JP4433741B2 - Similarity calculation system, similarity calculation program, and similarity calculation method - Google Patents
Similarity calculation system, similarity calculation program, and similarity calculation method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4433741B2 JP4433741B2 JP2003327756A JP2003327756A JP4433741B2 JP 4433741 B2 JP4433741 B2 JP 4433741B2 JP 2003327756 A JP2003327756 A JP 2003327756A JP 2003327756 A JP2003327756 A JP 2003327756A JP 4433741 B2 JP4433741 B2 JP 4433741B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- layout
- similarity
- information storage
- attribute
- storage frame
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Machine Translation (AREA)
- Document Processing Apparatus (AREA)
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
Description
本発明は、レイアウト結果の類似度を算出するシステムおよびプログラム、並びに方法に係り、特に、レイアウト結果の類似度を算出する場合に、読み手の主観を適切に反映した類似度を算出することができる類似度算出システムおよび類似度算出プログラム、並びに類似度算出方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a system, a program, and a method for calculating the similarity of layout results, and in particular, when calculating the similarity of layout results, the similarity that appropriately reflects the subjectivity of the reader can be calculated. The present invention relates to a similarity calculation system, a similarity calculation program, and a similarity calculation method.
従来、類似度を算出する技術としては、例えば、特許文献1に開示されている文書論理構造認識、特許文献2に開示されている類似画像検索システム、および特許文献3に開示されている標章作成支援システムがあった。
特許文献1記載の発明は、入力部、文書画像分割部、マッチング処理部、構造モデル管理部および内容認識部で構成されている。入力部により入力された文書画像は、文書画像分割部により複数の要素に分割される。マッチング処理部は、入力された文書画像の要素間の関係が構造モデル管理部に定義されているどの構造モデルと整合するかを調べ、各要素が構造モデルにおけるどの論理構造要素に該当するかを決定する。内容認識部は、マッチング処理部により認識された対応する構造モデルの論理構造要素の属性をパラメータとして内容の認識を行う。
Conventionally, as techniques for calculating the similarity, for example, document logical structure recognition disclosed in
The invention described in
特許文献2記載の発明は、画像データベース内の画像データまたは検索キーとなる例示画像データを前処理部で複数のサブブロックに分割し、濃淡情報検出部および特徴定量化部で、サブブロックにおける正規化濃淡情報に基づく濃淡レイアウトを定量化する。そして、類似画像検索部で、この定量化された濃淡レイアウトを用いて画像データベースに蓄積された画像データと例示画像データとの類否を判定する。 In the invention described in Patent Document 2, image data in an image database or exemplary image data serving as a search key is divided into a plurality of sub-blocks by a pre-processing unit, and the gray-scale information detection unit and the feature quantification unit Quantify shading layout based on scaled shading information. Then, the similar image search unit determines the similarity between the image data stored in the image database and the exemplary image data using the quantified grayscale layout.
特許文献3記載の発明は、発注者側の通信端末装置から送信されたデザインの対象文字を含む標章情報を受信し、対象文字について同一または類似する登録商標があるかを調査し、対象文字または対象文字にデザインを施したデザイン標章が商標登録される可能性の有無を判定する。同一または類似する登録商標の調査は、商標の称呼について行う。
一方、従来、文字や画像等のレイアウト要素をレイアウトする自動レイアウトシステムがある。自動レイアウトシステムは、複数のレイアウト要素を登録したレイアウト要素登録データベース(以下、データベースのことを単にDBと略記する。)と、レイアウト属性(配色、位置、サイズ等)と対応付けて情報格納枠を所定のレイアウト領域に配置したレイアウト状態を規定したレイアウトテンプレートを登録したテンプレート登録DBと、レイアウト要素登録DBのなかからレイアウト要素を選択するレイアウト要素選択部と、テンプレート登録DBのレイアウトテンプレートに従ってレイアウト要素選択部で選択したレイアウト要素を情報格納枠に格納することによりレイアウトを行うレイアウト部とで構成されている。このような自動レイアウトシステムは、例えば、特許文献4に開示されている。
On the other hand, there are conventional automatic layout systems that lay out layout elements such as characters and images. The automatic layout system associates an information storage frame with a layout element registration database in which a plurality of layout elements are registered (hereinafter, the database is simply abbreviated as DB) and layout attributes (color arrangement, position, size, etc.). A template registration DB that registers a layout template that defines a layout state arranged in a predetermined layout area, a layout element selection unit that selects a layout element from the layout element registration DB, and a layout element selection according to the layout template of the template registration DB And a layout unit that performs layout by storing the layout elements selected in the unit in an information storage frame. Such an automatic layout system is disclosed in Patent Document 4, for example.
自動レイアウトシステムから得られたレイアウト結果は、ユーザや顧客に対して提供する用途がある。そのとき、同一の業種に属する異なるユーザに対してレイアウト結果を提供する場合や、同一の顧客を抱えている異なるユーザがその顧客に対してレイアウト結果を提供する場合は、掲載内容が同一または類似したものであってもレイアウトは極力異ならせたい。そこで、例えば、それら提供先(以下、競合提供先という。)に提供するレイアウト結果について類似度を算出し、類似度が大きくなるように一方のレイアウト結果を生成・修正等することが考えられる。 The layout result obtained from the automatic layout system has a purpose of providing it to users and customers. At that time, if the layout results are provided to different users belonging to the same industry, or if different users who have the same customer provide the layout results to the customers, the posted contents are the same or similar. I want to make the layout as different as possible. Thus, for example, it is conceivable to calculate the similarity for the layout results provided to those providers (hereinafter referred to as competing providers), and to generate / correct one layout result so that the similarity is increased.
レイアウト結果の類否を読み手が判断する場合は、レイアウト結果全体の類否のほか、各情報格納枠ごとの類否、およびレイアウト要素の内容の類否を考慮して総合的に判断していると考えられる。そのため、レイアウト結果の類似度を算出する場合、読み手の主観を適切に反映させるには、これらの点を考慮して行うのが好ましい。
しかしながら、特許文献1記載の発明にあっては、文書の論理構造に基づいて類似度を算出する構成となっているため、レイアウト結果の類似度を算出する場合に適用しても、各情報格納枠ごとの類否、およびレイアウト要素の内容の類否が十分に考慮することができず、読み手の主観を適切に反映した類似度を算出することができないという問題があった。
When the reader determines the similarity of the layout result, the reader makes a comprehensive determination considering the similarity of the entire layout result, the similarity of each information storage frame, and the similarity of the contents of the layout elements. it is conceivable that. Therefore, when calculating the similarity of layout results, it is preferable to take these points into consideration in order to appropriately reflect the subjectivity of the reader.
However, in the invention described in
また、特許文献2記載の発明にあっては、画像の濃淡レイアウトを用いて類似度を算出する構成となっているため、レイアウト結果の類似度を算出する場合に適用しても、各情報格納枠ごとの類否、およびレイアウト要素の内容の類否が十分に考慮することができず、読み手の主観を適切に反映した類似度を算出することができないという問題があった。
また、特許文献3記載の発明にあっては、商標の称呼に基づいて類似度を算出する構成となっているため、レイアウト結果の類似度を算出する場合に適用しても、各情報格納枠ごとの類否、およびレイアウト要素の内容の類否が十分に考慮することができず、読み手の主観を適切に反映した類似度を算出することができないという問題があった。
Further, in the invention described in Patent Document 2, since the similarity is calculated using the shading layout of the image, each information storage is performed even when the similarity of the layout result is calculated. There is a problem that the similarity for each frame and the similarity of the contents of the layout elements cannot be sufficiently considered, and the similarity that appropriately reflects the subjectivity of the reader cannot be calculated.
Further, in the invention described in
そこで、本発明は、このような従来の技術の有する未解決の課題に着目してなされたものであって、レイアウト結果の類似度を算出する場合に、読み手の主観を適切に反映した類似度を算出することができる類似度算出システムおよび類似度算出プログラム、並びに類似度算出方法を提供することを目的としている。 Therefore, the present invention has been made paying attention to such unsolved problems of the conventional technology, and when calculating the similarity of layout results, the similarity that appropriately reflects the subjectivity of the reader It is an object to provide a similarity calculation system, a similarity calculation program, and a similarity calculation method.
〔手段1〕 上記目的を達成するために、手段1の類似度算出システムは、
情報格納枠を当該情報格納枠のレイアウト属性と対応付けて所定のレイアウト領域に配置したレイアウト結果の類似度を算出するシステムであって、
比較先となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて前記類似度を算出するレイアウト結果類似度算出手段を備えることを特徴とする。
[Means 1] In order to achieve the above object, the similarity calculation system of the
A system for calculating the similarity of layout results in which an information storage frame is arranged in a predetermined layout area in association with a layout attribute of the information storage frame,
A layout result similarity calculating unit that calculates the similarity based on a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison destination and a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison source is provided.
このような構成であれば、レイアウト結果類似度算出手段により、比較先レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいてレイアウト結果の類似度が算出される。
これにより、情報格納枠のレイアウト属性に基づいて類似度が算出されるので、各情報格納枠ごとの類否を考慮してレイアウト結果の類似度を算出することができる。したがって、従来に比して、読み手の主観を比較的適切に反映した類似度を算出することができるという効果が得られる。
With such a configuration, the layout result similarity calculation unit calculates the similarity of the layout result based on the layout attribute of the comparison destination layout result and the layout attribute of the comparison source layout result.
Thereby, since the similarity is calculated based on the layout attribute of the information storage frame, the similarity of the layout result can be calculated in consideration of the similarity for each information storage frame. Therefore, as compared with the prior art, it is possible to calculate the similarity that relatively reflects the reader's subjectivity.
ここで、レイアウトとは、例えば、画面上に表示することを目的としてレイアウトを行う場合にはその表示レイアウトを、紙面上に印刷することを目的としてレイアウトを行う場合にはその印刷レイアウトをいう。以下、手段2ないし5の類似度算出システム、手段6ないし10の類似度算出プログラム、並びに手段11ないし15の類似度算出方法において同じである。 Here, the layout refers to, for example, a display layout when performing layout for the purpose of displaying on a screen, and a print layout when performing layout for the purpose of printing on paper. The same applies to the similarity calculation system of means 2 to 5, the similarity calculation program of means 6 to 10, and the similarity calculation method of means 11 to 15.
また、本システムは、単一の装置、端末その他の機器として実現するようにしてもよいし、複数の装置、端末その他の機器を通信可能に接続したネットワークシステムとして実現するようにしてもよい。後者の場合、各構成要素は、それぞれ通信可能に接続されていれば、複数の機器等のうちいずれに属していてもよい。以下、手段2ないし5の類似度算出システムにおいて同じである。 Further, the present system may be realized as a single device, terminal, or other device, or may be realized as a network system in which a plurality of devices, terminals, or other devices are communicably connected. In the latter case, each component may belong to any one of a plurality of devices and the like as long as they are connected so as to communicate with each other. The same applies to the similarity calculation system of means 2 to 5 below.
〔手段2〕 さらに、手段2の類似度算出システムは、
異なる複数種の情報格納枠を当該情報格納枠のレイアウト属性と対応付けて所定のレイアウト領域に配置したレイアウト結果の類似度を算出するシステムであって、
比較先となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度を算出する属性類似度算出手段と、前記比較先レイアウト結果の情報格納枠の種別および前記比較元レイアウト結果の情報格納枠の種別に基づいて種別類似度を算出する種別類似度算出手段と、前記属性類似度算出手段で算出した属性類似度および前記種別類似度算出手段で算出した種別類似度に基づいて前記類似度を算出するレイアウト結果類似度算出手段とを備えることを特徴とする。
[Means 2] Furthermore, the similarity calculation system of the means 2 includes:
A system for calculating the similarity of layout results in which different types of information storage frames are arranged in a predetermined layout area in association with layout attributes of the information storage frame,
Attribute similarity calculation means for calculating attribute similarity based on the layout attribute of the layout result as the comparison destination and the layout attribute of the layout result as the comparison source, the type of information storage frame of the comparison destination layout result, and the Type similarity calculating means for calculating the type similarity based on the type of the information storage frame of the comparison source layout result, the attribute similarity calculated by the attribute similarity calculating means, and the type similarity calculated by the type similarity calculating means Layout result similarity calculating means for calculating the similarity based on the degree.
このような構成であれば、属性類似度算出手段により、比較先レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度が算出され、種別類似度算出手段により、比較先レイアウト結果の情報格納枠の種別および比較元レイアウト結果の情報格納枠の種別に基づいて種別類似度が算出される。そして、レイアウト結果類似度算出手段により、算出された属性類似度および種別類似度に基づいてレイアウト結果の類似度が算出される。 With such a configuration, the attribute similarity calculation unit calculates the attribute similarity based on the layout attribute of the comparison destination layout result and the layout attribute of the comparison source layout result, and the type similarity calculation unit calculates the comparison destination layout. The type similarity is calculated based on the type of the result information storage frame and the type of the information storage frame of the comparison source layout result. Then, the layout result similarity calculation means calculates the similarity of the layout results based on the calculated attribute similarity and type similarity.
これにより、情報格納枠のレイアウト属性および種別に基づいて類似度が算出されるので、各情報格納枠ごとの類否を考慮してレイアウト結果の類似度を算出することができる。したがって、従来に比して、読み手の主観を比較的適切に反映した類似度を算出することができるという効果が得られる。
〔手段3〕 さらに、手段3の類似度算出システムは、
情報格納枠を当該情報格納枠のレイアウト属性と対応付けかつ前記情報格納枠に情報を格納して所定のレイアウト領域に配置したレイアウト結果の類似度を算出するシステムであって、
比較先となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度を算出する属性類似度算出手段と、前記比較先レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容および前記比較元レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容に基づいて内容類似度を算出する内容類似度算出手段と、前記属性類似度算出手段で算出した属性類似度および前記内容類似度算出手段で算出した内容類似度に基づいて前記類似度を算出するレイアウト結果類似度算出手段とを備えることを特徴とする。
Thereby, since the similarity is calculated based on the layout attribute and type of the information storage frame, the similarity of the layout result can be calculated in consideration of the similarity of each information storage frame. Therefore, as compared with the prior art, it is possible to calculate the similarity that relatively reflects the reader's subjectivity.
[Means 3] Furthermore, the similarity calculation system of the
A system for associating an information storage frame with a layout attribute of the information storage frame and storing information in the information storage frame and calculating a similarity of layout results arranged in a predetermined layout area,
Attribute similarity calculation means for calculating attribute similarity based on the layout attribute of the layout result as the comparison destination and the layout attribute of the layout result as the comparison source, the contents of the storage information of the comparison destination layout result and the comparison Content similarity calculation means for calculating the content similarity based on the contents of the stored information of the original layout result, the attribute similarity calculated by the attribute similarity calculation means, and the content similarity calculated by the content similarity calculation means Layout result similarity calculation means for calculating the similarity on the basis thereof.
このような構成であれば、属性類似度算出手段により、比較先レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度が算出され、内容類似度算出手段により、比較先レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容および比較元レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容に基づいて内容類似度が算出される。そして、レイアウト結果類似度算出手段により、算出された属性類似度および内容類似度に基づいてレイアウト結果の類似度が算出される。 With this configuration, the attribute similarity calculation unit calculates the attribute similarity based on the layout attribute of the comparison destination layout result and the layout attribute of the comparison source layout result, and the content similarity calculation unit calculates the comparison destination layout. The content similarity is calculated based on the content of the storage information of the result and the content of the storage information of the comparison source layout result. Then, the layout result similarity calculation means calculates the similarity of the layout results based on the calculated attribute similarity and content similarity.
これにより、情報格納枠のレイアウト属性および格納情報の内容に基づいて類似度が算出されるので、各情報格納枠ごとの類否、および格納情報の内容の類否を考慮してレイアウト結果の類似度を算出することができる。したがって、従来に比して、読み手の主観を比較的適切に反映した類似度を算出することができるという効果が得られる。
ここで、格納情報には、文字情報、画像情報その他レイアウトを構成可能な要素が含まれる。以下、手段4および5の類似度算出システム、手段8ないし10の類似度算出プログラム、並びに手段13ないし15の類似度算出方法において同じである。
As a result, the similarity is calculated based on the layout attribute of the information storage frame and the content of the stored information. Therefore, the similarity of the layout results in consideration of the similarity of each information storage frame and the similarity of the content of the stored information The degree can be calculated. Therefore, as compared with the prior art, it is possible to calculate the similarity that relatively reflects the reader's subjectivity.
Here, the storage information includes character information, image information, and other elements that can constitute a layout. The same applies to the similarity calculation system of the means 4 and 5, the similarity calculation program of the means 8 to 10, and the similarity calculation method of the means 13 to 15.
〔手段4〕 さらに、手段4の類似度算出システムは、
複数の格納情報を記憶した格納情報記憶手段のなかから前記格納情報を選択する格納情報選択手段と、前記格納情報選択手段で選択した格納情報に基づいてレイアウトを行うレイアウト手段とを備え、前記レイアウト手段は、情報格納枠を当該情報格納枠のレイアウト属性と対応付けて所定のレイアウト領域に配置したレイアウト状態を規定したレイアウトテンプレートに従って前記情報格納枠に前記格納情報を格納することによりレイアウトを行うレイアウトシステムから得られたレイアウト結果の類似度を算出するシステムであって、
比較先となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度を算出する属性類似度算出手段と、前記比較先レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートおよび前記比較元レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートに基づいてテンプレート類似度を算出するテンプレート類似度算出手段と、前記属性類似度算出手段で算出した属性類似度および前記テンプレート類似度算出手段で算出したテンプレート類似度に基づいて前記類似度を算出するレイアウト結果類似度算出手段とを備えることを特徴とする。
[Means 4] Furthermore, the similarity calculation system of the means 4 includes:
A storage information selection means for selecting the storage information from storage information storage means for storing a plurality of storage information; and a layout means for performing a layout based on the storage information selected by the storage information selection means. A means for performing layout by storing the storage information in the information storage frame according to a layout template that defines a layout state in which the information storage frame is associated with a layout attribute of the information storage frame and arranged in a predetermined layout area. A system for calculating the similarity of layout results obtained from a system,
Attribute similarity calculation means for calculating an attribute similarity based on a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison destination and a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison source, and a layout template used for obtaining the comparison destination layout result And a template similarity calculating unit that calculates a template similarity based on a layout template used to obtain the comparison source layout result, an attribute similarity calculated by the attribute similarity calculating unit, and a template similarity calculating unit. Layout result similarity calculating means for calculating the similarity based on the calculated template similarity;
このような構成であれば、属性類似度算出手段により、比較先レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度が算出され、テンプレート類似度算出手段により、比較先レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートおよび比較元レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートに基づいてテンプレート類似度が算出される。そして、レイアウト結果類似度算出手段により、算出された属性類似度およびテンプレート類似度に基づいてレイアウト結果の類似度が算出される。 With such a configuration, the attribute similarity calculation unit calculates the attribute similarity based on the layout attribute of the comparison destination layout result and the layout attribute of the comparison source layout result, and the template similarity calculation unit calculates the comparison destination layout. The template similarity is calculated based on the layout template used to obtain the result and the layout template used to obtain the comparison source layout result. Then, the layout result similarity calculation means calculates the similarity of the layout results based on the calculated attribute similarity and template similarity.
これにより、情報格納枠のレイアウト属性およびレイアウトテンプレートに基づいて類似度が算出されるので、各情報格納枠ごとの類否を考慮してレイアウト結果の類似度を算出することができる。したがって、従来に比して、読み手の主観を比較的適切に反映した類似度を算出することができるという効果が得られる。
〔手段5〕 さらに、手段5の類似度算出システムは、
複数の格納情報を記憶した格納情報記憶手段のなかから前記格納情報を選択する格納情報選択手段と、前記格納情報選択手段で選択した格納情報に基づいてレイアウトを行うレイアウト手段とを備え、前記レイアウト手段は、情報格納枠を当該情報格納枠のレイアウト属性と対応付けて所定のレイアウト領域に配置したレイアウト状態を規定したレイアウトテンプレートに従って前記情報格納枠に前記格納情報を格納することによりレイアウトを行うレイアウトシステムから得られたレイアウト結果の類似度を算出するシステムであって、
比較先となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度を算出する属性類似度算出手段と、前記比較先レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートおよび前記比較元レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートに基づいてテンプレート類似度を算出するテンプレート類似度算出手段と、前記比較先レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容および前記比較元レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容に基づいて内容類似度を算出する内容類似度算出手段と、前記属性類似度算出手段で算出した属性類似度、前記テンプレート類似度算出手段で算出したテンプレート類似度および前記内容類似度算出手段で算出した内容類似度に基づいて前記類似度を算出するレイアウト結果類似度算出手段とを備えることを特徴とする。
Thereby, since the similarity is calculated based on the layout attribute and layout template of the information storage frame, the similarity of the layout result can be calculated in consideration of the similarity of each information storage frame. Therefore, as compared with the prior art, it is possible to calculate the similarity that relatively reflects the reader's subjectivity.
[Means 5] Furthermore, the similarity calculation system of the means 5 includes:
A storage information selection means for selecting the storage information from storage information storage means for storing a plurality of storage information; and a layout means for performing a layout based on the storage information selected by the storage information selection means. A means for performing layout by storing the storage information in the information storage frame according to a layout template that defines a layout state in which the information storage frame is associated with a layout attribute of the information storage frame and arranged in a predetermined layout area. A system for calculating the similarity of layout results obtained from a system,
Attribute similarity calculation means for calculating attribute similarity based on the layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison destination and the layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison source, and a layout template used to obtain the comparison destination layout result And template similarity calculation means for calculating a template similarity based on a layout template used to obtain the comparison source layout result, contents of storage information of the comparison destination layout result, and storage information of the comparison source layout result A content similarity calculating unit that calculates content similarity based on content; an attribute similarity calculated by the attribute similarity calculating unit; a template similarity calculated by the template similarity calculating unit; and the content similarity calculating unit Calculate the similarity based on the calculated content similarity Characterized in that it comprises a that layout result similarity calculation means.
このような構成であれば、属性類似度算出手段により、比較先レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度が算出され、テンプレート類似度算出手段により、比較先レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートおよび比較元レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートに基づいてテンプレート類似度が算出される。そして、内容類似度算出手段により、比較先レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容および比較元レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容に基づいて内容類似度が算出され、レイアウト結果類似度算出手段により、算出された属性類似度、テンプレート類似度および内容類似度に基づいてレイアウト結果の類似度が算出される。 With such a configuration, the attribute similarity calculation unit calculates the attribute similarity based on the layout attribute of the comparison destination layout result and the layout attribute of the comparison source layout result, and the template similarity calculation unit calculates the comparison destination layout. The template similarity is calculated based on the layout template used to obtain the result and the layout template used to obtain the comparison source layout result. Then, the content similarity calculation unit calculates the content similarity based on the contents of the storage information of the comparison destination layout result and the storage information of the comparison source layout result, and calculates the attribute calculated by the layout result similarity calculation unit. The similarity of the layout results is calculated based on the similarity, the template similarity, and the content similarity.
これにより、情報格納枠のレイアウト属性、レイアウトテンプレートおよび格納情報の内容に基づいて類似度が算出されるので、各情報格納枠ごとの類否、および格納情報の内容の類否を考慮してレイアウト結果の類似度を算出することができる。したがって、従来に比して、読み手の主観を比較的適切に反映した類似度を算出することができるという効果が得られる。 As a result, the similarity is calculated based on the layout attribute of the information storage frame, the layout template, and the content of the stored information. Therefore, the layout is determined in consideration of the similarity of each information storage frame and the similarity of the content of the stored information. The similarity of the results can be calculated. Therefore, as compared with the prior art, it is possible to calculate the similarity that relatively reflects the reader's subjectivity.
〔手段6〕 一方、上記目的を達成するために、手段6の類似度算出プログラムは、
情報格納枠を当該情報格納枠のレイアウト属性と対応付けて所定のレイアウト領域に配置したレイアウト結果の類似度を算出するプログラムであって、
比較先となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて前記類似度を算出するレイアウト結果類似度算出手段として実現される処理をコンピュータに実行させるためのプログラムであることを特徴とする。
[Means 6] On the other hand, in order to achieve the above object, the similarity calculation program of the means 6 is:
A program for calculating the similarity of layout results in which an information storage frame is arranged in a predetermined layout area in association with a layout attribute of the information storage frame,
A program for causing a computer to execute processing realized as layout result similarity calculation means for calculating the similarity based on a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison destination and a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison source It is characterized by being.
このような構成であれば、コンピュータによってプログラムが読み取られ、読み取られたプログラムに従ってコンピュータが処理を実行すると、手段1の類似度算出システムと同等の作用および効果が得られる。
〔手段7〕 さらに、手段7の類似度算出プログラムは、
異なる複数種の情報格納枠を当該情報格納枠のレイアウト属性と対応付けて所定のレイアウト領域に配置したレイアウト結果の類似度を算出するプログラムであって、
比較先となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度を算出する属性類似度算出手段、前記比較先レイアウト結果の情報格納枠の種別および前記比較元レイアウト結果の情報格納枠の種別に基づいて種別類似度を算出する種別類似度算出手段、並びに、前記属性類似度算出手段で算出した属性類似度および前記種別類似度算出手段で算出した種別類似度に基づいて前記類似度を算出するレイアウト結果類似度算出手段として実現される処理をコンピュータに実行させるためのプログラムであることを特徴とする。
With this configuration, when the program is read by the computer and the computer executes processing according to the read program, the same operation and effect as the similarity calculation system of the
[Means 7] Further, the similarity calculation program of the means 7 includes:
A program for calculating the similarity of layout results in which different types of information storage frames are arranged in a predetermined layout area in association with layout attributes of the information storage frames,
Attribute similarity calculation means for calculating attribute similarity based on the layout attribute of the layout result as the comparison destination and the layout attribute of the layout result as the comparison source, the type of the information storage frame of the comparison destination layout result, and the comparison Type similarity calculating means for calculating the type similarity based on the type of the information storage frame of the original layout result, the attribute similarity calculated by the attribute similarity calculating means, and the type similarity calculated by the type similarity calculating means It is a program for causing a computer to execute processing realized as layout result similarity calculation means for calculating the similarity based on degree.
このような構成であれば、コンピュータによってプログラムが読み取られ、読み取られたプログラムに従ってコンピュータが処理を実行すると、手段2の類似度算出システムと同等の作用および効果が得られる。
〔手段8〕 さらに、手段8の類似度算出プログラムは、
情報格納枠を当該情報格納枠のレイアウト属性と対応付けかつ前記情報格納枠に情報を格納して所定のレイアウト領域に配置したレイアウト結果の類似度を算出するプログラムであって、
比較先となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度を算出する属性類似度算出手段、前記比較先レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容および前記比較元レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容に基づいて内容類似度を算出する内容類似度算出手段、並びに、前記属性類似度算出手段で算出した属性類似度および前記内容類似度算出手段で算出した内容類似度に基づいて前記類似度を算出するレイアウト結果類似度算出手段として実現される処理をコンピュータに実行させるためのプログラムであることを特徴とする。
With such a configuration, when the program is read by the computer and the computer executes processing according to the read program, the same operation and effect as the similarity calculation system of the means 2 can be obtained.
[Means 8] Further, the similarity calculation program of the means 8 includes:
A program for associating an information storage frame with a layout attribute of the information storage frame, storing information in the information storage frame, and calculating a similarity of layout results arranged in a predetermined layout area,
Attribute similarity calculation means for calculating attribute similarity based on the layout attribute of the layout result as the comparison destination and the layout attribute of the layout result as the comparison source, the contents of the storage information of the comparison destination layout result, and the comparison source Content similarity calculating means for calculating the content similarity based on the contents of the storage information of the layout result, the attribute similarity calculated by the attribute similarity calculating means, and the content similarity calculated by the content similarity calculating means It is a program for causing a computer to execute processing realized as layout result similarity calculation means for calculating the similarity based on the above.
このような構成であれば、コンピュータによってプログラムが読み取られ、読み取られたプログラムに従ってコンピュータが処理を実行すると、手段3の類似度算出システムと同等の作用および効果が得られる。
〔手段9〕 さらに、手段9の類似度算出プログラムは、
複数の格納情報を記憶した格納情報記憶手段のなかから前記格納情報を選択する格納情報選択手段と、前記格納情報選択手段で選択した格納情報に基づいてレイアウトを行うレイアウト手段とを備え、前記レイアウト手段は、情報格納枠を当該情報格納枠のレイアウト属性と対応付けて所定のレイアウト領域に配置したレイアウト状態を規定したレイアウトテンプレートに従って前記情報格納枠に前記格納情報を格納することによりレイアウトを行うレイアウトプログラムから得られたレイアウト結果の類似度を算出するプログラムであって、
比較先となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度を算出する属性類似度算出手段、前記比較先レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートおよび前記比較元レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートに基づいてテンプレート類似度を算出するテンプレート類似度算出手段、並びに、前記属性類似度算出手段で算出した属性類似度および前記テンプレート類似度算出手段で算出したテンプレート類似度に基づいて前記類似度を算出するレイアウト結果類似度算出手段として実現される処理をコンピュータに実行させるためのプログラムであることを特徴とする。
With such a configuration, when the program is read by the computer and the computer executes processing according to the read program, the same operation and effect as the similarity calculation system of the
[Means 9] Further, the similarity calculation program of the means 9 includes:
A storage information selection means for selecting the storage information from storage information storage means for storing a plurality of storage information; and a layout means for performing a layout based on the storage information selected by the storage information selection means. A means for performing layout by storing the storage information in the information storage frame according to a layout template that defines a layout state in which the information storage frame is associated with a layout attribute of the information storage frame and arranged in a predetermined layout area. A program for calculating the similarity of layout results obtained from a program,
Attribute similarity calculation means for calculating an attribute similarity based on a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison destination and a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison source, a layout template used to obtain the comparison destination layout result, and A template similarity calculating unit that calculates a template similarity based on a layout template used to obtain the comparison source layout result, and an attribute similarity calculated by the attribute similarity calculating unit and the template similarity calculating unit. It is a program for causing a computer to execute processing realized as layout result similarity calculation means for calculating the similarity based on the calculated template similarity.
このような構成であれば、コンピュータによってプログラムが読み取られ、読み取られたプログラムに従ってコンピュータが処理を実行すると、手段4の類似度算出システムと同等の作用および効果が得られる。
〔手段10〕 さらに、手段10の類似度算出プログラムは、
複数の格納情報を記憶した格納情報記憶手段のなかから前記格納情報を選択する格納情報選択手段と、前記格納情報選択手段で選択した格納情報に基づいてレイアウトを行うレイアウト手段とを備え、前記レイアウト手段は、情報格納枠を当該情報格納枠のレイアウト属性と対応付けて所定のレイアウト領域に配置したレイアウト状態を規定したレイアウトテンプレートに従って前記情報格納枠に前記格納情報を格納することによりレイアウトを行うレイアウトプログラムから得られたレイアウト結果の類似度を算出するプログラムであって、
比較先となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度を算出する属性類似度算出手段、前記比較先レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートおよび前記比較元レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートに基づいてテンプレート類似度を算出するテンプレート類似度算出手段、前記比較先レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容および前記比較元レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容に基づいて内容類似度を算出する内容類似度算出手段、並びに、前記属性類似度算出手段で算出した属性類似度、前記テンプレート類似度算出手段で算出したテンプレート類似度および前記内容類似度算出手段で算出した内容類似度に基づいて前記類似度を算出するレイアウト結果類似度算出手段として実現される処理をコンピュータに実行させるためのプログラムであることを特徴とする。
With such a configuration, when the program is read by the computer and the computer executes processing according to the read program, the same operation and effect as the similarity calculation system of the means 4 can be obtained.
[Means 10] Further, the similarity calculation program of the
A storage information selection means for selecting the storage information from storage information storage means for storing a plurality of storage information; and a layout means for performing a layout based on the storage information selected by the storage information selection means. A means for performing layout by storing the storage information in the information storage frame according to a layout template that defines a layout state in which the information storage frame is associated with a layout attribute of the information storage frame and arranged in a predetermined layout area. A program for calculating the similarity of layout results obtained from a program,
Attribute similarity calculation means for calculating an attribute similarity based on a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison destination and a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison source, a layout template used to obtain the comparison destination layout result, and Template similarity calculation means for calculating a template similarity based on the layout template used to obtain the comparison source layout result, the content of the storage information of the comparison destination layout result, and the content of the storage information of the comparison source layout result Content similarity calculating means for calculating content similarity based on the above, attribute similarity calculated by the attribute similarity calculating means, template similarity calculated by the template similarity calculating means, and content similarity calculating means The similarity is calculated based on the content similarity Characterized in that the process is implemented as a layout result similarity calculation means for a program to be executed by a computer.
このような構成であれば、コンピュータによってプログラムが読み取られ、読み取られたプログラムに従ってコンピュータが処理を実行すると、手段5の類似度算出システムと同等の作用および効果が得られる。
〔手段11〕 一方、上記目的を達成するために、手段11の類似度算出方法は、
情報格納枠を当該情報格納枠のレイアウト属性と対応付けて所定のレイアウト領域に配置したレイアウト結果の類似度を算出する方法であって、
比較先となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて前記類似度を算出するレイアウト結果類似度算出ステップを含むことを特徴とする。
With such a configuration, when the program is read by the computer and the computer executes processing according to the read program, the same operation and effect as the similarity calculation system of the means 5 can be obtained.
[Means 11] On the other hand, in order to achieve the above object, the similarity calculation method of the means 11 is:
A method of calculating a similarity of layout results in which an information storage frame is associated with a layout attribute of the information storage frame and arranged in a predetermined layout area,
A layout result similarity calculating step of calculating the similarity based on a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison destination and a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison source;
これにより、手段1の類似度算出システムと同等の効果が得られる。
〔手段12〕 さらに、手段12の類似度算出方法は、
異なる複数種の情報格納枠を当該情報格納枠のレイアウト属性と対応付けて所定のレイアウト領域に配置したレイアウト結果の類似度を算出する方法であって、
比較先となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度を算出する属性類似度算出ステップと、前記比較先レイアウト結果の情報格納枠の種別および前記比較元レイアウト結果の情報格納枠の種別に基づいて種別類似度を算出する種別類似度算出ステップと、前記属性類似度算出ステップで算出した属性類似度および前記種別類似度算出ステップで算出した種別類似度に基づいて前記類似度を算出するレイアウト結果類似度算出ステップとを含むことを特徴とする。
Thereby, the same effect as the similarity calculation system of
[Means 12] Furthermore, the similarity calculation method of the
A method of calculating the similarity of layout results in which different types of information storage frames are arranged in a predetermined layout area in association with layout attributes of the information storage frames,
An attribute similarity calculating step of calculating an attribute similarity based on a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison destination and a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison source; a type of an information storage frame of the comparison destination layout result; and A type similarity calculation step for calculating the type similarity based on the type of the information storage frame of the comparison source layout result, the attribute similarity calculated in the attribute similarity calculation step, and the type similarity calculated in the type similarity calculation step And a layout result similarity calculation step for calculating the similarity based on the degree.
これにより、手段2の類似度算出システムと同等の効果が得られる。
〔手段13〕 さらに、手段13の類似度算出方法は、
情報格納枠を当該情報格納枠のレイアウト属性と対応付けかつ前記情報格納枠に情報を格納して所定のレイアウト領域に配置したレイアウト結果の類似度を算出する方法であって、
比較先となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度を算出する属性類似度算出ステップと、前記比較先レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容および前記比較元レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容に基づいて内容類似度を算出する内容類似度算出ステップと、前記属性類似度算出ステップで算出した属性類似度および前記内容類似度算出ステップで算出した内容類似度に基づいて前記類似度を算出するレイアウト結果類似度算出ステップとを含むことを特徴とする。
Thereby, the same effect as the similarity calculation system of means 2 can be obtained.
[Means 13] Furthermore, the similarity calculation method of the means 13 is as follows.
A method of calculating the similarity of a layout result in which an information storage frame is associated with a layout attribute of the information storage frame and information is stored in the information storage frame and arranged in a predetermined layout area.
An attribute similarity calculating step of calculating an attribute similarity based on a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison destination and a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison source, contents of the storage information of the comparison destination layout result, and the comparison The content similarity calculation step for calculating the content similarity based on the content of the stored information of the original layout result, the attribute similarity calculated in the attribute similarity calculation step, and the content similarity calculated in the content similarity calculation step And a layout result similarity calculation step for calculating the similarity based on the above.
これにより、手段3の類似度算出システムと同等の効果が得られる。
〔手段14〕 さらに、手段14の類似度算出方法は、
複数の格納情報を記憶した格納情報記憶手段のなかから前記格納情報を選択する格納情報選択手段と、前記格納情報選択手段で選択した格納情報に基づいてレイアウトを行うレイアウト手段とを備え、前記レイアウト手段は、情報格納枠を当該情報格納枠のレイアウト属性と対応付けて所定のレイアウト領域に配置したレイアウト状態を規定したレイアウトテンプレートに従って前記情報格納枠に前記格納情報を格納することによりレイアウトを行うレイアウトシステムから得られたレイアウト結果の類似度を算出する方法であって、
比較先となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度を算出する属性類似度算出ステップと、前記比較先レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートおよび前記比較元レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートに基づいてテンプレート類似度を算出するテンプレート類似度算出ステップと、前記属性類似度算出ステップで算出した属性類似度および前記テンプレート類似度算出ステップで算出したテンプレート類似度に基づいて前記類似度を算出するレイアウト結果類似度算出ステップとを含むことを特徴とする。
Thereby, the same effect as the similarity calculation system of
[Means 14] Furthermore, the similarity calculation method of the
Storage information selection means for selecting the storage information from storage information storage means for storing a plurality of storage information; and layout means for performing layout based on the storage information selected by the storage information selection means. A means for performing layout by storing the storage information in the information storage frame according to a layout template that defines a layout state in which the information storage frame is associated with a layout attribute of the information storage frame and arranged in a predetermined layout area. A method for calculating the similarity of layout results obtained from a system,
An attribute similarity calculation step for calculating an attribute similarity based on a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison destination and a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison source, and a layout template used to obtain the comparison destination layout result And a template similarity calculating step for calculating a template similarity based on a layout template used to obtain the comparison source layout result, an attribute similarity calculated in the attribute similarity calculating step, and a template similarity calculating step. And a layout result similarity calculation step for calculating the similarity based on the calculated template similarity.
これにより、手段4の類似度算出システムと同等の効果が得られる。
〔手段15〕 さらに、手段15の類似度算出方法は、
複数の格納情報を記憶した格納情報記憶手段のなかから前記格納情報を選択する格納情報選択手段と、前記格納情報選択手段で選択した格納情報に基づいてレイアウトを行うレイアウト手段とを備え、前記レイアウト手段は、情報格納枠を当該情報格納枠のレイアウト属性と対応付けて所定のレイアウト領域に配置したレイアウト状態を規定したレイアウトテンプレートに従って前記情報格納枠に前記格納情報を格納することによりレイアウトを行うレイアウトシステムから得られたレイアウト結果の類似度を算出する方法であって、
比較先となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度を算出する属性類似度算出ステップと、前記比較先レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートおよび前記比較元レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートに基づいてテンプレート類似度を算出するテンプレート類似度算出ステップと、前記比較先レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容および前記比較元レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容に基づいて内容類似度を算出する内容類似度算出ステップと、前記属性類似度算出ステップで算出した属性類似度、前記テンプレート類似度算出ステップで算出したテンプレート類似度および前記内容類似度算出ステップで算出した内容類似度に基づいて前記類似度を算出するレイアウト結果類似度算出ステップとを含むことを特徴とする。
Thereby, the same effect as the similarity calculation system of means 4 can be obtained.
[Means 15] Furthermore, the similarity calculation method of the
Storage information selection means for selecting the storage information from storage information storage means for storing a plurality of storage information; and layout means for performing layout based on the storage information selected by the storage information selection means. A means for performing layout by storing the storage information in the information storage frame according to a layout template that defines a layout state in which the information storage frame is associated with a layout attribute of the information storage frame and arranged in a predetermined layout area. A method for calculating the similarity of layout results obtained from a system,
An attribute similarity calculation step for calculating an attribute similarity based on a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison destination and a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison source, and a layout template used to obtain the comparison destination layout result And a template similarity calculation step for calculating a template similarity based on the layout template used to obtain the comparison source layout result, contents of storage information of the comparison destination layout result, and storage information of the comparison source layout result A content similarity calculation step for calculating content similarity based on content; an attribute similarity calculated in the attribute similarity calculation step; a template similarity calculated in the template similarity calculation step; and a content similarity calculation step. Calculated content similarity Zui and characterized in that it comprises a layout result similarity calculation step of calculating the degree of similarity.
これにより、手段5の類似度算出システムと同等の効果が得られる。 Thereby, an effect equivalent to the similarity calculation system of the means 5 is obtained.
以下、本発明の第1の実施の形態を図面を参照しながら説明する。図1ないし図13は、本発明に係る類似度算出システムおよび類似度算出プログラム、並びに類似度算出方法の第1の実施の形態を示す図である。
第1の実施の形態は、本発明に係る類似度算出システムおよび類似度算出プログラム、並びに類似度算出方法を、自動レイアウト処理のレイアウト結果を修正する場合について適用したものである。
Hereinafter, a first embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. 1 to 13 are diagrams showing a first embodiment of a similarity calculation system, a similarity calculation program, and a similarity calculation method according to the present invention.
In the first embodiment, the similarity calculation system, the similarity calculation program, and the similarity calculation method according to the present invention are applied to the case where the layout result of the automatic layout process is corrected.
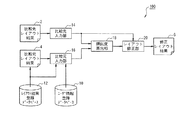
まず、本発明を適用するレイアウト装置100の機能概要を図1を参照しながら詳細に説明する。
図1は、レイアウト装置100の機能概要を示す機能ブロック図である。
レイアウト装置100は、図1に示すように、ユーザに関するユーザ情報を登録したユーザ情報登録DB10と、複数の比較元レイアウト結果4を登録したレイアウト結果登録DB12と、比較先レイアウト結果2を入力する比較先入力部14と、ユーザ情報登録DB10のユーザ情報に基づいて比較元レイアウト結果4をレイアウト結果登録DB12から入力する比較元入力部16と、比較先入力部14で入力した比較先レイアウト結果2と比較元入力部16で入力した比較元レイアウト結果4との類似度を算出する類似度算出部18と、類似度算出部18で算出した類似度に応じて比較先レイアウト結果2を修正するレイアウト修正部20とで構成されている。
First, the functional outline of the
FIG. 1 is a functional block diagram showing an outline of functions of the
As illustrated in FIG. 1, the
ユーザ情報登録DB10は、ユーザが属する業種を示すユーザ情報をユーザIDと対応付けて登録している。
レイアウト結果登録DB12は、比較元レイアウト結果4をユーザIDと対応付けて登録している。
比較元入力部16は、修正レイアウト結果6を利用する現在のユーザと同一の業種に属する他のユーザのユーザIDをユーザ情報登録DB10から検索し、検索により索出したユーザIDに対応する比較元レイアウト結果4をレイアウト結果登録DB12から読み出す。
The user
The layout
The comparison
レイアウト修正部20は、類似度算出部18で算出した類似度に応じて、比較先レイアウト結果2に対する修正の度合いが大きくなるように、比較先レイアウト結果2を修正する。
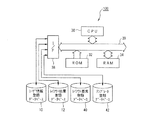
次に、レイアウト装置100の構成を図2を参照しながら説明する。
図2は、レイアウト装置100の構成を示すブロック図である。
The layout correction unit 20 corrects the comparison destination layout result 2 so that the degree of correction with respect to the comparison destination layout result 2 increases according to the similarity calculated by the
Next, the configuration of the
FIG. 2 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration of the
レイアウト装置100は、図2に示すように、制御プログラムに基づいて演算およびシステム全体を制御するCPU30と、所定領域にあらかじめCPU30の制御プログラム等を格納しているROM32と、ROM32等から読み出したデータやCPU30の演算過程で必要な演算結果を格納するためのRAM34と、外部装置に対してデータの入出力を媒介するI/F38とで構成されており、これらは、データを転送するための信号線であるバス39で相互にかつデータ授受可能に接続されている。
As shown in FIG. 2, the
I/F38には、外部装置として、ユーザ情報登録DB10と、レイアウト結果登録DB12と、文字情報、画像情報、タイトル情報その他レイアウトを構成可能な要素(以下、レイアウト要素という。)を複数登録したレイアウト要素登録DB40と、複数のレイアウトテンプレートを登録したテンプレート登録DB42とが接続されている。
次に、テンプレート登録DB42のデータ構造を図3を参照しながら詳細に説明する。
In the I /
Next, the data structure of the
テンプレート登録DB42は、レイアウトを規定したレイアウトテンプレートをそのファイル名と対応付けて複数登録している。レイアウトテンプレートは、例えば、レイアウト要素を格納するための情報格納枠の大きさおよびレイアウト領域での配置位置と、文字情報のフォントの大きさ、種類および色彩と、文字間隔や行ピッチと、画像の数、品質、大きさおよび割合とを定義しており、XML(eXtensible Markup Language)等により記述されている。なお、各レイアウトテンプレートは、それぞれ異なるデータ構造となっているが、ここでは、レイアウトテンプレートのなかから代表的なものを1つ取り上げて説明する。
The
図3は、レイアウトテンプレートのデータ構造を示す図である。
レイアウトテンプレートは、各ページごとにレイアウト領域360を有し、そのうち一つのレイアウト領域360は、図3に示すように、タイトル情報を格納するためのタイトル情報格納枠362と、画像情報を格納するための画像情報格納枠364と、文字情報を格納するための文字情報格納枠366と、画像情報格納枠368と、文字情報格納枠370と、フローオブジェクトを格納するためのフローオブジェクト格納枠372とを配置して構成されている。ここで、フローオブジェクトとは、現在のページよりも前のページで情報格納枠に格納しきれずに溢れた文字情報その他の溢れ情報をいう。
FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating a data structure of the layout template.
The layout template has a
タイトル情報格納枠362は、横方向ほぼ一杯の幅および縦方向1/5程度の高さを有する矩形の枠で、その左上角がレイアウト領域360の左上端近傍に位置するよう配置され、画像情報格納枠364、文字情報格納枠366および文字情報格納枠370と重なり合っている。
画像情報格納枠364は、横方向1/2程度の幅および縦方向1/4程度の高さを有する矩形の枠で、その左上角がタイトル情報格納枠362の左上角と比較して横方向が一致し縦方向がそれよりもやや下方に位置するよう配置され、タイトル情報格納枠362および文字情報格納枠366と重なり合っている。
The title
The image
文字情報格納枠366は、横方向1/2程度の幅および縦方向ほぼ一杯の高さを有する矩形の枠で、その左上角がタイトル情報格納枠362の左上角と一致するよう配置され、タイトル情報格納枠362、文字情報格納枠364および画像情報格納枠368と重なり合っている。
画像情報格納枠368は、横方向1/2程度の幅および縦方向1/4程度の高さを有する矩形の枠で、その左下角が文字情報格納枠366の左下角と一致するよう配置され、文字情報格納枠366と重なり合っている。
The character
The image
文字情報格納枠370は、横方向1/2程度の幅および縦方向ほぼ一杯の高さを有する矩形の枠で、その右上角がタイトル情報格納枠362の右上角と一致するよう配置され、タイトル情報格納枠362およびフローオブジェクト格納枠372と重なり合っている。
フローオブジェクト格納枠372は、横方向1/2程度の幅および縦方向1/4程度の高さを有する矩形の枠で、その右下角が文字情報格納枠370の右下角と一致するよう配置され、文字情報格納枠370と重なり合っている。
The character
The flow
なお、図3の例では、情報格納枠の種別として、タイトル情報格納枠、文字情報格納枠および画像情報格納枠を例示したが、それ以外にも、例えば、イラスト情報を格納するためのイラスト情報格納枠がある。イラスト情報格納枠は、画像情報格納枠が写真を格納するのに対してイラストを格納する点で用途が異なる。
また、テンプレート登録DB42は、レイアウト属性の重み付け係数を登録したレイアウト属性テーブル400を登録している。
In the example of FIG. 3, the title information storage frame, the character information storage frame, and the image information storage frame are illustrated as the types of information storage frames. However, for example, illustration information for storing illustration information is used. There is a storage frame. The illustration information storage frame has a different use in that the image information storage frame stores pictures while the image information storage frame stores pictures.
Further, the
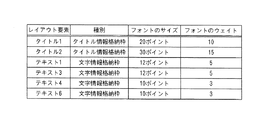
図4は、レイアウト属性テーブル400のデータ構造を示す図である。
レイアウト属性テーブル400には、図4に示すように、各レイアウト属性ごとに1つのレコードが登録されている。各レコードは、レイアウト属性を登録したフィールド402と、重み付け係数を登録したフィールド404とを含んで構成されている。
図4の例では、第1段目のレコードには、レイアウト属性として「配色」が、重み付け係数として「1.0」がそれぞれ登録されている。これは、配色の類似度を算出する場合に「1.0」の重み付けで類似度を算出することを示している。
FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating a data structure of the layout attribute table 400.
In the layout attribute table 400, as shown in FIG. 4, one record is registered for each layout attribute. Each record includes a
In the example of FIG. 4, “color scheme” is registered as the layout attribute and “1.0” is registered as the weighting coefficient in the first record. This indicates that the similarity is calculated with a weight of “1.0” when calculating the similarity of the color scheme.
次に、ユーザ情報登録DB10のデータ構造を図5を参照しながら詳細に説明する。
ユーザ情報登録DB10は、ユーザ情報をユーザIDと対応付けて登録したユーザ情報登録テーブル420を登録している。
図5は、ユーザ情報登録テーブル420のデータ構造を示す図である。
ユーザ情報登録テーブル420には、図5に示すように、各ユーザごとに1つのレコードが登録されている。各レコードは、ユーザIDを登録したフィールド422と、ユーザが属する業種を示す業種情報を登録したフィールド424とを含んで構成されている。
Next, the data structure of the user
The user
FIG. 5 is a diagram showing the data structure of the user information registration table 420.
In the user information registration table 420, as shown in FIG. 5, one record is registered for each user. Each record includes a
図5の例では、第1段目のレコードには、ユーザIDとして「USER1」が、業種情報として「建築」がそれぞれ登録されている。これは、ユーザID「USER1」のユーザが建築業に属していることを示している。
次に、レイアウト結果登録DB12のデータ構造を図6を参照しながら詳細に説明する。
In the example of FIG. 5, “USER1” is registered as the user ID and “Architecture” is registered as the business type information in the first record. This indicates that the user with the user ID “USER1” belongs to the building industry.
Next, the data structure of the layout
レイアウト結果登録DB12は、複数の比較元レイアウト結果4と、比較元レイアウト結果4のファイル名をユーザIDと対応付けて登録した利用履歴情報登録テーブル440を登録している。また、レイアウト結果登録DB12には、比較先レイアウト結果2を修正するごとに、その修正レイアウト結果6を比較元レイアウト結果4として登録する。
図6は、利用履歴情報登録テーブル440のデータ構造を示す図である。
The layout
FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating a data structure of the usage history information registration table 440.
利用履歴情報登録テーブル440には、図6に示すように、各比較元レイアウト結果4ごとに1つのレコードが登録されている。各レコードは、比較元レイアウト結果4のファイル名を登録したフィールド442と、比較元レイアウト結果4を利用したユーザのユーザIDを登録したフィールド444と、比較元レイアウト結果4の利用年月日を登録したフィールド446とを含んで構成されている。
In the usage history information registration table 440, one record is registered for each comparison source layout result 4 as shown in FIG. Each record registers a
図6の例では、第1段目のレコードには、ファイル名として「Layout1」が、ユーザIDとして「USER2」が、利用年月日として「2002/6/10」がそれぞれ登録されている。これは、「Layout1」というファイル名の比較元レイアウト結果4がユーザID「USER2」のユーザにより「2002/6/10」に利用されたことを示している。
次に、CPU30の構成およびCPU30で実行される処理を図7を参照しながら説明する。
In the example of FIG. 6, “Layout1” is registered as the file name, “USER2” is registered as the user ID, and “2002/6/10” is registered as the usage date in the first row record. This indicates that the comparison source layout result 4 with the file name “Layout1” was used for “2002/6/10” by the user with the user ID “USER2”.
Next, the configuration of the
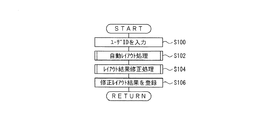
CPU30は、マイクロプロセッシングユニット(MPU)等からなり、ROM32の所定領域に格納されている所定のプログラムを起動させ、そのプログラムに従って、図7のフローチャートに示すレイアウト処理を実行するようになっている。
図7は、レイアウト処理を示すフローチャートである。
レイアウト処理は、CPU30において実行されると、図7に示すように、まず、ステップS100に移行するようになっている。
The
FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing the layout processing.
When the layout process is executed in the
ステップS100では、図示しない入力装置または通信装置を介して、修正レイアウト結果6を利用するユーザのユーザIDを入力し、ステップS102に移行する。
ステップS102では、レイアウト要素登録DB40のなかからレイアウト要素を選択し、テンプレート登録DB42のレイアウトテンプレートに従って、選択したレイアウト要素をレイアウト領域360に自動的に配置する自動レイアウト処理を実行し、ステップS104に移行する。
In step S100, the user ID of the user who uses the modified layout result 6 is input via an input device or communication device not shown, and the process proceeds to step S102.
In step S102, a layout element is selected from the layout
ステップS104では、ステップS102の自動レイアウト処理のレイアウト結果を比較先レイアウト結果2として取得し、取得した比較先レイアウト結果2を修正するレイアウト結果修正処理を実行し、ステップS106に移行する。
ステップS106では、ステップS104のレイアウト結果修正処理の修正レイアウト結果6をユーザIDと対応付けてレイアウト結果登録DB12に登録する。具体的には、修正レイアウト結果6を比較元レイアウト結果4としてレイアウト結果登録DB12に登録するとともに、そのファイル名、ステップS100で入力したユーザIDおよび現在の年月日を利用履歴情報登録テーブル440に登録する。
In step S104, the layout result of the automatic layout process in step S102 is acquired as the comparison destination layout result 2, the layout result correction process for correcting the acquired comparison destination layout result 2 is executed, and the process proceeds to step S106.
In step S106, the modified layout result 6 of the layout result correcting process in step S104 is registered in the layout
そして、ステップS106の処理が終了すると、一連の処理を終了して元の処理に復帰させる。
次に、ステップS102の自動レイアウト処理を図8を参照しながら詳細に説明する。
図8は、ステップS102の自動レイアウト処理を示すフローチャートである。
自動レイアウト処理は、ステップS102において実行されると、図8に示すように、まず、ステップS200に移行するようになっている。
When the process of step S106 is completed, the series of processes is terminated and the original process is restored.
Next, the automatic layout process in step S102 will be described in detail with reference to FIG.
FIG. 8 is a flowchart showing the automatic layout process in step S102.
When the automatic layout process is executed in step S102, as shown in FIG. 8, first, the process proceeds to step S200.
ステップS200では、テンプレート登録DB42からレイアウトテンプレートを読み出し、読み出したレイアウトテンプレートのレイアウト領域360のうち先頭ページのものを処理対象として設定し、ステップS202に移行する。
ステップS202では、ページ内に固定的に配置される固定線の位置を決定し、ステップS204に移行して、ページ内に固定的に配置される固定文字情報の形状および位置を決定し、ステップS206に移行して、ページ内に固定的に配置される固定画像情報の形状および位置を決定し、ステップS208に移行する。
In step S200, a layout template is read from the
In step S202, the position of the fixed line fixedly arranged in the page is determined, and the process proceeds to step S204 to determine the shape and position of fixed character information fixedly arranged in the page, and step S206. Then, the shape and position of the fixed image information fixedly arranged in the page are determined, and the process proceeds to step S208.
ステップS208では、未処理のフローオブジェクトが存在するか否かを判定し、未処理のフローオブジェクトが存在すると判定したときは、未処理のフローオブジェクトに基づいてフローオブジェクト格納枠の形状および位置を決定する処理を実行し、ステップS210に移行する。
ステップS210では、所定の選択規則に基づいてレイアウト要素登録DB40のなかからレイアウト領域360に配置すべきレイアウト要素を選択し、ステップS212に移行する。
In step S208, it is determined whether or not there is an unprocessed flow object. If it is determined that there is an unprocessed flow object, the shape and position of the flow object storage frame are determined based on the unprocessed flow object. Is executed, and the process proceeds to step S210.
In step S210, a layout element to be arranged in the
ステップS212では、ステップS210で選択した選択レイアウト要素がタイトル情報であるか否かを判定し、タイトル情報であると判定したときは、選択レイアウト要素に基づいてタイトル情報格納枠の形状および位置を決定する処理を実行し、ステップS214に移行する。
ステップS214では、選択レイアウト要素が画像情報であるか否かを判定し、画像情報であると判定したときは、選択レイアウト要素に基づいて画像情報格納枠またはイラスト情報格納枠の形状および位置を決定する処理を実行し、ステップS216に移行する。
In step S212, it is determined whether the selected layout element selected in step S210 is title information. If it is determined that the selected layout element is title information, the shape and position of the title information storage frame are determined based on the selected layout element. Is executed, and the process proceeds to step S214.
In step S214, it is determined whether the selected layout element is image information. If it is determined that the selected layout element is image information, the shape and position of the image information storage frame or the illustration information storage frame are determined based on the selected layout element. Is executed, and the process proceeds to step S216.
ステップS216では、選択レイアウト要素が文字情報であるか否かを判定し、文字情報であると判定したときは、選択レイアウト要素に基づいて文字情報格納枠の形状および位置を決定する処理を実行し、ステップS218に移行する。
ステップS218では、分界線の位置を決定する処理を実行し、ステップS220に移行して、レイアウト領域360内に未処理の情報格納枠が存在するか否かを判定し、未処理の情報格納枠が存在しないと判定したとき(No)は、ステップS222に移行する。
In step S216, it is determined whether or not the selected layout element is character information. If it is determined that the selected layout element is character information, processing for determining the shape and position of the character information storage frame based on the selected layout element is executed. The process proceeds to step S218.
In step S218, the process of determining the position of the demarcation line is executed, the process proceeds to step S220, it is determined whether or not an unprocessed information storage frame exists in the
ステップS222では、ステップS200で読み出したレイアウトテンプレートのすべてのページについてステップS202〜S220の処理が終了したか否かを判定し、すべてのページについて処理が終了したと判定したとき(Yes)は、ステップS224に移行する。
ステップS224では、未処理のフローオブジェクトが存在するか否かを判定し、未処理のフローオブジェクトが存在すると判定したときは、未処理のフローオブジェクトを掲載するのに必要なレイアウト領域360を追加ページとして作成し、未処理のフローオブジェクトを追加のレイアウト領域360に掲載する処理を実行し、一連の処理を終了して元の処理に復帰させる。
In step S222, it is determined whether or not the processing in steps S202 to S220 has been completed for all pages of the layout template read in step S200. If it is determined that the processing has been completed for all pages (Yes), step S222 is performed. The process proceeds to S224.
In step S224, it is determined whether or not there is an unprocessed flow object. If it is determined that there is an unprocessed flow object, a
一方、ステップS222で、ステップS200で読み出したレイアウトテンプレートのすべてのページについてステップS202〜S220の処理が終了していないと判定したとき(No)は、ステップS226に移行して、ステップS200で読み出したレイアウトテンプレートのレイアウト領域360のうち次のページのものを処理対象として設定し、ステップS202に移行する。
On the other hand, when it is determined in step S222 that the processing in steps S202 to S220 has not been completed for all pages of the layout template read in step S200 (No), the process proceeds to step S226 and is read in step S200. The next page of the
一方、ステップS220で、レイアウト領域360内に未処理の情報格納枠が存在すると判定したとき(Yes)は、ステップS210に移行する。
次に、ステップS104のレイアウト結果修正処理を図9を参照しながら詳細に説明する。
図9は、ステップS104のレイアウト結果修正処理を示すフローチャートである。
On the other hand, when it is determined in step S220 that an unprocessed information storage frame exists in the layout area 360 (Yes), the process proceeds to step S210.
Next, the layout result correction process in step S104 will be described in detail with reference to FIG.
FIG. 9 is a flowchart showing the layout result correction processing in step S104.
レイアウト結果修正処理は、ステップS104において実行されると、図9に示すように、まず、ステップS300に移行するようになっている。
ステップS300では、ステップS102の自動レイアウト処理のレイアウト結果を比較先レイアウト結果2として取得し、ステップS302に移行する。
ステップS302では、ステップS100で入力したユーザIDに対応する業種情報と同一の業種情報をユーザ情報登録DB10のなかから検索して該当の業種情報に対応するユーザIDを読み出す。該当の業種情報に対応するユーザIDが複数存在するときは、それらユーザIDをすべて読み出す。
When the layout result correction process is executed in step S104, the process first proceeds to step S300 as shown in FIG.
In step S300, the layout result of the automatic layout process in step S102 is acquired as the comparison destination layout result 2, and the process proceeds to step S302.
In step S302, the same industry information as the industry information corresponding to the user ID input in step S100 is searched from the user
次いで、ステップS304に移行して、利用履歴情報登録テーブル440を参照して、読み出したユーザIDに対応する比較元レイアウト結果4をレイアウト結果登録DB12から読み出す。読み出したユーザIDが複数存在するときは、それらユーザIDのうち先頭のものに対応する比較元レイアウト結果4を読み出す。
次いで、ステップS306に移行して、取得した比較先レイアウト結果2と、読み出した比較元レイアウト結果4との類似度を算出し、ステップS308に移行して、読み出したユーザIDに対応するすべての比較元レイアウト結果4についてステップS306の処理が終了したか否かを判定し、すべての比較元レイアウト結果4について処理が終了したと判定したとき(Yes)は、ステップS310に移行する。
Next, the process proceeds to step S304, with reference to the usage history information registration table 440, the comparison source layout result 4 corresponding to the read user ID is read from the layout
Next, the process proceeds to step S306, the similarity between the acquired comparison destination layout result 2 and the read comparison source layout result 4 is calculated, and the process proceeds to step S308, where all the comparisons corresponding to the read user ID are calculated. It is determined whether or not the process of step S306 is completed for the original layout result 4, and when it is determined that the process is completed for all the comparison source layout results 4 (Yes), the process proceeds to step S310.
ステップS310では、ステップS306の処理を1回だけ実行したときは、その類似度を、ステップS306の処理を複数回実行したときは、それら類似度のうち最大のものを、最終的に求めるべき類似度として算出し、ステップS312に移行する。
ステップS312では、算出した類似度に応じて、比較先レイアウト結果2に対する修正の度合いが大きくなるように、比較先レイアウト結果2を修正する。この場合、類似度が大きいときは、比較先レイアウト結果2に対する修正箇所を多くし、比較元レイアウト結果4に対する独自性を高める。逆に、類似度が小さいときは、比較元レイアウト結果4に対して既に独自性が高いものと考えられるので、比較先レイアウト結果2に対する修正箇所を少なくする。
In step S310, when the process of step S306 is executed only once, the degree of similarity is obtained. When the process of step S306 is executed a plurality of times, the maximum of the similarities is finally obtained. It calculates as a degree and transfers to step S312.
In step S312, the comparison target layout result 2 is corrected so that the degree of correction with respect to the comparison target layout result 2 is increased according to the calculated similarity. In this case, when the degree of similarity is large, the number of correction points for the comparison destination layout result 2 is increased, and the uniqueness of the comparison source layout result 4 is enhanced. On the other hand, when the degree of similarity is small, it is considered that the originality of the comparison source layout result 4 is already high.
比較先レイアウト結果2の修正は、例えば、複数の修正ルールを用意しておき、比較先レイアウト結果2に対して類似度に相当する数の修正ルールを適用することにより行うことができる。そうすると、類似度が大きいときは、多数の修正ルールが適用されることとなるので、比較先レイアウト結果2に対する修正箇所は多くなる。逆に、類似度が小さいときは、少数の修正ルールが適用されることとなるので、比較先レイアウト結果2に対する修正箇所は少なくなる。 The comparison destination layout result 2 can be corrected, for example, by preparing a plurality of correction rules and applying the number of correction rules corresponding to the similarity to the comparison destination layout result 2. Then, when the degree of similarity is large, a large number of correction rules are applied, and the number of correction points for the comparison destination layout result 2 increases. Conversely, when the degree of similarity is small, a small number of correction rules are applied, and the number of correction points for the comparison destination layout result 2 decreases.
また、類似度の大小は、所定の閾値を設けて判定することができる。例えば、類似度が「0」〜「1」の範囲の値を取り得る場合は、次の(a)〜(e)の条件に従って比較先レイアウト結果2を修正する。
(a)類似度が「0.8」以上であるときは、比較先レイアウト結果2に対する修正箇所は10カ所とする。
(b)類似度が「0.5」以上でかつ「0.8」未満であるときは、比較先レイアウト結果2に対する修正箇所は7カ所とする。
(c)類似度が「0.3」以上でかつ「0.5」未満であるときは、比較先レイアウト結果2に対する修正箇所は5カ所とする。
(d)類似度が「0.1」以上でかつ「0.3」未満であるときは、比較先レイアウト結果2に対する修正箇所は3カ所とする。
(e)類似度が「0.1」未満であるときは、比較先レイアウト結果2に対する修正箇所は0カ所とする。
The degree of similarity can be determined by providing a predetermined threshold. For example, when the similarity can take a value in the range of “0” to “1”, the comparison destination layout result 2 is corrected according to the following conditions (a) to (e).
(A) When the degree of similarity is “0.8” or more, the number of correction points for the comparison destination layout result 2 is 10.
(B) When the similarity is not less than “0.5” and less than “0.8”, the number of correction points for the comparison destination layout result 2 is seven.
(C) When the degree of similarity is “0.3” or more and less than “0.5”, the number of correction points for the comparison destination layout result 2 is five.
(D) When the similarity is “0.1” or more and less than “0.3”, the number of correction points for the comparison destination layout result 2 is three.
(E) When the degree of similarity is less than “0.1”, the number of correction points for the comparison destination layout result 2 is zero.
次いで、ステップS312の処理が終了すると、一連の処理を終了して元の処理に復帰させる。
一方、ステップS308で、読み出したユーザIDに対応するすべての比較元レイアウト結果4についてステップS306の処理が終了しないと判定したとき(No)は、ステップS314に移行して、読み出したユーザIDのうち次のものに対応する比較元レイアウト結果4をレイアウト結果登録DB12から読み出し、ステップS306に移行する。
Next, when the process of step S312 ends, the series of processes ends and the original process is restored.
On the other hand, when it is determined in step S308 that the process of step S306 is not completed for all the comparison source layout results 4 corresponding to the read user ID (No), the process proceeds to step S314, and among the read user IDs The comparison source layout result 4 corresponding to the following is read from the layout
次に、ステップS306の類似度算出処理を図10を参照しながら詳細に説明する。
図10は、ステップS306の類似度算出処理を示すフローチャートである。
類似度算出処理は、ステップS306において実行されると、図10に示すように、まず、ステップS400に移行するようになっている。
ステップS400では、レイアウト属性テーブル400のなかからレイアウト属性(以下、選択レイアウト属性という。)を選択し、ステップS402に移行する。
Next, the similarity calculation process in step S306 will be described in detail with reference to FIG.
FIG. 10 is a flowchart showing the similarity calculation process in step S306.
When the similarity calculation process is executed in step S306, as shown in FIG. 10, first, the process proceeds to step S400.
In step S400, a layout attribute (hereinafter referred to as a selected layout attribute) is selected from the layout attribute table 400, and the process proceeds to step S402.
ステップS402では、情報格納枠の各種別ごとに、比較先レイアウト結果2の情報格納枠の選択レイアウト属性と、比較元レイアウト結果4の情報格納枠の選択レイアウト属性との属性類似度を算出する。
(1)例えば、選択レイアウト属性がフォントサイズである場合、タイトル情報格納枠については、比較先レイアウト結果2のタイトル情報格納枠のフォントサイズ、および比較元レイアウト結果4のタイトル情報格納枠のフォントサイズに基づいて、下式(1)により属性類似度Simを算出する。
In step S402, the attribute similarity between the selected storage attribute of the information storage frame of the comparison destination layout result 2 and the selected layout attribute of the information storage frame of the comparison source layout result 4 is calculated for each type of information storage frame.
(1) For example, when the selected layout attribute is font size, for the title information storage frame, the font size of the title information storage frame of the comparison destination layout result 2 and the font size of the title information storage frame of the comparison source layout result 4 Based on the above, the attribute similarity Sim is calculated by the following equation (1).
ただし、上式(1)において、X(i)は、比較先レイアウト結果2のタイトル情報格納枠のフォントサイズ、iは、比較先レイアウト結果2に含まれるタイトル情報格納枠の個数である。また、Y(j)は、比較元レイアウト結果4のタイトル情報格納枠のフォントサイズ、jは、比較元レイアウト結果4に含まれるタイトル情報格納枠の個数である。また、f(X,Y)は、X≧YならばX−Yを、Y>XかつX≧Y−XならばY−Xを、それ以外ならばXをとる関数である。Max(n)は、n個の要素の値のうち最大のものを選択する関数である。 In the above equation (1), X (i) is the font size of the title information storage frame of the comparison destination layout result 2, and i is the number of title information storage frames included in the comparison destination layout result 2. Y (j) is the font size of the title information storage frame of the comparison source layout result 4, and j is the number of title information storage frames included in the comparison source layout result 4. Further, f (X, Y) is a function that takes XY if X ≧ Y, YY if Y> X and X ≧ YX, and X otherwise. Max (n) is a function that selects the maximum value among n element values.
文字情報格納枠についても、同様に、上式(1)により属性類似度を算出することができる。画像情報格納枠およびイラスト情報格納枠については、フォントサイズが規定されていないので、この場合は、属性類似度の算出対象とならない。
(2)また、例えば、選択レイアウト属性が情報格納枠のフォントウエイトである場合、タイトル情報格納枠については、比較先レイアウト結果2のタイトル情報格納枠のフォントウエイト、および比較元レイアウト結果4のタイトル情報格納枠のフォントウエイトに基づいて、上式(1)により属性類似度Simを算出する。
Similarly for the character information storage frame, the attribute similarity can be calculated by the above equation (1). For the image information storage frame and the illustration information storage frame, since the font size is not defined, in this case, the attribute similarity is not calculated.
(2) For example, when the selected layout attribute is the font weight of the information storage frame, for the title information storage frame, the font weight of the title information storage frame of the comparison destination layout result 2 and the title of the comparison source layout result 4 Based on the font weight of the information storage frame, the attribute similarity Sim is calculated by the above equation (1).
ただし、上式(1)において、X(i)は、比較先レイアウト結果2のタイトル情報格納枠のフォントウエイト、iは、比較先レイアウト結果2に含まれるタイトル情報格納枠の個数である。また、Y(j)は、比較元レイアウト結果4のタイトル情報格納枠のフォントウエイト、jは、比較元レイアウト結果4に含まれるタイトル情報格納枠の個数である。 In the above formula (1), X (i) is the font weight of the title information storage frame of the comparison destination layout result 2, and i is the number of title information storage frames included in the comparison destination layout result 2. Y (j) is the font weight of the title information storage frame of the comparison source layout result 4, and j is the number of title information storage frames included in the comparison source layout result 4.
文字情報格納枠についても、同様に、上式(1)により属性類似度を算出することができる。画像情報格納枠およびイラスト情報格納枠については、フォントウエイトが規定されていないので、この場合は、属性類似度の算出対象とならない。
(3)また、例えば、選択レイアウト属性が情報格納枠の配置位置である場合、タイトル情報格納枠については、比較先レイアウト結果2のタイトル情報格納枠の配置位置、および比較元レイアウト結果4のタイトル情報格納枠の配置位置に基づいて、例えば、特許文献1の技術により属性類似度を算出することができる。具体的には、比較先レイアウト結果2の構造モデルにおける情報格納枠と、比較元レイアウト結果4の構造モデルにおける同位置の情報格納枠との種別が一致している個数を算出し、算出した個数を情報格納枠の総数で除算した値を属性類似度として算出することができる。
Similarly for the character information storage frame, the attribute similarity can be calculated by the above equation (1). Since the font weight is not defined for the image information storage frame and the illustration information storage frame, in this case, the attribute similarity is not calculated.
(3) Also, for example, when the selected layout attribute is the arrangement position of the information storage frame, for the title information storage frame, the arrangement position of the title information storage frame of the comparison destination layout result 2 and the title of the comparison source layout result 4 Based on the arrangement position of the information storage frame, for example, the attribute similarity can be calculated by the technique of
文字情報格納枠、画像情報格納枠およびイラスト情報格納枠についても、同様に、属性類似度を算出することができる。
(4)また、例えば、選択レイアウト属性が情報格納枠のサイズである場合、タイトル情報格納枠については、比較先レイアウト結果2のタイトル情報格納枠のサイズ、および比較元レイアウト結果4のタイトル情報格納枠のサイズに基づいて、上式(1)により属性類似度Simを算出する。
Similarly, the attribute similarity can be calculated for the character information storage frame, the image information storage frame, and the illustration information storage frame.
(4) Also, for example, when the selected layout attribute is the size of the information storage frame, for the title information storage frame, the size of the title information storage frame of the comparison destination layout result 2 and the title information storage of the comparison source layout result 4 Based on the size of the frame, the attribute similarity Sim is calculated by the above equation (1).
ただし、上式(1)において、X(i)は、比較先レイアウト結果2のタイトル情報格納枠の面積、iは、比較先レイアウト結果2に含まれるタイトル情報格納枠の個数である。また、Y(j)は、比較元レイアウト結果4のタイトル情報格納枠の面積、jは、比較元レイアウト結果4に含まれるタイトル情報格納枠の個数である。
文字情報格納枠、画像情報格納枠およびイラスト情報格納枠についても、同様に、上式(1)により属性類似度を算出することができる。
However, in the above formula (1), X (i) is the area of the title information storage frame of the comparison destination layout result 2, and i is the number of title information storage frames included in the comparison destination layout result 2. Y (j) is the area of the title information storage frame of the comparison source layout result 4, and j is the number of title information storage frames included in the comparison source layout result 4.
Similarly, for the character information storage frame, the image information storage frame, and the illustration information storage frame, the attribute similarity can be calculated by the above equation (1).
次いで、ステップS404に移行して、算出した各種別ごとの属性類似度の平均値を代表属性類似度として算出し、ステップS406に移行する。
ステップS406では、レイアウト属性テーブル400のすべてのレイアウト属性についてステップS400〜S404の処理が終了したか否かを判定し、すべてのレイアウト属性について処理が終了したと判定したとき(Yes)は、ステップS408に移行する。
Next, the process proceeds to step S404, where the calculated average value of the attribute similarity for each type is calculated as the representative attribute similarity, and the process proceeds to step S406.
In step S406, it is determined whether or not the processing in steps S400 to S404 has been completed for all layout attributes in the layout attribute table 400. If it is determined that the processing has been completed for all layout attributes (Yes), step S408 is performed. Migrate to
ステップS408では、各レイアウト属性ごとに、レイアウト属性テーブル400から重み付け係数を読み出し、ステップS404で算出した代表属性類似度にその重み付け係数を乗算し、各乗算結果の平均値をレイアウト結果の類似度として算出し、一連の処理を終了して元の処理に復帰させる。
一方、ステップS406で、レイアウト属性テーブル400のすべてのレイアウト属性についてステップS400〜S404の処理が終了しないと判定したとき(No)は、ステップS400に移行する。
In step S408, for each layout attribute, the weighting coefficient is read from the layout attribute table 400, the representative attribute similarity calculated in step S404 is multiplied by the weighting coefficient, and the average value of each multiplication result is used as the similarity of the layout result. The calculation is completed, and a series of processing is terminated and the original processing is restored.
On the other hand, when it is determined in step S406 that the processing of steps S400 to S404 is not completed for all layout attributes in the layout attribute table 400 (No), the process proceeds to step S400.
次に、第1の実施の形態の動作を説明する。
自動レイアウト処理のレイアウト結果をユーザに提供する場合、レイアウト装置100において、レイアウト結果を提供するユーザのユーザIDを入力する。この場合、提供するレイアウト結果は、同一の業種に属する他のユーザに過去提供したことのあるレイアウト結果に対して独自性が高いものであることが望ましい。
Next, the operation of the first embodiment will be described.
When providing the layout result of the automatic layout process to the user, the
レイアウト装置100では、ユーザIDを入力すると、ステップS102を経て、自動レイアウト処理が実行される。自動レイアウト処理を、図3のレイアウトテンプレートを用いてレイアウトを行う場合を例にとって説明する。
まず、ステップS200〜S210を経て、固定線の位置、固定文字情報の形状および位置、並びに固定画像情報の形状および位置がその順で決定され、所定の選択規則に基づいてレイアウト要素登録DB40のなかからレイアウト要素が選択される。
In the
First, through steps S200 to S210, the position of the fixed line, the shape and position of the fixed character information, and the shape and position of the fixed image information are determined in that order, and are stored in the layout
次いで、選択レイアウト要素がタイトル情報である場合には、レイアウト領域360内にタイトル情報格納枠362が存在するので、ステップS212を経て、選択レイアウト要素に基づいてタイトル情報格納枠362の形状および位置を決定する処理が実行される。この決定処理では、タイトル情報の情報量が算出され、算出された情報量に基づいてタイトル情報格納枠362の形状および位置が決定され、タイトル情報がタイトル情報格納枠362に格納される。例えば、タイトルが比較的短い場合は、タイトル情報がちょうど収まるようにデフォルトのタイトル情報格納枠362を上方向に変形する。
Next, when the selected layout element is title information, since the title
また、選択レイアウト要素が画像情報である場合には、レイアウト領域360内に画像情報格納枠364が存在するので、ステップS214を経て、選択レイアウト要素に基づいて画像情報格納枠364の形状および位置を決定する処理が実行される。この決定処理では、画像情報の情報量が算出され、算出された情報量に基づいて、他の情報格納枠と重なり合わないように画像情報格納枠364の形状および位置が決定され、画像情報が画像情報格納枠364に格納される。例えば、画像の高さが幅に比して大きくかつ右寄せの指定がある場合は、タイトル情報格納枠362と重なり合わない最小限の位置までデフォルトの画像情報格納枠364を下方向(または可能であれば上方向)に変形した上で、その変形後の位置を上方向の移動上限として、画像情報格納枠364を、画像のアスペクト比を保持しつつ右方向に変形する。これにより、画像のアスペクト比を保持しつつ、許容し得る最大のサイズで画像を掲載することができる。
If the selected layout element is image information, the image
また、選択レイアウト要素が文字情報である場合には、レイアウト領域360内に文字情報格納枠366が存在するので、ステップS216を経て、選択レイアウト要素に基づいて文字情報格納枠366の形状および位置を決定する処理が実行される。この決定処理では、他の情報格納枠と重なり合わないように文字情報の情報量が算出され、算出された情報量に基づいて、文字情報格納枠366の形状および位置が決定され、文字情報が文字情報格納枠366に格納される。例えば、文字情報格納枠366の右上部分が画像情報格納枠364と重なり合っている場合は、文字情報格納枠366は、画像情報格納枠364と重なり合う部分とそうでない部分とで上下2つの枠に分割される。分割された文字情報格納枠366のうち上側部分は、その位置を下方向および左方向の移動上限として、画像情報格納枠364と重なり合わない最小限の位置まで左方向に変形するとともに、タイトル情報格納枠362と重なり合わない最小限の位置まで下方向(または可能であれば上方向)に変形する。また、分割された文字情報格納枠366のうち下側部分は、その位置を上方向の移動上限として、画像情報格納枠368と重なり合わない最小限の位置まで上方向に変形する。そして、文字情報は、まず、分割された文字情報格納枠366のうち上側部分に格納され、格納しきれなかった分は、分割された文字情報格納枠366のうち下側部分に格納される。これにより、他の情報格納枠と重なり合っても文字情報格納枠366を分割することで文字情報を効率的に格納することができるとともに、分割しても枠間の内容の連続性を保つことができる。
If the selected layout element is character information, a character
図11は、比較先レイアウト結果2および比較元レイアウト結果4を示す図である。
自動レイアウト処理が完了すると、ステップS300を経て、自動レイアウト処理のレイアウト結果が比較先レイアウト結果2として取得される。このとき、図11(a)に示すような比較先レイアウト結果2が取得されたとする。
図11(a)の例では、比較先レイアウト結果2には、タイトル1を格納したタイトル情報格納枠と、テキスト1を格納した文字情報格納枠と、テキスト3を格納した文字情報格納枠と、写真1を格納した画像情報格納枠と、イラストAを格納したイラスト情報格納枠とが配置されている。
FIG. 11 is a diagram illustrating the comparison destination layout result 2 and the comparison source layout result 4.
When the automatic layout process is completed, the layout result of the automatic layout process is acquired as the comparison destination layout result 2 through step S300. At this time, it is assumed that the comparison destination layout result 2 as shown in FIG.
In the example of FIG. 11A, the comparison destination layout result 2 includes a title information storage frame that stores the
次いで、ステップS302を経て、入力されたユーザIDに対応する業種情報と同一の業種情報がユーザ情報登録DB10のなかから検索されて該当の業種情報に対応するユーザIDが読み出される。
次いで、ステップS304を経て、読み出されたユーザIDに対応する比較元レイアウト結果4がレイアウト結果登録DB12から読み出される。このとき、図11(b)に示すような比較元レイアウト結果4が読み出されたとする。
Next, through step S302, the same industry information as the industry information corresponding to the input user ID is searched from the user
Next, through step S304, the comparison source layout result 4 corresponding to the read user ID is read from the layout
図11(b)の例では、比較元レイアウト結果4には、タイトル2を格納したタイトル情報格納枠と、イラストBを格納したイラスト情報格納枠と、テキスト4を格納した文字情報格納枠と、テキスト6を格納した文字情報格納枠と、写真3を格納した画像情報格納枠とが配置されている。
そして、ステップS306を経て、図11(a)の比較先レイアウト結果2と、図11(b)の比較元レイアウト結果4との類似度が算出される。以下の説明では、情報格納枠の種別として、タイトル情報格納枠、文字情報格納枠、画像情報格納枠およびイラスト情報格納枠の4種類を、レイアウト属性として、フォントサイズ、フォントウエイト、情報格納枠の配置位置および情報格納枠のサイズの4種類を取り扱うものとする。
In the example of FIG. 11B, the comparison source layout result 4 includes a title information storage frame storing title 2, an illustration information storage frame storing illustration B, a character information storage frame storing text 4, A character information storage frame storing text 6 and an image information storage
Then, through step S306, the similarity between the comparison destination layout result 2 in FIG. 11A and the comparison source layout result 4 in FIG. 11B is calculated. In the following description, four types of information storage frames, title information storage frame, character information storage frame, image information storage frame, and illustration information storage frame, are used as layout attributes, font size, font weight, and information storage frame. It is assumed that four types of arrangement positions and information storage frame sizes are handled.
まず、ステップS400,S402を経て、レイアウト属性としてフォントサイズが選択され、情報格納枠の各種別ごとに属性類似度が算出される。
図12は、比較先レイアウト結果2および比較元レイアウト結果4についてタイトル情報格納枠および文字情報格納枠のフォントサイズおよびフォントウエイトを解析した結果である。
First, through steps S400 and S402, a font size is selected as a layout attribute, and an attribute similarity is calculated for each type of information storage frame.
FIG. 12 shows the result of analyzing the font size and font weight of the title information storage frame and the character information storage frame for the comparison destination layout result 2 and the comparison source layout result 4.
タイトル情報格納枠については、図12に示すように、比較先レイアウト結果2のタイトル1のフォントサイズ「20」、および比較元レイアウト結果4のタイトル2のフォントサイズ「30」に基づいて、属性類似度Simは、上式(1)により、(20−10)/20=「0.5」として算出される。
文字情報格納枠については、図12に示すように、比較先レイアウト結果2のテキスト1のフォントサイズ「12」およびテキスト3のフォントサイズ「12」、並びに比較元レイアウト結果4のテキスト4のフォントサイズ「10」およびテキスト6のフォントサイズ「10」に基づいて、属性類似度Simは、上式(1)により、「1.0」として算出される。
For the title information storage frame, as shown in FIG. 12, the attribute similarity is based on the font size “20” of
For the character information storage frame, as shown in FIG. 12, the font size “12” and the font size “12” of the
そして、ステップS404を経て、算出された各種別ごとの属性類似度の平均値が代表属性類似度として算出される。タイトル情報格納枠の属性類似度が「0.5」、文字情報格納枠の属性類似度が「1.0」なので、フォントサイズの代表属性類似度は、「0.75」となる。
次に、ステップS400,S402を経て、レイアウト属性としてフォントウエイトが選択され、情報格納枠の各種別ごとに属性類似度が算出される。
Then, through step S404, the calculated average value of the attribute similarity for each type is calculated as the representative attribute similarity. Since the attribute similarity of the title information storage frame is “0.5” and the attribute similarity of the character information storage frame is “1.0”, the representative attribute similarity of the font size is “0.75”.
Next, through steps S400 and S402, a font weight is selected as a layout attribute, and an attribute similarity is calculated for each type of information storage frame.
タイトル情報格納枠については、図12に示すように、比較先レイアウト結果2のタイトル1のフォントウエイト「10」、および比較元レイアウト結果4のタイトル2のフォントウエイト「15」に基づいて、属性類似度Simは、上式(1)により、(10−5)/10=「0.5」として算出される。
文字情報格納枠については、図12に示すように、比較先レイアウト結果2のテキスト1のフォントウエイト「5」およびテキスト3のフォントウエイト「5」、並びに比較元レイアウト結果4のテキスト4のフォントウエイト「3」およびテキスト6のフォントウエイト「3」に基づいて、属性類似度Simは、上式(1)により、「1.0」として算出される。
For the title information storage frame, as shown in FIG. 12, the attribute similarity is based on the font weight “10” of
For the character information storage frame, as shown in FIG. 12, the font weight “5” of the
そして、ステップS404を経て、算出された各種別ごとの属性類似度の平均値が代表属性類似度として算出される。タイトル情報格納枠の属性類似度が「0.5」、文字情報格納枠の属性類似度が「1.0」なので、フォントウエイトの代表属性類似度は、「0.75」となる。
次に、ステップS400を経て、レイアウト属性として情報格納枠の配置位置が選択される。そして、ステップS402,S404を経て、特許文献1の技術により、比較先レイアウト結果2の構造モデルにおける情報格納枠と、比較元レイアウト結果4の構造モデルにおける同位置の情報格納枠との種別が一致している個数が算出され、算出された個数が情報格納枠の総数で除算され、その除算結果が属性類似度として算出される。構造化モデルでは、タイトル1,2が一致し、テキスト3,4が一致しているので、一致の個数は「2」となる。また、情報格納枠の総数が「5」なので、配置位置の代表属性類似度は、2/5=「0.4」となる。
Then, through step S404, the calculated average value of the attribute similarity for each type is calculated as the representative attribute similarity. Since the attribute similarity of the title information storage frame is “0.5” and the attribute similarity of the character information storage frame is “1.0”, the representative attribute similarity of the font weight is “0.75”.
Next, through step S400, the arrangement position of the information storage frame is selected as the layout attribute. Then, through steps S402 and S404, the type of the information storage frame in the structural model of the comparison destination layout result 2 and the information storage frame at the same position in the structural model of the comparison source layout result 4 are set to one by the technique of
次に、ステップS400,S402を経て、レイアウト属性として情報格納枠のサイズが選択され、情報格納枠の各種別ごとに属性類似度が算出される。ここで、タイトル情報格納枠については属性類似度Simが「1.0」として、文字情報格納枠については属性類似度Simが「0.8」として、画像情報格納枠については属性類似度Simが「0.8」として、イラスト情報格納枠については属性類似度Simが「0.8」としてそれぞれ算出されたとする。 Next, through steps S400 and S402, the size of the information storage frame is selected as the layout attribute, and the attribute similarity is calculated for each type of information storage frame. Here, the attribute similarity Sim is set to “1.0” for the title information storage frame, the attribute similarity Sim is set to “0.8” for the character information storage frame, and the attribute similarity Sim is set to the image information storage frame. Assume that the attribute similarity Sim is calculated as “0.8” for the illustration information storage frame as “0.8”.
そして、ステップS404を経て、算出された各種別ごとの属性類似度の平均値が代表属性類似度として算出される。タイトル情報格納枠の属性類似度が「1.0」、文字情報格納枠、画像情報格納枠およびイラスト情報格納枠の属性類似度がそれぞれ「0.8」なので、サイズの代表属性類似度は、「0.85」となる。
このように、すべてのレイアウト属性について代表属性類似度が算出されると、ステップS408を経て、各レイアウト属性ごとに、レイアウト属性テーブル400から重み付け係数が読み出され、算出された代表属性類似度にその重み付け係数が乗算され、各乗算結果の平均値がレイアウト結果の類似度として算出される。フォントサイズの代表属性類似度が「0.75」、フォントウエイトの代表属性類似度が「0.75」、配置位置の代表属性類似度が「0.4」、サイズの代表属性類似度が「0.85」であり、それぞれの重み付け係数が「0.8」、「0.3」、「0.3」および「0.7」なので、レイアウト結果の類似度は、(0.75×0.8+0.75×0.3+0.4×0.3+0.85×0.7)/4=「0.385」となる。
Then, through step S404, the calculated average value of the attribute similarity for each type is calculated as the representative attribute similarity. Since the attribute similarity of the title information storage frame is “1.0” and the attribute similarity of the character information storage frame, the image information storage frame, and the illustration information storage frame is “0.8”, the representative attribute similarity of the size is “0.85”.
As described above, when the representative attribute similarity is calculated for all layout attributes, the weighting coefficient is read from the layout attribute table 400 for each layout attribute through step S408, and the calculated representative attribute similarity is obtained. The weighting coefficient is multiplied, and the average value of the multiplication results is calculated as the similarity of the layout results. The font size representative attribute similarity is “0.75”, the font weight representative attribute similarity is “0.75”, the arrangement attribute representative attribute similarity is “0.4”, and the size representative attribute similarity is “0.75”. 0.85 ”and the respective weighting coefficients are“ 0.8 ”,“ 0.3 ”,“ 0.3 ”, and“ 0.7 ”, so the similarity of the layout results is (0.75 × 0). .8 + 0.75 × 0.3 + 0.4 × 0.3 + 0.85 × 0.7) / 4 = “0.385”.
レイアウト結果の類似度が算出されると、ステップS310,S312を経て、それら類似度のうち最大のものが最終的な類似度として算出され、算出された類似度に応じて、比較先レイアウト結果2に対する修正の度合いが大きくなるように、比較先レイアウト結果2が修正される。ユーザには、修正レイアウト結果6が提供される。また、ステップS106を経て、修正レイアウト結果6がユーザIDと対応付けられてレイアウト結果登録DB12に登録される。
When the similarity of the layout result is calculated, the maximum of the similarities is calculated as the final similarity through steps S310 and S312, and the comparison destination layout result 2 is determined according to the calculated similarity. The comparison destination layout result 2 is corrected so that the degree of correction with respect to increases. The user is provided with the modified layout result 6. Further, through step S106, the corrected layout result 6 is associated with the user ID and registered in the layout
[実施例]
第1の実施の形態の実施例を図13を参照しながら説明する。
図13は、比較先レイアウト結果2および比較元レイアウト結果4を示す図である。
図13(a)の比較先レイアウト結果2と、図13(b)の比較元レイアウト結果4との類似度を算出することを考える。
[Example]
An example of the first embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
FIG. 13 is a diagram showing the comparison destination layout result 2 and the comparison source layout result 4.
Consider calculating the similarity between the comparison destination layout result 2 in FIG. 13A and the comparison source layout result 4 in FIG.
まず、特許文献1の技術のように、相対位置のみを対象にレイアウトの類似度を求めると、情報格納枠の相対位置が変わっている(テキスト、画像では正反対、タイトルも正反対)ため、レイアウト結果の類似度は、かなり低い値(殆ど類似していないもの)として算出される。
また、特許文献2の技術のように、比較先レイアウト結果2および比較元レイアウト結果4を画像として扱い、画像の類似度として求めると、レイアウト結果の位置では、まったく違うレイアウト要素がレイアウトされているため、レイアウト結果の類似度は、かなり低い値(殆ど類似していないもの)として算出される。
First, as in the technique of
Further, as in the technique of Patent Document 2, when the comparison destination layout result 2 and the comparison source layout result 4 are treated as images and obtained as image similarity, completely different layout elements are laid out at the positions of the layout results. Therefore, the similarity of the layout results is calculated as a considerably low value (almost not similar).
したがって、従来の手法を利用すると、レイアウト結果の類似度は低く、独自性は高いと判定される。しかしながら、図13(a)の比較先レイアウト結果2と、図13(b)の比較元レイアウト結果4とを比較すると、情報格納枠の配置位置がただ単に変更されているだけなので、読み手には、それらレイアウト結果が類似していると判断される可能性が高い。そのため、読み手の主観を適切に反映した類似度とはいえない。 Therefore, when the conventional method is used, it is determined that the similarity of layout results is low and the originality is high. However, comparing the comparison destination layout result 2 in FIG. 13A and the comparison source layout result 4 in FIG. 13B, the arrangement position of the information storage frame is simply changed, so that the reader The layout results are likely to be determined to be similar. For this reason, it cannot be said that the degree of similarity appropriately reflects the reader's subjectivity.
これに対して、第1の実施の形態により類似度を算出すると、特許文献1,2の技術に比して、レイアウト結果の類似度を高い値として算出することができる。したがって、図13のようなレイアウト結果の類似度を算出する場合は、読み手の主観を比較的適切に反映した類似度を算出することができる。
このようにして、第1の実施の形態では、比較先レイアウト結果2のレイアウト属性および比較元レイアウト結果4のレイアウト属性に基づいてレイアウト結果の類似度を算出するようになっている。
On the other hand, when the similarity is calculated according to the first embodiment, the similarity of the layout result can be calculated as a higher value than the techniques of
In this way, in the first embodiment, the similarity of the layout results is calculated based on the layout attribute of the comparison target layout result 2 and the layout attribute of the comparison source layout result 4.
これにより、情報格納枠のレイアウト属性に基づいて類似度が算出されるので、各情報格納枠ごとの類否を考慮してレイアウト結果の類似度を算出することができる。したがって、従来に比して、読み手の主観を比較的適切に反映した類似度を算出することができる。
さらに、第1の実施の形態では、自動レイアウト処理のレイアウト結果を比較先レイアウト結果2として取得し、比較元レイアウト結果4をレイアウト結果登録DB12から読み出し、比較先レイアウト結果2と比較元レイアウト結果4との類似度を算出し、算出した類似度に応じて、比較先レイアウト結果2に対する修正の度合いが大きくなるように、比較先レイアウト結果2を修正するようになっている。
Thereby, since the similarity is calculated based on the layout attribute of the information storage frame, the similarity of the layout result can be calculated in consideration of the similarity for each information storage frame. Therefore, it is possible to calculate the degree of similarity reflecting the reader's subjectivity relatively appropriately as compared with the conventional case.
Furthermore, in the first embodiment, the layout result of the automatic layout process is acquired as the comparison destination layout result 2, the comparison source layout result 4 is read from the layout
これにより、同一の業種に属する異なるユーザに対してレイアウト結果を提供する場合は、一方のユーザに提供するレイアウト結果は、他方のユーザに提供するレイアウト結果との類似度に応じて修正の度合いが大きくなるように修正されるので、独自性の高いレイアウトを実現することができる。
さらに、第1の実施の形態では、入力したユーザIDと対応付けて修正レイアウト結果6を比較元レイアウト結果4としてレイアウト結果登録DB12に登録する一方、入力したユーザIDに対応する業種情報と同一の業種情報をユーザ情報登録DB10のなかから検索して該当の業種情報に対応するユーザIDを読み出し、読み出したユーザIDに対応する比較元レイアウト結果4をレイアウト結果登録DB12から読み出すようになっている。
Thus, when providing layout results to different users belonging to the same industry, the layout result provided to one user has a degree of correction depending on the degree of similarity with the layout result provided to the other user. Since it is corrected so as to be larger, a highly unique layout can be realized.
Furthermore, in the first embodiment, the corrected layout result 6 is registered as the comparison source layout result 4 in the layout
これにより、過去のレイアウト結果を比較元レイアウト結果4として用いることができるので、同一の業種に属する他のユーザに対して過去提供したことのあるレイアウト結果に対して独自性の高いレイアウトを実現することができる。
上記第1の実施の形態において、類似度算出部18およびステップS400〜S408は、手段1または6のレイアウト結果類似度算出手段に対応し、ステップS400〜S408は、手段11のレイアウト結果類似度算出ステップに対応している。
Thereby, since the past layout result can be used as the comparison source layout result 4, a highly unique layout can be realized with respect to the layout result that has been provided in the past to other users belonging to the same business type. be able to.
In the first embodiment, the
次に、本発明の第2の実施の形態を図面を参照しながら説明する。図14および図15は、本発明に係る類似度算出システムおよび類似度算出プログラム、並びに類似度算出方法の第2の実施の形態を示す図である。
第2の実施の形態は、本発明に係る類似度算出システムおよび類似度算出プログラム、並びに類似度算出方法を、自動レイアウト処理のレイアウト結果を修正する場合について適用したものであり、上記第1の実施の形態と異なるのは、属性類似度のほか、内容類似度およびテンプレート類似度に基づいてレイアウト結果の類似度を算出する点にある。以下、上記第1の実施の形態と異なる部分についてのみ説明し、上記第1の実施の形態と重複する部分については同一の符号を付して説明を省略する。
Next, a second embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. FIGS. 14 and 15 are diagrams showing a second embodiment of the similarity calculation system, the similarity calculation program, and the similarity calculation method according to the present invention.
In the second embodiment, the similarity calculation system, the similarity calculation program, and the similarity calculation method according to the present invention are applied to the case of correcting the layout result of the automatic layout process. The difference from the embodiment is that the similarity of the layout result is calculated based on the content similarity and the template similarity in addition to the attribute similarity. Hereinafter, only the parts different from the first embodiment will be described, and the same parts as those in the first embodiment will be denoted by the same reference numerals and the description thereof will be omitted.
CPU30は、ROM32の所定領域に格納されている所定のプログラムを起動させ、そのプログラムに従って、図10のフローチャートに示す類似度算出処理に代えて、図14のフローチャートに示す類似度算出処理を実行するようになっている。
図14は、ステップS306の類似度算出処理を示すフローチャートである。
類似度算出処理は、ステップS306において実行されると、図14に示すように、まず、ステップS500に移行するようになっている。
The
FIG. 14 is a flowchart showing the similarity calculation processing in step S306.
When the similarity calculation process is executed in step S306, as shown in FIG. 14, first, the process proceeds to step S500.
ステップS500では、情報格納枠の各種別ごとに、比較先レイアウト結果2のレイアウト要素の内容と、比較元レイアウト結果4のレイアウト要素の内容との内容類似度を算出する。
タイトル情報格納枠については、比較先レイアウト結果2のタイトル情報の内容、および比較元レイアウト結果4のタイトル情報の内容に基づいて、例えば、TFIDF(Term Frequency & Inverse Document Frequency)法により内容類似度を算出する。比較先レイアウト結果2または比較元レイアウト結果4に複数の文字情報格納枠が配置されている場合は、総当たりでそれぞれの内容類似度を算出し、それらの最大値を内容類似度として算出する。
In step S500, the content similarity between the content of the layout element of the comparison destination layout result 2 and the content of the layout element of the comparison source layout result 4 is calculated for each type of information storage frame.
For the title information storage frame, based on the content of the title information of the comparison destination layout result 2 and the content of the title information of the comparison source layout result 4, for example, the content similarity is calculated by the TFIDF (Term Frequency & Inverse Document Frequency) method. calculate. When a plurality of character information storage frames are arranged in the comparison destination layout result 2 or the comparison source layout result 4, each content similarity is calculated in a round robin manner, and the maximum value thereof is calculated as the content similarity.
画像情報格納枠については、比較先レイアウト結果2の画像情報の内容、および比較元レイアウト結果4の画像情報の内容に基づいて、例えば、特許文献1,2の技術により内容類似度を算出する。比較先レイアウト結果2または比較元レイアウト結果4に複数の画像情報格納枠が配置されている場合は、総当たりでそれぞれの内容類似度を算出し、それらの最大値を内容類似度として算出する。
For the image information storage frame, based on the content of the image information of the comparison destination layout result 2 and the content of the image information of the comparison source layout result 4, for example, the content similarity is calculated by the techniques of
文字情報格納枠についてはタイトル情報格納枠と同様に、イラスト情報格納枠については画像情報格納枠と同様に、それぞれ内容類似度を算出することができる。
次いで、ステップS502に移行して、算出した各種別ごとの内容類似度に基づいて、下式(2)により代表内容類似度Simを算出する。
Sim=a×S1+b×S2+c×S3+d×S4 …(2)
ただし、上式(2)において、S1〜S4は、タイトル情報格納枠、文字情報格納枠、画像情報格納枠およびイラスト情報格納枠の内容類似度であり、a〜dは、所定の重み付け係数である。
Similar to the title information storage frame for the character information storage frame, the content similarity can be calculated for the illustration information storage frame in the same manner as the image information storage frame.
Next, the process proceeds to step S502, and the representative content similarity Sim is calculated by the following equation (2) based on the calculated content similarity for each type.
Sim = a * S1 + b * S2 + c * S3 + d * S4 (2)
However, in the above formula (2), S1 to S4 are the content similarity of the title information storage frame, the character information storage frame, the image information storage frame and the illustration information storage frame, and a to d are predetermined weighting coefficients. is there.
次いで、ステップS504に移行して、情報格納枠の各種別ごとに、比較先レイアウト結果2の情報格納枠のレイアウト属性と、比較元レイアウト結果4の情報格納枠のレイアウト属性との属性類似度を算出する。
タイトル情報格納枠については、比較先レイアウト結果2のタイトル情報格納枠の面積、および比較元レイアウト結果4のタイトル情報格納枠の面積に基づいて、下式(3)により属性類似度Simを算出する。
Sim=2×s1∩s2/(s1+s2) …(3)
ただし、上式(3)において、s1は、比較先レイアウト結果2のタイトル情報格納枠の面積、s2は、比較元レイアウト結果4のタイトル情報格納枠の面積、s1∩s2は、比較先レイアウト結果2,4を重ね合わせた場合にタイトル情報格納枠の重なり合う領域の面積である。
Next, the process proceeds to step S504, and the attribute similarity between the layout attribute of the information storage frame of the comparison destination layout result 2 and the layout attribute of the information storage frame of the comparison source layout result 4 is set for each type of information storage frame. calculate.
For the title information storage frame, the attribute similarity Sim is calculated by the following equation (3) based on the area of the title information storage frame of the comparison destination layout result 2 and the area of the title information storage frame of the comparison source layout result 4. .
Sim = 2 × s1∩s2 / (s1 + s2) (3)
In the above equation (3), s1 is the area of the title information storage frame of the comparison destination layout result 2, s2 is the area of the title information storage frame of the comparison source layout result 4, and s1ss2 is the comparison destination layout result This is the area of the overlapping area of the title information storage frames when 2 and 4 are overlapped.
文字情報格納枠、画像情報格納枠およびイラスト情報格納枠についても、同様に、上式(3)により属性類似度を算出することができる。
次いで、ステップS506に移行して、算出した各種別ごとの属性類似度に基づいて、下式(4)により代表属性類似度Simを算出する。
Sim=e×P1+f×P2+g×P3+h×P4 …(4)
ただし、上式(4)において、P1〜P4は、タイトル情報格納枠、文字情報格納枠、画像情報格納枠およびイラスト情報格納枠の属性類似度であり、e〜hは、所定の重み付け係数である。
Similarly for the character information storage frame, the image information storage frame, and the illustration information storage frame, the attribute similarity can be calculated by the above equation (3).
Next, the process proceeds to step S506, and based on the calculated attribute similarity for each type, the representative attribute similarity Sim is calculated by the following equation (4).
Sim = e * P1 + f * P2 + g * P3 + h * P4 (4)
In the above equation (4), P1 to P4 are attribute similarity of the title information storage frame, the character information storage frame, the image information storage frame, and the illustration information storage frame, and e to h are predetermined weighting coefficients. is there.
次いで、ステップS508に移行して、情報格納枠の各種別ごとに、比較先レイアウト結果2を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートと、比較元レイアウト結果4を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートとのテンプレート類似度を算出する。
タイトル情報格納枠については、比較先レイアウト結果2を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートにおけるタイトル情報格納枠の面積、および比較元レイアウト結果4を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートにおけるタイトル情報格納枠の面積に基づいて、下式(5)により属性類似度Simを算出する。
Sim=2×s1∩s2/(s1+s2) …(5)
ただし、上式(5)において、s1は、比較先レイアウト結果2を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートにおけるタイトル情報格納枠の面積、s2は、比較元レイアウト結果4を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートにおけるタイトル情報格納枠の面積、s1∩s2は、比較先レイアウト結果2,4を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートを重ね合わせた場合にタイトル情報格納枠の重なり合う領域の面積である。
Next, the process proceeds to step S508, and the template similarity between the layout template used to obtain the comparison destination layout result 2 and the layout template used to obtain the comparison source layout result 4 for each type of information storage frame. Calculate the degree.
As for the title information storage frame, the area of the title information storage frame in the layout template used to obtain the comparison destination layout result 2 and the area of the title information storage frame in the layout template used to obtain the comparison source layout result 4 are used. Based on this, the attribute similarity Sim is calculated by the following equation (5).
Sim = 2 × s1∩s2 / (s1 + s2) (5)
In the above equation (5), s1 is the area of the title information storage frame in the layout template used to obtain the comparison destination layout result 2, and s2 is the layout template used to obtain the comparison source layout result 4. The area of the title information storage frame, s1∩s2, is the area of the overlapping area of the title information storage frames when the layout templates used to obtain the comparison destination layout results 2 and 4 are superimposed.
文字情報格納枠、画像情報格納枠およびイラスト情報格納枠についても、同様に、上式(5)により属性類似度を算出することができる。
なお、テンプレート類似度は、属性類似度の算出がレイアウト後の内容に基づいて行うのに対して、レイアウト前の内容に基づいて算出する点で異なる。すなわち、レイアウトの過程では、選択レイアウト要素によって情報格納枠の配置位置や大きさが変更されるが、テンプレート類似度は、その変更を考慮しない類似度であり、属性類似度は、その変更を考慮した類似度であることがいえる。
Similarly for the character information storage frame, the image information storage frame, and the illustration information storage frame, the attribute similarity can be calculated by the above equation (5).
The template similarity is different in that the attribute similarity is calculated based on the content before layout, whereas the attribute similarity is calculated based on the content after layout. In other words, in the layout process, the arrangement position and size of the information storage frame are changed depending on the selected layout element. It can be said that the degree of similarity.
次いで、ステップS510に移行して、算出した各種別ごとのテンプレート類似度に基づいて、下式(6)により代表テンプレート類似度Simを算出する。
Sim=i×T1+j×T2+k×T3+l×T4 …(6)
ただし、上式(6)において、T1〜T4は、タイトル情報格納枠、文字情報格納枠、画像情報格納枠およびイラスト情報格納枠のテンプレート類似度であり、i〜lは、所定の重み付け係数である。
Next, the process proceeds to step S510, and the representative template similarity Sim is calculated by the following equation (6) based on the calculated template similarity for each type.
Sim = i * T1 + j * T2 + k * T3 + l * T4 (6)
In the above equation (6), T1 to T4 are template similarities of the title information storage frame, the character information storage frame, the image information storage frame, and the illustration information storage frame, and i to l are predetermined weighting coefficients. is there.
次いで、ステップS512に移行して、算出した代表内容類似度、代表属性類似度および代表テンプレート類似度に基づいて、下式(7)によりレイアウト結果の類似度Simを算出する。
Sim=α×S+β×P+γ×T …(7)
ただし、上式(7)において、S,P,Tは、代表内容類似度、代表属性類似度および代表テンプレート類似度であり、α〜γは、所定の重み付け係数である。
Next, the process proceeds to step S512, and the similarity Sim of the layout result is calculated by the following equation (7) based on the calculated representative content similarity, representative attribute similarity, and representative template similarity.
Sim = α × S + β × P + γ × T (7)
However, in the above formula (7), S, P, and T are the representative content similarity, the representative attribute similarity, and the representative template similarity, and α to γ are predetermined weighting coefficients.
ステップS512の処理が終了すると、一連の処理を終了して元の処理に復帰させる。
次に、第2の実施の形態の動作を説明する。
図15は、比較先レイアウト結果2および比較元レイアウト結果4を示す図である。
自動レイアウト処理が完了すると、ステップS300を経て、自動レイアウト処理のレイアウト結果が比較先レイアウト結果2として取得される。このとき、図15(a)に示すような比較先レイアウト結果2が取得されたとする。
When the process of step S512 is completed, the series of processes is terminated and the original process is restored.
Next, the operation of the second embodiment will be described.
FIG. 15 is a diagram illustrating the comparison destination layout result 2 and the comparison source layout result 4.
When the automatic layout process is completed, the layout result of the automatic layout process is acquired as the comparison destination layout result 2 through step S300. At this time, it is assumed that the comparison destination layout result 2 as shown in FIG.
図15(a)の例では、比較先レイアウト結果2には、タイトル1を格納したタイトル情報格納枠と、テキスト1を格納した文字情報格納枠と、写真2を格納した画像情報格納枠と、テキスト3を格納した文字情報格納枠と、写真1を格納した画像情報格納枠と、テキスト2を格納した文字情報格納枠と、イラストAを格納したイラスト情報格納枠とが配置されている。
In the example of FIG. 15A, the comparison destination layout result 2 includes a title information storage
次いで、ステップS302を経て、入力されたユーザIDに対応する業種情報と同一の業種情報がユーザ情報登録DB10のなかから検索されて該当の業種情報に対応するユーザIDが読み出される。
次いで、ステップS304を経て、読み出されたユーザIDに対応する比較元レイアウト結果4がレイアウト結果登録DB12から読み出される。このとき、図15(b)に示すような比較元レイアウト結果4が読み出されたとする。
Next, through step S302, the same industry information as the industry information corresponding to the input user ID is searched from the user
Next, through step S304, the comparison source layout result 4 corresponding to the read user ID is read from the layout
図15(b)の例では、比較元レイアウト結果4には、タイトル2を格納したタイトル情報格納枠と、テキスト4を格納した文字情報格納枠と、写真3を格納した画像情報格納枠と、イラストBを格納したイラスト情報格納枠とが配置されている。
そして、ステップS306を経て、図15(a)の比較先レイアウト結果2と、図15(b)の比較元レイアウト結果4との類似度が算出される。
In the example of FIG. 15B, the comparison source layout result 4 includes a title information storage frame storing the title 2, a character information storage frame storing the text 4, an image information storage frame storing the
Then, through step S306, the similarity between the comparison destination layout result 2 in FIG. 15A and the comparison source layout result 4 in FIG. 15B is calculated.
まず、ステップS500を経て、情報格納枠の各種別ごとに内容類似度が算出される。
タイトル情報格納枠については、比較先レイアウト結果2にタイトル1のタイトル情報格納枠が、比較元レイアウト結果4にタイトル2のタイトル情報格納枠がそれぞれ存在するので、内容類似度は、タイトル1,2のタイトル情報格納枠の比較で算出された内容類似度となる。
First, through step S500, the content similarity is calculated for each type of information storage frame.
As for the title information storage frame, the title information storage frame of
文字情報格納枠については、比較先レイアウト結果2にテキスト1〜3の文字情報格納枠が、比較元レイアウト結果4にテキスト4,6のタイトル情報格納枠がそれぞれ存在するので、内容類似度は、次の(1)〜(6)の内容類似度のうち最大値となる。
(1)テキスト1,4の文字情報格納枠の比較により算出された内容類似度
(2)テキスト1,6の文字情報格納枠の比較により算出された内容類似度
(3)テキスト2,4の文字情報格納枠の比較により算出された内容類似度
(4)テキスト2,6の文字情報格納枠の比較により算出された内容類似度
(5)テキスト3,4の文字情報格納枠の比較により算出された内容類似度
(6)テキスト3,6の文字情報格納枠の比較により算出された内容類似度
画像情報格納枠については、比較先レイアウト結果2に写真1,2の画像情報格納枠が、比較元レイアウト結果4に写真3の画像情報格納枠がそれぞれ存在するので、内容類似度は、次の(1),(2)の内容類似度のうち最大値となる。
(1)写真1,3の画像情報格納枠の比較により算出された内容類似度
(2)写真2,3の画像情報格納枠の比較により算出された内容類似度
イラスト情報格納枠については、比較先レイアウト結果2にイラストAのイラスト情報格納枠が、比較元レイアウト結果4にイラストBのイラスト情報格納枠がそれぞれ存在するので、内容類似度は、イラストA,Bのイラスト情報格納枠の比較により算出された内容類似度となる。
As for the character information storage frames, the character information storage frames of
(1) Content similarity calculated by comparing character information storage frames of
(1) Content similarity calculated by comparing image information storage frames of
次いで、ステップS502を経て、算出された各種別ごとの内容類似度に基づいて代表内容類似度が算出される。
同様に、ステップS504,S506を経て、情報格納枠の各種別ごとに属性類似度が算出され、算出された各種別ごとの属性類似度に基づいて代表属性類似度が算出される。また、ステップS508,S510を経て、情報格納枠の各種別ごとにテンプレート類似度が算出され、算出された各種別ごとのテンプレート類似度に基づいて代表テンプレート類似度が算出される。
Next, through step S502, the representative content similarity is calculated based on the calculated content similarity for each type.
Similarly, through steps S504 and S506, the attribute similarity is calculated for each type of information storage frame, and the representative attribute similarity is calculated based on the calculated attribute similarity for each type. Further, through steps S508 and S510, the template similarity is calculated for each type of information storage frame, and the representative template similarity is calculated based on the calculated template similarity for each type.
そして、ステップS512を経て、算出された代表内容類似度、代表属性類似度および代表テンプレート類似度に基づいてレイアウト結果の類似度が算出される。
このようにして、第2の実施の形態では、比較先レイアウト結果2のレイアウト属性および比較元レイアウト結果4のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度を算出し、比較先レイアウト結果2を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートおよび比較元レイアウト結果4を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートに基づいてテンプレート類似度を算出し、比較先レイアウト結果2のレイアウト要素の内容および比較元レイアウト結果4のレイアウト要素の内容に基づいて内容類似度を算出し、算出した属性類似度、テンプレート類似度および内容類似度に基づいてレイアウト結果の類似度を算出するようになっている。
Then, through step S512, the similarity of the layout result is calculated based on the calculated representative content similarity, representative attribute similarity, and representative template similarity.
In this way, in the second embodiment, the attribute similarity is calculated based on the layout attribute of the comparison destination layout result 2 and the layout attribute of the comparison source layout result 4, and is used to obtain the comparison destination layout result 2. The template similarity is calculated based on the layout template used to obtain the layout template and the comparison source layout result 4, and based on the content of the layout element of the comparison destination layout result 2 and the content of the layout element of the comparison source layout result 4 The content similarity is calculated, and the similarity of the layout result is calculated based on the calculated attribute similarity, template similarity, and content similarity.
これにより、情報格納枠のレイアウト属性、レイアウトテンプレートおよびレイアウト要素の内容に基づいて類似度が算出されるので、各情報格納枠ごとの類否、およびレイアウト要素の内容の類否を考慮してレイアウト結果の類似度を算出することができる。したがって、従来に比して、読み手の主観を比較的適切に反映した類似度を算出することができる。 As a result, the similarity is calculated based on the layout attribute of the information storage frame, the layout template, and the content of the layout element. Therefore, the layout is considered in consideration of the similarity of each information storage frame and the content of the layout element. The similarity of the results can be calculated. Therefore, it is possible to calculate the degree of similarity reflecting the reader's subjectivity relatively appropriately as compared with the conventional case.
上記第2の実施の形態において、レイアウト要素登録DB40は、手段4、5、9、10、14または15の格納情報記憶手段に対応し、ステップS210は、手段4、5、9、10、14または15の格納情報選択手段に対応し、ステップS212〜S218は、手段4、5、9、10、14または15のレイアウト手段に対応している。また、ステップS500,S502は、手段5若しくは10の内容類似度算出手段、または手段15の内容類似度算出ステップに対応し、ステップS504,S506は、手段4、5、9若しくは10の属性類似度算出手段、または手段14若しくは15の属性類似度算出ステップに対応している。
In the second embodiment, the layout
また、上記第2の実施の形態において、ステップS508,S510は、手段4、5、9若しくは10のテンプレート類似度算出手段、または手段14若しくは15のテンプレート類似度算出ステップに対応し、ステップS512は、手段4、5、9若しくは10のレイアウト結果類似度算出手段、または手段14若しくは15のレイアウト結果類似度算出ステップに対応している。
In the second embodiment, steps S508 and S510 correspond to the template similarity calculating means of
次に、本発明の第3の実施の形態を図面を参照しながら説明する。図16および図17は、本発明に係る類似度算出システムおよび類似度算出プログラム、並びに類似度算出方法の第3の実施の形態を示す図である。
第3の実施の形態は、本発明に係る類似度算出システムおよび類似度算出プログラム、並びに類似度算出方法を、自動レイアウト処理のレイアウト結果を修正する場合について適用したものであり、上記第2の実施の形態と異なるのは、比較先レイアウト結果2の各情報格納枠ごとに、属性類似度、内容類似度およびテンプレート類似度を算出する点にある。以下、上記第2の実施の形態と異なる部分についてのみ説明し、上記第2の実施の形態と重複する部分については同一の符号を付して説明を省略する。
Next, a third embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. 16 and 17 are diagrams showing a third embodiment of the similarity calculation system, the similarity calculation program, and the similarity calculation method according to the present invention.
In the third embodiment, the similarity calculation system, the similarity calculation program, and the similarity calculation method according to the present invention are applied to the case where the layout result of the automatic layout processing is corrected. The difference from the embodiment is that the attribute similarity, content similarity, and template similarity are calculated for each information storage frame of the comparison destination layout result 2. Hereinafter, only the parts different from the second embodiment will be described, and the same parts as those in the second embodiment will be denoted by the same reference numerals and the description thereof will be omitted.
CPU30は、ROM32の所定領域に格納されている所定のプログラムを起動させ、そのプログラムに従って、図14のフローチャートに示す類似度算出処理に代えて、図16のフローチャートに示す類似度算出処理を実行するようになっている。
図16は、ステップS306の類似度算出処理を示すフローチャートである。
類似度算出処理は、ステップS306において実行されると、図16に示すように、まず、ステップS600に移行するようになっている。
The
FIG. 16 is a flowchart showing the similarity calculation processing in step S306.
When the similarity calculation process is executed in step S306, as shown in FIG. 16, first, the process proceeds to step S600.
ステップS600では、比較先レイアウト結果2のなかから先頭の情報格納枠を選択し、ステップS602に移行する。
ステップS602では、ステップS600,S614で選択した情報格納枠(以下、選択レイアウト属性という。)について、下式(8)により属性類似度Simを算出する。
Sim=2×s1∩s2/(s1+s2) …(8)
ただし、上式(8)において、s1は、選択情報格納枠の面積、s2は、比較元レイアウト結果4における選択情報格納枠と同種の情報格納枠の面積、s1∩s2は、比較先レイアウト結果2,4を重ね合わせた場合に選択情報格納枠と同種の情報格納枠とが重なり合う領域の面積である。
In step S600, the top information storage frame is selected from comparison target layout result 2, and the process proceeds to step S602.
In step S602, the attribute similarity Sim is calculated for the information storage frame selected in steps S600 and S614 (hereinafter referred to as the selected layout attribute) by the following equation (8).
Sim = 2 × s1∩s2 / (s1 + s2) (8)
However, in the above equation (8), s1 is the area of the selection information storage frame, s2 is the area of the information storage frame of the same type as the selection information storage frame in the comparison source layout result 4, and s1∩s2 is the comparison destination layout result This is the area of the area where the selected information storage frame and the same type of information storage frame overlap when 2 and 4 are overlapped.
次いで、ステップS604に移行して、選択情報格納枠に格納されているレイアウト要素の内容、および比較元レイアウト結果4における選択情報格納枠と同種の情報格納枠に格納されているレイアウト要素の内容に基づいて、例えば、TFIDF法により内容類似度を算出する。
次いで、ステップS606に移行して、比較先レイアウト結果2を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートにおける選択情報格納枠の面積、および比較元レイアウト結果4を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートにおける選択情報格納枠と同種の情報格納枠の面積に基づいて、下式(9)によりテンプレート類似度Simを算出する。
Sim=2×s1∩s2/(s1+s2) …(9)
ただし、上式(9)において、s1は、比較先レイアウト結果2を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートにおける選択情報格納枠の面積、s2は、比較元レイアウト結果4を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートにおける選択情報格納枠と同種の情報格納枠の面積、s1∩s2は、比較先レイアウト結果2,4を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートを重ね合わせた場合に選択情報格納枠と同種の情報格納枠とが重なり合う領域の面積である。
Next, the process proceeds to step S604, where the contents of the layout elements stored in the selected information storage frame and the contents of the layout elements stored in the same type of information storage frame as the selected information storage frame in the comparison source layout result 4 are displayed. Based on this, for example, the content similarity is calculated by the TFIDF method.
Next, the process proceeds to step S606, where the area of the selection information storage frame in the layout template used to obtain the comparison destination layout result 2 and the selection information storage frame in the layout template used to obtain the comparison source layout result 4 Based on the area of the information storage frame of the same type, the template similarity Sim is calculated by the following equation (9).
Sim = 2 × s1∩s2 / (s1 + s2) (9)
In the above equation (9), s1 is the area of the selection information storage frame in the layout template used to obtain the comparison destination layout result 2, and s2 is the layout template used to obtain the comparison source layout result 4. The area of the information storage frame of the same type as the selection information storage frame, s1∩s2 is the same type of information storage frame as the selection information storage frame when the layout templates used to obtain the comparison destination layout results 2 and 4 are superimposed. Is the area of the overlapping region.
次いで、ステップS608に移行して、算出した属性類似度、内容類似度およびテンプレート類似度に基づいて、上式(7)により選択情報格納枠の代表類似度を算出する。
ただし、上式(7)において、S,P,Tは、内容類似度、属性類似度およびテンプレート類似度であり、α〜γは、所定の重み付け係数である。
次いで、ステップS610に移行して、比較先レイアウト結果2のすべての情報格納枠についてステップS602〜S608の処理が終了したか否かを判定し、すべての情報格納枠について処理が終了したと判定したとき(Yes)は、ステップS612に移行して、各情報格納枠の代表類似度の平均値をレイアウト結果の類似度として算出し、一連の処理を終了して元の処理に復帰させる。
Next, the process proceeds to step S608, and the representative similarity of the selection information storage frame is calculated by the above equation (7) based on the calculated attribute similarity, content similarity, and template similarity.
However, in the above equation (7), S, P, and T are content similarity, attribute similarity, and template similarity, and α to γ are predetermined weighting coefficients.
Next, the process proceeds to step S610, where it is determined whether or not the processing of steps S602 to S608 has been completed for all information storage frames of the comparison destination layout result 2, and it is determined that the processing has been completed for all information storage frames. If yes (Yes), the process proceeds to step S612, the average value of the representative similarity of each information storage frame is calculated as the similarity of the layout result, the series of processes is terminated, and the process returns to the original process.
一方、ステップS610で、比較先レイアウト結果2のすべての情報格納枠についてステップS602〜S608の処理が終了しないと判定したとき(No)は、ステップS614に移行して、比較先レイアウト結果2のなかから次の情報格納枠を選択し、ステップS602に移行する。
次に、第3の実施の形態の動作を説明する。
On the other hand, when it is determined in step S610 that the processing of steps S602 to S608 is not completed for all the information storage frames of the comparison destination layout result 2 (No), the process proceeds to step S614, and the comparison destination layout result 2 includes The next information storage frame is selected from step S602, and the process proceeds to step S602.
Next, the operation of the third embodiment will be described.
図17は、比較先レイアウト結果2および比較元レイアウト結果4を示す図である。
自動レイアウト処理が完了すると、ステップS300を経て、自動レイアウト処理のレイアウト結果が比較先レイアウト結果2として取得される。このとき、図17(a)に示すような比較先レイアウト結果2が取得されたとする。
図17(a)の例では、比較先レイアウト結果2には、タイトル1を格納したタイトル情報格納枠と、テキスト1を格納した文字情報格納枠と、テキスト3を格納した文字情報格納枠と、写真1を格納した画像情報格納枠と、イラストAを格納したイラスト情報格納枠とが配置されている。
FIG. 17 is a diagram showing the comparison destination layout result 2 and the comparison source layout result 4.
When the automatic layout process is completed, the layout result of the automatic layout process is acquired as the comparison destination layout result 2 through step S300. At this time, it is assumed that the comparison destination layout result 2 as shown in FIG.
In the example of FIG. 17A, the comparison destination layout result 2 includes a title information storage frame that stores the
次いで、ステップS302を経て、入力されたユーザIDに対応する業種情報と同一の業種情報がユーザ情報登録DB10のなかから検索されて該当の業種情報に対応するユーザIDが読み出される。
次いで、ステップS304を経て、読み出されたユーザIDに対応する比較元レイアウト結果4がレイアウト結果登録DB12から読み出される。このとき、図17(b)に示すような比較元レイアウト結果4が読み出されたとする。
Next, through step S302, the same industry information as the industry information corresponding to the input user ID is searched from the user
Next, through step S304, the comparison source layout result 4 corresponding to the read user ID is read from the layout
図17(b)の例では、比較元レイアウト結果4には、タイトル2を格納したタイトル情報格納枠と、テキスト4を格納した文字情報格納枠と、テキスト6を格納した文字情報格納枠と、写真3を格納した画像情報格納枠と、イラストBを格納したイラスト情報格納枠とが配置されている。
そして、ステップS306を経て、図17(a)の比較先レイアウト結果2と、図17(b)の比較元レイアウト結果4との類似度が算出される。
In the example of FIG. 17B, the comparison source layout result 4 includes a title information storage frame that stores the title 2, a character information storage frame that stores the text 4, a character information storage frame that stores the text 6, An image information storage frame storing the
Then, through step S306, the similarity between the comparison destination layout result 2 in FIG. 17A and the comparison source layout result 4 in FIG. 17B is calculated.
まず、ステップS600〜S606を経て、比較先レイアウト結果2のなかからタイトル1のタイトル情報格納枠が選択され、選択タイトル情報格納枠の属性類似度、内容類似度およびテンプレート類似度が算出される。比較元レイアウト結果4にタイトル2のタイトル情報格納枠がそれぞれ存在するので、属性類似度、内容類似度およびテンプレート類似度は、タイトル1,2のタイトル情報格納枠の比較で算出された内容類似度となる。そして、ステップS608を経て、算出された属性類似度、内容類似度およびテンプレート類似度に基づいて、選択タイトル情報格納枠の代表類似度が算出される。
First, through steps S600 to S606, the title information storage frame of
次に、ステップS614,S602〜S606を経て、比較先レイアウト結果2のなかからテキスト1の文字情報格納枠が選択され、選択文字情報格納枠の属性類似度、内容類似度およびテンプレート類似度が算出される。比較元レイアウト結果4にテキスト4,6の文字情報格納枠がそれぞれ存在するので、属性類似度、内容類似度およびテンプレート類似度は、テキスト1,4の文字情報格納枠の比較で算出された内容類似度、およびテキスト1,6の文字情報格納枠の比較で算出された内容類似度のうち最大値となる。そして、ステップS608を経て、算出された属性類似度、内容類似度およびテンプレート類似度に基づいて、選択文字情報格納枠の代表類似度が算出される。
Next, through steps S614, S602 to S606, the character information storage frame of
同様に、ステップS614,S602〜S606を繰り返し経て、テキスト3の文字情報格納枠の代表類似度、写真1の画像情報格納枠の代表類似度、およびイラストAのイラスト情報格納枠の代表類似度が算出される。
そして、比較先レイアウト結果2のすべての情報格納枠について代表類似度が算出されると、ステップS612を経て、各情報格納枠の代表類似度の平均値がレイアウト結果の類似度として算出される。
Similarly, through steps S614, S602 to S606, the representative similarity of the character information storage frame of
When the representative similarity is calculated for all the information storage frames of the comparison destination layout result 2, the average value of the representative similarity of each information storage frame is calculated as the similarity of the layout result through step S612.
このようにして、第3の実施の形態では、比較先レイアウト結果2のレイアウト属性および比較元レイアウト結果4のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度を算出し、比較先レイアウト結果2を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートおよび比較元レイアウト結果4を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートに基づいてテンプレート類似度を算出し、比較先レイアウト結果2のレイアウト要素の内容および比較元レイアウト結果4のレイアウト要素の内容に基づいて内容類似度を算出し、算出した属性類似度、テンプレート類似度および内容類似度に基づいてレイアウト結果の類似度を算出するようになっている。 In this manner, in the third embodiment, the attribute similarity is calculated based on the layout attribute of the comparison destination layout result 2 and the layout attribute of the comparison source layout result 4, and is used to obtain the comparison destination layout result 2. The template similarity is calculated based on the layout template used to obtain the layout template and the comparison source layout result 4, and based on the content of the layout element of the comparison destination layout result 2 and the content of the layout element of the comparison source layout result 4 The content similarity is calculated, and the similarity of the layout result is calculated based on the calculated attribute similarity, template similarity, and content similarity.
これにより、情報格納枠のレイアウト属性、レイアウトテンプレートおよびレイアウト要素の内容に基づいて類似度が算出されるので、各情報格納枠ごとの類否、およびレイアウト要素の内容の類否を考慮してレイアウト結果の類似度を算出することができる。したがって、従来に比して、読み手の主観を比較的適切に反映した類似度を算出することができる。 As a result, the similarity is calculated based on the layout attribute of the information storage frame, the layout template, and the content of the layout element. Therefore, the layout is considered in consideration of the similarity of each information storage frame and the content of the layout element. The similarity of the results can be calculated. Therefore, it is possible to calculate the degree of similarity reflecting the reader's subjectivity relatively appropriately as compared with the conventional case.
上記第3の実施の形態において、レイアウト要素登録DB40は、手段4、5、9、10、14または15の格納情報記憶手段に対応し、ステップS210は、手段4、5、9、10、14または15の格納情報選択手段に対応し、ステップS212〜S218は、手段4、5、9、10、14または15のレイアウト手段に対応している。また、ステップS602は、手段4、5、9若しくは10の属性類似度算出手段、または手段14若しくは15の属性類似度算出ステップに対応し、ステップS604は、手段5若しくは10の内容類似度算出手段、または手段15の内容類似度算出ステップに対応している。
In the third embodiment, the layout
また、上記第3の実施の形態において、ステップS606は、手段4、5、9若しくは10のテンプレート類似度算出手段、または手段14若しくは15のテンプレート類似度算出ステップに対応し、ステップS612は、手段4、5、9若しくは10のレイアウト結果類似度算出手段、または手段14若しくは15のレイアウト結果類似度算出ステップに対応している。
In the third embodiment, step S606 corresponds to the template similarity calculating means of
なお、上記第1の実施の形態においては、比較先レイアウト結果2のレイアウト属性および比較元レイアウト結果4のレイアウト属性に基づいてレイアウト結果の類似度を算出するように構成したが、これに限らず、次のような構成とすることもできる。
第1の構成としては、比較先レイアウト結果2のレイアウト属性および比較元レイアウト結果4のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度を算出し、比較先レイアウト結果2の情報格納枠の種別および比較元レイアウト結果4の情報格納枠の種別に基づいて種別類似度を算出し、算出した属性類似度および算出した種別類似度に基づいてレイアウト結果の類似度を算出する。
In the first embodiment, the similarity of the layout result is calculated based on the layout attribute of the comparison destination layout result 2 and the layout attribute of the comparison source layout result 4. However, the present invention is not limited to this. The following configuration can also be adopted.
As a first configuration, the attribute similarity is calculated based on the layout attribute of the comparison destination layout result 2 and the layout attribute of the comparison source layout result 4, and the type of the information storage frame of the comparison destination layout result 2 and the comparison source layout result The type similarity is calculated based on the type of the information storage frame 4, and the similarity of the layout result is calculated based on the calculated attribute similarity and the calculated type similarity.
これにより、情報格納枠のレイアウト属性および種別に基づいて類似度が算出されるので、各情報格納枠ごとの類否を考慮してレイアウト結果の類似度を算出することができる。したがって、従来に比して、読み手の主観を比較的適切に反映した類似度を算出することができる。
第2の構成としては、比較先レイアウト結果2のレイアウト属性および比較元レイアウト結果4のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度を算出し、比較先レイアウト結果2の格納情報の内容および比較元レイアウト結果4の格納情報の内容に基づいて内容類似度を算出し、算出した属性類似度および内容類似度に基づいてレイアウト結果の類似度を算出する。
Thereby, since the similarity is calculated based on the layout attribute and type of the information storage frame, the similarity of the layout result can be calculated in consideration of the similarity of each information storage frame. Therefore, it is possible to calculate the degree of similarity reflecting the reader's subjectivity relatively appropriately as compared with the conventional case.
As a second configuration, the attribute similarity is calculated based on the layout attribute of the comparison destination layout result 2 and the layout attribute of the comparison source layout result 4, and the contents of the storage information of the comparison destination layout result 2 and the comparison source layout result 4 The content similarity is calculated based on the contents of the stored information, and the similarity of the layout results is calculated based on the calculated attribute similarity and content similarity.
これにより、情報格納枠のレイアウト属性および格納情報の内容に基づいて類似度が算出されるので、各情報格納枠ごとの類否、および格納情報の内容の類否を考慮してレイアウト結果の類似度を算出することができる。したがって、従来に比して、読み手の主観を比較的適切に反映した類似度を算出することができる。
また、上記第1の実施の形態においては、情報格納枠の各種別ごとに選択レイアウト属性の属性類似度を算出するように構成したが、これに限らず、情報格納枠の種別によらず、各レイアウト属性ごとに属性類似度を算出するように構成することもできる。
As a result, the similarity is calculated based on the layout attribute of the information storage frame and the content of the stored information. Therefore, the similarity of the layout results in consideration of the similarity of each information storage frame and the similarity of the content of the stored information The degree can be calculated. Therefore, it is possible to calculate the degree of similarity reflecting the reader's subjectivity relatively appropriately as compared with the conventional case.
Further, in the first embodiment, the attribute similarity of the selected layout attribute is calculated for each type of information storage frame. However, the present invention is not limited to this, regardless of the type of information storage frame. It can also be configured to calculate the attribute similarity for each layout attribute.
また、上記第1の実施の形態においては、最大値をとる関数maxを利用し、その関数により各レイアウト属性の属性類似度を算出するように構成したが、これに限らず、読み手の主観に対する影響度合いを表した関数を作成し、その関数により各レイアウト属性の属性類似度を算出するように構成することもできる。
また、上記第1の実施の形態においては、レイアウト属性として図4のレイアウト属性テーブル400のレイアウト属性を利用したが、これに限らず、ジャンプ率や黒率(黒の割合)、図版率などを利用することもできる。
In the first embodiment, the function max that takes the maximum value is used, and the attribute similarity of each layout attribute is calculated by the function. However, the present invention is not limited to this. It is also possible to create a function representing the degree of influence and calculate the attribute similarity of each layout attribute by the function.
In the first embodiment, the layout attribute of the layout attribute table 400 of FIG. 4 is used as the layout attribute. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and the jump rate, black rate (black rate), plate rate, etc. It can also be used.
また、上記第2の実施の形態においては、所定の重み付け係数を利用するように構成したが、より具体的には、重み付け係数として、例えば「視覚度」の高いイラスト、画像の重みを大きくすると、より人の感性に合った類似度が算出できるようになる。
また、上記第2および第3の実施の形態においては、各重み付けの結果を加算することによりレイアウト結果の類似度を算出するように構成したが、これに限らず、各重み付けの結果の平均値をとったり、それ以外の計算方法によりレイアウト結果の類似度を算出するように構成することもできる。
In the second embodiment, a predetermined weighting factor is used. More specifically, as the weighting factor, for example, an illustration with high “visibility” or an image weight is increased. Thus, it becomes possible to calculate a similarity that more suits the human sensitivity.
In the second and third embodiments, the similarity of the layout results is calculated by adding the weighting results. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and the average value of the weighting results is not limited thereto. Alternatively, the similarity of layout results can be calculated by other calculation methods.
また、上記第2の実施の形態においては、属性類似度の算出において、各情報格納枠のサイズと配置位置を一緒に扱ったが、これに限らず、サイズと配置位置それぞれで類似度を求め、平均や重み付け演算などによって、配置位置類似度を求めることもできる。
これにより、読み手の主観をさらに適切に反映した類似度を算出することができる。
また、上記第2および第3の実施の形態においては、TFIDF法により内容類似度を算出するように構成したが、これに限らず、表記的な類似度や、ひらがなの多さ、空白の多さなど、より見た目に影響しそうな内容の類似度を利用して内容類似度を算出するように構成することもできる。
In the second embodiment, the size and arrangement position of each information storage frame are handled together in the calculation of the attribute similarity. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and the similarity is obtained for each size and arrangement position. The arrangement position similarity can also be obtained by averaging or weighting calculation.
This makes it possible to calculate a similarity that more appropriately reflects the subjectivity of the reader.
In the second and third embodiments, the content similarity is calculated by the TFIDF method. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and the notation similarity, the number of hiragana, and the number of blanks are increased. The content similarity may be calculated using the similarity of the content that is likely to affect the appearance.
また、上記第1ないし第3の実施の形態においては、入力したユーザIDに対応する業種情報と同一の業種情報をユーザ情報登録DB10のなかから検索して該当の業種情報に対応するユーザIDを読み出し、読み出したユーザIDに対応する比較元レイアウト結果4をレイアウト結果登録DB12から読み出すように構成したが、これに限らず、図5のユーザ情報登録テーブル420に代えて図18のユーザ情報登録テーブル420を設け、入力したユーザIDに対応する顧客IDと同一の顧客IDをユーザ情報登録DB10のなかから検索して該当の顧客IDに対応するユーザIDを読み出し、読み出したユーザIDに対応する比較元レイアウト結果4をレイアウト結果登録DB12から読み出すように構成することもできる。
In the first to third embodiments, the same industry information as the industry information corresponding to the input user ID is searched from the user
図18は、ユーザ情報登録テーブル420のデータ構造を示す図である。
ユーザ情報登録テーブル420には、図18に示すように、各ユーザごとに1つのレコードが登録されている。各レコードは、ユーザIDを登録したフィールド422と、ユーザが管理する顧客を識別するための顧客IDを登録したフィールド426とを含んで構成されている。フィールド426には、複数の顧客IDを登録することが可能である。
FIG. 18 is a diagram showing the data structure of the user information registration table 420.
In the user information registration table 420, as shown in FIG. 18, one record is registered for each user. Each record includes a
図18の例では、第1段目のレコードには、ユーザIDとして「USER1」が、顧客IDとして「Client1」がそれぞれ登録されている。これは、ユーザID「USER1」のユーザが顧客ID「Client1」の顧客を抱えていることを示している。
ステップS302では、ステップS100で入力したユーザIDに対応する顧客IDと同一の顧客IDをユーザ情報登録DB10のなかから検索して該当の顧客IDに対応するユーザIDを読み出し、ステップS304に移行する。該当の顧客IDに対応するユーザIDが複数存在するときは、それらユーザIDをすべて読み出す。
In the example of FIG. 18, “USER1” is registered as the user ID and “Client1” is registered as the customer ID in the first record. This indicates that the user with the user ID “USER1” has a customer with the customer ID “Client1”.
In step S302, a user ID corresponding to the user ID input in step S100 is searched from the user
これにより、同一の顧客を抱えている異なるユーザがその顧客に対してレイアウト結果を提供する場合は、一方のユーザから提供されるレイアウト結果は、他方のユーザから提供されるレイアウト結果との類似度に応じて修正の度合いが大きくなるように修正されるので、従来に比して、独自性の高いレイアウトを実現することができる。
また、上記第1ないし第3の実施の形態においては、入力したユーザIDに対応する業種情報と同一の業種情報をユーザ情報登録DB10のなかから検索して該当の業種情報に対応するユーザIDを読み出し、読み出したユーザIDに対応する比較元レイアウト結果4をレイアウト結果登録DB12から読み出すように構成したが、これに限らず、業種間に類似関係を設定し、入力したユーザIDに対応する業種情報と類似の業種情報をユーザ情報登録DB10のなかから検索して該当の業種情報に対応するユーザIDを読み出し、読み出したユーザIDに対応する比較元レイアウト結果4をレイアウト結果登録DB12から読み出すように構成することもできる。
As a result, when different users who have the same customer provide layout results to the customer, the layout result provided by one user is similar to the layout result provided by the other user. Since the correction is made so that the degree of correction is increased according to the above, a unique layout can be realized as compared with the conventional case.
In the first to third embodiments, the same business type information as the business type information corresponding to the input user ID is searched from the user
このような改良は、同一の顧客を抱えている異なるユーザがその顧客に対してレイアウト結果を提供する場合の構成においても同様に行うことができる。すなわち、顧客間に類似関係を設定し、入力したユーザIDに対応する顧客IDと類似の顧客IDをユーザ情報登録DB10のなかから検索して該当の顧客IDに対応するユーザIDを読み出し、読み出したユーザIDに対応する比較元レイアウト結果4をレイアウト結果登録DB12から読み出すように構成することもできる。
Such an improvement can be similarly performed in a configuration in which different users who have the same customer provide layout results to the customer. That is, a similar relationship is set between customers, a customer ID similar to the customer ID corresponding to the input user ID is searched from the user
また、上記第1ないし第3の実施の形態においては、ユーザ情報登録テーブル420の利用年月日を利用することについて特に説明しなかったが、業種情報に基づいて読み出した比較元レイアウト結果4に代えて、現在の年月日を基準として過去所定日(例えば、過去1年間)以内に利用された比較元レイアウト結果4を競合のものとみなし、利用年月日および現在の年月日に基づいて対象期間内の比較元レイアウト結果4を読み出し、これを利用するように構成することもできる。例えば、図6の利用履歴情報登録テーブル440において「USER1」の場合、「Layout1 USER1 2002/10/23」、「Layout4 USER1 2003/2/14」と登録されているが、利用年月日が2003年11月でかつ1年以上前のものは、競合のものとは見なさない。 In the first to third embodiments, the use date of the user information registration table 420 is not particularly described. However, the comparison source layout result 4 read based on the business type information is used. Instead, the comparison source layout result 4 used within the past predetermined date (for example, the past one year) based on the current date is regarded as a competitor, and based on the use date and the current date The comparison source layout result 4 within the target period can be read out and used. For example, in the case of “USER1” in the usage history information registration table 440 of FIG. 6, “Layout1 USER1 2002/10/23” and “Layout4 USER1 2003/2/14” are registered, but the usage date is 2003. Those that were in November and more than a year ago are not considered to be competitors.
これにより、同じようなレイアウト結果がすぐに作られるのを抑制でき、かつ、少ないレイアウト結果の場合でも効率的に独自性の高いレイアウトを実現することができる。
このような改良は、同一の顧客を抱えている異なるユーザがその顧客に対してレイアウト結果を提供する場合の構成においても同様に行うことができる。
また、上記第1ないし第3の実施の形態においては、自動レイアウト処理のレイアウト結果を修正するように構成したが、これに限らず、例えば、デザイナ等が直接デザインしたレイアウト結果を修正するように構成することもできる。
Thereby, it is possible to suppress the generation of a similar layout result immediately, and it is possible to efficiently realize a highly unique layout even when there are few layout results.
Such an improvement can be similarly performed in a configuration in which different users having the same customer provide layout results to the customer.
In the first to third embodiments, the layout result of the automatic layout process is corrected. However, the present invention is not limited to this. For example, the layout result directly designed by a designer or the like is corrected. It can also be configured.
また、上記第1ないし第3の実施の形態においては、ユーザ情報登録DB10、レイアウト結果登録DB12、レイアウト要素登録DB40およびテンプレート登録DB42をレイアウト装置100の外部装置として設けたが、これに限らず、これらDBをネットワーク上の任意の端末に設け、レイアウト装置100とそれら端末とをネットワークで接続し、レイアウト装置100がそれら端末のDBを利用するように構成することもできる。
In the first to third embodiments, the user
また、上記第1ないし第3の実施の形態において、図7、図8、図9、図10、図14および図16のフローチャートに示す処理を実行するにあたってはいずれも、ROM32にあらかじめ格納されている制御プログラムを実行する場合について説明したが、これに限らず、これらの手順を示したプログラムが記憶された記憶媒体から、そのプログラムをRAM34に読み込んで実行するようにしてもよい。
In the first to third embodiments, the processes shown in the flowcharts of FIGS. 7, 8, 9, 10, 14, and 16 are all stored in the
ここで、記憶媒体とは、RAM、ROM等の半導体記憶媒体、FD、HD等の磁気記憶型記憶媒体、CD、CDV、LD、DVD等の光学的読取方式記憶媒体、MO等の磁気記憶型/光学的読取方式記憶媒体であって、電子的、磁気的、光学的等の読み取り方法のいかんにかかわらず、コンピュータで読み取り可能な記憶媒体であれば、あらゆる記憶媒体を含むものである。 Here, the storage medium is a semiconductor storage medium such as RAM or ROM, a magnetic storage type storage medium such as FD or HD, an optical reading type storage medium such as CD, CDV, LD, or DVD, or a magnetic storage type such as MO. / Optical reading type storage media, including any storage media that can be read by a computer regardless of electronic, magnetic, optical, or other reading methods.
また、上記第1ないし第3の実施の形態においては、本発明に係る類似度算出システムおよび類似度算出プログラム、並びに類似度算出方法を、自動レイアウト処理のレイアウト結果を修正する場合について適用したが、これに限らず、本発明の主旨を逸脱しない範囲で他の場合にも適用可能である。 In the first to third embodiments, the similarity calculation system, the similarity calculation program, and the similarity calculation method according to the present invention are applied to the case where the layout result of the automatic layout process is corrected. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and can be applied to other cases without departing from the gist of the present invention.
100…レイアウト装置,2…比較先レイアウト結果,4…比較元レイアウト結果,6…修正レイアウト結果,10…ユーザ情報登録DB,12…レイアウト結果登録DB,14…比較先入力部,16…比較元入力部,18…類似度算出部,20…レイアウト修正部,30…CPU,32…ROM,34…RAM,38…I/F,39…バス,40…レイアウト要素登録DB,42…テンプレート登録DB,360…レイアウト領域,362…タイトル情報格納枠,364,368…画像情報格納枠,366,370…文字情報格納枠,376…文字情報格納枠,372…フローオブジェクト格納枠,400…レイアウト属性テーブル,420…ユーザ情報登録テーブル,440…利用履歴情報登録テーブル
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (3)
比較先となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度を算出する属性類似度算出手段と、
前記比較先レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートおよび前記比較元レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートに基づいてテンプレート類似度を算出するテンプレート類似度算出手段と、
前記比較先レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容および前記比較元レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容に基づいて内容類似度を算出する内容類似度算出手段と、
前記属性類似度算出手段で算出した属性類似度、前記テンプレート類似度算出手段で算出したテンプレート類似度および前記内容類似度算出手段で算出した内容類似度に基づいて前記類似度を算出するレイアウト結果類似度算出手段とを備えることを特徴とする類似度算出システム。 A storage information selection means for selecting the storage information from storage information storage means for storing a plurality of storage information; and a layout means for performing a layout based on the storage information selected by the storage information selection means. A means for performing layout by storing the storage information in the information storage frame according to a layout template that defines a layout state in which the information storage frame is associated with a layout attribute of the information storage frame and arranged in a predetermined layout area. A system for calculating the similarity of layout results obtained from a system,
Attribute similarity calculating means for calculating attribute similarity based on the layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison destination and the layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison source;
A template similarity calculation means for calculating a template similarity based on a layout template used for obtaining the comparison destination layout result and a layout template used for obtaining the comparison source layout result;
Content similarity calculating means for calculating content similarity based on the content of the storage information of the comparison destination layout result and the content of the storage information of the comparison source layout result;
Layout result similarity that calculates the similarity based on the attribute similarity calculated by the attribute similarity calculation unit, the template similarity calculated by the template similarity calculation unit, and the content similarity calculated by the content similarity calculation unit A similarity calculation system comprising: a degree calculation means.
比較先となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度を算出する属性類似度算出手段、前記比較先レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートおよび前記比較元レイアウト
結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートに基づいてテンプレート類似度を算出するテンプレート類似度算出手段、前記比較先レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容および前記比較元レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容に基づいて内容類似度を算出する内容類似度算出手段、並びに、前記属性類似度算出手段で算出した属性類似度、前記テンプレート類似度算出手段で算出したテンプレート類似度および前記内容類似度算出手段で算出した内容類似度に基づいて前記類似度を算出するレイアウト結果類似度算出手段として実現される処理をコンピュータに実行させるためのプログラムであることを特徴とする類似度算出プログラム。 A storage information selection means for selecting the storage information from storage information storage means for storing a plurality of storage information; and a layout means for performing a layout based on the storage information selected by the storage information selection means. A means for performing layout by storing the storage information in the information storage frame according to a layout template that defines a layout state in which the information storage frame is associated with a layout attribute of the information storage frame and arranged in a predetermined layout area. A program for calculating the similarity of layout results obtained from a program,
Attribute similarity calculation means for calculating an attribute similarity based on a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison destination and a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison source, a layout template used to obtain the comparison destination layout result, and Template similarity calculation means for calculating a template similarity based on the layout template used to obtain the comparison source layout result, the content of the storage information of the comparison destination layout result, and the content of the storage information of the comparison source layout result Content similarity calculating means for calculating content similarity based on the above, attribute similarity calculated by the attribute similarity calculating means, template similarity calculated by the template similarity calculating means, and content similarity calculating means The similarity is calculated based on the content similarity Layout result similarity similarity calculation program, characterized in that the process is realized as calculating means is a program to be executed by a computer.
前記コンピュータが、比較先となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性および比較元となる前記レイアウト結果のレイアウト属性に基づいて属性類似度を算出する属性類似度算出ステップと、
前記コンピュータが、前記比較先レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートおよび前記比較元レイアウト結果を得るのに利用したレイアウトテンプレートに基づいてテンプレート類似度を算出するテンプレート類似度算出ステップと、
前記コンピュータが、前記比較先レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容および前記比較元レイアウト結果の格納情報の内容に基づいて内容類似度を算出する内容類似度算出ステップと、
前記コンピュータが、前記属性類似度算出ステップで算出した属性類似度、前記テンプレート類似度算出ステップで算出したテンプレート類似度および前記内容類似度算出ステップで算出した内容類似度に基づいて前記類似度を算出するレイアウト結果類似度算出ステップとを含むことを特徴とする類似度算出方法。 Storage information selection means for selecting the storage information from storage information storage means for storing a plurality of storage information; and layout means for performing layout based on the storage information selected by the storage information selection means. A means for performing layout by storing the storage information in the information storage frame according to a layout template that defines a layout state in which the information storage frame is associated with a layout attribute of the information storage frame and arranged in a predetermined layout area. A method of calculating the similarity of layout results obtained from a system by a computer ,
An attribute similarity calculating step in which the computer calculates an attribute similarity based on a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison destination and a layout attribute of the layout result as a comparison source;
A template similarity calculating step in which the computer calculates a template similarity based on a layout template used to obtain the comparison destination layout result and a layout template used to obtain the comparison source layout result;
A content similarity calculation step in which the computer calculates a content similarity based on the content of the storage information of the comparison destination layout result and the content of the storage information of the comparison source layout result;
The computer calculates the similarity based on the attribute similarity calculated in the attribute similarity calculation step, the template similarity calculated in the template similarity calculation step, and the content similarity calculated in the content similarity calculation step And a layout result similarity calculating step.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003327756A JP4433741B2 (en) | 2003-09-19 | 2003-09-19 | Similarity calculation system, similarity calculation program, and similarity calculation method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003327756A JP4433741B2 (en) | 2003-09-19 | 2003-09-19 | Similarity calculation system, similarity calculation program, and similarity calculation method |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005092707A JP2005092707A (en) | 2005-04-07 |
| JP2005092707A5 JP2005092707A5 (en) | 2006-10-12 |
| JP4433741B2 true JP4433741B2 (en) | 2010-03-17 |
Family
ID=34457531
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003327756A Expired - Fee Related JP4433741B2 (en) | 2003-09-19 | 2003-09-19 | Similarity calculation system, similarity calculation program, and similarity calculation method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4433741B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11494553B2 (en) | 2019-03-04 | 2022-11-08 | Fujifilm Business Innovation Corp. | Document creation assistance apparatus and non-transitory computer readable medium |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006318219A (en) * | 2005-05-12 | 2006-11-24 | Fujitsu Ltd | Similar slide search program and search method |
| JP4872079B2 (en) | 2006-05-19 | 2012-02-08 | 国立大学法人長岡技術科学大学 | Sentence update amount evaluation program |
| JP6551847B2 (en) * | 2016-09-14 | 2019-07-31 | 株式会社プロフィールド | Layout apparatus, layout method, and program |
| CN106844592A (en) * | 2017-01-12 | 2017-06-13 | 无线生活(杭州)信息科技有限公司 | A kind of databases comparison method and device |
| CN111694978B (en) * | 2020-05-20 | 2023-04-28 | Oppo(重庆)智能科技有限公司 | Image similarity detection method and device, storage medium and electronic equipment |
-
2003
- 2003-09-19 JP JP2003327756A patent/JP4433741B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11494553B2 (en) | 2019-03-04 | 2022-11-08 | Fujifilm Business Innovation Corp. | Document creation assistance apparatus and non-transitory computer readable medium |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2005092707A (en) | 2005-04-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4089655B2 (en) | Layout system, layout program, and layout method | |
| US10846524B2 (en) | Table layout determination using a machine learning system | |
| JP3835193B2 (en) | Digital content creation system and digital content creation program | |
| JP5623079B2 (en) | Automatic generation of form definitions from hardcopy forms | |
| JP4572669B2 (en) | Layout rule generation system, layout system, layout rule generation method, and layout rule generation program | |
| CN110874618B (en) | OCR template learning method and device based on small sample, electronic equipment and medium | |
| US7424672B2 (en) | System and method of specifying image document layout definition | |
| JP3835191B2 (en) | Digital content creation system and digital content creation program | |
| JP2012059248A (en) | System, method, and program for detecting and creating form field | |
| JP4079087B2 (en) | Layout system | |
| JP3835194B2 (en) | Digital content creation system and digital content creation program | |
| JP4146620B2 (en) | Digital content creation system and digital content creation program | |
| JP2007049388A (en) | Image processing apparatus and control method thereof, and program | |
| US20080131000A1 (en) | Method for generating typographical line | |
| JP4055494B2 (en) | Layout system, layout program, and layout method | |
| EP1278368A2 (en) | Document filing apparatus for storing information added to a document file | |
| JP4433741B2 (en) | Similarity calculation system, similarity calculation program, and similarity calculation method | |
| JP2009110500A (en) | Document processing apparatus, document processing method and program of document processing apparatus | |
| US20050055636A1 (en) | Dynamic editing of multimedia content for real-time applications | |
| JP2009031937A (en) | Form image processing apparatus and form image processing program | |
| JP4518212B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus and program | |
| JP4031189B2 (en) | Document recognition apparatus and document recognition method | |
| US20040205608A1 (en) | System and method for rearranging the layout of a business card | |
| JP4517822B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus and program | |
| KR20090111912A (en) | Online ordering method and system for real time cyan production |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20060825 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20060825 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20090811 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20091006 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20091027 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20091113 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20091208 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20091221 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130108 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |