JP4194130B2 - Color image forming apparatus - Google Patents
Color image forming apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4194130B2 JP4194130B2 JP09668998A JP9668998A JP4194130B2 JP 4194130 B2 JP4194130 B2 JP 4194130B2 JP 09668998 A JP09668998 A JP 09668998A JP 9668998 A JP9668998 A JP 9668998A JP 4194130 B2 JP4194130 B2 JP 4194130B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- intermediate transfer
- charge
- transfer
- charging
- applying
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Electrostatic Charge, Transfer And Separation In Electrography (AREA)
- Control Or Security For Electrophotography (AREA)
- Color Electrophotography (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、電子写真方式の複写機やレーザプリンタ等のカラー画像形成装置に関するものである。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
図8は、従来のカラー画像形成装置を示す概略図である。
【0003】
カラー画像形成装置は、像担持体として感光ドラム1を有し、この感光ドラム1は、図示しない駆動手段によって矢印方向に回転され、その回転過程で感光ドラム1に当接した一次帯電ローラ2により表面が一様に帯電される。ついで、露光装置3によりイエローの画像模様に従ったレーザ光Lが感光ドラム1の表面に照射され、感光ドラム1の表面に静電潜像が形成される。
【0004】
回転支持体11に4個の現像器4a、4b、4c、4dが支持されており、感光ドラム1の回転が進むと、回転支持体11の回転により、イエロートナーを収容した現像器4aが感光ドラム1と対向した位置(現像位置)に移動し、このように選択された現像器4aにより感光ドラム1上の潜像が現像される。潜像は現像によりイエロートナー像として可視化される。
【0005】
感光ドラム1に隣接して、感光ドラム1と略同速度で矢印方向に回転する中間転写ベルト5が設置されており、感光ドラム1上に形成されたイエロートナー像は、1次転写バイアスを印加した1次転写ローラ8aにより、中間転写ベルト5の表面に転写される(1次転写)。以上の行程をイエロー、マゼンタ、シアン、ブラックの4色について行うことにより、中間転写ベルト5上に4色のトナー像を重ね合わせて転写したカラー画像が形成される。
【0006】
つぎに転写材カセット12内からピックアップローラ13によって転写材が取り出され、所定のタイミングで中間転写ベルト5に供給される。これと同時に2次転写バイアスを印加された2次転写ローラ8bが転写材を挟んで中間転写ベルト5に当接し、中間転写ベルト5上の4色のトナー像が転写材の表面に一括して転写される(2次転写)。
【0007】
このようにして4色のトナー像を転写された転写材は、搬送ベルト14によって定着装置6まで搬送され、そこで加熱および加圧によりトナーが転写材に溶融固定されて、カラーの定着画像が得られる。4色のトナー像の転写が終了して、中間転写ベルト5の表面に残留した2次転写残りのトナーは、クリーニングローラ15により電荷が付与された後、1次転写ローラ8aにより感光ドラム1上に逆転写され、中間転写ベルト5から除去される。一方、感光ドラム1上の1次転写残りトナーおよび逆転写された2次転写残りトナーは、クリーニング装置の公知のブレード手段7により感光ドラム1から除去される。
【0008】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
ところで、上記の中間転写ベルト5は、高温高湿環境下や長期間の使用による抵抗変動で、ベルトの時定数τが下がる。ここで、時定数τとは、ベルトをVo (V)に帯電して、それがVo /e(V)(eは自然対数の底)に減衰するまでの時間である。
【0009】
この中間転写ベルト5の時定数が下がると、ドラムゴーストが発生する問題があった。
【0010】
すなわち、2色目以降の1次転写の際、中間転写ベルト5上に前色までの1次転写により所定の電荷が保持されており、中間転写ベルト5上の電位が下がっているので、これを前提に2色目以降の1次転写バイアスを決定している。中間転写ベルト5の時定数τが低下すると、中間転写ベルト5上に所定の電荷が保持できなくなり、中間転写ベルト5上の電位が高くなる。従って、上記で決定した転写バイアスと同一のバイアスを印加しても、所望の電位差以上の電位差になり、このため感光ドラム1へ過剰な電流が流れてしまい、ドラムゴーストが発生する。
【0011】
また、中間転写ベルト5の時定数τが顕著に低下すると、トナーの飛び散り等の不具合も発生し、画質が劣化する。
【0012】
このように、中間転写ベルト5の寿命を決める主たる要因は、中間転写ベルト5の時定数τの低下である。従って、時定数が所定値に低下したら、中間転写ベルト5の寿命をユーザーに知らせることが望ましい。
【0013】
しかしながら、従来は、プリント枚数や中間転写ベルトの回転数等の予め定めた条件が所定値に達したことにより、中間転写ベルト5が寿命に至ったものとしてユーザーに知らせていた。しかし、中間転写ベルト5の時定数の低下は、使用環境や使用モード等によって変動する。このため、正常にプリントできるにもかかわらず、中間転写ベルト5を交換してしまうことがあった。
【0014】
本発明の目的は、中間転写体の時定数τが下がっても、ドラムゴーストのない高品質の画像を得ることができ、また中間転写体の寿命告知を使用環境や使用モード等によらずに常に最適時期に行うことを可能としたカラー画像形成装置を提供することである。
【0015】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上記目的は、本発明にかかるカラー画像形成装置にて達成される。要約すれば、本発明は、像担持体と、中間転写体と、前記像担持体を一様に帯電する帯電手段と、帯電した前記像担持体を露光し、現像して各色のトナー像が得られるたびに、そのトナー像を前記中間転写体に重ね合わせて転写する1次転写手段と、前記中間転写体に転写された各色のトナー像を一括して転写材に転写する2次転写手段とを有するカラー画像形成装置において、複数の定電圧電源と、前記複数の定電圧電源からの電圧の印加により前記中間転写体に電圧を印加し、前記中間転写体に電荷を付与する複数の電荷付与手段と、前記複数の電荷付与手段による電圧の印加によって発生する前記中間転写体に流れる電流を検知する電流検知手段とを有し、前記電荷付与手段により前記中間転写体の回動過程で前記中間転写体の同一箇所に連続して複数回電圧を印加し、前記電流検知手段によって複数回検知したそれぞれの電流値に応じて、前記1次転写手段に印加する1次転写バイアスを制御することを特徴とするカラー画像形成装置である。
【0016】
本発明の一実施態様によれば、前記電荷付与手段が2つであり、前記1次転写手段が前記電荷付与手段の一方を兼ね、前記2次転写手段が前記電荷付与手段の他方を兼ねる。
【0017】
本発明の他の実施態様によれば、前記帯電手段とは別の第2の帯電手段と、第2の帯電手段からの帯電バイアスの印加により、前記中間転写体上の2次転写残りのトナーに電荷を付与するクリーニング部材とがさらに設置され、前記電荷を付与された2次転写残りのトナーは、前記1次転写手段によるトナー像の中間転写体への転写と同時に像担持体に逆転写されるようになっており、そして前記電荷付与手段が2つであり、前記第2の帯電手段が前記電荷付与手段の一方を兼ね、前記1次転写手段が前記電荷付与手段の他方を兼ねる。
本発明の他の実施態様によれば、前記帯電手段とは別の第2の帯電手段と、第2の帯電手段からの帯電バイアスの印加により、前記中間転写体上の2次転写残りのトナーに電荷を付与するクリーニング部材とがさらに設置され、前記電荷を付与された2次転写残りのトナーは、前記1次転写手段によるトナー像の中間転写体への転写と同時に像担持体に逆転写されるようになっており、そして前記電荷付与手段が2つであり、前記第2の帯電手段が前記電荷付与手段の一方を兼ね、前記2次転写手段が前記電荷付与手段の他方を兼ねる。
【0018】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明の実施例を図面に即して詳細に説明する。
【0019】
実施例1
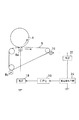
図1は、本発明のカラー画像形成装置の要部を示す概略図である。本発明は、中間転写体である中間転写ベルト5に電圧を印加して、そのときの電流値から中間転写ベルト5の時定数τを推定し、1次転写ローラ8aに印加する1次転写バイアス等を制御することが大きな特徴である。本発明のカラー画像形成装置の構成自体は、図8に示した従来のカラー画像形成装置と基本的に同じであるので、以下必要に応じて図8を援用して説明する。
【0020】
図8の従来のカラー画像形成装置では、1色目から4色目までのトナー像を1色目から4色目まで予め決められた転写バイアスにより、順次中間ベルト5上に1次転写していく。このときの転写バイアスは、中間転写ベルト5の表面電位と感光ドラム1の表面電位(暗部電位VD )の電位差が所定の電位になるように設定する。1色目の転写前には中間転写ベルト5上には前残留電荷がないように除電されているので、印加された1色目の転写バイアスVt1が中間転写ベルト5の表面電位となるため、差分Vt1−VD が所定の値になるようにVt1を設定する。2色目転写時には、中間転写ベルト5上には1色目転写時に与えられた電荷(転写バイアスとは逆極性)が残っているため、中間転写ベルトの表面電位は印加された2色目の転写バイアスよりも低くなる(Vt2−ΔV1 )。従って、Vt2−ΔV1 −VD が所定の値になるようにVt2を設定する。同様に、3色目、4色目の転写バイアスも、前色までの残留電荷を考慮して設定している。
【0021】
しかし、中間転写ベルト5はプリント枚数が進むにつれて表面に窒素酸化物等が付着し、それが吸湿することにより徐々に表面抵抗が下がり、時定数τも低下してしまう。これは、雰囲気の温湿度によっても変わり、高温高湿環境が最も顕著である。
【0022】
このように、中間転写ベルト5の時定数が下がると、電荷保持能力が低下してしまう。これにより、前色までの残留電荷が減るため、所望の電位差よりも大きな電位差が発生し、転写電流が増加してしまう。転写電流が増加する、すなわち感光ドラム1が付与される電荷が増加すると、感光ドラム1の次回の帯電で所望の電位に帯電されず、ドラムゴーストが発生する。
【0023】
そこで、本実施例では、図1に示すように、中間転写ベルト5に電荷を付与する手段として接離可能な電荷付与ローラ16を設置し、中間転写体5が2回転する間に、定電圧電源22からの電荷付与ローラ16への電圧の印加によって、電荷付与ローラ16で中間転写ベルト5の同一箇所に電圧を連続的に2回印加して中間転写ベルト5に2回電荷を付与し、そのとき中間転写ベルト5に流れる各電流値を電源22に接続された電流検知手段24により検知した。そして検知した2回分の電流値のそれぞれに応じて、CPU20により中間転写ベルト5の時定数τを推定し、これに基づき1次転写電源18により1次転写ローラ8aに印加する1次転写バイアスを制御するようにした。
【0024】
本実施例によれば、中間転写ベルト5は、体積抵抗105 Ωcm以下のNBR(ニトリルゴム)を厚さ1mm、幅230mm、周長140πmmの円筒状にシームレス成形し、その上に高抵抗の誘電体層を厚さ50μm程度にコートして構成した。1次転写ローラ8aには、体積抵抗105 Ωcm以下のEPDMによる直径14mm、幅220mmのローラを用いた。電荷付与ローラ16には、体積抵抗107 〜108 ΩcmのEPDMによる直径18mm、幅220mmのローラを用いた。
【0025】
1次転写バイアスを印加したときの中間転写ベルト5の時定数τの変化に対する転写電流It の変化を図2に示す。図2において、It1、It2、It3、It4は、1色目、2色目、3色目および4色目の転写電流で、それぞれ1次転写バイアスとして100V、550V、700Vおよび850Vを印加した。
【0026】
図2から明らかなように、各色とも中間転写ベルト5の時定数τが小さくなるほど多く、また転写電流は3色目、4色目と後の色ほど多く、時定数τの変化に対する転写電流の差分は3色目、4色目で特に大きく、4色目が最も大きい。ドラムゴーストは、転写電流が9μAを超える3色目、4色目で発生した。
【0027】
500Vの電圧を印加した電荷付与ローラ16により中間転写ベルト5の同一箇所に2回連続して電荷を付与したときの時定数τに対する転写電流I1 、I2 の変化を図3に示す。
【0028】
図3に示されるように、この場合も、図2の転写電流の変化と同様の傾向を示していることが分かる。また、2つの電流値の比I2 /I1 は、時定数τが大きくなるほど小さくなるような相関があることが分かる。
【0029】
そこで、本実施例では、1色目、2色目、3色目、4色目の1次転写バイアスVt10 、Vt20 、Vt30 、Vt40 を以下のように設定した。
【0030】
Vt10 =100(V)
Vt20 =500+100×(1−I2 /I1 )(V)
Vt30 =550+300×(1−I2 /I1 )(V)
Vt40 =600+500×(1−I2 /I1 )(V)
【0031】
これにより、転写電流It10 、It20 、It30 、It40 は図4のようになり、時定数τが下がっても、転写電流が9μAを超えることがなくなり、ドラムゴーストを防止することができる。
【0032】
以上では、電流の測定を2回行ったが、3回以上行うことができるのはいうまでもない。
【0033】
実施例2
前述したように、中間転写ベルト5の時定数τが下がると転写電流が多くなり、次回の帯電で感光ドラム1が所望の電位まで達せず、ドラムゴーストが発生する。つまり、ドラムゴーストは帯電能力以上の電荷が転写により付与されることにより発生する。そこで、本実施例では、転写電流が多い(中間転写ベルトの時定数τが低い)ときに、帯電能力を上げてやるように帯電ローラ2の帯電バイアスを制御した。
【0034】
従来、帯電バイアスはVdc=−550Vの直流成分にVpp=2.0kV、周波数1.2kHz の交流成分を重畳したものを用いていた。このバイアスでは、転写電流が9μA以上になると、ドラムゴーストが発生した。
【0035】
帯電バイアスのVppを変更し、転写電流に対するドラムゴーストの発生状況を実験した結果を表1に示す。表1において、符号の○はドラムゴーストが発生しないことを示し、×はドラムゴーストが発生することを示す。
【0036】
【表1】
【0037】
表1によれば、Vppを高くすることによって帯電能力が上がっていることが分かる。
【0038】
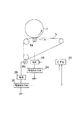
これを踏まえて、本実施例では、図5に示すように、電荷付与ローラ16により電圧を中間転写ベルト5の同一箇所に連続して印加し、その各印加時、中間転写ベルト5に流れる電流値を電流検知手段24で検知し、CPU20により中間転写ベルト5の時定数τを推定する。そして、それに基づき帯電バイアス電源26により帯電ローラ2に印加する帯電バイアスのVppを制御する。
【0039】
実施例1で説明したように、転写電流は中間転写ベルト5の時定数τと相関があり、τは実施例1と同様に電荷付与ローラ16から中間転写ベルト5の同一箇所に2回連続して電圧を印加したときの各電流値I1 、I2 の比I2 /I1 で推定することができる。
【0040】
そこで、本実施例では、帯電バイアスのVppを以下のように設定した。
【0041】
Vpp=2.6−1.2×(1−I2 /I1 )(kV)
これにより、中間転写ベルト5の時定数τが低下しても、ドラムゴーストを防止することができる。
【0042】
本実施例では、帯電バイアスのVppを変更したが、AC電流値やあるいはVdcや周波数を変更することによっても、同様の効果を得ることができる。
【0043】
実施例3
本実施例では、中間転写ベルト5の時定数τが所定の範囲から外れた場合に、中間転写ベルト5の寿命に関する信号を出力するようにした。
【0044】
詳述すると、中間転写ベルト5の寿命は時定数τの低下に基づいている。中間転写ベルト5のτが著しく低下すると、前述したドラムゴーストだけでなく飛び散り等の不具合も発生し、画質に大きな影響を与えるため、所望のτになったら寿命をユーザーに知らせていた。
【0045】
しかし、時定数τの低下は使用環境、使用モード等によってその速度が変わるが、従来はその中で最も速い条件でのプリント枚数を持って寿命としていた。従って、ほとんどの場合、中間転写ベルト5が依然として使用可能な状態であるにもかかわらず、寿命となってしまっていた。
【0046】
本実施例では、上記不具合を解決するために、図1等において、CPU20に中間転写ベルト5の寿命に関する図示しない報知手段を設置し、上述した方法で中間転写ベルト5の時定数τを推定し、この値が所定の範囲から外れた場合、報知手段に中間転写ベルト5が寿命に達する旨のメッセージを表示して、ユーザーに告知するようにした。
【0047】
本実施例によれば、これにより、使用環境、使用モードに応じて、中間転写ベルト5の最終的な交換時期を常に適切に知らせることができる。
【0048】
実施例4
本実施例では、図6に示すように、1次転写ローラ8aに1次転写バイアスを印加する1次転写電源18に電流検知手段24を接続し、1次転写ローラ8aにより中間転写ベルト5の同一箇所に2回連続して電圧を印加し、電流検知手段24によりそれぞれの電流値を検知して、中間転写ベルト5の時定数τを推定し、1次転写バイアスを制御するようにした。
【0049】
すなわち、前の実施例1では、電荷付与ローラ16、つまり電流測定用の電荷付与手段を設置していたが、本実施例では、1次転写ローラ8aに電荷付与手段に兼ねさせて、特別な電荷付与手段を設置することを省略した。これにより、コストアップをすることなく、実施例1と同様な効果を発揮することができる。
【0050】
本実施例では、1次転写ローラ8aが電荷付与手段を兼ねたが、2次転写ローラ8bや中間転写ベルト5のクリーニングローラ15に電荷付与手段を兼ねさせてもよく、同様な効果を得ることができる。
【0051】
実施例5
本実施例では、図7に示すように、1次転写ローラ8aと2次転写ローラ8bのそれぞれを電荷付与手段とし、1次転写電源18からの1次転写ローラ8aへの電圧の印加、2次転写電源28からの2次転写ローラ8bへの電圧の印加により、中間転写ベルト5の同一箇所に連続して電圧を印加する。そしてそれぞれの電流検知手段24、30により得られた各電流値から、CPU20により中間転写ベルト5の時定数τを推定し、それに基づき電源18により1次転写ローラ8aに印加する1次転写バイアスを制御するようにした。
【0052】
前の実施例1〜4では、1つの電荷付与手段により2回の電流測定を行っていたため、少なくとも中間転写ベルト5を2回転させる必要があったが、本実施例では、中間転写ベルト5の1回転で2回の電流測定が可能なため、制御工程の時間短縮が図れる。
【0053】
本実施例では、電流検知を行って1次転写ローラ8aの1次転写バイアスを制御したが、帯電ローラ2の帯電バイアス制御や、中間転写ベルト5の寿命決定を行ってもよい。
【0054】
また本実施例では、1次転写ローラ8aと2次転写ローラ8bのそれぞれに電荷付与手段を兼ねさせたが、電荷付与手段の1つを中間転写ベルト5のクリーニングローラ15で代用してもよい。さらに3つ以上の電荷付与手段を用いることもできる。
【0055】
本発明における電流検知は、画像形成行程の先頭の非画像部で毎回プリント中に行うのが好ましいが、電源投入時やジャム処理後の作動状態復帰時の前回転のときに行っても、あるいは濃度制御の前後で行ってもよい。
【0056】
【発明の効果】
以上説明したように、本発明によれば、複数の定電圧電源と、複数の定電圧電源からの電圧の印加により中間転写体に電圧を印加し、中間転写体に電荷を付与する複数の電荷付与手段と、複数の電荷付与手段による電圧の印加によって発生する中間転写体に流れる電流を検知する電流検知手段とを有し、電荷付与手段により中間転写体の回動過程で中間転写体の同一箇所に連続して複数回電圧を印加し、電流検知手段によって複数回検知したそれぞれの電流値に応じて、1次転写手段に印加する1次転写バイアスを制御するようにしたので、中間転写体の時定数τが下がっても、ドラムゴーストが発生するのを防止することができる。
【0058】
また、複数の電荷付与手段を設置して、中間転写体の同一箇所に連続して複数回電圧を印加するようにしたので、1次転写バイアス制御等の時間を短縮することができる。さらに、1次転写手段、2次転写手段もしくは中間転写体のクリーニング手段に電荷付与手段を兼ねさせた場合には、コストを上昇することなく、1次転写バイアス制御等を実施することができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明のカラー画像形成装置の一実施例における要部を示す概略構成図である。
【図2】図1の要部に設置された中間転写ベルトに1次転写バイアスを印加したときの中間転写ベルトの時定数τの変化に対する転写電流It の変化を示す図である。
【図3】図1の要部に設置された電荷付与ローラにより中間転写ベルトの同一箇所に2回連続して電荷を付与したときの時定数τに対する転写電流I1 、I2 の変化を示す図である。
【図4】図1の実施例における制御を行ったときの中間転写ベルトの時定数τに対する転写電流の変化を示す図である。
【図5】本発明の他の一実施例における要部を示す概略構成図である。
【図6】本発明のさらに他の一実施例における要部を示す概略構成図である。
【図7】本発明のさらに他の一実施例における要部を示す概略構成図である。
【図8】従来のカラー画像形成装置を示す概略図である。
【符号の説明】
1 感光ドラム
2 帯電ローラ
5 中間転写ベルト
8a 1次転写ローラ
8b 2次転写ローラ
16 電荷付与ローラ
18、22、26、28 電源
20 CPU
24、30 電流検知手段[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a color image forming apparatus such as an electrophotographic copying machine or a laser printer.
[0002]
[Prior art]
FIG. 8 is a schematic view showing a conventional color image forming apparatus.
[0003]
The color image forming apparatus has a
[0004]
Four developing
[0005]
An
[0006]
Next, the transfer material is taken out from the
[0007]
The transfer material onto which the four color toner images have been transferred in this manner is conveyed to the
[0008]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
By the way, the
[0009]
When the time constant of the
[0010]
That is, at the time of primary transfer for the second and subsequent colors, a predetermined charge is held on the
[0011]
In addition, when the time constant τ of the
[0012]
Thus, the main factor that determines the life of the
[0013]
However, conventionally, the user has been informed that the
[0014]
It is an object of the present invention to obtain a high-quality image without drum ghost even when the time constant τ of the intermediate transfer member is lowered, and to notify the life of the intermediate transfer member regardless of the use environment or use mode. It is an object of the present invention to provide a color image forming apparatus that can always be performed at an optimum time.
[0015]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The above object is achieved by a color image forming apparatus according to the present invention. In summary, the present invention includes an image bearing member, and the intermediate transfer member, a charging means for uniformly charging said image bearing member, exposing the charged the image bearing member, a toner image of each and developed color each time the resulting thereof and a toner image primary transfer means for transferring superimposed on the intermediate transfer member, second transfer means for transferring to the transfer material at once the color toner images transferred to the intermediate transfer member in the color image forming apparatus having the door, and a plurality of constant voltage power supply, voltage is applied to the intermediate transfer member by applying a voltage from the plurality of constant voltage power supply, a plurality of charge imparting a charge to said intermediate transfer member and applying means, and a current detecting means for detecting a current flowing through the intermediate transfer member caused by application of a voltage by the plurality of charging unit, said at turning the course of the intermediate transfer member by said charging unit Same part of intermediate transfer member And a voltage is applied a plurality of times continuously, and a primary transfer bias applied to the primary transfer unit is controlled in accordance with each current value detected a plurality of times by the current detection unit. Forming device.
[0016]
According to an embodiment of the present invention, there are two charge applying units, the primary transfer unit also serves as one of the charge providing units, and the secondary transfer unit also serves as the other of the charge providing units.
[0017]
According to another embodiment of the present invention, a secondary transfer remaining toner on the intermediate transfer member by applying a second charging unit different from the charging unit and a charging bias from the second charging unit. And a secondary transfer residual toner to which the charge is applied is reversely transferred to the image carrier simultaneously with the transfer of the toner image to the intermediate transfer member by the primary transfer unit. In addition, there are two charge applying units, the second charging unit also serves as one of the charge providing units, and the primary transfer unit also serves as the other of the charge providing units.
According to another embodiment of the present invention, a secondary transfer remaining toner on the intermediate transfer member by applying a second charging unit different from the charging unit and a charging bias from the second charging unit. And a secondary transfer residual toner to which the charge is applied is reversely transferred to the image carrier simultaneously with the transfer of the toner image to the intermediate transfer member by the primary transfer unit. In addition, there are two charge applying units, the second charging unit also serves as one of the charge providing units, and the secondary transfer unit also serves as the other of the charge providing units.
[0018]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
[0019]
Example 1
FIG. 1 is a schematic view showing a main part of a color image forming apparatus of the present invention. In the present invention, a voltage is applied to the
[0020]
In the conventional color image forming apparatus shown in FIG. 8, the toner images of the first color to the fourth color are sequentially primary-transferred onto the
[0021]
However, as the number of printed sheets advances, nitrogen oxide or the like adheres to the surface of the
[0022]
As described above, when the time constant of the
[0023]
Therefore, in this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 1, a
[0024]
According to this embodiment, the
[0025]
FIG. 2 shows changes in the transfer current It with respect to changes in the time constant τ of the
[0026]
As is clear from FIG. 2, the color transfer current increases as the time constant τ of the
[0027]
FIG. 3 shows changes in the transfer currents I1 and I2 with respect to the time constant .tau. When the electric
[0028]
As shown in FIG. 3, it can be seen that this case also shows the same tendency as the change in the transfer current in FIG. It can also be seen that the ratio of the two current values I2 / I1 has a correlation that decreases as the time constant τ increases.
[0029]
Therefore, in this embodiment, the primary transfer biases Vt10, Vt20, Vt30, and Vt40 for the first color, the second color, the third color, and the fourth color are set as follows.
[0030]
Vt10 = 100 (V)
Vt20 = 500 + 100 × (1−I 2 / I 1) (V)
Vt30 = 550 + 300 × (1−I 2 / I 1) (V)
Vt40 = 600 + 500 × (1-I2 / I1) (V)
[0031]
As a result, the transfer currents It10, It20, It30, and It40 are as shown in FIG. 4, and even if the time constant τ decreases, the transfer current does not exceed 9 μA, and drum ghosting can be prevented.
[0032]
In the above, the current measurement was performed twice, but it goes without saying that it can be performed three or more times.
[0033]
Example 2
As described above, when the time constant τ of the
[0034]
Conventionally, a charging bias in which an AC component of Vpp = 2.0 kV and a frequency of 1.2 kHz is superimposed on a DC component of Vdc = −550 V has been used. With this bias, when the transfer current was 9 μA or more, drum ghost was generated.
[0035]
Table 1 shows the results of experiments on the occurrence of drum ghost with respect to the transfer current by changing the charging bias Vpp. In Table 1, the symbol ◯ indicates that drum ghost is not generated, and x indicates that drum ghost is generated.
[0036]
[Table 1]
[0037]
According to Table 1, it can be seen that the charging ability is increased by increasing Vpp.
[0038]
Based on this, in this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 5, a voltage is continuously applied to the same portion of the
[0039]
As described in the first exemplary embodiment, the transfer current has a correlation with the time constant τ of the
[0040]
Therefore, in this embodiment, Vpp of the charging bias is set as follows.
[0041]
Vpp = 2.6-1.2.times. (1-I @ 2 / I @ 1) (kV)
As a result, even if the time constant τ of the
[0042]
In this embodiment, the charging bias Vpp is changed, but the same effect can be obtained by changing the AC current value, Vdc, or frequency.
[0043]
Example 3
In this embodiment, when the time constant τ of the
[0044]
More specifically, the life of the
[0045]
However, although the speed of the time constant τ varies depending on the use environment, use mode, etc., conventionally, the lifetime is determined with the number of prints under the fastest condition. Therefore, in most cases, the
[0046]
In this embodiment, in order to solve the above problem, in FIG. 1 and the like, a notifying means (not shown) relating to the life of the
[0047]
According to the present embodiment, this makes it possible to always appropriately notify the final replacement time of the
[0048]
Example 4
In this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 6, a current detecting
[0049]
That is, in the
[0050]
In the present embodiment, the
[0051]
Example 5
In this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 7, each of the
[0052]
In the previous Examples 1 to 4, since the current measurement was performed twice by one charge applying unit, it was necessary to rotate the
[0053]
In this embodiment, the current detection is performed to control the primary transfer bias of the
[0054]
In this embodiment, each of the
[0055]
The current detection in the present invention is preferably performed during printing every time at the top non-image portion of the image forming process, but it may be performed at the time of pre-rotation when the power is turned on or when the operation state is restored after jam processing, or You may carry out before and after density control.
[0056]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, a plurality of constant voltage power supplies and a plurality of charges for applying a voltage to the intermediate transfer body by applying voltages from the plurality of constant voltage power supplies and applying a charge to the intermediate transfer body. And a current detecting means for detecting a current flowing in the intermediate transfer member generated by applying a voltage from a plurality of charge applying means, and the intermediate transfer member is identical in the rotation process of the intermediate transfer member by the charge applying means. Since the primary transfer bias applied to the primary transfer unit is controlled according to the respective current values detected by the current detection unit a plurality of times , and the intermediate transfer member The drum ghost can be prevented from occurring even when the time constant τ decreases.
[0058]
Further, by installing a plurality of charging unit. Thus applying a plurality of times voltages in succession at the same position of the intermediate transfer member, it is possible to shorten the primary transfer bias control of the time. Further, when the primary transfer unit, the secondary transfer unit or the intermediate transfer member cleaning unit is also used as the charge applying unit, the primary transfer bias control and the like can be performed without increasing the cost.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a schematic configuration diagram showing a main part in an embodiment of a color image forming apparatus of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a diagram showing a change in transfer current It with respect to a change in time constant τ of the intermediate transfer belt when a primary transfer bias is applied to the intermediate transfer belt installed in the main part of FIG. 1;
3 is a graph showing changes in transfer currents I1 and I2 with respect to time constant τ when a charge is applied to the same portion of the intermediate transfer belt twice in succession by a charge application roller installed in the main part of FIG. is there.
4 is a diagram illustrating a change in transfer current with respect to a time constant τ of the intermediate transfer belt when the control in the embodiment of FIG. 1 is performed.
FIG. 5 is a schematic configuration diagram showing a main part in another embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 6 is a schematic configuration diagram showing a main part in still another embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 7 is a schematic configuration diagram showing a main part in still another embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 8 is a schematic view showing a conventional color image forming apparatus.
[Explanation of symbols]
DESCRIPTION OF
24, 30 Current detection means
Claims (4)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP09668998A JP4194130B2 (en) | 1998-03-25 | 1998-03-25 | Color image forming apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP09668998A JP4194130B2 (en) | 1998-03-25 | 1998-03-25 | Color image forming apparatus |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JPH11272093A JPH11272093A (en) | 1999-10-08 |
| JP4194130B2 true JP4194130B2 (en) | 2008-12-10 |
Family
ID=14171770
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP09668998A Expired - Fee Related JP4194130B2 (en) | 1998-03-25 | 1998-03-25 | Color image forming apparatus |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4194130B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20050069050A (en) * | 2003-12-30 | 2005-07-05 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Apparatus and method for controlling transfer voltage in image forming device |
| EP3246760A1 (en) * | 2016-05-18 | 2017-11-22 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Image forming apparatus |
-
1998
- 1998-03-25 JP JP09668998A patent/JP4194130B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPH11272093A (en) | 1999-10-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0391306B1 (en) | An image forming apparatus | |
| US5701551A (en) | Image forming apparatus including control means for controlling an output from en electrical power source to a charging member for charging an image bearing member | |
| JP4464092B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP2006003886A (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| KR20080047292A (en) | Image forming apparatus capable of controlling application voltage to adhering member | |
| JP2001282012A (en) | Image forming device | |
| JP5595226B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP6509032B2 (en) | Image forming device | |
| JP6418959B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JPH09114273A (en) | Transfer device for image forming device | |
| JP2008134393A (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP2007101980A (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JPH09185219A (en) | Electrostatic charging device and image forming device | |
| JPH06175514A (en) | Image recording and forming devices | |
| JP4194130B2 (en) | Color image forming apparatus | |
| JPH02264278A (en) | Image forming device | |
| JP2018120219A (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JPH10268590A (en) | Image forming device | |
| JPH10198131A (en) | Electrifier and image forming device | |
| US20200103782A1 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP2004163475A (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP5056202B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP3569155B2 (en) | Image forming device | |
| JP2009251171A (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP2004045897A (en) | Image forming apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20050314 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20050314 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20080403 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20080624 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20080825 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20080916 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20080922 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111003 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111003 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121003 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131003 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |