JP3607093B2 - Information management apparatus and recording medium on which program is recorded - Google Patents
Information management apparatus and recording medium on which program is recorded Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3607093B2 JP3607093B2 JP25721398A JP25721398A JP3607093B2 JP 3607093 B2 JP3607093 B2 JP 3607093B2 JP 25721398 A JP25721398 A JP 25721398A JP 25721398 A JP25721398 A JP 25721398A JP 3607093 B2 JP3607093 B2 JP 3607093B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- information
- importance
- keyword
- weight coefficient
- weighting factor
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、使用者に合わせて情報の重要度を変更しながら、様々な情報を管理する情報管理装置、および、そのプログラムが記録された記録媒体に関するものである。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
従来より、例えば、コンピュータなどを用いて、種々の情報を管理することは広く行われている。これらの情報管理装置にて管理される情報量は、例えば、CD−ROMなどの大容量な記録媒体の普及や、情報ネットワークの発達による情報データベースの巨大化などによって、益々増大する傾向にあり、人手によって整理・管理可能な情報量を越えつつある。それゆえ、近年では、情報管理装置自体による自動整理・管理の技術が提案されている。
【0003】
例えば、特開平5−20362号公報に記載の情報管理装置は、文書単位で格納されるテキストの内容を分析して、それぞれの情報の鍵となる語句(キーワード)を自動的に抽出すると共に、各キーワードの重要度に基づき、各文書間を自動的に関連付けることによって、各文書を整理している。このように、情報管理装置が支援することによって、使用者が大量の情報の中から必要な情報を取り出す際の手間を軽減できる。
【0004】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、使用者が感じる重要度は、多くの場合、使用者毎に異なるので、上記従来の情報管理装置では、各使用者の意思に適合した十分な支援が困難であるという問題を生じる。
【0005】
具体的には、上記構成の情報管理装置では、情報の内容から機械的にキーワードを抽出して各情報を管理しているため、各情報は、各使用者で共通の観点から分類される。これに対して、使用者が感じる重要度は、一般に、例えば、使用者の職種や興味など種々の要因により、使用者毎に異なっている。したがって、情報管理装置の管理する重要度と、当該情報管理装置の使用者が感じる重要度との間にズレが発生し、上記構成の情報管理装置が各使用者に応じた重要度で情報を管理することは難しい。この結果、上記情報管理装置では、使用者に適合した支援が難しく、使用者が必要な情報を取り出すための手間を十分に削減しているとは言い難い。
【0006】
ここで、上記問題点を克服する方法として、各使用者にキーワードの重要度を変更させる方法が挙げられる。ところが、使用者は、キーワードの重要度を認識する際、通常、他のキーワードの重要度との大小や比率などを認識しているだけであり、キーワードの重要度を所望の値に設定することは、使用者にとってさえ困難である。さらに、情報の量が多くなるに従って、キーワードの量が多くなるので、上記構成では、使用者は、大量のキーワードを管理することになる。したがって、使用者は、情報の重要度管理からは開放される一方で、新たに、キーワードを管理する必要がある。この結果、必要な情報を取り出すためには、依然として、多くの手間を必要であり、使用者の負担となっている。さらに、情報量の増大に伴って、キーワードを管理しきれなくなる虞れもある。
【0007】
一方、情報管理装置へ、使用者が感じる重要度を反映させる別の方法として、特開平6−130921号公報では、情報管理装置が算出した重要度に基づく表示レイアウトが、使用者の指示する表示レイアウトに一致するように、表示レイアウト算出時の重み係数を学習制御する構成が開示されている。ところが、当該構成では、情報管理装置が学習制御によって使用者が目標値を指定する必要があるため、一般的な操作には適用できない。
【0008】
さらに、当該公報に記載の重み係数は、例えば、構造的重要度関数や意味的重要度関数など、重要度算出における基本重要度関数を互いに結合する際のパラメータである。それゆえ、重み係数の修正は、表示レイアウトを決定する際の方針の修正として反映され、個々の情報自体の重要度を変更することは難しい。
【0009】
また、重要度に応じた表示レイアウトで表示することが不可欠なので、表示装置の種類と、情報管理装置の用途とが限定される。これらの結果、情報管理装置の適用範囲が限定されてしまう。
【0010】
本発明は、上記の問題点に鑑みてなされたものであり、その目的は、広い範囲に適用でき、かつ、使用者に合わせて重要度を変更しながら、情報を管理可能な情報管理装置を提供することにある。
【0011】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、上記課題を解決するために、各情報に応じて作成され、関連する情報の重要度算出に使用される重み係数を記憶する重み係数記憶手段と、情報に関連する重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出する重要度算出手段と、情報に関連する操作に応じて、上記重み係数を調整する重み係数調整手段とを備え、上記重み係数調整手段は、情報に関連する操作のうち、当該情報を重要視している際に頻出すると予め推定された第1種の操作の回数を、情報が作成されてからの経過時間で割った値が大きいほど、当該情報の重要度が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整することを特徴としている。
【0012】
また、上記構成に加えて、上記第1種の操作には、情報の表示、情報の情報管理装置外への出力、および、情報の内容変更のうちの少なくとも1つが含まれていてもよい。
【0013】
さらに、上記重み係数調整手段は、上記第1種の操作の操作内容に応じて、上記重み係数の調整量を変更してもよい。
【0014】
また、本発明に係る情報管理装置は、上記課題を解決するために、各情報に応じて作成され、関連する情報の重要度算出に使用される重み係数を記憶する重み係数記憶手段と、情報に関連する重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出する重要度算出手段と、情報に関連する操作に応じて、上記重み係数を調整する重み係数調整手段とを備え、上記重み係数調整手段は、情報に関連する操作のうち、当該情報を重要視している際に頻出すると予め推定された第1種の操作の回数が多いほど、当該情報の重要度が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整すると共に、上記重み係数調整手段は、上記第1種の操作の操作内容に応じて、上記重み係数の調整量を変更してもよい。
【0015】
さらに、上記構成に加えて、上記重み係数調整手段は、再表示が不要な表示操作よりも、再表示を必要とする表示操作の方が、情報の重要度の変動量が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整してもよい。
【0016】
また、上記構成に加えて、上記重み係数調整手段は、情報の表示操作よりも、情報の情報管理装置外への出力操作の方が、情報の重要度の変動量が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整してもよい。
【0017】
さらに、上記構成に加えて、上記重み係数調整手段は、情報の表示操作よりも、情報の内容変更操作の方が、情報の重要度の変動量が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整してもよい。
【0018】
また、上記構成に加えて、上記重み係数調整手段は、情報の内容変更操作よりも、情報の情報管理装置外への出力操作の方が、情報の重要度の変動量が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整してもよい。
【0019】
さらに、上記構成に加えて、上記重み係数記憶手段は、情報を構成するキーワード毎に設けられたキーワード重み係数が、上記重み係数として記憶されるキーワード重み係数記憶手段を備え、上記重要度算出手段は、情報を構成する各キーワードのキーワード重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出してもよい。
【0020】
また、上記構成に加えて、上記重み係数記憶手段は、情報の格納単位であるファイル毎に設けられたファイル重み係数が、上記重み係数として記憶されるファイル重み係数記憶手段を備え、上記重要度算出手段は、情報を蓄積するファイルのファイル重み係数と、当該情報を構成するキーワード重み係数とに基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出してもよい。
【0021】
さらに、上記構成に加えて、上記重み係数記憶手段は、情報の格納単位であるファイル毎に設けられたファイル重み係数が、上記重み係数として記憶されるファイル重み係数記憶手段を備え、上記重要度算出手段は、情報が蓄積されるファイルのファイル重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出してもよい。
【0022】
また、本発明に係る情報管理装置は、上記課題を解決するために、各情報に応じて作成され、関連する情報の重要度算出に使用される重み係数を記憶する重み係数記憶手段と、情報に関連する重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出する重要度算出手段と、情 報に関連する操作に応じて、上記重み係数を調整する重み係数調整手段とを備え、上記重み係数記憶手段は、情報を構成するキーワード毎に設けられたキーワード重み係数が、上記重み係数として記憶されるキーワード重み係数記憶手段を備え、上記重要度算出手段は、情報を構成する各キーワードのキーワード重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出すると共に、さらに、情報の操作部分を特定する部分特定手段を備え、上記重み係数調整手段は、当該操作部分に含まれるキーワードのキーワード重み係数を調整することを特徴としている。
【0023】
さらに、上記構成に加えて、上記部分特定手段は、操作部分として、情報の表示部分を特定し、上記重み係数調整手段は、当該操作部分に、あるキーワードが含まれる場合、当該キーワードが含まれていない場合よりも、当該キーワードの重要度が大きくなるように、キーワード重み係数を調整してもよい。
【0024】
また、上記構成に加えて、上記重み係数調整手段は、削除された操作部分に、あるキーワードが含まれている場合、当該キーワードが含まれていない場合よりも、当該キーワードの重要度が小さくなるように、キーワード重み係数を調整してもよい。
【0025】
さらに、本発明に係る情報管理装置は、上記課題を解決するために、各情報に応じて作成され、関連する情報の重要度算出に使用される重み係数を記憶する重み係数記憶手段と、情報に関連する重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出する重要度算出手段と、情報に関連する操作に応じて、上記重み係数を調整する重み係数調整手段とを備え、上記重み係数記憶手段は、情報を構成するキーワード毎に設けられたキーワード重み係数が、上記重み係数として記憶されるキーワード重み係数記憶手段を備え、上記重要度算出手段は、情報を構成する各キーワードのキーワード重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出すると共に、さらに、上記重み係数調整手段は、入力された文字列に、あるキーワードが含まれる場合、当該キーワードが含まれない場合よりも、当該キーワードの重要度が大きくなるように、キーワード重み係数を調整することを特徴としている。
【0026】
また、上記構成に加えて、上記入力文字列の用途を識別する識別手段を備え、上記重み係数調整手段は、上記入力文字列の用途に応じて、キーワード重み係数の調整量を変更してもよい。
【0027】
さらに、上記構成に加えて、上記重み係数調整手段は、上記入力文字列の用途が情報検索の場合、用途が情報の新規追加の場合よりも、キーワードの重要度の変動量が大きくなるように、上記キーワード重み係数を調整してもよい。
【0028】
また、上記構成に加えて、上記重み係数調整手段は、上記入力文字列の用途が情報の内容修正の場合、用途が情報の新規追加の場合よりも、キーワードの重要度が大きくなるように、上記キーワード重み係数を調整してもよい。
【0029】
さらに、上記構成に加えて、上記重み係数調整手段は、上記入力文字列の用途が情報検索の場合、用途が情報の内容修正の場合よりも、キーワードの重要度が大きくなるように、上記キーワード重み係数を調整してもよい。
【0030】
また、上記構成に加えて、上記重み係数記憶手段は、情報の格納単位であるファイル毎に設けられたファイル重み係数が、上記重み係数として記憶されるファイル重み係数記憶手段を備え、上記重要度算出手段は、情報を蓄積するファイルのファイル重み係数と、当該情報を構成するキーワード重み係数とに基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出してもよい。
【0031】
さらに、上記構成に加えて、情報に関連する操作の履歴を示す履歴情報が格納される履歴情報記憶手段を備え、上記重み係数調整手段は、履歴情報に基づいて、重み係数を調整してもよい。
【0032】
また、上記構成に加えて、上記重み係数調整手段は、操作が行われた時期に応じて、重み係数の調整量を変更してもよい。
【0033】
なお、重要度算出手段が情報の重要度算出を終了するまでの間に、重み係数を調整できれば、例えば、重み係数調整手段が重み係数記憶手段に格納された値を更新してもよいし、重み係数記憶手段から読み出された後で調整してもよい。また、ある情報の重要度を算出する際、複数の重み係数が使用される場合、重み係数の少なくとも1つを調整すればよい。また、各操作は、情報全体(ファイル)を操作対象としてもよいし、情報の一部を操作対象とすることもできる。
【0034】
上記各情報に応じて作成され、関連する情報の重要度算出に使用される重み係数を記憶する重み係数記憶手段と、情報に関連する重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出する重要度算出手段と、情報に関連する操作に応じて、上記重み係数を調整する重み係数調整手段とを備えている構成において、重み係数は、例えば、情報の蓄積単位であるファイル毎、あるいは、情報を構成する単位であるキーワード毎など、各情報に応じて作成され、重み係数記憶手段に格納される。また、重み係数調整手段は、例えば、表示されている情報への操作や、情報が蓄積されるファイルへの操作など、情報に関連する操作が行われた場合、上記重み係数を調整する。さらに、重要度算出手段は、情報に関連する重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出する。
【0035】
上記構成によれば、各情報の重要度は、使用者が特に重要度を指示しなくても、例えば、操作対象となる情報、ファイルまたはキーワードの分布、あるいは、操作の種類やタイミングなど、使用者の操作傾向に応じて、自動的に調整される。例えば、重み係数の調整方法として、情報が操作される毎に当該情報の重要度が大きくなるような方法を選択すれば、操作回数が多い情報ほど、相対的に重要度が大きくなる。これにより、使用者が検索用のキーワードを管理したり、各情報の重要度を管理しなくても、情報管理装置は、各使用者に適合した重要度を算出できる。この結果、使用者が必要な情報を探し出すために情報を整理する際の手間を大幅に削減できる。
【0036】
また、重み係数は、情報に応じて作成されており、操作の傾向に応じて調整される。このように、開放型の学習システムで各情報の重要度が学習されるので、情報の重要度に拘わらず、各情報の重み係数を調整できる。したがって、重要度に応じたレイアウトで各情報を表示すると共に、使用者から指示されたレイアウトに合致するように、システム固有の重み係数を学習制御する従来技術とは異なり、適用範囲が限定されず、情報に関連する操作が可能な情報管理装置に広く適用できる。
【0037】
さらに、上記情報に関連する操作の履歴を示す履歴情報が格納される履歴情報記憶手段を備え、上記重み係数調整手段は、履歴情報に基づいて、重み係数を調整する構成では、情報に関連する操作が行われると、当該操作を示す履歴情報が履歴情報記憶手段に格納される。ここで、重み係数調整手段は、履歴情報を参照すれば、例えば、使用者が情報の重要度算出を指示した時点など、操作時点から時間が経過した時点であっても、重み係数を調整できる。したがって、重要度算出を指示した時点で、重み係数の調整方法が指定されても、当該調整方法で重み係数を調整できる。この結果、情報管理装置は、より柔軟に情報の重要度を算出できる。
【0038】
一般に、使用者が感じる重要度は、時間の経過に伴って変化している。したがって、ある時期に重要と判断され、頻繁に操作された情報であっても、別の時期には、余り重要ではないと判断されることがある。
【0039】
上記重み係数調整手段は、操作が行われた時期に応じて、重み係数の調整量を変更する構成によれば、操作が行われた時期に応じて、重み係数の調整量を変更する。したがって、特定の時期の操作に起因する重み係数の調整量を、残余の時期での場合とは異なる値に設定できる。これにより、特定の時期において、使用者が重要と判断していると推測される情報の重要度を増大させることができる。この結果、使用者が所望の情報を発見する際の手間をさらに削減できる。
【0040】
上記重み係数記憶手段は、情報の格納単位であるファイル毎に設けられたファイル重み係数が、上記重み係数として記憶されるファイル重み係数記憶手段を備え、上記重要度算出手段は、情報が蓄積されるファイルのファイル重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出する構成では、重み係数となるファイル重み係数は、情報の蓄積単位となるファイル毎に設けられており、情報に関連する操作に応じて調整される。この結果、情報管理装置は、情報の重要度をファイル単位で増減できる。なお、重要度算出手段は、ファイル重み係数に基づいて情報の重要度を算出していれば、後述のキーワード重み係数など、他の重み係数を併用して、重要度を算出してもよい。
【0041】
ここで、使用者は、情報を操作する際、例えば、当該情報が蓄積されたファイルを開いて情報を表示するなど、ファイルを操作対象とすることが多い。したがって、情報管理装置がファイル単位で重要度を増減することで、使用者の操作傾向に適合した重要度を算出でき、使用者は、必要な情報をより早く発見できる。
【0042】
ところで、上記情報としては、文字だけではなく、画像や音声など、種々の形式の情報が考えられる。この中でも、文字からなる情報のように、意味を持つ単位であるキーワードから、情報が構成される場合、キーワードに対応する重み係数を設けると効果的である。
【0043】
すなわち、上記重み係数記憶手段は、情報を構成するキーワード毎に設けられたキーワード重み係数が、上記重み係数として記憶されるキーワード重み係数記憶手段を備え、上記重要度算出手段は、情報を構成する各キーワードのキーワード重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出する構成では、重み係数となるキーワード重み係数は、情報を構成するキーワード毎に設けられており、当該キーワードを含む情報に関連する操作に応じて調整される。したがって、ある情報が操作された場合、当該情報中のキーワードを含む他の情報の重要度が調整される。なお、キーワード重み係数に基づいて、情報の重要度を算出していれば、上記ファイル重み係数など、他の重み係数を併用してもよい。
【0044】
ここで、多くのキーワードが共通して含まれる情報は、互いに類似した内容であることが多く、使用者は、ある情報を重要と判断する場合、当該情報に類似した内容の情報も重要と判断することが多い。したがって、キーワード重み係数を調整することで、使用者の操作傾向に適合した重要度を算出でき、使用者は、必要な情報をより早く発見できる。
【0045】
ところで、重要度算出手段がファイル重み係数のみに基づいて重要度を算出する場合、ある情報が操作された場合、当該情報の重要度のみが変化して、他の情報の重要度は変化しない。したがって、当該情報に類似した内容を持った情報を検索する際に手間がかかる虞れがある。一方、キーワード重み係数のみに基づいて重要度を算出する場合、操作された情報の重要度と、当該情報に類似した内容を持った情報の重要度とが近くなり、操作した情報を見つけにくくなる虞れがある。
【0046】
これに対して、上記重み係数記憶手段は、情報の格納単位であるファイル毎に設けられたファイル重み係数が、上記重み係数として記憶されるファイル重み係数記憶手段を備え、上記重要度算出手段は、情報を蓄積するファイルのファイル重み係数と、当該情報を構成するキーワード重み係数とに基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出する構成では、重要度算出手段は、ファイル重み係数とキーワード重み係数とに基づいて重要度を算出する。したがって、ある情報が操作された場合、当該情報に類似した内容を持った情報の重要度を変化できると共に、操作された情報の重要度と、上記類似の情報の重要度との差を保つことができる。この結果、直接操作した情報と類似の情報との双方をより早く発見可能な情報管理装置を実現できる。なお、情報の重要度算出に、両重み係数が使用されていれば、他の重み係数を併用してもよい。
【0047】
また、上記重み係数調整手段は、情報の表示時間が長いほど、当該情報の重要度が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整する構成によれば、情報が表示されると、重み係数調整手段は、表示時間に応じて、重み係数を調整する。この結果、表示時間が長い情報が相対的に大きな重要度を持つように、重み係数を調整できる。
【0048】
一般に、使用者が重要と判断する情報は、不要と判断する情報に比べて頻繁に参照され、より長く表示される。ここで、上記構成では、重み係数が表示時間に応じて調整されるので、使用者の操作傾向に適合した重要度を算出でき、使用者は、必要な情報をより早く発見できる。
【0049】
なお、表示時間は、例えば、画面に表示されてから表示が終了するまでの時間であってもよいし、複数のウインドウをオーバーラップして表示可能な表示装置であれば、最も重なりが上のウインドウ(アクティブウインドウ)で表示される時間を表示時間としてもよい。また、各重なり状態での表示時間を別に計時すると共に、重なりが上の方が重みが大きくなるように、それぞれの表示時間へ重なり状態に応じた重みを付けて加算した値を表示時間としてもよい。
【0050】
さらに、上記重み係数調整手段は、情報に関連する操作のうち、当該情報を重要視している際に頻出すると予め推定された第1種の操作の回数が多いほど、当該情報の重要度が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整する構成によれば、例えば、表示に関連する操作、内容変更に関連する操作、情報の検索に関連する操作、情報管理装置外へ情報を出力する操作など、使用者が当該情報を重要と判断する際に頻出する操作が行われた場合、当該情報の重要度が大きくなる。この結果、情報管理装置は、使用者の操作傾向に適合した重要度を算出でき、使用者は、必要な情報をより早く発見できる。
【0051】
ここで、使用者は、一般に、最近作成され、頻繁に使用する情報ほど、現時点で重要視していることが多い。上記重み係数調整手段は、情報に関連する操作のうち、当該情報を重要視している際に頻出すると予め推定された第1種の操作の回数を、情報が作成されてからの経過時間で割った値が大きいほど、当該情報の重要度が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整する構成では、当該情報を重要と判断する際に頻出する操作が行われた場合、当該情報の重要度が大きくなる。また、情報が作成されてからの経過時間が増大するほど、当該情報の重要度は小さくなる。この結果、操作回数が同じ場合であっても、最近作成された情報の重要度を大きくでき、情報管理装置は、より使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できる。
【0052】
さらに、上記第1種の操作には、情報の表示、情報の情報管理装置外への出力、および、情報の内容変更のうちの少なくとも1つが含まれている構成によれば、情報の表示操作、出力操作、あるいは、内容変更操作が行われた場合、当該情報の重要度が大きくなる。ここで、表示操作としては、例えば、表示開始や表示停止、全体表示、部分表示、情報中の表示部分変更、拡大、縮小、あるいは、表示画面での表示位置変更などが挙げられる。また、出力操作には、例えば、印刷や通信または記録媒体への記録などが含まれる。さらに、内容変更操作としては、内容の追加、内容の修正、部分複写や部分削除などが存在する。情報に関連する操作のうちでも、これらの操作は、使用者が当該情報を重要視している際に頻繁に行われる。この結果、上記第1種の操作として、これらの操作を採用することで、情報管理装置は、より使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できる。
【0053】
ところで、上述したように、情報に関連する操作には、様々な種類の操作が存在し、それぞれの種類の操作は、操作頻度や、1回の操作が情報の重要度へ与える影響などが互いに異なっていることが多い。
【0054】
例えば、ある文書を編集している場合を例にすると、文字入力は、操作回数が極めて多く、1回の操作によって、情報の重要度が余り変化しないのに対して、文書を保存する操作は、使用者が情報の更新が必要と判断した時点で実施されるため、操作回数が比較的少ないにも拘わらず、情報の重要度が比較的大きく変化する。
【0055】
したがって、操作に応じて重み係数を調整する際、各種類の操作で一律に調整すると、情報管理装置が算出する重要度と、使用者が感じる重要度との間にズレが発生する虞れがある。
【0056】
これに対して、上記重み係数調整手段は、上記第1種の操作の操作内容に応じて、上記重み係数の調整量を変更する構成によれば、重み係数の調整量は、操作の種類に応じて変化する。この結果、情報が算出する重要度と、使用者が感じる重要度との間のズレを低減でき、情報管理装置は、より的確に、情報の重要度を算出できる。
【0057】
ここで、多くの情報を同時に表示したり、大きな情報を表示する場合、画面に必要な情報全てを同時に表示することは難しい。したがって、複数の情報を重ね合わせて表示したり、情報の一部だけを表示したりすることが多い。この場合、使用者は、所望の部分を表示させるために、画面を書き直したり、画面の表示領域から外れた情報をバックスクロール機能などを利用して再度表示させたりする。この結果、使用者にとって重要な情報ほど、情報の表示状態が頻繁に変更され、再表示される。
【0058】
上記重み係数調整手段は、再表示が不要な表示操作よりも、再表示を必要とする表示操作の方が、情報の重要度の変動量が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整する構成によれば、再表示が頻繁に行われる情報ほど、重要度が相対的に高くなる。これにより、情報管理装置は、より的確に、情報の重要度を算出できる。なお、再表示を必要とする表示操作としては、バックスクロール操作や表示位置の変更操作などが挙げられる。
【0059】
また、上記重み係数調整手段は、情報の表示操作よりも、情報の情報管理装置外への出力操作の方が、情報の重要度の変動量が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整する構成によれば、出力操作された情報ほど、重要度が相対的に大きくなる。ここで、使用者は、情報や情報の一部分を出力する場合、多くの人々に参照させることを意図していることが多く、当該情報は、情報管理装置内で使用している情報よりも、重要視されている。この結果、情報管理装置は、より使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できる。
【0060】
一方、上記重み係数調整手段は、情報の表示操作よりも、情報の内容変更操作の方が、情報の重要度の変動量が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整する構成によれば、内容が変更された場合、単に表示している場合よりも、情報の重要度が大きくなる。ここで、使用者が情報の内容を変更する場合、使用者は、この情報を重要と判断していることが多い。したがって、内容が変更された情報の重要度を相対的に大きくすることで、情報管理装置は、より的確に、情報の重要度を算出できる。
【0061】
さらに、上記重み係数調整手段は、情報の内容変更操作よりも、情報の情報管理装置外への出力操作の方が、情報の重要度の変動量が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整する構成によれば、出力された情報、内容が変更された情報、表示された情報の順番で、重要度が相対的に大きくなる。したがって、情報管理装置は、より的確に重要度を算出できる。
【0062】
一方、上記重み係数調整手段は、情報に関連する操作のうち、当該情報が不要な場合に頻出すると予め推定された第2種の操作が行われた場合、当該情報の重要度が小さくなるように、上記重み係数を調整する構成において、第2種の操作が行われると、操作されない場合よりも、情報の重要度が低下する。ここで、第2種の操作は、使用者が情報を不要と判断している場合に頻出する操作である。したがって、情報管理装置は、使用者の操作傾向に適合した重要度を算出でき、使用者は、必要な情報をより早く発見できる。なお、第2種の操作としては、例えば、情報が蓄積されたファイルを削除する操作など、情報を削除する操作が挙げられる。
【0063】
ところで、操作の対象が情報の一部分の場合、使用者は、情報の中でも操作部分に注意を払っていることが多い。したがって、情報よりも小さな単位に重み係数が対応している場合には、操作部分に含まれているか否かによって、重み係数の調整量を変更することで、情報管理装置は、使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できる。
【0064】
具体的には、上記情報の操作部分を特定する部分特定手段を備え、上記重み係数調整手段は、当該操作部分に含まれるキーワードのキーワード重み係数を調整する構成によれば、キーワード重み係数の調整量は、操作部分に含まれているか否かによって変更される。これにより、情報管理装置は、使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できる。
【0065】
さらに、上記部分特定手段は、操作部分として、情報の表示部分を特定し、上記重み係数調整手段は、当該操作部分に、あるキーワードが含まれる場合、当該キーワードが含まれていない場合よりも、当該キーワードの重要度が大きくなるように、キーワード重み係数を調整する構成によれば、キーワードの重要度は、表示部分に含まれる場合の方が大きくなる。したがって、頻繁に表示されるキーワードほど、重要度が相対的に大きくなる。この結果、情報管理装置は、使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できる。
【0066】
また、上記重み係数調整手段は、削除された操作部分に、あるキーワードが含まれている場合、当該キーワードが含まれていない場合よりも、当該キーワードの重要度が小さくなるように、キーワード重み係数を調整する構成によれば、キーワードの重要度は、削除部分に含まれる場合の方が小さくなる。したがって、情報の内容修正の結果、頻繁に削除されるキーワードほど、重要度が相対的に小さくなる。この結果、情報管理装置は、使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できる。
【0067】
ところで、キーワードは、情報だけではなく、例えば、情報を検索する際の文字列など、使用者によって入力される文字列にも含まれる。ここで、一般に、使用者は、文字列を入力する際、使用者自身が重要視する文字列を入力している。したがって、使用者の入力文字列中に含まれるか否かで、キーワードの重要度の変動量を変更すれば、使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できる。
【0068】
具体的には、上記重み係数調整手段は、入力された文字列に、あるキーワードが含まれる場合、当該キーワードが含まれない場合よりも、当該キーワードの重要度が大きくなるように、キーワード重み係数を調整する構成によれば、入力文字列に頻繁に含まれるキーワードほど、重要度が相対的に大きくなる。これにより、情報管理装置は、使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できる。
【0069】
さらに、上記入力文字列の用途を識別する識別手段を備え、上記重み係数調整手段は、上記入力文字列の用途に応じて、キーワード重み係数の調整量を変更する構成によれば、キーワード重み係数の調整量は、入力文字列の用途に応じて変更される。ここで、用途としては、例えば、情報の新規入力、情報の内容修正、検索などが挙げられ、入力文字列の長さと、入力文字列中のキーワードを使用者が重要視する程度とが異なっていることが多い。したがって、情報管理装置は、用途に応じて調整量を変更することで、使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できる。
【0070】
また、上記重み係数調整手段は、上記入力文字列の用途が情報検索の場合、用途が情報の新規追加の場合よりも、キーワードの重要度の変動量が大きくなるように、上記キーワード重み係数を調整する構成によれば、情報検索の際に使用されるキーワードは、新規入力に使用されるキーワードよりも、重要度が相対的に大きくなる。ここで、情報検索時には、使用者が特に重要視しているキーワードのみが入力されることが多く、新規入力時には、使用者が特に重要視しているキーワードだけではなく、当該キーワードに関連するキーワードも入力されることが多い。したがって、情報管理装置は、情報検索に使用されるキーワードの重要度を大きくすることで、使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できる。
【0071】
一方、上記重み係数調整手段は、上記入力文字列の用途が情報の内容修正の場合、用途が情報の新規追加の場合よりも、キーワードの重要度が大きくなるように、上記キーワード重み係数を調整する構成によれば、内容修正に使用されるキーワードは、新規入力に使用されるキーワードよりも、重要度が相対的に大きくなる。ここで、多くの場合、内容修正時には、新規入力時に比べて、入力文字列の長さが短く、より重要視されているキーワードの含有率が高い。したがって、情報管理装置は、内容修正に使用されるキーワードの重要度を大きくすることで、使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できる。
【0072】
さらに、上記重み係数調整手段は、上記入力文字列の用途が情報検索の場合、用途が情報の内容修正の場合よりも、キーワードの重要度が大きくなるように、上記キーワード重み係数を調整する構成によれば、情報検索に使用されるキーワードは、内容修正に使用されるキーワードに比べて、相対的な重要度がさらに大きくなる。ここで、多くの場合、情報検索時の入力文字列は、内容修正時の入力文字列に比べて、長さが短く、重要視されているキーワードの含有率が高い。したがって、情報管理装置は、情報検索に使用されるキーワードの重要度をさらに大きくでき、使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できる。
【0073】
また、本発明に係る記録媒体は、上記課題を解決するために、上記各情報管理装置の各手段として、コンピュータを動作させるプログラムが記録されていることを特徴としている。
【0074】
上記構成の当該プログラムがコンピュータで実行されると、上記情報管理装置と同様に、重み係数が情報に応じて作成され、操作の傾向に応じて調整される。したがって、各情報の重要度を管理しなくても、情報管理装置は、各使用者に適合した重要度を算出でき、使用者が必要な情報を探し出すために情報を整理する際の手間を大幅に削減できる。
【0075】
また、開放型の学習システムで各情報の重要度が学習されるので、情報の重要度に拘わらず、各情報の重み係数を調整できる。したがって、適用範囲が限定されず、情報に関連する操作が可能な情報管理装置に広く適用できる。
【0076】
【発明の実施の形態】
〔第1の実施形態〕
本発明の一実施形態について図1ないし図7に基づいて説明すると以下の通りである。すなわち、本実施形態に係る情報管理システムは、使用者に合わせて情報の重要度を変更しながら、様々な情報を管理するシステムであって、例えば、ある事柄に関する情報を使用者が必要と感じたときに、例えば、重要度の大きな情報を強調して表示するなどして、当該情報の発見を助けるために使用されている。
【0077】
図1に示すように、本実施形態に係る情報管理システム1は、情報Dを格納する情報管理装置2と、情報Dを表示する表示装置3と、例えば、キーボードやマウスなど、情報管理装置2を操作する操作入力装置4と、例えば、ネットワーク5aやディスク装置5bあるいはプリンタ5cなど、情報管理装置2の外部と情報Dをやり取りする外部入出力装置5とを備えており、使用者の操作に基づいて、情報管理装置2が算出する重要度Xsを、使用者が感じる重要度Xuに近づけることができる。
【0078】
具体的には、上記情報管理装置2は、記憶部11として、情報D自体を格納する情報蓄積部11aと、情報Dに応じて作成され、情報Dの重要度算出用の重み係数Pが格納される重み係数蓄積部11bと、使用者の操作に応じて更新される履歴記憶部11cとを備えている。なお、重み係数蓄積部11bが特許請求の範囲に記載の重み係数記憶手段、ファイル重み係数記憶手段およびキーワード重み係数記憶手段に対応する。また、履歴記憶部11cが履歴情報記憶手段に対応する。
【0079】
本実施形態に係る情報蓄積部11aは、情報Dとして、少なくとも文字列のフィールドを記憶している。なお、情報Dは、例えば、絵や音声など、文字以外のフィールドを含んでいてもよい。
【0080】
また、上記重み係数蓄積部11bは、重み係数Pとして、各情報Dの蓄積単位であるファイルF毎に設けられたファイル重み係数FPと、各情報Dを構成するキーワードK毎に設けられたキーワード重み係数KPとを格納しており、ある情報DA の重要度XsA は、当該情報DA が格納されるファイルFA のファイル重み係数FPA と、当該情報DA を構成するキーワードKA1…のキーワード重み係数KPA1…の合計とを加算して算出される。なお、以下では、説明の便宜上、情報Dの重要度算出に使用されるファイル重み係数FPおよびキーワード重み係数KPを、当該情報Dの重み係数Pと称する。
【0081】
さらに、履歴記憶部11cは、例えば、表示時間や操作回数など、使用者の操作に応じて、各重み係数Pを調整するための情報が記憶されるが、詳細については後述する。
【0082】
一方、上記各装置3〜5を制御するための入出力制御部12として、表示制御部12a、入力制御部12b、および、情報入出力制御部12cが設けられている。また、情報Dや操作を分析するための分析部13として、表示制御部12aの入出力に基づいて、表示装置3の表示を分析する表示分析部(部分特定手段)13aと、操作入力装置4から入力制御部12bを介して入力される使用者の操作を分析する操作分析部13bと、操作入力装置4や外部入出力装置5から入力制御部12bや情報入出力制御部12cを介して入力される情報Dを分析して、重み係数Pの初期値を算出する情報分析部13cとを備えている。
【0083】
また、重要度Xsを算出するための演算部14として、上記重み係数蓄積部11bに格納される重み係数Pを処理する重み係数処理部(重み係数調整手段)14aと、重み係数Pに基づいて、重要度Xsを算出する重要度計算部(重要度算出手段)14bとを備えている。さらに、上記各部11〜14を制御する情報制御部(識別手段)15が設けられている。
【0084】
上記各部11〜15は、例えば、コンピュータが所定のプログラムを実行することによって実現される機能モジュールであってもよいし、固有のハードウェアであってもよい。ただし、機能モジュールとして実現した場合は、上記プログラムが記録された記録媒体を配付するだけで、情報管理装置2を実現できる。
【0085】
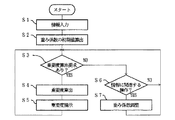
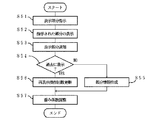
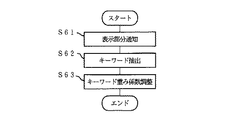
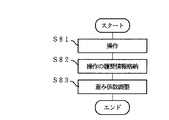
上記構成において、情報Dを入力する際の各部の動作について、図2に基づき説明すると以下の通りである。すなわち、S1において、情報管理装置2に情報Dが入力されると、情報管理装置2では、S2において、各情報Dの重要度Xsを算出するための重み係数Pが生成される。
【0086】
具体的には、図3に示すように、使用者が情報Dを生成する場合、S11において、情報管理装置2の入力制御部12bは、操作入力装置4からの入力が情報Dであると判断して、使用者が生成した情報Dを情報分析部13cへ出力する。一方、情報Dが外部入出力装置5から取り込まれる場合、S12において、情報管理装置2の情報入出力制御部12cは、ネットワーク5aやディスク装置5bなどの外部入出力装置5から、当該情報Dを受け取って、情報分析部13cへ出力する。
【0087】
いずれの場合であっても、情報分析部13cは、S13において、受け取った情報Dを、記憶部11の情報蓄積部11aへ蓄積する。情報Dは、テキスト情報からなる領域D1を含んでいれば、例えば、図4に示すように、画像など、文字列以外の情報からなる領域D2を含んでいてもよい。また、重み係数Pの1つとなるファイル重み係数FPが、情報Dの蓄積単位であるファイルFに対応して生成され、重み係数蓄積部11bに格納される(S14)。なお、ファイル重み係数FPの初期値は、例えば、操作入力装置4やネットワーク5aなど、情報Dの入手経路によって互いに異なる値に設定してもよいし、一定の値としてもよい。
【0088】
さらに、S15において、情報分析部13cは、入力された情報Dからテキスト情報を抽出し、S16では、抽出されたテキスト情報から、文字列処理により、キーワードKを切り出す。また、情報分析部13cは、S17において、例えば、出現頻度や、情報Dの中の出現箇所などによって、各キーワードKに重み付けを行う。これにより、例えば、以下の表1に示すように、各キーワードKの重み係数KPの初期値を算出する。なお、出現頻度に応じて重み付けが行われる場合、情報蓄積部11aに蓄積された他の情報Dでの出現頻度も参照される。
【0089】
【表1】
【0090】
この結果、情報Dの出現頻度が高く、多くの情報Dに平均的に出現するキーワードKは、出現頻度が低いキーワードKよりも低い重みが付けられる。また、テキスト情報が構造化されており、要約あるいは本文などの領域から構成されている場合、要約の領域に含まれるキーワードKは、本文の領域に含まれるキーワードKよりも高い重みが付けられる。なお、上記では、キーワード重み係数KPの初期値算出方法の一例として、出現頻度と出現箇所とに基づく方法を例示したが、これに限るものではなく、種々の方法を採用できる。
【0091】
一方、図2において、使用者が情報Dの重要度算出を指示した場合(S3にて YESの場合)、情報管理装置2は、S4において、重み係数Pに基づいて各情報Dの重要度Xsを算出し、S5において、例えば、重要度Xsの高い情報Dを強調して表示したり、重要度Xsの高い順番に順位付けて表示するなど、情報管理装置2が算出した重要度Xsを使用者が把握可能なように提示する。これにより、情報管理装置2が重要と判断する情報Dほど、使用者が取得しやすくなる。この結果、情報管理装置2が算出する重要度Xsと使用者が感じる重要度Xuとのズレが少ないほど、使用者は、少ない手間で所望の情報Dを取り出すことができる。なお、図2に示すS4が、特許請求の範囲に記載の重要度算出工程に対応し、S7が重み係数調整工程に対応する。
【0092】
上述したように、本実施形態に係る情報管理装置2では、重み係数Pの一例として、情報Dを構成する単位であるキーワード重み係数KPと、情報Dの蓄積単位であるファイルF毎に設けられるファイル重み係数FPとが使用されており、情報管理装置2は、上記S4において、ある情報Dに含まれる各キーワードKのキーワード重み係数KPの総和と、当該情報Dを格納するファイルFのファイル重み係数FPとを加算して、当該情報Dの重要度Xsを算出する。
【0093】
ここで、上記S2で算出された重み係数Pの初期値は、予め定められる算出方法と、S1にて入力される情報Dとから決定されるので、両者が同一であれば、各情報管理装置2間で同一である。したがって、これらから算出される情報Dの重要度Xsも、各情報管理装置2間で同一の値となる。一方、使用者が感じる情報Dの重要度Xuは、各使用者毎に異なっているため、重み係数Pが初期値のままの状態では、情報管理装置2が提示する情報Dの重要度Xsとの間にズレを生じる。
【0094】
ところが、本実施形態に係る情報管理装置2は、例えば、情報Dの表示や内容変更、あるいは、検索や出力など、情報Dに関連する操作が行われた場合(上記S6にて YESの場合)、上記S7において、当該情報Dの重要度Xsを算出するための重み係数Pを調整する。
【0095】
これにより、例えば、キーワードの重要度を入力するなど、情報Dの重要度Xsを管理するための操作が行われていないにも拘わらず、情報管理装置2は、使用者の感じる重要度Xuへ、自らが算出する重要度Xsを近づけることができる。この結果、使用者は、情報Dの重要度Xsを管理することなく、より少ない手間で所望の情報Dを取り出すことができる。
【0096】
ここで、上記S7における重み係数Pの調整方法としては、例えば、操作の内容や頻度、操作により情報Dが表示される時間など、情報Dに関連する操作に応じて調整する方法であれば、任意の方法を適用できるが、本実施形態では、調整方法の一例として、表示時間による重み付けについて説明する。
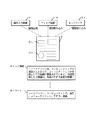
【0097】
具体的には、図5に示すように、S21において、ある情報DA の表示を使用者が指示すると、当該指示は、操作分析部13bにて識別され、情報制御部15へ伝えられる(S22)。情報制御部15は、S23において、当該通知を受け取ると、情報DA の画面表示を行うための指令を作成して、表示制御部12aへ発信する。これにより、表示装置3には、情報DA が表示される。
【0098】
さらに、S24において、情報制御部15は、表示分析部13aへ、情報DA の画面表示が開始されたことを通知し、S25において、表示分析部13aは、情報DA の表示時間計測を開始する。
【0099】
一方、S26において、使用者が情報DA の表示終了を指示すると、当該指示は、操作分析部13bにて識別され、情報制御部15へ伝えられる(S27)。情報制御部15は、S28において、情報DA の画面表示を終了するための指令を作成して、表示制御部12aへ発信する。これにより、情報DA の画面表示は終了する。
【0100】
さらに、本実施形態に係る情報制御部15は、S29において、情報DA の画面表示が終了されたことを表示分析部13aへ通知する。一方、S30において、表示分析部13aは、当該通知に基づいて、情報DA の表示時間計測を終了する。
【0101】
ここで、履歴記憶部11cには、過去に情報Dが表示された時間の総和を示す総表示時間Tが、各情報Dに対応して格納されている。表示分析部13aは、S31において、情報DA の総表示時間TA に、今回の表示時間を加算する。この加算結果は、新たな総表示時間TA として、履歴記憶部11cに格納される。なお、例えば、初めて表示された場合など、総表示時間TA が履歴記憶部11cに格納されていない場合は、表示分析部13aは、今回の表示時間を新たな総表示時間TA として格納する。
【0102】
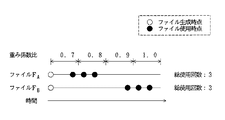
さらに、重み係数処理部14aは、S32において、履歴記憶部11cに格納された情報DA の総表示時間TA を参照して、総表示時間TA が長いほど、当該情報DA の重要度XsA が大きくなるように、当該情報DA の重み係数PA を調整する。
【0103】
例えば、以下の表2に示すように、情報DB の総表示時間TB が、情報DA の総表示時間TA の2倍の場合、重み係数処理部14aは、情報DA の重み係数PA の2倍に、情報DB の重み係数PB を増加させる。なお、表2では、比較のために、総表示時間Tのみが異なり、例えば、調整前の重み係数Pなど、他の条件が同一な情報DA ・DB ・DC を例示しており、重み係数比は、重み係数PA の値を1とした場合の比率である。
【0104】
【表2】
【0105】
本実施形態では、重み係数Pとして、ファイル重み係数FPとキーワード重み係数KPとが使用されているので、情報DB が格納されるファイルFB のファイル重み係数FPB は、情報DA が格納されるファイルFA のファイル重み係数FPA の2倍だけ増加し、情報DB に含まれるキーワードKB1のキーワード重み係数KPB1は、情報Aに含まれるキーワードKA1のキーワード重み係数KPA1の2倍だけ増加する。同様に、情報DC の重み係数PC は、情報DA の重み係数PA の1.5倍に増加する。
【0106】
上記S21〜S32の処理は、他の情報Dでも実施されるので、総表示時間Tが長い情報Dほど、重要度Xsが相対的に増大し、総表示時間Tが短い情報Dほど、重要度Xsが相対的に低下する。
【0107】
一般に、情報管理装置2の使用者は、主として、表示装置3の表示画面に表示された情報Dを見ながら、操作入力装置4を操作している。したがって、使用者が、ある情報Dに注意を払っているほど、当該情報Dの表示時間が長くなることが多い。ここで、情報管理装置2は、情報Dの総表示時間Tが長いほど、使用者が当該情報Dを重要視していると推測して重み係数Pを調整する。この結果、図2に示すS2の時点では、使用者の感じる情報Dの重要度Xuと、情報管理装置2が算出する重要度Xsとの間にズレが発生したとしても、上記S21〜S32(図2に示すS3〜S7)の処理を繰り返す毎に、ズレが縮小される。この結果、情報管理装置2は、各使用者に適合した重要度Xsを提示できる。
【0108】
なお、この例では、ファイル重み係数FPとキーワード重み係数KPとの双方を調整しているが、一方のみを調整してもよい。ただし、ファイル重み係数FPのみを調整する場合は、使用者が表示させた情報DA の重要度XsA のみが調整される。したがって、他の情報DB の内容が情報DA に類似していたとしても、当該情報DB の重要度XsB は変化せず、当該情報DB の検索に手間や時間がかかる虞れがある。
【0109】
一方、キーワード重み係数KPを調整する場合は、使用者が1つの情報Dに注目して操作するだけで、類似の内容を持つ情報DB の重要度XsB も上昇する。この結果、使用者が当該情報DB を発見しやすくなる。ところが、キーワード重み係数KPのみを調整する場合は、両情報DA ・DB の重要度XsA ・XsB が同様に変化するため、使用者は、直接指示した情報DA を他の情報DB から区別しにくくなる。この結果、直接指示した情報DA を検索したい場合には、手間や時間がかかる虞れがある。
【0110】
これに対して、本実施形態では、重み係数Pとして2つの重み係数FP・KPを併用し、双方を調整している。この結果、直接指示した情報DA の検索を妨げることなく、類似の情報DB を発見しやすくできる。
【0111】
また、上記の例では、重み係数Pの増加率と、総表示時間Tとが比例するように重み係数Pを調整したが、これに限るものではない。増加率に代えて、増加幅で調整してもよいし、他の数式を用いて調整してもよい。総表示時間Tのみが異なる場合で比較した場合、総表示時間Tが長くなるに従って、情報Dの重要度Xsが大きくなるような調整方法であれば、本実施形態と同様の効果が得られる。
【0112】
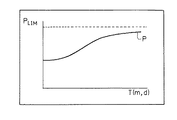
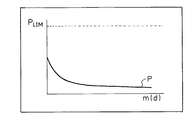
ただし、情報管理装置2がより使用者の感覚に近い重要度Xsを算出するためには、例えば、図6に示すように、総表示時間Tに対してS字状に変化するように重み係数Pを調整する方が望ましい。この場合は、総表示時間Tが少ないうちは、重み係数Pが徐々に増加し、総表示時間Tが増大すると、重み係数Pの傾きが急峻になる。さらに、重み係数Pが所定の上限値PLIM に近づくと、重み係数Pは、緩やかに上昇する。これにより、総表示時間Tに起因する重要度Xsの変動を使用者の感覚に近づけることができる。
【0113】
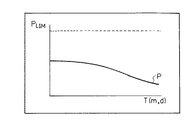
また、情報管理装置2が動作を開始してからの時間が長くなると、各情報Dの総表示時間Tが長くなり、各情報Dの重要度Xsが近づく虞れがある。したがって、ファイルFあるいはキーワードKに関連しない表示が続く場合は、図7に示すように、当該ファイルFあるいはキーワードKの重み係数P(KP・FP)を徐々に減少させる方がよい。これにより、時間が経過しても、各情報Dの重要度Xsを広い範囲に分散させることができ、使用者は、所望の情報Dを発見しやすくなる。
【0114】
なお、上記の例では、履歴記憶部11cへ、情報Dの総表示時間T自体を格納しているが、これに限るものではない。例えば、各情報Dの表示開始を指示した時刻と、各情報Dの表示停止を指示した時刻とを格納して、各情報Dの総表示時間を算出してもよい。また、表示装置3がマルチウィンドウ表示でき、複数の情報Dをオーバーラップして表示可能な場合は、表示時間を測定する際、表示の重なり順位に重みを付けてもよい。いずれの場合であっても、情報Dの表示時間に応じて、当該情報Dの重み係数Pを調整できれば、本実施形態と同様の効果が得られる。
【0115】
〔第2の実施形態〕
ところで、情報Dの総表示時間Tのみに基づいて、重み係数Pを調整する場合、例えば、画面の背景的に表示されている情報Dの重要度Xsも増加してしまう。また、例えば、使用者が情報管理装置2から離れている場合など、使用者が当該情報Dを注視していない場合であっても、重要度Xsが増大する虞れがある。
【0116】
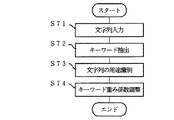
本実施形態では、重み係数Pを調整する際の別の尺度として、図6〜図9を参照しながら、情報Dの操作回数について説明する。なお、情報Dへの操作には、種々の操作が存在するが、以下では、情報Dの表示開始指示と表示停止指示とを例にして説明する。この場合、例えば、使用者の指示や画面表示に関する処理は、図5の処理と同様なので、同じ処理には同じ参照符号を付して説明を省略する。また、本実施形態および以下の実施形態では、情報管理装置2の構成は、第1の実施形態と同様で、各部の動作のみが異なっているため、図1を参照して説明する。
【0117】
すなわち、図8に示すS21〜S24において、情報管理装置2は、使用者の指示に応じて、表示装置3へ情報DA を表示し、情報制御部15は、表示分析部13aへ表示開始を通知する。一方、本実施形態に係る表示分析部13aは、S41において、履歴記憶部11cに格納されている情報DA の操作回数mA を1増加させる。
【0118】
また、使用者が表示終了を指示する場合、S26〜S29において、情報管理装置2は、表示装置3への情報DA の表示を停止し、情報制御部15は、表示分析部13aへ表示停止を通知する。この場合、上記S41と同様に、S42では、情報DA の操作回数mA を1増加させる。これにより、履歴記憶部11cには、各情報Dの操作回数mが格納される。
【0119】
さらに、重み係数処理部14aは、S43において、履歴記憶部11cに格納された情報DA の操作回数mA を参照して、操作回数mA が多いほど、当該情報DA の重要度XsA が大きくなるように、当該情報DA の重み係数PA を調整する。
【0120】
例えば、以下の表3に示すように、情報DB の操作回数mB が、情報DA の操作回数mA の2倍の場合、重み係数処理部14aは、図5に示すS32と同様に、情報DA の重み係数PA の2倍だけ、情報DB の重み係数PB を増加させる。なお、以下の表3では、比較のために、操作回数mA のみが異なり、他の条件が同一な情報DA ・DB ・DC を例示している。また、重み係数比は、重み係数PA を1とした場合の比率である。
【0121】
【表3】
【0122】
上記S21〜S43の処理は、他の情報Dでも実施されるので、操作回数mが多い情報Dほど、重要度Xsが相対的に増大し、操作回数mが少ない情報Dほど、重要度Xsが相対的に低下する。
【0123】
ここで、画面に表示されている情報Dであっても、使用者が何も操作しない情報Dは、頻繁に操作する情報Dに比べて、重要度が低いことが多い。例えば、画面の背景として表示され、操作されない情報Dは、多くの場合、画面の最も前のウィンドウに表示され、頻繁に操作される情報Dに比べて重要度が低い。また、情報Dが長時間表示されていても、使用者が情報管理装置2から離れている場合もある。
【0124】
本実施形態に係る情報管理装置2は、情報Dの操作回数mが多いほど、使用者が当該情報Dを重要視していると推測して、重み係数Pを調整する。したがって、使用者が情報管理装置2から離れている期間の長さに拘わらず、重み係数Pを調整できる。なお、操作回数mに応じて重み係数Pが調整されるので、第1の実施形態のように、総表示時間Tに基づく調整と併用した場合であっても、使用者が情報管理装置2から離れている期間に起因する重み係数Pの変動を相対的に抑制できる。これらの結果、使用者の感じる重要度Xuへ、情報管理装置2が算出する重要度Xsを近づけることができる。
【0125】
なお、上記では、表示開始操作および停止操作を数える場合を例にして説明したが、これに限るものではない。使用者にとって当該情報Dが重要であると推測された種類の操作を数えれば、同様の効果が得られる。一例として、例えば、再表示や拡大表示など、表示状態を変更する種類の操作、例えば、情報Dの内容の修正や追加、部分複写あるいは部分削除など、情報Dの内容を変更する種類の操作と、例えば、外部記録媒体への複写や印刷あるいは送信など、情報管理装置2外へ出力する種類の操作となどが挙げられる。さらに、操作の対象としては、表示している情報D、情報Dの一部分、あるいは、情報Dを格納するファイルFなどが挙げられる。例えば、ファイルFの操作回数を数える場合には、使用者がファイルFA を使用する度に、当該ファイルFの操作回数mA は、1ずつ加算され、各ファイルFの操作回数mに応じて、ファイルFに格納された情報Dの重み係数Pが調整される。いずれの場合であっても、使用者が当該情報Dを重要視している種類の操作は、予め推測できるので、情報管理装置2は、これらの種類の操作が行われた際、操作回数を数えて、操作に関連する情報Dの重み係数Pを調整できる。
【0126】
なお、第1の実施形態と同様に、操作回数mに応じた重み係数Pの調整方法は、増加幅や増加率、あるいは、比例関係や任意の関数など種々の方法を採用できる。いずれの場合であっても、操作回数が多いほど、ある情報Dの重要度Xsが上昇するような調整方法であれば、本実施形態と同様の効果が得られる。
【0127】
ただし、第1の実施形態と同様に、図6に示すように、操作回数mに対してS字状に変化するように重み係数Pを調整した方が、操作回数mに起因する重要度Xsの変動を使用者の感覚に近づけることができる。また、図7に示すように、ファイルFやキーワードKに関連しない操作が続く場合、当該ファイルFあるいはキーワードKの重み係数P(KP・FP)を徐々に減少させる方が、所望の情報Dを発見しやすくなる。
【0128】
一方、情報Dの削除など、使用者にとって、その情報Dが不要と推測される種類の操作が行われた場合、例えば、図9に示すように、情報管理装置2は、操作回数mの増加に伴って、当該情報Dの重み係数Pを低下させる方がよい。当該種類の操作も予め推測できるので、情報管理装置2は、これらの種類の操作が行われた際、何ら支障なく、操作に関連する情報Dの重み係数Pを調整できる。
【0129】
〔第3の実施形態〕
ところで、第2の実施形態では、操作回数の数え方の一例として、各操作を同等に数える場合について説明した。ところが、実際の操作には、例えば、バックスクロール操作など、使用者が情報Dを重要視しているときに頻出する特定種類の操作が存在する。したがって、当該特定種類の操作が行われた場合と、残余の操作が行われた場合とで、同じように重み係数Pを調整すると、情報管理装置2が算出する重要度Xsと使用者が感じる重要度Xuとの間にズレが発生する虞れがある。
【0130】
これに対して、本実施形態では、例えば、上記特定種類の操作を数えるなど、情報Dの操作内容に応じて重み係数Pを調整する場合について、図10〜図13を参照しながら説明する。なお、以下では、特定操作の一例として、バックスクロール操作など、情報Dの中の同じ部分を再表示させる操作について説明する。
【0131】
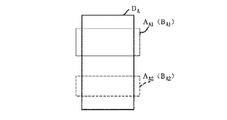
すなわち、図10に示すS51において、情報DA 中の、ある部分AA1を表示するように、使用者が指示した場合、情報制御部15は、S52において、使用者の指示に基づいて、当該部分AA1を表示するための指令を作成する。表示制御部12aは、当該指令に応じて、表示装置3の画面上に、例えば、図11に示すように、情報DA のうちの指示された部分AA1を表示する。
【0132】
さらに、情報制御部15は、S53において、当該部分AA1の画面表示が開始されたことを表示分析部13aへ通知する。また、表示分析部13aは、S54において、当該部分AA1を示す部分情報BA1が、履歴記憶部11cに格納されているか否かを照合して、当該部分AA1が過去に表示されたか否かを判定する。例えば、図12に示す例では、履歴記憶部11cに格納されている部分情報BA2は、部分AA2を示しており、現在、表示している部分AA1と異なっている。このように、上記部分AA1を示す部分情報BA1が、履歴記憶部11cに格納されていない場合、表示分析部13aは、当該部分AA1が過去に表示されていないと判定す。この場合、表示分析部13aは、部分情報BA1を作成して、履歴記憶部11cに格納する(S55)。
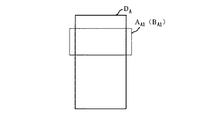
【0133】
一方、部分AA1が過去に表示されている場合(上記S54にて、 YESの場合)、例えば、図13に示すように、現在、表示している部分AA1を示す部分情報BA1は、既に、履歴記憶部11cに格納されている。この場合、表示分析部13aは、使用者が情報DA に対して再表示操作を行ったと判断し、情報DA の再表示操作回数dA を1増加させる。当該再表示操作回数dA は、履歴記憶部11cに格納される(S56)。
【0134】
さらに、重み係数処理部14aは、S57において、情報DA の再表示操作回数dA を参照して、再表示操作回数dA が多いほど、当該情報DA の重要度XsA が大きくなるように、当該情報DA の重み係数PA を調整する。
【0135】
例えば、比較のために、再表示操作回数dA のみが異なり、他の条件が同一な情報DA ・DB を例にして説明すると、情報DB の再表示操作回数dB が、情報DA の再表示操作回数dA の2倍の場合、重み係数処理部14aは、上述の表3と同様に、情報DA の重み係数PA の2倍だけ、情報DB の重み係数PB を増加させる。
【0136】
上記S51〜S57の処理は、他の情報Dでも実施されるので、再表示操作回数dが多い情報Dほど、重要度Xsが相対的に増大し、再表示操作回数dが少ない情報Dほど、重要度Xsが相対的に低下する。これにより、情報管理装置2は、使用者の感覚に近い重要度Xsを算出できる。
【0137】
なお、上記では、再表示操作回数dを数えたが、これに限るものではない。使用者が情報Dを重要視している場合に頻出する操作であれば、予め定められた特定種類の操作として他の操作を数えた場合でも同様の効果が得られる。
【0138】
さらに、特定種類の操作として、複数の種類の操作を数え、各操作毎に、重み係数Pを変化させてもよい。例えば、上記特定種類の操作として、情報Dを表示する操作と、情報Dの内容を修正する操作と、フロッピーディスクなど、可搬性の記録媒体へ情報Dを複写する操作と、電子メールなど、当該情報Dを通信する操作と、情報Dを印刷する操作とをそれぞれ数える。さらに、表示操作時の重み係数Pの増加割合を1として、修正操作時の重み係数Pの増加割合を1.5、複写操作時の増加割合を2、通信操作時の増加割合を2.5、印刷操作時の増加割合を3などのように、操作毎の重み係数Pの増加割合を変化させる。
【0139】
一般に、情報Dの印刷、通信、複写など、情報管理装置2の外部へ情報Dを出力する操作が行われた場合、使用者は、当該情報Dを多くの人々に活用させようとしていることが多く、情報管理装置2内部で情報Dを処理している場合に比べて、使用者が情報Dを重要視していると推測できる。また、使用者は、必要がない限り、情報Dの内容を修正しないことが多いので、使用者は、単に表示されている情報Dに比べて、内容を修正した情報Dの方を重要視していると推測される。したがって、上述のように、表示操作、修正操作、複写操作、通信操作、印刷操作の順番で重みを付けて、情報Dの重み係数Pを調整すれば、情報管理装置2は、使用者の感覚にさらに近い重要度Xsを算出できる。
【0140】
なお、上記では、それぞれの操作回数を別に数える場合を例にして説明したが、これに限るものではない。例えば、印刷操作を修正操作の3回分と数えるなど、計数の段階で重みを付けてもよい。操作回数を別にするか否かに拘わらず、上述の特定種類の操作毎に、重要度Xsの変動幅を変更できれば、本実施形態と同様の効果が得られる。
【0141】
〔第4の実施形態〕
ところで、上記第1ないし第3の実施形態では、操作対象が情報D全体であるか否かに拘わらず、情報D毎に、表示時間や操作回数を数え、情報Dの重要度算出に使用される重み係数Pが調整される場合について説明した。これに対して、本実施形態では、操作対象が情報Dの一部分の場合、当該部分に関連する重み係数Pを調整する場合について、図14および図15に基づき説明する。なお、情報Dの一部分を操作対象とする操作は、種々の操作が挙げられるが、以下では、部分表示を例にして説明する。
【0142】
すなわち、図14に示すS61において、表示分析部13aは、情報Dが画面表示される毎に、例えば、情報制御部15からの通知などに基づいて、情報Dのうち、どの部分Aが表示されているかを判定し、重み係数処理部14aへ通知する。一方、重み係数処理部14aは、S62において、情報分析部13cに依頼して、図15に示すように、当該部分Aに含まれているキーワードを抽出する。さらに、S63において、重み係数処理部14aは、例えば、各キーワードK毎に操作回数を数え、操作回数に応じて、キーワード重み係数KPを調整するなどして、当該キーワードKが部分Aに含まれていない場合よりも重要度Xsが大きくなるように、当該キーワードKのキーワード重み係数KPを調整する。
【0143】
なお、キーワード重み係数KPの調整方法は、第2あるいは第3の実施形態と同様に、各種操作を区別せずに調整してもよいし、操作の種類毎に重みを付けてもよい。また、操作対象の削除など、使用者が操作対象が不要と推測される操作の場合は、キーワードKの重要度Xsが減少するように、キーワード重み係数KPを調整する。
【0144】
いずれの場合であっても、情報Dの一部分が操作された場合、当該情報Dの中の各キーワードKが操作対象に含まれるか否かによって、キーワードKのキーワード重み係数KPを個別に調整できる。したがって、情報管理装置2は、より使用者の感覚に近い重要度Xsを算出できる。
【0145】
〔第5の実施形態〕
第4の実施形態では、情報Dの操作対象に含まれているか否かによって、キーワード重み係数KPを調整する場合について説明したが、キーワードKは、情報Dのみに含まれるものではなく、例えば、検索文字列など、使用者が入力する文字列にも含まれる。本実施形態では、図16を参照しながら、入力文字列に応じたキーワード重み係数KPの調整について説明する。
【0146】
すなわち、S71において、例えば、検索や情報Dの修正などのために、使用者が文字列を入力すると、情報管理装置2の入力制御部12bは、入力された文字列を情報分析部13cへ通知する。さらに、情報分析部13cは、S72において、入力文字列中に含まれているキーワードKを抽出する。
【0147】
一方、S73において、情報制御部15は、例えば、入力時点における情報管理装置2の状況(モード)を調査するなどして、当該入力文字列の用途を識別し、重み係数処理部14aへ通知する。さらに、重み係数処理部14aは、状況に応じて、各キーワードKのキーワード重み係数KPを調整する(S74)。
【0148】
例えば、情報管理装置2がファイルFを新規作成する状況であった場合、重み係数処理部14aは、キーワード重み係数KPを増加させる割合を1に設定する。これとは逆に、情報管理装置2が情報Dを更新する状況にあった場合、重み係数処理部14aは、キーワード重み係数KPを増加させる割合を1.5に設定する。また、情報Dを検索する状況の場合、キーワード重み係数KPは、2の割合で増加する。
【0149】
上記構成によれば、使用者が入力した文字列に含まれるキーワードKは、当該キーワードKが入力文字列に含まれない場合よりも、キーワード重み係数KPが大きくなる。さらに、入力文字列に含まれる場合であっても、キーワードKのキーワード重み係数KPは、新規作成、更新、検索の順番で大きくなる。
【0150】
一般に、使用者は、文字列を入力する際、使用者自身が重要視する文字列を入力している。したがって、使用者の入力文字列中に含まれるキーワードKの重要度を大きくすることで、情報管理装置2は、使用者の感覚に近い重要度Xsを算出できる。
【0151】
さらに、文字列の長さは、新規作成、更新、検索の順番で短くなることが多い。特に、検索時には、使用者が重要視しているキーワードKのみが入力されることが多く、新規作成時には、重要視しているキーワードKだけではなく、他のキーワードKも入力される。したがって、上述のように、文字列の用途に応じて、キーワード重み係数KPを調整することで、情報管理装置2は、さらに、使用者の感覚に近い重要度Xsを算出できる。
【0152】
〔第6の実施形態〕
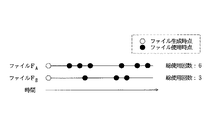
ところで、上記第1ないし第5の実施形態では、例えば、総表示時間Tや総操作回数m(d)など、情報D(ファイルF)が生成されてからの操作状況全てに応じて、重み係数Pを調整する方法(第1の方法)について説明した。この方法によれば、操作回数mに応じる場合、操作回数mが多い情報Dほど、重要度Xsが増加するので、情報管理装置2は、例えば、図17に示すように、操作回数mが異なる情報Dについて、互いに異なる重要度Xsを提示できる。
【0153】
ところが、この第1の方法では、例えば、図18に示すように、1年前に作成されて、その頃にn回操作されたファイルFA に格納された情報DA の重要度XsA は、最近作成され、n回操作されたファイルFB に格納された情報DB の重要度XsB と同一になってしまう。
【0154】
ここで、一般に最近頻繁に操作された情報DB は、かつて頻繁に操作された情報DA よりも、現時点での重要度Xsが高いことが多い。したがって、第1の方法で重み係数Pを調整すると、上記両重要度XsA ・XsB の値が近くなり、使用者が情報DB を発見しにくくなる虞れがある。
【0155】
これに対して、本実施形態に係る重み係数処理部14aは、第2の方法として、ファイルFが作成されてから現在に至るまでの経過時間Rで、総操作回数mを割った値(m/R)に応じて、重み係数Pを変更する。なお、経過時間Rは、情報Dの属性として格納される作成日時などから算出できる。
【0156】
本実施形態では、重み係数処理部14aは、操作回数mに代えて、m/Rに応じて、重み係数Pを調整する。したがって、経過時間Rが長い情報Dほど、重み係数Pの維持に必要な操作回数mが大きくなり、重要度Xsが相対的に低下する。この結果、情報管理装置2は、現時点での使用者の感覚にさらに近い重要度Xsを算出できる。
【0157】
〔第7の実施形態〕
ところで、第1ないし第6の実施形態では、履歴記憶部11cに格納された総表示時間Tや操作回数mなどが、操作時に更新される場合について説明したが、総表示時間Tや操作回数を求める方法は、これに限るものではない。
【0158】
本実施形態では、操作時には、操作時刻などを含む履歴情報Hが履歴記憶部11cに格納され、当該履歴情報Hに基づいて、重要度Xsを算出する場合について説明する。なお、以下では、説明の便宜上、第2の実施形態において、履歴情報Hを格納する場合を例にして説明する。
【0159】
すなわち、図19に示すように、S81において、使用者が情報Dを操作すると、情報制御部15は、S82において、操作の履歴情報Hを格納する。当該履歴情報Hには、操作の時期と、重要度Xsを後で算出する際、必要な情報とが含まれている。例えば、情報Dへ操作回数に基づいて重要度Xsを算出する場合は、履歴情報Hには、操作した日時と、操作対象となる情報Dとが含まれる。
【0160】
さらに、重要度Xsを算出する際、重み係数処理部14aは、S83において、各情報Dの履歴情報Hに基づいて、それぞれの重み係数Pを調整し、重要度Xsを算出する。
【0161】
ここで、本実施形態では、重み係数処理部14aは、履歴記憶部11cに格納された履歴情報Hから、各情報DA に関連する履歴情報Hをそれぞれ抽出すれば、各情報Dの操作回数mを算出できる。したがって、重み係数処理部14aは、上記第1の方法および第2の方法と同様に、操作回数m、あるいは、操作回数mを経過時間Rで割った値に応じて、各情報Dの重み係数Pを調整できる。
【0162】
さらに、本実施形態では、履歴情報Hが格納されているため、上記第1の方法および第2の方法に加えて、操作時期に応じて重みを付ける第3の方法を選択できる。
【0163】
例えば、最近1か月に1回使用した場合に、重み係数Pを増加させる割合を1とした場合、過去1か月前から2か月前までの期間に1回使用した場合を0.9、2か月前から3か月前までの期間を0.8のように、操作する時点が、現時点から離れるに従って重みが小さくなるように重みを付けて、重み係数Pを調整する。これにより、図20に示すように、経過時間Rと操作回数mとが同一であっても、より最近に操作された情報Dの重要度Xsを相対的に増加できる。この結果、情報管理装置2は、使用者の感覚にさらに適合した重要度Xsを算出できる。
【0164】
ここで、上記では、現時点との差に応じて重みを付ける場合について説明したが、これに限るものではない。任意の時点との差に応じて、重みを付ければ、当該時点における使用者の感覚に適合した重要度Xsを算出できる。一般に、使用者が感じる重要度Xuは、常に一貫している訳ではなく、時間の経過と共に変化することが多い。したがって、使用者は、ある時点において重要と考えていた情報Dに基づいて、情報Dを検索することがある。この場合には、情報管理装置2は、ある時点での使用者の感覚に近い重要度Xsを算出することが求められる。第3の方法では、履歴情報Hを算出することで、任意の時点での重要度Xsを算出できる。さらに、履歴記憶部11cが履歴情報Hを格納しているので、使用者の要求に応じて、第1の方法〜第3の方法のうちの任意の方法を選択できる。したがって、使用者が所望の情報Dを発見する際の手間を大幅に削減できる。
【0165】
なお、上記では、履歴情報Hとして、第2の実施形態での重要度算出に必要な情報が記憶されている場合を例にして説明したが、第1ないし第5の実施形態での重要度算出に必要な情報を記憶すれば、いずれに適用しても、同様の効果が得られる。
【0166】
特に、第3の実施形態に適用した場合、重要度算出時点で、特定種類の操作を特定できると共に、各種操作間の重み付けを変更できる。例えば、印刷操作の重みを重くすれば、通信操作された情報Dの重要度Xsを大きくできる。したがって、情報管理装置2が重要度Xsを算出する際の方法を、より柔軟に変化させることができ、使用者が所望の情報Dを発見する際の手間を大幅に削減できる。
【0167】
ところで、履歴情報Hを格納する場合は、総表示時間Tや操作回数m(d)を格納する場合に比べて、多くの記憶容量を必要とする。ところが、履歴情報Hの格納に必要な記憶容量は、情報Dの格納に必要な記憶容量よりも極めて小さいことが多いので、情報管理装置2全体の記憶容量は、余り増加しない。
【0168】
なお、上記各第1ないし第7の実施形態で説明した重み係数Pの調整方法は、任意の組み合わせで併用できる。この場合は、各種の操作に応じて、重み係数Pを調整できるので、情報管理装置2は、さらに使用者の感覚に近い重要度Xsを算出できる。特に、例えば、再表示の有無、外部出力の有無など、互いに異なる操作に基づいて、重み係数Pを調整すれば、広く一般の操作に応じて、重み係数Pを調整できるので、情報管理装置2は、より的確に重要度Xsを算出できる。
【0169】
また、上記各実施形態では、重み係数Pが増大すれば、情報Dの重要度Xsが増大する場合について説明したが、これに限るものではない。例えば、重み係数Pが増大した場合、情報Dの重要度Xsが減少する場合など、他の方法で重要度Xsを算出する場合であっても、上記各実施形態と情報Dの重要度Xsが同様に変化するように、重み係数Pを調整できれば、同様の効果が得られる。
【0170】
さらに、上記各実施形態では、情報Dに関連する操作が行われた場合、当該情報Dの重要度算出に使用される重み係数Pを調整する場合について説明したが、これに限らず、例えば、情報Dの重要度算出に使用されない重み係数Pを調整してもよい。重要度算出に使用される重み係数Pの大きさと、残余の重み係数Pの大きさとを、相対的に変更できれば、同様の効果が得られる。
【0171】
また、上記各実施形態に係る記録媒体は、各情報に応じて作成される重み係数のうち、 情報に関連する重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出する重要度算出工程と、情報に関連する操作に応じて、上記重要度算出工程で使用される重み係数を調整する重み係数調整工程とを実行するプログラムが記録されていることを特徴としている。
【0172】
【発明の効果】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、各情報に応じて作成され、関連する情報の重要度算出に使用される重み係数を記憶する重み係数記憶手段と、情報に関連する重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出する重要度算出手段と、情報に関連する操作に応じて、上記重み係数を調整する重み係数調整手段とを備えている構成である。
【0173】
上記構成によれば、重み係数が情報に応じて作成され、操作の傾向に応じて調整される。したがって、使用者が各情報の重要度を管理しなくても、情報管理装置は、各使用者に適合した重要度を算出できる。この結果、使用者が必要な情報を探し出すために情報を整理する際の手間を大幅に削減できるという効果を奏する。また、開放型の学習システムで各情報の重要度が学習されるので、情報に関連する操作が可能な情報管理装置に広く適用できるという効果を奏する。
【0174】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、情報に関連する操作の履歴を示す履歴情報が格納される履歴情報記憶手段を備え、上記重み係数調整手段は、履歴情報に基づいて、重み係数を調整する構成である。
【0175】
上記構成では、情報に関連する操作が行われると、当該操作を示す履歴情報が履歴情報記憶手段に格納される。したがって、重要度算出を指示した時点で、重み係数の調整方法が指定されても、当該調整方法で重み係数を調整でき、情報管理装置は、より柔軟に情報の重要度を算出できるという効果を奏する。
【0176】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、上記重み係数調整手段は、操作が行われた時期に応じて、重み係数の調整量を変更する構成である。
【0177】
上記構成によれば、特定の時期において、使用者が重要と判断していると推測される情報の重要度を増大させることができる。この結果、使用者が所望の情報を発見する際の手間をさらに削減できるという効果を奏する。
【0178】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、上記重要度算出手段は、情報が蓄積されるファイルのファイル重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出する構成である。
【0179】
上記構成では、重み係数となるファイル重み係数は、情報の蓄積単位となるファイル毎に設けられており、情報に関連する操作に応じて調整される。この結果、情報管理装置は、情報の重要度をファイル単位で増減でき、情報検索時の手間を削減できるという効果を奏する。
【0180】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、上記重要度算出手段は、情報を構成する各キーワードのキーワード重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出する構成である。
【0181】
上記構成では、ある情報が操作された場合、当該情報中のキーワードが含まれる他の情報の重要度を調整でき、情報検索時の手間を削減できるという効果を奏する。
【0182】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、上記重要度算出手段は、情報を蓄積するファイルのファイル重み係数と、当該情報を構成するキーワード重み係数とに基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出する構成である。
【0183】
上記構成によれば、操作された情報の重要度と、上記類似の情報の重要度との差を保ちながら、類似の情報の重要度を調整できる。この結果、直接操作した情報と類似の情報との双方をより早く発見可能な情報管理装置を実現できるという効果を奏する。
【0184】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、情報の表示時間が長いほど、当該情報の重要度が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整する構成である。
【0185】
上記構成によれば、表示時間が長い情報が相対的に大きな重要度を持つように、重み係数を調整でき、情報検索時の手間を削減できるという効果を奏する。
【0186】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、情報に関連する操作のうち、当該情報を重要視している際に頻出すると予め推定された第1種の操作の回数が多いほど、当該情報の重要度が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整する構成である。
【0187】
上記構成によれば、使用者が当該情報を重要と判断する際に頻出する操作が行われた場合、当該情報の重要度が大きくなる。この結果、情報管理装置は、使用者の操作傾向に適合した重要度を算出でき、情報検索時の手間を削減できるという効果を奏する。
【0188】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、情報に関連する操作のうち、第1種の操作の回数を経過時間で割った値が大きいほど、当該情報の重要度が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整する構成である。
【0189】
上記構成によれば、操作回数が同じ場合であっても、最近作成された情報の重要度を大きくできる。この結果、情報管理装置は、より使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できるという効果を奏する。
【0190】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、上記第1種の操作には、情報の表示、情報の情報管理装置外への出力、および、情報の内容変更のうちの少なくとも1つが含まれている構成である。
【0191】
上記構成では、表示、情報管理装置外への出力、あるいは、内容変更が行われた情報ほど、重要度が相対的に大きくなる。この結果、情報管理装置は、より使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できるという効果を奏する。
【0192】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、上記第1種の操作の操作内容に応じて、上記重み係数の調整量を変更する構成である。
【0193】
上記構成によれば、重み係数の調整量は、操作の種類に応じて変化するため、情報が算出する重要度と、使用者が感じる重要度との間のズレを低減できる。この結果、情報管理装置が、より的確な重要度を算出できるという効果を奏する。
【0194】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、再表示を必要とする表示操作の方が情報の重要度の変動量が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整する構成である。
【0195】
上記構成によれば、再表示が頻繁に行われる情報ほど、重要度が相対的に高くなる。これにより、情報管理装置は、より的確に、情報の重要度を算出できるという効果を奏する。
【0196】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、情報の表示操作よりも、情報の情報管理装置外への出力操作の方が、情報の重要度の変動量が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整する構成である。
【0197】
上記構成によれば、出力操作された情報ほど、重要度が相対的に大きくなる。この結果、情報管理装置は、より使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できるという効果を奏する。
【0198】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、情報の表示操作よりも、情報の内容変更操作の方が、情報の重要度の変動量が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整する構成である。
【0199】
上記構成によれば、内容が変更された情報の重要度を相対的に大きくできる。この結果、情報管理装置は、より的確に、情報の重要度を算出できるという効果を奏する。
【0200】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、情報の内容変更操作よりも、情報の情報管理装置外への出力操作の方が、情報の重要度の変動量が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整する構成である。
【0201】
上記構成によれば、出力された情報、内容が変更された情報、表示された情報の順番で、重要度が相対的に大きくなる。したがって、情報管理装置は、より的確に重要度を算出できるという効果を奏する。
【0202】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、情報に関連する操作のうち、当該情報が不要な場合に頻出すると予め推定された第2種の操作が行われた場合、当該情報の重要度が小さくなるように、上記重み係数を調整する構成である。
【0203】
上記構成によれば、使用者が情報を不要と判断している場合に頻出する操作が行われると、情報の重要度が小さくなる。したがって、情報管理装置は、使用者の操作傾向に適合した重要度を算出でき、情報検索時の手間を削減できるという効果を奏する。
【0204】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、情報の操作部分を特定する部分特定手段を備え、上記重み係数調整手段は、当該操作部分に含まれるキーワードのキーワード重み係数を調整する構成である。
【0205】
上記構成によれば、キーワード重み係数の調整量は、操作部分に含まれているか否かによって変更される。これにより、情報管理装置は、使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できるという効果を奏する。
【0206】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、情報の表示部分に、あるキーワードが含まれる場合、当該キーワードが含まれていない場合よりも、当該キーワードの重要度が大きくなるように、キーワード重み係数を調整する構成である。
【0207】
上記構成によれば、頻繁に表示部分に含まれるキーワードほど、重要度が相対的に大きくなる。この結果、情報管理装置は、使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できるという効果を奏する。
【0208】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、削除された操作部分に、あるキーワードが含まれている場合、当該キーワードが含まれていない場合よりも、当該キーワードの重要度が小さくなるように、キーワード重み係数を調整する構成である。
【0209】
上記構成によれば、情報の内容修正の結果、頻繁に削除されるキーワードほど、重要度が相対的に小さくなる。この結果、情報管理装置は、使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できるという効果を奏する。
【0210】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、入力された文字列に、あるキーワードが含まれる場合、当該キーワードが含まれない場合よりも、当該キーワードの重要度が大きくなるように、キーワード重み係数を調整する構成である。
【0211】
上記構成によれば、入力文字列に頻繁に含まれるキーワードほど、重要度が相対的に大きくなる。これにより、情報管理装置は、使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できるという効果を奏する。
【0212】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、上記入力文字列の用途を識別する識別手段を備え、上記重み係数調整手段は、上記入力文字列の用途に応じて、キーワード重み係数の調整量を変更する構成である。
【0213】
上記構成によれば、キーワード重み係数の調整量は、入力文字列の用途に応じて変更される。ここで、入力文字列の長さや、入力文字列中のキーワードを使用者が重要視する程度が、用途毎に異なる場合であっても、使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出でき、情報検索時の手間を削減できるという効果を奏する。
【0214】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、上記入力文字列の用途が情報検索の場合、用途が情報の新規追加の場合よりも、キーワードの重要度の変動量が大きくなるように、上記キーワード重み係数を調整する構成である。
【0215】
上記構成によれば、情報検索の際に使用されるキーワードの重要度が相対的に大きくなる。したがって、情報管理装置は、使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できるという効果を奏する。
【0216】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、上記入力文字列の用途が情報の内容修正の場合、用途が情報の新規追加の場合よりも、キーワードの重要度が大きくなるように、上記キーワード重み係数を調整する構成である。
【0217】
上記構成によれば、内容修正に使用されるキーワードの重要度が相対的に大きくなる。したがって、情報管理装置は、使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できるという効果を奏する。
【0218】
本発明に係る情報管理装置は、以上のように、上記構成に加えて、上記入力文字列の用途が情報検索の場合、用途が情報の内容修正の場合よりも、キーワードの重要度が大きくなるように、上記キーワード重み係数を調整する構成である。
【0219】
上記構成によれば、情報検索に使用されるキーワードは、内容修正に使用されるキーワードに比べて、相対的な重要度がさらに大きくなる。したがって、情報管理装置は、使用者の感覚に近い重要度を算出できるという効果を奏する。
【0220】
本発明に係る記録媒体は、以上のように、上記各情報管理装置の各手段として、コンピュータを動作させるプログラムが記録されている構成である。
【0221】
上記構成の当該プログラムがコンピュータで実行されると、上記情報管理装置と同様に、重み係数が情報に応じて作成され、操作の傾向に応じて調整される。また、開放型の学習システムで各情報の重要度が学習されるので、情報の重要度に拘わらず、各情報の重み係数を調整できる。したがって、各情報の重要度を管理しなくても、各使用者に適合した重要度を算出でき、かつ、広い範囲に適用可能な情報管理装置を実現できるという効果を奏する。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の一実施形態を示すものであり、情報管理システムの要部構成を示すブロック図である。
【図2】上記情報管理システムにおいて、情報管理装置の動作の概略を示すフローチャートである。
【図3】情報入力時における上記情報管理装置の動作を示すフローチャートである。
【図4】情報入力時における上記情報管理装置の動作を示すものであり、重み係数の算出方法を示す説明図である。
【図5】総表示時間に応じて重み係数が調整される場合において、上記情報管理装置の動作を示すフローチャートである。
【図6】上記情報管理システムにおいて、重み係数に関連する表示(操作)が行われた場合の重み係数の変化を示すグラフである。
【図7】上記情報管理システムにおいて、重み係数に関連しない表示(操作)が続いた場合の重み係数の変化を示すグラフである。
【図8】本発明の他の実施形態を示すものであり、操作回数に応じて重み係数を調整する場合における情報管理装置の動作を示すフローチャートである。
【図9】上記情報管理システムにおいて、情報が不要であると推測される操作が行われた場合の重み係数の変化を示すグラフである。
【図10】本発明のさらに他の実施形態を示すものであり、操作内容に応じて重み係数を調整する場合における情報管理装置の動作を示すフローチャートである。
【図11】上記情報管理装置の動作を示すものであり、新たな表示部分が指定された場合を示す説明図である。
【図12】上記情報管理装置の動作を示すものであり、指定された表示部分が、表示部分の履歴と一致しない場合を示す説明図である。
【図13】上記情報管理装置の動作を示すものであり、指定された表示部分が、表示部分の履歴と一致する場合を示す説明図である。
【図14】本発明のさらに他の実施形態を示すものであり、表示部分に含まれるキーワードのキーワード重み係数を調整する場合において、情報管理装置の動作を示すフローチャートである。
【図15】上記情報管理装置の動作を示す説明図である。
【図16】本発明のさらに他の実施形態を示すものであり、入力文字列に含まれるキーワードのキーワード重み係数を調整する場合において、情報管理装置の動作を示すフローチャートである。
【図17】情報の作成時点と操作時点との関係を示すものであり、操作回数が異なる場合を示すタイミングチャートである。
【図18】情報の作成時点と操作時点との関係を示すものであり、操作回数が同一で、作成時期が異なる場合を示すタイミングチャートである。
【図19】本発明のさらに他の実施形態を示すものであり、格納された履歴情報に基づいて、重み係数を調整する場合において、情報管理装置の動作を示すフローチャートである。
【図20】情報の作成時点と操作時点との関係を示すものであり、操作回数と作成時点とが互いに同一で、操作時点が異なる場合を示すタイミングチャートである。
【符号の説明】
2 情報管理装置
11b 重み係数蓄積部(重み係数記憶手段;ファイル重み係数記憶手段; キーワード重み係数記憶手段)
11c 履歴記憶部(履歴情報記憶手段)
13a 表示分析部(部分特定手段)
14a 重み係数処理部(重み係数調整手段)
14b 重要度計算部(重要度算出手段)
15 情報制御部(識別手段)[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to an information management apparatus that manages various types of information while changing the importance of information according to a user, and a recording medium on which the program is recorded.
[0002]
[Prior art]
Conventionally, for example, managing various information using a computer or the like has been widely performed. The amount of information managed by these information management devices tends to increase more and more due to, for example, the widespread use of large-capacity recording media such as CD-ROMs and the expansion of information databases due to the development of information networks. The amount of information that can be manually organized and managed is being exceeded. Therefore, in recent years, an automatic organization / management technique using the information management apparatus itself has been proposed.
[0003]
For example, the information management apparatus described in Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 5-20362 analyzes the contents of text stored in units of documents and automatically extracts the key words (keywords) that are the keys of each information, Each document is organized by automatically associating each document based on the importance of each keyword. In this way, the information management apparatus supports, so that it is possible to reduce the trouble for the user to extract necessary information from a large amount of information.
[0004]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, since the importance level felt by the user is often different for each user, the conventional information management apparatus has a problem that it is difficult to provide sufficient support adapted to the intention of each user.
[0005]
Specifically, in the information management apparatus configured as described above, since each keyword is managed by mechanically extracting a keyword from the content of the information, each information is classified from a common point of view by each user. On the other hand, the degree of importance felt by the user is generally different for each user due to various factors such as the job type and interest of the user. Therefore, there is a difference between the importance managed by the information management device and the importance felt by the user of the information management device, and the information management device configured as described above stores the information with the importance according to each user. It is difficult to manage. As a result, in the information management apparatus, it is difficult to support the user in conformity with the user, and it is difficult to say that the effort for the user to extract necessary information is sufficiently reduced.
[0006]
Here, as a method of overcoming the above problem, there is a method of allowing each user to change the importance of the keyword. However, when recognizing the importance of a keyword, the user usually only recognizes the magnitude or ratio of the importance with other keywords, and sets the importance of the keyword to a desired value. Is difficult even for the user. Furthermore, since the amount of keywords increases as the amount of information increases, in the above configuration, the user manages a large number of keywords. Therefore, the user is required to manage keywords newly while being freed from information importance management. As a result, in order to extract necessary information, it still requires a lot of time and is a burden on the user. Furthermore, as the amount of information increases, there is a possibility that keywords cannot be managed completely.
[0007]
On the other hand, as another method for reflecting the importance felt by the user to the information management apparatus, in Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 6-309291, the display layout based on the importance calculated by the information management apparatus is displayed by the user. A configuration is disclosed that learns and controls the weighting factor at the time of display layout calculation so as to match the layout. However, this configuration cannot be applied to general operations because the user needs to specify a target value by learning control of the information management apparatus.
[0008]
Furthermore, the weighting factor described in the publication is a parameter for combining basic importance functions in importance calculation such as structural importance functions and semantic importance functions. Therefore, the correction of the weighting factor is reflected as the correction of the policy when determining the display layout, and it is difficult to change the importance of each piece of information itself.
[0009]
Further, since it is indispensable to display in a display layout corresponding to the importance, the type of display device and the use of the information management device are limited. As a result, the application range of the information management apparatus is limited.
[0010]
The present invention has been made in view of the above problems, and an object of the present invention is to provide an information management apparatus that can be applied to a wide range and can manage information while changing the importance according to the user. It is to provide.
[0011]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The present inventionIn order to solve the above problem, the information management apparatus according toWeighting factor storage means for storing weighting factors that are created according to each information and used to calculate the importance of related information, and the importance that calculates the importance of the information based on the weighting factors related to the information A calculating means and a weighting coefficient adjusting means for adjusting the weighting coefficient according to an operation related to information, wherein the weighting coefficient adjusting means attaches importance to the information among the operations related to information The weighting factor is adjusted so that the greater the value obtained by dividing the number of operations of the first type that is presumed to occur frequently by the elapsed time since the information was created, the greater the importance of the information. It is characterized by doing.
[0012]
In addition to the above configuration, the first type of operation may include at least one of information display, information output outside the information management apparatus, and information content change.
[0013]
Further, the weight coefficient adjusting means may change the adjustment amount of the weight coefficient according to the operation content of the first type operation.
[0014]
Further, in order to solve the above problems, the information management device according to the present invention is a weighting coefficient storage unit that stores weighting coefficients that are created according to each information and used for calculating the importance of related information, An importance calculation means for calculating the importance of the information based on a weight coefficient related to the information, and a weight coefficient adjustment means for adjusting the weight coefficient according to an operation related to the information. The above means that the importance of the information increases as the number of times of the first type operation that is presumed to occur frequently when the information is important among the operations related to the information increases. While adjusting the weighting factor, the weighting factor adjusting means may change the adjustment amount of the weighting factor according to the operation content of the first type of operation.
[0015]
Further, in addition to the above-described configuration, the weighting factor adjusting unit is configured so that the amount of change in the importance of information is larger in a display operation that requires redisplay than in a display operation that does not require redisplay. The weighting factor may be adjusted.
[0016]
Further, in addition to the above configuration, the weighting factor adjusting unit is configured so that the amount of change in the importance of the information is larger in the output operation outside the information management apparatus than in the information display operation. The weighting factor may be adjusted.
[0017]
Further, in addition to the above configuration, the weighting factor adjusting unit adjusts the weighting factor so that the information content change operation has a larger amount of change in the importance of information than the information display operation. May be.
[0018]
Further, in addition to the above configuration, the weighting factor adjusting means is configured so that the amount of change in the importance of information is greater in the output operation outside the information management device than in the information content change operation. The weighting factor may be adjusted.
[0019]
Further, in addition to the above configuration, the weight coefficient storage means includes keyword weight coefficient storage means in which a keyword weight coefficient provided for each keyword constituting information is stored as the weight coefficient, and the importance calculation means May calculate the importance of the information based on the keyword weight coefficient of each keyword constituting the information.
[0020]
In addition to the above configuration, the weight coefficient storage means includes file weight coefficient storage means for storing a file weight coefficient provided for each file, which is a storage unit of information, as the weight coefficient, and the importance level The calculation means may calculate the importance of the information based on the file weight coefficient of the file for storing information and the keyword weight coefficient constituting the information.
[0021]
Further, in addition to the above configuration, the weight coefficient storage means includes file weight coefficient storage means for storing a file weight coefficient provided for each file as an information storage unit as the weight coefficient, and the importance level The calculation means may calculate the importance of the information based on the file weight coefficient of the file in which the information is stored.
[0022]
Further, in order to solve the above problems, the information management device according to the present invention is a weighting coefficient storage unit that stores weighting coefficients that are created according to each information and used for calculating the importance of related information, Importance calculating means for calculating the importance of the information based on the weighting factor related to Weighting coefficient adjusting means for adjusting the weighting coefficient according to an operation related to information, and the weighting coefficient storage means stores the keyword weighting coefficient provided for each keyword constituting the information as the weighting coefficient. Keyword weight coefficient storage means, and the importance level calculation means calculates the importance level of the information based on the keyword weight coefficient of each keyword constituting the information, and further specifies the operation part of the information It comprises a part specifying means, and the weight coefficient adjusting means adjusts the keyword weight coefficient of the keyword included in the operation part.
[0023]
Further, in addition to the above configuration, the part specifying unit specifies an information display part as an operation part, and the weight coefficient adjusting unit includes the keyword when the operation part includes a keyword. The keyword weighting factor may be adjusted so that the degree of importance of the keyword is greater than when it is not.
[0024]
In addition to the above-described configuration, the weight coefficient adjustment unit is less important when the deleted operation part includes a keyword than when the keyword is not included. As described above, the keyword weighting coefficient may be adjusted.
[0025]
Furthermore, in order to solve the above-described problem, the information management apparatus according to the present invention includes weighting factor storage means for storing a weighting factor that is created for each piece of information and used for calculating importance of related information, An importance calculation means for calculating the importance of the information based on a weight coefficient related to the information, and a weight coefficient adjustment means for adjusting the weight coefficient according to an operation related to the information, and the weight coefficient storage The means includes keyword weight coefficient storage means for storing a keyword weight coefficient provided for each keyword constituting the information as the weight coefficient, and the importance calculation means includes the keyword weight coefficient for each keyword constituting the information. The weighting factor adjustment means calculates the importance of the information based on the keyword, and if the input character string includes a keyword, the keyword Than not contain a de, so the importance of the keyword increases, is characterized by adjusting the keyword weighting factors.
[0026]
Further, in addition to the above configuration, an identification unit for identifying the use of the input character string is provided, and the weighting factor adjusting unit may change the adjustment amount of the keyword weighting factor according to the use of the input character string. Good.
[0027]
Further, in addition to the above-described configuration, the weighting factor adjusting unit may increase the amount of change in the importance of the keyword when the use of the input character string is information search, compared with the case where the use is a new addition of information. The keyword weight coefficient may be adjusted.
[0028]
Further, in addition to the above configuration, the weighting factor adjustment unit may increase the importance of the keyword when the use of the input character string is information content correction than when the use is a new addition of information. The keyword weighting factor may be adjusted.
[0029]
Further, in addition to the above-described configuration, the weight coefficient adjustment means may be configured such that when the use of the input character string is information retrieval, the importance of the keyword is greater than when the use is information content correction. The weighting factor may be adjusted.
[0030]
In addition to the above configuration, the weight coefficient storage means includes file weight coefficient storage means for storing a file weight coefficient provided for each file, which is a storage unit of information, as the weight coefficient, and the importance level The calculation means may calculate the importance of the information based on the file weight coefficient of the file for storing information and the keyword weight coefficient constituting the information.
[0031]
Further, in addition to the above configuration, there is provided history information storage means for storing history information indicating a history of operations related to information, and the weighting coefficient adjusting means can adjust the weighting coefficient based on the history information. Good.
[0032]
In addition to the above-described configuration, the weighting factor adjusting unit may change the adjustment amount of the weighting factor according to the time when the operation is performed.
[0033]
If the weighting factor can be adjusted before the importance level calculating unit finishes calculating the importance level of the information, for example, the weighting factor adjusting unit may update the value stored in the weighting factor storage unit, You may adjust, after reading from the weight coefficient memory | storage means. Further, when a plurality of weighting factors are used when calculating the importance of certain information, at least one of the weighting factors may be adjusted. In addition, for each operation, the entire information (file) may be the operation target, or part of the information may be the operation target.
[0034]
the aboveWeighting factor storage means for storing weighting factors created according to each information and used for calculating the importance of related information, and importance for calculating importance of the information based on the weighting factor related to information A calculating unit and a weighting factor adjusting unit configured to adjust the weighting factor according to an operation related to information.In the configuration, the weighting coefficient is created according to each information, for example, for each file that is an information storage unit or for each keyword that is a unit constituting information, and is stored in the weighting coefficient storage means. In addition, the weighting coefficient adjusting unit adjusts the weighting coefficient when an operation related to information such as an operation on displayed information or an operation on a file in which information is stored is performed. Furthermore, the importance level calculation means calculates the importance level of the information based on the weighting coefficient related to the information.
[0035]
According to the above configuration, the importance of each information can be used, for example, the information to be operated, the distribution of files or keywords, or the type and timing of the operation, without the user instructing the importance. It is automatically adjusted according to the user's operation tendency. For example, if a method that increases the importance of the information every time the information is manipulated is selected as the weighting coefficient adjustment method, the more important the information, the greater the importance. As a result, the information management apparatus can calculate the importance suitable for each user without the user managing the keyword for search or managing the importance of each information. As a result, it is possible to greatly reduce the time and effort required for the user to organize information in order to find out necessary information.
[0036]
The weighting factor is created according to the information and adjusted according to the operation tendency. In this way, since the importance of each information is learned by the open learning system, the weighting coefficient of each information can be adjusted regardless of the importance of the information. Therefore, unlike the conventional technique in which each information is displayed in a layout corresponding to the degree of importance, and learning control is performed on the system-specific weight coefficient so as to match the layout instructed by the user, the applicable range is not limited. The present invention can be widely applied to information management devices that can perform operations related to information.
[0037]
Furthermore, onHistory information storage means for storing history information indicating an operation history related to the recording information, and the weighting coefficient adjusting means adjusts the weighting coefficient based on the history information.StructureIn the configuration, when an operation related to information is performed, history information indicating the operation is stored in the history information storage unit. Here, the weighting factor adjusting means can adjust the weighting factor by referring to the history information, for example, even when the time has elapsed since the operation time point, such as the time point when the user instructs the importance calculation of information. . Therefore, even if a weighting factor adjustment method is specified at the time of instructing importance calculation, the weighting factor can be adjusted by the adjustment method. As a result, the information management apparatus can calculate the importance of information more flexibly.
[0038]
In general, the importance felt by the user changes with the passage of time. Therefore, information that is determined to be important at a certain time and frequently manipulated may be determined to be less important at another time.
[0039]
the aboveThe weighting factor adjusting means is configured to change the adjustment amount of the weighting factor according to the time when the operation is performed.According to this, the adjustment amount of the weighting coefficient is changed according to the time when the operation is performed. Therefore, the adjustment amount of the weighting coefficient resulting from the operation at a specific time can be set to a value different from that at the remaining time. Accordingly, it is possible to increase the importance of information that is estimated to be important by the user at a specific time. As a result, it is possible to further reduce the trouble for the user to find desired information.
[0040]
UpThe weighting coefficient storage means includes file weighting coefficient storage means for storing a file weighting coefficient provided for each file as a storage unit of information as the weighting coefficient, and the importance calculation means stores information. Calculate the importance of the information based on the file weighting factorIn the configuration, the file weighting coefficient serving as a weighting coefficient is provided for each file serving as an information storage unit, and is adjusted according to an operation related to information. As a result, the information management apparatus can increase or decrease the importance of information in units of files.Note that the importance calculation unit may calculate the importance using other weighting factors such as a keyword weighting factor described later as long as the importance of the information is calculated based on the file weighting factor.
[0041]
Here, when a user operates information, the file is often set as an operation target, for example, by opening a file in which the information is stored and displaying the information. Accordingly, the information management device can increase or decrease the importance level for each file, thereby calculating the importance level suitable for the user's operation tendency, and the user can find necessary information earlier.
[0042]
By the way, as said information, not only a character but the information of various formats, such as an image and an audio | voice, can be considered. Among these, when information is composed of keywords that are meaningful units, such as information consisting of characters, it is effective to provide a weighting coefficient corresponding to the keywords.
[0043]
IeThe weight coefficient storage means includes keyword weight coefficient storage means for storing, as the weight coefficient, a keyword weight coefficient provided for each keyword constituting the information, and the importance degree calculation means includes each of the importance degree calculation means. Calculate the importance of the information based on the keyword weighting factor of the keywordIn the configuration, a keyword weighting factor that is a weighting factor is provided for each keyword constituting the information, and is adjusted according to an operation related to information including the keyword. Therefore, when certain information is operated, the importance of other information including the keyword in the information is adjusted.If the importance of information is calculated based on the keyword weighting factor, other weighting factors such as the file weighting factor may be used together.
[0044]
Here, information that includes many keywords in common often has contents similar to each other, and when a user determines that certain information is important, the information having contents similar to the information is also determined to be important. Often to do. Therefore, by adjusting the keyword weighting coefficient, it is possible to calculate the degree of importance suitable for the operation tendency of the user, and the user can find necessary information earlier.
[0045]
By the way, when the importance calculation means calculates the importance based only on the file weight coefficient, when certain information is operated, only the importance of the information changes, and the importance of the other information does not change. Therefore, it may take time to search for information having contents similar to the information. On the other hand, when the importance is calculated based only on the keyword weighting factor, the importance of the operated information is close to the importance of information having contents similar to the information, and it becomes difficult to find the operated information. There is a fear.
[0046]
On the other handAnd aboveRecordThe weight coefficient storage means includes file weight coefficient storage means for storing a file weight coefficient provided for each file as a storage unit of information as the weight coefficient, and the importance calculation means is a file for storing information. The importance of the information is calculated based on the file weighting coefficient and the keyword weighting coefficient constituting the information.In the configuration, the importance level calculation means calculates the importance level based on the file weight coefficient and the keyword weight coefficient. Therefore, when certain information is manipulated, the importance of information having contents similar to the information can be changed, and the difference between the importance of manipulated information and the importance of the similar information is maintained. Can do. As a result, it is possible to realize an information management apparatus that can discover both information directly operated and similar information earlier.If both weighting factors are used for calculating the importance of information, other weighting factors may be used in combination.
[0047]
Also,UpThe weighting factor adjusting means adjusts the weighting factor so that the importance of the information increases as the information display time increases.StructureAccording to the above, when the information is displayed, the weighting factor adjusting means adjusts the weighting factor according to the display time. As a result, the weighting factor can be adjusted so that information with a long display time has a relatively high importance.
[0048]
In general, information that is determined to be important by the user is frequently referred to and displayed longer than information that is determined to be unnecessary. Here, in the above configuration, since the weighting coefficient is adjusted according to the display time, it is possible to calculate the degree of importance suitable for the operation tendency of the user, and the user can find necessary information earlier.
[0049]
Note that the display time may be, for example, the time from when it is displayed on the screen until the display ends, or if the display device can display a plurality of windows in an overlapping manner, the display time is the highest. The time displayed in the window (active window) may be set as the display time. In addition, the display time in each overlap state is counted separately, and the display time is a value obtained by adding a weight corresponding to the overlap state to each display time so that the weight is larger when the overlap is higher. Good.
[0050]
MoreOnThe weighting coefficient adjusting means increases the importance of the information as the number of operations of the first type preliminarily estimated to occur frequently when the information is important among the operations related to the information. Adjust the weighting factor so thatStructureAccording to the configuration, for example, the user determines that the information is important, such as an operation related to display, an operation related to content change, an operation related to information retrieval, and an operation to output information outside the information management apparatus. If an operation that occurs frequently is performed, the importance of the information increases. As a result, the information management apparatus can calculate the degree of importance suitable for the operation tendency of the user, and the user can find necessary information earlier.
[0051]
Here, in general, a user often places importance on information that has been recently created and frequently used. UpThe weighting coefficient adjustment means calculates the number of times of the first type of operation that is presumed to occur frequently when the information is important among the operations related to the information by the elapsed time after the information is created. The weight coefficient is adjusted so that the greater the divided value, the greater the importance of the information.In the configuration, when an operation that is frequently performed when the information is determined to be important is performed, the importance of the information increases. Moreover, the importance of the information becomes smaller as the elapsed time from the creation of the information increases. As a result, even when the number of operations is the same, the importance of recently created information can be increased, and the information management apparatus can calculate the importance closer to the sense of the user.
[0052]
further,UpThe first type of operation includes at least one of information display, information output outside the information management apparatus, and information content change.StructureAccording to the configuration, when an information display operation, an output operation, or a content change operation is performed, the importance of the information increases. Here, examples of the display operation include display start and display stop, whole display, partial display, display part change in information, enlargement and reduction, or display position change on the display screen. The output operation includes, for example, printing, communication, or recording on a recording medium. Furthermore, the content change operation includes content addition, content correction, partial copying, partial deletion, and the like. Among operations related to information, these operations are frequently performed when the user attaches importance to the information. As a result, by adopting these operations as the first type of operation, the information management apparatus can calculate the importance closer to the sense of the user.
[0053]
By the way, as described above, there are various types of operations related to information, and each type of operation has an influence on the frequency of operation and the influence of one operation on the importance of information. Often different.
[0054]
For example, in the case of editing a certain document, the number of operations for character input is extremely large, and the importance of information does not change much by one operation. Since the process is performed when the user determines that the information needs to be updated, the importance of the information changes relatively greatly even though the number of operations is relatively small.
[0055]
Therefore, when adjusting the weighting factor according to the operation, if the adjustment is made uniformly for each type of operation, there is a risk that a deviation will occur between the importance calculated by the information management device and the importance felt by the user. is there.
[0056]
On the other handAnd aboveThe weight coefficient adjusting means changes the adjustment amount of the weight coefficient according to the operation content of the first type operation.StructureAccording to the above, the adjustment amount of the weighting coefficient changes according to the type of operation. As a result, the deviation between the importance calculated by the information and the importance felt by the user can be reduced, and the information management apparatus can calculate the importance of the information more accurately.
[0057]
Here, when displaying a lot of information at the same time or displaying a large amount of information, it is difficult to display all necessary information on the screen at the same time. Therefore, it is often the case that a plurality of pieces of information are superimposed and displayed, or only a part of the information is displayed. In this case, in order to display a desired portion, the user rewrites the screen, or displays information out of the display area of the screen again using a back scroll function or the like. As a result, as the information is more important to the user, the information display state is frequently changed and redisplayed.
[0058]
the aboveThe weighting factor adjusting means adjusts the weighting factor so that the amount of change in the importance of information is larger in a display operation that requires redisplay than in a display operation that does not require redisplay.According to the configuration, the more frequently the information is redisplayed, the higher the importance. Thereby, the information management apparatus can calculate the importance of information more accurately.Note that examples of the display operation that requires re-display include a back scroll operation and a display position change operation.
[0059]
MaThe topThe weighting factor adjusting means adjusts the weighting factor so that the amount of change in the importance of information is greater in the operation of outputting information outside the information management device than in the operation of displaying information.StructureAccording to Sei, the importance of information that has been output is relatively increased. Here, when the user outputs information or a part of the information, the user is often intended to refer to many people, and the information is more than the information used in the information management device. It is important. As a result, the information management apparatus can calculate the importance closer to the sense of the user.
[0060]
oneWay upThe weighting factor adjusting means adjusts the weighting factor so that the amount of change in the importance of information is greater in the information content changing operation than in the information displaying operation.StructureAccording to the configuration, when the contents are changed, the importance of the information becomes larger than when the contents are simply displayed. Here, when the user changes the contents of the information, the user often determines that this information is important. Therefore, the information management apparatus can calculate the importance of the information more accurately by relatively increasing the importance of the information whose contents are changed.
[0061]
further,UpThe weighting factor adjusting means adjusts the weighting factor so that the amount of change in the importance of the information becomes larger in the operation of outputting the information outside the information management apparatus than in the operation of changing the information content.StructureAccording to the configuration, the importance is relatively increased in the order of the output information, the information whose contents are changed, and the displayed information. Therefore, the information management apparatus can calculate the importance more accurately.
[0062]
on the other handThe weight coefficient adjustment means is configured so that, when an operation related to information is performed and a second type operation that is presumed to occur frequently when the information is unnecessary is performed, the importance of the information is reduced. , Adjust the above weighting factorIn the configuration, when the second type operation is performed, the importance of the information is lower than when the operation is not performed. Here, the second type of operation is frequently performed when the user determines that information is unnecessary. Therefore, the information management apparatus can calculate the importance level adapted to the operation tendency of the user, and the user can find necessary information earlier.Note that examples of the second type of operation include an operation for deleting information, such as an operation for deleting a file in which information is stored.
[0063]
By the way, when the operation target is a part of the information, the user often pays attention to the operation part in the information. Therefore, EmotionWhen the weight coefficient corresponds to a unit smaller than the information, the information management device is close to the user's sense by changing the adjustment amount of the weight coefficient depending on whether or not it is included in the operation part. Importance can be calculated.
[0064]
In particular,Above informationPart specifying means for specifying the operation part of the report, and the weight coefficient adjusting means adjusts the keyword weight coefficient of the keyword included in the operation part.StructureAccording to the configuration, the adjustment amount of the keyword weighting coefficient is changed depending on whether or not it is included in the operation part. Thereby, the information management apparatus can calculate the importance close to the sense of the user.
[0065]
further,UpThe part specifying means specifies the information display part as the operation part, and the weight coefficient adjusting means is configured such that when the operation part includes a keyword, the keyword is included rather than when the keyword is not included. Adjust the keyword weighting factor so that the importance ofStructureAccording to this, the importance of the keyword is greater when it is included in the display part. Therefore, the more frequently the keywords are displayed, the greater the importance. As a result, the information management apparatus can calculate the importance level close to the user's sense.
[0066]
Also,UpThe weighting factor adjustment means adjusts the keyword weighting factor so that when the deleted operation part includes a certain keyword, the importance of the keyword is smaller than when the keyword is not included. YouStructureAccording to this, the importance of the keyword is smaller when it is included in the deleted part. Therefore, the importance is relatively reduced as the keyword is frequently deleted as a result of the information content correction. As a result, the information management apparatus can calculate the importance level close to the user's sense.
[0067]
By the way, the keyword is included not only in the information but also in a character string input by the user such as a character string used when searching for information. Here, generally, when a user inputs a character string, the user himself / herself inputs a character string that the user considers important. Therefore, if the amount of change in the importance of the keyword is changed depending on whether it is included in the user's input character string, the importance close to the user's sense can be calculated.
[0068]
In particular,UpThe weighting coefficient adjusting means adjusts the keyword weighting coefficient so that when the keyword is included in the input character string, the importance of the keyword is higher than when the keyword is not included.StructureAccording to Sei, keywords that are frequently included in the input character string have a relatively high importance. Thereby, the information management apparatus can calculate the importance close to the sense of the user.
[0069]
MoreOnIdentification means for identifying the use of the input character string, and the weight coefficient adjustment means changes the adjustment amount of the keyword weight coefficient according to the use of the input character string.StructureAccording to the above, the adjustment amount of the keyword weighting coefficient is changed according to the use of the input character string. Here, for example, new input of information, correction of information content, search, etc. can be mentioned, and the length of the input character string is different from the degree to which the user attaches importance to the keyword in the input character string. There are many. Therefore, the information management apparatus can calculate the importance close to the user's sense by changing the adjustment amount according to the application.
[0070]
Also,UpThe weighting factor adjusting means adjusts the keyword weighting factor so that when the use of the input character string is information retrieval, the amount of change in the importance of the keyword is larger than when the use is a new addition of information.StructureAccording to this, keywords used for information retrieval have a relatively higher importance than keywords used for new input. Here, when searching for information, only keywords that are particularly important to the user are often input, and for new input, not only keywords that are particularly important to the user but also keywords related to the keywords. Are often entered. Therefore, the information management device can calculate the importance level close to the user's sense by increasing the importance level of the keyword used for the information search.
[0071]
on the other hand,UpThe weighting factor adjustment means adjusts the keyword weighting factor so that the importance of the keyword is greater when the use of the input character string is the modification of information content than when the use is a new addition of information.StructureAccording to this, the keyword used for content correction is relatively more important than the keyword used for new input. Here, in many cases, at the time of content correction, the length of the input character string is shorter than that at the time of new input, and the content rate of keywords that are more important is high. Therefore, the information management apparatus can calculate the importance close to the user's sense by increasing the importance of the keyword used for content correction.
[0072]
further,UpThe weighting factor adjusting means adjusts the keyword weighting factor so that the importance of the keyword is greater when the usage of the input character string is information retrieval than when the usage is information content modification.StructureAccording to this, the keyword used for information retrieval has a greater relative importance than the keyword used for content correction. Here, in many cases, the input character string at the time of information retrieval is shorter in length than the input character string at the time of content correction, and the content rate of the keyword regarded as important is high. Therefore, the information management apparatus can further increase the importance of the keyword used for information retrieval, and can calculate the importance close to the user's sense.
[0073]
Also,Main departureIn order to solve the above problems, a recording medium according to MingIn addition, a program for operating a computer is recorded as each means of each information management apparatus.It is characterized by having.
[0074]
When the program of the above configuration is executed on a computer,Above informationSimilar to the information management apparatus, a weighting factor is created according to the information and adjusted according to the tendency of the operation. Therefore, even if the importance of each information is not managed, the information management device can calculate the importance suitable for each user, and greatly reduces the trouble of organizing the information to find the necessary information for the user. Can be reduced.
[0075]
Also, since the importance of each information is learned by an open learning system, the weighting coefficient of each information can be adjusted regardless of the importance of the information. Therefore, the application range is not limited, and the present invention can be widely applied to information management apparatuses that can perform operations related to information.
[0076]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
[First Embodiment]
An embodiment of the present invention will be described below with reference to FIGS. That is, the information management system according to the present embodiment is a system that manages various types of information while changing the importance of information according to the user. For example, the user feels that information related to a certain matter is necessary. When, for example, information with high importance is highlighted and displayed, it is used to assist in finding the information.
[0077]
As shown in FIG. 1, an
[0078]
Specifically, the
[0079]
The information storage unit 11a according to the present embodiment stores at least a character string field as the information D. Note that the information D may include fields other than characters, such as pictures and voices.
[0080]
In addition, the weight coefficient storage unit 11b uses, as the weight coefficient P, a file weight coefficient FP provided for each file F, which is a storage unit of each information D, and a keyword provided for each keyword K constituting each information D. Stores weighting coefficient KP and some information DA Importance XsA Is the information DA File F where is storedA File weighting factor FPA And the information DA K that constitutesA1Keyword weighting factor KP ...A1It is calculated by adding the sum of…. Hereinafter, for convenience of explanation, the file weight coefficient FP and the keyword weight coefficient KP used for calculating the importance of the information D are referred to as the weight coefficient P of the information D.
[0081]
Furthermore, the history storage unit 11c stores information for adjusting each weighting factor P according to the operation of the user, such as the display time and the number of operations, for example, which will be described in detail later.
[0082]
On the other hand, a display control unit 12a, an input control unit 12b, and an information input /
[0083]
Further, as the
[0084]
Each of the units 11 to 15 may be a functional module realized by a computer executing a predetermined program, or may be unique hardware. However, when realized as a functional module, the
[0085]
In the above configuration, the operation of each unit when inputting information D will be described with reference to FIG. That is, when information D is input to the
[0086]
Specifically, as illustrated in FIG. 3, when the user generates information D, in S <b> 11, the input control unit 12 b of the
[0087]
In any case, the information analysis unit 13c accumulates the received information D in the information accumulation unit 11a of the storage unit 11 in S13. As long as the information D includes a region D1 including text information, for example, as illustrated in FIG. 4, the information D may include a region D2 including information other than a character string, such as an image. A file weight coefficient FP, which is one of the weight coefficients P, is generated corresponding to the file F, which is the storage unit of information D, and stored in the weight coefficient storage unit 11b (S14). Note that the initial value of the file weight coefficient FP may be set to a different value depending on the acquisition route of the information D such as the
[0088]
In S15, the information analysis unit 13c extracts text information from the input information D. In S16, the keyword K is cut out from the extracted text information by character string processing. In S17, the information analysis unit 13c weights each keyword K according to, for example, the appearance frequency or the appearance location in the information D. Thereby, for example, as shown in Table 1 below, the initial value of the weighting coefficient KP of each keyword K is calculated. When weighting is performed according to the appearance frequency, the appearance frequency in the other information D stored in the information storage unit 11a is also referred to.
[0089]
[Table 1]
[0090]
As a result, the keyword K having a high appearance frequency of the information D and appearing on a large amount of information D on the average is given a lower weight than the keyword K having a low appearance frequency. When the text information is structured and is composed of areas such as a summary or text, the keyword K included in the summary area is given a higher weight than the keyword K included in the text area. In the above description, the method based on the appearance frequency and the appearance location is exemplified as an example of the method for calculating the initial value of the keyword weight coefficient KP. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and various methods can be adopted.
[0091]
On the other hand, in FIG. 2, when the user instructs the importance calculation of the information D (YES in S3), the
[0092]
As described above, in the
[0093]
Here, since the initial value of the weighting coefficient P calculated in S2 is determined from a predetermined calculation method and the information D input in S1, if each is the same, each information management device The same between the two. Accordingly, the importance level Xs of the information D calculated from these values is the same value between the
[0094]
However, the
[0095]
Thus, for example, the
[0096]
Here, as a method of adjusting the weighting factor P in S7, for example, if it is a method of adjusting according to the operation related to the information D such as the content and frequency of the operation, the time when the information D is displayed by the operation, Although any method can be applied, in this embodiment, weighting by display time will be described as an example of an adjustment method.
[0097]
Specifically, as shown in FIG. 5, in S21, certain information DA When the user instructs the display, the instruction is identified by the operation analysis unit 13b and transmitted to the information control unit 15 (S22). Upon receiving the notification in S23, the
[0098]
Further, in S24, the
[0099]
On the other hand, in S26, the user receives information D.A Is instructed by the operation analysis unit 13b and transmitted to the information control unit 15 (S27). In S28, the
[0100]
Furthermore, the
[0101]
Here, in the history storage unit 11c, a total display time T indicating the total of the time when the information D was displayed in the past is stored corresponding to each information D. In S31, the display analysis unit 13a performs information DA Total display time TA Is added to the current display time. The result of this addition is the new total display time TA Is stored in the history storage unit 11c. Note that the total display time T is displayed when, for example, it is displayed for the first time.A Is not stored in the history storage unit 11c, the display analysis unit 13a sets the current display time as a new total display time T.A Store as.
[0102]
Furthermore, the weight coefficient processing unit 14a receives the information D stored in the history storage unit 11c in S32.A Total display time TA Referring to the total display time TA The longer the is, the information DA Importance XsA The information D so that theA Weighting factor PA Adjust.
[0103]
For example, as shown in Table 2 below, information DB Total display time TB But information DA Total display time TA Is twice the weight coefficient processing unit 14a, the information DA Weighting factor PA Information DB Weighting factor PB Increase. In Table 2, for comparison, only the total display time T is different. For example, information D having the same other conditions such as a weighting factor P before adjustment.A ・ DB ・ DC And the weighting factor ratio is the weighting factor PA It is a ratio when the value of 1 is 1.
[0104]
[Table 2]
[0105]
In the present embodiment, since the file weight coefficient FP and the keyword weight coefficient KP are used as the weight coefficient P, the information DB File F where is storedB File weighting factor FPB Is information DA File F where is storedA File weighting factor FPA Information DB Keyword K included inB1Keyword weight coefficient KPB1Is the keyword K included in information AA1Keyword weight coefficient KPA1Increases by a factor of two. Similarly, information DC Weighting factor PC Is information DA Weighting factor PA It increases to 1.5 times.
[0106]
Since the processes of S21 to S32 are also performed on other information D, the importance Ds increases relatively as the information D with a longer total display time T, and the importance increases as the information D with a shorter total display time T. Xs relatively decreases.
[0107]
In general, the user of the
[0108]
In this example, both the file weight coefficient FP and the keyword weight coefficient KP are adjusted, but only one of them may be adjusted. However, when adjusting only the file weight coefficient FP, the information D displayed by the user is displayed.A Importance XsA Only adjusted. Therefore, other information DB Is the information DA Even if it is similar toB Importance XsB Does not change, the information DB It may take time and effort to search for.
[0109]
On the other hand, when adjusting the keyword weighting coefficient KP, the user simply operates by paying attention to one piece of information D, and information D having similar contents.B Importance XsB Also rises. As a result, the user receives the information DB Makes it easier to discover. However, when adjusting only the keyword weighting coefficient KP, both information DA ・ DB Importance XsA ・ XsB Changes in the same manner, so that the user can directly indicate the information DA The other information DB It becomes difficult to distinguish from. As a result, the directly designated information DA If you want to search for, there is a risk of taking time and effort.
[0110]
On the other hand, in the present embodiment, two weighting factors FP and KP are used together as the weighting factor P, and both are adjusted. As a result, the directly designated information DA Similar information D without interfering with the search forB Can be easily discovered.
[0111]
In the above example, the weighting factor P is adjusted so that the increasing rate of the weighting factor P is proportional to the total display time T, but the present invention is not limited to this. Instead of the increase rate, it may be adjusted by an increase width, or may be adjusted using another mathematical formula. When compared only when the total display time T is different, the same effect as in the present embodiment can be obtained if the adjustment method is such that the importance level Xs of the information D increases as the total display time T increases.
[0112]
However, in order for the
[0113]
Moreover, if the time after the
[0114]
In the above example, the total display time T of the information D itself is stored in the history storage unit 11c. However, the present invention is not limited to this. For example, the time when the display start of each information D is instructed and the time when the display stop of each information D is instructed may be stored to calculate the total display time of each information D. Further, when the
[0115]
[Second Embodiment]
By the way, when the weighting coefficient P is adjusted based only on the total display time T of the information D, for example, the importance Xs of the information D displayed on the background of the screen also increases. In addition, for example, even when the user is not paying attention to the information D, such as when the user is away from the
[0116]
In this embodiment, the number of operations of information D will be described with reference to FIGS. 6 to 9 as another measure for adjusting the weighting factor P. FIG. Various operations exist for the operation on the information D. In the following, a display start instruction and a display stop instruction for the information D will be described as examples. In this case, for example, processing related to the user's instruction and screen display is the same as the processing in FIG. 5, and thus the same processing is denoted by the same reference numeral and description thereof is omitted. Further, in the present embodiment and the following embodiments, the configuration of the
[0117]
That is, in S21 to S24 shown in FIG. 8, the
[0118]
When the user gives an instruction to end the display, the
[0119]
Further, the weight coefficient processing unit 14a receives the information D stored in the history storage unit 11c in S43.A Number of operations mA Refer to the number of operations mA The more information, the more information DA Importance XsA The information D so that theA Weighting factor PA Adjust.
[0120]
For example, as shown in Table 3 below, information DB Number of operations mB But information DA Number of
[0121]
[Table 3]
[0122]
Since the processing of S21 to S43 is also performed on other information D, the importance level Xs is relatively increased as the information D has a higher operation count m, and the importance level Xs is higher as the information D has a lower operation count m. Relatively decreases.
[0123]
Here, even if the information D is displayed on the screen, the information D that is not operated by the user is often less important than the information D that is frequently operated. For example, information D that is displayed as a screen background and is not operated is often displayed in the foremost window on the screen and is less important than information D that is frequently operated. Even if the information D is displayed for a long time, the user may be away from the
[0124]
The
[0125]
In the above description, the case where the display start operation and the stop operation are counted has been described as an example. However, the present invention is not limited to this. The same effect can be obtained by counting the types of operations presumed that the information D is important for the user. As an example, for example, a type of operation for changing the display state, such as redisplay or enlarged display, for example, a type of operation for changing the content of the information D, such as correction or addition of the content of the information D, partial copying, or partial deletion. For example, there are types of operations that are output to the outside of the
[0126]
As in the first embodiment, various methods such as an increase width, an increase rate, a proportional relationship, and an arbitrary function can be adopted as a method for adjusting the weighting coefficient P according to the number of operations m. In any case, the same effect as in the present embodiment can be obtained as long as the adjustment method increases the importance Xs of certain information D as the number of operations increases.
[0127]
However, as in the first embodiment, as shown in FIG. 6, it is more important that the weighting factor P is adjusted so as to change in an S shape with respect to the number of operations m. Can be brought closer to the user's sense. Further, as shown in FIG. 7, when an operation not related to the file F or the keyword K continues, the desired information D can be obtained by gradually decreasing the weighting factor P (KP · FP) of the file F or the keyword K. It becomes easy to discover.
[0128]
On the other hand, when the user performs an operation of a type in which it is assumed that the information D is unnecessary for the user, such as deleting the information D, for example, as shown in FIG. Accordingly, it is better to reduce the weighting factor P of the information D. Since this type of operation can also be estimated in advance, the
[0129]
[Third Embodiment]
By the way, 2nd Embodiment demonstrated the case where each operation was counted equally as an example of how to count operation frequency. However, the actual operation includes a specific type of operation that frequently appears when the user attaches importance to the information D, such as a back scroll operation. Therefore, when the weighting factor P is adjusted in the same manner when the specific type of operation is performed and when the remaining operation is performed, the user feels the importance Xs calculated by the
[0130]
On the other hand, in this embodiment, for example, the case where the weighting coefficient P is adjusted according to the operation content of the information D, such as counting the specific types of operations, will be described with reference to FIGS. Hereinafter, as an example of the specific operation, an operation for redisplaying the same portion in the information D such as a back scroll operation will be described.
[0131]
That is, in S51 shown in FIG.A Part A insideA1In S52, the
[0132]
Furthermore, the
[0133]
On the other hand, part AA1Is displayed in the past (in the case of YES in S54 above), for example, as shown in FIG.A1Partial information B indicatingA1Is already stored in the history storage unit 11c. In this case, the display analysis unit 13a indicates that the user has information DA It is determined that a re-display operation has been performed for information DA Redisplay operation count dA Increase by one. Redisplay operation count dA Is stored in the history storage unit 11c (S56).
[0134]
Furthermore, the weighting coefficient processing unit 14a performs information D in S57.A Redisplay operation count dA , The number of redisplay operations dA The more information, the more information DA Importance XsA The information D so that theA Weighting factor PA Adjust.
[0135]
For example, for comparison, the number of redisplay operations dA Information D that is different only in other conditionsA ・ DB As an example, information DB Redisplay operation count dB But information DA Redisplay
[0136]
Since the processing of S51 to S57 is also performed on other information D, the information D having a larger redisplay operation count d, the importance Xs is relatively increased, and the information D having a smaller redisplay operation count d is decreased. The importance level Xs decreases relatively. Thereby, the
[0137]
In the above description, the number of redisplay operations d is counted, but the present invention is not limited to this. If the operation is frequently performed when the user attaches importance to the information D, the same effect can be obtained even when other operations are counted as a predetermined specific type of operation.
[0138]
Further, a plurality of types of operations may be counted as specific types of operations, and the weighting coefficient P may be changed for each operation. For example, as the specific type of operation, an operation for displaying the information D, an operation for correcting the content of the information D, an operation for copying the information D to a portable recording medium such as a floppy disk, an e-mail, etc. The operation for communicating information D and the operation for printing information D are each counted. Further, the increasing rate of the weighting factor P during the display operation is 1, the increasing rate of the weighting factor P during the correcting operation is 1.5, the increasing rate during the copying operation is 2, and the increasing rate during the communication operation is 2.5. The increase rate of the weighting factor P for each operation is changed such that the increase rate during the printing operation is 3 or the like.
[0139]
Generally, when an operation for outputting the information D to the outside of the
[0140]
In the above description, the case where the number of operations is counted separately has been described as an example. However, the present invention is not limited to this. For example, the printing operation may be counted as three correction operations, and a weight may be given at the counting stage. Regardless of whether the number of operations is different or not, if the fluctuation range of the importance level Xs can be changed for each specific type of operation described above, the same effect as in the present embodiment can be obtained.
[0141]
[Fourth Embodiment]
In the first to third embodiments, regardless of whether the operation target is the entire information D or not, the display time and the number of operations are counted for each information D and used to calculate the importance of the information D. The case where the weighting coefficient P is adjusted has been described. On the other hand, in the present embodiment, when the operation target is a part of the information D, a case where the weighting coefficient P related to the part is adjusted will be described with reference to FIGS. Note that various operations can be cited as operations for which a part of the information D is to be operated, but in the following, partial display will be described as an example.
[0142]
That is, in S61 shown in FIG. 14, every time the information D is displayed on the screen, the display analysis unit 13a displays which part A of the information D is displayed based on, for example, a notification from the
[0143]
Note that the adjustment method of the keyword weighting coefficient KP may be adjusted without distinguishing various operations, as in the second or third embodiment, or may be weighted for each type of operation. In addition, in the case of an operation in which the user is assumed to not need the operation target, such as deletion of the operation target, the keyword weighting coefficient KP is adjusted so that the importance level Xs of the keyword K decreases.
[0144]
In any case, when a part of the information D is operated, the keyword weight coefficient KP of the keyword K can be individually adjusted depending on whether or not each keyword K in the information D is included in the operation target. . Therefore, the
[0145]
[Fifth Embodiment]
In the fourth embodiment, the case where the keyword weight coefficient KP is adjusted depending on whether or not the information D is included in the operation target has been described. However, the keyword K is not included only in the information D. It is also included in character strings entered by the user, such as search character strings. In the present embodiment, adjustment of the keyword weighting coefficient KP according to the input character string will be described with reference to FIG.
[0146]
That is, in S71, for example, when the user inputs a character string for search or correction of information D, the input control unit 12b of the
[0147]
On the other hand, in S73, the
[0148]
For example, when the
[0149]
According to the above configuration, the keyword weight coefficient KP of the keyword K included in the character string input by the user is larger than that in the case where the keyword K is not included in the input character string. Furthermore, even if it is included in the input character string, the keyword weight coefficient KP of the keyword K increases in the order of new creation, update, and search.
[0150]
Generally, when a user inputs a character string, the user himself / herself inputs a character string regarded as important by the user. Therefore, by increasing the importance of the keyword K included in the user's input character string, the
[0151]
Furthermore, the length of the character string is often shortened in the order of new creation, update, and search. In particular, at the time of search, only the keyword K that is regarded as important by the user is often input, and at the time of new creation, not only the keyword K that is emphasized but also other keywords K are input. Therefore, as described above, by adjusting the keyword weighting coefficient KP according to the use of the character string, the
[0152]
[Sixth Embodiment]
By the way, in the first to fifth embodiments, for example, the weighting coefficient is determined according to all the operation situations after the information D (file F) is generated, such as the total display time T and the total number of operations m (d). The method for adjusting P (first method) has been described. According to this method, when responding to the number of operations m, the information X having a larger number of operations m increases the importance level Xs. Therefore, the
[0153]
However, in this first method, for example, as shown in FIG. 18, a file F created one year ago and operated n times at that time.A Information D stored inA Importance XsA Is the file F recently created and manipulated n timesB Information D stored inB Importance XsB Will be the same.
[0154]
Here, in general, information D that has been frequently manipulated recentlyB Is information D that has been frequently manipulated onceA In many cases, the current importance level Xs is higher. Therefore, when the weighting factor P is adjusted by the first method, both the above-mentioned importance levels XsA ・ XsB The value of theB May be difficult to discover.
[0155]
In contrast, as a second method, the weight coefficient processing unit 14a according to the present embodiment divides the total number of operations m by the elapsed time R from the creation of the file F to the present (m / R), the weighting factor P is changed. The elapsed time R can be calculated from the creation date and time stored as an attribute of the information D.
[0156]
In the present embodiment, the weight coefficient processing unit 14a adjusts the weight coefficient P according to m / R instead of the number of operations m. Therefore, as the information D has a longer elapsed time R, the number of operations m necessary to maintain the weighting coefficient P increases, and the importance level Xs relatively decreases. As a result, the
[0157]
[Seventh Embodiment]
In the first to sixth embodiments, the total display time T and the number of operations m stored in the history storage unit 11c have been described as being updated at the time of operation. However, the total display time T and the number of operations are not limited. The method to obtain is not limited to this.
[0158]
In the present embodiment, a case will be described in which history information H including an operation time is stored in the history storage unit 11c and the importance level Xs is calculated based on the history information H during operation. In the following, for convenience of explanation, the case where the history information H is stored in the second embodiment will be described as an example.
[0159]
That is, as shown in FIG. 19, when the user operates the information D in S81, the
[0160]
Furthermore, when calculating the importance level Xs, the weighting factor processing unit 14a adjusts each weighting factor P based on the history information H of each information D in S83 to calculate the importance level Xs.
[0161]
Here, in the present embodiment, the weighting coefficient processing unit 14a receives each information D from the history information H stored in the history storage unit 11c.A If the history information H related to each is extracted, the number of operations m of each information D can be calculated. Therefore, the weighting coefficient processing unit 14a performs the weighting coefficient of each information D according to the number of operations m or the value obtained by dividing the number of operations m by the elapsed time R, as in the first method and the second method. P can be adjusted.
[0162]
Furthermore, in the present embodiment, since the history information H is stored, in addition to the first method and the second method, a third method for weighting according to the operation time can be selected.
[0163]
For example, when the rate of increasing the weighting coefficient P is 1 when used once a month recently, 0.9 is used when it is used once in the period from the past one month to two months ago. The weighting factor P is adjusted by assigning a weight so that the weighting becomes smaller as the operation time is away from the current time, such that the period from 2 months ago to 3 months ago is 0.8. As a result, as shown in FIG. 20, even when the elapsed time R and the number of operations m are the same, the importance level Xs of the information D that has been operated more recently can be relatively increased. As a result, the
[0164]
Here, the case where weighting is performed according to the difference from the current time has been described above, but the present invention is not limited to this. If weighting is applied according to the difference from an arbitrary time point, the importance level Xs suitable for the sense of the user at that time point can be calculated. In general, the importance Xu felt by the user is not always consistent and often changes with the passage of time. Therefore, the user may search for the information D based on the information D that is considered important at a certain time. In this case, the
[0165]
In the above description, the history information H has been described by taking as an example the case where information necessary for calculating the importance in the second embodiment is stored. However, the importance in the first to fifth embodiments is described. If information necessary for calculation is stored, the same effect can be obtained regardless of which information is applied.
[0166]
In particular, when applied to the third embodiment, a specific type of operation can be specified at the time of importance calculation, and the weighting between various operations can be changed. For example, if the weight of the printing operation is increased, the importance level Xs of the information D that has been subjected to the communication operation can be increased. Therefore, the method when the
[0167]
By the way, storing the history information H requires more storage capacity than storing the total display time T and the number of operations m (d). However, since the storage capacity required for storing the history information H is often much smaller than the storage capacity required for storing the information D, the storage capacity of the
[0168]
Note that the adjustment method of the weighting coefficient P described in each of the first to seventh embodiments can be used in any combination. In this case, since the weighting coefficient P can be adjusted according to various operations, the
[0169]
In each of the above embodiments, the case where the importance Xs of the information D increases as the weighting factor P increases has been described. However, the present invention is not limited to this. For example, even when the importance level Xs of the information D is calculated by other methods, such as when the weighting factor P increases or the importance level Xs of the information D decreases, the importance level Xs of the above embodiments and the information D is If the weighting coefficient P can be adjusted so as to change similarly, the same effect can be obtained.
[0170]
Furthermore, in each of the above-described embodiments, the case where the weighting coefficient P used for calculating the importance of the information D is adjusted when an operation related to the information D is performed has been described. The weighting factor P that is not used for calculating the importance of the information D may be adjusted. The same effect can be obtained if the magnitude of the weighting factor P used for the importance calculation and the magnitude of the remaining weighting factor P can be changed relatively.
[0171]
In addition, the recording medium according to each of the above embodiments includes a weighting factor created according to each information, Based on a weighting factor related to information, an importance calculation step for calculating the importance of the information, and a weighting factor adjustment for adjusting a weighting factor used in the importance calculation step according to an operation related to information A program for executing the process is recorded.
[0172]
【The invention's effect】
Main departureAs described above, the information management apparatus according to the invention includes weighting factor storage means for storing a weighting factor that is created for each piece of information and is used for calculating importance of related information, and a weighting factor related to information. Based on this, the degree of importance calculation means for calculating the degree of importance of the information and a weight coefficient adjustment means for adjusting the weight coefficient according to an operation related to the information are provided.
[0173]
According to the above configuration, the weighting coefficient is created according to the information and adjusted according to the tendency of the operation. Therefore, even if the user does not manage the importance of each information, the information management apparatus can calculate the importance suitable for each user. As a result, there is an effect that it is possible to drastically reduce the trouble in organizing the information in order for the user to find the necessary information. In addition, since the importance of each information is learned by an open learning system, there is an effect that it can be widely applied to information management devices capable of operations related to information.
[0174]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,History information storage means for storing history information indicating the history of operations related to information is provided, and the weight coefficient adjustment means is configured to adjust the weight coefficient based on the history information.
[0175]
In the above configuration, when an operation related to information is performed, history information indicating the operation is stored in the history information storage unit. Therefore, even when a weighting factor adjustment method is specified at the time of instructing importance calculation, the weighting factor can be adjusted by the adjustment method, and the information management apparatus can calculate the importance of information more flexibly. Play.
[0176]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,The weight coefficient adjusting means is configured to change the adjustment amount of the weight coefficient according to the time when the operation is performed.
[0177]
According to the above configuration, it is possible to increase the importance of information that is estimated to be important by the user at a specific time. As a result, there is an effect that it is possible to further reduce time and labor when the user discovers desired information.
[0178]
The present inventionAs described above, the information management apparatus according toIn addition to the above configuration,The importance level calculating means is configured to calculate the importance level of the information based on the file weight coefficient of the file in which the information is stored.
[0179]
In the above configuration, the file weighting coefficient serving as the weighting coefficient is provided for each file serving as the information storage unit, and is adjusted according to the operation related to the information. As a result, the information management apparatus can increase / decrease the importance of information in units of files, and there is an effect that it is possible to reduce time and effort during information retrieval.
[0180]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,The importance calculation means is configured to calculate the importance of the information based on the keyword weight coefficient of each keyword constituting the information.
[0181]
In the above configuration, when certain information is manipulated, the importance of other information including the keyword in the information can be adjusted, and the labor for searching information can be reduced.
[0182]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,The importance calculation means is configured to calculate the importance of the information based on the file weight coefficient of the file storing the information and the keyword weight coefficient forming the information.
[0183]
According to the above configuration, the importance of similar information can be adjusted while maintaining the difference between the importance of the operated information and the importance of the similar information. As a result, there is an effect that it is possible to realize an information management apparatus capable of discovering both directly operated information and similar information earlier.
[0184]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,In this configuration, the weight coefficient is adjusted so that the importance of the information increases as the information display time increases.
[0185]
According to the above configuration, it is possible to adjust the weighting coefficient so that information with a long display time has a relatively high importance, and there is an effect that it is possible to reduce time and effort during information retrieval.
[0186]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,Among the operations related to information, the weighting factor is set so that the greater the number of operations of the first type that are presumed to occur frequently when the information is important, the greater the importance of the information. It is the structure to adjust.
[0187]
According to the above configuration, when an operation frequently performed when the user determines that the information is important, the importance of the information increases. As a result, the information management apparatus can calculate the degree of importance suitable for the operation tendency of the user, and has the effect of reducing the labor for information retrieval.
[0188]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,Among the operations related to information, the weight coefficient is adjusted such that the greater the value obtained by dividing the number of times of the first type operation by the elapsed time is, the greater the importance of the information is.
[0189]
According to the above configuration, the importance of recently created information can be increased even when the number of operations is the same. As a result, the information management apparatus has an effect of calculating the importance closer to the user's sense.
[0190]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,The first type of operation includes at least one of information display, information output outside the information management apparatus, and information content change.
[0191]
In the above configuration, the degree of importance becomes relatively higher as the information is displayed, output to the outside of the information management apparatus, or information whose contents are changed. As a result, the information management apparatus has an effect of calculating the importance closer to the user's sense.
[0192]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,According to the operation content of the first type of operation, the weight coefficient adjustment amount is changed.
[0193]
According to the above configuration, since the adjustment amount of the weighting coefficient changes according to the type of operation, it is possible to reduce a deviation between the importance calculated by the information and the importance felt by the user. As a result, there is an effect that the information management apparatus can calculate a more appropriate importance level.
[0194]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,In this configuration, the weighting factor is adjusted so that the amount of change in the importance of information is larger in a display operation that requires redisplay.
[0195]
According to the above configuration, the more frequently the information is displayed again, the higher the importance. Thereby, the information management apparatus has an effect that the importance of information can be calculated more accurately.
[0196]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,In this configuration, the weighting factor is adjusted so that the amount of change in the importance of the information becomes larger in the output operation outside the information management apparatus than in the information display operation.
[0197]
According to the above configuration, the degree of importance is relatively increased as the output operation is performed. As a result, the information management apparatus has an effect of calculating the importance closer to the user's sense.
[0198]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,In this configuration, the weight coefficient is adjusted so that the amount of change in the importance of the information is larger in the information content changing operation than in the information displaying operation.
[0199]
According to the above configuration, the importance of the information whose contents are changed can be relatively increased. As a result, there is an effect that the information management apparatus can calculate the importance of information more accurately.
[0200]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,In this configuration, the weight coefficient is adjusted so that the amount of change in the importance of the information is larger in the operation of outputting the information outside the information management apparatus than in the operation of changing the information content.
[0201]
According to the above configuration, the importance is relatively increased in the order of the output information, the information whose contents are changed, and the displayed information. Therefore, the information management apparatus has an effect that the importance can be calculated more accurately.
[0202]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,A configuration in which the weighting factor is adjusted so that the importance of the information is reduced when a second type operation that is presumed to occur frequently when the information is unnecessary among operations related to the information is performed. It is.
[0203]
According to the above configuration, the importance of the information is reduced if an operation that frequently occurs when the user determines that the information is unnecessary is performed. Therefore, the information management apparatus can calculate the importance level adapted to the operation tendency of the user, and has the effect of reducing the labor for information retrieval.
[0204]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,A part specifying unit that specifies an operation part of the information is provided, and the weight coefficient adjusting unit is configured to adjust a keyword weight coefficient of a keyword included in the operation part.
[0205]
According to the above configuration, the adjustment amount of the keyword weight coefficient is changed depending on whether or not it is included in the operation part. Thereby, the information management apparatus has an effect that the importance close to the sense of the user can be calculated.
[0206]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,When a certain keyword is included in the information display portion, the keyword weighting coefficient is adjusted so that the importance of the keyword is higher than when the keyword is not included.
[0207]
According to the above configuration, the more frequently a keyword is included in a display portion, the greater the importance. As a result, the information management apparatus has an effect that the importance close to the user's sense can be calculated.
[0208]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,When the deleted operation part includes a certain keyword, the keyword weighting coefficient is adjusted so that the importance of the keyword is smaller than when the keyword is not included.
[0209]
According to the above configuration, as a result of the information content correction, keywords that are frequently deleted have a relatively low importance. As a result, the information management apparatus has an effect that the importance close to the user's sense can be calculated.
[0210]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,This is a configuration in which the keyword weight coefficient is adjusted so that the importance of the keyword is greater when the input character string includes a certain keyword than when the keyword is not included.
[0211]
According to the above configuration, the more frequently a keyword is included in the input character string, the greater the importance. Thereby, the information management apparatus has an effect that the importance close to the sense of the user can be calculated.
[0212]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,Identification means for identifying the use of the input character string is provided, and the weight coefficient adjusting means is configured to change the adjustment amount of the keyword weight coefficient according to the use of the input character string.
[0213]
According to the above configuration, the adjustment amount of the keyword weighting coefficient is changed according to the use of the input character string. Here, even if the length of the input string and the degree of importance of the keyword in the input string by the user are different for each application, the degree of importance close to the user's sense can be calculated and information retrieval There is an effect that time and effort can be reduced.
[0214]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,When the usage of the input character string is information retrieval, the keyword weighting coefficient is adjusted so that the amount of change in the importance of the keyword is larger than when the usage is new addition of information.
[0215]
According to the said structure, the importance of the keyword used in the case of an information search becomes relatively large. Therefore, the information management apparatus has an effect that the importance close to the sense of the user can be calculated.
[0216]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,When the usage of the input character string is information content correction, the keyword weighting coefficient is adjusted so that the importance of the keyword is greater than when the usage is new addition of information.
[0217]
According to the said structure, the importance of the keyword used for content correction becomes relatively large. Therefore, the information management apparatus has an effect that the importance close to the sense of the user can be calculated.
[0218]
Main departureAs described above, the information management device according to MingIn addition to the above configuration,When the use of the input character string is information retrieval, the keyword weighting coefficient is adjusted so that the importance of the keyword is greater than when the use is information content correction.
[0219]
According to the above configuration, the keyword used for information retrieval has a greater relative importance than the keyword used for content correction. Therefore, the information management apparatus has an effect that the importance close to the sense of the user can be calculated.
[0220]
Main departureAs described above, the recording medium according to Ming isAs each means of each information management apparatus, a program for operating a computer is recorded.It is the composition which is.
[0221]
When the program of the above configuration is executed on a computer,the aboveSimilar to the information management apparatus, the weighting coefficient is created according to the information and adjusted according to the tendency of the operation. Also, since the importance of each information is learned by an open learning system, the weighting coefficient of each information can be adjusted regardless of the importance of the information. Therefore, it is possible to calculate an importance suitable for each user without managing the importance of each information, and to realize an information management apparatus applicable to a wide range.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1, showing an embodiment of the present invention, is a block diagram showing a main configuration of an information management system.
FIG. 2 is a flowchart showing an outline of the operation of the information management apparatus in the information management system.
FIG. 3 is a flowchart showing the operation of the information management apparatus when inputting information.
FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating the operation of the information management apparatus when inputting information, and is an explanatory diagram illustrating a method of calculating a weighting factor.
FIG. 5 is a flowchart showing the operation of the information management apparatus when the weighting coefficient is adjusted according to the total display time.
FIG. 6 is a graph showing changes in weighting factors when display (operation) related to weighting factors is performed in the information management system.
FIG. 7 is a graph showing a change in weighting factor when display (operation) not related to the weighting factor continues in the information management system.
FIG. 8 shows another embodiment of the present invention, and is a flowchart showing the operation of the information management apparatus when the weighting coefficient is adjusted according to the number of operations.
FIG. 9 is a graph showing changes in weighting factors when an operation that is assumed to require no information is performed in the information management system.
FIG. 10 shows still another embodiment of the present invention, and is a flowchart showing the operation of the information management apparatus when adjusting the weighting coefficient according to the operation content.
FIG. 11 is an explanatory diagram showing an operation of the information management apparatus and showing a case where a new display portion is designated.
FIG. 12 is a diagram illustrating the operation of the information management apparatus, and is a diagram illustrating a case where a designated display portion does not match the history of the display portion.
FIG. 13 is a diagram illustrating the operation of the information management apparatus and is an explanatory diagram illustrating a case where a designated display portion matches a history of the display portion.
FIG. 14 shows still another embodiment of the present invention, and is a flowchart showing the operation of the information management apparatus when adjusting the keyword weighting coefficient of the keyword included in the display portion.
FIG. 15 is an explanatory diagram showing an operation of the information management apparatus.
FIG. 16 shows still another embodiment of the present invention, and is a flowchart showing an operation of the information management apparatus when adjusting a keyword weighting factor of a keyword included in an input character string.
FIG. 17 is a timing chart showing the relationship between the creation time of information and the operation time, and showing a case where the number of operations is different.
FIG. 18 is a timing chart showing the relationship between the creation time of information and the operation time, showing the case where the number of operations is the same and the creation time is different.
FIG. 19 shows still another embodiment of the present invention, and is a flowchart showing the operation of the information management apparatus when adjusting the weighting factor based on stored history information.
FIG. 20 is a timing chart showing the relationship between the creation time of information and the operation time, and shows the case where the number of operations and the creation time are the same and the operation time is different.
[Explanation of symbols]
2 Information management device
11b Weight coefficient storage unit (weight coefficient storage means; file weight coefficient storage means; keyword weight coefficient storage means)
11c History storage unit (history information storage means)
13a Display analysis unit (part identification means)
14a Weight coefficient processing unit (weight coefficient adjustment means)
14b Importance calculation part (importance calculation means)
15 Information control unit (identification means)
Claims (23)
情報に関連する重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出する重要度算出手段と、
情報に関連する操作に応じて、上記重み係数を調整する重み係数調整手段とを備え、
上記重み係数調整手段は、情報に関連する操作のうち、当該情報を重要視している際に頻出すると予め推定された第1種の操作の回数を、情報が作成されてからの経過時間で割った値が大きいほど、当該情報の重要度が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整することを特徴とする情報管理装置。A weighting factor storage means for storing a weighting factor that is created for each piece of information and used to calculate the importance of the related information;
Importance calculating means for calculating the importance of the information based on a weighting factor related to the information;
Weight coefficient adjustment means for adjusting the weight coefficient according to an operation related to information ,
The weighting factor adjusting means calculates the number of times of the first type of operation that is presumed to occur frequently when the information is important among the operations related to the information by the elapsed time after the information is created. as divided by the value is large, so that the importance of the information is increased, information management apparatus characterized by adjusting the weighting factors.
情報に関連する重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出する重要度算出手段と、
情報に関連する操作に応じて、上記重み係数を調整する重み係数調整手段とを備え、
上記重み係数調整手段は、情報に関連する操作のうち、当該情報を重要視している際に頻出すると予め推定された第1種の操作の回数が多いほど、当該情報の重要度が大きくなるように、上記重み係数を調整すると共に、
上記重み係数調整手段は、上記第1種の操作の操作内容に応じて、上記重み係数の調整量を変更することを特徴とする情報管理装置。 A weighting factor storage means for storing a weighting factor that is created for each piece of information and used to calculate the importance of the related information;
Importance calculating means for calculating the importance of the information based on a weighting factor related to the information;
Weight coefficient adjustment means for adjusting the weight coefficient according to an operation related to information ,
The weight coefficient adjusting means increases the importance of the information as the number of operations of the first type preliminarily estimated to occur frequently when the information is important among the operations related to the information. And adjusting the weighting factor,
The information management apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the weighting factor adjusting means changes an adjustment amount of the weighting factor according to the operation content of the first type of operation.
上記重要度算出手段は、情報を構成する各キーワードのキーワード重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出することを特徴とする請求項1〜8のいずれか1項記載の情報9. The information according to claim 1, wherein the importance level calculation unit calculates the importance level of the information based on a keyword weighting factor of each keyword constituting the information. 管理装置。Management device.
上記重要度算出手段は、情報を蓄積するファイルのファイル重み係数と、当該情報を構成するキーワード重み係数とに基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出することを特徴とする請求項9記載の情報管理装置。10. The information according to claim 9, wherein the importance calculation means calculates the importance of the information based on a file weight coefficient of a file for storing information and a keyword weight coefficient constituting the information. Management device.
上記重要度算出手段は、情報が蓄積されるファイルのファイル重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出することを特徴とする請求項1〜8記載の情報管理装置。9. The information management apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the importance calculation means calculates the importance of the information based on a file weighting coefficient of a file in which the information is stored.
情報に関連する重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出する重要度算出手段と、Importance calculating means for calculating the importance of the information based on a weighting factor related to the information;
情報に関連する操作に応じて、上記重み係数を調整する重み係数調整手段とを備え、Weight coefficient adjustment means for adjusting the weight coefficient according to an operation related to information,
上記重み係数記憶手段は、情報を構成するキーワード毎に設けられたキーワード重み係数が、上記重み係数として記憶されるキーワード重み係数記憶手段を備え、The weight coefficient storage means includes keyword weight coefficient storage means in which a keyword weight coefficient provided for each keyword constituting information is stored as the weight coefficient,
上記重要度算出手段は、情報を構成する各キーワードのキーワード重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出すると共に、The importance calculation means calculates the importance of the information based on the keyword weight coefficient of each keyword constituting the information,
さらに、情報の操作部分を特定する部分特定手段を備え、Furthermore, a part specifying means for specifying the operation part of the information is provided,
上記重み係数調整手段は、当該操作部分に含まれるキーワードのキーワード重み係数を調整することを特徴とする情報管理装置。The information management apparatus characterized in that the weight coefficient adjustment means adjusts a keyword weight coefficient of a keyword included in the operation part.
上記重み係数調整手段は、当該操作部分に、あるキーワードが含まれる場合、当該キーワードが含まれていない場合よりも、当該キーワードの重要度が大きくなるように、キーワード重み係数を調整することを特徴とする請求項12記載の情報管理装置。The weight coefficient adjustment means adjusts the keyword weight coefficient so that when the keyword is included in the operation part, the importance of the keyword is higher than when the keyword is not included. The information management apparatus according to claim 12.
情報に関連する重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出する重要度算出手段と、Importance calculating means for calculating the importance of the information based on a weighting factor related to the information;
情報に関連する操作に応じて、上記重み係数を調整する重み係数調整手段とを備え、Weight coefficient adjustment means for adjusting the weight coefficient according to an operation related to information,
上記重み係数記憶手段は、情報を構成するキーワード毎に設けられたキーワード重み係数が、上記重み係数として記憶されるキーワード重み係数記憶手段を備え、The weight coefficient storage means includes keyword weight coefficient storage means in which a keyword weight coefficient provided for each keyword constituting information is stored as the weight coefficient,
上記重要度算出手段は、情報を構成する各キーワードのキーワード重み係数に基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出すると共に、The importance calculation means calculates the importance of the information based on the keyword weight coefficient of each keyword constituting the information,
さらに、上記重み係数調整手段は、入力された文字列に、あるキーワードが含まれる場合、当該キーワードが含まれない場合よりも、当該キーワードの重要度が大きくなるように、キーワード重み係数を調整することを特徴とする情報管理装置。Further, the weighting factor adjusting means adjusts the keyword weighting factor so that when the input character string includes a certain keyword, the importance of the keyword is greater than when the keyword is not included. An information management apparatus characterized by that.
上記重み係数調整手段は、上記入力文字列の用途に応じて、キーワード重み係数の調整量を変更することを特徴とする請求項15記載の情報管理装置。16. The information management apparatus according to claim 15, wherein the weight coefficient adjustment means changes an adjustment amount of the keyword weight coefficient in accordance with the use of the input character string.
上記重要度算出手段は、情報を蓄積するファイルのファイル重み係数と、当該情報を構成するキーワード重み係数とに基づいて、当該情報の重要度を算出することを特徴とする請求項12〜19のいずれか1項記載の情報管理装置。20. The importance level calculation unit calculates the importance level of the information based on a file weighting factor of a file for storing information and a keyword weighting factor constituting the information. The information management device according to any one of claims.
上記重み係数調整手段は、履歴情報に基づいて、重み係数を調整することを特徴とする請求項1〜20のいずれか1項記載の情報管理装置。21. The information management apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the weighting factor adjusting unit adjusts the weighting factor based on history information.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP25721398A JP3607093B2 (en) | 1998-09-10 | 1998-09-10 | Information management apparatus and recording medium on which program is recorded |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP25721398A JP3607093B2 (en) | 1998-09-10 | 1998-09-10 | Information management apparatus and recording medium on which program is recorded |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2000090109A JP2000090109A (en) | 2000-03-31 |
| JP3607093B2 true JP3607093B2 (en) | 2005-01-05 |
Family
ID=17303243
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP25721398A Expired - Fee Related JP3607093B2 (en) | 1998-09-10 | 1998-09-10 | Information management apparatus and recording medium on which program is recorded |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3607093B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4699632B2 (en) * | 2001-05-15 | 2011-06-15 | ぴあ株式会社 | Mail magazine distribution system and computer program for realizing the same |
| US7716161B2 (en) | 2002-09-24 | 2010-05-11 | Google, Inc, | Methods and apparatus for serving relevant advertisements |
| JP4499735B2 (en) * | 2004-08-30 | 2010-07-07 | パイオニア株式会社 | Image display control apparatus and image display method |
| US20060085181A1 (en) * | 2004-10-20 | 2006-04-20 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Keyword extraction apparatus and keyword extraction program |
| US7693817B2 (en) * | 2005-06-29 | 2010-04-06 | Microsoft Corporation | Sensing, storing, indexing, and retrieving data leveraging measures of user activity, attention, and interest |
| JP2007183864A (en) * | 2006-01-10 | 2007-07-19 | Fujitsu Ltd | File search method and system |
| JP4830532B2 (en) * | 2006-02-22 | 2011-12-07 | 富士ゼロックス株式会社 | Information processing apparatus and program for calculating importance of computerized information |
| US8330830B2 (en) * | 2006-04-13 | 2012-12-11 | Eastman Kodak Company | Camera user input based image value index |
| JP4826331B2 (en) * | 2006-05-09 | 2011-11-30 | 富士ゼロックス株式会社 | Document usage tracking system |
| JP4946187B2 (en) * | 2006-06-09 | 2012-06-06 | 富士ゼロックス株式会社 | Related word display device, search device, method and program thereof |
| JP5046634B2 (en) * | 2006-12-15 | 2012-10-10 | 中国電力株式会社 | Information retrieval system |
| JP2009140108A (en) * | 2007-12-04 | 2009-06-25 | Yahoo Japan Corp | Method for evaluating the usefulness of bookmarks |
| JP4917061B2 (en) * | 2007-12-18 | 2012-04-18 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | Characteristic keyword detection apparatus, characteristic keyword detection method, program, and recording medium |
| JP4911536B2 (en) * | 2008-09-30 | 2012-04-04 | ヤフー株式会社 | Regional information retrieval device, regional information retrieval device control method, regional information retrieval system, and regional information retrieval system control method |
| JP5077574B2 (en) * | 2008-10-27 | 2012-11-21 | 日本電気株式会社 | Terminal device, Web content evaluation system, Web content evaluation method, and program |
| JP5367088B2 (en) * | 2008-11-28 | 2013-12-11 | イーストソフト コーポレーション | Web search system and method based on web page connection time and visit degree |
| JP2010128970A (en) * | 2008-11-28 | 2010-06-10 | Toshiba Corp | Content retrieval device, and method for retrieval of content in the same |
| JP5127066B2 (en) * | 2009-03-02 | 2013-01-23 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | Window operation activity detection device, window operation activity detection method, and program |
| JP5713567B2 (en) * | 2010-02-08 | 2015-05-07 | Necパーソナルコンピュータ株式会社 | Information processing apparatus, program, and recording medium |
| JP5635284B2 (en) * | 2010-03-19 | 2014-12-03 | 日本無線株式会社 | Disaster activity support device, program, and storage medium |
| JP5154623B2 (en) * | 2010-09-24 | 2013-02-27 | ヤフー株式会社 | Electronic book management apparatus and method |
| JP6042162B2 (en) * | 2012-10-05 | 2016-12-14 | 株式会社日立ソリューションズ | Web search device, web search method and program |
| JP7740976B2 (en) * | 2021-12-08 | 2025-09-17 | 矢崎総業株式会社 | Information provision system, server and program for information provision system |
-
1998
- 1998-09-10 JP JP25721398A patent/JP3607093B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2000090109A (en) | 2000-03-31 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP3607093B2 (en) | Information management apparatus and recording medium on which program is recorded | |
| US8078627B2 (en) | File management apparatus, method for controlling file management apparatus, computer program, and storage medium | |
| US7734638B2 (en) | File system updating metadata of files according to results of keyword search | |
| US20060197762A1 (en) | Scalable visualizer for heterogeneous data | |
| US8520096B2 (en) | Apparatus and method for learning photographing profiles of digital imaging device for recording personal life history | |
| US20080104040A1 (en) | Visually intuitive search method | |
| JP2008537254A (en) | Conflict resolution by synchronous manager | |
| US9372843B2 (en) | Document association device, document association method, and non-transitory computer readable medium | |
| US8701025B2 (en) | Interactive ring-shaped interface | |
| JP4745424B2 (en) | Document classification apparatus and document classification program | |
| US20130151555A1 (en) | Content reproduction device, control method for content reproduction device, control program, and recording medium | |
| JP2004355392A (en) | Screen autonomous optimization device, optimization method, recording medium, program | |
| US20120066257A1 (en) | Document management system, search designation method, and storage medium | |
| JP5551795B2 (en) | Search result providing system and method | |
| JP2012064207A (en) | Host device and content display method of the same | |
| JP4699148B2 (en) | Keyword extraction device, keyword extraction program | |
| JPH06342361A (en) | Icon display controller | |
| JP2009157537A (en) | Information processor, information processing system, and information processing program | |
| JP5097385B2 (en) | Building information retrieval system | |
| JP2004227221A (en) | Data management decision method, data management decision device, data management decision program, and recording medium recording data management decision program | |
| JP4788708B2 (en) | Information search device, information search method, and information search program | |
| JP2007207031A (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and image processing program | |
| JP3198941B2 (en) | Information processing device and recording medium | |
| JP2010097409A (en) | Electronic document conversion server, control method thereof and program | |
| JP4935848B2 (en) | File management program, file management method, and machine-readable recording medium on which file management program is recorded |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20040629 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20040830 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20041005 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20041006 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20071015 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20081015 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20081015 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20091015 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20091015 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20101015 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111015 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121015 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131015 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |