JP3633054B2 - Hot water storage water heater - Google Patents
Hot water storage water heater Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3633054B2 JP3633054B2 JP24287095A JP24287095A JP3633054B2 JP 3633054 B2 JP3633054 B2 JP 3633054B2 JP 24287095 A JP24287095 A JP 24287095A JP 24287095 A JP24287095 A JP 24287095A JP 3633054 B2 JP3633054 B2 JP 3633054B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- hot water
- heater
- bath
- temperature
- water storage
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Control For Baths (AREA)
- Heat-Pump Type And Storage Water Heaters (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【産業上の利用分野】
本発明は風呂保温機能付きの貯湯式給湯装置に関するものである。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
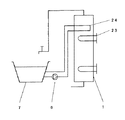
従来、この種の貯湯式給湯装置の第1の例のとしては実開平5−73453号公報に示すようなものがある。図9において、風呂加熱用熱交換器24および追い焚き用ヒータ23を貯湯槽1の上部に設け、風呂加熱用熱交換器24に導びかれてくる湯を追い焚き用ヒータ23で所定温度まで再加熱するようになっている。
【0003】
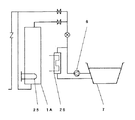
また、第2の例としては特開平5−1847号公報に示すようなものもある。図10において、ヒータ25で加熱する電気温水器1Aと、浴槽7の水を加熱する追い焚きヒータ26と追い焚きヒータ26に浴槽水を循環するポンプ6とを備え、この追い焚きヒータ26で風呂の追い焚きを行うようになっている。
【0004】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、上記従来の第1の例の構成では、貯湯槽からの出湯と風呂加熱運転が同時に行われると熱交換器24近傍の貯湯湯温は低下して出湯温度が下がり、湯の使い勝手が悪い。また、湯が大量に使用された場合には、追い焚き用ヒータ23の上部の水温が風呂加熱可能な温度まで昇温するのに時間を要するため、追い焚きに時間がかかる。
【0005】
また、第2の例の構成では、電気温水器1Aのヒータ25と風呂の追い焚き用ヒータ26を配設しているため、機器のコストが高くなるとともに電源の接続工事も多くなる。また、電気容量の観点から、ヒータ25と風呂の追い焚き用ヒータ26とは同時に通電しない制御が必要となる。
【0006】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明は上記従来の課題を解決するもので、貯湯槽と、加熱器と、風呂用加熱器と、循環ポンプとを有し、前記加熱器により加熱された湯を前記循環ポンプにより前記貯湯槽に貯湯する貯湯運転と、前記加熱器により加熱された湯を前記循環ポンプにより前記風呂用加熱器に流入させることにより浴槽の水を加熱する風呂保温加熱運転とを流路切換手段により切り換え可能としたものであって、前記加熱器の出口湯温は貯湯運転時より風呂保温加熱運転時の方が低くなるように制御するものである。
【0007】
また、請求項1記載の発明に加え、貯湯運転時と風呂保温加熱運転時とで循環ポンプの回転数を変化させるものである。
【0008】
また、昼間電力の消費量を少なくして、電力負荷の平準化をはかり、同様に蓄熱剤の耐久性向上をはかるため、加熱器の下流に設けられた温度検知器と、流路切換手段の流路方向が貯湯槽側の場合には前記温度検知器の検出温度が第1の温度となるように循環ポンプの回転数を制御し、前記流路切換手段の流路方向が風呂用加熱器側の場合には前記温度検知器の検出温度が前記第1の温度より低い第2の温度となるように循環ポンプの回転数を制御する回転数制御器とを備えたものである。
【0009】
また、同様に配管の凍結防止をはかるため、循環ポンプ、加熱器、流路切換手段、風呂用加熱器を接続した循環回路途中に設けられた温度検知器と、前記温度検知器が循環回路内の水が凍結温度に達したことを検出すると前記循環ポンプを通電するとともに前記流路切換手段の流路方向を前記風呂用加熱器側に切り換える制御を行う制御器とを備えたものである。
【0010】
また、同様に貯湯運転を開始した場合に貯湯槽の残湯温度が低下することを防止するため、加熱器の下流に設けられた温度検知器と、運転開始後に前記温度検知器の信号を受けて流路切換手段の流路方向を貯湯槽側に切り換える制御を行う制御器と、風呂用加熱器と熱交換関係を有する蓄熱熱交換器を備えたものである。
【0011】
また、同様に貯湯熱量の向上をはかるため、加熱器の下流に設けられを有し、貯湯運転終了間近になると、貯湯運転から風呂保温加熱運転へ切り換え制御する制御器とを備えたものである。
【0012】
また、昼間電力の消費量を少なくして、電力負荷の平準化をはかるため、請求項1〜4いずれか1項に記載の発明に加え、風呂用加熱器と熱交換関係を有する蓄熱熱交換器を備えたものである。
【0013】
また、前述の構成に加え、風呂保温加熱能力を確保するため、蓄熱熱交換器に設けた温度検知器と、前記温度検知器の信号を受けて加熱器を通電するとともに流路切換手段の流路方向を風呂用加熱器側に接続する制御器とを備えたものである。
【0014】
【作用】
上記第1、2の構成によると、貯湯運転時は、貯湯槽下部から流入した低温の水は加熱器で所定温度に加熱され、流路切換手段を通って貯湯槽の上部に貯湯される。また、風呂保温加熱運転時には、加熱器で加熱された水が流路切換手段を通り、風呂用加熱器に流入し、ここで風呂循環用の水を加熱する。そして、温度低下した水は循環ポンプを通り、再度加熱器に流入し昇温される。従って、風呂の保温加熱運転中に貯湯槽から出湯されても出湯温度は変化しない。また、貯湯槽を沸き上げる大能力の加熱器で風呂加熱運転を行うため、短時間で追い焚き保温加熱が可能となる。さらに、単一加熱器で貯湯および風呂保温加熱ができるため、機器のコンパクト化、低コスト化、省施工化がはかれる。
【0015】
上記第3の構成によれば、貯湯運転時は、流路切換手段の流路は加熱器から貯湯槽への流れ方向になっている。そして、加熱器の出口湯温が所定温度となるように制御器が温度検知器の第1信号(第1の温度)で循環ポンプの回転数を制御し、貯湯槽の上部に貯湯する。また、蓄熱運転時には、流路切換手段の流路は加熱器から風呂用加熱器への流れ方向になっている。そして、制御器は加熱器の出口湯温が第1信号より低温の第2信号(第2の温度)で循環ポンプの回転数を制御し、風呂用加熱器を介して蓄熱熱交換器を蓄熱する。従って、蓄熱剤の耐久性が確保できる所定温度で蓄熱できるようになり、信頼性が向上する。一方、貯湯運転時は高温湯が貯湯できるため、貯湯槽の小型化あるいは貯湯熱量の増大がはかれる。
【0016】
上記第4の構成によれば、冬季の運転停止時において、循環ポンプ、加熱器、流路切換手段、風呂用加熱器を接続した循環回路内の水が凍結温度に達したことを温度検知器が検出する。そして、制御器は温度検知器の信号を受けて循環ポンプを通電するとともに流路切換手段の流路を風呂用加熱器側に切り換え、蓄熱熱交換器から受熱しながら循環回路内の水を循環させる。したがって、冬季の運転停止時において凍結することもない。
【0017】
上記第5の構成によれば、運転開始後、加熱器から流出する湯温は少しづつ昇温し、所定温度に達したことを温度検知器が検出する。そして、制御器は温度検知器の信号を受けて流路切換手段を貯湯槽側に切り換える制御を行う。従って、運転開始時に貯湯温度に達しない中温水は蓄熱熱交換器に流入し、蓄熱を行い、所定温度に達した高温湯を貯湯槽の上部に流入させるため、残湯温度が低下することもない。
【0018】
上記第6の構成によれば、貯湯運転において、貯湯槽の下部から流出する給水された低温水を加熱器で加熱する。そして、加熱器の出口温度が温度検知器の第1信号(第1の温度)となるように回転数制御器は循環ポンプの回転数を制御し、所定温度の湯が貯湯槽の上部に流入し、上から次第に貯湯されていく。そして、この運転中に、貯湯槽内では貯湯槽上部から流入した湯と給水されている水が熱伝導をともない湯と水が混合した中温水の混合層を形成する。そして、貯湯運転終了間近になると、この混合層が貯湯槽から流出しはじめ、加熱器に流入する。そのため、加熱器の出口温度を一定にするため循環ポンプの回転数を増加させる制御を回転数制御器は行い、最大回転数まで運転を継続する。そして、さらに、高温湯が加熱器に流入しはじめると、加熱器の出口温度は上昇しはじめる。これを温度検知器の第2信号(第2の温度)が検出し、制御器に信号を送り、制御器は風呂用加熱器側に流路切換手段の流路を切り換える。よって、加熱器から流出した湯は流路切換手段を通り、風呂用加熱器に流入し、蓄熱熱交換器で蓄熱される。従って、貯湯槽には下部まで高温湯が貯湯され、その後に蓄熱運転に切り変わるため、給湯負荷を満足する貯湯熱量が確保できる。
【0019】
上記第7の構成によれば、深夜時間帯に加熱器で加熱した湯は風呂用加熱器に流入し、蓄熱熱交換器を蓄熱する。そして、昼間時間帯において、風呂保温加熱運転されると風呂循環用の水は蓄熱熱交換器に流入する。その際に蓄熱熱交換器は放熱して、循環水の加熱に利用される。よって、昼間時間帯に加熱器を運転することもなく、風呂保温加熱ができるため、昼間電力の消費量はなくなり、電力負荷の平準化が促進される。
【0020】
上記第8の構成によれば、蓄熱熱交換器の蓄熱熱量が低下したことを温度検知器が検出し、その信号を制御器に送る。そして、制御器は加熱器を通電するとともに流路切換手段の流路方向を風呂用加熱器に切り換える。よって、加熱器で加熱された水が風呂用加熱器に流入し、蓄熱熱交換器に蓄熱されるため、風呂加熱能力は常に確保される。
【0021】
【実施例】
以下本発明の第1の実施例を図1を参照して説明する。
【0022】
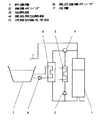
図1において、1は貯湯槽、2は循環ポンプ、3は加熱器であり、ヒータなどが熱源となっている。4は風呂用加熱器であり、循環ポンプ2および加熱器3と並列に設けられている。5は流路切換え手段であり、加熱器3の下流に設けられ、流路を貯湯槽1側あるいは風呂用加熱器4側に切換える。そして、貯湯槽1の下部、加熱器3、流路切換え手段5、貯湯槽1の上部は順次接続されて給湯回路を構成する。6は風呂循環ポンプであり、風呂用加熱器4と浴槽7の循環経路内の水を循環させる。
【0023】
上記構成において、最初に貯湯運転について述べる。貯湯槽1の下部の低温水は循環ポンプ2の作用で加熱器3に流入し、所定温度まで加熱される。そして、流路切換え手段5を通り、貯湯槽1の上部に流入し、貯湯される。この運転を繰り返しながら、貯湯槽1には上部からしだいに高温湯が貯湯されていく。次に、風呂保温加熱運転について述べる。この場合には、流路切換え手段5の流路方向は風呂用加熱器4側に切り換わっているため、加熱器3で加熱された湯は風呂用加熱器4に流入し、ここで、風呂循環ポンプ6から送られてきた浴槽7の水を加熱する。そして、風呂用加熱器4から流出した低温となった水は再度、加熱器3に流入し、加熱されて高温となる。この運転を繰り返しながら浴槽7の水温を所定温度に加熱する。
【0024】
従って、風呂の保温加熱運転中に貯湯槽1から出湯されても出湯温度は変化しない。また、貯湯槽1を沸き上げる大能力の加熱器3を用いて風呂保温加熱運転を行うため、追い焚き時間が短時間となる。さらに、単一加熱器で貯湯および風呂保温加熱ができるため、機器のコンパクト化、低コスト化、省施工化がはかれる。また、図2において、流路切換え手段5の代わりに、加熱器3から貯湯槽1の配管途中に第1開閉弁5A、加熱器3から風呂用加熱器4の配管途中に第2開閉弁5Bを設けて、貯湯運転時は第1開閉弁5Aを開放するとともに第2開閉弁5Bを閉止し、風呂の保温加熱運転時は第1開閉弁5Aを閉止するとともに第2開閉弁5Bを開放することによって同じ機能、作用が得られる。
【0025】
つぎに、第2の実施例について説明する。図3において、第1の実施例と同じ機能、動作するものについては同一符号で表し、説明は省略する。8は蓄熱熱交換器であり、風呂用加熱器4と熱交換関係を有し、風呂循環ポンプ6で送られてくる浴槽7の水を加熱する。
【0026】
上記構成において、最初に深夜時間帯における蓄熱運転について述べる。加熱器3で加熱された湯は風呂用加熱器4に流入し、風呂用加熱器4と熱交換関係にある蓄熱熱交換器8を蓄熱する。次に、昼間時間帯における風呂保温加熱運転について述べる。この場合には、風呂循環ポンプ6から送られてきた浴槽7の水は蓄熱熱交換器8に流入し、ここで蓄熱熱交換器8の熱を奪い昇温し、浴槽7にもどる。そしてこの運転を繰り返しながら、浴槽7内の湯は所定温度まで加熱される。従って、深夜時間帯に蓄熱された熱を昼間時間帯に風呂保温加熱に利用するため、昼間時間帯に加熱器3を運転する必要もなくなり、電力負荷の平準化がはかれる。
【0027】
次に、第3の実施例について説明する。図4において、第1、第2の実施例と同じ機能、動作するものについては同一符号で表し、説明は省略する。9は温度検知器であり、蓄熱熱交換器8に設けられ、ここの検出温度に基づき信号を発生する。10は制御器であり、温度検知器9の信号を受けて加熱器3を通電するとともに流路切換え手段5の流路方向を風呂用加熱器4側に切り換える。
【0028】
上記構成において、最初に風呂保温加熱運転について述べる。風呂循環ポンプ6から送られてきた浴槽7の水は蓄熱熱交換器8に流入し、ここで蓄熱熱交換器8の熱を奪い昇温し、浴槽7にもどる。この運転を繰り返しながら、浴槽7内の湯は所定温度まで加熱される。一方、熱を奪われた蓄熱熱交換器8は蓄熱熱量が低下すると温度が下がる。それを温度検知器9が検知し、その信号を制御器10に送り、加熱器3を通電するとともに、流路切換え手段5の流れ方向を風呂用加熱器4に切り換える。そして、加熱器3で加熱された湯は流路切換え手段5を通り、風呂用加熱器4に流入し、ここで風呂用加熱器4を介して蓄熱熱交換器8を蓄熱する。従って、常に蓄熱熱交換器8は蓄熱されているため、風呂保温加熱に必要な能力が確保される。
【0029】
次に第4の実施例について説明する。図5において、第1、第2および第3の実施例と同じ機能、動作するものについては同一符号で表し、説明は省略する。11は温度検知器であり、加熱器3の下流に設けられ、ここを流れる流体の検出温度に基づき第1の温度を示す第1信号と第1信号より低温の第2の温度を示す第2信号の複数の信号を発生する。12は制御器であり、流路切換え手段5の流路方向が貯湯槽1側の場合には温度検知器11の第1信号で、流路切換え手段5の流路方向が風呂用加熱器4側になっている場合には温度検知器11の第2信号で循環ポンプ2の回転数を制御する。
【0030】
上記構成において、最初に貯湯運転について述べる。この場合、流路切換手段5は加熱器3から貯湯槽1への流れ方向になっている。そして、制御器12は加熱器3の出口湯温が所定温度となるように温度検知器11の第1信号で循環ポンプ2の回転数を制御し、加熱器3から流出した高温湯を流路切換手段5を通り、貯湯槽1の上部に貯湯する。次に、蓄熱運転について述べる。この場合には、流路切換手段5は加熱器3から風呂用加熱器4への流れ方向になっている。そして、制御器12は加熱器3の出口湯温が第1信号より低温の第2信号で循環ポンプ2の回転数を制御し、流路切換手段5を通り、風呂用加熱器4に流入して、蓄熱熱交換器8を蓄熱する。そして、風呂用加熱器4から流出した水は加熱器3に再度流入して、加熱される。つまり、流路切換手段の流路方向が貯湯槽側の場合には第1の信号に基づく第1の温度となるように、前記流路切換手段の流路方向が風呂用加熱器側の場合には前記第1の温度より低い第2の信号に基づく第2の温度となるように循環ポンプの回転数を制御する。従って、貯湯運転時には高温で沸き上げることが可能であり、貯湯槽1の小型化あるいは貯湯熱量の増大がはかれる。また、蓄熱運転時には蓄熱剤の耐久性が確保できる所定温度で蓄熱できるため、信頼性が向上する。
【0031】
つぎに第5の実施例について説明する。図6において、第1、第2、第3および第4の実施例と同じ機能、動作するものについては同一符号で表し、説明は省略する。13は温度検知器であり、循環ポンプ2、加熱器3、流路切換手段5、風呂用加熱器5を接続した循環回路途中に設けられ、ここの温度を検出して信号を発生する。14は制御器であり、温度検知器13の信号を受けて循環ポンプ2を通電するとともに流路切換手段5の媒体流れ方向を風呂用加熱器4側に切り換える制御を行う。
【0032】
上記構成において、冬季の運転停止時において、循環ポンプ2、加熱器3、流路切換え手段5、風呂用加熱器4を接続した循環回路内の水が凍結温度に達したことを温度検知器13が検出する。そして、制御器14は温度検知器13の信号を受けて循環ポンプ2を通電するとともに流路切換手段5を風呂用加熱器4側に切り換え、蓄熱熱交換器8から受熱しながら循環回路内の水を循環させる。したがって、冬季の運転停止時において凍結することはない。
【0033】
つぎに第6の実施例について説明する。図7において、第1、第2、第3、第4および第5の実施例と同じ機能、動作するものについては同一符号で表し、説明は省略する。15は温度検知器であり、加熱器3の下流に設けられ、ここを流れる水の温度を検出して、信号を発生する。16は制御器であり、運転開始後に温度検知器15の信号を受けて流路切換手段5の媒体流れ方向を貯湯槽1側に切り換える制御を行う。
【0034】
上記構成において、運転開始後、加熱器3から流出する湯温は少しづつ昇温し、所定温度に達したことを温度検知器15が検出する。そして、制御器16は温度検知器15の信号を受けて流路切換え手段5を貯湯槽1側に切り換える制御を行う。そして、加熱器3で加熱された所定温度の湯が貯湯槽1に貯湯される。従って、運転開始時に貯湯温度に達しない中温水は蓄熱熱交換器8に流入し、蓄熱を行う。また、所定温度に達した高温湯が貯湯槽1の上部に流入するため、残湯温度が低下することはない。
【0035】
つぎに第7の実施例について説明する。図8において、第1、第2、第3、第4、第5および第6の実施例と同じ機能、動作するものについては同一符号で表し、説明は省略する。17は温度検知器であり、加熱器3の下流に設けられ、ここを流れる水の温度を検出する第1信号と第1信号より高温の第2信号の複数の信号を発生する。18は回転数制御器であり、温度検知器17の第1信号を受けて循環ポンプ2の回転数制御を行う。19は制御器であり、温度検知器17の第2信号を受けて流路切換え手段5の媒体流れ方向を風呂用加熱器4側に切り換える制御を行う。
【0036】
上記構成において、貯湯運転時、貯湯槽1の下部から流出する給水された低温水を加熱器3で加熱する。そして、加熱器3の出口温度が温度検知器17の第1信号となるように回転数制御器18は循環ポンプ2の回転数を制御し、所定温度の湯が貯湯槽1の上部に流入し、上から次第に貯湯されていく。そして、この運転中に、貯湯槽1内では上部から流入した湯と給水されている水が熱伝導をともない湯と水が混合した中温水の混合層を形成する。そして、沸き上げ運転終了間近になると、この混合層が貯湯槽1から流出しはじめ、加熱器3に流入する。そのため、加熱器3の出口温度を一定にするため循環ポンプ2の回転数を増加させる制御を回転数制御器18は行い、最大回転数まで運転を継続する。そして、さらに高温の湯が加熱器3に流入しはじめると、加熱器3の出口温度は上昇しはじめる。これを温度検知器17の第2信号が検出し、制御器19に信号を送り、制御器19は流路切換手段5の流路方向を風呂用加熱器4側に換える。よって、加熱器3から流出した湯は流路切換手段5を通り、風呂用加熱器4に流入し、蓄熱熱交換器8で蓄熱される。従って、貯湯槽1には下部まで高温湯が貯湯され、その後に蓄熱運転に切り変わるため、給湯負荷を満足する貯湯熱量が確保できる。
【0037】
【発明の効果】
以上の説明から明らかのように本発明の貯湯式給湯装置によれば、貯湯運転時は、貯湯槽下部から流入した低温の水は加熱器で所定温度に加熱され、流路切換手段を通って貯湯槽の上部に貯湯される。また、風用保温加熱運転時には、加熱器で加熱された水が流路切換手段を通り、風呂用加熱器に流入し、ここで風呂循環用の水を加熱する。そして、温度低下した風呂用加熱器から流出した水は循環ポンプを通り、再度、加熱器に流入し昇温される。従って、出湯中に風呂の保温加熱運転されても出湯温度は変化しない。
【0038】
そして、貯湯槽を沸き上げる大能力の加熱器で風呂保温加熱運転を行うため、追い焚き時間は短時間となり、さらに、単一加熱器で貯湯および風呂保温加熱ができるため、機器のコンパクト化、低コスト化、省施工化がはかれる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の第1の実施例における貯湯式給湯装置の構成図
【図2】同装置の流路切換手段を示す構成図
【図3】本発明の第2の実施例における貯湯式給湯装置の構成図
【図4】本発明の第3の実施例における貯湯式給湯装置の構成図
【図5】本発明の第4の実施例における貯湯式給湯装置の構成図
【図6】本発明の第5の実施例における貯湯式給湯装置の構成図
【図7】本発明の第6の実施例における貯湯式給湯装置の構成図
【図8】本発明の第7の実施例における貯湯式給湯装置の構成図
【図9】従来の貯湯式給湯装置の構成図
【図10】従来の他の貯湯式給湯装置の構成図
【符号の説明】
1 貯湯槽
2 循環ポンプ
3 加熱器
4 風呂用加熱器
5 流路切換え手段
5A 第1開閉弁
5B 第2開閉弁
6 風呂循環ポンプ
7 浴槽
8 蓄熱熱交換器
9、11、13、15、17 温度検知器
10、12、14、16、19 制御器
18 回転数制御器[0001]
[Industrial application fields]
The present invention relates to a hot water storage type hot water supply apparatus having a bath heat retaining function.
[0002]
[Prior art]
Conventionally, a first example of this type of hot water storage type hot water supply apparatus is shown in Japanese Utility Model Laid-Open No. 5-73453. In FIG. 9, a bath
[0003]
A second example is disclosed in Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 5-1847. In FIG. 10, an
[0004]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, in the configuration of the first conventional example described above, when the hot water from the hot water storage tank and the bath heating operation are performed simultaneously, the hot water temperature in the vicinity of the
[0005]
Further, in the configuration of the second example, since the
[0006]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The present invention solves the above-described conventional problems, and includes a hot water storage tank, a heater, a bath heater, and a circulation pump, and hot water heated by the heater is supplied to the hot water storage tank by the circulation pump. It is possible to switch between the hot water storage operation for storing hot water and the bath heat insulation heating operation for heating the water in the bathtub by flowing the hot water heated by the heater into the bath heater by the circulation pump. Therefore, the outlet hot water temperature of the heater is controlled so as to be lower during the bath heat insulation heating operation than during the hot water storage operation .
[0007]
Further, in addition to the invention described in
[0008]
Moreover, by reducing the consumption of daytime power, measure the leveling power load, for improving the durability of the same heat storage agent, and temperature detector provided downstream of the heater, the passage switching device When the direction of the flow path is on the hot water storage tank side, the rotational speed of the circulation pump is controlled so that the temperature detected by the temperature detector becomes the first temperature, and the flow path direction of the flow path switching means is the heating for the bath. In the case of the vessel side, a rotation speed controller for controlling the rotation speed of the circulation pump so that the temperature detected by the temperature detector becomes a second temperature lower than the first temperature is provided.
[0009]
Similarly, in order to prevent the pipe from freezing, a temperature detector provided in the circulation circuit to which a circulation pump, a heater, a flow path switching means, a bath heater are connected, and the temperature detector are disposed in the circulation circuit. And a controller for controlling to switch the flow path direction of the flow path switching means to the bath heater side when energizing the circulating pump when it is detected that the water has reached the freezing temperature .
[0010]
Similarly, in order to prevent the remaining hot water temperature in the hot water tank from decreasing when the hot water storage operation is started, a temperature detector provided downstream of the heater and a signal from the temperature detector after the start of operation are received. And a heat storage heat exchanger having a heat exchange relationship with the bath heater and a controller for controlling the flow direction of the flow path switching means to the hot water storage tank side.
[0011]
Similarly, in order to improve the amount of heat stored in the hot water, it is provided downstream of the heater and includes a controller that controls switching from the hot water storage operation to the bath heat insulation heating operation when the hot water storage operation is about to end. .
[0012]
In addition to reducing the amount of daytime power consumption and leveling the power load, in addition to the invention according to any one of
[0013]
In addition to the above-described configuration, in order to ensure the bath heat-retention capability, the temperature detector provided in the heat storage heat exchanger, and the heater is energized in response to the signal from the temperature detector, and the flow of the flow path switching means. And a controller for connecting the road direction to the bath heater side.
[0014]
[Action]
According to the first and second configurations, during the hot water storage operation, the low-temperature water flowing from the lower part of the hot water tank is heated to a predetermined temperature by the heater, and is stored in the upper part of the hot water tank through the flow path switching means. Moreover, at the time of bath insulation heating operation, the water heated by the heater passes through the flow path switching means and flows into the bath heater, where the water for bath circulation is heated. Then, the water whose temperature has decreased passes through the circulation pump and flows into the heater again to be heated. Therefore, even if the hot water is discharged from the hot water storage tank during the heat insulation and heating operation of the bath, the hot water temperature does not change. In addition, since the bath heating operation is performed with a large-capacity heater that boils the hot water storage tank, it is possible to reheat and keep warm in a short time. Furthermore, since the hot water can be stored and the bath can be heated with a single heater, the device can be made compact, low in cost and reduced in construction.
[0015]
According to the third configuration, during the hot water storage operation, the flow path of the flow path switching means is in the flow direction from the heater to the hot water storage tank. And a controller controls the rotation speed of a circulation pump with the 1st signal (1st temperature) of a temperature detector so that the outlet hot water temperature of a heater may become predetermined temperature, and stores hot water on the upper part of a hot water storage tank. Further, during the heat storage operation, the flow path of the flow path switching means is in the flow direction from the heater to the bath heater. The controller controls the number of rotations of the circulation pump with the second signal (second temperature) at which the outlet hot water temperature of the heater is lower than the first signal, and stores the heat storage heat exchanger via the bath heater. To do. Therefore, heat can be stored at a predetermined temperature at which the durability of the heat storage agent can be ensured, and the reliability is improved. On the other hand, since hot water can be stored during hot water storage operation, the hot water tank can be downsized or the amount of stored hot water can be increased.
[0016]
According to the fourth configuration, when the operation is stopped in winter, the temperature detector indicates that the water in the circulation circuit connected to the circulation pump, the heater, the flow path switching means, and the bath heater has reached the freezing temperature. Will detect. The controller receives a signal from the temperature detector, energizes the circulation pump, switches the flow path of the flow path switching means to the bath heater side, and circulates water in the circulation circuit while receiving heat from the heat storage heat exchanger. Let Therefore, it does not freeze when the operation is stopped in winter.
[0017]
According to the fifth configuration, the temperature of the hot water flowing out of the heater gradually increases after the operation is started, and the temperature detector detects that the temperature has reached a predetermined temperature. And a controller performs control which receives the signal of a temperature detector and switches a flow-path switching means to the hot water storage tank side. Therefore, the hot water that does not reach the hot water storage temperature at the start of operation flows into the heat storage heat exchanger, stores the heat, and the hot water that has reached the predetermined temperature flows into the upper part of the hot water storage tank. Absent.
[0018]
According to the sixth configuration, in the hot water storage operation, the supplied low-temperature water flowing out from the lower part of the hot water tank is heated by the heater. Then, the rotation speed controller controls the rotation speed of the circulation pump so that the outlet temperature of the heater becomes the first signal (first temperature) of the temperature detector, and hot water of a predetermined temperature flows into the upper part of the hot water tank. The hot water is gradually stored from above. During this operation, the hot water flowing in from the upper part of the hot water storage tank and the supplied water form a mixed layer of hot water and water with heat conduction in the hot water storage tank. When the hot water storage operation is about to end, the mixed layer begins to flow out of the hot water tank and flows into the heater. Therefore, the rotation speed controller performs control to increase the rotation speed of the circulation pump in order to make the outlet temperature of the heater constant, and the operation is continued up to the maximum rotation speed. Further, when hot water starts to flow into the heater, the outlet temperature of the heater starts to rise. This is detected by the second signal (second temperature) of the temperature detector, and a signal is sent to the controller. The controller switches the flow path of the flow path switching means to the bath heater side. Therefore, the hot water flowing out from the heater passes through the flow path switching means, flows into the bath heater, and is stored in the heat storage heat exchanger. Therefore, hot water is stored in the hot water storage tank up to the lower part and then switched to the heat storage operation, so that the amount of stored hot water satisfying the hot water supply load can be secured.
[0019]
According to the said 7th structure, the hot water heated with the heater at midnight time flows in into the heater for baths, and heat-stores a thermal storage heat exchanger. In the daytime period, when the bath is kept warm and heated, the water for bath circulation flows into the heat storage heat exchanger. At that time, the heat storage heat exchanger dissipates heat and is used for heating the circulating water. Therefore, since the bath can be kept warm without operating the heater during the daytime, the consumption of daytime power is eliminated and the leveling of the power load is promoted.
[0020]
According to the eighth configuration, the temperature detector detects that the amount of heat stored in the heat storage heat exchanger has decreased, and sends the signal to the controller. Then, the controller energizes the heater and switches the channel direction of the channel switching means to the bath heater. Therefore, water heated by the heater flows into the bath heater and is stored in the heat storage heat exchanger, so that the bath heating capability is always ensured.
[0021]
【Example】
A first embodiment of the present invention will be described below with reference to FIG.
[0022]
In FIG. 1, 1 is a hot water tank, 2 is a circulation pump, 3 is a heater, and a heater or the like serves as a heat source.
[0023]
In the above configuration, the hot water storage operation will be described first. The low temperature water in the lower part of the
[0024]
Therefore, even if the hot water is discharged from the hot
[0025]
Next, a second embodiment will be described. In FIG. 3, the same functions and operations as those of the first embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals, and description thereof is omitted. A heat
[0026]
In the above configuration, the heat storage operation in the midnight time zone will be described first. Hot water heated by the
[0027]
Next, a third embodiment will be described. In FIG. 4, the same functions and operations as those in the first and second embodiments are denoted by the same reference numerals, and the description thereof is omitted. A
[0028]
In the above configuration, first, the bath insulation heating operation will be described. The water in the
[0029]
Next, a fourth embodiment will be described. In FIG. 5, the same functions and operations as those of the first, second and third embodiments are denoted by the same reference numerals, and the description thereof is omitted.
[0030]
In the above configuration, the hot water storage operation will be described first. In this case, the flow path switching means 5 is in the flow direction from the
[0031]
Next, a fifth embodiment will be described. In FIG. 6, the same functions and operations as those of the first, second, third and fourth embodiments are denoted by the same reference numerals, and description thereof is omitted. A
[0032]
In the above configuration, when the operation is stopped in winter, the
[0033]
Next, a sixth embodiment will be described. In FIG. 7, the same functions and operations as those of the first, second, third, fourth and fifth embodiments are denoted by the same reference numerals, and description thereof is omitted. A
[0034]
In the above configuration, the temperature of the hot water flowing out of the
[0035]
Next, a seventh embodiment will be described. In FIG. 8, the same functions and operations as those of the first, second, third, fourth, fifth and sixth embodiments are denoted by the same reference numerals, and description thereof is omitted. A
[0036]
In the above-described configuration, the supplied low-temperature water flowing out from the lower part of the
[0037]
【The invention's effect】
As is apparent from the above description, according to the hot water storage type hot water supply apparatus of the present invention, during hot water storage operation, the low-temperature water flowing from the lower part of the hot water storage tank is heated to a predetermined temperature by the heater and passes through the flow path switching means. Hot water is stored in the upper part of the hot water tank. Further, at the time of the heat insulation heating operation for wind, the water heated by the heater passes through the flow path switching means and flows into the bath heater, where the water for bath circulation is heated. And the water which flowed out from the heater for baths which temperature fell passes through a circulation pump, flows into a heater again, and is heated up. Therefore, even if the bath is kept warm and heated during the hot water, the hot water temperature does not change.
[0038]
And since the bath heat insulation heating operation is performed with a large capacity heater that boils the hot water storage tank, the reheating time is short, and furthermore, the hot water storage and bath heat insulation heating can be performed with a single heater, so the equipment is made compact. Cost reduction and saving work can be achieved.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a configuration diagram of a hot water storage type hot water supply apparatus in a first embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 2 is a configuration diagram showing flow path switching means of the apparatus. FIG. 3 is a hot water storage type in a second embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 4 is a block diagram of a hot water storage type hot water supply apparatus in the third embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 5 is a block diagram of a hot water storage type hot water supply apparatus in the fourth embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 7 is a block diagram of a hot water storage type hot water supply apparatus according to the fifth embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 8 is a block diagram of a hot water storage type hot water supply apparatus according to the sixth embodiment of the present invention. Fig. 9 is a block diagram of a conventional hot water storage type hot water supply device. Fig. 10 is a block diagram of another conventional hot water storage type hot water supply device.
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (8)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP24287095A JP3633054B2 (en) | 1995-09-21 | 1995-09-21 | Hot water storage water heater |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP24287095A JP3633054B2 (en) | 1995-09-21 | 1995-09-21 | Hot water storage water heater |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JPH0989369A JPH0989369A (en) | 1997-04-04 |
| JP3633054B2 true JP3633054B2 (en) | 2005-03-30 |
Family
ID=17095473
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP24287095A Expired - Fee Related JP3633054B2 (en) | 1995-09-21 | 1995-09-21 | Hot water storage water heater |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3633054B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4849524B2 (en) * | 2006-04-03 | 2012-01-11 | 東芝キヤリア株式会社 | Water heater |
-
1995
- 1995-09-21 JP JP24287095A patent/JP3633054B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPH0989369A (en) | 1997-04-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4893070B2 (en) | Return hot water recovery method and hot water supply system | |
| JP5305714B2 (en) | Hot water heating system | |
| JP2004144327A (en) | Hot water storage type water heater | |
| JP3887781B2 (en) | Heat pump water heater | |
| JP3651942B2 (en) | Water heater | |
| JP3633054B2 (en) | Hot water storage water heater | |
| JP3740718B2 (en) | Hot water storage water heater | |
| JP2004257692A (en) | Water heater | |
| JP4710511B2 (en) | Hot water storage water heater | |
| JP3848142B2 (en) | Heat exchange heat storage control method and heat exchange heat storage device | |
| JP3888117B2 (en) | Hot water storage water heater | |
| JP5087417B2 (en) | Hot water storage water heater | |
| JP2002147870A (en) | Solar water heater | |
| JP4138712B2 (en) | Hot water storage hot water system | |
| JP3589118B2 (en) | Hot water storage type electric water heater | |
| JP4515883B2 (en) | Hot water storage water heater | |
| JP3034389B2 (en) | Electric water heater | |
| JP2004156845A (en) | Heat pump water heater device | |
| JP3930835B2 (en) | Multi-function heat pump hot water supply system | |
| JP5226622B2 (en) | Bath equipment | |
| JP4423440B2 (en) | Heat recovery system | |
| JP3901108B2 (en) | Hot water storage water heater | |
| JP4148909B2 (en) | Heat pump water heater / heater | |
| JP3920161B2 (en) | Hot water storage hot water heater | |
| JP4055695B2 (en) | Heat pump water heater |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20040402 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20040420 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20040727 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20040924 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20041207 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20041220 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20080107 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20090107 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100107 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110107 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |