JP4154986B2 - Resin pulley - Google Patents
Resin pulley Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4154986B2 JP4154986B2 JP2002291865A JP2002291865A JP4154986B2 JP 4154986 B2 JP4154986 B2 JP 4154986B2 JP 2002291865 A JP2002291865 A JP 2002291865A JP 2002291865 A JP2002291865 A JP 2002291865A JP 4154986 B2 JP4154986 B2 JP 4154986B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- guide surface
- belt guide
- resin
- hard carbon
- carbon film
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Pulleys (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、内径側に転がり軸受を一体に備える樹脂製プーリに関するものである。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
従来、自動車に搭載される補機類を駆動するベルトを案内するために樹脂製プーリが一般に使用されている。この樹脂製プーリは、転がり軸受と樹脂部とからなり、樹脂部は転がり軸受の外輪の外周に一体成形されている。この樹脂部は、内周側にある内径円筒部分、外周側にある外径円筒部分、内径円筒部分と外径円筒部分との間をつなぐ円板部分、円板部分上に形成された複数のリブとを有している。そして、外径円筒部分の外周面がベルト案内面となっており、このベルト案内面に補機類を駆動するゴム製のベルトが架けられて案内されている。
【0003】
この樹脂製プーリを使用する自動車が走行している最中に、砂塵などの異物がベルトとベルト案内面との間に挟まることがあり、樹脂製プーリに摩耗等を生じて損傷することがあった。このような損傷は自動車が悪路を連続走行する場合に特に発生しやすい。この問題を対処するために、SiO2及びAl2O3を主体とするセラミックス皮膜をベルト案内面に溶射して形成することがなされている(例えば、特許文献1を参照。)。
【0004】
また、ガラス繊維やマイカ粉等の充填材を添加した合成樹脂組成物により樹脂製プーリの樹脂部を形成し、樹脂部の耐摩耗性を向上させることも行われている(例えば、特許文献2を参照。)。
さらに、樹脂製プーリには、外径円筒部分の成形精度、ベルトの張力に耐え得る強度、連続負荷使用時に発生する熱に対する耐熱性が求められ、耐塩化カルシウム性等も要求されている。そこで、かかる成形精度、強度、耐熱性及び耐塩化カルシウム性の向上を目的として、樹脂製プーリの樹脂部を形成する合成樹脂組成物を、ガラス繊維等の充填材を15〜40質量%程度充填したポリアミド66、ポリアミド610、ポリアミド612、あるいはポニフェニレンサルファイドとミネラルの複合材料とすることが提案されている(例えば、特許文献3を参照。)。また、ガラス繊維の充填材を43質量%充填したポリアミド6、ポリアミド66、ポリアミド11、ポリアミド12等のポリアミド樹脂からなる合成樹脂組成物も提案されている(例えば、特許文献4を参照。)。
【0005】
【特許文献1】
特開平7―12206号公報(第2頁)
【特許文献2】
特開平8―145148号公報(第2〜3頁)
【特許文献3】
特開平7―63249号公報(第2頁の段落番号[0004])
【特許文献4】
特開平8―4883号公報(第7頁の段落番号[0043])
【0006】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、ベルト案内面にセラミックス皮膜を溶射して形成すると、以下の不具合を生じるものと想定される。すなわち、セラミックス皮膜は耐摩耗性に優れはするものの、セラミックス皮膜の厚さが50〜100μmと比較的厚い。このため、冷熱サイクルによってセラミックス皮膜中の内部応力が大きくなりやすい。したがって、樹脂製プーリが稼動するとセラミックス皮膜に亀裂や剥離を発生しやすいと考えられる。
【0007】
また、ガラス繊維等の充填材を添加した合成樹脂組成物によって樹脂製プーリの樹脂部を形成した場合、以下に述べる過程によりベルト案内面の摩耗が進行し、最終的に樹脂製プーリからベルトが外れてしまう不具合が想定される。すなわち、ベルトとベルト案内面の間に挟まった砂塵等の異物によって、ベルト案内面の充填材以外の部分において摩耗が進行し、充填材が比較的多く存在する部分がベルト案内面上の凸部として残り、ベルト案内面が荒れてしまう。その後、残った凸部も摩耗していき、結果的にベルト案内面の外径が小さくなり、ベルトが緩んでしまい、樹脂製プーリを交換しなくてはならなくなる。
【0008】
本発明は、上記した従来の技術の問題点を除くためになされたものであり、その目的とするところは、ベルトとベルト案内面との間に異物が挟まってもベルト案内面に摩耗を生じにくく、ベルト案内面に形成した皮膜の損傷を生じにくい樹脂製プーリを提供することである。
【0009】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明は、その課題を解決するために以下のような構成をとる。転がり軸受と、この転がり軸受の外周に設けられた樹脂部とからなる樹脂製プーリであって、前記樹脂部の外周に形成されて駆動ベルトと接触し、且つこの駆動ベルトを案内するベルト案内面上に、硬質炭素皮膜を形成し、前記硬質炭素皮膜の下にカーボンミキシング傾斜層を形成してあり、このカーボンミキシング傾斜層を介して前記硬質炭素皮膜を前記ベルト案内面に密着させている。
【0010】
請求項1の発明によると、ベルト案内面に形成した硬質炭素皮膜は硬度が非常に高く、耐摩耗性に優れるので、ベルト案内面の耐摩耗性は非常に大きい。
また、硬質炭素皮膜としては、たとえばHv1000〜5000の硬度を有するダイヤモンドライクカーボンを挙げることができる。そして、硬質炭素皮膜を形成する方法としてはプラズマCVD法、イオンビーム蒸着法、プラズマイオン注入法等の方法を挙げることができる。
【0011】
硬質炭素皮膜の膜厚が0.5μmよりも薄くなると、すべてのベルト案内面を硬質炭素皮膜によって覆うことが困難となり、ベルト案内面上で部分的に樹脂部が露出し、ベルト案内面の耐摩耗性が低下し、ベルト案内面で充分な耐摩耗性を発揮させることができない。また、膜厚が10μmよりも厚くなると、硬質炭素皮膜の中に大きな内部応力がたまりやすくなり、この内部応力によって硬質炭素皮膜に亀裂や剥離等を生じて自己破壊を起こしやすくなり、耐摩耗性を長期間に亙って発揮することが困難となる。したがって、硬質炭素皮膜の膜厚は0.5〜10μmとすることが望ましい。
【0012】
また、すべてのベルト案内面を硬質炭素皮膜によって確実に覆い、硬質炭素皮膜の自己破壊を一層確実に防止し、硬質炭素皮膜による耐摩耗性を安定して長期間に亙り発揮させる観点からは、硬質炭素皮膜の膜厚を1〜5μmとすることがより望ましい。そして、硬質炭素皮膜の形成時間や形成条件をコントロール等することを併せて考慮すると、硬質炭素皮膜の膜厚を1〜3μmとすることがより一層望ましい。
【0013】
本発明によれば、ベルト案内面の基底部をなす樹脂部の合成樹脂組成物と、ベルト案内面の表面に形成される硬質炭素皮膜との間にカーボンミキシング傾斜層が形成され、このカーボンミキシング傾斜層が合成樹脂組成物と硬質炭素皮膜との密着性を高める。したがって、硬質炭素皮膜の剥離等が防止され、硬質炭素皮膜は長期間に亙って安定してベルト案内面に存在する。
【0014】
なお、カーボンミキシング傾斜層を形成する方法として、プラズマイオン注入法を挙げることができる。プラズマイオン注入法を用いて硬質炭素皮膜を形成すると、カーボンミキシング傾斜層がベルト案内面の基底部をなす樹脂部の合成樹脂組成物とベルト案内面の表面の硬質炭素皮膜との間に形成される。
【0015】
【発明の実施の形態】
本発明の実施の形態を図面に基づいて説明する。
まず、図1ないし図3を参照して本実施の形態の構成を説明する。
図1及び図2に示すように、樹脂製プーリ10は、転がり軸受12と樹脂部24とからなる。転がり軸受12は、外輪14、内輪18、転動体20、保持器21及び接触ゴムシール22とからなる深溝玉軸受である。転動体20は外輪14と内輪18との間の空間に転動自在に保持器21によって保持されており、外輪14の外周面上には周方向に連続する凹溝16が環状に形成されている。
【0016】
外輪14、内輪18との間の前記空間は接触ゴムシール22によって外部から独立した空間となっており、この空間内にはグリースが充填されている。接触ゴムシール22を形成するゴム材として、ニトリルゴム、水素添加ニトリルゴム、アクリルゴム等を原料ゴムとし、各種充填材を添加したものを使用することが可能である。また、前記空間内に充填されるグリースとしては、ポリαオレフィン油、アルキルジフェニルエーテル油等を基油とし、ジウレア等を増ちょう剤とし、酸化防止剤や摩耗防止剤等を添加剤として加えたものを使用することが可能である。
【0017】
また、外輪14の外周上に、樹脂部24が後述の合成樹脂組成物から射出成形により一体形成されている。転がり軸受12の単体を図示しない金型のキャビティ内に配置し、このキャビティのゲートから溶融した合成樹脂組成物を流し入れて、樹脂部24は形成される。
樹脂部24は内径円筒部分26、外径円筒部分28、円板部分32及びリブ34とからなる。内径円筒部分26は樹脂部24の内径側に形成されており、内径円筒部分26の内周側には外輪14の凹溝16と対応して周方向に連続する突起が形成されており、この突起が外輪14の凹溝16に係合して樹脂部24は外輪14の外周上に固着されている。また、外径円筒部分28は樹脂部24の外径側に形成されており、円板部分32が内径円筒部分26の外周側と外径円筒部分28の内周側とをつないでいる。さらに、円板部分32には、内径円筒部分26の外周側と外径円筒部分28の内周側をつないで複数のリブ34が形成されている。
【0018】
樹脂部24を形成する合成樹脂組成物として、ガラス繊維等の強化繊維を充填材として15〜40質量%添加したポリアミド66やポリアミド46等を用いることができる。また、樹脂部24の成形時に生じる成形収縮の異方性を制御するとともに、機械的強度を保持するために、充填材としてガラス繊維等の繊維系充填材とシリカ等の粒子状充填材とを併用することも可能である。さらに、樹脂部24に耐塩化カルシウム性を付与するために、ポリアミド66やポリアミド46のポリアミドと低吸水ポリアミドとをポリマーアロイとし、このポリマーアロイに充填材を添加した合成樹脂組成物を用いることが可能である。低吸水ポリアミドとして、ポリアミド612、ポリアミド610、ポリアミド12、ポリアミド11等が挙げられる。また、直鎖状あるいは分岐状ポリフェニレンサルファイド等に充填材を添加した合成樹脂組成物を用いることも可能である。
【0019】
また、外径円筒部分28の外周面を軸方向から見るとほぼ真円をなし、この外周面がベルト案内面30をなす。ベルト案内面30は凹凸のない平坦な面が周方向に連続したフラット形状となっている。図3に示すように、ベルト案内面30にはダイヤモンドライクカーボンからなる硬質炭素皮膜36がプラズマイオン注入法によって形成されている。硬質炭素皮膜36の膜厚T1は1〜3μmであり、硬質炭素皮膜36とベルト案内面30をなす合成樹脂組成物との間には、後述するカーボンミキシング傾斜層38が存在する。このカーボンミキシング傾斜層38が合成樹脂組成物と硬質炭素皮膜との密着性を高めており、硬質炭素皮膜36はベルト案内面30の表面に強固に一体化して存在している。
【0020】
次に、この硬質炭素皮膜36をプラズマイオン注入法によってベルト案内面30に形成するプロセスについて説明する。
硬質炭素皮膜36を形成するプロセスは、クリーニングステージ、注入ステージ及び成膜ステージとからなる。最初のクリーニングステージでは、図示しないプラズマイオン注入装置の真空容器内に、未だベルト案内面30に硬質炭素皮膜36を形成していない樹脂製プーリ10をセットし、アルゴンとメタンの混合ガスプラズマ内において−5kVから−35kVのパルス電圧を樹脂製プーリ10に印加し、ベルト案内面30をスパッダリングによりクリーニングする。ベルト案内面30のクリーニングを終えたら、注入ステージに移る。この注入ステージで、−15kVから−35kVのパルス電圧を樹脂製プーリ10に印加し、ベルト案内面30にメタンガスプラズマによるイオン注入を行う。このイオン注入によって0.1μm程度の層厚T2を有するカーボンミキシング傾斜層38をベルト案内面30に形成する。そして、−15kVから−35kVのパルス電圧を樹脂製プーリ10に再び印加し、既に注入したカーボンの単原子とアセチレンガス等の直鎖状炭化水素とのバインディングを行う。その後、成膜ステージにおいて、−2kVから−5kVのパルス電圧を樹脂製プーリ10に印加するとともに、プラズマガス圧を0.5〜2Paとし、パルスの繰り返し数を毎秒2000〜10000パルスとして、ベルト案内面30にイオン注入を行い、カーボンミキシング傾斜層38の上に硬質炭素皮膜36を形成する。そして、必要に応じて、窒素やカーボン等のイオン注入、アルゴンによる硬質炭素皮膜36の表面トリートメントを施す。
【0021】
本実施の形態に係る樹脂製プーリ10は、上記のように形成されて構成されており、次にその作用について説明する。
樹脂製プーリ10のベルト案内面30には、図示しない平ベルトが架けられて案内されている。この平ベルトとベルト案内面30との間に砂塵等の異物が挟まっても、この異物がベルト案内面30を覆って形成された硬質炭素皮膜36と接触するだけであり、ベルト案内面30を形成する合成樹脂組成物と直接接触することは防止されている。硬質炭素皮膜36をなすダイヤモンドライクカーボンはHv1000〜5000の非常に高い硬度を有するので、前記異物によって硬質炭素皮膜36が摩耗することは殆どなく、ベルト案内面30を形成する合成樹脂組成物に損傷を生じることは防止されている。このため、樹脂製プーリ10の外径が変化しにくくなり、樹脂製プーリ10の外径が摩耗により縮小することは防止され、前記平ベルトがベルト案内面30から外れることも防止される。
【0022】
また、硬質炭素皮膜36の膜厚T1を1〜3μmとしているので、冷熱サイクルによって硬質炭素皮膜36中に大きな内部応力が生じることは防止されており、硬質炭素皮膜36に亀裂や剥離が生じることも防止されている。したがって、硬質炭素皮膜36は長期間に亙ってベルト案内面30を覆って存在し続けることが可能となり、ベルト案内面30の耐摩耗性が維持される。
【0023】
さらに、ベルト案内面30をなす合成樹脂組成物と硬質炭素皮膜36との間にはカーボンミキシング傾斜層38が形成されており、この合成樹脂組成物と硬質炭素皮膜36とは互いにカーボンミキシング傾斜層38を介して密着しているので、硬質炭素皮膜36がベルト案内面30から剥離等することは防止されている。
【0024】
また、樹脂部24を形成する合成樹脂組成物に、繊維系充填材と粒子状充填材を添加している場合は、樹脂部24の機械的強度が高くなる。したがって、ベルト案内面30に架けられるベルトの張力に対して、樹脂部24が変形したりすることが防止される。さらに、樹脂部24を射出成形する時に生じる成形収縮の異方性を制御することができ、ベルト案内面30の真円度を高めることができる。ベルト案内面30の真円度を高めることにより、ベルト案内面30に案内される平ベルトの振れが防止され、騒音も低減される。
【0025】
また、樹脂部24を形成する合成樹脂組成物に、ポリアミド66やポリアミド46のポリアミドと低吸水ポリアミドとからなるポリマーアロイを用いた場合は、樹脂性プーリ10は耐塩化カルシウム性に優れる。
また、転がり軸受12中に充填されるグリースとして、ポリαオレフィン油、アルキルジフェニルエーテル油等を基油とし、ジウレア等を増ちょう剤とし、酸化防止剤や摩耗防止剤等を添加剤として加えたものを使用すると、自動車の補機類について樹脂製プーリ10を使用する条件下で、転がり軸受12に焼きつき等を生じることが防止される。
【0026】
なお、本実施の形態において硬質炭素皮膜36をベルト案内面30に形成することとしたが、ベルト案内面30とともに、ベルト案内面30以外の樹脂部24の表面にも硬質炭素皮膜36を形成することが可能であることは勿論である。
また、本実施の形態において、ベルト案内面30は平坦なフラット形状であるとしたが、図4の変形例に示すように、Vの字状の断面を有する溝40が周方向に連続するVリブ形状とすることによりベルト案内面30を形成し、Vベルトを架けられるようにすることもできる。
【0027】
さらに、本実施の形態において、転がり軸受12を深溝玉軸受としたが、深溝玉軸受に限定されるものでないことは勿論であり、アンギュラ玉軸受等とすることが可能である。また、転がり軸受12の転動体20が玉に限定されるものではなく、ころによって転動体20を構成することが可能であることは勿論である。
次に、本実施の形態に係る樹脂製プーリの耐摩耗性能試験結果を示す。
【0028】
本耐摩耗性試験で使用した本実施の形態に係る樹脂製プーリ(以下、「本発明例の樹脂製プーリ」という)は、前述の本実施の形態において説明した樹脂製プーリ10と同様の構成を有する。本発明例の樹脂製プーリの樹脂部を形成する合成樹脂組成物の組成は以下のものとした。すなわち、ガラス繊維を33質量%添加したポリアミド66と、やはりガラス繊維を33質量%添加したポリアミド612とを質量比4:1の割合で混合して合成樹脂組成物とした。なお、ガラス繊維を33質量%添加したポリアミド66にはデュポンジャパン株式会社製のザイテル70G−33Lを使用し、ガラス繊維を33質量%添加したポリアミド612にはデュポンジャパン株式会社製のザイテル77G−33Lを使用した。
【0029】
そして、この合成樹脂組成物を280〜300℃で溶融し、75〜85℃とした金型のキャビティ内に流し入れ、90〜120MPaの射出圧力で樹脂部を転がり軸受の周りに一体成形し、ベルト案内面には未だ硬質炭素皮膜を形成していない樹脂製プーリを形成した。
そして、この樹脂製プーリの転がり軸受部分にマスキングを施した後、プラズマイオン注入装置によってベルト案内面に3μmの膜厚T1を有する硬質炭素皮膜を形成する処理を行った。なお、プラズマイオン注入装置には、株式会社栗田製作所製の3Dプラズマパック表面処理装置を使用した。まず、窒素を用いたスパッダリングによりベルト案内面のクリーニングを行い、クリーニング後にカーボンイオンの注入を行って0.1μmの層厚T2を有するカーボンミキシング傾斜層をベルト案内面に形成した。その後、カーボンミキシング傾斜層の上に硬質炭素皮膜を形成させて、本発明例の樹脂製プーリを得た。
【0030】
一方、本発明例の樹脂製プーリと耐摩耗性を比較するために、従来ある樹脂製プーリ(以下、「比較例の樹脂製プーリ」という)についても耐久試験を行った。比較例の樹脂製プーリの構成は、ベルト案内面に硬質炭素皮膜を形成しておらず、合成樹脂組成物が露出している点を除いて、本発明例の樹脂製プーリと同様である。
【0031】
また、本耐摩耗性試験で使用した耐摩耗性試験機の構成を図5に示す。耐摩耗性試験機42は駆動モータにつながった駆動輪44と従動輪46とを備え、駆動輪44と従動輪46とはベルト48が架け渡されて連結されている。そして、駆動輪44と従動輪46との間で、ベルト48に試験対象の樹脂製プーリ11のベルト案内面30を接触させて取り付け可能になっている。
【0032】
なお、この樹脂製プーリ11の転がり軸受には下方向きに100kgfの荷重がかけられており、この荷重によって樹脂製プーリ11のベルト案内面31はベルト48に押し付けられている。そして、駆動輪44が回転するとベルト48が回転し、従動輪46も回転し、ベルト48に押し付けられたベルト案内面30も回転する。
【0033】
さらに、耐摩耗性試験機42は恒温槽50中に収納されており、恒温槽50中の雰囲気は120℃に維持されている。また、この雰囲気中には、関東ローム粉JIS#8が空間容積で0.05%の条件を満足するようにファンによって漂わせてある。この恒温槽50中の雰囲気は、悪路を走行中の自動車に補機類に使用された樹脂製プーリが置かれる雰囲気を再現したものである。
【0034】
そして、本発明例の樹脂製プーリを耐摩耗性試験機42に取り付け、本発明例の樹脂製プーリを8000min−1で回転させた。回転時間が10時間経過するごとに、耐摩耗性試験機42を停止し、本発明例の樹脂製プーリを室温まで冷却し、本発明例の樹脂製プーリのベルト案内面の半径方向の寸法の累計摩耗量を測定した。そして、累計回転時間が100時間になるまで耐摩耗性試験を続けて行った。
【0035】
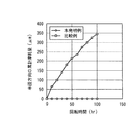
また、比較例の樹脂製プーリについても、本発明例の樹脂製プーリと同様の条件で耐摩耗性試験機42によって耐摩耗性試験を行った。
本耐摩耗性試験の試験結果を図6に示す。累計回転時間が100時間となった時点で、比較例の樹脂製プーリのベルト案内面の半径方向の累計摩耗量は約350μmであった。これに対して、本発明例の樹脂製プーリのベルト案内面の半径方向の累計摩耗量は約1.4μmであり、ほとんど摩耗の進行が認められなかった。
【0036】
したがって、本発明例の樹脂製プーリは耐摩耗性に優れ、悪路を走行する自動車に使用されるような場合に優れた耐久性を発揮できることが確認された。
【0037】
【発明の効果】
本発明は、上記のような樹脂製プーリであるので、ベルトとベルト案内面との間に異物が挟まってもベルト案内面に摩耗を生じにくく、ベルト案内面に形成した皮膜の損傷を生じにくい樹脂製プーリを提供できるという効果がある。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の実施の形態に係る樹脂製プーリの正面図である。
【図2】図1の樹脂製プーリのA−A線断面図である。
【図3】本発明の実施の形態に係るベルト案内面の構成図である。
【図4】本実施の形態の変形例に係る樹脂製プーリの断面図である。
【図5】耐摩耗性試験機の構成図である。
【図6】耐摩耗性試験の試験結果の説明図である。
【符号の説明】
10、11 樹脂製プーリ
12 転がり軸受
14 外輪
16 凹溝
18 内輪
20 転動体
21 保持器
22 接触ゴムシール
24 樹脂部
26 内径円筒部分
28 外径円筒部分
30、31 ベルト案内面
32 円板部分
34 リブ
36 硬質炭素皮膜
38 カーボンミキシング傾斜層
T1 硬質炭素皮膜の膜厚
T2 カーボンミキシング傾斜層の層厚
40 溝
42 耐摩耗性試験機
44 駆動輪
46 従動輪
48 ベルト
50 恒温槽[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a resin pulley provided integrally with a rolling bearing on the inner diameter side.
[0002]
[Prior art]
Conventionally, a resin pulley is generally used to guide a belt for driving auxiliary machines mounted on an automobile. This resin pulley is composed of a rolling bearing and a resin portion, and the resin portion is integrally formed on the outer periphery of the outer ring of the rolling bearing. The resin portion includes an inner diameter cylindrical portion on the inner peripheral side, an outer diameter cylindrical portion on the outer peripheral side, a disc portion connecting the inner diameter cylindrical portion and the outer diameter cylindrical portion, and a plurality of disc portions formed on the disc portion. And ribs. The outer peripheral surface of the outer diameter cylindrical portion serves as a belt guide surface, and a rubber belt for driving auxiliary machinery is laid on the belt guide surface for guidance.
[0003]
While a vehicle using this resin pulley is running, foreign matter such as dust may get caught between the belt and the belt guide surface, and the resin pulley may be worn and damaged. It was. Such damage is particularly likely to occur when an automobile runs continuously on a rough road. In order to cope with this problem, a ceramic film mainly composed of SiO 2 and Al 2 O 3 is formed by thermal spraying on the belt guide surface (see, for example, Patent Document 1).
[0004]
Moreover, the resin part of a resin pulley is formed with a synthetic resin composition to which a filler such as glass fiber or mica powder is added to improve the wear resistance of the resin part (for example, Patent Document 2). See).
Furthermore, the resin pulley is required to have a molding accuracy of the outer diameter cylindrical portion, a strength that can withstand the tension of the belt, heat resistance against heat generated during continuous load use, and calcium chloride resistance and the like. Therefore, for the purpose of improving the molding accuracy, strength, heat resistance and calcium chloride resistance, the synthetic resin composition forming the resin portion of the resin pulley is filled with about 15 to 40% by mass of a filler such as glass fiber. It has been proposed to use polyamide 66, polyamide 610, polyamide 612, or a composite material of poniphenylene sulfide and mineral (see, for example, Patent Document 3). A synthetic resin composition made of a polyamide resin such as polyamide 6, polyamide 66,
[0005]
[Patent Document 1]
JP 7-12206 A (page 2)
[Patent Document 2]
JP-A-8-145148 (pages 2 and 3)
[Patent Document 3]
JP 7-63249 A (paragraph number [0004] on page 2)
[Patent Document 4]
JP-A-8-4883 (paragraph number [0043] on page 7)
[0006]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, when the ceramic coating is sprayed on the belt guide surface, it is assumed that the following problems occur. That is, although the ceramic film is excellent in wear resistance, the thickness of the ceramic film is relatively thick at 50 to 100 μm. For this reason, the internal stress in the ceramic film tends to increase due to the thermal cycle. Therefore, it is considered that cracking and peeling are likely to occur in the ceramic film when the resin pulley is operated.
[0007]
In addition, when the resin portion of the resin pulley is formed by a synthetic resin composition to which a filler such as glass fiber is added, the wear of the belt guide surface proceeds through the process described below, and finally the belt is removed from the resin pulley. It is assumed that there will be a problem that will come off. That is, due to foreign matter such as dust sandwiched between the belt and the belt guide surface, wear proceeds in a portion other than the filler on the belt guide surface, and a portion where the filler is relatively present is a convex portion on the belt guide surface. As a result, the belt guide surface becomes rough. After that, the remaining convex portion is also worn out. As a result, the outer diameter of the belt guide surface is reduced, the belt is loosened, and the resin pulley must be replaced.
[0008]
The present invention has been made to eliminate the above-described problems of the prior art, and the object of the present invention is to cause wear on the belt guide surface even if foreign matter is caught between the belt and the belt guide surface. It is an object of the present invention to provide a resin pulley that is difficult to cause damage to the film formed on the belt guide surface.
[0009]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The present invention adopts the following configuration in order to solve the problem. A resin pulley comprising a rolling bearing and a resin portion provided on the outer periphery of the rolling bearing, the belt guide surface being formed on the outer periphery of the resin portion and in contact with the drive belt and guiding the drive belt A hard carbon film is formed thereon, a carbon mixing gradient layer is formed under the hard carbon film, and the hard carbon film is in close contact with the belt guide surface via the carbon mixing gradient layer .
[0010]
According to the first aspect of the present invention, the hard carbon film formed on the belt guide surface has a very high hardness and excellent wear resistance. Therefore, the wear resistance of the belt guide surface is very large.
Examples of the hard carbon film include diamond-like carbon having a hardness of Hv 1000 to 5000. Examples of the method for forming the hard carbon film include plasma CVD, ion beam evaporation, and plasma ion implantation.
[0011]
When the thickness of the hard matter carbon film is thinner than 0.5 [mu] m, all the belt guide surface becomes difficult to be covered by the hard carbon film, partially resin portion is exposed on the belt guiding surface, the belt guide surface The wear resistance is lowered, and sufficient wear resistance cannot be exhibited on the belt guide surface. Also, if the film thickness is thicker than 10 μm, large internal stress tends to be accumulated in the hard carbon film, and this internal stress easily causes self-destruction due to cracks and peeling in the hard carbon film, resulting in wear resistance. It is difficult to exert the effect over a long period of time. Therefore, the film thickness of the hard carbon film is preferably 0.5 to 10 μm.
[0012]
In addition, from the viewpoint of reliably covering all belt guide surfaces with a hard carbon film, further preventing self-destruction of the hard carbon film, and stably exhibiting the wear resistance of the hard carbon film over a long period of time, The film thickness of the hard carbon film is more preferably 1 to 5 μm. In consideration of controlling the formation time and formation conditions of the hard carbon film, it is even more desirable to set the film thickness of the hard carbon film to 1 to 3 μm.
[0013]
According to the present invention, the carbon mixing gradient layer is formed between the synthetic resin composition of the resin portion forming the base portion of the belt guide surface and the hard carbon film formed on the surface of the belt guide surface. The inclined layer enhances the adhesion between the synthetic resin composition and the hard carbon film. Therefore, peeling of the hard carbon film is prevented, and the hard carbon film is stably present on the belt guide surface over a long period of time.
[0014]
An example of a method for forming the carbon mixing gradient layer is a plasma ion implantation method. When a hard carbon film is formed using the plasma ion implantation method, a carbon mixing gradient layer is formed between the synthetic resin composition of the resin part forming the base of the belt guide surface and the hard carbon film on the surface of the belt guide surface. The
[0015]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
First, the configuration of the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS.
As shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, the
[0016]
The space between the
[0017]
A
The
[0018]
As the synthetic resin composition for forming the
[0019]
Further, when the outer peripheral surface of the outer diameter
[0020]
Next, a process for forming the
The process for forming the
[0021]
The
A flat belt (not shown) is hung on the
[0022]
Further, since the film thickness T1 of the
[0023]
Further, a carbon mixing
[0024]
Moreover, when the fiber type filler and the particulate filler are added to the synthetic resin composition forming the
[0025]
Moreover, when the polymer alloy which consists of polyamide 66, the
Further, as grease filled in the rolling
[0026]
In the present embodiment, the
In the present embodiment, the
[0027]
Furthermore, in this embodiment, the rolling
Next, the abrasion resistance performance test result of the resin pulley according to the present embodiment is shown.
[0028]
The resin pulley according to the present embodiment used in the wear resistance test (hereinafter referred to as “resin pulley of the present invention example”) has the same configuration as the
[0029]
Then, this synthetic resin composition is melted at 280 to 300 ° C. and poured into a cavity of a mold having a temperature of 75 to 85 ° C., and the resin part is integrally molded around the rolling bearing with an injection pressure of 90 to 120 MPa. A resin pulley having a hard carbon film not yet formed is formed on the guide surface.
Then, after masking the rolling bearing portion of the resin pulley, a process of forming a hard carbon film having a film thickness T1 of 3 μm on the belt guide surface was performed by a plasma ion implantation apparatus. As the plasma ion implantation apparatus, a 3D plasma pack surface treatment apparatus manufactured by Kurita Manufacturing Co., Ltd. was used. First, the belt guide surface was cleaned by sputtering using nitrogen, and after the cleaning, carbon ions were implanted to form a carbon mixing gradient layer having a layer thickness T2 of 0.1 μm on the belt guide surface. Thereafter, a hard carbon film was formed on the carbon mixing gradient layer to obtain a resin pulley of the present invention.
[0030]
On the other hand, in order to compare the wear resistance with the resin pulley of the present invention, a conventional resin pulley (hereinafter referred to as “resin pulley of comparative example”) was also subjected to a durability test. The structure of the resin pulley of the comparative example is the same as that of the resin pulley of the present invention except that the hard carbon film is not formed on the belt guide surface and the synthetic resin composition is exposed.
[0031]
FIG. 5 shows the configuration of the wear resistance tester used in this wear resistance test. The
[0032]
A load of 100 kgf is applied to the rolling bearing of the
[0033]
Furthermore, the
[0034]
Then, the resin pulley of the present invention example was attached to the
[0035]
The comparative example of the resin pulley was also subjected to an abrasion resistance test by the
The test results of this wear resistance test are shown in FIG. When the cumulative rotation time reached 100 hours, the cumulative wear amount in the radial direction of the belt guide surface of the resin pulley of the comparative example was about 350 μm. On the other hand, the cumulative wear amount in the radial direction of the belt guide surface of the resin pulley of the present invention was about 1.4 μm, and almost no progress of wear was observed.
[0036]
Therefore, it was confirmed that the resin pulley of the present invention example has excellent wear resistance and can exhibit excellent durability when used in an automobile traveling on a rough road.
[0037]
【The invention's effect】
Since the present invention is a resin pulley as described above, even if a foreign object is caught between the belt and the belt guide surface, the belt guide surface is hardly worn, and the film formed on the belt guide surface is not easily damaged. There is an effect that a resin pulley can be provided.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a front view of a resin pulley according to an embodiment of the present invention.
2 is a cross-sectional view of the resin pulley of FIG. 1 taken along line AA.
FIG. 3 is a configuration diagram of a belt guide surface according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view of a resin pulley according to a modification of the present embodiment.
FIG. 5 is a configuration diagram of an abrasion resistance tester.
FIG. 6 is an explanatory diagram of test results of an abrasion resistance test.
[Explanation of symbols]
10, 11
Claims (1)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002291865A JP4154986B2 (en) | 2002-10-04 | 2002-10-04 | Resin pulley |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002291865A JP4154986B2 (en) | 2002-10-04 | 2002-10-04 | Resin pulley |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2004125102A JP2004125102A (en) | 2004-04-22 |
| JP2004125102A5 JP2004125102A5 (en) | 2005-09-29 |
| JP4154986B2 true JP4154986B2 (en) | 2008-09-24 |
Family
ID=32283305
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002291865A Expired - Lifetime JP4154986B2 (en) | 2002-10-04 | 2002-10-04 | Resin pulley |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4154986B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007071319A (en) * | 2005-09-08 | 2007-03-22 | Nsk Ltd | Rolling bearing with pulley |
| DE102006039363A1 (en) * | 2006-08-22 | 2008-03-06 | Schaeffler Kg | Strip tension roller for a traction drive unit comprises a plastic running roller having a running surface with a physical vapor deposition coating |
| WO2009084231A1 (en) * | 2007-12-28 | 2009-07-09 | Bando Chemical Industries, Ltd. | Belt transmission device and transmission belt used for the same |
| FR3078131B1 (en) * | 2018-02-19 | 2020-01-31 | Aktiebolaget Skf | PULLEY DEVICE FOR TENSIONER OR ROLLER |
-
2002
- 2002-10-04 JP JP2002291865A patent/JP4154986B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2004125102A (en) | 2004-04-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7785013B2 (en) | High-accuracy sliding bearing | |
| US20190178386A1 (en) | Sliding component | |
| JP2011117609A (en) | Crown-shaped retainer for ball bearing, method of manufacturing the same, and ball bearing | |
| US6213476B1 (en) | Bi-modulus composite seal and its method of manufacture | |
| RU2599687C2 (en) | Sliding element with coating of diamond-like carbon | |
| JPH11170397A (en) | Thrust washer for high speed and high surface pressure slide | |
| JP2008506902A (en) | Sealing device | |
| JP4154986B2 (en) | Resin pulley | |
| US6296393B1 (en) | Lubricant-containing polymer-filled rolling bearing and process for the production thereof | |
| JP7265431B2 (en) | Structure | |
| CN1488869A (en) | Resin pulley | |
| US20090110339A1 (en) | Bearing Device with Sliding Bearing | |
| JP2010180971A (en) | Rolling bearing and manufacturing method | |
| JP4171899B2 (en) | Resin pulley | |
| JPH0942461A (en) | Oil seal and its manufacturing method | |
| JP2003314561A (en) | Ball bearing | |
| JP2007192386A (en) | Pulley device | |
| JP3772944B2 (en) | Roller bearings filled with polymer containing lubricant | |
| JP4013016B2 (en) | Lubricant supply composition and rolling bearing filled with the same | |
| JP2006316973A (en) | Synthetic resin-made pulley | |
| JP2007255492A (en) | Rolling bearing | |
| JPH11117758A (en) | Member for engine electric equipment accessory | |
| Rubenstein et al. | Wear assessment of epoxy composites used for machine slideways | |
| JP2001289330A (en) | Slide contact structure of sealing part of construction and civil engineering machine | |
| JP2004205016A (en) | Linear motion device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20050426 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20050426 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20080207 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20080212 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20080314 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20080617 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20080630 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110718 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110718 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120718 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120718 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130718 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| S801 | Written request for registration of abandonment of right |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R311801 |
|
| R371 | Transfer withdrawn |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R371 |
|
| S801 | Written request for registration of abandonment of right |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R311801 |
|
| ABAN | Cancellation due to abandonment | ||
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |