JP3848150B2 - Image processing apparatus and method - Google Patents
Image processing apparatus and method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3848150B2 JP3848150B2 JP2001386137A JP2001386137A JP3848150B2 JP 3848150 B2 JP3848150 B2 JP 3848150B2 JP 2001386137 A JP2001386137 A JP 2001386137A JP 2001386137 A JP2001386137 A JP 2001386137A JP 3848150 B2 JP3848150 B2 JP 3848150B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- character
- characters
- extracting
- image processing
- image
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、1文字が複数の文字片から成る文字を含む文書画像に対して電子透かしの埋め込みを行う画像処理装置、1文字が複数の文字片から成る文字を含む文書画像に対して埋め込まれた電子透かしを抽出する画像処理装置及び画像処理方法に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
近年プリンタ、複写機などのデジタル画像形成装置において、その画質の向上は著しく、容易に高画質の印刷物を手にすることができるようになってきている。つまり誰もが高性能スキャナ、プリンタ、複写機そしてコンピュータによる画像処理により、要求される印刷物を得ることが可能となってきている。そのため、文書の不正コピー、改ざん等の問題が発生し、それらを防止、あるいは抑止させるため、印刷物そのものにアクセス制御情報を埋め込もうという動きが近年活発となってきている(電子透かし)。
【0003】
このような機能としては、印刷物にアクセス制御情報を目に見えないように埋め込むもの(不可視タイプ)、文書の余白にアクセス制御情報に対応したビットマップパターンを埋め込むもの、文書画像にスクランブル暗号をかけるもの等が現在一般的である。そのうち、アクセス制御情報を目に見えないように埋め込むものは、一般的な実現方法として、英文字列のスペースの量をコントロールすることにより情報を埋め込むタイプ、文字を回転するタイプ、文字を拡大縮小するタイプ、また文字を変形させて情報を埋め込むタイプ等が提案されている。
【0004】
図8は、英文文字列のスペースの量をコントロールするタイプの印刷物である。ここで、801をスペ−スと呼ぶ。また、このスペースは、埋め込む透かしビットが0ならば、p←(1+p)(p+s)/2s←(1−p)(p+s)/2とし、透かしビットが1ならば、p←(1−p)(p+s)/2s←(1+p)(p+s)/2とする。
【0005】
図9は、文字を回転するタイプの印刷物である。ここで、(a)は回転前の状態、(b)は回転後の状態を示している。901は、文字の回転角度を示す。
【0006】
図10は、文字を拡大縮小するタイプの印刷例である。1001は、元のサイズを示す。1002は、拡大縮小後のサイズを示す。
【0007】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、上記のアクセス制御情報を目に見えないように埋め込むものは、特に文章画像においては、画像的に冗長度が少ない文章自体(通常2値画像)に情報を埋め込むため、文字、スペースに違和感を生じ、原稿品位の劣化が目立ちやすくなる。また、一般にそのような画像は読み出し耐性が弱い。
【0008】
本発明は以上の問題に鑑みてなされたものであり、字体の劣化を最小限に抑えつつ、一定以上の情報埋め込み精度、量を確保することを目的とする。
【0009】
【課題を解決するための手段】
この発明は下記の構成を備えることにより上記課題を解決できるものである。
(1)1文字が複数の文字片から成る文字を含む文書画像に対して透かし情報を埋め込む画像処理装置であって、前記文書画像から文字を抽出する抽出手段と、前記抽出手段により抽出された文字のうち、文字の文字片構成が所定の構成をとる文字を選択する選択手段と、前記選択手段により選択された文字の文字片の相対形状を変化させることで、前記選択された文字に透かし情報を埋め込む埋め込み手段を備えることを特徴とする画像処理装置。
【0010】
(2)1文字が複数の文字片から成る文字を含む文書画像に対して埋め込まれた透かし情報を抽出する画像処理装置であって、前記文書画像から文字を抽出する文字抽出手段と、前記文字抽出手段により抽出された文字のうち、文字の文字片構成が所定の構成をとる文字を選択する選択手段と、前記選択手段が選択した文字の文字片の相対形状に基づいて、前記透かし情報を抽出する透かし情報抽出手段を備えることを特徴とする画像処理装置。
【0011】
(3)1文字が複数の文字片から成る文字を含む文書画像に対して透かし情報を埋め込む画像処理方法であって、前記文書画像から文字を抽出する抽出工程と、前記抽出工程で抽出された文字のうち、文字の文字片構成が所定の構成をとる文字を選択する選択工程と、前記選択手段により選択された文字の文字片の相対形状を変化させることで、前記選択された文字に透かし情報を埋め込む埋め込み工程を備えることを特徴とする画像処理方法。
【0012】
(4)1文字が複数の文字片から成る文字を含む文書画像に対して埋め込まれた透かし情報を抽出する画像処理方法であって、前記文書画像から文字を抽出する文字抽出工程と、前記文字抽出工程で抽出された文字のうち、文字の文字片構成が所定の構成をとる文字を選択する選択工程と、前記選択手段が選択した文字の文字片の相対形状に基づいて、前記透かし情報を抽出する透かし情報抽出工程を備えることを特徴とする画像処理方法。
【0026】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、図面を参照して本発明の実施形態を詳細に説明する。
【0027】
(実施例1)
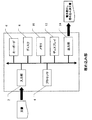
図1は、本発明の実施の形態に係る電子透かし装置の概略構成を示すブロック図である。(a)は電子透かし埋め込み部のブロック図、(b)は電子透かし読み出し部のブロック図である。
【0028】
(a)において、2は電子透かしを埋め込む対象文書を入力するスキャナ、カメラ、あるいはファイル読み込み装置などの画像入力手段(入力部)、4は各種処理を行うプロセッサ、6はプロセッサ4への命令を入力するキーボード、8は埋め込み情報、あるいは読み込んだ文書画像を保存するディスク、10はプロセッサ4において為される各種処理の一時データ記憶、あるいは画像入力手段(入力部)2で読み込んだ文書画像を蓄積するメモリ、12はプロセッサ4への命令入力、および処理の状態を示すディスプレイ、14はアクセス制御情報が埋め込まれた文書画像を出力するプリンタ等の出力手段(出力部)である。
【0029】
(b)において、22は電子透かしが埋め込まれた文書を入力するスキャナ、カメラ、あるいはファイル読み込み装置などの画像入力手段(入力部)、24は各種処理を行うプロセッサ、26はプロセッサ24への命令を入力するキーボード、28は読み込んだ文書画像を保存、あるいは読み込んだ文書のオリジナルファイル検索のためのディスク、30はプロセッサ24において為される各種処理用の一時データ記憶、あるいは画像入力手段(入力部)22で読み込んだ文書画像を蓄積するメモリ、32はプロセッサ24への命令入力、および処理の状態を示すディスプレイ、34、36はそれぞれ読み取った文書アクセス制御情報を活用するためのネットワークインターフェース、プリンタである。
【0030】
次に動作について説明する。電子透かし埋め込み時は、キーボード6から入力された命令に従い、まず、画像入力手段(入力部)2より電子化された被埋め込み文書画像を取得し、メモリ10に展開する。
【0031】
さらに埋め込み情報(文書アクセス制御情報)をキーボード6、あるいはディスク8より入力し、プロセッサ4によりその情報をメモリ10上に展開されている文書画像に埋め込む。所定の文書アクセス制御情報が埋め込まれた文書画像は、出力手段(出力部)14により電子透かし埋め込み済文書として出力される。
【0032】
一方電子透かし読み出し時は、キーボード26から入力された命令に従い、まず、画像入力手段(入力部)22より電子透かし埋め込み済文書を電子化し、メモリ30に展開する。次にプロセッサ24によりメモリ30上に展開された文書画像から埋め込まれた文書アクセス制御情報を読み出し、その指示に基づいて所定の処理を行う。所定の処理とは、例えば、不正読み取りが発覚した場合に外部ヘ通報する、オリジナル文書の検索を内部ディスク28、または外部に対し行う、あるいは属性情報をプリントアウトする等であり、これらの処理のためネットワークI/F34、プリンタ36は使用される。
【0033】
以下図2,図3,図4,図5,図6を参照して本実施形態の電子透かし装置、特にプロセッサ4,24が実行する各種制御処理の動作を説明する。
【0034】
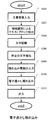
図2は、プロセッサ4が1枚の文書に電子透かしを埋め込む際の全体流れ図である。
【0035】
S200は、文章画像入力手段(入力部)2から文書を取込み、電子画像データとしてメモリ10に転送する制御を行うルーチンである。このルーチンは、読み込んだ文書の方向、傾斜補正等の前処理も含む。
【0036】
S202は、S200においてメモリ10に展開された文書画像に対し領域識別を施し、画像中の文字ブロックをすべて抽出するルーチンである。これは例えば特開平6−068301号公報に記述されているブロックセレクション技術等を応用して実現させることが可能である。
【0037】
S204は、S202で抽出された全ての文字ブロックに文字認識を施すルーチンである。
【0038】
S206は、S204で文字コードに変換された各々の文字の中から文書アクセス制御情報を埋め込むべき対象文字を抽出するルーチンである。
【0039】
S208は、S206で抽出された文字に埋め込まれるべき文書アクセス制御情報を入力するルーチンである。ここで、文書アクセス制御情報とは、例えば、複写制限情報、改ざん防止情報、オリジナル文書管理情報等である。
【0040】
S210は、S208で入力された文書アクセス制御情報をS206で抽出された文字に埋め込むルーチンである。
【0041】
S206とS210は本発明の主眼を為すルーチンで、後ほど詳しく説明する。
【0042】
S212は、S210で文書アクセス制御情報が埋め込まれた文字画像を出力するルーチンである。
【0043】
図3は、プロセッサ24が1枚の電子透かし埋め込み済文書から所望の情報を取り出す際の全体流れ図である。
【0044】
S300は、文章画像入力手段(入力部)22から電子透かし埋め込み済文書を取込み、電子画像データとしてメモリ30に転送する制御を行うルーチンである。このルーチンは、S200同様読み込んだ文書の方向、傾斜補正等の前処理も含む。
【0045】
S302は、S300においてメモリ30に展開された電子透かし埋め込み済文書画像に対し領域識別を施し、文書画像中の文字ブロックをすべて抽出するルーチンである。
【0046】
S304は、S302で抽出された全ての文字ブロックに文字認識を施すルーチンである。
【0047】
S306は、S304で文字コードに変換された各々の文字の中から文書アクセス制御情報が埋め込まれている文字のみを抽出するルーチンである。
【0048】
S302,S304,S306はそれぞれS202,S204,S206と同じ処理ルーチンである。
【0049】
S308は、S306で抽出された文字から文書アクセス制御情報を読み出すルーチンである。
【0050】
S306,S308はS206,S210と同様本発明の主眼を為すルーチンで、後ほど詳しく説明する。
【0051】
S310は、S308で読み出された文書アクセス制御情報に従って所定の制御を行うルーチンで、例えば、コピー禁止処理、文書検索処理等を指令する。
【0052】
図4は本発明の主眼を為す電子透かし埋め込み/読み込みの対象文字抽出ルーチン(S206,S306)の詳細流れ図である。
【0053】
S400は、文字認識結果より文字コードを文字抽出用ワークメモリに転送する制御を行うルーチンである。
【0054】
S402は、文書中に含まれる全ての文字コードを文字抽出用ワークメモリに転送したか否かを判定するルーチンである。転送が全て終了している場合はS404へ、そうでない場合はS400へ制御を移行させる。
【0055】
S404は、あらかじめ設定されている文書アクセス制御情報を埋め込むべき対象文字を文字毎にカウントするルーチンである。ここで、あらかじめ設定されているとは、例えば、構成部首が3個以上の漢字というように、ある程度複雑な部首構成をとっている漢字をあらかじめ設定しておくことである。このような設定を行うことにより、一定以上の情報を目立たないようにしかも確実に埋め込むことが可能となる。これについては後ほど詳しく説明する。
【0056】
S406は、S404でカウントされた対象文字をカウント数によりソーティングするルーチンである。
【0057】
S408は、カウント数がある程度以上、すなわち文書中に出現頻度の多い埋め込み対象文字が一定以上あるか否かを判定するルーチンである。これは、埋め込み/読み出し精度を確保するため対象とする文字を一定数以上とり、すなわち同じ文字に対し同じ情報を繰り返し埋め込むための措置である。ここでいう一定数以上とは多ければ多いほど精度が上がるが、例えば図6(3)で説明されているように2文字程度でも良い。このようにすることにより、読み込み時の精度が大幅に改善する。
【0058】
また、そのような対象文字が一定数以上とは、埋め込み情報量を保証するため、例えば図5に示すように一文字あたり3ビットの情報を埋め込むことが可能とすると、図6(3)に示すように11文字だと30ビットの情報を埋め込むことが可能となるが、そのように文字数を限定することである。
【0059】
ここで、一定以上対象文字数がないと判断された場合、所定の情報量の埋め込みは不可能と判断し、S414へ、そうでない場合はS410へ制御を移行させる。
【0060】
S410は、埋め込み対象文字の中で文書中最も出現頻度の高い文字を選択し、埋め込み/読み込み操作のための基準値を算出するルーチンである(図6(4)に相当)。この基準値については後ほど説明する。
【0061】
S412は、基準値を求めた文字以外、すなわち2番目以降、例えば30ビットの場合11番目までの埋め込み対象文字をS406でソーティングした結果より求め、情報の埋め込み/読み出し操作を行うルーチンである。具体的な手法は、図5、図6を用い後ほど詳しく説明する。
【0062】
S414は、S408で埋め込み対象文字が少なく、埋め込み不可と判断された場合所定の処理を行うルーチンである。所定の処理とは、例えば警告を発する等である。
【0063】
図5は、S412で行われている情報の埋め込み/読み出し手法の原理を説明する図、図6は実際にある文書に30ビットの情報量を埋め込む場合の説明図である。
【0064】
図5、図6では、例えば部首の個数が3個の例えば“型”という文字のパターンのような、小さな部首が上部に2個、大きな部首が下部に1個あるようなパターンを取り上げ説明する。なお、図は説明のために多少誇張して表現されている。
【0065】
まず、抽出された文字画像を個々の部首に分解しその基準値を求める。基準値とは、本発明において文書アクセス情報を目に見えない形で埋め込む際に最も重要な値である。
【0066】
具体的には、図5(a)に記載されているように、文字画像の絶対高さ、幅に対する分解された各部首の幅、高さの割合で表される。さらに説明すると、ここでは各部首といいつつも、上部2つの部首のみで、下部の部首についてはその大きさの割合を定義していない。これは、全ての部首で定義してしまうと、相対的な基準値が変動してしまい、さらには、字の変形も大きくなり劣化が目立つことになるので、このように最も主要な部首を一つ残し、他の2つの部首(この場合は)のみ使用しているのである。
【0067】
具体的な情報の埋め込み手法であるが、ここで先ほど定義した4つの基準値k,m,n,pを使用して1文字あたり3ビットの情報を埋め込むことを考える。図4、S410で最も信頼度の高い、すなわち出現頻度の高い文字の基準値k,m,n,pを求める(図6(4)に相当)。これに対し、埋め込まれるべき文書アクセス制御、例えば30ビットを用意し、図4、S412で選択した2番目以降の文字に、図5の右半分に表されているよう規則にのっとり、順番に3ビット毎にk′,m′,n′,p′を求め、その結果を反映させるよう対象文字の各部首の縦横比を変化させる(図6(5)に相当)。このような手順で任意の情報を埋め込むことが可能となる。
【0068】
読み出し時は、文字認識を行い、文字を抽出し、ソーティングし、第一位の基準値を求めるところまではまったく埋め込み時と同様で、最後に第二位以降の各部首の縦横比を基準値と比較し、割り振られたビット配列を再現させる。通常これを複数回行い(ここでは最低2回以上)、その多数決等で判断し、精度をより高めることが可能である。
【0069】
図6では、“001 100 111 000 010 011 111 101 111 000”のような30ビットの情報を、実際に埋め込む手順を表している。
【0070】
以上述べてきたように本発明では、領域識別、文字認識を行った上で、部首構成の複雑な漢字の部首毎の相対形状変化を巧みに活用することにより、字体の劣化を最小限に抑えつつも、出現頻度による対象文字のソーティングにより一定以上の情報埋め込み精度、量を確保し、読み取り時においてもノイズ耐性の高い電子透かし装置を実現させることが可能となった。また、フォントサイズの依存性も原理的に全くないため、文字数の少ない原稿に対しても、有効な手法であることは明白である。
【0071】
(実施例2)
第1の実施例では、埋め込み対象として採用した部首構成は図5で示されたような単一のパターンだったが、何もこれに限ることはなく、図7に示すように一定以上の部首を持つ複数の漢字パターンを同時に設定しても良い。この場合は埋め込み情報量はさらに増大する。
【0072】
【発明の効果】
以上述べてきたように本発明では、1文字が複数の文字片から成る文字を含む文書画像に対して文字片の相対形状変化を巧みに活用することにより、字体の劣化を最小限に抑えつつも、出現頻度による対象文字のソーティングにより一定以上の情報埋め込み精度、量を確保し、読み取り時においてもノイズ耐性の高い電子透かし装置を実現させることが可能となった。また、フォントサイズの依存性も原理的に全くないため、文字数の少ない原稿に対しても、有効な手法であることは明白である。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1(a)】 本発明の実施の形態に係る電子透かし装置の電子透かし埋め込み部の概略構成を示すブロック図
【図1(b)】 本発明の実施の形態に係る電子透かし装置の電子透かし読み出し部の概略構成を示すブロック図
【図2】 プロセッサ4が1枚の文書に電子透かしを埋め込む際の全体流れ図
【図3】 プロセッサ24が1枚の電子透かし埋め込み済文書から所望の情報を取り出す際の全体流れ図
【図4】 本発明の主眼を為す電子透かし埋め込み/読み込みの対象文字抽出ルーチン(S206,S306)の詳細流れ図
【図5】 S412で行われている情報の埋め込み/読み出し手法の原理の説明図
【図6】(1),(2),(3),(4),(5) 実際にある文書に30ビットの情報量を埋め込む場合の説明図
【図7】 第2の実施例の説明図(その他の埋め込み/読み出し部首パターン)
【図8】 従来の技術の説明図
【図9】(a),(b) 従来の技術の説明図
【図10】 従来の技術の説明図
【符号の説明】
2 画像入力手段(入力部)
4 プロセッサ
6 キーボード
8 ディスク
10 メモリ
12 ディスプレイ
14 出力手段(出力部)
22 画像入力手段(入力部)
24 プロセッサ
26 キーボード
28 ディスク
30 メモリ
32 ディスプレイ
34 ネットワークインターフェース
36 プリンタ[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to an image processing apparatus that embeds a digital watermark into a document image including a character composed of a plurality of character pieces, and is embedded into a document image including a character composed of a plurality of character pieces. The present invention relates to an image processing apparatus and an image processing method for extracting a digital watermark.
[0002]
[Prior art]
In recent years, in digital image forming apparatuses such as printers and copying machines, the image quality has been remarkably improved, and it has become possible to easily obtain high-quality printed materials. That is, anyone can obtain the required printed matter by image processing using a high-performance scanner, printer, copier, and computer. For this reason, problems such as illegal copying and falsification of documents have occurred, and in recent years, there has been an active movement to embed access control information in the printed matter itself in order to prevent or prevent them (digital watermark).
[0003]
Such functions include embedding access control information in an invisible form (invisible type), embedding a bitmap pattern corresponding to the access control information in the margin of the document, and applying scramble encryption to the document image. Things are now common. Of these, those that embed access control information invisibly are generally implemented as a method of embedding information by controlling the amount of space in the English character string, a type of rotating characters, and scaling characters A type that embeds information by deforming characters or the like has been proposed.
[0004]
FIG. 8 shows a type of printed matter that controls the amount of space in the English character string. Here, 801 is called a space. If the watermark bit to be embedded is 0, this space is set to p ← (1 + p) (p + s) / 2s ← (1-p) (p + s) / 2, and if the watermark bit is 1, p ← (1-p ) (P + s) / 2s ← (1 + p) (p + s) / 2.
[0005]
FIG. 9 shows a printed matter of a type that rotates characters. Here, (a) shows a state before rotation, and (b) shows a state after rotation.
[0006]
FIG. 10 shows an example of printing that enlarges or reduces characters. 1001 indicates the original size.
[0007]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, the above-mentioned access control information that is embedded invisible is embedded in the text itself (usually a binary image) with less redundancy, particularly in a text image, so that characters and spaces are uncomfortable. And the deterioration of the document quality becomes conspicuous. In general, such an image has low read resistance.
[0008]
The present invention is more has been made in view of the problems, while minimizing the deterioration of the typeface, an object of ensuring to Rukoto certain level of information embedding accuracy and amount.
[0009]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The present invention can solve the above problems by providing the following configuration.
(1) An image processing apparatus that embeds watermark information in a document image that includes characters each consisting of a plurality of character pieces, the extraction unit extracting characters from the document image, and the extraction unit extracting the characters Among the characters, a selection unit that selects a character having a predetermined character fragment configuration, and a watermark on the selected character by changing a relative shape of the character fragment selected by the selection unit. An image processing apparatus comprising an embedding unit for embedding information.
[0010]
(2) An image processing apparatus for extracting watermark information embedded in a document image including a character in which one character is composed of a plurality of character pieces, the character extracting means for extracting a character from the document image, and the character The watermark information is selected based on the selection means for selecting a character whose character fragment configuration has a predetermined configuration among the characters extracted by the extraction means, and the relative shape of the character fragment of the character selected by the selection means. An image processing apparatus comprising watermark information extracting means for extracting.
[0011]
(3) An image processing method for embedding watermark information in a document image including a character consisting of a plurality of character pieces, wherein the character is extracted from the document image, and extracted in the extraction step Among the characters, a selection step of selecting a character whose character fragment configuration has a predetermined configuration, and changing the relative shape of the character fragment of the character selected by the selection means, thereby watermarking the selected character. An image processing method comprising an embedding step of embedding information.
[0012]
(4) An image processing method for extracting watermark information embedded in a document image including a character in which one character is composed of a plurality of character pieces, the character extracting step for extracting a character from the document image, and the character Based on the selection step of selecting a character whose character fragment configuration has a predetermined configuration from among the characters extracted in the extraction step, and the watermark information based on the relative shape of the character fragment of the character selected by the selection means An image processing method comprising a watermark information extracting step of extracting.
[0026]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
[0027]
Example 1
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a schematic configuration of a digital watermark apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention. (A) is a block diagram of a digital watermark embedding unit, and (b) is a block diagram of a digital watermark reading unit.
[0028]
In (a), 2 is an image input means (input unit) such as a scanner, a camera, or a file reading device for inputting a target document for embedding a digital watermark, 4 is a processor for performing various processes, and 6 is a command to the processor 4. Keyboard for input, 8 is a disk for storing embedded information or a read document image, 10 is a temporary data storage for various processes performed in the processor 4, or a document image read by the image input means (input unit) 2 is stored. A
[0029]
In (b), 22 is an image input means (input unit) such as a scanner, camera, or file reading device for inputting a document in which a digital watermark is embedded, 24 is a processor for performing various processes, and 26 is a command to the
[0030]
Next, the operation will be described. When embedding a digital watermark, according to a command input from the keyboard 6, first, an embedded document image digitized by the image input means (input unit) 2 is acquired and developed in the
[0031]
Further, embedded information (document access control information) is input from the keyboard 6 or the
[0032]
On the other hand, at the time of reading the digital watermark, the digital watermark embedded document is first digitized by the image input means (input unit) 22 in accordance with a command input from the
[0033]
The operations of various control processes executed by the digital watermarking apparatus of this embodiment, particularly the
[0034]
FIG. 2 is an overall flowchart when the processor 4 embeds a digital watermark in one document.
[0035]
S200 is a routine for performing control for taking a document from the text image input means (input unit) 2 and transferring it to the
[0036]
S202 is a routine for performing region identification on the document image developed in the
[0037]
S204 is a routine for performing character recognition on all the character blocks extracted in S202.
[0038]
S206 is a routine for extracting a target character to be embedded with the document access control information from each character converted into the character code in S204.
[0039]
S208 is a routine for inputting document access control information to be embedded in the characters extracted in S206. Here, the document access control information is, for example, copy restriction information, falsification prevention information, original document management information, and the like.
[0040]
S210 is a routine for embedding the document access control information input in S208 in the characters extracted in S206.
[0041]
S206 and S210 are routines that are the main subject of the present invention, and will be described in detail later.
[0042]
S212 is a routine for outputting the character image in which the document access control information is embedded in S210.
[0043]
FIG. 3 is an overall flowchart when the
[0044]
S300 is a routine for performing control to take a digital watermark embedded document from the text image input means (input unit) 22 and transfer it to the
[0045]
S302 is a routine for performing region identification on the digital watermark embedded document image developed in the
[0046]
S304 is a routine for performing character recognition on all the character blocks extracted in S302.
[0047]
S306 is a routine for extracting only the character in which the document access control information is embedded from each character converted into the character code in S304.
[0048]
S302, S304, and S306 are the same processing routines as S202, S204, and S206, respectively.
[0049]
S308 is a routine for reading the document access control information from the characters extracted in S306.
[0050]
Similar to S206 and S210, S306 and S308 are routines that focus on the present invention, and will be described in detail later.
[0051]
S310 is a routine for performing predetermined control according to the document access control information read in S308, and instructs, for example, copy prohibition processing, document search processing, and the like.
[0052]
FIG. 4 is a detailed flowchart of a character extraction routine (S206, S306) for embedding / reading a digital watermark which is the main object of the present invention.
[0053]
S400 is a routine for performing control to transfer the character code to the character extraction work memory based on the character recognition result.
[0054]
S402 is a routine for determining whether or not all character codes included in the document have been transferred to the character extraction work memory. If all the transfers have been completed, the process proceeds to S404. If not, the process proceeds to S400.
[0055]
S404 is a routine for counting, for each character, target characters to be embedded with document access control information set in advance. Here, “preliminarily set” means that, for example, a Chinese character having a somewhat complicated radical configuration, such as a Chinese character having three or more constituent radicals, is set in advance. By performing such a setting, it becomes possible to embed information of a certain level without making it conspicuous. This will be described in detail later.
[0056]
S406 is a routine for sorting the target characters counted in S404 by the number of counts.
[0057]
S408 is a routine for determining whether or not the number of counts exceeds a certain level, that is, whether or not there are a certain number of embedding target characters frequently appearing in the document. This is a measure for taking a predetermined number or more of characters to ensure embedding / reading accuracy, that is, repeatedly embedding the same information for the same character. Although the accuracy increases as the number is more than a certain number here, for example, as illustrated in FIG. By doing so, the reading accuracy is greatly improved.
[0058]
Further, if the number of such target characters exceeds a certain number, in order to guarantee the amount of embedded information, for example, if it is possible to embed 3 bits of information per character as shown in FIG. Thus, if it is 11 characters, it becomes possible to embed 30-bit information, but this is to limit the number of characters.
[0059]
Here, if it is determined that there is no target character number above a certain level, it is determined that embedding of a predetermined amount of information is impossible, and control is shifted to S414, and if not, control is shifted to S410.
[0060]
S410 is a routine for selecting a character having the highest appearance frequency in the document from among the embedding target characters and calculating a reference value for embedding / reading operation (corresponding to (4) in FIG. 6). This reference value will be described later.
[0061]
S412 is a routine for performing information embedding / reading operations by obtaining the result of the sorting in S406 of characters to be embedded other than the character for which the reference value has been obtained, that is, the second and subsequent characters, for example, up to 11th in the case of 30 bits. A specific method will be described in detail later with reference to FIGS.
[0062]
S414 is a routine for performing a predetermined process when it is determined in S408 that there are few characters to be embedded and it is impossible to embed. The predetermined process is, for example, issuing a warning.
[0063]
FIG. 5 is a diagram for explaining the principle of the information embedding / reading method performed in S412, and FIG. 6 is an explanatory diagram in the case of embedding a 30-bit information amount in an actual document.
[0064]
In FIG. 5 and FIG. 6, for example, a pattern with three small radicals at the top and two large radicals at the bottom, such as a pattern of three letters, for example, “type”. Take up and explain. Note that the drawings are exaggerated for the sake of explanation.
[0065]
First, the extracted character image is decomposed into individual radicals to obtain the reference value. The reference value is the most important value when embedding document access information in an invisible form in the present invention.
[0066]
More specifically, as described in FIG. 5A, the absolute height and width of the character image are represented by the ratio of the width and height of each decomposed radical. To explain further, although it is referred to as each radical here, only the upper two radicals are used, and the proportion of the size of the lower radical is not defined. If this is defined for all radicals, the relative reference value will fluctuate, and further, the deformation of the character will become large and the deterioration will be conspicuous. One is used and only the other two radicals (in this case) are used.
[0067]
As a specific information embedding method, consider embedding information of 3 bits per character using the four reference values k, m, n, and p defined earlier. In FIG. 4, S410, the reference values k, m, n, and p of the character having the highest reliability, that is, the appearance frequency are obtained (corresponding to FIG. 6 (4)). On the other hand, document access control to be embedded, for example, 30 bits are prepared, and the second and subsequent characters selected in FIG. 4 and S412 are set in order according to the rule shown in the right half of FIG. K ′, m ′, n ′, and p ′ are obtained for each bit, and the aspect ratio of each radical of the target character is changed to reflect the result (corresponding to FIG. 6 (5)). Arbitrary information can be embedded by such a procedure.
[0068]
At the time of reading, character recognition is performed, the characters are extracted, sorted, and until the first reference value is obtained, it is exactly the same as when embedding, and finally the aspect ratio of each radical after the second is the reference value And the allocated bit array is reproduced. Usually, this is performed a plurality of times (here, at least two times or more), and it is possible to make a judgment based on the majority vote or the like to further improve accuracy.
[0069]
FIG. 6 shows a procedure for actually embedding 30-bit information such as “001 100 111 000 010 011 111 101 111 000”.
[0070]
As described above, according to the present invention, after performing region identification and character recognition, skillful use of the relative shape change for each radical of a complex Chinese character having a radical structure makes it possible to minimize deterioration of the font. However, it is possible to achieve a digital watermarking device with high noise resistance even at the time of reading by ensuring the accuracy and amount of information embedding beyond a certain level by sorting target characters according to appearance frequency. Further, since there is no dependency on the font size in principle, it is clear that this is an effective method even for an original with a small number of characters.
[0071]
(Example 2)
In the first embodiment, the radical configuration adopted as the embedding target was a single pattern as shown in FIG. 5, but nothing is limited to this, as shown in FIG. A plurality of Chinese character patterns having radicals may be set simultaneously. In this case, the amount of embedded information further increases.
[0072]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, by utilizing the relative shape change of a character piece with respect to a document image including a character composed of a plurality of character pieces, the deterioration of the font is minimized. However, it is possible to secure a certain degree of information embedding accuracy and amount by sorting the target characters based on the appearance frequency, and to realize a digital watermark device having high noise resistance even at the time of reading. Further, since there is no dependency on the font size in principle, it is clear that this is an effective method even for an original with a small number of characters.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 (a) is a block diagram showing a schematic configuration of a digital watermark embedding unit of a digital watermark apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 1 (b) is an electronic diagram of a digital watermark apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing a schematic configuration of a watermark reading unit. FIG. 2 is an overall flow chart when the processor 4 embeds a digital watermark in one document. FIG. 3 shows that the
FIG. 8 is an explanatory diagram of a conventional technique. FIG. 9 is an explanatory diagram of a conventional technique. FIG. 10 is an explanatory diagram of a conventional technique.
2 Image input means (input unit)
4 processor 6
22 Image input means (input unit)
24
Claims (11)
前記文書画像から文字を抽出する抽出手段と、 Extraction means for extracting characters from the document image;
前記抽出手段により抽出された文字のうち、文字の文字片構成が所定の構成をとる文字を選択する選択手段と、 A selection means for selecting a character whose character fragment configuration has a predetermined configuration among the characters extracted by the extraction means;
前記選択手段により選択された文字の文字片の相対形状を変化させることで、前記選択された文字に透かし情報を埋め込む埋め込み手段を備えることを特徴とする画像処理装置。 An image processing apparatus comprising: an embedding unit that embeds watermark information in the selected character by changing a relative shape of a character piece selected by the selecting unit.
前記文書画像から文字ブロックを抽出する文字ブロック抽出手段と、 A character block extracting means for extracting a character block from the document image;
前記文字ブロック抽出手段により抽出された文字ブロックに含まれる文字に対して文字認識を行い、認識結果として文字コードを生成し、前記文字の画像を前記文字ブロックから抽出する文字認識手段を備えることを特徴とする請求項1に記載の画像処理装置。 Character recognition is performed for characters included in the character block extracted by the character block extraction means, a character code is generated as a recognition result, and character recognition means for extracting an image of the character from the character block is provided. The image processing apparatus according to claim 1, wherein:
前記カウント手段によるカウント数が所定のカウント数以上である文字の数が一定数以上である場合に、前記埋め込み手段は前記選択手段により選択された文字に前記透かし情報を埋め込むことを特徴とする請求項1又は2に記載の画像処理装置。 The embedding unit embeds the watermark information in the character selected by the selecting unit when the number of characters whose count by the counting unit is equal to or greater than a predetermined number. Item 3. The image processing apparatus according to Item 1 or 2.
前記文書画像から文字を抽出する文字抽出手段と、 Character extraction means for extracting characters from the document image;
前記文字抽出手段により抽出された文字のうち、文字の文字片構成が所定の構成をとる文字を選択する選択手段と、 A selection means for selecting a character whose character fragment configuration has a predetermined configuration among the characters extracted by the character extraction means;
前記選択手段が選択した文字の文字片の相対形状に基づいて、前記透かし情報を抽出する透かし情報抽出手段を備えることを特徴とする画像処理装置。 An image processing apparatus comprising: watermark information extraction means for extracting the watermark information based on a relative shape of a character piece selected by the selection means.
前記文書画像から文字ブロックを抽出する文字ブロック抽出手段と、A character block extracting means for extracting a character block from the document image;
前記文字ブロック抽出手段により抽出された文字ブロックに含まれる文字に対して文字認識を行い、認識結果として文字コードを生成し、前記文字の画像を前記文字ブロックから抽出する文字認識手段を備えることを特徴とする請求項6に記載の画像処理装置。Character recognition is performed for characters included in the character block extracted by the character block extraction means, a character code is generated as a recognition result, and character recognition means for extracting an image of the character from the character block is provided. The image processing apparatus according to claim 6.
前記文書画像から文字を抽出する抽出工程と、 An extraction step of extracting characters from the document image;
前記抽出工程で抽出された文字のうち、文字の文字片構成が所定の構成をとる文字を選択する選択工程と、 Among the characters extracted in the extraction step, a selection step of selecting a character whose character fragment configuration has a predetermined configuration;
前記選択手段により選択された文字の文字片の相対形状を変化させることで、前記選択された文字に透かし情報を埋め込む埋め込み工程を備えることを特徴とする画像処理方法。 An image processing method comprising: an embedding step of embedding watermark information in the selected character by changing a relative shape of a character piece of the character selected by the selection means.
前記文書画像から文字を抽出する文字抽出工程と、 A character extraction step of extracting characters from the document image;
前記文字抽出工程で抽出された文字のうち、文字の文字片構成が所定の構成をとる文字を選択する選択工程と、 Of the characters extracted in the character extraction step, a selection step of selecting a character whose character fragment configuration has a predetermined configuration;
前記選択手段が選択した文字の文字片の相対形状に基づいて、前記透かし情報を抽出する透かし情報抽出工程を備えることを特徴とする画像処理方法。 An image processing method comprising: a watermark information extraction step for extracting the watermark information based on a relative shape of a character piece selected by the selection means.
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001386137A JP3848150B2 (en) | 2001-12-19 | 2001-12-19 | Image processing apparatus and method |
| CNB021419965A CN1226860C (en) | 2001-09-03 | 2002-09-02 | Image processing apparatus and image processing method and program and storage media |
| KR10-2002-0052878A KR100485554B1 (en) | 2001-09-03 | 2002-09-03 | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and recording medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001386137A JP3848150B2 (en) | 2001-12-19 | 2001-12-19 | Image processing apparatus and method |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2003189085A JP2003189085A (en) | 2003-07-04 |
| JP2003189085A5 JP2003189085A5 (en) | 2005-07-14 |
| JP3848150B2 true JP3848150B2 (en) | 2006-11-22 |
Family
ID=27595371
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001386137A Expired - Fee Related JP3848150B2 (en) | 2001-09-03 | 2001-12-19 | Image processing apparatus and method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3848150B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4772888B2 (en) * | 2009-03-27 | 2011-09-14 | シャープ株式会社 | Image processing apparatus, image forming apparatus, image processing method, program, and recording medium thereof |
| JP5598120B2 (en) * | 2010-06-30 | 2014-10-01 | 株式会社リコー | Image processing device |
-
2001
- 2001-12-19 JP JP2001386137A patent/JP3848150B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2003189085A (en) | 2003-07-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1956823B1 (en) | A method and device for embedding digital watermark into a text document and detecting it | |
| JP4136731B2 (en) | Information processing method and apparatus, computer program, and computer-readable storage medium | |
| JP4854491B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus and control method thereof | |
| JP4343968B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus and method | |
| US20090021793A1 (en) | Image processing device, image processing method, program for executing image processing method, and storage medium for storing program | |
| CN100505821C (en) | Image processing apparatus, method for controlling same | |
| JP2004265384A (en) | Image processing system, information processing device, control method, computer program, and computer-readable storage medium | |
| KR20060003027A (en) | Watermark information detection method | |
| JP2004334339A (en) | Information processor, information processing method, and storage medium, and program | |
| US7411702B2 (en) | Method, apparatus, and computer program product for embedding digital watermark, and method, apparatus, and computer program product for extracting digital watermark | |
| Tan et al. | Print-Scan Resilient Text Image Watermarking Based on Stroke Direction Modulation for Chinese Document Authentication. | |
| JP4227432B2 (en) | Image processing method | |
| US8351086B2 (en) | Two-dimensional code generating device | |
| WO2008052430A1 (en) | Method of digital watermark embedding and extracting and device thereof | |
| JP4327188B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP3848150B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus and method | |
| JP3833154B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, program, and storage medium | |
| KR100485554B1 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and recording medium | |
| JP4164458B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus and method, computer program, and computer-readable storage medium | |
| JP2005149097A (en) | Image processing system and image processing method | |
| JP4185858B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, control method therefor, and program | |
| JP2004334340A (en) | Image processing method and device | |
| JP3943925B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for embedding a digital watermark in a document file | |
| JP2007166333A (en) | Apparatus and method for processing image | |
| JP2004336220A (en) | Apparatus and method for image generating image recording medium, and image generating program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20041117 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20041117 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20060719 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20060815 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20060824 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20090901 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100901 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110901 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110901 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120901 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120901 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130901 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |