JP4187100B2 - Mobile phone system - Google Patents
Mobile phone system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4187100B2 JP4187100B2 JP2003118666A JP2003118666A JP4187100B2 JP 4187100 B2 JP4187100 B2 JP 4187100B2 JP 2003118666 A JP2003118666 A JP 2003118666A JP 2003118666 A JP2003118666 A JP 2003118666A JP 4187100 B2 JP4187100 B2 JP 4187100B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- base station
- signal strength
- handoff
- signal
- station
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、符号分割多元接続(CDMA)方式の通信システムの移動局及び当該移動局の通信方法に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
近年、符号分割多元接続(CDMA)方式を利用した携帯電話システムが広く普及してきている。CDMA方式では、送信局が、擬似雑音(PN)系列という特殊なコードを用いて信号を広帯域に拡散変調して送信し、受信局では、受信した信号を送信側と同一のPN系列を用いて逆拡散復調することによって、所要の信号を復元する。ここで、PN系列とは、直交性を有し、他の系列との相互相関値は0になるという性質を有する。そして、このようなPN系列の性質により、複数の送信局が、それぞれ異なるPN系列を用いて拡散変調した信号を送信している場合でも、受信局は、所望する送信局に対応するPN系列で受信した信号を逆拡散変調することで、所望する送信局からの信号のみを分離抽出することができる。
【0003】
次に、移動局が、通信接続する基地局を切替える方法について説明する。まず、基地局では、移動局の通信接続先のサーチに供するためのパイロット信号(制御信号)をその基地局固有のPN系列で拡散変調して送信している。ここで、PN系列のオフセット値はPN番号と呼ばれ、0〜511の値をとる。このPN番号により基地局は一意に特定できるので、PN番号(オフセット値)がnのPN系列を用いる基地局を基地局nと呼ぶことにする。通信接続中の基地局をアクティブ基地局と呼ぶ。そして、アクティブ基地局は、自局の近傍に位置する基地局の番号を示すネイバーリストを移動局に送信する。当該ネイバーリストに含まれる基地局をネイバー基地局と呼び、アクティブ基地局でもネイバー基地局でもない遠隔に位置する基地局をリメイン基地局と呼ぶ。また、アクティブ基地局は、移動局が通信接続先のサーチ時において利用する、リメイン基地局をサーチするPN番号の間隔を表わす数R_INCも送信する。
【0004】
移動局では、通話中において、現在のアクティブ基地局よりも、より良好な基地局がないかを常にサーチしている。すなわち、移動局では、すべてのネイバー基地局と、PN番号がR_INCごとのリメイン基地局からの信号強度を測定する。そして、移動局では、アクティブ基地局よりも信号強度が大きな基地局がある場合には、その基地局へハンドオフ(接続切替え)する。従って、遠隔にあるリメイン基地局にハンドオフすることもありうる。
【0005】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
ところで、遠隔にあるリメイン基地局にハンドオフした場合には、次のような問題がある。
【0006】
第1に、リメイン基地局は移動局から遠隔に位置するので、移動局からの信号(上り信号)が届きにくい。移動局では、強いエネルギーで信号を送出できないからである。その結果、リメイン基地局と移動局との間で、通信接続が確立できずに再度ハンドオフ先を決定しなくてはならなかったり、通信接続ができても通信品質が極端に悪かったりする。
【0007】
第2に、遠隔のリメイン基地局がアクティブ基地局になった場合には、その基地局のネイバー基地局も遠隔の基地局になる。そのような場合には、現在地の近傍の基地局はリメイン基地局とされるので、必ずしも次回のサーチ対象とはならない(リメイン基地局は、R_INCごとに飛び飛びにサーチされる。)。従って、現在地の近傍の基地局(一般には、遠隔よりも信号強度が大きい。)へなかなかハンドオフされないことである。
【0008】
一方、移動局の移動に伴って、フェージング、つまり、電波の伝播環境が変化し、受信する信号の強度が変動することがある。また、リメイン基地局は、移動局からの距離が長く、その信号は多様な伝播環境の下を通過してくるので、その分だけ信号強度も時間的な変動を受け易いといえる。従って、測定したときに信号強度が大きくても、たまたまその時だけ大きかっただけかもしれず、測定した以外の時点でも確実に信号強度が高いとの保証はない。
【0009】
以上のように、リメイン基地局へハンドオフした場合には、多くの弊害があるので可能な限りリメイン基地局へハンドオフするのを避けたいところだが、従来の基地局の切替え方法では、リメイン基地局がアクティブ基地局よりも信号強度が一度でも大きくなれば、それ以外の時点でも継続して信号強度が大きいかどうかにかかわりなく、即座にそのリメイン基地局へハンドオフするものとしていた。
【0010】
そこで、本発明は、かかる問題点に鑑みてなされたものであり、信号強度が継続して高くはないようなリメイン基地局にハンドオフするのを回避するCDMA通信システムの移動局を提供することを目的とする。
【0011】
【課題を解決するための手段】
請求項1に係る本発明の移動局は、上記の目的を達成するために、少なくとも移動局と基地局で構成された符号分割多元接続方式を利用した携帯電話システムにおいて、前記移動局は、前記基地局からの信号の強度を検出する検出手段と、現に通信接続中の基地局からの信号強度よりも大きい信号強度をもつ他の基地局をサーチする手段と、前記サーチした基地局が、現に通信接続している基地局の近傍に位置するネイバー基地局であるか、それ以外のリメイン基地局であるかを判定する手段と、リメイン基地局と判定したときには、当該リメイン基地局へのハンドオフを一時的に禁止するハンドオフ制御手段とを具備し、前記ハンドオフ制御手段は、ハンドオフを一時的に禁止している状態で、そのリメイン基地局からの信号強度を前記検出手段に所定回数検出させ、所定回数の信号強度の平均値が現に通信接続中の基地局からの信号強度よりも大きい場合に、前記禁止を解除して当該リメイン基地局にハンドオフすることを特徴とする。
【0012】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明の実施の形態について図面を用いて説明する。
<移動局の構成>
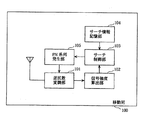
図1は、本実施の形態に係るCDMA通信システムにおける移動局の構成を示すブロック図である。同図に示すように、CDMA通信システムにおける移動局100は、逆拡散変調部101と、信号強度算出部102と、サーチ制御部103と、サーチ情報記憶部104と、PN系列発生部105とから構成される。
【0013】
サーチ情報記憶部104は、通信中の基地局の番号と、アクティブ基地局から送られたネイバー基地局の番号のリスト(ネイバーリストと呼ぶ)と、リメイン基地局をサーチする間隔数R_INCとからなるサーチ情報を記憶する。ネイバーリストとR_INCとは、アクティブ基地局から送信されたものを受信して記憶している。図2は、サーチ情報の例を示す。同図に示すように、アクティブ基地局が基地局7であり、ネイバー基地局が基地局2、基地局8、基地局10、基地局12、基地局14であり、リメイン基地局をサーチする間隔数が5である状態を示している。
【0014】
PN系列発生部105は、サーチ制御部103から基地局の番号を指示されると、当該番号をオフセットにもつPN系列(拡散符号)を発生し、逆拡散変調部101に送る。
【0015】
逆拡散変調部101は、PN系列発生部105から送られてくるPN系列で逆換算変調し、そのPN系列で拡散変調している基地局からのパイロット信号を抽出する。
【0016】
信号強度算出部102は、逆拡散変調部101より送られてきた基地局ごとののパイロット信号の強度を算出する。より具体的には、基地局ごとの信号のエネルギーEcを信号の総エネルギーIoで除算した値Ec/Ioを算出し、これを信号強度とする。
【0017】
サーチ制御部103は、本実施の形態における最も特徴的な構成要素であり、サーチ制御情報記憶部104を参照して、サーチすべき基地局を特定し、当該基地局の番号をPN系列発生部105に送る。
【0018】
サーチ制御部103は、以下の(A1)に示す順番でサーチを行う。(A1)アクティブ基地局、すべてのネイバー基地局、R_INCごとのリメイン基地局の順番に、これを1サイクルとしてサーチを繰り返す。
【0019】
例えば、図2に示す状態のように、アクティブ基地局が7、ネイバー基地局が{2、8、10、12、14}で、R_INCが5のときには、{7、2、8、10、12、14、0}、{7、2、8、10、12、14、5}、{7、2、8、10、12、14、15}…の順番でサーチを行う。ここで、3サイクル目のリメインについては、基地局10がネイバー基地局なので、これを飛ばして、さらにR_INC(=5)を加算した番号の基地局15を選択したものである。
【0020】
また、サーチ制御部103は、以下の(B1)、(B2)の基準で、基地局のハンドオフを決定する。
(B1)ネイバー基地局の信号強度の最大値がアクティブ基地局の信号強度よりも大きければ、当該最大のネイバー基地局へハンドオフする。
【0021】
つまり、ネイバー基地局の信号強度は、たまたま測定した時点で大きかっただけで、もともと小さいものであったとしても、ハンドオフした後には、直ぐにより適した近傍の基地局へハンドオフされ、信号強度が大きいことが継続しているとの保証がなくても弊害は少ないので、即座にハンドオフするものとする。(B2)リメイン基地局の信号強度がアクティブ基地局の信号強度よりも大きければ、当該リメイン基地局を確認対象リメインとして確認モードに移行する。
【0022】
つまり、リメイン基地局の信号強度が大きかったときには、直ぐには、そのリメイン基地局へハンドオフせずに、なんどかその基地局の信号強度を確認するという確認モードに移行する。ここで、確認モードと区別する上で、確認モードに移行する前の状態を通常モードと呼ぶことにする。
【0023】
次に、確認モード中のサーチ方法について説明する。
【0024】
サーチ制御部103は、確認モード時には、以下の(C1)に示す順番でサーチを行う。(C1)アクティブ基地局とすべてのネイバー基地局のセットを所定回数Nだけサーチした後、確認対象リメイン基地局のサーチを行い、これを1サイクルとし
てサーチを繰り返す。
【0025】
例えば、図2に示す状態のように、アクティブ基地局が7、ネイバー基地局が{2、8、10、12、14}のときに、所定回数N=3とし、基地局15が確認対象リメインとなったときには、{7、2、8、10、12、14、7、2、8、10、12、14、7、2、8、10、12、14、15}の順番に、これを1サイクルとしてサーチを行う。
【0026】
また、サーチ制御部103は、確認モード時には、以下の(D1)、(D2)の基準で、基地局のハンドオフを決定する。(D1)ネイバー基地局の信号強度の最大値がアクティブ基地局の信号強度よりも大きければ、当該最大のネイバー基地局へハンドオフする。
【0027】
つまり、確認モード時においても、信号強度の大きなネイバー基地局が見付かれば、そのネイバー基地局へハンドオフするものとする。(D2)確認対象リメイン基地局の信号強度がアクティブ基地局の信号強度よりも大きければカウンタをインクリメントし、カウンタ値が所定値Rになれば、当該リメイン基地局にハンドオフする。途中で、確認対象リメイン基地局の信号強度がアクティブ基地局の信号強度以下になったときには、その時点で確認モードを終了して、通常モードに戻る。
【0028】
つまり、リメイン基地局の信号強度は変動しやすい上に、リメイン基地局へのハンドオフは弊害が大きいので、信号強度が大きいことが継続していることが確実であることを確認したときに限り、ハンドオフするものとする。
【0029】
<通常モード時のサーチ動作>
次に、本実施の形態に係る移動局における通常モード時のサーチ動作について説明する。
【0030】
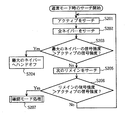
図3は、通常モード時のサーチの動作手順を示すフロチャートである。
【0031】
まず、サーチ制御部103は、サーチ情報記憶部104を参照して、アクティブ基地局となる基地局を特定し、当該アクティブ基地局のPN系列を発生させることにより、逆拡散変調部101からアクティブ基地局の信号を取り出させ、信号強度算出部102からアクティブ基地局からの信号の強度を得る(ステップS201)。
【0032】
次に、サーチ制御部103は、サーチ情報記憶部104を参照して、ネイバー基地局となる基地局を特定し、アクティブ基地局のときと同様にして、すべてのネイバー基地局についてその信号の強度を得る(ステップS202)。
【0033】
サーチ制御部103は、ネイバー基地局からの信号の強度のうちの最大値が、アクティブ基地局からの信号の強度よりも大きいときには、当該強度が最大となる信号を出しているネイバー基地局へハンドオフする(ステップS203、S204)。
【0034】
一方、サーチ制御部103は、当該信号の強度の最大値がアクティブ基地局からの信号の強度以下のときには、1つのリメインのサーチを行う。すなわち、サーチ制御部103は、サーチ情報記憶部104を参照して、アクティブでもネイバーでもない任意の1つの基地局(リメイン基地局)を選択し、当該基地局について信号の強度を得る(ステップS205)。
【0035】
サーチ制御部103は、リメイン基地局からの信号の強度がアクティブ基地局からの信号の強度よりも大きいときには、当該リメイン基地局を確認対象リメインとして確認モードへ移行する(ステップS206、S207)。
【0036】
一方、サーチ制御部103は、当該信号の強度の最大値がアクティブ基地局からの信号の強度以下のときには、ステップS201に戻り処理を繰り返す(ステップS206)。
【0037】
そして、次回のステップS205においては、サーチ制御部103は、サーチ情報記憶部103中のサーチ間隔数を前回選択したリメイン基地局の番号に加えた番号の基地局を特定し、当該基地局がアクティブでもネイバーでもない(リメイン)なら、当該基地局をサーチし、当該基地局がリメインでないのなら、さらにサーチ間隔数を加えた番号の基地局がリメインであるかを調べることによって、サーチすべきリメインを決めて、そのリメインのサーチを実施する。
【0038】
<確認モード時のサーチ動作>
次に、本実施の形態に係る移動局における確認モード時のサーチ動作について説明する。
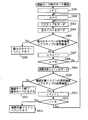
図4は、確認モード時のサーチの動作手順を示すフロチャートである。
【0039】
まず、サーチ制御部103は、確認対象リメインの確認した回数(信号強度がアクティブよりも大きくなった回数)を示すrを0にセットし、ネイバー基地局のサーチした回数を示すnを0にセットする(ステップS301、S302)。
【0040】
次に、サーチ制御部103は、サーチ情報記憶部104を参照して、アクティブ基地局となる基地局を特定し、当該アクティブ基地局のPN系列を発生させることにより、逆拡散変調部101からアクティブ基地局の信号を取り出させ、信号強度算出部102からアクティブ基地局からの信号の強度を得る(ステップS303)。
【0041】
次に、サーチ制御部103は、サーチ情報記憶部104を参照して、ネイバー基地局となる基地局を特定し、アクティブ基地局のときと同様にして、すべてのネイバー基地局についてその信号の強度を得る(ステップS304)。
【0042】
サーチ制御部103は、ネイバー基地局からの信号の強度のうちの最大値が、アクティブ基地局からの信号の強度よりも大きいときには、当該強度が最大となる信号を出しているネイバー基地局へハンドオフする(ステップS305、S306)。
【0043】
一方、サーチ制御部103は、当該信号の強度の最大値がアクティブ基地局からの信号の強度以下のときには、ネイバー基地局のサーチした回数nをインクリメントする(ステップS307)。
【0044】
サーチ制御部103は、サーチした回数nがサーチすべき回数N未満のときには、ステップS303に戻り、アクティブとネイバーのサーチを繰り返す(ステップS308、S303)。
【0045】
一方、サーチ制御部103は、サーチした回数nがサーチすべき回数Nとなったときには、確認対象リメインのサーチを行う。すなわち、サーチ制御部103は、アクティブ基地局のときと同様にして、確認対象リメイン基地局についてその信号の強度を得る(ステップS309)。
【0046】
サーチ制御部103は、確認対象リメイン基地局の信号の強度がアクティブ基地局からの信号の強度以下のときには、確認モードを終了し、通常モードに移行し、図3に示す通常モードのステップS201からの処理を行う(ステップS310、S311)。
【0047】
一方、サーチ制御部103は、確認対象リメイン基地局の信号の強度がアクティブ基地局からの信号の強度よりも大きいときには、確認対象リメインの確認した回数rをインクリメントする(ステップS312)。
【0048】
サーチ制御部103は、確認した回数rが確認すべき回数R未満のときには、ステップS302に戻り、アクティブのサーチからの処理を繰り返す(ステップS313、S302)。
【0049】
一方、サーチ制御部103は、確認した回数rが確認すべき回数Rとなったときには、確認対象リメインへハンドオフする(ステップS313、S314)。<まとめ>
以上のように、本実施の形態に係るCDMA通信システムにおける移動局では、リメイン基地局の信号強度がアクティブ基地局の信号強度よりも大きかったときには、直ぐにはそのリメイン基地局へハンドオフせずに、所定回数そのリメイン基地局の信号強度を検出し、いずれもアクティブ基地局の信号強度よりも大きいときに限り、そのリメイン基地局にハンドオフするので、そのリメイン基地局が、たまたま一時点で信号強度が大きく、継続しては大きくはないのにも係らず、そのリメイン基地局にハンドオフしてしまう事態を回避することができる。
<変形例>
(1)確認方法について
本実施の形態では、リメイン基地局からの信号強度のアクティブ基地局からの信号強度よりも所定回数すべてにわたって大きくなることを条件に、そのリメイン基地局へハンドオフするものとしたが、これに限定するものではない。例えば、所定回数測定した平均値が、アクティブ基地局の信号強度よりも大きくなれば、当該リメイン基地局へハンドオフするものとしてもよい。あるいは、所定回数測定したうちの何回かが、アクティブ基地局の信号強度よりも大きければ、当該リメイン基地局へハンドオフするものとしてもよい。
(2)確認モードの維持
本実施の形態では、確認モードにおいて、ネイバー基地局へハンドオフした後において、前回の確認対象リメイン基地局の確認対象となった事実については、なんらサーチ上考慮しないものとしていたが、これに限定するものではない。
【0050】
確認モードにおいて、ネイバー基地局へハンドオフしたときには、その後のリメイン基地局のサーチについては、前回の確認モードで確認対象となったリメイン基地局からサーチするものとしてよく、あるいは、確認対象となったリメイン基地局のみをサーチし続けるものとしてもよい。
【0051】
また、確認モードにおいて、ネイバー基地局へハンドオフした後、前回と同一のリメインが確認対象リメインとして選択されたときには、前回のカウンタ値からカウントするものとしてもよい。例えば、10回まで確認していたときには、当該カウンタ値を10からインクリメントさせるものとしてもよい。
【0052】
【発明の効果】
以上の説明から明らかなように、本発明に係るCDMA通信システムの移動局は、基地局からの信号の強度を検出する検出手段と、現に通信接続中の基地局からの信号強度よりも大きい信号強度をもつ他の基地局をサーチする手段と、前記サーチした基地局が、現に通信接続している基地局の近傍に位置するネイバー基地局であるか、それ以外のリメイン基地局であるかを判定する手段と、リメイン基地局と判定したときには、当該リメイン基地局へのハンドオフを一時的に禁止するハンドオフ制御手段とを備えたことを特徴とする。
【0053】
これにより、リメイン基地局からの信号強度が通信接続中の基地局からの信号強度よりも大きいときには、直ぐにそのリメイン基地局へハンドオフするのではなく、信号強度が大きいことが継続していることが確実に保証されるまでそのリメイン基地局へのハンドオフを猶予するので、信号強度が大きいことが継続していることが確実に保証されないリメイン基地局へハンドオフするのを回避することができる。
【0054】
ここで、前記ハンドオフ制御手段は、ハンドオフを一時的に禁止している状態で、そのリメイン基地局からの信号強度を前記検出手段に所定回数検出させ、所定回数の信号強度の平均値が現に通信接続中の基地局からの信号強度よりも大きい場合に、前記禁止を解除して当該リメイン基地局にハンドオフすることを特徴とする。
【0055】
これにより、リメイン基地局からの信号強度が、通信接続中の基地局からの信号強度よりも所定回数検出したすべてにわたって大きいときには、かなりの確実性をもって、そのリメイン基地局からの信号強度が継続して大きいことが保証されるので、継続して信号強度が大きいことが確実に保証されないリメイン基地局はハンドオフするのを回避することができる。
【0056】
ここで、前記ハンドオフ制御手段は、ハンドオフを一時的に禁止している状態で、そのリメイン基地局からの信号強度を前記検出手段に繰り替えし検出させ、所定回数連続して前記リメイン基地局からの信号強度が現に通信接続中の基地局からの信号強度よりも大きい場合に、前記禁止を解除して当該リメイン基地局にハンドオフすることを特徴とする。
【0057】
これにより、リメイン基地局からの信号強度を所定回数検出した平均値が、通信接続中の基地局からの信号強度よりも大きいときには、かなりの確実性をもって、そのリメイン基地局からの信号強度が継続して大きいことが保証されるので、継続して信号強度が大きいことが確実に保証されないリメイン基地局はハンドオフするのを回避することができる。
【0058】
ここで、前記ハンドオフ制御手段は、さらに、前記リメイン基地局からの信号強度を検出する合間にネイバー基地局からの信号強度を前記検出手段に検出させ、ネイバー基地局からの信号強度が現に通信接続中の基地局からの信号強度よりも大きければ、当該ネイバー基地局にハンドオフすることを特徴とする。
【0059】
これにより、リメイン基地局からの信号強度が継続して大きいかを確認している間に、ネイバー基地局からの信号強度が通信接続中の基地局からの信号強度よりも大きくなれば、そのネイバー基地局へハンドオフするので、リメイン基地局よりもハンドオフ後に弊害が少ないネイバー基地局にハンドオフすることができる。
【0060】
ここで、前記ハンドオフ制御手段は、前記検出手段にネイバー基地局からの信号強度を検出する頻度を前記リメイン基地局からの信号強度を検出する頻度よりも多くして検出させることを特徴とする。
【0061】
これにより、リメイン基地局からの信号強度が継続して大きいかを確認している間における、ネイバー基地局からの信号強度を検出する頻度が高いので、信号伝播環境が良好になったネイバー基地局に迅速に発見して、そのネイバー基地局にハンドオフすることができる。
【0062】
ここで、前記ハンドオフ制御手段は、ネイバー基地局にハンドオフした後も、前記検出手段に前記リメイン基地局からの信号強度の検出を優先して行わせることを特徴とする。
【0063】
これにより、ネイバー基地局にハンドオフしたときにも、前回にハンドオフを猶予したリメイン基地局は、ハンドオーバできる基地局の候補として最も有力なので、そのリメイン基地局からの信号強度を優先的に検出することで、ハンドオーバするのに適した基地局を迅速に発見することができる。
【0064】
また、本発明に係るCDMA通信システムの移動局の通信方法は、基地局からの信号の強度を検出するステップと、現に通信接続中の基地局からの信号強度よりも大きい信号強度をもつ他の基地局をサーチするステップと、前記サーチした基地局が、現に通信接続している基地局の近傍に位置するネイバー基地局であるか、それ以外のリメイン基地局であるかを判定するステップと、リメイン基地局と判定したときには、当該リメイン基地局へのハンドオフを一時的に禁止するステップとを含むことを特徴とする。
【0065】
これにより、リメイン基地局からの信号強度が通信接続中の基地局からの信号強度よりも大きいときには、直ぐにそのリメイン基地局へハンドオフするのではなく、信号強度が大きいことが継続していることが確実に保証されるまでそのリメイン基地局へのハンドオフを猶予するので、信号強度が大きいことが継続していることが確実に保証されないリメイン基地局へハンドオフするのを回避することができる。
【0066】
以上のように本発明は、適切でない基地局と通信接続してしまうというCDMA方式を用いた移動通信システムにおける最も切実な問題点を解消でき、その実用的効果は極めて大きい。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の実施の形態に係るCDMA通信システムにおける移動局の構成を示すブロック図である。
【図2】サーチ情報の例を示す。
【図3】通常モード時のサーチの動作手順を示すフロチャートである。
【図4】確認モード時のサーチの動作手順を示すフロチャートである。
【符号の説明】
100 移動局
101 逆拡散変調部
102 信号強度算出部
103 サーチ制御部
104 サーチ情報記憶部
105 PN系列発生部[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a mobile station of a code division multiple access (CDMA) communication system and a communication method of the mobile station.
[0002]
[Prior art]
In recent years, mobile phone systems using a code division multiple access (CDMA) system have become widespread. In the CDMA system, a transmitting station uses a special code called a pseudo-noise (PN) sequence to spread and modulate a signal over a wide band, and the receiving station uses the same PN sequence as that on the transmitting side. The required signal is restored by despreading demodulation. Here, the PN sequence has the property that it has orthogonality and the cross-correlation value with other sequences is zero. Due to the nature of such a PN sequence, even when a plurality of transmitting stations transmit signals that are spread-modulated using different PN sequences, the receiving station uses a PN sequence corresponding to the desired transmitting station. By despreading the received signal, only the signal from the desired transmitting station can be separated and extracted.
[0003]
Next, a method for the mobile station to switch base stations to be connected for communication will be described. First, in a base station, a pilot signal (control signal) for use in searching for a communication connection destination of a mobile station is spread-modulated with a PN sequence unique to the base station and transmitted. Here, the offset value of the PN sequence is called a PN number and takes a value of 0 to 511. Since a base station can be uniquely identified by this PN number, a base station using a PN sequence having a PN number (offset value) of n is called a base station n. A base station in communication connection is called an active base station. Then, the active base station transmits a neighbor list indicating the numbers of base stations located in the vicinity of the active station to the mobile station. A base station included in the neighbor list is called a neighbor base station, and a remotely located base station that is neither an active base station nor a neighbor base station is called a main base station. The active base station also transmits a number R_INC that represents the interval of the PN numbers for searching the remote base station, which is used when the mobile station searches for a communication connection destination.
[0004]
The mobile station always searches for a better base station than the current active base station during a call. That is, the mobile station measures the signal strength from all the neighbor base stations and the main base station whose PN number is R_INC. Then, when there is a base station having a signal strength higher than that of the active base station, the mobile station performs handoff (connection switching) to the base station. Therefore, it may be handed off to a remote base station that is remote.
[0005]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
By the way, when handing off to a remote remote base station, there are the following problems.
[0006]
First, since the remote base station is located remotely from the mobile station, a signal (uplink signal) from the mobile station is difficult to reach. This is because a mobile station cannot transmit a signal with strong energy. As a result, the communication connection cannot be established between the remote base station and the mobile station, and the handoff destination must be determined again, or the communication quality is extremely poor even if the communication connection is established.
[0007]
Second, when a remote main base station becomes an active base station, its neighbor base station also becomes a remote base station. In such a case, since the base station in the vicinity of the current location is the main base station, the base station is not necessarily the next search target (the main base station is searched every R_INC). Therefore, it is difficult to handoff to a base station in the vicinity of the current location (generally, the signal strength is higher than that of a remote location).
[0008]
On the other hand, as the mobile station moves, fading, that is, the radio wave propagation environment changes, and the intensity of the received signal may vary. In addition, the re-main base station has a long distance from the mobile station, and the signal passes through various propagation environments. Therefore, it can be said that the signal intensity is likely to be subject to temporal fluctuations accordingly. Therefore, even if the signal strength is high when measured, it may happen that it is only high at that time, and there is no guarantee that the signal strength is high at any time other than when it is measured.
[0009]
As described above, when handing off to the main base station, there are many adverse effects, so it is desirable to avoid handing off to the main base station as much as possible. However, in the conventional base station switching method, the main base station If the signal strength becomes higher than that of the active base station even once, it will be handed off immediately to the remote base station regardless of whether the signal strength is continuously high at other times.
[0010]
Therefore, the present invention has been made in view of such problems, and provides a mobile station of a CDMA communication system that avoids handing off to a remaining base station whose signal strength is not continuously high. Objective.
[0011]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In order to achieve the above object, the mobile station of the present invention according to
[0012]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
<Configuration of mobile station>
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a mobile station in the CDMA communication system according to the present embodiment. As shown in the figure,
[0013]
The search
[0014]
When the
[0015]
[0016]
The signal
[0017]
The
[0018]
The
[0019]
For example, when the active base station is 7, the neighbor base station is {2, 8, 10, 12, 14} and R_INC is 5, as in the state shown in FIG. 2, {7, 2, 8, 10, 12 , 14, 0}, {7, 2, 8, 10, 12, 14, 5}, {7, 2, 8, 10, 12, 14, 15}... Here, regarding the third cycle, since the base station 10 is a neighbor base station, this is skipped, and the base station 15 having a number obtained by adding R_INC (= 5) is selected.
[0020]
Further, the
(B1) If the maximum value of the signal strength of the neighbor base station is greater than the signal strength of the active base station, handoff to the maximum neighbor base station is performed.
[0021]
In other words, the signal strength of the neighbor base station was high when it happened to be measured, and even if it was originally small, it was handed off to a nearby base station that was more suitable immediately after handoff, and the signal strength was high. Even if there is no guarantee that this is continuing, there will be little adverse effects, so we will hand off immediately. (B2) If the signal strength of the main base station is greater than the signal strength of the active base station, the main base station is shifted to the confirmation mode with the main base station as the confirmation target main.
[0022]
That is, when the signal strength of the main base station is high, the mode immediately shifts to a confirmation mode in which the signal strength of the base station is confirmed without any handoff to the main base station. Here, in order to distinguish from the confirmation mode, the state before shifting to the confirmation mode is referred to as a normal mode.
[0023]
Next, a search method in the confirmation mode will be described.
[0024]
In the confirmation mode, the
[0025]
For example, as in the state shown in FIG. 2, when the active base station is 7 and the neighbor base station is {2, 8, 10, 12, 14}, the predetermined number N is set to 3 and the base station 15 performs the confirmation target Then, in the order {7, 2, 8, 10, 12, 14, 7, 2, 8, 10, 12, 14, 7, 2, 8, 10, 12, 14, 15} Search is performed as one cycle.
[0026]
In the confirmation mode, the
[0027]
That is, even in the confirmation mode, if a neighbor base station having a high signal strength is found, the handoff to that neighbor base station is assumed. (D2) If the signal strength of the main base station to be confirmed is greater than the signal strength of the active base station, the counter is incremented, and if the counter value reaches a predetermined value R, handoff to the main base station is performed. On the way, when the signal strength of the confirmation target main base station becomes equal to or lower than the signal strength of the active base station, the confirmation mode is terminated at that time and the normal mode is restored.
[0028]
In other words, the signal strength of the remaining base station is likely to fluctuate and the handoff to the remaining base station is bad, so only when it is confirmed that it is certain that the signal strength is high, It shall be handed off.
[0029]
<Search operation in normal mode>
Next, a search operation in the normal mode in the mobile station according to the present embodiment will be described.
[0030]
FIG. 3 is a flowchart showing a search operation procedure in the normal mode.
[0031]
First, the
[0032]
Next, the
[0033]
When the maximum value of the signal strengths from the neighbor base station is larger than the signal strength from the active base station, the
[0034]
On the other hand, when the maximum value of the intensity of the signal is equal to or less than the intensity of the signal from the active base station, the
[0035]
When the strength of the signal from the main base station is larger than the strength of the signal from the active base station, the
[0036]
On the other hand, when the maximum value of the signal strength is less than or equal to the signal strength from the active base station, the
[0037]
In the next step S205, the
[0038]
<Search operation in confirmation mode>
Next, the search operation in the confirmation mode in the mobile station according to the present embodiment will be described.
FIG. 4 is a flowchart showing a search operation procedure in the confirmation mode.
[0039]
First, the
[0040]
Next, the
[0041]
Next, the
[0042]
When the maximum value of the signal strengths from the neighbor base station is larger than the signal strength from the active base station, the
[0043]
On the other hand, when the maximum value of the intensity of the signal is equal to or less than the intensity of the signal from the active base station, the
[0044]
When the number n of searches is less than the number N to be searched, the
[0045]
On the other hand, when the number n of searches reaches the number N of times to be searched, the
[0046]
When the signal strength of the confirmation target main base station is equal to or lower than the signal strength from the active base station, the
[0047]
On the other hand, when the strength of the signal of the confirmation target main base station is larger than the strength of the signal from the active base station, the
[0048]
When the number r of confirmed times is less than the number of times R to be confirmed, the
[0049]
On the other hand, when the number r of times of confirmation becomes the number of times R to be confirmed, the
As described above, in the mobile station in the CDMA communication system according to the present embodiment, when the signal strength of the main base station is larger than the signal strength of the active base station, immediately without handing off to the main base station, The signal strength of the remote base station is detected a predetermined number of times, and only when both of them are larger than the signal strength of the active base station, handoff to the remote base station is performed. Although it is large and is not large continuously, it is possible to avoid a situation in which handoff is performed to the main base station.
<Modification>
(1) About the confirmation method In this embodiment, the signal strength from the main base station is handed off to the main base station on condition that the signal strength from the active base station becomes larger all the time than the signal strength from the active base station. However, the present invention is not limited to this. For example, when the average value measured a predetermined number of times becomes larger than the signal strength of the active base station, the handoff to the main base station may be performed. Alternatively, if the number of times measured a predetermined number of times is larger than the signal strength of the active base station, handoff to the main base station may be performed.
(2) Maintenance of confirmation mode In the present embodiment, the fact that it was the confirmation target of the previous confirmation target main base station after handing off to the neighbor base station in the confirmation mode is not considered in the search. However, it is not limited to this.
[0050]
In the confirmation mode, when handing off to the neighbor base station, the subsequent search for the main base station may be performed from the main base station that was the confirmation target in the previous confirmation mode, or the The search may be continued only for the base station.
[0051]
Further, in the confirmation mode, after hand-off to the neighbor base station, when the same residual as the previous one is selected as the confirmation target residual, the counting may be performed from the previous counter value. For example, when it has been confirmed up to 10 times, the counter value may be incremented from 10.
[0052]
【The invention's effect】
As is apparent from the above description, the mobile station of the CDMA communication system according to the present invention includes a detecting means for detecting the strength of the signal from the base station, and a signal larger than the signal strength from the base station that is currently in communication connection. Means for searching for another base station having strength, and whether the searched base station is a neighbor base station located in the vicinity of the currently connected base station or another main base station. It is characterized in that it comprises means for determining and handoff control means for temporarily prohibiting handoff to the main base station when it is determined to be the main base station.
[0053]
As a result, when the signal strength from the remote base station is higher than the signal strength from the base station in communication connection, the signal strength continues rather than immediately handing off to the remote base station. Since the handoff to the remote base station is postponed until it is surely guaranteed, it is possible to avoid handing off to the remote base station that is not reliably guaranteed that the signal strength continues to be high.
[0054]
Here, the handoff control means causes the detection means to detect the signal strength from the remote base station a predetermined number of times while handoff is temporarily prohibited, and the average value of the signal strength of the predetermined number of times is actually communicated. When the signal strength from the connected base station is larger, the prohibition is canceled and the handoff to the main base station is performed.
[0055]
As a result, when the signal strength from the remote base station is larger than the signal strength from the base station in communication connection over all of the detected times, the signal strength from the remote base station continues with considerable certainty. Therefore, it is possible to avoid the handoff of the re-main base station that is not surely guaranteed that the signal strength is continuously high.
[0056]
Here, the handoff control means, while handoff is temporarily prohibited, causes the detection means to repeatedly detect the signal strength from the main base station and continuously detect the signal from the main base station a predetermined number of times. When the signal strength is larger than the signal strength from the currently connected base station, the prohibition is canceled and handoff to the relevant base station is performed.
[0057]
As a result, when the average value obtained by detecting the signal strength from the re-main base station a predetermined number of times is larger than the signal strength from the base station in communication connection, the signal strength from the re-main base station continues with considerable certainty. Therefore, it is possible to avoid the hand-off of the re-main base station that is not surely guaranteed that the signal strength is continuously high.
[0058]
Here, the handoff control means further causes the detection means to detect the signal strength from the neighbor base station between detection of the signal strength from the main base station, and the signal strength from the neighbor base station is actually connected to the communication. If it is larger than the signal strength from the base station in the middle, handoff to the neighbor base station is performed.
[0059]
As a result, if the signal strength from the neighbor base station becomes larger than the signal strength from the base station in communication connection while checking whether the signal strength from the remaining base station is continuously high, the neighbor Since handoff is performed to the base station, it is possible to handoff to a neighbor base station with less harmful effect after handoff than the main base station.
[0060]
Here, the handoff control means causes the detection means to detect the signal strength from the neighbor base station more frequently than the frequency to detect the signal strength from the main base station.
[0061]
As a result, the frequency of detecting the signal strength from the neighbor base station while checking whether the signal strength from the main base station is continuously high is high, so the neighbor base station in which the signal propagation environment is improved Can quickly discover and handoff to its neighbor base station.
[0062]
Here, the handoff control means is characterized in that, even after handing off to a neighbor base station, the detection means gives priority to detection of the signal strength from the remote base station.
[0063]
As a result, even when a handoff is performed to a neighbor base station, the main base station that has suspended the handoff last time is the most promising candidate for a base station that can be handed over, so the signal strength from the main base station should be detected with priority. Thus, a base station suitable for handover can be quickly found.
[0064]
Further, the communication method of the mobile station of the CDMA communication system according to the present invention includes a step of detecting the strength of a signal from the base station, and another signal having a signal strength greater than the signal strength from the currently connected base station. A step of searching for a base station, and a step of determining whether the searched base station is a neighbor base station located in the vicinity of the currently connected base station, or a remaining base station other than that, A step of temporarily prohibiting handoff to the remote base station when it is determined that the remote base station is determined.
[0065]
As a result, when the signal strength from the remote base station is higher than the signal strength from the base station in communication connection, the signal strength continues rather than immediately handing off to the remote base station. Since the handoff to the main base station is postponed until it is guaranteed with certainty, it is possible to avoid handing off to the main base station that is not reliably guaranteed that the signal strength continues to be high.
[0066]
As described above, the present invention can solve the most serious problem in the mobile communication system using the CDMA system in which communication connection with an inappropriate base station is established, and its practical effect is extremely large.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a mobile station in a CDMA communication system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 shows an example of search information.
FIG. 3 is a flowchart showing a search operation procedure in a normal mode.
FIG. 4 is a flowchart showing a search operation procedure in a confirmation mode.
[Explanation of symbols]
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (1)
前記移動局は、
前記基地局からの信号の強度を検出する検出手段と、
現に通信接続中の基地局からの信号強度よりも大きい信号強度をもつ他の基地局をサーチする手段と、
前記サーチした基地局が、現に通信接続している基地局の近傍に位置するネイバー基地局であるか、それ以外のリメイン基地局であるかを判定する手段と、
リメイン基地局と判定したときには、当該リメイン基地局へのハンドオフを一時的に禁止するハンドオフ制御手段とを具備し、
前記ハンドオフ制御手段は、ハンドオフを一時的に禁止している状態で、そのリメイン基地局からの信号強度を前記検出手段に所定回数検出させ、所定回数の信号強度の平均値が現に通信接続中の基地局からの信号強度よりも大きい場合に、前記禁止を解除して当該リメイン基地局にハンドオフすること、
を特徴とする携帯電話システム。In a mobile phone system using a code division multiple access method composed of at least a mobile station and a base station,
The mobile station
Detecting means for detecting the intensity of the signal from the base station;
Means for searching for another base station having a signal strength greater than the signal strength from the currently connected base station;
Means for determining whether the searched base station is a neighbor base station located in the vicinity of the currently connected base station, or another main base station;
When it is determined as a remote base station, it comprises handoff control means for temporarily prohibiting handoff to the remote base station,
The handoff control means causes the detection means to detect the signal strength from the remote base station a predetermined number of times while handoff is temporarily prohibited, and the average value of the signal strength of the predetermined number of times is currently in communication connection. Canceling the prohibition and handing off to the concerned base station when the signal strength from the base station is larger than the signal strength;
A mobile phone system characterized by
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003118666A JP4187100B2 (en) | 2003-04-23 | 2003-04-23 | Mobile phone system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003118666A JP4187100B2 (en) | 2003-04-23 | 2003-04-23 | Mobile phone system |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000092291A Division JP3454775B2 (en) | 2000-03-29 | 2000-03-29 | Mobile station and handoff method for CDMA communication system |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2003333670A JP2003333670A (en) | 2003-11-21 |
| JP2003333670A5 JP2003333670A5 (en) | 2005-10-20 |
| JP4187100B2 true JP4187100B2 (en) | 2008-11-26 |
Family
ID=29707416
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003118666A Expired - Fee Related JP4187100B2 (en) | 2003-04-23 | 2003-04-23 | Mobile phone system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4187100B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20090011795A1 (en) * | 2006-02-08 | 2009-01-08 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Radio communication base station device, radio communication terminal device, and radio communication system |
| JP6433467B2 (en) * | 2016-08-08 | 2018-12-05 | ソフトバンク株式会社 | Relay device and mobile communication system |
-
2003
- 2003-04-23 JP JP2003118666A patent/JP4187100B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2003333670A (en) | 2003-11-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR100560982B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for performing mobile assisted hard handoff between communication systems | |
| CA2203256C (en) | Pilot signal searching technique for a cellular communications system | |
| KR100746871B1 (en) | Soft handoff algorithm and wireless communication system for third generation cdma systems | |
| KR100414409B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for providing a mobile device supporting hard handoff from a CDMA communication system to another access communication system | |
| JP4108759B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for avoiding loss of communication with mobile station | |
| US6667962B1 (en) | Method for recovering dropped call in mobile station for CDMA system and method for informing recovery of the dropped call | |
| CA2383956C (en) | Method and system for initiating idle handoff in a wireless communications system | |
| US7324479B2 (en) | Cell search method in UMTS | |
| US7146164B2 (en) | Intelligent base station antenna beam-steering using mobile multipath feedback | |
| US20050272425A1 (en) | Maintaining and searching sets of cells in a wireless communication system | |
| JP2002513527A (en) | Method and apparatus for performing soft handoff in a wireless communication system | |
| NO316998B1 (en) | Handover during waiting in a multi-access connection system | |
| KR100338339B1 (en) | Spread spectrum communication system and handover method therein | |
| US6539006B1 (en) | Mobile station capable of determining base station suitability | |
| JP3454775B2 (en) | Mobile station and handoff method for CDMA communication system | |
| US6718171B1 (en) | Robust and efficient reacquisition after call release | |
| JP4187100B2 (en) | Mobile phone system | |
| KR100422236B1 (en) | Pilot search method of mobile station in the mobile communication system | |
| JPH07298332A (en) | Mobile communication cell deciding method and its mobile station device | |
| KR100292712B1 (en) | Method for decoding of traffic channel in softer handoff |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A712 Effective date: 20040922 |
|
| A072 | Dismissal of procedure [no reply to invitation to correct request for examination] |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A072 Effective date: 20050315 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20050617 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20050617 |
|
| RD01 | Notification of change of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7421 Effective date: 20051226 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20080715 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A712 Effective date: 20080801 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20080903 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110919 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110919 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120919 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130919 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |