JP4126907B2 - Liquid crystal display device and electronic device - Google Patents
Liquid crystal display device and electronic device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4126907B2 JP4126907B2 JP2001394903A JP2001394903A JP4126907B2 JP 4126907 B2 JP4126907 B2 JP 4126907B2 JP 2001394903 A JP2001394903 A JP 2001394903A JP 2001394903 A JP2001394903 A JP 2001394903A JP 4126907 B2 JP4126907 B2 JP 4126907B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- liquid crystal
- layer
- reflective
- region
- display
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Liquid Crystal (AREA)
- Devices For Indicating Variable Information By Combining Individual Elements (AREA)
- Optical Elements Other Than Lenses (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、液晶表示装置及び電子機器に関し、特に反射型と透過型の両方の構造を具備させた半透過反射型の液晶表示装置において、反射表示と透過表示の境界付近におけるディスクリネーションの発生を抑制し、明るく高コントラストな表示を得られるようにした技術に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
反射型と透過型の表示方式を兼ね備えた半透過反射型液晶表示装置は、周囲の明るさに応じて反射モード又は透過モードのいずれかの表示方式に切り替えることにより、消費電力を低減しつつ周囲が暗い場合でも明瞭な表示を行うことができるものである。
【0003】
このような半透過反射型液晶表示装置としては、透光性の上基板と下基板との間に液晶層が挟持された構成を備えるとともに、例えばアルミニウム等の金属膜に光透過用のスリットを形成した反射膜を下基板の内面に備え、この反射膜を半透過反射膜として機能させる液晶表示装置が提案されている。この場合、反射モードでは上基板側から入射した外光が、液晶層を通過した後に下基板の内面に配された反射膜により反射され、再び液晶層を通過して上基板側から表示に供される。一方、透過モードでは下基板側から入射したバックライトからの光が、反射膜に形成されたスリットから液晶層を通過した後に、上基板側から外部に表示され得る。したがって、反射膜のスリットが形成された領域が透過表示領域で、反射膜のスリットが形成されていない領域が反射表示領域とされている。
【0004】
上記構成の半透過反射型液晶表示装置において、例えば液晶層の厚さをd1、液晶の屈折率異方性をΔn、これらの積算値として示される液晶のリタデーションをΔnd1とすると、反射表示を行う部分の液晶のリタデーションΔnd1は、入射光が液晶層を2回通過してから観測者に到達するので2×Δnd1で示されるが、透過表示を行う部分の液晶のリタデーションΔnd1は、バックライトからの光が1回のみ液晶層を通過するので1×Δnd1となる。
【0005】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
このように反射表示領域と透過表示領域とにおいてリタデーションの値が異なる構造であるのに対し、液晶層の液晶分子の配向制御を行う場合に、各表示モードで同じ駆動電圧で液晶に電界を印加して配向制御を行っており、液晶において表示形態の異なる状態、換言すると、透過型表示領域と反射型表示領域においてリタデーションの異なる状態の液晶を同一の駆動電圧で配向したのでは高コントラストの表示を得ることができない場合があった。
【0006】
そこで、反射表示領域において下基板の上側にアクリル樹脂を形成し、液晶層厚を透過表示領域よりも小さくし、リタデーションの均一化を図る技術が提案されている。この場合、液晶層の層厚を制御するためのアクリル樹脂層は、反射表示領域と透過表示領域とにおいて自身の層厚が異なる構成とされているため、各領域の境界付近において段差が生じ、したがって液晶層にも各領域の境界付近で段差が生じていた。このように液晶層に段差が生じると、その段差部において液晶配向が乱れ、ディスクリネーションが発生する惧れがあり、ひいてはコントラスト低下等の表示不良の一因となる惧れがある。
【0007】
本発明は、上記の課題を解決するためになされたものであって、半透過反射型液晶表示装置として、反射表示領域と透過表示領域との境界付近において、ディスクリネーションの発生を抑制可能な構成であって、明るくコントラストの高い表示を得ることが可能な液晶表示装置と、その液晶表示装置を備えた電子機器を提供することを目的とする。
【0008】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上記課題を解決するために、本発明の液晶表示装置は、一対の基板間に液晶層が挟持されており、反射表示に利用される反射表示領域と、透過表示に利用される透過表示領域とを個別に備えてなる液晶表示装置において、前記一対の基板のうちの少なくとも一方の基板に設けられ、前記反射表示領域における前記液晶層の層厚と前記透過表示領域における前記液晶層の層厚とを異ならせる絶縁層と、前記一方の基板に設けられてなるカラーフィルタと、前記一対の基板のうちの他方の基板に形成されてなり、前記透過表示領域に対応する開口部が形成された反射層と、を具備し、前記絶縁層は、当該絶縁層の層厚を連続的に変化させた傾斜面を有する傾斜領域を備え、前記傾斜領域は、前記反射層の縁と重なるように配置されることにより、前記透過表示領域と前記反射表示領域との境界部及び当該境界部付近に位置し、前記カラーフィルタは、前記傾斜領域を含む前記透過表示領域および反射表示領域にわたって設けられ、前記透過表示領域における色純度が前記反射表示領域における色純度より高く設定されてなることを特徴とする。
【0009】
この場合、絶縁層が少なくとも反射表示領域に形成されて、反射表示領域における液晶層層厚を透過表示領域における液晶層層厚よりも小さくしているため(反射側液晶層薄層化手段として機能している)、反射表示と透過表示とにおいて表示に寄与する光が通過する液晶層の層厚が異なる場合においても、そのリタデーションの差を小さく若しくはゼロとすることが可能となる。さらに、絶縁層を、反射表示領域と透過表示領域との境界付近において、自身の層厚が連続的に変化するべく傾斜面を備えた傾斜領域を含む構成としたため、反射表示領域と透過表示領域との境界付近において絶縁層の段差が生じず、したがって境界付近における液晶層の段差が生じ難い構成となり、液晶配向の乱れ等が生じ難く、ディスクリネーションの発生が抑制される。本発明においては、前記絶縁層は、絶縁層の層厚を連続的に変化させた傾斜面を有する傾斜領域を備え、傾斜領域は、透過表示領域と反射領域との境界部及び境界部付近に形成されてなり、カラーフィルタは、傾斜領域を含む透過表示領域および反射表示領域に対応して設けられ、透過表示領域における色純度が反射表示領域における色純度より高く設定されてなる。そのため、透過表示においては透過光がカラーフィルタを1回通過した後に表示に供され、反射表示においては外光がカラーフィルタを入射の際と反射の際に1回ずつ計2回通過するため、上記のように透過表示領域においてカラーフィルタの色純度を反射表示領域よりも相対的に高くすることで、透過表示と反射表示とにおいて色の濃淡を同程度にすることが可能となる。
【0010】
なお、絶縁層は、例えばアクリル樹脂等の透光性絶縁材料を主体として構成することが可能で、液晶層は、絶縁層の傾斜面が形成された面側に配設され、この液晶層の層厚が、傾斜面に沿って反射表示領域と透過表示領域との境界付近において連続的に変化しているものとすることができる。また、反射表示領域には、入射した光を反射することが可能な反射層が形成されているものとすることができ、例えば太陽光、照明光等の外光が入射する側と異なる側の基板(内部側基板)と液晶層との間に反射層が形成されているものとすることができる。この場合、外光は、液晶層を通過した後に反射層にて反射され、再び液晶層を通過して計2回液晶層を通過して表示に供される一方、内部側基板から入射される光源光(バックライト)は、液晶層を1回通過して表示に供されるため、本発明の構成を採用して、例えば、絶縁層にて反射表示領域における液晶層層厚を透過表示領域における液晶層層厚の概ね半分とすることで、各領域におけるリタデーションの値を略等しいものとすることが可能となる。
【0011】
また前記絶縁層は、前記反射表示領域に位置し、膜厚が略均一で且つ前記液晶層側の面が平坦面とされた反射側平坦領域を備え、前記傾斜面は平面状、又は曲面状に形成されるとともに、前記反射側平坦領域に形成された前記絶縁層の層厚をdとした場合、前記傾斜領域における前記絶縁層の層厚がd/2となる位置における前記傾斜面の接線と、前記平坦面とのなす角度αが、10°〜50°とされていることを特徴とする。反射側平坦領域においては安定した液晶配向が得られるとともに、隣接する傾斜領域においては上述した通り、絶縁層の段差が生じず、したがって境界付近における液晶層の段差が生じ難い構成となり、液晶配向の乱れ等が生じ難くなる。なお、透過表示領域においても、液晶層に接する面を平坦面とすることで、ディスクリネーションの発生等が生じ難い、均一な液晶配向を実現することが可能となる。
【0012】
また、前記傾斜面が平面状、又は曲面状に形成されるとともに、前記反射側平坦領域に形成された前記絶縁層の層厚をdとした場合、前記傾斜領域における前記絶縁層の層厚がd/2となる位置における前記傾斜面の接線と、前記平坦面とのなす角度αが、10°〜50°とされているので、良好な表示が得られるようになる。例えば、角度αが50°を超えると、反射表示領域と透過表示領域との境界付近において、すなわち傾斜領域においてディスクリネーションが発生する場合があり、これにより表示の明るさが低下する場合がある。一方、角度αが10°未満の場合、液晶配向の欠陥は生じ難いものの、平坦な領域が減り、反射表示領域及び透過表示領域の液晶層層厚が所望の厚さと異なる領域が増すため、表示の明るさがディスクリネーションが発生した場合よりも低下してしまう場合がある。なお、角度αは、好ましくは30゜〜45゜程度とするのが良い。
【0013】
また、前記反射表示領域には反射層が形成されているとともに、当該反射層の縁が前記傾斜領域に含まれて配置されていることを特徴とする。例えば、上記反射層が開口部を備え、その開口部に透過表示領域が形成されるとともに、開口部の開口縁が上記傾斜領域に含まれるものとすることができる。すなわち、反射表示領域と透過表示領域との境界となる反射層の開口部の開口縁を、上記傾斜領域に含ませることで、反射表示領域と透過表示領域のいずれにも、液晶層の層厚が変化する領域(傾斜領域)を含ませることが可能となり、したがって、リタデーションの差を小さくすることが可能となる。なお、上記d/2の位置において開口部の開口縁を設けることにより、リタデーションの差を一層小さくすることが可能となり、コントラスト低下等の少ない良好な表示を得ることが可能となる。
【0014】
次に、一対の基板のうち外光が入射する側を上基板、他方を下基板とした場合、反射表示領域には、下基板側から、反射層と、絶縁層と、下側電極と、液晶層と、上側電極とが少なくともこの順で含まれているものとすることができる。また、反射表示領域には、下基板側から、反射層と、下側電極と、液晶層と、上側電極と、絶縁層とが少なくともこの順で含まれているものとすることもできる。
【0015】
ここで下側電極、上側電極としては例えばITO(Indium-Tin-Oxide)等の透明電極を例示することができる。このような構成の場合、上基板(表示側基板、若しくは外側基板)から入射した外光が少なくとも上側電極、液晶層、下側電極、絶縁層を介して反射層に達し、この反射層で反射された後に同様の過程を経て外部に出射され、反射表示が実現される。
【0016】
なお、透過表示領域には下基板(バックライト側基板、若しくは内側基板)側から下側電極と、液晶層と、上側電極とがこの順で積層配置されているものとすることができる。このように、透過表示領域には絶縁層を設けないものとした場合、絶縁層を設けた反射表示領域よりも液晶層が相対的に厚くなり、反射表示にかかる往復分の液晶層層厚を透過表示において確保することが可能となる。したがって、透過表示と反射表示において同程度のリタデーションを確保可能となる。
【0017】
次に、上記一対の基板間にカラーフィルタが設けられ、反射表示領域と透過表示領域とにおいて、カラーフィルタの分光特性が異なるものとされ、透過表示領域においてカラーフィルタの色純度が反射表示領域よりも相対的に高くされているものとすることができる。透過表示においては透過光がカラーフィルタを1回通過した後に表示に供され、反射表示においては外光がカラーフィルタを入射の際と反射の際に1回ずつ計2回通過するため、上記のように透過表示領域においてカラーフィルタの色純度を反射表示領域よりも相対的に高くすることで、透過表示と反射表示とにおいて色の濃淡を同程度にすることが可能となる。
【0018】
また、上記下基板の液晶層側(上基板側)の面には凹凸が形成されているものとすることができる。すなわち、例えば凹凸を形成した下基板の上層に反射層を形成するものとすることができ、この場合、下基板に形成された凹凸により外光は散乱を伴って反射されるため、一層明るく高コントラストの反射表示を行うことが可能となる。
【0019】
次に、本発明の電子機器は上記構成の液晶表示装置を備えたことを特徴とする。この構成によれば、透過表示と反射表示とを切換可能であって、その透過表示及び反射表示において共に明るく高コントラストな表示を可能であって、さらにこれら透過と反射の表示に利用される各領域の境界付近においても、明るく高コントラストな表示を実現可能な電子機器を提供することができる。
【0020】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明の実施形態について図面に基づいて説明する。
[第1実施形態]
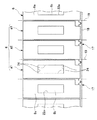
図1は、本発明の構成をアクティブマトリクスタイプの液晶表示装置に適用した第1実施形態を示すもので、この第1実施形態の液晶表示装置Aは、図1に示す断面構造の如く上下に対向配置された透明のガラス等からなる基板1,2の間に液晶層3が挟持された基本構造を具備している。なお、図面では省略されているが、実際には基板1,2の周縁部側にシール材が介在されていて、液晶層3を基板1,2とシール材とで取り囲むことにより液晶層3が基板1,2間に封入された状態で挟持されている。また、下方の基板2の更に下方側には光源及び導光板等を備えたバックライト4が設けられている。
【0021】
上側の基板1の上面側(観測者側)には位相差板12と偏光板13とが配置されるとともに、下側の基板2の下面側(内部光源側)にも位相差板14と偏光板15とが配置されている。偏光板13,15は、上面側から入射する外光、及び下面側から入射するバックライト4の光に対し一方向の直線偏光のみを透過させ、位相差板12,14は、偏光板13,15を透過した直線偏光を円偏光(楕円偏光を含む)に変換する。したがって、偏光板13,15及び位相差板12,14は円偏光入射手段として機能している。なお、本実施形態においては、バックライト4を備える側を下側とし、一方の外光が入射する側を上側としており、基板1を上基板1、基板2を下基板2と言うこともある。
【0022】
一方、上基板1の液晶層3側にはカラーフィルタ10を介してITO(Indium-Tin-Oxide)等からなる透明電極5が形成され、さらに透明電極5の液晶層3側には、この透明電極5を覆う態様で配向膜11が形成されている。また、下基板2の液晶層3側には反射層16が形成され、この反射層16は所定の間隔毎に開口部16aを具備し、その開口部16aが図1の紙面左右方向及び紙面垂直方向に相互に離間して透過表示領域に対応するように平面視矩形状に分割された態様で複数形成されている。なお、反射層16はAl、Ag等の光反射性の、すなわち反射率の高い金属材料により平面視矩形枠状に構成されており、配向膜11はポリイミド等の高分子材料膜に対して所定のラビング処理を施したものを用いている。
【0023】
また、下基板2の液晶層3側表面にはフロスト加工が施されて凹凸部2eが形成されており、この凹凸部2eに沿って反射層16の液晶層3側表面も凹凸部16eを形成している。このような基板2に対する凹凸形成は、例えば基板2となるガラス基板上にレジストを塗布した後にフッ酸を用いたエッチング処理を行い、エッチング処理後にレジストを剥離するフォトリソ工程を行うことで形成することができる。
【0024】
反射層16の上層側には、液晶層3について層厚の大きな領域と層厚の小さな領域とを形成するための液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bが所定の間隔毎に突出形態にて形成されている。液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bは、アクリル樹脂等の透光性絶縁材料を主体として構成されており、この液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bにより反射層16の上面が覆われるとともに、凸状の各液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bの間には凹状部22aが形成されている。また、液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bは、凹状部22aの谷底たる凹状底面23から10°〜50°の角度で傾斜した傾斜面24を備えた傾斜領域と、凸状部の丘部分たる平坦面25を備えた平坦領域とを有している。したがって、液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bは、傾斜領域において自身の層厚が平面方向に連続的に変化するものとされており、平坦領域において自身の層厚が平面方向に略均一な構成とされている。なお、これら傾斜領域と平坦領域とは隣接して、傾斜面と平坦面とが連続するべく形成されている。
【0025】
液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bの液晶層3側の表面、及び凹状部22aの底面(すなわち下基板2の凹部22aが形成されている面)23には透明電極6が形成され、透明電極6の上には電極を覆う態様で配向膜7が形成されている。透明電極6は例えばITO(Indium-Tin-Oxide)等を用いることができ、配向膜7は例えばポリイミド等の高分子材料膜に対して所定のラビング処理を施したものを用いることができる。なお、透明電極6は図2に示すスイッチング素子としての薄膜トランジスタ17により駆動制御され、したがって本実施形態では下側の透明電極6が画素電極、上側の透明電極5が対向電極、さらに下基板2が素子基板、上基板1が対向基板とされている。この場合、薄膜トランジスタ17等のスイッチング素子は例えば下基板2側に形成することができるが、本実施形態では図示を省略している。
【0026】
次に、本実施形態の液晶表示装置Aでは、液晶層3において表示に利用される領域が反射表示領域Rと透過表示領域Tを含み、これらの表示部がそれぞれ異なる液晶層厚で形成されている。具体的には、上述の液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bが反射表示領域Rに形成され、凹状部22aが透過表示領域Tに形成されており、この液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bの形成に基づき反射表示領域Rにおける液晶層3の厚さが、透過表示領域Tにおける液晶層3の厚さよりも小さく構成されている。すなわち、液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bの厚みに基づき反射表示領域Rにおける液晶層厚が小さくされ、この液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bが反射表示領域Rの液晶層3を薄層化する反射側液晶層薄層化手段として機能している。
【0027】
ここで、反射表示領域Rには上述の反射層16が形成され、反射層16の開口部16aの開口縁が反射表示領域Rと透過表示領域Tの境界部とされている。したがって、透過表示領域Tは開口部16aに形成され、この開口部16aを介してバックライト4から光が入射され、入射光は液晶層3を通過して透過表示に供されるものとされている。
【0028】
また、反射層16において開口部16aの開口縁は、上記液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bの傾斜面24を備えた傾斜領域に形成されており、この傾斜領域は反射表示領域Rと透過表示領域Tとの境界部を含む構成とされている。したがって、液晶層3の層厚は、傾斜領域の傾斜面24に沿って、反射表示領域Rと透過表示領域Tとの境界付近において連続的に変化している。具体的には、凹状部22aの底面23若しくは傾斜面24の上層に位置する液晶層3の層厚は、液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bの平坦面25の上層に位置する液晶層3の層厚よりも大きくされている。
【0029】
傾斜面24は、本実施形態では平面状に形成されており、その傾斜角が10°〜50°とされているが、図8に示すように緩やかに湾曲した曲面状に形成することも可能である。この場合、傾斜角は、上記平坦面25を備える平坦領域の層厚をdとして、傾斜領域の層厚がd/2となる位置における傾斜面の接線と、平坦面25とのなす角度αにて定義することが可能で、この角度αが10°〜50°となるように液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bを形成している。なお、本実施形態では、例えば平坦領域の層厚dは2μm、傾斜領域の傾斜幅(平面方向における幅)lは10μm程度とされている。
【0030】
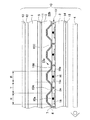
次に、図2は図1に示した液晶表示装置Aの電極6の平面模式図であって、液晶表示装置Aにおいて表示領域は図2に示すように多数の画素gが集合して構成され、各画素gは電極6を平面視した場合に縦長の3つの電極6が集合した略正方形状の部分により区画される。本実施形態の液晶表示装置Aはカラー表示を前提とした構造とされているので、具体的には図2に示す3つの電極6で区画される平面視略正方形状の1つの画素gが、3つのドットg1、g2、g3に分割されている。そして、これらのドットg1〜g3に対応する電極6の中央部分にそれぞれ長方形状の凹状部22aが形成され、これら凹状部22aの底側にも電極6が形成されている。この長方形状の凹状部22aにおいて、四辺各部において上述の傾斜面24を備えており、その内縁が透過表示領域Tとされている。
【0031】
ここで、電極6は、凹部22aに対応する位置に、詳しくは凹部22aの底部から傾斜領域中間部(詳しくは反射層16の開口縁16a)に至る位置に設けられた透過表示用電極6bと、平坦領域の層厚d(図8参照)に対応する位置に、詳しくは液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bの上面部に設けられた反射表示用電極6aとに機能的に分けることができ、それぞれ透過表示及び反射表示に寄与するものとされている。また、透過表示用電極6aは図1に示した開口部16aの開口内部に位置し、反射表示用電極6bは開口部16aを備えた反射層16の上層側に液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bを挟んで位置している。
【0032】
反射層16に形成された開口部16aの大きさは、ドットg1、g2、g3のいずれか1つの大きさに対し、各ドットの縦幅と横幅をいずれも数分の一程度とした大きさに形成される。また、各ドットg1、g2、g3の横幅は、例えば80μmとされており、各ドットg1、g2、g3にて構成される画素gの横幅は例えば240μmとされ、各ドットg1、g2、g3の縦幅、すなわち画素gの縦幅は例えば240μmとされている。なお、開口部16aの開口横幅は例えば30μm、開口縦幅は例えば100μm程度とすることができる。
【0033】
各ドットの周囲のコーナ部分には、電極6を駆動するためのスイッチング素子としての薄膜トランジスタ17が形成され、更に薄膜トランジスタ17に給電するためのゲート線18とソース線19とが配線されている。なお、本実施形態ではスイッチング素子として薄膜トランジスタ17が設けられているが、このスイッチング素子として2端子型の線形素子、あるいは、その他の構造のスイッチング素子を適用することも可能である。
【0034】
また、各ドットg1、g2、g3の平面位置に対応するようにカラーフィルタ10(図1参照)の各着色部分が配置される。カラーフィルタ10は「R(赤色)、G(緑色)、B(青色)」のいずれかに着色された着色部10A、10B、10Cと、これら着色部の境界部分に配置された遮光層(ブラックマトリクス)10aとから構成されている。なお、図1に示すカラーフィルタ10の構造においては、着色部が10A(赤)、10B(緑)、10C(青)の順に繰り返し配列されているが、これら着色部の配列順序は一例であって、ランダム配置、モザイク配置、あるいは他の順序の配列等のいずれの配列であっても良い。
【0035】
次に、図1と図2に示した構造の半透過反射型の液晶表示装置Aの作用効果について説明する。液晶表示装置Aにおいて、反射表示を行う場合には、装置の外部側から入射する光が利用され、この入射光が基板1の外部側からカラーフィルタ10、電極5、配向膜11を介して液晶層3側に導かれる。
【0036】
ここで、反射表示領域Rにおいては、上記入射光が液晶層3を通過した後に、配向膜7、電極6、液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bを通過し、反射層16で反射される。そして、反射された光は再度液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22b、電極6、配向膜7、液晶層3を通過した後、更に配向膜11、電極5、カラーフィルタ10、基板1、位相差板12、偏光板13を介して装置外部に戻されることにより観察者に到達し反射型のカラー表示が行われるものとされている。一方、透過型表示部Tにおいては、上記外部からの入射光は液晶層3を通過した後に、配向膜7、電極6を通過し、さらに反射層16の開口部16aを通過する。そして、開口部16aを通過した光は下側の基板2及び位相差板12を通過した後に、偏光板13に吸収される。このような反射型のカラー表示においては、電極5、6によって液晶層3の液晶を配向制御することで、液晶層3を通過する光の透過率を変えて明暗表示を行うものとされている。
【0037】
また、透過表示を行う場合には、バックライト4から発せられた光が偏光板15、位相差板14、基板2を介して入射する。この場合、透過表示領域Tにおいては、基板2から入射した光が電極6、配向膜7、液晶層3、配向膜11、電極5、カラーフィルタ10、基板1、位相差板12、偏光板13の順に透過して透過カラー表示が行われるものとされている。一方、反射表示領域Rにおいては、基板2から入射した光は、反射層16で反射され、反射された光は位相差板14を通過した後、偏光板15に吸収される。このような透過型のカラー表示においても、電極5、6によって液晶層3の液晶を配向制御することで、液晶層3を通過する光の透過率を変えて明暗表示することができる。
【0038】
これらの表示形態において、反射型の表示形態においては入射光が液晶層3を2回通過するが、透過光に関してはバックライト4から発せられた光が液晶層3を1回しか通過しない。ここで液晶層3のリタデーションを考慮すると、反射型の表示形態と透過型の表示形態では同じ電圧を電極5、6から印加して配向制御した場合に、液晶のリタデーションの違いにより液晶の透過率の状態に違いを生じる。しかしながら、本実施形態の構造では反射表示を行う領域、即ち、図1に示す反射層16を備えた領域である反射表示領域Rに液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bを設けたため、その反射表示領域Rの液晶層3の厚さよりも、透過表示を行う透過表示領域、即ち、図1に示す開口部16aに相当する領域である透過表示領域Tの液晶層3の厚さが大きくなり、反射表示領域Rと透過表示領域Tでの液晶層3の透過表示と反射表示に係る状態、すなわち各領域における液晶層3を光が通過する距離を揃えることができる。したがって、液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bの形成により、反射表示領域Rと透過表示領域Tにおけるリタデーションの均一化を図ることが可能とり、反射表示及び透過表示共に明るく高コントラストの表示が得られるようになる。
【0039】
また、反射表示領域Rと透過表示領域Tとの境界付近においては、液晶層3の層厚変化が急峻となり、液晶配向不良が生じる惧れがある。しかしながら、本実施形態では、各領域の境界付近において液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bを傾斜面を備えて形成したため、液晶層の急峻な層厚変化がなくなり、液晶配向不良が生じ難い構成となっている。したがって、本実施形態の液晶表示装置Aは半透過反射型の液晶表示装置であって、液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bの形成に基づき、反射表示と透過表示のいずれにおいても明るく高コントラストの表示を行うことが可能となり、特に反射表示領域と透過表示領域との境界付近における表示不良等も生じ難い表示装置となる。
【0040】
[第2実施形態]
以下、本発明の第2の実施形態を図3を参照して説明する。なお、図1に示した第1の実施形態と同じ符号については、特に断り書きのない限り同様の構成を有するものとして説明を省略する。第2実施形態の液晶表示装置Bは、反射表示領域Rにおいて下基板(バックライト側の基板)2の上層に、透光性凹凸層16bと、反射本体層16cとが形成されている。
【0041】
透光性凹凸層16bはアクリル樹脂を主体として構成されており、その表層部(液晶層側表面)には凹凸が形成され、その凹凸にしたがって反射本体層16cにも凹凸部が形成されている。このように反射本体層16cに凹凸を形成したことにより、外部から入射した光を確実に散乱反射させることが可能となる。なお、この凹凸部は0.5〜0.8μmの範囲の表面粗さとされてランダムに凹凸が形成されたものである。
【0042】
このような液晶表示装置Bにあっても、第1実施形態の液晶表示装置Aと同様に透過表示と反射表示を利用した表示形態をとることができる。その場合の効果としても、透過表示領域Tと反射表示領域Rとで液晶層の厚さを先の第1実施形態の場合と同様に変えているので、同等の効果を得ることができ、液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bには傾斜面を備えた傾斜領域が形成されているため、同領域において液晶配向不良等も生じ難い。更に本第2実施形態においては、反射本体層16cにランダムな凹凸を形成するための透光性凹凸層16bを形成したので、反射表示を行う場合に、反射本体層16cにおいて入射光を様々な方向に反射させることができ、一層広視野角の反射表示を得ることが可能となる。
【0043】
[第3実施形態]
以下、本発明の第3の実施形態を図4を参照して説明する。なお、図1に示した第1の実施形態と同じ符号については、特に断り書きのない限り同様の構成を有するものとして説明を省略する。第3実施形態の液晶表示装置Cにおいては、下基板2の上層側(液晶層3側)に反射層16が形成されるとともに、その反射層16の上層側であって、且つ反射層16の開口部16aを充填する態様にてカラーフィルタ10が形成されている。そして、カラーフィルタ10の上層には上述の液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22b、電極6、配向膜7、液晶層3が反射表示領域Rにおいて形成され、電極6、配向膜7、液晶層3が透過表示領域Tにおいて形成されている。
【0044】
このような液晶表示装置Cにあっても、第1実施形態の液晶表示装置Aと同様に透過表示と反射表示を利用した表示形態をとることができる。その場合の効果としても、反射表示領域Rに液晶層層厚制御層22bを形成し、透過表示領域Tと反射表示領域Rとで液晶層の厚さを先の第1実施形態の場合と同様に変えているので、同等の効果を得ることができる。さらに、液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bには傾斜面を備えた傾斜領域が形成されているため、同領域において液晶配向不良等が生じ難い構成となる。
【0045】
[第4実施形態]
以下、本発明の第4の実施形態を図5を参照して説明する。なお、図1に示した第1の実施形態と同じ符号については、特に断り書きのない限り同様の構成を有するものとして説明を省略する。第4実施形態の液晶表示装置Dにおいては、上基板1の内面にはR(赤)、G(緑)、B(青)からなるカラーフィルタ10が形成され、さらにそのカラーフィルタ10の液晶層3側には、液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bが形成されている。すなわち、上基板1の液晶層側内面に設けられたカラーフィルタ10と液晶層3との間に、液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22b、電極5、配向膜11が形成されている。
【0046】
このような液晶表示装置Dにあっても、第1実施形態の液晶表示装置Aと同様に、反射表示領域Rに液晶層層厚制御層22bを形成し、透過表示領域Tの液晶層3の厚さを反射表示領域Rの液晶層3の厚さよりも大きくしたため、第1実施形態と同等の効果を得ることができる。また、液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bには傾斜面を備えた傾斜領域が形成されているため、同領域において液晶配向不良等が生じ難い構成となる。
【0047】
[第5実施形態]
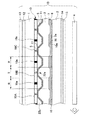
以下、本発明の第5の実施形態を図6及び図7を参照して説明する。なお、図1に示した第1の実施形態と同じ符号については、特に断り書きのない限り同様の構成を有するものとして説明を省略する。図6及び図7は、本発明に係る半透過反射型の液晶表示装置を単純マトリクスタイプの液晶表示装置に適用した第5実施形態を示すものである。この第5実施形態の液晶表示装置Eは、図6に示す断面構造の如く上下に対向配置された透明のガラス等からなる基板1、2の間に液晶層3が挟持された基本構造とされている点については先の各実施形態と同等であり、下方の基板2の更に下方側にはバックライト4が設けられている。
【0048】
図6に示す液晶表示装置Eにおいて基板1の液晶層3側には平面視短冊状の透明電極50が、図6の紙面垂直方向に伸びるように、かつ、図6の紙面左右方向に相互に離間して表示領域に対応するように形成されている。一方、基板2の液晶層3側には平面視短冊状の複数の電極60が、図6の紙面左右方向に伸びるように、且つ、図6の紙面垂直方向に相互に離間して表示領域に対応するように形成され、上下の電極50、60は平面視90゜に交差するように配置されている。
【0049】
液晶表示装置Eにおいて表示領域は多数の画素gが集合して構成され、各画素gは図7に示すように電極50、60を平面視した場合に電極50と電極60とが交差した部分により区画される。本実施形態の液晶表示装置Eはカラー表示を前提とした構造とされているので、具体的に図7に示す鎖線で区画される平面視略正方形状の1つの画素gが、3本の電極50と1本の電極60との交差部分で区画され、1つの画素gは1本の電極50と1本の電極60とで区画されるドットg1、g2、g3に分割されている。そして、これらのドットg1〜g3に対応する電極60の中央部分に個々に長方形状の凹状部22aが形成され、第1実施形態と同様にその凹状部22aに対応する位置が透過表示用電極60bを備えた透過表示領域T、凹状部22aを取り囲む凸状の液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bに対応する位置が反射表示用電極60aを備えた反射表示領域Rとされている。なお、本実施形態の如くカラー表示を前提とするのではなく、白黒表示に対応した構造の場合は、電極50、60を同じ幅の短冊状の電極としてカラーフィルタ10を省略すれば良い。
【0050】
このような液晶表示装置Eにあっても、第1実施形態の液晶表示装置Aと同様に透過表示と反射表示を利用した表示形態をとることができる。その場合の効果としても、反射表示領域Rに液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bを形成し、透過表示領域Tと反射表示領域Rとで液晶層の厚さを先の第1実施形態の場合と同様に変えているので、同等の効果を得ることができる。さらに、液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bには傾斜面を備えた傾斜領域が形成されているため、同領域において液晶配向不良等が生じ難い構成となる。
【0051】
[各実施形態に共通の変形例]
次に、以上のような第1実施形態〜第5実施形態の液晶表示装置A〜Eにおいては、カラーフィルタ10について、反射表示領域Rと透過表示領域Tとにおいてその分光特性を異なるものとすることができる。具体的には、図9及び図10に示すように、透過表示領域T(図9に示す透過型CF仕様)においてカラーフィルタ10の色純度を反射表示領域R(図10に示す反射型CF仕様)よりも相対的に高くすることができる。例えば、透過表示を行う場合、透過光がカラーフィルタ10を1回通過した後に表示に供され、一方、反射表示を行う場合、外光がカラーフィルタを入射の際と反射の際に1回ずつ計2回通過するため、図9及び図10のように透過表示領域Tにおいてカラーフィルタ10の色純度を反射表示領域Rよりも相対的に高くすることで、透過表示と反射表示とにおいて色の濃淡を同程度にすることが可能となる。
【0052】
[電子機器]
上記実施の形態の液晶表示装置を備えた電子機器の例について説明する。
図11(a)は、携帯電話の一例を示した斜視図である。図11(a)において、符号500は携帯電話本体を示し、符号501は上記の液晶表示装置A〜Eを用いた液晶表示部を示している。
【0053】
図11(b)は、ワープロ、パソコンなどの携帯型情報処理装置の一例を示した斜視図である。図11(b)において、符号600は情報処理装置、符号601はキーボードなどの入力部、符号603は情報処理装置本体、符号602は上記の液晶表示装置A〜Eを用いた液晶表示部を示している。
【0054】
図11(c)は、腕時計型電子機器の一例を示した斜視図である。図11(c)において、符号700は時計本体を示し、符号701は上記の液晶表示装置A〜Eを用いた液晶表示部を示している。
【0055】
このように図11に示す電子機器は、上記実施の形態の液晶表示装置A〜Eを用いた液晶表示部を備えているので、様々な環境下で明るく高コントラストの表示部を有する電子機器を実現することができる。また、反射と透過の表示領域の境界においても表示不良の少ない表示部を備えた電子機器を実現することが可能となる。
【0056】
[実施例]
次に、上記実施形態の効果を確認するために以下の評価を行った。すなわち、図8に示すように、液晶層層厚制御層22bの平坦領域の層厚dと、傾斜領域の領域幅(平面方向横幅)lを表1及び表2に示すように変化させ、傾斜角αの異なる第1実施形態に係る液晶表示装置Aを用意した。
【0057】
【表1】
【0058】
【表2】
【0059】
このように傾斜角αの異なる各液晶表示装置について、液晶層3における液晶の配向均一性、及び透過表示における明るさ(cd/m2)を評価した。配向均一性については、顕微鏡観察により配向状態に不連続部分が観察された場合に×、観察されなかった場合に○として評価を行った。その結果、傾斜角αが50°を超える63.4°、68.2°、84.3°、87.1°のものについては液晶の配向が不均一でディスクリネーションの発生が確認され、透過表示の明るさについても31cd/m2以下で相対的に低いものであった。また、傾斜角αが10°未満の7.6°、5.7°のものについては液晶の配向性は均一であるものの、透過表示における明るさが30cd/m2以下で相対的に低いものであった。
【0060】
一方、傾斜角αが10°〜50°のものについては、液晶の配向が均一性に優れ、透過表示における明るさも相対的に明るいものであった。したがって、傾斜角10°〜50°の液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)22bを備える液晶表示装置は、液晶の配向乱れが少なく、ディスクリネーションの発生が少ない表示特性に優れることが確認された。
【0061】
【発明の効果】
以上、詳細に説明したように、本発明によれば、液晶層の層厚を反射表示領域において小さくするべく、少なくとも反射表示領域において液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)を設けたために、反射表示領域と透過表示領域におけるリタデーションの均一化を図ることが可能とり、反射表示及び透過表示共に明るく高コントラストの表示が得られるようになった。また、反射表示領域と透過表示領域の境界付近において、液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)を自身の層厚を連続的に変化させるべく傾斜面を備えた形態にて構成したため、各領域境界付近における液晶層の急峻な層厚変化がない構成となった。したがって、この反射表示領域と透過表示領域の境界付近における液晶配向の乱れが生じ難く、明るく高コントラストの表示が得られるようになった。なお、液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)は透過表示領域に設けることも可能で、その場合、反射表示領域に形成される液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)の層厚よりも小さい層厚であれば良い。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】 本発明の第1の実施形態に係る液晶表示装置の部分断面構造を模式的に示す図。
【図2】 図1の液晶表示装置の反射層を拡大して示す部分拡大平面図。
【図3】 本発明の第2の実施形態に係る液晶表示装置の部分断面構造を模式的に示す図。
【図4】 本発明の第3の実施形態に係る液晶表示装置の部分断面構造を模式的に示す図。
【図5】 本発明の第4の実施形態に係る液晶表示装置の部分断面構造を模式的に示す図。
【図6】 本発明の第5の実施形態に係る液晶表示装置の部分断面構造を模式的に示す図。
【図7】 図6の液晶表示装置の反射層を拡大して示す部分拡大平面図。
【図8】 液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)の傾斜領域における傾斜角について示す説明図。
【図9】 透過表示に用いるカラーフィルタの分光特性を示す図。
【図10】 反射表示に用いるカラーフィルタの分光特性を示す図。
【図11】 本発明に係る電子機器について幾つかの例を示す斜視図。
【符号の説明】
A〜E 液晶表示装置
1 上基板
2 下基板
3 液晶層
10 カラーフィルタ
16 反射層
16a 開口部
22b 液晶層層厚制御層(絶縁層)
24 傾斜面
25 平坦面
R 反射表示領域
T 透過表示領域[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a liquid crystal display device and an electronic apparatus, and in particular, in a transflective liquid crystal display device having both a reflective type and a transmissive type, occurrence of disclination near the boundary between the reflective display and the transmissive display. The present invention relates to a technology that suppresses the image and makes it possible to obtain a bright and high-contrast display.
[0002]
[Prior art]
The transflective liquid crystal display device that combines the reflective and transmissive display modes can be switched to either the reflective mode or the transmissive mode depending on the ambient brightness, reducing the power consumption. A clear display can be performed even when the is dark.
[0003]
Such a transflective liquid crystal display device has a configuration in which a liquid crystal layer is sandwiched between a translucent upper substrate and a lower substrate, and a light transmission slit is formed in a metal film such as aluminum, for example. A liquid crystal display device has been proposed in which the formed reflective film is provided on the inner surface of the lower substrate, and this reflective film functions as a semi-transmissive reflective film. In this case, in the reflection mode, external light incident from the upper substrate side passes through the liquid crystal layer, is reflected by the reflection film disposed on the inner surface of the lower substrate, passes through the liquid crystal layer again, and is displayed from the upper substrate side. Is done. On the other hand, in the transmissive mode, light from the backlight incident from the lower substrate side can be displayed outside from the upper substrate side after passing through the liquid crystal layer through the slit formed in the reflective film. Therefore, a region where the slit of the reflective film is formed is a transmissive display region, and a region where the slit of the reflective film is not formed is a reflective display region.
[0004]
In the transflective liquid crystal display device having the above configuration, for example, the thickness of the liquid crystal layer is set to d.1The refractive index anisotropy of the liquid crystal is Δn, and the retardation of the liquid crystal expressed as an integrated value of these is Δnd1Then, the retardation Δnd of the liquid crystal of the portion that performs the reflective display1Is 2 × Δnd because the incident light reaches the observer after passing through the liquid crystal layer twice.1The retardation Δnd of the liquid crystal in the portion where transmissive display is performed11 × Δnd because the light from the backlight passes through the liquid crystal layer only once1It becomes.
[0005]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
In this way, the reflective display area and the transmissive display area have different retardation values, but when controlling the orientation of the liquid crystal molecules in the liquid crystal layer, an electric field is applied to the liquid crystal with the same drive voltage in each display mode. The alignment is controlled, and the liquid crystal in different display forms, in other words, the liquid crystal with different retardation in the transmissive display area and the reflective display area is aligned with the same driving voltage, so that high contrast display is achieved. There was a case that could not get.
[0006]
Therefore, a technique has been proposed in which an acrylic resin is formed on the upper side of the lower substrate in the reflective display region, the liquid crystal layer thickness is made smaller than that in the transmissive display region, and the retardation is made uniform. In this case, the acrylic resin layer for controlling the layer thickness of the liquid crystal layer has a structure in which the layer thickness is different between the reflective display region and the transmissive display region. Therefore, the liquid crystal layer also has a step near the boundary between the regions. When a step is generated in the liquid crystal layer in this way, the liquid crystal alignment is disturbed at the step, and disclination may occur, which may cause a display defect such as a decrease in contrast.
[0007]
The present invention has been made to solve the above-described problem, and as a transflective liquid crystal display device, the occurrence of disclination can be suppressed near the boundary between the reflective display area and the transmissive display area. An object of the present invention is to provide a liquid crystal display device having a configuration and capable of obtaining a bright and high-contrast display, and an electronic apparatus including the liquid crystal display device.
[0008]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In order to solve the above problems, a liquid crystal display device of the present invention includes a reflective display region used for reflective display, a transmissive display region used for transmissive display, and a liquid crystal layer sandwiched between a pair of substrates. Are prepared individuallyIn liquid crystal display devicesAn insulating layer that is provided on at least one of the pair of substrates and makes the thickness of the liquid crystal layer in the reflective display region different from the thickness of the liquid crystal layer in the transmissive display region;One boardA color filter provided inA reflective layer formed on the other of the pair of substrates and having an opening corresponding to the transmissive display region;Equipped withAndThe insulating layer includes an inclined region having an inclined surface in which the layer thickness of the insulating layer is continuously changed, and the inclined region isBy being arranged so as to overlap the edge of the reflective layer,At the boundary between the transmissive display area and the reflective display area and in the vicinity of the boundaryPosition to,The color filter is provided over the transmissive display region and the reflective display region including the inclined region, and the color purity in the transmissive display region is set higher than the color purity in the reflective display region.
[0009]
In this case, since the insulating layer is formed at least in the reflective display area, the liquid crystal layer thickness in the reflective display area is smaller than the liquid crystal layer thickness in the transmissive display area (functions as a means for thinning the reflective liquid crystal layer). However, even when the thickness of the liquid crystal layer through which the light contributing to the display passes is different between the reflective display and the transmissive display, the difference in retardation can be made small or zero. Furthermore, since the insulating layer includes an inclined region having an inclined surface so that its layer thickness continuously changes in the vicinity of the boundary between the reflective display region and the transmissive display region, the reflective display region and the transmissive display region are provided. Therefore, the step of the insulating layer does not occur in the vicinity of the boundary, and therefore the step of the liquid crystal layer does not easily occur in the vicinity of the boundary, the liquid crystal alignment is hardly disturbed, and the occurrence of disclination is suppressed.In the present invention, the insulating layer includes an inclined region having an inclined surface in which the thickness of the insulating layer is continuously changed, and the inclined region is located at and near the boundary between the transmissive display region and the reflective region. The color filter is formed so as to correspond to the transmissive display area and the reflective display area including the inclined area, and the color purity in the transmissive display area is set higher than the color purity in the reflective display area. Therefore, in transmissive display, transmitted light is provided for display after passing through the color filter once, and in reflective display, external light passes through the color filter once and twice when reflected, for a total of two times. As described above, by making the color purity of the color filter relatively higher than that of the reflective display region in the transmissive display region, it is possible to make the color density of the transmissive display and the reflective display comparable.
[0010]
The insulating layer can be mainly composed of a light-transmitting insulating material such as acrylic resin, and the liquid crystal layer is disposed on the surface side where the inclined surface of the insulating layer is formed. The layer thickness may be continuously changed near the boundary between the reflective display region and the transmissive display region along the inclined surface. In addition, the reflective display area may be formed with a reflective layer capable of reflecting incident light. For example, the reflective display area may have a different side from the side on which external light such as sunlight or illumination light enters. A reflective layer may be formed between the substrate (inner side substrate) and the liquid crystal layer. In this case, external light is reflected by the reflective layer after passing through the liquid crystal layer, passes through the liquid crystal layer again, passes through the liquid crystal layer a total of two times, and is used for display, and is incident from the inner side substrate. Since the light source light (backlight) passes through the liquid crystal layer once and is used for display, the structure of the present invention is adopted, and the thickness of the liquid crystal layer in the reflective display region is changed to the transmissive display region by the insulating layer, for example. By setting the thickness of the liquid crystal layer to about half the thickness, the retardation value in each region can be made substantially equal.
[0011]
AlsoThe insulating layer includes a reflective-side flat region that is located in the reflective display region, has a substantially uniform film thickness, and has a flat surface on the liquid crystal layer side, and the inclined surface is planar or curved. And the tangent of the inclined surface at a position where the thickness of the insulating layer in the inclined region is d / 2, where d is the thickness of the insulating layer formed in the reflective-side flat region. The angle α formed with the flat surface is 10 ° to 50 °.In the reflection side flat region, stable liquid crystal alignment is obtained, and in the adjacent inclined region, the step of the insulating layer does not occur as described above. Disturbances are less likely to occur. Note that even in the transmissive display region, by making the surface in contact with the liquid crystal layer flat, it is possible to realize uniform liquid crystal alignment in which disclination hardly occurs.
[0012]
In addition, when the inclined surface is formed in a planar shape or a curved surface, and the layer thickness of the insulating layer formed in the reflection-side flat region is d, the layer thickness of the insulating layer in the inclined region is Since the angle α formed between the tangent line of the inclined surface at the position of d / 2 and the flat surface is 10 ° to 50 °, a good display can be obtained.For example, when the angle α exceeds 50 °, disclination may occur in the vicinity of the boundary between the reflective display area and the transmissive display area, that is, in the inclined area, which may reduce the display brightness. . On the other hand, when the angle α is less than 10 °, the liquid crystal alignment defect is hardly generated, but the flat area is reduced, and the liquid crystal layer thickness of the reflective display area and the transmissive display area is different from the desired thickness. The brightness may be lower than when disclination occurs. The angle α is preferably about 30 ° to 45 °.
[0013]
In addition, a reflective layer is formed in the reflective display region, and an edge of the reflective layer is included in the inclined region. For example,The reflective layer may include an opening, a transmissive display area may be formed in the opening, and an opening edge of the opening may be included in the inclined area. That is, by including the opening edge of the opening of the reflective layer, which becomes the boundary between the reflective display region and the transmissive display region, in the inclined region, the layer thickness of the liquid crystal layer in both the reflective display region and the transmissive display region. It is possible to include a region (inclined region) in which changes occur, and therefore, the retardation difference can be reduced. In addition, by providing the opening edge of the opening at the position of d / 2, it is possible to further reduce the difference in retardation, and it is possible to obtain a good display with little reduction in contrast.
[0014]
Next, in the case where the outside light incident side of the pair of substrates is the upper substrate, and the other is the lower substrate, the reflective display area includes the reflective layer, the insulating layer, the lower electrode, and the lower substrate side. The liquid crystal layer and the upper electrode may be included at least in this order. Further, the reflective display region may include a reflective layer, a lower electrode, a liquid crystal layer, an upper electrode, and an insulating layer in this order from the lower substrate side.
[0015]
Here, examples of the lower electrode and the upper electrode include transparent electrodes such as ITO (Indium-Tin-Oxide). In such a configuration, external light incident from the upper substrate (display side substrate or outer substrate) reaches the reflective layer via at least the upper electrode, the liquid crystal layer, the lower electrode, and the insulating layer, and is reflected by this reflective layer. Then, the light is emitted to the outside through a similar process, and a reflective display is realized.
[0016]
In the transmissive display region, the lower electrode, the liquid crystal layer, and the upper electrode may be stacked in this order from the lower substrate (backlight side substrate or inner substrate) side. Thus, when the insulating layer is not provided in the transmissive display region, the liquid crystal layer is relatively thicker than the reflective display region in which the insulating layer is provided, and the liquid crystal layer thickness for the reciprocating display is reduced. It can be ensured in the transmissive display. Therefore, the same degree of retardation can be secured in the transmissive display and the reflective display.
[0017]
Next, a color filter is provided between the pair of substrates, and the spectral characteristics of the color filter are different between the reflective display region and the transmissive display region. The color purity of the color filter in the transmissive display region is higher than that of the reflective display region. Can also be relatively high. In transmissive display, transmitted light is used for display after passing through the color filter once. In reflective display, external light passes through the color filter once and twice when reflected, so that the above-mentioned As described above, by making the color purity of the color filter relatively higher than that of the reflective display region in the transmissive display region, it is possible to make the color density of the transmissive display and the reflective display comparable.
[0018]
In addition, irregularities may be formed on the surface of the lower substrate on the liquid crystal layer side (upper substrate side). That is, for example, the reflective layer can be formed on the upper layer of the lower substrate on which the unevenness is formed. In this case, since the external light is reflected with scattering by the unevenness formed on the lower substrate, Contrast reflection display can be performed.
[0019]
Next, an electronic apparatus according to the present invention includes the liquid crystal display device having the above-described configuration. According to this configuration, it is possible to switch between transmissive display and reflective display, and both the transmissive display and the reflective display can be bright and high-contrast display. An electronic device capable of realizing bright and high-contrast display even in the vicinity of the boundary of the region can be provided.
[0020]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
[First Embodiment]
FIG. 1 shows a first embodiment in which the configuration of the present invention is applied to an active matrix type liquid crystal display device. The liquid crystal display device A of this first embodiment is vertically arranged as shown in the sectional structure of FIG. It has a basic structure in which a
[0021]
A
[0022]
On the other hand, a
[0023]
Further, the surface of the
[0024]
On the upper layer side of the
[0025]
The
[0026]
Next, in the liquid crystal display device A of the present embodiment, a region used for display in the
[0027]
Here, the
[0028]
In addition, the opening edge of the
[0029]
The
[0030]
Next, FIG. 2 is a schematic plan view of the
[0031]
Here, the
[0032]
The size of the
[0033]
A
[0034]
In addition, the colored portions of the color filter 10 (see FIG. 1) are arranged so as to correspond to the planar positions of the dots g1, g2, and g3. The
[0035]
Next, functions and effects of the transflective liquid crystal display device A having the structure shown in FIGS. 1 and 2 will be described. When performing reflective display in the liquid crystal display device A, light incident from the outside of the device is used, and this incident light is transmitted from the outside of the
[0036]
Here, in the reflective display region R, after the incident light passes through the
[0037]
When performing transmissive display, light emitted from the
[0038]
In these display forms, incident light passes through the
[0039]
Further, in the vicinity of the boundary between the reflective display region R and the transmissive display region T, the layer thickness change of the
[0040]
[Second Embodiment]
Hereinafter, a second embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. Note that the same reference numerals as those of the first embodiment shown in FIG. 1 are omitted because they have the same configuration unless otherwise specified. In the liquid crystal display device B of the second embodiment, a translucent
[0041]
The translucent
[0042]
Even in such a liquid crystal display device B, it is possible to take a display form using transmissive display and reflective display as in the liquid crystal display device A of the first embodiment. Also in this case, since the thickness of the liquid crystal layer is changed between the transmissive display region T and the reflective display region R in the same manner as in the first embodiment, the same effect can be obtained. In the layer thickness control layer (insulating layer) 22b, since an inclined region having an inclined surface is formed, a liquid crystal alignment defect or the like hardly occurs in the same region. Further, in the second embodiment, since the light-transmitting
[0043]
[Third Embodiment]
Hereinafter, a third embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. Note that the same reference numerals as those of the first embodiment shown in FIG. 1 are omitted because they have the same configuration unless otherwise specified. In the liquid crystal display device C according to the third embodiment, the
[0044]
Even in such a liquid crystal display device C, it is possible to adopt a display form using transmissive display and reflective display, similar to the liquid crystal display device A of the first embodiment. In this case as well, the liquid crystal layer
[0045]
[Fourth Embodiment]
Hereinafter, a fourth embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. Note that the same reference numerals as those of the first embodiment shown in FIG. 1 are omitted because they have the same configuration unless otherwise specified. In the liquid crystal display device D of the fourth embodiment, a
[0046]
Even in such a liquid crystal display device D, as in the liquid crystal display device A of the first embodiment, the liquid crystal layer
[0047]
[Fifth Embodiment]
The fifth embodiment of the present invention will be described below with reference to FIGS. Note that the same reference numerals as those of the first embodiment shown in FIG. 1 are omitted because they have the same configuration unless otherwise specified. 6 and 7 show a fifth embodiment in which the transflective liquid crystal display device according to the present invention is applied to a simple matrix type liquid crystal display device. The liquid crystal display device E according to the fifth embodiment has a basic structure in which a
[0048]
In the liquid crystal display device E shown in FIG. 6, a
[0049]
In the liquid crystal display device E, the display area is configured by a collection of a large number of pixels g. Each pixel g is formed by a portion where the
[0050]
Even in such a liquid crystal display device E, it is possible to take a display form using a transmissive display and a reflective display as in the liquid crystal display device A of the first embodiment. Also in this case, the liquid crystal layer thickness control layer (insulating layer) 22b is formed in the reflective display region R, and the thickness of the liquid crystal layer is changed between the transmissive display region T and the reflective display region R in the first embodiment. Since it is changed similarly to the case of, the same effect can be obtained. Furthermore, since the liquid crystal layer thickness control layer (insulating layer) 22b has an inclined region having an inclined surface, the liquid crystal alignment defect or the like hardly occurs in the region.
[0051]
[Modification common to each embodiment]
Next, in the liquid crystal display devices A to E of the first to fifth embodiments as described above, the spectral characteristics of the
[0052]
[Electronics]
Examples of electronic devices provided with the liquid crystal display device of the above embodiment will be described.
FIG. 11A is a perspective view showing an example of a mobile phone. In FIG. 11A,
[0053]
FIG. 11B is a perspective view illustrating an example of a portable information processing apparatus such as a word processor or a personal computer. In FIG. 11B,
[0054]
FIG. 11C is a perspective view showing an example of a wristwatch type electronic device. In FIG. 11C,
[0055]
As described above, since the electronic apparatus illustrated in FIG. 11 includes the liquid crystal display unit using the liquid crystal display devices A to E according to the above-described embodiments, the electronic apparatus having a bright and high-contrast display unit under various environments. Can be realized. In addition, it is possible to realize an electronic device including a display portion with few display defects even at the boundary between the reflective and transmissive display areas.
[0056]
[Example]
Next, in order to confirm the effect of the above embodiment, the following evaluation was performed. That is, as shown in FIG. 8, the thickness d of the flat region of the liquid crystal layer
[0057]
[Table 1]
[0058]
[Table 2]
[0059]
Thus, for each liquid crystal display device having different inclination angles α, the alignment uniformity of the liquid crystal in the
[0060]
On the other hand, when the inclination angle α is 10 ° to 50 °, the alignment of the liquid crystal is excellent in uniformity, and the brightness in transmissive display is relatively bright. Therefore, it is confirmed that the liquid crystal display device including the liquid crystal layer thickness control layer (insulating layer) 22b having an inclination angle of 10 ° to 50 ° is excellent in display characteristics with less liquid crystal alignment disorder and less disclination. It was.
[0061]
【The invention's effect】
As described above in detail, according to the present invention, since the liquid crystal layer thickness control layer (insulating layer) is provided at least in the reflective display region in order to reduce the thickness of the liquid crystal layer in the reflective display region, It is possible to make the retardation uniform in the display area and the transmissive display area, and a bright and high-contrast display can be obtained for both the reflective display and the transmissive display. In addition, since the liquid crystal layer thickness control layer (insulating layer) is configured with an inclined surface to continuously change its own layer thickness in the vicinity of the boundary between the reflective display region and the transmissive display region, The configuration was such that there was no sharp change in the thickness of the liquid crystal layer in the vicinity. Therefore, liquid crystal alignment is hardly disturbed near the boundary between the reflective display area and the transmissive display area, and a bright and high-contrast display can be obtained. Note that the liquid crystal layer thickness control layer (insulating layer) can also be provided in the transmissive display region, in which case the layer is smaller than the liquid crystal layer thickness control layer (insulating layer) formed in the reflective display region. It only needs to be thick.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a diagram schematically showing a partial cross-sectional structure of a liquid crystal display device according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a partially enlarged plan view showing an enlarged reflection layer of the liquid crystal display device of FIG. 1;
FIG. 3 is a diagram schematically showing a partial cross-sectional structure of a liquid crystal display device according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 4 is a diagram schematically showing a partial cross-sectional structure of a liquid crystal display device according to a third embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 5 is a diagram schematically showing a partial cross-sectional structure of a liquid crystal display device according to a fourth embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 6 is a diagram schematically showing a partial cross-sectional structure of a liquid crystal display device according to a fifth embodiment of the present invention.
7 is a partially enlarged plan view showing a reflection layer of the liquid crystal display device of FIG. 6 in an enlarged manner.
FIG. 8 is an explanatory diagram showing a tilt angle in a tilt region of a liquid crystal layer thickness control layer (insulating layer).
FIG. 9 is a diagram illustrating spectral characteristics of a color filter used for transmissive display.
FIG. 10 is a diagram illustrating spectral characteristics of a color filter used for reflective display.
FIGS. 11A and 11B are perspective views illustrating some examples of an electronic apparatus according to the invention. FIGS.
[Explanation of symbols]
A to E Liquid crystal display device
1 Upper substrate
2 Lower substrate
3 Liquid crystal layer
10 Color filter
16 Reflective layer
16a opening
22b Liquid crystal layer thickness control layer (insulating layer)
24 Inclined surface
25 flat surface
R Reflective display area
T Transparent display area
Claims (4)
前記一対の基板のうちの少なくとも一方の基板に設けられ、前記反射表示領域における前記液晶層の層厚と前記透過表示領域における前記液晶層の層厚とを異ならせる絶縁層と、
前記一方の基板に設けられてなるカラーフィルタと、
前記一対の基板のうちの他方の基板に形成されてなり、前記透過表示領域に対応する開口部が形成された反射層と、を具備し、
前記絶縁層は、当該絶縁層の層厚を連続的に変化させた傾斜面を有する傾斜領域を備え、
前記傾斜領域は、前記反射層の縁と重なるように配置されることにより、前記透過表示領域と前記反射表示領域との境界部及び当該境界部付近に位置し、
前記カラーフィルタは、前記傾斜領域を含む前記透過表示領域および反射表示領域にわたって設けられ、前記透過表示領域における色純度が前記反射表示領域における色純度より高く設定されてなることを特徴とする液晶表示装置。And the liquid crystal layer is sandwiched between a pair of substrates, a reflective display area used for reflection display, the liquid crystal display device ing provided separately and a transmissive display area used for transmissive display,
An insulating layer provided on at least one of the pair of substrates, wherein the thickness of the liquid crystal layer in the reflective display region is different from the thickness of the liquid crystal layer in the transmissive display region;
A color filter provided on the one substrate ;
A reflection layer formed on the other of the pair of substrates and having an opening corresponding to the transmissive display region ;
The insulating layer includes an inclined region having an inclined surface in which the layer thickness of the insulating layer is continuously changed,
The inclined region is located so as to overlap with the edge of the reflective layer, and is located at and near the boundary between the transmissive display region and the reflective display region ,
The color filter is provided over the transmissive display area and the reflective display area including the inclined area, and the color purity in the transmissive display area is set higher than the color purity in the reflective display area. apparatus.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001394903A JP4126907B2 (en) | 2001-12-26 | 2001-12-26 | Liquid crystal display device and electronic device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001394903A JP4126907B2 (en) | 2001-12-26 | 2001-12-26 | Liquid crystal display device and electronic device |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007194589A Division JP4127317B2 (en) | 2007-07-26 | 2007-07-26 | Liquid crystal display device and electronic device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2003195287A JP2003195287A (en) | 2003-07-09 |
| JP2003195287A5 JP2003195287A5 (en) | 2005-07-28 |
| JP4126907B2 true JP4126907B2 (en) | 2008-07-30 |
Family
ID=27601494
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001394903A Expired - Fee Related JP4126907B2 (en) | 2001-12-26 | 2001-12-26 | Liquid crystal display device and electronic device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4126907B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100628254B1 (en) | 2000-04-12 | 2006-09-27 | 엘지.필립스 엘시디 주식회사 | Liquid Crystal Display |
| JP4167963B2 (en) | 2003-10-09 | 2008-10-22 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Liquid crystal display device and electronic device |
| JP3903980B2 (en) * | 2003-11-06 | 2007-04-11 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Liquid crystal display device and electronic device |
| JP2005173037A (en) * | 2003-12-09 | 2005-06-30 | Fujitsu Display Technologies Corp | Liquid crystal display device and its manufacturing method |
| JP2006209087A (en) * | 2004-12-27 | 2006-08-10 | Alps Electric Co Ltd | Liquid crystal display apparatus |
-
2001
- 2001-12-26 JP JP2001394903A patent/JP4126907B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2003195287A (en) | 2003-07-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4123208B2 (en) | Liquid crystal display device, electronic equipment | |
| US7352420B2 (en) | Liquid crystal display and electronic appliance | |
| KR100568197B1 (en) | Liquid crystal display device and method of manufacturing the same | |
| US7528910B2 (en) | Liquid crystal display device and electronic apparatus | |
| US8120738B2 (en) | Liquid crystal display device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP3692445B2 (en) | Liquid crystal device and electronic device | |
| JP3674579B2 (en) | Liquid crystal display device and electronic device | |
| JP3900141B2 (en) | Liquid crystal display device and electronic device | |
| JP2004361825A (en) | Liquid crystal display device, and electronic appliance | |
| JP3915792B2 (en) | Liquid crystal display device and electronic device | |
| JP3901172B2 (en) | Liquid crystal display device and electronic device | |
| JP2004341486A (en) | Liquid crystal display and electronic equipment | |
| JP4126907B2 (en) | Liquid crystal display device and electronic device | |
| JP4127317B2 (en) | Liquid crystal display device and electronic device | |
| JP2008077108A (en) | Liquid crystal display and electronic apparatus | |
| JP2008145664A (en) | Liquid crystal device and electronic device | |
| JP2007334085A (en) | Liquid crystal display device, and electronic apparatus | |
| JP4036026B2 (en) | Liquid crystal display device and electronic device | |
| JP4379081B2 (en) | Liquid crystal display device and electronic device | |
| JP4067026B2 (en) | Liquid crystal display device and electronic device | |
| JP2003215561A (en) | Liquid crystal display and electronic appliance | |
| JP2003255348A (en) | Liquid crystal display and electronic appliance | |
| JP2003295178A (en) | Liquid crystal display device and electronic equipment | |
| JP2008293050A (en) | Liquid crystal device and electronic appliance | |
| JP2003302631A (en) | Liquid crystal display device and electronic apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20041221 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20041221 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A821 Effective date: 20041222 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20070122 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20070605 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070726 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20070904 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20071017 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20080122 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20080306 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20080422 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20080505 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110523 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120523 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120523 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130523 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140523 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |