JP3624583B2 - Manufacturing method of electrode plate for sealed lead-acid battery - Google Patents
Manufacturing method of electrode plate for sealed lead-acid battery Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3624583B2 JP3624583B2 JP28537296A JP28537296A JP3624583B2 JP 3624583 B2 JP3624583 B2 JP 3624583B2 JP 28537296 A JP28537296 A JP 28537296A JP 28537296 A JP28537296 A JP 28537296A JP 3624583 B2 JP3624583 B2 JP 3624583B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- electrode plate
- glass
- battery
- present
- sealed lead
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/10—Energy storage using batteries
Landscapes
- Battery Electrode And Active Subsutance (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、密閉形鉛蓄電池用ペースト式極板とその製造方法に関するものである。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
従来、鉛蓄電池を密閉化する場合、正・負極板間に微細なガラスマットを配置して、このガラスマットに電解液を保持させるリテーナ方式とSiO2 等の無機酸化物を添加したゾル状の希硫酸を電池内でゲル化させ電解液の非流動化を図るゲル電解液方式の2種類が存在するが、現在は主にリテーナ方式が採用されている。
【0003】
リテーナ方式においては、電池組み立て時に高い圧力で極板群を組み立て極板表面の凹凸に従いガラスマットの表面に凹凸を形成させ、極板表面とガラスマットの接触を良好にしている。しかし、このような極群を電槽内へ収納し電解液を注液すると、ガラス繊維の毛細管現象により極板表面とガラスマットの接触性が低下する。また、電池の充電中のガス発生や、充放電サイクル中の電解液の減液により極群の圧力低下が見られ、極板表面とセパレータとのイオン伝導率が低下し、放電容量が低下するという問題を有している。この様な問題を解決するため実開昭57−192065にて極板表面に耐酸性を有する繊維を付着した密閉形鉛蓄電池が提案されている。
【0004】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかし、上記提案の極板は、極板表面に耐酸性の繊維を吹き付け、またはばらまき等で付着させ、プレスしたもので、乾燥工程や電池の充放電により、極板表面と繊維の結合力が低下し、イオン伝導率が低下する問題点を有していた。
【0005】
本発明は、上記問題点に鑑みてなされたものであって、その目的とするところは、極板の乾燥工程や電池に組み込み充放電した場合に、極板表面と極板表面のガラス繊維との結合力が低下しない密閉形鉛蓄電池用極板とその製造法を提供することにある。
【0006】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上記目的を達成するために本発明の極板は、ガラス繊維が極板表面に起毛状に埋設され、該ガラス繊維と該ガラス繊維より細いガラス繊維が極板表面で交差結合していることを特徴とするものである。
【0007】
また、本発明の製造方法は、ガラス繊維を裁断したガラスチョップを極板表面に起毛状に埋設し、次いで、前記ガラスチョップ間に耐酸性を有する有機バインダーと該ガラスチョップより細いガラス繊維とを含むエマルジョンを含浸させ、この極板を乾燥工程で加熱し、ガラスチョップと細ガラス繊維の交点、および細ガラス繊維同士の交点を結合させることを特徴とするものである。
【0008】
【作用】
ガラス繊維が極板表面に埋設されているので、乾燥工程などで該ガラス繊維と極板との結合力が低下することがない。また、極板表面のガラス繊維と細いガラス繊維がガラスマットと接触するので、極群の圧力が低下しても極板とガラスマットの間のイオン伝導率の低下が抑制される。
【0009】
さらに、ガラス繊維と細いガラス繊維、および細いガラス繊維同士が有機バインダーを加熱して結合しているので、結合力が優れ、乾燥工程などで分離することがない。
【0010】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明の一実施形態について図面を参考にしながら説明する。
【0011】
図1は本発明の製造方法を示す説明図、図2は本発明の極板の一実施形態を示す一部拡大断面図である。
【0012】
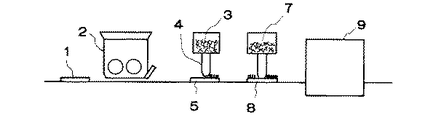
図1のように、集電体1をペースト状活物質が充填されている充填機2の下部を通過させ、集電体1にペースト状活物質を充填する。その後、予め含珪酸塩ガラス繊維を裁断した直径5〜30μm、長さ約1〜1.5mmのチョップ状のガラス繊維(以下、ガラスチョップと称する。)3をエアガン4により極板5表面に噴射し、ガラスチョップ3を極板5に埋設する。次いで、該ガラスチョップ3間に耐酸性を有する有機バインダー及び0.3〜1.0μmの細いガラス繊維6を含むエマルジョン7を極板8に含浸させ、乾燥機9に送る。乾燥機9で温度100〜300℃にて加熱しバインダーを融解させ、細いガラス繊維6とガラスチョップ3同士および細いガラス繊維6,6同士の交点を接着させる。その後、該極板を反転して裏面にもガラスチョップ3を埋設し、該ガラスチョップ3の間に前記エマルジョン7を含浸させて乾燥する。このようにして図2のような本発明の極板10を作製する。
【0013】
この極板10を用いて公称仕様12V−60Ahの密閉形鉛蓄電池を作製し、従来製法の極板(極板表面にガラス繊維が付着していない極板)を用いた密閉形鉛蓄電池も同時に作製し、サイクル寿命試験に供した。サイクル寿命試験は3時間率電流にて2.4時間放電し、充電は放電容量の110%とした。図3に寿命試験中の3時間率容量試験の推移を示す。
【0014】
また、図4に寿命試験中の3CA放電電流(Cは定格容量値)による高率放電容量試験結果を示す。
【0015】
なお、図3、図4の容量は、電池Aの初期容量を100%とした時の比率で表している。
【0016】
図3から分かる様に本発明に係る電池Aの寿命特性は従来の電池Bより優れていた。また、図4より高率放電性能については本発明に係る電池Aと従来電池Bとの差は顕著である。
【0017】
図5に寿命試験中の内部抵抗の変化を示すが、本発明に係る電池Aの内部抵抗増加率は従来電池B品に比べ低く、これが高率放電性能へ大きく影響していると思われる。なお、内部抵抗は電池Bの初期値を100として%表示してある。
【0018】
【発明の効果】
以上のように本発明の極板は、ガラス繊維が極板表面に起毛状に埋設され、該ガラス繊維と細いガラス繊維が交差結合しているので、これらガラス繊維が極板表面から容易に離れ落ちることがなく、本発明の極板を用いた密閉形鉛蓄電池は優れた寿命性能を示す。
【0019】
また、本発明の方法によれば、ガラス繊維と細いガラス繊維とを強固に結合できる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の方法を示す説明図である。
【図2】本発明の極板の一実施形態を示す一部拡大断面図である。
【図3】本発明による電池Aと従来の電池Bの3時間率容量試験の結果を示すグラフである。
【図4】本発明による電池Aと従来の電池Bの高率放電容量試験の結果を示すグラフである。
【図5】本発明による電池Aと従来の電池Bの高率放電容量試験中の内部抵抗の変化を示すグラフである。
【符号の説明】
3 ガラスチョップ
5,8,10 極板
6 細いガラス繊維
7 エマルジョン[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a paste-type electrode plate for a sealed lead-acid battery and a method for producing the same.
[0002]
[Prior art]
Conventionally, when sealing a lead-acid battery, a fine glass mat is disposed between the positive and negative electrode plates, and a retainer method for holding an electrolytic solution on the glass mat and a sol-like form added with an inorganic oxide such as SiO 2 There are two types of gel electrolyte solutions, in which dilute sulfuric acid is gelled in the battery to make the electrolyte non-fluid, but currently the retainer method is mainly used.
[0003]
In the retainer system, the electrode plate group is assembled at a high pressure during battery assembly, and irregularities are formed on the surface of the glass mat in accordance with the irregularities on the surface of the electrode plate, so that the contact between the electrode plate surface and the glass mat is improved. However, when such an electrode group is accommodated in a battery case and an electrolyte solution is injected, the contact between the electrode plate surface and the glass mat decreases due to the capillary action of glass fibers. In addition, the pressure of the electrode group is reduced due to gas generation during charging of the battery and reduction of the electrolyte during the charge / discharge cycle, the ionic conductivity between the electrode plate surface and the separator is reduced, and the discharge capacity is reduced. Has the problem. In order to solve such problems, Japanese Utility Model Laid-Open No. 57-192065 proposes a sealed lead-acid battery in which acid-resistant fibers are attached to the electrode plate surface.
[0004]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, the electrode plate proposed above is produced by spraying acid-resistant fibers on the surface of the electrode plate, or attaching them with a duster, etc., and pressing them. The bonding force between the electrode plate surface and the fibers is reduced by the drying process or charging / discharging of the battery. It had the problem that it decreased and the ionic conductivity fell.
[0005]
The present invention has been made in view of the above-mentioned problems, and the object of the present invention is that the electrode plate surface and the electrode plate surface glass fiber when the electrode plate drying process and the battery are charged and discharged. Another object is to provide an electrode plate for a sealed lead-acid battery and a method for manufacturing the same.
[0006]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In order to achieve the above object, the electrode plate of the present invention is such that the glass fiber is buried in a brushed shape on the surface of the electrode plate, and the glass fiber and glass fiber thinner than the glass fiber are cross-bonded on the electrode plate surface. It is a feature.
[0007]
Further, in the production method of the present invention, a glass chop obtained by cutting glass fibers is buried in a brushed shape on the surface of the electrode plate, and then an organic binder having acid resistance between the glass chops and glass fibers thinner than the glass chops. The emulsion is impregnated, and this electrode plate is heated in a drying step to bond the intersection of the glass chop and the fine glass fiber and the intersection of the fine glass fibers.
[0008]
[Action]
Since the glass fiber is embedded in the surface of the electrode plate, the bonding force between the glass fiber and the electrode plate is not reduced in the drying process or the like. Moreover, since the glass fiber on the surface of the electrode plate and the thin glass fiber come into contact with the glass mat, even if the pressure of the electrode group decreases, the decrease in ionic conductivity between the electrode plate and the glass mat is suppressed.
[0009]
Furthermore, since the glass fiber, the thin glass fiber, and the thin glass fiber are bonded by heating the organic binder, the bonding force is excellent and the glass fiber is not separated in the drying step or the like.
[0010]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
[0011]
FIG. 1 is an explanatory view showing the manufacturing method of the present invention, and FIG. 2 is a partially enlarged sectional view showing an embodiment of the electrode plate of the present invention.
[0012]
As shown in FIG. 1, the
[0013]
A sealed lead-acid battery having a nominal specification of 12V-60Ah is produced using this
[0014]
FIG. 4 shows the results of a high rate discharge capacity test using a 3CA discharge current (C is a rated capacity value) during the life test.
[0015]
3 and 4 are expressed as a ratio when the initial capacity of the battery A is 100%.
[0016]
As can be seen from FIG. 3, the life characteristics of the battery A according to the present invention were superior to those of the conventional battery B. Further, the difference between the battery A according to the present invention and the conventional battery B is remarkable in the high rate discharge performance as shown in FIG.
[0017]
FIG. 5 shows the change in internal resistance during the life test. The increase rate of the internal resistance of the battery A according to the present invention is lower than that of the conventional battery B product, which seems to have a great influence on the high rate discharge performance. The internal resistance is indicated in% with the initial value of the battery B being 100.
[0018]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, in the electrode plate of the present invention, the glass fibers are embedded in the brushed surface on the electrode plate surface, and the glass fibers and the thin glass fibers are cross-bonded, so that these glass fibers are easily separated from the electrode plate surface. The sealed lead-acid battery using the electrode plate of the present invention does not fall and exhibits excellent life performance.
[0019]
Moreover, according to the method of the present invention, glass fibers and thin glass fibers can be firmly bonded.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is an explanatory diagram showing a method of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a partially enlarged sectional view showing an embodiment of the electrode plate of the present invention.
FIG. 3 is a graph showing the results of a 3-hour rate capacity test of a battery A according to the present invention and a conventional battery B.
FIG. 4 is a graph showing the results of a high rate discharge capacity test of battery A according to the present invention and conventional battery B.
FIG. 5 is a graph showing changes in internal resistance during a high rate discharge capacity test of battery A according to the present invention and conventional battery B.
[Explanation of symbols]
3
Claims (1)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP28537296A JP3624583B2 (en) | 1996-10-28 | 1996-10-28 | Manufacturing method of electrode plate for sealed lead-acid battery |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP28537296A JP3624583B2 (en) | 1996-10-28 | 1996-10-28 | Manufacturing method of electrode plate for sealed lead-acid battery |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JPH10134803A JPH10134803A (en) | 1998-05-22 |
| JP3624583B2 true JP3624583B2 (en) | 2005-03-02 |
Family
ID=17690703
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP28537296A Expired - Fee Related JP3624583B2 (en) | 1996-10-28 | 1996-10-28 | Manufacturing method of electrode plate for sealed lead-acid battery |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3624583B2 (en) |
-
1996
- 1996-10-28 JP JP28537296A patent/JP3624583B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPH10134803A (en) | 1998-05-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5092272B2 (en) | Lead-acid battery and method for producing lead-acid battery | |
| JP2001508916A (en) | Lithium ion battery and method of manufacturing the same | |
| CN113594538A (en) | Safe lithium ion battery and preparation method thereof | |
| KR20030005759A (en) | Electrode for lead storage battery and method for manufacturing thereof | |
| JPS59121787A (en) | Conductive partition wall and manufacture for bipolar electrode of lead battery | |
| JP3624583B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of electrode plate for sealed lead-acid battery | |
| CN216563254U (en) | Lithium ion battery | |
| JP3388265B2 (en) | Lead-acid battery separator | |
| JP2002075379A (en) | Lead-acid battery | |
| JPH03285263A (en) | Collector for lead-acid battery | |
| JP2002025540A (en) | Manufacturing method of nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery and electrode plate for nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery | |
| JPS634562A (en) | Paste type nickel positive electrode | |
| JP2001273886A (en) | Sealed lead storage battery | |
| KR100238443B1 (en) | The structure for lithium polymer secondary batteries unit cell using the electrode material slurry of including polymer and method thereof | |
| JPH01187778A (en) | Manufacture of secondary battery | |
| CN203456543U (en) | Reinforced positive plate of power lead-acid storage battery | |
| JP2773311B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of sealed lead-acid battery | |
| JPS63187561A (en) | Manufacture of sealed lead acid battery | |
| CN115588771A (en) | Lithium ion battery and manufacturing method thereof | |
| CN110534703A (en) | A kind of high capacity silicon cathode lithium ion battery | |
| JP2785321B2 (en) | Lead-acid battery separator and lead-acid battery | |
| JPH07240229A (en) | Clad-type sealed lead-acid battery and its manufacturing method | |
| JPH03173065A (en) | Sealed lead-acid battery | |
| JPH1173985A (en) | Lead-acid battery | |
| JP2001068118A (en) | Sealed lead-acid battery and manufacturing method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20040917 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20041109 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20041122 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313111 |
|
| R371 | Transfer withdrawn |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R371 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313111 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20081210 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20091210 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |