005]
An object of the present invention is to provide a mobile phone that is easy to shift to the misplaced mode and that can be operated without having to connect the line many times. The object is to provide a mobile phone that does not leak.
[0006]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
To achieve the above object, the present invention includes a mating terminal determination means for determining a call type of the remote terminal, the caller's telephone number when an incoming call, and setting means arrival time and number of incoming calls , when the incoming from the same of the remote terminal is turned many times counting means for counting there was the value of the number of incoming calls the count value of the count means is the set of the set arrival time processing means for the own device and call inhibition mode, the state of being a call prohibition mode by the processing unit, comprises a call control means for allowing only call to a preset telephone number, the A mobile phone is provided.
[0007]
Further, the present invention provides a counterpart terminal determination means for determining the call type and caller telephone number of the counterpart terminal when there is an incoming call, a means for setting the incoming time and the number of incoming calls, and an incoming call from the same counterpart terminal Counting means for counting the number of times the mobile phone is within the set incoming time, and a process for setting the own device to a call prohibition mode when the count value of the counting means reaches the set number of incoming calls and means, in the state of being a call prohibition mode by said processing means, display control means so as not to display at least one of the apparatus itself memory dial information registered in, 2-touch dialing information or local telephone number, , to provide a mobile telephone, characterized in that it comprises a.
[0008]
According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a mobile phone characterized by displaying a preset misplacement message in a state in which the processing means is in a call prohibition mode.
[0009]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing a schematic configuration of a mobile phone according to the present invention, a
[0010]
The control unit 2 has a mode
[0011]
The misplacement
[0012]
When the input of the misplaced message is completed, the screen of FIG. 3B is displayed next, and the incoming call counting method when shifting to the misplaced mode is set as the incoming call method. If you select "Normal" here, you can receive calls from the same phone number (for number notification) or from the same model (public, analog phone, etc.), even if there is an incoming call from another phone or other model. If the count is ignored and “continuous” is selected, if there is an incoming call from another number or other model in between, the incoming call system starts over from 1.
[0013]
Next, the incoming time is set. This will be described in detail later in the description of the
[0014]
When the mobile phone set by the misplacement
[0015]
If the value j of the incoming call counter is not 0 (No in step 104), the current time tb is obtained from the system clock (step 106), and the incoming time ta before j times is obtained by referring to the incoming call history (step 106). 107). Then, it is checked whether the value of tb-ta is smaller than the incoming time T set in the
[0016]
When the call type is different from the previous time (No in Step 109), or when the telephone number is not the same in the number notification (No in Step 111), the incoming call method set in the
[0017]
When the value j of the incoming call counter is equal to the number of incoming calls jmax (Yes in step 113), the number of incoming calls within the incoming time T from the telephone of the same call type, and particularly from the telephone of the same telephone number for number notification. This indicates that there are incoming calls equal to jmax. This is done to prevent a mistaken transition to the misplaced mode if there is an incoming call jmax times within the incoming time T, such as when the mobile phone has not been lost but is left at home. This means that the telephone number was checked when the type and number were notified. At this time, the mode shifts to the misplacement mode because there is an instruction from the owner. That is, first, the value j of the incoming call counter is reset to 0 (step 115), and the incoming sound is sounded at the maximum level for 20 seconds, for example (step 116). Thereby, it can be notified that there is a person around that there is a mobile phone that has been misplaced. Next, the misplacement message set by the misplacement
[0018]
However, even if the outgoing call restriction or key lock state is set, if any key (for example, a call key) is pressed while the misplaced message is displayed as shown in FIG. 4, the call is made to the contact telephone number displayed in the misplaced message. Be ready to call. This makes it possible to contact the owner of the mobile phone by a simple method without burdening the financial user, such as when the mobile phone is lost. Note that the telephone number need not be displayed in the misplaced message, and in this case, leakage of personal information of the owner of the mobile phone can be prevented.
[0019]
As described above, if a lost mobile phone is placed in a call-prohibited state, calls can only be made to contact telephone numbers that have been registered in advance, and otherwise only reception is possible. . Thus, according to the processing of FIG. 1, a mobile phone lost due to a call from a nearby telephone can be placed in a call prohibition state, that is, a misplacement mode without using a personal identification number. No call charges are required. In addition, even when an incoming call from another device is assumed during an operation for prohibiting outgoing calls, it is easy to shift to the misplaced mode by setting the incoming call method. Furthermore, private information registered in the mobile phone can be protected. Note that the release of the misplaced mode can be performed by assigning a function key to the release mode and inputting the personal identification number in the release mode. Canceling the misplaced mode is not as urgent as shifting to call prohibition to prevent abuse when lost, and if you forget your PIN, just wait for use until you see a note etc. The use of a personal identification number is necessary for preventing others from leaving the misplaced mode.
[0020]
【The invention's effect】
According to the present invention, a lost mobile phone can be placed in a call-forbidden forgetting mode without calling charges even without using a personal identification number, and an unfair charge can be prevented from being added. Also, the operation for setting the misplacement mode becomes easy, and there is an effect that the registered private information can be prevented from being leaked to others.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a flowchart of a mode switching process that is a feature of the present invention;
FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing a schematic configuration of a mobile phone according to the present invention.
3 is an explanatory diagram of a misplacement
FIG. 4 is a display example of a misplaced message.
[Explanation of symbols]
2
Claims (3)
着信時間及び着信回数の設定手段と、
同一の相手端末からの着信が前記設定された着信時間の内に何回あったかをカウントするカウント手段と、
このカウント手段のカウント値が前記設定された着信回数の値になったときに自機を発呼禁止モードとする処理手段と、
前記処理手段により発呼禁止モードとされた状態では、予め設定された電話番号への発呼のみを可能とする発呼制御手段と、
を備えたことを特徴とする携帯電話機。A partner terminal determination means for determining a call type of a partner terminal and a calling party telephone number when there is an incoming call;
Means for setting the incoming time and number of incoming calls;
Counting means for the same incoming call from the partner terminal to count whether a number of times within the set arrival time,
A processing means for setting the own apparatus to a call prohibition mode when the count value of the counting means reaches the set number of incoming calls;
In the state where the processing means is set to the call prohibition mode, a call control means that enables only a call to a preset telephone number;
A mobile phone comprising:
着信時間及び着信回数の設定手段と、
同一の相手端末からの着信が前記設定された着信時間の内に何回あったかをカウントするカウント手段と、
このカウント手段のカウント値が前記設定された着信回数の値になったときに自機を発呼禁止モードとする処理手段と、
前記処理手段により発呼禁止モードとされた状態では、自機内に登録されたメモリダイヤル情報、ツータッチダイヤル情報、あるいは自局電話番号の少なくとも1つを表示しないようにする表示制御手段と、
を備えたことを特徴とする携帯電話機。 A partner terminal determination means for determining a call type of a partner terminal and a calling party telephone number when there is an incoming call;
Means for setting the incoming time and number of incoming calls;
Counting means for counting how many times an incoming call from the same partner terminal has occurred within the set incoming time;
A processing means for setting the own device to a call prohibition mode when the count value of the counting means reaches the set number of incoming calls;
Display control means for preventing display of at least one of memory dial information, two-touch dial information, or own telephone number registered in the own device in a state where the calling means is set to the calling prohibit mode by the processing means;
A mobile phone comprising:
前記処理手段により発呼禁止モードとされた状態では、予め設定された置忘れメッセージを表示することを特徴とする携帯電話機。 The mobile phone according to claim 1 or 2,
A cellular phone characterized by displaying a preset misplaced message in a state in which the calling means is set to the call prohibit mode by the processing means .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000128906A JP4454099B2 (en) | 2000-04-28 | 2000-04-28 | Mobile phone |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000128906A JP4454099B2 (en) | 2000-04-28 | 2000-04-28 | Mobile phone |
Related Child Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008332765A Division JP4452754B2 (en) | 2008-12-26 | 2008-12-26 | Mobile phone and mobile phone control method |
| JP2009287030A Division JP2010110000A (en) | 2009-12-18 | 2009-12-18 | Cellular phone and method of controlling the same |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2001313980A JP2001313980A (en) | 2001-11-09 |
| JP2001313980A5 JP2001313980A5 (en) | 2009-03-05 |
| JP4454099B2 true JP4454099B2 (en) | 2010-04-21 |
Family
ID=18638271
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000128906A Expired - Lifetime JP4454099B2 (en) | 2000-04-28 | 2000-04-28 | Mobile phone |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4454099B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4026397B2 (en) | 2002-04-09 | 2007-12-26 | 日本電気株式会社 | Mobile communication terminal remote control system, mobile communication terminal, remote control method, and remote control program |
| KR100551120B1 (en) * | 2002-08-19 | 2006-02-13 | 주식회사 엘지텔레콤 | Apparatus and method for detecting terminal of mobile telephone |
| JP4627047B2 (en) * | 2006-05-16 | 2011-02-09 | 京セラ株式会社 | Mobile communication terminal |
-
2000
- 2000-04-28 JP JP2000128906A patent/JP4454099B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2001313980A (en) | 2001-11-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP3621612B2 (en) | Mobile phone | |
| CN1416257B (en) | Communication equipment | |
| KR0143122B1 (en) | Cellular phone | |
| US5745559A (en) | Restricted access telephones for logical telephone networks | |
| KR101062392B1 (en) | Recording media recording electronic devices and programs | |
| JP2000270376A (en) | Mobile phone maintenance service system and method for maintenance service | |
| JPWO2003084189A1 (en) | Information device with telephone function, incoming call history processing method and program | |
| JPH11298600A (en) | Portable telephone set | |
| CN108924335B (en) | Call control method, system and mobile terminal | |
| JP4454099B2 (en) | Mobile phone | |
| JPH11331366A (en) | Portable telephone set | |
| JP4452754B2 (en) | Mobile phone and mobile phone control method | |
| JP5113445B2 (en) | Mobile communication device | |
| JP4150302B2 (en) | Mobile phone | |
| JP2010110000A (en) | Cellular phone and method of controlling the same | |
| KR100621748B1 (en) | Method for storing calling number of mobile communication terminal | |
| JP2002101189A (en) | Portable telephone | |
| JP4159069B2 (en) | Wireless telephone equipment | |
| KR100606774B1 (en) | Method for setting restrict call of mobile communication terminal | |
| KR100598354B1 (en) | Incoming call number protecting method for mobile handset | |
| JP3005044U (en) | Long phone prevention control device | |
| JP2004056423A (en) | Portable communication device | |
| JP3056113B2 (en) | Mobile phone | |
| JP2002291041A (en) | Portable terminal and mobile communication system | |
| JP2004104548A (en) | Portable telephone and its call termination display controlling method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070330 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090116 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A132 Effective date: 20091020 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20091130 |
|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20091209 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20091218 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20100120 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20100202 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130212 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4454099 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130212 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313113 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130212 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130212 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140212 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313111 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313113 |
|
| S533 | Written request for registration of change of name |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313533 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| EXPY | Cancellation because of completion of term |