JP3848151B2 - Imaging apparatus, imaging method, program, and storage medium - Google Patents
Imaging apparatus, imaging method, program, and storage medium Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3848151B2 JP3848151B2 JP2001388153A JP2001388153A JP3848151B2 JP 3848151 B2 JP3848151 B2 JP 3848151B2 JP 2001388153 A JP2001388153 A JP 2001388153A JP 2001388153 A JP2001388153 A JP 2001388153A JP 3848151 B2 JP3848151 B2 JP 3848151B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- information
- image
- setting
- reproduction
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、画像のプリントを容易に行なえるようにすることができる撮像装置に関するものである。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
近年、デジタルカメラで撮影した画像について、モニタ等の表示装置に表示するとともに、観賞用としてプリンター等で印刷する機会が増えている。このような状況下において、ユーザメリットという観点からDPOF(Digital Print Order Format)と呼ばれる規格が発表されている。DPOF規格は、プリントするのに必要なプリント情報を電子化し、プリント情報を画像ファイルととともに記録媒体に保存するというもので、プリント情報の記述形式を統一化している。
【0003】
プリント情報を保存するファイル(DPOFファイルと呼ばれる)は、画像ファイルとは別のテキストファイル形式で記録媒体に記録することが規定されている。規格が拡張されて、プリント情報だけでなくスライドショーや画像ファイルの送信などについても再生情報、及び送信情報として記述形式を統一化している。
【0004】
このような規格に従ってプリント情報、及び再生情報、及び送信情報を画像ファイルとともに記録媒体に保存することで、パーソナルプリンタとのダイレクトプリントや、異なる機種間でのスライドショーの実現、画像ファイルの送信といったユーザメリットの実現に効果がある。
【0005】
一方撮影画像は、撮影レンズを通過した被写体光束が固体撮像素子(CCDなど)に到達し、被写体像を電気信号に変換し映像信号として出力される。出力された画像について、画像処理回路内でさまざまな変換処理が施され、最後に記録媒体に画像ファイルとして保存される。
【0006】
一般的なデジタルカメラは、画像ファイルをデジタルカメラに内蔵の液晶モニタ(LCD)で再生(表示)する機能を有し、例えば特開平10-126724号公報に開示されているように、この再生画像を液晶モニタに一覧表示し、プリントする画像を指定する装置が提案されている。
【0007】
また、特開2001-045339号公報には、撮影モードでの撮影画像の確認画面上で、プリント指示を行う手段が開示されている。
【0008】
また、特開2001-069454号公報には、メモリカードなどの記録媒体に設けた固定ファイルに予め付加情報を格納し、撮影時に前記固定ファイルに格納された付加情報を自動的に取得し、利用する方法が開示されている。
【0009】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
従来のプリント設定では、撮影画像についてユーザが確認しながら、プリント指示を行っている。そのため、撮影画像を必ずプリントすると決めている場合においても、画像毎にプリント枚数の指定を行う必要があり、回転やトリミングなどの設定なども別途行う必要がある。
【0010】
コンパクト性が重視されるデジタルカメラにおいては、物理的な制約などによって、機能毎に対応するボタンを用意することは困難であるため、プリント設定の操作がわかりずらいなどの問題点を抱えている。
【0011】
また、プリント設定を容易に行えるようにするため、ボタンなど入力キーを特別に設定することは、カメラサイズが大きくなる、撮影時の不具合をもたらす可能性がある、といった問題を引き起こすことになる。
【0012】
また、プリント指示を全画像に対して行う方法もあるが、プリント指示を全画像に対して設定し、プリント情報が確定した後でも、もう一度撮影モードで画像を撮影した場合は、再度全画像に対してプリント指定の指示をするなどのユーザ操作が必要となる。
【0013】
また、撮影時に、付加情報を自動的に取得し、利用する方法も存在するが、撮影画像に対してプリント情報を設定することは想定されていないため容易には適用できないという問題点を抱えている。
【0014】
従って、本発明は上述した課題に鑑みてなされたものであり、その目的は、デジタルカメラにおいて、画像のプリントを容易に行なえるようにすることである。
【0015】
異なる機種間で画像の再生及び送信をする場合にユーザの操作の手間を低減することである。
【0016】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上述した課題を解決し、目的を達成するために、本発明に係わる撮像装置は、記憶媒体に記憶される画像に対するプリント条件が記述されたプリント情報、再生条件が記述された再生情報、送信条件が記述された送信情報とを記憶可能な設定記憶手段と、前記プリント情報、前記再生情報、前記送信情報のいずれかに対して情報を追記するための追記情報を記憶する情報記憶手段と、撮像手段によって画像を取得する前に、前記画像のプリント情報、前記再生情報、前記送信情報のいずれに情報を追記するかを選択する選択手段と、前記撮像手段による画像の取得に応じて、前記選択手段で選択された情報に前記追記情報に基づく情報を自動的に追記する追記手段と、を有することを特徴としている。
【0017】
また、この発明に係わる撮像装置において、前記プリント情報は、前記画像のプリント時におけるプリント枚数、回転角度、トリミング、日付入力、及びファイル名入力のうち少なくとも1つの設定のためのプリント情報であることを特徴としている。
【0018】
また、この発明に係わる撮像装置において、前記再生情報は、前記画像の再生時における再生間隔、効果音、ファイル番号表示、及び日付表示のうち少なくとも1つの設定のための再生情報であることを特徴としている。
【0019】
また、この発明に係わる撮像装置において、前記送信情報は、前記画像の送信時における送信先、本文、題、及びファイル名のうち少なくとも1つの設定のための送信情報であることを特徴としている。
【0020】
また、この発明に係わる撮像装置において、前記プリント情報、前記再生情報、前記送信情報に追記する情報の内容を設定する追記情得設定手段をさらに有することを特徴としている。
【0021】
また、この発明に係わる撮像装置において、前記追記情報の設定内容を表示する表示手段をさらに有することを特徴としている。
【0022】
また、本発明に係わる撮像方法は、記憶媒体に記憶される画像に対するプリント条件が記述されたプリント情報、再生条件が記述された再生情報、送信条件が記述された送信情報とを記憶する設定記憶工程と、前記プリント情報、前記再生情報、前記送信情報のいずれかに対して情報を追記するための追記情報を記憶する情報記憶工程と、撮像手段によって画像を取得する前に、前記画像のプリント情報、前記再生情報、前記送信情報のいずれに情報を追記するかを選択する選択工程と、前記撮像手段による画像の取得に応じて、前記選択工程において選択された情報に前記追記情報に基づく情報を自動的に追記する追記工程と、を有することを特徴としている。
【0023】
また、この発明に係わる撮像方法において、前記プリント情報、前記再生情報、前記送信情報に追記する情報の内容を設定する追記情得設定工程をさらに有することを特徴としている。
【0024】
また、この発明に係わる撮像方法において、前記追記情報の設定内容を表示する表示工程をさらに有することを特徴としている。
【0027】
また、本発明に係わるプログラムは、上記の撮像方法をコンピュータに実行させることを特徴としている。
また、本発明に係わる記憶媒体は、上記のプログラムをコンピュータ読み取り可能に記憶したことを特徴としている。
【0028】
以上のような構成により、ユーザは撮影画像に対していちいちプリント設定をすることなく、撮影した画像全てを、わずらわしい設定処理をすることなくプリント設定することが可能である。同様に、画像のスライドショー、及び画像の送信についてもわずらわしい設定処理をしないで済む。
【0029】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明の好適な実施形態について、添付図面を参照して説明する。
【0030】
(第1の実施形態)
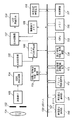
図1は、本発明のデジタルカメラの第1の実施形態の構成を示すブロック図である。
【0031】
図1において、101は図示していない被写体からの光を結像するレンズ、102はレンズ101からの入射光量を調節する絞り機構、103はレンズ101から絞り機構102を通って入射した光を電気信号に変換する撮像素子、104は撮像素子103により光電変換された信号をサンプリングしてゲインコントロールするCDS・AGC回路、105はCDS・AGC回路104から出力されるアナログ信号をデジタル信号に変換するアナログ・デジタル変換器(以降、A/D変換器と記述)、106はA/D変換器105によりA/D変換された信号に対して所定の処理を施すカメラ信号処理回路、121はカメラ信号処理回路106などの装置から出力されたデジタル信号をメモリ116などの他の装置へ転送するためのデータバス、115は本デジタルカメラ全体を制御するマイクロコンピュータ(以降、CPUと記述)、120はCPU115から出力される制御信号を伝達する制御バス、116はデータバス121から送られる画像データなどのデジタル信号を一時的に記憶する記録装置(以降、メモリと記述)、117はメモリ116上に一時的に記憶されている画像データを画像ファイルの形で保存するメモリカードやディスクなどの2次記録装置、118はカメラ信号処理回路106から出力した生の画像データをJPEGなどの圧縮アルゴリズムを用いて圧縮したりその逆に伸張したりする画像圧縮・伸張装置、108はLCD液晶表示装置109に出力する映像信号を保持する画像表示メモリ、107は画像表示メモリに出力されたデジタル信号をアナログ信号に変換するデジタル・アナログ変換器(以降、D/A変換器と記述)、109はD/A変換器107から出力されるアナログ映像信号をユーザに対して表示するLCD液晶表示装置である。
【0032】
送信設定選択部110、再生設定選択部111、及びプリント設定選択部112は、単独のボタンキー、タッチパネルまたは十字ボタンが用いられる。114はプリント情報、再生情報、送信情報をなどの設定情報を作成、及び取得する設定情報作成・取得装置、119は撮影画像に対して、自動的にプリント情報、再生情報、送信情報の設定が行えるようにするための自動追記情報を作成、及び取得する自動追記情報作成・取得装置、113は自動追記情報作成・取得装置119で、取得した設定情報に基づいて、プリント情報、再生情報、送信情報を自動的に追記する設定情報自動追記装置である。
【0033】
図2に電源がオンされてから設定情報自動追記装置113で、設定情報が自動追記されるまでの撮影モードでのメインルーチンのフローチャートを示す。
【0034】
電源がオンされると処理が開始され(ステップS100)、ステップS101では、後述の自動追記情報取得ルーチンを、ステップS102では、ステップS101で取得した自動追記情報、及びユーザ選択結果に基づいて、設定情報自動追記装置113に対して、画像の撮影後、設定情報を自動作成するよう指示する。
【0035】
図6に、ステップS101で、自動追記情報を取得しようとした結果、プリント情報、及び再生情報については取得でき、送信情報については取得できなかった場合のLCD液晶表示装置109に表示される画面のイメージ図を示す。
【0036】
ユーザは、前もって自動追記情報が設定してある設定について、撮影の前に設定情報を自動追記するかを選択する。
【0037】
図7に、プリントのみ設定情報を自動追記するとした場合(ステップS102)のLCD液晶表示装置109に表示される画面のイメージ図を示す。
【0038】
ステップS103で、LCD液晶表示109への動画表示などの撮影前処理を行い、ステップS104で、シャッターボタンが押されると、ステップS105で、撮像素子103から出力された画像信号を、A/D変換器105やカメラ信号処理回路106で処理し、JPEGなどの画像ファイルを作成する。ステップS106で、画像ファイルを記録装置117に記録し、ステップS107で、後述の設定情報自動追記ルーチンを実行した後、ステップS103からステップS107を繰り返す。
【0039】
図2で示すように、今まで撮影後に行っていた各種設定処理は、自動追記情報を適用するか否かの選択処理(ステップS102)だけで済み、ユーザは各画像に必要だったプリント設定、再生設定、送信設定についてのわずらわしい処理をしないで済む。
【0040】
図3は、図2のステップS101の自動追記情報取得ルーチンのフローチャートである。
【0041】
本ルーチンは、記録装置117内を検索し、自動追記情報があればその内容を解釈し、LCD液晶表示装置109を用いてユーザに対し現在設定されている自動追記情報を表示するためのルーチンである。
【0042】
ステップS151で、記録装置117内を検索して自動追記情報が記録されていれば、自動追記情報をメモリ116に読み出す。ステップS152では、自動追記情報が記録されていなければステップS156でメインルーチンへ戻り、自動追記情報が見つかりメモリ116へ読み出すことに成功していれば、ステップS153以降を実行する。
【0043】
ステップS153で、デジタルカメラにおける機種依存情報を取得し、ステップS154におけるパラメータとなる情報を生成する。機種依存情報には、プリント設定、及び再生設定、及び送信設定ができるか、プリント設定において紙の設定ができるか、再生設定において再生間隔の設定ができるか、送信設定において送信先にどのような宛先を設定できるか等がある。
【0044】
ステップS154で、メモリ116に読み出されている自動追記情報を解釈し、ステップS153で取得した機種依存情報を元に、デジタルカメラ毎に自動追記可能な設定内容を取得する。
【0045】
プリント設定を自動追記する場合には、図8にあるような自動追記情報を自動追記情報作成・取得装置119で前もって編集、及び新規作成を行う(ステップS154)。同様に、再生設定の場合は、図9のような自動追記情報を、送信設定の場合は、図10のような自動追記情報を、自動追記情報作成・取得装置119で前もって編集、及び新規作成を行う(ステップS154)。
【0046】
図11に、プリント設定におけるステップS153で取得した機種依存情報のLCD液晶表示装置109に表示される画像のイメージ図を示す。
【0047】
図12に、ステップS153で取得した機種依存情報と記録装置117に存在した自動追記情報をもとに、設定情報自動追記装置113を備えるデジタルカメラにおいて自動追記の内容がLCD液晶表示装置109に表示される画面のイメージ図を示す。
【0048】
図12では、記録装置117内の自動追記情報では、トリミングの指定を設定しているが(図8)、デジタルカメラにトリミングの設定を行う機能がない場合(図11)、最終的に自動追記情報となっていないことを示している。ステップS155で、ステップS154で取得した自動追記情報の内容をLCD液晶表示装置109で表示する。ステップS156で、メインルーチンへ戻る。
【0049】
図4は、図2のステップS107の設定情報自動追記ルーチンのフローチャートである。
【0050】
本ルーチンは、図2のステップS105で撮影された画像に対して、自動追記情報が有効であれば自動的に設定情報を追記するためのルーチンである。設定情報自動追記装置113において、ステップS201では、図2のS102の結果より、設定情報を自動追記しない場合は、ステップS205でメインルーチンへ戻り、設定情報を自動追記する場合は、ステップS202以降を実行する。ステップS202で、図2のステップS105で撮影された画像に関する情報、撮影画像のパス名、及びファイルフォーマットを取得する。ステップS203で、ステップS202で取得した撮影画像データ、及び図2のステップS102で選択された自動追記情報を元に、設定情報を作成し、記録装置117に記録する。ステップS204で、LCD液晶表示装置109へ設定情報の記録結果を表示する。ステップS205で、メインルーチンへ戻る。
【0051】
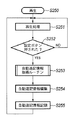
図5に電源がオンされてから自動追記情報を編集するまでの再生モードでのメインルーチンのフローチャートを示す。
【0052】
電源がオンされると処理が開始され(ステップS250)、ステップS251で、撮影画像についてLCD液晶表示装置109で表示する。ステップS252で、設定ボタンが押されるとステップS253で、前述の自動追記情報取得ルーチンが実行される。
【0053】
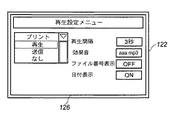
図8、図9、及び図10は、ステップS253で取得した自動追記情報を元にした設定情報を自動的に追記するための設定を行う編集画面のイメージ図である。プリント設定を自動追記する場合には、図8にあるような自動追記情報を自動追記情報作成・取得装置119で前もって編集、及び新規作成を行う(ステップS254)。同様に、再生設定の場合は、図9のような自動追記情報を、送信設定の場合は、図10のような自動追記情報を、自動追記情報作成・取得装置119で前もって編集、及び新規作成を行う(ステップS254)。ステップS255で、自動追記情報記録処理を行い記録装置117へ自動追記情報を保存し、ステップS251以降を繰り返す。
【0054】
撮影前に自動追記情報作成・取得装置119で追記内容を取得することで、前もって編集した自動追記情報の結果を反映し、画像の撮影後に行っていたわずらわしい操作を行うことなく自動的に設定情報を追記する操作を実現する。
【0055】
(第2の実施形態)
以下、本発明の第2の実施形態を図面及びフローチャートを参照して説明する。本発明の第1の実施形態で示した手段に加え、設定情報作成(図4のステップS203)において、設定情報自動追記装置113で作成するプリント情報、及び再生情報、及び送信情報をDPOF規格に従った記述形式とする。自動追記情報作成・取得装置119で作成した自動追記情報から、設定情報自動追記装置113で設定情報が作成されるまでのDPOF規格に従った設定情報を追記する場合のフローチャート図を図13に示す。
【0056】
図13で電源がオンされると処理が開始され(ステップS300)、ステップS301では、前述の自動追記情報取得ルーチンを実行する。ステップS302では、ステップS301で取得した自動追記情報、及びユーザ選択結果に基づいて、設定情報自動追記装置113に対して、画像の撮影後、DPOF規格に従った設定情報を自動追記するよう指示する。ステップS303では、設定情報を記録するためのDPOF規格に従った記録ファイルが記録装置117上に存在しなければ、新規に前記記録ファイルを作成する。ステップS304で、LCD液晶表示装置109への動画表示などの撮影前処理を行い、ステップS305で、シャッターボタンが押されると、ステップS306で、撮像素子103から出力された画像信号を、A/D変換器105やカメラ信号処理回路106で処理し、JPEGなどの画像ファイルを作成する。ステップS307で、画像ファイルを記録装置117に記録する。ステップS308で、自動追記する設定情報の中で画像ファイルに依存せず自動追記情報だけで済む内容を取得し、DPOF規格に従った記述形式を作成する。ステップS309で、画像ファイル固有の設定情報、及び自動追記情報から自動追記する設定情報を取得し、DPOF規格に従った記述形式を作成する。ステップS310で、ステップS308、及びステップS309で作成したDPOF規格に従った設定情報を、前記記録ファイルに書き込む。上記記録ファイルに設定情報を書き込んだ後、ステップS304からステップS310を繰り返す。
【0057】
図13に示すように、今まで撮影後に行っていた各種設定処理は、自動追記情報を適用するか否かの選択処理(ステップS302)だけで済む。第2の実施形態についても、第1の実施形態と同じくユーザは各画像に必要だったプリント設定、再生設定、送信設定についてのわずらわしい操作は必要ない。
【0058】
(第3の実施形態)
以下、本発明の第3の実施形態を図面及びフローチャートを参照して説明する。
【0059】
本発明の第1の実施形態で示した手段に加え、自動追記情報作成・取得装置119で作成される自動追記情報を、DPOF規格のベンダーユニークリージョンの領域内に作成するようにしたものである。
【0060】
図14に、自動追記情報をDPOF規格のベンダーユニークリージョン内に作成するフローチャート図を示す。
【0061】
図14で電源がオンされると処理が開始され(ステップS350)、ステップS351で、撮影画像についてLCD液晶表示装置109で表示する。撮影画像を再生中に設定ボタンが押されると(ステップS352)、ステップS353で、自動追記情報を記述するDPOF規格に従った記録ファイルを検索する。ステップS354で、自動追記情報を記録している前記記録ファイルが存在すれば、ステップS355以降を実行し、存在しなければステップS357以降を実行する。ステップS355では、前記記録ファイル内をDPOF規格に従って解析し、ベンダーユニークリージョンを見つける。ステップS356で、ベンダーユニークリージョン内に自動追記情報が記述してあれば、自動追記情報を取得する。
【0062】
自動追記情報の設定メニューについて、ステップS356で取得した自動追記情報は、LCD液晶表示装置109に図8、及び図9、及び図10のように表示される。プリント設定は、図8のような表示画面について、ステップS357で、自動追記情報を編集し、その結果をベンダーユニークリージョン内に記述する。同様に再生設定は、図9のような表示画面に対して、送信設定は、図10のような表示画面に対して、ステップS357で自動追記情報を編集し、その結果をベンダーユニークリージョン内に記述する。ステップS354で、DPOF規格に従った記録ファイルがない場合は、新規にDPOF規格に従った記録ファイルを作成する(ステップS357)。ステップS358で、ステップS357で編集、又は新規作成した自動追記情報を記録装置117で記録する。自動追記情報を記録後はステップS351以降を繰り返す。
【0063】
(第4の実施形態)
以下、本発明の第4の実施形態を図面及びフローチャートを参照して説明する。
【0064】
本発明の第1の実施形態で示した手段に加え、自動追記情報作成・取得装置119で自動追記情報を複数作成・取得し、複数の自動追記情報の中から選択する。
【0065】
図15は、図8の自動追記情報設定メニューにおいて、プリント設定の自動追記を複数の中から選択できることをLCD液晶表示装置109で表示しているイメージ図である。新規追加ボタンを押すと自動追記を行う設定情報について、別の設定で保存できる。
【0066】
以上説明したように、上記の各実施形態によれば、プリント設定機能を有するデジタルカメラにおいて、ユーザによるプリント指示を行うのではなく、プリント情報を自動的に追記することによって、プリント設定におけるユーザ操作の手間の低減を図り、撮影画像を容易にプリント設定できるデジタルカメラを提供することができる。同様に、異なる機種間での再生設定、及び画像ファイルの送信を想定した送信設定についても設定情報を自動的に追記し、ユーザ操作の手間を低減するデジタルカメラを提供することができる。
【0067】
言い換えれば、記録媒体に前もってどのようなプリント設定を行うのかを記述することによって、画像撮影後のプリント設定にかかるユーザ操作の手間を省くことができる。
【0068】
また、プリント設定の自動追記にあたりDPOF規格にしたがっているため、DPOF規格に対応している機種間で設定内容を利用することが可能である。プリント設定だけでなく、再生設定、送信設定についても同様である。
【0069】
【他の実施形態】
また、各実施形態の目的は、前述した実施形態の機能を実現するソフトウェアのプログラムコードを記録した記憶媒体(または記録媒体)を、システムあるいは装置に供給し、そのシステムあるいは装置のコンピュータ(またはCPUやMPU)が記憶媒体に格納されたプログラムコードを読み出し実行することによっても、達成されることは言うまでもない。この場合、記憶媒体から読み出されたプログラムコード自体が前述した実施形態の機能を実現することになり、そのプログラムコードを記憶した記憶媒体は本発明を構成することになる。また、コンピュータが読み出したプログラムコードを実行することにより、前述した実施形態の機能が実現されるだけでなく、そのプログラムコードの指示に基づき、コンピュータ上で稼働しているオペレーティングシステム(OS)などが実際の処理の一部または全部を行い、その処理によって前述した実施形態の機能が実現される場合も含まれることは言うまでもない。
【0070】
さらに、記憶媒体から読み出されたプログラムコードが、コンピュータに挿入された機能拡張カードやコンピュータに接続された機能拡張ユニットに備わるメモリに書込まれた後、そのプログラムコードの指示に基づき、その機能拡張カードや機能拡張ユニットに備わるCPUなどが実際の処理の一部または全部を行い、その処理によって前述した実施形態の機能が実現される場合も含まれることは言うまでもない。
【0071】
本発明を上記記憶媒体に適用する場合、その記憶媒体には、先に説明したフローチャートに対応するプログラムコードが格納されることになる。
【0072】
【発明の効果】
以上説明したように、本発明によれば、デジタルカメラにおいて、画像のプリントを容易に行なえるようにすることができる。
【0073】
また、異なる機種間で画像の再生及び送信をする場合にユーザの操作の手間を低減することができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の第1の実施形態のデジタルカメラの構成を示すブロック図である。
【図2】デジタルカメラの撮影モードでのメインルーチンのフローチャートである。
【図3】自動追記情報を取得するルーチンのフローチャートである。
【図4】設定情報を自動追記するルーチンのフローチャートである。
【図5】デジタルカメラの再生モードでのメインルーチンのフローチャートである。
【図6】自動追記情報を編集するためのメニュー画面のイメージ図である。
【図7】自動追記を選択するためのメニュー画面のイメージ図である。
【図8】プリント設定メニュー画面のイメージ図である。
【図9】再設定メニュー画面のイメージ図である。
【図10】送信設定メニュー画面のイメージ図である。
【図11】機種依存情報の表示画面のイメージ図である。
【図12】自動追記情報の表示画面のイメージ図である。
【図13】撮影ルーチンのフローチャートである。
【図14】再生ルーチンのフローチャートである。
【図15】図8の自動追記情報設定メニューにおいて、プリント設定の自動追記を複数の中から選択できることをLCD液晶表示装置で表示しているイメージ図である。
【符号の説明】
122 LCD液晶表示部
123 自動追記情報取得結果メニュー
124 自動追記選択ボタン
125 自動追記決定状態
126 自動追記情報設定メニュー
127 機種依存情報
128 自動追記情報[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to an imaging device that can easily print an image.
[0002]
[Prior art]
In recent years, an image taken with a digital camera is displayed on a display device such as a monitor, and an opportunity to print with a printer or the like for viewing is increasing. Under such circumstances, a standard called DPOF (Digital Print Order Format) has been announced from the viewpoint of user merit. In the DPOF standard, print information necessary for printing is digitized, and the print information is stored in a recording medium together with an image file, and the print information description format is unified.
[0003]
A file for storing print information (referred to as a DPOF file) is specified to be recorded on a recording medium in a text file format different from an image file. The standard has been expanded to standardize the description format for reproduction information and transmission information not only for print information but also for slide show and image file transmission.
[0004]
By storing print information, playback information, and transmission information together with image files in a recording medium in accordance with these standards, users such as direct printing with a personal printer, realization of a slide show between different models, and transmission of image files Effective in realizing the benefits.
[0005]
On the other hand, in the captured image, the subject luminous flux that has passed through the photographing lens reaches a solid-state imaging device (CCD or the like), and the subject image is converted into an electrical signal and output as a video signal. The output image is subjected to various conversion processes in the image processing circuit, and finally stored in the recording medium as an image file.
[0006]
A typical digital camera converts an image file to a digital camera. Built-in The display has a function of reproducing (displaying) on a liquid crystal monitor (LCD). For example, as disclosed in Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 10-126724, a list of the reproduced images is displayed on the liquid crystal monitor and an image to be printed is designated. A device has been proposed.
[0007]
Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 2001-045339 discloses means for issuing a print instruction on a confirmation screen for a photographed image in the photographing mode.
[0008]
Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 2001-066944 discloses that additional information is stored in advance in a fixed file provided on a recording medium such as a memory card, and the additional information stored in the fixed file is automatically acquired and used at the time of shooting. A method is disclosed.
[0009]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
In conventional print settings, a user issues a print instruction while confirming a captured image. For this reason, even when it is decided to print a photographed image, it is necessary to designate the number of prints for each image, and to perform settings such as rotation and trimming separately.
[0010]
In digital cameras where compactness is important, it is difficult to prepare buttons corresponding to each function due to physical restrictions, etc., so there are problems such as difficult to understand print setting operations. .
[0011]
Also, in order to make it easy to perform print settings, specially setting input keys such as buttons causes problems such as an increase in camera size and the possibility of causing problems during shooting.
[0012]
In addition, there is a method of giving a print instruction to all images, but if the print instruction is set for all images and the print information is confirmed, if the image is taken again in the shooting mode, it is changed to all images again. A user operation such as instructing print designation is required.
[0013]
There is also a method of automatically acquiring and using additional information at the time of shooting, but there is a problem that it is not easily applied because it is not assumed that print information is set for a shot image. Yes.
[0014]
Accordingly, the present invention has been made in view of the above-described problems, and an object thereof is to make it possible to easily print an image in a digital camera.
[0015]
This is to reduce the time and effort of the user's operation when reproducing and transmitting images between different models.
[0016]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In order to solve the above-described problems and achieve the object, an imaging apparatus according to the present invention includes: Setting storage means capable of storing print information describing print conditions for images stored in a storage medium, reproduction information describing reproduction conditions, and transmission information describing transmission conditions, the print information, and the reproduction Information storage means for storing additional information for adding information to any one of the information and the transmission information; Before acquiring images by imaging means A selection unit that selects whether to add information to the print information of the image, the reproduction information, or the transmission information, and the information selected by the selection unit according to the acquisition of the image by the imaging unit. An additional recording means for automatically adding information based on the additional information; It is characterized by having.
[0017]
In the imaging apparatus according to the present invention, The print information is print information for setting at least one of print number, rotation angle, trimming, date input, and file name input when the image is printed. It is characterized by that.
[0018]
In the imaging apparatus according to the present invention, The reproduction information is reproduction information for setting at least one of a reproduction interval, a sound effect, a file number display, and a date display when the image is reproduced. It is characterized by that.
[0019]
In the imaging apparatus according to the present invention, The transmission information is transmission information for setting at least one of a transmission destination, a body, a subject, and a file name at the time of transmission of the image. It is characterized by that.
[0020]
In the imaging apparatus according to the present invention, Additional information acquisition setting means for setting contents of information to be added to the print information, the reproduction information, and the transmission information. It is characterized by that.
[0021]
Also, The imaging apparatus according to the present invention further includes display means for displaying the setting contents of the additional information. It is characterized by that.
[0022]
Also, An imaging method according to the present invention includes a setting storage step for storing print information describing a print condition for an image stored in a storage medium, reproduction information describing a reproduction condition, and transmission information describing a transmission condition. An information storage step for storing additional information for adding information to any one of the print information, the reproduction information, and the transmission information, and before the image is acquired by the imaging unit, the print information of the image, A selection step for selecting whether to add information to the reproduction information or the transmission information, and information based on the additional information is automatically added to the information selected in the selection step in accordance with acquisition of an image by the imaging means. And an additional recording step for additional recording It is characterized by that.
[0023]
Also related to this invention The imaging method further includes an additional information acquisition setting step for setting contents of information to be additionally recorded in the print information, the reproduction information, and the transmission information. It is characterized by that.
[0024]
Also related to this invention The imaging method further includes a display step of displaying the setting content of the additional information. It is characterized by that.
[0027]
A program according to the present invention is characterized by causing a computer to execute the above imaging method.
A storage medium according to the present invention is characterized in that the above program is stored in a computer-readable manner.
[0028]
With the configuration as described above, the user can perform print settings for all the captured images without performing complicated setting processing without performing print settings for each captured image. Similarly, troublesome setting processing is not required for image slideshows and image transmissions.
[0029]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
[0030]
(First embodiment)
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing the configuration of the first embodiment of the digital camera of the present invention.
[0031]
In FIG. 1, 101 is a lens that forms an image of light from a subject (not shown), 102 is a diaphragm mechanism that adjusts the amount of incident light from the
[0032]
The transmission
[0033]
FIG. 2 shows a flowchart of the main routine in the photographing mode from when the power is turned on until the setting information is automatically added by the setting information automatic adding
[0034]
When the power is turned on, the process is started (step S100). In step S101, an automatic additional information acquisition routine described later is set, and in step S102, the automatic additional information acquired in step S101 is set based on the user selection result. The automatic
[0035]
FIG. 6 shows a screen displayed on the LCD liquid
[0036]
The user selects whether to automatically add the setting information before shooting for the setting in which the automatic additional information is set in advance.
[0037]
FIG. 7 shows an image diagram of a screen displayed on the LCD liquid
[0038]
In step S103, pre-shooting processing such as moving image display on the LCD
[0039]
As shown in FIG. 2, the various setting processes that have been performed up to now are only a selection process (step S <b> 102) for whether or not to apply the automatic additional information, and the user can set the print settings necessary for each image, There is no need for cumbersome processing for playback settings and transmission settings.
[0040]
FIG. 3 is a flowchart of the automatic additional information acquisition routine in step S101 of FIG.
[0041]
This routine is a routine for searching the
[0042]
In step S151, if automatic additional information is recorded by searching the
[0043]
In step S153, model-dependent information in the digital camera is acquired, and information serving as a parameter in step S154 is generated. In the model-dependent information, whether print settings, playback settings, and transmission settings can be set, whether paper settings can be set in print settings, playback intervals can be set in playback settings, and what kind of destination is specified in transmission settings It is possible to set the destination.
[0044]
In step S154, the automatic additional information read to the
[0045]
When the print setting is automatically added, automatic additional information as shown in FIG. 8 is edited and newly created in advance by the automatic additional information creation / acquisition device 119 (step S154). Similarly, in the case of reproduction setting, automatic additional information as shown in FIG. 9 is created, and in the case of transmission setting, automatic additional information as shown in FIG. 10 is edited and newly created by the automatic additional information creation /
[0046]
FIG. 11 shows an image diagram of an image displayed on the LCD liquid
[0047]
In FIG. 12, based on the model-dependent information acquired in step S153 and the automatic additional information existing in the
[0048]
In FIG. 12, although the designation of trimming is set in the automatic additional information in the recording device 117 (FIG. 8), if the digital camera does not have a function for setting the trimming (FIG. 11), the automatic additional recording is finally performed. Indicates that it is not information. In step S155, the content of the automatic additional information acquired in step S154 is displayed on the LCD liquid
[0049]
FIG. 4 is a flowchart of the setting information automatic addition routine in step S107 of FIG.
[0050]
This routine is a routine for automatically adding setting information to the image captured in step S105 of FIG. 2 if the automatic additional information is valid. In step S201, if the setting information is not automatically added in step S201 in step S201, the process returns to the main routine in step S205. If the setting information is automatically added, step S202 and subsequent steps are performed. Execute. In step S202, information on the image captured in step S105 of FIG. 2, the path name of the captured image, and the file format are acquired. In step S203, setting information is created based on the captured image data acquired in step S202 and the automatic additional recording information selected in step S102 in FIG. In step S204, the recording result of the setting information is displayed on the LCD liquid
[0051]
FIG. 5 shows a flowchart of the main routine in the reproduction mode from when the power is turned on until the automatic additional information is edited.
[0052]
When the power is turned on, the process is started (step S250), and the captured image is displayed on the LCD liquid
[0053]
8, FIG. 9, and FIG. 10 are image diagrams of an editing screen for performing settings for automatically adding setting information based on the automatic additional information acquired in step S253. When the print setting is automatically added, the automatic additional information as shown in FIG. 8 is edited and newly created in advance by the automatic additional information creation / acquisition device 119 (step S254). Similarly, in the case of reproduction setting, automatic additional information as shown in FIG. 9 is created, and in the case of transmission setting, automatic additional information as shown in FIG. 10 is edited and newly created by the automatic additional information creation /
[0054]
By acquiring the content of additional recording with the automatic additional information creation /
[0055]
(Second Embodiment)
The second embodiment of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings and flowcharts. In addition to the means shown in the first embodiment of the present invention, in the setting information creation (step S203 in FIG. 4), the print information, reproduction information, and transmission information created by the setting information
[0056]
When the power is turned on in FIG. 13, the process is started (step S300). In step S301, the above-described automatic additional information acquisition routine is executed. In step S302, based on the automatic additional information acquired in step S301 and the user selection result, the setting information automatic
[0057]
As shown in FIG. 13, the various setting processes that have been performed up to now are only a selection process (step S <b> 302) for determining whether or not to apply the automatic additional information. Also in the second embodiment, similarly to the first embodiment, the user does not need troublesome operations for print setting, reproduction setting, and transmission setting that are necessary for each image.
[0058]
(Third embodiment)
The third embodiment of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings and flowcharts.
[0059]
In addition to the means shown in the first embodiment of the present invention, the automatic additional information created by the automatic additional information creation /
[0060]
FIG. 14 is a flowchart for creating automatic additional recording information in the vendor unique region of the DPOF standard.
[0061]
When the power is turned on in FIG. 14, the process is started (step S350), and the captured image is displayed on the LCD liquid
[0062]
For the automatic additional information setting menu, the automatic additional information acquired in step S356 is displayed on the LCD liquid
[0063]
(Fourth embodiment)
The fourth embodiment of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings and flowcharts.
[0064]
In addition to the means shown in the first embodiment of the present invention, the automatic additional information creation /
[0065]
FIG. 15 is an image diagram displayed on the LCD liquid
[0066]
As described above, according to each of the above-described embodiments, the user operation in the print setting is performed by automatically adding the print information instead of performing the print instruction by the user in the digital camera having the print setting function. Therefore, it is possible to provide a digital camera that can easily print a captured image. Similarly, it is possible to provide a digital camera that automatically adds setting information for reproduction settings between different models and transmission settings assuming transmission of image files, thereby reducing the effort of user operations.
[0067]
In other words, by describing what kind of print settings are to be performed on the recording medium in advance, it is possible to save time and effort for user operations for print settings after image shooting.
[0068]
In addition, since the print settings are automatically added according to the DPOF standard, the setting contents can be used between models that support the DPOF standard. The same applies not only to print settings but also to playback settings and transmission settings.
[0069]
[Other Embodiments]
In addition, an object of each embodiment is to supply a storage medium (or recording medium) on which a program code of software that realizes the functions of the above-described embodiments is recorded to a system or apparatus, and a computer (or CPU) of the system or apparatus Needless to say, this can also be achieved by reading and executing the program code stored in the storage medium. In this case, the program code itself read from the storage medium realizes the functions of the above-described embodiments, and the storage medium storing the program code constitutes the present invention. Further, by executing the program code read by the computer, not only the functions of the above-described embodiments are realized, but also an operating system (OS) running on the computer based on the instruction of the program code. It goes without saying that a case where the function of the above-described embodiment is realized by performing part or all of the actual processing and the processing is included.
[0070]
Furthermore, after the program code read from the storage medium is written into a memory provided in a function expansion card inserted into the computer or a function expansion unit connected to the computer, the function is determined based on the instruction of the program code. It goes without saying that the CPU or the like provided in the expansion card or the function expansion unit performs part or all of the actual processing and the functions of the above-described embodiments are realized by the processing.
[0071]
When the present invention is applied to the storage medium, the storage medium stores program codes corresponding to the flowcharts described above.
[0072]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, it is possible to easily print an image in a digital camera.
[0073]
Further, it is possible to reduce the time and effort of the user's operation when reproducing and transmitting an image between different models.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a digital camera according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a flowchart of a main routine in a shooting mode of the digital camera.
FIG. 3 is a flowchart of a routine for acquiring automatic additional recording information.
FIG. 4 is a flowchart of a routine for automatically adding setting information.
FIG. 5 is a flowchart of a main routine in a playback mode of the digital camera.
FIG. 6 is an image diagram of a menu screen for editing automatic additional information.
FIG. 7 is an image diagram of a menu screen for selecting automatic appending.
FIG. 8 is an image diagram of a print setting menu screen.
FIG. 9 is an image diagram of a reset menu screen.
FIG. 10 is an image diagram of a transmission setting menu screen.
FIG. 11 is an image diagram of a display screen for model-dependent information.
FIG. 12 is an image diagram of a display screen of automatic additional information.
FIG. 13 is a flowchart of an imaging routine.
FIG. 14 is a flowchart of a reproduction routine.
FIG. 15 is an image diagram showing that an automatic addition of print settings can be selected from a plurality of options in the automatic additional information setting menu of FIG. 8 on an LCD liquid crystal display device.
[Explanation of symbols]
122 LCD liquid crystal display
123 Automatic additional information acquisition result menu
124 Automatic append selection button
125 Auto-append decision state
126 Automatic additional information setting menu
127 Model-dependent information
128 Automatic additional information
Claims (11)
前記プリント情報、前記再生情報、前記送信情報のいずれかに対して情報を追記するための追記情報を記憶する情報記憶手段と、
撮像手段によって画像を取得する前に、前記画像のプリント情報、前記再生情報、前記送信情報のいずれに情報を追記するかを選択する選択手段と、
前記撮像手段による画像の取得に応じて、前記選択手段で選択された情報に前記追記情報に基づく情報を自動的に追記する追記手段と、
を有することを特徴とする撮像装置。 Setting storage means capable of storing print information describing print conditions for images stored in the storage medium, reproduction information describing reproduction conditions, and transmission information describing transmission conditions;
Information storage means for storing additional information for adding information to any one of the print information, the reproduction information, and the transmission information;
A selection means for selecting whether to add information to the print information of the image, the reproduction information, or the transmission information before acquiring an image by the imaging means ;
In accordance with acquisition of an image by the imaging means, additional recording means for automatically adding information based on the additional information to the information selected by the selection means;
An imaging device comprising:
前記プリント情報、前記再生情報、前記送信情報のいずれかに対して情報を追記するための追記情報を記憶する情報記憶工程と、An information storage step of storing additional information for adding information to any one of the print information, the reproduction information, and the transmission information;
撮像手段によって画像を取得する前に、前記画像のプリント情報、前記再生情報、前記送信情報のいずれに情報を追記するかを選択する選択工程と、A selection step of selecting whether to add information to the print information of the image, the reproduction information, or the transmission information before acquiring the image by the imaging means;
前記撮像手段による画像の取得に応じて、前記選択工程において選択された情報に前記追記情報に基づく情報を自動的に追記する追記工程と、An additional recording step of automatically adding information based on the additional recording information to the information selected in the selection step in response to acquisition of an image by the imaging means;
を有することを特徴とする撮像方法。An imaging method characterized by comprising:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001388153A JP3848151B2 (en) | 2001-12-20 | 2001-12-20 | Imaging apparatus, imaging method, program, and storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001388153A JP3848151B2 (en) | 2001-12-20 | 2001-12-20 | Imaging apparatus, imaging method, program, and storage medium |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2003189212A JP2003189212A (en) | 2003-07-04 |
| JP2003189212A5 JP2003189212A5 (en) | 2005-07-14 |
| JP3848151B2 true JP3848151B2 (en) | 2006-11-22 |
Family
ID=27596760
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001388153A Expired - Fee Related JP3848151B2 (en) | 2001-12-20 | 2001-12-20 | Imaging apparatus, imaging method, program, and storage medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3848151B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5571944B2 (en) | 2009-01-16 | 2014-08-13 | キヤノン株式会社 | Imaging apparatus, control method therefor, and program |
| JP5377050B2 (en) * | 2009-04-16 | 2013-12-25 | キヤノン株式会社 | Image processing apparatus, control method therefor, and program |
-
2001
- 2001-12-20 JP JP2001388153A patent/JP3848151B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2003189212A (en) | 2003-07-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8698821B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, computer program, and storage medium | |
| JP5147424B2 (en) | Image display apparatus, control method therefor, and program | |
| JP2004304425A (en) | Electronic camera | |
| US20120176512A1 (en) | Image storage apparatus, image storage method, and control program executed in image storage apparatus | |
| JP2009199586A (en) | Information processing apparatus and control method thereof | |
| JP2004157647A (en) | Image transmission-and-reception system, image transmission device and image reception device | |
| JP2004159293A (en) | Imaging recording apparatus, image processing apparatus, imaging recording control program, image processing program, image-pickup recording method and image processing method | |
| JP4616500B2 (en) | Image transmitting apparatus, method and program | |
| JP3747914B2 (en) | Image recording apparatus, image recording method, and program | |
| JP2004222236A (en) | Image pickup device, image editing method and program | |
| US20110279690A1 (en) | Electronic device, camera, and computer program product of image processing | |
| JP2007048214A (en) | Print preview display method and print system | |
| JP3848151B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, imaging method, program, and storage medium | |
| JP4888711B2 (en) | Scene selection screen generation device, scene selection screen addition system, scene selection screen generation method, scene selection screen addition method, and program | |
| JP2001333363A (en) | Device, system and method for information communication | |
| JP2007013881A (en) | Imaging apparatus | |
| JP2004056707A (en) | Method of creating folder and program therefor | |
| US20040130635A1 (en) | Image processing apparatus and image processing method | |
| JP4211764B2 (en) | Electronic camera, image recording apparatus, image recording method and program | |
| JP4025525B2 (en) | Electronic camera | |
| JP5338516B2 (en) | Image processing system and communication device | |
| JP2014115982A (en) | Photographing device, security release method and program | |
| JP3988075B2 (en) | Image transmission equipment | |
| JP2005167547A (en) | Image outputting device, electronic camera, and program thereof | |
| JP2003274237A (en) | Digital camera |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20041119 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20041119 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20060406 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20060418 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20060619 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20060804 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20060824 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20090901 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100901 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110901 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110901 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120901 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120901 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130901 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |