JP4433827B2 - Resin gear - Google Patents
Resin gear Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4433827B2 JP4433827B2 JP2004054889A JP2004054889A JP4433827B2 JP 4433827 B2 JP4433827 B2 JP 4433827B2 JP 2004054889 A JP2004054889 A JP 2004054889A JP 2004054889 A JP2004054889 A JP 2004054889A JP 4433827 B2 JP4433827 B2 JP 4433827B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- resin
- gear
- heat stabilizer
- cast nylon
- monomer cast
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Power Steering Mechanism (AREA)
- Gears, Cams (AREA)
Description
本発明は、動力伝達に適した樹脂製歯車に関する。 The present invention relates to a resin gear suitable for power transmission.
車両用の電動パワーステアリング装置では、電動モータに比較的高回転・低トルクのものが使用されることから、電動モータとステアリングシャフトとの間に歯車減速機構が組み込まれている。歯車減速機構としては、平歯車等の歯車を使用したものも知られているが、一組で大きな減速比が得られる等の理由から、電動モータの回転軸に連結される駆動側歯車であるウォームと、このウォームに噛み合うウォームホイールと、で構成されるウォーム歯車減速機構(以下、減速ギヤと記すこともある)が一般的に使用されている。 In an electric power steering apparatus for a vehicle, a gear reduction mechanism is incorporated between the electric motor and the steering shaft since an electric motor having a relatively high rotation and low torque is used. As a gear reduction mechanism, a gear using a gear such as a spur gear is also known, but it is a drive-side gear connected to the rotating shaft of an electric motor for the reason that a large reduction ratio can be obtained by one set. A worm gear speed reduction mechanism (hereinafter sometimes referred to as a speed reduction gear) composed of a worm and a worm wheel meshing with the worm is generally used.
このような減速ギヤにおいては、ウォームホイールとウォームとの両方を金属製とすると、ハンドル操作時に歯打ち音や振動音等の不快音が発生するという問題があった。そこで、ウォームが金属製である場合には、樹脂製の歯を有するウォームホイールを使用することにより、不快音の発生を抑制していた。このウォームホイールは、金属製のハブ(すなわち芯金)の外周に樹脂製のブランク円板を一体に形成し、このブランク円板の円周部に切削等の手段で歯を形成したものである。 In such a reduction gear, if both the worm wheel and the worm are made of metal, there has been a problem that unpleasant noise such as rattling noise and vibration noise is generated when the handle is operated. Therefore, when the worm is made of metal, the generation of unpleasant noise is suppressed by using a worm wheel having resin teeth. In this worm wheel, a resin blank disc is integrally formed on the outer periphery of a metal hub (that is, a metal core), and teeth are formed on the circumferential portion of the blank disc by means such as cutting. .
歯を構成する樹脂としては、例えば特許文献1に示されるように、ポリアミド6,ポリアミド66,ポリアセタール,ポリエーテルエーテルケトン(PEEK),ポリフェニレンサルファイド(PPS)等のベース樹脂にガラス繊維や炭素繊維等の繊維補強材を配合した材料の他、繊維補強材を含有しないモノマーキャストナイロン(MCナイロン),ポリアミド6,ポリアミド66等が使用されている。
As a resin constituting the teeth, for example, as disclosed in
これらの樹脂材料の中でも、寸法安定性やコストを考慮して、繊維補強材を含有しないMCナイロンや、ガラス繊維を含有するポリアミド6,ポリアミド66,ポリアミド46等が主に使用されている。
しかしながら、コラムタイプの電動パワーステアリング装置に最も多く使用されているモノマーキャストナイロン樹脂を用いた樹脂製歯車は、歯が形成された樹脂部と金属製のハブの外周とが融着(接着)されているため、吸水による寸法変化は抑制されているものの、樹脂自体には耐熱性を格段に改善する熱安定剤等が配合されていないことから、使用温度である60〜80℃では強度の低下等が生じるおそれがあった。 However, resin gears using monomer cast nylon resin, which is most often used in column-type electric power steering devices, have a resin part where teeth are formed and the outer periphery of a metal hub fused (adhered). Therefore, although the dimensional change due to water absorption is suppressed, the resin itself does not contain a heat stabilizer or the like that remarkably improves heat resistance. Etc. may occur.
このような強度の低下が生じると、低温時における衝撃等のような大きな負荷が作用した際に樹脂製の歯が破損するおそれがあり、最悪の場合には電動パワーステアリング装置が機能しなくなってしまうおそれがあった。
そこで、本発明は、上記のような従来技術が有する問題点を解決し、耐熱性に優れ歯の破損等の不具合が生じにくい高信頼性の樹脂製歯車を提供することを課題とする。
If such a decrease in strength occurs, there is a risk of damage to the resin teeth when a large load such as an impact at low temperatures is applied. In the worst case, the electric power steering device will not function. There was a risk of it.
Accordingly, an object of the present invention is to solve the above-described problems of the prior art and to provide a highly reliable resin gear that has excellent heat resistance and is unlikely to cause problems such as tooth breakage.
前記課題を解決するため、本発明は次のような構成からなる。すなわち、本発明に係る請求項1の樹脂製歯車は、ハブと、該ハブの外周に一体的に設けられ歯が形成された樹脂部と、を備える樹脂製歯車において、前記樹脂部は、空気中に120℃で2000時間放置することによる引張強度の低下率が10%未満であるモノマーキャストナイロン樹脂で構成されていることを特徴とする。
また、本発明に係る請求項2の樹脂製歯車は、請求項1に記載の樹脂製歯車において、ウォームホイール,はすば歯車,平歯車,傘歯車,又はハイポイドギヤであることを特徴とする。
さらに、本発明に係る請求項3の樹脂製歯車は、請求項1又は請求項2に記載の樹脂製歯車において、前記モノマーキャストナイロン樹脂の結晶化度がアニーリング処理により50〜60%とされていることを特徴とする。
さらに、本発明に係る請求項4の樹脂製歯車は、請求項1〜3のいずれか一項に記載の樹脂製歯車において、前記モノマーキャストナイロン樹脂が、銅系熱安定剤,フェノール系熱安定剤,リン系熱安定剤,硫黄系熱安定剤,及びアミン系熱安定剤のうち少なくとも1種を含有することを特徴とする。
さらに、本発明に係る請求項5の樹脂製歯車は、請求項1〜4のいずれか一項に記載の樹脂製歯車において、電動パワーステアリング装置に用いられることを特徴とする。
In order to solve the above-described problems, the present invention has the following configuration. In other words, the resin gear according to
A resin gear according to a second aspect of the present invention is the resin gear according to the first aspect, wherein the resin gear is a worm wheel, a helical gear, a spur gear, a bevel gear, or a hypoid gear.
Furthermore, the resin gear according to claim 3 according to the present invention is the resin gear according to
Furthermore, the resin-made gear of Claim 4 which concerns on this invention is a resin-made gear as described in any one of Claims 1-3. WHEREIN: The said monomer cast nylon resin is a copper-type heat stabilizer, a phenol-type heat stability. It contains at least one of an agent, a phosphorus heat stabilizer, a sulfur heat stabilizer, and an amine heat stabilizer.
Furthermore, the resin gear of Claim 5 which concerns on this invention is used for an electric power steering apparatus in the resin gear as described in any one of Claims 1-4.
本発明の樹脂製歯車は、優れた耐熱性を有しているので、歯の破損等の不具合が生じにくく信頼性が高い。 Since the resin gear of the present invention has excellent heat resistance, problems such as tooth breakage are less likely to occur and the reliability is high.
本発明に係る樹脂製歯車の実施の形態を、図面を参照しながら詳細に説明する。
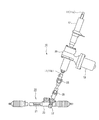
図1は、本実施形態の樹脂製歯車を減速機構に用いた自動車のコラム式電動パワーステアリング装置10の構成を説明する図である。舵輪軸11は、上部舵輪軸11aと下部舵輪軸11bとで構成され、舵輪軸ハウジング12の内部に、軸心を中心に回転自在に支承されている。また、舵輪軸ハウジング12は、下部を車両の前方に向けて傾斜した姿勢で、車室内部の所定位置に固定されている。さらに、上部舵輪軸11aの上端には、図示されない舵輪が固定されている。
さらに、上部舵輪軸11aと下部舵輪軸11bとは、図示されないトーションバーで連結されている。舵輪から上部舵輪軸11aを経て下部舵輪軸11bに伝達された操舵トルクは、トーションバーにより検出され、検出された操舵トルクに基づいて、電動モータ13の出力が制御される。
An embodiment of a resin gear according to the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of a column-type electric
Further, the upper
ラック・ピニオン式運動変換機構20は、軸方向に移動可能なラック軸21と、ラック軸21の軸心に対して斜めに支承されてラック軸21の歯に噛み合う歯を備えたピニオンを有するピニオン軸22と、ラック軸21及びピニオン軸22を支承する筒状のラック軸ケース23と、で構成される。そして、ラック・ピニオン式運動変換機構20は、その長手方向が車両の左右方向に沿うようにして、車両の前部のエンジンルーム内にほぼ水平に配置されている。
ピニオン軸22と下部舵輪軸11bの下部とは、2個の自在継手25,26で連結されている。また、下部舵輪軸11bの中間部分には、後述するウォーム歯車減速機構30が配置されていて、電動モータ13から下部舵輪軸11bに対して操舵補助力が供給されるようになっている。
The rack-and-pinion type
The
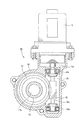
次に、ウォーム歯車減速機構30の構成を、図2の部分断面図を参照しながら説明する。ウォームホイール31と噛み合うウォーム32の両端には、ウォーム軸32a,32bが一体的に形成されており、これらウォーム軸32a,32bはそれぞれ、ギヤケース33に装着された玉軸受34a,34bによって回転自在に支承されている。また、ウォーム軸32bは、電動モータ13の駆動軸13aにスプライン結合又はセレーション結合している。
ウォームホイール31の芯金42(本発明の構成要件であるハブに相当する)は、下部舵輪軸11bと連結しているので、電動モータ13の回転が、ウォーム32及びウォームホイール31を経て下部舵輪軸11bに伝達されることとなる。
Next, the configuration of the worm
Since the
次に、ウォームホイール31の構成を、図3の斜視図を参照しながら説明する。ウォームホイール31は、芯金42と、芯金42の外周に一体的に設けられた樹脂部43と、で構成されている。そして、樹脂部43の外径面には、金属製のウォーム32と噛み合う歯44が形成されている。
この樹脂部43はモノマーキャストナイロン樹脂製で、円筒形をなしており、芯金42を加熱圧入することによりウォームホイール31が得られる。この時、芯金42の外周面には、適宜クロスローレット加工等の加工を施すことが好ましく、その加工面を円筒形の樹脂部43に加熱圧入するとよい。そして、外周面にシランカップリング剤等のカップリング剤が塗布された芯金42を加熱圧入し、その後に高周波融着を行えば、芯金42と樹脂部43とが一体的に接合(接着)される。また、樹脂部43の外径面の歯44は、芯金42と樹脂部43とを融着等により一体化した後に、切削加工等で形成する。なお、カップリング剤を芯金42に塗布する方法としては、メタノール等の溶剤で希釈した溶液を塗布する方法等があげられる。
Next, the configuration of the
The
シランカップリング剤は、加水分解性基であるアルコキシ基を一端に有する化学構造を有している。このアルコキシ基は加水分解して水酸基に変化し、その水酸基が金属表面の水酸基と脱水縮合反応を起こすことにより、金属との間で高い結合力を持つ共有結合を形成する。
また、シランカップリング剤は他端に有機官能基を有しており、この有機官能基が、ε−カプロラクタムの重合によってモノマーキャストナイロン樹脂を得る過程において、約1質量%程度残る未反応のε−カプロラクタムや、モノマーキャストナイロン樹脂のアミド結合等と結合する。そして、これらの結合により芯金42と樹脂部43とが強固に結合される。なお、有機官能基としては、反応性を考慮するとアミノ基を有するものが好適である。このような有機官能基を有するシランカップリング剤の具体例としては、γ−アミノプロピルトリエトキシシラン,N−β−アミノエチル−γ−アミノプロピルトリメトキシシラン,γ−ウレイドプロピルトリエトキシシラン等があげられる。
The silane coupling agent has a chemical structure having an alkoxy group which is a hydrolyzable group at one end. This alkoxy group is hydrolyzed to change to a hydroxyl group, and the hydroxyl group causes a dehydration condensation reaction with a hydroxyl group on the metal surface, thereby forming a covalent bond having a high binding force with the metal.
Further, the silane coupling agent has an organic functional group at the other end, and this organic functional group remains about 1% by mass in the process of obtaining a monomer cast nylon resin by polymerization of ε-caprolactam. -Bonds with caprolactam and amide bond of monomer cast nylon resin. And the
モノマーキャストナイロン樹脂はε−カプロラクタムの重合体であるが、本発明において使用されるモノマーキャストナイロン樹脂は、結晶化度の向上と熱安定剤の均一分散との少なくとも一方がなされているので、従来のモノマーキャストナイロン樹脂に比べて樹脂自体の耐熱性が優れている。さらに、機械的強度及び寸法安定性にも優れている。このようなモノマーキャストナイロン樹脂が有する耐熱性は、以下の通りである。すなわち、モノマーキャストナイロン樹脂は高温に曝されると劣化して引張強度等の物性が低下する傾向があるが、前述のようなモノマーキャストナイロン樹脂は、空気中に120℃で2000時間放置されても、引張強度の低下率が10%未満である。 Although the monomer cast nylon resin is a polymer of ε-caprolactam, since the monomer cast nylon resin used in the present invention has at least one of improvement in crystallinity and uniform dispersion of the heat stabilizer, The heat resistance of the resin itself is superior to that of the monomer cast nylon resin. Furthermore, it is excellent in mechanical strength and dimensional stability. The heat resistance of such a monomer cast nylon resin is as follows. That is, the monomer cast nylon resin has a tendency to deteriorate when exposed to high temperature, and the physical properties such as tensile strength decrease. However, the monomer cast nylon resin as described above is left in the air at 120 ° C. for 2000 hours. However, the rate of decrease in tensile strength is less than 10%.
ウォームホイール31の樹脂部43は、このような耐熱性に優れたモノマーキャストナイロン樹脂で構成されているので、大きな負荷等が作用しても歯の破損等の不具合が生じにくい。よって、このウォーム歯車減速機構30は、信頼性が高く長寿命であり、電動パワーステアリング装置10の高性能化に寄与する。
ここで、結晶化度の向上について説明する。ε−カプロラクタムをモノマーキャスト法で重合して得られたモノマーキャストナイロン樹脂(通常の方法で得られた重合体)を、アニーリング処理すると、結晶化度は40〜45%程度から50〜60%へ向上する。これにより、引張強度等の機械的強度が向上するとともに、耐疲労性や耐熱性が改善される。結晶化度が50%未満であると、上記のような改善効果が不十分となる。一方、60%を超えると、機械的強度は向上するものの弾性率が高くなりすぎるため、歯車の歯面の面圧が向上してしまう。また、アニーリング処理の処理温度を高めたり、処理時間を長くしたりする必要があるため、実用性が低い。
Since the
Here, the improvement of the crystallinity will be described. When a monomer cast nylon resin (polymer obtained by a normal method) obtained by polymerizing ε-caprolactam by a monomer cast method is annealed, the crystallinity is increased from about 40 to 45% to 50 to 60%. improves. Thereby, mechanical strength such as tensile strength is improved, and fatigue resistance and heat resistance are improved. When the degree of crystallinity is less than 50%, the above improvement effect is insufficient. On the other hand, if it exceeds 60%, the mechanical strength is improved, but the elastic modulus is too high, so that the surface pressure of the gear tooth surface is improved. Moreover, since it is necessary to raise the processing temperature of annealing processing or to lengthen processing time, its practicality is low.
アニーリング処理の条件は特に限定されるものではないが、以下のようなものが一例としてあげられる。すなわち、2〜15時間かけて室温から160〜200℃まで昇温し、該温度で1〜15時間程度保持した後に、3〜30時間かけて室温まで徐冷する、という条件である。このようなアニーリング処理により、モノマーキャストナイロン樹脂の結晶化度を、40〜45%程度から50〜60%へ向上させることができる。 The conditions for the annealing treatment are not particularly limited, but examples include the following. That is, the temperature is raised from room temperature to 160 to 200 ° C. over 2 to 15 hours, held at the temperature for about 1 to 15 hours, and then gradually cooled to room temperature over 3 to 30 hours. By such annealing treatment, the crystallinity of the monomer cast nylon resin can be improved from about 40 to 45% to 50 to 60%.
次に、熱安定剤の均一分散について説明する。モノマーキャストナイロン樹脂中に熱安定剤を均一に分散させるためには、熱安定剤の混合方法を工夫する必要がある。モノマーキャスト法で得られたε−カプロラクタムの重合体(モノマーキャストナイロン樹脂)とε−カプロラクタム(モノマー)とを加熱しながら混合し、高粘度な均一溶液とする。この時の加熱温度は、ε−カプロラクタムの融点である69℃以上とする必要があり、より好ましくは160〜210℃程度である。この溶液に熱安定剤を分散させ、熱安定剤の沈降や濃度むらを防止した状態で、さらにモノマーキャスト法で重合を進行させる。これにより、モノマーキャストナイロン樹脂中に熱安定剤を均一に分散させることができる。
なお、モノマーキャストナイロン樹脂の数平均分子量は60000〜300000が好ましく、100000〜200000がより好ましい。
Next, the uniform dispersion of the heat stabilizer will be described. In order to uniformly disperse the heat stabilizer in the monomer cast nylon resin, it is necessary to devise a method for mixing the heat stabilizer. A polymer of ε-caprolactam (monomer cast nylon resin) obtained by the monomer casting method and ε-caprolactam (monomer) are mixed while heating to obtain a highly viscous uniform solution. The heating temperature at this time needs to be 69 ° C. or higher, which is the melting point of ε-caprolactam, more preferably about 160 to 210 ° C. In a state where the heat stabilizer is dispersed in this solution and precipitation of the heat stabilizer and uneven concentration are prevented, the polymerization is further advanced by a monomer cast method. Thereby, the heat stabilizer can be uniformly dispersed in the monomer cast nylon resin.
The number average molecular weight of the monomer cast nylon resin is preferably 60000 to 300000, more preferably 100000 to 200000.
熱安定剤の種類は特に限定されるものではなく、銅系熱安定剤,フェノール系熱安定剤,リン系熱安定剤,硫黄系熱安定剤,アミン系熱安定剤等を使用することができる。
銅系熱安定剤として用いることができる銅化合物としては、塩化銅,臭化銅,ヨウ化銅,硫酸銅,硝酸銅,リン酸銅等の無機酸の塩や、酢酸銅,ステアリン酸銅,ミスチリン酸銅,ナフテン酸銅,パルミチン酸銅等の有機酸の塩等があげられる。これらの銅系熱安定剤は単独で使用してもよいし、二種以上を併用してもよい。なお、銅系熱安定剤として用いた銅化合物と同種の塩(例えば、ヨウ化銅の場合であればヨウ化カリウム)を添加すると、重合時の溶解性を向上させることができる。
The type of heat stabilizer is not particularly limited, and copper heat stabilizers, phenol heat stabilizers, phosphorus heat stabilizers, sulfur heat stabilizers, amine heat stabilizers, and the like can be used. .
Copper compounds that can be used as copper-based heat stabilizers include inorganic acid salts such as copper chloride, copper bromide, copper iodide, copper sulfate, copper nitrate, copper phosphate, copper acetate, copper stearate, Examples thereof include salts of organic acids such as copper myristylate, copper naphthenate, and copper palmitate. These copper heat stabilizers may be used alone or in combination of two or more. In addition, the solubility at the time of superposition | polymerization can be improved by adding the same kind of salt as a copper compound used as a copper-type heat stabilizer (for example, potassium iodide in the case of copper iodide).
フェノール系熱安定剤としては、N,N’−ヘキサメチレンビス(3,5−ジ−t−ブチル−4−ヒドロキシヒドロシンナマミド)、1,3,5−トリス(4−t−ブチル−3−ヒドロキシ−2,6−ジメチルベンジル)イソシアネレート、トリエチレングリコ―ル−ビス[3−(3−t−ブチル−5−メチル−4−ヒドロキシフェニル)プロピオネート]、1−オキシ−3−メチル−4−イソプロピルベンゼン、2,6−ジ−t−ブチル−4−エチルフェノール等を用いることができる。 Phenol-based heat stabilizers include N, N′-hexamethylenebis (3,5-di-t-butyl-4-hydroxyhydrocinnamamide), 1,3,5-tris (4-t-butyl- 3-hydroxy-2,6-dimethylbenzyl) isocyanate, triethylene glycol bis [3- (3-tert-butyl-5-methyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) propionate], 1-oxy-3- Methyl-4-isopropylbenzene, 2,6-di-t-butyl-4-ethylphenol and the like can be used.
リン系熱安定剤としては、亜リン酸エステル系化合物が好適であり、具体的には、ジフェニルイソデシルホスファイト、ジフェニルイソオクチルホスファイト、トリフェニルホスファイト、トリイソデシルホスファイト、トリス(2,4−ジ−t−ブチルフェニル)ホスファイト、テトラフェニルテトラ(トリデシル)ペンタエリスリトールテトラホスファイト、環状ネオペンタンテトライルビス(2,4−ジ−t−ブチルフェニルホスファイト)、ジステアリルペンタエリスリトールジホスファイト等を用いることができる。 As the phosphorus-based heat stabilizer, a phosphite-based compound is preferable. Specifically, diphenylisodecyl phosphite, diphenylisooctyl phosphite, triphenyl phosphite, triisodecyl phosphite, tris (2 , 4-Di-t-butylphenyl) phosphite, tetraphenyltetra (tridecyl) pentaerythritol tetraphosphite, cyclic neopentanetetraylbis (2,4-di-t-butylphenylphosphite), distearyl pentaerythritol Diphosphite or the like can be used.
硫黄系熱安定剤としては、ジラウリルチオジプロピオネート、ジステアリルチオジプロピオネート、ジミリスチル−3,3’−チオジプロピネート、ジトリデシル−3,3’−チオジプロピオネート、ジラウリルチオジプロピオネート等を用いることができる。
アミン系熱安定剤としては、4,4’−ジオクチルジフェニルアミン等のアルキル置換されたジフェニルアミンや、N,N’−ジ−2−ナフチル−p−フェニレンジアミン等の置換基を有するp−フェニレンジアミン等を用いることができる。
Examples of sulfur-based heat stabilizers include dilauryl thiodipropionate, distearyl thiodipropionate, dimyristyl-3,3′-thiodipropionate, ditridecyl-3,3′-thiodipropionate, dilauryl thiodipropionate. Nate etc. can be used.
Examples of the amine heat stabilizer include alkyl-substituted diphenylamine such as 4,4′-dioctyldiphenylamine, and p-phenylenediamine having a substituent such as N, N′-di-2-naphthyl-p-phenylenediamine. Can be used.
これらの各種熱安定剤は単独で使用してもよいし、二種以上を併用してもよいが、好適な含有量は熱安定剤の種類によって異なる。銅系熱安定剤の場合は、モノマーキャストナイロン樹脂を主成分とする樹脂組成物全体に対して、0.0005〜0.3質量%とすることが好ましい。含有量が0.0005質量%未満であると、耐熱性の改善効果が乏しい。一方、含有量が0.3質量%を超えても、耐熱性の改善効果はそれ以上向上しない上、含有量が多すぎるために十分に均一な分散を行うことが困難となり、一部に粒子の凝集が発生するおそれがある。そして、凝集が発生すると、その凝集点を起点として耐疲労性等の物性低下を起こすおそれある。このような不都合がより生じにくくするためには、銅系熱安定剤の含有量は0.001〜0.1質量%とすることがより好ましい。 These various heat stabilizers may be used alone or in combination of two or more, but the preferred content varies depending on the type of heat stabilizer. In the case of a copper-based heat stabilizer, the content is preferably 0.0005 to 0.3% by mass with respect to the entire resin composition containing a monomer cast nylon resin as a main component. When the content is less than 0.0005% by mass, the effect of improving heat resistance is poor. On the other hand, even if the content exceeds 0.3% by mass, the effect of improving the heat resistance is not improved any more, and since the content is too large, it becomes difficult to perform sufficiently uniform dispersion, and some of the particles May occur. When aggregation occurs, physical properties such as fatigue resistance may be deteriorated starting from the aggregation point. In order to make such inconvenience less likely to occur, the content of the copper-based heat stabilizer is more preferably 0.001 to 0.1% by mass.
銅系熱安定剤以外の上記の有機系熱安定剤の場合は、モノマーキャストナイロン樹脂を主成分とする樹脂組成物全体に対して、0.05〜4質量%とすることが好ましい。含有量が0.05質量%未満であると、耐熱性の改善効果が乏しい。一方、含有量が4質量%を超えても、耐熱性の改善効果はそれ以上向上しない上、モノマーキャストナイロン樹脂に相溶させることが難しくなる。このような不都合がより生じにくくするためには、熱安定剤の含有量は0.1〜2質量%とすることがより好ましい。 In the case of the above organic heat stabilizers other than the copper heat stabilizer, it is preferably 0.05 to 4% by mass with respect to the entire resin composition containing the monomer cast nylon resin as a main component. When the content is less than 0.05% by mass, the effect of improving heat resistance is poor. On the other hand, even if the content exceeds 4% by mass, the effect of improving the heat resistance is not further improved, and it becomes difficult to make it compatible with the monomer cast nylon resin. In order to make such inconvenience less likely to occur, the content of the heat stabilizer is more preferably 0.1 to 2% by mass.
なお、モノマーキャストナイロン樹脂には、上記の熱安定剤の他に、紫外線吸収剤,難燃剤,抗菌剤等の各種添加剤を含有させてもよい。また、ウォラストナイト,チタン酸カリウムウィスカー,ホウ酸アルミニウムウィスカー,炭酸カルシウム(アラゴナイト),塩基性硫酸マグネシウム(モスハイジ),セピオライト,ゾノトライト等の針状充填剤や、カーボンブラック等の着色剤等を含有させてもよい。 The monomer cast nylon resin may contain various additives such as an ultraviolet absorber, a flame retardant, and an antibacterial agent in addition to the heat stabilizer. Also contains acicular fillers such as wollastonite, potassium titanate whisker, aluminum borate whisker, calcium carbonate (aragonite), basic magnesium sulfate (mosheidi), sepiolite, zonotolite, and colorants such as carbon black. You may let them.
本実施形態は本発明の一例を示したものであって、本発明は本実施形態に限定されるものではない。例えば、本実施形態においては、ウォームホイールを例示して本発明を説明したが、本発明の樹脂製歯車はウォームホイールに限定されるものではなく、他の形式の歯車にも適用できることは言うまでもない。例えば、図4に示す平歯車、図5に示すはすば歯車、図6に示す傘歯車、図7に示すハイポイドギヤ等へ適用することができる。 This embodiment shows an example of the present invention, and the present invention is not limited to this embodiment. For example, in the present embodiment, the present invention has been described by exemplifying a worm wheel. However, it goes without saying that the resin gear of the present invention is not limited to a worm wheel and can be applied to other types of gears. . For example, the present invention can be applied to the spur gear shown in FIG. 4, the helical gear shown in FIG. 5, the bevel gear shown in FIG. 6, the hypoid gear shown in FIG.
〔実施例〕
以下に、実施例を示して、本発明をさらに具体的に説明する。表1に示すような組成の樹脂組成物を用いて、後述するような方法により、2種(実施例及び比較例)のウォームホイール試験体を作製した。なお、表1から分かるように、実施例のウォームホイール試験体は、2.0質量%の熱安定剤を含有するモノマーキャストナイロン樹脂からなり、比較例のウォームホイール試験体は、熱安定剤を含有しないモノマーキャストナイロン樹脂からなる。
〔Example〕
Hereinafter, the present invention will be described more specifically with reference to examples. Two types (Examples and Comparative Examples) of worm wheel specimens were produced by using the resin compositions having the compositions shown in Table 1 by the method described below. As can be seen from Table 1, the worm wheel specimens of the examples are made of a monomer cast nylon resin containing 2.0% by mass of a thermal stabilizer, and the worm wheel specimens of the comparative examples are made of a thermal stabilizer. It consists of a monomer cast nylon resin that does not contain.
表1に示す配合組成のモノマーキャストナイロン樹脂で、ドーナツ状の樹脂ブランクを成形した。実施例については、樹脂ブランクをシリコンオイル中に浸漬してアニーリング処理を行い、結晶化度を向上させた。温度条件は以下の通りである。すなわち、4時間かけて室温から170℃まで昇温し、170℃で3時間保持した後、4 時間かけて室温まで徐冷した。 A donut-shaped resin blank was molded with the monomer cast nylon resin having the composition shown in Table 1. About the Example, the resin blank was immersed in silicone oil, the annealing process was performed, and the crystallinity degree was improved. The temperature conditions are as follows. That is, the temperature was raised from room temperature to 170 ° C. over 4 hours, held at 170 ° C. for 3 hours, and then gradually cooled to room temperature over 4 hours.
また、クロスローレット加工を施した芯金を用意し、シランカップリング剤のメタノール溶液(濃度は5質量%)に浸漬した。シランカップリング剤としては、日本ユニカー株式会社製のA−1122(N−β−アミノエチル−γ−アミノプロピルトリメトキシシラン)を用いた。
樹脂ブランクを140℃で1時間加熱し膨張させ、そこに前述の芯金を圧入した。その後、直ちに高周波融着を行い、シランカップリング剤を介して芯金と樹脂ブランクとを完全に接合した。接合の後、樹脂部(樹脂ブランク)の外周を切削加工して歯を形成し、ウォームホイール試験体を得た。
Moreover, the core metal which gave the cross knurling process was prepared, and it was immersed in the methanol solution (concentration is 5 mass%) of a silane coupling agent. As a silane coupling agent, A-1122 (N-β-aminoethyl-γ-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane) manufactured by Nippon Unicar Co., Ltd. was used.
The resin blank was heated at 140 ° C. for 1 hour to expand, and the above-described core metal was press-fitted therein. Thereafter, high frequency fusion was performed immediately, and the cored bar and the resin blank were completely joined via the silane coupling agent. After joining, the outer periphery of the resin part (resin blank) was cut to form teeth, and a worm wheel specimen was obtained.
これらのウォームホイール試験体を、図2に示すような電動パワーステアリング装置のウォーム歯車減速機構に組み込んだ。そして、ウォームホイール試験体に破損が生じるまで操舵を繰り返し行うことにより、耐久性を評価した。この耐久試験の温度条件は120℃である。表1に示すように、実施例の場合は10万回操舵を繰り返してもウォームホイール試験体に破損が生じなかったのに対して、比較例の場合は1万回の操舵で歯底にクラックが発生した。 These worm wheel specimens were incorporated into a worm gear reduction mechanism of an electric power steering apparatus as shown in FIG. The durability was evaluated by repeatedly performing steering until the worm wheel specimen was damaged. The temperature condition of this durability test is 120 ° C. As shown in Table 1, in the case of the example, the worm wheel specimen was not damaged even after repeating 100,000 times of steering, whereas in the case of the comparative example, the tooth bottom was cracked by 10,000 times of steering. There has occurred.
また、2種の樹脂組成物の引張強度,結晶化度,吸水率,耐熱性試験結果も、表1に併せて示す。なお、引張強度は、23℃及び120℃の両温度条件下での測定結果が示してある。また、吸水率は、水中に24時間浸漬した場合の数値である。さらに、耐熱性試験は、120℃の空気中に2000時間放置して、該熱処理による引張強度の低下率を測定する試験である。 Table 1 also shows the tensile strength, crystallinity, water absorption rate, and heat resistance test results of the two resin compositions. The tensile strength is the result of measurement under both temperature conditions of 23 ° C. and 120 ° C. The water absorption is a numerical value when immersed in water for 24 hours. Furthermore, the heat resistance test is a test in which the rate of decrease in tensile strength due to the heat treatment is measured by leaving in air at 120 ° C. for 2000 hours.
表1に示す結果から分かるように、実施例のモノマーキャストナイロン樹脂は、熱安定剤を含有し、結晶化度を向上させていることから、引張強度等の機械的強度に優れるとともに、耐熱性に優れ、吸水率が低い。よって、吸水による歯車の寸法変化が抑制されるとともに、従来のモノマーキャストナイロン製の樹脂歯車では、耐熱性不足及び高温での強度不足のために使用が不可能であった120℃程度の高温でも、使用が可能である。 As can be seen from the results shown in Table 1, the monomer cast nylon resin of the example contains a thermal stabilizer and has improved crystallinity, so that it has excellent mechanical strength such as tensile strength and heat resistance. Excellent water absorption rate. Therefore, the gear dimensional change due to water absorption is suppressed, and the conventional monomer cast nylon resin gear cannot be used due to insufficient heat resistance and insufficient strength at high temperature even at a high temperature of about 120 ° C. Can be used.
本発明の樹脂製歯車は、例えば、電動パワーステアリング装置のパワーアシスト部を構成する歯車減速機構等に好適である。 The resin gear of the present invention is suitable, for example, for a gear reduction mechanism that constitutes a power assist portion of an electric power steering device.
10 電動パワーステアリング装置
30 ウォーム歯車減速機構
31 ウォームホイール
32 ウォーム
42 芯金(ハブ)
43 樹脂部
44 歯
DESCRIPTION OF
43
Claims (5)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004054889A JP4433827B2 (en) | 2004-02-27 | 2004-02-27 | Resin gear |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004054889A JP4433827B2 (en) | 2004-02-27 | 2004-02-27 | Resin gear |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005240973A JP2005240973A (en) | 2005-09-08 |
| JP2005240973A5 JP2005240973A5 (en) | 2006-10-05 |
| JP4433827B2 true JP4433827B2 (en) | 2010-03-17 |
Family
ID=35022914
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004054889A Expired - Fee Related JP4433827B2 (en) | 2004-02-27 | 2004-02-27 | Resin gear |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4433827B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5059750B2 (en) | 2006-04-28 | 2012-10-31 | ユニチカ株式会社 | Polyamide resin composition |
| JP2017081462A (en) * | 2015-10-29 | 2017-05-18 | 株式会社ジェイテクト | Worm decelerator and electric power steering device |
| CN106633831A (en) * | 2015-11-03 | 2017-05-10 | 株洲时代新材料科技股份有限公司 | Preparation method of cast nylon EPS (electrical power steering) worm gear |
-
2004
- 2004-02-27 JP JP2004054889A patent/JP4433827B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2005240973A (en) | 2005-09-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2004083015A1 (en) | Electric power steering device and resin gear used for the same | |
| JP4433827B2 (en) | Resin gear | |
| JP2006194296A (en) | Composite gear and its manufacturing method and electric-powered power steering including composite gear | |
| JP2005030462A (en) | Gear, reduction gear using the same, and electric power steering device equipped therewith | |
| JP2005240940A (en) | Resin gear | |
| JP2007331662A (en) | Electric power steering device | |
| JP5857628B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of electric power steering apparatus | |
| JP5104001B2 (en) | Telescopic shaft for vehicle steering | |
| JP2006077809A (en) | Resin gear | |
| JP4370973B2 (en) | Electric power steering device | |
| JP2011111112A (en) | Telescopic shaft for vehicle steering | |
| WO2011158941A1 (en) | Electric power steering apparatus | |
| JP4352706B2 (en) | Resin gear suitable for power transmission | |
| JP5098167B2 (en) | Reduction gear for electric power steering device | |
| JP2007168718A (en) | Reduction gear for electric power steering device | |
| JP2002156025A (en) | Electric power steering unit | |
| KR101065976B1 (en) | Glass fiber reinforced polyamide resin composition and reduction gear for vehicles using the same | |
| JP2003083423A (en) | Reduction gear for electric power steering device | |
| JP2003343696A (en) | Speed reduction gear for electric power steering device | |
| JP2006290062A (en) | Reduction gear for electric power steering device | |
| JP2006232111A (en) | Speed reduction gear for electric power steering device | |
| JP5610015B2 (en) | Electric power steering device | |
| JP4475879B2 (en) | Gear, speed reducer using the same, and electric power steering apparatus including the same | |
| JP4918954B2 (en) | Electric power steering device | |
| JP2013095221A (en) | Gear for electric power steering device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20060823 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20060823 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20090319 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20090324 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090415 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20091208 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20091221 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130108 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130108 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140108 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |