JP4124591B2 - Solid expansible sealant and baffle component with wide tolerance for expansion temperature and method for producing the same - Google Patents
Solid expansible sealant and baffle component with wide tolerance for expansion temperature and method for producing the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4124591B2 JP4124591B2 JP2001526604A JP2001526604A JP4124591B2 JP 4124591 B2 JP4124591 B2 JP 4124591B2 JP 2001526604 A JP2001526604 A JP 2001526604A JP 2001526604 A JP2001526604 A JP 2001526604A JP 4124591 B2 JP4124591 B2 JP 4124591B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- component
- baffle
- polymer
- acid anhydride
- temperature
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J9/00—Working-up of macromolecular substances to porous or cellular articles or materials; After-treatment thereof
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R13/00—Elements for body-finishing, identifying, or decorating; Arrangements or adaptations for advertising purposes
- B60R13/08—Insulating elements, e.g. for sound insulation
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K3/00—Materials not provided for elsewhere
- C09K3/10—Materials in mouldable or extrudable form for sealing or packing joints or covers
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K2200/00—Chemical nature of materials in mouldable or extrudable form for sealing or packing joints or covers
- C09K2200/04—Non-macromolecular organic compounds
- C09K2200/0458—Nitrogen-containing compounds
- C09K2200/047—Amides, imides, imines, N-oxides
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K2200/00—Chemical nature of materials in mouldable or extrudable form for sealing or packing joints or covers
- C09K2200/06—Macromolecular organic compounds, e.g. prepolymers
- C09K2200/0607—Rubber or rubber derivatives
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K2200/00—Chemical nature of materials in mouldable or extrudable form for sealing or packing joints or covers
- C09K2200/06—Macromolecular organic compounds, e.g. prepolymers
- C09K2200/0615—Macromolecular organic compounds, e.g. prepolymers obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds
- C09K2200/0617—Polyalkenes
- C09K2200/062—Polyethylene
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K2200/00—Chemical nature of materials in mouldable or extrudable form for sealing or packing joints or covers
- C09K2200/06—Macromolecular organic compounds, e.g. prepolymers
- C09K2200/0615—Macromolecular organic compounds, e.g. prepolymers obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds
- C09K2200/0622—Polyvinylalcohols, polyvinylacetates
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K2200/00—Chemical nature of materials in mouldable or extrudable form for sealing or packing joints or covers
- C09K2200/06—Macromolecular organic compounds, e.g. prepolymers
- C09K2200/0615—Macromolecular organic compounds, e.g. prepolymers obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds
- C09K2200/0635—Halogen-containing polymers, e.g. PVC
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K2200/00—Chemical nature of materials in mouldable or extrudable form for sealing or packing joints or covers
- C09K2200/06—Macromolecular organic compounds, e.g. prepolymers
- C09K2200/0687—Natural resins, e.g. rosin
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Acoustics & Sound (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Sealing Material Composition (AREA)
- Manufacture Of Porous Articles, And Recovery And Treatment Of Waste Products (AREA)
- Compositions Of Macromolecular Compounds (AREA)
- Epoxy Resins (AREA)
- Body Structure For Vehicles (AREA)
- Paints Or Removers (AREA)
Abstract
Description
【0001】
発明の背景
[発明の分野]
本発明は、膨張温度に対する許容範囲が広く、固形であって、初期非粘着性である自動車車体キャビティ部のシール用の膨張性シーラントおよびバッフル構成材に関し、本発明のシーラントおよびバッフル構成材は、車体に適用されるプライマー、シーラーおよびトップコートの焼付硬化時に、車体キャビティ部が経験する温度で、粘着性になり、かつ膨張することができる。本発明は、また従来よりも広い温度範囲で、所望の度合まで完全に膨張することができるシーラントおよびバッフル構成材を形成する改良された組成物に関する。ある特定の態様において、本発明は、改善された構造的健全性(structual integrity)を有し、車体キャビティを定義する構造に補強を与える所望の特性のシーラントおよびバッフル構成材を含む。本発明は、また膨張性シーラントおよびバッフル構成材を作製するための新規な方法に関し、本発明の方法は、連続処理をベースとすることで、バッチ型の処理でしばしば認められた変異性を減少させる。
【0002】
[従来技術の説明]
自動車車体は、様々な中空の柱部、キャビティ、通路部および同様な部位を有し、これらの部位は、雑音または汚染物質の侵入を防止するためにシールしなければ、望ましくない雑音、空気の流れ、湿気、ほこりおよび他の気中微粒子が通過しうる。米国特許第5,373,027号公報には、固形で初期非粘着性の熱膨張性シーラントおよびバッフル構成材が開示されており、このシーラントおよびバッフル構成材は、車体の支柱部、キャビティまたは通路中に挿入した後、自動車製造工程のプライマーまたは塗料硬化工程の一部をなす焼付けがまに車体を通過させて移送する際に、熱誘導で膨張し、所望の形状に成形することができる。
【0003】
同公報によれば、固形の膨張性シーラントおよびバッフル構成材を作製するための組成物は、一部が亜鉛のような金属イオンで中和されたα,β位にエチレン基を含んだ多量のエチレン・不飽和カルボン酸共重合体と、変性されたアゾジカルボンアミドのような少量の発泡剤、少量の低分子量樹脂粘着付与剤を含み、粘着付与剤が高温になると、構成材の外表面に粘着性が付与され、発泡剤によって膨張する。
【0004】
固形の膨張性シーラントおよびバッフル構成材を形成する組成物は、従来の塗料またはプライマー焼付けがまに車体を通過させて移送する際に、車体のキャビティ内で膨張した形状を形成するように機能する。自動車車体に適用される仕上げ塗装の焼付けまたは硬化用の従来のかまは、乾燥される、または硬化されるコーティングに応じて、通常約140℃から約200℃までの範囲の温度で操作される。自動車車体は、通常約10〜15分間から2時間までの時間でそれぞれの焼付けがまを通過する。この目的のために、従来の膨張性バッフル構成材は、約135℃から約185℃までの温度で好ましく膨張するように設計されていた。上記公報に開示されている固形の膨張性シーラントおよびバッフル構成材は、自動車製造分野において、実質的な商業的成功を享受している。バッフル構成材は、その使用の容易さと、適当な大きさに作製し、修正して、個々の車体キャビティ部の形状に個別に適合させることができるため、現場膨張可能な自動車用シーラントおよびバッフル構成材に対する人気が近年加速している。さらに、バッフル構成材の膨張は、この目的のための追加の機器や製造上の操作を与える必要なしに、自動車を焼付けがまに通過させながら現場で実施することができる。
【0005】
予想させる通り、自動車製造手順における塗料および/またはプライマーの焼付け処理の主眼は、自動車車体の表面に適用した塗料および/またはプライマーを適切に、かつ効果的に硬化させることである。自動車および同様の車両の製造時、処理時間は絶対不可欠であり、塗料および/またはプライマー焼付けがまへの車体の滞留時間は、要求される塗料および/またはプライマーの硬化を最短の時間で行うために注意深く調節されている。自動車車体には、位置、長さ、および塗料若しくはプライマーを焼付けするために熱処理される車体表面からの相対距離のいずれもが異なる多数のキャビティおよび通路が存在するため、塗料および/またはプライマーの焼付け硬化時に車体の特定のキャビティおよび通路が経験する実際の温度は有意に異なっており、焼付けサイクル時の他のキャビティまたは通路よりも実質的に高い温度まで上昇する場合もあれば、膨張性バッフル構成材の完全な膨張を保証するのに適切な温度まで上昇しない場合もある。
【0006】
技術者は、膨張性バッフル構成材に関して、望ましくない雑音または汚染物質がキャビティを通過しやすいか否かに基づいて、最も都合のよい車体のキャビティ部を選択する。このバッフル位置の選択では、通常は焼付けまたは硬化サイクル時におけその位置の加熱の程度の差は考慮されない。例えば、金属質量が高い部位では、金属質量が低い部位よりも熱エネルギーの放散が速い。したがって、焼き付け用および硬化用のかまに対して、車体の出口よりも前方では、膨張性バッフル構成材が、バッフル生成物を完全に膨張させるのに必要な十分に高い温度レベルまで到達しない。他方、他のバッフル製品の位置では、熱源に直接近接している、膨張性バッフル構成材を囲んでいるキャビティを定義する金属の性質、またはキャビティが車体の外表面からどれだけ離れているかといった理由により、バッフル材料が過熱される可能性もある。垂直の支柱は、煙突効果を発揮し、車体キャビティ部の到達温度に影響する可能性がある。
【0007】
したがって、好適な固形の膨張性シーラントおよびバッフル生成物の組成は、複数の多様で、かつ機能的に異なったパラメータおよび条件を満足することが必要となる。このような組成物は、経済的に構成され、好ましくは既存の機器を用いて、効率的な方法で処理できることが必要である。組成物は、所定の形状および大きさを有する自立の成形体へと容易に作製できることが必要である。成形体は、キャビティを効果的にシールするために、それが配置される担体や、成形体に関連する好適なバッフル構造に制限されることなしに、元の大きさから全方向に実質的に均一に膨張することができる。膨張性の組成物から形成された成形体は、自動車車体の各キャビティ中に挿入する目的で形成されるため、固形で、非粘着性であることが必須である。
【0008】
特に、自動車車体中のキャビティは、互いにその到達温度が異なるため、膨張性シーラントおよびバッフル構成材を作製するための組成物は、膨張性の部材が設置されたキャビティが経験する可能性のある最も低い温度でも高度に膨張できることが必要である。同様に、膨張性シーラントおよびバッフル生成物は、車体の塗料および/またはプライマーの硬化サイクル中に、膨張性の部材を収容するキャビティのいずれか1つが経験する可能性がある最も高い温度でも炭化および/または燃焼してはならない。
【0009】
さらに、組成物は、自動車車体のキャビティに挿入され、塗料またはプライマーの焼付けがまで硬化される膨張性の部材に形成された際に、物理的な網目状の構造を有することが必要である。この網目状の構造は、組成物中に組み込まれた発泡剤によって発生したガスの封じ込めを高めて、それによって部材が、使用の際に高度の膨張性を保持していることを保証する。
【0010】
また、膨張性シーラントおよびバッフル構成材の特定態様において、雑音、空気および湿気に対するバリア特性を保持しつつ、車体のキャビティを定義する構造に追加の補強を与える機能的特性を有することが望ましい。
【0011】
[発明の要約]
本発明は、膨張温度に対する許容範囲が広く、固形で、初期非粘着性である自動車車体キャビティ部のシール用の膨張性シーラントおよび吸音バッフル構成材を与える。このシーラントおよびバッフル構成材は、膨張性の部材が存在することで利益が予想される自動車車体のキャビティの、仮にその全てではなくとも、その大半が経験する温度の実質的全範囲で粘着性になり、膨張することができる。したがって、本発明のシーラントおよび吸音バッフル構成材は、同様の用途に従来利用可能な製品よりも実質的により広い時間および温度に対する許容範囲を有する。
【0012】
具体的には、本発明は、自動車車体キャビティ用の新規の膨張性シーラントおよび吸音バッフル構成材に関し、このシーラントおよびバッフル構成材は、所望の初期形状に前もって成形されていてもよく、車体全体について見た場合に、自動車製造操作の塗料および/またはプライマーの焼付けサイクル中でキャビティが到達する温度がキャビティ間で実質的に異なるにもかかわらず、シーラントおよびバッフル構成材を収納するキャビティの位置とは実質的に関係なしに、該サイクル中に個々の車体キャビティが通常経験する温度まで上昇した際に、比較的高度に膨張する。
また、本発明は、以下の(1)〜(28)を提供するものである。
(1)固形で、初期非粘着性の自動車車体キャビティのシール用の膨張性吸音バッフル構成材であって、
前記構成材は、前記車体に適用されるコーティング材の焼付硬化時に前記車体キャビティ部が経験する110℃〜191℃の温度で膨張することができ、
前記構成材は、酸無水物がグラフト結合されたある量の酸無水物ポリマーと、
前記構成材が前記膨張することができる110℃〜191℃の温度に加熱された際に、前記酸無水物ポリマーの少なくとも一部と反応する末端エポキシドを含んだある量のポリマー添加物と、
前記構成材が自動車車体キャビティ内で前記110℃〜191℃の温度に加熱された際に、前記構成材の成分を膨張させる十分な量の発泡剤と、を含む膨張性吸音バッフル構成材。
(2)前記構成材が、選択された自動車車体キャビティ内に相補的に受け入れられるべく設計された充填成型構成材である前記(1)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(3)前記酸無水物ポリマーは、グラフト結合されたオレフィンベースのポリマーであって、前記オレフィンベースのポリマーの少なくとも一部が酸無水物と反応している前記(1)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(4)前記グラフト結合されたオレフィンベースのポリマーは、エチレンビニルアセテート、エチレン−n−ブチルアクリレート、エチレン・オクタン共重合体およびポリエチレンからなる群から選択される前記(3)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(5)前記酸無水物は、無水マレイン酸である前記(1)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(6)前記発泡剤は、変性アゾジカルボンアミドおよび未変性のアゾジカルボンアミドからなる群から選択される前記(1)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(7)前記発泡剤は、p,p’−オキシビス(ベンゼンスルホニル)ヒドラジド、p−トルエンスルホニルヒドラジドおよびジニトロソペンタメチレン−tert−アミンからなる群から選択される前記(1)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(8)前記酸無水物がグラフト結合されたポリマーは、前記構成材中に10質量%から60質量%の範囲で存在する前記(1)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(9)前記ポリマー添加物は、前記構成材中に1質量%から10質量%の範囲で存在する前記(1)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(10)前記発泡剤は、前記構成材中に1質量%から10質量%の範囲で存在する前記(1)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(11)前記オレフィンベースのポリマーは、前記構成材中に1質量%から50質量%の範囲で存在する前記(3)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(12)ある量の合成ゴム状物質を含んだ前記(1)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(13)前記合成ゴム状物質は、スチレンブタジエンゴム、エチレンプロピレンゴム、エチレンプロピレンジエンゴム、ブタジエンゴム、スチレン−イソプレン−スチレンブロック共重合体、スチレン−ブタジエン−スチレンブロック共重合体、スチレン−エチレン/ブチレン−スチレンブロック共重合体、スチレン−エチレン/プロピレンブロック共重合体、ニトリルゴムおよび塩素化ポリエチレンからなる群から選択される前記(12)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(14)前記ゴム状物質は、前記構成材中に1質量%から15質量%の範囲で存在する前記(12)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(15)脂肪族炭化水素樹脂、芳香族炭化水素樹脂、脂肪族/芳香族炭化水素樹脂、水素化された炭化水素樹脂、ポリテルペン樹脂、ロジンエステル樹脂、クマロンインデン樹脂、α−メチルスチレン樹脂およびポリスチレン樹脂からなる群から選択される添加物を含む前記(1)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(16)前記脂肪族炭化水素樹脂は、C 5 、C7 およびC9 の炭化水素で構成される前記(15)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(17)前記添加物は、ビスフェノールAジグリシジルエーテルポリマー、ビスフェノールFジグリシジルエーテルポリマー、二量体脂肪酸とビスフェノールAのジグリシジルエーテルとの付加物、二量体脂肪酸とビスフェノールFのジグリシジルエーテルとの付加物および末端エポキシド化されたアクリロブタジエンニトリルゴム付加物からなる群から選択される前記(15)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(18)前記構成材は、ある量のワックス生成物を含む前記(1)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(19)前記ワックス生成物は、パラフィンワックス、ミクロワックス、ポリエチレンワックス、ポリアミドワックスおよび天然ワックスからなる群から選択される前記(18)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(20)前記ワックス生成物は、前記構成材中に1質量%から15質量%の範囲内で存在する前記(19)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(21)前記構成材は、充填剤を含む前記(1)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(22)前記充填剤は、炭酸カルシウム、硫酸バリウム、シリカ、硫酸カルシウム、ケイ酸アルミニウム、ケイ酸マグネシウム、カリウムアルミニウムシリケート、カルシウムメタシリケート、軽石、ガラス小球および有機物充填剤からなる群から選択される前記(21)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(23)前記充填剤は、前記構成材中に1質量%から20質量%の範囲内で存在する前記(22)に記載のバッフル構成材。
(24)自動車車体に適用されるコーティング材の焼付硬化時に前記車体キャビティ部が経験する110℃〜191℃の温度で膨張することができる、固形で、初期非粘着性である、自動車車体キャビティのシール用の膨張性吸音バッフル構成材を形成するための組成物を作製する方法であって、
酸無水物がグラフト結合されたある量の酸無水物ポリマーと、末端エポキシドを含んだある量のポリマー添加物と、前記構成材を自動車車体キャビティ内で前記110℃〜191℃の温度に加熱した際に、前記構成材の成分を膨張させる十分な量の発泡剤と、の混和物を連続して混合する区域を通過させて移送する工程と、
前記混合物を混合しつつ、前記末端エポキシドの少なくとも一部と前記酸無水物がグラフト結合されたポリマーとを反応させるのに十分な時間前記混和物が前記区域にあるようにする工程と、を含んだ方法。
(25)前記移送する工程が、前記混和物をオーガ型の連続練りミキサを通過させて移送する工程を含む前記(24)に記載の方法。
(26)前記移送する工程が、前記混和物を連続して混合する区域に導入した際の温度に保持した状態で、前記連続して混合する区域を通過させて移送する工程を含む前記(24)に記載の方法。
(27)前記移送する工程が、前記混和物を、1分間から2分間の時間で、前記連続して混合する区域を通過させて移送する工程を含む前記(24)に記載の方法。
(28)固形で、初期非粘着性の自動車車体キャビティのシール用の膨張性吸音バッフル構成材であって、
前記構成材は、前記車体に適用されるコーティング材の焼付硬化時に前記車体キャビティ部が経験する温度で膨張することができ、
前記構成材は、酸無水物がグラフト結合されたある量のオレフィンベースの酸無水物ポリマーと、
前記構成材が前記膨張することができる温度に加熱された際に、前記酸無水物ポリマーの少なくとも一部と反応する末端エポキシドを含んだある量のポリマー添加物と、
前記構成材が自動車車体キャビティ内で前記温度に加熱された際に、前記構成材の成分を膨張させる十分な量の発泡剤と、
を含み、前記オレフィンベースの酸無水物ポリマーが、エチレンビニルアセテート、エチレン−n−ブチルアクリレート、エチレン・オクタン共重合体およびポリエチレンからなる群から選択される、膨張性吸音バッフル構成材。
【0013】
ある特定の態様に独自に設計された組成物は、初期固形で、非粘着性の膨張性組成物を加熱して構成材を作製した場合に、膨張性の構成材は、それを収納するキャビティを定義する自動車車体の壁面構造物に構造的健全性を付加するように作用する。
【0014】
膨張温度に対する許容範囲が広い膨張性シーラントおよびバッフル構成材の作製に用いる組成物は、無水物がグラフト結合されたある量のポリマーを含む。該ポリマーは、初期非粘着性であっても、自動車車体が塗料および/またはプライマーの焼付けがまを通過する際に、車体キャビティが経験する温度の全範囲で、膨張性構成材の粘着性および接着性を向上させる特性を有する。したがって、自動車車体内に配置された膨張性構成材は、焼付けがまでの塗料および/またはプライマーの硬化時に構成材が膨張すると、キャビティの壁面にしっかりと接着する。無水マレイン酸がグラフト結合されたエチレンビニルアセテートは、組成物の無水物がグラフト結合されたポリマーとして好ましい。これは、例えば約120℃未満の、比較的低い融点を持つ。これは膨張性構成材が実質的に膨張する温度よりも低い温度である。同じく重要な点として、グラフト結合されたEVAポリマーは、塗料および/またはプライマーの硬化サイクル時にシーラントおよびバッフルを収納するキャビティが経験する最も高い温度でも、燃焼または炭化することなく、粘着性を向上させる特性と所望の粘度特性を保持している。
【0015】
固形で、非粘着性である膨張性構成材を作製するための組成物は、また末端エポキシドを有するポリマー添加物を含む。このエポキシドは、シーラントおよび吸音バッフル構成材を膨張させるのに十分な高温で無水物ポリマーの少なくとも一部と反応することができる。車体の塗料および/またはプライマーの焼付け時にキャビティ内のシーラントおよび吸音バッフル構成材が経験する温度で起る無水物ポリマーおよびエポキシポリマー間の架橋反応は、三次元的な網目構造および橋掛け構造を有する構成要素を形成し、構成材が、その中に組み込まれた発泡剤によって膨張するのを容易にし、膨張後の最終生成物のガス保持特性を向上させる。従来技術のポリマーでの実施とは対照的に、末端エポキシド化されたポリマーと無水物がグラフト結合されたポリマーとの反応は触媒なしで実施される。結果的に、ポリマーの適切な架橋が起こり、発泡剤から放出されたガスを効果的に封じ込める多孔性の格子状生成物を与える。しかし、2つの構成要素間での架橋および共重合体のフリーラジカル重合は、シーラントおよびバッフル組成物から作製されたバッフル生成物の柔軟性および膨張特性を減少させるほど顕著ではない。
【0016】
固形で、初期非粘着性である膨張性シーラントおよび吸音バッフル構成材は、その融点で膨張後の生成物の粘着性を向上させる作用をする無水物がグラフト結合されたポリマーを含んだ組成物からバッチ型のミキサ処理により作製してもよい。成分として無水物がグラフト結合されたポリマーを含んだ組成物のバッチ式によるミキサ処理は、自動車の塗料および/またはプライマーの焼付けがまで経験される温度の範囲内で要求される程度まで膨張することができる最終生成物を作製する。しかし、従来の連続練りミキサを用いて、無水物がグラフト結合されたポリマーを含んだ成分から組成物を作製する試みは成功していない。連続練りミキサで作製した材料からなり、焼付けがま温度で硬化させた部品は、高い流動性と低い膨張性を示し、得られる生成物は所望の用途に有用ではない。
【0017】
膨張温度に対する許容範囲が広く、固形で、初期非粘着性である膨張性シーラントおよび吸音バッフル構成材の作製に使用される組成物に、末端エポキシドを有するポリマーと、無水物がグラフト結合されたポリマーを含めることにより、成形後の未膨張の生成物を焼付けがまレベルの温度を加えた際に、該組成物から成形された組成物の膨張の程度に悪影響することなく連続型の練りミキサで処理できることを予期せず発見した。シーラントおよび吸音バッフル構成材として、無水物がグラフト結合されたポリマーおよび末端エポキシドポリマーの組み合わせで制限された反応を行うと、構成材の焼付けがま内での熱誘導による膨張と溶融粘度を増加させる。
【0018】
[好ましい実施形態の詳細な説明]
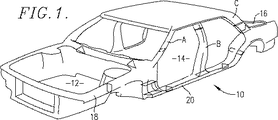
図1の自動車車体10は、エンジン区画12、乗員区画14およびトランク区域16を定義する複数の内部接続され、中空形状のフレーム部材、支柱、またはレールを含む。引用することで本明細書の一部をなす米国特許5,506,025号公報で説明されているように、乗員区画14を囲む垂直の支柱は、従来A、BおよびCのような符号で呼ばれる。一方、前方に伸びるフレーム部材18は、エンジンレールと呼ばれる。同様に、車体10の下部の水平方向に伸びる筒状構成材20は、通常ロッカーパネルレールとして識別される。
【0019】
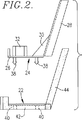
本発明は、膨張温度に対する許容範囲が広く、固形で、初期非粘着性である改善された膨張性シーラントおよび吸音バッフル構成材に関し、例えば、図2〜図4に示すように、成形された構成材22の形態であってもよい。構成材22は、金属またはナイロンのような様々な材料製であってよい担体24に相補的に配置されるように設計されている。担体24の機能は、自動車車体10が、自動車製造工程の一部をなす従来の塗料および/またはプライマー焼付けがまを通過させて移送する際に、成形された膨張性構成材22を車体10の選択された車体キャビティに保持し、構成材22を膨張させるまでの間所定の位置に固定することともに、膨張性構成材の車体10の特定のキャビティ内における膨張後の形状を選択的に調節するガイドバリアとして作用することである。
【0020】
図2に最もよく示されているように、特別に設計された担体24は、例えば、主プレート部分26と、ガセットプレート30によって主プレート部分26と接続される垂直延長部分32とを有していてもよい。所望により、プレート26には、破線で示したクランプ34を受けるためのクランプ取り付け要素32が与えられてもよい。これにより、自動車車体10の壁面構造36に、担体24およびその上に配置された構成材22を固定するのが容易になる。プレート26は、成形された膨張性構成材22の主体部分42の各開口部40を受けられる多数のとげ部(barb)を含む。これにより構成材22が担体24のプレート26に接続される。図2〜図4に図示した例において、成形された構成材22は、担体24の延長部分28の反対方向に置かれ、該延長部分28と相補的に係合する垂直方向の腕部44を有する。
【0021】
この点に関して、上記で参照した米国特許5,506,025号公報で詳細に説明されているように、構成材22は、好ましくは射出成形または、その膨張時に、車体10のキャビティ内に現場で発泡されたシーラントおよびバッフルバリアを形成する自立の成形体を作製するための同等の手法を用いて所望の形状を作製することが好ましい。図示の成形された構成材22の形状は、単に説明を目的としており、個々の構成材22の寸法および形状は、膨張性の構成材22が配置される車体キャビティの断面形状に一致するように選択的に変更してもよい。構成材22の具体的な形状および大きさは、車体キャビティ内で膨張された形態で実施されるシーリングおよびバッフル機能で示される多くの例である。
【0022】
図1〜図4は、特に成形可能な膨張性バッフル生成物が好適な比較的剛直な担体上に配置された形態で示しているが、本発明は相補的な担体に配置されるように設計された膨張性バッフル生成物に限定されないと理解される。特にキャビティの通路が全体において、基本的に水平方向となっているある用途において、成形された膨張性のバッフル要素は、その通路の所望の位置に単に諸条件を考慮して配置してもよい。これらの例において多くの場合、バッフル製品は、きわめて正確な位置に配置することは必要ではない。
【0023】
要求される物理特性および化学特性を有する膨張性構成材22を作製するための成形可能な組成物は、無水物がグラフト結合されたある量のポリマーと、末端エポキシドを含んだある量のポリマー添加物とを含む。自動車車体を自動車製造操作の一部をなす従来の塗料および/またはプライマー焼付けがまを通過させて移送する際に、膨張性構成材がそれを収納する自動車車体キャビティが経験する温度まで加熱されると、末端エポキシドは、無水物ポリマーの少なくとも一部と反応する。さらに、成形可能な組成物は、構成材が焼付けがま内での自動車車体の焼付け時に加熱された場合に、組成物から成形された構成材を膨張させる好適な発泡剤を含む。望ましくは、成形可能な組成物は、固形で、初期非粘着性である成形された構成材22が、焼付けがま中で加熱されて膨張する時に、その外表面に粘着性を付与する。成形された構成材22中の無水物がグラフト結合されたポリマーは、焼付けがま中で加熱する際に、接着剤のような形でいくらか機能し、成形された構成材が膨張する際に、その粘着特性を向上させる。
【0024】
本発明の改善された組成物を作製するのに有用な無水物がグラフト結合されたポリマーの具体例は、酸無水物が官能基としてグラフト結合されたエチレンビニルアセテート、酸無水物が官能基としてグラフト結合されたエチレン−n−ブチルアセテート、酸無水物が官能基としてグラフト結合されたエチレン・オクタン共重合体、酸無水物が官能基としてグラフト結合されたポリエチレン、酸無水物が官能基としてグラフト結合されたポリプロピレン、酸無水物が官能基としてグラフト結合されたエチレンプロピレンゴムを含む。個々の例において、好ましい酸無水物は、マレイン酸無水物である。好ましいオレフィンベースのグラフト結合されたポリマーは、マレイン酸無水物が官能基としてグラフト結合されたエチレンビニルアセテートである。無水物がグラフト結合されたオレフィンベースのポリマーは、組成物中に約10質量%から約60質量%存在する。
【0025】
末端エポキシドを含むポリマー添加物は、好ましくはエポキシ当量約400超で特徴付けられる固体ビスフェノールAジグリシジルエーテルポリマーまたは固体ビスフェノールFジグリシジルエーテルポリマー(ビスフェノールAまたはビスフェノールFと、エピクロロヒドリンから誘導される)からなる群、エポキシ当量約150から約220で特徴付けられる液体ビスフェノールAジグリシジルエーテルポリマーまたは固体ビスフェノールFジグリシジルエーテルポリマー(ビスフェノールAまたはビスフェノールFと、エピクロロヒドリンから誘導される)からなる群、二量体脂肪酸と、ビスフェノールAまたはビスフェノールFのジグリシジルエーテルとの付加物(EpikoteまたはEpon 872)、末端エポキシドのアクリロニトリルブタジエンゴムの付加物(CTBN、Hycar 1300×8、1300×13)から選択される。好ましい添加物は、ビスフェノールAジグリシジルエーテルポリマーである。末端エポキシドを有するポリマーは、組成物中に好ましくは約1質量%から約10質量%存在する。
【0026】
組成物は、また好適な発泡剤も与えられている。発泡剤は、 好ましくは変性アゾジカルボンアミド、未変性のアゾジカルボンアミド、p, p’−オキシビス(ベンゼンスルホニル)ヒドラジド、p−トルエンスルホニルヒドラジドおよびジニトロソペンタメチレン−tert−アミンからなる群から選択される。好ましい発泡剤は、アゾジカルボンアミドである。発泡剤は、 組成物中に好ましくは約1質量%から約10質量%存在する。
【0027】
従来の膨張性の組成物よりも膨張温度に対する許容範囲が広い、固形で、初期非粘着性である膨張性シーラントおよび吸音バッフル構成材を作製するための組成物は、また充填剤ポリマーを含んでもよい。充填剤ポリマーは、好ましくはエチレンビニルアセテート、エチレン−n−ブチルアセテート、エチレン・オクタン共重合体、ポリエチレン、ポリプロピレンおよびエチレン・メタクリル酸共重合体からなる群から選択される。好ましい充填剤ポリマーは、エチレンビニルアセテートである。組成物に組み込まれる場合に、充填剤ポリマーは、約1質量%から約50質量%存在してもよい。
【0028】
ゴム状成分もまた、膨張性構成材を作製するための組成物に含んでもよい。ゴム状成分は、好ましくはスチレンブタジエンゴム、エチレンプロピレンゴム、エチレン・プロピレン・ジエンゴム、ブタジエンゴム、スチレン・イソプレン・スチレンブロック共重合体、スチレン・ブタジエン・スチレンブロック共重合体、スチレン・エチレン/プロピレンブロック共重合体、ニトリルゴム、および塩素化ポリエチレンからなる群から選択される。好ましいゴム状成分は、スチレンブタジエンゴムである。ゴム状成分は、組成物中に約1質量%から約15質量%存在してもよい。
【0029】
成形および処理助剤も組成物中に含めてもよい。助剤は、好ましくはパラフィンワックス、ミクロワックス、ポリエチレンワックス、ポリアミドワックス、および天然ワックスからなる群から選択される。組成物に使用する場合、好ましい成形および処理補助物はポリエチレンワックスである。成形および処理助剤は、組成物中に約1質量%から約15質量%存在してもよい。
【0030】
膨張開始に続いて、膨張性の構成材の粘着性を向上させる粘着付与剤を組成物中に含めてもよい。粘着付与剤を使用する場合、脂肪族炭化水素樹脂、芳香族炭化水素樹脂、脂肪族/芳香族炭化水素樹脂、水素化された炭化水素樹脂、ポリテルペン樹脂、ロジンエステル樹脂、クマロンインデン樹脂、α−メチルスチレン樹脂およびポリスチレン樹脂からなる群から選択される。脂肪族炭化水素樹脂および芳香族炭化水素樹脂の主要部分は、好ましくは脂肪族炭化水素の場合、主としてC5 、C7 およびC9 の炭化水素で構成され、芳香族炭化水素の場合、主として等価の炭化水素で構成される。粘着付与剤の量は、約1質量%から約15質量%であってもよい。
【0031】
無機充填剤または有機充填剤を、約1質量%から約20質量%の範囲の量で組成物中に含めてもよい。充填剤は、好ましくは炭酸カルシウム、硫酸バリウム、シリカ、硫酸カルシウム、ケイ酸アルミニウム、ケイ酸マグネシウム、カリウムカルシウムシリケート、カルシウムメタシリケート、軽石、ガラス小球、有機充填剤からなる群から選択される。好ましい充填剤は、炭酸カルシウムである。無機充填剤または有機充填剤の量は、組成物中に約1質量%から約20質量%であってもよい。
【0032】
本発明の必須パラメータに適合する膨張性のシーラントおよびバッフル構成材を作製する際、具体的に使用される組成物は、各成分を押し出し機のような従来の連続操作可能な機械に導入して作製してもよい。機械の具体例は、単軸配合機、往復動単軸押出機、二軸押出機を含む。この種の押出機は、従来その長手方向に沿って、2個〜4個のインレットを含み、バレルの長さに対する軸の径の比は、約7:1から約18:1の範囲である。好ましくは、発泡剤を含む反応性の試薬を除いた組成物の成分は、全て押し出し機の第1の入口ポートに添加される。反応性の試薬および発泡剤は、通常4個入口ポートを有する押し出し機の第3の入口ポートに添加される。第3の入口ポートは、第1の入口ポートから通常押し出し機のバレルの長さに沿って約50%から約75%離れている。残留時間は、名目上の処理時間が約2分間である場合に、通常約1分間から3分間の範囲である。
【0033】
連続押出機は、押出し物を一連のペレットに切断するためのナイフが備え付けられている。望ましくは、押出機から放出された押出し物は、水浴に浸して冷却することで、実質的に固体の状態を保証することができる。または、連続押出機からの押出し物は、ストランドとしてストランドペレット成形機に導き、小型の円筒形のペレットに切断することもできる。
【0034】
押出機からのペレットは、通常は120℃未満の温度で、好ましくは80℃から100℃の範囲の温度で、射出成形機により複合物の膨張性シーラントおよびバッフル生成物に成形することができる。
【0035】
本発明の改良された膨張性バッフル構成材は、自動車車体の通路を定義するキャビティでの使用に関する特定の有用性について記載したが、膨張性構成材は、製造時および/または処理時に生成物の温度が上昇する他の生成物に使用した場合にも利益を提供すると理解される。例えば、多くの装置は、通路を与える構造保持部材を有し、この構造物が定義する通路にシーラントおよびバッフル要素を組み込むことで、通路への望ましくない汚染物質の侵入または該通路を介しての汚染物質の通過が防止される利益が得られる。さらに、これらの装置の多くは、焼付けがまで乾燥され、および/または硬化される塗料またはコーティング材が適用される。冷蔵庫は、装置の保持構造物に本発明の改良されたシーラントおよびバッフル部品を適用するのが好都合な装置の一例である。
【0036】
【表1】
【0037】
1 基質:冷延鋼、溶融亜鉛めっき、ガルバニール、電着コートされた鋼、リン酸処理された鋼
Bynel CXA−E418:無水マレイン酸が官能基としてグラフト結合されたエチレンビニルアセテート
Elvax 265:エチレンビニルアセテート
SBR:スチレンブタジエンゴム
Tylin 2136P:塩素化ポリエチレン
Nevtac 100:脂肪族炭化水素樹脂(C5 、C7 およびC9 )
Microsere:ミクロワックス
Marcus M200:ポリエチレンワックス
Epon 1001F:ビスフェノールAジグリシジルエーテルポリマー
Ardite GT 9654:ビスフェノールAジグリシジルエーテルポリマー
Celogen 765A:変性アゾジカルボンアミド
Unicell DL75N:変性アゾジカルボンアミド
Unicell OH:p、 p’オキシビス(ベンゼンスルホニル)ヒドラジド
Unicell GP3:ジニトロソペンタメチレン−tert−アミン
ZnO:酸化亜鉛
Polar9910:カリウムアルミニウムシリケート
Quincy White325:炭酸カルシウム
容積拡張 “高”:200%以下
“低”:800%以上
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】 自動車車体の斜視図であり、車体キャビティを与える様々な支柱、エンジンレールおよび車体側面の筒状構造を示している。個々のキャビティは、望ましくは湿気、雑音および微細物質に対して効果的にシールするシーラントおよびバッフル構成材を含む。
【図2】 図1に示す自動車車体のキャビティ内に相補して一致するように特に設計された、成形された構造材用の担体の側面図とともに、成形された、固形で、初期非粘着性である膨張性シーラントおよび吸音バッフル構成材の組み合わせを示す側面分解図との合成図である。
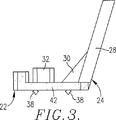
【図3】 図2の構成材および担体の側面図であり、両者が組み合わされた状態で示されている。
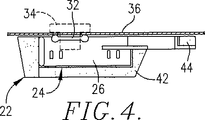
【図4】 図3の構成材および担体の平面図であり、アセンブリは、車体のキャビティの一部を定義する自動車車体のパネル上に配置された状態で示されている。[0001]
Background of the Invention
[Field of the Invention]
The present invention relates to an expandable sealant and baffle component for sealing an automobile body cavity portion that has a wide tolerance for expansion temperature, is solid, and is initially non-adhesive, and the sealant and baffle component of the present invention includes: When the primer, sealer and topcoat applied to the vehicle body are baked and cured, it becomes sticky and expands at the temperature experienced by the vehicle body cavity. The present invention also relates to an improved composition that forms a sealant and baffle component that can be fully expanded to a desired degree over a wider temperature range. In certain aspects, the present invention includes sealants and baffle components of desired characteristics that have improved structural integrity and provide reinforcement to the structure defining the vehicle body cavity. The present invention also relates to a novel method for making expandable sealants and baffle components, which reduces the variability often observed in batch-type processing by being based on continuous processing. Let
[0002]
[Description of prior art]
The car body has various hollow pillars, cavities, passages and similar parts that must be sealed to prevent intrusion of noise or contaminants. Flow, moisture, dust and other airborne particulates can pass through. U.S. Pat. No. 5,373,027 discloses a solid, initially non-adhesive, thermally expandable sealant and baffle component, which sealant and baffle component can be used for vehicle body struts, cavities or passages. After being inserted into the car body, it is expanded by heat induction and formed into a desired shape when the car body is passed through and transferred to a baking pot that forms part of the primer or paint curing process in the automobile manufacturing process.
[0003]
According to the publication, a composition for producing a solid expandable sealant and a baffle component is a large amount containing ethylene groups at α and β positions partially neutralized with metal ions such as zinc. Ethylene / unsaturated carboxylic acid copolymer and modified azodicarboNIncluding a small amount of foaming agent such as amide and a small amount of low molecular weight resin tackifier, when the tackifier becomes high temperature, the outer surface of the constituent material is imparted with tackiness and is expanded by the foaming agent.
[0004]
The composition that forms a solid inflatable sealant and baffle component functions to form an expanded shape within the cavity of the vehicle body as it is transported through a vehicle through a conventional paint or primer baking kettle. . Conventional kilns for baking or curing finishes applied to automobile bodies are usually operated at temperatures ranging from about 140 ° C. to about 200 ° C., depending on the coating being dried or cured. The car body usually passes through each stove for about 10-15 minutes up to 2 hours. For this purpose, conventional expandable baffle components have been designed to preferably expand at temperatures from about 135 ° C to about 185 ° C. The solid expandable sealant and baffle components disclosed in the above publication have enjoyed substantial commercial success in the automotive manufacturing field. The baffle components are easy to use and can be made to the appropriate size, modified and individually adapted to the shape of the individual car body cavities, so that in-situ inflatable automotive sealants and baffle configurations The popularity of timber has been accelerating in recent years. In addition, the expansion of the baffle component can be performed on-site while the automobile is being passed through a baking kettle without the need to provide additional equipment or manufacturing operations for this purpose.
[0005]
As expected, the focus of the paint and / or primer baking process in automotive manufacturing procedures is to properly and effectively cure the paint and / or primer applied to the surface of the automobile body. During the manufacture of automobiles and similar vehicles, processing time is absolutely essential, and the residence time of the vehicle body in the paint and / or primer baking bake ensures that the required paint and / or primer is cured in the shortest possible time. Has been carefully adjusted. The car body has many cavities and passages that differ in location, length, and relative distance from the body surface that is heat treated to bake the paint or primer, so that paint and / or primer baking The actual temperature experienced by certain cavities and passages in the car body during curing is significantly different and may rise to substantially higher temperatures than other cavities or passages during the baking cycle, or an inflatable baffle configuration In some cases, the temperature does not rise to an appropriate temperature to ensure complete expansion of the material.
[0006]
The technician selects the most convenient body cavity portion for the inflatable baffle component based on whether undesirable noise or contaminants are likely to pass through the cavity. This selection of baffle position usually does not take into account the difference in the degree of heating at that position during the bake or cure cycle. For example, the heat energy is dissipated faster in the part with a high metal mass than in the part with a low metal mass. Thus, for the baking and curing kilns, in front of the vehicle exit, the inflatable baffle component does not reach a sufficiently high temperature level necessary to fully expand the baffle product. On the other hand, at other baffle product locations, the nature of the metal that defines the cavity surrounding the inflatable baffle component, in direct proximity to the heat source, or how far the cavity is from the exterior surface of the car body As a result, the baffle material may be overheated. The vertical strut has a chimney effect and may affect the temperature reached in the body cavity.
[0007]
Accordingly, suitable solid expandable sealant and baffle product compositions are required to satisfy a variety of diverse and functionally different parameters and conditions. Such compositions need to be economically configured and can be processed in an efficient manner, preferably using existing equipment. The composition needs to be able to be easily produced into a self-supporting molded body having a predetermined shape and size. The molded body is substantially omnidirectional from its original size without being limited to the carrier on which it is placed or a suitable baffle structure associated with the molded body in order to effectively seal the cavity. It can expand uniformly. Since the molded body formed from the expandable composition is formed for the purpose of being inserted into each cavity of the automobile body, it is essential that the molded body is solid and non-adhesive.
[0008]
In particular, since the cavities in the car body differ in the temperature reached, the composition for making the inflatable sealant and the baffle component is most likely experienced by the cavity in which the inflatable member is installed. It must be highly expandable at low temperatures. Similarly, the expandable sealant and baffle product is carbonized and formed at the highest temperature that any one of the cavities containing the expandable member may experience during the car paint and / or primer cure cycle. Do not burn.
[0009]
Furthermore, the composition needs to have a physical network structure when formed into an inflatable member that is inserted into the cavity of an automobile body and cured to a stove of paint or primer. This network structure enhances the containment of gas generated by the blowing agent incorporated in the composition, thereby ensuring that the member retains a high degree of expansibility in use.
[0010]
It is also desirable for certain aspects of the inflatable sealant and baffle components to have functional characteristics that provide additional reinforcement to the structure defining the body cavity while retaining barrier characteristics against noise, air and moisture.
[0011]
[Summary of Invention]
The present invention provides an expandable sealant and sound-absorbing baffle component for sealing an automobile body cavity that is wide in tolerance to expansion temperature, solid, and initially non-sticky. This sealant and baffle component is tacky over substantially the full range of temperatures experienced by most if not all of the car body cavities expected to benefit from the presence of inflatable components. Can expand. Thus, the sealant and sound absorbing baffle components of the present invention have a substantially wider time and temperature tolerance than products conventionally available for similar applications.
[0012]
Specifically, the present invention relates to a novel inflatable sealant and sound-absorbing baffle component for an automobile body cavity, which sealant and baffle component may be pre-shaped to a desired initial shape and for the entire vehicle body. When viewed, what is the position of the cavity containing the sealant and baffle components, even though the temperature reached by the cavity during the paint and / or primer baking cycle in an automotive manufacturing operation is substantially different between the cavities? Substantially unrelated, when the individual body cavities rise to the temperatures normally experienced during the cycle, they expand to a relatively high degree.
The present invention also provides the following (1) to (28).
(1) An inflatable sound-absorbing baffle component for sealing a solid, initial non-adhesive car body cavity,
The component material can expand at a temperature of 110 ° C. to 191 ° C. experienced by the vehicle body cavity portion during bake hardening of a coating material applied to the vehicle body,
The component isacidAn amount of anhydride graftedacidAn anhydride polymer;
When the component is heated to a temperature of 110 ° C. to 191 ° C. capable of expanding,acidAn amount of a polymer additive comprising a terminal epoxide that reacts with at least a portion of the anhydride polymer;
An expandable sound-absorbing baffle component comprising a sufficient amount of a foaming agent that expands the components of the component when the component is heated to a temperature of 110 ° C. to 191 ° C. in a vehicle body cavity.
(2) The baffle component according to (1), wherein the component is a filling molding component designed to be complementarily received in a selected automobile body cavity.
(3) The aboveacidAn anhydride polymer is a graft-bonded olefin-based polymer wherein at least a portion of the olefin-based polymer isacidThe baffle component according to (1), which reacts with an anhydride.
(4) The baffle component according to (3), wherein the grafted olefin-based polymer is selected from the group consisting of ethylene vinyl acetate, ethylene-n-butyl acrylate, ethylene-octane copolymer, and polyethylene. .
(5) The aboveacidThe baffle component according to (1), wherein the anhydride is maleic anhydride.
(6) The baffle component according to (1), wherein the foaming agent is selected from the group consisting of modified azodicarbonamide and unmodified azodicarbonamide.
(7) The baffle composition according to (1), wherein the blowing agent is selected from the group consisting of p, p′-oxybis (benzenesulfonyl) hydrazide, p-toluenesulfonylhydrazide, and dinitrosopentamethylene-tert-amine. Wood.
(8) saidacidThe polymer grafted with anhydride is contained in the component.10% by massEt al 6The baffle constituent material according to (1), which exists in a range of 0% by mass.
(9) The polymer additive is contained in the constituent material.1Mass%Et 1The baffle constituent material according to (1), which exists in a range of 0% by mass.
(10) The foaming agent is contained in the constituent material.1Mass%Et 1The baffle constituent material according to (1), which exists in a range of 0% by mass.
(11) The olefin-based polymer is in the component1Mass%Et al 5The baffle constituent material according to (3), which exists in a range of 0% by mass.
(12) The baffle component according to (1), which includes a certain amount of a synthetic rubber-like substance.
(13) The synthetic rubber-like substance includes styrene butadiene rubber, ethylene propylene rubber, ethylene propylene diene rubber, butadiene rubber, styrene-isoprene-styrene block copolymer, styrene-butadiene-styrene block copolymer, styrene-ethylene / The baffle component according to (12), selected from the group consisting of butylene-styrene block copolymer, styrene-ethylene / propylene block copolymer, nitrile rubber, and chlorinated polyethylene.
(14) The rubbery substance is contained in the constituent material.1Mass%Et 1The baffle constituent material according to (12), which exists in a range of 5% by mass.
(15) Aliphatic hydrocarbon resins, aromatic hydrocarbon resins, aliphatic / aromatic hydrocarbon resins, hydrogenated hydrocarbon resins, polyterpene resins, rosin ester resins, coumarone indene resins, α-methylstyrene resins and The baffle constituent material according to (1), including an additive selected from the group consisting of polystyrene resins.
(16) The aliphatic hydrocarbon resin, C Five, C7And C9The baffle constituent material according to (15), which is composed of the following hydrocarbon.
(17) The additive includes bisphenol A diglycidyl ether polymer, bisphenol F diglycidyl ether polymer, an adduct of dimer fatty acid and diglycidyl ether of bisphenol A, diglycidyl ether of dimer fatty acid and bisphenol F, and The baffle component according to (15), which is selected from the group consisting of an adduct of the above and a terminal epoxidized acrylobutadiene nitrile rubber adduct.
(18) The baffle component according to (1), wherein the component includes a certain amount of a wax product.
(19) The baffle component according to (18), wherein the wax product is selected from the group consisting of paraffin wax, microwax, polyethylene wax, polyamide wax, and natural wax.
(20) The wax product is in the constituent material.1Mass%Et 1The baffle constituent material according to (19), which exists within a range of 5% by mass.
(21) The constituent material according to (1), wherein the constituent material includes a filler.
(22) The filler is selected from the group consisting of calcium carbonate, barium sulfate, silica, calcium sulfate, aluminum silicate, magnesium silicate, potassium aluminum silicate, calcium metasilicate, pumice, glass globules and organic filler. (21The baffle constituent material according to).
(23) The filler is in the constituent material1Mass%Et al 2The baffle constituent material according to (22), which is present within a range of 0% by mass.
(24) A solid, initial non-adhesive, automotive body cavity that can expand at a temperature of 110 ° C. to 191 ° C. experienced by the body cavity portion during bake hardening of a coating material applied to an automobile body. A method for producing a composition for forming an inflatable sound absorbing baffle component for sealing,
acidAn amount of anhydride graftedacidSufficient to expand the components of the component when the component is heated to a temperature between 110 ° C. and 191 ° C. in an automobile body cavity, with an anhydride polymer, an amount of polymer additive including terminal epoxide, and the component Transporting the admixture of an appropriate amount of foaming agent through a continuous mixing zone;
While mixing the mixture, at least a portion of the terminal epoxide and theacidAllowing the admixture to be in the zone for a sufficient time to allow the anhydride to react with the grafted polymer.
(25) The method according to (24), wherein the transferring step includes a step of transferring the mixture through an auger-type continuous kneading mixer.
(26) Temperature at which the transferring step is introduced into an area where the admixture is continuously mixedKeepThe method according to (24), further comprising the step of transporting through the continuously mixing section while holding the container.
(27) The step of transferring comprises transferring the mixture.1MinutesEt al 2The method according to (24), comprising the step of transferring through the continuously mixing zone for a time of minutes.
(28) An inflatable sound absorbing baffle component for sealing a solid, initial non-adhesive automobile body cavity,
The component material can expand at a temperature experienced by the vehicle body cavity portion during bake hardening of a coating material applied to the vehicle body,
The component isacidAn amount of olefin-based grafted anhydrideacidAn anhydride polymer;
When the component is heated to a temperature at which it can expand,acidAn amount of a polymer additive comprising a terminal epoxide that reacts with at least a portion of the anhydride polymer;
A sufficient amount of foaming agent to expand the components of the component when the component is heated to the temperature in the automobile body cavity;
Including the olefinBase anhydrideAn expandable sound-absorbing baffle component, wherein the polymer is selected from the group consisting of ethylene vinyl acetate, ethylene-n-butyl acrylate, ethylene-octane copolymer and polyethylene.
[0013]
A composition uniquely designed for a particular embodiment is an initial solid, non-adhesive, intumescent composition that is heated to produce the component, the expansible component is a cavity that houses it It acts to add structural integrity to the wall structure of the car body that defines
[0014]
Compositions used to make expandable sealants and baffle components that are well tolerated by expansion temperatures include an amount of polymer grafted with anhydride. The polymer, even if it is initially non-tacky, has the stickiness of the expandable component and the entire range of temperatures experienced by the car body cavity as the car body passes through the paint and / or primer bake. It has the property of improving adhesiveness. Thus, the expandable component disposed within the automobile body adheres firmly to the cavity wall when the component expands upon curing of the paint and / or primer until baking. Ethylene vinyl acetate grafted with maleic anhydride is preferred as the polymer grafted with the anhydride of the composition. This has a relatively low melting point, for example below about 120 ° C. This is a temperature lower than the temperature at which the expandable component substantially expands. Also importantly, the grafted EVA polymer improves adhesion without burning or carbonizing even at the highest temperatures experienced by the cavity containing the sealant and baffle during the paint and / or primer cure cycle. Maintains properties and desired viscosity properties.
[0015]
The composition for making a solid, non-tackable expandable component also includes a polymer additive having a terminal epoxide. The epoxide is capable of reacting with at least a portion of the anhydride polymer at a temperature high enough to expand the sealant and sound absorbing baffle component. The cross-linking reaction between the anhydride polymer and the epoxy polymer that occurs at the temperature experienced by the sealant and sound absorbing baffle components in the cavity during baking of the car body paint and / or primer has a three-dimensional network and cross-linked structure Forms the component and facilitates expansion of the component by the blowing agent incorporated therein, improving the gas retention properties of the final product after expansion. In contrast to practice with prior art polymers, the reaction of terminal epoxidized polymer with anhydride grafted polymer is carried out without a catalyst. As a result, proper crosslinking of the polymer occurs, giving a porous lattice-like product that effectively contains the gas released from the blowing agent. However, crosslinking between the two components and free radical polymerization of the copolymer are not significant enough to reduce the flexibility and expansion properties of baffle products made from sealant and baffle compositions.
[0016]
A solid, initial non-tackable expandable sealant and sound absorbing baffle component is obtained from a composition comprising an anhydride grafted polymer that acts to improve the stickiness of the product after expansion at its melting point. You may produce by a batch type mixer process. Batch mixer processing of compositions containing an anhydride grafted polymer as a component expands to the required level within the temperature range at which automotive paint and / or primer baking is experienced. To produce a final product that can be However, attempts to make compositions from components containing polymers grafted with anhydrides using conventional continuous kneader mixers have not been successful. Parts made of materials made with a continuous kneader and cured at the stove temperature show high fluidity and low expansion, and the resulting product is not useful for the desired application.
[0017]
Polymers with terminal epoxides and anhydride grafted polymers in compositions used to make expandable sealants and sound-absorbing baffle components that are broadly tolerant to expansion temperature, solid and initially non-sticky In the continuous kneading mixer without adversely affecting the degree of expansion of the composition molded from the composition when the temperature of the unexpanded product after molding is applied to the temperature of the baking scale. Unexpectedly found that it can be processed. As a sealant and sound-absorbing baffle component, a limited reaction with a combination of anhydride grafted polymer and terminal epoxide polymer increases the thermal induction expansion and melt viscosity of the component in the stove. .
[0018]
Detailed Description of Preferred Embodiments
The
[0019]
The present invention relates to an improved expandable sealant and sound-absorbing baffle component that is broadly tolerant to expansion temperature, solid, and initially non-tacky, for example, as shown in FIGS. The form of the material 22 may be sufficient. The
[0020]
Specially designed carrier as best shown in FIG.24May have, for example, a
[0021]
In this regard, as described in detail in US Pat. No. 5,506,025 referenced above, the components22Preferably produces the desired shape using injection molding or an equivalent technique for producing a self-supporting molded body that forms an in-situ foamed sealant and baffle barrier in the cavity of the
[0022]
1-4 show in particular the formable expandable baffle product in a form disposed on a suitable relatively rigid carrier, the present invention is designed to be disposed on a complementary carrier. It is understood that the present invention is not limited to expanded baffle products. In certain applications, particularly where the cavity passageway is essentially horizontal in its entirety, the shaped inflatable baffle element may simply be placed at a desired location in the passageway, taking into account various conditions. . In many cases in these examples, the baffle product need not be placed in a very precise location.
[0023]
A moldable composition for making an
[0024]
Specific examples of anhydride grafted polymers useful for making the improved compositions of the present invention include ethylene vinyl acetate grafted with acid anhydrides as functional groups, acid anhydrides as functional groups Graft-bonded ethylene-n-butyl acetate, ethylene-octane copolymer grafted with acid anhydride as functional group, polyethylene grafted with acid anhydride as functional group, acid anhydride grafted as functional group Bonded polypropylene, ethylene propylene rubber grafted with acid anhydrides as functional groups. In particular examples, the preferred acid anhydride is maleic anhydride. A preferred olefin-based grafted polymer is ethylene vinyl acetate grafted with maleic anhydride as a functional group. The anhydride grafted olefin-based polymer is present in the composition from about 10% to about 60% by weight.
[0025]
Polymer additives containing terminal epoxides are preferably derived from solid bisphenol A diglycidyl ether polymer or solid bisphenol F diglycidyl ether polymer (bisphenol A or bisphenol F and epichlorohydrin characterized by an epoxy equivalent of greater than about 400. A liquid bisphenol A diglycidyl ether polymer or a solid bisphenol F diglycidyl ether polymer (derived from bisphenol A or bisphenol F and epichlorohydrin) characterized by an epoxy equivalent weight of about 150 to about 220 The adducts of dimer fatty acids and diglycidyl ethers of bisphenol A or bisphenol F (Epikote or Epon 872), terminal epoxides Acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber adduct (CTBN, Hycar 1300 × 8,1300 × 13) is selected from. A preferred additive is bisphenol A diglycidyl ether polymer. The polymer with terminal epoxide is preferably present in the composition from about 1% to about 10% by weight.
[0026]
The composition is also provided with a suitable blowing agent. The blowing agent is preferably a modified azodicarboNAmides, unmodified azodicarboNIt is selected from the group consisting of amide, p, p'-oxybis (benzenesulfonyl) hydrazide, p-toluenesulfonylhydrazide and dinitrosopentamethylene-tert-amine. Preferred foaming agents are azodicarboNAmide. The blowing agent is preferably present in the composition from about 1% to about 10% by weight.
[0027]
Compositions for making solid, initially non-sticky expandable sealants and sound absorbing baffle components that have a wider tolerance to expansion temperature than conventional expandable compositions may also include a filler polymer. Good. The filler polymer is preferably selected from the group consisting of ethylene vinyl acetate, ethylene-n-butyl acetate, ethylene / octane copolymer, polyethylene, polypropylene and ethylene / methacrylic acid copolymer. A preferred filler polymer is ethylene vinyl acetate. When incorporated into the composition, the filler polymer may be present from about 1% to about 50% by weight.
[0028]
A rubbery component may also be included in the composition for making the expandable component. The rubbery component is preferably styrene butadiene rubber, ethylene propylene rubber, ethylene / propylene / diene rubber, butadiene rubber, styrene / isoprene / styrene block copolymer, styrene / butadiene / styrene block copolymer, styrene / ethylene / propylene block Selected from the group consisting of copolymers, nitrile rubber, and chlorinated polyethylene. A preferred rubbery component is styrene butadiene rubber. The rubbery component may be present in the composition from about 1% to about 15% by weight.
[0029]
Molding and processing aids may also be included in the composition. The auxiliary is preferably selected from the group consisting of paraffin wax, microwax, polyethylene wax, polyamide wax, and natural wax. When used in the composition, the preferred molding and processing aid is polyethylene wax. Molding and processing aids may be present from about 1% to about 15% by weight in the composition.
[0030]
Subsequent to the start of expansion, a tackifier that improves the tackiness of the expandable component may be included in the composition. When using tackifiers, aliphatic hydrocarbon resins, aromatic hydrocarbon resins, aliphatic / aromatic hydrocarbon resins, hydrogenated hydrocarbon resins, polyterpene resins, rosin ester resins, coumarone indene resins, α -Selected from the group consisting of methylstyrene resin and polystyrene resin. The main part of the aliphatic hydrocarbon resin and the aromatic hydrocarbon resin is preferably C, mainly in the case of aliphatic hydrocarbons.Five , C7 And C9 In the case of aromatic hydrocarbons, it is mainly composed of equivalent hydrocarbons. The amount of tackifier may be from about 1% to about 15% by weight.
[0031]
Inorganic or organic fillers may be included in the composition in amounts ranging from about 1% to about 20% by weight. The filler is preferably selected from the group consisting of calcium carbonate, barium sulfate, silica, calcium sulfate, aluminum silicate, magnesium silicate, potassium calcium silicate, calcium metasilicate, pumice, glass globules, organic filler. A preferred filler is calcium carbonate. The amount of inorganic or organic filler may be from about 1% to about 20% by weight in the composition.
[0032]
In making inflatable sealant and baffle components that meet the essential parameters of the present invention, the specifically used composition is introduced by introducing each component into a conventional continuously operable machine such as an extruder. It may be produced. Specific examples of the machine include a single screw blender, a reciprocating single screw extruder, and a twin screw extruder. This type of extruder conventionally includes 2 to 4 inlets along its length, and the ratio of shaft diameter to barrel length ranges from about 7: 1 to about 18: 1. . Preferably, all of the components of the composition except for the reactive reagent including the blowing agent are added to the first inlet port of the extruder. Reactive reagents and blowing agents are added to the third inlet port of the extruder, which usually has four inlet ports. The third inlet port is about 50% to about 75% away from the first inlet port, usually along the length of the extruder barrel. The remaining time is usually in the range of about 1 minute to 3 minutes when the nominal processing time is about 2 minutes.
[0033]
A continuous extruder is equipped with a knife for cutting the extrudate into a series of pellets. Desirably, the extrudate discharged from the extruder can be cooled by immersion in a water bath to ensure a substantially solid state. Alternatively, the extrudate from the continuous extruder can be led as a strand to a strand pellet forming machine and cut into small cylindrical pellets.
[0034]
Pellets from the extruder can be formed into composite expandable sealants and baffle products by an injection molding machine, usually at temperatures below 120 ° C, preferably in the range of 80 ° C to 100 ° C.
[0035]
Although the improved inflatable baffle component of the present invention has been described for particular utility with respect to use in cavities that define the passage of an automobile body, the inflatable component may be produced at the time of manufacture and / or processing. It is understood that it also provides benefits when used for other products with elevated temperatures. For example, many devices have a structural retention member that provides a passageway and incorporates sealant and baffle elements into the passage defined by the structure, thereby allowing unwanted contaminants to enter or pass through the passageway. The benefit is that the passage of contaminants is prevented. Furthermore, many of these devices are applied with paints or coatings that are dried and / or cured until baking. A refrigerator is an example of a device that advantageously applies the improved sealant and baffle parts of the present invention to the holding structure of the device.
[0036]
[Table 1]
[0037]
1Substrate: Cold-rolled steel, hot-dip galvanized, galvanil, electrodeposited steel, phosphated steel
Bynel CXA-E418: ethylene vinyl acetate grafted with maleic anhydride as a functional group
Elvax 265: Ethylene vinyl acetate
SBR: Styrene butadiene rubber
Tylin 2136P: Chlorinated polyethylene
Nevtac 100: Aliphatic hydrocarbon resin (CFive, C7And C9)
Microsere: Microwax
Marcus M200: Polyethylene wax
Epon 1001F: bisphenol A diglycidyl ether polymer
Ardite GT 9654: Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether polymer
Celogen 765A: Modified azodicarboNAmide
Unicell DL75N: Modified AzodicarboNAmide
Unicell OH: p, p'oxybis (benzenesulfonyl) hydrazide
Unicell GP3: dinitrosopentamethylene-tert-amine
ZnO: Zinc oxide
Polar 9910: Potassium aluminum silicate
Quincy White 325: calcium carbonate
Volume expansion “High”: 200% or less
“Low”: 800% or more
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a perspective view of an automobile body, showing various struts, engine rails, and tubular structures on the side of the body that provide a body cavity. Individual cavities desirably include sealant and baffle components that effectively seal against moisture, noise and fine materials.
2 is a molded, solid, initial non-adhesive with side view of a molded structural carrier specifically designed to complementarily fit within the cavity of the automobile body shown in FIG. It is a synthetic | combination figure with the side surface exploded view which shows the combination of the expandable sealant which is and a sound-absorbing baffle component material.
FIG. 3 is a side view of the component and carrier of FIG. 2 shown in a combined state.
4 is a plan view of the components and carrier of FIG. 3, with the assembly shown disposed on a panel of the automobile body defining a portion of the body cavity. FIG.
Claims (28)
前記構成材は、前記車体に適用されるコーティング材の焼付硬化時に前記車体キャビティ部が経験する110℃〜191℃の温度で膨張することができ、
前記構成材は、酸無水物がグラフト結合されたある量の酸無水物ポリマーと、
前記構成材が前記膨張することができる110℃〜191℃の温度に加熱された際に、前記酸無水物ポリマーの少なくとも一部と反応する末端エポキシドを含んだある量のポリマー添加物と、
前記構成材が自動車車体キャビティ内で前記110℃〜191℃の温度に加熱された際に、前記構成材の成分を膨張させる十分な量の発泡剤と、を含む膨張性吸音バッフル構成材。An inflatable sound absorbing baffle component for sealing a solid, initial non-stick car body cavity,
The component material can expand at a temperature of 110 ° C. to 191 ° C. experienced by the vehicle body cavity portion during bake hardening of a coating material applied to the vehicle body,
The construction material is an acid anhydride polymer an amount of the acid anhydride is grafted,
An amount of a polymer additive comprising a terminal epoxide that reacts with at least a portion of the acid anhydride polymer when the component is heated to a temperature of 110 ° C. to 191 ° C. capable of expanding;
An expandable sound-absorbing baffle component comprising a sufficient amount of a foaming agent that expands the components of the component when the component is heated to a temperature of 110 ° C. to 191 ° C. in a vehicle body cavity.
酸無水物がグラフト結合されたある量の酸無水物ポリマーと、末端エポキシドを含んだある量のポリマー添加物と、前記構成材を自動車車体キャビティ内で前記110℃〜191℃の温度に加熱した際に、前記構成材の成分を膨張させる十分な量の発泡剤と、の混和物を連続して混合する区域を通過させて移送する工程と、
前記混合物を混合しつつ、前記末端エポキシドの少なくとも一部と前記酸無水物がグラフト結合されたポリマーとを反応させるのに十分な時間前記混和物が前記区域にあるようにする工程と、を含んだ方法。For the sealing of automobile body cavities that are solid and initially non-adhesive that can expand at a temperature of 110 ° C. to 191 ° C. experienced by the body cavity portion during baking and curing of coating materials applied to automobile bodies A method of making a composition for forming an intumescent sound absorbing baffle component comprising:
An amount of acid anhydride polymer grafted with acid anhydride, an amount of polymer additive including terminal epoxide, and the component was heated to a temperature of 110 ° C. to 191 ° C. in an automobile body cavity. A sufficient amount of a blowing agent to expand the components of the component, and a step of transferring the mixture through a continuous mixing zone; and
While mixing the mixture, it includes the steps of sufficient time said admixture to at least a portion of the acid anhydride of the terminal epoxide reacting the polymer grafted bonds as in the zone That way.
前記構成材は、前記車体に適用されるコーティング材の焼付硬化時に前記車体キャビティ部が経験する温度で膨張することができ、
前記構成材は、酸無水物がグラフト結合されたある量のオレフィンベースの酸無水物ポリマーと、
前記構成材が前記膨張することができる温度に加熱された際に、前記酸無水物ポリマーの少なくとも一部と反応する末端エポキシドを含んだある量のポリマー添加物と、
前記構成材が自動車車体キャビティ内で前記温度に加熱された際に、前記構成材の成分を膨張させる十分な量の発泡剤と、
を含み、前記オレフィンベースの酸無水物ポリマーが、エチレンビニルアセテート、エチレン−n−ブチルアクリレート、エチレン・オクタン共重合体およびポリエチレンからなる群から選択される膨張性吸音バッフル構成材。An inflatable sound absorbing baffle component for sealing a solid, initial non-stick car body cavity,
The component material can expand at a temperature experienced by the vehicle body cavity portion during bake hardening of a coating material applied to the vehicle body,
The construction material, and a quantity of the olefin-based anhydride polymer acid anhydride is grafted,
An amount of a polymer additive comprising a terminal epoxide that reacts with at least a portion of the acid anhydride polymer when the component is heated to a temperature capable of expanding;
A sufficient amount of foaming agent to expand the components of the component when the component is heated to the temperature in the automobile body cavity;
And wherein the olefin-based acid anhydride polymer is selected from the group consisting of ethylene vinyl acetate, ethylene-n-butyl acrylate, ethylene-octane copolymer and polyethylene.
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US09/407,820 US6150428A (en) | 1999-09-28 | 1999-09-28 | Expansion temperature tolerant dry expandable sealant and baffle product and method of preparing same |
| US09/407,820 | 1999-09-28 | ||
| PCT/US2000/026209 WO2001023461A1 (en) | 1999-09-28 | 2000-09-22 | Expansion temperature tolerant dry expandable sealant and baffle product and method of preparing same |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2003510434A JP2003510434A (en) | 2003-03-18 |
| JP4124591B2 true JP4124591B2 (en) | 2008-07-23 |
Family
ID=23613649
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001526604A Expired - Lifetime JP4124591B2 (en) | 1999-09-28 | 2000-09-22 | Solid expansible sealant and baffle component with wide tolerance for expansion temperature and method for producing the same |
Country Status (9)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US6150428A (en) |
| EP (1) | EP1090813B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP4124591B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR100546093B1 (en) |
| AT (1) | ATE287808T1 (en) |
| AU (1) | AU7611000A (en) |
| DE (1) | DE60017663T2 (en) |
| ES (1) | ES2237370T3 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2001023461A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (110)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6103341A (en) | 1997-12-08 | 2000-08-15 | L&L Products | Self-sealing partition |
| US6131897A (en) | 1999-03-16 | 2000-10-17 | L & L Products, Inc. | Structural reinforcements |
| TW517260B (en) * | 1999-05-15 | 2003-01-11 | Semiconductor Energy Lab | Semiconductor device and method for its fabrication |
| US6830799B1 (en) * | 1999-10-26 | 2004-12-14 | Orbseal Llc | Expandable compositions and methods of making and using the compositions |
| EP1230299B1 (en) * | 1999-10-26 | 2006-12-27 | Henkel Corporation | Expandable compositions and methods of making and using the compositions |
| US6358584B1 (en) | 1999-10-27 | 2002-03-19 | L&L Products | Tube reinforcement with deflecting wings and structural foam |
| US6668457B1 (en) | 1999-12-10 | 2003-12-30 | L&L Products, Inc. | Heat-activated structural foam reinforced hydroform |
| US6467834B1 (en) | 2000-02-11 | 2002-10-22 | L&L Products | Structural reinforcement system for automotive vehicles |
| EP1265778B1 (en) | 2000-02-11 | 2016-10-05 | Zephyros Inc. | Structural reinforcement system for automotive vehicles |
| US6482486B1 (en) | 2000-03-14 | 2002-11-19 | L&L Products | Heat activated reinforcing sleeve |
| US6422575B1 (en) | 2000-03-14 | 2002-07-23 | L&L Products, Inc. | Expandable pre-formed plug |
| US6296298B1 (en) | 2000-03-14 | 2001-10-02 | L&L Products, Inc. | Structural reinforcement member for wheel well |
| US6321793B1 (en) | 2000-06-12 | 2001-11-27 | L&L Products | Bladder system for reinforcing a portion of a longitudinal structure |
| US6319964B1 (en) * | 2000-06-30 | 2001-11-20 | Sika Corporation | Acoustic baffle with predetermined directional expansion characteristics |
| US6820923B1 (en) | 2000-08-03 | 2004-11-23 | L&L Products | Sound absorption system for automotive vehicles |
| US6634698B2 (en) | 2000-08-14 | 2003-10-21 | L&L Products, Inc. | Vibrational reduction system for automotive vehicles |
| US6561571B1 (en) | 2000-09-29 | 2003-05-13 | L&L Products, Inc. | Structurally enhanced attachment of a reinforcing member |
| US6419305B1 (en) | 2000-09-29 | 2002-07-16 | L&L Products, Inc. | Automotive pillar reinforcement system |
| US6471285B1 (en) | 2000-09-29 | 2002-10-29 | L&L Products, Inc. | Hydroform structural reinforcement system |
| USD457120S1 (en) | 2001-01-08 | 2002-05-14 | Sika Corporation | Ribbed structural reinforcing member |
| GB0106911D0 (en) | 2001-03-20 | 2001-05-09 | L & L Products | Structural foam |
| GB2375328A (en) * | 2001-05-08 | 2002-11-13 | L & L Products | Reinforcing element for hollow structural member |
| US6502821B2 (en) | 2001-05-16 | 2003-01-07 | L&L Products, Inc. | Automotive body panel damping system |
| US6855652B2 (en) | 2001-08-24 | 2005-02-15 | L&L Products, Inc. | Structurally reinforced panels |
| US6729425B2 (en) | 2001-09-05 | 2004-05-04 | L&L Products, Inc. | Adjustable reinforced structural assembly and method of use therefor |
| KR100410939B1 (en) * | 2001-09-12 | 2003-12-18 | 현대자동차주식회사 | Mastic Sealer Composition having foam-type |
| US6786533B2 (en) | 2001-09-24 | 2004-09-07 | L&L Products, Inc. | Structural reinforcement system having modular segmented characteristics |
| EP1300291A3 (en) * | 2001-09-28 | 2005-10-26 | CWW-GERKO Akustik GmbH & Co. KG | Process for applying a sound absorbing covering material based on epoxy resins to a vehicle body |
| US6793274B2 (en) | 2001-11-14 | 2004-09-21 | L&L Products, Inc. | Automotive rail/frame energy management system |
| US7041355B2 (en) | 2001-11-29 | 2006-05-09 | Dow Global Technologies Inc. | Structural reinforcement parts for automotive assembly |
| AU2002361136A1 (en) * | 2001-12-21 | 2003-07-09 | Henkel Teroson Gmbh | Expandable epoxy resin-based systems modified with thermoplastic polymers |
| JP4391826B2 (en) | 2002-01-22 | 2009-12-24 | ダウ グローバル テクノロジーズ インコーポレイティド | Reinforced structure and manufacturing method thereof |
| US7318873B2 (en) | 2002-03-29 | 2008-01-15 | Zephyros, Inc. | Structurally reinforced members |
| CA2482168A1 (en) | 2002-04-15 | 2003-10-30 | Dow Global Technologies Inc. | Improved vehicular structural members and method of making the members |
| US6969551B2 (en) * | 2002-04-17 | 2005-11-29 | L & L Products, Inc. | Method and assembly for fastening and reinforcing a structural member |
| US7169344B2 (en) | 2002-04-26 | 2007-01-30 | L&L Products, Inc. | Method of reinforcing at least a portion of a structure |
| US7077460B2 (en) | 2002-04-30 | 2006-07-18 | L&L Products, Inc. | Reinforcement system utilizing a hollow carrier |
| WO2003093064A1 (en) | 2002-05-02 | 2003-11-13 | Dow Global Technologies, Inc. | Vehicle body cavity filler |
| GB0211268D0 (en) * | 2002-05-17 | 2002-06-26 | L & L Products Inc | Hole plugs |
| GB0211287D0 (en) * | 2002-05-17 | 2002-06-26 | L & L Products Inc | Improved baffle precursors |
| GB0211775D0 (en) | 2002-05-23 | 2002-07-03 | L & L Products Inc | Multi segment parts |
| US20040011282A1 (en) * | 2002-07-18 | 2004-01-22 | Myers Robert D. | System and method for manufacturing physical barriers |
| US6920693B2 (en) | 2002-07-24 | 2005-07-26 | L&L Products, Inc. | Dynamic self-adjusting assembly for sealing, baffling or structural reinforcement |
| US7390845B2 (en) * | 2002-07-26 | 2008-06-24 | Illinois Tool Works Inc | Sealing system and process therefor |
| US7004536B2 (en) | 2002-07-29 | 2006-02-28 | L&L Products, Inc. | Attachment system and method of forming same |
| US20040034982A1 (en) * | 2002-07-30 | 2004-02-26 | L&L Products, Inc. | System and method for sealing, baffling or reinforcing |
| US6923499B2 (en) | 2002-08-06 | 2005-08-02 | L & L Products | Multiple material assembly for noise reduction |
| US6883858B2 (en) | 2002-09-10 | 2005-04-26 | L & L Products, Inc. | Structural reinforcement member and method of use therefor |
| US6692347B1 (en) | 2002-09-27 | 2004-02-17 | L&L Products, Inc. | Filter housing assembly for transportation vehicles |
| US7026410B2 (en) * | 2002-10-17 | 2006-04-11 | Henkel Corporation | Solventless method for preparation of carboxylic polymers |
| US7105112B2 (en) | 2002-11-05 | 2006-09-12 | L&L Products, Inc. | Lightweight member for reinforcing, sealing or baffling |
| CA2509629A1 (en) | 2002-12-27 | 2004-07-22 | Dow Global Technologies Inc. | Heat activated epoxy adhesive and use in a structural foam insert |
| GB0300159D0 (en) | 2003-01-06 | 2003-02-05 | L & L Products Inc | Improved reinforcing members |
| US7313865B2 (en) | 2003-01-28 | 2008-01-01 | Zephyros, Inc. | Process of forming a baffling, sealing or reinforcement member with thermoset carrier member |
| WO2004078451A1 (en) * | 2003-03-05 | 2004-09-16 | Dow Global Technologies Inc. | Structural reinforcement article and process for prepareation thereof |
| JP4406540B2 (en) * | 2003-03-28 | 2010-01-27 | シャープ株式会社 | Thin film transistor substrate and manufacturing method thereof |
| US7111899B2 (en) | 2003-04-23 | 2006-09-26 | L & L Products, Inc. | Structural reinforcement member and method of use therefor |
| GB2401349A (en) | 2003-05-08 | 2004-11-10 | L & L Products | Reinforcement for a vehicle panel |
| US7041193B2 (en) | 2003-05-14 | 2006-05-09 | L & L Products, Inc. | Method of adhering members and an assembly formed thereby |
| US7784186B2 (en) | 2003-06-26 | 2010-08-31 | Zephyros, Inc. | Method of forming a fastenable member for sealing, baffling or reinforcing |
| US7249415B2 (en) | 2003-06-26 | 2007-07-31 | Zephyros, Inc. | Method of forming members for sealing or baffling |
| JP3771567B2 (en) * | 2003-09-02 | 2006-04-26 | 日東電工株式会社 | Filling foam composition, filled foam member and filling foam |
| US7469459B2 (en) | 2003-09-18 | 2008-12-30 | Zephyros, Inc. | System and method employing a porous container for sealing, baffling or reinforcing |
| US20050102815A1 (en) * | 2003-11-03 | 2005-05-19 | L&L Products, Inc. | Reinforced members formed with absorbent mediums |
| US20050127145A1 (en) * | 2003-11-20 | 2005-06-16 | L&L Products, Inc. | Metallic foam |
| US20050166532A1 (en) * | 2004-01-07 | 2005-08-04 | L&L Products, Inc. | Structurally reinforced panels |
| US20050172486A1 (en) * | 2004-02-05 | 2005-08-11 | L&L Products, Inc. | Member for sealing, baffling or reinforcing and method of forming same |
| GB2415658A (en) | 2004-06-21 | 2006-01-04 | L & L Products Inc | An overmoulding process |
| US20050012280A1 (en) * | 2004-08-13 | 2005-01-20 | L&L Products, Inc. | Sealing member, sealing method and system formed therewith |
| US20060043772A1 (en) * | 2004-08-26 | 2006-03-02 | L&L Products, Inc. | Baffle and system formed therewith |
| US7374219B2 (en) | 2004-09-22 | 2008-05-20 | Zephyros, Inc. | Structural reinforcement member and method of use therefor |
| US20060065483A1 (en) * | 2004-09-29 | 2006-03-30 | L&L Products, Inc. | Baffle with flow-through medium |
| US7494179B2 (en) * | 2005-04-26 | 2009-02-24 | Zephyros, Inc. | Member for baffling, reinforcement or sealing |
| US7503620B2 (en) | 2005-05-12 | 2009-03-17 | Zephyros, Inc. | Structural reinforcement member and method of use therefor |
| US8381403B2 (en) * | 2005-05-25 | 2013-02-26 | Zephyros, Inc. | Baffle for an automotive vehicle and method of use therefor |
| US7428774B2 (en) * | 2005-05-25 | 2008-09-30 | Zephyros, Inc. | Baffle for an automotive vehicle and method of use therefor |
| US7597382B2 (en) * | 2005-06-07 | 2009-10-06 | Zephyros, Inc. | Noise reduction member and system |
| CN102585439B (en) * | 2005-07-01 | 2016-06-15 | Sika技术股份公司 | Solid thermally expansible material |
| US20070110951A1 (en) * | 2005-07-20 | 2007-05-17 | Frank Hoefflin | Thermally expansible material substantially free of tackifier |
| US7926179B2 (en) | 2005-08-04 | 2011-04-19 | Zephyros, Inc. | Reinforcements, baffles and seals with malleable carriers |
| EP1772480B1 (en) * | 2005-10-06 | 2013-12-04 | Henkel AG & Co. KGaA | Reduction of transfer of vibrations |
| GB0600901D0 (en) | 2006-01-17 | 2006-02-22 | L & L Products Inc | Improvements in or relating to reinforcement of hollow profiles |
| JP5342444B2 (en) * | 2006-09-20 | 2013-11-13 | ヘンケル・アクチェンゲゼルシャフト・ウント・コムパニー・コマンディットゲゼルシャフト・アウフ・アクチェン | Solid expansible composition |
| DE102007038659A1 (en) | 2007-08-15 | 2009-02-19 | Henkel Ag & Co. Kgaa | Expandable filler insert for filling hollow spaces, comprises self-supporting continuous structure including polymer matrix containing polymer(s) or polymer precursor and latent blowing agent(s), and spacer and/or fixing element |
| CA2670642A1 (en) * | 2006-12-28 | 2008-07-10 | Henkel Ag & Co. Kgaa | Acoustic baffle |
| US20090001758A1 (en) * | 2007-06-29 | 2009-01-01 | Sika Technology Ag | Expandable insert for hollow structure |
| WO2009091953A2 (en) | 2008-01-16 | 2009-07-23 | Sika Technology Ag | Extruded expandable barrier |
| EP2262664A4 (en) * | 2008-03-07 | 2012-05-09 | Henkel Corp | Acoustic baffle assembly |
| GB0806434D0 (en) | 2008-04-09 | 2008-05-14 | Zephyros Inc | Improvements in or relating to structural adhesives |
| EP2154052A1 (en) | 2008-08-12 | 2010-02-17 | Sika Technology AG | Structural reinforcement system |
| KR20110065499A (en) * | 2008-09-05 | 2011-06-15 | 헨켈 아게 운트 코. 카게아아 | Edge-encapsulated panel with high damping foam |
| US8430448B2 (en) | 2008-11-07 | 2013-04-30 | Zephyros, Inc. | Hybrid reinforcement structure |
| GB0916205D0 (en) | 2009-09-15 | 2009-10-28 | Zephyros Inc | Improvements in or relating to cavity filling |
| JP6283163B2 (en) * | 2009-12-17 | 2018-02-21 | マルチマティック パテントコ エルエルシー | Method and structure for forming a butt-joined closed cross-section hollow structure |
| JP2013521163A (en) | 2010-03-04 | 2013-06-10 | ゼフィロス インコーポレイテッド | Structural composite laminate |
| BR112013013989B1 (en) | 2010-12-08 | 2022-02-08 | Zephyros, Inc | SEALING DEVICE FOR A CAVITY AND METHOD FOR SEALING A CAVITY |
| ES2782194T3 (en) | 2011-06-10 | 2020-09-11 | Henkel Ag & Co Kgaa | Effective vibration damping over a wide temperature range |
| WO2013142145A1 (en) | 2012-03-20 | 2013-09-26 | Zephyros, Inc. | Baffle assembly |
| EP3483046A1 (en) | 2012-06-08 | 2019-05-15 | Zephyros Inc. | Baffle with expanding material |
| WO2014040913A1 (en) | 2012-09-11 | 2014-03-20 | Sika Technology Ag | Thermoplastic foaming agent |
| US10577522B2 (en) | 2013-07-26 | 2020-03-03 | Zephyros, Inc. | Thermosetting adhesive films including a fibrous carrier |
| GB201417985D0 (en) | 2014-10-10 | 2014-11-26 | Zephyros Inc | Improvements in or relating to structural adhesives |
| BR112017023238B1 (en) | 2015-04-30 | 2023-03-28 | Zephyros, Inc | ARTICLE AND METHOD FOR FORMING AN ARTICLE |
| JP7007260B2 (en) | 2015-09-02 | 2022-01-24 | シーカ テクノロジー アクチェンゲゼルシャフト | Thermally expandable foam material |
| EP3486146B1 (en) | 2017-11-15 | 2021-04-14 | Sika Technology Ag | Device for reinforcing and sealing a structural element |
| JPWO2019181336A1 (en) * | 2018-03-22 | 2021-03-18 | 東洋紡株式会社 | Aqueous dispersion composition |
| CN108727816A (en) * | 2018-04-03 | 2018-11-02 | 南阳国宇密封发展有限公司 | A kind of no asbestos latex sealing material and preparation method thereof |
| USD879701S1 (en) | 2018-05-14 | 2020-03-31 | Zephyros, Inc. | Sealing device |
| USD879007S1 (en) | 2018-05-14 | 2020-03-24 | Zephyros, Inc. | Sealing device |
| USD938887S1 (en) | 2018-06-21 | 2021-12-21 | Zephyros, Inc. | Sealing device |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0459866A (en) * | 1990-06-29 | 1992-02-26 | Kanegafuchi Chem Ind Co Ltd | Thermoplastic resin composition |
| JPH04117467A (en) * | 1990-09-06 | 1992-04-17 | Shinto Paint Co Ltd | Formable powder coating composition |
| CA2112410C (en) * | 1991-06-26 | 2003-12-09 | Norman E. Blank | Reactive hot-melt adhesive |
| US5266133A (en) * | 1993-02-17 | 1993-11-30 | Sika Corporation | Dry expansible sealant and baffle composition and product |
| JPH07188445A (en) * | 1993-11-16 | 1995-07-25 | Sumitomo Chem Co Ltd | Rubber composition for sponge |
| US5506025A (en) * | 1995-01-09 | 1996-04-09 | Sika Corporation | Expandable baffle apparatus |
| US6221928B1 (en) | 1996-11-15 | 2001-04-24 | Sentinel Products Corp. | Polymer articles including maleic anhydride |
-
1999
- 1999-09-28 US US09/407,820 patent/US6150428A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2000
- 2000-06-30 US US09/607,311 patent/US6281260B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-09-22 KR KR1020027004008A patent/KR100546093B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-09-22 WO PCT/US2000/026209 patent/WO2001023461A1/en not_active Ceased
- 2000-09-22 AU AU76110/00A patent/AU7611000A/en not_active Abandoned
- 2000-09-22 JP JP2001526604A patent/JP4124591B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-09-25 AT AT00120829T patent/ATE287808T1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2000-09-25 EP EP00120829A patent/EP1090813B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-09-25 ES ES00120829T patent/ES2237370T3/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-09-25 DE DE60017663T patent/DE60017663T2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| AU7611000A (en) | 2001-04-30 |
| US6150428A (en) | 2000-11-21 |
| JP2003510434A (en) | 2003-03-18 |
| ES2237370T3 (en) | 2005-08-01 |
| WO2001023461A1 (en) | 2001-04-05 |
| KR100546093B1 (en) | 2006-01-24 |
| EP1090813A1 (en) | 2001-04-11 |
| DE60017663D1 (en) | 2005-03-03 |
| EP1090813B1 (en) | 2005-01-26 |
| ATE287808T1 (en) | 2005-02-15 |
| DE60017663T2 (en) | 2006-03-30 |
| KR20020063870A (en) | 2002-08-05 |
| US6281260B1 (en) | 2001-08-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4124591B2 (en) | Solid expansible sealant and baffle component with wide tolerance for expansion temperature and method for producing the same | |
| US6319964B1 (en) | Acoustic baffle with predetermined directional expansion characteristics | |
| JP5342444B2 (en) | Solid expansible composition | |
| JP2538529B2 (en) | Inflatable dry sealant / baffle composition | |
| EP1599527A2 (en) | Epoxy/elastomer adduct, method of forming same and materials and articles formed therewith | |
| MX2008012897A (en) | Adhesion-modified expandable polyolefin compositions and insulated vehicle parts containing expanded adhesion-modified polyolefin compositions. | |
| JP2005289063A (en) | Method for utilizing material which can be activated to member | |
| CN107922661B (en) | heat expandable foam | |
| US20240327589A1 (en) | Low Odor Heat-Expandable Materials | |
| US20240059359A1 (en) | Cavity Sealing System for Automotive Vehicles | |
| JP2006176668A (en) | Foamable filler composition | |
| CN118475643A (en) | Multistage processing of sealant materials |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20040910 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20040921 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20041215 |
|
| A602 | Written permission of extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A602 Effective date: 20041227 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20050322 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20071002 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20071217 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20080408 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20080502 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4124591 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110516 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120516 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130516 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| EXPY | Cancellation because of completion of term |