JP3925054B2 - Camera device - Google Patents
Camera device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3925054B2 JP3925054B2 JP2000226095A JP2000226095A JP3925054B2 JP 3925054 B2 JP3925054 B2 JP 3925054B2 JP 2000226095 A JP2000226095 A JP 2000226095A JP 2000226095 A JP2000226095 A JP 2000226095A JP 3925054 B2 JP3925054 B2 JP 3925054B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- image
- shooting
- storage means
- mode
- sample
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Cameras In General (AREA)
- Camera Data Copying Or Recording (AREA)
- Television Signal Processing For Recording (AREA)
- Studio Devices (AREA)
- Details Of Cameras Including Film Mechanisms (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、カメラ装置及び記録媒体、撮影モード設定データ作成装置に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
従来、例えば電子スチルカメラにおいては、シャッタースピード、絞り値といった装置側における各種の撮影条件を自動的に設定したり、又は撮影者の好みに応じて手動で設定したりできるようになっている。さらには、例えばポートレート、風景、夜景といった被写体の種別に適した撮影条件を自動的に設定する複数の撮影モードを用意しておき、かかる撮影モードを事前に撮影者に選択させることにより、シャッタースピード、絞り値等の専門的な知識を有していない初心者等であっても、より適切な撮影条件が設定できるようにしたものが多い。
【0003】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、前述した各種の撮影条件を撮影者が手動で設定した場合、必ずしも撮影者の意図にあった撮影結果が得られるとは限らなかった。また、予め用意されている撮影モードにより撮影条件を自動的に設定する場合においても、その撮影条件の設定内容が最大公約数的なものであることから、撮影者の好みに応じ撮影結果が得られるとは限らないという問題があった。
【0004】
本発明は、かかる従来の課題に鑑みてなされたものであり、撮影者の好みに応じ撮影結果が得られる適切な撮影条件を容易に設定することができるカメラ装置、及び記録媒体、撮影モード設定データ作成装置を提供することを目的とする。
【0005】
【課題を解決するための手段】
前記課題を解決するために請求項1の発明にあっては、被写体の種別に応じた複数の撮影モードが選択的に設定可能なカメラ装置であって、撮影した画像を撮影条件とともに画像データとして記録する画像記憶手段と、前記撮影モード毎に応じて撮影時における装置の撮影条件を制御する制御手段と、予め、前記撮影モードに対応した複数の見本画像と撮影条件の内容を説明する説明情報とを記憶する撮影条件記憶手段と、前記画像記憶手段に記憶された画像の縮小画像撮影した画像の撮影条件とこの縮小画像撮影条件と対応した撮影条件と画像とを前記撮影条件記憶手段に追加記憶させる手段と、前記撮影条件記憶手段に記憶された見本画像とこの見本画像に対応する説明情報、および前記縮小画像とを表示する表示手段と、この表示手段に表示される前記見本画像および前記縮小画像を送り表示させるための操作手段と、この表示手段に表示されている前記見本画像あるいは前記縮小画像を選択する選択手段と、この選択手段により選択された前記見本画像あるいは前記縮小画像に対応する撮影モードを設定する設定する設定手段とを備えたものとした。
【0006】
かかる構成においては、使用者の要求があると、設定手段は表示中の画像を撮影した時点と同一の撮影条件を設定するため、使用者は、撮影結果のイメージを過去に撮影された画像で確認しながら、その画像の撮影時と同一の撮影条件を設定することができる。
【0007】
また、請求項2の発明にあっては、撮影した画像の画像データと撮影条件とを含む所定のフォーマット形式を有するファイルが前記画像記憶手段に記憶され、前記画像記憶手段は前記撮影条件記憶手段として機能するものとした。かかる構成においては、装置の撮影条件を設定するときには、同種の装置によって撮影された画像を利用することができる。
【0008】
また、請求項3の発明にあっては、前記撮影条件記憶手段は前記撮影した画像が縮小された見本画像を記憶し、所定のモードで前記見本画像を前記表示手段に表示させる前記制御手段を備えるとともに、前記設定手段は、前記見本画像が前記表示手段に表示された状態での使用者の要求に応じて、当該見本画像とに対応するする撮影条件に基づき装置の撮影条件を設定するものとした。
【0009】
また、請求項4の発明にあっては、前記撮影条件記憶手段には、予め複数組の前記画像記憶手段に記憶された画像の縮小画像とこの縮小画像と対応した撮影条件とを記憶させる領域が確保されていることとした。
【0015】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明の第1の実施の形態を図にしたがって説明する。図1は、本発明にかかる電子スチルカメラ1の外観を示す図であって、同図(a)は背面図、同図(b)は平面図、同図(c)は正面図である。
【0016】
電子スチルカメラ1は、正面側に固定レンズ4、背面側にTFT液晶モニタ18を有し、さらに光学ファインダ51とストロボ19とを有している。また、電子スチルカメラ1の背面部及び上面部には、電源スイッチ52、シャッターキー53、ズーム操作スイッチ54、録画モード(RECモード)と再生モード(PLAYモード)の切り替え行う動作モード切り替えスイッチ55、液晶モニタ・スイッチ56、フラッシュ・キー57、セルフタイマ・キー58、メニュー・キー59の各種スイッチが設けられている。
【0017】
図2は、前記電子スチルカメラ1の電気的構成の概略を示すブロック構成図であり、電子スチルカメラ1は、撮像手段であるCCD2により撮像した画像を所定の規格に基づく符号化データに変換する等の画像処理機能を備えたMPU3を中心に構成されている。CCD2の受光面には、固定レンズ4、フォーカスレンズ5、絞り6を通過して被写体の光学像が結像される。フォーカスレンズ5はAFモータ等からなる駆動機構7に保持されており、MPU3からの制御信号によりAFドライバー8が出力する駆動信号が駆動機構7に供給されることにより光軸上を前後に移動する合焦動作を行う。絞り6は、MPU3からの制御信号に基づき絞り駆動部9が発生する駆動信号により駆動しCCD2に入射する被写体像の光量を調整する。
【0018】
また、MPU3には、タイミング信号を発生するTG(Timming Generater)10が接続されており、TG10が発生したタイミング信号に基づきVドライバー11(垂直方向ドライバー)がCCD2を駆動し、それに伴いCCD2により被写体像の輝度に応じたアナログの撮像信号が出力されユニット回路12へ送られる。ユニット回路12は、CCD2から出力された撮像信号を保持するCDSと、CDSから撮像信号を供給されるアナログアンプであるゲイン調整アンプ(AGC)と、ゲイン調整アンプに増幅され調整された撮像信号を画像データに変換するA/D変換器(AD)とからなり、CCD2の出力信号は、ここで黒レベルを合わせてサンプリングされデジタル信号としてMPU3に送られる。送られたデジタル信号(撮像信号)はDRAM13に一時保存されるとともに、MPU3によって各種の画像処理が施された後、最終的には圧縮された映像信号データからなる画像ファイルとして本発明の画像記憶手段である、着脱可能なフラッシュメモリ(FLASH)14に保存される。
【0019】
図3は、フラッシュメモリ14は保存される画像ファイル100のフォーマットを示す概念図である。このフォーマットは、例えば統一規格DCF(Design rule for Camera File system)に合致する画像フォーマットであって、主として符号化された画像データ(画像データ本体)、及び画像データの復号化に際して使用される符号/復号化テーブル等のデータを格納する画像データ格納領域100aと、撮影時の日付、及びシャッタ速度や絞り値といった撮影条件データ等の当該画像の付加的なデータを格納する付加データ格納領域100bと、ユーザーが自由に使用できるユーザーデータ格納領域100cから構成されている。そして、本実施の形態において前記画像ファイル100の保存時には、記録する画像の縮小画像を生成し、生成した縮小画像の映像信号データを前記ユーザーデータ格納領域100cに格納する。また、画像ファイル100として保存された本体画像及び縮小画像の映像信号データは、必要に応じてMPU3に読み出され、伸長処理、輝度信号及び色信号の付加等の処理を経てデジタルビデオ信号やアナログビデオ信号に生成される。
【0020】
さらに、MPU3にはMROM15と、電源回路16、図1に示した各種のスイッチ群を含む操作キー部17、前記TFT液晶モニター18、前記ストロボ19が接続されている。MROM15は、MPU3の動作プログラムが記録されたプログラムROMである。また、MROM9には撮影時の適正な露出値(EV)に対応する絞り値(F)とシャッタースピードとの組み合わせを示すプログラム線図を構成するプログラムAEデータが格納されている。MPU3は、内蔵するRAMをワーキングメモリとして前記動作プログラムに従い動作することにより本発明の設定手段、制限手段として機能する。また、前記プログラム線図に従って前記CCD2の電荷蓄積時間や、前記絞り6の開放度、前記ユニット回路12のゲイン調整アンプ(AGC)のゲイン設定等を行う。MPU3が設定した電荷蓄積時間はシャッターパルスとして、TG10を介してVドライバー11に供給され、これに従いVドライバー11がCCD2を駆動することにより電荷蓄積時間すなわち露光時間が制御される。つまりCCD2は電子シャッターとして機能する。また、MROM9に格納された動作プログラムには、オートフォーカス制御に関するプログラムが含まれており、かかるプログラムに基づきMPU3は、前記フォーカスレンズ5を駆動させピント合わせ(オートフォーカス)を行う。
【0021】
なお、MROM15に記憶されているプログラムデータ等は、その記録内容の保持が可能であれば、別途固定的に設けたもの、若しくは脱着自在に装着可能なICカード等の他の記録媒体に記録される構成にしてもよく、更に、前記プログラムデータ等をパソコン等の他の機器から供給可能な構成としてもよい。
【0022】
TFT液晶モニター18は、録画モードにおいては逐次撮像された画像をスルー画像として表示し、再生モードにおいては前記フラッシュメモリ14に記録された画像データから生成されたアナログビデオ信号に基づく映像を表示する。ストロボ19は、映像取り込みキーの操作時(撮影時)に必要に応じて駆動され補助光を発する。
【0023】
次に、以上の構成からなる電子スチルカメラ1において、撮影者が、所定のキー操作により撮影条件の設定モードを選択して撮影条件を設定した後、撮影を行う場合における動作の一例を図4のフローチャートにしたがって説明する。
【0024】
すなわち、撮影条件の設定モードが設定された状態で、TFT液晶モニター18に表示されたメニュー画面(図示せず)から「再生画像から設定」が選択されると(ステップSA1でYES)、再生画面選択モードに移行し前記フラッシュメモリ14に記録されている画像をTFT液晶モニター18に表示する(ステップSA2)。また、このときには撮影者のキー操作により画面切り替え指定された場合には、フラッシュメモリ14に記録されている画像を逐次再生してTFT液晶モニター18に表示する。なお、このときには撮影者の要求に応じて前述した縮小画像を複数同時に表示させるようにしてもよい。
【0025】
そして、かかる状態において、撮影者の所定のキー操作により表示されたいずれかの画像(又は縮小画像)が選択されると(ステップSA3でYES)、前述した画像ファイル100の付加データ格納領域100bから、選択された画像を撮影したときに取得された撮影条件データを読み込み(ステップSA4)、その撮影条件データに基づいて撮影条件を設定すとともに、RECモードに移行して撮影待機状態となる(ステップSA5)。しかる後、撮影者がシャッターキー53を押することにより、前述した撮影条件の下での撮影が完了する(ステップSA6)。
【0026】
すなわち撮影者は、新たな撮影を行うとき、撮影結果のイメージをTFT液晶モニター18に表示されている過去に撮影された画像で確認しながら、その画像の撮影時と同一の撮影条件を設定することができる。これにより、撮影者は、自己の好みに応じ撮影結果が得られる適切な撮影条件を容易に設定することができる。なお、本実施の形態においては、撮像した画像を前述した画像フォーマット100(図3参照)の形式で保存しており、撮影条件の設定に用いられる撮影条件データが画像データと一体不可分にフラッシュメモリ14に保存する構成される場合を示したが、画像データとの対応関係が確認できる状態であれば、前記撮影条件データを画像データと分離して記憶させるようにしても構わない。但し、本実施の形態のように、両者を画像ファイル内に一体不可分に記憶させた方が、電子スチルカメラ1と同種の他の電子スチルカメラによって、自己又は他人が撮影した画像を撮影条件の設定に用いることができる点で有利である。
【0027】
次に、本発明の第2の実施の形態を図にしたがって説明する。すなわち、本実施の形態は、図1及び図2に示したと同様の構成を有する電子スチルカメラに関するものである。
【0028】
すなわち本実施の形態における電子スチルカメラにあっては、前述したMROM15に、第1の実施の形態で既説したデータとは別に、図4及び図5に示した撮影条件データ101、図6に示した付加情報データ102、図7(a)〜(c)に例示したような複数の見本画像103を構成する画像データが記憶されている。前記撮影条件データ101は、後述するシーンセレクトモードの設定時に選択可能な複数のシーン撮影モード(本実施の形態では24種類)の各々に対応して予め設定されている電子スチルカメラの撮影条件を示す本発明における設定データであって、より具体的には、図示したような以下のデータから構成されている。すなわち、フォーカス制御、シャッター速度、絞り、EVシフト量、感度、・・・といった電子スチルカメラ1において制御可能な複数の制御項目の制御内容を示すパラメータ、つまり第1の実施の形態における撮影条件データと同様のデータにより構成されている。
【0029】
前記付加情報データ102(図7)は、撮影条件データとともに上記シーン撮影モードに対応して記憶されている付加情報データであり、具体的には、「風景と人物を写します。」といったシーン説明、「ズームを使うと背景がキレイにボケます。」といったアドバイス情報、「マクロモードになり、彩度が高めに設定されます。」といった制御説明の3種類のコメントデータによって構成されている。図8に示した複数の見本画像103は、前記撮影条件データ、前記付加情報データと共に各シーン撮影モードに対応するとともに、各シーン撮影モードでの撮影に適した被写体の見本となる画像である。なお、図8(a)は、シーン撮影モードの「1」(人と風景1)に対応する見本画像、同図(b)は、シーン撮影モードの「2」(人と風景2)に対応する見本画像、同図(c)は、シーン撮影モードの「3」(アップ)に対応する見本画像の例である。
【0030】
また、これらの各データは、電子スチルカメラの使用開始時には、前述したDRAM13の所定記憶領域に展開され、全体として単一の撮影条件データテーブルを構成されるものであって、DRAM13に転記された状態においては、前述した24種類のシーン撮影モードとは別に、ユーザーが使用可能な5種類のシーン撮影モード、すなわち撮影モード番号が「25」〜「29」の使用領域が確保されるようになっている。
【0031】
次に、以上の構成からなる本実施の形態において、使用者が新たなシーン撮影モードを設定(登録)する場合の手順を図9のフローチャートに従って説明する。すなわち、使用者による所定のキー操作によって撮影条件プリセットモードが設定されると(ステップSB1でYES)、プリセット選択画面選択モードに移行し前記フラッシュメモリ14に記録されている画像をTFT液晶モニター18に表示する(ステップSB2)。また、このときには撮影者のキー操作により画面切り替え指定された場合には、フラッシュメモリ14に記録されている画像を逐次再生してTFT液晶モニター18に表示する。なお、このときには撮影者の要求に応じて前述した縮小画像を複数同時に表示させるようにしてもよい。
【0032】
そして、かかる状態において、撮影者の所定のキー操作により、表示されたいずれかの画像(又は縮小画像)が選択されると(ステップSB3でYES)、前述した画像ファイル100の付加データ格納領域100bから、選択された画像を撮影したときに取得された撮影条件データを読み込み、その撮影条件データを、前述した撮影条件データテーブルの撮影モード番号が「25」〜「29」のうちの未だデータが記憶されていない使用領域に記憶する(ステップSB4)。さらに、選択された画像をTFT液晶モニター18に表示するサイズに変換し、変換した縮小画像、又は画像ファイル100から読み出した縮小画像をそのまま見本画像として前記撮影条件データテーブルの構成データとしてDRAM13に記憶する(ステップSB5)。しかる後、撮影者による所定のキー操作によって画像のプリセット操作が完了されることにより、新たなシーン撮影モードの設定(登録)を終了する(ステップSB6)。
【0033】
なお、以上の説明においては、画像ファイル100から得られる撮影条件データと見本画像とをDRAM13に記憶させるようにしたが、例えばユーザーが使用可能な5種類のシーン撮影モード(撮影モード番号「25」〜「29」)の使用領域を前記フラッシュメモリ14の所定領域に設定しておき、その所定領域に撮影条件データと見本画像とを記憶させるようにしてもよい。その場合には、フラッシュメモリ14を本実施の形態と同種の他の電子スチルカメラに装着することにより、上記のシーン撮影モードの設定操作で設定(登録)した新たなシーン撮影モードの使用が可能となる。
【0034】
一方、図10は、シーン撮影モードの設定操作が行われた後、前述したメニュー・キー59の操作によりモード選択が指定された場合の動作を示すフローチャートである。
【0035】
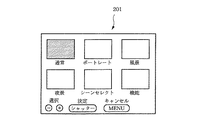
すなわち、本実施の形態の電子スチルカメラにあっては撮影モードの設定モードが選択されると、先ず、TFT液晶モニター18に図11に示したようなモード選択画面201を表示する(ステップSC1)。モード選択画面201は、撮影者に従来技術で説明したと同様の「通常(フルオート)」、「ポートレート」、「風景」、「夜景」の3つの撮影モードと、前述した撮影条件データテーブルを利用した撮影モードを指定するためのシーンセレクトモードと、所定の機能設定モードとのいずれかを選択させるための画面であって、これらの選択候補を示す表示するとともに、この画面を表示した状態において所定の操作に割り当てられているキーの説明を同時に表示する。
【0036】
次に、シーンセレクトモードが選択されたか否かを判別し(ステップSC2)。ここで、シーンセレクトモードが選択されなければ(ステップSC2でNO)、ステップSC1へ戻って他のモードが選択されれば、そのモードの動作に移行する。一方、シーンセレクトモードが選択されていたときには、TFT液晶モニター18の表示を、図12に示したシーンセレクト選択画面202へ切り替える(ステップSC3)。
【0037】
ここで表示されるシーンセレクト選択画面202には、撮影モードのシーン番号「1」と、これに対応する見本画像103、付加情報つまりシーン説明(「風景と人物を写します。」)、アドバイス情報(「フレームが表示されます。」)を表示する。なお、対応する制御説明が存在するシーン番号の見本画像103を表示する場合には、その制御説明も表示する。また、シーンセレクト選択画面202にも、所定の操作に割り当てられているキーの説明も引き続き表示する。しかる後、選択ボタン(本実施の形態では、ズームボタン54の[+]と[−])の操作に応じて、シーンセレクト選択画面202を構成するシーン番号「1」と見本画像103と付加情報とをシーン番号順に昇順又は降順に変更しながら変更、つまり送り表示を行う(ステップSC4)。この間には、前述したシーン撮影モードの設定操作で設定された見本画像(縮小画像)も表示される。
【0038】
一方、その間に、いずれかの見本画像103等が表示された状態、つまりいずれかの撮影モードが選択されている状態でシャッターキー53(決定キー)が押されると(ステップSC5でYES)、電子スチルカメラにおける撮影時の撮影条件を、選択された見本画像103が対応するシーン番号に応じて設定されているパラメータに基づき設定するとともに、RECモードに移行しTFT液晶モニター18にスルー画像を表示し(ステップSC6)、撮影待機状態となる。
【0039】
つまり、撮影者によって、これから撮影しようとする被写体に対応する見本画像103が選択されると、その被写体の撮影に適した撮影条件が自動的に設定される。これにより、撮影者は、自己の好みに応じた撮影結果を簡単に得ることができる。
【0040】
そして、シャッターキー53が押されるまで前述したスルー画像301の表示状態を維持するとともに(ステップSC7でNO)、その間に、シャッターキー53が押されれば(ステップSC7でYES)、前述したステップSC6で設定された撮影条件下での撮像を行うとともに、撮像した画像を記録する(ステップSC8)。しかる後、シーンセレクトモードが解除されるまで(ステップSC9でNO)、前述したステップS4以降の動作を繰り返し行うとともに、シーンセレクトモードが解除された場合にはステップS1へ戻り前述した処理を繰り返す。
【0041】
ここで、本実施の形態においては、前述したシーン撮影モードの設定操作において、使用者が過去に撮影した画像(画像ファイル100)を用いて設定された新たな撮影条件は、その画像を消去した後であっても使用することができる。また、使用者は、予め用意されている既存の撮影条件における見本画像103(本実施の形態では撮影モード番号が「1」〜「24」の見本画像)を参考にしながら、自己の好みに応じた新たな撮影条件を設定することができる。したがって、前述した第1の実施の形態に比較すると、撮影者が好みに応じ撮影結果が得られる適切な撮影条件を設定し、かつそれを使用する場合における使用環境が良好である。
【0042】
なお、本実施の形態においては、予め用意された既存の撮影条件のデータMROM15に記憶されている場合について説明したが、例えばパソコンなどの他の装置から、或いはインターネット等を用いた通信手段を介して他の装置から供給される構成であっても構わない。
【0043】
【発明の効果】
以上説明したように本発明においては、使用者が撮影結果のイメージを過去に撮影された画像で確認しながら、その画像の撮影時と同一の撮影条件を設定することができるようにした。よって、使用者(撮影者)は、自己の好みに応じ撮影結果が得られる適切な撮影条件を容易に設定することが可能となる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の実施の形態に係る電子スチルカメラの外観を示す図である。
【図2】同電子スチルカメラのブロック構成図である。
【図3】フラッシュメモリに記憶する画像データのフォーマットを示す概念図である。
【図4】本発明の第1の実施の形態に係る電子スチルカメラの動作を示すフローチャートである。
【図5】本発明の第2の実施の形態に係るプログラムROMに記録されている撮影条件データを示す概念図である。
【図6】図5の下に続く図である。
【図7】同プログラムROMに記録されている付加情報データを示す概念図である。
【図8】同プログラムROMに記録されている見本画像を示す図である。
【図9】撮影条件データの登録動作を示すフローチャートである。
【図10】シーンセレクトモードを用いた撮影時における電子スチルカメラの動作を示すフローチャートである。
【図11】モードの選択画面を示す図である。
【図12】シーンセレクト選択画面、及びその変化を示す図である。
【符号の説明】
1 電子スチルカメラ
2 CCD
3 MPU
13 DRAM
14 フラッシュメモリ
15 MROM
101 撮影条件データ
102 付加情報データ
103 見本画像
104 選択履歴テーブル
202 シーンセレクト選択画面
204 フレーム画像
301 スルー画像[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a camera device, a recording medium, and a shooting mode setting data creation device.
[0002]
[Prior art]
2. Description of the Related Art Conventionally, for example, in an electronic still camera, various photographing conditions such as shutter speed and aperture value can be automatically set or manually set according to a photographer's preference. Furthermore, for example, a plurality of shooting modes that automatically set shooting conditions suitable for the type of subject such as portrait, landscape, and night scene are prepared, and the photographer selects the shooting mode in advance, thereby enabling the shutter. Many beginners who do not have specialized knowledge such as speed and aperture value can set more appropriate shooting conditions.
[0003]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, when the photographer manually sets the above-described various photographing conditions, it is not always possible to obtain a photographing result that is intended by the photographer. In addition, even when shooting conditions are automatically set using a shooting mode prepared in advance, the shooting conditions are set to the greatest common divisor, so that shooting results can be obtained according to the photographer's preference. There was a problem that it was not always possible.
[0004]
The present invention has been made in view of the conventional problems, and a camera device, a recording medium, and a shooting mode setting capable of easily setting an appropriate shooting condition for obtaining a shooting result according to a photographer's preference. An object is to provide a data creation device.
[0005]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In order to solve the above-mentioned problem, the invention of
[0006]
In such a configuration, when the user requests it, the setting unit sets the same shooting conditions as when the currently displayed image was shot. Therefore, the user can use the image obtained as a result of shooting in the past. While confirming, it is possible to set the same shooting conditions as when shooting the image.
[0007]
According to a second aspect of the present invention, a file having a predetermined format including image data of a photographed image and photographing conditions is stored in the image storage means, and the image storage means is the photographing condition storage means. To function as. In such a configuration, when setting the shooting conditions of the apparatus, an image shot by the same type of apparatus can be used.
[0008]
Further, in the invention of
[0009]
According to a fourth aspect of the present invention, the shooting condition storage means stores a reduced image of an image stored in advance in a plurality of sets of the image storage means and shooting conditions corresponding to the reduced image. Has been secured .
[0015]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, a first embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. FIG. 1 is an external view of an electronic
[0016]
The electronic
[0017]
FIG. 2 is a block configuration diagram showing an outline of the electrical configuration of the electronic
[0018]
The MPU 3 is connected with a TG (Timing Generator) 10 that generates a timing signal, and the V driver 11 (vertical driver) drives the
[0019]
FIG. 3 is a conceptual diagram showing the format of the
[0020]
Further, the
[0021]
Note that the program data and the like stored in the
[0022]
The TFT liquid crystal monitor 18 displays sequentially captured images as through images in the recording mode, and displays images based on analog video signals generated from the image data recorded in the
[0023]
Next, in the electronic still
[0024]
That is, when “setting from playback image” is selected from a menu screen (not shown) displayed on the TFT liquid crystal monitor 18 in a state where the shooting condition setting mode is set (YES in step SA1), the playback screen is displayed. The mode is changed to the selection mode, and the image recorded in the
[0025]
In this state, when any image (or reduced image) displayed by the photographer's predetermined key operation is selected (YES in step SA3), the additional
[0026]
That is, the photographer sets the same photographing conditions as when photographing a new image while confirming the image of the photographing result with an image photographed in the past displayed on the TFT
[0027]
Next, a second embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. That is, this embodiment relates to an electronic still camera having the same configuration as that shown in FIGS.
[0028]
That is, in the electronic still camera according to the present embodiment, in addition to the data already described in the first embodiment, the
[0029]
The additional information data 102 (FIG. 7) is additional information data stored corresponding to the above-described scene shooting mode together with shooting condition data, and specifically, a scene description such as “photographs a landscape and a person”. , Is composed of three types of comment data, such as advice information such as “The background is clearly blurred when using zoom”, and control explanation such as “macro mode is set and the saturation is set higher”. A plurality of
[0030]
Each of these data is expanded in the predetermined storage area of the above-described
[0031]
Next, in the present embodiment configured as described above, a procedure when the user sets (registers) a new scene shooting mode will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG. That is, when the shooting condition preset mode is set by a predetermined key operation by the user (YES in step SB1), the mode is shifted to the preset selection screen selection mode, and the image recorded in the
[0032]
In this state, when any one of the displayed images (or reduced images) is selected by a predetermined key operation of the photographer (YES in step SB3), the additional
[0033]
In the above description, the shooting condition data and the sample image obtained from the
[0034]
On the other hand, FIG. 10 is a flowchart showing the operation when the mode selection is designated by the operation of the
[0035]
In other words, in the electronic still camera of the present embodiment, when the shooting mode setting mode is selected, first, the
[0036]
Next, it is determined whether or not the scene select mode has been selected (step SC2). If the scene select mode is not selected (NO in step SC2), the process returns to step SC1 and if another mode is selected, the operation proceeds to that mode. On the other hand, when the scene select mode is selected, the display on the TFT liquid crystal monitor 18 is switched to the scene
[0037]
On the scene
[0038]
On the other hand, if one of the
[0039]
That is, when the photographer selects the
[0040]
The display state of the through image 301 described above is maintained until the
[0041]
Here, in the present embodiment, in the above-described scene shooting mode setting operation, a new shooting condition set using an image (image file 100) shot by the user in the past is deleted. It can be used even later. In addition, the user can respond to his / her preference while referring to the sample image 103 (sample images with the shooting mode numbers “1” to “24” in the present embodiment) in the existing shooting conditions prepared in advance. New shooting conditions can be set. Therefore, as compared with the first embodiment described above, the use environment is better when the photographer sets appropriate shooting conditions for obtaining shooting results according to his / her preference and uses them.
[0042]
In the present embodiment, the case where data of existing photographing conditions prepared in advance is stored in the
[0043]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, in the present invention, the user can set the same shooting conditions as when shooting the image while checking the image of the shooting result with the image shot in the past. Therefore, the user (photographer) can easily set an appropriate photographing condition for obtaining a photographing result according to his / her preference.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing an external appearance of an electronic still camera according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a block configuration diagram of the electronic still camera.
FIG. 3 is a conceptual diagram showing a format of image data stored in a flash memory.
FIG. 4 is a flowchart showing an operation of the electronic still camera according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 5 is a conceptual diagram showing photographing condition data recorded in a program ROM according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
6 is a diagram continuing from the bottom of FIG. 5;
FIG. 7 is a conceptual diagram showing additional information data recorded in the program ROM.
FIG. 8 is a diagram showing a sample image recorded in the program ROM.
FIG. 9 is a flowchart showing an operation for registering shooting condition data.
FIG. 10 is a flowchart showing an operation of the electronic still camera at the time of shooting using the scene select mode.
FIG. 11 is a diagram showing a mode selection screen.
FIG. 12 is a diagram showing a scene select selection screen and its change.
[Explanation of symbols]
1 Electronic still
3 MPU
13 DRAM
14
101
Claims (4)
撮影した画像を撮影条件とともに画像データとして記録する画像記憶手段と、 Image storage means for recording captured images as image data together with shooting conditions;
前記撮影モード毎に応じて撮影時における装置の撮影条件を制御する制御手段と、 Control means for controlling the shooting conditions of the apparatus at the time of shooting according to each shooting mode;
予め、前記撮影モードに対応した複数の見本画像と撮影条件の内容を説明する説明情報とを記憶する撮影条件記憶手段と、 Shooting condition storage means for storing in advance a plurality of sample images corresponding to the shooting mode and explanation information explaining the contents of the shooting conditions;
前記画像記憶手段に記憶された画像の縮小画像とこの縮小画像と対応した撮影条件とを前記撮影条件記憶手段に追加記憶させる手段と、 Means for additionally storing a reduced image of the image stored in the image storage means and a shooting condition corresponding to the reduced image in the shooting condition storage means;
前記撮影条件記憶手段に記憶された見本画像とこの見本画像に対応する説明情報、および前記縮小画像とを表示する表示手段と、 Display means for displaying a sample image stored in the photographing condition storage means, explanation information corresponding to the sample image, and the reduced image;
この表示手段に表示される前記見本画像および前記縮小画像を送り表示させるための操作手段と、 Operation means for sending and displaying the sample image and the reduced image displayed on the display means;
この表示手段に表示されている前記見本画像あるいは前記縮小画像を選択する選択手段と、 Selecting means for selecting the sample image or the reduced image displayed on the display means;
この選択手段により選択された前記見本画像あるいは前記縮小画像に対応する撮影モードを設定する設定する設定手段と Setting means for setting a shooting mode corresponding to the sample image or the reduced image selected by the selection means;
を備えたことを特徴とするカメラ装置。 A camera device comprising:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000226095A JP3925054B2 (en) | 2000-06-21 | 2000-06-21 | Camera device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000226095A JP3925054B2 (en) | 2000-06-21 | 2000-06-21 | Camera device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2002010134A JP2002010134A (en) | 2002-01-11 |
| JP2002010134A5 JP2002010134A5 (en) | 2004-09-16 |
| JP3925054B2 true JP3925054B2 (en) | 2007-06-06 |
Family
ID=18719766
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000226095A Expired - Fee Related JP3925054B2 (en) | 2000-06-21 | 2000-06-21 | Camera device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3925054B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4007052B2 (en) | 2002-05-07 | 2007-11-14 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Image processing control data update device |
| JP2004254256A (en) | 2003-02-24 | 2004-09-09 | Casio Comput Co Ltd | Camera apparatus, display method, and program |
| JP2006115475A (en) * | 2004-09-15 | 2006-04-27 | Seiko Epson Corp | Image processor, image processing method and image processing program |
| JP2006332789A (en) * | 2005-05-23 | 2006-12-07 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Video photographing method, apparatus, and program, and storage medium for storing the program |
| JP4826217B2 (en) * | 2005-11-08 | 2011-11-30 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | Imaging apparatus and program |
| JP5164327B2 (en) * | 2005-12-26 | 2013-03-21 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | Imaging apparatus and program |
| JP4792985B2 (en) * | 2006-01-18 | 2011-10-12 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | Camera device, photographing condition setting method, and program |
| JP4888711B2 (en) | 2006-05-19 | 2012-02-29 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | Scene selection screen generation device, scene selection screen addition system, scene selection screen generation method, scene selection screen addition method, and program |
| JP5076695B2 (en) | 2006-09-29 | 2012-11-21 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | Image correction apparatus, image correction method, and program |
| JP5352994B2 (en) * | 2007-12-07 | 2013-11-27 | 株式会社ニコン | Imaging device |
| JP4811449B2 (en) * | 2008-11-10 | 2011-11-09 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | Image storage system, image storage device, and program |
| JP2009141978A (en) * | 2009-02-04 | 2009-06-25 | Casio Comput Co Ltd | Camera apparatus, through-image display method ,and program therefor |
| JP5109996B2 (en) * | 2009-02-04 | 2012-12-26 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | Camera device, through image display method and program thereof |
| JP2010200362A (en) * | 2010-04-26 | 2010-09-09 | Olympus Imaging Corp | Camera, and device and method for display control of the same |
| JP5187416B2 (en) * | 2011-06-24 | 2013-04-24 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | Imaging apparatus, imaging condition setting method and program |
| JP5522214B2 (en) * | 2012-08-03 | 2014-06-18 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | Camera device and through image display method |
| WO2018011898A1 (en) * | 2016-07-12 | 2018-01-18 | オリンパス株式会社 | Image processing device and image acquisition apparatus |
-
2000
- 2000-06-21 JP JP2000226095A patent/JP3925054B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2002010134A (en) | 2002-01-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP3925054B2 (en) | Camera device | |
| JP4395619B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, imaging condition setting method, and program | |
| JP3543135B2 (en) | Camera device | |
| US7492405B2 (en) | Camera apparatus, displaying method, and storage medium containing displaying method | |
| EP1363447A2 (en) | Photographing method and camera device equipped with temporary photographing | |
| JP4617417B2 (en) | Electronic camera, photographing and recording method, and program | |
| JP2005229326A (en) | Camera apparatus and through-image display method | |
| JP4041407B2 (en) | Digital camera | |
| JP4888711B2 (en) | Scene selection screen generation device, scene selection screen addition system, scene selection screen generation method, scene selection screen addition method, and program | |
| JP4509829B2 (en) | Camera device | |
| JP3890897B2 (en) | Camera device and recording medium | |
| JP3721965B2 (en) | Electronic still camera, image recording method thereof, and recording medium | |
| JP4070414B2 (en) | Camera device, data supply device, camera system, method, and recording medium | |
| JP3630104B2 (en) | CAMERA DEVICE, SAMPLE IMAGE DISPLAY METHOD, AND RECORDING MEDIUM | |
| JP4725075B2 (en) | CAMERA DEVICE, SAMPLE IMAGE DISPLAY METHOD, AND RECORDING MEDIUM | |
| JP4288858B2 (en) | Camera device and camera system, photographing condition capturing device and method, sample image management method, and recording medium | |
| JP3913046B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| JP3997970B2 (en) | Camera device | |
| JP4063313B2 (en) | Camera device | |
| JP2003230090A (en) | Electronic camera | |
| JP2002300513A (en) | Electronic camera | |
| JP4301151B2 (en) | Camera apparatus and photographing scene registration method | |
| JP2005109569A (en) | Photographing instrument | |
| JP4063312B2 (en) | Camera device | |
| JP4535389B2 (en) | Camera device, display control method thereof, and control program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20050711 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20050726 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20050922 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20070206 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20070219 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Ref document number: 3925054 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110309 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110309 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120309 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130309 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130309 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140309 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |