JP2020108661A - Game machine - Google Patents
Game machine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2020108661A JP2020108661A JP2019000413A JP2019000413A JP2020108661A JP 2020108661 A JP2020108661 A JP 2020108661A JP 2019000413 A JP2019000413 A JP 2019000413A JP 2019000413 A JP2019000413 A JP 2019000413A JP 2020108661 A JP2020108661 A JP 2020108661A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- state
- combination
- game
- stop operation
- winning combination
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Abstract
Description
本発明は、パチスロ機などの遊技機に関する。 The present invention relates to a gaming machine such as a pachi-slot machine.
従来、遊技者により、メダルやコインなどの遊技媒体が投入(以下、「投入操作」という。)され、スタートレバーが操作(以下、「開始操作」という。)されると、複数の図柄がそれぞれの表面に配された複数のリールの回転が開始し、ストップボタンが操作(以下、「停止操作」という。)されると、複数のリールの回転が停止し、その結果表示された図柄の組合せに応じて特典が付与される、いわゆるパチスロ機と称される遊技機が知られている。 Conventionally, when a player inserts a game medium such as a medal or a coin (hereinafter, referred to as “insertion operation”) and operates a start lever (hereinafter, referred to as “start operation”), a plurality of symbols are respectively generated. The rotation of multiple reels arranged on the surface of the reel starts, and when the stop button is operated (hereinafter referred to as "stop operation"), the rotation of the multiple reels stops, and the combination of symbols displayed as a result. A gaming machine known as a so-called pachi-slot machine, in which a privilege is given in accordance with the above, is known.
このような遊技機においては、開始操作をスタートスイッチにより検出すると、乱数値を抽出して抽籤を行う(以下、この抽籤の結果を「内部当籤役」という。)とともに、ステッピングモータを駆動制御して複数のリールの回転を開始させる制御を行い、停止操作をストップスイッチにより検出すると、ステッピングモータを駆動制御し、内部当籤役に基づいて複数のリールの回転を停止させる制御を行う。 In such a gaming machine, when the start operation is detected by the start switch, a random number value is extracted and lottery is performed (hereinafter, the result of this lottery is referred to as an "internal winning combination"), and the stepping motor is drive-controlled. When the stop operation is detected by the stop switch, the stepping motor is drive-controlled and the rotation of the plurality of reels is stopped based on the internal winning combination.
また、近年、内部当籤役に決定された役を取りこぼすことがないように、内部当籤役を成立させるための情報など遊技者にとって有利な情報を、遊技者に対して報知する遊技機が知られている。なお、このように遊技者が有利となるような情報を報知することを、一般にナビする(ナビを行う)などといい、ナビが行われる期間をAT(assist time)という。 In addition, in recent years, a gaming machine that informs the player of information advantageous to the player such as information for establishing an internal winning combination is known so as not to drop the winning combination determined as the internal winning combination. Has been. It should be noted that such notification of information that is advantageous to the player is generally referred to as navigating (navigating) or the like, and the period during which navigating is performed is referred to as AT (assist time).
こうしたAT機能を搭載した遊技機によれば、ナビを行うか否かを制御することで遊技者に払い出す遊技媒体の数が制御されるため、遊技者は、ATを継続するATゲーム数(ナビゲーム数)が増加することを望むことになる。ATゲーム数を増加させるための工夫はこれまで様々な観点からなされてきており、例えば、特許文献1には、内部当籤役としてスイカやチェリーなどの特定の役が決定されるとATゲーム数を増加させる(ATゲーム数を上乗せさせる)遊技機が開示されている。
According to the gaming machine equipped with such an AT function, the number of gaming media to be paid out to the player is controlled by controlling whether or not to perform the navigation. We hope that the number of navigation games) will increase. Various measures have been taken so far to increase the number of AT games. For example, in
ところで、従来の遊技機では、今回の遊技において決定された当籤役に応じてATなどの有利な状態の継続期間を延長させるだけであり、有利な状態の継続期間の長さに関して遊技者が介入する余地が少なかった。 By the way, in the conventional gaming machine, only the duration of the advantageous state such as AT is extended according to the winning combination determined in this game, and the player intervenes with respect to the duration of the advantageous state. There was little room to do it.
本発明はこのような問題に鑑みてなされたものであり、有利な状態の継続期間の長さに関して遊技者が介入可能な遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of such a problem, and an object of the present invention is to provide a gaming machine in which a player can intervene regarding the length of an advantageous state duration.
本発明に係る遊技機は、複数の識別表示を変動表示可能な可変表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、複数の役の中から決定された当籤役に応じて前記可変表示手段を用いた遊技の進行を制御する遊技制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を備える遊技機であって、当籤役として決定された場合に、所定の操作態様で停止操作が行われると第1の結果表示を導出可能、かつ、前記所定の操作態様とは異なる操作態様で停止操作が行われると第2の結果表示を導出可能な報知対象役を有し、遊技に関する遊技状態として、第1状態(例えば、非報知状態)と第2状態(例えば、報知状態)とを有し、前記第1状態において所定条件を満たすと、遊技状態を前記第2状態に移行可能な状態制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記報知対象役が当籤役として決定された遊技において前記第1の結果表示が導出されると、所定数量の遊技用価値を付与可能である一方で、当該遊技において前記第2の結果表示が導出されると、前記所定数量よりも少ない遊技用価値を付与可能な利益付与手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記第2状態において前記報知対象役が当籤役として決定されると、前記第1の結果表示を導出するために必要な前記所定の操作態様を報知可能な報知手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記第2状態の継続期間を定める数値情報である、前記第2状態において前記利益付与手段により付与された遊技用価値の総数を計数可能な継続期間計数手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記第2状態において前記利益付与手段により付与された遊技用価値の数量に応じて前記数値情報を更新可能であるとともに、更新の結果、前記数値情報が終了閾値に達すると、前記第2状態を終了可能な継続期間管理手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記第2状態において、前記第2状態の継続期間が延長されるように前記数値情報を更新する上乗せ制御を実行可能な上乗せ制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を更に備え、前記継続期間管理手段は、前記第2状態の前記報知対象役が当籤役として決定された遊技において前記報知手段が前記所定の操作態様を報知した場合であっても、遊技者の停止操作の結果として前記第2の結果表示が導出された場合には、導出された前記第2の結果表示に応じて付与される遊技用価値の数量に応じて、前記数値情報を更新することを特徴とする。
The gaming machine according to the present invention includes a variable display means (for example,
このような遊技機によれば、報知対象役が当籤役として決定された際に所定の操作態様を報知可能な第2状態(有利な状態)は、第2状態において付与された遊技用価値の総数(数値情報)が終了閾値に達すると終了するため、所謂、有利な状態を当該状態中の差枚数又は獲得枚数により管理することができる。このとき、本発明に係る遊技機では、第2状態中に報知対象役に応じた報知を行っただけでは、数値情報(差枚数や獲得枚数)を更新せず、停止操作の結果として停止した結果表示に伴い実際に付与された遊技用価値の数量に応じて数値情報を更新する。遊技者にとってみれば、報知に従い停止操作を行うことで、多くの遊技用価値を獲得できる一方で有利な状態(第2状態)の終了が早まってしまい、反対に、報知に逆らって停止操作を行うことで、遊技用価値の獲得は減るものの有利な状態を継続させることができるため、有利な状態の継続期間の長さに関して遊技者が介入することができる。また、本発明に係る遊技機では、第2状態において、継続期間を延長する上乗せ制御を実行可能であるため、報知に逆らい有利な状態を継続させることで、一時的には遊技用価値の獲得を減らしてしまうものの、報知に逆らって伸ばした期間において上乗せ制御を受けることにより、最終的には多くの遊技用価値を獲得する可能性もあるため、従来にない戦略性を持った遊技性を実現することができる。 According to such a gaming machine, the second state (advantageous state) in which the predetermined operation mode can be notified when the notification target combination is determined as the winning combination is the gaming value given in the second state. Since the process ends when the total number (numerical value information) reaches the end threshold, a so-called advantageous state can be managed by the difference number or the acquired number in the state. At this time, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, the numerical information (the difference number or the acquired number) is not updated only by performing the notification according to the notification target combination during the second state, and the game is stopped as a result of the stop operation. Numerical information is updated according to the quantity of the gaming value actually given along with the result display. For the player, by performing the stop operation according to the notification, a lot of gaming value can be obtained, but the advantageous state (second state) ends earlier, and conversely, the stop operation is performed against the notification. By doing so, it is possible to continue the advantageous state although the acquisition of the gaming value is reduced, so that the player can intervene regarding the length of the duration of the advantageous state. Further, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, in the second state, it is possible to execute additional control for extending the duration, so by continuing the advantageous state against the notification, the gaming value is temporarily obtained. However, it is possible to eventually gain a lot of gaming value by receiving additional control during the extended period against the notification, so a gameplay with a strategy that has never existed is possible. Can be realized.
また、本発明に係る遊技機において、当籤役として決定されると、停止操作の態様に関わらず前記利益付与手段により特定数量の遊技用価値が付与される第3の結果表示を導出可能な特定役(例えば、引込1の役)を更に有し、継続期間管理手段は、複数の役のうちの前記特定役が当籤役として決定されたことに応じて前記利益付与手段により遊技用価値が付与された場合には、前記数値情報を更新しないことを特徴とする。 Further, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, when it is determined as a winning combination, a third result display in which a specific amount of gaming value is given by the profit giving means regardless of the mode of the stop operation can be derived. It further has a winning combination (for example, a winning combination 1), and the continuation period management means gives the gaming value by the profit giving means in response to the specific winning combination of a plurality of winning combinations being determined as a winning combination. In the case of being performed, the numerical information is not updated.
このような遊技機によれば、上述と同様に、報知に逆らい有利な状態を継続させることで、一時的には遊技用価値の獲得を減らしてしまうものの、報知に逆らって伸ばした期間において上乗せ制御を受けることにより、最終的には多くの遊技用価値を獲得する可能性もあるため、従来にない戦略性を持った遊技性を実現することができる。 According to such a gaming machine, similarly to the above, by continuing the advantageous state against the notification, although it temporarily reduces the acquisition of the gaming value, the addition in the period extended against the notification By receiving the control, there is a possibility that a large amount of gaming value will eventually be obtained, so that it is possible to realize a gaming property with a strategy that has never been seen before.
本発明によれば、有利な状態の継続期間の長さに関して遊技者が介入することができる。 The present invention allows the player to intervene with regard to the length of the advantageous state duration.
以下、本発明の一実施形態に係る遊技機としてパチスロを例に挙げ、図面を参照しながら、その構成及び動作について説明する。なお、本実施形態では、ボーナス作動機能、AT機能及びART機能を備えたパチスロについて説明する。 A pachi-slot is taken as an example of a gaming machine according to an embodiment of the present invention, and its configuration and operation will be described with reference to the drawings. In the present embodiment, a pachi-slot having a bonus operation function, an AT function, and an ART function will be described.
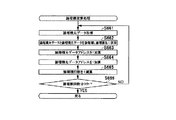
<機能フロー>
まず、図1を参照して、パチスロの機能フローについて説明する。本実施形態のパチスロでは、遊技を行うための遊技媒体としてメダルを用いる。なお、遊技媒体としては、メダル以外にも、例えば、コイン、遊技球、遊技用のポイントデータ又はトークン等を適用することもできる。また、遊技媒体は、「遊技価値」、あるいは「遊技用価値」と称されることもある。
<Function flow>
First, the functional flow of the pachi-slot will be described with reference to FIG. In the pachi-slot of the present embodiment, medals are used as a game medium for playing a game. In addition to medals, for example, coins, game balls, game point data, tokens, or the like can be applied as the game medium. The game medium may also be referred to as "game value" or "game value".
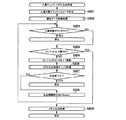
遊技者によりパチスロにメダルが投入され、スタートレバーが操作されると、予め定められた数値範囲(例えば、0〜65535)の乱数から1つの値(以下、乱数値という)が抽出される。 When a player inserts a medal into a pachi-slot and operates a start lever, one value (hereinafter referred to as a random number value) is extracted from random numbers in a predetermined numerical range (for example, 0 to 65535).
内部抽籤手段は、抽出された乱数値に基づいて抽籤を行い、内部当籤役を決定する。この内部抽籤手段は、後述の主制御回路が備える各種処理手段(処理機能)の1つである。内部当籤役の決定により、後述の有効ライン(入賞判定ライン)に沿って表示を行うことを許可する図柄の組合せが事前に決定される。なお、図柄の組合せの種別としては、メダルの払い出し、再遊技(リプレイ)の作動、ボーナスの作動等といった特典が遊技者に与えられる「入賞」に係るものと、それ以外のいわゆる「はずれ」に係るものとが設けられる。なお、以下では、メダルの払い出しに係る役を「小役」と称し、再遊技(リプレイ)の作動に係る役を「リプレイ役」と称する。また、ボーナスの作動(ボーナスゲーム)に係る役を「ボーナス役」ともいう。また、内部当籤し得る役(すなわち、成立が許可される図柄の組合せ)は、単に「役」と称されることがあり、内部当籤役は、「当籤役」、「事前決定結果」、あるいは「導出許容条件」と称されることがある。また、内部抽籤手段は、「役決定手段」、「当籤役決定手段」、「事前決定手段」、あるいは「導出許容条件決定手段」と称されることがある。 The internal lottery means performs lottery based on the extracted random number value and determines an internal winning combination. The internal lottery means is one of various processing means (processing functions) included in the main control circuit described later. By the determination of the internal winning combination, a combination of symbols that is allowed to be displayed along an activated line (winning determination line) described later is determined in advance. The types of symbol combinations are classified into those related to "winning prizes" in which benefits such as payout of medals, operation of replay (replay), operation of bonuses, etc. are given to the player, and so-called "outliers". The related items are provided. In the following, the winning combination relating to the payout of medals is referred to as a “small winning combination”, and the winning combination relating to the operation of the replay (replay) is referred to as a “replay winning combination”. In addition, a winning combination (bonus game) is also referred to as a “bonus winning combination”. In addition, a winning combination that can be internally won (that is, a combination of symbols that are allowed to be established) is sometimes simply referred to as a “winning combination”, and an internal winning combination is a “winning combination”, a “predetermined result”, or It is sometimes called "derivation permission condition". Further, the internal lottery means may be referred to as a “winning combination determining means”, a “winning winning combination determining means”, a “preliminary determining means”, or a “derivation permissible condition determining means”.
また、スタートレバーが操作されると、複数のリールの回転が行われる。その後、遊技者により所定のリールに対応するストップボタンが押されると、リール停止制御手段は、内部当籤役とストップボタンが押されたタイミングとに基づいて、該当するリールの回転を停止する制御を行う。このリール停止制御手段は、後述の主制御回路が備える各種処理手段(処理機能)の1つである。なお、開始操作を行うための操作手段は、スタートレバーのようにレバー形状をしたものに限られず、遊技者が開始操作を行うことが可能であれば、どのような操作手段であってもよい。また、停止操作を行うための操作手段は、ストップボタンのようにボタン形状をしたものに限られず、遊技者が停止操作を行うことが可能であれば、どのような操作手段であってもよい。 Further, when the start lever is operated, the plurality of reels are rotated. After that, when the player presses the stop button corresponding to the predetermined reel, the reel stop control means performs control for stopping the rotation of the corresponding reel based on the internal winning combination and the timing when the stop button is pressed. To do. The reel stop control means is one of various processing means (processing functions) included in the main control circuit described later. The operation means for performing the start operation is not limited to a lever-shaped one such as a start lever, and any operation means may be used as long as the player can perform the start operation. .. Further, the operation means for performing the stop operation is not limited to a button shape like a stop button, and any operation means may be used as long as the player can perform the stop operation. ..
パチスロでは、基本的に、ストップボタンが押されたときから規定時間(190msec)内に、該当するリールの回転を停止する制御が行われる。本実施形態では、この規定時間内にリールの回転に伴って移動する図柄の数を「滑り駒数」という。そして、本実施形態では、規定期間が190msecである場合には、滑り駒数の最大数(最大滑り駒数)を図柄4個分に定める。 In the pachi-slot, basically, control is performed to stop the rotation of the corresponding reel within a specified time (190 msec) from when the stop button is pressed. In the present embodiment, the number of symbols that move with the rotation of the reel within this specified time is referred to as the “number of sliding pieces”. Then, in the present embodiment, when the prescribed period is 190 msec, the maximum number of sliding pieces (maximum number of sliding pieces) is set to four symbols.
リール停止制御手段は、入賞に係る図柄の組合せ表示を許可する内部当籤役が決定されているときは、通常、190msec(図柄4駒分)の規定時間内に、その図柄の組合せが有効ラインに沿って極力表示されるようにリールの回転を停止させる。また、リール停止制御手段は、規定時間を利用して、内部当籤役によってその表示が許可されていない図柄の組合せが有効ラインに沿って表示されないようにリールの回転を停止させる。なお、リールの回転が停止したときに表示された図柄は、「停止表示」、あるいは「表示結果」と称されることがある。また、リールの回転が停止したときに有効ラインに図柄が表示されることを、「停止表示の導出」、あるいは「表示結果の導出」などと表現する場合がある。 The reel stop control means, when the internal winning combination permitting the combination display of the symbols relating to the winning is determined, the combination of the symbols is normally placed on the activated line within a prescribed time of 190 msec (for 4 symbols). The rotation of the reel is stopped so as to be displayed as much as possible. Further, the reel stop control means uses the stipulated time to stop the rotation of the reel so that a combination of symbols which is not permitted to be displayed by the internal winning combination is not displayed along the activated line. The symbol displayed when the reel rotation is stopped may be referred to as "stop display" or "display result". In addition, displaying a symbol on the activated line when the rotation of the reel is stopped may be expressed as “deriving a stop display” or “deriving a display result”.
また、リール停止制御手段は、リールが回転してから、予め定められた自動停止時間が経過した場合には、遊技者が停止操作を行っていない場合でも、自動的に各リールを停止させる自動停止制御を行うようにしてもよい。この場合には、遊技者の停止操作を介さずにリールが停止することとなるため、いずれかの内部当籤役が決定されている場合であっても、いずれの入賞に係る図柄の組合せも有効ラインに沿って表示されていないようにリールの回転を停止させることが望ましい。 Further, the reel stop control means automatically stops each reel when a predetermined automatic stop time has elapsed since the reel was rotated, even if the player has not performed a stop operation. You may make it perform stop control. In this case, since the reels will be stopped without the player's stop operation, even if any internal winning combination is determined, any combination of symbols related to winning is effective. It is desirable to stop spinning the reel so that it is not displayed along the line.
このようにして、複数のリールの回転が全て停止されると、入賞判定手段は、有効ラインに沿って表示された図柄の組合せが、入賞に係るもの(あるいは、その他予め定められたもの)であるか否かの判定を行う。すなわち、入賞に係る図柄の組合せ(あるいは、その他予め定められた図柄の組合せ)が成立したか否かの判定を行う。この入賞判定手段もまた、後述の主制御回路が備える各種処理手段(処理機能)の1つである。そして、表示された図柄の組合せが、入賞判定手段により入賞に係るもの(あるいは、その他予め定められたもの)である(すなわち、入賞に係る図柄の組合せ(あるいは、その他予め定められた図柄の組合せ)が成立した)と判定されると、メダルの払い出し等の特典が遊技者に与えられ、あるいは、それを契機として各種の制御が行われる。パチスロでは、以上のような一連の流れが1回の遊技(単位遊技)として行われる。 In this way, when the rotation of the plurality of reels is all stopped, the winning determination means determines that the combination of symbols displayed along the activated line is related to winning (or other predetermined one). It is determined whether or not there is. That is, it is determined whether or not a winning symbol combination (or other predetermined symbol combination) has been established. This winning determination means is also one of various processing means (processing functions) included in the main control circuit described later. Then, the combination of the symbols displayed is the one relating to the winning by the winning determination means (or other predetermined one) (that is, the combination of the symbols relating to the winning (or other predetermined combination of symbols). ) Is established), a bonus such as payout of medals is given to the player, or various controls are performed in response to the privilege. In the pachi-slot, the above-described series of flows is performed as one game (unit game).
なお、入賞判定手段は、有効ラインに沿って表示された図柄の組合せが、単に予め定められた複数の図柄の組合せのうちのいずれかの図柄の組合せに該当するか否かを判定するものであってもよいし、内部抽籤手段によって決定された内部当籤役に係る図柄の組合せに該当するか否かを判定するものであってもよい。すなわち、前者では、内部当籤役と切り離して、入賞に係る図柄の組合せであるか否かを判定するものであってもよい。この場合、リール停止制御手段によって適切に停止制御が行われる限り、誤入賞の発生の防止は十分に担保され得ることから、誤入賞検知に係る制御負担を低減させることが可能となる。一方、後者では、入賞に係る図柄の組合せが、入賞が許可されていた図柄の組合せであるか否かも判定可能とすることで、リールの不具合等により誤入賞が発生した場合に、その誤入賞を検知することができるため、セキュリティ性を向上させることが可能となる。 The winning determination means determines whether or not the symbol combination displayed along the activated line corresponds to any symbol combination among a plurality of predetermined symbol combinations. It may be possible to determine whether or not it corresponds to the combination of symbols related to the internal winning combination determined by the internal lottery means. That is, in the former case, it may be determined whether or not it is a combination of symbols related to winning, separately from the internal winning combination. In this case, as long as the reel stop control means appropriately controls the stop, the prevention of the false prize can be sufficiently ensured, so that the control load related to the false prize detection can be reduced. On the other hand, in the latter case, it is possible to determine whether or not the combination of symbols related to winning is a combination of symbols for which winning is permitted. Can be detected, so that it is possible to improve security.
また、パチスロでは、前述した一連の遊技動作の流れの中で、表示装置などによる映像の表示、各種ランプによる光の出力、スピーカによる音の出力、或いは、これらの組合せを利用して様々な演出が行われる。 Also, in the pachi-slot, in the sequence of the game operation described above, various effects are displayed by using the display of images by a display device, the output of light by various lamps, the output of sound by the speaker, or a combination of these. Is done.
具体的には、スタートレバーが操作されると、上述した内部当籤役の決定に用いられた乱数値とは別に、演出用の乱数値が抽出される。演出用の乱数値が抽出されると、演出内容決定手段は、内部当籤役に対応づけられた複数種類の演出内容の中から今回実行する演出を抽籤により決定する。この演出内容決定手段は、後述の副制御回路が備える各種処理手段(処理機能)の1つである。また、後述の主制御回路が演出内容を決定する場合には、この演出内容決定手段を、後述の主制御回路が備える各種処理手段(処理機能)の1つとすることもできる。 Specifically, when the start lever is operated, a random number value for effect is extracted in addition to the random number value used for determining the internal winning combination described above. When the random number value for effect is extracted, the effect content determination means randomly determines the effect to be executed this time from among a plurality of kinds of effect content associated with the internal winning combination. The effect content determining means is one of various processing means (processing functions) included in the sub-control circuit described later. Further, when the main control circuit described later determines the effect content, the effect content determination means may be one of various processing means (processing functions) included in the main control circuit described later.
次いで、演出内容決定手段により演出内容が決定されると、演出実行手段は、リールの回転開始時、各リールの回転停止時、入賞の有無の判定時等の各契機に連動させて対応する演出を実行する。このように、パチスロでは、例えば、内部当籤役に対応づけられた演出内容を実行することによって、決定された内部当籤役(言い換えると、狙うべき図柄の組合せ)を知る機会又は予想する機会が遊技者に提供され、遊技者の興味の向上を図ることができる。 Next, when the effect content is determined by the effect content determining means, the effect executing means responds to each of the triggers such as when the reel starts rotating, when each reel stops rotating, and when the presence or absence of a prize is determined. To execute. As described above, in the pachi-slot, for example, by executing the effect contents associated with the internal winning combination, the opportunity to know or predict the determined internal winning combination (in other words, the combination of the symbols to be aimed) is a game. It is provided to the player and the interest of the player can be improved.
<パチスロの構造>
次に、図2〜図5を参照して、本発明の一実施形態に係るパチスロの構造について説明する。
<Pachislot structure>
Next, the structure of the pachi-slot according to the embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS.
[外観構造]
図2は、パチスロ1の外部構造を示す斜視図である。
[Appearance structure]
FIG. 2 is a perspective view showing an external structure of the pachi-
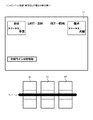
パチスロ1は、図2に示すように、外装体(遊技機本体)2を備える。外装体2は、リールや回路基板等を収容するキャビネット(筐体)2aと、キャビネット2aの開口を開閉可能に取り付けられるフロントドア(前面扉)2bと、を有する。
As shown in FIG. 2, the pachi-
キャビネット2aの内部には、3つのリール3L,3C,3R(変動表示手段、表示列)が横一列に並べて設けられている。以下、各リール3L,3C,3R(メインリール)を、それぞれ左リール3L、中リール3C、右リール3Rともいう。各リール3L,3C,3Rは、円筒状に形成されたリール本体と、リール本体の周面に装着された透光性のシート材を有する。そして、シート材の表面には、複数(例えば20個)の図柄が周方向(リールの回転方向)に沿って所定の間隔をあけて描かれている。なお、各リール3L,3C,3Rは、「図柄表示手段」、「可変表示手段」、あるいは「可変表示器」などと表現される場合もある。また、これらの構成要素として、後述の図柄表示領域4を含む場合もある。また、「図柄」は、遊技者が視認により識別可能な情報であればよく、その意味において「識別情報」などと表現される場合もある。
Inside the
フロントドア2bは、ドア本体9と、フロントパネル10と、腰部パネル12と、台座部13とを備える。ドア本体9は、ヒンジ(不図示)を用いてキャビネット2aに開閉可能に取り付けられる。ヒンジは、パチスロ1の前方側(遊技者側)から見て、ドア本体9の左側の側端部に設けられる。なお、キャビネット2aは、単に「箱体」と称することもできるし、フロントドア2bは、単に「扉」、あるいは「前面扉」と称することもできる。また、キャビネット2aは、フロントドア2bを支持、あるいは固定する枠体として機能するため、「支持体」、「支持枠」、あるいは「固定枠」などと表現される場合もある。また、フロントドア2bは、複数の扉部材によって構成されるものであってもよい。例えば、キャビネット2aの開口の上方側に取り付けられる上扉部材と、キャビネット2aの開口の下方側に取り付けられる下扉部材とによって構成されるものであってもよいし、遊技機の前面側からみて、キャビネット2aの開口側に取り付けられる内側扉部材と、遊技機の前面側に取り付けられる外側扉部材とによって構成されるものであってもよい。
The
フロントパネル10は、ドア本体9の上部に設けられている。このフロントパネル10は、開口10aを有する枠状部材で構成される。フロントパネル10の開口10aは、表示装置カバー30によって塞がれ、表示装置カバー30は、キャビネット2aの内部に配置された後述の表示装置11と対向して配置される。
The
表示装置カバー30は、黒色の半透明な合成樹脂により形成される。それゆえ、遊技者は、後述の表示装置11により表示された映像(画像)を、表示装置カバー30を介して視認することができる。 また、本実施形態では、表示装置カバー30を黒色の半透明な合成樹脂で形成することにより、キャビネット2a内への外光の入り込みを抑制して、表示装置11により表示された映像(画像)を鮮明に視認できるようにしている。
The
フロントパネル10には、ランプ群21が設けられている。ランプ群21は、例えば、遊技者側から見て、フロントパネル10の上部に設けられたランプ21a、21bを含む。ランプ群21を構成する各ランプは、LED(Light Emitting Diode)等で構成され(後述の図6中のLED群85参照)、演出内容に対応するパターンで、光を点灯及び消灯する。
A
腰部パネル12は、ドア本体9の略中央部に設けられる。腰部パネル12は、任意の画像が描かれた装飾パネルと、この装飾パネルを背面側から照明するための光を出射する光源(後述のLED群85に含まれるLED)とを有する。
The
台座部13は、フロントパネル10と腰部パネル12との間に設けられる。台座部13には、図柄表示領域4と、遊技者による操作の対象となる各種装置(メダル投入口14、MAXベットボタン15a、1ベットボタン15b、スタートレバー16、3つのストップボタン17L,17C,17R、精算ボタン(不図示)等)とが設けられる。
The
図柄表示領域4は、正面から見て、3つのリール3L,3C,3Rに重畳する領域で、かつ、3つのリール3L,3C,3Rより遊技者側の位置に配置されており、3つのリール3L,3C,3Rにおける所定領域を視認可能とする。この図柄表示領域4は、表示窓としての機能を果たすものであり、その背後に設けられた各リール3L,3C,3Rを視認することが可能な構成になっている。以下、図柄表示領域4を、リール表示窓4という。
The
リール表示窓4は、その背後に設けられた3つのリール3L,3C,3Rの回転が停止されたとき、各リールの周面に設けられた複数の図柄のうち、連続して配置された3つの図柄がその枠内に表示されるように構成されている。すなわち、3つのリール3L,3C,3Rの回転が停止されたとき、リール表示窓4の枠内には、リール毎に上段、中段及び下段の各領域にそれぞれ1個の図柄(合計で3個)が表示される(リール表示窓4の枠内には、3行×3列の態様で図柄が表示される)。
The
そして、本実施形態では、リール表示窓4の枠内において、左リール3Lの中段領域、中リール3Cの中段領域、及び、右リール3Rの中段領域を結ぶライン(センターライン)、左リール3Lの上段領域、中リール3Cの上段領域、及び、右リール3Rの上段領域を結ぶライン(トップライン)、並びに、左リール3Lの下段領域、中リール3Cの下段領域、及び、右リール3Rの下段領域を結ぶライン(ボトムライン)を、入賞か否かの判定を行う有効ラインとして定義(規定)する。なお、有効ラインは、「入賞ライン」、あるいは「判定ライン」とも称されることがある。
In the present embodiment, in the frame of the
なお、本実施形態では、他のライン、例えば、左リール3Lの下段領域、中リール3Cの中段領域、及び、右リール3Rの上段領域を結ぶライン(クロスアップライン)、並びに、左リール3Lの上段領域、中リール3Cの中段領域、及び、右リール3Rの下段領域を結ぶライン(クロスダウンライン)を、さらに有効ラインとして定義してもよい。また、本実施形態では、有効ラインは上述の3つのラインである(あるいは、ここで説明したように5つのラインであってもよい)が、そのライン数は適宜増減できるものとする。例えば、センターラインの1つのラインのみを有効ラインとしてもよいし、トップライン及びボトムラインの2つのラインのみを有効ラインとしてもよい。また、有効ラインを定義する際には、上述した図柄が一直線に並ぶ各ラインに替えて、あるいはこれとともに、図柄が一直線に並ばないラインを有効ラインとして定義することもできる。すなわち、各列(左リール3L,中リール3C,右リール3R)ごとのいずれか一の図柄(の領域)を通るラインであれば、直線又は折れ線で結んで構成される一又は複数のラインを有効ラインとして設定可能である。
In the present embodiment, other lines, for example, a line (cross-up line) connecting the lower region of the
例えば、左リール3Lの中段領域、中リール3Cの下段領域、及び、右リール3Rの上段領域を結ぶライン(変則ライン)などを有効ラインとして定義するようにしてもよい。すなわち、本実施形態では、リール表示窓4の枠内に、3行×3列の態様で図柄が表示されるようになっていることから、27通りの有効ラインを定義することが可能であり、そのうち少なくともいずれか1つのラインが有効ラインとして定義されるようにすればよい。
For example, a line (irregular line) connecting the middle region of the
リール表示窓4は、台座部13に設けられた枠部材31の開口により形成される。また、リール表示窓4を画成する枠部材31の下方には、略水平面の台座領域が設けられる。そして、遊技者側から見て、台座領域の右側にはメダル投入口14が設けられ、左側にはMAXベットボタン15a及び1ベットボタン15bが設けられる。
The
メダル投入口14は、遊技者によって外部からパチスロ1に投下されるメダルを受け入れるために設けられる。メダル投入口14から受け入れられたメダルは、予め設定された所定枚数(例えば3枚)を上限として1回の遊技に使用され、所定枚数を超えたメダルの枚数分は、パチスロ1の内部に預けることができる(いわゆるクレジット機能(遊技媒体貯留手段))。
The
MAXベットボタン15a及び1ベットボタン15bは、キャビネット2aの内部に預けられているメダルから1回の遊技に使用する枚数を決定するために設けられる。なお、MAXベットボタン15aの内部には、メダル投入が可能な時に点灯するベットボタンLED(不図示)が設けられている。また、精算ボタンは、パチスロ1の内部に預けられているメダルを外部に引き出す(排出する)ために設けられる。
The
なお、遊技者がMAXベットボタン15aを押下操作すると、単位遊技のベット枚数(3枚)のメダルが投入され、有効ラインが有効化される。一方、1ベットボタン15bが1回、押下操作される度に1枚のメダルが投入される。1ベットボタン15bが3回操作されると、単位遊技のベット枚数(3枚)のメダルが投入され、有効ラインが有効化される。
When the player presses the
なお、以下では、MAXベットボタン15aの操作、1ベットボタン15bの操作及びメダル投入口14にメダルを投入する操作(遊技を行うためにメダルを投入する操作)をいずれも「投入操作」という。
In the following, the operation of the
スタートレバー16は、全てのリール(3L,3C,3R)の回転を開始するために設けられる。ストップボタン17L,17C,17Rは、それぞれ、左リール3L、中リール3C、右リール3Rに対応づけて設けられ、各ストップボタンは対応するリールの回転を停止するために設けられる。以下、ストップボタン17L,17C,17Rを、それぞれ左ストップボタン17L、中ストップボタン17C、右ストップボタン17Rともいう。
The
また、リール表示窓4の下方の略水平面の台座領域の略中央には、情報表示器6が設けられる。なお、情報表示器6は、透明の窓カバー(不図示)によって覆われている。
In addition, an
情報表示器6には、特典として遊技者に対して払い出されるメダルの枚数(以下、「払出枚数」という)の情報を遊技者に対してデジタル表示(報知)するための2桁の7セグメントLED(以下、「7セグLED」という)や、パチスロ1の内部に預けられているメダルの枚数(以下、「クレジット枚数」という)などの情報を遊技者に対してデジタル表示(報知)するための2桁の7セグLEDが設けられる。なお、本実施形態では、メダルの払出枚数表示用の2桁の7セグLEDは、エラー発生及びエラー種別の情報を遊技者に対してデジタル表示(報知)するための2桁の7セグLEDとしても用いられる。それゆえ、エラー発生時には、メダルの払出枚数表示用の2桁の7セグLEDの表示態様は、払出枚数の表示態様からエラー種別の情報の表示態様に切り替わる。
The
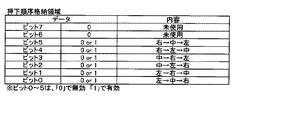
また、情報表示器6には、内部当籤役として決定された役に応じた図柄組合せを有効ラインに沿って表示するために必要な停止操作の情報を報知する指示モニタ(不図示)が設けられている。指示モニタ(指示表示器)は、例えば、2桁の7セグLEDにより構成される。そして、指示モニタでは、報知する停止操作の情報と一義的に対応する態様で、2桁の7セグLEDが点灯、点滅又は消灯することにより、遊技者に対して必要な停止操作の情報を報知する。
In addition, the
なお、ここでいう、報知する停止操作の情報と一義的に対応する態様とは、例えば、押し順「1st(第1停止操作を左リール3Lに対して行うこと)」を報知する場合には指示モニタに数値「1」を表示し、押し順「2nd(第1停止操作を中リール3Cに対して行うこと)」を報知する場合には指示モニタに数値「2」を表示し、押し順「3rd(第1停止操作を右リール3Rに対して行うこと)」を報知する場合には指示モニタに数値「3」を表示するなどの態様のことである。なお、指示モニタにおける停止操作の情報の報知態様(後述のメイン側で決定されるナビデータ)については、後述の図45等を参照しながら後で詳述する。
Note that, here, the mode uniquely corresponding to the information of the stop operation to be notified means, for example, when the pressing order “1st (perform the first stop operation on the
また、情報表示器6には、遊技者にとって有利な有利区間(後述の「通常有利区間」及び「有利区間」を含む。後述の図14参照)であること報知する状態表示器(不図示)が設けられている。状態表示器は、例えば、7セグLEDにより構成される。状態表示器は、原則として、有利区間に移行することが決定された遊技中の所定のタイミング(例えば、遊技開始時〜遊技終了時までのいずれかのタイミング)で点灯し、有利区間が継続している間はその点灯が継続する。そして、有利区間が終了したときにその点灯が終了し、消灯するようになっている。これにより、遊技者にとって有利な有利区間が開始すること、当該有利区間中であること、及び当該有利区間が終了することが全ての遊技者に報知されるため、遊技の公平性が担保される。
In addition, the
情報表示器6は、後述の図6に示すように、ドア中継端子板68及び遊技動作表示基板81を介して主制御基板71に電気的に接続され、情報表示器6の表示動作は、主制御基板71内の後述の主制御回路90により制御される。また、上述した各種7セグLEDの制御方式は、ダイナミック点灯制御である。
The
なお、本実施形態のパチスロ1では、主制御基板71により制御される指示モニタに加えて、副制御基板72により制御される他の手段を用いて停止操作の情報を報知する構成を設ける。具体的には、後述のプロジェクタ機構211及び表示ユニット212(図3及び後述の図6参照)により構成される後述の表示装置11により停止操作の情報を報知する。
In the pachi-
このような構成を適用した場合、指示モニタにおける報知の態様と、副制御基板72により制御されるその他の手段における報知の態様とは、互いに異なる態様であってもよい。すなわち、指示モニタでは、報知する停止操作の情報と一義的に対応する態様で報知すればよく、必ずしも、停止操作の情報を直接的に報知する必要はない(例えば、指示モニタにおいて数値「1」が表示されたとしても、遊技者によっては報知内容を特定できない可能性もあり、直接的な報知とはいえない)。一方、後述の表示装置11等のその他の手段によるサブ側(副制御基板側)での報知では、停止操作の情報を直接的に報知してもよい。例えば、押し順「1st」を報知する場合、指示モニタでは報知する押し順と一義的に対応する数値「1」を表示するが、その他の手段(例えば、表示装置11等)では、左リール3Lに対して第1停止操作を行わせるための指示情報を直接的に報知してもよい。
When such a configuration is applied, the notification mode in the instruction monitor and the notification mode in the other means controlled by the
このような構成のパチスロ1では、副制御基板72の制御だけでなく、主制御基板71の制御によっても、内部当籤役に応じた必要な停止操作の情報を報知することができる。また、このような停止操作の情報の報知の有無は、遊技状態に応じて制御することができる。例えば、後述の通常区間における遊技状態(通常状態)では停止操作の情報が報知されずに、後述の通常有利区間及び有利区間における各遊技状態では停止操作の情報が報知され得るようにすることができる。
In the pachi-
また、遊技者側から見て、リール表示窓4の左方には、サブ表示装置18が設けられる。サブ表示装置18は、図2に示すように、ドア本体9の前面部のうち、台座部13の略水平面の台座領域から略垂直に立設するように設けられる。サブ表示装置18は、液晶ディスプレイや有機EL(Electro-Luminescence)ディスプレイで構成され、各種情報を表示する。
A
また、サブ表示装置18の表示面上には、タッチセンサ19が設けられている(後述の図6参照)。タッチセンサ19は、静電容量方式などの所定の動作原理に従い動作し、遊技者の操作を受け付けると、タッチ入力情報として当該操作に応じた信号を出力する。そして、本実施形態のパチスロ1は、タッチセンサ19を介して受け付けた遊技者の操作(タッチセンサ19から出力されるタッチ入力情報)に応じて、サブ表示装置18の表示を切り替え可能にする機能を有する。なお、サブ表示装置18は、タッチセンサ19から出力されるタッチ入力情報に基づいて後述の副制御基板72(後述の図6参照)により制御される。
Further, a
ドア本体9の下部には、メダル払出口24、メダル受皿25、2つのスピーカ用孔20L,20R等が設けられる。メダル払出口24は、後述のホッパー装置51(メダル払出装置)の駆動により排出されるメダルを外部に導く。メダル受皿25は、メダル払出口24から排出されたメダルを貯める。また、2つのスピーカ用孔20L,20Rからは、演出内容に対応する効果音や楽曲等の音声が出力される。
A
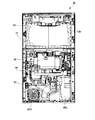
[内部構造]
次に、パチスロ1の内部構造を、図3〜図5を参照しながら説明する。図3は、キャビネット2aの内部構造を示す図であり、図4は、フロントドア2bの裏面側の内部構造を示す図であり、図5は、フロントドア2bの裏面側に設けられた後述のセレクタ66の構造を示す図である。
[Internal structure]
Next, the internal structure of the pachi-
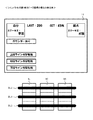
キャビネット2aは、図3に示すように、上面板27aと、底面板27bと、左右の側面板27c,27dと、背面板27eとを有する。そして、キャビネット2a内の上部には、表示装置11が配設される。
As shown in FIG. 3, the
表示装置11は、プロジェクタ機構211と、プロジェクタ機構211から投射された映像光が投影される箱状の被投影部材212aとを有し、プロジェクションマッピングによる映像表示を行う。具体的には、表示装置11では、立体物となる被投影部材212aの位置(投影距離や角度など)や形状に基づいて映像光を生成し、その映像光が、プロジェクタ機構211により被投影部材212aの表面に投影される。このような演出機能を設けることにより、高度で且つ迫力のある演出を行うことができる。また、図3には示さないが、箱状の被投影部材212aの裏側には、表示面が湾曲した別の被投影部材が設けられ、遊技状態に応じて、どちらか一方の被投影部材が、映像光が投影されるスクリーンとして使用される。それゆえ、キャビネット2a内は、遊技状態に応じて、被投影部材を切り換える機能(不図示)も設けられる。なお、表示装置11は、遊技者にとって画像を表示可能な装置であれば、他の種々の表示装置(例えば、液晶表示装置)を用いることもできる。
The
キャビネット2a内の下部には、メダル払出装置(以下、ホッパー装置という)51と、メダル補助収納庫52と、電源装置53とが配設される。
A medal payout device (hereinafter referred to as a hopper device) 51, a medal
ホッパー装置51は、キャビネット2aにおける底面板27bの中央部に取り付けられる。このホッパー装置51は、多量のメダルを収容可能で、それらを1枚ずつ排出可能な構造を有する。ホッパー装置51は、貯留されたメダルが例えば50枚を超えたとき、又は、精算ボタンが押下されてメダルの精算が実行されるときに、メダルを払い出す。そして、ホッパー装置51によって払い出されたメダルは、メダル払出口24(図2参照)から排出される。
The
メダル補助収納庫52は、ホッパー装置51から溢れ出たメダルを収納する。このメダル補助収納庫52は、キャビネット2a内部を正面から見て、ホッパー装置51の右側に配置される。また、メダル補助収納庫52は、キャビネット2aの底面板27bに対して着脱可能に取り付けられている。
The medal
電源装置53は、電源スイッチ53aと、電源基板53b(電源供給手段)とを有している(後述の図6参照)。この電源装置53は、キャビネット2a内部を正面から見て、ホッパー装置51の左側に配置されており、左側面板27cに取り付けられている。電源装置53は、サブ電源装置(不図示)から供給された交流電圧100Vの電力を各部で必要な直流電圧の電力に変換して、変換した電力を各部へ供給する。
The
また、キャビネット2a内の電源装置53の上方には、副制御基板72(後述の図6参照)を収容する副制御基板ケース57が配設される。副制御基板ケース57に収納された副制御基板72には、後述の副制御回路200(後述の図9参照)が搭載されている。この副制御回路200は、映像の表示等による演出の実行を制御する回路である。副制御回路200の具体的な構成については後述する。
Further, above the
キャビネット2a内の副制御基板ケース57の上方には、副中継基板61が配設される。この副中継基板61は、副制御基板72と後述の主制御基板71とを接続する配線が実装された中継基板である。また、副中継基板61は、副制御基板72と副制御基板72の周辺に配設された基板や各種装置部(ユニット)などとを接続する配線が実装された中継基板である。
A
また、図3には示さないが、キャビネット2a内には、キャビネット側中継基板44(後述の図6参照)が配設される。このキャビネット側中継基板44は、主制御基板71(後述の図6参照)と、ホッパー装置51、メダル補助収納庫スイッチ75(後述の図6参照)及びメダル払出カウントスイッチ(不図示)のそれぞれとを接続する配線が実装された中継基板である。
Although not shown in FIG. 3, a cabinet-side relay board 44 (see FIG. 6 described later) is arranged in the
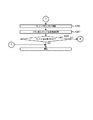
フロントドア2bの裏面側の中央部には、図4に示すように、ミドルドア41が、配設され、リール表示窓4(図2参照)を裏側から開閉可能に取り付けられている。また、図4には示さないが、ミドルドア41のリール表示窓4側には、3つのリール3L,3C,3Rが取り付けられ、ミドルドア41のリール表示窓4側とは反対側には、主制御基板71(後述の図6参照)が収納された主制御基板ケース55が取り付けられている。なお、3つのリール3L,3C,3Rには、所定の減速比をもったギアを介してステッピングモータ(不図示)が接続されている。
As shown in FIG. 4, a
主制御基板ケース55に収納された主制御基板71は、後述する主制御回路90(後述の図7及び図8参照)を有する。主制御回路90(主制御手段)は、内部当籤役の決定、各リール3L,3C,3Rの回転及び停止、入賞の有無の判定といった、パチスロ1における遊技の主な流れを制御する回路である。また、本実施形態では、例えば、ATあるいはARTに関する決定に係る処理、ナビ情報の指示モニタへの表示処理、各種試験信号の送信処理などの制御も主制御回路90により行われる。なお、主制御回路90の具体的な構成は後述する。
The
フロントドア2bの裏面側において、ミドルドア41の下方には、スピーカ65L,65Rが配設される。スピーカ65L,65Rは、それぞれスピーカ用孔20L,20R(図2参照)と対向する位置に配置されている。
また、スピーカ65Lの上方には、セレクタ66と、ドア開閉監視スイッチ67とが配設される。セレクタ66は、メダル投入口14に投入されたメダルを検出する装置であるとともに、投入されたメダルが適正なメダルであるか否かを選別する装置であり、適正なメダルであると選別される場合には、そのメダルがホッパー装置51側へと案内されてホッパー装置51内に収容されるように駆動し、適正なメダルでないと選別される場合には、そのメダルがメダル払出口24側へと案内されてメダル払出口24から排出されるように駆動する。すなわち、セレクタ66は、メダル投入口14に投入されたメダルを、ホッパー装置51側又はメダル払出口24側に振り分ける装置でもある。
A
図5に示すように、セレクタ66は、メダルが通過するメダルレール(メダル通路)802が形成されたベース803と、投入されたメダルをホッパー装置51側又はメダル払出口24側に案内するセレクトプレート804と、投入されたメダルが適正なメダルでない場合にそのメダルをメダル払出口24側に押し出すメダルプッシャ805と、投入されたメダルをメダルレール802の上流側で検出する上流側メダルセンサ(第1メダルセンサ)806と、投入されたメダルをメダルレール802の下流側で検出する下流側メダルセンサ(第2メダルセンサ)807と、を備える。
As shown in FIG. 5, the
また、図5には示さないが、セレクタ66には、セレクトプレート804によってメダルがホッパー装置51側に案内される場合に、セレクタ66からホッパー装置51へのメダルの流路を形成するメダルガイド(不図示)と、セレクトプレート804によってメダルがメダル払出口24側にされる場合に、セレクタ66からメダル払出口24へのメダルの流路を形成するキャンセルシュート(不図示)と、が着脱可能に取り付けられている。
Although not shown in FIG. 5, the
セレクトプレート804は、セレクタ66が備えるソレノイド(不図示)によって駆動する。セレクトプレート804は、ソレノイドが駆動しているときには、通過するメダルをホッパー装置51側に案内するガイド位置に移動する一方、ソレノイドが駆動していないときには、通過するメダルをホッパー装置51側に案内しない(すなわち、メダル払出口24側に案内する)排出位置に移動する。具体的には、ソレノイドが駆動しているとき、セレクトプレート804はパチスロ1の後側方向に移動してメダルの上方をガイドする一方、ソレノイドが駆動していないとき、セレクトプレート804はパチスロ1の前側方向に移動してメダルの上方をガイドしないようになっている。なお、セレクトプレート804によるメダルのガイド手法はこれに限られるものでなく、例えば、パチスロ1の上下方向に移動可能な機構とすることで、ガイド位置及び排出位置の移動を可能とするものであってもよい。すなわち、セレクトプレート804は、ソレノイドあるいはその他の駆動源により、メダルレール802上において、通過するメダルがホッパー装置51側に移動することを妨げないガイド位置と、通過するメダルがホッパー装置51側に移動することを妨げてメダル払出口24側に案内する排出位置との間で変移可能とする機構であれば、いずれの機構を採用することもできる。
The
メダルプッシャ805は、例えば、セレクトプレート804がガイド位置に移動している場合には、パチスロ1の後側方向に突出しないように動作し、セレクトプレート804がガイド位置に移動していない(排出位置に移動している)場合には、パチスロ1の後側方向に突出するように動作する。すなわち、メダルプッシャ805が、パチスロ1の後側方向に突出しない位置にあるときには、通過するメダルをホッパー装置51側に案内するガイド位置となり、パチスロ1の後側方向に突出する位置にあるときには、通過するメダルをホッパー装置51側に案内しない(すなわち、メダル払出口24側に案内する)排出位置となる。
For example, when the
上流側メダルセンサ806及び下流側メダルセンサ807は、メダルが通過したことを検出する遊技媒体検出手段を構成する。各メダルセンサは、例えば、一対の、あるいは複数対の発光素子及び受光素子から構成される反射型センサで構成され、発光素子からメダルに対して光を照射し、メダルから反射された反射光を受光素子が受光することでメダルの通過を検出する。なお、センサの構成は適宜変更可能であり、例えば、透過型センサ等を採用することもできる。また、上流側メダルセンサ806を設けることなく、下流側メダルセンサ807のみによってメダルの通過を検出するようにしてもよい。また、各メダルセンサの検出結果(メダルセンサ入力状態)に基づく具体的な制御については後述する。
The
ドア開閉監視スイッチ67は、フロントドア2bを裏面側から見て、セレクタ66の左斜め下に配置される。このドア開閉監視スイッチ67は、フロントドア2bの開閉を報知するためのセキュリティ信号をパチスロ1の外部に出力する。
The door open/
また、図4には示さないが、フロントドア2bを裏面において、ミドルドア41により開閉された領域であり且つリール表示窓4の下方には、ドア中継端子板68が配設される(後述の図6参照)。このドア中継端子板68は、主制御基板ケース55内の主制御基板71と、各種のボタンやスイッチ、副中継基板61、セレクタ66、遊技動作表示基板81、試験機用第1インターフェースボード301及び試験機用第2インターフェースボード302のそれぞれとを接続する配線が実装された中継基板である。なお、各種のボタン及びスイッチとしては、例えば、MAXベットボタン15a、1ベットボタン15b、ドア開閉監視スイッチ67、後述のBETスイッチ77、スタートスイッチ79等が挙げられる。
Although not shown in FIG. 4, a door
<パチスロが備える制御系>
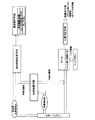
次に、パチスロ1が備える制御系について、図6を参照して説明する。図6は、パチスロ1の制御系の構成を示す回路ブロック図である。
<Control system of pachi-slot>
Next, the control system included in the pachi-
パチスロ1は、ミドルドア41に設けられた主制御基板71と、フロントドア2bに設けられた副制御基板72とを有する。また、パチスロ1は、主制御基板71に接続された、リール中継端子板74、設定用鍵型スイッチ54(設定スイッチ)及びキャビネット側中継基板44を有する。さらに、パチスロ1は、キャビネット側中継基板44を介して主制御基板71に接続された外部集中端子板47、ホッパー装置51、メダル補助収納庫スイッチ75、リセットスイッチ76及び電源装置53を有する。なお、ホッパー装置51の構成については上述したので、ここでは、その説明を省略する。
The pachi-
リール中継端子板74は、各リール3L,3C,3Rのリール本体の内側に配設されている。リール中継端子板74は、各リール3L,3C,3Rのステッピングモータ(不図示)に電気的に接続されており、主制御基板71からステッピングモータに出力される信号を中継する。
The reel
設定用鍵型スイッチ54は、主制御基板ケース55に設けられる。設定用鍵型スイッチ54は、パチスロ1の設定値(設定1〜設定6)を変更するとき、もしくは、パチスロ1の設定を確認するときに使用される。なお、設定値は、遊技に関する遊技者の有利さの度合いを示すものであり、通常は、設定値が低いほど(例えば、設定1に近いほど)遊技者の有利さの度合いが相対的に低くなり、設定値が高いほど(例えば、設定6に近いほど)遊技者の有利さの度合いが相対的に高くなる。なお、本実施形態では、設定値が高いほど後述のボーナス役の当籤確率が高まるようにして遊技者の有利さの度合いを変動させることもできるし、設定値が高いほど後述のATやARTに係る抽籤の当籤確率が高まるようにして遊技者の有利さの度合いを変動させることもできる。
The setting
キャビネット側中継基板44は、主制御基板71と、外部集中端子板47、ホッパー装置51、メダル補助収納庫スイッチ75、リセットスイッチ76及び電源装置53のそれぞれとを接続する配線が実装された中継基板である。外部集中端子板47は、メダル投入信号、メダル払出信号及びセキュリティ信号などの信号をパチスロ1の外部へ出力するために設けられる。メダル補助収納庫スイッチ75は、メダル補助収納庫52に設けられ、メダル補助収納庫52がメダルで満杯になっているか否かを検出する。リセットスイッチ76は、例えば、パチスロ1の設定を変更する際に用いられる。
The cabinet-
電源装置53は、電源基板53bと、電源基板53bに接続された電源スイッチ53aとを有する。電源スイッチ53aは、パチスロ1に必要な電源を供給するときに押下される。電源基板53bは、キャビネット側中継基板44を介して主制御基板71に接続されるとともに、副中継基板61を介して副制御基板72にも接続される。
The
また、パチスロ1は、ドア中継端子板68、並びに、該ドア中継端子板68を介して、主制御基板71に接続された、セレクタ66、ドア開閉監視スイッチ67、BETスイッチ77、精算スイッチ78、スタートスイッチ79、ストップスイッチ基板80、遊技動作表示基板81、副中継基板61、試験機用第1インターフェースボード301及び試験機用第2インターフェースボード302を有する。なお、セレクタ66、ドア開閉監視スイッチ67及び副中継基板61については、上述したので、ここでは、それらの説明を省略する。
Further, the pachi-
BETスイッチ77(投入操作検出手段)は、MAXベットボタン15a又は1ベットボタン15bが遊技者により押下されたことを検出する。精算スイッチ78は、精算ボタン(不図示)が遊技者により押下されたことを検出する。スタートスイッチ79(開始操作検出手段)は、スタートレバー16が遊技者により操作されたこと(開始操作)を検出する。
The BET switch 77 (insertion operation detecting means) detects that the player has pressed the
ストップスイッチ基板80(停止操作検出手段)は、回転しているメインリールを停止させるための回路と、停止可能なメインリールをLEDなどにより表示するための回路とを備える。また、ストップスイッチ基板80には、ストップスイッチ(不図示)が設けられる。ストップスイッチは、各ストップボタン17L,17C,17Rが遊技者により押下されたこと(停止操作)を検出する。
The stop switch board 80 (stop operation detecting means) includes a circuit for stopping the rotating main reel and a circuit for displaying the stoppable main reel with an LED or the like. A stop switch (not shown) is provided on the
遊技動作表示基板81は、情報表示器(7セグ表示器)6及びLED82に接続される。LED82には、例えば、今回の遊技に投入されたメダルの枚数(以下、「投入枚数」という)に対応して点灯する、メダル投入枚数表示用の3つのLED(以下、「第1LED」〜「第3LED」という)や、遊技動作表示基板81から入力される信号に基づいて、メダル投入が可能であることを表示するマーク、遊技開始を表示するマーク、再遊技を行うマークなどを点灯させるLEDなどが含まれる。第1LED〜第3LED(表示手段)では、メダルが1枚投入されると、第1LEDが点灯し、メダルが2枚投入されると、第1及び第2LEDが点灯し、メダルが3枚(遊技開始可能枚数)投入されると、第1LED〜第3LEDが点灯する。なお、情報表示器6については、上述したので、ここでは、それらの説明を省略する。
The game
試験機用第1インターフェースボード301及び試験機用第2インターフェースボード302はともに、パチスロ1の検定試験(試射試験)において、遊技に関する各種信号を試験機に出力する際に用いられる中継基板である(なお、販売用のリリース製品としてのパチスロ1にはこれらの中継基板は搭載されていないので、販売用の主制御基板71の主制御回路90には、試験機用第1インターフェースボード301及び試験機用第2インターフェースボード302に接続するために必要な各種電子部品もまた実装されていない)。例えば、遊技に係る主要な動作(例えば、内部抽籤、リール停止制御等)を制御するための試験信号は、試験機用第1インターフェースボード301を介して出力され、例えば、主制御基板71で決定された押し順ナビに係る試験信号などは、試験機用第2インターフェースボード302を介して出力される。
Both the
副制御基板72は、ドア中継端子板68及び副中継基板61を介して主制御基板71に接続される。また、パチスロ1は、副中継基板61を介して副制御基板72に接続された、スピーカ群84、LED群85、24hドア開閉監視ユニット63、タッチセンサ19及び表示ユニット212を有する。なお、タッチセンサ19については、上述したので、ここでは、その説明を省略する。
The
スピーカ群84は、スピーカ65L,65Rや図示しない各種スピーカを含んで構成される。LED群85は、フロントパネル10に設けられたランプ群21や、腰部パネル12の装飾パネルを背面側から照明するための光を出射する光源などを含んで構成される。24hドア開閉監視ユニット63は、ミドルドア41の開閉の履歴情報を保存する。また、24hドア開閉監視ユニット63は、ミドルドア41が開放されたときに、表示装置11によりエラー表示を行うための信号を副制御基板72(副制御回路200)に出力する。表示ユニット212は、例えば、表示装置11を構成する被投影部材212a、及び、被投影部材212aの裏側に設けられた表示面が湾曲した別の被投影部材を含んで構成される。
The
また、パチスロ1は、副制御基板72に接続された、ロムカートリッジ基板86及び液晶中継基板87を有する。なお、ロムカートリッジ基板86及び液晶中継基板87は、副制御基板72とともに副制御基板ケース57に収納されている。
Further, the pachi-
ロムカートリッジ基板86は、サブCPU201により実行される各種制御プログラムと、演出用の画像(映像)、音声(スピーカ群84)、光(LED群85)及び通信のデータを管理するための基板である。液晶中継基板87は、副制御基板72と、表示装置11を構成するプロジェクタ機構211、及び、サブ表示装置18との間の接続配線を中継する基板である。なお、プロジェクタ機構211及びサブ表示装置18については、上述したので、ここでは、それらの説明を省略する。
The
<主制御回路>
次に、図7を参照して、主制御基板71に実装される主制御回路90の構成について説明する。図7は、パチスロ1の主制御回路90の構成例を示すブロック図である。
<Main control circuit>
Next, the configuration of the
主制御回路90は、遊技動作を制御する遊技制御部として機能し、マイクロプロセッサ91と、クロックパルス発生回路92と、電源管理回路93と、スイッチングレギュレータ94(電源供給手段)と、役比モニタ(不図示)とを備える。
The
マイクロプロセッサ91は、遊技機用のセキュリティ機能付きマイクロプロセッサである。なお、本実施形態のマイクロプロセッサ91では、プログラム上で規定可能な該マイクロプロセッサ91に特有の様々な命令コード(以下、「メインCPU101専用命令コード」という)が設けられている。本実施形態では、このメインCPU101専用命令コードを用いることにより、処理の効率化やプログラム容量の削減などを実現している。マイクロプロセッサ91の内部構成については、後述の図8を参照して詳述し、マイクロプロセッサ91に設けられているメインCPU101専用命令コードについては、後述の主制御回路が実行する各種処理において詳述する。
The
クロックパルス発生回路92は、メインCPU作動用のクロックパルス信号を生成し、該生成したクロックパルス信号をマイクロプロセッサ91に出力する。マイクロプロセッサ91は、入力されたクロックパルス信号に基づいて、制御プログラムを実行する。
The clock
電源管理回路93は、電源基板53b(図6参照)から供給される直流12Vの電源電圧の変動を管理する。そして、電源管理回路93は、例えば、電源が投入された際(電源電圧が0Vから起動電圧値(10V)を上回った際)には、リセット信号をマイクロプロセッサ91の「XSRST」端子に出力し、電断が発生した際(電源電圧が12Vから停電電圧値(10.5V)を下回った際)には、電断検知信号をマイクロプロセッサ91の「XINT」端子に出力する。すなわち、電源管理回路93は、電源投入時に、マイクロプロセッサ91にリセット信号(起動信号)を出力する手段(起動手段)、及び、電断発生時に、マイクロプロセッサ91に電断検知信号(停電信号)を出力する手段(停電手段)も兼ねる。
The
スイッチングレギュレータ94は、DC/DC変換回路であり、マイクロプロセッサ91の直流駆動電圧(直流5Vの電源電圧)を生成し、該生成した直流駆動電圧をマイクロプロセッサ91の「VCC」端子に出力する。
The switching
役比モニタ(不図示)は、例えば、4桁の7セグメントLEDにより構成され、後述のメインCPU101によって集計された遊技情報に関する集計結果に対して、後述の演算回路107が所定の比率計算を行い、その比率計算の結果を比率情報として表示する。本実施形態では、複数種類の比率計算が行われ、役比モニタは、その結果に基づいて、複数種類の比率情報を順次表示する。
The winning ratio monitor (not shown) is composed of, for example, a 4-digit 7-segment LED, and the
なお、役比モニタの上位2桁には、その比率情報の種別を示す種別情報である「略記」が表示され、下位2桁には、その種別情報に対応する比率情報である「比率」が表示されるようになっている。例えば、役比モニタの第1の桁(略記10の位)に「7」が表示され、第2の桁(略記1の位)に「U」が表示される場合(すなわち、略記「7U」が表示される場合)、役比モニタの下位2桁には、比率情報として、所定の総遊技数(175000回)の間に占める、ART機能が作動した(すなわち、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の手順が報知されていた有利区間の)遊技数の比率(有利区間比率)が表示される。具体的には、有効区間比率が10%である場合、第3の桁(比率10の位)には「1」が表示され、第4の桁(比率1の位)には「0」が表示される。なお、有利区間比率は、AT機能及びART機能が作動した遊技数の比率を表示するものであってもよい。 In the upper two digits of the combination ratio monitor, "abbreviation", which is the type information indicating the type of the ratio information, is displayed, and in the lower two digits, "ratio", which is the ratio information corresponding to the type information. It is supposed to be displayed. For example, when “7” is displayed in the first digit (the place of the abbreviation 10) and “U” is displayed in the second digit (the place of the abbreviation 1) of the combination ratio monitor (that is, the abbreviation “7U”). Is displayed), the lower two digits of the winning ratio monitor, as ratio information, occupies a predetermined total number of games (175,000 times), and the ART function is activated (that is, a stop operation advantageous for the player). The ratio of the number of games (of the advantageous section for which the procedure was notified) (the advantageous section ratio) is displayed. Specifically, when the effective section ratio is 10%, "1" is displayed in the third digit (the 10th digit of the ratio) and "0" is displayed in the 4th digit (the 1st digit of the ratio). Is displayed. In addition, the advantageous section ratio may display a ratio of the number of games in which the AT function and the ART function are activated.
また、例えば、役比モニタの第1の桁(略記10の位)に「6」が表示され、第2の桁(略記1の位)に「Y」が表示される場合(すなわち、略記「6Y」が表示される場合)、役比モニタの下位2桁には、比率情報として、特定の総遊技数(6000回)の間で払い出された遊技媒体の払出枚数に占める、役物連続作動装置(本実施形態ではBB。なお、第2種特別役物(CB)が連続で作動する役物連続作動装置(MB)が搭載されている場合には、それを含む。以下同じ)が作動して払い出された遊技媒体の払出枚数の比率(中時間連役比率)が表示される。具体的には、中時間連役比率が59%である場合、第3の桁(比率10の位)には「5」が表示され、第4の桁(比率1の位)には「9」が表示される。 Further, for example, when "6" is displayed in the first digit (the place of the abbreviation 10) and "Y" is displayed in the second digit (the place of the abbreviation 1) of the winning ratio monitor (that is, the abbreviation " 6Y” is displayed), in the lower two digits of the winning ratio monitor, as ratio information, the winning character continuation occupies in the payout number of game media paid out within a specific total number of games (6000 times). The operating device (BB in the present embodiment, including the accessory continuous operating device (MB) that continuously operates the second type special accessory (CB), including it. The same applies hereinafter). The ratio of the number of paid-out game media that has been activated (middle-time combination ratio) is displayed. Specifically, when the medium-time combination ratio is 59%, "5" is displayed in the third digit (the 10th digit of the ratio) and "9" is displayed in the 4th digit (the 1st digit of the ratio). Is displayed.
また、例えば、役比モニタの第1の桁(略記10の位)に「7」が表示され、第2の桁(略記1の位)に「Y」が表示される場合(すなわち、略記「7Y」が表示される場合)、役比モニタの下位2桁には、比率情報として、特定の総遊技数(6000回)の間で払い出された遊技媒体の払出枚数に占める、全ての役物(本実施形態ではBB。なお、上述のMBの他、上述の第一種特別役物(RB)が単独で搭載されている場合、上述の第2種特別役物(CB)が単独で搭載されている場合、普通役物(SB)が搭載されている場合には、それら全てを含む。以下同じ)が作動して払い出された遊技媒体の払出枚数の比率(中時間役物比率)が表示される。具体的には、中時間役物比率が59%である場合、第3の桁(比率10の位)には「5」が表示され、第4の桁(比率1の位)には「9」が表示される。 Further, for example, when "7" is displayed in the first digit (the place of the abbreviation 10) and "Y" is displayed in the second digit (the place of the abbreviation 1) of the ratio monitor (that is, the abbreviation " "7Y" is displayed), the lower two digits of the combination ratio monitor show, as ratio information, all combinations of the number of game media paid out within a specific total number of games (6000 times). (In the present embodiment, BB. In addition to the above MB, when the above-described first-class special accessory (RB) is installed alone, the above-mentioned second-class special accessory (CB) is alone. If it is installed, if the normal accessory (SB) is installed, all of them are included. The same applies hereafter) Ratio of the number of paid-out game media (medium-time accessory ratio) ) Is displayed. Specifically, when the medium-time role product ratio is 59%, "5" is displayed in the third digit (the tenth place of the ratio), and "9" is displayed in the fourth digit (the ones place of the ratio). Is displayed.
また、例えば、役比モニタの第1の桁(略記10の位)に「6」が表示され、第2の桁(略記1の位)に「A」が表示される場合(すなわち、略記「6A」が表示される場合)、役比モニタの下位2桁には、比率情報として、所定の総遊技数(175000回)の間で払い出された遊技媒体の払出枚数に占める、役物連続作動装置が作動して払い出された遊技媒体の払出枚数の比率(総連役比率)が表示される。具体的には、総連役比率が25%である場合、第3の桁(比率10の位)には「2」が表示され、第4の桁(比率1の位)には「5」が表示される。 Also, for example, when "6" is displayed in the first digit (the place of the abbreviation 10) and "A" is displayed in the second digit (the place of the abbreviation 1) of the ratio monitor (that is, the abbreviation " 6A” is displayed), in the lower two digits of the winning ratio monitor, as the ratio information, the winning character continuous in the payout number of game media paid out within a predetermined total number of games (175000 times) The ratio of the number of paid-out game media paid out by the actuation of the actuating device (total combination ratio) is displayed. Specifically, when the total combination ratio is 25%, "2" is displayed in the third digit (the 10th place of the ratio) and "5" is displayed in the 4th digit (the 1st place of the ratio). Is displayed.
また、例えば、役比モニタの第1の桁(略記10の位)に「7」が表示され、第2の桁(略記1の位)に「A」が表示される場合(すなわち、略記「7A」が表示される場合)、役比モニタの下位2桁には、比率情報として、所定の総遊技数(175000回)の間で払い出された遊技媒体の払出枚数に占める、全ての役物が作動して払い出された遊技媒体の払出枚数の比率(総役物比率)が表示される。具体的には、総役物比率が25%である場合、第3の桁(比率10の位)には「2」が表示され、第4の桁(比率1の位)には「5」が表示される。 Further, for example, when "7" is displayed in the first digit (the place of the abbreviation 10) and "A" is displayed in the second digit (the place of the abbreviation 1) of the ratio monitor (that is, the abbreviation " 7A” is displayed), the lower two digits of the combination ratio monitor show, as ratio information, all combinations of the number of game media paid out within a predetermined total number of games (175000 times). The ratio of the number of paid-out game media (total prize ratio) is displayed. Specifically, when the total accessory ratio is 25%, "2" is displayed in the third digit (the 10th digit of the ratio) and "5" is displayed in the 4th digit (the 1st digit of the ratio). Is displayed.
なお、本実施形態では、主制御回路90が直接的に役比モニタを備える構成を例に挙げて説明しているが、役比モニタは、主制御回路90によってその表示内容が制御され、また、必要なとき(例えば、主制御基板ケース55を視認したとき)にその表示内容を認識可能であれば足り、主制御回路90が直接的に備えない構成を採用することもできる。例えば、役比モニタが遊技動作表示基板81に接続され、主制御回路90が遊技動作表示基板81を介してその表示内容を制御するようにしてもよい。また、この場合、役比モニタが、情報表示器6、LED82、又は指示モニタ(指示表示器)と兼用されるようにし、それらのうち、一又は複数を用いて所定の比率情報が表示されるようにしてもよい。
In the present embodiment, the
また、本実施形態では、役比モニタに表示される所定の比率情報として、有利区間比率、中時間連役比率、中時間役物比率、総連役比率、及び総役物比率を例に挙げて説明しているが、これら以外の比率情報を表示可能としてもよい。例えば、所定の総遊技数(175000回)の間で払い出された遊技媒体の払出枚数に占める、ART機能が作動して払い出された遊技媒体の払出枚数の比率(総有利区間獲得比率)、特定の総遊技数(6000回)の間で払い出された遊技媒体の払出枚数に占める、ART機能が作動して払い出された遊技媒体の払出枚数の比率(中時間有利区間獲得比率)、特定の総遊技数(6000回)の間に占める、役物連続作動装置が作動した遊技数の比率(中時間連役区間比率)、特定の総遊技数(6000回)の間に占める、全ての役物が作動した遊技数の比率(中時間役物区間比率)、所定の総遊技数(175000回)の間に占める、役物連続作動装置が作動した遊技数の比率(総連役区間比率)、所定の総遊技数(175000回)の間に占める、全ての役物が作動した遊技数の比率(総役物区間比率)等も所定の比率計算を行って表示することができる。 Further, in the present embodiment, as the predetermined ratio information displayed on the role ratio monitor, the advantageous section ratio, the medium-time role combination ratio, the medium-time role ratio, the total role ratio, and the total role ratio are taken as an example. Although described, ratio information other than these may be displayed. For example, the ratio of the number of game media paid out by the ART function operating to the number of game media paid out within a predetermined total number of games (175,000 times) (total advantageous section acquisition ratio) , Ratio of the number of paid-out game media paid out by the ART function to the number of paid-out game media during a specific total number of games (6000 times) (intermediate time advantageous section acquisition ratio) , Ratio of the number of games in which the character continuous operating device has operated (medium-time continuous combination section ratio), occupying in the specific total number of games (6000 times), occupying in the specific total number of games (6000 times), The ratio of the number of games in which all the accessory operated (the middle-time role section ratio), the ratio of the number of games in which the accessory continuous operation device operated among the predetermined total number of games (175000 times) (total combined section) The ratio), the ratio of the number of games in which all the auctions occupy in the predetermined total number of games (175,000 times) (total amusement section ratio), and the like can also be displayed by performing a predetermined ratio calculation.
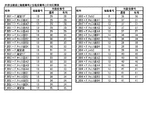
また、本実施形態では、役比モニタに表示される所定の比率情報の母数(分母)として、所定の総遊技数を「175000回」とし、特定の総遊技数を「6000回」として説明しているが、所定の総遊技数及び特定の総遊技数はこれに限られない。例えば、上述した各種比率のうち、一部又は全部を算出するための母数(分母)として、所定の総遊技数を「17500回」とし、特定の総遊技数を「3000回」としてもよい。もっとも、遊技店では様々な種類の遊技機が設置され運用されており、比率計算に最適な遊技数も異なる場合もあること等から、上述した各種比率を算出するための各遊技数は、上述したものに限られず適宜変更可能である。なお、この場合、各種比率のうち、一部又は全部を算出するための母数(分母)及び子数(分子)となりうる遊技数を、遊技店側で任意に設定可能とするようにしてもよい。 Further, in the present embodiment, as the parameter (denominator) of the predetermined ratio information displayed on the winning ratio monitor, the predetermined total number of games is set to “175,000” and the specific total number of games is set to “6000”. However, the predetermined total number of games and the specific total number of games are not limited to this. For example, as a parameter (denominator) for calculating a part or all of the above-mentioned various ratios, a predetermined total number of games may be set to “17500” and a specific total number of games may be set to “3000”. .. However, since various types of gaming machines are installed and operated in game stores, and the optimal number of games for ratio calculation may differ, the number of games for calculating the various ratios described above is It is not limited to the above and can be changed appropriately. In this case, the number of games that can be a parameter (denominator) and a child number (numerator) for calculating some or all of the various ratios can be arbitrarily set on the game store side. Good.
また、本実施形態では、中時間役物比率及び総役物比率において対象としている全ての役物の中に、ART機能の作動を含ませないようにしているが、ART機能の作動を役物の作動としてとらえ、中時間役物比率及び総役物比率の比率計算を行うようにすることもできる。また、上述したもの以外であっても、それが有益な情報である限り、2つの値を集計して比率計算を行い、その比率計算の結果を比率情報として表示可能であることはいうまでもない。また、役比モニタの説明において、「ART機能が作動」として説明している箇所については、「AT機能の作動」が含まれるようにしてもよいし、除かれるようにしてもよい。 In addition, in the present embodiment, the operation of the ART function is not included in all the targeted effects in the medium-time character ratio and the total character ratio, but the operation of the ART function is not included. It is also possible to calculate the ratio of the medium time character effect ratio and the total character effect ratio, as an operation of. Moreover, it goes without saying that other than the above, as long as it is useful information, it is possible to aggregate two values to perform ratio calculation and display the result of the ratio calculation as ratio information. Absent. Further, in the description of the ratio monitor, the portion described as “the ART function operates” may include the “operation of the AT function” or may be excluded.
<マイクロプロセッサ>
次に、図8を参照して、マイクロプロセッサ91の内部構成について説明する。図8は、マイクロプロセッサ91の内部構成を示すブロック図である。
<Microprocessor>
Next, the internal configuration of the
マイクロプロセッサ91は、メインCPU101(演算処理部)と、メインROM102(第1記憶部)と、メインRAM103(第2記憶部)と、外部バスインターフェース104と、クロック回路105と、リセットコントローラ106と、演算回路107と、乱数回路110と、パラレルポート111と、割込みコントローラ112と、タイマー回路113と、第1シリアル通信回路114と、第2シリアル通信回路115と、を有する。そして、マイクロプロセッサ91を構成するこれらの各部は信号バス116を介して互いに接続されている。
The
メインCPU101は、クロック回路105で生成されたクロックパルスに基づいて、各種制御プログラムを実行して、遊技動作全般に係る制御を行う。ここで、メインCPU101の制御動作の一例としてリール停止制御について説明する。
The
メインCPU101は、リールインデックスを検出してから各リール3L,3C,3L(メインリール)のステッピングモータに対してパルスを出力した回数をカウントする。これにより、メインCPU101は、各リールの回転角度(主に、リールが図柄何個分だけ回転したか)を管理する。なお、リールインデックスとは、リールが一回転したことを示す情報である。このリールインデックスは、例えば、発光部及び受光部を有する光センサと、各リールの所定の位置に設けられ、各メインリールの回転により発光部と受光部との間に介在される検知片とを備えたリール位置検出部(不図示)により検出される。
After detecting the reel index, the
ここで、各リール3L,3C,3L(メインリール)の回転角度の管理について、具体的に説明する。ステッピングモータに対して出力されたパルスの数は、メインRAM103に設けられたパルスカウンタによって計数される。そして、図柄1つ分の回転に必要な所定回数のパルスの出力がパルスカウンタで計数される毎に、メインRAM103に設けられた図柄カウンタが1ずつ加算される。図柄カウンタは、各リールに応じて設けられている。図柄カウンタの値は、リール位置検出部(不図示)によってリールインデックスが検出されるとクリアされる。
Here, the management of the rotation angle of each
すなわち、本実施形態では、図柄カウンタを管理することにより、リールインデックスが検出されてから図柄何個分の回転が行われたのかを管理する。したがって、各リールの各図柄の位置は、リールインデックスが検出される位置を基準として検出される。 That is, in the present embodiment, by managing the symbol counter, it is managed how many symbols are rotated after the reel index is detected. Therefore, the position of each symbol on each reel is detected based on the position where the reel index is detected.
メインROM102には、メインCPU101により実行される各種制御プログラム、各種データテーブル、副制御回路200に対して各種制御指令(コマンド)を送信するためのデータ等が記憶される。メインRAM103には、制御プログラムの実行により決定された内部当籤役等の各種データを格納する格納領域が設けられる。なお、メインROM102及びメインRAM103の内部構成(メモリマップ)については、後述の図11を参照して詳述する。
The
外部バスインターフェース104は、マイクロプロセッサ91の外部に設けられた各種構成部(例えば、各リール等)が接続された外部信号バス(不図示)と、マイクロプロセッサ91とを電気的に接続するためのインターフェース回路である。クロック回路105は、例えば分周器(不図示)等を含んで構成され、クロックパルス発生回路92から入力されたCPU作動用のクロックパルス信号を、その他の構成部(例えば、タイマー回路113)で使用される周波数のクロックパルス信号に変換する。なお、クロック回路105で生成されたクロックパルス信号は、リセットコントローラ106にも出力される。
The
リセットコントローラ106は、電源管理回路93から入力されたリセット信号に基づいて、IAT(Illegal Address Trap)やWDT(watchdog timer)のリセットを行う。演算回路107は、乗算回路及び除算回路を含んで構成される。例えば、プログラム上において、「MUL(乗算)」命令を実行するときには、演算回路107がこの「MUL」命令に基づく乗算処理を実行する。
The
乱数回路110は、予め定められた範囲の乱数(例えば、0〜65535又は0〜255)を発生させる。また、図示しないが、乱数回路110は、2バイトのハードラッチ乱数を得るための乱数レジスタ0と、2バイトのソフトラッチ乱数を得るための乱数レジスタ1と、1バイトのソフトラッチ乱数を得るための乱数レジスタ2〜7とで構成されている。なお、メインCPU101は、乱数回路110で発生させた所定範囲の乱数の中から1つの値を、例えば内部抽籤用の乱数値として抽出する。パラレルポート111は、マイクロプロセッサ91と、マイクロプロセッサ91の外部に設けられた各種回路(例えば、電源管理回路93等)との間で入出力される信号のポート(メモリーマップI/O)である。また、パラレルポート111は、乱数回路110及び割込みコントローラ112にも接続される。スタートスイッチ79はパラレルポート111のPI0〜PI4のいずれかの入力ポートにも接続され、スタートスイッチ79がオン状態になったタイミング(オンエッジ)で、パラレルポート111から乱数回路110の乱数レジスタ0へラッチ信号が出力される。そして、乱数回路110では、ラッチ信号が入力されることにより乱数レジスタ0がラッチされ、2バイトのハードラッチ乱数が取得される。
The
割込みコントローラ112は、パラレルポート111を介して電源管理回路93から入力される電断検知信号、又は、タイマー回路113から1.1172ms周期で入力されるタイムアウト信号に基づいて、メインCPU101による割込処理の実行タイミングを制御する。電源管理回路93から電断検知信号が入力された場合、又は、タイマー回路113からタイムアウト信号が入力された場合には、割込みコントローラ112は、割込処理開始指令を示す割込要求信号をメインCPU101に出力する。メインCPU101は、タイマー回路113からのタイムアウト信号に応じて割込みコントローラ112から入力される割込要求信号に基づいて、入力ポートチェック処理、リール制御処理、通信データ送信処理、7セグLED駆動処理、タイマー更新処理等の各種割込処理(後述の図79参照)を行う。
The interrupt
タイマー回路113(PTC)は、クロック回路105で生成されたクロックパルス信号(メインCPU作動用のクロックパルス信号を分周器(不図示)で分周された周波数のクロックパルス信号)で動作する(経過時間をカウントする)。そして、タイマー回路113は、1.1172msecの周期で割込みコントローラ112にタイムアウト信号(トリガー信号)を出力する。
The timer circuit 113 (PTC) operates with a clock pulse signal generated by the clock circuit 105 (a clock pulse signal having a frequency obtained by dividing the clock pulse signal for operating the main CPU by a frequency divider (not shown)) ( Count elapsed time). Then, the
第1シリアル通信回路114は、主制御基板71から副制御基板72にデータ(各種制御指令(コマンド))を送信する際のシリアル送信動作を制御する回路である。第2シリアル通信回路115は、主制御基板71から試験機用第2インターフェースボード302にデータを送信する際のシリアル送信動作を制御する回路である。
The first serial communication circuit 114 is a circuit that controls a serial transmission operation when transmitting data (various control commands (commands)) from the
<副制御回路>
次に、図9を参照して、副制御基板72に実装される副制御回路200(副制御手段)の構成について説明する。図9は、パチスロ1の副制御回路200の構成例を示すブロック図である。
<Sub control circuit>
Next, the configuration of the sub control circuit 200 (sub control means) mounted on the
副制御回路200は、主制御回路90と電気的に接続されており、主制御回路90から送信されるコマンドに基づいて演出内容の決定や実行等の処理を行う。副制御回路200は、演出動作を制御する演出制御部として機能し、基本的に、サブCPU201、サブRAM202、レンダリングプロセッサ203、描画用RAM204、ドライバ205を含んで構成される。
The
なお、サブCPU201は、ロムカートリッジ基板86に接続される。ドライバ205は、液晶中継基板87に接続される。すなわち、ドライバ205は、液晶中継基板87を介してプロジェクタ機構211及びサブ表示装置18に接続される。
The
サブCPU201は、主制御回路90から送信されたコマンドに応じて、ロムカートリッジ基板86に記憶されている制御プログラムに従い、映像、音、光の出力の制御を行う。ロムカートリッジ基板86は、基本的に、プログラム記憶領域とデータ記憶領域とによって構成される。
The
プログラム記憶領域には、サブCPU201が実行する制御プログラムが記憶される。例えば、制御プログラムには、主制御回路90との通信を制御するための主基板通信タスクや、演出用の乱数値を抽出し、演出内容(演出データ)の決定及び登録を行うための演出登録タスクを実行するための各種プログラムが含まれる。また、制御プログラムには、決定した演出内容に基づいて表示装置11による映像の表示を制御する描画制御タスク、LED群85等の光源による光の出力を制御するランプ制御タスク、スピーカ群84による音の出力を制御する音声制御タスク等を実行するための各種プログラムも含まれる。
The control program executed by the
データ記憶領域には、各種データテーブルを記憶する記憶領域、各演出内容を構成する演出データを記憶する記憶領域、映像の作成に関するアニメーションデータを記憶する記憶領域が含まれる。また、データ記憶領域には、BGMや効果音に関するサウンドデータを記憶する記憶領域、光の点消灯のパターンに関するランプデータを記憶する記憶領域等も含まれる。 The data storage area includes a storage area for storing various data tables, a storage area for storing effect data constituting each effect content, and a storage area for storing animation data related to image creation. The data storage area also includes a storage area for storing sound data regarding BGM and sound effects, a storage area for storing lamp data regarding a pattern of turning on/off light, and the like.
サブRAM202には、決定された演出内容や演出データを登録する格納領域や、主制御回路90から送信されるサブフラグ(内部当籤役)等の各種データを格納する格納領域が設けられる。
The
サブCPU201、レンダリングプロセッサ203、描画用RAM(フレームバッファを含む)204及びドライバ205は、演出内容により指定されたアニメーションデータに従って映像を作成し、作成した映像を表示装置11(プロジェクタ機構211)及び/又はサブ表示装置18に表示させる。なお、表示装置11(プロジェクタ機構211)及びサブ表示装置18は、副制御基板72により、それぞれ個別に制御される。
The
また、サブCPU201は、演出内容により指定されたサウンドデータに従ってBGMなどの音をスピーカ群84により出力させる。また、サブCPU201は、演出内容により指定されたランプデータに従ってLED群85の点灯及び消灯を制御する。
In addition, the
<メインCPUが有する各種レジスタ>
次に、図10を参照しながら、メインCPU101が有する各種レジスタについて説明する。なお、図10は、メインCPU101に含まれる各種レジスタの概略構成図である。
<Various registers of main CPU>
Next, various registers included in the
メインCPU101は、メイン・レジスタとして、アキュームレータA(以下、「Aレジスタ」という)、フラグ・レジスタF(フラグレジスタ)、汎用レジスタB(以下、「Bレジスタ」という)、汎用レジスタC(以下、「Cレジスタ」という)、汎用レジスタD(以下、「Dレジスタ」という)、汎用レジスタE(以下、「Eレジスタ」という)、汎用レジスタH(以下、「Hレジスタ」という)及び汎用レジスタL(以下、「Lレジスタ」という)を有する。また、メインCPU101は、サブ・レジスタとして、アキュームレータA′、フラグ・レジスタF′、汎用レジスタB′、汎用レジスタC′、汎用レジスタD′、汎用レジスタE′、汎用レジスタH′及び汎用レジスタL′を汎用レジスタとして有する。なお、各レジスタは、1バイトのレジスタで構成される。
The
また、本実施形態では、BレジスタとCレジスタとをペアレジスタ(以下、「BCレジスタ」という)として用い、DレジスタとEレジスタとをペアレジスタ(以下、「DEレジスタ」という)として用いる。さらに、本実施形態では、HレジスタとLレジスタとをペアレジスタ(以下、「HLレジスタ」という)として用いる。 Further, in this embodiment, the B register and the C register are used as a pair register (hereinafter referred to as “BC register”), and the D register and the E register are used as a pair register (hereinafter referred to as “DE register”). Further, in this embodiment, the H register and the L register are used as a pair register (hereinafter, referred to as “HL register”).
フラグ・レジスタF,F′の各ビットには、図10に示すように、演算処理の結果等を示す所定のフラグ情報がセットされる。例えばビット6(D6)には、演算結果の判定処理において演算結果が「0」であるか否かを示すデータ(ゼロフラグ)がセットされる。具体的には、演算結果が「0」である場合、ビット6にデータ「1」がセットされ、演算結果が「0」でない場合には、ビット6にデータ「0」がセットされる。そして、演算結果の判定処理では、メインCPU101は、ビット6のデータ「0」/「1」を参照して判定(YES/NO)を行う。
As shown in FIG. 10, predetermined flag information indicating the result of arithmetic processing is set in each bit of the flag registers F and F'. For example, in bit 6 (D6), data (zero flag) indicating whether or not the operation result is “0” in the operation result determination process is set. Specifically, when the operation result is "0", the data "1" is set in the
また、メインCPU101は、拡張レジスタQ(以下、「Qレジスタ」という)を有する。Qレジスタは、1バイトのレジスタで構成される。なお、本実施形態では、後述の各種処理フローの中で説明するように、プログラム上において、このQレジスタを用いてアドレス指定を行う各種メインCPU101専用命令コードが設けられており、この命令コードの使用により、処理の効率化やメインROM102の容量削減などを実現している。なお、Qレジスタを用いてアドレス指定を行う各種メインCPU101専用命令コードでは、Qレジスタには、アドレスの上位側のアドレスデータ(アドレス値)が格納される。なお、Qレジスタには、メインCPU101のリセット直後に、初期値として「F0H」がセットされる。また、Qレジスタを用いた「LDQ,n(8ビットデータ)」命令において、「n」に任意の1バイトのデータをセットして該命令を実行することにより、Qレジスタの値を変更することができる。
Further, the
さらに、メインCPU101は、1バイトのレジスタで構成された、インタラプト・ページアドレス・レジスタI及びメモリ・リフレッシュ・レジスタR、並びに、2バイトのレジスタで構成された、インデックス・レジスタIX、インデックス・レジスタIY、スタックポインタSP及びプログラムカウンタPCを専用レジスタとして有する。
Further, the
<メインROM及びメインRAMの内部構成(メモリマップ)>
次に、図11A〜図11Cを参照しながら、主制御回路90(マイクロプロセッサ91)に含まれるメインROM102及びメインRAM103の内部構成(以下「メモリマップ」という)について説明する。なお、図11Aは、メモリ全体のメモリマップを示す図であり、図11Bは、メインROM102のメモリマップを示す図であり、図11Cは、メインRAM103のメモリマップを示す図である。
<Internal configuration of main ROM and main RAM (memory map)>
Next, with reference to FIG. 11A to FIG. 11C, the internal configuration (hereinafter referred to as “memory map”) of the
主制御回路90(マイクロプロセッサ91)が備えるメモリ全体のメモリマップでは、図11Aに示すように、アドレスの先頭(0000H)側から、メインROM102のメモリ領域、メインRAM103のメモリ領域、内蔵レジスタエリア及びXCSデコードエリアが、不使用領域を間に挟んでこの順で、それぞれ所定のアドレスに配置される。
In the memory map of the entire memory included in the main control circuit 90 (microprocessor 91), as shown in FIG. 11A, the memory area of the
メインROM102のメモリマップでは、図11Bに示すように、メインROM102のアドレスの先頭(0000H)側から、プログラムエリア、データエリア、規定外エリア、商標記録エリア、プログラム管理エリア及びセキュリティ設定エリアが、この順で、それぞれ所定のアドレスに配置される。
In the memory map of the
なお、プログラムエリアには、遊技者により実施される遊技の遊技性に関連する各種制御処理において、メインCPU101により実行される各種処理の制御プログラムが記憶される。データエリアには、遊技者により実施される遊技の遊技性に関連する各種制御処理において、メインCPU101により使用される各種データ(例えば、内部抽籤テーブル等のデータテーブル、副制御回路200に対して各種制御指令(コマンド)を送信するためのデータ等)が記憶される。すなわち、プログラムエリアとデータエリアとからなる遊技用ROM領域(遊技用記憶領域)には、遊技店で遊技者が実際に行う遊技の遊技性に関連する制御処理(遊技性に関する処理)に必要な各種プログラム及び各種データが格納される。
The program area stores control programs for various processes executed by the
また、規定外エリアには、遊技者により実施される遊技の遊技性に直接関与しない各種処理(遊技性に影響を与えない処理)の制御プログラム及びデータが記憶される。例えば、パチスロ1の検定試験(試射試験)で使用されるプログラム及びデータ、電断時のチェックサム生成処理や電源復帰時のサムチェック処理などで使用される制御プログラム及びデータ、並びに、不正対策プログラム及びそれに必要なデータ等が、規定外エリアに格納される。
In the non-regulated area, control programs and data of various processes (processes that do not affect the game play) that are not directly related to the game play of the game performed by the player are stored. For example, programs and data used in the pachi-
また、プログラム管理エリア及びセキュリティ設定エリアには、制御プログラムの実行、あるいは、セキュリティ機能に関する各種の設定及び管理情報が記憶される。例えば、プログラムエリアに記憶された制御プログラムの開始アドレス及び終了アドレス(すなわち、データ範囲)の設定及び管理情報、読み出し可能なRAM領域のアドレス数の設定及び管理情報、WDTのリセット設定及び管理情報、割込み設定及び管理情報、プログラムエリアに記憶された制御プログラムの読み出しの許可/不許可の設定及び管理情報、乱数回路110の起動、更新方法等に関する設定及び管理情報、並びに、後述のセキュリティモードの設定及び管理情報等が、プログラム管理エリア及びセキュリティ設定エリアに格納される。なお、本実施形態では、プログラム管理エリアにセキュリティ機能に関連しないその他の設定及び管理情報が記憶され、セキュリティ設定エリアにセキュリティ機能に関連する設定及び管理情報が記憶されるものしているが、これに限られるものでなく、例えば、単一の管理エリアとしてこれらの設定及び管理情報が記憶されるようにしてもよい。
In the program management area and the security setting area, various settings and management information regarding execution of the control program or security functions are stored. For example, setting and management information of the start address and end address (that is, data range) of the control program stored in the program area, setting and management information of the number of addresses in the readable RAM area, reset setting and management information of WDT, Interrupt setting and management information, setting and management information of permission/non-permission of reading of the control program stored in the program area, setting and management information regarding activation and updating method of the
メインRAM103のメモリマップでは、図11Cに示すように、メインRAM103のアドレスの先頭(F000H)側から、遊技用RAM領域(所定格納領域、遊技用一時記憶領域)及び規定外RAM領域(規定外一時記憶領域)が、この順で、それぞれ所定のアドレスに配置される。
In the memory map of the
遊技用RAM領域には、遊技者により実施される遊技の遊技性に関連する制御プログラムの実行により決定された例えば内部当籤役等の各種データを一時的に格納する作業領域及びスタックエリアが設けられる。そして、各種データのそれぞれは、遊技用RAM領域内の所定アドレスの作業領域に格納される。 The game RAM area is provided with a work area and a stack area for temporarily storing various data such as an internal winning combination determined by the execution of a control program related to the playability of the game executed by the player. .. Then, each of the various data is stored in the work area at a predetermined address in the game RAM area.
また、規定外RAM領域には、遊技者により実施される遊技の遊技性に直接関与しない各種処理の作業領域となる規定外作業領域と、規定外スタックとが設けられる。本実施形態では、この規定外RAM領域を使用して、例えばサムチェック処理等の遊技者により実施される遊技の遊技性に直接関与しない各種処理が実行される。 In addition, the non-regular RAM area is provided with an non-regular work area and a non-regular stack, which are work areas of various processes not directly related to the game playability of the game performed by the player. In the present embodiment, using this non-regular RAM area, various processes such as a sum check process that are not directly related to the game playability of the game performed by the player are executed.
上述のように、本実施形態のパチスロ1では、メインROM102内において、遊技者により実施される遊技の遊技性に直接関与しない各種処理に使用される各種プログラム及び各種データ(テーブル)を、遊技用ROM領域とは異なるアドレスに配置された規定外ROM領域(規定外記憶領域)に格納する。また、そのような遊技者により実施される遊技の遊技性に直接関与しない各種処理は、メインRAM103内において、遊技用RAM領域とは異なるアドレスに配置された規定外RAM領域を使用して行われる。
As described above, in the pachi-
このようなメインROM102の構成では、従来の規則上においてプログラム等の配置不可とされていたROM領域(規定外ROM領域)に、遊技者が実際に行う遊技そのものには不要なプログラム及びデータを配置することができる。それゆえ、本実施形態では、遊技用ROM領域の容量の圧迫を回避することができる。
With such a configuration of the
<セキュリティモード>
次に、図12を参照しながら、主制御回路90(マイクロプロセッサ91)が有するセキュリティ機能の一部である、セキュリティモードについて説明する。なお、図12は、セキュリティモードを説明するための図である。
<Security mode>
Next, the security mode, which is a part of the security function of the main control circuit 90 (microprocessor 91), will be described with reference to FIG. Note that FIG. 12 is a diagram for explaining the security mode.
セキュリティモードは、例えば、パチスロ1の電源が投入され、電源管理回路93からリセット信号が入力されたときに、マイクロプロセッサ91が動作する動作状態である。このセキュリティモード中は、セキュリティ設定エリアに記憶された設定に応じた期間、メインCPU101の起動を遅延させる(すなわち、メインCPU101によって電源投入時の処理(後述の図46参照)の実行が開始されることを遅延させる)。このセキュリティモードを経てメインCPU101が起動することにより、マイクロプロセッサ91のセキュリティ性を担保し、また、電源投入時の起動制御に必要な時間を確保してメインCPU101を安定的に起動させる。
The security mode is an operating state in which the
なお、本実施形態では、例えば、リセットコントローラ106が、電源投入時に入力されたリセット信号を所定期間遅延させることによって、メインCPU101の起動を遅延させるようにするここともできるし、割込みコントローラ112が、電源投入時のリセット割込処理(後述の図46参照)の割込許可を所定期間遅延させることによって、メインCPU101の起動を遅延させるようにすることもできる。また、各コントローラが協働してメインCPU101の起動を遅延させるようにすることもできる。また、例えば、マイクロプロセッサ91内(あるいは、リセットコントローラ106若しくは割込みコントローラ112内)に、遅延回路を設け、この遅延回路によってメインCPU101の起動を遅延させるようにすることもできる。すなわち、マイクロプロセッサ91内でセキュリティ機能を実行する構成(セキュリティ部)は、その仕様に応じて適宜変形して適用することができる。
In the present embodiment, for example, the
図12に示すように、セキュリティモード中の遅延期間は、固定延長時間(固定期間)とランダム延長時間(可変期間)とが設定可能となっている。本実施形態では、例えば、各々異なる固定延長時間が対応付けられたモード1〜モード8のうち、いずれかのモードを選択して設定することで、複数の固定延長時間の中から一の固定延長時間が設定可能となっているとともに、各々異なるランダム延長時間の範囲が対応付けられたモード1〜モード4のうち、いずれかのモードを選択して設定することで、複数のランダム延長時間の範囲中から一のランダム延長時間の範囲が設定可能となっている。
As shown in FIG. 12, a fixed extension time (fixed period) and a random extension time (variable period) can be set as the delay period in the security mode. In the present embodiment, for example, by selecting and setting any one of the
例えば、固定延長時間として「モード4」、ランダム延長時間として「モード4」が選択され、セキュリティ設定エリアにこれらの設定が記憶されている場合、マイクロプロセッサ91は、パチスロ1の電源が投入され、電源管理回路93からリセット信号が入力されたときに、まず、固定延長時間として約4秒(4000ms)、メインCPU101の起動を遅延させ、次に、ランダム延長時間として0〜500msの範囲の中からランダムに一の延長時間が選択され、当該選択された時間、メインCPU101の起動を遅延させる。
For example, when “
なお、固定延長時間及びランダム延長時間の範囲は適宜設定可能であるが、本実施形態では、パチスロ1の電源投入時に設定変更が可能となるまでの時間を短縮する観点より、ランダム延長時間の範囲としてランダム延長時間が必ず「0」となる「モード1」が設定されることが望ましい。
The range of the fixed extension time and the random extension time can be set as appropriate, but in the present embodiment, the range of the random extension time is shortened from the viewpoint of shortening the time until the setting can be changed when the power of the pachi-
<遊技状態の遷移フロー>
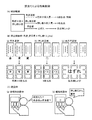
次に、図13及び図14を参照しながら、本実施形態のパチスロ1の主制御回路90(メインCPU101)により管理される各種遊技状態及びその遷移フローについて説明する。なお、図13は、パチスロ1の基本的な遊技状態の遷移フロー図であり、図14は、報知(AT・ART)機能の作動の有無を考慮した(すなわち、遊技の区間として、通常区間と有利区間とを区別した)遊技状態の遷移フロー図である。
<Game state transition flow>
Next, with reference to FIG. 13 and FIG. 14, various game states managed by the main control circuit 90 (main CPU 101) of the pachi-
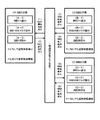
[基本的な遊技状態の遷移フロー]
本実施形態のパチスロ1では、ボーナスゲームの種類として、ビッグボーナス(以下、「BB」と記す)が設けられる。BBは、第一種特別役物と呼ばれるレギュラーボーナス(以下、「RB」と記す)に係る役物連続作動装置であり、RBを連続して作動させる。
[Basic game state transition flow]
In the pachi-
それゆえ、本実施形態では、主制御回路90は、ボーナス役の当籤/作動(入賞)の有無に基づいて遊技状態を管理する。具体的には、図13に示すように、主制御回路90は、ボーナス役(後述の名称「F_BB1」,「F_BB2」,「F_BB3」,「F_BB4」の内部当籤役)の当籤/作動(入賞)の有無に基づいて、「ボーナス非当籤状態」、「フラグ間状態」及び「ボーナス状態」と称する3種類の遊技状態を管理する。
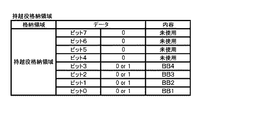
Therefore, in the present embodiment, the
なお、ボーナス非当籤状態は、ボーナスに非当籤であり、かつ、ボーナスが作動(入賞)していない状態であり、ボーナス状態は、ボーナスが作動している状態である。また、本実施形態では、ボーナス役が内部当籤役として決定されると、ボーナスが入賞するまで複数回の遊技に渡りボーナス役が内部当籤役として持ち越された状態が発生する。フラグ間状態は、ボーナス役が内部当籤役として持ち越されている状態、すなわち、ボーナス役が当籤し、かつ、ボーナスが作動していない状態である。 The bonus non-winning state is a state where the bonus is non-winning, the bonus is not activated (winning), and the bonus state is a state where the bonus is activated. Further, in the present embodiment, when the bonus combination is determined as the internal winning combination, a state occurs in which the bonus combination is carried over as the internal winning combination over a plurality of games until the bonus is won. The inter-flag state is a state in which the bonus combination is carried over as an internal winning combination, that is, the bonus combination is won and the bonus is not activated.
なお、ボーナス役の当籤の有無は、メインRAM103に設けられる後述の当り要求フラグ格納領域(後述の図25参照)及び持越役格納領域(後述の図26参照)に格納されるデータに基づいて管理される。また、ボーナスの作動(入賞)の有無は、メインRAM103に設けられる後述の遊技状態フラグ格納領域(後述の図27参照)に格納されるデータに基づいて管理される。
Whether or not the bonus combination is won is managed based on data stored in a hit request flag storage area (see FIG. 25 described later) and a carryover combination storage area (see FIG. 26 described later) provided in the
また、本実施形態では、図13に示すように、ボーナスが作動していない遊技状態(ボーナス非当籤状態及びフラグ間状態)において、リプレイに係る内部当籤役の種別及びその当籤確率が互いに異なる、RT0遊技状態〜RT5遊技状態の6種類の状態(以下、それぞれ「RT0状態」〜「RT5状態」という)が設けられる。なお、RT1状態及びRT4状態は、リプレイ役が内部当籤役として決定される確率が低確率となる遊技状態であり、RT5状態はリプレイ役が内部当籤役として決定される確率が中程度の中確率となる遊技状態である。また、RT0状態、RT2状態及びRT3状態は、リプレイ役が内部当籤役として決定される確率が高確率となる遊技状態である。なお、本実施形態では、ボーナス非当籤状態のRT状態は、RT0状態〜RT4状態のいずれかとなり、フラグ間状態のRT状態はRT5状態となる。 Further, in the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 13, in a gaming state in which a bonus is not operated (a bonus non-winning state and a state between flags), the type of the internal winning combination relating to the replay and its winning probability are different from each other. Six kinds of states of RT0 gaming state to RT5 gaming state (hereinafter, respectively referred to as "RT0 state" to "RT5 state") are provided. The RT1 state and the RT4 state are gaming states in which the probability that the replay combination is determined as the internal winning combination is low, and the RT5 state is the medium probability that the replay combination is determined as the internal winning combination. The game state is as follows. Further, the RT0 state, the RT2 state, and the RT3 state are gaming states in which the probability that the replay combination is determined as the internal winning combination is high. In the present embodiment, the RT state of the bonus non-winning state is any one of the RT0 state to the RT4 state, and the RT state of the inter-flag state is the RT5 state.
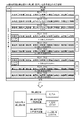
それゆえ、本実施形態では、主制御回路90は、ボーナスが作動していない遊技状態(ボーナス非当籤状態及びフラグ間状態)において、さらに、リプレイに係る内部当籤役の種別及びその当籤確率に基づいて、RT0状態〜RT5状態の6種類の状態も管理する。
Therefore, in the present embodiment, the
なお、RT0状態〜RT5状態は、メインRAM103に設けられる後述の遊技状態フラグ格納領域(後述の図27参照)に格納されるデータに基づいて管理される。具体的には、本実施形態のパチスロ1では、RT0状態フラグ〜RT5状態フラグの6つのRT状態を示すフラグが設けられ、これらのフラグのオン/オフ状態をメインRAM103により管理することによりRT状態が管理される。そして、主制御回路90は、オン状態であるRT状態フラグに対応するRT状態を現在のRT状態として特定する。なお、RT0状態フラグを設けないようにし、全てのRT状態フラグがオフ状態である場合には、主制御回路90は、現在のRT状態がRT0状態であると特定するようにしてもよい。
The RT0 state to the RT5 state are managed based on data stored in a game state flag storage area (see FIG. 27 described later) provided in the
図13に示すように、ボーナス非当籤状態(RT0〜RT4状態)においてボーナス役(後述の名称「F_BB1」,「F_BB2」,「F_BB3」,「F_BB4」の内部当籤役)が内部当籤役として決定されると(図13中、「ボーナス当籤」)、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をボーナス非当籤状態からフラグ間状態(RT5状態)に移行させる。また、フラグ間状態においてボーナス役が入賞すると(図13中、「ボーナス成立」)、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をフラグ間状態からボーナス状態に移行させる。
As shown in FIG. 13, in a bonus non-winning state (RT0 to RT4 state), a bonus combination (internal winning combination of names “F_BB1”, “F_BB2”, “F_BB3”, and “F_BB4” described later) is determined as an internal winning combination. When this is done (“bonus winning” in FIG. 13), the
ここで、ボーナス状態としては、BB1遊技状態(BB1状態)、BB2遊技状態(BB2状態)、BB3遊技状態(BB3状態)、及びBB4遊技状態(BB4状態)が設けられる。なお、主制御回路90は、RT状態と同様に、後述の遊技状態フラグ格納領域(後述の図27参照)に格納されるBB1状態フラグ、BB2状態フラグ、BB3状態フラグ、及びBB4状態フラグのオン/オフ状態によってボーナス状態を管理する。また、後述するように、BB1〜BB4状態中は常にRB遊技状態(RB状態)となることから、これも同様に、後述の遊技状態フラグ格納領域(後述の図27参照)に格納されるRB状態フラグのオン/オフ状態によって管理する。
Here, as the bonus state, a BB1 gaming state (BB1 state), a BB2 gaming state (BB2 state), a BB3 gaming state (BB3 state), and a BB4 gaming state (BB4 state) are provided. The
ボーナス非当籤状態において、後述の名称「F_BB1」が内部当籤役として決定され、フラグ間状態において、対応する図柄の組合せ「C_赤同色BB」が有効ライン上に表示されると、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をフラグ間状態からBB1状態に移行させる。BB1状態では、常にRB状態となり、BB1状態において規定枚数「240」枚を超えるメダルが払い出されると、BB1状態が終了し(図13中、「ボーナス終了」)、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をボーナス状態からRT4状態に移行させる。
In the bonus non-winning state, the name “F_BB1” described later is determined as the internal winning combination, and in the inter-flag state, when the corresponding symbol combination “C_red same color BB” is displayed on the activated line, the
また、ボーナス非当籤状態において、後述の名称「F_BB2」が内部当籤役として決定され、フラグ間状態において、対応する図柄の組合せ「C_青同色BB」が有効ライン上に表示されると、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をフラグ間状態からBB2状態に移行させる。BB2状態では、常にRB状態となり、BB2状態において規定枚数「240」枚を超えるメダルが払い出されると、BB2状態が終了し(図13中、「ボーナス終了」)、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をボーナス状態からRT4状態に移行させる。
Further, in the bonus non-winning state, the name “F_BB2” described later is determined as an internal winning combination, and in the inter-flag state, the corresponding symbol combination “C_blue same color BB” is displayed on the activated line. The
また、ボーナス非当籤状態において、後述の名称「F_BB3」が内部当籤役として決定され、フラグ間状態において、対応する図柄の組合せ「C_赤異色BB」が有効ライン上に表示されると、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をフラグ間状態からBB3状態に移行させる。BB3状態では、常にRB状態となり、BB3状態において規定枚数「165」枚を超えるメダルが払い出されると、BB3状態が終了し(図13中、「ボーナス終了」)、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をボーナス状態からRT4状態に移行させる。
Further, in the bonus non-winning state, the name “F_BB3” described later is determined as an internal winning combination, and in the inter-flag state, the corresponding symbol combination “C_red different color BB” is displayed on the activated line. The
また、ボーナス非当籤状態において、後述の名称「F_BB4」が内部当籤役として決定され、フラグ間状態において、対応する図柄の組合せ「C_青異色BB」が有効ライン上に表示されると、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をフラグ間状態からBB4状態に移行させる。BB4状態では、常にRB状態となり、BB4状態において規定枚数「165」枚を超えるメダルが払い出されると、BB4状態が終了し(図13中、「ボーナス終了」)、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をボーナス状態からRT4状態に移行させる。
Further, in the bonus non-winning state, the name “F_BB4” described later is determined as the internal winning combination, and in the inter-flag state, the corresponding symbol combination “C_blue different color BB” is displayed on the activated line. The
RT4状態において、後述の図柄の組合せ「R_RT1移行目」が有効ライン上に表示されると(図13中、「RT1移行目成立」)、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をRT4状態からRT1状態に移行させる。また、RT4状態において、後述の図柄の組合せ「S_RT3移行目」が有効ライン上に表示されると(図13中、「RT3移行目成立」)、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をRT4状態からRT3状態に移行させる。
In the RT4 state, when the later-described symbol combination “R_RT1 transition” is displayed on the activated line (“RT1 transition is established” in FIG. 13), the
RT1状態において、後述の図柄の組合せ「S_RT3移行目」が有効ライン上に表示されると(図13中、「RT3移行目成立」)、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をRT1状態からRT3状態に移行させる。また、RT1状態において、後述の図柄の組合せ「S_RT0移行リプ」が有効ライン上に表示されると(図13中、「RT0移行リプ成立」)、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をRT1状態からRT0状態に移行させる。
In the RT1 state, when the later-described symbol combination “S_RT3 transition eye” is displayed on the activated line (“RT3 transition eye is established” in FIG. 13), the
RT0状態において、後述の図柄の組合せ「S_RT3移行目」が有効ライン上に表示されると(図13中、「RT3移行目成立」)、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をRT0状態からRT3状態に移行させる。また、RT0状態において、後述の図柄の組合せ「R_RT1移行目」が有効ライン上に表示されるか、後述の図柄の組合せ「S_RT1移行リプ」が有効ライン上に表示されると(図13中、「RT1移行目 RT1移行リプ成立」)、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をRT0状態からRT1状態に移行させる。また、RT0状態において、後述の図柄の組合せ「S_RT2移行リプ」が有効ライン上に表示されると(図13中、「RT2移行リプ成立」)、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をRT0状態からRT2状態に移行させる。なお、設定値が変更された場合、あるいは後述の「RAM異常」などの初期化条件が成立した場合(図13中、「設定変更・初期化条件成立」)には、初期状態として、遊技状態がRT0状態となる。
In the RT0 state, when a later-described symbol combination "S_RT3 transition" is displayed on the activated line (in FIG. 13, "RT3 transition established"), the
RT2状態において、後述の図柄の組合せ「S_RT3移行目」が有効ライン上に表示されると(図13中、「RT3移行目成立」)、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をRT2状態からRT3状態に移行させる。また、RT2状態において、後述の図柄の組合せ「R_RT1移行目」が有効ライン上に表示されるか、後述の図柄の組合せ「S_RT1移行リプ」が有効ライン上に表示されると(図13中、「RT1移行目 RT1移行リプ成立」)、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をRT2状態からRT1状態に移行させる。
In the RT2 state, when the later-described symbol combination “S_RT3 transition eye” is displayed on the activated line (“RT3 transition eye establishment” in FIG. 13), the
RT3状態において、予め定められた期間(本実施形態では、「8」ゲーム。すなわち、8回の遊技の間)の遊技が行われると(図13中、「8ゲーム消化」)、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をRT3状態からRT0状態に移行させる。なお、RT3状態が継続する期間は適宜設定可能である。また、RT3状態が継続する期間を特に定めないものとしてもよい。この場合、RT3状態において、後述の図柄の組合せ「S_RT0移行リプ」が有効ライン上に表示され得る内部当籤役が所定の確率で決定されるようにすればよい。
In the RT3 state, when a game is played for a predetermined period (in the present embodiment, “8” game, that is, during 8 games) (“8 game digestion” in FIG. 13), the
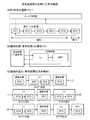
[報知(AT・ART)機能の作動の有無を考慮した遊技状態の遷移フロー]
本実施形態では、主制御回路90(メインCPU101)により、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作を報知する機能(AT・ART機能)の作動の有無が決定される。それゆえ、本実施形態では、上述したボーナス非当籤状態、フラグ間状態、及びボーナス状態のみならず、AT・ART機能の作動/非作動状態も遊技状態として管理する。なお、本実施形態では、AT機能が作動している遊技の区間を「通常有利区間」と称し、ART機能が作動している遊技の区間を「有利区間」と称し、AT機能及びART機能のいずれも作動していない遊技の区間を「非有利区間」あるいは「通常区間」と称する。
[Game state transition flow considering whether the notification (AT/ART) function is activated]
In the present embodiment, the main control circuit 90 (main CPU 101) determines whether or not the function (AT/ART function) for notifying a stop operation advantageous to the player is activated. Therefore, in the present embodiment, not only the above-mentioned bonus non-winning state, inter-flag state, and bonus state, but also the operating/non-operating state of the AT/ART function is managed as a game state. In the present embodiment, the game section in which the AT function is operating is referred to as a “normal advantage section”, and the game section in which the ART function is operating is referred to as an “advantage section”. A section of the game in which neither is operating is called a "non-advantageous section" or a "normal section".
また、本実施形態では、有利区間(「通常有利区間」及び「有利区間」を含む)においてボーナス状態となった場合、遊技者にとって一連の有利な遊技の区間であるとして、当該ボーナス状態は有利区間に含まれ、上述した状態表示器の点灯が継続する期間(有利区間中報知期間)となるとともに、有利区間が強制的に終了される(継続が規制される)ための遊技回数が計数される期間(規制監視期間)(本実施形態では、「1500」回の遊技)ともなる。もっとも、後述するように、「非有利区間」においてボーナス状態となった場合、当該ボーナス状態の終了後に「通常有利区間」や「有利区間」に移行する場合があり、この場合には、当該ボーナス状態は上述した期間に含まれるものとする。なお、非有利区間においてボーナス状態となった場合、当該ボーナス状態の終了後に「通常有利区間」や「有利区間」に移行しない場合(「非有利区間」が継続する場合)には、遊技者にとって一連の有利な遊技の区間でないとして、当該ボーナス状態は有利区間に含まれず、当該ボーナス状態は上述した期間に含まれないものとする。もっとも、ボーナス状態はそれ自体で遊技者にとって有利な遊技状態であることから、その前後で「通常有利区間」や「有利区間」となっているか否かにかかわらず、ボーナス状態は常に有利区間に含まれ、上述した期間に含まれるようにすることもできる。 Further, in the present embodiment, when the bonus state is set in the advantageous section (including the “normal advantageous section” and the “advantageous section”), the bonus state is advantageous as a series of advantageous game sections for the player. It is included in the section and becomes a period during which the above-mentioned status indicator lights up (information period during the advantageous period), and the number of games for forcibly ending the advantageous period (regulation of continuation) is counted. It also becomes a period (regulation monitoring period) (in this embodiment, "1500" games). However, as will be described later, when the bonus state is set in the "non-advantageous section", the bonus state may shift to the "normal advantageous section" or the "advantageous section". The state shall be included in the above-mentioned period. If the player enters the bonus state in the non-advantageous section and does not move to the “normal advantage section” or the “advantageous section” after the bonus state ends (when the “non-advantageous section” continues), It is assumed that the bonus state is not included in the advantageous section and the bonus state is not included in the period described above, as it is not a series of advantageous game sections. However, since the bonus state is a gaming state that is advantageous for the player by itself, the bonus state is always the advantageous zone regardless of whether it is the "normal advantageous zone" or the "advantageous zone" before and after that. It may be included and included in the period described above.
本実施形態のパチスロ1では、図14に示すように、主制御回路90は、非有利区間(通常区間)の遊技状態として「通常状態」、通常有利区間の遊技状態として「高確1状態」〜「高確4状態」及び「本前兆状態」、有利区間の遊技状態として「ラインバトル準備状態」、「ラインバトル状態」、「権利獲得抽籤準備状態」、「権利獲得抽籤状態」、「権利獲得状態」、「エンディング準備状態」、「エンディング1状態」及び「エンディング2状態」を管理する。
In the pachi-
(非有利区間(通常区間)の遊技状態)
非有利区間(通常区間)の遊技状態である通常状態は、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報が報知されない遊技状態(非AT・非ART)であり、遊技者にとって不利な遊技状態である。通常状態において、通常有利区間に移行することが決定されると(図14中、「通常有利区間移行当籤」)、主制御回路90は、その決定契機に応じて、遊技状態を通常有利区間のいずれかの遊技状態に移行させる。なお、通常状態における遊技の流れの詳細は、後述の図33を参照しながら後で説明する。
(Game state of non-advantageous section (normal section))
The normal state, which is the game state of the non-advantageous section (normal section), is a gaming state (non-AT/non-ART) in which the information of the stop operation advantageous to the player is not notified, and is a disadvantageous gaming state to the player. In the normal state, when it is determined to shift to the normal advantageous zone (in FIG. 14, "normal advantageous zone shift winning"), the
なお、本実施形態では、通常状態のボーナス非当籤状態において、ボーナス役以外の特定役(後述の図33参照)に当籤した場合、通常有利区間のいずれかの遊技状態(高確4状態以外)に移行することが決定され、各設定値間で同一の当籤確率が設定されているボーナス役を含む内部当籤役(「F_BB3+F_スイカ2」及び「F_BB4+F_スイカ2」以外)に当籤した場合、通常有利区間の高確4状態に移行することが決定され、また、当該ボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態の終了後、有利区間に移行することが決定されている場合には有利区間のラインバトル状態に移行することが決定され、有利区間に移行することが決定されていない場合には通常有利区間の高確4状態が所定期間(32ゲーム)継続するようになっている。
In the present embodiment, in the normal bonus non-winning state, when a specific winning combination other than the bonus winning combination (see FIG. 33 described later) is won, one of the normal advantageous sections is in the gaming state (other than the high-probability state 4). It is usually advantageous to win an internal winning combination (other than “F_BB3+
また、通常状態のボーナス非当籤状態において、各設定値間で異なる当籤確率が設定されているボーナス役を含む内部当籤役(「F_BB3+F_スイカ2」及び「F_BB4+F_スイカ2」)に当籤した場合、通常有利区間に移行することは決定されず、当該ボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態の終了後、非有利区間の通常状態が継続する。また、通常状態のフラグ間状態においては、いずれの役が内部当籤役として決定された場合にも、通常有利区間に移行することは決定されない。
Further, in the normal non-bonus winning state, when the internal winning combination (“F_BB3+
また、本実施形態では、非有利区間の通常状態から通常有利区間のいずれかの遊技状態に移行した場合、上述した有利区間中報知期間が開始される(すなわち、状態表示器の点灯が開始される)とともに、上述した規制監視期間が開始される(すなわち、一連の有利な遊技の区間が継続する上限となる「1500」回の遊技回数の計数が開始される)。 Further, in the present embodiment, when the game state shifts from the normal state of the non-advantageous section to one of the gaming states of the normal advantageous section, the above-mentioned advantageous section during notification period is started (that is, the lighting of the state indicator is started. Along with this, the regulation monitoring period described above is started (that is, counting of the number of games “1500” times, which is the upper limit for continuing a series of advantageous game sections, is started).
(通常有利区間の遊技状態)
通常有利区間の各遊技状態は、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報が報知され得る遊技状態(AT)であり、通常状態と比較して、遊技者にとって有利な遊技状態である。通常有利区間の各遊技状態において、有利区間に移行することが決定された場合(通常状態においてすでに有利区間に移行することが決定されている場合を含む)であって、通常有利区間が終了した場合(図14中、「通常有利区間終了 有利区間移行当籤」)、主制御回路90は、その決定契機に応じて、遊技状態を有利区間のいずれかの遊技状態に移行させる。また、通常有利区間の各遊技状態において、有利区間に移行することが決定されていない場合であって、通常有利区間が終了した場合(図14中、「通常有利区間終了 有利区間移行非当籤」)、主制御回路90は、遊技状態を非有利区間の通常状態に移行させる。なお、通常有利区間の各遊技状態における遊技の流れの詳細は、後述の図34を参照しながら後で説明する。
(Normally advantageous section game state)
Each gaming state in the normal advantageous section is a gaming state (AT) in which information of the stop operation advantageous to the player can be notified, and is a gaming state advantageous to the player as compared with the normal state. In each game state of the normal advantage section, when it is determined to shift to the advantage section (including the case where it is already determined to shift to the advantage section in the normal state), the normal advantage section has ended In this case (in FIG. 14, “normal advantageous section end/advantageous section transition winning”), the
通常有利区間の各遊技状態では、主制御回路90は、押し順小役(後述の「F_上段左ベル1」,「F_上段左ベル2」,「F_上段中ベル1」,「F_上段中ベル2」,「F_上段右左ベル1」,「F_上段右左ベル2」,「F_上段右中ベル1」,「F_上段右中ベル2」,「F_中段左ベル1」,「F_中段左ベル2」,「F_中段中ベル1」,「F_中段中ベル2」,「F_中段右左ベル1」,「F_中段右左ベル2」,「F_中段右中ベル1」,「F_中段右中ベル2」,「F_下段中ベル1」,「F_下段中ベル2」,「F_下段右左ベル1」,「F_下段右左ベル2」,「F_下段右中ベル1」,「F_下段右中ベル2」の内部当籤役)のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合に、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知するか否かの決定を行い、報知することが決定された場合、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報(すなわち、遊技者が最も多くメダルを得ることができる停止操作の情報)を報知する(後述の図45参照)。
In each gaming state of the normal advantageous section, the
また、通常有利区間の各遊技状態では、主制御回路90は、押し順リプレイ(後述の「F_RT0中リプレイ1」〜「F_RT0中リプレイ6」,「F_RT1中リプレイ1」〜「F_RT1中リプレイ6」,「F_RT2中リプレイ1」〜「F_RT2中リプレイ3」の内部当籤役)のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合に、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知するか否かの決定を行わず、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報(すなわち、遊技者にとって有利なRT状態に移行させ、あるいは当該有利なRT状態を維持することができる停止操作の情報)を報知しない(後述の図45参照)。この意味において、RT機能は作動せず(偶発的に押し順が正解したときを除く)、AT機能のみが作動する状態(AT遊技状態)となっている。
Further, in each gaming state of the normal advantageous section, the
ここで、本実施形態では、通常有利区間の各遊技状態において、RT3状態又はRT5状態であるとき(すなわち、後述のRT3移行目が表示されてから8ゲームの間、あるいはフラグ間状態であるとき)には、通常有利区間が終了するまで、押し順小役の押し順報知が行われるようになっている。一方、通常有利区間の各遊技状態において、RT3状態及びRT5状態以外のRT状態であるときには、1回に限り、押し順小役の押し順報知が行われるようになっている。したがって、同じ通常有利区間の遊技状態であっても、RT状態が異なれば、押し順小役の押し順報知が行われる回数も変動するため、それに基づく遊技者の利益も変動するようになっている。 Here, in the present embodiment, in each gaming state of the normal advantageous section, when in the RT3 state or the RT5 state (i.e., during the eight games or the inter-flag state after the RT3 transition to be described later is displayed). ), the push order notification of the push order small winning combination is performed until the normal advantageous section ends. On the other hand, in each gaming state of the normal advantageous section, when the RT state is other than the RT3 state and the RT5 state, the push order notification of the push order small winning combination is performed only once. Therefore, even in the game state of the same normal advantageous section, if the RT state is different, the number of times the push order notification of the push order small winning combination is performed also changes, so that the profit of the player based on it also changes. There is.
また、本実施形態では、通常有利区間の各遊技状態においてボーナス状態となったとき(より詳細には、通常有利区間中にボーナス役に当籤したとき)には、通常状態においてボーナス状態となったとき(より詳細には、非有利区間中にボーナス役に当籤したとき)と同様、当該ボーナス状態においては、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報(すなわち、遊技者が最も多くメダルを得ることができる停止操作の情報)を報知しない(後述の図45参照)。具体的には、ボーナス状態の押し順小役(後述の「F_JAC1_1」〜「F_JAC1_6」の内部当籤役)のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合に、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知するか否かの決定を行わない。 Further, in the present embodiment, when the gaming state in each of the normal advantageous sections is in the bonus state (more specifically, when the bonus combination is won during the normal advantageous section), the bonus state is in the normal state. As in the above (more specifically, when the bonus combination is won during the non-advantageous section), information on the stop operation advantageous to the player in the bonus state (that is, the player can obtain the most medals) The information of possible stop operation) is not notified (see FIG. 45 described later). Specifically, when any one of the push order small winning combinations in the bonus state (the internal winning combinations of “F_JAC1_1” to “F_JAC1_6” described later) is determined as the internal winning combination, the information on the stop operation advantageous to the player Is not determined.
なお、本実施形態では、通常有利区間の各遊技状態のボーナス非当籤状態において、ボーナス役以外の特定役(後述の図34参照)に当籤した場合、通常有利区間中の各遊技状態間でも遊技状態の移行が行われ、また、通常有利区間が継続する期間(ゲーム数)も変動するようになっている。また、ボーナス役に当籤した場合、すでに有利区間に移行することが決定されていなければ、有利区間に移行するか否かが決定され、有利区間に移行することが決定されている場合には有利区間のラインバトル状態に移行することが決定され、有利区間に移行することが決定されていない場合には通常有利区間の高確4状態が継続するようになっている。
In the present embodiment, in the bonus non-winning state of each game state of the normal advantage section, when a specific combination other than the bonus combination (see FIG. 34 described later) is won, the game is performed even between the game states of the normal advantage section. The state is changed, and the period (the number of games) during which the normal advantageous section continues is also changed. In addition, when the bonus combination is won, if it is not already decided to shift to the advantageous zone, it is decided whether or not to shift to the advantageous zone, and it is advantageous if it is decided to shift to the advantageous zone. When it is decided to shift to the line battle state of the section and it is not decided to shift to the advantageous section, the high-
ここで、通常有利区間の各遊技状態では、ボーナス役が、各設定値間で同一の当籤確率が設定されているボーナス役を含む内部当籤役(「F_BB3+F_スイカ2」及び「F_BB4+F_スイカ2」以外)に当籤したことに基づいて当籤した場合のみならず、各設定値間で異なる当籤確率が設定されているボーナス役を含む内部当籤役(「F_BB3+F_スイカ2」及び「F_BB4+F_スイカ2」)に当籤したことに基づいて当籤した場合であっても、有利区間に移行する否かが決定されるようになっている。すなわち、通常有利区間においては、通常有利区間中の共通処理として、当籤確率に設定差のあるボーナス役を含む内部当籤役が決定されたか否かにかかわらず、ボーナス役に当籤した場合には、有利区間に移行するか否かが決定されるようになっている。この意味においても、通常有利区間の各遊技状態は、非有利区間の遊技状態よりも有利な遊技状態となっている。
Here, in each game state of the normal advantageous section, the bonus winning combination is an internal winning combination (including “F_BB3+
また、本実施形態では、通常有利区間の各遊技状態は、上述した有利区間中報知期間中である(すなわち、状態表示器の点灯中である)とともに、上述した規制監視期間中でもある(すなわち、一連の有利な遊技の区間が継続する上限となる「1500」回の遊技回数の計数中である)状態となっている。もっとも、有利区間に移行することなく、通常有利区間が終了した場合には、上述した有利区間中報知期間が終了される(すなわち、状態表示器の点灯が終了され、消灯される)とともに、上述した規制監視期間が終了される(すなわち、一連の有利な遊技の区間が継続する上限となる「1500」回の遊技回数の計数が終了され、計数結果が初期化(クリア)される)。 In addition, in the present embodiment, each game state of the normal advantageous section is in the above-described advantageous section during the notification period (that is, the state indicator is lit) and also during the above-mentioned regulation monitoring period (that is, It is in the state of “1500” times of counting the number of games, which is the upper limit for continuing a series of advantageous games. However, when the normal advantageous period ends without shifting to the advantageous period, the above-described advantageous period notification period ends (that is, the state indicator is turned off and turned off), and The regulated monitoring period is ended (that is, the counting of the number of games “1500” times, which is the upper limit for continuing a series of advantageous games, is ended, and the counting result is initialized (cleared)).
(有利区間の遊技状態)
有利区間の各遊技状態は、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報が報知され得る遊技状態(ART)であり、通常状態及び通常有利区間の各遊技状態と比較して、遊技者にとって有利な遊技状態である。有利区間の各遊技状態では、主制御回路90は、基本的に、上述した押し順小役及び押し順リプレイのいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合に、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報(すなわち、遊技者が最も多くメダルを得ることができ、遊技者にとって有利なRT状態に移行させ、あるいは当該有利なRT状態を維持することができる停止操作の情報)を報知する(後述の図45参照)。この意味において、ART機能が作動する状態(ART遊技状態)となっている。なお、有利区間の各遊技状態において、有利区間が延長(継続)することなく終了した場合(後述の有利区間が強制的に終了される場合を含む)(図14中、「有利区間終了」)、主制御回路90は、遊技状態を非有利区間の通常状態に移行させる。
(Game state of advantageous section)
Each gaming state of the advantageous section is a gaming state (ART) in which information of a stop operation advantageous to the player can be notified, and a gaming advantageous to the player as compared with the normal state and each gaming state of the normal advantageous section. It is in a state. In each gaming state of the advantageous section, the
ここで、有利区間の各遊技状態では、上述した押し順小役及び押し順リプレイの押し順報知が行われる結果、基本的なRT状態としてはRT2状態が対応する(維持される)ようになっている。また、ボーナス状態終了後のRT4状態、後述のRT3移行目が表示されたことに基づくRT3状態、RT3状態終了後のRT0状態を除き、通常有利区間の各遊技状態から有利区間の各遊技状態に移行する場合には、ほとんどの場合、通常有利区間の各遊技状態におけるRT状態がRT1状態に対応するようになっている。したがって、有利区間の遊技状態であるラインバトル準備状態、権利獲得抽籤準備状態、及びエンディング準備状態は、それぞれ、ラインバトル状態、権利獲得抽籤状態、及びエンディング1状態若しくはエンディング2状態に移行することが決定されていて、かつ、RT状態がRT2状態でない場合に、RT状態をRT2状態まで上昇させるための準備状態として位置付けられる。 Here, in each gaming state of the advantageous section, as a result of the push order notification of the push order small combination and the push order replay described above, the RT2 state corresponds (is maintained) as the basic RT state. ing. Also, except for the RT4 state after the bonus state ends, the RT3 state based on the display of the RT3 transition described later, and the RT0 state after the RT3 state ends, from the normal advantageous zone each gaming state to the advantageous zone each gaming state. When transitioning, in most cases, the RT state in each gaming state of the normal advantage section corresponds to the RT1 state. Therefore, the line battle preparation state, the right acquisition lottery preparation state, and the ending preparation state, which are the game states of the advantageous section, can be shifted to the line battle state, the right acquisition lottery state, and the ending 1 state or the ending 2 state, respectively. If it is determined and the RT state is not the RT2 state, it is positioned as a preparation state for raising the RT state to the RT2 state.
主制御回路90は、基本的に、ラインバトル準備状態、権利獲得抽籤準備状態、及びエンディング準備状態において、RT状態がRT2状態に移行すると、遊技状態をそれぞれ、ラインバトル状態、権利獲得抽籤状態、及びエンディング1状態若しくはエンディング2状態に移行させる。なお、有利区間の各遊技状態における遊技の流れの詳細は、後述の図35〜図44を参照しながら後で説明する。
When the RT state shifts to the RT2 state in the line battle preparation state, the right acquisition lottery preparation state, and the ending preparation state, the
ここで、本実施形態では、有利区間の各遊技状態においてボーナス状態となったとき(より詳細には、有利区間中にボーナス役に当籤したとき)には、非有利区間及び通常有利区間とは異なり、当該ボーナス状態においては、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報(すなわち、遊技者が最も多くメダルを得ることができる停止操作の情報)を報知する(後述の図45参照)。具体的には、ボーナス状態の押し順小役(後述の「F_JAC1_1」〜「F_JAC1_6」の内部当籤役)のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合に、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報が必ず報知される。それゆえ、有利区間においてボーナス状態となったときには、非有利区間及び通常有利区間においてボーナス状態となったときよりも、遊技者に付与される利益が多くなる。この意味においても、有利区間の各遊技状態は、非有利区間及び通常有利区間の各遊技状態よりも有利な遊技状態となっている。 Here, in the present embodiment, when the bonus state is set in each gaming state of the advantageous section (more specifically, when the bonus combination is won during the advantageous section), the non-advantageous section and the normal advantageous section are defined. Differently, in the bonus state, information of the stop operation advantageous to the player (that is, information of the stop operation by which the player can obtain the most medals) is notified (see FIG. 45 described later). Specifically, when any one of the push order small winning combinations in the bonus state (the internal winning combinations of “F_JAC1_1” to “F_JAC1_6” described later) is determined as the internal winning combination, the information on the stop operation advantageous to the player Will be informed. Therefore, when the bonus state is set in the advantageous section, more profit is given to the player than when the bonus state is set in the non-advantageous section and the normal advantageous section. In this sense as well, each gaming state of the advantageous section is a gaming state more advantageous than each gaming state of the non-advantageous section and the normal advantageous section.
また、本実施形態では、有利区間の各遊技状態は、上述した有利区間中報知期間中である(すなわち、状態表示器の点灯中である)とともに、上述した規制監視期間中でもある(すなわち、一連の有利な遊技の区間が継続する上限となる「1500」回の遊技回数の計数中である)状態となっている。なお、有利区間中(ボーナス状態中を含む)の遊技回数が上限の「1500」回に達することなく、有利区間が終了した場合には、上述した有利区間中報知期間が終了される(すなわち、状態表示器の点灯が終了され、消灯される)とともに、上述した規制監視期間が終了される(すなわち、一連の有利な遊技の区間が継続する上限となる「1500」回の遊技回数の計数が終了され、計数結果が初期化(クリア)される)。また、有利区間中(ボーナス状態中を含む)の遊技回数が上限の「1500」回に達した場合には、有利区間が強制的に終了され(ボーナス状態中である場合には、ボーナス状態のみが継続する)、この場合にも、上述した有利区間中報知期間が終了される(すなわち、状態表示器の点灯が終了され、消灯される)とともに、上述した規制監視期間が終了される(すなわち、一連の有利な遊技の区間が継続する上限となる「1500」回の遊技回数の計数が終了され、計数結果が初期化(クリア)される)。 Further, in the present embodiment, each gaming state of the advantageous section is in the advantageous section notification period described above (that is, the state indicator is lit), and also in the regulation monitoring period described above (that is, a series). The state of "1500" is being counted, which is the upper limit at which the advantageous game section continues. In addition, when the advantageous period ends without reaching the upper limit of “1500” times of the number of games during the advantageous period (including the bonus state), the above-described advantageous period notification period ends (that is, The status indicator is turned off and then turned off, and the above-mentioned regulation monitoring period is ended (that is, the number of "1500" games is counted, which is the upper limit for continuing a series of advantageous games. The counting result is initialized (cleared) after the end. Further, when the number of games in the advantageous section (including the bonus state) reaches the upper limit of "1500", the advantageous section is forcibly ended (only in the bonus state when in the bonus state). Is continued), and in this case as well, the above-mentioned advantageous period notification period is ended (that is, the state indicator is turned off and turned off), and the above-mentioned regulation monitoring period is ended (that is, , The count of the number of games “1500” times, which is the upper limit for continuing a series of advantageous games, is finished, and the count result is initialized (cleared).
なお、本実施形態では、有利区間中(ボーナス状態中を含む)の遊技回数が上限の「1500」回に達したことに基づいて、有利区間が強制的に終了される場合、例えば、有利区間中の各遊技状態を継続させることが決定され(継続させるための権利が付与され)、あるいは、有利区間中の各遊技状態の残りの遊技回数が残存している場合であっても、それらは全て初期化(クリア)された上で、非有利区間の通常状態に移行するようになっている。また、有利区間のボーナス状態中であるときに、有利区間が強制的に終了された場合には、当該ボーナス状態における上述した押し順小役の押し順報知も直ちに終了されるようになっている。もっとも、この場合には、例外的に、当該ボーナス状態が終了するまで上述した押し順小役の押し順報知が行われるようにしてもよい。また、規制監視期間に対応する遊技回数も「1500」回に限られず、その値は適宜変更可能である。 In the present embodiment, when the advantageous section is forcibly ended based on the number of games in the advantageous section (including the bonus state) reaching the upper limit “1500” times, for example, the advantageous section Even if it is decided to continue each gaming state in (the right is given to continue), or if the remaining number of games in each gaming state in the advantageous section remains, After all are initialized (cleared), the normal state of the non-advantageous section is entered. Further, when the advantageous section is forcibly ended while in the bonus section of the advantageous section, the above-mentioned pushing order notification of the pushing order small winning combination in the bonus state is also immediately ended. .. However, in this case, exceptionally, the pushing order notification of the pushing order small winning combination may be performed until the bonus state ends. Further, the number of games played corresponding to the regulation monitoring period is not limited to "1500", and its value can be changed appropriately.
また、本実施形態では、基本的に、上述した通常有利区間及び有利区間に対応する各遊技状態が継続する期間、あるいは各遊技状態が延長される期間(継続する期間)を遊技回数(ゲーム数)により管理しているが、各遊技状態の期間を管理する手法はこれに限られない。例えば、上述した通常有利区間及び有利区間に対応する各遊技状態のうち、一又は複数の遊技状態の期間を、その期間中に払い出されたメダルの払出枚数や、そこからメダルの投入枚数を減じた差枚数(純増数)により管理してもよいし、メダルの払い出しに影響を与える報知(すなわち、上述した押し順小役が当籤した場合の報知)を行った回数(報知回数)により管理してもよい。 In addition, in the present embodiment, basically, the number of games (the number of games) is defined as a period during which each gaming state corresponding to the above-described normal advantageous section and the advantageous section continues or a period during which each gaming state is extended (continuous period). ), but the method of managing the period of each game state is not limited to this. For example, among the above-mentioned normal advantageous section and each gaming state corresponding to the advantageous section, the period of one or a plurality of gaming states, the payout number of medals paid out during that period, and the number of inserted medals from that period are set. It may be managed by the subtracted number of coins (net increase), or by the number of times (the number of times of notification) the notification that affects the payout of medals (that is, the notification when the above-mentioned small push winning combination wins) is performed. You may.
<メインROMに記憶されているデータテーブルの構成>
次に、図15〜図22を参照して、メインROM102に記憶されている各種データテーブルの構成について説明する。なお、図14で説明した遊技性に係る各遊技状態で行われる各種抽籤で用いられる各種データテーブルについては、別途、各遊技性の説明と一緒に後述する。
<Structure of data table stored in main ROM>
Next, the configuration of various data tables stored in the
[図柄配置テーブル]
まず、図15を参照して、図柄配置テーブルについて説明する。図柄配置テーブルは、左リール3L、中リール3C及び右リール3Rのそれぞれの回転方向における各図柄の位置と、各位置に配置された図柄の種類を特定するデータ(以下、図柄コード(図15中の図柄コード表を参照)という)との対応関係を規定する。
[Design placement table]
First, the symbol arrangement table will be described with reference to FIG. The symbol arrangement table, the position of each symbol in the respective rotation directions of the
図柄配置テーブルでは、リールインデックスが検出されたときに、リール表示窓4の枠内における各リールの中段領域に位置する図柄の位置を「0」と規定する。そして、各リールにおいて、図柄位置「0」を基準としてリールの回転方向(図15中の図柄位置「19」から図柄位置「0」に向かう方向)に進む順に、図柄カウンタの値に対応する「0」〜「19」が、図柄位置として、各図柄に割り当てられる。
In the symbol arrangement table, the position of the symbol located in the middle area of each reel in the frame of the
すなわち、図柄カウンタの値(「0」〜「19」)と、図柄配置テーブルとを参照することにより、リール表示窓4の枠内における各リールの上段領域、中段領域及び下段領域に表示されている図柄の種類を特定することができる。なお、本実施形態では、図柄として、「赤7」、「青7」、「BAR」、「チェリー1」、「チェリー2」、「ベル」、「スイカ」、「リプレイ」及び「ブランク」の9種類の図柄を用いる。
That is, by referring to the value (“0” to “19”) of the symbol counter and the symbol arrangement table, the reels are displayed in the upper area, middle area and lower area of each reel in the frame of the
また、本実施形態では、図柄コード表に示すように、図柄「赤7」(図柄コード1)には、データとして「00000001」が割り当てられ、図柄「青7」(図柄コード2)には、データとして「00000010」が割り当てられている。図柄「BAR」(図柄コード3)には、データとして「00000011」が割り当てられ、図柄「チェリー1」(図柄コード4)には、データとして「00000100」が割り当てられ、図柄「チェリー2」(図柄コード5)には、データとして「00000101」が割り当てられている。
Further, in the present embodiment, as shown in the symbol code table, "00000001" is assigned as data to the symbol "red 7" (symbol code 1), and the symbol "blue 7" (symbol code 2), “00000010” is assigned as data. The symbol "BAR" (symbol code 3) is assigned "00000011" as data, the symbol "
図柄「ベル」(図柄コード6)には、データとして「00000110」が割り当てられている。図柄「スイカ」(図柄コード7)には、データとして「00000111」が割り当てられ、図柄「リプレイ」(図柄コード8)には、データとして「00001000」が割り当てられ、図柄「ブランク」(図柄コード9)には、データとして「00001001」が割り当てられている。 The data "0000110" is assigned to the symbol "bell" (symbol code 6). The symbol "watermelon" (symbol code 7) is assigned "00000111" as data, the symbol "Replay" (symbol code 8) is assigned "00001000" as data, and the symbol "blank" (symbol code 9) ) Is assigned "00001001" as data.
[内部抽籤テーブル]
次に、図16〜図18を参照して、内部当籤役を決定する際に参照される内部抽籤テーブルについて説明する。なお、図16及び図17は、RT0状態〜RT5状態のそれぞれにおいて参照される内部抽籤テーブルである。また、図18は、ボーナス状態において参照される内部抽籤テーブルである。
[Internal lottery table]
Next, with reference to FIG. 16 to FIG. 18, an internal lottery table that is referred to when determining an internal winning combination will be described. 16 and 17 are internal lottery tables that are referred to in each of the RT0 state to the RT5 state. Further, FIG. 18 is an internal lottery table referred to in the bonus state.
内部抽籤テーブルは、遊技状態(図13参照)毎に設けられ、各種内部当籤役と、各内部当籤役が決定されるときの抽籤値との対応関係を規定する。なお、抽籤値は、予め設定されたボーナス役や小役等の内部当籤の期待値を調整するための設定値(設定1〜6)毎に規定される。この設定は、例えば、リセットスイッチ76及び設定用鍵型スイッチ54(図7参照)を用いて変更される。
The internal lottery table is provided for each gaming state (see FIG. 13), and defines the correspondence relationship between various internal winning combinations and the lottery value when each internal winning combination is determined. The lottery value is defined for each set value (
本実施形態の内部抽籤処理では、まず、乱数回路110の乱数レジスタ0により、予め定められた数値の範囲(例えば、0〜65535)から抽出される乱数値を、各内部当籤役に対応して規定された抽籤値で順次加算する。次いで、抽籤結果(抽籤値+乱数値)が65535を超えたか否か(抽籤結果がオーバーフローしたか否か)の判定を行う。そして、所定の内部当籤役において、抽籤結果が65535を超えた場合、該内部当籤役が当籤したと判定される。なお、本実施形態の内部抽籤処理では、抽出した乱数値に抽籤値を加算して抽籤を行う例を説明したが、本発明はこれに限定されず、乱数値から抽籤値を減算して、減算結果(抽籤結果)が「0」を下回ったか否か(抽籤結果がアンダーフローしたか否か)を判定して、内部抽籤の当籤/非当籤を決定してもよい。
In the internal lottery process of the present embodiment, first, a random number value extracted from a predetermined numerical value range (for example, 0 to 65535) by the
それゆえ、本実施形態の内部抽籤処理では、抽籤値として規定されている数値が大きい内部当籤役ほど、決定される確率が高い。なお、各内部当籤役の当籤確率は、「各当籤番号に規定された抽籤値/抽出される可能性のある全ての乱数値の個数(乱数分母:65536)」によって表すことができる。 Therefore, in the internal lottery process of the present embodiment, the larger the numerical value defined as the lottery value, the higher the probability of being determined. The winning probability of each internal winning combination can be represented by “lottery value defined for each winning number/the number of all random number values that may be extracted (random number denominator: 65536)”.
RT0状態〜RT5状態のそれぞれにおいて参照される内部抽籤テーブルでは、図16に示すように、基本的には、RT状態の種別に応じて、内部当籤役として決定されるリプレイ役の種別及び当籤確率が変化する。例えば、名称「F_RT0中リプレイ1(No.40)」〜「F_RT0中リプレイ6(No.45)」に係るリプレイ役は、RT0状態以外では内部当籤役として決定されることなく、RT0状態で内部当籤役として決定される。
In the internal lottery table referred to in each of the RT0 state to the RT5 state, as shown in FIG. 16, basically, the type and winning probability of the replay combination determined as the internal winning combination are determined according to the type of the RT state. Changes. For example, the replay combinations associated with the names “
図16及び図17において、「No.1」〜「No.38」が示す内部当籤役は、ボーナス役とリプレイ役又は小役とが重複して当籤する内部当籤役となっている。例えば、「F_BB1+F_確定リプ(No.1)」は、ボーナス役「F_BB1」と、リプレイ役「F_確定リプ」とが重複して当籤し、ボーナス役「F_BB1」に対応する図柄の組合せ「BB01」(後述の図19〜図22参照)と、リプレイ役「F_確定リプ」に対応する図柄の組合せ「REP01」〜「REP09」(後述の図19〜図22参照)の導出が許容される(入賞が許可される)内部当籤役となっている。 16 and 17, the internal winning combination indicated by "No. 1" to "No. 38" is an internal winning combination in which the bonus combination and the replay combination or the small combination overlap. For example, in “F_BB1+F_confirmation rep (No. 1)”, the bonus combination “F_BB1” and the replay combination “F_confirmation rep” are won, and the symbol combination “BB01” corresponding to the bonus combination “F_BB1” is won. (See FIGS. 19 to 22 described later) and the combination of symbols “REP01” to “REP09” (see FIGS. 19 to 22 described later) corresponding to the replay combination “F_confirmed rep” (see FIGS. 19 to 22 described later) are allowed to be derived (winning) Is allowed) has become an internal winning combination.
また、図16及び図17において、「No.39」〜「No.60」が示す内部当籤役は、リプレイ役が当籤する内部当籤役となっている。例えば、「F_維持リプ(No.40)」は、リプレイ役「F_維持リプ」が当籤し、リプレイ役「F_維持リプ」に対応する図柄の組合せ「REP02」(後述の図19〜図22参照)の導出が許容される(入賞が許可される)内部当籤役となっている。 16 and 17, the internal winning combinations indicated by "No. 39" to "No. 60" are the internal winning combinations that the replay winning combination wins. For example, “F_maintenance rep (No. 40)” is won by the replay combination “F_maintenance rep”, and the symbol combination “REP02” corresponding to the replay combination “F_maintenance rep” (see FIGS. 19 to 22 described later). ) Is allowed to derive (winning is allowed) is an internal winning combination.
また、図16及び図17において、「No.61」〜「No.98」が示す内部当籤役は、小役が当籤する内部当籤役となっている。例えば、「F_チャンス目A1(No.61)」は、小役「F_チャンス目A1」が当籤し、小役「F_チャンス目A1」に対応する図柄の組合せ「NML14」、「NML22」、「NML26」及び「NML30」(後述の図19〜図22参照)の導出が許容される(入賞が許可される)内部当籤役となっている。 16 and 17, the internal winning combinations indicated by "No. 61" to "No. 98" are the internal winning combinations that the small winning combination wins. For example, “F_chance eye A1 (No. 61)” is won by the small win “F_chance eye A1”, and the symbol combination “NML14”, “NML22”, and “NML22” corresponding to the small win “F_chance eye A1”. It is an internal winning combination that allows derivation of “NML26” and “NML30” (see FIGS. 19 to 22 described later) (winning is permitted).
なお、図示は省略しているが、「F_チャンス目A1(No.61)」〜「F_チャンス目B4(No.68)」が内部当籤役として決定された場合、後述の「NZR01」(後述の図19〜図22参照)の導出も許容される(停止表示が許可される)ようになる。ここで、「HZR01」は、入賞に係る図柄の組合せではなくはずれの図柄の組合せの一部であるが、遊技状態を他のRT状態からRT3状態に移行させる図柄の組合せ(RT3移行目)として規定された図柄の組合せであり、基本的に「No.61」〜「No.68」が示す内部当籤役のうちのいずれかが決定された場合以外には導出が許容されることがない。それゆえ、「NZR01」は、「No.61」〜「No.68」が示す内部当籤役に対応する図柄の組合せであるともいい得る。 Although illustration is omitted, when “F_chance eye A1 (No. 61)” to “F_chance eye B4 (No. 68)” are determined as the internal winning combination, “NZR01” described later (later described. 19 to 22) is permitted (stop display is permitted). Here, "HZR01" is not a combination of symbols related to winning, but a part of a combination of deviating symbols, but as a combination of symbols for shifting the gaming state from another RT state to the RT3 state (RT3 transition eye) It is a combination of defined symbols, and basically, derivation is not permitted except when any of the internal winning combinations indicated by "No. 61" to "No. 68" is determined. Therefore, "NZR01" can be said to be a combination of symbols corresponding to the internal winning combination indicated by "No. 61" to "No. 68".
また、同様に、「F_上段左ベル1(No.77)」〜「F_下段右中ベル2(No.98)」が内部当籤役として決定された場合、後述の「NZR02」(後述の図19〜図22参照)の導出も許容される(停止表示が許可される)ようになる。ここで、「HZR02」は、入賞に係る図柄の組合せではなくはずれの図柄の組合せの一部であるが、遊技状態を他のRT状態からRT1状態に移行させる図柄の組合せ(RT1移行目)として規定された図柄の組合せであり、基本的に「No.77」〜「No.98」が示す内部当籤役のうちのいずれかが決定された場合以外には導出が許容されることがない。それゆえ、「NZR02」は、「No.77」〜「No.98」が示す内部当籤役に対応する図柄の組合せであるともいい得る。 Similarly, when “F_upper left bell 1 (No. 77)” to “F_lower right middle bell 2 (No. 98)” are determined as the internal winning combination, “NZR02” (to be described later in FIG. 19 to FIG. 22) is also allowed to be derived (stop display is allowed). Here, "HZR02" is not a combination of symbols related to winning, but a part of a combination of deviating symbols, but as a combination of symbols for shifting the gaming state from another RT state to the RT1 state (RT1 transition eye) It is a combination of defined symbols, and basically, derivation is not permitted except when any of the internal winning combinations indicated by "No. 77" to "No. 98" is determined. Therefore, "NZR02" can be said to be a combination of symbols corresponding to the internal winning combination indicated by "No. 77" to "No. 98".
なお、本実施形態では、フラグ間状態(RT5状態)、すなわち、すでにボーナス役が内部当籤役として決定されている(持ち越されている)状態では、さらに、ボーナス役が決定されることはない。それゆえ、図16及び図17に示す内部抽籤テーブルにおいて、フラグ間状態(RT5状態)における「No.1」〜「No.38」が示す内部当籤役の抽籤値には「0」が設定されている。もっとも、フラグ間状態(RT5状態)とボーナス非当籤状態(RT0〜RT4状態)とで小役の当籤確率が変動しないように、「No.2」〜「No.10」、「No.12」〜「No.38」が示す内部当籤役において割り当てられていた小役に係る抽籤値は、その分がフラグ間状態(RT5状態)における「No.61」〜「No.68」、「No.72」及び「No.73」が示す内部当籤役の抽籤値に加算されるようになっている。すなわち、「No.61」〜「No.68」、「No.72」及び「No.73」が示す内部当籤役は、フラグ間状態(RT5状態)において当籤確率が高くなるのではなく、ボーナス状態以外の遊技状態間で同一の確率となるようになっている。 In this embodiment, the bonus combination is not further determined in the inter-flag state (RT5 state), that is, in the state where the bonus combination has already been determined as the internal winning combination (carried over). Therefore, in the internal lottery table shown in FIG. 16 and FIG. 17, “0” is set to the lottery value of the internal winning combination indicated by “No. 1” to “No. 38” in the inter-flag state (RT5 state). ing. However, "No. 2" to "No. 10" and "No. 12" are set so that the winning probability of the small winning combination does not change between the inter-flag state (RT5 state) and the bonus non-winning state (RT0 to RT4 state). The lottery values related to the small wins assigned in the internal winning combination indicated by "No. 38" to "No. 38" are "No. 61" to "No. 68" and "No. 68" in the inter-flag state (RT5 state). 72” and “No. 73” are added to the lottery value of the internal winning combination. That is, the internal winning combinations indicated by “No. 61” to “No. 68”, “No. 72” and “No. 73” do not have a high winning probability in the inter-flag state (RT5 state), but the bonus. It has become the same probability among the game states other than the state.
また、図16及び図17において、「No.0」は、規定されたいずれの図柄の組合せ(後述の図19〜図22参照)の導出も許容されない「はずれ」を示すものであり、この「はずれ」の割り当て(抽籤値)が高いほど、遊技者にとっては不利となる。なお、RT0状態及びRT2状態では、「はずれ」が決定される場合はない。また、RT5状態では、「はずれ」が決定される確率が「22289/65536」として表記しているが、実際には、いずれかのボーナス役がすでに内部当籤役として決定されている(持ち越されている)状態であることから、その意味において「はずれ」が決定される場合はない。 Further, in FIGS. 16 and 17, “No. 0” indicates “off” in which derivation of any defined combination of symbols (see FIGS. 19 to 22 described later) is not allowed. The higher the allocation (lottery value) of “out”, the more disadvantageous to the player. It should be noted that in the RT0 state and the RT2 state, there is no case where “out” is determined. Further, in the RT5 state, the probability that the “out” is determined is described as “22289/65536”, but in reality, one of the bonus combinations has already been determined as the internal winning combination (carried over). Since it is in a state of being), “out” is not determined in that sense.
なお、図16及び図17では、設定値が「1」(設定1)の場合の内部抽籤テーブルを例に挙げて説明しているが、「No.21」、「No.30」、「No.39」及び「No.74」に示す内部当籤役以外の内部当籤役については、各設定値間で共通の抽籤値が設定されている。すなわち、同一の当籤確率となっている。一方、「No.21」、「No.30」、「No.39」及び「No.74」に示す内部当籤役については、各設定値間(あるいは、所定の設定値と特定の設定値との間)で異なる抽籤値が設定されている。すなわち、異なる当籤確率となっている(図16及び図17中、(※1)、(※2)及び(※3)参照)。 16 and 17, the internal lottery table when the setting value is "1" (setting 1) is described as an example, but "No. 21", "No. 30", "No" .39” and “No. 74”, internal lottery combinations other than the internal winning combinations shown in FIG. That is, they have the same winning probability. On the other hand, regarding the internal winning combinations shown in “No. 21,” “No. 30,” “No. 39,” and “No. 74,” between each set value (or between a predetermined set value and a specific set value). Different lottery values have been set. That is, the winning probabilities are different (see (*1), (*2) and (*3) in FIGS. 16 and 17).
具体的には、例えば、「No.21」及び「No.30」に示す内部当籤役は、設定値が「1」の場合、各々「22」という抽籤値が設定されているのに対し、設定値が「6」の場合、各々「77」という抽籤値が設定される(すなわち、設定値が高くなるのにしたがって、「No.21」及び「No.30」に示す内部当籤役では抽籤値が「11」ずつ増加している)。なお、図示は省略しているが、フラグ間状態(RT5状態)では、「No.21」、及び「No.30」に示す内部当籤役に設定される抽籤値が増加するのにしたがって、「No.72」に示す内部当籤役に設定される抽籤値も増加する。 Specifically, for example, in the case of the internal winning combinations shown in “No. 21” and “No. 30”, when the set value is “1”, the lottery value of “22” is set, respectively. When the set value is "6", a lottery value of "77" is set respectively (that is, as the set value becomes higher, the lottery results in the internal winning combinations shown in "No. 21" and "No. 30"). The value is increasing by "11"). Although illustration is omitted, in the flag-to-flag state (RT5 state), as the lottery value set for the internal winning combination shown in “No. 21” and “No. 30” increases, “ The lottery value set for the internal winning combination shown in No. 72” also increases.
また、例えば、「No.74」に示す内部当籤役は、設定値が「1」、「3」及び「5」の場合よりも、設定値が「2」、「4」及び「6」の場合のほうが相対的に抽籤値が高くなるように設定されるとともに、設定値が高くなるのにしたがって抽籤値が増加するように設定される。 Further, for example, the internal winning combination shown in “No. 74” has setting values of “2”, “4” and “6” more than the setting values of “1”, “3” and “5”. In this case, the lottery value is set to be relatively high, and the lottery value is set to increase as the set value increases.
また、例えば、「No.39」に示す内部当籤役は、設定値が「1」、「3」及び「5」の場合よりも、設定値が「2」、「4」及び「6」の場合のほうが相対的に抽籤値が低くなるように設定されるとともに、設定値が高くなるのにしたがって抽籤値が減少するように設定される。これは、「No.21」、「No.30」及び「No.74」に示す内部当籤役の抽籤値の増加分を調整するためである。したがって、例えば、RT0状態及びRT2状態において、「はずれ」が決定される確率が変動することはなく「0」が維持される。なお、これらは、設定値間で、特定の内部当籤役の当籤確率を異ならせる一例である。 In addition, for example, the internal winning combination shown in “No. 39” has setting values “2”, “4” and “6” rather than setting values “1”, “3” and “5”. In this case, the lottery value is set to be relatively low, and the lottery value is set to decrease as the set value increases. This is for adjusting the increment of the lottery value of the internal winning combination shown in “No. 21”, “No. 30” and “No. 74”. Therefore, for example, in the RT0 state and the RT2 state, “0” is maintained without changing the probability that “off” is determined. Note that these are examples of different winning probabilities of a specific internal winning combination between the set values.
図18において、「No.1」〜「No.7」が示す内部当籤役は、小役が当籤する内部当籤役となっており、当籤した場合には、図18に示した対応する図柄の組合せの導出が許容される(入賞が許可される)ようになる。なお、本実施形態では、RB状態(すなわち、BB1〜BB4状態)において、リプレイ役が内部当籤役として決定されないように構成されているが、図16及び図17に示したリプレイ役のうち、一又は複数のリプレイ役が内部当籤役として決定されるようにしてもよい。 In FIG. 18, the internal winning combination indicated by “No. 1” to “No. 7” is an internal winning combination in which the small winning combination is won, and in the case of winning, the corresponding symbols shown in FIG. Derivation of combinations is allowed (winning is allowed). In the present embodiment, in the RB state (that is, the BB1 to BB4 states), the replay combination is not determined as the internal winning combination, but one of the replay combinations shown in FIG. 16 and FIG. Alternatively, a plurality of replay combinations may be determined as internal winning combinations.
[図柄組合せテーブル]
次に、図19〜図22を参照して、本実施形態における入賞等に係る図柄の組合せを規定する図柄組合せテーブルについて説明する。なお、本実施形態では、複数の図柄の組合せを予め規定するデータとして、図柄組合せテーブルを設けることを例に挙げて説明しているが、主制御回路90側で表示される図柄の組合せが識別可能な態様であれば、他の手法によってデータを規定することもできる。例えば、図柄コードの組合せを定め、これにより表示される図柄の組合せを識別可能としてもよい。
[Design combination table]
Next, with reference to FIG. 19 to FIG. 22, a symbol combination table that defines symbol combinations relating to winning and the like in the present embodiment will be described. In addition, in the present embodiment, as an example of providing a symbol combination table as the data that predefines a combination of a plurality of symbols, the symbol combination displayed on the
図柄組合せテーブルは、図19〜図22に示すように、複数の図柄の組合せを予め規定しており、これらの図柄の組合せの種別を示すデータを、表示役(入賞作動フラグ)として規定している。また、図柄組合せテーブルは、当り要求フラグ格納領域、入賞作動フラグ格納領域(後述の図25参照)、及び図柄コード格納領域(後述の図30参照)と対応するように、9バイトのデータで構成されるとともに、各格納領域の各ビットに異なる表示役(入賞作動フラグ)を示すデータを規定している。 As shown in FIGS. 19 to 22, the symbol combination table predefines a combination of a plurality of symbols, and defines data indicating the type of the symbol combination as a display combination (winning operation flag). There is. Further, the symbol combination table is composed of 9-byte data so as to correspond to the hit request flag storage area, the winning operation flag storage area (see FIG. 25 described later), and the symbol code storage area (see FIG. 30 described later). In addition, data indicating different display combinations (winning action flags) is defined in each bit of each storage area.
なお、図19〜図22においては、規定される図柄の組合せ内で「/」が付された箇所があるが、これは、表記された図柄のうちいずれの図柄でもその図柄の組合せを構成することを示す。例えば、「HZR01」の組合せは、左リールの図柄が「チェリー1」、中リールの図柄が「チェリー1」、右リールの図柄が「チェリー1」である図柄の組合せ(すなわち、「チェリー1−チェリー1−チェリー1」)と、左リールの図柄が「チェリー2」、中リールの図柄が「チェリー1」、右リールの図柄が「チェリー1」である図柄の組合せ(すなわち、「チェリー2−チェリー1−チェリー1」)と、が対応する図柄の組合せであることを示している。
It should be noted that in FIGS. 19 to 22, there is a portion marked with "/" in the prescribed symbol combination, but this constitutes the symbol combination in any of the symbols shown. Indicates that. For example, the combination of “HZR01” is a combination of symbols in which the symbol of the left reel is “
表示役(入賞作動フラグ)「HZR01」は、はずれの図柄組合せであるが、当該図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に表示された場合に、RT状態を他のRT状態からRT3状態に移行させる図柄の組合せ(「RT3移行目」)として規定された図柄の組合せである。 The display combination (winning operation flag) "HZR01" is an outlying symbol combination, but when the symbol combination is displayed on the activated line, the RT state is shifted from another RT state to the RT3 state. It is a combination of symbols defined as a combination (“RT3 transition”).
表示役(入賞作動フラグ)「HZR02」は、はずれの図柄組合せであるが、当該図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に表示された場合に、RT状態を他のRT状態からRT1状態に移行させる図柄の組合せ(「RT1移行目」)として規定された図柄の組合せである。 The display combination (winning operation flag) "HZR02" is an outlying symbol combination, but when the symbol combination is displayed on the activated line, the RT state is shifted from another RT state to the RT1 state. It is a combination of symbols defined as a combination (“RT1 transition”).
表示役(入賞作動フラグ)「BB01」、「BB02」、「BB03」及び「BB04」は、ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せであり、各々の図柄の組合せが表示有効ライン上に表示された場合に、対応するボーナス状態を作動させる。 Display combinations (winning operation flags) "BB01", "BB02", "BB03" and "BB04" are combinations of symbols related to the bonus combination, and when each combination of symbols is displayed on the display effective line. , Activate the corresponding bonus state.
表示役(入賞作動フラグ)「REP01」〜「REP06」は、リプレイ役に係る図柄の組合せであり、これらのうちのいずれかの図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に表示された場合に、再遊技を作動させる。なお、「REP01」の図柄の組合せは、「平行リプ」あるいは「直線リプ」と称することができ、「REP02」の図柄の組合せは、「通常リプ」と称することができ、「REP03」の図柄の組合せは、「被弾リプ」と称することができ、「REP04」の図柄の組合せは、「特殊リプ」と称することができ、「REP05」の図柄の組合せは、「フェイクリプ」と称することができ、「REP06」の図柄の組合せは、「BAR揃いリプ」と称することができる。 The display combination (winning operation flag) "REP01" to "REP06" is a combination of symbols related to the replay combination, and when any one of these symbols is displayed on the activated line, the replay is performed. Activate. The combination of symbols "REP01" can be referred to as "parallel lip" or "straight line lip", and the combination of symbols "REP02" can be referred to as "normal lip" and symbol "REP03". The combination of symbols can be referred to as "bullied lip", the symbol combination of "REP04" can be referred to as "special lip", and the symbol combination of "REP05" can be referred to as "fake lip". , The combination of symbols of "REP06" can be referred to as "BAR matching lip".
表示役(入賞作動フラグ)「REP07」は、リプレイ役に係る図柄の組合せであり、当該図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に表示された場合に、再遊技を作動させるとともに、RT状態を他のRT状態(例えば、RT1状態)からRT0状態に移行させる図柄の組合せ(「RT0移行リプ」)として規定された図柄の組合せである。 The display combination (winning operation flag) "REP07" is a combination of symbols related to the replay combination, and when the combination of the symbols is displayed on the activated line, the re-game is activated and the RT state is set to another RT. It is a combination of symbols defined as a symbol combination (“RT0 transition rip”) to be shifted from the state (for example, RT1 state) to the RT0 state.
表示役(入賞作動フラグ)「REP08」は、リプレイ役に係る図柄の組合せであり、当該図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に表示された場合に、再遊技を作動させるとともに、RT状態を他のRT状態(例えば、RT0状態及びRT2状態)からRT1状態に移行させる図柄の組合せ(「RT1移行リプ」)として規定された図柄の組合せである。 The display combination (winning operation flag) "REP08" is a combination of symbols related to the replay combination, and when the combination of the symbols is displayed on the activated line, the replay is activated and the RT state is set to another RT. The state (for example, RT0 state and RT2 state) is a symbol combination defined as a symbol combination (“RT1 transition lip”) to be shifted from the RT1 state.
表示役(入賞作動フラグ)「REP09」は、リプレイ役に係る図柄の組合せであり、当該図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に表示された場合に、再遊技を作動させるとともに、RT状態を他のRT状態(例えば、RT0状態)からRT2状態に移行させる図柄の組合せ(「RT2移行リプ」)として規定された図柄の組合せである。 The display combination (winning operation flag) "REP09" is a combination of symbols related to the replay combination, and when the combination of the symbols is displayed on the activated line, the re-game is activated and the RT state is set to another RT. It is a combination of symbols defined as a combination of symbols (“RT2 transition lip”) to be shifted from the state (for example, RT0 state) to the RT2 state.
表示役(入賞作動フラグ)「NML01」は、小役に係る図柄の組合せであり、当該図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に表示された場合に、8枚のメダルが払い出される。なお、「NML01」の図柄の組合せは、「ベル」の図柄の組合せと称することができる。 The display combination (winning action flag) "NML01" is a combination of symbols related to the small combination, and when the combination of the symbols is displayed on the activated line, eight medals are paid out. The combination of symbols "NML01" can be referred to as the combination of symbols "bell".
表示役(入賞作動フラグ)「NML02」〜「NML13」は、小役に係る図柄の組合せであり、これらのうちのいずれかの図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に表示された場合に、1枚のメダルが払い出される。なお、「NML02」〜「NML13」の図柄の組合せは、「打順役」の図柄の組合せと総称することができる。 The display combination (winning operation flag) "NML02" to "NML13" is a combination of symbols related to the small combination, and when one of these symbols is displayed on the activated line, one of the symbols is displayed. Medals will be paid out. The symbol combinations of "NML02" to "NML13" can be collectively referred to as the symbol combinations of "batting order combination".
表示役(入賞作動フラグ)「NML14」〜「NML30」は、小役に係る図柄の組合せであり、これらのうちのいずれかの図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に表示された場合に、1枚のメダルが払い出される。なお、「NML14」〜「NML30」の図柄の組合せは、「チャンス役」の図柄の組合せと総称することができる。 The display combination (winning operation flag) "NML14" to "NML30" is a combination of symbols related to the small combination, and when one of these symbols is displayed on the activated line, one of the symbols is displayed. Medals will be paid out. The symbol combinations of "NML14" to "NML30" can be collectively referred to as the symbol combinations of "chance combination".
表示役(入賞作動フラグ)「NML31」〜「NML33」は、小役に係る図柄の組合せであり、これらのうちのいずれかの図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に表示された場合に、5枚のメダルが払い出される。なお、「NML31」〜「NML33」の図柄の組合せは、「特殊役」の図柄の組合せと総称することができる。 The display combination (winning operation flag) "NML31" to "NML33" is a combination of symbols related to the small combination, and when any one of these symbols is displayed on the activated line, five symbols are displayed. Medals will be paid out. The combination of symbols "NML31" to "NML33" can be collectively referred to as the combination of symbols "special combination".
表示役(入賞作動フラグ)「NML34」は、小役に係る図柄の組合せであり、当該図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に表示された場合に、8枚のメダルが払い出される。なお、「NML34」の図柄の組合せは、「クロスダウンベル」の図柄の組合せと称することができる。 The display combination (winning operation flag) "NML34" is a combination of symbols related to the small combination, and when the combination of the symbols is displayed on the activated line, eight medals are paid out. The symbol combination of "NML34" can be referred to as a symbol combination of "cross down bell".
表示役(入賞作動フラグ)「NML35」は、小役に係る図柄の組合せであり、当該図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に表示された場合に、5枚のメダルが払い出される。なお、「NML35」の図柄の組合せは、「スイカ」の図柄の組合せと称することができる。 The display combination (winning operation flag) "NML35" is a combination of symbols related to the small combination, and when the combination of the symbols is displayed on the activated line, five medals are paid out. The symbol combination of “NML35” can be referred to as the symbol combination of “watermelon”.
表示役(入賞作動フラグ)「NML36」及び「NML37」は、小役に係る図柄の組合せであり、これらのうちのいずれかの図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に表示された場合に、8枚のメダルが払い出される。なお、「NML36」及び「NML37」の図柄の組合せは、「JACA」の図柄の組合せと総称することができる。 The display combination (winning operation flag) "NML36" and "NML37" is a combination of symbols related to the small combination, and when any one of these symbols is displayed on the activated line, eight pieces are displayed. Medals will be paid out. The combination of symbols "NML36" and "NML37" can be collectively referred to as the symbol combination "JACA".
表示役(入賞作動フラグ)「NML38」〜「NML40」は、小役に係る図柄の組合せであり、これらのうちのいずれかの図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に表示された場合に、2枚のメダルが払い出される。なお、「NML38」〜「NML40」の図柄の組合せは、「JACB」の図柄の組合せと総称することができる。 The display combination (winning operation flag) "NML38" to "NML40" is a combination of symbols relating to a small combination, and when any one of these symbols is displayed on the activated line, two symbols are displayed. Medals will be paid out. The symbol combinations of “NML38” to “NML40” can be collectively referred to as the symbol combinations of “JACB”.
なお、本実施形態では、一の表示役(入賞作動フラグ)を示すデータとして、複数の図柄の組合せ(コンビネーション)が割り当てられるものが含まれる例について説明しているが、一の表示役(入賞作動フラグ)を示すデータには、一の図柄の組合せ(コンビネーション)のみが割り当てられるようにデータを構成することもできる。 In the present embodiment, an example in which data indicating one display combination (winning operation flag) to which a combination (combination) of a plurality of symbols is assigned is described, but one display combination (winning prize) The data indicating the operation flag) may be configured such that only one symbol combination (combination) is assigned.
[内部当籤役と停止操作順序(打順)と表示役等との対応関係]
次に、図23及び図24を参照して、内部当籤役と停止操作順序(打順)と表示役等との対応について説明する。
[Correspondence between internal winning combination, stop operation sequence (batting order), display combination, etc.]
Next, with reference to FIG. 23 and FIG. 24, correspondence between the internal winning combination, the stop operation sequence (batting order), the display combination and the like will be described.
本実施形態のパチスロ1では、遊技者の停止操作順序(押し順)に応じて表示される図柄組合せが異なる役、いわゆる「押し順役」(例えば、上述した「押し順小役」や「押し順リプレイ」)を設ける。なお、リール3L,3C,3Rに対応するストップボタン17L,17C,17Rが設けられているため、最大6通りの停止操作順序(押し順)がある。
In the pachi-
図23及び図24においては、停止操作順序(押し順)が「左、中、右」の順であることを「打順1」として示し、停止操作順序(押し順)が「左、右、中」の順であることを「打順2」として示し、停止操作順序(押し順)が「中、左、右」の順であることを「打順3」として示し、停止操作順序(押し順)が「中、右、左」の順であることを「打順4」として示し、停止操作順序(押し順)が「右、左、中」の順であることを「打順5」として示し、停止操作順序(押し順)が「右、中、左」の順であることを「打順6」として示している。
In FIG. 23 and FIG. 24, the stop operation order (pushing order) is “left, middle, right” as “
図23及び図24に示すように、「F_確定リプ」は、押し順役でなく、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序、及び停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、当籤している「特殊リプ」が成立する。なお、停止操作のタイミングに応じて、当籤しているその他のリプレイ役のうちいずれかが成立するようにしてもよい。 As shown in FIG. 23 and FIG. 24, “F_confirmed lip” is won regardless of the stop operation sequence and the timing of the stop operation when it is determined as an internal winning combination instead of the push order combination. "Special Lip" is established. Depending on the timing of the stop operation, one of the other winning replay combinations may be established.
ここで、「停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず」とは、有効ラインを「センターライン」、「トップライン」及び「ボトムライン」の3ラインとし、最大滑り駒数を「4」としたときに、最大滑り駒数の範囲内で、対応する図柄がいずれかの有効ライン上に停止表示可能となるように配置されている(例えば、図柄5個分の範囲内で配置されている)ことを意味するものである。なお、例えば、左リール3Lにおいて、「チェリー1」の図柄は、最大滑り駒数の範囲内で停止表示されない箇所(例えば、図柄位置「10」〜「12」が中段にあるタイミングで停止操作が行われたとき)もあるが、その箇所で停止操作が行われた場合には「チェリー2」の図柄が停止表示され得るように、図柄位置「13」に「チェリー2」の図柄が配置されている。したがって、内部当籤役が決定される際に、これに対応する図柄の組合せを構成する図柄として、例えば、「チェリー1」と「チェリー2」の図柄が停止表示されることを重複して許可することにより、全体としては最大滑り駒数の範囲内で、対応する図柄がいずれかの有効ライン上に停止表示可能となっている場合も、「停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず」当該図柄の組合せが成立するといえる。以下、他の表示役(入賞作動フラグ)等においても同様である。もっとも、押し順役にあっては、停止操作順序に基づいて優先的に停止制御される図柄の組合せが変動することから、上述したように図柄が配置されていたとしても、停止操作順序の種別によってその図柄が有効ライン上に停止表示されない場合もある。
Here, "regardless of the timing of the stop operation" means that when the effective line is three lines of "center line", "top line" and "bottom line" and the maximum number of sliding pieces is "4", It means that the corresponding symbols are arranged so that they can be stopped and displayed on any of the activated lines within the range of the maximum number of sliding pieces (for example, they are arranged within the range of 5 symbols). To do. Note that, for example, on the
「F_維持リプ」は、押し順役でなく、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序、及び停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、当籤している「通常リプ」のうちいずれかが成立する。 If "F_Maintain Lip" is determined as an internal winning combination instead of a push order combination, one of the winning "normal Lip" is established regardless of the stop operation order and the stop operation timing. To do.
「F_RT0中リプレイ1」は、押し順役であり、RT0状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順1」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT2移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT2状態に移行する。一方、停止操作順序が「打順1」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT1移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT1状態に移行する。
"F_RT0
「F_RT0中リプレイ2」は、押し順役であり、RT0状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順2」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT2移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT2状態に移行する。一方、停止操作順序が「打順2」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT1移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT1状態に移行する。
“F_RT0
「F_RT0中リプレイ3」は、押し順役であり、RT0状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順3」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT2移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT2状態に移行する。一方、停止操作順序が「打順3」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT1移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT1状態に移行する。
"F_RT0
「F_RT0中リプレイ4」は、押し順役であり、RT0状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順4」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT2移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT2状態に移行する。一方、停止操作順序が「打順4」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT1移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT1状態に移行する。
“F_RT0
「F_RT0中リプレイ5」は、押し順役であり、RT0状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順5」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT2移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT2状態に移行する。一方、停止操作順序が「打順5」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT1移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT1状態に移行する。
"F_RT0
「F_RT0中リプレイ6」は、押し順役であり、RT0状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順6」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT2移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT2状態に移行する。一方、停止操作順序が「打順6」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT1移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT1状態に移行する。
"F_RT0
「F_RT1中リプレイ1」は、押し順役であり、RT1状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順1」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT0移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT0状態に移行する。一方、停止操作順序が「打順1」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、当籤している「RT0移行リプ」以外のリプレイ役のうちいずれかが成立し、RT状態がRT0状態に移行せず、RT1状態が維持される(維持リプ)。なお、停止操作順序が「打順5」及び「打順6」のとき、他の「維持リプ」よりも「フェイクリプ」が優先的に停止するように停止制御が行われる。すなわち、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングであれば「フェイクリプ」が成立し、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングでなければ他の「維持リプ」が成立するようになっている。これは、「F_RT1中リプレイ2」及び「F_RT1中リプレイ3」においても同様である。
"F_RT1
「F_RT1中リプレイ2」は、押し順役であり、RT1状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順2」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT0移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT0状態に移行する。一方、停止操作順序が「打順2」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、当籤している「RT0移行リプ」以外のリプレイ役のうちいずれかが成立し、RT状態がRT0状態に移行せず、RT1状態が維持される(維持リプ)。
"F_RT1
「F_RT1中リプレイ3」は、押し順役であり、RT1状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順3」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT0移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT0状態に移行する。一方、停止操作順序が「打順3」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、当籤している「RT0移行リプ」以外のリプレイ役のうちいずれかが成立し、RT状態がRT0状態に移行せず、RT1状態が維持される(維持リプ)。
"F_RT1
「F_RT1中リプレイ4」は、押し順役であり、RT1状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順4」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT0移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT0状態に移行する。一方、停止操作順序が「打順4」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、当籤している「RT0移行リプ」以外のリプレイ役のうちいずれかが成立し、RT状態がRT0状態に移行せず、RT1状態が維持される(維持リプ)。
"F_RT1
「F_RT1中リプレイ5」は、押し順役であり、RT1状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順5」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT0移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT0状態に移行する。一方、停止操作順序が「打順5」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、当籤している「RT0移行リプ」以外のリプレイ役のうちいずれかが成立し、RT状態がRT0状態に移行せず、RT1状態が維持される(維持リプ)。
"F_RT1
「F_RT1中リプレイ6」は、押し順役であり、RT1状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順6」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT0移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT0状態に移行する。一方、停止操作順序が「打順6」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、当籤している「RT0移行リプ」以外のリプレイ役のうちいずれかが成立し、RT状態がRT0状態に移行せず、RT1状態が維持される(維持リプ)。
"F_RT1
なお、本実施形態では、「RT0移行リプ」が成立するとき、同時に「RT1移行リプ」も成立する場合があるが、この場合、主制御回路90は、「RT0移行リプ」の成立を「RT1移行リプ」の成立よりも優先して判断する。すなわち、「RT0移行リプ」と「RT1移行リプ」が同時に成立した場合には、「RT0移行リプ」が成立したと判断してRT状態をRT0状態に移行させ、「RT1移行リプ」が成立したとは判断しない。
In the present embodiment, when the “RT0 transition lip” is established, the “RT1 transition lip” may be established at the same time, but in this case, the
「F_RT2中リプレイ1」は、押し順役であり、RT2状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順1」及び「打順2」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、当籤している「RT1移行リプ」以外のリプレイ役(例えば、「通常リプ」)が成立し、RT状態がRT1状態に移行せず、RT2状態が維持される(維持リプ)。一方、停止操作順序が「打順1」及び「打順2」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT1移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT1状態に移行する。
"F_RT2
「F_RT2中リプレイ2」は、押し順役であり、RT2状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順3」及び「打順4」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、当籤している「RT1移行リプ」以外のリプレイ役(例えば、「通常リプ」)が成立し、RT状態がRT1状態に移行せず、RT2状態が維持される(維持リプ)。一方、停止操作順序が「打順3」及び「打順4」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT1移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT1状態に移行する。
"F_RT2
「F_RT2中リプレイ3」は、押し順役であり、RT2状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順5」及び「打順6」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、当籤している「RT1移行リプ」以外のリプレイ役(例えば、「通常リプ」)が成立し、RT状態がRT1状態に移行せず、RT2状態が維持される(維持リプ)。一方、停止操作順序が「打順5」及び「打順6」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT1移行リプ」が成立し、RT状態がRT1状態に移行する。
"F_RT2
「F_上段リプ」は、押し順役でなく、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序、及び停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「平行リプ」がトップラインで成立する(すなわち、「リプレイ」の図柄が各リールの上段に一直線に表示される「上段リプ」となる)。 When the "F_upper lip" is determined as the internal winning combination instead of the push winning combination, the "parallel lip" is established at the top line regardless of the stop operation order and the stop operation timing (that is, " The "Replay" symbol is displayed in a straight line on the upper row of each reel, which is "Upper Lip".
「F_中段リプ1」は、押し順役でなく、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序、及び停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「平行リプ」がセンターラインで成立する(すなわち、「リプレイ」の図柄が各リールの中段に一直線に表示される「中段リプ」となる)。
When "F_Middle-
「F_中段リプ2」は、押し順役であり、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順1」〜「打順4」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「中段リプ」が成立し、停止操作順序が「打順1」〜「打順4」以外であり、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングであれば「フェイクリプ」が成立し、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングでなければ「中段リプ」が成立する。なお、いずれのリプレイ役が成立しても遊技状態の移行は行われないことから、「F_中段リプ2」は、押し順役であるが、停止操作順序によって遊技者の利益は変動しない内部当籤役である。
"
「F_中段リプ3」は、押し順役であり、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順1」及び「打順2」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「中段リプ」が成立し、停止操作順序が「打順1」及び「打順2」以外であり、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングであれば「BAR揃いリプ」が成立し、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングでなければ「中段リプ」が成立する。なお、いずれのリプレイ役が成立しても遊技状態の移行は行われないことから、「F_中段リプ3」は、押し順役であるが、停止操作順序によって遊技者の利益は変動しない内部当籤役である。
"
「F_下段リプ」は、押し順役でなく、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序、及び停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「平行リプ」がボトムラインで成立する(すなわち、「リプレイ」の図柄が各リールの下段に一直線に表示される「下段リプ」となる)。 When "F_lower lip" is determined as an internal winning combination rather than a push order combination, a "parallel lip" is established at the bottom line regardless of the stop operation order and the stop operation timing (that is, " The "Replay" symbol is displayed in a straight line at the bottom of each reel, which is "Lower Lip".
「F_被弾リプ」は、押し順役でなく、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序、及び停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「被弾リプ」がセンターラインで成立する(すなわち、「リプレイ」の図柄が左リール3L及び中リール3Cの中段に一直線に表示されるものの、右リール3Rでは中段に表示されないように成立する)。
When "F_Bullet Lip" is determined as an internal winning combination rather than a push order combination, the "Bullet Lip" is established at the center line regardless of the stop operation sequence and the timing of the stop operation (that is, " The symbol "replay" is displayed in a straight line in the middle row of the
「F_JAC1_1」は、押し順役であり、RB状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順1」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」及び当籤している「JACA」のうちいずれかが成立し、15枚のメダルが払い出される。一方、停止操作順序が「打順1」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、当籤している「JACB」全てが成立し(すなわち、「S_JACB1」、「C_JACB2」及び「S_JACB3」のそれぞれが同時に有効ライン上に表示され)、6枚のメダルが払い出される。
"F_JAC1_1" is a push order combination, and when it is determined as an internal winning combination in the RB state, if the stop operation sequence is "
なお、「ベル」と「JACA」は、それぞれ8枚のメダルが払い出される図柄の組合せとなっているため、上述のように同時に成立した場合、本来は「8+8=16枚」のメダルが払い出されることになるが、本実施形態では、1回の遊技で払出可能なメダルの上限を「15」枚として定め、15枚を超える分の入賞が発生した場合であっても15枚のメダルを払い出すようにしている。これは、「F_JAC1_2」〜「F_JAC1_6」においても同様である。 Since "bell" and "JACA" are combinations of symbols in which eight medals are paid out, if they are simultaneously established as described above, originally "8+8=16 medals" will be paid out. However, in the present embodiment, the upper limit of medals that can be paid out in one game is set to "15", and even if a prize for more than 15 coins is generated, 15 medals are paid out. I'm trying to put it out. The same applies to "F_JAC1_2" to "F_JAC1_6".
「F_JAC1_2」は、押し順役であり、RB状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順2」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」及び当籤している「JACA」のうちいずれかが成立し、15枚のメダルが払い出される。一方、停止操作順序が「打順2」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、当籤している「JACB」全てが成立し(すなわち、「S_JACB1」、「C_JACB2」及び「S_JACB3」のそれぞれが同時に有効ライン上に表示され)、6枚のメダルが払い出される。
"F_JAC1_2" is a push order combination, and when it is determined as an internal winning combination in the RB state, if the stop operation sequence is "
「F_JAC1_3」は、押し順役であり、RB状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順3」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」及び当籤している「JACA」のうちいずれかが成立し、15枚のメダルが払い出される。一方、停止操作順序が「打順3」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、当籤している「JACB」全てが成立し(すなわち、「S_JACB1」、「C_JACB2」及び「S_JACB3」のそれぞれが同時に有効ライン上に表示され)、6枚のメダルが払い出される。
"F_JAC1_3" is a push order combination, and when it is determined as an internal winning combination in the RB state, if the stop operation sequence is "
「F_JAC1_4」は、押し順役であり、RB状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順4」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」及び当籤している「JACA」のうちいずれかが成立し、15枚のメダルが払い出される。一方、停止操作順序が「打順4」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、当籤している「JACB」全てが成立し(すなわち、「S_JACB1」、「C_JACB2」及び「S_JACB3」のそれぞれが同時に有効ライン上に表示され)、6枚のメダルが払い出される。
"F_JAC1_4" is a push order combination, and when it is determined as an internal winning combination in the RB state, if the stop operation sequence is "
「F_JAC1_5」は、押し順役であり、RB状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順5」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」及び当籤している「JACA」のうちいずれかが成立し、15枚のメダルが払い出される。一方、停止操作順序が「打順5」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、当籤している「JACB」全てが成立し(すなわち、「S_JACB1」、「C_JACB2」及び「S_JACB3」のそれぞれが同時に有効ライン上に表示され)、6枚のメダルが払い出される。
"F_JAC1_5" is a push order combination, and when it is determined as an internal winning combination in the RB state, if the stop operation sequence is "
「F_JAC1_6」は、押し順役であり、RB状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順6」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」及び当籤している「JACA」のうちいずれかが成立し、15枚のメダルが払い出される。一方、停止操作順序が「打順6」以外であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、当籤している「JACB」全てが成立し(すなわち、「S_JACB1」、「C_JACB2」及び「S_JACB3」のそれぞれが同時に有効ライン上に表示され)、6枚のメダルが払い出される。
"F_JAC1_6" is a push order combination, and when it is determined as an internal winning combination in the RB state, if the stop operation sequence is "
なお、本実施形態では、RB状態において、押し順が正解した場合(遊技者に有利な停止操作の手順で停止操作が行われた場合)に、「ベル」と「JACA」が重複して入賞することで15枚のメダルが払い出されるようにしているが、これに限られず、例えば、「JACA」のメダルの払出枚数を「15」枚として定め、押し順が正解した場合に、当籤している「JACA」のうちいずれかが成立することで、15枚のメダルが払い出されるようにしてもよい。 In the present embodiment, in the RB state, when the pressing order is correct (when the stop operation is performed according to the procedure of the stop operation that is advantageous to the player), the “bell” and the “JACA” are overlapped and the prize is won. By doing so, 15 medals are paid out, but the present invention is not limited to this. For example, if the payout number of "JACA" medals is set to "15" and the pushing order is correct, it is won. If one of the existing “JACA” is established, 15 medals may be paid out.
また、本実施形態では、RB状態において、押し順が正解しなかった場合(遊技者に有利な停止操作の手順で停止操作が行われなかった場合)に、複数の「JACB」が重複して入賞することで6枚(2枚×3ライン)のメダルが払い出されるようにしているが、これに限られず、例えば、「JACB」のメダルの払出枚数を「6」枚として定め、押し順が正解しなかった場合に、当籤している「JACB」のうちいずれかが成立することで、6枚のメダルが払い出されるようにしてもよい。 Further, in the present embodiment, in the RB state, when the pressing order is not correct (when the stop operation is not performed in the procedure of the stop operation advantageous to the player), a plurality of “JACB” are duplicated. Although 6 medals are paid out by winning (2 lines x 3 lines), the present invention is not limited to this. For example, the payout number of "JACB" medals is set to "6", and the pushing order is If the correct answer is not obtained, six medals may be paid out by establishing one of the winning "JACB".
「F_JAC2」は、押し順役でなく、RB状態において内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」及び当籤している「JACA」のうちいずれかが成立し、15枚のメダルが払い出される。なお、これも同様に、例えば、「JACA」のメダルの払出枚数を「15」枚として定め、当籤している「JACA」のうちいずれかが成立することで、15枚のメダルが払い出されるようにしてもよい。 If "F_JAC2" is determined as an internal winning combination in the RB state instead of the pushing order combination, either "bell" or winning "JACA" is irrespective of the stop operation order and the stop operation timing. Is established, and 15 medals are paid out. Note that similarly, for example, the payout number of medals of "JACA" is set to "15", and if any of the winning "JACA" is established, 15 medals are paid out. You may
「F_チャンス目A1」〜「F_チャンス目A4」及び「F_チャンス目B1」〜「F_チャンス目B4」は、押し順役でなく、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングであれば、「チャンス役」の取りこぼしが発生し、「RT3移行目」が有効ライン上に表示される。この場合、メダルの払い出しはないが、RT状態がRT3状態に移行する可能性があるため、「チャンス役」を取りこぼして「RT3移行目」を表示させる停止操作を行ったほうが遊技者にとって有利となる可能性が高い。ここでは、その意味において、「チャンス役」の取りこぼしを発生させたほうが「適切な」停止操作のタイミングであると説明している。一方、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングでなければ、当籤している「チャンス役」のうちいずれかが成立し、1枚のメダルが払い出されるものの、RT状態はRT3状態に移行することはない。 When the “F_chance eye A1” to “F_chance eye A4” and the “F_chance eye B1” to “F_chance eye B4” are determined as the internal winning combination instead of the push winning combination, the timing of the stop operation is If the timing is appropriate, the "chance part" is missed and "RT3 transition" is displayed on the activated line. In this case, the medal is not paid out, but the RT state may shift to the RT3 state. Therefore, it is advantageous for the player to perform the stop operation in which the “chance hand” is dropped and the “RT3 shift eye” is displayed. Is likely to be. Here, in that sense, it is explained that it is the "appropriate" timing of the stop operation that the "chance part" is missed. On the other hand, if the timing of the stop operation is not appropriate, one of the winning "chance combinations" is established and one medal is paid out, but the RT state does not shift to the RT3 state. ..
ここで、「F_チャンス目A1」〜「F_チャンス目A4」及び「F_チャンス目B1」〜「F_チャンス目B4」のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングであるか否かは、例えば、第3停止操作時の停止操作のタイミングに基づいて定められる。具体的には、第3停止操作時における全ての停止操作のタイミングのうちの3/4のタイミングが適切なタイミングとして定められ、当該タイミングで停止操作がなされた場合には「RT3移行目」が成立し、残りの1/4のタイミングで停止操作がなされた場合には、停止操作のタイミングが適切でないとして「チャンス役」が成立するようになっている。なお、このような停止操作のタイミングは、原則として、「F_チャンス目A1」〜「F_チャンス目A4」及び「F_チャンス目B1」〜「F_チャンス目B4」間で少なくとも一部が異なるようになっているものを含んでいる。したがって、どの内部当籤役に当籤したかによって、適切なタイミングも異ならせることができ、停止操作に関する遊技の興趣を向上させることが可能となっている。 Here, when any one of “F_chance eye A1” to “F_chance eye A4” and “F_chance eye B1” to “F_chance eye B4” is determined as the internal winning combination, the timing of the stop operation is appropriate. Whether or not this timing is determined based on, for example, the timing of the stop operation during the third stop operation. Specifically, 3/4 of the timings of all the stop operations at the time of the third stop operation is determined as an appropriate timing, and when the stop operation is performed at the timing, the “RT3 transition” is performed. When it is satisfied and the stop operation is performed at the remaining 1/4 timing, the "chance hand" is established because the timing of the stop operation is not appropriate. In addition, as a general rule, the timing of such a stop operation should be at least partially different among the “F_chance eye A1” to “F_chance eye A4” and the “F_chance eye B1” to “F_chance eye B4”. It includes what has become. Therefore, it is possible to change the appropriate timing depending on which internal winning combination is won, and it is possible to improve the enjoyment of the game regarding the stop operation.
なお、本実施形態では、「F_チャンス目A1」〜「F_チャンス目A4」及び「F_チャンス目B1」〜「F_チャンス目B4」が内部当籤役として決定された場合、停止操作のタイミングに応じて、「RT3移行目」又は「チャンス役」が成立するものとしているが、これに限られない。例えば、正解となる押し順で停止操作が行われた場合に「RT3移行目」が成立し、正解となる押し順で停止操作が行われなかった場合に「チャンス役」が成立するようにしてもよい。また、停止操作順序、及び停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「RT3移行目」が成立するようにしてもよい。この場合、「RT3移行目」をメダルの払い出しがある(例えば、1枚のメダルが払い出される)図柄の組合せとして定義するようにしてもよい。 In the present embodiment, when the “F_chance eye A1” to “F_chance eye A4” and the “F_chance eye B1” to “F_chance eye B4” are determined as the internal winning combination, depending on the timing of the stop operation. Thus, the "RT3 transition point" or the "chance role" is established, but the present invention is not limited to this. For example, the "RT3 transition" is established when the stop operation is performed in the correct pressing order, and the "chance hand" is established when the stop operation is not performed in the correct pressing order. Good. In addition, the “RT3 transition point” may be established regardless of the stop operation order and the stop operation timing. In this case, the “RT3 shift” may be defined as a combination of symbols with which medals are paid out (for example, one medal is paid out).
「F_弱レア役A」及び「F_弱レア役B」は、押し順役でなく、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序、及び停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、当籤している「チャンス役」のうちいずれかが成立し、1枚のメダルが払い出される。なお、「F_チャンス目A1」〜「F_チャンス目A4」及び「F_チャンス目B1」〜「F_チャンス目B4」と同様に、停止操作のタイミングに応じて「チャンス役」の取りこぼしが発生し得るようにしてもよい。この場合、「RT3移行目」が表示されないようにすればよい。本実施形態では、「F_チャンス目A1」〜「F_チャンス目A4」及び「F_チャンス目B1」〜「F_チャンス目B4」のいずれかに当籤した場合であって、停止操作のタイミングが適切でなく「チャンス役」が表示される場合と、「F_弱レア役A」及び「F_弱レア役B」のいずれかに当籤した場合であって、「チャンス役」が表示される場合と、があることから、内部当籤役及び停止操作態様によって、ボーナス役重複当籤の期待感やRT3移行の期待感を変動させることができ、遊技の興趣を向上させることが可能となっている。 "F_weak rare combination A" and "F_weak rare combination B" are won regardless of the stop operation order and the stop operation timing when it is determined as the internal winning combination instead of the push order combination. One of the "chance roles" is established and one medal is paid out. As in the case of “F_chance eye A1” to “F_chance eye A4” and “F_chance eye B1” to “F_chance eye B4”, the “chance hand” may be missed depending on the timing of the stop operation. You may do it. In this case, the "RT3 shift" may not be displayed. In the present embodiment, the timing of the stop operation is appropriate when the winning of any of “F_chance eye A1” to “F_chance eye A4” and “F_chance eye B1” to “F_chance eye B4” is successful. There is a case where the "chance part" is displayed without a case, and a case where the "F_weak rare part A" or "F_weak rare part B" is won and the "chance part" is displayed. Therefore, it is possible to change the expectation of the bonus winning combination winning combination and the expectation of the transition to RT3 depending on the internal winning combination and the stop operation mode, and it is possible to improve the enjoyment of the game.
「F_スイカ1」及び「F_スイカ2」は、押し順役でなく、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序、及び停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「スイカ」が成立し、5枚のメダルが払い出される。なお、停止操作のタイミングに応じて「スイカ」の取りこぼしが発生し得るようにしてもよい。
When “
「F_確定役」は、押し順役でなく、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序、及び停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、当籤している「特殊役」全てが成立し(すなわち、「S_特殊役1」、「C_特殊役2」及び「S_特殊役3」のそれぞれが同時に有効ライン上に表示され)、15枚のメダルが払い出される。なお、例えば、「特殊役」のメダルの払出枚数を「15」枚として定め、当籤している「特殊役」のうちいずれかが成立することで、15枚のメダルが払い出されるようにしてもよい。
When the "F_determination winning combination" is determined as the internal winning combination instead of the push winning combination, all the winning "special winning combinations" are established regardless of the stop operation order and the timing of the stop operation (that is, , "
「F_特殊ベル」は、押し順役でなく、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序、及び停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「クロスダウンベル」が成立し、8枚のメダルが払い出される。 When the "F_Special Bell" is determined as the internal winning combination instead of the push order combination, the "cross down bell" is established regardless of the stop operation order and the stop operation timing, and eight medals are won. Be paid out.
「F_上段共通ベル」は、押し順役でなく、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序、及び停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」がトップラインで成立し(すなわち、「ベル」の図柄が各リールの上段に一直線に表示される「上段ベル」となり)、8枚のメダルが払い出される。 When the "F_upper common bell" is determined as the internal winning combination rather than the push order combination, the "bell" is established at the top line regardless of the stop operation order and the stop operation timing (that is, " The "Bell" symbol is displayed in a straight line on the upper row of each reel and becomes the "upper bell"), and 8 medals are paid out.
「F_中段共通ベル」は、押し順役でなく、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序、及び停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」がセンターラインで成立し(すなわち、「ベル」の図柄が各リールの中段に一直線に表示される「中段ベル」となり)、8枚のメダルが払い出される。 When the "F_middle-stage common bell" is determined as the internal winning combination instead of the push order combination, the "bell" is established on the center line regardless of the stop operation order and the stop operation timing (that is, " The "Bell" symbol is displayed in a straight line on the middle row of each reel, and becomes the "middle bell"), and 8 medals are paid out.
なお、本実施形態では、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序、及び停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」がボトムラインで成立し(すなわち、「ベル」の図柄が各リールの下段に一直線に表示される「下段ベル」となり)、8枚のメダルが払い出される、例えば、「F_下段共通ベル」の内部当籤役を設けていないが、この「F_下段共通ベル」の内部当籤役を設け、ボーナス状態以外の遊技状態において、所定の確率で当籤するように構成することもできる。 In the present embodiment, when the internal winning combination is determined, the "bell" is established at the bottom line regardless of the stop operation sequence and the timing of the stop operation (that is, the "bell" symbol is applied to each reel). It becomes a "lower bell" displayed in a straight line in the lower row), and 8 medals are paid out. For example, although there is no internal winning combination of "F_lower common bell", the inside of this "F_lower common bell" It is also possible to provide a winning combination and to win with a predetermined probability in a game state other than the bonus state.
「F_上段左ベル1」及び「F_上段左ベル2」は、押し順役であり、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順1」及び「打順2」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」がトップラインで成立し(すなわち、「ベル」の図柄が各リールの上段に一直線に表示される「上段ベル」となり)、8枚のメダルが払い出される。一方、停止操作順序が「打順1」及び「打順2」以外であり、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングであれば、当籤している「打順役」のうちいずれかが成立し、1枚のメダルが払い出され、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングでなければ、「RT1移行目」が成立し(RT1移行)、メダルは払い出されない。この場合、RT状態がRT0状態、RT2状態及びRT4状態であれば、RT1状態に移行する。
“F_upper left
「F_上段中ベル1」及び「F_上段中ベル2」は、押し順役であり、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順3」及び「打順4」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」がトップラインで成立し(すなわち、「ベル」の図柄が各リールの上段に一直線に表示される「上段ベル」となり)、8枚のメダルが払い出される。一方、停止操作順序が「打順3」及び「打順4」以外であり、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングであれば、当籤している「打順役」のうちいずれかが成立し、1枚のメダルが払い出され、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングでなければ、「RT1移行目」が成立し(RT1移行)、メダルは払い出されない。この場合、RT状態がRT0状態、RT2状態及びRT4状態であれば、RT1状態に移行する。
"F_upper
「F_上段右左ベル1」及び「F_上段右左ベル2」は、押し順役であり、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順5」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」がトップラインで成立し(すなわち、「ベル」の図柄が各リールの上段に一直線に表示される「上段ベル」となり)、8枚のメダルが払い出される。一方、停止操作順序が「打順5」以外であり、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングであれば、当籤している「打順役」のうちいずれかが成立し、1枚のメダルが払い出され、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングでなければ、「RT1移行目」が成立し(RT1移行)、メダルは払い出されない。この場合、RT状態がRT0状態、RT2状態及びRT4状態であれば、RT1状態に移行する。
"F_upper right/
「F_上段右中ベル1」及び「F_上段右中ベル2」は、押し順役であり、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順6」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」がトップラインで成立し(すなわち、「ベル」の図柄が各リールの上段に一直線に表示される「上段ベル」となり)、8枚のメダルが払い出される。一方、停止操作順序が「打順6」以外であり、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングであれば、当籤している「打順役」のうちいずれかが成立し、1枚のメダルが払い出され、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングでなければ、「RT1移行目」が成立し(RT1移行)、メダルは払い出されない。この場合、RT状態がRT0状態、RT2状態及びRT4状態であれば、RT1状態に移行する。
"F_upper right
なお、本実施形態では、押し順が正解したときに「上段ベル」となる押し順小役として、「打順1」及び「打順2」(すなわち、左第1停止)が正解となる「F_上段左ベル1」及び「F_上段左ベル2」と、「打順3」及び「打順4」(すなわち、中第1停止)が正解となる「F_上段中ベル1」及び「F_上段中ベル2」と、「打順5」が正解となる「F_上段右左ベル1」及び「F_上段右左ベル2」と、「打順6」が正解となる「F_上段右中ベル1」及び「F_上段右中ベル2」と、が設けられている。すなわち、最大6通り(6択)の押し順のうちで、正解となる押し順が4通り(4択)となるように規定されているが、これは、押し順小役において正解となる押し順の一例であり、正解となる押し順のパターン(択数)はこれに限られない。
In addition, in this embodiment, as the press order small win that becomes the “upper bell” when the press order is correct, “
例えば、正解となる押し順が6通り(6択)となるように規定してもよいし、3通り(3択)となるように規定してもよい。3通り(3択)とする場合には、左第1停止(「打順1」及び「打順2」)、中第1停止(「打順3」及び「打順4」)、及び右第1停止(「打順5」及び「打順6」)のうちいずれかが正解の押し順となるように、「上段ベル」に係る内部当籤役を構成すればよい。上述した「RT0移行リプ」〜「RT2移行リプ」に係る内部当籤役、以下に示す、「中段ベル」に係る内部当籤役、及び「下段ベル」に係る内部当籤役についても同様である。すなわち、押し順役において、正解となる押し順のパターン(択数)は適宜設定することができ、そのパターン(択数)は、図23及び図24で説明したものに限られない。
For example, the correct pressing order may be defined to be 6 ways (6 options) or 3 ways (3 options). When there are three ways (three choices), the left first stop ("
「F_中段左ベル1」及び「F_中段左ベル2」は、押し順役であり、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順1」及び「打順2」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」がセンターラインで成立し(すなわち、「ベル」の図柄が各リールの中段に一直線に表示される「中段ベル」となり)、8枚のメダルが払い出される。一方、停止操作順序が「打順1」及び「打順2」以外であり、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングであれば、当籤している「打順役」のうちいずれかが成立し、1枚のメダルが払い出され、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングでなければ、「RT1移行目」が成立し(RT1移行)、メダルは払い出されない。この場合、RT状態がRT0状態、RT2状態及びRT4状態であれば、RT1状態に移行する。
"F_middle-stage
「F_中段中ベル1」及び「F_中段中ベル2」は、押し順役であり、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順3」及び「打順4」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」がセンターラインで成立し(すなわち、「ベル」の図柄が各リールの中段に一直線に表示される「中段ベル」となり)、8枚のメダルが払い出される。一方、停止操作順序が「打順3」及び「打順4」以外であり、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングであれば、当籤している「打順役」のうちいずれかが成立し、1枚のメダルが払い出され、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングでなければ、「RT1移行目」が成立し(RT1移行)、メダルは払い出されない。この場合、RT状態がRT0状態、RT2状態及びRT4状態であれば、RT1状態に移行する。
“F_middle-stage
「F_中段右左ベル1」及び「F_中段右左ベル2」は、押し順役であり、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順5」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」がセンターラインで成立し(すなわち、「ベル」の図柄が各リールの中段に一直線に表示される「中段ベル」となり)、8枚のメダルが払い出される。一方、停止操作順序が「打順5」以外であり、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングであれば、当籤している「打順役」のうちいずれかが成立し、1枚のメダルが払い出され、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングでなければ、「RT1移行目」が成立し(RT1移行)、メダルは払い出されない。この場合、RT状態がRT0状態、RT2状態及びRT4状態であれば、RT1状態に移行する。
"F_middle-stage right/
「F_中段右中ベル1」及び「F_中段右中ベル2」は、押し順役であり、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順6」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」がセンターラインで成立し(すなわち、「ベル」の図柄が各リールの中段に一直線に表示される「中段ベル」となり)、8枚のメダルが払い出される。一方、停止操作順序が「打順6」以外であり、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングであれば、当籤している「打順役」のうちいずれかが成立し、1枚のメダルが払い出され、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングでなければ、「RT1移行目」が成立し(RT1移行)、メダルは払い出されない。この場合、RT状態がRT0状態、RT2状態及びRT4状態であれば、RT1状態に移行する。
"F_middle-stage right
「F_下段中ベル1」及び「F_下段中ベル2」は、押し順役であり、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順3」及び「打順4」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」がボトムラインで成立し(すなわち、「ベル」の図柄が各リールの下段に一直線に表示される「下段ベル」となり)、8枚のメダルが払い出される。一方、停止操作順序が「打順3」及び「打順4」以外であり、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングであれば、当籤している「打順役」のうちいずれかが成立し、1枚のメダルが払い出され、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングでなければ、「RT1移行目」が成立し(RT1移行)、メダルは払い出されない。この場合、RT状態がRT0状態、RT2状態及びRT4状態であれば、RT1状態に移行する。
“F_lower-
「F_下段右左ベル1」及び「F_下段右左ベル2」は、押し順役であり、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順5」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」がボトムラインで成立し(すなわち、「ベル」の図柄が各リールの下段に一直線に表示される「下段ベル」となり)、8枚のメダルが払い出される。一方、停止操作順序が「打順5」以外であり、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングであれば、当籤している「打順役」のうちいずれかが成立し、1枚のメダルが払い出され、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングでなければ、「RT1移行目」が成立し(RT1移行)、メダルは払い出されない。この場合、RT状態がRT0状態、RT2状態及びRT4状態であれば、RT1状態に移行する。
"F_lower row right/
「F_下段右中ベル1」及び「F_下段右中ベル2」は、押し順役であり、内部当籤役として決定された場合に、停止操作順序が「打順6」であれば、停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」がボトムラインで成立し(すなわち、「ベル」の図柄が各リールの下段に一直線に表示される「下段ベル」となり)、8枚のメダルが払い出される。一方、停止操作順序が「打順6」以外であり、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングであれば、当籤している「打順役」のうちいずれかが成立し、1枚のメダルが払い出され、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングでなければ、「RT1移行目」が成立し(RT1移行)、メダルは払い出されない。この場合、RT状態がRT0状態、RT2状態及びRT4状態であれば、RT1状態に移行する。
"F_lower right
なお、本実施形態では、「F_上段左ベル1」〜「F_下段右中ベル2」のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合であって、正解となる押し順で停止操作が行われなかった場合に、停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングであるか否かは、例えば、第3停止操作時の停止操作のタイミングに基づいて定められる。具体的には、第3停止操作時における全ての停止操作のタイミングのうちの1/2のタイミングが適切なタイミングとして定められ、当該タイミングで停止操作がなされた場合には、当籤している「打順役」のうちいずれかが成立し、残りの1/2のタイミングで停止操作がなされた場合には、停止操作のタイミングが適切でないとして「RT1移行目」が成立するようになっている。
In the present embodiment, when any of “F_upper left
また、本実施形態では、「F_上段左ベル1」〜「F_上段右中ベル2」のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合であって、フラグ間状態(RT5状態)であるときには、停止操作順序、及び停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」がトップラインで成立し(すなわち、「ベル」の図柄が各リールの上段に一直線に表示される「上段ベル」となり)、8枚のメダルが払い出される。また、「F_中段左ベル1」〜「F_中段右中ベル2」のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合であって、フラグ間状態(RT5状態)であるときには、停止操作順序、及び停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」がセンターラインで成立し(すなわち、「ベル」の図柄が各リールの中段に一直線に表示される「中段ベル」となり)、8枚のメダルが払い出される。また、「F_下段中ベル1」〜「F_下段右中ベル2」のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合であって、フラグ間状態(RT5状態)であるときには、停止操作順序、及び停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず、「ベル」がボトムラインで成立し(すなわち、「ベル」の図柄が各リールの下段に一直線に表示される「下段ベル」となり)、8枚のメダルが払い出される。
In addition, in the present embodiment, when any of the “F_upper left
すなわち、フラグ間状態(RT5状態)であるときには、押し順小役が押し順役ではなくなる(押し順役が不問となる)ようになっている。もっとも、必ずしもこのように構成する必要はなく、フラグ間状態(RT5状態)であるときにも、上述したように正解となる押し順であれば8枚のメダルが払い出される図柄の組合せ(「上段ベル」、「中段ベル」又は「下段ベル」)が停止表示され、正解となる押し順でなければ、停止操作のタイミングが適切であれば1枚のメダルが払い出される「打順役」が停止表示され、停止操作のタイミングが適切でなければ取りこぼしが発生するようにしてもよい。この場合、「RT1移行目」が表示されても遊技状態がRT1状態には移行しないことから、「RT1移行目」を表示させないようにしてもよい。 That is, in the flag-to-flag state (RT5 state), the push-order small winning combination is no longer the push-down winning combination (the push-down winning combination is unquestioned). However, it is not always necessary to configure in this way, and even in the flag-to-flag state (RT5 state), as described above, if the pushing order is the correct answer, eight medals will be paid out. "Bell", "middle bell" or "lower bell") is displayed as a stop, and if it is not the correct pressing order, one medal is paid out if the timing of the stop operation is appropriate "Stop batting" is displayed Therefore, if the timing of the stop operation is not appropriate, the omission may be generated. In this case, since the game state does not shift to the RT1 state even if the "RT1 shift" is displayed, the "RT1 shift" may not be displayed.
また、本実施形態では、リプレイ役又は小役とボーナス役とが重複して内部当籤役として決定される場合(ボーナス役が持ち越されている場合を含む)、ボーナス役よりもリプレイ役又は小役を優先的に成立させる停止制御が行われるが、リプレイ役又は小役よりもボーナス役を優先的に成立させる停止制御が行われるようにしてもよい。 Further, in the present embodiment, when the replay combination or the small combination and the bonus combination are overlapped and determined as the internal winning combination (including the case where the bonus combination is carried over), the replay combination or the small combination is more preferable than the bonus combination. However, the stop control for preferentially establishing the bonus combination over the replay combination or the small combination may be performed.
ここで、本実施形態のパチスロ1におけるリールの停止制御(停止図柄位置の決定手法)について簡単に説明する。本実施形態では、ストップスイッチにより停止操作が検出された後、該当するリールの回転が190msec以内に停止するようにリールの停止制御が行われる。具体的には、停止操作が検出されたときの該当リールに応じた図柄カウンタの値に、滑り駒数「0」〜「4」のうちの何れかを加算し、得られた値に対応する図柄位置を、リールの回転が停止する図柄位置(以下、「停止予定位置」という)として決定する。なお、停止操作が検出されたときの該当リールに応じた図柄カウンタの値に対応する図柄位置は、リールの回転の停止が開始される図柄位置(以下、「停止開始位置」という)である。
Here, the reel stop control (stop symbol position determination method) in the pachi-
すなわち、滑り駒数は、ストップスイッチにより停止操作が検出されてから該当するリールの回転が停止するまでのリールの回転量である。言い換えれば、ストップスイッチにより停止操作が検出されてから該当するリールの回転が停止するまでの期間において、リール表示窓4の該当するリールの中段領域を通過する図柄の数である。これは、ストップスイッチにより停止操作が検出されてから更新された図柄カウンタの値により把握される。
That is, the number of sliding pieces is the amount of rotation of the reel after the stop operation is detected by the stop switch until the rotation of the corresponding reel stops. In other words, it is the number of symbols that pass through the middle region of the reel of the
図示しない停止テーブルを参照すると、各リールの停止開始位置に応じて滑り駒数が取得される。なお、本実施形態では、停止テーブルに基づいて滑り駒数が取得されるが、これは仮のものであり、取得した滑り駒数が直ちにリールの停止予定位置が決定されるものではない。本実施形態では、停止テーブルに基づいて取得された滑り駒数(以下、「滑り駒数決定データ」という)より適切な滑り駒数が存在する場合には、図示しない引込優先順位テーブルを参照して滑り駒数を変更する。そして、滑り駒数決定データは、停止開始位置から最大滑り駒数である4個先の図柄位置までの各図柄について、優先順位の比較を行う際の検索順序を決定するために参照される。 By referring to a stop table (not shown), the number of sliding pieces is acquired according to the stop start position of each reel. In the present embodiment, the number of sliding pieces is acquired based on the stop table, but this is tentative, and the obtained number of sliding pieces does not immediately determine the scheduled stop position of the reel. In the present embodiment, when there is a more appropriate number of sliding pieces than the number of sliding pieces (hereinafter referred to as “slip piece number determination data”) acquired based on the stop table, a pull-in priority table (not shown) is referred to. Change the number of sliding pieces. Then, the number-of-slip-pieces determination data is referred to in order to determine the search order when comparing the priorities of the respective symbols from the stop start position to the symbol position which is the maximum number of four slides ahead.
本実施形態のリール停止制御では、まず、停止テーブル(不図示)に基づいて滑り駒数が取得される。しかしながら、優先順位に基づいて、この滑り駒数の他に、より適切な滑り駒数が存在する場合には、その適切な滑り駒数に変更する。すなわち、本実施形態では、停止テーブルにより取得された滑り駒数に関係なく、内部当籤役によって停止表示を許可する図柄組合せの優先順位に基づいて、より適切な滑り駒数を決定する。 In the reel stop control of the present embodiment, first, the number of sliding pieces is acquired based on a stop table (not shown). However, if there is a more appropriate number of sliding pieces other than this number of sliding pieces based on the priority, the number of sliding pieces is changed to the appropriate number of sliding pieces. That is, in the present embodiment, the more appropriate number of sliding pieces is determined based on the priority of the symbol combination that allows the stop display by the internal winning combination, regardless of the number of sliding pieces acquired by the stop table.
<メインRAMに設けられている格納領域の構成>
次に、図25〜図30を参照して、メインRAM103に設けられる各種格納領域の構成について説明する。
<Structure of storage area provided in main RAM>
Next, with reference to FIGS. 25 to 30, the configuration of various storage areas provided in the
[当り要求フラグ格納領域及び入賞作動フラグ格納領域]
まず、図25を参照して、当り要求フラグ格納領域(内部当籤役格納領域)及び入賞作動フラグ格納領域(表示役格納領域)の構成について説明する。なお、本実施形態では、当り要求フラグ格納領域(フラグデータ格納領域、当籤フラグデータ格納領域)と、入賞作動フラグ格納領域(入賞フラグデータ格納領域)とは、互いに同じ構成を有する。
[Hit request flag storage area and winning action flag storage area]
First, the configurations of the hit request flag storage area (internal winning combination storage area) and the winning operation flag storage area (display combination storage area) will be described with reference to FIG. In the present embodiment, the hit request flag storage area (flag data storage area, winning flag data storage area) and the winning operation flag storage area (winning flag data storage area) have the same configuration.
本実施形態では、当り要求フラグ格納領域は、それぞれ1バイトのデータにより表される当り要求格納領域1〜9で構成され、入賞作動フラグ格納領域は、それぞれ1バイトのデータにより表される入賞作動格納領域1〜9で構成される。なお、当り要求フラグ格納領域及び入賞作動フラグ格納領域の各格納領域に格納されるデータは、図25中の「データ」欄の1バイトデータのみであるが、図25では、説明の便宜上、各格納領域のビットに対応付けられた、各リールの図柄組合せを示す「コンビネーション」(図中では、左リール3Lの図柄、中リール3Cの図柄及び右リール3Rの図柄の順で記載)、及びその内容(図19〜図22参照)も併せて記載する。
In the present embodiment, the hit request flag storage areas are made up of hit
当り要求フラグ格納領域1〜9のそれぞれにおいて、所定のビットに「1」が格納されているとき、その所定のビットに対応する内部当籤役が内部当籤したことを示す。また、入賞作動格納領域1〜9のそれぞれにおいて、所定のビットに「1」が格納されているとき、その所定のビットに対応する表示役(入賞作動フラグ)が入賞したことを示す。すなわち、所定のビットに「1」が格納されているとき、その所定のビットに対応する内部当籤役の各種図柄組合せが有効ライン上に表示されたことを示す。
In each of the hit request
なお、当り要求フラグ格納領域及び入賞作動フラグ格納領域では、各格納領域内の1つのビット(フラグ)に対して、複数の図柄の組合せ(コンビネーション)が割り当てられるものを含むが、上述したように、各格納領域内の1つのビット(フラグ)に対して、1つの図柄の組合せ(コンビネーション)が割り当てられるようにしてもよい。 In addition, in the hit request flag storage area and the winning operation flag storage area, one bit (flag) in each storage area includes one in which a combination of a plurality of symbols is assigned, but as described above. Alternatively, one symbol (flag) in each storage area may be assigned to one symbol combination (combination).
[持越役格納領域]
次に、図26を参照して、持越役格納領域の構成について説明する。本実施形態では、持越役格納領域は、1バイトのデータ格納領域で構成される。
[Carryover storage area]
Next, with reference to FIG. 26, the configuration of the carryover combination storing area will be described. In this embodiment, the internal carryover combination storage area is composed of a 1-byte data storage area.
内部抽籤の結果、内部当籤役「F_BB1」、「F_BB2」、「F_BB3」又は「F_BB4」が決定されたときには、その内部当籤役(BB役)は、持越役として持越役格納領域に格納される。持越役格納領域に格納された持越役は、対応する図柄組合せが有効ライン上に表示されるまでクリアされずに保持される。また、持越役格納領域に持越役が格納されている間、内部抽籤によって決定された内部当籤役に加えて、持越役が当り要求格納領域に格納される。 As a result of the internal lottery, when the internal winning combination "F_BB1", "F_BB2", "F_BB3" or "F_BB4" is determined, the internal winning combination (BB combination) is stored in the carryover combination storing area as a carryover combination. .. The internal carryover combination stored in the internal carryover combination storage area is held without being cleared until the corresponding symbol combination is displayed on the activated line. Further, while the carry-over combination is stored in the carry-over combination storing area, the carry-over combination is stored in the hit request storage area in addition to the internal winning combination determined by the internal lottery.
[遊技状態フラグ格納領域]
次に、図27を参照して、遊技状態フラグ格納領域の構成について説明する。遊技状態フラグ格納領域は、2バイトのデータ格納領域で構成される。本実施形態では、図27に示すように、遊技状態フラグ格納領域の各ビットに対して固有のボーナスの種別又はRTの種別が割り当てられる。
[Game status flag storage area]
Next, with reference to FIG. 27, the configuration of the game state flag storage area will be described. The game state flag storage area is composed of a 2-byte data storage area. In the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 27, a unique bonus type or RT type is assigned to each bit of the game state flag storage area.
遊技状態フラグ格納領域において、所定のビットに「1」が格納されているとき、その所定のビットに該当するボーナス状態又はRT状態の作動が行われていることを示す。例えば、遊技状態フラグ格納領域1のビット0に「1」が格納されているときには、遊技状態がBB1状態であることを示す。また、例えば、遊技状態フラグ格納領域2のビット0に「1」が格納されているときは、遊技状態がRT3状態であることを示す。
When "1" is stored in the predetermined bit in the game state flag storage area, it indicates that the bonus state or the RT state corresponding to the predetermined bit is being operated. For example, when "1" is stored in
[作動ストップボタン格納領域]
次に、図28を参照して、作動ストップボタン格納領域の構成について説明する。作動ストップボタン格納領域は、1バイトのデータ格納領域で構成され、1バイトからなる作動ストップボタンフラグを格納する。作動ストップボタンフラグにおいて、各ビットには、ストップボタンの操作状態が割り当てられる。
[Operation stop button storage area]
Next, the configuration of the operation stop button storage area will be described with reference to FIG. The operation stop button storage area is configured by a 1-byte data storage area and stores an operation stop button flag consisting of 1 byte. In the operation stop button flag, the operation state of the stop button is assigned to each bit.
例えば、左ストップボタン17Lが今回押されたストップボタン、つまり、作動ストップボタンである場合には、作動ストップボタン格納領域のビット0に「1」が格納される。また、例えば、左ストップボタン17Lが未だに押されていないストップボタン、つまり、有効ストップボタンである場合には、ビット4に「1」が格納される。メインCPU101は、作動ストップボタン格納領域に格納されているデータに基づいて、今回押されたストップボタンと未だに押されていないストップボタンとを識別する。
For example, when the left stop button 17L is the stop button pressed this time, that is, the operation stop button, "1" is stored in
[押下順序格納領域]
次に、図29を参照して、押下順序格納領域の構成について説明する。押下順序格納領域は、1バイトのデータ格納領域で構成され、1バイトからなる押下順序フラグを格納する。
[Pressing order storage area]
Next, with reference to FIG. 29, the configuration of the pressing order storage area will be described. The pressing order storage area is composed of a 1-byte data storage area and stores a pressing order flag of 1 byte.
押下順序フラグにおいて、各ビットには、ストップボタンの押下順序の種別が割り当てられる。例えば、ストップボタンの押下順序が「左、中、右」である場合には、押下順序格納領域のビット0に「1」が格納される。
In the press order flag, the type of the stop button press order is assigned to each bit. For example, if the pressing order of the stop buttons is "left, center, right", "1" is stored in
[図柄コード格納領域]
次に、図30を参照して、図柄コード格納領域の構成について説明する。本実施形態では、図柄コード格納領域は、それぞれ1バイトのデータにより表される図柄コード格納領域1〜9で構成される。なお、図柄コード格納領域は、当り要求フラグ格納領域及び入賞作動フラグ格納領域(図25参照)と同様の構成となる。
[Design code storage area]
Next, the configuration of the symbol code storage area will be described with reference to FIG. In the present embodiment, the symbol code storage areas are composed of symbol
図柄コード格納領域では、有効ライン上に停止可能な図柄の組合せ(コンビネーション)に対応するビットに「1」が格納される。なお、全てのリールが停止後、図柄コード格納領域1〜9には、表示役(入賞作動フラグ)に対応する図柄コードが格納される。
In the symbol code storage area, "1" is stored in the bit corresponding to the symbol combination (combination) that can be stopped on the activated line. In addition, after all reels are stopped, the symbol codes corresponding to the display combination (winning operation flag) are stored in the symbol
[内部当籤役と抽籤番号と当籤役番号との関係]
上述した遊技性に関する各種遊技状態において、主制御回路90による各種抽籤では各種データテーブルを参照するが、この際に用いるパラメータとして、本実施形態では、内部当籤役だけでなく、内部当籤役に対応する別の名称の各パラメータ(以下、「抽籤番号」という)も用いる。抽籤番号は、主制御回路90による遊技性に関する各種抽籤において、同様の役割(抽籤対象役であるかや当籤確率など)を担う内部当籤役をグループ化して同じ抽籤番号を割り当てることで、そのグループを識別可能とするための情報である。これにより、本実施形態では、内部当籤役ごとに(例えば、図16及び図17に示す、「No.0」〜「No.98」のそれぞれについて)各種データテーブルを設ける必要がなく、抽籤番号ごとに各種データテーブルを設ければよいため、データ量を圧縮することができ、遊技用ROM領域の容量の圧迫を回避することができる。
[Relationship between internal winning combination, lottery number and winning combination number]
In the above-mentioned various game states related to game play, various data tables are referred to in various lottery by the
また、本実施形態では、内部当籤役について、副制御回路200側で今回の単位遊技における内部当籤役を識別させるための別の名称の各パラメータ(以下、「当籤役番号」という)も用いる。当籤役番号は、遊技状態(より詳細には、非有利区間であるか、通常有利区間及び有利区間であるか)に応じて、内部当籤役のうち少なくとも一部の内部当籤役をグループ化して同じ当籤役番号を割り当てることで、そのグループを認識可能とするための情報である。これにより、本実施形態では、内部当籤役ごとに(例えば、図16及び図17に示す、「No.0」〜「No.98」のそれぞれについて)、それを識別させるための固有の情報を副制御回路200側に送信する必要がなくなるため、データ量を圧縮することができ、制御負担を低減することができるのみならず、遊技状態に応じて適切な情報を送信することができる。
Further, in the present embodiment, with respect to the internal winning combination, each parameter of another name (hereinafter, referred to as “winning combination number”) for identifying the internal winning combination in the unit game of this time on the side of the
ここで、図31及び図32を参照して、内部当籤役と抽籤番号と当籤役番号との対応関係について説明する。図31及び図32は、内部当籤役と抽籤番号と当籤役番号との基本的な対応関係の一例を示す図である。 Here, the correspondence relationship between the internal winning combination, the lottery number, and the winning combination number will be described with reference to FIGS. 31 and 32. 31 and 32 are diagrams showing an example of a basic correspondence relationship between an internal winning combination, a lottery number, and a winning combination number.
図31に示すように、ボーナス役とリプレイ役又は小役とが同時に当籤する(ボーナス役を含む)内部当籤役(図16及び図17に示した「No.1」〜「No.38」が示す内部当籤役)については、各設定値間で異なる当籤確率となっている「F_BB3+F_スイカ2」及び「F_BB4+F_スイカ2」を除き、抽籤番号「13」が割り当てられている。また、「F_BB3+F_スイカ2」及び「F_BB4+F_スイカ2」については抽籤番号「0」が割り当てられている。
As shown in FIG. 31, an internal winning combination (including a bonus combination) in which a bonus combination and a replay combination or a small combination are simultaneously won (“No. 1” to “No. 38” shown in FIGS. 16 and 17 are The lottery number “13” is assigned to the internal winning combination shown) except for “F_BB3+
なお、本実施形態では、非有利区間(図31及び図32中、「通常」。以下同じ)と、通常有利区間及び有利区間(図31及び図32中、「有利」。以下同じ)と、で抽籤番号を異ならせていないが、例えば、「通常」と「有利」とで異なる抽籤や処理が行われる場合には、「通常」と「有利」とで異なる抽籤番号を割り当てることもできる。例えば、非有利区間においては、「F_BB3+F_スイカ2」及び「F_BB4+F_スイカ2」に当籤した場合、ART抽籤は行われず、通常有利区間に移行することも決定されないが、通常有利区間及び有利区間においては、「F_BB3+F_スイカ2」及び「F_BB4+F_スイカ2」が当籤した場合にも、他のボーナス役を含む内部当籤役と同様の抽籤が行われるため、「通常」においては上述のように抽籤番号を割り当て、「有利」においては共通の抽籤番号「13」を割り当てるようにしてもよい。
In the present embodiment, a non-advantageous section (“normal” in FIGS. 31 and 32, the same applies hereinafter), a normal advantageous section and an advantageous section (“advantage” in FIGS. 31 and 32, the same applies below), Although the lottery numbers are not made different in, for example, different lottery numbers can be assigned to “normal” and “advantageous” when different lottery or processing is performed for “normal” and “advantageous”. For example, in the non-advantageous section, when the winnings of “F_BB3+
また、図31に示すように、ボーナス役を含む内部当籤役では、そのボーナス役の種別と同時に当籤するリプレイ役又は小役の種別とに応じて、当籤役番号「28」〜「41」のいずれかの当籤役番号が割り当てられている。これにより、副制御回路200側では、当籤したボーナス役の種別、及び当籤したリプレイ役又は小役の種別に応じて、異なる演出を実行することが可能となる。
Further, as shown in FIG. 31, in the internal winning combination including the bonus combination, the winning combination numbers “28” to “41” are assigned according to the type of the bonus combination and the type of the replay combination or the small combination to be won. One of the winning combination numbers is assigned. As a result, on the side of the
また、図32に示すように、リプレイ又は小役の内部当籤役(図16及び図17に示した「No.39」〜「No.98」が示す内部当籤役、図18に示した「No.1」〜「No.7」が示す内部当籤役)については、それぞれ「0」〜「12」のいずれかの抽籤番号が割り当てられている。 Further, as shown in FIG. 32, the internal winning combination of the replay or the small winning combination (the internal winning combination shown by “No. 39” to “No. 98” shown in FIG. 16 and FIG. 17) and the “No winning shown by FIG. .1” to “No. 7”), a lottery number of any of “0” to “12” is assigned.
ここで、例えば、リプレイ役が内部当籤役として決定される確率が高確率となる遊技状態であるRT0状態及びRT2状態で当籤する「F_RT0中リプレイ1」〜「F_RT0中リプレイ6」及び「F_RT2中リプレイ1」〜「F_RT2中リプレイ3」には、同じ抽籤番号「1」が割り当てられている。また、例えば、RT5状態以外のRT状態において、RT3状態に移行する可能性があり、また、非有利区間から通常有利区間に移行することとなる「F_チャンス目A1」〜「F_チャンス目B4」には、同じ抽籤番号「6」が割り当てられている。
Here, for example, "
また、例えば、同じ「上段ベル」が表示される可能性がある「F_上段共通ベル」及び「F_上段左ベル1」〜「F_上段右中ベル2」には、同じ抽籤番号「10」が割り当てられ、同じ「中段ベル」が表示される可能性がある「F_中段共通ベル」及び「F_中段左ベル1」〜「F_中段右中ベル2」には、同じ抽籤番号「11」が割り当てられ、同じ「下段ベル」が表示される可能性がある「F_下段中ベル1」〜「F_下段右中ベル2」には、同じ抽籤番号「12」が割り当てられている。
Further, for example, the same lottery number “10” is assigned to “F_upper common bell” and “F_upper left
また、図32に示すように、リプレイ又は小役の内部当籤役(図16及び図17に示した「No.39」〜「No.98」が示す内部当籤役、図18に示した「No.1」〜「No.7」が示す内部当籤役)については、「通常」又は「有利」においてそれぞれ「0」〜「27」のいずれかの当籤役番号が割り当てられている。 Further, as shown in FIG. 32, the internal winning combination of the replay or the small winning combination (the internal winning combination shown by “No. 39” to “No. 98” shown in FIG. 16 and FIG. 17) and the “No winning shown by FIG. .1” to “No. 7”), a winning combination number of “0” to “27” is assigned to “normal” or “advantageous”, respectively.
ここで、「F_上段左ベル1」〜「F_下段右中ベル2」に割り当てられた当籤役番号に着目すると、「通常」においては、それぞれ同じ当籤役番号「22」が割り当てられているのに対し、「有利」においては、「F_上段左ベル1」〜「F_上段右中ベル2」について当籤役番号「23」が割り当てられ、「F_中段左ベル1」〜「F_中段右中ベル2」について当籤役番号「24」が割り当てられ、「F_下段中ベル1」〜「F_下段右中ベル2」について当籤役番号「25」が割り当てられている点で異なっている。
Here, focusing on the winning combination numbers assigned to “F_upper left
すなわち、本実施形態では、有利区間のラインバトル状態(後述の図35参照)において、これらの内部当籤役に当籤した場合、各リールの中段に「ベル」の図柄が並ぶ場合(「中段ベル」が成立する場合)と、各リールの上段に「ベル」の図柄が並ぶ場合(「上段ベル」が成立する場合)と、各リールの下段に「ベル」の図柄が並ぶ場合(「下段ベル」が成立する場合)と、でいずれもメダルの払出枚数は同じであるが、ラインバトル状態の継続度合いが変動する場合があることから、上述したように、通常有利区間及び有利区間である場合に、「F_上段左ベル1」〜「F_上段右中ベル2」と、「F_中段左ベル1」〜「F_中段右中ベル2」と、「F_下段中ベル1」〜「F_下段右中ベル2」と、で異なる当籤番号を割り当てることにより、副制御回路200側で、図柄の停止表示前(停止操作前)に、いずれの有効ライン上に「ベル」の図柄が並ぶ可能性があるのかを認識させることができ、ラインバトル状態において、この当籤役番号を受信したことに基づき期待度の異なる演出を行わせることができる。なお、ラインバトル状態における演出の一例については、後述の図37〜図41を用いて、後で説明する。
That is, in the present embodiment, in the line battle state of the advantageous section (see FIG. 35 described later), when these internal winning combinations are won, when the symbols of “bell” are lined up in the middle of each reel (“middle bell”) When the "bel" symbols are lined up in the upper row of each reel (when the "upper bell" is established), and when the "bell" symbols are lined up in the lower row of each reel ("lower bell") However, since the number of medals paid out is the same in both cases, the degree of continuation of the line battle state may fluctuate. , "F_upper left
なお、同様の観点より、例えば、「F_上段リプ」、「F_中段リプ1」〜「F_中段リプ3」及び「F_下段リプ」について、「通常」においては、それぞれ同じ当籤役番号が割り当てられ、「有利」においては、それぞれ異なる当籤役番号が割り当てられるようにしてもよい。
From the same viewpoint, for example, the same winning combination number is assigned to each of “F_upper lip”, “
また、本実施形態では、主制御回路90により、内部当籤役に関する情報として、当籤役番号がスタートコマンドの通信パラメータにセットされ、主制御回路90から副制御回路200に送信されるとともに、後述のナビデータ(後述の図45参照)に相当する情報がスタートコマンド(あるいは、他のコマンドであってもよい)の通信パラメータにセットされ、主制御回路90から副制御回路200に送信されるようになっているが、副制御回路200側で、内部当籤役あるいはナビデータを認識可能な情報を送信する態様はこれに限られない。
Further, in the present embodiment, the
例えば、「F_RT0中リプレイ1」〜「F_RT0中リプレイ6」について、非有利区間及び通常有利区間においては、同じ当籤役番号が割り当てられ、有利区間においては、それぞれ異なる当籤役番号が割り当てられるようにしてもよい。また、「F_RT1中リプレイ1」〜「F_RT1中リプレイ6」について、非有利区間及び通常有利区間においては、同じ当籤役番号が割り当てられ、有利区間においては、それぞれ異なる当籤役番号が割り当てられるようにしてもよい。また、「F_RT2中リプレイ1」〜「F_RT2中リプレイ3」について、非有利区間及び通常有利区間においては、同じ当籤役番号が割り当てられ、有利区間においては、それぞれ異なる当籤役番号が割り当てられるようにしてもよい。すなわち、押し順リプレイについて、遊技者に有利な停止操作の情報が報知され得る各遊技状態(有利区間)においては、内部当籤役が特定可能な情報として当籤役番号を送信し、遊技者に有利な停止操作の情報が報知され得ない各遊技状態(非有利区間及び通常有利区間)においては、内部当籤役が特定不可能な情報として当籤役番号を送信するようにしてもよい。
For example, regarding “
これは、押し順小役についても同様である。この場合、非有利区間においては、同じ当籤役番号が割り当てられ、通常有利区間及び有利区間においては、それぞれ異なる当籤役番号が割り当てられるようにすればよい。そして、通常有利区間及び有利区間における当籤役番号の割り当てについては、例えば、「ベル」の図柄がいずれの有効ライン上に表示される可能性があるかと、遊技者に有利な停止操作の種別の双方が特定可能となるように、当籤役番号をさらに細分化して割り当てるようにすればよい。 This is the same for the push order small win. In this case, the same winning combination number may be assigned to the non-advantageous section, and different winning combination numbers may be assigned to the normal advantageous section and the advantageous section. And about the allocation of the winning combination number in the normal advantageous section and the advantageous section, for example, on which effective line the symbol of "bell" may be displayed, and the type of the stop operation advantageous to the player, The winning combination number may be further subdivided and assigned so that both parties can be identified.
このように、例えば、押し順小役や押し順リプレイについて、遊技者に有利な停止操作の情報が報知され得る各遊技状態では、内部当籤役が特定可能な情報として当籤役番号を送信し、遊技者に有利な停止操作の情報が報知され得ない各遊技状態においては、内部当籤役が特定不可能な情報として当籤役番号を送信するようにすれば、後述のナビデータ(後述の図45参照)に相当する情報を副制御回路200に送信する必要がなくなる可能性がある。この場合には、後述のナビデータ(後述の図45参照)に相当する情報を副制御回路200に送信する処理を省略することができ、制御負担を軽減することが可能となる。
Thus, for example, for each push-order small combination or push-order replay, in each gaming state in which the information of the stop operation advantageous to the player can be informed, the internal winning combination is transmitted as a winning combination number that can be specified, In each gaming state in which the information of the stop operation advantageous to the player cannot be notified, if the winning combination number is transmitted as the information in which the internal winning combination cannot be specified, the navigation data described later (see FIG. 45 described later). It may not be necessary to send information corresponding to the reference) to the
なお、図32においては、内部当籤役と抽籤番号と当籤役番号との対応関係の一例として、ボーナス役の当籤(持ち越し)の有無を考慮しないものとして説明しているが、ボーナス役が持ち越されているか否かに応じて、内部当籤役と抽籤番号と当籤役番号との対応関係を変更するようにしてもよい。例えば、フラグ間状態では、基本的に遊技性に関する各種の抽籤が行われなくなるため、フラグ間状態では、抽籤番号を全て「0」に割り当てるようにしてもよい。 Note that, in FIG. 32, as an example of the correspondence relationship between the internal winning combination, the lottery number, and the winning combination number, it is described that the presence/absence of the winning (carrying over) of the bonus combination is not taken into consideration, but the bonus combination is carried over. Depending on whether or not the internal winning combination, the lottery number, and the winning combination number may be changed. For example, in the flag-to-flag state, various lottery related to game characteristics is basically not performed. Therefore, in the flag-to-flag state, all lottery numbers may be assigned to “0”.
<非有利区間(通常状態)中の遊技性>
次に、図33を参照して、非有利区間(通常状態)の遊技の流れについて説明する。なお、図33では、通常状態において、同図に示す各内部当籤役に当籤した場合に、遷移される遊技状態の概要を示している。
<Game play during non-advantageous section (normal state)>
Next, with reference to FIG. 33, the flow of the game in the non-advantageous section (normal state) will be described. In addition, in FIG. 33, in the normal state, an outline of the game state to be transitioned to when each of the internal winning combinations shown in the figure is won is shown.
(弱レア役当籤時)
非有利区間であり、ボーナス非当籤状態であるときに、弱レア役(「F_弱レア役A」及び「F_弱レア役B」)に当籤した場合、メインCPU101は、遊技状態を高確1状態(通常有利区間)に移行させるとともに、通常有利区間の遊技期間に「9」ゲームをセットする。これにより、次回遊技から少なくとも9回の遊技の間、次回遊技から高確1状態に制御される。
(When winning a rare role)
In the non-advantageous section, when the bonus rare winning state is reached, when the weak rare combination (“F_weak rare combination A” and “F_weak rare combination B”) is won, the
(チャンス目当籤時)
非有利区間であり、ボーナス非当籤状態であるときに、チャンス目(「F_チャンス目A1」〜「F_チャンス目A4」及び「F_チャンス目B1」〜「F_チャンス目B4」)に当籤した場合、メインCPU101は、遊技状態を高確2状態(通常有利区間)に移行させるとともに、通常有利区間の遊技期間に「9」ゲームをセットする。これにより、次回遊技から少なくとも9回の遊技の間、高確2状態に制御される。
(At the chance of winning)
In the non-advantageous section and when the bonus is not won, the chance chance (“F_chance eye A1” to “F_chance eye A4” and “F_chance eye B1” to “F_chance eye B4”) is won. , The
このとき、遊技者の停止操作の結果、「RT3移行目」が表示されてRT状態がRT3状態に移行する場合と、「RT3移行目」が表示されずRT状態がRT3状態に移行しない場合(すなわち、RT3状態以外のRT状態が継続する場合)がある。いずれも高確2状態に移行することにかわりはないものの、RT状態がRT3状態であるほうが遊技者に有利となる。この点は、後で詳述する。 At this time, as a result of the player's stop operation, the "RT3 shift eye" is displayed and the RT state shifts to the RT3 state, and the "RT3 shift eye" is not displayed and the RT state does not shift to the RT3 state ( That is, there is a case where RT states other than the RT3 state continue). Although there is no change in shifting to the highly accurate 2 state, it is more advantageous for the player that the RT state is the RT3 state. This point will be described in detail later.
なお、チャンス目は、ボーナス役と重複して当籤し得る内部当籤役であるが、ボーナス役と重複して当籤した場合には、そのボーナス役に係る処理(後述の「ボーナス役当籤時」参照)が優先されるため、高確2状態に移行させる制御は行われない。
It should be noted that the chance chance is an internal winning combination that can be won in combination with the bonus combination. However, in the case where the winning combination is won in combination with the bonus combination, the processing relating to that bonus combination (see "When winning bonus combination" below). ) Is given priority, so control for shifting to the high-
(スイカ1当籤時)
非有利区間であり、ボーナス非当籤状態であるときに、スイカ1(「F_スイカ1」)に当籤した場合、メインCPU101は、ART抽籤を行う。具体的には、例えば、8/256の確率で、通常有利区間の本前兆状態を経由して有利区間のエンディング1状態に移行させることを決定し(すなわち、ART当籤を決定し)、248/256の確率で、通常有利区間の高確3状態に移行させるが、有利区間には移行させないことを決定する(すなわち、ART非当籤を決定する)。なお、この場合、さらに、所定の確率で、通常有利区間の本前兆状態を経由して有利区間のラインバトル状態に移行させることを決定可能としてもよい。
(At the time of winning one watermelon)
When the watermelon 1 (“
ART当籤が決定された場合、及びART非当籤が決定された場合、いずれの場合にも、メインCPU101は、スイカ1当籤に基づいて移行する通常有利区間の遊技期間(前兆期間)を決定するための抽籤を行う。具体的には、例えば、前兆期間「9」〜「16」ゲームのうちのいずれか一の前兆期間を抽籤により決定する。この場合、例えば、前兆期間「9」ゲームが決定されると、通常有利区間の遊技期間に「9」ゲームがセットされ、前兆期間「16」ゲームが決定されると、通常有利区間の遊技期間に「16」ゲームがセットされる。なお、この場合、移行先が本前兆状態であるか、高確3状態であるかに応じて、異なる確率で一のゲーム数が決定されるようにすればよい。例えば、本前兆状態に移行する場合には、高確3状態に移行する場合よりも相対的に長い前兆期間が決定されやすいように抽籤確率を設定することができる。
In either case when the ART winning is determined and when the ART non-winning is determined, the
このように、スイカ1に当籤した場合、ART当籤が決定されれば、次回遊技から少なくとも前兆期間抽籤で決定された回数の遊技の間、通常有利区間の本前兆状態に制御され、本前兆状態の終了後は、有利区間のエンディング準備状態に制御される(後述の図34参照)。また、ART非当籤が決定されれば、次回遊技から少なくとも前兆期間抽籤で決定された回数の遊技の間、通常有利区間の高確3状態に制御される。
In this way, if the winning of the
(ボーナス役当籤時)
非有利区間であり、ボーナス非当籤状態であるときに、ボーナス役(「F_BB1」、「F_BB2」、「F_BB3」及び「F_BB4」)に当籤した場合、メインCPU101は、ART抽籤を行う。なお、各設定値間で当籤確率の異なる「F_BB3+F_スイカ2」又は「F_BB4+F_スイカ2」が内部当籤役として決定された場合には、ART抽籤は行われない。すなわち、「F_BB3+F_スイカ2」又は「F_BB4+F_スイカ2」が内部当籤役として決定された場合には、通常有利区間の各遊技状態に移行することなく、非有利区間(通常状態)のフラグ間状態となり、その後非有利区間(通常状態)のボーナス状態となり、当該ボーナス状態が終了すると、非有利区間(通常状態)のボーナス非当籤状態に戻る。
(When winning the bonus role)
When the bonus combination (“F_BB1”, “F_BB2”, “F_BB3” and “F_BB4”) is won in the non-advantageous section and the bonus non-winning state, the
ボーナス役当籤時のART抽籤では、具体的には、例えば、64/256の確率で、ボーナス状態の終了後に有利区間のラインバトル準備状態を経由して有利区間のラインバトル状態に移行させることを決定し(すなわち、ART当籤を決定し)、192/256の確率で、通常有利区間の高確4状態に移行させるが、有利区間には移行させないことを決定する(すなわち、ART非当籤を決定する)。なお、この場合、さらに、所定の確率で、ボーナス状態の終了後に有利区間のエンディング準備状態を経由して有利区間のエンディング1状態に移行させることを決定可能としてもよい。
In the ART lottery at the time of winning the bonus role, specifically, for example, with the probability of 64/256, it is possible to shift to the line battle state of the advantageous section via the line battle preparation state of the advantageous section after the bonus state ends. It is determined (that is, ART winning is determined), and with a probability of 192/256, it is determined to shift to the high-
ART当籤が決定された場合、及びART非当籤が決定された場合、いずれの場合にも、メインCPU101は、まず、遊技状態を高確4状態(通常有利区間)に移行させる。これにより、次回遊技から高確4状態に制御される。なお、フラグ間状態において高確4状態が継続する期間は、フラグ間状態からボーナス状態に移行するまで(持ち越されたボーナス役が成立するまで)としてもよいし、高確4状態となってから「9」ゲームの間(すなわち、高確1状態や高確2状態と同様)としてもよい。また、ART当籤が決定された場合には、フラグ間状態を、高確4状態でなく、本前兆状態(通常有利区間)に移行させるようにしてもよい。また、フラグ間状態では、実際には高確4状態としての各種の抽籤は行われないことから、このフラグ間状態を、通常有利区間であるが、高確1〜高確4状態及び本前兆状態とは異なる状態(例えば、「フラグ間通常有利状態」)として定義し、ボーナス役当籤時には、このフラグ間通常有利状態(通常有利区間)に移行させるようにしてもよい。
In either case when the ART winning is determined and when the ART non-winning is determined, the
そして、ボーナス状態となった後、当該ボーナス状態が終了したとき、メインCPU101は、ART当籤が決定されていれば、有利区間のラインバトル準備状態に移行させ、ART非当籤が決定されていれば、通常有利区間の高確4状態を継続させるとともに、通常有利区間の遊技期間に「32」ゲームをセットする。これにより、ボーナス終了後から少なくとも32回の遊技の間、高確4状態に制御される。
When the bonus state ends after the bonus state, the
<通常有利区間中の遊技性>
次に、図34を参照して、通常有利区間中の遊技の流れについて説明する。なお、図34では、通常有利区間中の遊技の流れの概要を示している。本実施形態では、上述したように、非有利区間の通常状態において、弱レア役に当籤したことに基づいて移行される高確1状態、チャンス目に当籤したことに基づいて移行される高確2状態、スイカ1に当籤したことに基づいて移行される高確3状態、ボーナス役に当籤したことに基づいて移行される高確4状態、及び有利区間(ART)に移行することが決定されている本前兆状態を有する。
<Game play during normal advantage section>
Next, with reference to FIG. 34, the flow of the game in the normal advantage section will be described. In addition, in FIG. 34, the outline of the flow of the game in the normal advantageous section is shown. In the present embodiment, as described above, in the normal state of the non-advantageous section, the high-
まず、メインCPU101は、フラグ間状態(RT5状態)又はボーナス状態である場合、及びボーナス非当籤状態であって本前兆状態である場合(すなわち、すでに有利区間に移行することが決定されている場合)を除き、単位遊技ごとにART移行可能状態抽籤を行う。このART移行可能状態抽籤では、通常有利区間においてボーナス役に当籤した場合に、有利区間に移行することが決定される状態(ART移行可能状態)であるか否かが決定される。このART移行可能状態抽籤において、ART移行可能状態とすることが決定されている場合(ART移行可能状態抽籤に当籤している場合)に、ボーナス役が当籤した場合には、そのボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態の終了後に有利区間に移行させることが決定され、ART移行可能状態とすることが決定されていない場合(ART移行可能状態抽籤に当籤していない場合)に、ボーナス役が当籤した場合には、そのボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態の終了後に有利区間に移行させず、通常有利区間(より詳細には、高確4状態)が継続することが決定される。
First, the
ART移行可能状態抽籤では、具体的には、例えば、高確1状態及び高確2状態であれば、64/256の確率で、ART移行可能状態を設定し(ART移行可能状態に当籤させ)、192/256の確率で、ART移行可能状態を設定しない(ART移行可能状態に非当籤させる)。また、例えば、高確3状態及び高確4状態であれば、128/256の確率で、ART移行可能状態を設定し(ART移行可能状態に当籤させ)、128/256の確率で、ART移行可能状態を設定しない(ART移行可能状態に非当籤させる)。なお、ART移行可能状態の当籤確率は上述したものに限られず、適宜設定可能である。例えば、高確1状態、高確2状態、高確3状態、高確4状態の順に、順次当籤確率が高まるように設定することもできるし、単に、各々の遊技状態で当籤確率が異なるように設定することもできる。
In the ART transferable state lottery, specifically, for example, in the case of the highly accurate 1 state and the highly accurate 2 state, the ART transferable state is set with a probability of 64/256 (the ART transferable state is won). , With a probability of 192/256, do not set the ART transferable state (not win the ART transferable state). Further, for example, if there are 3 highly accurate states and 4 highly accurate states, the ART transferable state is set with a probability of 128/256 (the ART transferable state is won), and the ART transfer is performed with a probability of 128/256. Do not set the possible state (not win to the ART transferable state). The winning probability of the ART transferable state is not limited to the above-mentioned one, and can be set as appropriate. For example, it is possible to set the winning probability to increase sequentially in the order of high-
また、ART移行可能状態抽籤は、単位遊技ごとに行われるものとなっているが、通常有利区間において、一度ART移行可能状態が設定された場合には、当該通常有利区間が終了するまで、そのART移行可能状態が維持されるようにすることもできる。この場合には、一度ART移行可能状態が設定されると、以降当該通常有利区間が終了するまで、ART移行可能状態抽籤を行う必要はない。一方、単位遊技ごとに行なう場合には、単位遊技の開始時であって、ボーナス役に当籤したか否かを判別する前に、まず、当該単位遊技をART移行可能状態とするか否かを抽籤し、その後、当該単位遊技においてボーナス役に当籤したか否かを判別するようにすればよい。 Also, the ART transferable state lottery is performed for each unit game, but if the ART transferable state is set once in the normal advantageous section, until the normal advantageous section ends, The ART transferable state can be maintained. In this case, once the ART transferable state is set, it is not necessary to perform the ART transferable state lottery thereafter until the normal advantageous section ends. On the other hand, in the case of playing for each unit game, at the start of the unit game and before determining whether or not the bonus combination is won, first, whether or not the unit game can be set to the ART transferable state is determined. It may be determined by lottery, and then whether or not the bonus combination is won in the unit game.
また、非有利区間では、各設定値間で当籤確率の異なる「F_BB3+F_スイカ2」又は「F_BB4+F_スイカ2」が内部当籤役として決定された場合には、有利区間に移行するか否かが決定されないようになっていたが、通常有利区間では、「F_BB3+F_スイカ2」又は「F_BB4+F_スイカ2」が内部当籤役として決定された場合にも、ART移行可能状態となっていれば、当該ボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態の終了後に有利区間に移行することが決定される。
In addition, in the non-advantageous section, if “F_BB3+
次に、メインCPU101は、状態間移行等制御処理を行う。この状態間移行等制御処理では、内部当籤役に基づいて、通常有利区間内における各遊技状態の移行制御を行うとともに、所定の条件にしたがって通常有利区間の遊技期間を再セットするなどの処理を行う。この状態間移行等制御処理の内容については、以下に詳述する。
Next, the
(チャンス目当籤時)
通常有利区間であり、ボーナス非当籤状態であるときに、チャンス目(「F_チャンス目A1」〜「F_チャンス目A4」及び「F_チャンス目B1」〜「F_チャンス目B4」)に当籤した場合、メインCPU101は、現在の状態が高確1状態又は高確2状態であり、RT状態がRT3状態でなければ、高確2状態をセットし、通常有利区間の遊技期間に「9」ゲームを再セットする。例えば、高確1状態(9ゲーム)で、5回の遊技を行ったときに、チャンス目に当籤した場合には、「9」ゲームが再セットされることで、実質的には通常有利区間の遊技期間が5ゲーム分延長されることとなる。
(At the chance of winning)
When it is a normal advantageous section and the bonus is not won, the chance chance (“F_chance eye A1” to “F_chance eye A4” and “F_chance eye B1” to “F_chance eye B4”) is won. , The
また、現在の状態が高確3状態であり、RT状態がRT3状態でなければ、通常有利区間の遊技期間に「9」ゲームを再セットする。また、現在の状態が高確4状態であり、RT状態がRT3状態でなければ、現在の通常有利区間の遊技期間の残りゲーム数が8ゲーム以下であれば、通常有利区間の遊技期間に「9」ゲームを再セットする。すなわち、チャンス目に当籤したことに基づいて通常有利区間の遊技期間が適宜延長される。
If the current state is the highly accurate 3 state and the RT state is not the RT3 state, the "9" game is reset in the game period of the normal advantageous section. In addition, if the current state is the high-
なお、上記において、RT状態がRT3状態であるとき、チャンス目に当籤しても通常有利区間の遊技期間が再セットされないのは、RT3状態は、遊技者に有利なリプレイ役の当籤確率が設定された遊技状態であるが、基本的に8ゲーム間しか継続しない遊技状態となっており、また、後述するように、通常有利区間のRT3状態では、フラグ間状態(RT5状態)と同様に、制限なく押し順小役の押し順報知が行われるようになっていることから、通常有利区間の終了とRT3状態の終了とを連動させ、RT3状態であっても遊技者のボーナス役当籤に対する期待感を損なわないようにするためである。 In addition, in the above, when the RT state is the RT3 state, the game period of the normal advantageous section is not reset even if the chance is won. The RT3 state sets the winning probability of the replay combination advantageous to the player. Although it is a game state that has been played, it is basically a game state that continues only for 8 games, and as will be described later, in the RT3 state of the normal advantageous section, like the flag state (RT5 state), Since the push order notification of the push order small winning combination is made without any limitation, the end of the normal advantage section and the end of the RT3 state are linked, and the expectation for the bonus winning of the player even in the RT3 state. This is so as not to impair the feeling.
もっとも、通常有利区間のRT3状態であるとき、通常有利区間の終了が、RT3状態の終了よりも必ず1ゲーム遅くなるように、通常有利区間の遊技期間が設定される。すなわち、通常有利区間の遊技期間は、少なくともRT3状態の遊技期間(8ゲーム)よりも長い期間に設定される。本実施形態では、通常有利区間が開始されると状態表示器の点灯が開始され、通常有利区間から有利区間に移行した場合にはその点灯が継続する一方、通常有利区間において有利区間に移行しなかった場合には通常有利区間が終了するときにその点灯が終了するようになっている。 However, in the RT3 state of the normal advantageous section, the game period of the normal advantageous section is set such that the end of the normal advantageous section is always one game later than the end of the RT3 state. That is, the game period of the normal advantage section is set to be a period longer than at least the game period (8 games) in the RT3 state. In the present embodiment, the lighting of the status indicator is started when the normal advantageous section is started, and when the normal advantageous section is shifted to the advantageous section, the lighting is continued, while the normal advantageous section is shifted to the advantageous section. If not, the lighting is normally terminated when the advantageous zone ends.
したがって、例えば、通常有利区間のRT3状態、あるいは通常有利区間のRT5状態において、同様の期待感演出(ボーナス役当籤、あるいはART当籤を遊技者に期待させる演出)を行う場合、通常有利区間とRT3状態とが同じゲームで終了させるようにした場合には、その期待感演出の実行中に、状態表示器の点灯が終了してしまう場合がある。この場合、期待感演出によって最終的にその当否が報知される前に、非当籤であることが遊技者に認識されてしまうことになる。そこで、本実施形態では、例えば、通常有利区間のRT3状態、及び通常有利区間のRT5状態においては、8ゲーム間にわたって同様の期待感演出を実行し、この期待感演出により、8ゲーム目に最終的な当否を報知するようにしているが、通常有利区間をその後も1ゲーム継続させることで、状態表示器の点灯態様によってはその当否が認識できないようにし、遊技者の興趣の維持を図ることを可能としている。 Therefore, for example, in the RT3 state of the normal advantageous section or the RT5 state of the normal advantageous section, when performing the same expected feeling effect (a bonus winning combination or an effect that makes the player expect the ART winning), the normal advantageous section and RT3 When the game is finished in the same state as the state, the lighting of the state indicator may be finished while the expectation effect is being executed. In this case, the player will recognize that the winning is non-winning before the result is finally notified by the expected feeling production. Therefore, in the present embodiment, for example, in the RT3 state of the normal advantageous section and the RT5 state of the normal advantageous section, the same expected feeling effect is executed over eight games, and by this expected effect effect, the final feeling is given to the eighth game. While the normal advantageous section is continued for one game after that, it is not possible to recognize whether it is right or wrong depending on the lighting mode of the status indicator, and the interest of the player is maintained. Is possible.
また、通常有利区間において、RT3状態が終了した場合であっても、残りの期間(例えば、1ゲーム間)は未だ通常有利区間であるため、ここでの内部当籤役の種別によっては、通常有利区間が延長される場合もあることから、例えば、期待感演出においてボーナス役に当籤していないことが報知された場合であっても、遊技者は通常有利区間の延長を願って遊技を継続しようと考える。この意味においても、遊技者の興趣の維持を図ることを可能としている。 Further, even if the RT3 state is ended in the normal advantageous section, the remaining period (for example, one game) is still the normal advantageous section, and therefore, depending on the type of the internal winning combination here, the normal advantageous section is usually advantageous. Since the section may be extended, for example, even when it is informed that the bonus combination is not won in the expected effect production, the player normally hopes to extend the advantageous section and continues the game. I think. In this sense, it is possible to maintain the interest of the player.
なお、実行され得る期待感演出は、例えば、表示装置11に表示される映像による連続演出であってもよいし、その他演出装置(例えば、スピーカ群84やLED群85)によって行われる連続演出であってもよい。また、必ずしも連続演出である必要もなく、遊技者の期待感を高めるために行われる演出であれば、どのような演出であってもよい。例えば、通常有利区間のRT3状態、あるいは通常有利区間のRT5状態における所定回数目(例えば、8ゲーム目)遊技において、その当否が報知されるものであってもよい。この場合、所定回数目の遊技が何ゲーム目であるかを8ゲームを超えない範囲で任意に、あるいは抽籤により決定するようにしてもよい。
The expectation effect that can be executed may be, for example, a continuous effect by the image displayed on the
また、RT状態にかかわらず通常有利区間の本前兆状態にあっては、上述した期待感演出が行われるようにしてもよい。この場合、期待感演出が実行され得る期間は、通常有利区間のRT3状態、あるいはRT5状態と同様としてもよいし、それよりも長い期間にわたって実行されるものとしてもよい。 In addition, regardless of the RT state, the above-described expectation effect may be performed in the normal sign section of the normal advantageous section. In this case, the period in which the expectation effect can be executed may be the same as the RT3 state or the RT5 state in the normal advantageous section, or may be executed for a longer period than that.
また、現在の状態が本前兆状態であり、RT状態がRT3状態に移行した場合(すなわち、「RT3移行目」が表示された場合)には、通常有利区間の遊技期間に「8」ゲームを再セットする。この場合、通常有利区間が終了すると有利区間に移行するため、RT3状態の終了と通常有利区間の終了を完全に連動させることで、(通常有利区間を残存させず)遊技者により有利な有利区間への移行が優先される。また、この場合、すでに上述した期待感演出が行われている場合には、そのまま当該期待感演出がその終了まで行われるようにしてもよいし、再度新たな期待感演出が8ゲーム間にわたって行われるようにしてもよい。また、RT状態がRT3状態に移行したことに基づいて期待感演出も延長され得るようにしてもよい。 Further, when the current state is this omen state and the RT state shifts to the RT3 state (that is, when the “RT3 shift eye” is displayed), the “8” game is normally played during the game period of the advantageous section. Reset it. In this case, since the normal advantageous section is shifted to the advantageous section when the normal advantageous section ends, by completely interlocking the end of the RT3 state and the end of the normal advantageous section, the advantageous section which is more advantageous to the player (without leaving the normal advantageous section) Is prioritized. Further, in this case, when the above-described expected feeling effect has already been performed, the expected feeling effect may be continuously performed until the end, or a new expected feeling effect is performed again for eight games. You may want to be told. Further, the anticipation effect may be extended based on the transition from the RT state to the RT3 state.
(スイカ1当籤時)
通常有利区間であり、ボーナス非当籤状態であるときに、スイカ1(「F_スイカ1」)に当籤した場合、メインCPU101は、本前兆状態でなければ(すなわち、未だART当籤が決定されていなければ)、非有利区間と同様にART抽籤を行う。
(At the time of winning one watermelon)
When the watermelon 1 (“
そして、メインCPU101は、現在の状態が高確1〜高確3状態のいずれかの状態であり、RT状態がRT3状態であり、ART非当籤であれば、高確3状態をセットするが、通常有利区間の遊技期間の再セットは行わない。また、現在の状態が高確1〜高確4状態のいずれかの状態であり、RT状態がRT3状態であり、ART当籤であれば、本前兆状態をセットし、RT3状態の残りゲーム数分のゲーム数を通常有利区間の遊技期間に再セットする。
Then, the
また、現在の状態が高確1又は高確2状態であり、RT状態がRT3状態でなく、ART非当籤であれば、高確3状態をセットし、再度上述した前兆期間抽籤を行って再セットされる通常有利区間の遊技期間を決定する。また、現在の状態が高確1〜高確4状態のいずれかの状態であり、RT状態がRT3状態でなく、ART当籤であれば、本前兆状態をセットし、高確1状態、高確2状態又は高確4状態であった場合には、再度上述した前兆期間抽籤を行って再セットされる通常有利区間の遊技期間を決定する。なお、高確3状態であった場合には、通常有利区間の遊技期間の再セットは行わない。
If the current state is the high-
(ボーナス役当籤時)
通常有利区間であり、ボーナス非当籤状態であるときに、ボーナス役(「F_BB1」、「F_BB2」、「F_BB3」及び「F_BB4」)に当籤した場合、メインCPU101は、現在の通常有利区間がART移行可能状態でなければ、高確4状態をセットし、ボーナス状態終了後の高確4状態における通常有利区間の遊技期間に「32」ゲームを再セットする。また、現在の通常有利区間がART移行可能状態であれば、本前兆状態をセットし、ボーナス状態終了後の本前兆状態における通常有利区間の遊技期間に「0」ゲームを再セットする(すなわち、ボーナス状態終了後、すぐに有利区間のラインバトル準備状態に移行させる)。
(When winning the bonus role)
When the bonus combination (“F_BB1”, “F_BB2”, “F_BB3”, and “F_BB4”) is won in the bonus non-winning state, the
通常有利区間であり、ボーナス非当籤状態及びフラグ間状態であるときに、押し順小役に当籤した場合、メインCPU101は、押し順小役の押し順報知を行う。具体的には、指示モニタにおいて、ナビデータに対応する数値を表示するとともに、副制御回路200側で押し順報知が可能となるように、ナビデータに相当する情報を含むコマンドを送信する。
When it is a normal advantageous section and the bonus non-winning state and the state between the flags are achieved and the winning combination of the pressing order is won, the
ここで、本実施形態では、RT状態がRT3状態又はRT5状態であれば、当該通常有利区間が終了するまで、押し順小役に当籤する度に押し順報知が行われる一方、RT状態がRT3状態及びRT5状態以外であれば、当該通常有利区間中、1回に限り、押し順小役の押し順報知が行われるようになっている。なお、RT状態がRT3状態及びRT5状態以外である場合の押し順報知の上限回数は1回に限られるものではなく、適宜設定可能である。例えば、「2回」としてもよいし、「3回」としてもよい。 Here, in the present embodiment, if the RT state is the RT3 state or the RT5 state, the push order notification is performed each time the push order small winning combination is won until the normal advantageous section ends, while the RT state is RT3. If it is other than the state and the RT5 state, the push order notification of the push order small winning combination is performed only once in the normal advantageous section. It should be noted that the upper limit of the push order notification when the RT state is other than the RT3 state and the RT5 state is not limited to one, and can be set as appropriate. For example, it may be “twice” or “three times”.
また、本実施形態では、RT状態がRT3状態であるとき、当該通常有利区間が終了するまで、押し順小役に当籤する度に押し順報知が行われるものとしているが、例えば、RT状態がRT3状態となって8ゲームが消化された後、RT3状態は終了するが、通常有利区間は継続する場合もある。この場合、一旦RT3状態となった後は、RT3状態の終了後であっても当該通常有利区間が終了するまで押し順小役の押し順報知が継続されるようにしてもよいし、RT3状態が終了したことに連動して押し順小役の押し順報知も終了され、通常有利区間のみが継続するようにしてもよい。すなわち、RT状態がRT3状態である期間のみ、押し順報知が行われるようにすることもできる。 Further, in the present embodiment, when the RT state is the RT3 state, the push order notification is performed each time the push order small winning combination is won until the normal advantageous section ends, but for example, the RT state is After 8 games have been exhausted in the RT3 state, the RT3 state ends, but the normal advantageous section may continue in some cases. In this case, after the RT3 state is once entered, the push order notification of the push order small winning combination may be continued until the normal advantageous section ends even after the RT3 state ends, or the RT3 state. It may be configured such that the push order notification of the push order small winning combination is also terminated in association with the completion of the above, and only the normal advantageous section continues. That is, the push order notification may be performed only during the period when the RT state is the RT3 state.
また、例えば、RT状態がRT3状態でないときに通常有利区間に移行し、通常有利区間においてRT状態がRT3状態となる場合もある。この場合、すでに1回の押し順報知が行われる場合には、その後のRT3状態でもその上限回数を有効として押し順報知が行われないようにしてもよいし、その後のRT3状態ではその上限回数を無効として押し順報知が行われるようにしてもよい。また、この場合、1回も押し順報知が行われていない場合には、その後のRT3状態でもその上限回数を有効として押し順報知が1回に限って行われるようにしてもよいし、その後のRT3状態ではその上限回数を無効として押し順報知が行われるようにしてもよい。RT状態がRT5状態でないときに通常有利区間に移行し、通常有利区間においてRT状態がRT5状態となる場合も同様である。 Further, for example, when the RT state is not the RT3 state, the normal advantageous section may be shifted to, and the RT state may become the RT3 state in the normal advantageous section. In this case, if the push order notification has already been performed once, the upper limit number may be valid in the subsequent RT3 state and the push order notification may not be performed. In the subsequent RT3 state, the upper limit number may be set. May be invalidated and the push order notification may be performed. Further, in this case, if the push order notification is not performed even once, the upper limit number may be valid even in the subsequent RT3 state, and the push order notification may be performed only once. In the RT3 state, the upper limit number of times may be invalidated and the push order notification may be performed. The same applies when the RT state is not the RT5 state and the normal advantageous section is entered, and the RT state becomes the RT5 state in the normal advantageous section.
RT状態がRT3状態及びRT5状態以外である場合の押し順報知の上限回数が1回であるとした場合、通常有利区間において2回以上の押し順報知が行われると、RT状態がRT3状態又はRT5状態であることが確定する。本実施形態では、チャンス目はボーナス役とも重複して当籤可能となっていることから、例えば、非有利区間において、チャンス目に当籤し、RT3移行目が表示されずに通常有利区間に移行していた場合、1回目の押し順報知が行われたときには、ボーナス役に当籤しているか否か(すなわち、フラグ間状態であるRT5状態であるか否か)は認識することは難しい。2回目の押し順報知が行われたときに、RT3状態でないことが確定し、結果としてボーナス役に当籤していることが認識可能になっている。 When the upper limit number of push order notifications when the RT state is other than the RT3 state and the RT5 state is 1, and when the push order notification is normally performed twice or more in the advantageous section, the RT state is the RT3 state or The RT5 state is confirmed. In the present embodiment, the chances can be won in the same manner as the bonus combination. Therefore, for example, in the non-advantageous section, the chance is won, and the RT3 transition is not displayed, and the normal advantageous section is moved to. In this case, it is difficult to recognize whether or not the bonus combination is won (that is, whether or not the state is the RT5 state between the flags) when the first push order notification is performed. When the second push order notification is performed, it is determined that the player is not in the RT3 state, and as a result, it is possible to recognize that the bonus combination is won.
一方、例えば、RT3移行目が表示されて通常有利区間に移行していた場合、押し順報知の回数では、ボーナス役に当籤しているか否か(すなわち、フラグ間状態であるRT5状態であるか否か)は認識することが難しく、例えば、上述した期待感演出の最終的な演出内容などによってボーナス役に当籤していることが認識可能となっている。 On the other hand, for example, when the transition to the third RT3 is displayed and the normal advantageous section is transitioned, whether or not the bonus combination is won in the number of push order notifications (that is, whether the RT5 state is the inter-flag state or not). Whether or not) is difficult to recognize, and for example, it is possible to recognize that the bonus combination is won based on the final effect contents of the above-described expected feeling effect.
すなわち、RT3状態は、リプレイ役の当籤確率が高く、また、例えば、RT1移行目やRT1移行リプが表示されてもRT状態の変動がない遊技状態であるとともに、通常有利区間であれば回数に限度なく押し順小役の押し順報知が行われるため、他のRT状態で通常有利区間の遊技を行うよりも、通常有利区間中の遊技を有利に進めることができるが、その一方で、通常有利区間においては、ボーナス役に当籤しているか否かが認識しにくい遊技状態となっている。 That is, the RT3 state is a gaming state in which the winning probability of the replay combination is high, and for example, the RT state does not change even when the RT1 transition eye or the RT1 transition lip is displayed. Since there is no limit to the notification of the pushing order of the small pushing order, it is possible to advance the game in the normal advantageous section more advantageously than the game in the normal advantageous section in other RT states, but on the other hand, In the advantageous section, it is difficult to recognize whether or not the winning combination is won.
なお、本実施形態では、有利区間中においてボーナス役に当籤し、当該ボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態が作動した場合、当該ボーナス状態においては、遊技者に有利な停止操作の情報(押し順)が報知されるようになっている一方、非有利区間及び通常有利区間中においてボーナス役に当籤し、当該ボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態が作動した場合、当該ボーナス状態においては、遊技者に有利な停止操作の情報(押し順)が報知されないようになっている。これは、通常有利区間においてART移行可能状態であるときにボーナス役に当籤した場合であっても同様である。この場合、ボーナス状態の終了後は有利区間に移行するものの、当該ボーナス状態中には遊技者に有利な停止操作の情報(押し順)が報知されない。押し順報知の具体的内容については、後述の図45を用いて後で説明する。 In the present embodiment, when the bonus combination is won during the advantageous section and the bonus state based on the bonus combination is activated, the information (stop order) of the stop operation advantageous to the player is notified in the bonus state. On the other hand, when the bonus combination is won in the non-advantageous section and the normal advantageous section and the bonus state based on the bonus combination is activated, in the bonus state, the stop operation advantageous to the player is performed. Information (pushing order) is not notified. This is the same even when the bonus combination is won when the ART transition is possible in the normal advantage section. In this case, after the bonus state ends, the advantageous section is shifted to, but during the bonus state, information (stop order) of the advantageous stop operation is not notified to the player. The specific content of the push order notification will be described later with reference to FIG. 45 described later.
また、本実施形態では、図24で説明したように、フラグ間状態において押し順小役に当籤した場合、ボーナス非当籤状態とは異なり、停止操作順序にかかわらず、「上段ベル」、「中段ベル」又は「下段ベル」が成立し、8枚のメダルが払い出されるようになっているが、この前提においても、通常有利区間のフラグ間状態(RT5状態)中では、通常有利区間が終了するまで、ボーナス非当籤状態と同様の押し順報知がなされる。すなわち、通常有利区間のRT5状態においては、押し順役の当籤時に、実際に押し順によって付与される利益が変動するか否かにかかわらず、通常有利区間のRT3状態と同様の押し順報知が行われるようになっている。これは、上述したように、ボーナス役に当籤しているか否かを認識しづらくし、その期待感をより継続させようとする観点からなされるものである。 Further, in the present embodiment, as described with reference to FIG. 24, when the push order small winning combination is won in the inter-flag state, unlike the bonus non-winning state, the “upper bell” and the “middle row” are irrespective of the stop operation order. The "bell" or "lower bell" is established, and eight medals are paid out. Even in this premise, the normal advantage section ends in the flag state (RT5 state) of the normal advantage section. Up to, the push order notification similar to the bonus non-winning state is made. That is, in the RT5 state of the normal advantage section, when the push order winning is won, the same push order notification as in the RT3 state of the normal advantage section is issued regardless of whether the profit actually given by the push order changes. It is supposed to be done. As described above, this is done from the viewpoint of making it difficult to recognize whether or not the bonus combination is won, and to further maintain the expectation.
なお、上述したように、フラグ間状態において押し順小役に当籤した場合、ボーナス非当籤状態と同様に、停止操作順序に応じて払い出させるメダルの枚数を変動させるようにすることもできる。この場合には、通常有利区間のフラグ間状態(RT5状態)中において、押し順報知が行われることにより付与される利益も増加する可能性が高まるようになるので、ボーナス役に当籤しているか否かの期待感を高めるのみならず、付与される利益に関する期待感も高めることができる。 Note that, as described above, in the case of winning the small winning combination in the pressing order in the inter-flag state, the number of medals to be paid out can be changed according to the stop operation order, as in the bonus non-winning state. In this case, it is likely that the profit to be given by the push order notification is also increased during the flag-to-flag state (RT5 state) of the normal advantageous section. Not only can the expectations about whether or not to be raised be raised, but also the expectations regarding the profits to be granted can be increased.
また、通常有利区間であり、ボーナス非当籤状態であるとき、メインCPU101は、単位遊技毎に通常有利区間の遊技期間を更新する。具体的には、通常有利区間の遊技期間の遊技回数を「1」ずつ減算し、続いて、通常有利区間の遊技期間が消化されたか(すなわち、減算結果が「0」となったか)否かを判定する。なお、通常有利区間の遊技期間の更新においては、単位遊技毎に遊技回数を「1」ずつ加算していき、続いて、加算結果が通常有利区間の遊技期間の遊技回数に達したか否かの判定によって、通常有利区間の遊技期間が消化されたか否かを判定するようにしてもよい。
In addition, in the normal advantageous section and in the bonus non-winning state, the
通常有利区間の遊技期間更新の結果、通常有利区間の遊技期間が消化されていない場合(図34中、「期間未消化」)には、通常有利区間を継続させ、通常有利区間のボーナス非当籤状態における遊技が繰り返されることとなる。 As a result of the update of the game period of the normal advantageous section, if the game period of the normal advantageous section has not been exhausted (in FIG. 34, “period not yet exhausted”), the normal advantageous section is continued and the bonus non-winning of the normal advantageous section. The game in the state will be repeated.
また、通常有利区間の遊技期間更新の結果、通常有利区間の遊技期間が消化された場合であって、有利区間に移行することが決定されていない場合(図34中、「期間消化 ART非当籤」)には、通常有利区間を終了させ、非有利区間のボーナス非当籤状態に移行させる。 Further, as a result of the game period update of the normal advantageous section, when the game period of the normal advantageous section has been exhausted and it is not decided to shift to the advantageous section (in FIG. 34, “period exhaustion ART non-winning) )), the normal advantageous section is ended and the bonus non-winning state of the non-advantageous section is entered.
なお、通常有利区間の遊技期間更新の結果、通常有利区間の遊技期間が消化された場合であっても、通常有利区間において1回も押し順小役の押し順報知が行われなかった場合(すなわち、押し順小役に当籤しなかった場合)には、押し順小役の押し順報知が1回行われるまで、通常有利区間が継続されるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、通常有利区間において、遊技者が最低限の利益を得ることを保障することができるのみならず、期間消化後押し順小役の押し順報知が行われるまでの間に、例えば、ART移行可能状態となってボーナス役に当籤させることができれば、ボーナス状態終了後に有利区間に移行させることも可能となることから、遊技性をより多様なものとし、遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。 In addition, even if the game period of the normal advantageous section is exhausted as a result of the update of the game period of the normal advantageous section, if the push order notification of the push order small winning combination is not performed even once in the normal advantageous section ( That is, in the case of not winning the push order small winning combination), the normal advantageous section may be continued until the push order small winning combination is notified once. By so doing, it is possible not only to guarantee that the player obtains the minimum profit in the normal advantage section, but also before the push order notification of the push order small winning combination after the period is exhausted, for example, , If it is possible to win the bonus combination in the ART transitionable state, it is possible to shift to the advantageous section after the bonus state ends, so that the amusement of games can be made more diverse and the enjoyment of the game can be improved. You can
また、通常有利区間の遊技期間更新の結果、通常有利区間の遊技期間が消化された場合であって、有利区間のラインバトル状態に移行することが決定されている場合(図34中、「期間消化 ラインバトル当籤」)には、通常有利区間を終了させ、有利区間のラインバトル準備状態(ボーナス非当籤状態)に移行させる。なお、有利区間は基本的にRT2状態に対応するため、本実施形態では、有利区間のラインバトル状態に移行させる前に、RT2状態に移行するまでの準備期間としてラインバトル準備状態に移行させるようにしているが、通常有利区間が終了するときに偶発的にRT2状態となっていれば、ラインバトル準備状態を経由せず直接ラインバトル状態に移行させるようにしてもよい。また、RT0状態とRT2状態とは、ともにリプレイ役の当籤確率が最も高い遊技状態であることから(図16及び図17参照)、通常有利区間が終了するときに偶発的にRT0状態となっていれば(あるいは、RT3状態が終了したことに基づいてRT0状態に移行していれば)、ラインバトル準備状態を経由せず直接ラインバトル状態に移行させるようにしてもよい。 Further, when the game period of the normal advantageous section is exhausted as a result of the update of the game period of the normal advantageous section, and it is determined to shift to the line battle state of the advantageous section (in FIG. 34, “period”). In the "digest line battle winning", the normal advantageous section is ended, and the line battle preparation state (bonus non-winning state) of the advantageous section is entered. Since the advantageous section basically corresponds to the RT2 state, in the present embodiment, before the transition to the line battle state of the advantageous section, the line battle preparation state is set as a preparation period until the RT2 state is set. However, if the RT2 state is accidentally set at the end of the normal advantageous section, the line battle state may be directly entered without going through the line battle preparation state. Further, since the RT0 state and the RT2 state are both game states in which the winning probability of the replay combination is the highest (see FIGS. 16 and 17), the RT0 state is accidentally set to the RT0 state when the normal advantageous section ends. If so (or if the RT0 state is entered based on the termination of the RT3 state), the line battle state may be directly entered without going through the line battle preparation state.
また、通常有利区間の遊技期間更新の結果、通常有利区間の遊技期間が消化された場合であって、有利区間のエンディング1状態に移行することが決定されている場合(図34中、「期間消化 エンディング1当籤」)には、通常有利区間を終了させ、有利区間のエンディング準備状態(ボーナス非当籤状態)に移行させる。なお、通常有利区間が終了するときに、なお、有利区間は基本的にRT2状態に対応するため、本実施形態では、有利区間のエンディング1状態に移行させる前に、RT2状態に移行するまでの準備期間としてエンディング準備状態に移行させるようにしているが、通常有利区間が終了するときに偶発的にRT2状態となっていれば、エンディング準備状態を経由せず直接エンディング1状態に移行させるようにしてもよい。また、RT0状態とRT2状態とは、ともにリプレイ役の当籤確率が最も高い遊技状態であることから(図16及び図17参照)、通常有利区間が終了するときに偶発的にRT0状態となっていれば(あるいは、RT3状態が終了したことに基づいてRT0状態に移行していれば)、エンディング準備状態を経由せず直接エンディング1状態に移行させるようにしてもよい。 Further, as a result of the game period update of the normal advantageous section, when the game period of the normal advantageous section has been exhausted and it is determined to shift to the ending 1 state of the advantageous section (in FIG. 34, “period”). In the "digest ending 1 win", the normal advantageous section is ended and the ending section of the advantageous section is shifted to the ending preparation state (bonus non-winning state). Note that when the normal advantageous section ends, the advantageous section basically corresponds to the RT2 state. Therefore, in the present embodiment, before the transition to the RT2 state is performed before the transition to the advantageous 1 ending 1 state. Although it is arranged to shift to the ending preparation state as a preparation period, if it is accidentally in the RT2 state when the normal advantageous section ends, it is arranged to directly shift to the ending 1 state without going through the ending preparation state. May be. Further, since the RT0 state and the RT2 state are both game states in which the winning probability of the replay combination is the highest (see FIGS. 16 and 17), the RT0 state is accidentally set to the RT0 state when the normal advantageous section ends. If so (or if the RT0 state is entered based on the termination of the RT3 state), the ending 1 state may be directly entered without going through the ending preparation state.
<非有利区間及び通常有利区間の遊技性のまとめ>
以下では、非有利区間及び通常有利区間中の遊技性(一部、有利区間中の遊技性を含む)について、その要部を簡潔にまとめて説明する。
<Summary of game characteristics of non-advantageous section and normal advantageous section>
In the following, with regard to the game characteristics in the non-advantageous section and the normal advantage section (including a part of the game characteristics in the advantage section), the main parts thereof will be briefly summarized.
(1)「チャンス目」は、ボーナス役と同時に内部当籤役として決定可能となっている。
(2)「チャンス目」に当籤した場合、ボーナス役も同時に内部当籤役として決定されている場合には、RT状態がRT5状態となる。この場合、非有利区間であれば、通常有利区間(例えば、「高確4状態」、あるいは「フラグ間通常有利状態」)に移行させる。
(3)「チャンス目」に当籤した場合、ボーナス役が同時に内部当籤役として決定されていない場合であって、停止操作が特定の態様で行われたことに基づいて「RT3移行目」が表示された場合には、RT状態がRT3状態となる。この場合、「RT3移行目」が表示されたか否かにかかわらず、非有利区間であれば、通常有利区間(例えば、「高確2状態」)に移行させる。
(4)「チャンス目」に当籤して移行した通常有利区間(例えば、「高確2状態」)は、少なくともRT3状態が継続する期間(例えば、8ゲーム間)よりも長い期間(例えば、9ゲーム間)、継続可能となっている。
(1) The “chance eye” can be determined as an internal winning combination as well as a bonus combination.
(2) If the "winning chance" is won and the bonus combination is also determined as an internal winning combination, the RT state becomes the RT5 state. In this case, if it is a non-advantageous section, it is shifted to a normal advantageous section (for example, “high-
(3) If the winning combination is a “chance eye”, the bonus winning combination is not determined as an internal winning combination at the same time, and the “RT3 transition eye” is displayed based on that the stop operation is performed in a specific mode. If so, the RT state becomes the RT3 state. In this case, regardless of whether or not the “RT3 shift eye” is displayed, if it is a non-advantageous section, it is shifted to a normal advantageous section (for example, “
(4) The normal advantageous section (e.g., "
(5)非有利区間でボーナス役に当籤し、当該ボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態が終了したとき、ART当籤が決定されていれば、有利区間(例えば、「ラインバトル準備状態」)に移行させる。
(6)非有利区間でボーナス役に当籤し、当該ボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態が終了したとき、ART当籤が決定されていなければ(ART非当籤が決定されていれば)、特定期間(例えば、32ゲーム間)、通常有利区間(例えば、「高確4状態」)に移行する。
(7)非有利区間でボーナス役に当籤した場合、そのボーナス役が、複数の設定値間で当籤確率が同じであるボーナス役である場合には、有利区間(ART)に移行させるか否かが決定されるが、複数の設定値間で当籤確率が異なるボーナス役である場合には、有利区間(ART)に移行させるか否かが決定されない。
(8)通常有利区間でボーナス役に当籤した場合、そのボーナス役が、複数の設定値間で当籤確率が同じであるボーナス役である場合、及び複数の設定値間で当籤確率が異なるボーナス役である場合のいずれの場合であっても、有利区間(ART)に移行させるか否かが決定される。
(5) When the bonus winning combination based on the bonus combination is won in the non-advantageous section and the bonus state based on the bonus combination ends, and the ART winning is determined, the section is shifted to the advantageous section (for example, “line battle preparation state”).
(6) When the bonus combination is won in the non-advantageous section and the bonus state based on the bonus combination ends, if the ART winning is not determined (if the ART non-winning is determined), a specific period (for example, During 32 games), a normal advantageous section (for example, “high-
(7) Whether or not to shift to the advantageous section (ART) when the bonus combination is won in the non-advantageous section and when the bonus combination has the same winning probability among a plurality of setting values However, in the case of a bonus combination having different winning probabilities among a plurality of setting values, it is not determined whether or not to shift to the advantageous section (ART).
(8) When a bonus combination is won in a normal advantageous section, the bonus combination is a bonus combination having a same winning probability among a plurality of setting values, and a bonus combination having a different winning probability between a plurality of setting values In either case, it is determined whether to shift to the advantageous section (ART).
(9)通常有利区間において、RT状態がRT3状態である場合、通常有利区間が終了するまで、押し順小役の押し順報知が行われる。
(10)通常有利区間において、RT状態がRT5状態である場合、通常有利区間が終了するまで、押し順小役の押し順報知が行われる。
(11)通常有利区間において、RT状態がRT3状態又はRT5状態でない場合、所定回数(例えば、1回)に限り、押し順小役の押し順報知が行われる。
(12)有利区間でボーナス役に当籤した場合、当該ボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態においては、押し順小役の押し順報知が行われるが、非有利区間及び通常有利区間でボーナス役に当籤した場合、当該ボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態においては、有利区間に移行させることが決定されているか否かにかかわらず、押し順小役の押し順報知は行われない。
(9) When the RT state is the RT3 state in the normal advantage section, the push order notification of the push order small winning combination is performed until the normal advantage section ends.
(10) When the RT state is the RT5 state in the normal advantageous section, the push order notification of the push order small winning combination is performed until the normal advantageous section ends.
(11) In the normal advantageous section, when the RT state is not the RT3 state or the RT5 state, the pushing order notification of the pushing order small winning combination is performed only a predetermined number of times (for example, once).
(12) When the winning combination is won in the advantageous section, in the bonus state based on the bonus combination, the pushing order notification of the small pushing order is performed, but when the winning combination is won in the non-advantageous section and the normal advantageous section. In the bonus state based on the bonus hand, the push order notification of the push order small combination is not performed regardless of whether it is determined to shift to the advantageous section.
このように、本実施形態では、「チャンス目」が内部当籤役として決定された場合に、少なくとも9ゲーム間、通常有利区間に制御可能であるとともに、ART当籤が決定された場合に、有利区間に制御可能であり、「RT3移行目」が表示された場合に、RT状態をRT3状態に変移させることが可能であるとともに、ボーナス役が内部当籤役として決定された場合に、RT状態をRT5状態に変移させることが可能となっている。また、「チャンス目」とボーナス役とを同時に内部当籤役として決定可能となっている。そして、通常有利区間であってRT3状態及びRT5状態である場合には、押し順小役について、遊技者に有利な停止操作の手順が報知されるようになっている。 As described above, in the present embodiment, when the “chance eye” is determined as the internal winning combination, it is possible to control the normal advantageous section for at least nine games, and when the ART winning is determined, the advantageous section is obtained. When the "RT3 transition" is displayed, the RT state can be changed to the RT3 state, and when the bonus combination is determined as the internal winning combination, the RT state is changed to RT5. It is possible to change to a state. In addition, it is possible to determine the "chance eye" and the bonus combination at the same time as an internal winning combination. Then, when the normal advantageous section is in the RT3 state and the RT5 state, the procedure of the stop operation advantageous to the player for the small push order combination is informed.
これにより、通常有利区間では、非有利区間よりも付与されるメダルの枚数が増加する可能性が高まるとともに、ボーナス状態に遷移するか否かの期待感も高まることから、遊技者に有利な状態の移行に関する興趣の向上を図ることができる。 As a result, in the normal advantage section, the number of medals to be given increases as compared with the non-advantageous section, and the expectation whether or not to shift to the bonus state also increases. It is possible to improve interest in the transition of.
また、本実施形態では、通常有利区間が継続可能な期間(9ゲーム)が、RT3状態が継続可能な期間(8ゲーム)よりも長い期間に設定されている。 Further, in the present embodiment, the period during which the normal advantageous period can be continued (9 games) is set to be longer than the period during which the RT3 state can be continued (8 games).
これにより、特定の遊技状態(RT3状態)が終了するか否かにかかわらず、遊技者の期待感を維持させることが可能となるため、さらに遊技者に有利な状態の移行に関する興趣の向上を図ることができる。 As a result, the player's expectation can be maintained regardless of whether or not the specific game state (RT3 state) ends, and thus the interest in transition to a state more advantageous to the player can be further improved. Can be planned.
また、本実施形態では、「チャンス目」は、停止操作が特定の態様(例えば、適切なタイミング)で行われた場合に「RT3移行目」が表示され、特定の態様で行われなかった場合に「RT3移行目」が表示されない内部当籤役であり、通常有利区間であってRT3状態及びRT5状態である場合には、当該通常有利区間が終了するまで、押し順小役について遊技者に有利な停止操作の手順が報知され、通常有利区間であってRT3状態及びRT5状態でない場合には、所定回数(例えば、1回)に限り、押し順小役について遊技者に有利な停止操作の手順が報知されるようになっている。 Further, in the present embodiment, the “opportunity” is displayed when the stop operation is performed in a specific mode (for example, appropriate timing), and is not performed in the specific mode. In the case of an internal winning combination in which the "RT3 transition eye" is not displayed, and the normal advantageous section is in the RT3 state and the RT5 state, it is advantageous to the player about the pushing order small combination until the normal advantageous section ends. The procedure of the stop operation is notified, and when the normal advantageous section is not in the RT3 state and the RT5 state, the procedure of the stop operation advantageous to the player for the small pushing order is limited to a predetermined number of times (for example, once). Is notified.
これにより、「チャンス目」が当籤したときに、ボーナス役も同時に内部当籤役として決定されているか否かと、「RT3移行目」が表示されたか否かと、によって通常有利区間の有利度合いや内容を変動させることができるため、さらに遊技者に有利な状態の移行に関する興趣の向上を図ることができる。 As a result, when the "chance eye" is won, whether or not the bonus combination is also determined as an internal winning combination at the same time and whether or not the "RT3 transition" is displayed, the advantage degree and contents of the normal advantage section are determined. Since it can be changed, it is possible to further enhance the interest in the transition to a state advantageous to the player.
また、本実施形態では、非有利区間において当籤したボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態が終了した場合に、ART当籤が決定されている場合には有利区間に移行させ、ART当籤が決定されていない場合には、特定期間(例えば、32ゲーム間)、通常有利区間(例えば、高確4状態)に移行させるようになっている。
In addition, in the present embodiment, when the bonus state based on the bonus combination that has been won in the non-advantageous section is ended, if the ART winning is determined, it is shifted to the advantageous section, and if the ART winning is not determined. Is designed to shift to a normal advantageous section (for example, high-
また、本実施形態では、通常有利区間のいずれかの遊技状態であるとき、複数の設定値間で当籤確率が同じであるボーナス役、及び複数の設定値間で当籤確率が異なるボーナス役のいずれに当籤した場合であっても、有利区間に移行させるか否かが決定されるが、非有利区間であるときには、複数の設定値間で当籤確率が異なるボーナス役に当籤した場合には、有利区間に移行させるか否かが決定されないようになっている。 Further, in the present embodiment, when the gaming state of any of the normal advantageous sections, whichever of the bonus combinations the winning probability is the same among the plurality of setting values and the winning probability which is different among the plurality of setting values. Even if the winning combination is won, it is decided whether or not to shift to the advantageous section, but when it is a non-advantageous section, it is advantageous when winning a bonus combination having different winning probabilities among a plurality of set values. It is not decided whether or not to shift to the section.
これにより、ボーナス役に当籤したときの遊技状態やその種別によって、その後の遊技状態(遊技区間)の遷移をより多様なものとすることができるため、さらに遊技者に有利な状態の移行に関する興趣の向上を図ることができる。 As a result, the transition of the subsequent game state (game section) can be made more diverse depending on the game state when the bonus combination is won and the type thereof. Can be improved.
また、本実施形態では、通常有利区間及び有利区間では、押し順小役について遊技者に有利な停止操作の手順を報知可能であり、有利区間においてボーナス状態に制御された場合にも押し順小役について遊技者に有利な停止操作の手順を報知可能であるが、非有利区間及び通常有利区間においてボーナス状態に制御された場合には押し順小役について遊技者に有利な停止操作の手順を報知可能としないようになっている。 Further, in the present embodiment, in the normal advantageous section and the advantageous section, it is possible to inform the player of the procedure of the stop operation which is advantageous for the small pushing order combination, and the pushing order is small even when the bonus state is controlled in the advantageous section. It is possible to inform the player of the stop operation procedure that is advantageous for the winning combination, but when the bonus state is controlled in the non-advantageous section and the normal advantage section, the procedure of the stopping operation that is advantageous for the player for the small pushing order combination is displayed. Notification is not possible.
これにより、有利区間に移行する期待度が高まるとともに、付与されるメダルの枚数が増加する可能性も高まる遊技区間である通常有利区間を設けることができるため、遊技者に有利な状態の移行に関する興趣の向上を図ることができるとともに、このような遊技区間を設ける場合であっても、遊技者に付与される利益が過度となってしまうことを抑制し、遊技者の射幸心が過度に煽られることを抑制することもできる。 As a result, it is possible to provide a normal advantageous section, which is a game section in which the degree of expectation of shifting to the advantageous section is increased and the possibility of increasing the number of medals to be given is increased. It is possible to improve the enjoyment of the game, and even when such a game section is provided, it is possible to prevent the profit given to the player from becoming excessive, and to excessively encourage the player's ambition. It can also be suppressed.
<ラインバトル状態中の遊技性>
次に、図35〜図41を参照して、有利区間のラインバトル状態中の遊技の流れについて説明する。なお、図35では、有利区間のラインバトル状態中の遊技の流れの概要を示している。また、図36では、少なくとも有利区間のラインバトル準備状態及びラインバトル状態において参照される各種テーブルであって、メインROM102に格納されている各種データテーブルの一例を示している。また、図37〜図41では、ラインバトル状態を継続させるか否かの継続度合いが変動する態様について説明するために、表示装置11の表示例を示している。本実施形態では、ラインバトル状態は、インターバル状態、バトル状態、及び継続抽籤状態を有する。また、本実施形態では、ラインバトル状態は、基本的にラインバトル準備状態を経由して移行される遊技状態となっている。
<Playability during line battle>
Next, with reference to FIGS. 35 to 41, the flow of the game during the line battle state of the advantageous section will be described. Note that FIG. 35 shows an outline of the flow of the game during the line battle state of the advantageous section. Further, FIG. 36 shows an example of various data tables stored in the
(ラインバトル準備状態)
メインCPU101は、非有利区間又は通常有利区間において、ボーナス役に当籤したことに基づいてART当籤が決定された場合、当該ボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態が終了したときに、ラインバトル準備状態に移行させる。また、有利区間のラインバトル準備状態及びラインバトル状態において、ボーナス役に当籤し、当該ボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態が終了したときに、ラインバトル準備状態に移行させる(すなわち、ラインバトル状態に復帰させる)。この場合、ボーナス状態が終了したときのRT状態はRT4状態であり(図13参照)、RT状態がRT2状態に移行するまでラインバトル準備状態を維持する。
(Line battle preparation state)
When the ART winning is determined based on the winning of the bonus combination in the non-advantageous section or the normal advantageous section, the
なお、この場合、RT4状態において「RT1移行目」を表示させるため、RT4状態において「RT1移行目」が表示されるまでは、押し順小役及び押し順リプレイについての押し順報知は行われず、RT状態がRT1状態に移行してから、押し順小役及び押し順リプレイについての押し順報知が開始される。また、この場合、RT4状態において「RT3移行目」が表示されてRT3状態に移行した場合にも、押し順小役及び押し順リプレイについての押し順報知が開始される。なお、RT3状態に移行したときに、ラインバトル準備状態を終了させ、ラインバトル状態に移行させるようにしてもよい。 In this case, since the "RT1 transition" is displayed in the RT4 state, the push order notification regarding the push sequence small win and the push sequence replay is not performed until the "RT1 transition" is displayed in the RT4 state. After the RT state shifts to the RT1 state, the push order notification of the push order small combination and the push order replay is started. Further, in this case, even when the "RT3 shift eye" is displayed in the RT4 state and the state shifts to the RT3 state, the push order notification regarding the push order minor combination and the push order replay is started. The line battle preparation state may be terminated and the line battle state may be set when the RT3 state is entered.
また、上述したように、例えば、非有利区間又は通常有利区間において、ボーナス役以外の特定役(例えば、「スイカ1」)に当籤したことに基づいてART抽籤が行われる場合に、その当籤結果としてラインバトル状態に移行させることを決定可能とする場合には、通常有利区間が終了したとき、ラインバトル準備状態に移行させる。この場合も、RT状態がRT2状態に移行するまでラインバトル準備状態を維持する。
In addition, as described above, for example, when the ART lottery is performed based on the fact that a specific combination other than the bonus combination (for example, “
もっとも、例えば、RT状態がRT0状態である場合に、押し順小役及び押し順リプレイについての押し順報知が行われたにもかかわらず、その押し順報知にしたがわずに停止操作が行われた結果、「RT1移行目」や「RT1移行リプ」が表示され、RT状態がRT1状態に移行した場合、RT状態がRT2状態とはなっていなくとも、ラインバトル状態に移行させるようにしてもよい。権利獲得抽籤準備状態及びエンディング準備状態においても同様である。すなわち、各準備状態において押し順ミスが発生した場合には、RT状態がRT2状態となっていない場合であっても、対応する遊技状態に移行させるようにしてもよい。 However, for example, in the case where the RT state is the RT0 state, although the push order notification about the push order minor combination and the push order replay was performed, the stop operation was performed without following the push order notification. As a result, “RT1 transition eye” or “RT1 transition lip” is displayed, and when the RT state is transited to the RT1 state, the line battle state may be transited even if the RT state is not the RT2 state. .. The same applies to the right acquisition lottery preparation state and the ending preparation state. That is, when a pressing order error occurs in each preparation state, even if the RT state is not the RT2 state, the game state may be shifted to the corresponding gaming state.
ラインバトル準備状態では、敵選択テーブル抽籤、味方選択テーブル抽籤、及び味方獲得抽籤が行われる。なお、これらの遊技性に関する抽籤は一例であり、ラインバトル準備状態においては他の抽籤も行うことが可能である。また、これらの遊技性に関する抽籤は、通常有利区間の各遊技状態においても行われるようにすることが可能である。この場合、通常有利区間から有利区間に移行した場合には、通常有利区間における抽籤結果がラインバトル状態において反映され、通常有利区間から有利区間に移行しなかった場合には、通常有利区間における抽籤結果が破棄(クリア)されるようにすればよい。 In the line battle preparation state, the enemy selection table lottery, the ally selection table lottery, and the ally acquisition lottery are performed. Note that the lottery related to these game characteristics is an example, and other lottery can be performed in the line battle preparation state. In addition, the lottery regarding these game characteristics can be performed even in each game state of the normal advantageous section. In this case, when the normal advantageous zone is shifted to the advantageous zone, the lottery result in the normal advantageous zone is reflected in the line battle state, and when the normal advantageous zone is not shifted to the advantageous zone, the lottery in the normal advantageous zone is drawn. The result should be discarded (cleared).
敵選択テーブル抽籤では、後述のバトル状態においてバトルの対象となる敵キャラクタに対応する情報を選択するための敵選択テーブルが決定される。具体的には、メインCPU101は、図36Aに示す敵選択テーブル抽籤テーブルを参照し、敵撃破回数と、抽籤値と、に基づいて、敵選択テーブル1〜8のいずれかのテーブルを選択する。ここで、敵撃破回数は、後述のバトル状態において敵HPが「0」となって権利獲得状態に移行された回数、及び後述の継続抽籤状態においてラインバトル状態が継続することが決定された回数の累計回数(すなわち、ラインバトル状態が継続した回数)として、メインRAM103内の所定領域に記憶された回数を示す。
In the enemy selection table lottery, an enemy selection table for selecting information corresponding to an enemy character to be a battle target in a later-described battle state is determined. Specifically, the
図36Aに示す敵選択テーブル1〜8では、それぞれ敵撃破回数に応じて、ラインバトル状態の継続度合いを変動させることが可能となるように、各情報が割り当てられている。図36Aに示す敵選択テーブル1〜8内において、「低」は、ラインバトル状態の継続度合いについて遊技者の有利度合いが相対的に低いことを示し、「中」は、ラインバトル状態の継続度合いについて遊技者の有利度合いが中程度であることを示し、「高」は、ラインバトル状態の継続度合いについて遊技者の有利度合いが高いことを示している。 In the enemy selection tables 1 to 8 shown in FIG. 36A, each information is assigned so that the degree of continuation of the line battle state can be changed according to the number of times the enemy is destroyed. In the enemy selection tables 1 to 8 shown in FIG. 36A, "Low" indicates that the player's advantage degree is relatively low with respect to the continuation degree of the line battle state, and "Medium" indicates the continuation degree of the line battle state. Indicates that the degree of advantage of the player is moderate, and “high” indicates that the degree of advantage of the player is high regarding the degree of continuation of the line battle state.
本実施形態では、バトルの対象となる敵キャラクタに対応する情報として、「A」(敵キャラクタA)、「B」(敵キャラクタB)、「C」(敵キャラクタC)、及び「D」(敵キャラクタD)が設定されており、後述のバトル突入時敵種別抽籤においてそのいずかが決定される。ここで、本実施形態では、後述するように、「A」、「B」、「C」、「D」の順にラインバトル状態が継続する期待度が順次高まるようになっている。すなわち、「A」、「B」、「C」、「D」の順で遊技者の有利度合いが順次高まるようになっている。 In the present embodiment, as information corresponding to the enemy character that is the target of the battle, "A" (enemy character A), "B" (enemy character B), "C" (enemy character C), and "D" ( Enemy character D) is set, and one of them is determined in the lottery for enemy type at the time of entering a battle, which will be described later. Here, in the present embodiment, as will be described later, the degree of expectation that the line battle state will continue in the order of “A”, “B”, “C”, and “D” gradually increases. That is, the advantage degree of the player is sequentially increased in the order of “A”, “B”, “C”, and “D”.
そして、後述のバトル突入時敵種別抽籤では、決定された敵選択テーブルが示す情報が「低」であれば、遊技者の有利度合いが相対的に低い敵キャラクタ(例えば、「A」)が決定されやすく、遊技者の有利度合いが相対的に高い敵キャラクタ(例えば、「D」)は決定されにくくなっており、決定された敵選択テーブルが示す情報が「高」であれば、遊技者の有利度合いが相対的に低い敵キャラクタ(例えば、「A」)は決定されにくく、遊技者の有利度合いが相対的に高い敵キャラクタ(例えば、「D」)が決定されやすくなっている。また、決定された敵選択テーブルが示す情報が「中」であれば、その間の確率となる。このようにして、ラインバトル状態の継続度合いについての遊技者の有利度合いを変動させることが可能となっている。 Then, in the later-described battle entry type lottery, if the information indicated by the determined enemy selection table is "low", an enemy character (for example, "A") with a relatively low player's advantage is determined. The enemy character (for example, “D”) that is easy to be played and the player's advantage degree is relatively high is hard to be determined, and if the information indicated by the determined enemy selection table is “high”, the player's advantage level is high. An enemy character (for example, "A") having a relatively low advantage degree is difficult to be determined, and an enemy character (for example, "D") having a relatively high advantage degree for the player is easily determined. Further, if the information indicated by the determined enemy selection table is "medium", the probability is in the meantime. In this way, it is possible to change the degree of advantage of the player regarding the degree of continuation of the line battle state.
味方選択テーブル抽籤では、後述のバトル状態においてバトルを有利に進めるための味方キャラクタに対応する情報を選択するための味方選択テーブルが決定される。具体的には、メインCPU101は、図36Bに示す味方選択テーブル抽籤テーブルを参照し、敵撃破回数と、抽籤値と、に基づいて、味方選択テーブル1〜8のいずれかのテーブルを選択する。なお、敵撃破回数はすでに説明したため、ここでの説明は省略する。
In the ally selection table lottery, a ally selection table for selecting information corresponding to the ally character for advancing the battle in an advantageous manner in the later-described battle state is determined. Specifically, the
本実施形態では、バトルを有利に進めるための味方キャラクタに対応する情報として、「1」(味方キャラクタ1)、「2」(味方キャラクタ2)、「3」(味方キャラクタ3)、及び「4」(味方キャラクタ4)が設定されており、後述のバトル突入時味方種別抽籤において、一又は複数の味方キャラクタが付与されるか、あるいは付与されないかが決定される。ここで、本実施形態では、後述するように、付与された味方キャラクタの数が多いほどラインバトル状態が継続する期待度が順次高まるようになっている。すなわち、付与された味方キャラクタの数が多いほどで遊技者の有利度合いが順次高まるようになっている。 In the present embodiment, as information corresponding to the ally character for advancing the battle advantageously, "1" (ally character 1), "2" (ally character 2), "3" (ally character 3), and "4". (Allied character 4) is set, and it is determined in the later-described battle entry ally type lottery whether one or a plurality of ally characters are given or not. Here, in the present embodiment, as will be described later, the greater the number of assigned ally characters, the higher the degree of expectation that the line battle state will continue will be successively increased. That is, as the number of alliance characters provided increases, the degree of advantage of the player gradually increases.
そして、後述のバトル突入時味方種別抽籤では、決定された味方選択テーブルが示す情報が「激低」であれば、味方キャラクタが付与されることがほとんどなく、決定された味方選択テーブルが示す情報が「低」であれば、味方キャラクタが付与されにくく、また、付与されたとしても1つであり、決定された味方選択テーブルが示す情報が「中」であれば、味方キャラクタが付与されやすいが、複数の味方キャラクタは付与されにくく、決定された味方選択テーブルが示す情報が「高」であれば、味方キャラクタが付与されやすく、複数の味方キャラクタが付与されやすくなっている。このようにして、ラインバトル状態の継続度合いについての遊技者の有利度合いを変動させることが可能となっている。 Then, in the later-described battle ally type lottery, if the information indicated by the determined ally selection table is "extremely low", the ally character is rarely given and the information indicated by the determined ally selection table is displayed. Is low, the ally character is hard to be given, and even if it is given, if the information shown in the decided ally selection table is "medium", the ally character is easily given. However, it is difficult to attach a plurality of ally characters, and if the information indicated by the determined ally selection table is “high”, the ally character is likely to be attached and the plurality of ally characters are likely to be attached. In this way, it is possible to change the degree of advantage of the player regarding the degree of continuation of the line battle state.
味方獲得抽籤では、後述のバトル突入時味方種別抽籤とは別に、予め味方キャラクタを獲得させるか否かの権利を付与するか否かが決定される。メインCPU101は、例えば、特定役(例えば、「チャンス目」や「スイカ1」)に当籤したことに基づいて、所定確率(例えば、1/2の確率)で味方キャラクタを獲得させるか否かを決定する。なお、味方獲得抽籤において参照されるテーブルについては、図示を省略している。
In the ally acquisition lottery, in addition to the ally type lottery at the time of entering a battle, which will be described later, whether or not to grant a right to previously acquire an ally character is determined. For example, the
ここで、味方獲得抽籤の結果、当該権利を付与することが決定された場合、バトル状態の突入時において、後述のバトル突入時味方種別抽籤の結果付与されなかった味方キャラクタの番号のうち、最も小さい番号の味方キャラクタが付与される。例えば、後述のバトル突入時味方種別抽籤において、味方キャラクタ「2」が付与されていた場合、当該権利を獲得していれば、さらに味方キャラクタ「1」が付与されるようになる。すなわち、後述のバトル突入時味方種別抽籤では、具体的な味方キャラクタの種別を含めて付与されるか否かが決定されるのに対し、味方獲得抽籤では、少なくともいずれかの味方キャラクタが付与されることを決定するか否かが決定される。 Here, if it is decided as a result of the ally acquisition lottery to grant the right, at the time of entering the battle state, among the numbers of the ally characters not given as the result of the ally type lottery at the time of entering the battle, the number is the most. A ally character with a small number is added. For example, in the case of a ally type lottery at the time of entering a battle to be described later, when the ally character “2” is given, if the right is acquired, the ally character “1” is further given. That is, in the later-described battle entry ally type lottery, it is determined whether or not the specific ally character type is included, whereas in the ally acquisition lottery, at least one ally character is provided. Whether or not to decide is decided.
なお、味方獲得抽籤の結果付与することが決定された権利は、基本的に、その後のバトル状態が終了したときに消滅し、再度当該権利を得るには再度味方獲得抽籤に当籤する必要がある。この意味において、当該権利は、後述の「永続権利」とは異なる「限定的権利」であるともいい得る。 The right decided to be granted as a result of the ally acquisition lottery basically disappears when the subsequent battle state ends, and it is necessary to win the ally acquisition lottery again in order to obtain the right again. .. In this sense, the right can be said to be a “limited right” different from the “perpetual right” described later.
(インターバル状態)
上述したように、ラインバトル準備状態が終了したときに、メインCPU101は、まず、ラインバトル状態開始時のインターバル状態に移行させる。インターバル状態は、3ゲーム間継続する状態となっており、インターバル状態における遊技期間が3ゲームを経過すると、バトル状態に移行する。インターバル状態では、上述した味方獲得抽籤が行われる。
(Interval state)
As described above, when the line battle preparation state ends, the
インターバル状態が終了したとき、バトル突入時敵種別抽籤、及びバトル突入時味方種別抽籤が行われる。 When the interval state ends, the lottery type for enemies at the time of battle entry and the lottery type for allies at the time of battle entry are performed.
バトル突入時敵種別抽籤では、上述した敵選択テーブル抽籤の結果決定された敵選択テーブル(1〜8のいずれか)に基づき、現在の敵撃破回数に応じた期待度の情報(「低」〜「高」のいずれか)が参照され、バトルの対象となる敵キャラクタに対応する情報(「A」〜「D」のいずれか)が決定される。なお、バトル突入時敵種別抽籤において参照されるテーブルについては、図示を省略している。 In the enemies type lottery at the time of battle entry, based on the enemy selection table (any one of 1 to 8) determined as a result of the above-mentioned lottery of the enemy selection table, information on the degree of expectation according to the current number of defeated enemies (“low” The information (one of “A” to “D”) corresponding to the enemy character that is the target of the battle is determined by referring to “one of “high”). It should be noted that the tables referred to in the lottery on the enemy type at the time of entering the battle are not shown.
バトル突入時味方種別抽籤では、上述した味方選択テーブル抽籤の結果決定された味方選択テーブル(1〜8のいずれか)に基づき、現在の敵撃破回数に応じた期待度の情報(「激低」〜「高」のいずれか)が参照され、バトルを有利に進めるための味方キャラクタに対応する情報が決定される。なお、バトル突入時味方種別抽籤では、例えば、『「1」に当籤』、『「2」に当籤』、『「3」に当籤』、『「4」に当籤』、『「1・2」に当籤』、・・・『「1〜4」に当籤』、といったように、複数の味方キャラクタが付与されることが決定され得る一方で、後述の永続権利(あるいは、限定的権利)として「1」が付与されている場合に、『「1」に当籤』が決定された場合には、その抽籤結果は破棄される(反映されない)ようになっている。また、この場合、『「1・2」に当籤』が決定された場合には、そのうちの『「1」に当籤』の部分のみが破棄され(反映されず)、『「2」に当籤』の部分は反映されるようになっている。したがって、味方獲得抽籤で他に権利が付与されていなければ、この場合の味方キャラクタは「1」と「2」となる。なお、バトル突入時味方種別抽籤において参照されるテーブルについては、図示を省略している。 In the ally type lottery at the time of battle entry, based on the ally selection table (any one of 1 to 8) determined as a result of the ally selection table lottery described above, information on the degree of expectation according to the current number of enemy defeats (“extremely low”) ~ "High") is referred to, and information corresponding to the teammate character for advancing the battle is determined. In addition, in the ally type lottery at the time of battle entry, for example, ““1” is won”, ““2” is won”, “3” is won”, “4” is won”, “1.2”. While it is possible to determine that a plurality of ally characters are given, such as “winning winning”,... “Winning “1 to 4””, a permanent right (or a limited right) described later is “ When "1" is given and "win" is determined, the lottery result is discarded (not reflected). Further, in this case, when “winning for “1.2” is decided, only the part of “winning for “1”” is discarded (not reflected) and “winning for “2””. The part of is reflected. Therefore, if no other right is given in the team acquisition lottery, the teammate characters in this case are “1” and “2”. The tables referred to in the ally type lottery at the time of battle entry are not shown.
また、インターバル状態が終了したとき、敵HPと味方HPとに初期値「32」がセットされる。そして、バトル突入時敵種別抽籤の結果に応じた敵種別がセットされるとともに、バトル突入時味方種別抽籤の結果、味方獲得抽籤の結果に基づき付与された限定的権利の有無、及び後述の永続権利獲得抽籤の結果に基づき付与された永続権利の有無に応じた味方種別がセットされる。 Further, when the interval state ends, the initial value “32” is set to the enemy HP and the friend HP. Then, the enemy type according to the result of the lottery type at the time of entering the battle is set, and the result of the lottery type at the time of entering the battle, the presence or absence of the limited right granted based on the result of the lottery for obtaining the ally, and the permanence described later. Based on the result of the right acquisition lottery, the ally type according to the presence or absence of the permanent right granted is set.
(バトル状態)
上述したように、インターバル状態が終了したときに、メインCPU101は、次に、ラインバトル状態中のバトル状態に移行させる。バトル状態は、少なくとも31ゲーム間継続する状態となっており、この間に、味方側が攻撃をすれば、その攻撃のダメージ分敵HPが減少し、敵側が攻撃をすれば、その攻撃のダメージ分味方HPが減少するという遊技性を有する。そして、バトル状態の終了前に敵HPが「0」以下となった場合には、権利獲得抽籤状態に移行させ、バトル状態の終了前に敵HPが「0」以下とならなかった場合には、後述の継続抽籤状態に移行させる。
(Battle state)
As described above, when the interval state ends, the
なお、バトル状態では、「弱レア役」又は「チャンス目」に当籤した場合、その当籤した遊技は、バトル状態の遊技期間のカウント対象には含まれないようになっている。すなわち、「弱レア役」又は「チャンス目」に当籤した回数だけ、バトル状態の遊技期間が延長されるようになっている。また、バトル状態では、「チャンス目」に当籤し、「RT3移行目」が表示されてRT状態がRT3状態となった場合、このRT3状態の8ゲーム間は、バトル状態の遊技期間のカウント対象には含まれないようになっている。すなわち、RT3状態が継続する遊技回数分、バトル状態の遊技期間が延長されるようになっている。 In the battle state, when a "weak rare role" or "chance eye" is won, the winning game is not included in the count of the game period in the battle state. That is, the game period in the battle state is extended by the number of times of winning the “weak rare role” or the “chance eye”. In addition, in the battle state, if the “chance eye” is won and the “RT3 transition eye” is displayed and the RT state becomes the RT3 state, the eight games in the RT3 state will be counted during the game period in the battle state. Is not included in. That is, the game period in the battle state is extended by the number of games in which the RT3 state continues.
バトル状態では、被弾リプ時カウンター抽籤、カウンター時与ダメージ抽籤、被弾リプ時防御抽籤、被弾リプ時被ダメージ抽籤、及び与ダメージ抽籤が行われ得る。なお、これらの遊技性に関する抽籤は一例であり、バトル状態においては他の抽籤も行うことが可能である。 In a battle state, a counter lottery for hitting rep, a lottery damage for countering lottery, a defense lottery for hitting lip, a damage lottery for hitting lip, and a damage lottery for hitting can be performed. Note that the lottery related to these game characteristics is an example, and other lottery can be performed in the battle state.
ここで、図37〜図41も参照しながら、バトル状態で行われる各種の遊技性に関する抽籤と、味方キャラクタに対応する情報との関係性について説明する。 Here, with reference to FIGS. 37 to 41, the relationship between the lottery related to various game properties performed in the battle state and the information corresponding to the teammate character will be described.
図37は、ラインバトル状態(より詳細には、バトル状態)において、味方なしの場合(すなわち、味方キャラクタに対応する情報として、「1」〜「4」のいずれもが付与されていない場合)の、表示装置11の表示内容の一例を示す図である。
FIG. 37 is a case where there is no ally in the line battle state (more specifically, the battle state) (that is, when neither “1” to “4” is given as the information corresponding to the ally character). 6 is a diagram showing an example of display contents of the
まず、表示装置11は、バトル状態中の基本的な表示内容として、遊技者自身に相当する味方側の自己キャラクタ(図37〜図41中、「自分」)の現在の「ステータス」を表示するとともに、上述したバトル突入時敵種別抽籤の結果決定された敵側の敵キャラクタ(図37〜図41中、「敵A」。この場合、敵種別「A」が選択されているものとする)の現在の「ステータス」を表示する。
First, the
ステータスは、バトル状態突入時にセットされた、味方HP及び敵HPの残りの数値範囲に対応する情報であり、本実施形態では、味方HP及び敵HPのそれぞれについて、残りの数値範囲が「32〜25」であるとき、ステータス「平常」が設定され、残りの数値範囲が「24〜17」であるとき、ステータス「小破」が設定され、残りの数値範囲が「16〜9」であるとき、ステータス「中破」が設定され、残りの数値範囲が「8〜1」であるとき、ステータス「大破」が設定され、残りの数値範囲が「0」以下となったとき、ステータス「撃破」が設定される。なお、敵HPについてはステータス「撃破」が設定される場合があるが、味方HPについてはステータス「撃破」が設定される場合はなく、味方HPの残り数値範囲が「1」以下となるときには、味方HPは「1」に固定され、それ以下に減算されることはない。 The status is information corresponding to the remaining numerical range of the friendly HP and the enemy HP set at the time of entering the battle state. In the present embodiment, the remaining numerical range of each of the friendly HP and the enemy HP is “32 to When the status is "25", the status "normal" is set, when the remaining numerical value range is "24 to 17", the status "small break" is set, and when the remaining numerical value range is "16 to 9" , When the status "Medium damage" is set and the remaining numerical value range is "8 to 1", the status "Great damage" is set, and when the remaining numerical value range is "0" or less, the status "Destroyed" Is set. Although the status "destroy" may be set for the enemy HP, the status "defeat" may not be set for the ally HP, and when the remaining numerical range of the ally HP is "1" or less, The ally HP is fixed at "1" and cannot be subtracted below it.
そして、表示装置11は、味方なしの場合、「中段ライン攻撃有効」と表示している。これは、バトル状態において「1」〜「4」のいずれの味方キャラクタも付与されていない場合、センターライン(図37〜図41中、「DL1」)のみがラインバトル状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインとして機能することを意味している。
Then, the
それゆえ、本実施形態では、味方なしの場合、上述した「中段リプ」又は「中段ベル」が表示されるとき(すなわち、「中段リプ」又は「中段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定されたとき)には、味方側の攻撃となり、後述の与ダメージ抽籤が行われる一方、上述した「中段リプ」又は「中段ベル」が表示されず(すなわち、「中段リプ」又は「中段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定されず)、「被弾リプ」(「F_被弾リプ」)に当籤した場合には、敵側の攻撃となり、後述する与ダメージ抽籤は行われず、後述する被弾リプ時被ダメージ抽籤が行われるようになっている。 Therefore, in the present embodiment, when there is no ally, when the above-mentioned "middle-level lip" or "middle-level bell" is displayed (that is, the internal winning combination in which the "middle-level lip" or "middle-level bell" can be displayed is determined. When it is done), it becomes an attack on the ally side, and the damage damage lottery described later is performed, while the above-mentioned "middle-stage lip" or "middle-stage bell" is not displayed (that is, "middle-stage lip" or "middle-stage bell"). If the internal winning combination that can be displayed is not determined), and if you win the “Billed Lip” (“F_Billed Lip”), it becomes an attack on the enemy side and the damage damage lottery described below is not performed The damage damage lottery is now performed.
図38は、ラインバトル状態(より詳細には、バトル状態)において、味方「1」獲得の場合(すなわち、味方キャラクタに対応する情報として「1」が付与されている場合)の、表示装置11の表示内容の一例を示す図である。なお、基本的な表示内容については、図37におけるものと同一であるため、ここでの説明は省略している。
FIG. 38 shows the
表示装置11は、味方「1」獲得の場合、「中段ライン攻撃有効」及び「上段ライン攻撃有効」と表示している。これは、バトル状態において味方キャラクタ「1」が付与されている場合、センターライン(図37〜図41中、「DL1」)及びトップライン(図38〜図41中、「DL2」)がラインバトル状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインとして機能することを意味している。
When the ally "1" is acquired, the
それゆえ、本実施形態では、味方「1」獲得の場合、上述した「中段リプ」又は「中段ベル」が表示されるとき(すなわち、「中段リプ」又は「中段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定されたとき)、及び上述した「上段リプ」又は「上段ベル」が表示されるとき(すなわち、「上段リプ」又は「上段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定されたとき)には、味方側の攻撃となり、後述の与ダメージ抽籤が行われる一方、上述した「中段リプ」又は「中段ベル」が表示されず(すなわち、「中段リプ」又は「中段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定されず)、上述した「上段リプ」又は「上段ベル」が表示されず(すなわち、「上段リプ」又は「上段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定されず)、「被弾リプ」(「F_被弾リプ」)に当籤した場合には、敵側の攻撃となり、後述する与ダメージ抽籤は行われず、後述する被弾リプ時被ダメージ抽籤が行われるようになっている。 Therefore, in the present embodiment, when the ally "1" is acquired, when the above-mentioned "middle lip" or "middle bell" is displayed (that is, the "middle lip" or "middle bell" may be displayed, the internal winnings may be displayed). When the winning combination is determined), and when the above-mentioned “upper lip” or “upper bell” is displayed (that is, when the internal winning combination that can display the “upper lip” or “upper bell” is determined) Will be an attack on the ally side, and the damage damage lottery described below will be performed, while the above-mentioned "middle-stage lip" or "middle-stage bell" is not displayed (that is, "middle-stage lip" or "middle-stage bell" may be displayed. The internal winning combination is not determined), the above-mentioned “upper lip” or “upper bell” is not displayed (that is, the internal winning combination for which “upper lip” or “upper bell” can be displayed is not determined), “ In the case where the hit bullet "(F_ bullet hit)" is won, it becomes an attack on the enemy side and the damage damage lottery described below is not performed, but the damage damage lottery described below is performed.
図39は、ラインバトル状態(より詳細には、バトル状態)において、味方「1」及び「2」獲得の場合(すなわち、味方キャラクタに対応する情報として「1」及び「2」が付与されている場合)の、表示装置11の表示内容の一例を示す図である。なお、基本的な表示内容については、図37におけるものと同一であるため、ここでの説明は省略している。
In FIG. 39, in the line battle state (more specifically, in the battle state), when the teammates “1” and “2” are acquired (that is, “1” and “2” are added as the information corresponding to the teammate character). FIG. 8 is a diagram showing an example of display contents of the
表示装置11は、味方「1」及び「2」獲得の場合、「中段ライン攻撃有効」、「上段ライン攻撃有効」、及び「下段ライン攻撃有効」と表示している。これは、バトル状態において味方キャラクタ「1」及び「2」が付与されている場合、センターライン(図37〜図41中、「DL1」)、トップライン(図38〜図41中、「DL2」)、及びボトムライン(図39〜図41中、「DL3」)がラインバトル状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインとして機能することを意味している。
When the teammates “1” and “2” are acquired, the
それゆえ、本実施形態では、味方「1」及び「2」獲得の場合、上述した「中段リプ」又は「中段ベル」が表示されるとき(すなわち、「中段リプ」又は「中段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定されたとき)、上述した「上段リプ」又は「上段ベル」が表示されるとき(すなわち、「上段リプ」又は「上段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定されたとき)、上述した「下段リプ」又は「下段ベル」が表示されるとき(すなわち、「下段リプ」又は「下段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定されたとき)には、味方側の攻撃となり、後述の与ダメージ抽籤が行われる一方、上述した「中段リプ」又は「中段ベル」が表示されず(すなわち、「中段リプ」又は「中段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定されず)、上述した「上段リプ」又は「上段ベル」が表示されず(すなわち、「上段リプ」又は「上段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定されず)、上述した「下段リプ」又は「下段ベル」が表示されず(すなわち、「下段リプ」又は「下段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定されず)、「被弾リプ」(「F_被弾リプ」)に当籤した場合には、敵側の攻撃となり、後述する与ダメージ抽籤は行われず、後述する被弾リプ時被ダメージ抽籤が行われるようになっている。 Therefore, in this embodiment, when the teammates “1” and “2” are acquired, when the above-mentioned “middle-stage lip” or “middle-stage bell” is displayed (that is, “middle-stage lip” or “middle-stage bell” is displayed). When an internal winning combination that can be performed is determined), when the above-mentioned “upper lip” or “upper bell” is displayed (that is, an internal winning combination that can display “upper lip” or “upper bell” is determined). When the above-mentioned “lower lip” or “lower bell” is displayed (that is, when the internal winning combination for which “lower lip” or “lower bell” can be displayed is determined), While the damage damage lottery described below is performed, the above-mentioned "middle-stage lip" or "middle-stage bell" is not displayed (that is, the internal winning combination in which "middle-stage lip" or "middle-stage bell" can be displayed is determined. No), the above "upper lip" or "upper bell" is not displayed (that is, the internal winning combination for which "upper lip" or "upper bell" can be displayed is not determined), and the above "lower lip" Or, if the “lower bell” is not displayed (that is, the internal winning combination for which the “lower lip” or the “lower bell” can be displayed is not determined), and if the winning hit is “Billed Lip” (“F_Billed Lip”) Is an attack on the enemy side, and the damage damage lottery described below is not performed, but the damage damage lottery during the bullet-received lip described below is performed.
図40は、ラインバトル状態(より詳細には、バトル状態)において、味方「1」〜「3」獲得の場合(すなわち、味方キャラクタに対応する情報として「1」〜「3」が付与されている場合)の、表示装置11の表示内容の一例を示す図である。なお、基本的な表示内容については、図37におけるものと同一であるため、ここでの説明は省略している。
In FIG. 40, in the line battle state (more specifically, in the battle state), when the teammates “1” to “3” are acquired (that is, “1” to “3” are added as information corresponding to the teammate character). FIG. 8 is a diagram showing an example of display contents of the
表示装置11は、味方「1」〜「3」獲得の場合、「中段ライン攻撃有効」、「上段ライン攻撃有効」、「下段ライン攻撃有効」、及び「カウンターあり」と表示している。これは、バトル状態において味方キャラクタ「1」〜「3」が付与されている場合、センターライン(図37〜図41中、「DL1」)、トップライン(図38〜図41中、「DL2」)、及びボトムライン(図39〜図41中、「DL3」)がラインバトル状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインとして機能するとともに、「被弾リプ」(「F_被弾リプ」)に当籤した場合に、後述の被弾リプ時カウンター抽籤及びカウンター時与ダメージ抽籤が行われ得ることを意味している。
When the teammates “1” to “3” are acquired, the
それゆえ、本実施形態では、味方「1」〜「3」獲得の場合、味方「1」及び「2」獲得の場合と後述の与ダメージ抽籤及び後述の被弾リプ時被ダメージ抽籤が行われる態様は同じであるが、それに加え、上述した「中段リプ」又は「中段ベル」が表示されず(すなわち、「中段リプ」又は「中段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定されず)、上述した「上段リプ」又は「上段ベル」が表示されず(すなわち、「上段リプ」又は「上段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定されず)、上述した「下段リプ」又は「下段ベル」が表示されず(すなわち、「下段リプ」又は「下段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定されず)、「被弾リプ」(「F_被弾リプ」)に当籤した場合に、後述の被弾リプ時被ダメージ抽籤が行われる前に、カウンター攻撃を発動させるか否かを決定するための被弾リプ時カウンター抽籤が行われ、これに当籤すると、味方側の攻撃となり、後述のカウンター時与ダメージ抽籤が行われ、後述の被弾リプ時被ダメージ抽籤は行われないようになっている。 Therefore, in the present embodiment, a mode in which when the teammates “1” to “3” are acquired, when the teammates “1” and “2” are acquired, and the damage damage lottery described later and the damage-received lottery at the time of a hit lip described below are performed Is the same, but in addition, the above-mentioned "middle-stage lip" or "middle-stage bell" is not displayed (that is, the internal winning combination for which "middle-stage lip" or "middle-stage bell" can be displayed is not determined), and The “upper lip” or “upper bell” is not displayed (that is, the internal winning combination for which the “upper lip” or “upper bell” can be displayed is not determined), and the “lower lip” or “lower bell” described above is not determined. Is not displayed (that is, the internal winning combination for which “lower lip” or “lower bell” can be displayed is not determined), and if the winning hit is “Billed Lip” (“F_Billed Lip”), Before the damage damage lottery is performed, a hit lottery counter lottery is performed to determine whether to activate a counter attack, and if you win this, it becomes an ally's attack and the counter damage damage lottery described later. Is performed, and damage damage lottery will not be performed at the time of hitting rips described later.
図41は、ラインバトル状態(より詳細には、バトル状態)において、味方「1」〜「4」獲得の場合(すなわち、味方キャラクタに対応する情報として「1」〜「4」が付与されている場合)の、表示装置11の表示内容の一例を示す図である。なお、基本的な表示内容については、図37におけるものと同一であるため、ここでの説明は省略している。
In FIG. 41, in the line battle state (more specifically, in the battle state), when the teammates “1” to “4” are acquired (that is, “1” to “4” are added as information corresponding to the teammate character). FIG. 8 is a diagram showing an example of display contents of the
表示装置11は、味方「1」〜「4」獲得の場合、「中段ライン攻撃有効」、「上段ライン攻撃有効」、「下段ライン攻撃有効」、「カウンターあり」、及び「防御あり」と表示している。これは、バトル状態において味方キャラクタ「1」〜「4」が付与されている場合、センターライン(図37〜図41中、「DL1」)、トップライン(図38〜図41中、「DL2」)、及びボトムライン(図39〜図41中、「DL3」)がラインバトル状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインとして機能するとともに、「被弾リプ」(「F_被弾リプ」)に当籤した場合に、後述の被弾リプ時カウンター抽籤及びカウンター時与ダメージ抽籤が行われ得ること、後述の被弾リプ時カウンター抽籤に当籤しない場合であっても後述の被弾リプ時防御抽籤が行われ得ることを意味している。
When the allies "1" to "4" are acquired, the
それゆえ、本実施形態では、味方「1」〜「4」獲得の場合、味方「1」及び「2」獲得の場合と後述の与ダメージ抽籤、後述の被弾リプ時被ダメージ抽籤、後述の被弾リプ時カウンター抽籤、及びカウンター時与ダメージ抽籤が行われる態様は同じであるが、それに加え、上述した「中段リプ」又は「中段ベル」が表示されず(すなわち、「中段リプ」又は「中段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定されず)、上述した「上段リプ」又は「上段ベル」が表示されず(すなわち、「上段リプ」又は「上段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定されず)、上述した「下段リプ」又は「下段ベル」が表示されず(すなわち、「下段リプ」又は「下段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定されず)、「被弾リプ」(「F_被弾リプ」)に当籤した場合に、後述の被弾リプ時被ダメージ抽籤が行われる前に、カウンター攻撃を発動させるか否かを決定するための被弾リプ時カウンター抽籤が行われ、これに当籤しなかった場合には、被弾リプ時防御抽籤が行われ、これに当籤すると、敵側の攻撃となるが、防御成功となり、後述の被弾リプ時被ダメージ抽籤は行われないようになっている。 Therefore, in the present embodiment, when the teammates “1” to “4” are acquired, when the teammates “1” and “2” are acquired, and the damage damage lottery described later, the damage damage lottery at the time of hitting a lip described later, and the hit damage later described The counter lottery at the time of rip and the damage damage lottery at the time of counter are performed in the same way, but in addition to that, the above-mentioned "middle-stage lip" or "middle-stage bell" is not displayed (that is, "middle-stage lip" or "middle-stage bell"). Is not determined), the above-mentioned “upper lip” or “upper bell” is not displayed (that is, the internal winning combination in which “upper lip” or “upper bell” can be displayed is determined) No), the above-mentioned “lower lip” or “lower bell” is not displayed (that is, the internal winning combination for which “lower lip” or “lower bell” can be displayed is not determined), “bounced lip” (“ F_Billed Lip”), if a lottery for hitting a rep is performed, a lottery for hitting a ripping is performed to determine whether to activate a counter attack before the damage lottery during a ripping hit is described later. If you do not do it, the defense lottery at the time of hitting rip is performed, and if you win this, it will be an attack on the enemy side, but it will be a defense success and the damage lottery at the time of hitting rep will not be performed. ..
なお、本実施形態では、判定ラインとして設定されたラインに、実際に「リプレイ」の図柄や「ベル」の図柄が揃った場合にのみ後述の与ダメージ抽籤が行われ、例えば、押し順小役について押し順報知が行われたにもかかわらず、遊技者の押し順ミスによって実際には「ベル」の図柄が揃わなかった場合には後述の与ダメージ抽籤が行われないようにしてもよいし、判定ラインとして設定されたラインに、「リプレイ」の図柄や「ベル」の図柄が揃い得る(表示され得る)内部当籤役が決定された場合には、実際に「リプレイ」の図柄や「ベル」の図柄が揃うか否かにかかわらず後述の与ダメージ抽籤が行われるようにしてもよい。これらの手法のいずれを採用することもできる。後者の手法を採用する場合には、「判定ライン」は実際に「判定」そのものが行われるラインではなくなるものの、例えば、遊技者に与ダメージ抽籤が行われることを報知可能とするといった意義を有するものとなることから、遊技者にとって重要な意味を持つことには変わりがない。 In the present embodiment, the damage determination lottery described below is performed only when the “replay” symbol and the “bell” symbol are actually aligned on the line set as the determination line, and for example, the pushing order small winning combination. Despite the fact that the push order is informed about, the player may not be allowed to perform the damage damage lottery described below if the "bell" symbols are not actually aligned due to the player's mistake in the push order. , If the internal winning combination in which the “Replay” symbol and the “Bell” symbol can be aligned (can be displayed) is determined on the line set as the judgment line, the “Replay” symbol or the “Bell symbol” is actually determined. The damage damage lottery described below may be performed regardless of whether or not the symbols of “” are aligned. Any of these methods can be adopted. In the case of adopting the latter method, the "judgment line" is not the line on which the "judgment" itself is actually performed, but it has the meaning of being able to inform the player that the damage lottery will be performed, for example. It will still be important to the player as it becomes a thing.
また、図37〜図41では、味方キャラクタ「1」〜「4」が順に増加する例を挙げて説明しているが、味方キャラクタは、バトル突入時味方種別抽籤の結果によっては、例えば、「2」のみ、「3」のみ、「4」のみ、あるいは、「2」及び「3」、「3」及び「4」といったように付与される場合もあり得る。したがって、以下では、味方キャラクタに対応する情報「1」〜「4」の機能を再度簡潔に説明する。 37 to 41, an example in which the teammate characters "1" to "4" are sequentially increased is described, but the teammate character may be, for example, " There may be a case where only "2", "3" only, "4" only, or "2" and "3", "3" and "4" are given. Therefore, in the following, the functions of the information “1” to “4” corresponding to the teammate character will be briefly described again.
味方キャラクタに対応する情報「1」が設定されると、センターライン(図37〜図41中、「DL1」)に加え、トップライン(図38〜図41中、「DL2」)がラインバトル状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインとして機能するようになる。 When the information “1” corresponding to the ally character is set, the top line (“DL2” in FIGS. 38 to 41) in addition to the center line (“DL1” in FIGS. 37 to 41) is in the line battle state. It will function as a judgment line regarding the variation of the continuation degree.
味方キャラクタに対応する情報「2」が設定されると、センターライン(図37〜図41中、「DL1」)に加え、ボトムライン(図39〜図41中、「DL3」)がラインバトル状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインとして機能するようになる。 When the information “2” corresponding to the teammate character is set, the bottom line (“DL3” in FIGS. 39 to 41) in addition to the center line (“DL1” in FIGS. 37 to 41) is in the line battle state. It will function as a judgment line regarding the variation of the continuation degree.
味方キャラクタに対応する情報「3」が設定されると、本来は敵側の攻撃となって味方HPが減少される場合であっても、逆に味方側の攻撃となって敵HPが減少される場合があるようになる。 When the information “3” corresponding to the ally character is set, even if the ally HP is originally reduced by the enemy side attack, the ally side attack is reduced and the enemy HP is reduced. There will be cases where
味方キャラクタに対応する情報「4」が設定されると、本来は敵側の攻撃となって味方HPが減少される場合であっても、味方HPが減少されない場合があるようになる。 When the information “4” corresponding to the ally character is set, even if the ally HP is originally reduced as an attack on the enemy side, the ally HP may not be reduced in some cases.
ここで、味方キャラクタに対応する情報「1」及び「2」のいずれが設定されているか否かにかかわらず、メインCPU101(主制御回路90側)からサブCPU201(副制御回路200側)に対して、当籤役番号「7」、「8」又は「24」が送信された場合(図32参照)、サブCPU201は、例えば、表示装置11において「中段ライン攻撃有効」と表示された箇所を点滅させたり、あるいは強調して表示するなどの処理を行う。これにより、味方側が攻撃することを期待させる演出を行うことができる。
Here, regardless of whether the information “1” or “2” corresponding to the teammate character is set, the main CPU 101 (
また、味方キャラクタに対応する情報「1」が設定されている場合であって、メインCPU101(主制御回路90側)からサブCPU201(副制御回路200側)に対して、当籤役番号「6」又は「23」が送信された場合(図32参照)、サブCPU201は、例えば、表示装置11において「上段ライン攻撃有効」と表示された箇所を点滅させたり、あるいは強調して表示するなどの処理を行う。これにより、味方側が攻撃することを期待させる演出を行うことができる。
Also, when the information “1” corresponding to the teammate character is set, the winning combination number “6” is sent from the main CPU 101 (
また、味方キャラクタに対応する情報「2」が設定されている場合であって、メインCPU101(主制御回路90側)からサブCPU201(副制御回路200側)に対して、当籤役番号「10」又は「25」が送信された場合(図32参照)、サブCPU201は、例えば、表示装置11において「下段ライン攻撃有効」と表示された箇所を点滅させたり、あるいは強調して表示したりするなどの処理を行う。これにより、味方側が攻撃することを期待させる演出を行うことができる。
In the case where the information “2” corresponding to the teammate character is set, the winning combination number “10” is sent from the main CPU 101 (
もっとも、味方側が攻撃することを期待させる演出の態様はこれに限られない。例えば、その他演出装置(例えば、スピーカ群84やLED群85)によって行われる演出であってもよい。また、上述した対応関係にない内部当籤役の当籤役番号が送信された場合であっても、所定確率で上述した演出のうちいずれかの演出が行われるようにしてもよい。
However, the aspect of the effect that the ally side expects to attack is not limited to this. For example, it may be an effect performed by another effect device (for example, the
なお、味方キャラクタに対応する情報の種類や機能は、上述したものに限られない。例えば、特定の味方キャラクタに対応する情報(例えば、「5」)が設定されると、後述の与ダメージ抽籤において決定される与ダメージが増加する(例えば、決定された与ダメージが2倍となる)ような機能を持たせてもよい。また、例えば、特定の味方キャラクタに対応する情報(例えば、「6」)が設定されると、後述の被弾リプ時被ダメージ抽籤において決定される被ダメージが減少する(例えば、決定された被ダメージが1/2となる)ような機能を持たせてもよい。 The type and function of information corresponding to the teammate character are not limited to those described above. For example, when information (for example, “5”) corresponding to a specific ally character is set, the amount of damage determined in the damage damage lottery described later increases (for example, the amount of damage determined is doubled). ) May have a function like this. Further, for example, when the information (for example, “6”) corresponding to a specific ally character is set, the damage received determined in the damage received lottery at the time of the bullet-received rip described below decreases (for example, the determined damage received). May be reduced to 1/2).
また、判定ラインとして機能するラインは、有効ラインに限られない。例えば、特定の味方キャラクタに対応する情報が設定された場合には、有効ラインとは異なるラインであっても、それを特別ラインとし、この特別ラインを判定ラインとして機能させるようにしてもよい。具体的には、例えば、特定の味方キャラクタに対応する情報(例えば、「5」)が設定されると、センターラインに加え、クロスダウンラインがラインバトル状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインとして機能するようにしてもよい。また、例えば、特定の味方キャラクタに対応する情報(例えば、「6」)が設定されると、センターラインに加え、クロスアップラインがラインバトル状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインとして機能するようにしてもよい。 The line functioning as the determination line is not limited to the valid line. For example, when the information corresponding to a specific ally character is set, even if it is a line different from the effective line, it may be set as a special line and this special line may be made to function as a determination line. Specifically, for example, when information (for example, “5”) corresponding to a specific ally character is set, the cross-down line functions as a determination line related to the variation of the continuation degree of the line battle state in addition to the center line. You may do so. Further, for example, when information (for example, “6”) corresponding to a specific ally character is set, the cross-up line functions as a determination line regarding the variation of the continuation degree of the line battle state in addition to the center line. May be.
このような場合、実際の有効ライン上に表示される図柄は、「リプレイ」の図柄揃い、あるいは「ベル」の図柄揃いではないが、このような特別ライン上に表示される図柄が、「リプレイ」の図柄揃い、あるいは「ベル」の図柄揃いとなるように構成されていれば、遊技者は有効ラインと同様に有利さの度合いが変動することを認識できるため、実際の有効ライン数にかかわらず、同様の遊技性を提供することが可能となる。なお、このような観点からは、ラインバトル状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインには、必ずしも有効ラインが含まれる必要はなく、例えば、有効ラインがクロスアップラインの1ラインであるとき、ラインバトル状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインが、センターライン、トップライン、及びボトムラインの最大3ラインから構成されていてもよい。すなわち、ラインバトル状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインを、有効ラインとは異なる特別ラインのみから構成することも可能である。 In such a case, the symbol displayed on the actual activated line is not the "Replay" symbol group or the "Bell" symbol group, but the symbol displayed on such a special line is "Replay". If it is configured so as to be the same as the "Bell" symbol arrangement, the player can recognize that the degree of advantage changes similarly to the activated line, so that the actual number of activated lines is not affected. Instead, it becomes possible to provide the same playability. From this point of view, the determination line regarding the variation in the continuation degree of the line battle state does not necessarily include the effective line. For example, when the effective line is one cross-up line, the line battle The determination line regarding the variation of the degree of continuation of the state may be composed of a maximum of three lines of a center line, a top line and a bottom line. That is, it is possible to configure the determination line regarding the variation of the continuation degree of the line battle state from only a special line different from the effective line.
また、判定ラインを定義する際には、上述した有効ラインと同様に、図柄が一直線に並ぶ各ラインに替えて、あるいはこれとともに、図柄が一直線に並ばないラインを有効ラインとして定義することもできる。すなわち、各列(左リール3L,中リール3C,右リール3R)ごとのいずれか一の図柄(の領域)を通るラインであれば、直線又は折れ線で結んで構成される一又は複数のラインを判定ラインとして設定可能である。
Further, when defining the determination line, similarly to the above-mentioned effective line, instead of each line in which the symbols are arranged in a straight line, or together with this, a line in which the symbols are not in a straight line can be defined as an effective line. .. That is, as long as it is a line that passes through (any area of) one of the symbols in each column (left
例えば、左リール3Lの上段領域、中リール3Cの下段領域、及び、右リール3Rの上段領域を結ぶライン(V時の変則ライン)などを判定ラインとして定義するようにしてもよい。すなわち、本実施形態では、リール表示窓4の枠内に、3行×3列の態様で図柄が表示されるようになっていることから、27通りの判定ラインを定義することが可能であり、そのうち少なくともいずれか1つのラインが判定ラインとして定義されるようにすればよい。
For example, a line (an irregular line at V time) connecting the upper region of the
ここで、再度バトル状態の説明に戻る。上述したように、味方キャラクタに対応する情報「3」が設定されている場合には、「被弾リプ」(「F_被弾リプ」)に当籤した場合に、被弾リプ時カウンター抽籤が行われる。被弾リプ時カウンター抽籤では、メインCPU101は、所定確率で、カウンター攻撃を発動させること(当籤)、又はカウンター攻撃を発動させないこと(非当籤)のいずれかを決定する。なお、被弾リプ時カウンター抽籤において参照されるテーブルについては、図示を省略している。
Here, let us return to the explanation of the battle state again. As described above, when the information “3” corresponding to the teammate character is set, when the “ball hit rep” (“F_ball hit rep”) is won, the ball hit rep counter lottery is performed. In the hit lottery counter lottery, the
被弾リプ時カウンター抽籤に当籤した場合には、続いて、カウンター時与ダメージ抽籤が行われる。カウンター時与ダメージ抽籤では、メインCPU101は、図36Cに示すカウンター時与ダメージ抽籤テーブルを参照し、抽籤値に基づいて、いずれか1つの与ダメージの値を決定する。なお、与ダメージの値が決定されると、その値が敵HPの値から減算され、敵HPの値が更新される。また、これにともなって、上述した敵の「ステータス」が適宜更新される。また、この場合には、被弾リプ時被ダメージ抽籤は行われない。
If you win the counter lottery at the time of a hit rip, the damage damage lottery at the time of the counter is subsequently performed. In the counter-time given damage lottery, the
一方、被弾リプ時カウンター抽籤に当籤しなかった場合であって、味方キャラクタに対応する情報「4」が設定されている場合、及び味方キャラクタに対応する情報「3」は設定されていないが「4」が設定されている場合には、被弾リプ時防御抽籤が行われる。被弾リプ時カウンター抽籤では、メインCPU101は、所定確率で、防御を発動させること(当籤)、又は防御を発動させないこと(非当籤)のいずれかを決定する。なお、被弾リプ時防御抽籤において参照されるテーブルについては、図示を省略している。
On the other hand, when the player does not win the counter lottery at the time of hitting a rip, the information “4” corresponding to the ally character is set, and the information “3” corresponding to the ally character is not set. When "4" is set, defense lottery is performed at the time of ripping a bullet. In the hit lot counter at random, the
被弾リプ時防御抽籤に当籤した場合には、被弾リプ時被ダメージ抽籤は行われない。一方、被弾リプ時防御抽籤に当籤しなかった場合、味方キャラクタに対応する情報「4」は設定されていないが「3」が設定されている場合であって、被弾リプ時カウンター抽籤に当籤しなかった場合、並びに味方キャラクタに対応する情報「3」及び「4」が設定されていない場合であって、「被弾リプ」(「F_被弾リプ」)に当籤した場合には、被弾リプ時被ダメージ抽籤が行われる。 If you win the lottery for defensive defense during hit rep, the damage lottery for hit rep will not be performed. On the other hand, if the player does not win the defensive lottery at the time of hitting rep, and the information “4” corresponding to the ally character is not set but “3” is set, the counter lottery at the time of hitting rep is won. If there is not, or if the information “3” and “4” corresponding to the teammate character is not set and the player has won the “Bullet Lip” (“F_Bullet Lip”), the player will receive The damage lottery is performed.
被弾リプ時被ダメージ抽籤では、メインCPU101は、図36Dに示す被弾リプ時被ダメージ抽籤テーブルを参照し、敵種別と、抽籤値と、に基づいて、いずれか1つの被ダメージの値を決定する。なお、被ダメージの値が決定されると、その値が味方HPの値から減算され、味方HPの値が更新される。また、これにともなって、上述した味方の「ステータス」が適宜更新される。
In the lottery for damage received during bullet ripping, the
味方キャラクタに対応する情報「1」及び「2」が設定されていない場合であって、「中段リプ」又は「中段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定された場合、及びスイカ(この場合、「F_スイカ1」のみであってもよいし、「F_スイカ2」を含んでいてもよい。以下、この項において同じ)が内部当籤役として決定された場合には、与ダメージ抽籤が行われる。
When the information "1" and "2" corresponding to the teammate character is not set, and when an internal winning combination that can display "middle lip" or "middle bell" is determined, and watermelon (in this case) , “
味方キャラクタに対応する情報「1」が設定されている場合であって、「中段リプ」若しくは「中段ベル」、又は「上段リプ」若しくは「上段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定された場合、及びスイカが内部当籤役として決定された場合には、与ダメージ抽籤が行われる。 In the case where the information “1” corresponding to the ally character is set, the “intermediate lip” or “middle bell”, or the internal winning combination in which the “upper lip” or the “upper bell” can be displayed is determined. In the case, and when the watermelon is determined as the internal winning combination, the damage damage lottery is performed.
味方キャラクタに対応する情報「2」が設定されている場合であって、「中段リプ」若しくは「中段ベル」、又は「下段リプ」若しくは「下段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定された場合、及びスイカが内部当籤役として決定された場合には、与ダメージ抽籤が行われる。 In the case where the information “2” corresponding to the ally character is set, the internal winning combination in which “middle lip” or “middle bell” or “lower lip” or “lower bell” can be displayed is determined. In the case, and when the watermelon is determined as the internal winning combination, the damage damage lottery is performed.
味方キャラクタに対応する情報「1」及び「2」が設定されている場合であって、「中段リプ」若しくは「中段ベル」、「上段リプ」若しくは「上段ベル」、又は「下段リプ」若しくは「下段ベル」が表示され得る内部当籤役が決定された場合、及びスイカが内部当籤役として決定された場合には、与ダメージ抽籤が行われる。 When the information "1" and "2" corresponding to the teammate character is set, "middle lip" or "middle bell", "upper lip" or "upper bell", or "lower lip" or " When the internal winning combination that can display “lower bell” is determined, and when the watermelon is determined as the internal winning combination, the damage damage lottery is performed.
与ダメージ抽籤では、メインCPU101は、図36Eに示す与ダメージ抽籤テーブルを参照し、内部当籤役と、抽籤値と、に基づいて、いずれか1つの与ダメージの値を決定する。なお、与ダメージの値が決定されると、その値が敵HPの値から減算され、敵HPの値が更新される。また、これにともなって、上述した敵の「ステータス」が適宜更新される。
In the damage damage lottery, the
ここで、RT状態に着目すると、有利区間のラインバトル状態は、基本的にはRT2状態に対応するものであるが、「RT3移行目」が表示された場合にはRT3状態ともなり得る。図16を参照すると、RT2状態では、「F_中段リプ1」の抽籤値が「5000」であり、「F_上段リプ」及び「F_下段リプ」の抽籤値が「2450」であり、「F_被弾リプ」の抽籤値が「8970」であるのに対し、RT3状態では、「F_中段リプ2」の抽籤値が「32768」であり、「F_被弾リプ」の抽籤値は「0」である。
Here, paying attention to the RT state, the line battle state of the advantageous section basically corresponds to the RT2 state, but when the “RT3 transition eye” is displayed, it can be the RT3 state. Referring to FIG. 16, in the RT2 state, the lottery value of “
すなわち、有利区間のラインバトル状態(より詳細には、バトル状態)において、RT3状態に移行させることができれば、味方キャラクタに対応する情報「1」又は「2」が設定されているか否かにかかわらず、「中段リプ」が表示され得る内部当籤役が高確率で決定される結果、与ダメージ抽籤が高確率で行われるようにすることができるとともに、「被弾リプ」が表示され得る内部当籤役は決定されない結果、被弾リプ時被ダメージ抽籤が行われないようにすることができる。したがって、有利区間のラインバトル状態(より詳細には、バトル状態)では、RT3状態が最も有利なRT状態となっている。 That is, in the line battle state of the advantageous section (more specifically, the battle state), if it is possible to shift to the RT3 state, it may be determined whether the information “1” or “2” corresponding to the ally character is set. Instead, the internal winning combination that can display "middle rip" is determined with a high probability, and as a result, the damage lottery can be performed with a high probability, and the internal winning combination that can display "hit rep" is displayed. As a result of not being determined, it is possible to prevent the damage lottery from taking place when the bullet is ripped. Therefore, in the line battle state of the advantageous section (more specifically, the battle state), the RT3 state is the most advantageous RT state.
バトル状態において、バトル状態が終了する前に敵HPが「0」以下(すなわち、ステータスとして「撃破」)となった場合、メインCPU101は、次回遊技から有利区間の権利付与抽籤状態に移行させる。また、敵HPが「0」以下となっておらず、バトル状態の遊技期間が終了していない場合には、バトル状態を継続させる。また、敵HPが「0」以下となっておらず、バトル状態の遊技期間が終了した場合には、次回遊技からラインバトル状態中の継続抽籤状態に移行させる。
In the battle state, when the enemy HP becomes "0" or less (that is, "destroy" as the status) before the battle state ends, the
なお、本実施形態では、「被弾リプ」(「F_被弾リプ」)に当籤した場合に、被弾リプ時カウンター抽籤、被弾リプ時防御抽籤及び被弾リプ時被ダメージ抽籤が行われるものとしているが、バトル状態における抽籤手法はこれに限られない。例えば、与ダメージ抽籤の対象なっていない内部当籤役(但し、「弱レア役」、「チャンス目」、ボーナス役は除く)が決定された場合には、「被弾リプ」(「F_被弾リプ」)に当籤したと同様に、被弾リプ時カウンター抽籤、被弾リプ時防御抽籤及び被弾リプ時被ダメージ抽籤が行われるようにしてもよい。 In addition, in the present embodiment, when the "bullet hit lip" ("F_ bullet hit lip") is won, it is assumed that the ball lottery counter lottery, the bullet hit rep defense lottery, and the bullet hit damage damage lottery are performed. The lottery method in the battle state is not limited to this. For example, if an internal winning combination that is not subject to the damage damage lottery (however, except for the “weak rare combination”, the “chance eye”, and the bonus combination) has been determined, the “ball hit lip” (“F_ball hit lip”) In the same manner as when the winning lottery) is won, a random lottery during a bullet-hit rip, a defense lottery during a bullet-hit rip, and a damage-hit lottery during a bullet-hist rip may be performed.
また、本実施形態では、「被弾リプ」(「F_被弾リプ」)に当籤した場合に、「被弾リプ」の図柄の組合せがセンターラインに表示されるようになっているが、例えば、複数の異なる内部当籤役として構成し、あるいは「被弾リプ」(「F_被弾リプ」)を押し順リプレイとして構成し、停止操作の手順に応じて、「被弾リプ」の図柄の組合せがトップラインに表示され、あるいはボトムラインに表示される場合があるようにしてもよい。この場合に、トップラインやボトムラインが判定ラインとなっている場合には、被弾リプ時カウンター抽籤、被弾リプ時防御抽籤及び被弾リプ時被ダメージ抽籤が行われるようにしてもよいし、これらの抽籤は行われないようにしてもよい。また、トップラインやボトムラインが判定ラインとなっている場合には、「被弾リプ」の図柄の組合せがトップラインやボトムラインに表示されないように、停止操作の手順が報知されるようにしてもよい。 In addition, in the present embodiment, when the winning ball is hit, the combination of the symbols of the “hits lip” is displayed on the center line. It is configured as a different internal winning combination, or is configured as a push order replay of "Bullet Lip" ("F_Bullet Lip"), and a combination of symbols of "Bullet Lip" is displayed on the top line according to the procedure of the stop operation. Alternatively, it may be displayed on the bottom line. In this case, if the top line or the bottom line is the judgment line, it may be possible to perform counter lottery at the time of hitting rep, lottery for defense at hitting rep, and damage lottery at hitting rep The lottery may not be performed. Also, if the top line or bottom line is the judgment line, even if the procedure of the stop operation is notified so that the combination of the symbols of “shot bullets” is not displayed on the top line or bottom line Good.
(継続抽籤状態)
上述したように、敵HPが「0」以下となっておらず、バトル状態の遊技期間が終了したときに、メインCPU101は、次に、ラインバトル状態中の継続抽籤状態に移行させる。継続抽籤状態は、4ゲーム又は7ゲーム間継続する状態となっており、最終的に、ラインバトル状態から権利獲得抽籤状態に移行させることが決定されている場合には、権利獲得抽籤状態に移行させ、ラインバトル状態を継続させることが決定されている場合には、再度ラインバトル状態中のインターバル状態に移行させ、これらのいずれの決定もなされていない場合には、ラインバトル状態が終了し(すなわち、有利区間が終了し)、非有利区間の通常状態に移行させる。
(Continuous lottery status)
As described above, when the enemy HP is not "0" or less and the game period in the battle state ends, the
継続抽籤状態では、敵種別とダメージ状態に応じた継続抽籤及び継続抽籤結果書換抽籤が行われ得る。なお、これらの遊技性に関する抽籤は一例であり、継続抽籤状態においては他の抽籤も行うことが可能である。 In the continuous lottery state, continuous lottery and continuous lottery result rewriting lottery can be performed according to the enemy type and the damage state. It should be noted that the lottery relating to these game characteristics is an example, and other lottery can be performed in the continuous lottery state.
まず、メインCPU101は、バトル状態から継続抽籤状態に移行する際に、敵種別とダメージ状態に応じた継続抽籤を行う。敵種別とダメージ状態に応じた継続抽籤では、メインCPU101は、図36Fに示す継続抽籤テーブルを参照し、敵種別と、ダメージ状態(すなわち、上述した「ステータス」と同義)と、抽籤値と、に基づいて、継続抽籤状態の遊技期間は4ゲームであるが、権利獲得抽籤状態に移行させることもラインバトル状態を継続させることも決定されないこと(「4G敗北」)、継続抽籤状態の遊技期間は7ゲームであるが、権利獲得抽籤状態に移行させることもラインバトル状態を継続させることも決定されないこと(「7G敗北」)、継続抽籤状態の遊技期間は4ゲームであり、ラインバトル状態を継続させることが決定されること(「4G継続」)、継続抽籤状態の遊技期間は7ゲームであり、ラインバトル状態を継続させることが決定されること(「7G継続」)、継続抽籤状態の遊技期間は4ゲームであり、権利獲得抽籤状態に移行させることが決定されること(「4G昇格」)、及び継続抽籤状態の遊技期間は7ゲームであり、権利獲得抽籤状態に移行させることが決定されること(「7G昇格」)、のいずれかが決定される。
First, when shifting from the battle state to the continuous lottery state, the
なお、敵種別とダメージ状態に応じた継続抽籤では、少なくとも有利区間が終了されない抽籤結果(上述した「4G継続」、「7G継続」、「4G昇格」、及び「7G昇格」)が決定される確率が、原則として、敵種別が「A」、「B」、「C」、「D」の順に順次高まるようになっており、また、味方ステータスが「大破」、「中破」、「小破」、「平常」の順に順次高まるようになっており、また、敵ステータスが「平常」、「小破」、「中破」、「大破」の順に順次高まるようになっている。すなわち、敵種別と、味方ステータスと、敵ステータスと、の3つのパラメータが参照され、有利区間が継続するか否かが決定されるようになっている。 In the continuous lottery depending on the enemy type and the damage state, the lottery result (“4G continuation”, “7G continuation”, “4G promotion”, and “7G promotion” described above) in which at least the advantageous zone is not ended is determined. As a general rule, the probability of enemies increases in the order of “A”, “B”, “C”, “D”, and the ally status is “major”, “medium”, “small”. The order is to gradually increase in the order of “break” and “normal”, and the enemy statuses are sequentially increased in the order of “normal”, “small break”, “medium break”, and “major break”. That is, the three parameters of the enemy type, the ally status, and the enemy status are referred to and it is determined whether or not the advantageous section continues.
それゆえ、本実施形態では、バトル状態突入時に、いずれの敵キャラクタに対応する情報が設定されるか、バトル状態中に味方ステータスがどのように変移するか、及びバトル状態中に敵ステータスがどのように変移するかに応じて、ラインバトル状態が継続する継続度合いを変動させることが可能となっている。また、味方ステータス及び敵ステータスの変移に際しては、味方キャラクタに対応する情報の種類(例えば、判定ライン数)が重要となり、これによって、ラインバトル状態が継続する継続度合いが、遊技者に有利な度合いに変動させたり、遊技者に不利な度合いに変動させたりする確率も変動するようになっている。 Therefore, in the present embodiment, when entering the battle state, information corresponding to which enemy character is set, how the ally status changes during the battle state, and which enemy status is determined during the battle state. It is possible to change the continuation degree in which the line battle state continues depending on the transition. In addition, when the ally status and the enemy status change, the type of information corresponding to the ally character (for example, the number of determination lines) becomes important, whereby the degree of continuation of the line battle state is advantageous to the player. The probability of changing the value to a certain degree or changing the degree to a disadvantage to the player is also changed.
なお、図36Fに示す継続抽籤テーブルでは、味方ステータスが「大破」、及び敵ステータスが「大破」であるときには、例外的に、少なくとも有利区間が終了されない抽籤結果が決定されることが確定するようになっている。このように、味方ステータスが特定のステータスであり、敵ステータスが特定のステータスであるとき、上述した原則に反して、有利区間が継続する確率を高めたり、有利区間が継続する確率を低めたりすることもできる。 Note that, in the continuous lottery table shown in FIG. 36F, when the ally status is “defeat” and the enemy status is “defeat”, it is decided that the lottery result in which at least the advantageous zone is not ended is exceptionally determined. It has become. In this way, when the ally status is a specific status and the enemy status is a specific status, the probability that the advantageous section continues will be increased or the probability that the advantageous section will continue will be reduced, contrary to the principle described above. You can also
また、メインCPU101は、バトル状態から継続抽籤状態に移行する際に、敵種別とダメージ状態に応じた継続抽籤の抽籤結果が、有利区間が終了される抽籤結果(上述した「4G敗北」及び「7G敗北」)である場合には、継続抽籤状態において、継続抽籤結果書換抽籤を行う。具体的には、継続抽籤状態において、「チャンス目」又はボーナス役に当籤した場合、継続抽籤の抽籤結果として、例えば「4G敗北」が決定されている場合には「4G継続」に書き換え、例えば「7G敗北」が決定されている場合には「7G継続」に書き換える。また、スイカ(この場合、「F_スイカ1」のみであってもよいし、「F_スイカ2」を含んでいてもよい)に当籤した場合、所定確率(例えば、1/2)で、継続抽籤の抽籤結果を書き換えることを決定する。継続抽籤の抽籤結果を書き換えることが決定された場合、上記と同様に継続抽籤の抽籤結果が適宜書き換えられる。
Further, when the
なお、本実施形態では、敵種別とダメージ状態に応じた継続抽籤が行われた後、継続抽籤結果書換抽籤が行われるが、継続抽籤状態における抽籤手法はこれに限られない。例えば、継続抽籤状態では、まず、継続抽籤結果書換抽籤が行われ(すなわち、内部当籤役に基づいて遊技毎にラインバトル状態を継続させる否かを決定するための抽籤が行われ)、当該抽籤の結果ラインバトル状態を継続させることが決定されなかった場合に、継続抽籤状態が終了するときに、敵種別とダメージ状態に応じた継続抽籤が行われるようにしてもよい。 In the present embodiment, the continuous lottery result rewriting lottery is performed after the continuous lottery according to the enemy type and the damage state is performed, but the lottery method in the continuous lottery state is not limited to this. For example, in the continuous lottery state, first, the continuous lottery result rewriting lottery is performed (that is, the lottery is performed to determine whether to keep the line battle state for each game based on the internal winning combination), and the relevant lottery is performed. When it is not determined to continue the line battle state, the continuous lottery may be performed according to the enemy type and the damage state when the continuous lottery state ends.
このように、本実施形態では、有利区間のラインバトル状態において、一又は複数のいずれかのライン(有効ラインであるかを問わない)を有利区間の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインとするかを決定可能とし、ラインバトル状態中のバトル状態において、決定された判定ラインに「リプレイ」又は「ベル」の図柄が並んで表示される場合に、有利区間の継続度合いを遊技者に有利な度合いに変動させることを可能とし、ラインバトル状態中の継続抽籤状態において、決定された有利区間の継続度合いに基づいて有利区間を継続させるか否かを決定することが可能となっている。 As described above, in the present embodiment, in the line battle state of the advantageous section, whether one or a plurality of lines (regardless of whether the line is an effective line) is set as the determination line regarding the variation of the continuation degree of the advantageous section is determined. It is possible to decide, and in the battle state during the line battle state, when the symbols of "Replay" or "Bell" are displayed side by side on the determined judgment line, the degree of continuation of the advantageous section is set to the degree advantageous to the player. It is possible to change, and in the continuous lottery state during the line battle state, it is possible to decide whether or not to continue the advantageous section based on the determined degree of continuation of the advantageous section.
これにより、判定ラインの決定結果に応じて有利区間の継続度合いを変動させることができるため、遊技者に有利な状態の継続に関する興趣の向上を図ることができる。 As a result, the degree of continuation of the advantageous section can be changed according to the determination result of the determination line, so that it is possible to improve the interest in continuing the advantageous state for the player.
また、本実施形態では、ラインバトル状態中のバトル状態において、決定された判定ラインに、例えば、「被弾リプ」の図柄の組合せが表示される場合に、有利区間の継続度合いを遊技者に不利な度合いに変動させることが可能となっている。 Further, in the present embodiment, in the battle state during the line battle state, for example, when the combination of the symbols “shot bullets” is displayed on the determined determination line, the degree of continuation of the advantageous section is disadvantageous to the player. It can be changed to any degree.
これにより、有利区間中(例えば、ラインバトル状態中のバトル状態中)における緊張感を高めることができ、有利区間中の遊技が単調とならず、さらに遊技者に有利な状態の継続に関する興趣の向上を図ることができる。 As a result, it is possible to increase the tension in the advantageous section (for example, during the battle state in the line battle state), the game in the advantageous section is not monotonous, and there is an interest in continuing the state advantageous to the player. It is possible to improve.
また、本実施形態では、有利区間のラインバトル状態におけるRT状態をRT2状態に変移させることが可能であるとともに、「RT3移行目」が表示された場合に、有利区間のラインバトル状態におけるRT状態をRT3状態に変移させることが可能となっており、決定された判定ラインに「中段リプ」の図柄の組合せが表示され得る特定の内部当籤役(例えば、「F_中段リプ1」及び「F_中段リプ2」のいずれか)を決定する確率は、RT2状態よりもRT3状態のほうが高くなっている。
Further, in the present embodiment, the RT state in the line battle state of the advantageous section can be changed to the RT2 state, and when the “RT3 transition eye” is displayed, the RT state in the line battle state of the advantageous section is displayed. Can be changed to the RT3 state, and a specific internal winning combination (for example, "
また、本実施形態では、RT2状態においては、「被弾リプ」の図柄の組合せが表示され得る所定の内部当籤役(例えば、「F_被弾リプ」)を決定可能とし、RT3状態においては、この所定の内部当籤役を決定可能としないようになっている。 Further, in the present embodiment, in the RT2 state, it is possible to determine a predetermined internal winning combination (for example, “F_ball hit lip”) in which a combination of symbols of “ball hit lip” can be displayed, and in the RT3 state, the predetermined internal winning combination can be determined. The internal winning combination of is not allowed to be decided.
これにより、有利区間中(例えば、ラインバトル状態中のバトル状態中)においては、いずれのRT状態であるかによって遊技者の有利さの度合いがさらに変動するようになるため、有利区間中の遊技をより多彩なものとし、さらに遊技者に有利な状態の継続に関する興趣の向上を図ることができる。 As a result, during the advantageous section (for example, during the battle state during the line battle state), the degree of advantage of the player is further changed depending on which RT state, so that the game during the advantageous section is performed. Can be made more diversified, and the interest in continuing a state advantageous to the player can be improved.
また、本実施形態では、例えば、「打順1」で停止操作が行われた場合に、トップラインで「ベル」の図柄の組合せが表示される「F_上段左ベル1」と、「打順1」で停止操作が行われた場合に、センターラインで「ベル」の図柄の組合せが表示される「F_中段左ベル1」と、「打順3」で停止操作が行われた場合に、トップラインで「ベル」の図柄の組合せが表示される「F_上段中ベル1」と、「打順3」で停止操作が行われた場合に、センターラインで「ベル」の図柄の組合せが表示される「F_中段中ベル1」と、を少なくとも内部当籤役として決定可能であり、図32に示したように、有利区間において、例えば、「F_上段左ベル1」又は「F_上段中ベル1」が決定された場合には、当籤役番号として「23」を送信し、「F_中段左ベル1」又は「F_中段中ベル1」が決定された場合には、当籤役番号として「24」を送信するようになっている。そして、本実施形態では、送信された当籤役番号に応じて異なる演出を実行することが可能となっている。
Further, in the present embodiment, for example, when the stop operation is performed in the "
これにより、例えば、有利区間のラインバトル状態のような図柄が表示されるラインによって遊技者の有利さの度合いが変動するような遊技性を有する場合に、表示される図柄の組合せに関連した演出を行うことができるため、制御負担を増大させることなく、より適切な演出を行うことができる。 Thereby, for example, in the case where the player has a playability in which the degree of the advantage of the player changes depending on the line on which the symbol is displayed, such as the line battle state of the advantageous section, the effect associated with the combination of the symbols displayed Since it is possible to perform, it is possible to perform a more appropriate effect without increasing the control load.
<権利獲得抽籤状態及び権利獲得状態中の遊技性>
次に、図42を参照して、有利区間の権利獲得抽籤状態及び権利獲得状態中の遊技の流れについて説明する。なお、図42では、権利獲得抽籤状態及び権利獲得状態中の遊技の流れの概要を示している。
<Right acquisition lottery state and game play in right acquisition state>
Next, with reference to FIG. 42, the flow of the game during the right acquisition lottery state and the right acquisition state of the advantageous section will be described. Note that FIG. 42 shows an outline of a game flow in the right acquisition lottery state and the right acquisition state.
(権利獲得抽籤準備状態)
メインCPU101は、有利区間の権利獲得抽籤準備状態、権利獲得抽籤状態、及び権利獲得状態において、ボーナス役に当籤し、当該ボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態が終了したときに、権利獲得抽籤準備状態に移行させる(すなわち、これらの状態に復帰させる)。この場合、ボーナス状態が終了したときのRT状態はRT4状態であり(図13参照)、RT状態がRT4状態からRT2状態に移行するまで権利獲得抽籤準備状態を維持する。RT状態がRT2状態に移行したとき、ボーナス役に当籤したのが権利獲得状態であれば権利獲得状態に移行させ、ボーナス役に当籤したのが権利獲得抽籤状態であれば権利獲得抽籤状態に移行させる。
(Right acquisition lottery preparation state)
The
なお、この場合、RT4状態において「RT1移行目」を表示させるため、RT4状態において「RT1移行目」が表示されるまでは、押し順小役及び押し順リプレイについての押し順報知は行われず、RT状態がRT1状態に移行してから、押し順小役及び押し順リプレイについての押し順報知が開始される。また、この場合、RT4状態において「RT3移行目」が表示されてRT3状態に移行した場合にも、押し順小役及び押し順リプレイについての押し順報知が開始される。なお、RT3状態に移行したときに、権利獲得抽籤準備状態を終了させ、権利獲得状態に復帰させる場合には権利獲得状態に復帰させ、権利獲得抽籤状態に復帰させる場合には権利獲得抽籤状態に復帰させるようにしてもよい。 In this case, since the "RT1 transition" is displayed in the RT4 state, the push order notification regarding the push sequence small win and the push sequence replay is not performed until the "RT1 transition" is displayed in the RT4 state. After the RT state shifts to the RT1 state, the push order notification of the push order small combination and the push order replay is started. Further, in this case, even when the "RT3 shift eye" is displayed in the RT4 state and the state shifts to the RT3 state, the push order notification regarding the push order minor combination and the push order replay is started. When the state shifts to the RT3 state, the right acquisition lottery preparation state is ended, the right acquisition state is returned to the right acquisition state, and the right acquisition lottery state is returned to the right acquisition lottery state. You may make it return.
(権利獲得抽籤状態)
上述したように、権利獲得抽籤準備状態が終了したとき、及びラインバトル状態において権利獲得抽籤状態に移行させることが決定されたときに、メインCPU101は、権利獲得抽籤状態に移行させる。権利獲得抽籤状態は、20ゲーム間継続する状態となっており、この間にはもちろん遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報が報知される。そして、権利獲得状態に移行しない場合であってもラインバトル状態に戻るようになっている。したがって、この権利獲得抽籤状態は、それ自体が有利区間の遊技期間を延長させ得る遊技状態となっている。権利獲得抽籤状態では、権利獲得状態移行抽籤が行われる。
(Right acquisition lottery status)
As described above, when the right acquisition lottery preparation state is completed and when it is determined to shift to the right acquisition lottery state in the line battle state, the
権利獲得状態移行抽籤では、例えば、メインCPU101は、権利獲得抽籤状態において、「チャンス目」又はスイカ(この場合、「F_スイカ1」のみであってもよいし、「F_スイカ2」を含んでいてもよい)に当籤した場合、次回遊技から権利獲得状態に移行させることを決定する。また、共通ベル(「F_上段共通ベル」及び「F_中段共通ベル」)に当籤した場合、所定確率(例えば、1/4)で、次回遊技から権利獲得状態に移行させることを決定する。なお、権利獲得状態に移行させることが決定された場合であっても、権利獲得状態に移行するのは、権利獲得抽籤状態の遊技期間(20ゲーム)が終了したときであってもよい。また、権利獲得状態に移行させることが決定された場合に、権利獲得抽籤状態の遊技期間の残りゲーム数の範囲で前兆期間を決定し、この前兆期間が経過したときに権利獲得状態に移行させるようにしてもよい。また、権利獲得抽籤状態から権利獲得状態に移行させる際に、権利獲得抽籤状態の遊技期間の残りゲーム数が生じる場合には、その残りゲーム数が、権利獲得状態の遊技期間に付加されるようにしてもよいし、次回(権利獲得状態から権利獲得抽籤状態に戻ったとき)の権利獲得抽籤状態の遊技期間に付加されるようにしてもよい。
In the right acquisition lottery, the
(権利獲得状態)
上述したように、権利獲得抽籤状態において権利獲得状態に移行させることが決定されたとき、及び権利獲得抽籤準備状態から復帰したときに、メインCPU101は、権利獲得状態に移行させる。権利獲得状態は、10ゲーム間継続する状態となっており、この間にはもちろん遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報が報知される。そして、永続権利を獲得するか否かにかかわらず権利獲得抽籤状態に戻るようになっている。したがって、この権利獲得状態は、それ自体が有利区間の遊技期間を延長させ得る遊技状態となっている。権利獲得状態では、永続権利獲得抽籤が行われる。
(Right acquisition status)
As described above, the
永続権利獲得抽籤では、後述のバトル突入時味方種別抽籤とは別に、予め味方キャラクタを永続的に(当該有利区間が終了するまで)獲得させるか否かの権利を付与するか否かが決定される。メインCPU101は、例えば、権利獲得状態においてボーナス役に当籤した場合に、永続権利を付与することを決定する。なお、例えば、特定役(例えば、「スイカ1」)に当籤したことに基づいて、所定確率(例えば、1/4)で、永続権利を付与することを決定するようにしてもよい。
In the permanent right acquisition lottery, it is determined whether or not to grant the right to permanently acquire the ally character (until the advantageous section ends) in advance, separately from the ally type lottery at the time of entering the battle, which will be described later. It For example, the
ここで、永続権利抽籤の結果、当該永続権利を付与することが決定された場合、バトル状態に突入する度に、バトル突入時味方種別抽籤の結果付与されなかった味方キャラクタの番号のうち、最も小さい番号の味方キャラクタが付与される。例えば、後述のバトル突入時味方種別抽籤において、味方キャラクタ「2」が付与されていた場合、当該永続権利を獲得していれば、さらに味方キャラクタ「1」が付与されるようになる。なお、付与された永続権利の機能はこれに限られない。例えば、永続権利抽籤の結果、当該永続権利を付与することが決定された場合、永続権利が付与されていない味方キャラクタの番号のうち、最も小さい番号の味方キャラクタが固定的に付与されるようにしてもよい。例えば、最初に永続権利が付与された場合、この永続権利の権利内容として味方キャラクタ「1」が付与され、次に永続権利が付与された場合、この永続権利の権利内容として味方キャラクタ「2」が付与されるようにしてもよい。 Here, if it is determined as a result of the permanent right lottery that the permanent right is given, the number of the ally characters that are not given as a result of the ally type lottery at the time of entering the battle is the most A ally character with a small number is added. For example, when the teammate character “2” is given in the team-type lottery at the time of battle entry described later, if the permanent right is acquired, the teammate character “1” is further provided. The function of the granted permanent right is not limited to this. For example, when it is determined as a result of the permanent right lottery that the permanent right is given, the ally character having the smallest number among the numbers of the ally characters to which the permanent right is not given is fixedly given. May be. For example, when the permanent right is first granted, the ally character "1" is given as the right content of this permanent right, and when the permanent right is given next, the ally character "2" is given as the right content of this permanent right. May be added.
なお、本実施形態では、権利獲得状態において、永続権利が付与されるか否かが決定されるようになっているが、これに限られず、権利獲得状態において、上述した限定的権利が付与されるか否かが決定されるようにしてもよい。この場合、例えば、上述した味方獲得抽籤と同様の抽籤が行われるようにしてもよいし、上述した味方獲得抽籤よりも限定的権利が付与される確率が高まるように、上述した限定的権利が付与されるか否が決定されるようにしてもよい。また、例えば、権利獲得状態においては、単位遊技ごとに、内部当籤役にかかわらず所定確率(例えば、1/10)で、上述した限定的権利が付与されるか否が決定されるようにしてもよい。なお、ボーナス役当籤以外の契機で永続権利あるいは限定的権利が付与されるようにした場合には、権利獲得状態において複数個の権利を獲得させることができる。 It should be noted that in the present embodiment, whether or not a permanent right is granted is determined in the right acquisition state, but the present invention is not limited to this, and the limited right described above is granted in the right acquisition state. It may be determined whether or not to execute. In this case, for example, a lottery similar to the ally acquisition lottery described above may be performed, or the limited right described above may be provided so that the probability that the limited right is granted is higher than the ally acquisition lottery described above. It may be determined whether or not it is given. Further, for example, in the right acquisition state, whether or not the above-described limited right is granted is determined for each unit game with a predetermined probability (for example, 1/10) regardless of the internal winning combination. Good. If a permanent right or a limited right is granted by a trigger other than the bonus winning, a plurality of rights can be acquired in the right acquisition state.
この場合、上述したように、例えば、2個の権利が付与された場合(味方キャラクタに対応する情報「1」及び「2」が設定される場合)には、バトル状態において判定ラインが上限数(DL1〜DL3)まで設定されることとなる。また、例えば、3個の権利が付与された場合(味方キャラクタに対応する情報「1」〜「3」が設定される場合)には、これに加え、バトル状態においてカウンターが発動する場合があるようになる。また、例えば、4個の権利が付与された場合(味方キャラクタに対応する情報「1」〜「4」が設定される場合)には、これに加え、バトル状態に防御が発動する場合があるようになる。ここで、例えば、権利獲得状態において5個以上の権利が付与された場合には、4個を超える分の権利については、次回のバトル状態まで持ち越されるようにしてもよいし、破棄(クリア)されるようにしてもよい。また、例えば、権利獲得状態において5個以上の権利が付与された場合には、次回のバトル状態終了後の継続抽籤状態において、必ず有利区間が継続することが決定されるようにしてもよい。 In this case, as described above, for example, when two rights are granted (when the information "1" and "2" corresponding to the teammate character are set), the determination line has the upper limit number in the battle state. (DL1 to DL3) will be set. Further, for example, when three rights are granted (when information “1” to “3” corresponding to the teammate character is set), in addition to this, the counter may be activated in the battle state. Like Further, for example, when four rights are granted (when information “1” to “4” corresponding to the teammate character is set), in addition to this, defense may be activated in the battle state. Like Here, for example, when 5 or more rights are granted in the right acquisition state, the rights of more than 4 may be carried over to the next battle state, or discarded (cleared). It may be done. Further, for example, when five or more rights are granted in the right acquisition state, it may be determined that the advantageous section is always continued in the continuous lottery state after the end of the next battle state.
また、本実施形態では、権利獲得状態において、有利区間のラインバトル状態が有利に進められるようになる(味方キャラクタに対応する情報が設定され得る)永続権利が付与されるか否かが決定されるようになっているが、権利獲得状態において、付与され得る権利内容はこれに限られない。例えば、ラインバトル状態の継続抽籤状態において、抽籤結果にかかわらず強制的にラインバトル状態が継続することとなる継続権利(すなわち、有利区間を延長させるための権利。「ストック」や「セット数」などと称される場合がある)が付与されるか否かが決定されるようにしてもよいし、権利獲得抽籤状態において、抽籤結果にかかわらず強制的に権利獲得抽籤状態が継続することとなる継続権利(すなわち、有利区間を延長させるための権利。「ストック」や「セット数」などと称される場合がある)が付与されるか否かが決定されるようにしてもよい。すなわち、権利獲得状態において、付与され得る権利内容は、遊技者に特典をもたらすものであれば、適宜設定することができる。 Further, in the present embodiment, in the right acquisition state, it is determined whether or not the permanent right that allows the line battle state of the advantageous section to be advantageously advanced (the information corresponding to the ally character can be set) is granted. However, the content of rights that can be granted in the right acquisition state is not limited to this. For example, in the continuous lottery state of the line battle state, the continuation right that the line battle state is forcibly continued regardless of the lottery result (that is, the right to extend the advantageous section. “stock” or “number of sets”) It may be determined whether or not the right acquisition lottery state is forcibly continued regardless of the lottery result in the right acquisition lottery state. It may be determined whether or not a continuous right (that is, a right to extend the advantageous section, which may be referred to as “stock” or “number of sets”) is granted. That is, in the right acquisition state, the content of the right that can be granted can be appropriately set as long as it gives the player a privilege.
このように、本実施形態では、有利区間のラインバトル状態において、一又は複数のいずれかのライン(有効ラインであるかを問わない)を有利区間の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインとするかを決定可能としており、その決定結果は、権利獲得状態において権利が付与されたか否かによって変動するようになっている。すなわち、権利獲得状態において付与された権利に基づいて判定ラインを決定することが可能となっている。 As described above, in the present embodiment, in the line battle state of the advantageous section, whether one or a plurality of lines (regardless of whether the line is an effective line) is set as the determination line regarding the variation of the continuation degree of the advantageous section is determined. It is possible to make a decision, and the decision result changes depending on whether or not the right is granted in the right acquisition state. That is, it is possible to determine the determination line based on the right granted in the right acquisition state.
また、本実施形態では、権利獲得状態において判定ラインの上限数以上の権利が付与された場合には、まず、上限数分の権利を用いて上限数の判定ラインが決定される。そして、ラインバトル状態中のバトル状態において、決定された判定ラインに、例えば、「被弾リプ」の図柄の組合せが表示される場合に、付与された権利が残存していなければ、有利区間の継続度合いを遊技者に不利な度合いに変動させ、付与された権利が残存していれば、有利区間の継続度合いを遊技者に不利な度合いに変動させないことが可能となっている。 Further, in the present embodiment, when the number of rights equal to or more than the upper limit number of the determination lines is given in the right acquisition state, the upper limit number of determination lines are first determined using the upper right number of rights. Then, in the battle state during the line battle state, for example, when the combination of the symbols “Bullet Lip” is displayed on the determined determination line, if the granted right does not remain, the advantageous section is continued. It is possible to change the degree to a degree unfavorable to the player and not to change the degree of continuation of the advantageous section to a degree unfavorable to the player as long as the granted right remains.
また、本実施形態では、永続権利が付与されている場合には、複数の判定ラインが必ず決定され、永続権利が付与されていない場合には、判定ラインを決定するときに、一又は複数のいずれかのラインが判定ラインとして決定されるようになっている。 Further, in the present embodiment, when the permanent right is granted, a plurality of determination lines are always determined, and when the permanent right is not granted, one or a plurality of determination lines are determined when determining the determination line. Either line is set as the determination line.
これにより、有利区間中の各遊技状態の役割を多様化させ、また、有利区間が継続する継続度合いを多様に変動させることができるため、遊技者に有利な状態の継続に関する興趣の向上を図ることができる。 This makes it possible to diversify the role of each gaming state in the advantageous section, and to vary the continuation degree of the advantageous section in various ways, thereby improving the interest in continuing the advantageous state for the player. be able to.
<エンディング1状態及びエンディング2状態中の遊技性>
次に、図43及び図44を参照して、有利区間のエンディング1状態及びエンディング2状態中の遊技の流れについて説明する。なお、図43では、エンディング1状態及びエンディング2状態中の遊技の流れの概要を示している。また、図44では、エンディング1状態及びエンディング2状態中に行われるエンディング演出の概要を示している。
<Playability during ending 1 state and ending 2 state>
Next, with reference to FIG. 43 and FIG. 44, the flow of the game during the ending 1 state and the ending 2 state of the advantageous section will be described. Note that FIG. 43 shows an outline of the flow of the game in the ending 1 state and the ending 2 state. Further, FIG. 44 shows an outline of the ending effect performed in the ending 1 state and the ending 2 state.
(エンディング準備状態)
メインCPU101は、有利区間のエンディング準備状態、エンディング1状態、及びエンディング2状態において、ボーナス役に当籤し、当該ボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態が終了したときに、エンディング準備状態に移行させる(すなわち、これらの状態に復帰させる)。この場合、ボーナス状態が終了したときのRT状態はRT4状態であり(図13参照)、RT状態がRT4状態からRT2状態に移行するまでエンディング状態を維持する。RT状態がRT2状態に移行したとき、ボーナス役に当籤したのがエンディング1状態であればエンディング1状態に移行させ、ボーナス役に当籤したのがエンディング2状態であればエンディング2状態に移行させる。
(Ending preparation state)
The
なお、この場合、RT4状態において「RT1移行目」を表示させるため、RT4状態において「RT1移行目」が表示されるまでは、押し順小役及び押し順リプレイについての押し順報知は行われず、RT状態がRT1状態に移行してから、押し順小役及び押し順リプレイについての押し順報知が開始される。また、この場合、RT4状態において「RT3移行目」が表示されてRT3状態に移行した場合にも、押し順小役及び押し順リプレイについての押し順報知が開始される。なお、RT3状態に移行したときに、エンディング準備状態を終了させ、エンディング1状態に復帰させる場合にはエンディング1状態に復帰させ、エンディング2状態に復帰させる場合にはエンディング2状態に復帰させるようにしてもよい。 In this case, since the "RT1 transition" is displayed in the RT4 state, the push order notification regarding the push sequence small win and the push sequence replay is not performed until the "RT1 transition" is displayed in the RT4 state. After the RT state shifts to the RT1 state, the push order notification of the push order small combination and the push order replay is started. Further, in this case, even when the "RT3 shift eye" is displayed in the RT4 state and the state shifts to the RT3 state, the push order notification regarding the push order minor combination and the push order replay is started. At the time of transition to the RT3 state, the ending preparation state is ended, and when returning to the ending 1 state, the ending 1 state is restored, and when returning to the ending 2 state, the ending 2 state is restored. May be.
また、メインCPU101は、非有利区間及び通常有利区間において、例えば、スイカ1当籤時のART抽籤で、エンディング1状態に移行させることが決定された場合には、通常有利区間の遊技期間が消化されたときに、エンディング準備状態に移行させる(すなわち、RT2状態に移行するまでエンディング1状態への移行を待機する)。
Further, in the non-advantageous section and the normal advantageous section, for example, when it is decided to shift to the ending 1 state by the ART lottery when the
(エンディング1状態)
上述したように、エンディング準備状態が終了したときであってエンディング1状態に移行(復帰)させる場合、メインCPU101は、エンディング1状態に移行させる。エンディング1状態は、100ゲーム間継続する状態となっており、この間にはもちろん遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報が報知される。そして、エンディング1状態が終了したときにはラインバトル状態に移行するようになっている。非有利区間及び通常有利区間から移行する有利区間の遊技状態である点についてはラインバトル状態と同じであるが、ラインバトル状態よりも遊技者に有利な遊技状態となっている。エンディング1状態では、権利獲得状態と同様に永続権利獲得抽籤が行われる。
(Ending 1 state)
As described above, when the ending preparation state is completed and the state is changed (returned) to the ending 1 state, the
なお、権利獲得状態における抽籤と同様に、エンディング1状態では、上述した限定的権利が付与されるか否かが決定されるようにしてもよいし、有利区間を延長させるための継続権利が付与されるか否かが決定されるようにしてもよい As in the case of lottery in the right acquisition state, in the ending 1 state, it may be determined whether or not the limited right described above is granted, or the continuation right for extending the advantageous section is granted. Whether or not it may be determined
また、例えば、エンディング1状態において、ボーナス役に当籤し、当該ボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態が終了して、エンディング準備状態を経由してエンディング1状態に復帰された場合、100ゲームの遊技期間は再度最初からカウントされるようにしてもよいし、ボーナス役に当籤した遊技における遊技期間を引き継いでカウントされるようにしてもよい。後者の場合、例えば、エンディング1状態の10ゲーム目(残り90ゲーム)でボーナス役に当籤し、当該ボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態が終了して、エンディング準備状態を経由してエンディング1状態に復帰された場合、当該エンディング1状態の遊技期間が90ゲームとなるようにすればよい。 Further, for example, in the ending 1 state, when the bonus combination is won, the bonus state based on the bonus combination is finished, and the ending 1 state is returned to via the ending preparation state, the game period of 100 games is again performed. It may be counted from the beginning, or may be counted by taking over the game period in the game in which the winning combination is won. In the latter case, for example, in the 10th game in the ending 1 state (90 games remaining), a bonus combination is won, the bonus state based on the bonus combination ends, and the ending 1 state is restored via the ending preparation state. In this case, the game period in the ending 1 state may be 90 games.
また、さらに、ボーナス状態中の遊技期間もエンディング1状態の遊技期間に含まれるようにしてもよい。例えば、エンディング1状態の10ゲーム目(残り90ゲーム)でボーナス役に当籤し、当該ボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態の遊技期間が17ゲームであり、当該ボーナス状態が終了して、エンディング準備状態を経由してエンディング1状態に復帰された場合、当該エンディング1状態の遊技期間が73ゲームとなるようにすればよい。 Further, the game period in the bonus state may be included in the game period in the ending 1 state. For example, a winning combination is won in the 10th game in the ending 1 state (90 games remaining), the game period of the bonus state based on the bonus combination is 17 games, the bonus state ends, and the ending preparation state is passed. Then, when the game is returned to the ending 1 state, the game period of the ending 1 state may be 73 games.
(エンディング2状態)
有利区間中の遊技回数が「1200」回以上となった場合であって、ラインバトル状態のインターバル状態が終了したとき、メインCPU101は、エンディング2状態に移行させる。エンディング2状態は、131ゲーム間継続する状態となっており、この間にはもちろん遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報が報知される。そして、エンディング2状態が終了したときには有利区間自体も終了し、非有利区間に移行するようになっている。
(Ending 2 state)
When the number of games in the advantageous section is “1200” times or more, and when the interval state of the line battle state ends, the
なお、この場合、上述した規制監視期間が「1200」回(あるいは、それよりも多い回数、例えば、「1369」回)の遊技回数となったときに、エンディング2状態に移行させるようにしてもよい。また、この場合、有利区間の他の遊技状態である場合にも、これらの遊技状態からエンディング2状態に移行させるようにしてもよい。また、エンディング2状態における遊技期間のカウントの態様も、エンディング1状態の遊技期間のカウントの態様と同様である。 In this case, the game may be moved to the ending 2 state when the above-mentioned regulation monitoring period reaches "1200" times (or more times than that, for example, "1369" times). Good. Further, in this case, even in the other gaming state of the advantageous section, the gaming state may be shifted to the ending 2 state. Further, the mode of counting the game period in the ending 2 state is the same as the mode of counting the game period in the ending 1 state.
また、本実施形態では、エンディング2状態が終了すると有利区間自体も終了し、非有利区間に移行させるようにしているが、これに限られない。エンディング2状態が終了するとき、上述した規制監視期間が未だ「1500」回となっていなければ、再度ラインバトル状態に移行させるようにしてもよい。あるいは、上述した規制監視期間が「1500」回となるまで、エンディング2状態を継続させるようにしてもよい。 Further, in the present embodiment, when the ending 2 state ends, the advantageous section itself ends and the non-advantageous section is entered, but the present invention is not limited to this. When the ending 2 state ends, if the above-mentioned regulation monitoring period has not reached “1500” times, the line battle state may be re-entered. Alternatively, the ending 2 state may be continued until the above-mentioned regulation monitoring period reaches “1500” times.
(エンディング演出)
次に、図44を参照しながら、エンディング1状態及びエンディング2状態で行われ得るエンディング演出について説明する。
(Ending production)
Next, with reference to FIG. 44, an ending effect that can be performed in the ending 1 state and the ending 2 state will be described.
エンディング演出は、その字句が示すように、基本的には、有利区間に制御されている期間が「1200」回以上となったときに、当該有利区間がもうじき終了されることを示唆する演出となっている。また、有利区間に制御されている期間が「1200」回以上となる確率を鑑みれば、実行される確率が他の演出よりも低い特別な演出となっている。 The ending effect is basically an effect that suggests that the advantageous section will soon end when the period controlled by the advantageous section becomes “1200” times or more, as the phrase indicates. Has become. Further, considering the probability that the period controlled in the advantageous section is “1200” times or more, the special effect has a lower probability of being executed than other effects.
エンディング演出は、例えば、第1話〜第8話及び最終話からなる一連のストーリー演出として構成され、エンディング2状態での遊技期間が進行するのにしたがって、ストーリーの内容も進行するようになっている。なお、上述したように、エンディング2状態が、有利区間に制御されている期間が「1200」回となってから、規制監視期間が「1500」回となるまで継続可能に構成する場合には、規制監視期間が「1500」回となるまでの遊技期間に応じて、ストーリーの内容を進行させるようにすればよい。 The ending effect is configured as a series of story effects including, for example, the first to eighth episodes and the final episode, and as the game period in the ending 2 state progresses, the content of the story also progresses. There is. As described above, in the case where the ending 2 state is configured to be able to continue until the regulation monitoring period becomes “1500” times after the period controlled to the advantageous section becomes “1200” times, The content of the story may be advanced according to the game period until the regulation monitoring period reaches "1500" times.
ここで、本実施形態では、有利区間が開始されるときに、エンディング1状態に移行させることが決定されている場合には、当該有利区間が開始されたばかりであるにもかかわらず、エンディング1状態中はエンディング演出が実行されるようになっている。 Here, in the present embodiment, when it is determined to shift to the ending 1 state when the advantageous section is started, the ending 1 state is set although the advantageous section is just started. The ending production is executed inside.
ただし、エンディング1状態では、上述した一連のストーリー演出のうちの一部が実行され、全部は実行されないようになっている。具体的には、第1話〜第8話及び最終話のうちの第1話〜第8話は実行されるが、最終話は実行されないようになっている。なお、この場合にも、エンディング2状態と同様、基本的には、エンディング1状態での遊技期間が進行するのにしたがって、ストーリーの内容が進行するようになっている。 However, in the ending 1 state, part of the series of story effects described above is executed, and not all of them are executed. Specifically, the first to eighth episodes of the first to eighth episodes and the final episode are executed, but the final episode is not executed. Note that, in this case also, basically, as in the ending 2 state, the content of the story progresses as the game period in the ending 1 state progresses.
エンディング1状態において、上述した一連のストーリー演出のうちの一部が実行される具体例を、図44を参照しながら説明する。例えば、エンディング準備状態では、エンディング演出の導入演出が行われる。そして、エンディング1状態が開始されるとき(ART開始)、エンディング演出が開始され、第1話、第2話、・・・第8話といったように、順次ストーリーが進行していく。そして、第8話が終了したとき、表示装置11に「つづく」といった文字が表示され、ストーリーが完結していないことが示される。
A specific example in which a part of the series of story effects described above is executed in the ending 1 state will be described with reference to FIG. For example, in the ending preparation state, the introduction effect of the ending effect is performed. Then, when the ending 1 state is started (ART start), the ending effect is started, and the story sequentially progresses like the first episode, the second episode,... The eighth episode. Then, when the eighth episode ends, a character such as "continue" is displayed on the
一方、エンディング2状態では、エンディング2状態が開始されるとき(有利区間≧1200 インターバル状態終了)、エンディング演出が開始され、第1話、第2話、・・・第8話といったように、順次ストーリーが進行していく。そして、第8話が終了すると、次に最終話のストーリーが展開され、最終話のストーリーが終了したとき、表示装置11に「THE END」といった文字が表示され、ストーリーが完結したことが示される。
On the other hand, in the ending 2 state, when the ending 2 state is started (advantageous interval ≧1200 interval state end), the ending effect is started, and the first, second,... The story progresses. Then, when the eighth episode ends, the story of the final episode is developed next, and when the story of the final episode ends, characters such as “THE END” are displayed on the
なお、上述したエンディング演出の演出内容は、複数回数の遊技にわたって実行可能なエンディング演出の演出内容の一例を示すものであり、エンディング演出の演出内容はこれに限られない。遊技者にとって価値を有する演出内容であれば、どのような演出内容であってもよい。 In addition, the above-mentioned ending production effect contents show one example of the ending effect production contents that can be executed over a plurality of times of games, and the ending production effect contents are not limited to this. Any production content may be used as long as it is production content that is valuable to the player.
例えば、パチスロ1のモチーフとして用いられているアニメーションやキャラクタなどがあれば、エンディング2状態におけるエンディング演出では、通常は見ることができないアニメーションの特別映像やキャラクタの特別映像が表示装置11に表示されるものとすればよい。この場合、エンディング1状態におけるエンディング演出では、これらの映像の内容をエンディング2状態におけるエンディング演出よりも短くして(例えば、要約し、その途中までとし、あるいは別内容として)表示装置11に表示されるものとすればよい。もっとも、これらに替えて、あるいはこれらとともに、スピーカ群84から出力される楽曲や音声、LED群85による発光態様によって各エンディング演出が行われるようにすることもできる。
For example, if there is an animation or a character used as the motif of the pachi-
また、エンディング演出は、残りの遊技回数にかかわらず演出内容が進行するものであってもよい。例えば、単位遊技に要する時間を、仮に「6秒」(この値は任意)と定め、エンディング2状態におけるエンディング演出を、「6秒×131回の遊技=786秒」の一連の演出として定め、エンディング2状態に制御されたタイミングでこの一連の演出を開始するようにし、また、エンディング1状態におけるエンディング演出を、「6秒×100回の遊技=600秒」の一連の演出の一部の演出として定め、エンディング1状態に制御されたタイミングでこの一連の演出の一部の演出を開始するようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、エンディング演出を遊技回数に合わせて進行させる必要がなくなることから、演出に係る制御負担を軽減することができる。また、この場合、有利区間が終了するよりも前のタイミングで上述した一連の演出の実行が終了した場合には、その終了時の画面がそのまま有利区間が終了するときまで表示されるようにしてもよいし、上述した一連の演出が再度最初から(あるいは、中途から)開始されるようにしてもよい(すなわち、ループして実行されるようにしてもよい)。また、この場合、上述した一連の演出の実行が終了する前のタイミングで有利区間が終了した場合には、上述した一連の演出をその中途であっても強制的に終了させるようにしてもよいし、上述した一連の演出が最後まで実行されるようにしてもよい。 Further, the ending effect may be one in which the effect content proceeds regardless of the number of remaining games. For example, the time required for the unit game is temporarily set to "6 seconds" (this value is arbitrary), and the ending effect in the ending 2 state is set as a series of effects of "6 seconds x 131 times game = 786 seconds", This series of effects is started at the timing controlled to the ending 2 state, and the ending effects in the ending 1 state are part of the series of effects of "6 seconds x 100 games = 600 seconds". As a result, a part of the series of effects may be started at the timing controlled to the ending 1 state. By doing so, it is not necessary to advance the ending effect according to the number of games, so that the control load related to the effect can be reduced. Further, in this case, when the execution of the series of effects described above is finished at a timing before the end of the advantageous section, the screen at the end is displayed as it is until the end of the advantageous section. Alternatively, the series of effects described above may be started again from the beginning (or from the middle) (that is, may be executed in a loop). Further, in this case, when the advantageous section ends at the timing before the execution of the series of effects described above ends, the series of effects described above may be forcibly ended even in the middle thereof. However, the series of effects described above may be executed until the end.
また、図44においては図示を省略しているが、本実施形態では、有利区間において、当該有利区間おける遊技期間が「1200」回の遊技となるまで(あるいは、エンディング1状態に移行するまで)、当該有利区間を継続させることが決定される(例えば、ラインバトル状態の継続抽籤状態においてラインバトル状態を継続させることが決定され、あるいは、権利獲得抽籤状態が終了し、その後インターバル状態に移行した)度に、表示装置11において、有利区間に制御されている期間の目安を示唆する示唆演出が実行されるようになっている。
Although not shown in FIG. 44, in the present embodiment, in the advantageous section, until the game period in the advantageous section becomes "1200" games (or until the ending 1 state is entered). , It is decided to continue the advantageous section (for example, it is decided to continue the line battle state in the continuous lottery state of the line battle state, or the right acquisition lottery state ends, and then shifts to the interval state. ) Each time, the
具体的には、例えば、12マスに区画されたプログレスバーやマップなどを表示装置11内に所定の領域に表示するとともに、有利区間における遊技期間の遊技回数が100ゲーム進行する度に、1マスずつその表示態様を異なるものとしていく、といったような示唆演出が実行される。このようにすれば、有利区間における遊技期間の概数が把握できるようになる。なお、例えば、プログレスバーやマップなどの区画を15マスとし、規制監視期間の消化度合いが表示されるようにしてもよい。また、これらは示唆演出の表示内容の一例であり、その表示内容はこれに限られない。例えば、有利区間における遊技期間の実数の遊技回数が表示されるようにしてもよい。
Specifically, for example, a progress bar or a map divided into 12 squares is displayed in a predetermined area in the
また、示唆演出は、インターバル状態の最初の遊技中のみ表示されるようにしてもよいし、インターバル状態中(3ゲーム間)にわたって表示されるようにしてもよい。また、有利区間が終了する可能性のあるラインバトル状態でのみ表示されるようにしてもよいし、有利区間中の各遊技状態で常に表示されるようにしてもよい。 Further, the suggestive effect may be displayed only during the first game in the interval state, or may be displayed over the interval state (between three games). Further, it may be displayed only in a line battle state in which the advantageous section may end, or may be always displayed in each game state in the advantageous section.
このように、本実施形態では、エンディング2状態となったときに、エンディング演出(特別演出)が実行されることを可能とするとともに、有利区間に移行することが決定された場合に、エンディング1状態に移行させることが決定されている場合には、エンディング1状態において、エンディング演出の一部の演出(特殊演出)が実行されることを可能としている。 As described above, in the present embodiment, the ending effect (special effect) can be executed when the ending 2 state is entered, and the ending 1 When it is determined to shift to the state, in the ending 1 state, a part of the ending effect (special effect) can be executed.
すなわち、本実施形態では、通常、遊技者に有利な状態中の遊技の終盤に実行され得るようになっている特別演出の一部である特殊演出が、所定の実行条件が成立した場合には、遊技者に有利な状態中の遊技の序盤において実行され得るようになっている。これにより、遊技者は特別演出を全て見たいと望みながら遊技を行うようになるため、遊技者の遊技意欲を高め、演出の興趣を向上させることができる。 That is, in the present embodiment, when the special execution, which is a part of the special effect that can be normally executed at the end of the game in the advantageous state for the player, satisfies the predetermined execution condition, , Can be executed in the early stage of the game in a state advantageous to the player. As a result, the player comes to play the game while wanting to see all the special effects, so that the player's motivation for the game can be increased and the interest of the effect can be improved.
また、本実施形態では、エンディング2状態となったときから131ゲームが経過して有利区間が終了するまで、あるいは、エンディング2状態となったときから規制監視期間が「1500」回となって有利区間が終了するまで、エンディング演出(特別演出)が実行されることを可能としている。これにより、遊技媒体の獲得を規制する場合であっても、遊技者の興趣が低下してしまうことを軽減することができる。 Further, in the present embodiment, the regulation monitoring period becomes “1500” times from the time the game enters the ending 2 state to the end of the advantageous section after 131 games have passed, or from the time the game enters the ending 2 state to “1500” times. The ending effect (special effect) can be executed until the section ends. As a result, even if the acquisition of the game medium is restricted, it is possible to reduce the decrease in the interest of the player.
また、本実施形態では、有利区間おける遊技期間が「1200」回の遊技となるまであるいは、エンディング1状態に移行するまで、有利区間を継続させることが決定される度に、有利区間に制御されている期間の目安を示唆する示唆演出を実行可能としている。これにより、特別演出の実行が開始される時期や有利区間が終了する時期などを遊技者が概ね把握できるようになるため、遊技の興趣を高めつつ、遊技者に適切な情報を提供することができる。 Further, in the present embodiment, the advantageous period is controlled every time it is determined that the advantageous period is continued until the game period in the advantageous period becomes “1200” games or until the ending 1 state is entered. It is possible to execute suggestive production that suggests a guide for the period of time. This makes it possible for the player to generally understand the time when the execution of the special effect starts, the time when the advantageous section ends, etc. Therefore, it is possible to provide the player with appropriate information while enhancing the interest of the game. it can.
(エンディング制御の他の例)
本実施形態では、有利区間が開始されてから例えば1500Gに達すると、残りゲーム数がたとえ残存していても有利区間を終了するリミット処理を実行するが、リミット処理を将来行うことが確定した段階(例えば、有利区間の消化済みゲーム数と残りゲーム数との合算値が規定値以上になった段階)で、主制御基板71は、出玉状態を「エンディング」(例えば、エンディング2状態)に移行する。一方で、副制御基板72は、メイン側において出玉状態を「エンディング」に移行した場合であっても、直ぐにはサブ側の演出状態を「エンディング(END)」に移行させることなく、所定の条件を契機に演出状態を「エンディング」に移行させる。以下では、特に、副制御基板72が演出状態を「エンディング」に移行させる制御の詳細について説明する。なお、本実施形態では、有利区間が「通常有利区間」などを含む場合があるが、この例では「有利区間」と「ART」とが全く同一の遊技状態であるものとして説明する。
(Other example of ending control)
In the present embodiment, when, for example, 1500 G is started after the advantageous section is started, limit processing for ending the advantageous section is executed even if the number of remaining games remains, but it is decided that the limit processing will be performed in the future. (For example, when the total value of the number of completed games and the number of remaining games in the advantageous section becomes equal to or more than the specified value), the
この例では、有利区間に関連してメイン(主制御基板71)側で計数するメイン側カウンタと、サブ(主制御基板71)側で計数するサブ側カウンタとを設けるものとする。主制御基板71は、第1のカウンタを用いて有利区間中に経過したゲーム数(消化済みゲーム数)を計数するとともに、第2のカウンタを用いて有利区間を継続可能な期間(残りゲーム数)を計数する。主制御基板71は、第1のカウンタの値が「1500」に達するとリミット処理を行い、第2のカウンタの値に関係なく有利区間を終了し、第1のカウンタの値が「1500」に達する前に、第2のカウンタの値が「0」になると、有利区間を終了する。
In this example, a main-side counter that counts on the main (main control board 71) side and a sub-side counter that counts on the sub (main control board 71) side are provided in association with the advantageous section. The
一方で、副制御基板72は、第3のカウンタを用いて有利区間中に経過したゲーム数(消化済みゲーム数)を計数するとともに、第4のカウンタを用いて有利区間を継続可能な期間(残りゲーム数)のうちの遊技者に対して報知した期間(報知済みゲーム数)を計数し、また、第5のカウンタを用いて有利区間を継続可能な期間(残りゲーム数)のうちの遊技者に対して未報知の期間(未報知ゲーム数(=潜伏させている上乗せゲーム数))を計数する。なお、副制御基板72は、潜伏させている上乗せゲーム数を報知した場合には、報知したゲーム数分だけ、報知済みゲーム数を加算するとともに、未報知ゲーム数を減算する。
On the other hand, the
メイン・サブの双方において計数する消化済みゲーム数は、基本的には一致するため、メイン側の第1のカウンタの値とサブ側の第3のカウンタの値とは一致する(なお、有利区間と「ART」とが一致しない場合、リミット処理はサブ側では行わないため、サブ側では有利区間の消化済みゲーム数を計数する必要が無く、「ART」中の消化済みゲーム数を計数することになるため、両カウンタの値は完全には一致しないものの、以下に説明する制御には関係が無い)。 Since the number of consumed games counted in both main and sub basically match, the value of the first counter on the main side matches the value of the third counter on the sub side (note that the advantageous interval is If the value and "ART" do not match, the limit process is not performed on the sub side, so it is not necessary for the sub side to count the number of completed games in the advantageous section, and the number of completed games in "ART" must be counted. Therefore, the values of both counters do not completely match, but are not related to the control described below).
また、サブ側では、報知済みの残りゲーム数と、未報知のまま保持している残りゲーム数とを個別に計数するため、メイン側の第2のカウンタの値と、サブ側の第4カウンタの値とは一致せず、また、メイン側の第2のカウンタの値と、サブ側の第5カウンタの値とも一致しない。ただし、報知済みの残りゲーム数と未報知のまま保持している残りゲーム数との和は、メイン側で計数する残りゲーム数と一致するため、メイン側の第2のカウンタの値と、サブ側の第4カウンタの値及び第5カウンタの値の和とは、一致する。 Further, on the sub-side, since the number of notified remaining games and the number of remaining games held unreported are individually counted, the value of the second counter on the main side and the fourth counter on the sub-side are counted. Does not match, and the value of the second counter on the main side does not match the value of the fifth counter on the sub side. However, since the sum of the number of remaining games that has been notified and the number of remaining games that have not been notified matches the number of remaining games that is counted on the main side, the value of the second counter on the main side and The sum of the value of the fourth counter and the value of the fifth counter on the side matches.
主制御基板71は、有利区間の消化済みゲーム数と残りゲーム数との合算値に基づいて「エンディング」への移行制御を行っており、例えば、ゲーム数の上乗せが行われた結果、有利区間の消化済みゲーム数と残りゲーム数との合算値が規定値以上になった段階で出玉状態を「エンディング」に移行する。
The
一方で、副制御基板72は、有利区間の消化済みゲーム数と報知済みゲーム数との合算値(すなわち、未報知ゲーム数を除いた合算値)に応じてサブ側の演出状態を「エンディング(END)」に移行させる。ここで、副制御基板72は、例えば、図示しないサブ_エンディング移行抽籤テーブルを参照して演出状態を「エンディング」に移行させる。
On the other hand, the
例えば、サブ_エンディング移行抽籤テーブルは、参照項目として消化済みゲーム数と報知済みゲーム数との合算値を規定し、合算値ごとに「エンディング」に移行させるか否かの抽籤結果(非当籤、当籤)についての抽籤値の情報を規定する。このようなサブ_エンディング移行抽籤テーブルによれば、例えば消化済みゲーム数と報知済みゲーム数との合算値が「1000〜1199G」である場合には、24576/32768の確率で「エンディング」への移行抽籤に非当籤し、8192/32768の確率で「エンディング」への移行抽籤に当籤する。 For example, the sub_ending transition lottery table defines a total value of the consumed game number and the notified game number as a reference item, and a lottery result (non-winning lottery, whether or not to shift to “ending” for each total value). Information on the lottery value for winning is defined. According to such a sub_ending transition lottery table, for example, when the total value of the number of consumed games and the number of notified games is “1000 to 1199G”, there is a probability of 24576/32768 to “ending”. Win the transition lottery without winning the transition lottery and have a probability of 8192/32768.
また、例えば、副制御基板72は、有利区間の消化済みゲーム数と報知済みゲーム数との合算値が大きくなるほど高い確率で演出状態を「エンディング」に移行させる。そして、副制御基板72は、演出状態を「エンディング」に移行させると、演出ステージを専用の“エンディングステージ”に移行し、有利区間が終了するまで当該“エンディングステージ”のまま維持する。なお、メイン側において出玉状態が「エンディング」に移行していない場合には、サブ側において「エンディング」への移行抽籤を行う必要がないため、副制御基板72は、メイン側において出玉状態が「エンディング」に移行した場合(すなわち、メイン側の管理するカウンタにおいて、有利区間の消化済みゲーム数と残りゲーム数との合算値が規定値以上になった場合)に限り、サブ側の演出状態を「エンディング」に移行させるか否かの抽籤を行うこととしてもよい。
Further, for example, the
このように「エンディング」移行時に専用の演出ステージに移行させることで、遊技者は、リミット処理が行われることを予め把握することができる。なお、“エンディングステージ”に移行した後は、リミット処理が行われることが確定しているため、ゲーム数の上乗せ報知演出を行う意味がない。そのため、副制御基板72は、“エンディングステージ”に移行した後は、上乗せ報知演出を行わない。
In this way, by shifting to the special effect stage when shifting to "ending", the player can know in advance that the limit process will be performed. Since it is determined that the limit process will be performed after shifting to the “ending stage”, it is meaningless to perform the additional notification effect of the number of games. Therefore, the
また、“エンディングステージ”への移行は、メイン側の合算値が規定値以上に達している状態で、サブ側の合算値(未報知ゲーム数を除く)が大きくなるほど高い確率で行われる。そのため、“エンディングステージ”への移行確率は、未報知のまま保持している上乗せゲーム数(未報知ゲーム数)が少ないほど高い確率となり、未報知のまま保持している上乗せゲーム数が多いほど低い確率となる。 Further, the transition to the "ending stage" is performed with a higher probability as the summed value on the sub side (excluding the number of uninformed games) becomes larger in a state where the summed value on the main side reaches or exceeds the specified value. Therefore, the probability of transition to the "ending stage" is higher as the number of additional games (unannounced games) held unannounced is higher, and the number of additional games held unannounced is higher. It has a low probability.
また、“エンディングステージ”に移行した後は、原則として有利区間の終了まで“エンディングステージ”の演出を継続し、有利区間が終了するゲームにおいて“エンディングステージ”の演出を終了し、当該ゲームの終了時又は次ゲームの開始時などに通常区間に対応する演出ステージへと移行させる。 In addition, after the transition to the "ending stage", as a general rule, the production of the "ending stage" is continued until the end of the advantageous section, and the production of the "ending stage" is finished in the game in which the advantageous section ends and the game ends. Time or at the start of the next game, the stage is shifted to the production stage corresponding to the normal section.
また、“エンディングステージ”の滞在中は、ボーナスが作動した場合でも依然としてリミット処理が近いうちに行われるという状況に変わりはないため“エンディングステージ”を維持することが望ましい。ここで、有利区間終了の直前のゲーム(例えば、第1のカウンタの値が「1499」のゲーム)においてBB1〜BB4などのように所定ゲーム数を消化に要するボーナスに当籤し、ボーナスが作動した場合、ボーナスの作動中に第1のカウンタが「1500」に達してリミット処理が行われ、有利区間が終了することになる。このとき、出玉が増加する状態であるボーナス作動中にも関わらず“エンディングステージ”を終了させて別の演出ステージ(通常区間に対応する演出ステージやボーナス作動中の演出ステージ)へ移行させると、遊技者に違和感を与える恐れがある。そこで、副制御基板72は、ボーナスの作動中にリミット処理により有利区間が終了する場合には、当該ボーナスの終了まで“エンディングステージ”のまま演出ステージを継続し、ボーナスの終了時に(有利区間の終了報知や、のめり込み防止表示などを行って)通常区間に対応する演出ステージへと移行させることとしてもよい。
In addition, it is desirable to maintain the "ending stage" during the stay of the "ending stage", since the limit processing will still be performed soon even if the bonus is activated. Here, in a game immediately before the end of the advantageous period (for example, a game in which the value of the first counter is “1499”), a bonus such as BB1 to BB4 required to consume a predetermined number of games is won and the bonus is activated. In this case, the first counter reaches “1500” during the bonus operation, the limit process is performed, and the advantageous period ends. At this time, if the "ending stage" is ended and the production stage is changed to another production stage (the production stage corresponding to the normal section or the production stage in bonus operation), even though the bonus operation, which is a state in which the payout increases, , There is a risk that the player feels uncomfortable. Therefore, if the advantageous section ends due to the limit process during the bonus operation, the
さらに、第1のカウンタの値が「1498」〜「1500」などリミット処理発動の直前でボーナス役が内部当籤役として決定され、入賞されずに持ち越された場合にも、副制御基板72は、“エンディングステージ”を継続して、当該持ち越し中のボーナス役が入賞して作動したボーナスの終了を待って“エンディングステージ”を終了させるというエンディング状態終了の遅延処理を行うことが好ましい。なお、この場合、リミット処理により有利区間が終了し、押し順などの報知を行わない状況(通常区間)となっても“エンディングステージ”が一時的に継続されてしまうため、副制御基板72は、このような非有利区間の“エンディングステージ”では有利区間中の“エンディングステージ”と演出を異ならせて、遊技者に機械の故障ではない旨を明示することが好ましい。また、副制御基板72は、非有利区間の“エンディングステージ”では、ボーナス役の入賞が可能な遊技(リプレイなどのボーナス役の入賞を阻害する役に当籤していない遊技)でボーナス役の入賞を促す旨の報知や、指示機能が終了しており、ボーナスの終了後に“エンディングステージ”が終了する旨の報知などを行って、遊技者に状況を分かり易く伝えることとしてもよい。また、ボーナス作動中にリミット処理により有利区間が終了した場合、又は、ボーナス作動中にリミット処理が行われる可能性が高い場合などは、副制御基板72は、それ以外のボーナス作動中とは異なる演出(例えば、大量獲得を祝福する演出や設定示唆情報など何らかの有利な情報を含む演出など)を、当該ボーナスの開始時、作動中、ないしは終了時に行うこととしてもよい。
Further, when the bonus combination is determined as the internal winning combination immediately before the limit process is activated such as the value of the first counter is “1498” to “1500” and the bonus winning combination is carried over without winning, the
また、有利区間が終了する際に、主制御基板71は、全リールの停止後などに所定時間、遊技操作(例えば、次遊技のメダルの投入操作や再遊技の作動による自動再投入、開始操作など)を受け付けない有利区間終了時のフリーズ処理を行うこととしてもよい。このとき、副制御基板72は、有利区間終了時のフリーズの時間を利用して、当該有利区間中に獲得したメダルの枚数、消化ゲーム数、ないしはセット数のように当該有利区間に関する情報を表示することとしてもよく、また、のめり込み防止表示をこれらに合わせて表示することとしてもよい。また、上述のように、リミット処理による有利区間の終了がボーナス作動中に発生する場合は、主制御基板71は、ボーナスの消化を妨げないようにリミット処理による有利区間の終了時にフリーズを発生させずに、ボーナスの終了時に有利区間終了時のフリーズを行うこととしてもよい。なお、有利区間の終了とは関係なく、ボーナス終了時に有利区間中に獲得したメダルの枚数などの有利区間に関する情報などを表示する表示用の時間を確保するなどの目的で、ボーナス終了時に所定時間のフリーズが設けられている場合は、有利区間の終了がボーナス作動中に発生する場合は、有利区間終了時のフリーズを有利区間終了時にも、ボーナス終了時にも行わず、主制御基板71は、ボーナス終了時のフリーズのみをボーナス終了時に行い、このボーナス終了時のフリーズ中に副制御基板72は、有利区間に関する情報やのめり込み防止表示などを表示することとしてもよい。フリーズによる遊技の遅延が複数発生することを抑制することで、遊技のテンポが悪くなってしまうことを防止できる。なお、ここまで説明した内容は、後述する別例のリミット処理によりボーナス作動中に有利区間が終了する場合においても適用することとしてもよく、また、仕様設計者は発動するリミッタの種別により上記の処理を適用するか、不適用とするか演出の流れなどを考慮して任意に決定することができる。
In addition, when the advantageous section ends, the
(可変リミッタ)
ここまで、有利区間を終了するリミット処理を実行する条件を有利区間が開始されてから例えば1500Gに達した場合など、リミット処理の実行条件が一定の場合を前提として説明を行った。しかし、主制御基板71によるリミット処理の実行条件は必ずしも一定である必要はなく、少なくとも上限値(例えば有利区間開始から1500G)を超えて有利区間が継続しないようにすれば十分に過度の射幸性を抑制するという効果を発揮することができる。そこで、主制御基板71は、第1のカウンタ(消化済みゲーム数)が所定の終了条件を満たした場合に、第1のカウンタ(消化済みゲーム数)が上限値を超えるより前に有利区間を終了させるリミット処理を行うこととしてもよい。
(Variable limiter)
Up to this point, the conditions for executing the limit process for ending the advantageous period have been described on the premise that the limit process execution condition is constant, for example, 1500 G has been reached after the advantageous period was started. However, the execution condition of the limit processing by the
例えば、「ART」が1セットあたり50G固定のセット数管理タイプのパチスロでは、「通常有利区間」の期間や「ART」中のボーナスなどにより、1セットのゲーム数に対して中途半端なタイミング(例えば、上限値まで残り20Gである1480G)で今回のセットの「ART」が終了することがある。このようなケースでは、次セットの「ART」を1セット全て(50G)行うことができず、セットの途中でリミット処理を行うことになってしまう。次セットの「ART」が開始されたにも関わらず、直ぐに強制的に終了させられてしまったのでは遊技者が不満を感じる可能性もある。そこで、主制御基板71は、上限値に達する前ではあるものの、区切りが良い今回のセットの「ART」終了時に、有利区間のリミット処理を行うこととしてもよい。これにより、有利区間(「ART」)は、必ず区切りの良いタイミングで終了することになるため、遊技者が不満を感じる可能性を軽減することができる。
For example, in a pachi-slot of a set number management type in which "ART" is fixed at 50 G per set, a timing that is halfway to the number of games in one set (due to the period of the "normal advantage section" or the bonus in "ART" ( For example, the “ART” of the current set may end when the remaining upper limit value is 20 G (1480 G). In such a case, the entire "ART" of the next set cannot be performed (50G), and the limit process is performed during the set. Even if the "ART" of the next set is started, if it is forcibly ended immediately, the player may feel dissatisfied. Therefore, the
また、パチスロによっては、リミット処理を行う場合に所定のエンディング制御を行うことも考えられるため、このようなエンディング制御を行うケースについても説明する。例えば、「ART」が1セットあたり50G固定のセット数管理タイプのパチスロにおいて、有利区間開始からの消化済みゲーム数及び残りゲーム数の値の合計値が1400〜1450Gの範囲(所定の終了条件の設定範囲)に達した場合に、主制御基板71は、残りの未消化セット数にかかわらずエンディング用の1セットとして50Gの有利区間(「ART」)を設定し、当該エンディング用の1セットが終了した時点で所定の終了条件を満たしたとしてリミット処理を実行し、有利区間を終了させるものとしてもよい。つまり、リミット処理は有利区間の開始から1400〜1450Gの時点で予約され、1450〜1500Gまでで実行されることとなる。このようにある程度、リミット処理の実行タイミングに幅を持つことを許容することで、不自然なタイミングで有利区間が終了して遊技者に違和感を与えることを防ぎつつ、射幸性を適切に抑制できる。また、「ART」1セットあたりのゲーム数を固定としても、途中でボーナスの作動や基本のセットと異なる上乗せ特化状態などの消化が加わることで、エンディング用の1セットが決定されるタイミングは必ずしも50の倍数である1400ゲームちょうどとはならないため、所定の終了条件の設定範囲(リミット処理を予約可能である期間)にも幅を持たせることが好ましい。
In addition, depending on the pachi-slot, it may be possible to perform a predetermined ending control when performing the limit processing, so a case of performing such ending control will also be described. For example, in a pachi-slot of a set number management type in which "ART" is fixed at 50 G per set, the total value of the number of completed games and the number of remaining games from the start of the advantageous section is in the range of 1400 to 1450 G (the predetermined end condition is satisfied). When the setting range) is reached, the
なお、後述するようにリミット処理は、ゲーム数に限らず有利区間中に遊技者が獲得したメダルの差枚数やナビの発生回数に基づいて行うことができる(後述の枚数リミッタ、払出枚数リミッタ、ナビ回数リミッタ)。上述の可変リミッタの説明は、リミット処理の種類に関係なく適用可能である。すなわち、主制御基板71は、リミット処理の実行タイミングをリミット処理発動用のカウンタ(ゲーム数カウンタ、払出枚数カウンタ、ナビ回数カウンタなど)がリミッタ発動の閾値(上限値)に達した場合に限らず、所定の終了条件を充足した場合には、リミッタ発動の閾値に達するよりも前にリミット処理を行うものとしてもよい。なお、所定の終了条件は任意であるが、一例として、セット数管理タイプの「ART」において、次セットの「ART」を開始してしまうと、次セットの「ART」の途中でリミッタが発動してしまうことが予測されることを採用することができる(パチスロでは、「ART」中の1ゲームあたりのメダルの増加量やそれぞれの役の当籤確率などが設計仕様から把握することができるため、後述の枚数リミッタ、払出枚数リミッタ又はナビ回数リミッタを用いる場合であっても、次セットの「ART」の途中でリミッタが発動してしまうことを予測することができる)。
Note that, as will be described later, the limit process can be performed not only on the number of games but also on the basis of the number of medals obtained by the player during the advantageous section and the number of times the navigation occurs (number limiter, payout number limiter described later, Navi count limiter). The above description of the variable limiter can be applied regardless of the type of limit processing. That is, the
この点についての技術的思想を整理すると、以下のようになる。
特定の遊技状態(有利区間)を継続可能な残り期間を示す第2数値(有利区間継続可能な残りゲーム数、差枚数、ナビ回数)が終了閾値(残り0ゲーム、0枚、0回)に達すると前記特定の遊技状態を終了するとともに、少なくとも前記計数手段が計数する前記第1数値(消化済みのゲーム数等)が所定の終了条件(例えば、リミット処理の実行となる有利区間1500ゲーム消化または、変形例のようにリミット処理の実行タイミングに幅が許容される場合は設定された1450〜1500までのゲーム数のいずれかの到達等)を満たす場合は前記第2数値の値が前記終了閾値に達していないときであっても前記特定の遊技状態を終了させる特定状態終了手段(主制御基板71)。
なお、特定状態終了手段は、「ART」など有利区間の権利がゼロとなったことに基づいて有利区間を終わらせる処理と、リミット処理により有利区間を終わらせる場合の双方についてまとめて記載したが、プログラム上、別の処理として持たせるものとしてもよい。
The technical ideas regarding this point are summarized as follows.
The second numerical value (remaining number of games that can continue the advantageous period, difference number, number of times of navigation) that indicates the remaining period in which the specific game state (advantageous period) can be continued is set as the end threshold (0 games remaining, 0 sheets, 0 times) When it reaches, the specific game state is ended, and at least the first numerical value (the number of completed games, etc.) counted by the counting means is a predetermined end condition (for example, an
Note that the specific state ending means collectively describes both the process of ending the advantageous period based on the fact that the right of the advantageous period such as “ART” has become zero, and the case of ending the advantageous period by the limit process. The program may be provided as another process.
なお、本実施形態では、これまでに説明した各種データテーブル(図示を省略したものを含む)を用いた抽籤(特にテーブルを用いた抽籤として説明していない抽籤を含む)において、乱数回路110の乱数レジスタ2〜7により、予め定められた数値の範囲(0〜255)から抽出される抽籤用乱数値(演出用乱数値)を、規定された抽籤値で順次減算し、減算の結果が負となったか否か(いわゆる「桁かり」が生じたか否か)の判定を行うことによって内部的な抽籤が行われる。すなわち、抽籤用乱数値から抽籤値を減算して当籤/非当籤を判定しているが、抽籤の手法はこれに限定されず、抽出した抽籤用乱数値に抽籤値を加算し、加算結果が256を超えたか否か(いわゆる「桁あふれ」が生じたか否か)を判定して、当籤/非当籤を決定してもよい。
In the present embodiment, in the lottery using the various data tables described above (including those not shown) (including lottery not particularly described as the lottery using the table), the
<メイン側の制御による報知機能>
従来のパチスロでは、遊技者に有利な停止操作の情報(押し順など)を報知するか否かの決定がサブ(副制御基板72)側の制御によりなされていた。しかしながら、この報知の有無が遊技者の利益(いわゆる、出玉)に影響を与えるため、近年では、遊技者の利益を管理するメイン(主制御基板71)側で制御することが求められている。そこで、本実施形態のパチスロ1では、上述のように、メイン側で制御される情報表示器6に停止操作の情報を報知するための指示モニタ(不図示)を設け、メイン側の制御により、リールの停止操作の情報を報知(指示)する機能が設けられている。
<Notification function by main control>
In the conventional pachi-slot, the sub-(sub-control board 72) side determines whether or not to inform the player of advantageous stop operation information (pushing order, etc.). However, since the presence or absence of this notification affects the profit of the player (so-called payout), in recent years, the main (main control board 71) side that manages the profit of the player is required to control. .. Therefore, in the pachi-
ここで、図45に、本実施形態のパチスロ1において、メイン側で制御される各遊技状態と内部当籤役とナビデータとの対応関係を示す。なお、図45に示すナビデータ「1」〜「6」は、指示モニタに表示される数値を表すとともに、停止操作の情報の報知内容を表す。また、図45に示すナビデータ「0」は、停止操作の情報が報知されないことを表す。また、図45では、押し順小役及び押し順リプレイのみを摘記して説明している。もっとも、押し順小役及び押し順リプレイ以外の内部当籤役については、基本的にナビデータが「0」となっている。
Here, in FIG. 45, in the pachi-
非有利区間の各遊技状態においては、図45に示すいずれの内部当籤役が決定された場合であっても、ナビデータ「0」がセットされ、停止操作の情報は報知されない。なお、ナビデータ「0」がセットされる場合、本実施形態では、指示モニタにいずれの数値も表示しないこととしているが、これに限られず、例えば、指示モニタに「0」の数値を表示するようにしてもよい。また、ナビデータ「0」がセットされる場合、本実施形態では、これに相当する情報をサブ側に送信しないようにしているが、これに限られず、これに相当する情報をサブ側に送信するようにしてもよい。 In each gaming state of the non-advantageous section, no matter which internal winning combination shown in FIG. 45 is determined, the navigation data “0” is set and the information of the stop operation is not notified. Note that when the navigation data “0” is set, in the present embodiment, no numerical value is displayed on the instruction monitor, but the present invention is not limited to this, and for example, a numerical value “0” is displayed on the instruction monitor. You may do it. Further, when the navigation data “0” is set, in the present embodiment, the information corresponding to this is not transmitted to the sub side, but the present invention is not limited to this, and the information corresponding to this is transmitted to the sub side. You may do so.
通常有利区間のボーナス非当籤状態及びフラグ間状態において、「F_上段左ベル1」及び「F_中段左ベル1」のいずれかの内部当籤役が決定された場合、ナビデータ「1」がセットされる。ナビデータ「1」は、「打順1」に対応する。また、「F_上段左ベル2」及び「F_中段左ベル2」のいずれかの内部当籤役が決定された場合、ナビデータ「2」がセットされる。ナビデータ「2」は、「打順2」に対応する。
When the internal winning combination of either "F_upper left
また、「F_上段中ベル1」、「F_中段中ベル1」、及び「F_下段中ベル1」のいずれかの内部当籤役が決定された場合、ナビデータ「3」がセットされる。ナビデータ「3」は、「打順3」に対応する。また、「F_上段中ベル2」、「F_中段中ベル2」、及び「F_下段中ベル2」のいずれかの内部当籤役が決定された場合、ナビデータ「4」がセットされる。ナビデータ「4」は、「打順4」に対応する。
Further, when the internal winning combination of any one of "F_upper
また、「F_上段右左ベル1」、「F_上段右左ベル2」、「F_中段右左ベル1」、「F_中段右左ベル2」、「F_下段右左ベル1」、及び「F_下段右左ベル2」、のいずれかの内部当籤役が決定された場合、ナビデータ「5」がセットされる。ナビデータ「5」は、「打順5」に対応する。また、「F_上段右中ベル1」、「F_上段右中ベル2」、「F_中段右中ベル1」、「F_中段右中ベル2」、「F_下段右中ベル1」、及び「F_下段右中ベル2」、のいずれかの内部当籤役が決定された場合、のいずれかの内部当籤役が決定された場合、ナビデータ「6」がセットされる。ナビデータ「6」は、「打順6」に対応する。
Also, "F_upper right
なお、本実施形態では、例えば、「F_上段左ベル1」及び「F_上段左ベル2」のいずれかの内部当籤役が決定された場合、「打順1」又は「打順2」であれば、押し順正解となるため、ナビデータを共通のナビデータとすることもできる。しかしながら、本実施形態では、内部当籤役の構成上、押し順小役について本来であれば最大6択の押し順を設定できるところを4択の押し順として設定していることから、これに対して違和感が生じないように、「F_上段左ベル1」が内部当籤役が決定された場合にはナビデータ「1」をセットし、「F_上段左ベル2」が内部当籤役が決定された場合にはナビデータ「2」をセットするようにしている。他の押し順小役も同様である。
In the present embodiment, for example, in the case where an internal winning combination of either “F_upper left
また、通常有利区間のボーナス非当籤状態及びフラグ間状態において、押し順リプレイのいずれかの内部当籤役が決定された場合、ナビデータ「0」がセットされる。すなわち、通常有利区間のボーナス非当籤状態及びフラグ間状態では、押し順リプレイの押し順報知は行われない。また、通常有利区間のボーナス状態において、押し順小役のいずれかの内部当籤役が決定された場合、ナビデータ「0」がセットされる。すなわち、通常有利区間のボーナス状態では、押し順小役の押し順報知は行われない。 Further, in the bonus non-winning state and the inter-flag state of the normal advantageous section, when any internal winning combination of the push order replay is determined, the navigation data “0” is set. That is, in the bonus non-winning state and the inter-flag state of the normal advantageous section, the push order notification of the push order replay is not performed. In addition, in the bonus state of the normal advantageous section, if any internal winning combination of the pushing order small combination is determined, the navigation data “0” is set. That is, in the bonus state of the normal advantageous section, the push order notification of the push order small win is not performed.
有利区間の各遊技状態において、「F_RT0中リプレイ1」及び「F_RT1中リプレイ1」のいずれかの内部当籤役が決定された場合、ナビデータ「1」がセットされる。ナビデータ「1」は、「打順1」に対応する。また、「F_RT2中リプレイ1」の内部当籤役が決定された場合であって、抽籤(1/2の確率)によりナビデータ「1」がセットされることが決定された場合にもナビデータ「1」がセットされる。なお、押し順小役(ボーナス非当籤状態及びフラグ間状態)において、ナビデータ「1」がセットされる態様は、通常有利区間におけるものと同様である。また、ボーナス状態において、「F_JAC1_1」の内部当籤役が決定された場合、ナビデータ「1」がセットされる。
In each gaming state of the advantageous section, when the internal winning combination of either "
また、「F_RT0中リプレイ2」及び「F_RT1中リプレイ2」のいずれかの内部当籤役が決定された場合、ナビデータ「2」がセットされる。ナビデータ「2」は、「打順2」に対応する。また、「F_RT2中リプレイ1」の内部当籤役が決定された場合であって、抽籤(1/2の確率)によりナビデータ「2」がセットされることが決定された場合にもナビデータ「2」がセットされる。なお、押し順小役(ボーナス非当籤状態及びフラグ間状態)において、ナビデータ「2」がセットされる態様は、通常有利区間におけるものと同様である。また、ボーナス状態において、「F_JAC1_2」の内部当籤役が決定された場合、ナビデータ「2」がセットされる。
If the internal winning combination of either "
また、「F_RT0中リプレイ3」及び「F_RT1中リプレイ3」のいずれかの内部当籤役が決定された場合、ナビデータ「3」がセットされる。ナビデータ「3」は、「打順3」に対応する。また、「F_RT2中リプレイ2」の内部当籤役が決定された場合であって、抽籤(1/2の確率)によりナビデータ「3」がセットされることが決定された場合にもナビデータ「3」がセットされる。なお、押し順小役(ボーナス非当籤状態及びフラグ間状態)において、ナビデータ「3」がセットされる態様は、通常有利区間におけるものと同様である。また、ボーナス状態において、「F_JAC1_3」の内部当籤役が決定された場合、ナビデータ「3」がセットされる。
Further, when the internal winning combination of either "
また、「F_RT0中リプレイ4」及び「F_RT1中リプレイ4」のいずれかの内部当籤役が決定された場合、ナビデータ「4」がセットされる。ナビデータ「4」は、「打順4」に対応する。また、「F_RT2中リプレイ2」の内部当籤役が決定された場合であって、抽籤(1/2の確率)によりナビデータ「4」がセットされることが決定された場合にもナビデータ「4」がセットされる。なお、押し順小役(ボーナス非当籤状態及びフラグ間状態)において、ナビデータ「4」がセットされる態様は、通常有利区間におけるものと同様である。また、ボーナス状態において、「F_JAC1_4」の内部当籤役が決定された場合、ナビデータ「4」がセットされる。
If the internal winning combination of either "
また、「F_RT0中リプレイ5」及び「F_RT1中リプレイ5」のいずれかの内部当籤役が決定された場合、ナビデータ「5」がセットされる。ナビデータ「5」は、「打順5」に対応する。また、「F_RT2中リプレイ3」の内部当籤役が決定された場合であって、抽籤(1/2の確率)によりナビデータ「5」がセットされることが決定された場合にもナビデータ「5」がセットされる。なお、押し順小役(ボーナス非当籤状態及びフラグ間状態)において、ナビデータ「5」がセットされる態様は、通常有利区間におけるものと同様である。また、ボーナス状態において、「F_JAC1_5」の内部当籤役が決定された場合、ナビデータ「5」がセットされる。
When the internal winning combination of either "
また、「F_RT0中リプレイ6」及び「F_RT1中リプレイ6」のいずれかの内部当籤役が決定された場合、ナビデータ「6」がセットされる。ナビデータ「6」は、「打順6」に対応する。また、「F_RT2中リプレイ3」の内部当籤役が決定された場合であって、抽籤(1/2の確率)によりナビデータ「6」がセットされることが決定された場合にもナビデータ「6」がセットされる。なお、押し順小役(ボーナス非当籤状態及びフラグ間状態)において、ナビデータ「6」がセットされる態様は、通常有利区間におけるものと同様である。また、ボーナス状態において、「F_JAC1_6」の内部当籤役が決定された場合、ナビデータ「6」がセットされる。
If the internal winning combination of either "
このように、本実施形態では、メイン(主制御基板71)側は、指示モニタに「1」〜「6」の数値を表示することにより、リールの停止操作の情報を報知する。また、指示モニタに表示されるこの「1」〜「6」の数値は、それぞれが報知する停止操作の内容に一義的に対応している。 As described above, in the present embodiment, the main (main control board 71) side notifies the information of the reel stop operation by displaying the numerical values of “1” to “6” on the instruction monitor. Further, the numerical values of "1" to "6" displayed on the instruction monitor uniquely correspond to the contents of the stop operation notified by each.
なお、メイン側(指示モニタ)で報知する数値「1」〜「6」は、報知する停止操作の内容に一義的に対応しているものの、全ての遊技者が、その数値に基づいて、明確に報知内容を把握できるとは限らない。例えば、メイン側で指示モニタに数値「6」を表示しただけでは、遊技者によっては報知内容を把握できない可能性もある。 Although the numbers "1" to "6" notified on the main side (instruction monitor) uniquely correspond to the contents of the stop operation to be notified, all the players are clear based on the values. It is not always possible to understand the content of the notification. For example, there is a possibility that the player may not be able to comprehend the content of the notification just by displaying the numerical value "6" on the instruction monitor on the main side.
そこで、本実施形態のパチスロ1では、メイン側の報知と併せてサブ側でもストップボタンの停止操作に係る情報を報知する。具体的には、サブ側で制御される表示装置11(プロジェクタ機構211及び表示ユニット212)を用いて、サブ側の制御により停止操作に係る情報の報知を行う。
Therefore, in the pachi-
例えば、押し順「中、左、右」(打順3)を報知する場合、メイン側で指示モニタに数値「3」を表示するとともに、サブ側では、表示装置11の表示画面内の中リール3Cの上方に数値「1」を表示し、左リール3Lの上方に数値「2」を表示し、右リール3Rの上方に数値「3」を表示し、この表示により押し順が「中、左、右」の順であることを報知する。
For example, when notifying the pressing order "middle, left, right" (stroke order 3), the numerical value "3" is displayed on the instruction monitor on the main side and the
なお、メイン側で報知を行うタイミングは、少なくとも報知を行う一遊技の期間であれば任意のタイミングに設定することができる。例えば、遊技者の開始操作を検知した(受け付けた)タイミングでメイン側の報知を行ってもよいし、リールの回転開始時にメイン側の報知を行ってもよいし、第1停止操作〜第3停止操作のいずれかを検知したタイミングでメイン側の報知を行ってもよい。一方、サブ側で報知を行うタイミングは、少なくとも第1停止操作よりも前のタイミングであることが好ましい。それゆえ、本実施形態のパチスロ1では、有利区間中の停止操作の情報を報知する遊技においては、内部抽籤処理(後述の図56のS204参照)の後、リール停止制御処理(後述の図56のS213)が開始される前に、メイン(主制御基板71)側からサブ(副制御基板72)側に、このナビデータ(あるいは、これに相当する情報)をパラメータに含むコマンドを送信するようにすればよい。なお、この場合、既存のコマンド(例えば、スタートコマンド、あるいはリール回転開始コマンド)にナビデータ(あるいは、これに相当する情報)のパラメータを含ませてもよいし、ナビデータ(あるいは、これに相当する情報)を送信するための専用のコマンドを送信してもよい。これにより、メイン側の指示モニタ及びサブ側の表示装置11の双方において停止操作の情報を報知することが可能となる。
The timing of notification on the main side can be set to any timing as long as it is at least one game period for notification. For example, the main side may be notified at the timing when the player's start operation is detected (accepted), the main side may be notified when the reel starts rotating, or the first stop operation to the third stop operation. The main side may be notified at the timing of detecting any one of the stop operations. On the other hand, it is preferable that the timing at which the notification is given on the sub side is at least a timing before the first stop operation. Therefore, in the pachi-
また、別の手法として、有利区間中の停止操作の情報を報知する遊技においては、上述したように、内部当籤役を特定できる情報として当籤役番号をメイン側からサブ側へ送信するものとしてもよい。この手法によれば、ナビデータに相当する情報を送るまでもなく、サブ側は遊技者に有利な停止操作の手順を特定できるため、送信するデータ量を減らすこともできる。 Further, as another method, in the game in which the information of the stop operation in the advantageous section is notified, as described above, the winning combination number may be transmitted from the main side to the sub side as the information for identifying the internal winning combination. Good. According to this method, the sub side can specify the procedure of the stop operation that is advantageous to the player without sending information corresponding to the navigation data, so that the amount of data to be transmitted can be reduced.
<主制御回路の動作説明>
次に、図46〜図84を参照して、主制御回路90のメインCPU101が、プログラムを用いて実行する各種処理の内容について説明する。
<Description of operation of main control circuit>
Next, the contents of various processes executed by the
[電源投入(リセット割込)時処理]
まず、メインCPU101の制御により行われるパチスロ1の電源投入(リセット割込)時処理を、図46を参照して説明する。図46は、電源投入(リセット割込)時処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。なお、図46に示す電源投入(リセット割込)時処理は、電源管理回路93が、マイクロプロセッサ91に電源電圧の供給が開始されたことを検知した際に、リセット信号をマイクロプロセッサ91の「XSRST」端子に出力し、セキュリティモードによる遅延動作を経た後、マイクロプロセッサ91の割込みコントローラ112からメインCPU101に出力される割込要求信号に基づいて、実行される。
[Process at power-on (reset interrupt)]
First, the power-on (reset interrupt) process of the pachi-
まず、メインCPU101は、タイマー回路113(PTC)の初期化処理を行う(S1)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、タイマー回路113の初期設定を行う。具体的には、メインCPU101は、タイマー用プリスケーラレジスタ(不図示)に分周比をセットし、タイマー用制御レジスタ(不図示)に割り込み可等の設定を行い、タイマー用カウンタ(不図示)の初期カウント値を設定する。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、主制御回路90及び副制御回路200間用の第1シリアル通信回路114(SCU1)の初期化処理、及び、第2インターフェースボード用の第2シリアル通信回路115(SCU2)の初期化処理を行う(S2)。次いで、メインCPU101は、乱数回路110(RDG)の初期化処理を行う(S3)。次いで、メインCPU101は、メインRAM103の書き込みテストを行う(S4)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、書き込みテストの結果、メインRAM103への書き込みが正常に行われたか否かを判別する(S5)。
Next, the
S5において、メインCPU101が、メインRAM103への書き込みが正常に行われなかったと判別したとき(S5がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS13の処理を行う。一方、S5において、メインCPU101が、メインRAM103への書き込みが正常に行われたと判別したとき(S5がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、タイマー回路113のタイマー用制御レジスタ(不図示)の状態を取得する(S6)。
When the
次いで、メインCPU101は、取得したタイマー用制御レジスタの状態に基づいて、現在の状態が割込処理の発生タイミングであるか否かを判別する(S7)。具体的には、メインCPU101は、取得したタイマー用制御レジスタの状態に基づいて、タイマーカウント開始後から1.1172ms経過したか否かを判別する。
Next, the
なお、本実施形態では、S2のタイマー回路113の初期化処理によりタイマー時間1.1172msがセットされると、CPU内蔵タイマーのカウント処理が開始される。その後、タイマー用制御レジスタ(不図示)の情報を読み込むことによりタイマー回路113のステータスを取得することができる。そして、本実施形態では、タイマー用制御レジスタに、現在の状態が割込処理の発生タイミングであるか否か(タイマー割込状態であるか否か)を判別(参照)可能なビット(判別ビット)が設けられる。
In the present embodiment, when the timer time of 1.1172 ms is set by the initialization process of the
それゆえ、上記S6の処理では、メインCPU101は、タイマー用制御レジスタ(不図示)の情報を読み込み、上記S7の処理では、メインCPU101は、タイマー用制御レジスタ内の判別ビットのオン/オフ状態(「1」/「0」)を参照することにより、現在の状態が割込処理の発生タイミングであるか否かを判別する。なお、タイマー回路113によるカウント開始から1.1172ms経過したとき(タイマー回路113のカウント値が0であれば)、該判別ビットはオン状態となる。
Therefore, in the process of S6, the
S7において、メインCPU101が、現在の状態が割込処理の発生タイミングでないと判別したとき(S7がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS6の処理に戻し、S6以降の処理を繰り返す。
In S7, when the
一方、S7において、メインCPU101が、現在の状態が割込処理の発生タイミングであると判別したとき(S7がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、コマンド送信開始タイマをセットする(S8)。コマンド送信開始タイマは、後述の起動遅延期間(後述の図85参照)を管理するためのタイマであり、このコマンド送信開始タイマがセットされてから0となるまでの期間は、主制御回路90(主制御基板71)から副制御回路200(副制御基板72)に対してコマンドデータが送信されないようになっている(後述の図80参照)。これにより、パチスロ1の電源投入時に、サブCPU201の起動制御に必要な時間(コマンドが受信可能となるまでの時間)が確保される。すなわち、コマンド送信開始タイマがセットされることにより、これに応じた期間、通信データ送信処理による通信データ(コマンドデータ)の送信が遅延される。なお、本実施形態では、S8において、コマンド送信開始タイマの値として「21801」(21801×1.1172ms=約24.3561秒)がセットされる。もっとも、コマンド送信開始タイマの値は、同時に搭載される副制御回路200の仕様に応じて、適宜変更することが可能である。
On the other hand, when the
なお、コマンド送信開始タイマは、メインRAM103の遊技用RAM領域内に2バイトで割り当てられたソフトウェアタイマであり、後述の設定変更確認処理(図48参照)では消去されないアドレスに配置されている。
The command transmission start timer is a software timer allocated in 2 bytes in the game RAM area of the
次いで、メインCPU101は、サムチェック処理(規定外)を行う(S9)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、メインRAM103のサムチェック処理を行うが、この処理の作業は、メインRAM103内の規定外作業領域(図11C参照)で行われる。また、このサムチェック処理で用いられるプログラムはメインROM102内の規定外エリアに格納されている(図11B参照)。なお、サムチェック処理の詳細については、後述の図54及び図55を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
S9の処理後、メインCPU101は、設定用鍵型スイッチ54がオン状態であるか否かを判別する(S10)。
After the processing of S9, the
S10において、メインCPU101が、設定用鍵型スイッチ54がオン状態であると判別したとき(S10がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS15の処理を行う。一方、S10において、メインCPU101が、設定用鍵型スイッチ54がオン状態でないと判別したとき(S10がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、S9のサムチェック処理の結果に基づいて、サムチェック判定結果が正常であったか否かを判別する(S11)。
In S10, when the
S11において、メインCPU101が、サムチェック判定結果が正常でないと判別したとき(S11がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS13の処理を行う。一方、S11において、メインCPU101が、サムチェック判定結果が正常であると判別したとき(S11がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、遊技復帰処理を行う(S12)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、遊技の状態を電断検知前の状態に戻す処理を行う。なお、遊技復帰処理の詳細については、後述の図47を参照しながら後で説明する。
In S11, when the
S5又はS11がNO判定の場合、メインCPU101は、情報表示器6(7セグLED表示器)に、エラー発生を意味する文字列「88」を表示する(S13)。その後、メインCPU101は、WDTのクリア処理を繰り返す(S14)。
If NO is determined in S5 or S11, the
ここで再度、S10の処理に戻って、S10がYES判定の場合、メインCPU101は、設定変更確認処理を行う(S15)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、主に、設定変更開始時における設定変更コマンドの生成格納処理を行う。なお、設定変更確認処理の詳細については、後述の図48を参照しながら後で説明する。
Here, returning to the process of S10 again, when the determination of S10 is YES, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、RAM初期化処理を行う(S16)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、図11Cに示すメインRAM103の遊技用RAM領域内の「RAM異常時又は設定変更開始時」のアドレスを、初期化開始の先頭アドレスとして設定し、該先頭アドレスから遊技用RAM領域の最終アドレスまでの情報を消去(クリア)する。そして、S16の処理後、メインCPU101は、後述のメイン処理(後述の図56参照)を開始する。
Next, the
[遊技復帰処理]
次に、図47を参照して、電源投入(リセット割込)時処理(図46参照)中のS12で行う遊技復帰処理について説明する。なお、図47は、遊技復帰処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Game return processing]
Next, with reference to FIG. 47, the game return processing performed in S12 during the power-on (reset interrupt) processing (see FIG. 46) will be described. Note that FIG. 47 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the game return processing.
まず、メインCPU101は、スタックポインタ(SP)に、電断時のスタックポインタをセットする(S21)。次いで、メインCPU101は、コマンド送信開始タイマはカウントアップしたか否かを判別する(S22)。S22において、メインCPU101が、コマンド送信開始タイマはカウントアップしていないと判別したとき(S22がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、S22の処理を繰り返す。
First, the
一方、S22において、メインCPU101が、コマンド送信開始タイマはカウントアップしたと判別したとき(S22がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、入力ポートの1割込処理前のオンエッジデータ、及び、現在セットされているオンエッジデータをクリア(オフ)する(S23)。次いで、メインCPU101は、メインRAM103の出力ポートバックアップ格納領域(不図示)から出力ポートのバックアップデータを読み出し、出力ポートにセットする(S24)。次いで、メインCPU101は、入力ポートのデータを読み込み、該データを、入力ポートの現在及び1割込処理前のデータ格納領域(入力ポート格納領域1及び入力ポート格納領域2)に保存する(S25)。
On the other hand, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、回胴制御データ格納領域のアドレスをセットする(S26)。次いで、メインCPU101は、チェックするリール数(本実施形態では「3」)をセットする(S27)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、セットされた回胴制御データ格納領域のアドレスに基づいて、所定のリールのリール制御管理情報(電断発生時の表示列の変動制御に関するデータ)を取得する(S28)。なお、リール制御管理情報(表示列の変動制御管理情報)は、各リールの制御状態(回転状況)に関する情報であり、電断時には、バックアップされて保存される。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、リール制御管理情報がリールの加速中、定速待ち又は定速中の回転状況に対応する情報であるか否かを判別する(S29)。
Next, the
S29において、メインCPU101が、S29の条件を満たさないと判別したとき(S29がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS32の処理を行う。一方、S29において、メインCPU101が、S29の条件を満たすと判別したとき(S29がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、回胴制御データ(リール制御管理情報)をクリアする(S30)。この処理により、遊技復帰後、リールの回転制御が加速処理から開始される。次いで、メインCPU101は、リールの作動タイミング値(回胴制御データの実行開始タイミング「1」)をセットする(S31)。なお、リールの作動タイミングに「1」がセットされると、リール制御処理(後述の図79中のS903参照)内で、励磁変更タイミングとなるため、メインCPU101は、リールの回転制御を加速処理から開始する。
In S29, when the
S31の処理後又はS29がNO判定の場合、メインCPU101は、リール数の値を1減算する(S32)。次いで、メインCPU101は、減算後のリール数の値が「0」であるか否かを判別する(S33)。
After the processing of S31 or when the determination of S29 is NO, the
S33において、メインCPU101が、減算後のリール数の値が「0」でないと判別したとき(S33がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、チェック対象のリールを変えて、処理をS28の処理に戻し、S28以降の処理を繰り返す。
In S33, when the
一方、S33において、メインCPU101が、減算後のリール数の値が「0」であると判別したとき(S33がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、RAM初期化処理を行う(S34)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、図11Cに示すメインRAM103の遊技用RAM領域内の「電源復帰時」のアドレスを、初期化開始の先頭アドレスとして設定し、該先頭アドレスから遊技用RAM領域の最終アドレスまでの情報を消去(クリア)する。
On the other hand, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、電断検知時に退避させた全てのレジスタのデータを全てのレジスタに復帰させる(S35)。そして、S35の処理後、メインCPU101は、遊技復帰処理を終了し、処理を電断検知時の処理に戻す。
Next, the
本実施形態では、上述のようにして遊技復帰処理が行われる。本実施形態の遊技復帰処理では、上述のように、電断発生時の各ポートの入出力状態を電源復帰時に担保するとともに、電断時にリール回転中の場合には、電源復帰時にリール制御管理情報を取得してリールの再回転開始に必要な処理も行う(S26〜S33の処理参照)。それゆえ、本実施形態では、回胴回転中の電断から復帰したときであっても、安定して、リールの再回転制御を行うことができ、遊技者に不快感を与えることが無くなる。 In the present embodiment, the game return processing is performed as described above. In the game return processing of the present embodiment, as described above, the input/output state of each port at the time of power failure is secured at the time of power recovery, and if the reel is rotating at the time of power failure, reel control management at power recovery The processing required to acquire the information and start the re-rotation of the reel is also performed (see the processing of S26 to S33). Therefore, in the present embodiment, the reel re-rotation control can be stably performed even when the power is restored from the power interruption during the rotation of the spinning drum, and the player does not feel uncomfortable.
[設定変更確認処理]
次に、図48を参照して、電源投入(リセット割込)時処理(図46参照)中のS15で行う設定変更確認処理について説明する。図48は、設定変更確認処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。なお、遊技機の電源投入後に、設定用鍵型スイッチ54がオン状態となった場合(すなわち、現在の設定値を確認する「設定確認」の場合)には、後述のS44からこの設定変更確認処理が開始されるようにすればよい。
[Setting change confirmation processing]
Next, with reference to FIG. 48, the setting change confirmation process performed in S15 during the power-on (reset interrupt) process (see FIG. 46) will be described. FIG. 48 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the setting change confirmation process. In addition, when the setting
まず、メインCPU101は、メインRAM103内の規定外RAM領域の初期化処理を行う(S41)。次いで、メインCPU101は、1割り込み待ち処理を行う(S42)。この処理では、コマンド送信開始タイマがカウントアップしている場合、後述の通信データ送信処理(図80参照)により無操作コマンドが副制御回路200に送信される。なお、コマンド送信開始タイマがカウントアップしていない場合には、いずれのコマンドも副制御回路200に送信されないため、コマンド送信開始タイマがカウントアップしていない場合には、この処理を省略するようにしてもよい。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、RAM初期化処理を行う(S43)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、図11Cに示すメインRAM103の遊技用RAM領域内の「RAM異常時又は設定変更開始時」のアドレスを、初期化開始の先頭アドレスとして設定し、該先頭アドレスから遊技用RAM領域の最終アドレスまでの情報を消去(クリア)する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、設定用鍵型スイッチ54がオン状態であるか否かを判別する(S44)。なお、設定用鍵型スイッチ54に差し込まれる設定キー(不図示)は、パチスロ1の設定値(設定1〜6)を設定するための操作キーであり、設定キーがオンされていると、設定用鍵型スイッチ54がオン状態となる。
Next, the
S44において、メインCPU101が、設定用鍵型スイッチ54がオン状態でないと判別したとき(S44がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、設定変更確認処理を終了し、処理を電源投入(リセット割込)時処理(図46参照)のS16の処理に移す。一方、S44において、メインCPU101が、設定用鍵型スイッチ54がオン状態であると判別したとき(S44がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、メダル受付禁止の処理を行う(S45)。この処理により、セレクタ66(図5参照)のソレノイドの駆動が行われず、投入されたメダルがメダル払出口24(図2参照)から排出される。
In S44, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、Lレジスタに設定変更開始又は設定確認開始の情報(005H:第1の値)をセットし、設定変更コマンド(設定変更/設定確認開始)の生成格納処理を行う(S46)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、設定変更処理又は設定確認処理の開始時に主制御回路90から副制御回路200に送信される設定変更コマンドデータ(第1のコマンドデータ)を生成し、該コマンドデータをメインRAM103に設けられた通信データ格納領域に保存する。なお、設定変更コマンド生成格納処理の詳細については、後述の図49を参照しながら後で説明する。また、通信データ格納領域に保存された設定変更コマンド(設定変更/設定確認開始)は、後述の図80で説明する通信データ送信処理により、主制御回路90から副制御回路200に送信される。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、エラーカウントリレーをオン状態にセットする(S47)。次いで、メインCPU101は、設定値の7セグ表示設定処理を行う(S48)。この処理により、現在の設定値が情報表示器6内の7セグLEDで表示可能になる。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、設定変更及び設定確認のいずれが行われたかを判別する(S49)。S49において、メインCPU101が、設定変更が行われていない(設定確認が行われた)と判別したとき(S49がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS54の処理を行う。
Next, the
一方、S49において、メインCPU101が、設定変更が行われた(設定確認が行われていない)と判別したとき(S49がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、リセットスイッチ76がオン状態であるか否かを判別する(S50)。
On the other hand, when the
S50において、メインCPU101が、リセットスイッチ76がオン状態であると判別したとき(S50がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、設定値を更新する(S51)。すなわち、メインCPU101は、リセットスイッチ76が操作される度に、設定値を「1」〜「6」の範囲内で順次更新する。S51の処理後、メインCPU101は、処理をS48の処理に戻し、S48以降の処理を繰り返す。一方、S50において、メインCPU101が、リセットスイッチ76がオン状態でないと判別したとき(S50がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、スタートスイッチ79がオン状態であるか否かを判別する(S52)。
In S50, when the
S52において、メインCPU101が、スタートスイッチ79がオン状態でないと判別したとき(S52がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS48の処理に戻し、S48以降の処理を繰り返す。一方、S52において、メインCPU101が、スタートスイッチ79がオン状態であると判別したとき(S52がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、メインRAM103に設けられた設定値格納領域(不図示)に設定値を格納する(S53)。
In S52, when the
S49がNO判定の場合又はS53の処理後、メインCPU101は、設定用鍵型スイッチ54がオフ状態であるか否かを判別する(S54)。
When the determination in S49 is NO or after the processing in S53, the
S54において、メインCPU101が、設定用鍵型スイッチ54がオフ状態でないと判別したとき(S54がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、S54の処理を繰り返す。一方、S54において、メインCPU101が、設定用鍵型スイッチ54がオフ状態であると判別したとき(S54がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、設定変更及び設定確認のいずれが行われたか否かを判別する(S55)。
In S54, when the
S55において、メインCPU101が、設定変更が行われていない(設定確認が行われた)と判別したとき(S55がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS57の処理を行う。一方、S55において、メインCPU101が、設定変更が行われた(設定確認が行われていない)と判別したとき(S55がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、RAM初期化処理を行う(S56)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、図11Cに示すメインRAM103の遊技用RAM領域内の図示しない「設定変更終了時」のアドレス(設定値格納領域の次のアドレス)を、初期化開始の先頭アドレスとして設定し、該先頭アドレスから遊技用RAM領域の最終アドレスまでの情報を消去(クリア)する。
In S55, when the
S56の処理後又はS55がNO判定の場合、メインCPU101は、Lレジスタに設定変更終了又は設定確認終了の情報(004H:第2の値)をセットし、設定変更コマンド(設定変更/設定確認終了)の生成格納処理を行う(S57)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、設定変更処理又は設定確認処理の終了時に主制御回路90から副制御回路200に送信される設定変更コマンドデータ(第2のコマンドデータ)を生成し、該コマンドデータをメインRAM103に設けられた通信データ格納領域に保存する。なお、設定変更コマンド生成格納処理の詳細については、後述の図49を参照しながら後で説明する。また、通信データ格納領域に保存された設定変更コマンド(設定変更/設定確認終了)は、後述の図80で説明する通信データ送信処理により、主制御回路90から副制御回路200に送信される。そして、S57の処理後、メインCPU101は、設定変更確認処理を終了し、処理を電源投入(リセット割込)時処理(図46参照)のS16の処理に移す。
After the processing of S56 or when the determination of S55 is NO, the
[設定変更コマンド生成格納処理]
次に、図49を参照して、設定変更確認処理(図48参照)中のS46及びS57で行う設定変更コマンド生成格納処理について説明する。なお、図49は、設定変更コマンド生成格納処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Setting change command generation and storage processing]
Next, with reference to FIG. 49, the setting change command generation/storing process performed in S46 and S57 in the setting change confirmation process (see FIG. 48) will be described. Note that FIG. 49 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the setting change command generation/storage process.
まず、メインCPU101は、設定値(1〜6)の情報をEレジスタにセットする(S61)。次いで、メインCPU101は、RT状態の情報をCレジスタにセットする(S62)。次いで、メインCPU101は、設定変更コマンドのコマンド種別情報(02H)をAレジスタにセットする(S63)。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、通信データ格納処理を行う(S64)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、S61〜S63で各レジスタにセットされた情報と、S46又はS58(図48参照)でLレジスタにセットされた情報(設定ステータスである設定変更開始/設定変更終了/設定確認開始/設定確認終了)とを用いて、設定変更コマンドデータを生成し、該生成されたコマンドデータを通信データ格納領域に保存する。なお、通信データ格納処理の詳細については、後述の図50を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
S64の処理後、メインCPU101は、設定変更コマンド生成格納処理を終了する。なお、設定変更確認処理(図48参照)中のS46で行う設定変更コマンド生成格納処理を終了する際には、メインCPU101は、S64の処理後、処理を設定変更確認処理(図48参照)のS47の処理に移す。また、設定変更確認処理(図48参照)中のS57で行う設定変更コマンド生成格納処理を終了する際には、メインCPU101は、S64の処理後、設定変更コマンド生成格納処理を終了するとともに、設定変更確認処理(図48参照)も終了する。
After the processing of S64, the
[通信データ格納処理]
次に、図50を参照して、例えば、設定変更コマンド生成格納処理(図49参照)中のS64で行う通信データ格納処理について説明する。なお、通信データ格納処理は、設定変更コマンド生成時だけでなく、他のコマンド生成時にも実行される。図50は、通信データ格納処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Communication data storage processing]
Next, with reference to FIG. 50, for example, the communication data storage processing performed in S64 of the setting change command generation storage processing (see FIG. 49) will be described. The communication data storage process is executed not only when the setting change command is generated, but also when another command is generated. FIG. 50 is a flowchart showing the procedure of communication data storage processing.
まず、メインCPU101は、Aレジスタにセットされているデータを通信コマンド種別のデータとして、メインRAM103内の通信データ一時格納領域(不図示)に格納する(S71)。次いで、メインCPU101は、Hレジスタ及びLレジスタにセットされているデータを、それぞれ通信コマンドのパラメータ1及び2として、メインRAM103内の通信データ一時格納領域に格納する(S72)。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、Dレジスタ及びEレジスタにセットされているデータを、それぞれ通信コマンドのパラメータ3及び4として、メインRAM103内の通信データ一時格納領域に格納する(S73)。次いで、メインCPU101は、Bレジスタ及びCレジスタにセットされているデータを、それぞれ通信コマンドのパラメータ5及びRT状態のデータとして、メインRAM103内の通信データ一時格納領域に格納する(S74)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、Aレジスタ〜Lレジスタにセットされているデータ値から通信コマンドのBCCデータ(サム値)を生成する(S75)。次いで、メインCPU101は、生成したBCCデータをメインRAM103内の通信データ一時格納領域に格納する(S76)。
Next, the
S76の処理後、メインCPU101は、メインRAM103内の通信データ格納領域に空きがあるか否かを判別する(S77)。なお、本実施形態では、通信データ格納領域に最大9個のコマンドデータが格納可能である。
After the processing of S76, the
S77において、メインCPU101が、通信データ格納領域に空きがないと判別したとき(S77がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、通信データ格納処理を終了するとともに、例えば、設定変更コマンド生成格納処理(図49参照)も終了する。
When the
一方、S77において、メインCPU101が、通信データ格納領域に空きがあると判別したとき(S77がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、上述したS71〜S76の処理により通信データ一時格納領域に格納された各データを通信データ(コマンドデータ)として、通信データ格納領域に格納(登録)する(S78)。
On the other hand, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、通信データポインタ更新処理を行う(S79)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、主に、通信データ格納領域内における通信データの格納アドレスを示す通信データポインタの更新処理を行う。なお、通信データポインタ更新処理の詳細については、後述の図51を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
そして、S79の処理後、メインCPU101は、通信データ格納処理を終了するとともに、例えば、設定変更コマンド生成格納処理(図49参照)も終了する。
Then, after the processing of S79, the
上述のように、本実施形態では、1パケット(8バイト)の通信データ(コマンドデータ)を作成する際に、各種パラメータをレジスタから転送して通信データ一時格納領域(通信バッファ)に格納する。このようなコマンドデータの作成手法では、コマンド生成時に各レジスタに格納されているデータがそのままコマンドデータの各種パラメータとして通信データ一時格納領域に格納される。それゆえ、未使用パラメータを含むコマンドデータを作成した時には、作成時毎に、未使用パラメータの値が不定値となる。これにより、通信データの解析を困難にしてゴト等の不正行為を抑止することができるとともに、不必要なゴト対策処理を加える必要がないため、ゴト対策処理の追加による、主制御回路90のプログラム容量の圧迫を抑制することができる。
As described above, in the present embodiment, when one packet (8 bytes) of communication data (command data) is created, various parameters are transferred from the register and stored in the communication data temporary storage area (communication buffer). In such a method of creating command data, the data stored in each register at the time of command generation is stored as it is in the communication data temporary storage area as various parameters of the command data. Therefore, when the command data including the unused parameter is created, the value of the unused parameter becomes an undefined value every time it is created. This makes it difficult to analyze the communication data and suppress fraudulent acts such as goto, and since it is not necessary to add unnecessary goto countermeasure processing, the program of the
[通信データポインタ更新処理]
次に、図51を参照して、通信データ格納処理(図50参照)中のS79で行う通信データポインタ更新処理について説明する。なお、図51は、通信データポインタ更新処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Communication data pointer update processing]
Next, with reference to FIG. 51, the communication data pointer updating process performed in S79 in the communication data storing process (see FIG. 50) will be described. Note that FIG. 51 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the communication data pointer update processing.
まず、メインCPU101は、現在、セットされている通信データポインタの値を取得する(S81)。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、通信データポインタの値を1パケット分(8バイト)加算更新する(S82)。なお、この処理において、更新後の通信データポインタの値が、通信データ格納領域の上限サイズ以上となる場合には、メインCPU101は、更新後の通信データポインタの値を「0」にセットし、これにより、通信データ格納領域に格納されているコマンドデータを全て無効にする(破棄した状態と同様の状態にする)。
Next, the
本実施形態では、1回の送信動作で送信されるデータ量(1パケット)は8バイトである。すなわち、本実施形態では、1つの送信動作で1つのコマンドデータを送信することができる。また、本実施形態では、通信データ格納領域に最大9個のコマンドデータを格納可能であるので、通信データ格納領域の上限サイズは、72バイト(=8バイト×9)となる。それゆえ、本実施形態では、通信データポインタの範囲を「0」〜「71」とし、S82の処理において、更新後(通信データポインタを+8更新した場合)の通信データポインタの値が「71(上限値)」を超えるような値となる場合には、更新後の通信データポインタの値を「0」にセットして(通信データの格納先のアドレスを先頭アドレスに戻して)、通信データ格納領域に格納されているコマンドデータを全て無効にする(破棄した状態と同様の状態にする)。なお、通信データポインタの値を「0」にセットすると、次にコマンドデータを通信データ格納領域に格納する場合には、通信データ格納領域の先頭アドレスから格納されるので、その前に格納されていたコマンドデータは新たなコマンドデータで上書きされることになる。それゆえ、本実施形態では、通信データポインタの値が「71(上限値)」を超えた場合に、通信データ格納領域を初期化(クリア)する必要はない。 In this embodiment, the amount of data (one packet) transmitted in one transmission operation is 8 bytes. That is, in this embodiment, one command data can be transmitted by one transmission operation. Further, in the present embodiment, since a maximum of 9 command data can be stored in the communication data storage area, the upper limit size of the communication data storage area is 72 bytes (=8 bytes×9). Therefore, in the present embodiment, the range of the communication data pointer is set to “0” to “71”, and the value of the communication data pointer after updating (when the communication data pointer is updated by +8) is “71 ( Upper limit value)”, set the value of the updated communication data pointer to “0” (return the communication data storage address to the start address) and store the communication data. Invalidates all command data stored in the area (sets the same state as the discarded state). If the value of the communication data pointer is set to "0", the next time command data is stored in the communication data storage area, it will be stored from the start address of the communication data storage area. The new command data will be overwritten by the new command data. Therefore, in the present embodiment, it is not necessary to initialize (clear) the communication data storage area when the value of the communication data pointer exceeds "71 (upper limit value)".
そして、S82の処理後、メインCPU101は、通信データポインタ更新処理を終了するとともに、通信データ格納処理(図50参照)も終了する。
Then, after the processing of S82, the
[電断時(外部)処理]
次に、メインCPU101の制御により行われるパチスロ1の電断時(外部)処理を、図52を参照して説明する。図52は、電断時(外部)処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。なお、図52に示す電断時(外部)処理は、電源管理回路93が、マイクロプロセッサ91に供給される電源電圧の低下(電断)を検知した際に、電断検知信号をマイクロプロセッサ91の「XINT」端子に出力し、これにより、マイクロプロセッサ91の割込みコントローラ112からメインCPU101に出力される割込要求信号に基づいて、実行される。
[Disconnect (external) processing]
Next, the power-off (external) processing of the pachi-
まず、メインCPU101は、全てのレジスタにセットされているデータを退避させる(S91)。次いで、メインCPU101は、電断検知ポートにセットされているデータを読み込む(S92)。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、電断検知ポートがオン状態であるか否かを判別する(S93)。
Next, the
S93において、メインCPU101が、電断検知ポートがオン状態でないと判別したとき(S93がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、割込処理許可をセットする(S94)。そして、S94の処理後、メインCPU101は、電断時(外部)処理を終了する。なお、S93がNO判定である場合に行われるこれらの処理は、電源管理回路93が瞬間的に電断を検知した場合等に発生する瞬停対策の処理に対応する。
In S93, when the
一方、S93において、メインCPU101が、電断検知ポートがオン状態であると判別したとき(S93がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、メダル投入不可を設定し、ホッパー装置51の停止を設定する(S95)。
On the other hand, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、現在セットされているスタックポインタ(SP)の値をメインRAM103内の遊技用RAM領域のスタックエリアに保存する(S96)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、メインRAM103のチェックサム生成処理を行う(S97)。なお、この処理は、メインRAM103内の規定外作業領域(図11C参照)で行われる。また、このチェックサム生成処理で用いられるプログラムはメインROM102内の規定外エリアに格納されている(図11B参照)。なお、チェックサム生成処理の詳細については、後述の図53を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、メインRAM103へのアクセス禁止を設定する(S98)。そして、S98の処理後、電源が停止するまで(電源電圧が、メインCPU101が動作できない電圧に達するまで)無限ループ処理が行われる。
Next, the
[チェックサム生成処理(規定外)]
次に、図53を参照して、電断時(外部)処理(図52参照)中のS97で行うチェックサム生成処理について説明する。なお、図53は、チェックサム生成処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Checksum generation processing (non-standard)]
Next, with reference to FIG. 53, the checksum generation process performed in S97 during the power interruption (external) process (see FIG. 52) will be described. Note that FIG. 53 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the checksum generation process.
まず、メインCPU101は、現在のスタックポインタ(SP)の値(遊技用RAM領域のスタックエリアの使用中アドレス)をメインRAM103の規定外RAM領域の規定外スタックエリアに保存する(S101)。次いで、メインCPU101は、スタックポインタに規定外スタックエリアのアドレスをセットする(S102)。次いで、メインCPU101は、RAMアドレス(規定外スタックエリアのアドレス)の上位側のアドレス値(F0H)をQレジスタにセットする(S103)。次いで、メインCPU101は、電断発生フラグを設定する(S104)。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、スタックポインタに、遊技用RAM領域内のサム値の計算開始アドレスをセットし、サム算出カウンタに、サム値の算出対象格納領域のバイト数を「2」で除算した値をセットする(S105)。なお、サム算出カウンタは、サム値算出の終了契機を判定するためのカウンタであり、メインRAM103に設けられる。そして、S105で設定されたサム算出カウンタが「0」になれば、メインRAM103の遊技用RAM領域のサム値算出処理を終了する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、HLレジスタを0クリア(値「0」をセット)する(S106)。この処理により、サム値の初期値「0」がセットされる。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、「POP命令」と呼ばれる命令コードを実行し、スタックポインタ(SP)にセットされたメインRAM103の格納領域のアドレスから2バイト分の領域のデータ(保存値)をDEレジスタに読み出す(S107)。
Next, the
なお、「POP」命令が実行されると、スタックポインタで指定されたアドレスの1バイト領域に保存されているデータ(メモリ内容)が、ペアレジスタの下位側のレジスタにロードされ、スタックポインタで指定されたアドレスを1更新したアドレスの1バイト領域に保存されているデータ(メモリ内容)が、ペアレジスタの上位側のレジスタにロードされる。また、「POP」命令が実行されると、スタックポインタ(SP)にセットされたアドレスに対して2バイト分のアドレス更新処理(アドレスを「2」加算する処理)が行われる。 When the "POP" instruction is executed, the data (memory contents) saved in the 1-byte area of the address specified by the stack pointer is loaded into the lower register of the pair register and specified by the stack pointer. The data (memory contents) stored in the 1-byte area of the address obtained by updating the created address by 1 is loaded into the register on the upper side of the pair register. When the "POP" instruction is executed, an address update process (process of adding "2" to the address) for 2 bytes is performed on the address set in the stack pointer (SP).
それゆえ、S107の処理では、スタックポインタで指定されたアドレスに保存されているデータ(メモリ内容)がEレジスタにロードされ、スタックポインタで指定されたアドレスに「1」を加算したアドレスに保存されているデータ(メモリ内容)がDレジスタにロードされる。 Therefore, in the process of S107, the data (memory content) saved at the address designated by the stack pointer is loaded into the E register and is saved at the address obtained by adding "1" to the address designated by the stack pointer. Data (memory contents) being loaded into the D register.
S107の処理後、メインCPU101は、サム値の算出処理を行う(S108)。具体的には、メインCPU101は、HLレジスタに格納されている値にDEレジスタに格納されている値を加算し、該加算された値をサム値としてHLレジスタに格納する。
After the process of S107, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、サム算出カウンタの値を1減算する(S109)。次いで、メインCPU101は、更新後のサム算出カウンタの値が「0」であるか否かを判別する(S110)。
Next, the
S110において、メインCPU101が、サム算出カウンタの値が「0」でないと判別したとき(S110がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS107の処理に戻し、S107以降の処理を繰り返す。すなわち、メインRAM103の遊技用RAM領域のサム値算出処理が終了するまで、S107〜S110の処理が繰り返される。
In S110, when the
一方、S110において、メインCPU101が、サム算出カウンタの値が「0」であると判別したとき(S110がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、DEレジスタに、メインRAM103内の規定外RAM領域のサム値の計算開始アドレスをセットし、サム算出カウンタに、規定外用サムカウント値をセットする(S111)。なお、規定外用サムカウント値は、規定外用格納領域のバイト数となる。それゆえ、S111で設定されたサム算出カウンタが「0」になれば、メインRAM103の規定外RAM領域のサム値算出処理、すなわち、メインRAM103全体のサム値算出処理が終了する。
On the other hand, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、DEレジスタにセットされた規定外RAM領域のアドレスから1バイト分の領域のデータ(保存値)をAレジスタに読み出す(S112)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、サム値の算出処理を行う(S113)。具体的には、メインCPU101は、HLレジスタに格納されている値にAレジスタに格納されている値を加算し、該加算された値をサム値としてHLレジスタに格納する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、DEレジスタに格納されているアドレスを1加算し、サム算出カウンタの値を1減算する(S114)。次いで、メインCPU101は、更新後のサム算出カウンタの値が「0」であるか否かを判別する(S115)。
Next, the
S115において、メインCPU101が、サム算出カウンタの値が「0」でないと判別したとき(S115がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS112の処理に戻し、S112以降の処理を繰り返す。すなわち、メインRAM103の規定外RAM領域のサム値を遊技用RAM領域のサム値に加算する処理が終了するまで、S112〜S115の処理が繰り返される。
When the
一方、S115において、メインCPU101が、サム算出カウンタの値が「0」であると判別したとき(S115がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、HLレジスタに格納されている値を電断発生時のサム値として、メインRAM103内のサム値格納領域(不図示)に保存する(S116)。次いで、メインCPU101は、S101で規定外スタックエリアに保存されたスタックポインタ(SP)の値をスタックポインタにセットする(S117)。そして、S117の処理後、メインCPU101は、チェックサム生成処理を終了し、処理を電断時(外部)処理(図52参照)のS98の処理に移す。
On the other hand, when the
[サムチェック処理(規定外)]
次に、図54及び図55を参照して、電源投入時処理(図46参照)中のS9で行うサムチェック処理について説明する。なお、図54及び図55は、サムチェック処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Sum check processing (non-standard)]
Next, with reference to FIGS. 54 and 55, the sum check process performed in S9 of the power-on process (see FIG. 46) will be described. 54 and 55 are flowcharts showing the procedure of the sum check process.
まず、メインCPU101は、現在のスタックポインタ(SP)の値を規定外スタックエリアに保存する(S121)。次いで、メインCPU101は、スタックポインタにサム値格納領域のアドレスをセットし、サム算出カウンタに、サム値の算出対象格納領域のバイト数を「2」で除算した値をセットする(S122)。なお、ここでセットされるサム算出カウンタは、サム値算出(サム値の減算処理)の終了契機を判定するためのカウンタであり、メインRAM103に設けられる。次いで、メインCPU101は、サム値格納領域からサム値(チェックサム)を取得する(S123)。この処理により、電断発生時に生成されたチェックサム(減算前の初期値)がHLレジスタに格納される。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、「POP」命令を実行し、スタックポインタ(SP)にセットされたメインRAM103の格納領域のアドレスから2バイト分の領域のデータ(保存値)をDEレジスタに読み出す(S124)。なお、この際、「POP」命令の実行により、スタックポインタで指定されたアドレスの1バイト領域に保存されているデータ(メモリ内容)が、Eレジスタにロードされ、スタックポインタで指定されたアドレスを1更新したアドレスの1バイト領域に保存されているデータ(メモリ内容)が、Dレジスタにロードされる。また、「POP」命令が実行されると、スタックポインタ(SP)にセットされたアドレスに対して2バイト分のアドレス更新処理(アドレスを2加算する処理)が行われる。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、サム値の算出(減算)処理を行う(S125)。具体的には、メインCPU101は、HLレジスタに格納されている値(サム値の初期値又は前回の減算処理後のサム値)からDEレジスタに格納されている値を減算し、該減算された値をサム値としてHLレジスタに格納する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、サム算出カウンタの値を1減算する(S126)。次いで、メインCPU101は、更新後のサム算出カウンタの値が「0」であるか否かを判別する(S127)。
Next, the
S127において、メインCPU101が、サム算出カウンタの値が「0」でないと判別したとき(S127がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS124の処理に戻し、S124以降の処理を繰り返す。すなわち、メインRAM103の遊技用RAM領域の全域に渡ってサム値の減算処理が終了するまで、S124〜S127の処理が繰り返される。
In S127, when the
一方、S127において、メインCPU101が、サム算出カウンタの値が「0」であると判別したとき(S127がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、DEレジスタに、メインRAM103内の規定外RAM領域のサム値の計算開始アドレスをセットし、サム算出カウンタに、規定外用サムカウント値をセットする(S128)。なお、規定外用サムカウント値は、規定外RAM領域のバイト数となる。
On the other hand, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、DEレジスタにセットされた規定外RAM領域のアドレスから1バイト分の領域のデータ(保存値)をAレジスタに読み出す(S129)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、サム値の算出(減算)処理を行う(S130)。具体的には、メインCPU101は、HLレジスタに格納されている値からAレジスタに格納されている値を減算し、該減算された値をサム値としてHLレジスタに格納する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、DEレジスタに格納されているアドレスを1加算し、サム算出カウンタの値を1減算する(S131)。次いで、メインCPU101は、更新後のサム算出カウンタの値が「0」であるか否かを判別する(S132)。
Next, the
S132において、メインCPU101が、サム算出カウンタの値が「0」でないと判別したとき(S132がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS129の処理に戻し、S129以降の処理を繰り返す。すなわち、メインRAM103の規定外RAM領域の全域に渡ってサム値の減算処理が終了するまで、S129〜S132の処理が繰り返される。
In S132, when the
一方、S132において、メインCPU101が、サム算出カウンタの値が「0」であると判別したとき(S132がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、サムチェック処理の判定結果に「サム異常」をセットする(S133)。次いで、メインCPU101は、算出されたサム値が「0」であるか否かを判別する(S134)。
On the other hand, when the
なお、この処理では、メインCPU101は、フラグ・レジスタFのゼロフラグ(ビット6)の状態(1/0)を参照して、サム値が「0」であるか否かを判別する。本実施形態では、S128でセットされたサム算出カウンタの値が「0」になった時点、すなわち、メインRAM103の全域に渡ってサム値の減算処理が終了した時点において、サム値が「0」である場合には、フラグ・レジスタFのゼロフラグには「1」がセットされ、サム値が「0」でない場合には、フラグ・レジスタFのゼロフラグには「0」がセットされている。それゆえ、S134の処理の時点において、フラグ・レジスタFのゼロフラグに「1(オン状態)」がセットされていれば、メインCPU101はサム値が「0」であると判定する。
In this process, the
S134において、メインCPU101が、算出されたサム値が「0」でないと判別したとき(S134がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS139の処理を行う。一方、S134において、メインCPU101が、算出されたサム値が「0」であると判別したとき(S134がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、判定結果に「電断異常」をセットする(S135)。
When the
次いで、メインCPU101は、電断発生フラグを取得する(S136)。次いで、メインCPU101は、電断発生フラグが電断なしの状態(オフ状態)であるか否かを判別する(S137)。
Next, the
S137において、メインCPU101が、電断発生フラグが電断なしの状態であると判別したとき(S137がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS139の処理を行う。一方、S137において、メインCPU101が、電断発生フラグが電断なしの状態でないと判別したとき(S137がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、判定結果に「正常」をセットする(S138)。
In S137, when the
S138の処理後、S134がNO判定の場合、又は、S137がYES判定の場合、メインCPU101は、サムチェック判定結果に判定結果を保存し、電断発生フラグをクリア(オフ)する(S139)。次いで、メインCPU101は、S121で規定外スタックエリアに保存されたスタックポインタ(SP)の値をスタックポインタにセットする(S140)。そして、S140の処理後、メインCPU101は、サムチェック処理を終了し、処理を電源投入時処理(図46参照)のS10の処理に移す。
After the processing of S138, if S134 is NO, or if S137 is YES, the
[メインCPUの制御によるパチスロのメイン処理]
次に、図56を参照して、メインCPU101の制御により実行されるパチスロ1のメイン処理(主要動作処理)について説明する。なお、図56は、メイン処理の手順を示すフローチャート(以下、メインフローという)である。
[Main processing of pachi-slot by control of main CPU]
Next, with reference to FIG. 56, the main processing (main operation processing) of the pachi-
まず、メインCPU101は、RAM初期化処理を行う(S201)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、図11Cに示すメインRAM103の遊技用RAM領域内の「一遊技終了時」のアドレスを、初期化開始の先頭アドレスとして設定し、該先頭アドレスから遊技用RAM領域の最終アドレスまでの情報を消去(クリア)する。なお、この範囲の格納領域は、例えば、内部当籤役格納領域や表示役格納領域などの1回の単位遊技(ゲーム)ごとにデータの消去が必要な格納領域である。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、メダル受付・スタートチェック処理を行う(S202)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、各メダルセンサ(図5参照)やスタートスイッチ79などの入力チェック処理等を行う。なお、メダル受付・スタートチェック処理の詳細については、後述の図57及び図58を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、乱数値取得処理を行う(S203)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、内部当籤役抽籤用の乱数値(0〜65535:ハードラッチ乱数となる乱数回路110の乱数レジスタ0の値)や遊技性に関する各種抽籤で用いられる演出用乱数値(0〜65535:ソフトラッチ乱数となる乱数回路110の乱数レジスタ1の値、0〜255:ソフトラッチ乱数となる乱数回路110の乱数レジスタ2〜7の各値)などを抽出し、該抽出した各種乱数値をメインRAM103に設けられた乱数値格納領域(不図示)に格納する。なお、乱数値取得処理の詳細については、後述の図63を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、内部抽籤処理を行う(S204)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、S203で抽出した乱数値(ハードラッチ乱数)に基づいた抽籤により内部当籤役の決定処理を行う。なお、内部抽籤処理の詳細については、後述の図64を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、図柄設定処理を行う(S205)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、例えば、当り要求フラグステータス(フラグステータス情報)から内部当籤役を生成する処理、当り要求フラグデータの展開処理、当り要求フラグデータを当り要求フラグ格納領域を格納する処理等を行う。なお、図柄設定処理の詳細については、後述の図65を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、スタートコマンド生成格納処理を行う(S206)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、副制御回路200に送信するスタートコマンドのデータを生成し、該コマンドデータをメインRAM103に設けられた通信データ格納領域に保存する。通信データ格納領域に保存されたスタートコマンドは、後述の図80で説明する通信データ送信処理により、主制御回路90から副制御回路200に送信される。なお、スタートコマンドは、内部当籤役等を特定するパラメータ(当籤役番号等)を含んで構成される。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、第2インターフェースボード制御処理を行う(S207)。なお、第2インターフェースボード制御処理は、メインRAM103の規定外用作業領域で実行される。この処理では、メインCPU101は、例えば、主制御基板71で決定された押し順ナビに係る試験信号などを、試験機用第2インターフェースボード302を介して出力するための処理等を行う。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、遊技開始時状態別制御処理を行う(S208)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、図33〜図44を用いて説明した、非有利区間の通常状態、通常有利区間の各遊技状態、及び有利区間の各遊技状態における各種制御のうち、遊技開始時に行う必要がある各種制御を行うための各種処理を行う。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、リール停止初期設定処理を行う(S209)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、リール停止初期設定テーブル(不図示)を参照し、内部当籤役及び遊技状態に基づいて、引込優先順位テーブル選択テーブル番号、引込優先順位テーブル番号、停止テーブル番号を取得する処理や、ストップボタン未作動カウンタに「3」を格納する処理などを行う。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、リール回転開始処理を行う(S210)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、全リールの回転開始を要求する。そして、全リールの回転開始が要求されると、一定の周期(1.1172msec)で実行される後述の割込処理(後述の図79参照)により、3つのステッピングモータ(不図示)の駆動が制御され、左リール3L、中リール3C及び右リール3Rの回転が開始される。次いで、各リールは、その回転速度が定速度に達するまで加速制御され、その後、該定速度が維持されるように制御される。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、リール回転開始コマンド生成格納処理を行う(S211)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、副制御回路200に送信するリール回転開始コマンドのデータを生成し、該コマンドデータをメインRAM103に設けられた通信データ格納領域に保存する。通信データ格納領域に保存されたリール回転開始コマンドは、後述の図80で説明する通信データ送信処理により、主制御回路90から副制御回路200に送信される。なお、リール回転開始コマンドは、リールの回転開始動作開始されたことを示すパラメータを含んで構成される。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、引込優先順位格納処理を行う(S212)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、引込優先順位データを取得して、引込優先順位データ格納領域に格納する。なお、引込優先順位格納処理の詳細については、後述の図67を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、リール停止制御処理を行う(S213)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、左ストップボタン17L、中ストップボタン17C及び右ストップボタン17Rがそれぞれ押されたタイミングと内部当籤役とに基づいて該当するリールの回転の停止制御を行う。なお、リール停止制御処理の詳細については、後述の図72を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、入賞検索処理を行う(S214)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、図柄コード格納領域(図30参照)のデータを入賞作動フラグ格納領域(図25参照)に格納する。また、この処理では、メインCPU101は、有効ラインに表示役が表示されたか否かを判定し、その判定結果に基づいて、メダルの払出枚数をセットする。なお、入賞検索処理の詳細については、後述の図73を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、イリーガルヒットチェック処理を行う(S215)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、当り要求フラグ(内部当籤役)と入賞作動フラグ(表示役)とを合成し、その合成結果に基づいてイリーガルヒットエラーの有無を判定する。なお、イリーガルヒットチェック処理の詳細については、後述の図74を参照しながら後で説明する。また、リール停止制御処理(後述の図72参照)によって誤入賞が発生することなく各リールが停止される限りにおいては、制御負担軽減の観点からこのイリーガルヒットチェック処理を省略することもできる。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、入賞チェック・メダル払出処理を行う(S216)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、入賞作動コマンドの生成処理を行う。また、この処理では、メインCPU101は、S214において決定された表示役の払出枚数に基づいて、ホッパー装置51の駆動やクレジット枚数の更新を行い、メダルの払い出し処理を行う。なお、入賞チェック・メダル払出処理の詳細については、後述の図75を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、BBチェック処理を行う(S217)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、ボーナス状態の作動及び終了を制御する。なお、BBチェック処理の詳細については、後述の図77を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、RTチェック処理を行う(S218)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、有効ライン上に停止表示された図柄組合せに基づいてRT状態の移行制御を行う。なお、RTチェック処理の詳細については、後述の図78を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、遊技終了時状態別制御処理を行う(S219)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、図33〜図44を用いて説明した、非有利区間の通常状態、通常有利区間の各遊技状態、及び有利区間の各遊技状態における各種制御のうち、遊技終了時に行う必要がある各種制御を行うための各種処理を行う。そして、S219の処理後(一遊技終了後)、メインCPU101は、処理をS201の処理に戻す。
Next, the
[メダル受付・スタートチェック処理]
次に、図57及び図58を参照して、メインフロー(図56参照)中のS202で行うメダル受付・スタートチェック処理について説明する。なお、図57及び図58は、メダル受付・スタートチェック処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Medal reception/start check processing]
Next, with reference to FIGS. 57 and 58, the medal acceptance/start check processing performed in S202 in the main flow (see FIG. 56) will be described. 57 and 58 are flowcharts showing the procedure of medal acceptance/start check processing.
まず、メインCPU101は、自動投入メダルカウンタの値が「0」であるか否か(自動投入要求はあるか否か)を判別する(S221)。なお、この処理において、自動投入メダルカウンタが「1」以上であるときは、メインCPU101は、自動投入要求があると判別する。また、自動投入メダルカウンタは、前回の単位遊技において再遊技(リプレイ)に係る表示役が成立したか否かを識別するためのデータである。再遊技に係る表示役が成立したときには、前回の単位遊技において投入された枚数分のメダルが自動投入メダルカウンタに自動的に投入される。
First, the
S221において、メインCPU101が、自動投入メダルカウンタの値が「0」であると判別したとき(S221がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS225の処理を行う。
In S221, when the
一方、S221において、メインCPU101が、自動投入メダルカウンタの値が「0」でないと判別したとき(S221がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、メダル投入処理を行う(S222)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、メダル投入コマンドの生成格納処理やメダル投入枚数のLED点灯制御処理などを行う。なお、メダル投入処理の詳細については、後述の図59を参照しながら後で説明する。
On the other hand, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、自動投入メダルカウンタの値を減算する(S223)。なお、この処理では、メインCPU101は、自動投入メダルカウンタの値を一度に(例えば、「3」を)減算するようにしてよいし、「1」ずつ減算するようにしてもよい。次いで、減算後の自動投入メダルカウンタの値が「0」であるか否かを判別する(S224)。
Next, the
S224において、メインCPU101が、自動投入メダルカウンタの値が「0」でないと判別したとき(S224がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS222の処理に戻し、S222以降の処理を繰り返す。
When the
一方、S224において、メインCPU101が、自動投入メダルカウンタの値が「0」であると判別したとき(S224がYES判定の場合)、又は、S221がYES判定の場合、メインCPU101は、メダル補助収納庫スイッチチェック処理を行う(S225)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、メダル補助収納庫スイッチ75のオン/オフ状態に基づいて、メダル補助収納庫52がメダルで満杯になっているか否かを検出する。
On the other hand, in S224, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、メダル投入状態チェック処理を行う(S226)。次いで、メインCPU101は、メダル投入状態チェック処理の結果に基づいて、メダル投入可能な状態であるか否かを判別する(S227)。
Next, the
S227において、メインCPU101が、メダル投入可能な状態でないと判別したとき(S227がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS231の処理を行う。
In S227, when the
一方、S227において、メインCPU101が、メダル投入可能な状態であると判別したとき(S227がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、メダル投入チェック処理を行う(S228)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、例えば、メダルセンサ入力状態に基づいて、メダルが正常に通過したか否かの判定処理や、規定数を超えてメダル投入が行われた場合に該メダルをクレジットする処理などを行う。なお、メダル投入チェック処理の詳細については、後述の図60及び図61を参照しながら後で説明する。
On the other hand, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、メダル投入チェック処理の結果に基づいて、メダル投入又はクレジット可能な状態であるか否かを判別する(S229)。
Next, the
S229において、メインCPU101が、メダル投入又はクレジット可能な状態であると判別したとき(S229がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS231の処理を行う。一方、S229において、メインCPU101が、メダル投入又はクレジット可能な状態でないと判別したとき(S229がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、メダル受付禁止の処理を行う(S230)。この処理により、セレクタ66(図5参照)のソレノイドの駆動が行われなくなり(励磁されていたソレノイドが消磁され)、セレクトプレート804がガイド位置から排出位置に変移することで、投入されたメダルがメダル払出口24から排出されるようになる。
In S229, when the
S230の処理後、S227がNO判定の場合、又は、S229がYES判定の場合、メインCPU101は、現在のメダルの投入枚数が遊技可能開始枚数であるか否かを判別する(S231)。なお、本実施形態では、遊技状態にかかわらず遊技開始可能枚数は3枚である(すなわち、3枚投入のときのみ遊技を開始することが可能となる)。
After the process of S230, if the determination of S227 is NO, or if the determination of S229 is YES, the
S231において、メインCPU101が、現在のメダルの投入枚数が遊技可能開始枚数であると判別したとき(S231がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS234の処理を行う。一方、S231において、メインCPU101が、現在のメダルの投入枚数が遊技可能開始枚数でないと判別したとき(S231がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、メダル投入があるか否かを判別する(S232)。
In S231, when the
S232において、メインCPU101が、メダル投入があると判別したとき(S232がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS226に戻し、S226以降の処理を繰り返す。一方、S232において、メインCPU101が、メダル投入がないと判別したとき(S232がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、図48で説明した設定変更確認処理を行う(S233)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、設定確認開始時の設定変更コマンドの生成格納処理などを行う。これにより、遊技状態がボーナス状態(特賞作動状態)であるか否かにかかわらず、設定値及びホールメニュー(各種履歴データ(エラー、電断履歴等))を確認することができ、ゴト等の不正行為を抑制することができる。なお、このS233で行われる設定変更確認処理では、設定用鍵型スイッチ54がオフ状態であっても、少なくとも現在の設定値の情報を含む設定変更コマンド(設定確認開始)の生成格納処理が行われ、該コマンドデータがメインRAM103に設けられた通信データ格納領域に保存されるようにしてもよい。これにより、遊技毎に設定値が適切か(設定1〜6の範囲内であるか)否かをチェックすることが可能としてもよい。
In S232, when the
S233の処理後又はS231がYES判定の場合、メインCPU101は、スタートスイッチ79がオン状態であるか否かを判別する(S234)。
After the processing of S233 or when the determination of S231 is YES, the
S234において、メインCPU101が、スタートスイッチ79がオン状態でないと判別したとき(S234がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS226に戻し、S226以降の処理を繰り返す。
In S234, when the
一方、S234において、メインCPU101が、スタートスイッチ79がオン状態であると判別したとき(S234がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、メダル受付禁止の処理を行う(S235)。この処理により、セレクタ66(図5参照)のソレノイドの駆動が行われなくなり(励磁されていたソレノイドが消磁され)、セレクトプレート804がガイド位置から排出位置に変移することで、投入されたメダルがメダル払出口24から排出されるようになる。
On the other hand, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、メダル監視タイマにタイマ値(本実施形態では、「72」)をセットする(S236)。メダル監視タイマは、セレクタ66において、励磁されていたソレノイドが消磁完了となるまでの期間(すなわち、セレクトプレート804が、ガイド位置から排出位置に移動するまでの期間)を監視するためのタイマであり(後述の図86参照)、例えば、励磁されていたソレノイドが消磁完了となるまでの期間が80msである場合に、少なくともそれ以上の期間(「約80.44ms」)を計測するためのタイマ値が設定される。すなわち、メダル監視タイマは、遊技可能開始枚数分のメダルが投入されている場合に、スタートレバー16が操作され(スタートスイッチ79がオン状態となり)、メダル受付禁止の制御が開始されてから、実際にメダルの受付が(物理的に)禁止されるまでの特定期間を監視する。これにより、後述のスタートレバーONフラグや、後述のメダル投入チェック2処理等と合わせて、該特定期間においてメダルが投入された場合に、そのメダルが誤って飲み込まれてしまう(すなわち、メダルを投入したが、カウントされることなくホッパー装置51に収容されてしまう)ことを防止している。なお、メダル監視タイマの値は、セレクタ66(主にソレノイド)の仕様に応じて、適宜変更することが可能である。また、メダルの飲み込みを防止することが担保される限り、励磁されていたソレノイドが消磁完了となるまでの期間未満の期間に設定することもできる。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、スタートレバーONフラグをオン状態にセットする(S237)。スタートレバーONフラグは、遊技可能開始枚数分のメダルが投入されている場合に、スタートレバー16が操作された(スタートスイッチ79がオン状態となった)か否かを識別するための情報である。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、メダル投入チェック2処理を行う(S238)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、基本的に、メダル投入チェック処理と同様の処理を行う。なお、メダル投入チェック処理及びメダル投入チェック2処理の詳細については、後述の図60及び図61を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、スタートレバーONフラグがオフ状態であるか否かを判別する(S239)。S239において、メインCPU101が、スタートレバーONフラグがオフ状態であると判別したとき(S239がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS226に戻し、S226以降の処理を繰り返す。
Next, the
一方、S239において、メインCPU101が、スタートレバーONフラグがオフ状態でない(すなわち、オン状態である)と判別したとき(S239がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、メダル監視タイマは「0」であるか否かを判別する(S240)。S239において、メインCPU101が、メダル監視タイマは「0」でない(すなわち、「1」以上である)と判別したとき(S240がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS238に戻し、S238以降の処理を繰り返す。
On the other hand, when the
一方、S240において、メインCPU101が、メダル監視タイマは「0」であると判別したとき(S240がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、メダル受付・スタートチェック処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)のS203に移す。
On the other hand, in S240, when the
[メダル投入処理]
次に、図59を参照して、メダル受付・スタートチェック処理(図57及び図58参照)中のS222、及び後述のメダル投入チェック処理(図60及び図61参照)中のS265で行うメダル投入処理について説明する。なお、図59は、メダル投入処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Medal insertion process]
Next, referring to FIG. 59, the medal insertion performed in S222 during the medal acceptance/start check process (see FIGS. 57 and 58) and the later-described medal insertion check process (see FIGS. 60 and 61) performed in S265. The processing will be described. Note that FIG. 59 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the medal insertion process.
まず、メインCPU101は、メダルカウンタの値に「1」を加算する(S241)。なお、メダルカウンタは、メダルの投入枚数をカウント(計数)するためのカウンタであり、メインRAM103に設けられる。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、メダル投入コマンド生成格納処理を行う(S242)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、副制御回路200に送信するメダル投入コマンドのデータを生成し、該コマンドデータをメインRAM103に設けられた通信データ格納領域に保存する。通信データ格納領域に保存されたメダル投入コマンドは、後述の図80で説明する通信データ送信処理により、主制御回路90から副制御回路200に送信される。すなわち、メダル投入コマンドは、メダルが1枚投入される度に、主制御回路90から副制御回路200に送信される。なお、メダル投入コマンドは、投入枚数等を特定するためのパラメータを含んで構成される。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、LED82(図6参照)に含まれるメダル投入枚数表示用の第1〜第3LEDを消灯させる(S243)。次いで、メインCPU101は、メダル投入枚数(メダルカウンタの値)に基づいて、該メダル投入枚数に対応するLED点灯データ(点灯制御データ)を算出する(S244)。この処理において、例えば、メダル投入枚数が1枚である場合には、メダル投入枚数表示用の第1LEDのみを点灯させるLED点灯データが算出され、また、例えば、メダル投入枚数が3枚である場合には、メダル投入枚数表示用の第1〜第3LEDの全てを点灯させるLED点灯データが算出される。なお、このLED点灯データの算出手法については、後で詳述する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、算出されたLED点灯データを用いて、対応するメダル投入枚数表示用のLEDを点灯させる(S245)。そして、S245の処理後、メインCPU101は、メダル投入処理を終了し、処理をメダル受付・スタートチェック処理(図57及び図58参照)のS223、又は後述のメダル投入チェック処理(図60及び図61参照)のS253に移す。
Next, the
[メダル投入チェック処理]
次に、図60及び図61を参照して、メダル受付・スタートチェック処理(図57及び図58参照)中のS228で行うメダル投入チェック処理、及びメダル受付・スタートチェック処理(図57及び図58参照)中のS238で行うメダル投入チェック2処理について説明する。図60及び図61は、メダル投入チェック処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。なお、メダル投入チェック2処理は、メダル投入チェック処理のS253から処理が開始されるものであり、S253〜S268の処理はメダル投入チェック処理におけるものと同一の処理であることから、以下では、メダル投入チェック処理の手順として説明する。
[Medal insertion check processing]
Next, referring to FIGS. 60 and 61, the medal insertion check process and the medal acceptance/start check process (FIGS. 57 and 58) performed in S228 of the medal acceptance/start check process (see FIGS. 57 and 58). The
まず、メインCPU101は、再遊技中であるか否かを判別する(S251)。
First, the
S251において、メインCPU101が、再遊技中であると判別したとき(S251がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、メダル投入チェック処理を終了し、処理をメダル受付・スタートチェック処理(図57及び図58参照)のS229に移す。
In S251, when the
一方、S251において、メインCPU101が、再遊技中でないと判別したとき(S251がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、メダル受付許可を行う(S252)。この処理では、セレクタ66(図5参照)のソレノイドの駆動が行われ(消磁されていたソレノイドが励磁され)、セレクトプレート804が排出位置からガイド位置に変移することで、メダル投入口14から投入されたメダルが計数され、ホッパー装置51に収容されるようになる。
On the other hand, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、ベットボタンチェック処理を行う(S253)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、BETスイッチ77のオン/オフ状態に基づいて、ベットボタン(MAXベットボタン15a又は1ベットボタン15b)の操作が行われたか否かを判別する。次いで、メインCPU101は、S253のベットボタンチェック処理の結果に基づいて、ベット動作が完了したか否かを判別する(S254)。
Next, the
S254において、メインCPU101が、ベット動作が完了したと判別したとき(S254がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、メダル投入チェック処理(又はメダル投入チェック2処理)を終了し、処理をメダル受付・スタートチェック処理(57及び図58参照)のS229(又はメダル受付・スタートチェック処理(図57及び図58参照)のS239)に移す。
In S254, when the
一方、S254において、メインCPU101が、ベット動作が完了していないと判別したとき(S254がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、現処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態(遊技媒体の受付状態)と、前回処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態とを取得する(S255)。なお、メダルセンサ入力状態は、メダル投入口14に受け入れられたメダルのセレクタ66内の通過状況を示す情報であり、セレクタ66の各メダルセンサ(図5参照)の検知結果により生成される。
On the other hand, in S254, when the
本実施形態では、メダルセンサ入力状態は、1バイト(8ビット)のデータで表され、セレクタ66の出口にメダルの通過方向に並んで設けられた上流側の第1メダルセンサ806の検知結果がビット0の情報(「0」又は「1」)に対応し、下流側の第2メダルセンサ807の検知結果がビット1の情報(「0」又は「1」)に対応する。第1メダルセンサによりメダルの通過が検知された場合には、ビット0に「1」がセットされ、第2メダルセンサによりメダルの通過が検知された場合には、ビット1に「1」がセットされる。それゆえ、メダルセンサ入力状態「00000000B」は、メダル通過前又は通過後(通過時)の状態を示し、メダルセンサ入力状態「00000001B」は、メダル通過開始時の状態を示し、メダルセンサ入力状態「00000011B」は、メダル通過中の状態を示し、メダルセンサ入力状態「00000010B」は、メダル通過完了直前の状態を示す。
In the present embodiment, the medal sensor input state is represented by 1-byte (8-bit) data, and the detection result of the upstream
次いで、メインCPU101は、現処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態が前回処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態から変化したか否かを判別する(S256)。
Next, the
S256において、メインCPU101が、現処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態が前回処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態から変化していないと判別したとき(S256がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS262の処理を行う。
In S256, when the
一方、S256において、メインCPU101が、現処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態が前回処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態から変化したと判別したとき(S256がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、スタートレバーONフラグがオン状態であれば、スタートレバーONフラグをオフ状態にセットする(S257)。すなわち、この処理では、メインCPU101は、開始操作が行われ、メダル受付禁止の制御が開始されてから、実際にメダルの受付が(物理的に)禁止されるまでの特定期間においてメダルの投入を検知した場合には、該開始操作を無効にする処理を行う。
On the other hand, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、前回処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態に基づいて、演算処理により、現処理時で得られるメダルセンサ入力状態の正常値(正常変化値)を生成する(S258)。
Next, the
なお、この処理において、前回処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態が「00000000B」である場合(第1及び第2メダルセンサがともにメダル未検知である場合)には、メダルセンサ入力状態の正常変化値として「00000001B」(第1メダルセンサがメダル検知であり、第2メダルセンサがメダル未検知である場合)が生成され、前回処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態が「00000001B」である場合には、メダルセンサ入力状態の正常変化値として「00000011B」(第1及び第2メダルセンサがともにメダル検知である場合)が生成される。また、この処理において、前回処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態が「00000011B」である場合には、メダルセンサ入力状態の正常変化値として「00000010B」(第1メダルセンサがメダル未検知であり、第2メダルセンサがメダル検知である場合)が生成され、前回処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態が「00000010B」である場合には、メダルセンサ入力状態の正常変化値として「00000000B」(第1及び第2メダルセンサがともにメダル未検知である場合)が生成される。 In this process, when the medal sensor input state at the previous process is “00000000B” (when both the first and second medal sensors have not detected medals), the normal change value of the medal sensor input state is determined. "00000001B" (when the first medal sensor detects medals and the second medal sensor does not detect medals) is generated, and the medal sensor input state at the time of the previous processing is "00000001B", the medal sensor As a normal change value of the input state, "00000011B" (when both the first and second medal sensors detect medals) is generated. In this process, when the medal sensor input state at the previous process is "00000011B", the normal change value of the medal sensor input state is "00000010B" (the first medal sensor has not detected the medal, If the medal sensor is for medal detection) and the medal sensor input state during the previous processing is "00000010B", the normal change value of the medal sensor input state is "00000000B" (first and second medals). (When both sensors have not detected medals).
次いで、メインCPU101は、現処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態がS258で生成された正常変化値と同じであるか否かを判別する(S259)。なお、この判定処理では、メダル逆行エラーの発生の有無が判定され、S259の判定条件が満たされない場合には、メインCPU101は、メダル逆行エラーが発生したと判定する。
Next, the
S259において、メインCPU101が、現処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態がS258で生成された正常変化値と同じでないと判別したとき(S259がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS263の処理を行う。
In S259, when the
一方、S259において、メインCPU101が、現処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態がS258で生成された正常変化値と同じであると判別したとき(S259がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、現処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態がメダル通過時の状態(「00000000B」)であるか否かを判別する(S260)。S260において、メインCPU101が、現処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態がメダル通過時の状態であると判別したとき(S260がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS264の処理を行う。
On the other hand, when the
S260において、メインCPU101が、現処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態がメダル通過時の状態でないと判別したとき(S260がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、メダル通過チェックタイマをセットする(S261)。この処理でメダル通過チェックタイマにセットされる時間は、メダルがセレクタ66を通過したか否かを判別可能な時間であれば、任意の時間に設定することができる。また、この処理でセットされるタイマ値は、例えば、現処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態に応じて変化させてもよい。
In S260, when the
S261の処理後又はS256がNO判定の場合、メインCPU101は、現処理時のメダルセンサ入力状態がメダル通過中の状態(「00000011B」)であり、かつ、メダル通過チェックタイマが停止しているか否かを判別する(S262)。この判定処理では、メダル通過エラー(投入メダル通過時間エラー)の発生の有無が判定され、S262の判定条件が満たされた場合、メインCPU101は、メダル通過エラーが発生したと判定する。
After the processing of S261 or when the determination of S256 is NO, the
S262において、メインCPU101が、S262の判定条件が満たされないと判別したとき(S262がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS253の処理に戻し、S253以降の処理を繰り返す。
In S262, when the
一方、S262において、メインCPU101が、S262の判定条件が満たされると判別したとき(S262がYES判定の場合)、又は、S259がNO判定の場合、すなわち、メダル通過エラー又はメダル逆行エラーが発生したと判定された場合、メインCPU101は、エラー処理を行う(S263)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、例えば、エラーコマンド生成格納処理等のエラー発生時の各種処理を行う。なお、エラー処理の詳細については、後述の図62を参照しながら後で説明する。そして、S263の処理後、メインCPU101は、処理をS253の処理に戻し、S253以降の処理を繰り返す。
On the other hand, in S262, when the
ここで再度、S260の処理に戻って、S260がYES判定の場合、メインCPU101は、規定数(本実施形態では3枚)のメダルが投入済みの状態であるか否かを判別する(S264)。
Here, returning to the process of S260 again, when the determination of S260 is YES, the
S264において、メインCPU101が、規定数のメダルが投入済みの状態でないと判別したとき(S264がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、図59で説明したメダル投入処理を行う(S265)。そして、S265の処理後、メインCPU101は、処理をS253の処理に戻し、S253以降の処理を繰り返す。
When the
一方、S264において、メインCPU101が、規定数のメダルが投入済みの状態であると判別したとき(S264がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、クレジットカウンタの値に「1」を加算する(S266)。次いで、メインCPU101は、メダル投入コマンド生成格納処理を行う(S267)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、副制御回路200に送信するメダル投入コマンドのデータを生成し、該コマンドデータをメインRAM103に設けられた通信データ格納領域に保存する。通信データ格納領域に保存されたメダル投入コマンドは、後述の図80で説明する通信データ送信処理により、主制御回路90から副制御回路200に送信される。
On the other hand, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、クレジットカウンタの値に基づいて、メダルのクレジット枚数が上限値(本実施形態では50枚)であるか否かを判別する(S268)。
Next, the
S268において、メインCPU101が、メダルのクレジット枚数が上限値でないと判別したとき(S268がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS253の処理に戻し、S253以降の処理を繰り返す。一方、S268において、メインCPU101が、メダルのクレジット枚数が上限値であると判別したとき(S268がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、メダル投入チェック処理(又はメダル投入チェック2処理)を終了し、処理をメダル受付・スタートチェック処理(図57及び図58参照)のS229(又はメダル受付・スタートチェック処理(図57及び図58参照)のS239)に移す。
In S268, when the
[エラー処理]
次に、図62を参照して、例えば、メダル投入チェック処理(図60及び図61参照)中のS263で行うエラー処理について説明する。図62は、エラー処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Error handling]
Next, with reference to FIG. 62, for example, the error processing performed in S263 in the medal insertion check processing (see FIGS. 60 and 61) will be described. FIG. 62 is a flowchart showing the procedure of error processing.
まず、メインCPU101は、メダルソレノイドのオフ処理を行う(S271)。具体的には、メインCPU101は、セレクタ66(図5参照)のソレノイドの駆動を停止する。次いで、メインCPU101は、メダルの払出枚数表示データの退避処理を行う(S272)。次いで、メインCPU101は、エラーテーブルのセット処理を行う(S273)。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、エラー要因を取得する(S274)。なお、この処理で取得されるエラー要因は、現在処理中のエラー処理を読み出した処理に応じて変化する。なお、本実施形態で対象とするエラー要因としては、「ホッパーエンプティエラー」、「ホッパージャムエラー」、「投入メダル通過カウントエラー」、「投入メダル通過チェックエラー」、「投入メダル通過チェックエラー」、「投入メダル通過時間エラー」、「投入メダル逆行エラー」、「投入メダル補助収納庫満杯エラー」、「イリーガルヒットエラー」が規定される。例えば、メダル投入チェック処理中のS259の処理後にエラー処理が読み出された場合には、この処理において、エラー要因として「投入メダル逆行エラー(Cr)」が取得される。また、例えば、メダル投入チェック処理中のS262の処理後にエラー処理が読み出された場合には、この処理において、エラー要因として「投入メダル通過時間エラー(CE)」が取得される。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、エラーテーブルとエラー要因とから、エラー表示データを取得する(S275)。例えば、エラー要因が「投入メダル逆行エラー(Cr)」である場合、この処理において、2桁の7セグLEDのうち、上位桁の7セグLEDに出力するエラー表示データとして、1バイトデータ「01001110B」が取得され、下位桁の7セグLEDに出力するエラー表示データとして、1バイトデータ「00001001B」が取得される。この場合、2桁の7セグLEDには、「Cr」の2文字がエラー情報として表示される。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、エラーコマンド(発生)生成格納処理を行う(S276)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、副制御回路200に送信する、エラー発生時のエラーコマンドのデータを生成し、該コマンドデータをメインRAM103に設けられた通信データ格納領域に保存する。通信データ格納領域に保存されたエラー発生時のエラーコマンドは、後述の図80で説明する通信データ送信処理により、主制御回路90から副制御回路200に送信される。なお、エラー発生時のエラーコマンドには、エラー発生を示すパラメータを含んで構成される。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、1割込時間(1.1172ms)の待機処理を行う(S277)。次いで、メインCPU101は、エラーが解除されたか否かを判別する(S278)。
Next, the
S278において、メインCPU101が、エラーが解除されていないと判別したとき(S278がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS277の処理に戻し、S277以降の処理を繰り返す。
When the
一方、S278において、メインCPU101が、エラーが解除されたと判別したとき(S278がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、エラー要因のクリア処理を行う(S279)。なお、この処理は、メインRAM103の規定外作業領域で行われる。次いで、メインCPU101は、S272で退避させたメダルの払出枚数表示データの復帰処理を行う(S280)。
On the other hand, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、エラーコマンド(解除)生成格納処理を行う(S281)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、副制御回路200に送信する、エラー解除時のエラーコマンドのデータを生成し、該コマンドデータをメインRAM103に設けられた通信データ格納領域に保存する。通信データ格納領域に保存されたエラー解除時のエラーコマンドは、後述の図80で説明する通信データ送信処理により、主制御回路90から副制御回路200に送信される。なお、エラー解除時のエラーコマンドには、エラー解除を示すパラメータを含んで構成される。そして、S281の処理後、メインCPU101は、エラー処理を終了し、処理を例えばメダル投入チェック処理(図60及び図61参照)中のS253に移す。なお、エラー解除では、発生したエラー要因が解除され、リセットスイッチ76が押下されることにより、エラー状態が解除される。
Next, the
[乱数値取得処理]
次に、図63を参照して、メインフロー(図56参照)中のS203で行う乱数値取得処理について説明する。なお、図63は、乱数値取得処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Random value acquisition process]
Next, with reference to FIG. 63, the random value acquisition processing performed in S203 in the main flow (see FIG. 56) will be described. Note that FIG. 63 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the random value acquisition process.
まず、メインCPU101は、乱数回路の乱数レジスタ0のハードラッチ乱数(0〜65535)を取得し、取得した乱数値を内部当籤役抽籤用の乱数値として、メインRAM103内の乱数値格納領域(不図示)に保存する(S291)。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、乱数回路の乱数レジスタ1〜7のソフトラッチ乱数(0〜65535又は0〜255)を生成するためのソフトラッチ乱数取得レジスタのセット処理を行う(S292)。次いで、メインCPU101は、ソフトラッチ乱数の取得個数(例えば、7)をセットする(S293)。なお、取得個数は、一遊技において行われ得る抽籤の数に応じて適宜増減して設定することができる。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、取得個数分のソフトラッチ乱数を一括で取得し、取得個数分のソフトラッチ乱数を乱数値格納領域に保存する(S294)。なお、この際、乱数回路110の乱数レジスタ1〜7から取得されるソフトラッチ乱数(演出用乱数値)は、乱数値格納領域内において、乱数回路の乱数レジスタ0から取得されるハードラッチ乱数(内部当籤役抽籤用の乱数値)が格納された領域とは異なる領域に保存される。そして、S294の処理後、メインCPU101は、乱数値取得処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)のS204に移す。なお、本実施形態では、1つの2バイト乱数(内部当籤役抽籤用の乱数値)と、6つの1バイト乱数(演出用乱数値)を格納するために、メインRAM103に8バイトの格納領域が乱数格納領域として割り当てられている。また、本実施形態では、2バイト乱数のソフトラッチ乱数は使用されていない。
Next, the
[内部抽籤処理]
次に、図64を参照して、メインフロー(図56参照)中のS204で行う内部抽籤処理について説明する。なお、図64は、内部抽籤処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Internal lottery processing]
Next, with reference to FIG. 64, the internal lottery process performed in S204 in the main flow (see FIG. 56) will be described. 64. FIG. 64 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the internal lottery process.
まず、メインCPU101は、設定値・メダル投入枚数チェック処理を行う(S301)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、現遊技の設定値(1〜6のいずれか)及びメダル投入枚数(本実施形態では3枚)のチェック処理を行う。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、一般遊技中用の内部抽籤テーブル(図16及び図17に示した「RT0」状態における内部抽籤テーブル参照)及び抽籤回数(本実施形態では98回)をセットする(S302)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、RB作動中であるか否かを判別する(S303)。S303において、メインCPU101が、RB作動中でないと判別したとき(S303がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS305の処理を行う。
Next, the
一方、S303において、メインCPU101が、RB作動中であると判別したとき(S303がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、RB中用の内部抽籤テーブル(図18に示した内部抽籤テーブル参照)及び抽籤回数(本実施形態では7回)をセットする(S304)。この処理では、S302でセットされた一般遊技中用の内部抽籤テーブル及び抽籤回数をRB中用の内部抽籤テーブル及び抽籤回数で上書きする。
On the other hand, when the
S304の処理後又はS303がNO判定の場合、メインCPU101は、セットされている内部抽籤テーブルから抽籤対象役の判定データ(アドレスに関するデータ)を取得し、抽籤テーブルアドレスを更新する(S305)。
After the process of S304 or when the determination of S303 is NO, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、判定データがRT状態別データであるか否かを判別する(S306)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、現在取得されている抽籤対象役がRT状態に応じて抽籤値が変化する内部当籤役であるか否かを判別する。具体的には、メインCPU101は、現在取得されている抽籤対象役の判定データに規定されているアドレスが、RT状態別抽籤値選択テーブル(不図示)内のアドレスであるか否かを判別する。
Next, the
S306において、メインCPU101が、判定データがRT状態別データでないと判別したとき(S306がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS308の処理を行う。一方、S306において、メインCPU101が、判定データがRT状態別データであると判別したとき(S306がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、判定データに基づいて、RT状態抽籤値選択テーブルから選択データを取得し、該取得した選択データを判定データにセットする(S307)。
In S306, when the
S307の処理後又はS306がNO判定の場合、メインCPU101は、抽籤対象役の判定データが設定別データであるか否かを判別する(S308)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、現在取得されている抽籤対象役が、設定値に応じて抽籤値が変化する内部当籤役であるか否かを判別する。具体的には、メインCPU101は、現在取得されている抽籤対象役の判定データに規定されているアドレスが、設定別内部抽籤値テーブル(不図示)内のアドレスであるか否かを判別する。
After the processing of S307 or when the determination of S306 is NO, the
S308において、メインCPU101が、判定データが設定別データでないと判別したとき(S308がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS310の処理を行う。一方、S308において、メインCPU101が、判定データが設定別データであると判別したとき(S308がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、判定データに設定値データ(0〜5のいずれか)を加算し、該加算した値を判定データにセットする(S309)。なお、この処理で判定データに加算される設定値データは、設定値に対応付けられたデータであるが、設定値そのものの値ではなく、設定値データ「0」〜「5」は、それぞれ「設定1」〜「設定6」に対応するデータである。
In S308, when the
S309の処理後又はS308がNO判定の場合、メインCPU101は、セットされている判定データ(アドレスデータ)に基づいて、抽籤対象役の抽籤値が格納された領域のアドレスを算出し、該アドレスに格納された抽籤値を取得する(S310)。
After the process of S309 or when the determination of S308 is NO, the
なお、例えば、その抽籤値がRT状態及び設定値の両方に応じて変化する内部当籤役の場合には、RT状態抽籤値選択テーブル及び設定別内部抽籤値テーブルの両方を参照して、抽籤値が取得される。すなわち、例えば、一般遊技状態用の内部抽籤テーブル(図16及び図17参照)において、RT0状態を基準とし、RT状態が異なる場合に抽籤値が変動する内部当籤役(例えば、「F_維持リプ」など)については、遊技状態(RT1〜RT5状態)に応じて抽籤値を変動させるとともに、設定値が異なる場合に抽籤値が変動する内部当籤役(例えば、「F_維持リプ」など)については、設定値(設定1〜6)に応じて抽籤値を変動させる。
For example, in the case of an internal winning combination in which the lottery value changes according to both the RT state and the set value, both the RT state lottery value selection table and the internal lottery value table for each setting are referred to to determine the lottery value. Is obtained. That is, for example, in the internal lottery table for the normal gaming state (see FIG. 16 and FIG. 17), the internal lottery combination (for example, “F_maintenance lip”) in which the lottery value changes when the RT state is different with the RT0 state as a reference Etc.), the lottery value is changed according to the game state (RT1 to RT5 state), and the lottery value is changed when the set value is different, for the internal winning combination (for example, “F_maintenance lip”, etc.), The lottery value is changed according to the set value (
次いで、メインCPU101は、乱数格納領域に格納された内部当籤役抽籤用の乱数値(0〜65535のいずれか)を取得する(S311)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、抽籤実行処理を行う(S312)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、S310で取得された抽籤値に、S311で取得された乱数値を加算し、その加算結果を抽籤結果(抽籤対象役の当籤/非当籤)とする。なお、この抽籤実行処理において、抽籤値と乱数値との和が65535を超えた場合(オーバーフローした場合)、抽籤対象役が当籤した(抽籤対象役が内部当籤役として決定された)と判定される。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、乱数値に抽籤値を加算した値(抽籤実行後の乱数値)を新たな乱数値として、乱数格納領域に保存する(S313)。次いで、メインCPU101は、抽籤実行処理で当籤したか否か(オーバーフローが発生したか否か)を判別する(S314)。
Next, the
S314において、メインCPU101が、抽籤実行処理で当籤したと判別したとき(S314がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、内部抽籤テーブルを参照して当籤した内部当籤役に対応する当り要求フラグステータス(例えば、図16〜図18中「No.」に対応する、特賞当籤番号(すなわち、当籤したボーナス役の種別を識別可能な情報)及び小役当籤番号(すなわち、当籤した小役又はリプレイ役の種別を識別可能な情報)の値)を取得する(S315)。そして、S315の処理後、メインCPU101は、内部抽籤処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)のS205に移す。
In S314, when the
一方、S314において、メインCPU101が、抽籤実行処理で当籤していないと判別したとき(S314がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、内部抽籤テーブルにおいて抽籤対象役を次の役に更新し、抽籤回数を1減算する(S316)。次いで、メインCPU101は、減算後の抽籤回数が「0」であるか否かを判別する(S317)。
On the other hand, in S314, when the
S317において、メインCPU101が、減算後の抽籤回数が「0」でないと判別したとき(S317がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS305の処理に戻し、S305以降の処理を繰り返す。
In S317, when the
一方、S317において、メインCPU101が、減算後の抽籤回数が「0」であると判別したとき(S317がYES判定の場合)、すなわち、内部当籤役が「はずれ」である場合、メインCPU101は、ハズレステータスをセットする(S318)。なお、「ハズレステータス」は、特賞当籤番号及び小役当籤番号のいずれもが「0」となる当り要求フラグステータスに対応する。そして、S318の処理後、メインCPU101は、内部抽籤処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)のS205に移す。
On the other hand, in S317, when the
[図柄設定処理]
次に、図65を参照して、メインフロー(図56参照)中のS205で行う図柄設定処理について説明する。なお、図65は、図柄設定処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Design setting process]
Next, with reference to FIG. 65, the symbol setting process performed in S205 in the main flow (see FIG. 56) will be described. Note that FIG. 65 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the symbol setting process.
まず、メインCPU101は、内部抽籤処理で取得された当り要求フラグステータスに基づいて、特賞当籤番号及び小役当籤番号を抽出し、該抽出された特賞当籤番号及び小役当籤番号をメインRAM103内の当籤番号格納領域(不図示)に保存する(S321)。
First, the
本実施形態では、特賞当籤番号「1」〜「4」には、それぞれ、内部当籤役「F_BB1」、「F_BB2」、「F_BB3」及び「F_BB4」が対応付けられている。また、小役当籤番号「1」〜「23」には、それぞれ、内部当籤役「F_確定リプ」〜「F_被弾リプ」が対応付けられ(図23参照)、小役当籤番号「24」〜「61」には、それぞれ、内部当籤役「F_チャンス目A1」〜「F_下段右中ベル2」が対応付けられ(図24参照)、小役当籤番号「62」〜「68」には、それぞれ、内部当籤役「F_JAC1_1」〜「F_JAC2」が対応付けられている(図23参照)。そして、当り要求フラグステータスの値は、これらの値を示す特賞番号に特賞当籤番号の値を乗算し、小役当籤番号を加算した値で構成される。それゆえ、S321の処理において、当り要求フラグステータスの値から特賞当籤番号及び小役当籤番号を抽出するため、本実施形態では、メインCPU101は、当り要求フラグステータスの値を特賞番号で除算する。なお、これは内部当籤役を識別するためのデータ圧縮の一例であり、特賞当籤番号及び小役当籤番号を抽出可能であれば、その他のデータ構成も適宜採用することができる。
In this embodiment, the internal winning combinations “F_BB1”, “F_BB2”, “F_BB3”, and “F_BB4” are associated with the special winning numbers “1” to “4”, respectively. In addition, the internal winning combinations “F_confirmed rep” to “F_ballistic rep” are respectively associated with the small winning combinations “1” to “23” (see FIG. 23), and the small winning combinations “24” to. “61” is associated with the internal winning combination “F_chance eye A1” to “F_lower right
次いで、メインCPU101は、抽出された小役当籤番号に基づいて、小役(又はリプレイ役)が当籤したか否かを判別する(S322)。この処理において、小役当籤番号が1〜68のいずれかである場合には、メインCPU101は、小役(又はリプレイ役)が当籤したと判定し、小役当籤番号が0である場合には、メインCPU101は、小役(又はリプレイ役)が当籤しなかったと判定する。
Next, the
S322において、メインCPU101が、小役(又はリプレイ役)が当籤していないと判別したとき(S322がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS331の処理を行う。一方、S322において、メインCPU101が、小役(又はリプレイ役)が当籤したと判別したとき(S322がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、小役当籤番号を減算結果の初期値としてセットする(S323)。
In S322, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、当り要求フラグテーブル(不図示)をセットする(S324)。次いで、メインCPU101は、減算結果を1減算し、該減算結果を更新する(S325)。次いで、メインCPU101は、減算結果が「0」未満であるか否かを判別する(S326)。
Next, the
S326において、メインCPU101が、減算結果が「0」未満でないと判別したとき(S326がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、ビット数算出処理を行う(S327)。なお、S327のビット数算出処理では、当り要求フラグテーブルに規定されている、小役当籤番号に対応する当り要求フラグデータの格納領域のブロック数を取得する。
When the
次いで、メインCPU101は、ビット数算出処理を行う(S328)。なお、S328のビット数算出処理では、当り要求フラグテーブルにおいて規定されるブロック単位の当り要求フラグデータのバイト数を算出する。
Next, the
なお、上述したS325〜S328の処理は、小役当籤番号の回数だけ繰り返される。また、S325〜S328の処理が複数回繰り返される場合には、S327及びS328のビット数算出処理でそれぞれ取得されるブロック数及びブロック単位の当り要求フラグデータのバイト数は、別の格納領域に保存される。また、上述したS325〜S328の処理により得られたブロック数及びブロック単位の当り要求フラグデータのバイト数は、当り要求フラグデータの格納先を指定する情報(オンビット情報)となる。 Note that the above-described processing of S325 to S328 is repeated for the number of small winning combinations. Further, when the processes of S325 to S328 are repeated a plurality of times, the number of blocks and the number of bytes of the hit request flag data in block units respectively acquired in the bit number calculation process of S327 and S328 are saved in another storage area. To be done. Also, the number of blocks and the number of bytes of the hit request flag data in block units obtained by the above-described processing of S325 to S328 are information (on-bit information) that specifies the storage destination of the hit request flag data.
ここで再度、S326の処理に戻って、S326において、メインCPU101が、減算結果が「0」未満であると判別したとき(S326がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、当り要求フラグ格納領域(内部当籤役格納領域)のセット処理を行う(S329)。この際、メインCPU101は、上述したS325〜S328の処理により得られたブロック数及びブロック単位の当り要求フラグデータのバイト数(オンビット情報)に基づいて、チェック(更新)対象となる当り要求フラグ格納領域のみをセットする。具体的には、チェック(更新)対象となる当り要求フラグ格納領域のアドレスをDEレジスタに格納する。
Here, returning again to the processing of S326, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、圧縮データ格納処理を行う(S330)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、主に、当り要求フラグデータをチェック(更新)対象となる当り要求フラグ格納領域内の所定の格納領域に転送(展開)する処理を行う。圧縮データ格納処理の詳細については、後述の図66を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
S330の処理後又はS322がNO判定の場合、メインCPU101は、持越役格納領域(図26参照)を参照して、持越役があるか否かを判別する(S331)。S331において、メインCPU101が、持越役があると判別したとき(S331がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS334の処理を行う。
After the processing of S330 or when the determination of S322 is NO, the
一方、S331において、メインCPU101が、持越役がないと判別したとき(S331がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、S321の処理で抽出された特賞当籤番号に基づいて、ボーナス役(BB1〜BB4)が当籤したか否かを判別する(S332)。
On the other hand, when the
S332において、メインCPU101が、ボーナス役が当籤していないと判別したとき(S332がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、図柄設定処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)のS206に移す。
In S332, when the
一方、S332において、メインCPU101が、ボーナス役が当籤したと判別したとき(S332がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、当籤した特賞当籤番号を持越役格納領域に格納する(S333)。
On the other hand, when the
S333の処理後又はS331がNO判定の場合、メインCPU101は、特賞当籤番号を当籤番号格納領域(不図示)にセットし、当り要求フラグ格納領域に当り要求フラグデータをセットし、RT状態をRT5状態にセットする(S334)。そして、S334の処理後、メインCPU101は、図柄設定処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)のS206に移す。
After the processing of S333 or when the determination of S331 is NO, the
[圧縮データ格納処理]
次に、図66を参照して、例えば、図柄設定処理(図65参照)中のS330で行う圧縮データ処理について説明する。図66は、圧縮データ格納処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Compressed data storage processing]
Next, with reference to FIG. 66, for example, the compressed data processing performed in S330 in the symbol setting processing (see FIG. 65) will be described. FIG. 66 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the compressed data storage processing.
なお、図66に示す圧縮データ格納処理は、図柄設定処理(図65参照)中のS330だけでなく、後述の図柄コード取得処理(後述の図68参照)中のS649においても実行される。図柄設定処理(図65参照)中のS330で実行される圧縮データ格納処理では、処理対象となるフラグデータは当り要求フラグデータ(当籤役に係るフラグデータ)となるが、後述の図柄コード取得処理(後述の図68参照)中のS649で実行される圧縮データ格納処理では、処理対象となるフラグデータは入賞作動フラグデータ(入賞役に係るフラグデータ)である。そして、処理対象となるフラグデータの種別が異なること以外は、両者の処理は同じ処理になる。 The compressed data storage processing shown in FIG. 66 is executed not only in S330 during the symbol setting processing (see FIG. 65) but also in S649 during the later-described symbol code acquisition processing (see later-described FIG. 68). In the compressed data storage process executed in S330 of the symbol setting process (see FIG. 65), the flag data to be processed becomes the hit request flag data (flag data related to the winning combination), but the symbol code acquisition process described later. In the compressed data storage processing executed in S649 in (see FIG. 68 described later), the flag data to be processed is winning operation flag data (flag data relating to winning combinations). Then, both processes are the same except that the types of flag data to be processed are different.
それゆえ、図66のフローチャートでは、処理対象とするフラグデータを「処理対象フラグデータ」と記し、処理対象となるフラグテーブルを「処理対象フラグテーブル」と記す。また、この記載に合わせて、以下の圧縮データ格納処理の説明においても、当り要求フラグデータ又は入賞作動フラグデータを「処理対象フラグデータ」と称し、当り要求フラグテーブル又は後述の図柄対応入賞作動テーブル(不図示)を「処理対象フラグテーブル」と称す。 Therefore, in the flowchart of FIG. 66, the flag data to be processed is referred to as “processing target flag data”, and the flag table to be processed is referred to as “processing target flag table”. In addition, in accordance with this description, in the following description of the compressed data storage processing, the hit request flag data or the winning operation flag data is referred to as "processing target flag data", and the hit request flag table or the symbol corresponding winning operation table described later. (Not shown) is referred to as a "processing target flag table".
まず、メインCPU101は、格納先チェックビットをセットする(S341)。この処理では、格納先チェックビットはAレジスタ以外のレジスタに格納される。
First, the
格納先チェックビットは、処理対象フラグデータの格納先(転送先)となるブロックを指定するための1バイトのデータである。本実施形態では、当り要求フラグ格納領域及び入賞作動フラグ格納領域はともに、2つのブロック(格納領域1〜8のブロック及び格納領域9のブロック)で構成される。そして、例えば、内部当籤役「F_JAC1_1」が決定された場合には、格納先のブロック数が「2」になるので、S341の処理では、格納先チェックビットとして、「00000011B」がセットされる。なお、この1バイトのデータのビット0の値(1/0)が格納領域1〜8のブロック内の格納先の有無に対応し、ビット1の値(1/0)が格納領域9のブロック内の格納先の有無に対応する。
The storage destination check bit is 1-byte data for designating a block as a storage destination (transfer destination) of the processing target flag data. In this embodiment, both the hit request flag storage area and the winning operation flag storage area are composed of two blocks (a
次いで、メインCPU101は、バイト単位の転送カウンタの値を「8」にセットする(S342)。本実施形態では、少なくとも1つのブロックのバイト数が「8」であるので、転送カウンタの初期値には「8」がセットされる。
Next, the
次いで、格納先チェックビットから転送指示ビットの値を抽出する(S343)。なお、転送指示ビットは、格納先チェックビット内のビット0のデータに対応し、S343の処理では、1バイトのレジスタに格納されている格納先チェックビットを1回(1ビット分)右シフトすることにより、転送指示ビットが抽出される。具体的には、格納先チェックビットが格納された1バイトのレジスタ(Aレジスタ以外のレジスタ)を1回右シフトすると、ビット7〜ビット1に格納されているデータがそれぞれビット6〜ビット0に移動するとともに、シフト前のビット0のデータが出力される。そして、このシフト処理により出力されたデータが転送指示ビットの値となる。
Next, the value of the transfer instruction bit is extracted from the storage destination check bit (S343). Note that the transfer instruction bit corresponds to the data of
次いで、メインCPU101は、抽出された転送指示ビットの値に基づいて、転送指示があるか否かを判別する(S344)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、抽出された転送指示ビットの値が「1」である場合に転送指示があると判定する。例えば、格納先チェックビットとして、「00000011B」がセットされた場合、1回目(格納領域の1ブロック目に対応)及び2回目(格納領域の2ブロック目に対応)のS344の判定処理で、転送指示ありの判定となる。
Next, the
S344において、メインCPU101が、転送指示がないと判別したとき(S344がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS354の処理を行う。
In S344, when the
一方、S344において、メインCPU101が、転送指示があると判別したとき(S344がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理対象フラグテーブルからバイト単位格納先指定情報を取得する(S345)。この処理では、バイト単位格納先指定情報として、処理対象フラグテーブル内の処理対象役(当籤役又は入賞役)のフラグデータが格納された領域の先頭アドレスに格納されている、転送先を示す1バイトのデータが取得される。
On the other hand, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、処理対象フラグテーブル内で参照するアドレスの更新処理(アドレスを1加算する処理)を行う(S346)。また、この処理では、メインCPU101は、処理対象フラグデータの格納(転送)先となるブロックの先頭格納領域を指定するアドレスを初期アドレスとしてセットする。例えば、1ブロック目の処理では、S346の処理において、初期アドレスとして格納領域1のアドレスがセットされ、2ブロック目の処理では、S346の処理において、初期アドレスとして格納領域9のアドレスがセットされる。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、バイト単位格納先指定情報から転送指示ビットの値を抽出する(S347)。なお、ここでいう転送指示ビットは、バイト単位格納先指定情報のビット0に対応し、S347の処理では、1バイトのレジスタに格納されているバイト単位格納先指定情報を1回右シフトすることにより、転送指示ビットの値を抽出する(ビット0のデータを出力する)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、S347の処理で抽出された転送指示ビットの値に基づいて、転送指示があるか否かを判別する(S348)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、抽出された転送指示ビットの値が「1」である場合、転送指示があると判定する。例えば、バイト単位格納先指定情報として、「00000001B」がセットされた場合、1回目(1ブロック目の格納領域1又は2ブロック目の格納領域9)のS347の処理でビット1のデータ「1」が転送指示ビットの値として出力され転送指示ありの判定となるが、2〜8回目のS347の処理では、転送指示なしの判定となる。
Next, the
S348において、メインCPU101が、転送指示がないと判別したとき(S348がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS351の処理を行う。
In S348, when the
一方、S348において、メインCPU101が、転送指示があると判別したとき(S348がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、現在セットされている処理対象フラグテーブル内のアドレスに格納されている処理対象フラグデータ(当り要求フラグデータ又は入賞作動フラグデータ)を、指定された格納領域に転送(コピー)する(S349)。
On the other hand, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、処理対象フラグテーブル内で参照するアドレスの更新処理(アドレスを1加算する処理)を行う(S350)。
Next, the
S350の処理後又はS348がNO判定の場合、メインCPU101は、処理対象フラグデータの格納先となる格納領域を指定するアドレスの更新処理(アドレスを1加算する処理)を行う(S351)。次いで、メインCPU101は、転送カウンタの値を1減算する(S352)。
After the process of S350 or when the determination of S348 is NO, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、転送カウンタの値が「0」であるか否かを判別する(S353)。S353において、メインCPU101が、転送カウンタの値が「0」でないと判別したとき(S353がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS347の処理に戻し、S347以降の処理を繰り返す。
Next, the
一方、S353において、メインCPU101が、転送カウンタの値が「0」であると判別したとき(S353がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、現在の格納先チェックビットに転送指示対象が残っているか否かを判別する(S354)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、現処理時点において、格納先チェックビット内に「1」が格納されているビットが残っているか否かを判別する。そして、メインCPU101は、格納先チェックビット内に「1」が格納されているビットが残っている場合、すなわち、処理対象となるブロックが存在する場合には、現在の格納先チェックビットに転送指示対象が残っていると判定する。
On the other hand, in S353, when the
S354において、メインCPU101が、現在の格納先チェックビットに転送指示対象が残っていると判別したとき(S354がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS342の処理に戻し、S342以降の処理を繰り返す。一方、S354において、メインCPU101が、現在の格納先チェックビットに転送指示対象が残っていないと判別したとき(S354がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、圧縮データ格納処理を終了し、処理を例えば図柄設定処理(図65参照)中のS331に移す。
In S354, when the
[引込優先順位格納処理]
次に、図67を参照して、メインフロー(図56参照)中のS212で行う引込優先順位格納処理について説明する。図67は、引込優先順位格納処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Import priority storage processing]
Next, with reference to FIG. 67, the attraction-in priority storage processing performed in S212 in the main flow (see FIG. 56) will be described. FIG. 67 is a flow chart showing the procedure of the attraction-in priority storage processing.
まず、メインCPU101は、検索リール数に「3」をセットする(S621)。次いで、メインCPU101は、引込優先順位テーブル選択処理を行う(S622)。この処理では、内部当籤役及び作動ストップボタンに基づいて、引込優先順位テーブル(不図示)が選択される。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、引込優先順位格納領域選択処理を行う(S623)。この処理では、検索対象のリールの引込優先順位データ格納領域が選択される。次いで、メインCPU101は、図柄チェック数(回数)として「20」をセットする(S624)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、図柄コード取得処理を行う(S625)。この処理では、図柄チェック数に対応した入賞作動フラグ格納領域及び図柄コード格納領域を参照して、図柄コードを取得する。なお、図柄コード取得処理の詳細については、後述の図68を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、論理積演算処理を行う(S626)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、入賞作動フラグデータの生成処理を行う。論理積演算処理の詳細については、後述の図69を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、引込優先順位取得処理を行う(S627)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、入賞作動フラグ(入賞役)格納領域(図25参照)内においてビットが「1」にセットされており、かつ、当り要求フラグ格納領域でビットが「1」にされている役について、引込優先順位テーブル(不図示)を参照して、引込優先順位データを取得する。なお、引込優先順位取得処理の詳細については、後述の図70及び図71を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、取得した引込優先順位データをメインRAM103内の引込優先順位データ格納領域(不図示)に格納する(S628)。この際、引込優先順位データは、各優先順位の値と、格納領域のビットとが対応するように引込優先順位データ格納領域に格納される。
Next, the
なお、引込優先順位データ格納領域には、メインリールの種類毎に優先順位データの格納領域が設けられる。各引込優先順位データ格納領域には、対応するメインリールの各図柄位置「0」〜「19」に応じて決定された引込優先順位データが格納される。本実施形態では、この引込優先順位データ格納領域を参照することにより、停止テーブルに基づいて決定された滑り駒数の他に、より適切な滑り駒数が存在するか否かを検索する。 The pull-in priority data storage area is provided with a storage area for priority data for each type of main reel. In each attraction priority data storage area, attraction priority data determined according to each symbol position “0” to “19” of the corresponding main reel is stored. In the present embodiment, by referring to this attraction-in priority data storage area, it is searched whether or not there is a more appropriate number of sliding pieces in addition to the number of sliding pieces determined based on the stop table.
引込優先順位データ格納領域に格納される優先順位引込データの内容は、引込優先順位データを決定する際に参照された引込優先順位テーブル内の引込優先順位テーブル番号の種類によって異なる。また、引込優先順位データは、その値が大きいほど優先順位が高いことを表す。引込優先順位データを参照することにより、メインリールの周面に配された各図柄間における優先順位の相対的な評価が可能となる。すなわち、引込優先順位データとして最も大きい値が決定されている図柄が最も優先順位の高い図柄となる。したがって、引込優先順位データは、メインリールの周面に配された各図柄間の順位を示すものともいえる。なお、引込優先順位データの値が等しい図柄が複数存在する場合には、優先順序テーブルが規定する優先順序に従って1つの図柄が決定される。 The contents of the priority attraction-in data stored in the attraction-in priority data storage area differ depending on the type of attraction-in priority table number in the attraction-in priority table referred to when determining the attraction-in priority data. The larger the value of the attraction-in priority data, the higher the priority. By referring to the attraction-in priority data, it is possible to make a relative evaluation of the priority among the symbols arranged on the peripheral surface of the main reel. That is, the symbol for which the largest value is determined as the attraction-in priority data is the symbol with the highest priority. Therefore, it can be said that the attraction-in priority data indicates the order between the symbols arranged on the peripheral surface of the main reel. If there are a plurality of symbols having the same value of the attraction-in priority data, one symbol is determined according to the priority order defined by the priority order table.
次いで、メインCPU101は、引込優先順位格納領域の更新処理を行う(S629)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、次のチェック図柄の引込優先順位データ格納領域をセットする。次いで、メインCPU101は、図柄チェック数を1減算する(S630)。次いで、メインCPU101は、図柄チェック数が「0」であるか否かを判別する(S631)。
Next, the
S631において、メインCPU101が、図柄チェック数が「0」でないと判別したとき(S631がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS625の処理に戻し、S625以降の処理を繰り返す。一方、S631において、メインCPU101が、図柄チェック数が「0」であると判別したとき(S631がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、検索対象リールの変更処理を行う(S632)。
In S631, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、検索リール数を1減算する(S633)。次いで、メインCPU101は、検索リール数が「0」であるか否か、すなわち、全てのメインリールに対して上述した一連の処理が行われたか否かを判別する(S634)。
Next, the
S634において、メインCPU101が、検索リール数が「0」でないと判別したとき(S634がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS622の処理に戻し、S622以降の処理を繰り返す。一方、S634において、メインCPU101が、検索リール数が「0」であると判別したとき(S634がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、引込優先順位格納処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)のS213に移す。
In S634, when the
[図柄コード取得処理]
次に、図68を参照して、引込優先順位格納処理(図67参照)中のS625で行う図柄コード取得処理について説明する。図68は、図柄コード取得処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Design code acquisition process]
Next, with reference to FIG. 68, the symbol code acquisition processing performed in S625 during the attraction-in priority storage processing (see FIG. 67) will be described. FIG. 68 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the symbol code acquisition process.
まず、メインCPU101は、入賞作動フラグ格納領域のクリア処理を行う(S641)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、入賞作動フラグ格納領域(図25参照)内の全ての格納領域に「0」をセットする。次いで、メインCPU101は、第1リール図柄配置テーブル(不図示)をセットする(S642)。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、第1リール(左リール3L)の停止時であるか否かを判別する(S643)。
Next, the
S643において、メインCPU101が、第1リール(左リール3L)の停止時であると判別したとき(S643がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS647の処理を行う。一方、S643において、メインCPU101が、第1リール(左リール3L)の停止時でないと判別したとき(S643がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、第2リール図柄配置テーブル(不図示)をセットする(S644)。この処理では、S642の処理でセットされた第1リール図柄配置テーブルが、第2リール図柄配置テーブルで上書きされる。
In S643, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、第2リール(中リール3C)の停止時であるか否かを判別する(S645)。
Next, the
S645において、メインCPU101が、第2リール(中リール3C)の停止時であると判別したとき(S645がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS647の処理を行う。一方、S645において、メインCPU101が、第2リール(中リール3C)の停止時でないと判別したとき(S645がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、第3リール図柄配置テーブル(不図示)をセットする(S646)。この処理では、S644の処理でセットされた第2リール図柄配置テーブルが、第3リール図柄配置テーブルで上書きされる。
In S645, when the
S646の処理後、又は、S643或いはS645がYES判定の場合、メインCPU101は、停止制御対象のリールに対する停止操作実行時の図柄チェック処理を行い、図柄チェック処理により取得された図柄に対応する図柄対応入賞作動テーブル(不図示)を取得する(S647)。図柄対応入賞作動テーブルは、停止制御対象のリールにおいて、対応する図柄が有効ライン上に停止したならば入賞となり得る入賞役(図柄組合せ)の種別を識別可能とするためのテーブルである。
After the processing of S646, or when YES is determined in S643 or S645, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、入賞作動フラグ格納領域をセットする(S648)。次いで、メインCPU101は、図66で説明した圧縮データ格納処理を行う(S649)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、主に、図柄対応入賞作動テーブルに格納された入賞可能な入賞作動フラグデータを、入賞作動フラグ格納領域内の対応する格納領域に転送(展開)する処理を行う。
Next, the
例えば、第1リール(左リール3L)停止時であり、停止操作時に有効ライン上に位置する図柄が「ブランク」である場合には、入賞可能な図柄組合せ(コンビネーション)は、図19〜図22に示すように、「S_XDリプ」、「S_バーリプ2」、「S_RT1移行リプ」、及び「S_特殊役1」である。
For example, when the first reel (the
S649の処理後、メインCPU101は、圧縮データ格納処理により更新された入賞作動フラグ格納領域をセットし、図柄コード格納領域をセットし、入賞作動フラグ格納領域のデータ長(本実施形態では9バイト)をセットする(S650)。そして、S650の処理後、メインCPU101は、図柄コード取得処理を終了し、処理を引込優先順位格納処理(図67参照)のS626に移す。
After the processing of S649, the
[論理積演算処理]
次に、図69を参照して、例えば、引込優先順位格納処理(図67参照)中のS626で行う論理積演算処理について説明する。図69は、論理積演算処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。なお、図69に示す論理積演算処理は、引込優先順位格納処理(図67参照)中のS626だけでなく、後述の引込優先順位取得処理(後述の図70及び図71参照)中のS686においても実行される。
[AND operation processing]
Next, with reference to FIG. 69, for example, the AND operation process performed in S626 during the pull-in priority storage process (see FIG. 67) will be described. FIG. 69 is a flow chart showing the procedure of the AND operation processing. Note that the logical product arithmetic processing shown in FIG. 69 is performed not only in S626 in the attraction priority order storage processing (see FIG. 67) but also in S686 in the attraction priority order acquisition processing (see FIGS. 70 and 71 below). Is also executed.
引込優先順位格納処理(図67参照)中のS626で実行される論理積演算処理において、論理積演算される2つのデータは、上述した図柄コード取得処理中のS650でセットされた入賞作動フラグ格納領域のデータ、及び、図柄コード格納領域のデータである。そして、前者のデータが後述の「論理積先データ」に対応し、後者のデータが後述の「論理積元データ」に対応する。また、この場合、上述した図柄コード取得処理中のS650でセットされたデータ長(9バイト)のバイト数「9」が後述の「論理積回数」に対応する。 In the logical product calculation process executed in S626 of the attraction-in priority storage process (see FIG. 67), the two data items that are logical product calculated are the winning operation flag storage set in S650 in the above-mentioned symbol code acquisition process. It is the data of the area and the data of the symbol code storage area. The former data corresponds to "logical product destination data" described later, and the latter data corresponds to "logical product source data" described later. Further, in this case, the number of bytes "9" of the data length (9 bytes) set in S650 during the above-described symbol code acquisition processing corresponds to the "number of logical product" described later.
一方、後述の引込優先順位取得処理(後述の図70及び図71参照)中のS686で実行される論理積演算処理において、論理積演算される2つのデータは、当り(引込)要求フラグ格納領域のデータ、及び、入賞作動フラグ格納領域のデータである。そして、前者のデータが後述の「論理積先データ」に対応し、後者のデータが後述の「論理積元データ」に対応する。また、この場合、後述のRT作動組み合わせ表示フラグのデータ長(1バイト)のバイト数「1」が後述の「論理積回数」に対応する。 On the other hand, in the AND operation processing executed in S686 of the attraction priority acquisition processing (see FIGS. 70 and 71 to be described later) described later, the two pieces of data to be ANDed are the hit (attraction) request flag storage area. And the data of the winning operation flag storage area. The former data corresponds to "logical product destination data" described later, and the latter data corresponds to "logical product source data" described later. Further, in this case, the number of bytes “1” of the data length (1 byte) of the RT operation combination display flag described later corresponds to the “number of logical product” described later.
まず、メインCPU101は、論理積元データ(例えば、図柄コード格納領域のデータ)を取得する(S661)。次いで、メインCPU101は、論理積元データと論理積先データ(例えば、入賞作動フラグ格納領域のデータ)との論理積演算を行い、その演算結果を論理積先データとして保存する(S662)。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、取得する論理積元データのアドレスを1加算する(S663)。次いで、メインCPU101は、参照する論理積先データのアドレスを1加算する(S664)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、論理積回数を1減算する(S665)。次いで、メインCPU101は、論理積回数が「0」であるか否かを判別する(S666)。
Next, the
S666において、メインCPU101が、論理積回数が「0」でないと判別したとき(S666がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS661の処理に戻し、S661以降の処理を繰り返す。一方、S666において、メインCPU101が、論理積回数が「0」であると判別したとき(S666がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、論理積演算処理を終了し、処理を例えば引込優先順位格納処理(図67参照)のS627に移す。
In S666, when the
[引込優先順位取得処理]
次に、図70及び図71を参照して、引込優先順位格納処理(図67参照)中のS627で行う引込優先順位取得処理について説明する。なお、図70及び図71は、引込優先順位取得処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Acquisition priority acquisition processing]
Next, with reference to FIGS. 70 and 71, the attraction-in priority order acquisition processing performed in S627 in the attraction-in priority order storage processing (see FIG. 67) will be described. 70 and 71 are flowcharts showing the procedure of the attraction-in priority order acquisition process.
まず、メインCPU101は、右リール3R(特定の表示列)のチェック時であるか否かを判別する(S671)。
First, the
S671において、メインCPU101が、右リール3Rのチェック時でないと判別したとき(S671がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS674の処理を行う。一方、S671において、メインCPU101が、右リール3Rのチェック時であると判別したとき(S671がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、内部当籤役に係る図柄組合せ(入賞役)に「ANY役」(所定の図柄の組合せ)が含まれるか否かを判別する(S672)。なお、ここでいう「ANY役」とは、少なくとも右リール3Rの停止図柄に関係なく入賞が確定する役(少なくとも右リール3Rの停止図柄が任意の図柄である入賞役)のことをいう。もっとも、本実施形態では、「ANY役」は規定されていない。
When the
S672において、メインCPU101が、内部当籤役に係る図柄組合せに「ANY役」が含まれないと判別したとき(S672がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS674の処理を行う。一方、S672において、メインCPU101が、内部当籤役に係る図柄組合せに「ANY役」が含まれると判別したとき(S672がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、入賞作動フラグ格納領域内の「ANY役」に対応する格納領域をマスクする(S673)。具体的には、メインCPU101は、入賞作動フラグ格納領域内の「ANY役」に対応するビットに「1」をセットする。なお、内部当籤役に係る図柄組合せ(入賞役)に「ANY役」を規定しない場合には、S671〜S673の処理を不要としてもよい。また、「ANY役」が、左リール3L又は中リール3Cの停止図柄を任意の図柄として規定する場合には、左リール3L又は中リール3Cのチェック時である場合にもS672及びS673の処理を行うようにすればよい(後述のS681〜S683の処理も同様)。
In S672, when the
S673の処理後、又は、S671或いはS672がNO判定の場合、メインCPU101は、入賞作動フラグ格納領域(図25参照)のアドレスとして、その最後尾の格納領域のアドレスに「1」を加算したアドレスをセットし、停止禁止データをセットし、入賞作動フラグデータ長(入賞作動フラグ格納領域のデータ長:本実施形態では、9バイト)をセットする(S674)。次いで、メインCPU101は、ストックボタン作動カウンタの値、及び、ストップボタン作動状態を取得する(S675)。なお、ストップボタン作動カウンタは、停止操作が検出されているストップボタンの数を管理するためのカウンタである。また、ストップボタン作動状態は、作動ストップボタン格納領域(図28参照)を参照することにより取得される。
After the processing of S673, or when the determination of S671 or S672 is NO, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、セットされている入賞作動フラグ格納領域のアドレスを1減算(−1更新)する(S676)。次いで、メインCPU101は、セットされている入賞作動フラグ格納領域とそれに対応する当り要求フラグ格納領域(図25参照)とから当り要求フラグデータを生成し、該生成された当り要求フラグデータに基づいて禁止入賞作動位置を生成する(S677)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、停止操作位置が禁止入賞作動位置であるか否かを判別する(S678)。
Next, the
S678において、メインCPU101が、停止操作位置が禁止入賞作動位置でないと判別したとき(S678がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS684の処理を行う。一方、S678において、メインCPU101が、停止操作位置が禁止入賞作動位置であると判別したとき(S678がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、ストップボタン作動カウンタの値が第3停止の値であるか否かを判別する(S679)。
In S678, when the
S679において、メインCPU101が、ストップボタン作動カウンタの値が第3停止の値であると判別したとき(S679がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS705の処理を行う。一方、S679において、メインCPU101が、ストップボタン作動カウンタの値が第3停止の値でないと判別したとき(S679がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、ストップボタン作動カウンタの値が第2停止の値であるか否かを判別する(S680)。
In S679, when the
S680において、メインCPU101が、ストップボタン作動カウンタの値が第2停止の値でないと判別したとき(S680がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS684の処理を行う。一方、S680において、メインCPU101が、ストップボタン作動カウンタの値が第2停止の値であると判別したとき(S680がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、右リール3Rの停止後であるか否かを判別する(S681)。
When the
S681において、メインCPU101が、右リール3Rの停止後であると判別したとき(S681がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS684の処理を行う。一方、S681において、メインCPU101が、右リール3Rの停止後でないと判別したとき(S681がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、当り要求フラグが「ANY役」の干渉を受ける可能性があるフラグでないか否か(内部当籤役に係る図柄組合せ(入賞役)に「ANY役」が含まれないか否か)を判別する(S682)。
When the
S682において、メインCPU101が、当り要求フラグが「ANY役」の干渉を受ける可能性があるフラグでないと判別したとき(S682がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS684の処理を行う。一方、S682において、メインCPU101が、当り要求フラグが「ANY役」の干渉を受ける可能性があるフラグであると判別したとき(S682がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、現チェックが「ANY役」を含む当り要求フラグのチェック時であるか否かを判別する(S683)。
In S682, when the
S683において、メインCPU101が、現チェックが「ANY役」を含む当り要求フラグのチェック時であると判別したとき(S683がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS705の処理を行う。
In S683, when the
一方、S683において、メインCPU101が、現チェックが「ANY役」を含む当り要求フラグのチェック時でないと判別したとき(S683がNO判定の場合)、S678或いはS680がNO判定の場合、又は、S681或いはS682がYES判定の場合、メインCPU101は、入賞作動フラグデータ長を1減算する(S684)。次いで、メインCPU101は、入賞作動フラグデータ長が「0」であるか否かを判別する(S685)。
On the other hand, in S683, when the
S685において、メインCPU101が、入賞作動フラグデータ長が「0」でないと判別したとき(S685がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS676の処理に戻し、S676以降の処理を繰り返す。
In S685, when the
一方、S685において、メインCPU101が、入賞作動フラグデータ長が「0」であると判別したとき(S685がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、停止制御用引込要求フラグ設定処理を行う(S686)。この処理では、例えば、メインCPU101は、図69で説明した論理積演算処理を行う。なお、S686の処理内で実行される論理積演算処理では、上述のように、当り(引込)要求フラグ格納領域のデータが「論理積先データ」にセットされ、入賞作動フラグ格納領域のデータが「論理積元データ」にセットされ、「論理積回数」には、RT作動組み合わせ表示フラグのデータ長(1バイト)のバイト数「1」がセットされる。RT作動組み合わせ表示フラグは、入賞作動フラグ格納領域において、RT移行に係る図柄組合せが規定された格納領域のことであり、本実施形態では、図25に示すように格納領域1のみとなる。
On the other hand, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、引込優先順位テーブルアドレス格納領域を参照して、引込優先順位テーブルを取得する(S687)。この処理では、現在セットされているアドレスに、引込優先順位データの初期値「1(001H)」が設定されるとともに、いずれかの引込優先順位テーブルが取得される。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、現在セットされているアドレスに格納されている引込優先順位テーブルのデータが、エンドコード(000H)であるか否かを判別する(S688)。
Next, the
S688において、メインCPU101が、現在セットされているアドレスに格納されている引込優先順位テーブルのデータが、エンドコードであると判別したとき(S688がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS705の処理を行う。一方、S688において、メインCPU101が、現在セットされているアドレスに格納されている引込優先順位テーブルのデータが、エンドコードでないと判別したとき(S688がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、入賞作動フラグ格納領域をセットする(S689)。
In S688, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、現在セットされているアドレスに格納されている引込優先順位テーブルに基づいて、引込優先順位データを取得する(S690)。次いで、メインCPU101は、引込優先順位テーブルのブロックカウンタをセットする(S691)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、引込優先順位テーブルのチェック回数をセットし、参照する引込優先順位テーブルのアドレスを1加算(+1更新)する(S692)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、更新された引込優先順位テーブルのアドレスに基づいて、チェックデータを取得し、チェックデータからチェックビットを抽出する(S693)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、抽出されたチェックビットの値が「1」であるか否かを判別する(S694)。
Next, the
S694において、メインCPU101が、抽出されたチェックビットの値が「1」でないと判別したとき(S694がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS699の処理を行う。一方、S694において、メインCPU101が、抽出されたチェックビットの値が「1」であると判別したとき(S694がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、参照する引込優先順位テーブルのアドレスを1加算(+1更新)し、更新後のアドレスに基づいて、引込優先順位テーブルから判定データを取得する(S695)。
When the
次いで、メインCPU101は、S695で取得した判定データに基づいて、現在取得されている入賞作動フラグデータが判定対象であるか否かを判別する(S696)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、現在取得されている入賞作動フラグデータと、判定データとを比較し、前者が後者に対応するものである否かを判定し、前者が後者に対応するものである場合には、現在取得されている入賞作動フラグデータが判定対象であると判定する。
Next, the
S696において、メインCPU101が、入賞作動フラグデータが判定対象でないと判別したとき(S696がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS699の処理を行う。一方、S696において、メインCPU101が、入賞作動フラグデータが判定対象であると判別したとき(S696がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、引込優先順位データの更新処理を行う(S697)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、S697で取得した判定データに対応付けられた引込優先順位データで、現在セットされている引込優先順位データを更新(上書き)する。
In S696, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、チェックデータの更新処理を行う(S698)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、チェックデータを1ビットだけ右方向(ビット7からビット0に向かう方向)にシフトする。なお、この処理において、シフト後のチェックデータのビット7には、「0」がセットされる。
Next, the
S698の処理後、又は、S694或いはS696がNO判定の場合、メインCPU101は、チェックデータにチェック対象のビット(「1」がセットされているビット)があるか否かを判別する(S699)。
After the processing of S698, or when S694 or S696 makes a NO determination, the
S699において、メインCPU101が、チェックデータにチェック対象のビットがないと判別したとき(S699がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS702の処理を行う。一方、S699において、メインCPU101が、チェックデータにチェック対象のビットがあると判別したとき(S699がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、チェックする入賞作動フラグ格納領域のアドレスを1加算(+1更新)し、チェック回数を1減算する(S700)。
When the
次いで、メインCPU101は、チェック回数が「0」であるか否かを判別する(S701)。S701において、メインCPU101が、チェック回数が「0」でないと判別したとき(S701がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS698の処理に戻し、S698以降の処理を繰り返す。
Next, the
一方、S701において、メインCPU101が、チェック回数が「0」であると判別したとき(S701がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、現在参照している入賞作動フラグ格納領域のアドレスにチェック回数を加算して入賞作動フラグ格納領域のアドレスを更新し、ブロックカウンタの値を1減算する(S702)。次いで、メインCPU101は、ブロックカウンタの値が「0」であるか否かを判別する(S703)。
On the other hand, when the
S703において、メインCPU101が、ブロックカウンタの値が「0」でないと判別したとき(S703がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS692の処理に戻し、S692以降の処理を繰り返す。
In S703, when the
一方、S703において、メインCPU101が、ブロックカウンタの値が「0」であると判別したとき(S703がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、参照する引込優先順位テーブルのアドレスを1加算(+1更新)する(S704)。そして、S704の処理後、メインCPU101は、処理をS688の処理に戻し、S688以降の処理を繰り返す。
On the other hand, in S703, when the
ここで再度、S679、S683又はS688の処理に戻って、S679、S683又はS688がYES判定の場合、メインCPU101は、この時点でセットされている引込順位データを、最終的な引込優先順位データとしてセットする(S705)。なお、S679又はS683がYES判定の場合、メインCPU101は、最終的な引込優先順位データとして「0(00H)」をセットする。この場合、引込優先順位データ「0(00H)」にはエンドコードが割り付けられているので、引込データ無し(停止禁止)がセットされる。そして、S705の処理後、メインCPU101は、引込優先順位取得処理を終了し、処理を引込優先順位格納処理(図67参照)のS628に移す。
Here, again returning to the processing of S679, S683 or S688, when S679, S683 or S688 is YES, the
[リール停止制御処理]
次に、図72を参照して、メインフロー(図56参照)中のS213で行うリール停止制御処理について説明する。なお、図72は、リール停止制御処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Reel stop control processing]
Next, with reference to FIG. 72, the reel stop control process performed in S213 in the main flow (see FIG. 56) will be described. Note that FIG. 72 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the reel stop control processing.
まず、メインCPU101は、リール停止可能信号OFF処理を行う(S711)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、主に、リール停止可能信号OFFデータのポート出力処理を行う。また、この処理は、メインRAM103の規定外作業領域を使用して行われる。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、全リールの回転速度が所定の一定速度に到達したか否か(「定速」になったか否か)を判別する(S712)。S712において、メインCPU101が、全リールの回転速度が「定速」になっていないと判別したとき(S712がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、S712の処理を繰り返す。
Next, the
一方、S712において、メインCPU101が、全リールの回転速度が「定速」になったと判別したとき(S712がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、リール停止可能信号ON処理を行う(S713)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、主に、リール停止可能信号ONデータのポート出力処理を行う。また、この処理は、メインRAM103の規定外作業領域を使用して行われる。
On the other hand, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、有効なストップボタンが押されたか否かを判別する(S714)。
Next, the
S714において、メインCPU101が、有効なストップボタンが押されていないと判別したとき(S714がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS713の処理に戻し、S713以降の処理を繰り返す。一方、S714において、メインCPU101が、有効なストップボタンが押されたと判別したとき(S714がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、作動ストップボタン格納領域(図28参照)を更新し、ストップボタン未作動カウンタの値を1減算する(S715)。
In S714, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、作動ストップボタンから検索対象リールを決定する(S716)。また、この処理では、検索対象リールのリール制御管理情報が格納される回胴制御データ格納領域のアドレス(先頭アドレス)セット処理も行われる。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、リール停止可能信号OFF処理を行う(S717)。この処理は、上記S711と同様に、メインRAM103の規定外作業領域を使用して行われる。次いで、メインCPU101は、図柄カウンタの値に基づいて停止開始位置をメインRAM103に格納する(S718)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、リール停止選択処理を行う(S719)。詳細な説明は省略するが、この処理では、メインCPU101は、滑り駒数の選択処理を行う。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、停止開始位置と、S719で決定された滑り駒数とに基づいて停止予定位置を決定し、該決定した停止予定位置をメインRAM103に格納する(S720)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、停止開始位置に滑り駒数を加算し、その加算結果を停止予定位置とする。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、図柄コード格納処理を実行する(S721)。この処理では、停止予定位置に対応する図柄コードが図柄コード格納領域に格納される。次いで、メインCPU101は、制御対象のリールが最終停止(第3停止)のリールであるか否かを判別する(S722)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、ストップボタン未作動カウンタの値に基づいて、制御対象のリールが最終停止(第3停止)のリールであるか否かを判別し、ストップボタン未作動カウンタの値が「0」であるときには、制御対象のリールが最終停止のリールであると判定する。
Next, the
S722において、メインCPU101が、制御対象のリールが最終停止のリールでないと判別したとき(S722がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、制御変更処理を行う(S723)。この処理では、特定の停止位置にあった場合に、リールの停止に用いる停止情報群が更新される。次いで、メインCPU101は、図67で説明した引込優先順位格納処理を行う(S724)。
In S<b>722, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、停止間隔残時間待機処理を行う(S725)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、予め設定された所定のリール停止間隔時間が経過するまで、待機処理を行う。そして、S725の処理後、メインCPU101は、処理をS711の処理に戻し、S711以降の処理を繰り返す。
Next, the
ここで再度、S722の処理に戻って、S722において、メインCPU101が、制御対象のリールが最終停止のリールであると判別したとき(S722がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、全リールの励磁が停止状態であるか否かを判別する(S726)。S726において、メインCPU101が、全リールの励磁が停止状態でないと判別したとき(S726がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、S726の処理を繰り返す。
Here, returning again to the processing of S722, when the
一方、S726において、メインCPU101が、全リールの励磁が停止状態であると判別したとき(S726がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、第3停止操作されたストップボタンがオン状態のままである(ストップボタンが放されていない)か否かを判別する(S727)。S727において、メインCPU101が、第3停止操作されたストップボタンがオン状態のままであると判別したとき(S727がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、S727の処理を繰り返す。一方、S727において、メインCPU101が、第3停止操作されたストップボタンがオン状態のままでないと判別したとき(S727がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、リール停止制御処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)のS214に移す。
On the other hand, in S726, when the
[入賞検索処理]
次に、図73を参照して、メインフロー(図56参照)中のS214で行う入賞検索処理について説明する。なお、図73は、入賞検索処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Prize search processing]
Next, with reference to FIG. 73, the winning combination search process performed in S214 in the main flow (see FIG. 56) will be described. It should be noted that FIG. 73 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the prize winning search process.
まず、メインCPU101は、図柄コード格納領域(図30参照)に格納された各格納領域のデータを、入賞作動フラグ格納領域(図25参照)の対応する格納領域に転送して保存する(S761)。そして、この処理終了時点では、DEレジスタに入賞作動フラグ格納領域の最後尾のアドレスがセットされる。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、入賞役(図柄組合せ)の払出枚数(図19〜図22参照)を規定する払出枚数データテーブル(不図示)のアドレスをHLレジスタにセットする(S762)。次いで、メインCPU101は、払出枚数テーブル数(例えば、本実施形態では「4」)を入賞検索カウンタの初期値とし、該初期値をBレジスタにセットする(S763)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、HLレジスタにセットされたアドレスに基づいて、メダルの払出枚数(本実施形態では、1枚、2枚、5枚及び8枚のいずれか)のデータをCレジスタにセットし、判定対象データをAレジスタにセットし、HLレジスタにセットされているアドレスに「2」を加算(+2更新)する(S764)。なお、払出枚数データテーブルにおいて、メダルの払出枚数のデータは、例えば「払出枚数(1,2,5又は8)*2+0」と規定される。また、以下では、Cレジスタにセットされたメダルの払出枚数のデータ「払出枚数(1,2,5又は8)*2+0」内のデータ「0」を「判定ビット」という。この判定ビットは入賞検索の判定対象ブロックであるか否かを示す情報である。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、Cレジスタにセットされたメダルの払出枚数のデータから判定ビットの値を抽出する(S765)。次いで、メインCPU101は、抽出した判定ビットの値に基づいて、判定対象ブロックであるか否かを判別する(S766)。この処理において、メインCPU101は、抽出した判定ビットの値が「1」である場合に、判定対象ブロックであると判定する。なお、本実施形態では、メダルの払出枚数にかかわらず、判定ビットの値は常に「0」が規定されるようにしているため、S766の処理は必ずNO判定となる。
Next, the
S766において、メインCPU101が、判定対象ブロックでないと判別したとき(S766がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS768の処理を行う。一方、S766において、メインCPU101が、判定対象ブロックであると判別したとき(S766がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、DEレジスタにセットされている入賞作動フラグ格納領域のアドレスを1減算(−1更新)する(S767)。
In S766, when the
S767の処理後又はS766がNO判定の場合、メインCPU101は、DEレジスタにセットされた入賞作動フラグ格納領域のアドレスで指定される格納領域のデータを判定データとして抽出する(S768)。
After the processing of S767 or when the determination of S766 is NO, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、S764でAレジスタにセットされた判定対象データと、S768で抽出した判定データとに基づいて、判定の結果が入賞であるか否かを判別する(S769)。この処理において、メインCPU101は、S764でAレジスタにセットされた判定対象データが、S768で抽出した判定データと同じであれば、判定の結果が入賞であると判定する。
Next, the
S769において、メインCPU101が、判定の結果が入賞でないと判別したとき(S769がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS776の処理を行う。一方、S769において、メインCPU101が、判定の結果が入賞であると判別したとき(S769がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、現遊技が3枚遊技(メダルのベット枚数が3枚である遊技)であるか否かを判別する(S770)。
In S769, when the
S770において、メインCPU101が、現遊技が3枚遊技であると判別したとき(S770がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS772の処理を行う。一方、S770において、メインCPU101が、現遊技が3枚遊技でないと判別したとき(S770がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、2枚遊技(メダルのベット枚数が2枚である遊技)の払出枚数をCレジスタにセットする(S771)。なお、本実施形態では、2枚遊技がないため、S770及びS771の処理は不要となる。
In S770, when the
S771の処理後又はS770がYES判定の場合、メインCPU101は、払出枚数の更新処理を行う(S772)。具体的には、メインCPU101は、現在の入賞枚数カウンタの値に、Cレジスタにセットされたメダルの払出枚数を加算し、加算後の値を払出枚数にセットする。
After the processing of S771 or in the case of YES determination in S770, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、払出枚数の値が最大払出枚数「15」未満であるか否かを判別する(S773)。
Next, the
S773において、メインCPU101が、払出枚数の値が最大払出枚数「15」未満であると判別したとき(S773がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS775の処理を行う。一方、S773において、メインCPU101が、払出枚数の値が最大払出枚数「15」未満でないと判別したとき(S773がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、払出枚数に最大払出枚数「15」をセットする(S774)。
When the
S774の処理後又はS773がYES判定の場合、メインCPU101は、払出枚数を入賞枚数カウンタに保存する(S775)。
After the processing of S774 or when the determination in S773 is YES, the
S775の処理後又はS769がNO判定の場合、メインCPU101は、他の入賞があるか否かを判別する(S776)。S776において、メインCPU101が、他の入賞があると判別したとき(S776がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS769の処理に戻し、S769以降の処理を繰り返す。
After the processing of S775 or if NO in S769, the
一方、S776において、メインCPU101が、他の入賞がないと判別したとき(S776がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、入賞検索カウンタの値を1減算(−1更新)する(S777)。なお、例えば、有効ラインが1本である場合には、複数の小役が重複して入賞することがないので、S776の判定処理は必ずNO判定となる。
On the other hand, in S776, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、入賞検索カウンタの値が「0」であるか否かを判別する(S778)。
Next, the
S778において、メインCPU101が、入賞検索カウンタの値が「0」でないと判別したとき(S778がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS764の処理に戻し、S764以降の処理を繰り返す。一方、S778において、メインCPU101が、入賞検索カウンタの値が「0」であると判別したとき(S778がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、入賞検索処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)中のS215の処理に移す。
In S778, when the
[イリーガルヒットチェック処理]
次に、図74を参照して、メインフロー(図56参照)中のS215で行うイリーガルヒットチェック処理について説明する。なお、図74は、イリーガルヒットチェック処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。なお、イリーガルヒットとは、内部抽籤処理(図64参照)で抽籤され、図柄設定処理(図65参照)で当籤番号格納領域に格納された特賞当籤番号及び小役当籤番号(内部当籤役)に基づいて、左リール3L、中リール3C及び右リール3Rが、成立しえない図柄の組合せで有効ライン上に停止(図柄組合せ不成立)したことを示す用語である。
[Illegal hit check processing]
Next, with reference to FIG. 74, the illegal hit check processing performed in S215 in the main flow (see FIG. 56) will be described. Note that FIG. 74 is a flowchart showing the procedure of illegal hit check processing. It should be noted that the illegal hit is the special lottery number and the small winning combination number (internal winning combination) that is randomly selected in the internal lottery process (see FIG. 64) and is stored in the winning number storage area in the symbol setting process (see FIG. 65). Based on this, the
まず、メインCPU101は、入賞作動フラグ格納領域(図25参照)のアドレスをセットする(S781)。次いで、メインCPU101は、入賞作動フラグ格納領域のサイズ(バイト数、本実施形態では「9」)を、チェックカウンタの値にセットする(S782)。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、現在セットされている入賞作動フラグ格納領域のアドレスに基づいて、該アドレスに対応する当り要求フラグ格納領域(内部当籤役格納領域)内の格納領域に格納された内部当籤役のデータ(当り要求フラグデータ)を取得する(S783)。次いで、メインCPU101は、現在セットされている入賞作動フラグ格納領域のアドレスに格納された入賞役のデータ(入賞作動フラグデータ)と、内部当籤役のデータ(当り要求フラグデータ)とを合成する(S784)。
Next, the
なお、この合成処理では、まず、メインCPU101は、入賞役のデータ(入賞作動フラグデータ)と内部当籤役のデータ(当り要求フラグデータ)との排他的論理和を求める。次いで、メインCPU101は、求められた排他的論理和の算出結果と入賞役のデータ(入賞作動フラグデータ)との論理積を求め、論理積の算出結果を合成結果とする。なお、イリーガルヒットエラーが発生していない場合、この合成結果の値は「0」となる。
In this synthesizing process, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、S784の合成処理の結果に基づいて、イリーガルヒットエラーが発生しているか否かを判別する(S785)。
Next, the
S785において、メインCPU101が、イリーガルヒットエラーが発生していないと判別したとき(S785がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、参照する入賞作動フラグ格納領域のアドレスを+1更新する(S786)。次いで、メインCPU101は、チェックカウンタの値を1減算する(S787)。次いで、メインCPU101は、チェックカウンタの値が「0」であるか否かを判別する(S788)。
When the
S788において、メインCPU101が、チェックカウンタの値が「0」でないと判別したとき(S788がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS783の処理に戻し、S783以降の処理を繰り返す。一方、S788において、メインCPU101が、チェックカウンタの値が「0」であると判別したとき(S788がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、イリーガルヒットチェック処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)中のS216の処理に移す。
When the
ここで再度、S785の処理に戻って、S785において、メインCPU101が、イリーガルヒットエラーが発生していると判別したとき(S785がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、図62で説明したエラー処理を行う(S789)。この処理により、情報表示器6に含まれる2桁の7セグLED(払出枚数表示用及びエラー表示用兼用)に、イリーガルヒットエラーの発生を示す2文字「EE」をエラー情報として表示するためのエラー表示データが出力される。なお、イリーガルヒットエラーの発生状態(エラー状態)は、リセットスイッチ76(図6参照)を押下することにより解除される。
Here, returning again to the processing of S785, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、入賞枚数カウンタの値及び当り要求フラグ格納領域のデータをクリアする(S790)。そして、S790の処理後、メインCPU101は、イリーガルヒットチェック処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)中のS216の処理に移す。
Next, the
なお、本実施形態では、図25に示すように、入賞作動フラグ格納領域(表示役格納領域)の構成が当り要求フラグ格納領域(内部当籤役格納領域)のそれと同じであるので、入賞作動フラグ格納領域の役と内部当籤役との合成処理時にメインRAM103に配置される当り要求フラグ格納領域と入賞作動フラグ格納領域とを同一構成にすることができる。それゆえ、本実施形態のイリーガルヒットチェック処理におけるS784の演算結果(入賞役のデータと内部当籤役のデータとを合成結果)は、入賞役のデータと内部当籤役のデータとを単純に論理積(例えば、「AND」命令で実行する)することにより求められる。その結果、本実施形態では、イリーガルヒットチェック処理を効率化及び簡略化することができ、主制御プログラムの空き容量を確保する(増やす)ことができ、増えた空き容量を使用して遊技性を高めることが可能になる。
In the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 25, the winning operation flag storage area (display combination storing area) has the same structure as that of the hit request flag storing area (internal winning combination storing area). The winning request flag storage area and the winning operation flag storage area, which are arranged in the
[入賞チェック・メダル払出処理]
次に、図75を参照して、メインフロー(図56参照)中のS216で行う入賞チェック・メダル払出処理について説明する。なお、図75は、入賞チェック・メダル払出処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Prize check/medal payout processing]
Next, with reference to FIG. 75, the winning check/medal payout processing performed in S216 in the main flow (see FIG. 56) will be described. Note that FIG. 75 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the winning check/medal payout processing.
まず、メインCPU101は、入賞作動コマンド生成処理を行う(S801)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、副制御回路200に送信する入賞作動コマンドに含まれる、種別データおよび各種通信パラメータを生成する。なお、入賞作動コマンドは、入賞作動フラグ(表示役)等を特定するパラメータを含んで構成される。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、図50で説明した通信データ格納処理を行う(S802)。この処理により、入賞作動コマンドデータがメインRAM103に設けられた通信データ格納領域に保存される。なお、入賞作動コマンドは、後述の図80で説明する通信データ送信処理により、主制御回路90から副制御回路200に送信される。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、入賞枚数カウンタの値が「0」であるか否かを判別する(S803)。S803において、メインCPU101が、入賞枚数カウンタの値が「0」であると判別したとき(S803がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、入賞チェック・メダル払出処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)中のS217の処理に移す。
Next, the
一方、S803において、メインCPU101が、入賞枚数カウンタの値が「0」でないと判別したとき(S803がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、メダルのクレジット枚数(貯留枚数)がその上限枚数(本実施形態では50枚)以上であるか否かを判別する(S804)。
On the other hand, in S803, when the
S804において、メインCPU101が、メダルのクレジット枚数がその上限枚数以上でないと判別したとき(S804がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、クレジットカウンタの値に「1」を加算(+1更新)する(S805)。加算されたクレジットカウンタの値は、情報表示器6に含まれる貯留枚数表示用の2桁の7セグLED(不図示)により表示される。次いで、メインCPU101は、メダル払出枚数チェック処理を行う(S806)。なお、メダル払出枚数チェック処理の詳細については、後述の図76を参照しながら後で説明する。
In S804, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、メダルの払い出しが終了したか否かを判別する(S807)。S807において、メインCPU101が、メダルの払い出しが終了したと判別したとき(S807がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、入賞チェック・メダル払出処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)中のS217の処理に移す。
Next, the
一方、S807において、メインCPU101が、メダルの払い出しが終了していないと判別したとき(S807がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、払出間隔待機処理を行う(S808)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、予め設定されたメダル払出間隔時間(本実施形態では60.33msec:後述の図79で説明する割込処理(1.1172msec周期)の54周期分)が経過するまでウェイトする。そして、S808の処理後、メインCPU101は、処理をS803の処理に戻し、S803以降の処理を繰り返す。
On the other hand, when the
ここで再度、S804の処理に戻って、S804において、メインCPU101が、メダルのクレジット枚数がその上限枚数(50枚)以上であると判別したとき(S804がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、メダルの払出処理を行う(S809)。この処理により、クレジット枚数として貯留されなかった分のメダルが払い出される。なお、S809の処理においても、メダルの払い出しが終了するまで、メダルが1枚払い出される度にS806〜806の処理が繰り返されるようにすればよい。そして、S809の処理後、メインCPU101は、入賞チェック・メダル払出処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)中のS217の処理に移す。
Here, again returning to the processing of S804, when the
[メダル払出枚数チェック処理]
次に、図76を参照して、入賞チェック・メダル払出処理(図75参照)中のS806で行うメダル払出枚数チェック処理について説明する。なお、図76は、メダル払出枚数チェック処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Medal payout number check process]
Next, with reference to FIG. 76, the medal payout number check process performed in S806 of the prize check/medal payout process (see FIG. 75) will be described. Note that FIG. 76 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the medal payout number check processing.
まず、メインCPU101は、メダルOUTカウンタの値に「1」を加算(+1更新)する(S811)。なお、メダルOUTカウンタは、メダルの払出回数を計数するためのカウンタである。次いで、メインCPU101は、払出枚数カウンタの値に「1」を加算(+1更新)する(S812)。なお、払出枚数カウンタは、メダルの払出枚数を計数するためのカウンタである。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、払出枚数7SEG表示処理を行う(S813)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、払出枚数カウンタの値を、情報表示器6に含まれる払出枚数表示用の2桁の7セグLED(不図示)により表示させる制御処理を行う。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、役連終了枚数カウンタの更新処理を行う(S814)。なお、役連終了枚数カウンタは、ボーナス役が入賞する(コンビネーション「C_赤同色BB」、「C_青同色BB」、「C_赤異色BB」又は「C_青異色BB」の図柄組合せが揃う)ことで、ボーナス遊技が開始する時にボーナス遊技で払い出すことが可能な払出枚数がセットされ(後述の図77参照)、ボーナス遊技中のメダルの払出枚数の残り枚数を計数し、ボーナス遊技の終了を判断する(後述の図77のS822参照)ためのカウンタである。この処理では、メインCPU101は、役連終了枚数カウンタの値とその下限値「0」とを比較し、役連終了枚数カウンタの値が下限値「0」より大きい場合には、役連終了枚数カウンタの値を1減算(−1更新)し、役連終了枚数カウンタの値が下限値「0」以下である場合には、役連終了枚数カウンタの値を「0」に保持する。なお、役連終了枚数カウンタにセットされる払出枚数は、実際に遊技者に払い出される枚数となる訳ではない、例えば、役連終了枚数カウンタに240枚がセットされ、役連終了枚数カウンタが240となった状態で、15枚のメダルが払い出された場合、実際の払い出される払出枚数は255枚となる。役連終了枚数カウンタは240枚払い出された後「0」となり、以降、役連終了枚数カウンタの値の下限値「0」が維持される。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、入賞枚数カウンタの値を1減算(−1更新)する(S815)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、クレジット情報コマンド生成処理を行う(S816)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、副制御回路200に送信するクレジット情報コマンドに含まれる、種別データ及び各種通信パラメータを生成する。なお、クレジット情報コマンドは、メダルのクレジット枚数を特定するパラメータを含んで構成される。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、図50で説明した通信データ格納処理を行う(S817)。この処理により、クレジット情報コマンドデータがメインRAM103に設けられた通信データ格納領域に保存される。なお、クレジット情報コマンドは、後述の図80で説明する通信データ送信処理により、主制御回路90から副制御回路200に送信される。そして、S817の処理後、メインCPU101は、メダル払出枚数チェック処理を終了し、処理を入賞チェック・メダル払出処理(図75参照)中のS807の処理に移す。
Next, the
[BBチェック処理]
次に、図77を参照して、メインフロー(図56参照)中のS217で行うBBチェック処理について説明する。なお、図77は、BBチェック処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[BB check process]
Next, with reference to FIG. 77, the BB check process performed in S217 in the main flow (see FIG. 56) will be described. Note that FIG. 77 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the BB check process.
まず、メインCPU101は、現在の遊技状態がボーナス状態であるか否かを判別する(S821)。S821において、メインCPU101が、現在の遊技状態がボーナス状態でないと判別したとき(S821がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS831の処理を行う。
First, the
一方、S821において、メインCPU101が、現在の遊技状態がボーナス状態であると判別したとき(S821がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、役連終了枚数カウンタの値が「0」以下であるか否かを判別する(S822)。S822において、メインCPU101が、役連終了枚数カウンタの値が「0」以下でないと判別したとき(S822がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、BBチェック処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)中のS218の処理に移す。
On the other hand, in S821, when the
一方、S822において、メインCPU101が、役連終了枚数カウンタの値が「0」以下であると判別したとき(S822がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、ボーナス終了時処理を行う(S823)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、ボーナス状態中の各種情報をクリアする。次いで、メインCPU101は、RT4状態フラグをオン状態にセットする(S824)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、ボーナス状態終了後のRT状態をRT4状態とする。そして、S824の処理後、メインCPU101は、BBチェック処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)中のS218の処理に移す。
On the other hand, when the
ここで再度、S821の処理に戻って、S821がNO判定の場合、メインCPU101は、BB役に係る図柄組合せ(コンビネーション「C_赤同色BB」、「C_青同色BB」、「C_赤異色BB」又は「C_青異色BB」の図柄組合せ)が表示されたか否かを判別する(S825)。S825において、メインCPU101が、BB役に係る図柄組合せが表示されなかったと判別したとき(S825がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、BBチェック処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)中のS218の処理に移す。
Here, again returning to the processing of S821, when the determination of S821 is NO, the
一方、S825において、メインCPU101が、BB役に係る図柄組合せが表示されたと判別したとき(S825がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、ボーナス作動時処理を行う(S826)。この処理では、次遊技の遊技状態にボーナス状態をセットするなどのボーナスの作動開始に必要な各種処理を行う。次いで、メインCPU101は、役連終了枚数カウンタの値に所定値(ボーナス終了契機となる払出枚数:本実施形態では、BB1及びBB2において「240」、BB3及びBB4において「165」)をセットする(S827)。次いで、メインCPU101は、RT5状態フラグをオフ状態にセットする(S828)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、ボーナス状態開始前のRT状態をクリアする。そして、S828の処理後、メインCPU101は、BBチェック処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)中のS218の処理に移す。
On the other hand, in S825, when the
[RTチェック処理]
次に、図78を参照して、メインフロー(図56参照)中のS218で行うRTチェック処理について説明する。なお、図78は、RTチェック処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[RT check processing]
Next, the RT check processing performed in S218 in the main flow (see FIG. 56) will be described with reference to FIG. 78. 78. FIG. 78 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the RT check process.
まず、メインCPU101は、現在の遊技状態がボーナス状態中であるか否かを判別する(S831)。S831において、メインCPU101が、現在の遊技状態がボーナス状態中であると判別したとき(S831がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、RTチェック処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)中のS219の処理に移す。
First, the
一方、S831において、メインCPU101が、現在の遊技状態がボーナス状態中でないと判別したとき(S831がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、RT状態がRT5状態(フラグ間状態)であるか否かを判別する(S832)。S832において、メインCPU101が、RT状態がRT5状態であると判別したとき(S832がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、RTチェック処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)中のS219の処理に移す。
On the other hand, in S831, when the
一方、S832において、メインCPU101が、RT状態がRT5状態でないと判別したとき(S832がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、RT状態がRT3状態であるか否かを判別する(S833)。S833において、メインCPU101が、RT状態がRT3状態でないと判別したとき(S833がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、S837の処理に移す。
On the other hand, when the
一方、S833において、メインCPU101が、RT状態がRT3状態であると判別したとき(S833がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、RT遊技数カウンタを1減算する(S834)。すなわち、メインCPU101は、RT3状態の遊技期間を管理する。次いで、メインCPU101は、RT遊技数カウンタは0となったか否かを判別する(S835)。S835において、メインCPU101が、RT遊技数カウンタは0となっていないと判別したとき(S835がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、RTチェック処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)中のS219の処理に移す。
On the other hand, in S833, when the
一方、S835において、メインCPU101が、RT遊技数カウンタは0となったと判別したとき(S835がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、RT0状態フラグをオン状態にセットし、RT3状態フラグをオフ状態にセット(クリア)する(S836)。この処理により、RT状態がRT0状態となる。そして、S836の処理後、メインCPU101は、RTチェック処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)中のS219の処理に移す。
On the other hand, in S835, when the
S833において、メインCPU101が、RT状態がRT3状態でないと判別したとき(S833がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、RT3移行目に係る図柄の組合せ(コンビネーション「S_RT3移行目」)が表示されたか否かを判別する(S837)。S837において、メインCPU101が、RT3移行目に係る図柄の組合せが表示されたと判別したとき(S837がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、RT3状態フラグをオン状態にセットし、RT遊技数カウンタに8をセットする(S838)。なお、この場合、他のRT状態フラグはオフ状態にセットされる。この処理により、RT状態がRT3状態となる。そして、S838の処理後、メインCPU101は、RTチェック処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)中のS219の処理に移す。
In S833, when the
一方、S837において、メインCPU101が、RT3移行目に係る図柄の組合せが表示されなかったと判別したとき(S837がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、RT1移行目に係る図柄の組合せ(コンビネーション「R_RT1移行目」の図柄組合せ)が表示されたか否かを判別する(S839)。S839において、メインCPU101が、RT1移行目に係る図柄の組合せが表示されなかったと判別したとき(S839がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、RT1移行リプに係る図柄の組合せ(コンビネーション「S_RT1移行リプ」の図柄組合せ)が表示されたか否かを判別する(S840)。
On the other hand, in S837, when the
S839において、メインCPU101が、RT1移行目に係る図柄の組合せが表示されたと判別したとき(S839がYES判定の場合)、及びS840において、メインCPU101が、RT1移行リプに係る図柄の組合せが表示されたと判別したとき(S840がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、RT1状態フラグをオン状態にセットする(S841)。なお、この場合、他のRT状態フラグはオフ状態にセットされる。この処理により、RT状態がRT1状態となる。そして、S841の処理後、メインCPU101は、RTチェック処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)中のS219の処理に移す。
In S839, when the
一方、S840において、メインCPU101が、RT1移行リプに係る図柄の組合せが表示されなかったと判別したとき(S840がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、RT2移行リプに係る図柄の組合せ(コンビネーション「S_RT2移行リプ」の図柄の組合せ)が表示されたか否かを判別する(S842)。S842において、メインCPU101が、RT2移行リプに係る図柄の組合せが表示されたと判別したとき(S842がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、RT2状態フラグをオン状態にセットする(S843)。なお、この場合、他のRT状態フラグはオフ状態にセットされる。この処理により、RT状態がRT2状態となる。そして、S843の処理後、メインCPU101は、RTチェック処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56照)中のS219の処理に移す。
On the other hand, in S840, when the
一方、S842において、メインCPU101が、RT2移行リプに係る図柄の組合せが表示されなかったと判別したとき(S842がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、RT0移行リプに係る図柄の組合せ(コンビネーション「S_RT0移行リプ」の図柄の組合せ)が表示されたか否かを判別する(S844)。S844において、メインCPU101が、RT0移行リプに係る図柄の組合せが表示されたと判別したとき(S844がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、RT0状態フラグをオン状態にセットする(S845)。なお、この場合、他のRT状態フラグはオフ状態にセットされる。この処理により、RT状態がRT0状態となる。そして、S845の処理後、メインCPU101は、RTチェック処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)中のS219の処理に移す。一方、S844において、メインCPU101が、RT0移行リプに係る図柄の組合せが表示されなかったと判別したとき(S844がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、RTチェック処理を終了し、処理をメインフロー(図56参照)中のS219の処理に移す。
On the other hand, in S842, when the
[メインCPUの制御による割込処理(1.1172msec)] 次に、図79を参照して、1.1172msec周期で、メインCPU101が行う割込処理について説明する。なお、図79は、割込処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。1.1172msec周期で繰り返し実行される割込処理は、タイマー回路113(PTC)の初期化処理(図46中のS2参照)で設定されたタイマー回路113のタイムアウト信号の出力タイミングに基づいて発生する割込みコントローラ112からの割込要求信号がメインCPU101に入力された際に実行される処理である。
[Interrupt Processing Under Control of Main CPU (1.1172 msec)] Next, with reference to FIG. 79, the interrupt processing performed by the
まず、メインCPU101は、レジスタの退避処理を行う(S901)。次いで、メインCPU101は、入力ポートチェック処理を行う(S902)。この処理では、外部バスインターフェース104を介して接続されたスタートスイッチ79、ストップスイッチ等の各種スイッチや、左リール3L、中リール3C及び右リール3Rの各々に設けられたインデックスセンサ(不図示)等の各種センサから入力される信号がチェックされる。本実施形態では、キャビネット側中継基板44、ドア中継端子板68、及びリール中継端子板74等を経由し、これらの各種スイッチや各種センサが、外部バスインターフェース104を介して入力ポート用IC(不図示)の出力端子に接続された入力用のICの入力端子に接続されている。また、メインRAM103には、メインCPU101が、外部バスインターフェース104に接続された入力ポート用IC(本実施形態では、単に「入力ポート」という)の状態を格納するための入力ポート格納領域(不図示)が割り当てられている。ここで、入力ポート格納領域は、例えば、入力ポートの現在の状態を格納するための入力ポート格納領域1と、入力ポートの1割込処理前の状態を格納するための入力ポート格納領域2とで構成される。そして、メインCPU101は、この処理において、まず、入力ポート格納領域1に格納された各種情報を入力ポート格納領域2に保存し、次いで、入力ポートから読み込んだ各種情報を入力ポート格納領域1に格納する。なお、各種スイッチや各種センサの接続構成や入力ポート格納領域の構成は、上述したものに限られない。すなわち、メインCPU101側で、各種スイッチや各種センサのオン/オフ状態を認識可能な構成であればよい。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、リール制御処理を行う(S903)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、全リールの回転開始が要求されたときに、左リール3L、中リール3C及び右リール3Rの回転を開始し、その後、各リールが一定速度で回転するように、3つのステッピングモータを駆動制御する。また、滑り駒数が決定されたときは、メインCPU101は、該当するリールの図柄カウンタを滑り駒数分だけ更新する。そして、メインCPU101は、更新された図柄カウンタが停止予定位置に対応する値に一致する(停止予定位置の図柄が表示窓の有効ライン上の領域に到達する)のを待って、該当するリールの回転の減速及び停止が行われるように、対応するステッピングモータを駆動制御する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、通信データ送信処理を行う(S904)。この処理では、主に、通信データ格納領域に格納された各種コマンドを主制御回路90の第1シリアル通信回路114(図8参照)を介して副制御回路200に送信する。なお、通信データ送信処理の詳細については、後述の図80を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、投入メダル通過チェック処理を行う(S905)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、各メダルセンサ(図5参照)の検出結果(メダルセンサ入力状態)に基づいて、投入メダルがセレクタ66を通過したか否かのチェック処理を行う。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、7セグLED駆動処理を行う(S906)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、情報表示器6に含まれる各種7セグLEDを駆動制御して、例えば、メダルの払出枚数やクレジット枚数、ストップボタンの押し順データなどを表示する。なお、7セグLED駆動処理の詳細については、後述の図82を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、タイマー更新処理を行う(S907)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、セットされた各種タイマーのカウント(減算)処理を行う。なお、タイマー更新処理の詳細については、後述の図84を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、エラー検知処理を行う(S908)。次いで、メインCPU101は、ドア開閉チェック処理を行う(S909)。ドア開閉チェック処理では、メインCPU101は、ドア開閉監視スイッチ67のオン(ドア閉)/オフ(ドア開)状態をチェックすることにより、フロントドア2b(図2参照)の開閉状態をチェックする。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、試射試験信号制御処理を行う(S910)。この処理では、第2インターフェースボート等を介して試験機に各種試験信号の出力する際の制御処理が行われる。また、この処理は、メインRAM103の規定外作業領域(図11C参照)を用いて実行される。なお、本実施形態では、この処理は、試射試験時以外のとき(パチスロ1が遊技店に設置された後)にも行われるが、この時には、主制御基板71が第2インターフェースボート等を介して試験機に接続されていないので、各種試験信号は生成されても出力はされない。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、レジスタの復帰処理を行う(S911)。そして、S912の処理後、メインCPU101は、割込処理を終了する。
Next, the
[通信データ送信処理]
次に、図80を参照して、割込処理(図79参照)中のS904で行う通信データ送信処理について説明する。なお、図80は、通信データ送信処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Communication data transmission process]
Next, with reference to FIG. 80, the communication data transmission process performed in S904 during the interrupt process (see FIG. 79) will be described. Note that FIG. 80 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the communication data transmission process.
まず、メインCPU101は、WDT設定処理を行う(S961)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、リセットコントローラ106内のWDTをリスタートさせる処理などを行う。なお、WDT設定処理の詳細については、後述の図81を参照しながら後で説明する。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、コマンド送信開始タイマはカウントアップしたか否かを判別する(S962)。すなわち、メインCPU101は、通信データの送信の遅延中であるか否かを判別する。S962において、メインCPU101が、コマンド送信開始タイマはカウントアップしていないと判別したとき(S962がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、通信データ送信処理を終了し、処理を割込処理(図79参照)中のS905の処理に移す。
Next, the
一方、S962において、メインCPU101が、コマンド送信開始タイマはカウントアップしたと判別したとき(S962がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、通信データは送信完了しているか否かを判別する(S963)。具体的には、メインCPU101は、第1シリアル通信回路114(SCU1)のコマンドステータスレジスタ(不図示)に格納されているデータを参照し、送信完了を示すデータが格納されていれば、通信データは送信完了していると判別し、送信完了を示すデータが格納されていなければ、通信データは送信完了していないと判別する。
On the other hand, when the
S963において、メインCPU101が、通信データは送信完了していないと判別したとき(S963がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、通信データ送信処理を終了し、処理を割込処理(図79参照)中のS905の処理に移す。一方、S963において、メインCPU101が、通信データは送信完了していると判別したとき(S963がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、通信データ取得処理を行う(S964)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、メインRAM103の通信データ格納領域から通信データ(コマンドデータ)を取得する処理を行う。
When the
次いで、メインCPU101は、取得した通信データの中に未送信データがあるか否かを判別する(S965)。S965において、メインCPU101が、取得した通信データの中に未送信データがあると判別したとき(S965がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS969の処理を行う。
Next, the
一方、S965において、メインCPU101が、取得した通信データの中に未送信データがないと判別したとき(S965がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、無操作コマンドデータを各レジスタにセットする(S966)。無操作コマンドデータは、遊技者の遊技操作(例えば、遊技を進行させるための操作としての、投入操作、開始操作、及び停止操作など)に関連する情報(例えば、これらの操作が行われたことを示す情報、あるいは、例えば、開始操作に基づき決定された内部当籤役を示す情報など)を含まないように各パラメータが設定されている。なお、無操作コマンドデータの各パラメータには、例えば、パチスロ1における、各スイッチのオン状態/オフ状態を示すパラメータや、各センサのオン状態/オフ状態を示すパラメータ(例えば、入力ポート格納領域1及び入力ポート格納領域2に格納された情報)が設定されるようにすればよい。これにより、副制御回路200側でこれらのスイッチやセンサなどの誤作動や故障などの可能性が判定されるようにしてもよい。
On the other hand, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、通信データ格納処理(図50参照)を行う(S967)。すなわち、メインCPU101は、S966で生成された無操作コマンドデータをメインRAM103の通信データ格納領域に格納する処理を行う。次いで、メインCPU101は、通信データ取得処理を行う(S968)。すなわち、メインCPU101は、S967で通信データ格納領域に格納された無操作コマンドデータを取得する処理を行う。
Next, the
このように、本実施形態では、主制御回路90から副制御回路200に送信する通信データがない場合であっても、割込処理(図79参照)毎に、少なくとも無操作コマンドが送信されるようになっている。したがって、主制御回路90から副制御回路200に送信する通信データがないことに起因して、外部から不正な通信データが送信されてしまうことを防止することが可能となる。なお、このような観点より、無操作コマンドデータは、遊技者の遊技操作に関連する情報を含まないものとしているが、設定される各パラメータの内容はこれに限られるものではなく、適宜変更可能である。
As described above, in this embodiment, at least a non-operation command is transmitted for each interrupt process (see FIG. 79) even when there is no communication data to be transmitted from the
S968の処理後又はS965がYES判定の場合、メインCPU101は、1パケット分のバッファサイズを送信カウンタにセットする(S969)。なお、本実施形態では、1パケット分の送信データは8バイトであることから、1パケット分のバッファサイズも同様に8バイトで構成されている。また、本実施形態では、通信データ格納領域に複数の通信データ(コマンドデータ)が格納されている場合には、格納された順序で(格納が古いものから先に)送信される(FIFO形式)。
After the processing of S968 or if the determination of S965 is YES, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、通信バッファから送信データを取得して送信データレジスタにセットする(S970)。具体的には、メインCPU101は、第1シリアル通信回路114(SCU1)の送信データレジスタ(不図示)に送信データを1バイト単位でセットする。これにより、セットされた送信データは、第1シリアル通信回路114(SCU1)の送信シフトレジスタ(不図示)に転送され、1パケット分ずつ送信される。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、通信バッファのアドレスを「1」更新(+1)する(S971)。次いで、メインCPU101は、送信カウンタを「1」減算する(S972)。次いで、メインCPU101は、送信カウンタは「0」であるか否かを判別する(S973)。すなわち、メインCPU101は、1パケット分の送信データの送信が完了したか否かを判別する。S973において、メインCPU101が、送信カウンタは「0」でないと判別したとき(S973がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS970の処理に戻し、S970以降の処理を繰り返す。
Next, the
一方、S973において、メインCPU101が、送信カウンタは「0」であると判別したとき(S973がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、通信データポインタ更新処理(例えば、図51参照)を行う(S974)。そして、S974の処理後、メインCPU101は、通信データ送信処理を終了し、処理を割込処理(図79参照)中のS905の処理に移す。
On the other hand, when the
[WDT設定処理]
次に、図81を参照して、通信データ送信処理(図80参照)中のS961で行うWDT設定処理について説明する。なお、図81は、WDT設定処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[WDT setting process]
Next, with reference to FIG. 81, the WDT setting process performed in S961 during the communication data transmission process (see FIG. 80) will be described. Note that FIG. 81 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the WDT setting process.
まず、メインCPU101は、リセットコントローラ106内のWDTにおけるWDTクリアレジスタ(不図示)のアドレスをセットする(S981)。次いで、メインCPU101は、セットしたアドレスにクリアデータ(例えば、「55H」)をセットする(S982)。次いで、メインCPU101は、セットしたアドレスにリスタートデータ(例えば、「AAH」)をセットする(S983)。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、コマンド送信開始タイマとその下限値「0」とを比較し、コマンド送信開始タイマが下限値「0」より大きい場合には、コマンド送信開始タイマを1減算(−1更新)し、コマンド送信開始タイマが下限値「0」以下である場合には、コマンド送信開始タイマを「0」に保持する(S984)。そして、S984の処理後、メインCPU101は、WDT設定処理を終了し、処理を通信データ送信処理(図80参照)のS962の処理に移す。
Next, the
上述したように、本実施形態では、WDTのリセット設定及び管理情報(WDTの許可/禁止、基準クロック、タイムアウト時間(例えば、419.4ms)など)がプログラム管理エリアに記憶されており、S982及びS983の処理が行われることにより、設定されているタイムアウト時間が再計測される。なお、タイムアウトによりリセット信号が出力されてメインCPU101が再起動される場合には、電断時(外部)処理(図52参照)が実行されることなく再起動するため、チェックサム生成処理(図53参照)によって算出されるサム値がメインRAM103(サム値格納領域)に格納されない。したがって、この場合、電源投入時処理(図46のS11参照)におけるサムチェック判定結果は正常とならず(すなわち、「RAM異常」として)、情報表示器6(7セグLED表示器)に、エラー発生を意味する文字列「88」が表示される。
As described above, in the present embodiment, the WDT reset setting and management information (WDT enable/disable, reference clock, timeout time (for example, 419.4 ms), etc.) are stored in the program management area, and S982 and By performing the processing in S983, the set timeout time is remeasured. When the reset signal is output due to the timeout and the
[7セグLED駆動処理]
次に、図82を参照して、割込処理(図79参照)中のS906で行う7セグLED駆動処理について説明する。なお、図82は、7セグLED駆動処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[7-segment LED drive processing]
Next, with reference to FIG. 82, the 7-segment LED drive process performed in S906 in the interrupt process (see FIG. 79) will be described. Note that FIG. 82 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the 7-segment LED drive processing.
まず、メインCPU101は、割込カウンタの値に「1」を加算(+1更新)する(S921)。次いで、メインCPU101は、割込カウンタの値が奇数であるか否かを判別する(S922)。
First, the
S922において、メインCPU101が、割込カウンタの値が奇数でないと判別したとき(S922がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、7セグLED駆動処理を終了し、処理を割込処理(図79参照)中のS907の処理に移す。すなわち、本実施形態では、2回の割込周期毎に、7セグLED駆動処理が行われる。なお、本実施形態では、7セグLED駆動処理を割込みカウンタの値が偶数の場合に実行する例を説明したが、本発明はこれに限定されず、割込みカウンタの値が奇数の場合に7セグLED駆動処理を実行してもよいし、また、任意の整数で割込みカウンタの値を除算したときの商又は余りを用いて、7セグLED駆動処理の実行タイミングを決定してもよい。
When the
一方、S922において、メインCPU101が、割込カウンタの値が奇数であると判別したとき(S922がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、ナビデータ格納領域からナビデータを取得する(S923)。次いで、メインCPU101は、7セグLEDの各カソードに出力される押し順表示データを格納するための押し順表示データ格納領域のアドレスをセットする(S924)。
On the other hand, in S922, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、7セグ表示データ生成処理を行う(S925)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、ナビデータに基づいて、押し順表示データ(7セグ表示データ)を作成し、生成された押し順表示データを押し順表示データ格納領域に格納する。なお、7セグ表示データ生成処理の詳細については、後述の図83を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、クレジットカウンタの値を取得する(S926)。次いで、メインCPU101は、7セグLEDの各カソードに出力されるクレジット表示データを格納するためのクレジット表示データ格納領域のアドレスをセットする(S927)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、7セグ表示データ生成処理を行う(S928)。この処理では、メインCPU101は、クレジットカウンタの値に基づいて、クレジット表示データ(7セグ表示データ)を生成し、生成されたクレジット表示データをクレジット表示データ格納領域に格納する。なお、7セグ表示データ生成処理の詳細については、後述の図83を参照しながら後で説明する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、後述の7セグコモンカウンタの値を格納するための7セグコモンカウンタ格納領域のアドレスをセットする(S929)。次いで、メインCPU101は、7セグコモンカウンタの値に「1」を加算(+1更新)する(S930)。なお、この処理において、更新後の7セグコモンカウンタの値が「8」となった場合には、メインCPU101は、7セグコモンカウンタの値に「0」をセットする。本実施形態では、7セグLEDをダイナミック制御するため、8回周期で7セグコモンカウンタの値が更新される。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、7セグコモンカウンタの値に基づいて、コモン選択データを作成し、対象のカソードデータ格納領域(押し順表示データ格納領域又はクレジット表示データ格納領域内の対象格納領域)のアドレスをセットする(S931)。次いで、メインCPU101は、7セグLEDのカソードにクリアデータを出力する(S932)。この処理は、7セグLEDを一旦消灯して、残像の影響を無くすために行われる。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、対象のカソードデータ格納領域から7セグカソード出力データを取得してセットする(S933)。次いで、メインCPU101は、7セグコモンバックアップデータとコモン選択データとから、7セグコモン出力データを生成する(S934)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、7セグコモンバックアップデータ及び7セグカソードバックアップデータにそれぞれ7セグコモン出力データ及び7セグカソード出力データを保存する(S935)。次いで、メインCPU101は、7セグカソード出力データ及び7セグコモン出力データを出力する(S936)。そして、S936の処理後、メインCPU101は、7セグLED駆動処理を終了し、処理を割込処理(図79参照)中のS907の処理に移す。
Next, the
[7セグ表示データ生成処理]
次に、図83を参照して、7セグLED駆動処理(図82参照)中のS925及びS928で行う7セグ表示データ生成処理について説明する。なお、図83は、7セグ表示データ生成処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[7-segment display data generation process]
Next, the 7-segment display data generation process performed in S925 and S928 in the 7-segment LED drive process (see FIG. 82) will be described with reference to FIG. 83. Note that FIG. 83 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the 7-segment display data generation process.
なお、7セグLED駆動処理(図82参照)中のS925で行われる7セグ表示データ生成処理で生成される後述の「表示データ」は押し順表示データに対応し、7セグLED駆動処理(図82参照)中のS928で行われる7セグ表示データ生成処理で生成される後述の「表示データ」はクレジット表示データに対応する。 The "display data" described below, which is generated in the 7-segment display data generation process performed in S925 of the 7-segment LED drive process (see FIG. 82), corresponds to the push-order display data, and the 7-segment LED drive process (see FIG. “Display data”, which will be described later, generated by the 7-segment display data generation process performed in S928 of (see 82) corresponds to the credit display data.
まず、メインCPU101は、カソードデータ格納領域にセットされた表示データを「10」で除算し、その除算結果の商の値を、2桁の7セグLEDの上位桁の表示データとして取得し、除算結果の余の値を下位桁の表示データとして取得する(S941)。次いで、メインCPU101は、取得した上位桁の表示データに基づいて、上位桁表示を行うか否かを判別する(S942)。
First, the
S942において、メインCPU101が、上位桁表示を行うと判別したとき(S942がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、後述のS944の処理を行う。一方、S942において、メインCPU101が、上位桁表示を行わないと判別したとき(S942がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、上位桁の表示無しをセットする(S943)。
In S942, when the
S943の処理後又はS942がYES判定の場合、メインCPU101は、7セグカソードテーブル(不図示)を参照して、上位桁の表示データを取得する(S944)。次いで、メインCPU101は、上位桁の表示データ格納領域(不図示)に取得した上位桁の表示データを保存する(S945)。
After the processing of S943 or when the determination of S942 is YES, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、7セグカソードテーブル(不図示)を参照して、下位桁の表示データを取得する(S946)。次いで、メインCPU101は、下位桁の表示データ格納領域(不図示)に取得した下位桁の表示データを保存する(S947)。
Next, the
そして、S947の処理後、メインCPU101は、7セグ表示データ生成処理を終了する。この際、実行した7セグ表示データ生成処理が7セグLED駆動処理(図82参照)中のS925の処理である場合には、メインCPU101は、処理を7セグLED駆動処理中のS926の処理に移す。一方、実行した7セグ表示データ生成処理が7セグLED駆動処理(図82参照)中のS928の処理である場合には、メインCPU101は、処理を7セグLED駆動処理中のS929の処理に移す。
Then, after the processing of S947, the
[タイマー更新処理]
次に、図84を参照して、割込処理(図79参照)中のS907で行うタイマー更新処理について説明する。なお、図84は、タイマー更新処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[Timer update processing]
Next, with reference to FIG. 84, the timer updating process performed in S907 during the interrupt process (see FIG. 79) will be described. Note that FIG. 84 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the timer updating process.
まず、メインCPU101は、HLレジスタに2バイトタイマー格納領域(不図示)の更新開始アドレスをセットし、Bレジスタに2バイトタイマー数をセットする(S951)。2バイトタイマー格納領域は、286ms(256×1.1172ms)以上の時間(すなわち、1バイトを超えるタイマ値)を管理するために用いられる。
First, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、2バイトタイマー数とその下限値「0」とを比較し、2バイトタイマー数が下限値「0」より大きい場合には、2バイトタイマー数を1減算(−1更新)し、2バイトタイマー数が下限値「0」以下である場合には、2バイトタイマー数を「0」に保持する(S952)。さらに、S952の処理では、メインCPU101は、HLレジスタにセットされている2バイトタイマー格納領域の更新開始アドレスを2減算(−2更新)する。なお、例えば、コマンド送信開始タイマも2バイトタイマあることから、この処理においてその更新が行われるようにしてもよい(図81参照)。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、Bレジスタにセットされた2バイトタイマー数を1減算(−1更新)する(S953)。次いで、メインCPU101は、Bレジスタにセットされた2バイトタイマー数が「0」であるか否かを判別する(S954)。
Next, the
S954において、メインCPU101が、Bレジスタにセットされた2バイトタイマー数が「0」でないと判別したとき(S954がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS952の処理に戻し、S952以降の処理を繰り返す。
When the
一方、S954において、メインCPU101が、Bレジスタにセットされた2バイトタイマー数が「0」であると判別したとき(S954がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、HLレジスタに1バイトタイマー格納領域の更新開始アドレスをセットし、Bレジスタに1バイトタイマー数をセットする(S955)。1バイトタイマー格納領域は、286ms(256×1.1172ms)未満の時間(すなわち、1バイトを超えないタイマ値)を管理するために用いられる。例えば、メダル監視タイマなどは1バイトタイマとしてその更新が行われる。
On the other hand, when the
次いで、メインCPU101は、1バイトタイマー数とその下限値「0」とを比較し、1バイトタイマー数が下限値「0」より大きい場合には、1バイトタイマー数を1減算(−1更新)し、1バイトタイマー数が下限値「0」以下である場合には、1バイトタイマー数を「0」に保持する(S956)。さらに、S956の処理では、メインCPU101は、HLレジスタにセットされている1バイトタイマー格納領域の更新開始アドレスを1減算(−1更新)する。
Next, the
次いで、メインCPU101は、Bレジスタにセットされた1バイトタイマー数を1減算(−1更新)する(S957)。次いで、メインCPU101は、Bレジスタにセットされた1バイトタイマー数が「0」であるか否かを判別する(S958)。
Next, the
S958において、メインCPU101が、Bレジスタにセットされた1バイトタイマー数が「0」でないと判別したとき(S958がNO判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、処理をS956の処理に戻し、S956以降の処理を繰り返す。
When the
一方、S958において、メインCPU101が、Bレジスタにセットされた1バイトタイマー数が「0」であると判別したとき(S958がYES判定の場合)、メインCPU101は、電磁カウンタ制御処理を行う(S959)。この処理では、メダルのIN/OUTを示す信号を外部集中端子板47に出力する際の出力制御処理が行われる。そして、S959の処理後、メインCPU101は、タイマー更新処理を終了し、処理を割込処理(図79参照)中のS908の処理に移す。
On the other hand, when the
<電源投入時の動作説明>
次に、図85を参照しながら、本発明の一実施形態に係るパチスロの電源投入時の動作について説明する。図85は、パチスロ1の電源投入時の動作の例を示すタイミングチャートである。
<Explanation of operation when power is turned on>
Next, the operation of the pachi-slot according to the embodiment of the present invention when the power is turned on will be described with reference to FIG. FIG. 85 is a timing chart showing an example of the operation of the pachi-
なお、図85中、「MainCPU」は、メインCPU101(主制御回路90)を示し、「SubCPU」は、サブCPU201(副制御回路200)を示している。 In FIG. 85, “MainCPU” indicates the main CPU 101 (main control circuit 90), and “SubCPU” indicates the sub CPU 201 (sub control circuit 200).
また、図85中、「MainCPU」の動作状態「セキュリティモード」は、上述したセキュリティモード中である状態を示し、「MainCPU」の動作状態「起動遅延期間」は、セキュリティモードの終了後、上述したコマンド送信開始タイマがセットされ、セットされたコマンド送信開始タイマが「0」となるまでの期間(すなわち、設定変更は可能であるが、通信データの送信を遅延させている期間)を示し、「MainCPU」の動作状態「通常動作期間」は、通信データの送信の遅延が終了し、サブCPU201(副制御回路200)に対して通信データの送信が可能となった状態を示している。 Further, in FIG. 85, the operation state "security mode" of "MainCPU" indicates the above-described security mode, and the operation state "start delay period" of "MainCPU" is as described above after the end of the security mode. The command transmission start timer is set, and the period until the set command transmission start timer becomes "0" (that is, the period during which the setting can be changed but the transmission of communication data is delayed) is shown. The operation state “normal operation period” of “MainCPU” indicates a state in which the delay of the transmission of the communication data is completed and the communication data can be transmitted to the sub CPU 201 (sub control circuit 200).
また、図85中、「SubCPU」の動作状態「初期化」は、サブCPU201(副制御回路200)の電源投入時の初期化(起動)処理(ハード起動時間、バイオス(ドライバ)初期化、カーネル(OS)起動など)中である状態(すなわち、メインCPU101(主制御回路90)から送信される通信データの受信が可能でない状態)を示し、「SubCPU」の動作状態「通常動作期間」は、電源投入時の初期化(起動)処理が終了し、メインCPU101(主制御回路90)から送信される通信データの受信が可能となった状態を示している。 Further, in FIG. 85, the operation state “initialization” of the “SubCPU” is the initialization (startup) process (hardware start-up time, BIOS (driver) initialization, kernel) when the sub-CPU 201 (sub-control circuit 200) is powered on. (OS) startup (that is, a state in which communication data transmitted from the main CPU 101 (main control circuit 90) cannot be received), and the operating state “normal operating period” of “SubCPU” is This shows a state in which the initialization (startup) processing at the time of turning on the power is completed and the communication data transmitted from the main CPU 101 (main control circuit 90) can be received.
また、図85中、「設定動作A」は、「起動遅延期間」において設定変更が開始され(例えば、設定用鍵型スイッチ54がオン状態でパチスロ1の電源が投入され)、その後、「通常動作期間」において設定変更が終了された場合の動作を示し、「送信態様A」は、「設定動作A」の場合の、設定変更コマンド(設定変更/設定確認開始)(COM1)、及び設定変更コマンド(設定変更/設定確認終了)(COM2)の送信タイミングを示している。また、「送信態様A」の下の「MainCPU設定変更処理」は、「送信態様A」の場合の、メインCPU101による設定変更確認処理(図48参照)内において、設定変更コマンドがメインRAM103の通信データ格納領域に格納(登録)されるタイミング(図49の設定変更コマンド生成格納処理及び図50の通信データ格納処理も参照)を示している。
Further, in FIG. 85, in the “setting operation A”, the setting change is started in the “start delay period” (for example, the setting
また、図85中、「設定動作B」は、「起動遅延期間」において設定変更が開始され(例えば、設定用鍵型スイッチ54がオン状態でパチスロ1の電源が投入され)、その後、当該「起動遅延期間」において設定変更が終了された場合の動作を示し、「送信態様B」は、「設定動作B」の場合の、設定変更コマンド(設定変更/設定確認開始)(COM1)、及び設定変更コマンド(設定変更/設定確認終了)(COM2)の送信タイミングを示している。また、「送信態様B」の下の「MainCPU設定変更処理」は、「送信態様B」の場合の、メインCPU101による設定変更確認処理(図48参照)内において、設定変更コマンドがメインRAM103の通信データ格納領域に格納(登録)されるタイミング(図49の設定変更コマンド生成格納処理及び図50の通信データ格納処理も参照)を示している。
Also, in FIG. 85, in the “setting operation B”, the setting change is started in the “start delay period” (for example, the setting
パチスロ1の電源が投入されリセット信号が入力されると、マイクロプロセッサ91のセキュリティ部(不図示)によってセキュリティモードの動作状態に制御される。メインCPU101は、セキュリティモード中においては、セキュリティ設定エリア記憶された設定に応じた期間、起動が遅延させられる。セキュリティモードが終了すると、メインCPU101は、所定期間、通信データの送信を遅延させる。なお、メインCPU101は、通信データの送信を遅延させている場合であっても、設定変更を可能としている。
When the power of the pachi-
ここで、「設定動作A」に示すように、通信データの送信の遅延中に設定変更が開始され、通信データの送信の遅延が終了した後に設定変更が終了された場合、メインCPU101は、通信データの送信の遅延が終了したときに、設定変更コマンド(設定変更/設定確認開始)(COM1)を副制御回路200に対して送信し、設定変更が終了されたときに、設定変更コマンド(設定変更/設定確認終了)(COM2)を副制御回路200に対して送信する。
Here, as shown in "setting operation A", when the setting change is started during the delay of the transmission of the communication data and the setting change is ended after the delay of the transmission of the communication data is ended, the
一方、「設定動作B」に示すように、通信データの送信の遅延中に設定変更が開始され、同じく通信データの送信の遅延中に設定変更が終了された場合、メインCPU101は、通信データの送信の遅延が終了したときに、設定変更コマンド(設定変更/設定確認開始)(COM1)、及び設定変更コマンド(設定変更/設定確認終了)(COM2)を副制御回路200に対して順次送信する。すなわち、通信データの送信の遅延が終了したときに、通信データ格納領域に設定変更コマンド(設定変更/設定確認開始)(COM1)、及び設定変更コマンド(設定変更/設定確認終了)(COM2)が登録されている場合には、これらの通信データを登録された順序で送信する。
On the other hand, as shown in “setting operation B”, when the setting change is started during the delay of transmission of communication data and the setting change is ended during the delay of transmission of communication data as well, the
このように、本実施形態のパチスロ1によれば、パチスロ1の電源投入時にメインCPU101の起動を遅延させることで、主制御回路90を安定的に起動させることができるとともに、メインCPU101の起動の遅延が終了した後、通信データの送信を遅延させることで、副制御回路200の起動に要する時間を確保して副制御回路200も安定的に起動させることができる。
As described above, according to the pachi-
そして、メインCPU101の起動の遅延が終了した後は、通信データの送信の遅延が終了する前であっても設定変更を可能としたことから、例えば、遊技店における開店作業を行う際に、パチスロ1の電源を投入した場合(すなわち、これにともなってリセット信号が入力された場合)には、副制御回路200の起動完了を待つことなく先立って設定変更を行うことができるため、電源投入時における作業効率を向上させることが可能となる。
After the delay of the start of the
さらに、通信データの送信の遅延が終了する前に設定変更が行われた場合には、設定変更の開始時や設定変更の終了時にこれらを示す通信データが登録され、通信データの送信の遅延が終了したときに、これらの通信データが登録された順序で送信されるようになっていることから、副制御回路200の起動完了を待つことなく先立って設定変更を行った場合であっても、それによって主制御回路90と副制御回路200との間で保有する情報に齟齬が生じることを防止することができる。また、例えば、副制御回路200において、主制御回路90から送信される通信データの順序によって不正行為やエラー等の判定が行われるように構成される場合であっても、このような判定の結果に影響を及ぼさず、正確な判定を行わせることが可能となる。
Furthermore, if the settings are changed before the delay of the transmission of communication data ends, the communication data indicating these are registered at the start of the setting change or at the end of the setting change, and the delay of the transmission of communication data will be delayed. Since these communication data are transmitted in the order in which they are registered when they are completed, even if the setting is changed in advance without waiting for the completion of the activation of the
また、本実施形態のパチスロ1によれば、通信データの送信処理が行われる際に、通信データが登録されていない場合であっても、少なくとも無操作コマンドデータが送信されるようにしたことから、例えば、主制御回路90と副制御回路200との間の接続線に不正にアクセスする等、不正の手段によって外部から通信データが送信されてしまうことを防止することが可能となる。また、通信データの送信の遅延が終了する前は、当該無操作コマンドデータの登録・送信を行わないようにしたことから、パチスロ1の電源投入時の制御負担を軽減することが可能となる。なお、不正行為防止を主目的とする観点より、当該無操作コマンドデータは、遊技者の遊技操作に関連する情報を含まないようにすればよい。
Further, according to the pachi-
また、本実施形態のパチスロ1によれば、メインCPU101の起動の遅延期間が、固定期間及び可変期間で構成され、また、これらの期間(あるいはその範囲)を適宜選択して設定可能としたことから、主制御回路90や副制御回路200のスペックに応じて、適切な遅延時間を設定することが可能となる。なお、設定変更が可能となるまでの期間をより短くするという観点より、可変期間として必ず0が決定される所定の期間の範囲(例えば、ランダム延長期間における「設定なし」)を設定可能である場合には、当該所定の期間の範囲が設定されるものとすればよい。
According to the pachi-
なお、本実施形態では、セキュリティモードの終了後、通信データの送信を遅延させている期間(「起動遅延期間」)において、設定値の設定操作(設定変更操作)を可能とした例について説明しているが、通信データの送信を遅延させている期間(「起動遅延期間」)において実行可能とする操作はこれに限られるものではない。例えば、設定用鍵型スイッチ54がオフ状態でパチスロ1の電源が投入され、通信データの送信を遅延させている期間(「起動遅延期間」)において設定用鍵型スイッチ54がオン状態となった場合、当該期間において設定値の確認操作(設定確認操作)を可能とするようにしてもよい。これにより、例えば、遊技店における開店作業を行う際に、設定変更は行わないが現在の設定値を確認したい等の場合においても、副制御回路200の起動完了を待つことなく先立って設定確認を行うことができるため、電源投入時における作業効率を向上させることが可能となる。
Note that, in the present embodiment, an example will be described in which after the security mode ends, the setting value setting operation (setting change operation) is possible during the period in which the transmission of communication data is delayed (“start delay period”). However, the operation that can be executed during the period in which the transmission of the communication data is delayed (“activation delay period”) is not limited to this. For example, the setting
<メダル投入時の動作説明>
次に、図86を参照しながら、本発明の一実施形態に係るパチスロのメダル投入時の動作について説明する。図86は、パチスロ1のメダル投入時の動作の例を示すタイミングチャートである。
<Explanation of operation when inserting medals>
Next, with reference to FIG. 86, an operation of the pachi-slot according to the embodiment of the present invention at the time of inserting a medal will be described. FIG. 86 is a timing chart showing an example of the operation of the pachi-
なお、図86中、「スタートスイッチ」は、スタートスイッチ79を示し、「メダルセンサ」は、上流側メダルセンサ(第1メダルセンサ)806及び下流側メダルセンサ(第2メダルセンサ)807の検知状態(メダルセンサ入力状態)を示し、「メダル受付信号」は、オン状態(「ON」)がメダルの受付が許可されている状態(メダル受付許可)を示し、オフ状態(「OFF」)がメダルの受付が禁止されている状態(メダル受付禁止)を示している(図57及び図58参照)。
In FIG. 86, a “start switch” indicates the
また、図86中、「ソレノイド」は、セレクタ66のソレノイド(セレクトプレート804をガイド位置又は排出位置に変移させる駆動源)を示し、「監視タイマ」は、メダル監視タイマを示し(図57及び図58参照)、「動作状態」は、パチスロ1における、開始操作後の遊技の進行を可能とする状態(「遊技中」)と、開始操作後の遊技の進行を可能としない状態(「遊技待」)と、を示している。
Further, in FIG. 86, “solenoid” indicates the solenoid of the selector 66 (driving source that shifts the
メインCPU101は、遊技開始可能枚数(本実施形態では3枚)のメダルが投入されると、スタートレバー16に対する開始操作を受付可能とする。なお、図86に示すように、この状態において、クレジット枚数としてメダルを貯留可能であれば(クレジットが50枚未満であれば)、スタートレバー16に対する開始操作が行われるまで(スタートスイッチ79により開始操作が検出されるまで)、メダルの受付が許可されている状態(メダル受付信号が「ON」である状態)が継続する。なお、図示は省略しているが、この状態において、クレジット枚数としてメダルを貯留可能でなければ(クレジットが50枚であれば)、メダルの受付が禁止されている状態(メダル受付信号が「OFF」である状態)に変移している。
When the number of medals that can be started in the game (three in the present embodiment) is inserted, the
メインCPU101は、遊技開始可能枚数(本実施形態では3枚)のメダルが投入され、クレジット枚数としてメダルを貯留可能な状態において、スタートスイッチ79により開始操作(図86中、左側の1回目の開始操作(スタートスイッチ79の「OFF」から「ON」への変移)を「開始操作A」とする)が検出されると、メダルの受付が許可されている状態(メダル受付信号が「ON」である状態)からメダルの受付が禁止されている状態(メダル受付信号が「OFF」である状態)に変移させ、セレクタ66のソレノイドを消磁状態に変移させることを開始し、メダル監視タイマによる監視(計測)を開始する。また、このとき、上述したスタートレバーONフラグをオン状態とする。
The
メインCPU101は、メダル監視タイマによる監視(計測)中に(すなわち、セレクタ66のソレノイドが励磁状態から消磁状態に変移完了となる前に)、メダルが投入された場合(各メダルセンサのメダルセンサ入力状態に基づきメダルが投入されたと判別される場合)には、励磁状態から消磁状態に変移途中であったセレクタ66のソレノイドを再度励磁状態に変移させるようにして、投入されたメダルが計数され、ホッパー装置51内に案内されるようにする。また、この場合、スタートスイッチ79により「開始操作A」は検出されているが、当該検出に基づいて、動作状態を開始操作後の遊技の進行を可能とする状態(「遊技中」)には変移させない。また、このとき、上述したスタートレバーONフラグをオフ状態とする。すなわち、この場合には、「開始操作A」を無効とする。
When the medal is inserted (that is, before the solenoid of the
なお、メインCPU101は、メダル監視タイマによる監視(計測)中に(すなわち、セレクタ66のソレノイドが励磁状態から消磁状態に変移完了となる前に)、メダルが投入された場合(各メダルセンサのメダルセンサ入力状態に基づきメダルが投入されたと判別される場合)には、さらに、メダルの受付が禁止されている状態(メダル受付信号が「OFF」である状態)からメダルの受付が許可されている状態(メダル受付信号が「ON」である状態)に変移させるようにしてもよい。
It should be noted that the
その後、メインCPU101は、再度スタートスイッチ79により開始操作(図86中、右側の2回目の開始操作(スタートスイッチ79の「OFF」から「ON」への変移)を「開始操作B」とする)が検出されると、再度セレクタ66のソレノイドを励磁状態から消磁状態に変移させ、再度メダル監視タイマによる監視(計測)を開始する。また、このとき、再度上述したスタートレバーONフラグをオン状態とする。
Thereafter, the
そして、メインCPU101は、メダル監視タイマによる監視(計測)中に(すなわち、セレクタ66のソレノイドが励磁状態から消磁状態に変移完了となる前に)、メダルが投入されなかった場合(各メダルセンサのメダルセンサ入力状態に基づきメダルが投入されたと判別されない場合)には、メダル監視タイマによる監視(計測)終了後(すなわち、セレクタ66のソレノイドが励磁状態から消磁状態に変移完了後)に、動作状態を開始操作後の遊技の進行を可能とする状態(「遊技中」)に変移させ、遊技を進行させることを可能とする(すなわち、メダル受付・スタートチェック処理(図57及び図58参照)以後の処理を実行可能とする)。
Then, the
なお、図示は省略しているが、メインCPU101は、スタートスイッチ79により「開始操作A」が検出され、メダルの受付が許可されている状態(メダル受付信号が「ON」である状態)からメダルの受付が禁止されている状態(メダル受付信号が「OFF」である状態)に変移し、セレクタ66のソレノイドを消磁状態に変移させることを開始し、メダル監視タイマによる監視(計測)を開始した後、メダル監視タイマによる監視(計測)中に(すなわち、セレクタ66のソレノイドが励磁状態から消磁状態に変移完了となる前に)、メダルが投入されなかった場合(各メダルセンサのメダルセンサ入力状態に基づきメダルが投入されたと判別されない場合)にも、スタートスイッチ79により「開始操作B」が検出された場合と同様、メダル監視タイマによる監視(計測)終了後(すなわち、セレクタ66のソレノイドが励磁状態から消磁状態に変移完了後)に、動作状態を開始操作後の遊技の進行を可能とする状態(「遊技中」)に変移させ、遊技を進行させることを可能とする(すなわち、メダル受付・スタートチェック処理(図57及び図58参照)以後の処理を実行可能とする)。
Although illustration is omitted, the
このように、本実施形態のパチスロ1によれば、遊技者の開始操作にともなって遊技が開始される場合に、例えば、メダルの「飲込み」などの発生を防止するためのメダル監視タイマがセットされる。このメダル監視タイマにより、セレクタ66において、投入されたメダルが遊技機内部に貯留される状態(ソレノイドが励磁状態であることによりセレクトプレート804がガイド位置にある状態)から遊技機外部に排出される状態(ソレノイドが消磁状態であることによりセレクトプレート804が排出位置にある状態)に物理的に変移するまでの時間が確保される。
As described above, according to the pachi-
そして、メダル監視タイマによる監視(計測)中にメダルが投入された場合には、そのもととなった開始操作は無効とされ、また、セレクタ66においては、投入されたメダルが遊技機内部に貯留される状態に戻る。したがって、メダルの「飲込み」などの発生を防止して、投入されたメダルを適切に処理することが可能となる。
Then, when a medal is inserted during the monitoring (measurement) by the medal monitoring timer, the starting operation which is the basis of the medal is invalidated, and in the
また、本実施形態のパチスロ1によれば、メダル監視タイマによる監視(計測)中にメダルが投入された場合であっても、そのメダルが計数されるようにしたことから、投入されたメダルの計数漏れを防止でき、投入されたメダルをより適切に処理することが可能となる。
Further, according to the pachi-
また、本実施形態のパチスロ1によれば、メダル監視タイマのタイマ値(例えば、「72」)を、投入されたメダルが遊技機内部に貯留される状態から遊技機外部に排出される状態に物理的に変移するまでの期間(例えば、80ms)以上の期間(例えば、「72」×1.1172ms)に設定するようにしたことから、メダルの「飲込み」などの発生を確実に防止して、投入されたメダルをより適切に処理することが可能となる。なお、本実施形態のように、駆動部がソレノイドである場合には、このような効果はより顕著となる。
Further, according to the pachi-
<本実施形態で実行可能なその他の演出>
次に、図87〜図91を参照しながら、上述した演出の他に、本実施形態で実行可能なその他の演出の一例について説明する。なお、以下では、その他の演出の一例として、ボーナス役に当籤しているか否かを報知するためのボーナス役当籤報知演出が実行可能であることについて説明しているが、その用途はボーナス役に当籤しているか否かを報知するものに限定されない。
<Other effects that can be executed in this embodiment>
Next, with reference to FIGS. 87 to 91, examples of other effects that can be executed in the present embodiment will be described in addition to the effects described above. In the following, as an example of other effects, it is explained that a bonus winning combination winning notification effect for notifying whether or not a bonus winning combination is won can be executed, but its use is a bonus winning combination. The present invention is not limited to the one for notifying whether or not the winning has been won.
例えば、非有利区間及び通常有利区間において、有利区間に移行することが決定されているか否かを報知するために実行されるものであってもよいし、有利区間のラインバトル状態において、有利区間が継続することが決定されているか否かを報知するために実行されるものであってもよい。また、有利区間の権利獲得抽籤状態において、権利獲得状態に移行することが決定されているか否かを報知するために実行されるものであってもよいし、有利区間の権利獲得状態おいて、権利を付与することが決定されているか否かを報知するために実行されるものであってもよい。すなわち、遊技者に特典が付与されるか否かを報知するために実行される演出として用いることができる。 For example, in the non-advantageous section and the normal advantageous section, it may be executed to notify whether or not it is decided to shift to the advantageous section, or in the line battle state of the advantageous section, the advantageous section. May be executed to notify whether or not is decided to continue. Further, in the right acquisition lottery state of the advantageous section, it may be executed to inform whether or not it is determined to shift to the right acquisition state, or in the right acquisition state of the advantageous section, It may be executed to inform whether or not it has been decided to grant the right. That is, it can be used as an effect executed to inform the player whether or not the privilege is awarded.
(ボーナス役当籤報知演出の演出例(その1))
まず、図87及び図88を参照して、ボーナス役当籤報知演出の演出例(その1)について説明する。図87及び図88は、例えば、ボーナス役の(同時)当籤を期待させる内部当籤役(例えば、「チャンス目」)が決定された場合に、所定確率で表示装置11に表示され得るボーナス役当籤報知演出の演出例(その1)を示している。なお、図87では、ボーナス役に当籤していない場合(ボーナス役非当籤の場合)の表示例を示し、図88では、ボーナス役に当籤している場合(ボーナス役当籤の場合)の表示例を示している。
(Example of a bonus winning combination notification effect (No. 1))
First, with reference to FIG. 87 and FIG. 88, an example of the bonus winning combination notification effect (No. 1) will be described. 87 and 88 show, for example, a bonus winning combination that can be displayed on the
図87及び図88に示すように、ボーナス役当籤報知演出の演出例(その1)では、「間違い探し演出」と題した演出が行われるようになっている。この「間違い探し演出」は、例えば、パチスロ1のモチーフとして使用されている、漫画、アニメーション、あるいはゲームなどの原作品がある場合に、当該原作品における所定の画像と同一又は近似の画像をベース画像とし、当該ベース画像に対して異なっている点(すなわち、間違い)があるか否かを遊技者に探させる演出となっている。この場合、所定の画像は、原作品のままの(すなわち、同一の)画像であってもよいし、原作品の画像に対して、A/D変換し、アクペクト比を変更し、解像度を変更し、あるいはリマスターした(すなわち、近似の)画像であってもよい。また、あくまでも原作品に依拠した画像であるが、パチスロ1の演出に用いるために新たに制作された画像であってもよい。
As shown in FIG. 87 and FIG. 88, in the example of the bonus winning combination notification effect (No. 1), an effect entitled “Find Mistakes Effect” is performed. For example, if there is an original work such as a manga, animation, or game that is used as a motif of Pachi-
なお、ベース画像は、上述したものに限られず、適宜設定することができる。例えば、原作品がない場合(例えば、オリジナルのモチーフである場合)であっても、パチスロ1における他の演出において表示され得る画像と同一又は近似の画像を設定するようにしてもよい。また、例えば、パチスロ1の仕様を説明するために遊技店で配布される小冊子内に印刷された画像と同一又は近似の画像を設定するようにしてもよい。また、例えば、ベース画像は静止画でなくともよく、動画であってもよいし、静止画がスライド形式で順次表示されるものであってもよい。
The base image is not limited to the one described above, and can be set as appropriate. For example, even when there is no original work (for example, when it is an original motif), an image that is the same as or close to the image that can be displayed in another effect in the pachi-
図87の上段には、「全員集合!」という文字とともに、5体のキャラクタが表示された画像が表示されている。当該画像は、ベース画像と同じ画像となっている。また、当該画像の下方には、「知っている画像と違う箇所があったらカーソルを合わせて決定してね!」といったように、ベース画像と相違する点を指摘すべきことを促すメッセージとカーソルとが表示される。 In the upper part of FIG. 87, an image in which five characters are displayed is displayed together with the characters “all together!”. The image is the same as the base image. Also, below the image, a message and a cursor prompting you to point out the points that are different from the base image, such as "Please set the cursor if there is a part that is different from the image you know!" And are displayed.
このとき、遊技者は、タッチセンサ19が設けられたサブ表示装置18の表示面上の所定領域を指でなぞるなどしてカーソルを所望の箇所まで移動させ(選択操作を行い)、同じくサブ表示装置18の表示面上に表示された決定ボタン(不図示)をタッチ操作し(決定操作を行い)、自身が間違いだと思う箇所を指定する。
At this time, the player moves the cursor to a desired position (by performing a selection operation) by tracing a predetermined area on the display surface of the
なお、遊技者の選択操作や決定操作などの演出に係る各種操作を検出する手段は、サブ表示装置18に限られるものではない。例えば、表示装置11が、液晶表示装置のような表示装置である場合には、表示装置11の少なくとも一部(例えば、図87の上段の表示が行われる箇所)にタッチセンサを設けるようにし、当該タッチセンサが、遊技者の指の移動を検出した場合(選択操作が行われた場合)にはそれに応じてカーソルを移動させ、また、当該タッチセンサが設けられた箇所に表示された決定ボタン(不図示)が押下操作された場合(決定操作が行われた場合)にはそれに応じて結果を報知する演出が行われるようにしてもよい。また、例えば、選択操作や決定操作などの演出に係る各種操作が検出可能な物理的操作手段(例えば、十字キー及び演出ボタン、ジョグダイヤルなど)が設けられる場合には、このような物理的操作手段によって選択操作や決定操作が検出されるようにしてもよい。すなわち、遊技者の演出に係る各種操作を検出可能な手段であれば、どのような手段であっても適用することが可能である。
It should be noted that the means for detecting various operations related to the production such as the player's selection operation and determination operation is not limited to the
ここで、例えば、図87の上段に表示された画像において、右端のキャラクタが表示されている部分を遊技者が指定したとする。そうすると、図87の上段に表示された画像にはベース画像と異なる部分はないため、図87の下段に示すように、「間違い探し演出」における間違い探しの結果が失敗であったことを報知するための「はずれ〜残念」というメッセージが表示される。 Here, for example, in the image displayed in the upper part of FIG. 87, it is assumed that the player designates the portion where the character at the right end is displayed. Then, since the image displayed in the upper part of FIG. 87 has no difference from the base image, as shown in the lower part of FIG. 87, the fact that the error search result in the “error search effect” has failed is notified. "I'm sorry ~ sorry" message is displayed.
一方、図88の上段には、「全員集合!」という文字とともに、4体のキャラクタが表示された画像が表示されている。当該画像は、ベース画像とは右端のキャラクタが表示されていない部分において異なる画像となっている。また、当該画像の下方には、図87と同様に、「知っている画像と違う箇所があったらカーソルを合わせて決定してね!」といったように、ベース画像と相違する点を指摘すべきことを促すメッセージとカーソルとが表示される。 On the other hand, in the upper part of FIG. 88, an image in which four characters are displayed is displayed together with the characters “all gathering!”. The image is different from the base image in the portion where the rightmost character is not displayed. Also, similar to FIG. 87, a point different from the base image should be pointed out as in the case of FIG. 87, such as “If there is a part different from the image you know, move the cursor to make a decision!”. A message prompting the user and a cursor are displayed.
ここで、例えば、図88の上段に表示された画像において、右端のキャラクタが表示されていない部分を遊技者が指定したとする。この場合、当該指定された部分は、ベース画像と異なる部分であるため、図88の下段に示すように、「間違い探し演出」における間違い探しの結果が成功であったことを報知するための「あたり〜」というメッセージとともに、ボーナス役に当籤していることを報知するための「ボーナス確定!」というメッセージが表示される。 Here, for example, in the image displayed in the upper part of FIG. 88, it is assumed that the player designates a portion where the rightmost character is not displayed. In this case, since the designated portion is a portion different from the base image, as shown in the lower part of FIG. 88, a message “Notification of mistake” indicates that the result of the error search is successful. Along with the message "around", a message "bonus confirmed!" for notifying that the bonus combination has been won is displayed.
これに対し、例えば、図88の上段に表示された画像において、左端のキャラクタが表示されている部分を遊技者が指定したとする。この場合、当該指定された部分は、ベース画像と異なる部分ではないため、図87の下段と同様に、「間違い探し演出」における間違い探しの結果が失敗であったことを報知するための「はずれ〜残念」というメッセージが表示され、ボーナス役に当籤している場合であってもボーナス役に当籤していることは報知されない。 On the other hand, for example, in the image displayed in the upper part of FIG. 88, it is assumed that the player designates the portion where the character at the left end is displayed. In this case, since the designated part is not a part different from the base image, as in the lower part of FIG. 87, “off” for notifying that the result of the error search in the “error search effect” is a failure has occurred. A message "~ sorry" is displayed, and even if the winning combination is won, it is not notified that the winning combination is won.
なお、図87及び図88に示した演出態様は、「間違い探し演出」における演出態様の一例を示すものであり、例えば、以下に示すような演出態様を採用することもできる。 It should be noted that the effect modes shown in FIGS. 87 and 88 are examples of the effect modes in the “error search effect”, and, for example, the following effect modes can also be adopted.
例えば、ベース画像が、原作品における所定のテーマ(例えば、原作品における第1話)に基づくものであり、複数(例えば、5枚)の画像(例えば、ダイジェスト画像)がスライド形式で表示されるものであるとする。そして、ボーナス役に当籤していない場合には、そのスライド画像がそのまま順次表示された後、そのスライドの各画像がサムネイル状に表示される。一方、ボーナス役に当籤している場合には、そのスライド画像のうち一部の画像が異なるスライド画像が順次表示された後、そのスライドの各画像がサムネイル状に表示される。 For example, the base image is based on a predetermined theme in the original work (for example, the first episode in the original work), and a plurality of (for example, five) images (for example, digest images) are displayed in a slide format. It is assumed to be a thing. Then, when the bonus combination is not won, the slide images are sequentially displayed as they are, and then each image of the slide is displayed in a thumbnail shape. On the other hand, when the bonus combination is won, slide images in which some of the slide images are different are sequentially displayed, and then each image of the slide is displayed in a thumbnail shape.
遊技者は、サムネイル状に表示された各画像において、所定のテーマとは異なるテーマ(例えば、原作品における第1話とは異なる話数)に基づくものが含まれているかどうかを検索し、所定のテーマとは異なるテーマの画像であると思ったものに対し、選択操作及び決定操作を行う。そして、所定のテーマとは異なるテーマの画像が含まれている場合であって、遊技者が当該画像を指定した場合には、「間違い探し演出」における間違い探しの結果が成功となるようにすればよい。具体的には、例えば、原作品における第1話においては、キャラクタA及びキャラクタBしか登場しないにもかかわらず、ボーナス役に当籤した場合に表示されるスライド画像では、原作品における第3話以降にしか登場しないキャラクタCが表示された画像が含まれるようにすればよい。このようにすれば、例えば、原作品に愛着のある遊技者は、特に思い入れをもって「間違い探し演出」を行うことができるため、演出に関する興趣をより向上させることが可能となる。 The player searches each image displayed in a thumbnail form for a theme based on a theme different from the predetermined theme (for example, the number of stories different from the first story in the original work), and determines whether or not the predetermined theme is included. The selection operation and the determination operation are performed for an image that is thought to be an image of a theme different from that of. Then, when an image of a theme different from the predetermined theme is included and the player specifies the image, the result of the error search in the “error search effect” should be successful. Good. Specifically, for example, in the first episode of the original work, although only the characters A and B appear, in the slide images displayed when the winning combination is won, the third and subsequent episodes of the original work are shown. It suffices to include an image in which the character C that appears only in is displayed. By doing so, for example, a player who is attached to the original work can perform the “error search performance” with particular feelings, and thus it is possible to further enhance the interest in the performance.
また、上述のように、「間違い探し演出」においてベース画像と少なくとも一部が異なる画像を表示する場合、ベース画像と異なる部分は1箇所のみである必要はなく、複数箇所が異なっていてもよい。この場合、例えば、当籤したボーナス役の種類に応じて、異なる箇所の数が異なる場合があるようにしてもよい。例えば、ベース画像と異なる部分が1箇所である場合、BB3又はBB4に当籤している可能性が高く、ベース画像と異なる部分が複数箇所である場合、BB1又はBB2に当籤している可能性が高くなるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、当籤しているボーナス役の種類まで示唆することができる。 Further, as described above, in the case of displaying an image at least partially different from the base image in the “error search effect”, the portion different from the base image does not have to be only one location, and a plurality of locations may be different. .. In this case, for example, the number of different parts may be different depending on the type of winning combination. For example, if there is one part different from the base image, it is highly likely that BB3 or BB4 is won, and if there are multiple parts different from the base image, there is a possibility that BB1 or BB2 is won. It may be higher. By doing this, it is possible to suggest even the type of bonus combination that has been won.
また、「間違い探し演出」における間違い探しの結果が失敗であったことを報知する場合、例えば、「???」などのメッセージを表示して、間違い探しの結果が失敗であったことを明示しないようにしてもよい。 In addition, when notifying that the result of the error search in the “error search production” was a failure, for example, a message such as “???” is displayed to clearly indicate that the error search result was a failure. You may not.
また、ベース画像を複数種類設けるようにし、例えば、「チャンス目」に当籤した場合、これらの複数種類のベース画像のうちの1つのベース画像を決定し、その後、ボーナス役に当籤しているか否かに応じて、ベース画像のまま表示するか、あるいは、少なくとも一部は異なる部分を有する画像として表示するかが決定されるようにしてもよい。また、この場合、決定されるベース画像の種類に応じて、間違い探しの難易度が異なるようにしてもよい。 In addition, if a plurality of types of base images are provided and, for example, if the "chance eye" is won, one of the plurality of types of base images is determined, and thereafter, whether or not the bonus combination is won. Depending on whether to display the base image as it is, or to display as an image having a different portion at least in part, it may be determined. Further, in this case, the difficulty level for finding an error may be different depending on the type of the determined base image.
このように、本実施形態では、遊技者に有利なボーナス状態に制御可能となる所定の有利条件(例えば、ボーナス役に当籤したこと)が成立したか否かを報知するため、所定の有利条件が成立している場合には、第1特定画像(例えば、ベース画像と一部が異なる画像)が表示され、所定の有利条件が成立していない場合には第2特定画像(例えば、ベース画像と同じ画像)が表示されることが可能となっており、第1特定画像が表示された場合に、遊技者が第2特定画像と異なる部分を指定する操作を行った場合には、所定の有利条件が成立していることを報知する特別画像(例えば、「ボーナス確定!」のメッセージ)が表示されることが可能となっている。 As described above, in the present embodiment, in order to notify whether or not a predetermined advantageous condition (for example, winning a bonus combination) that enables control to a bonus state advantageous to the player is established, the predetermined advantageous condition is given. Is satisfied, the first specific image (for example, an image partially different from the base image) is displayed, and when the predetermined advantageous condition is not satisfied, the second specific image (for example, the base image) is displayed. The same image) can be displayed, and when the player performs an operation of designating a part different from the second specific image when the first specific image is displayed, It is possible to display a special image (for example, a message of "bonus confirmed!") for informing that the advantageous condition is established.
これにより、遊技者の所定の操作も関与させた新規な演出態様によって、所定の有利条件が成立したか否かを報知することができるため、遊技者に有利な状態の移行に関する興趣の向上を図ることができる。 With this, it is possible to inform whether or not the predetermined advantageous condition is satisfied by the new effect mode in which the predetermined operation of the player is also involved, so that the interest for the transition to the advantageous state for the player is improved. Can be planned.
また、本実施形態では、第2特定画像が、遊技機のモチーフとして使用された原作品における所定の画像と同一又は近似の画像となっている。これにより、原作品に愛着のある遊技者は、所定の有利条件が成立したか否かを認識しやすくなるため、遊技意欲を高めることができるとともに、演出に関する興趣をより高めることができる。 Further, in the present embodiment, the second specific image is the same as or similar to the predetermined image in the original work used as the motif of the game machine. As a result, a player who is attached to the original work can easily recognize whether or not a predetermined advantageous condition is established, and thus, it is possible to increase the motivation for the game and further increase the interest in the production.
(ボーナス役当籤報知演出の演出例(その2))
次に、図89及び図90を参照して、ボーナス役当籤報知演出の演出例(その2)について説明する。図89は、例えば、ボーナス役の(同時)当籤を期待させる内部当籤役(例えば、「チャンス目」)が決定された場合に、所定確率で表示装置11に表示され得るボーナス役当籤報知演出の演出例(その2)のタイミングチャートを示し、図90は、ボーナス役当籤報知演出の演出例(その2)の表示例を示している。なお、ボーナス役当籤報知演出の演出例(その2)では、表示装置11によって演出が実行される例を挙げて説明しているが、これに限られず、その他演出装置(例えば、スピーカ群84やLED群85)によって演出が実行されるようにすることもできる。
(Example of a bonus winning combination notification effect (No. 2))
Next, with reference to FIG. 89 and FIG. 90, a description will be given of an example (No. 2) of the bonus winning combination notification effect. FIG. 89 shows a bonus winning combination notification effect that can be displayed on the
図89及び図90に示すように、ボーナス役当籤報知演出の演出例(その2)では、「長押し演出」と題した演出が行われるようになっている。この「長押し演出」は、例えば、第3停止操作における停止操作が、以下に示すような態様で長押しされた場合、長押しされない場合とは異なる演出が行われるようになっているものである。 As shown in FIGS. 89 and 90, in the example of the bonus winning combination notification effect (No. 2), an effect entitled “long press effect” is performed. In this "long press effect", for example, when the stop operation in the third stop operation is long pressed in the following manner, a different effect from that in the case where it is not long pressed is performed. is there.
なお、本実施形態では、「長押し」の対象となる操作手段を、第3停止操作におけるストップボタン(左ストップボタン17L、中ストップボタン17C及び右ストップボタン17Rのいずれか)としているが、これに限られるものではない。例えば、第1停止操作におけるストップボタン(左ストップボタン17L、中ストップボタン17C及び右ストップボタン17Rのいずれか)としてもよいし、第2停止操作におけるストップボタン(左ストップボタン17L、中ストップボタン17C及び右ストップボタン17Rのいずれか)としてもよい。また、停止操作と直接関連しないタイミングで操作されたストップボタンとしてもよい。すなわち、いずれかのストップボタンが操作されたときに、「長押し演出」が行われ得るようにすることができる。
In addition, in the present embodiment, the operation means that is the target of the "long press" is the stop button in the third stop operation (any one of the left stop button 17L, the middle stop button 17C, and the
また、例えば、「長押し」の対象となる操作手段は、ベットボタン(MAXベットボタン15a又は1ベットボタン15b)であってもよいし、スタートレバー16であってもよい。この場合、ベットボタンについて、メダルの投入操作のタイミングで操作されたときを「長押し」の対象とすることもできるし、メダルの投入操作のタイミングとは異なるタイミングで操作されたときを「長押し」の対象とすることもできる。また、この場合、スタートレバー16について、開始操作のタイミングで操作されたときを「長押し」の対象とすることもできるし、開始操作のタイミングとは異なるタイミングで操作されたときを「長押し」の対象とすることもできる。
Further, for example, the operation means that is the target of the “long press” may be the bet button (
また、例えば、「長押し」の対象となる操作手段は、上述した遊技に関する操作を行うための操作手段に限られず、演出に関する操作を行うための操作手段であってもよい。例えば、タッチセンサ19が設けられたサブ表示装置18、上述した少なくとも一部にタッチセンサが設けられた表示装置11、あるいは、上述した物理的操作手段であってもよい。
Further, for example, the operating means that is the target of "long pressing" is not limited to the operating means for performing the above-described game-related operation, and may be an operating means for performing an effect-related operation. For example, it may be the
図89に示すように、例えば、「長押し演出」が実行されることが決定されている場合に、第3停止操作におけるストップボタンの押下が開始され、ストップスイッチがオン状態(オンエッジ)となった状態で3秒間経過したとき(長押し時)、「演出1」が実行され、その後、第3停止操作におけるストップボタンの押下が終了し、ストップスイッチがオフ状態(オフエッジ)となったとき、「演出2」が実行される。すなわち、第3停止操作におけるストップボタンが所定期間(3秒間)長押しされた場合には、「演出1」及び「演出2」が実行される。なお、「演出1」の実行中に、ストップスイッチがオフ状態(オフエッジ)となったときには、中途であっても「演出1」の実行が終了され、「演出2」の実行が開始される。
As shown in FIG. 89, for example, when it is determined that the “long press effect” is to be executed, the pressing of the stop button in the third stop operation is started, and the stop switch is turned on (on edge). When 3 seconds have passed (long press) in this state, "
一方、例えば、「長押し演出」が実行されることが決定されている場合に、第3停止操作におけるストップボタンの押下が開始されたが、ストップスイッチがオン状態(オンエッジ)となった状態で3秒間経過する前に、第3停止操作におけるストップボタンの押下が終了し、ストップスイッチがオフ状態(オフエッジ)となったとき(短押し時)には、「演出1」は実行されず、「演出2」のみが実行される。
On the other hand, for example, when it is determined that the "long press effect" is to be executed, the pressing of the stop button in the third stop operation is started, but the stop switch is in the on state (on edge). Before 3 seconds have elapsed, when the pressing of the stop button in the third stop operation is completed and the stop switch is in the off state (off edge) (short press), "
なお、「長押し演出」の演出パターンは上述したものに限られない。例えば、第3停止操作におけるストップボタンの押下が開始され、ストップスイッチがオン状態(オンエッジ)となった状態で3秒間経過したとき(長押し時)、「演出1」とそれに続いて「演出2」と実行される演出パターンを有していてもよい。すなわち、第3停止操作におけるストップボタンの押下が開始され、ストップスイッチがオン状態(オンエッジ)となった状態で3秒間経過したとき(長押し時)には、ストップスイッチがオフ状態(オフエッジ)となるか否かにかかわらず、「演出1」及び「演出2」が実行される演出パターンを有していてもよい。また、例えば、第3停止操作におけるストップボタンの押下が開始され、ストップスイッチがオン状態(オンエッジ)となった状態で3秒間経過したとき(長押し時)、「演出2」のみが実行される演出パターンを有していてもよい。
The effect pattern of "long press effect" is not limited to the one described above. For example, when pressing the stop button in the third stop operation is started and the stop switch is in the on state (on edge) for 3 seconds (long press), "
また、例えば、第3停止操作におけるストップボタンの押下が開始されたが、ストップスイッチがオン状態(オンエッジ)となった状態で3秒間経過する前に、第3停止操作におけるストップボタンの押下が終了し、ストップスイッチがオフ状態(オフエッジ)となったとき(短押し時)、「演出1」とそれに続いて「演出2」と実行される演出パターンを有していてもよい。すなわち、ストップスイッチがオン状態(オンエッジ)となった状態で3秒間経過する前であっても、ストップスイッチがオフ状態(オフエッジ)となった場合には、「演出1」及び「演出2」が実行される演出パターンを有していてもよい。また、例えば、ストップスイッチがオン状態(オンエッジ)となった状態で3秒間経過する前であっても、ストップスイッチがオフ状態(オフエッジ)となった場合には、「演出1」のみが実行される演出パターンを有していてもよい。
Further, for example, although the pressing of the stop button in the third stop operation is started, the pressing of the stop button in the third stop operation ends before 3 seconds elapse with the stop switch in the on state (on edge). However, when the stop switch is in the off state (off edge) (short press), there may be an effect pattern that is executed as "
なお、このように複数の演出パターンを有する場合には、例えば、ボーナス役に当籤しているか否かによって異なる選択確率で、これらの複数の演出パターンのうちいずれかの演出パターンが選択されるようにすればよい。また、このような場合、第3停止操作におけるストップボタンの押下が開始され、ストップスイッチがオン状態(オンエッジ)となった状態で3秒間経過したときであっても、「演出2」が既に実行されている場合には、「演出1」は実行されないようにすればよい。
When a plurality of effect patterns are provided in this way, for example, one of these effect patterns is selected with different selection probabilities depending on whether or not the bonus combination is won. You can do this. Further, in such a case, even when the stop button is started to be pressed in the third stop operation and the stop switch is in the on state (on edge) for 3 seconds, the “
図89に示した「演出1」及び「演出2」が実行される態様の一例を、図90を参照しながら説明する。なお、図90では、ボーナス役に当籤している場合の、長押し時及び短押し時それぞれの表示例について説明する。
An example of a mode in which the “
まず、「長押し演出」が実行されることが決定されている場合、まず、少なくとも第3停止操作の停止操作が行われる前の所定のタイミングで、例えば、「押し続けて〜」といったようなメッセージが表示され、第3停止操作の停止操作時においてはストップボタンを長押しすべきであることを促す演出が実行される。 First, when it is determined that the "long press effect" is to be executed, first, at least at a predetermined timing before the stop operation of the third stop operation is performed, such as "hold and hold ~" A message is displayed, and an effect is urged that the stop button should be held down during the stop operation of the third stop operation.
その後、第3停止操作の停止操作時において、遊技者がストップボタンを3秒以上押下し続けた場合には、例えば、「STEP1」〜「STEP3」といったような表示が順次行われる「演出1」が実行される。そして、遊技者がストックボタンの押下を終了させた場合には、例えば、「WIN!」といった表示によりボーナス役に当籤していることを報知するための「演出2」が実行される。なお、ボーナス役に当籤していない場合には、「演出2」において、ボーナス役に当籤していないことが報知される、例えば、「LOSE」といった表示がなされるようにすればよい。また、「演出1」では、例えば、ボーナス役に当籤していることの期待度が報知されるようにすればよい。この場合、例えば、「STEP1」まで表示される演出パターンと、「STEP2」まで表示される演出パターンと、「STEP3」まで表示される演出パターンと、を有し、ボーナス役に当籤している場合には、「STEP3」まで表示される演出パターンが選択されやすく、ボーナス役に当籤していない場合には、「STEP3」まで表示される演出パターンが選択されにくくすればよい。このようにすれば、長押しにすることによってボーナス役に当籤している期待度が報知されるようになるため、遊技者の操作に応じてその内容が変化する演出に関する興趣をより向上させることができる。
Then, at the time of the stop operation of the third stop operation, if the player continues to press the stop button for 3 seconds or more, for example, "
一方、第3停止操作の停止操作時において、遊技者がストップボタンを3秒以上押下し続けなかった場合には、例えば、上述したようなボーナス役に当籤している期待度が報知される「演出1」は実行されず、ボーナス役に当籤しているか否かが報知される「演出2」のみが実行される。
On the other hand, at the time of the stop operation of the third stop operation, if the player does not continue to press the stop button for 3 seconds or more, for example, the degree of expectation of winning the bonus combination as described above is notified. "
なお、サブCPU201(副制御回路200側)で、ストップボタンの押下時間を認識させる手法は種々の手法を採用することができる。例えば、リール停止制御処理(図72参照)において、有効なストップボタンが押下されたことをストップスイッチが検出する度に、メインCPU101がリール停止コマンドを送信するようにした場合、サブCPU201は、第3停止操作のストップボタンが押下されたことに基づくリール停止コマンドを受信したときに、計時を開始し、計時時間が3秒となった場合には「演出1」を実行し、第3停止操作のストップボタンの押下が終了して、メインCPU101から送信された入賞作動コマンドを受信したときに、「演出2」を実行するようにすればよい。また、サブCPU201は、メインCPU101から送信された無操作コマンドに含まれるストップスイッチのオン状態/オフ状態を示すパラメータに基づいて、「演出1」を実行するか否か、及び「演出2」の実行タイミングの制御を行うようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、メインCPU101(主制御回路90側)では、ストップボタンの押下時間を計時する必要がなくなることから、遊技者の操作に応じてその内容が変化する演出に関する制御負荷を軽減することができる。
It should be noted that various methods can be adopted for the sub CPU 201 (
なお、サブCPU201(副制御回路200側)によって制御される、例えば、上述したタッチパネルや物理的操作手段などに対する操作時間によって「長押し演出」が制御される場合には、サブCPU201は独立して操作手段が操作されている時間を計時し、その計時結果に応じて演出内容を制御することが可能となる。ここで、本実施形態で説明しているような遊技機では、主制御回路90側では容量の制限があるが、副制御回路200側では特段の制限がないのが一般的であるため、少なくともサブCPU201によってこのような演出が制御されるようにすれば、演出に関する制御負荷の軽減を図ることができる。
Note that when the "long press effect" is controlled by the sub CPU 201 (
また、「演出2」を実行する制御が行われるための所定条件は、操作手段への操作が終了したことに限られず、適宜設定することが可能である。例えば、対象となる操作手段とは異なる操作手段に対する操作が行われたことを所定条件とすることもできるし、対象となる操作手段への操作回数が所定回数未満である場合には、「演出1」、「演出2」の順に演出を発生させ、対象となる操作手段への操作回数が所定回数となった場合には、所定条件を成立させ、「演出1」を発生させずに「演出2」を発生させるようにしてもよい。
Further, the predetermined condition for performing the control for executing the "
このように、本実施形態では、特定の操作手段の操作(例えば、オンエッジ)を検出したときに、計時を開始し、当該計時の開始から所定時間(例えば、3秒)が経過した場合に「演出1」を実行する制御を行い、所定条件が成立したとき(例えば、オフエッジを検出したとき)に、「演出2」を実行する制御を行い、計時の開始から所定時間が経過するよりも前に所定条件が成立した場合は、「演出1」を実行する制御を行わないことが可能となっている。
As described above, in the present embodiment, when the operation (for example, the on-edge) of the specific operation unit is detected, the time counting is started, and when a predetermined time (for example, 3 seconds) has elapsed from the start of the time counting, Before performing a control for executing “
これにより、特定の操作手段の操作態様によって演出を変化させる場合であっても、当該演出に関する制御負荷の軽減を図ることができる。 Accordingly, even when the effect is changed according to the operation mode of the specific operation means, it is possible to reduce the control load related to the effect.
(ボーナス役当籤報知演出の演出例(その3))
次に、図91を参照して、ボーナス役当籤報知演出の演出例(その3)について説明する。図90は、例えば、ボーナス役の(同時)当籤を期待させる内部当籤役(例えば、「スイカ2」)が決定された場合であって、ボーナス役にも当籤した場合に、所定確率で表示装置11に表示され得るボーナス役当籤報知演出の演出例(その3)の表示例を示している。なお、ボーナス役当籤報知演出の演出例(その3)では、表示装置11によって演出が実行される例を挙げて説明しているが、これに限られず、その他演出装置(例えば、情報表示器6、LED82、又は指示モニタ(指示表示器))によって演出が実行されるようにすることもできる。
(Example of a bonus winning combination notification effect (No. 3))
Next, with reference to FIG. 91, an example (part 3) of the bonus winning combination notification effect will be described. FIG. 90 shows a display device with a predetermined probability when, for example, an internal winning combination (for example, “
例えば、図91に示す遊技価値表示部(VL)は、表示装置11において、小役が成立した場合にその払出枚数が表示され得る所定の領域(払出枚数表示部)に表示されてもよいし、有利区間であれば有利区間中の払出枚数の累計枚数が表示され得る所定の領域(獲得枚数表示部)に表示されてもよいし、これら払出枚数表示部や獲得枚数表示部とは異なる領域の所定の領域に表示されてもよい。また、上述したように、主制御回路90側で制御される情報表示器6などの7セグ表示器が、当該演出が実行されるときに、遊技価値表示部(VL)として機能するようにすればよい。
For example, the game value display unit (VL) shown in FIG. 91 may be displayed on the
図91に示すように、ボーナス役当籤報知演出の演出例(その3)では、「枚数先表示演出」と題した演出が行われるようになっている。この「枚数先表示演出」は、例えば、ボーナス状態において払い出され得るメダルの枚数(獲得予定枚数)が、ボーナス状態の作動が開始する前に報知されることで、遊技者にボーナス役に当籤したことが報知される演出となっている。 As shown in FIG. 91, in the example of the bonus winning combination notification effect (No. 3), an effect entitled "number-of-firsts display effect" is performed. In this "number-of-numbers display effect", for example, the number of medals that can be paid out in the bonus state (the expected number of medals) is notified before the operation in the bonus state is started, so that the player wins the bonus role. It is a performance that informs you that you have done it.
なお、以下では、「枚数先表示演出」において報知される獲得予定枚数として、役連終了枚数カウンタの値が表示される例を挙げて説明しているが、「枚数先表示演出」において報知される獲得予定枚数の態様はこれに限られない。例えば、BB3状態又はBB4状態において、役連終了枚数カウンタの値は「165」枚であるが、仮にボーナス状態中の毎遊技で全て「15枚」のメダルが払い出されるとしたならば、BB3状態又はBB4状態では「12回」の遊技が行えることになり、実際の払出枚数は「180」枚となる。したがって、この実際の払出枚数である「180」枚を獲得予定回数として表示するようにしてもよい。また、BB3状態又はBB4状態においても、3枚のメダルを投入して遊技を行う必要があるため、役連終了枚数カウンタの値が「165」枚の場合、仮にボーナス状態中の毎遊技で全て「15枚」のメダルが払い出されるとしたならば、毎遊技の純増枚数は「15−3=12枚」となる。したがって、役連終了枚数カウンタの値に合わせたかたちで、純増枚数の累計予定枚数を「12枚」×「11回」=「132」枚とし、この「132」枚を獲得予定回数として表示するようにしてもよい。また、上述したように、実際には「12回」の遊技が行えるため、実際に遊技が行える回数に合わせたかたちで、純増枚数の累計予定枚数を「12枚」×「12回」=「144」枚とし、この「144」枚を獲得予定回数として表示するようにしてもよい。 In the following, an example in which the value of the combination end number counter is displayed as the expected number of sheets to be notified in the "number destination display effect" is described, but it is notified in the "number destination display effect". The mode of the expected number of sheets to be acquired is not limited to this. For example, in the BB3 state or the BB4 state, the value of the combination end number counter is "165", but if all the "15" medals are paid out in each game in the bonus state, the BB3 state Alternatively, in the BB4 state, the game can be played "12 times", and the actual payout number is "180". Therefore, "180", which is the actual payout number, may be displayed as the scheduled acquisition number. Further, even in the BB3 state or the BB4 state, it is necessary to insert three medals to play a game. Therefore, if the value of the combination end number counter is "165", all the games in the bonus state are assumed. If "15" medals are paid out, the net additional number of each game is "15-3=12". Therefore, the cumulative total number of the net increase number is set to “12”ד11 times”=“132” in accordance with the value of the combination end number counter, and this “132” is displayed as the expected number of acquisitions. You may do it. In addition, as described above, since the game can be actually played “12 times”, the cumulative total number of net increase is “12 sheets”ד12 times”=“according to the number of times the game can be actually played”. The number of 144 sheets may be set, and this “144” sheet may be displayed as the scheduled acquisition number.
また、本実施形態では、BB1〜BB4状態において、押し順小役が当籤するようになっているため、この押し順小役の当籤時に押し順が正解したか否かによって遊技毎に払い出されるメダルの枚数も変動する(「15枚」又は「6枚」。図23参照)ようになっている。また、非有利区間及び通常有利区間においてボーナス役に当籤した場合には、当該ボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態においては押し順報知は行われず、有利区間においてボーナス役に当籤した場合には、当該ボーナス役に基づくボーナス状態においては押し順報知が行われるようになっている。 In addition, in the present embodiment, in the BB1 to BB4 states, since the push order small winning combination is won, the medals to be paid out for each game depending on whether or not the pushing order is correct when the push order small winning combination is won. The number of sheets also changes ("15 sheets" or "6 sheets", see FIG. 23). In addition, when the bonus combination is won in the non-advantageous section and the normal advantageous section, the pushing order is not notified in the bonus state based on the bonus combination, and when the bonus combination is won in the advantageous section, the bonus combination is won. In the bonus state based on, the push order notification is performed.
したがって、例えば、有利区間においてボーナス役(例えば、「F_BB3」)に当籤した場合には、上述した「144」枚(投入枚数を考慮しない場合には、「180」枚)を獲得予定回数として表示し、非有利区間及び通常有利区間においてボーナス役(例えば、「F_BB3」)に当籤した場合であって、ボーナス状態において押し順報知が行われない場合に「15枚」のメダルが払い出される確率を仮に50%とした場合には、(「12枚」×「8回」=96枚)+(「3枚」×「8回」=24枚)=「120」枚(投入枚数を考慮しない場合には、(「15枚」×「8回」=120枚)+(「6枚」×「8回」=48枚)=「168」枚)を獲得予定枚数として表示するようにしてもよい。すなわち、「枚数先表示演出」において報知される獲得予定枚数は、ボーナス状態における払出枚数(あるいは、純増枚数)の期待値であってもよい。 Therefore, for example, when a bonus combination (for example, “F_BB3”) is won in the advantageous section, the above-mentioned “144” sheets (“180” sheets when the number of thrown-in sheets is not considered) are displayed as the expected number of times of acquisition. However, when a bonus combination (for example, “F_BB3”) is won in the non-advantageous section and the normal advantageous section, and the probability that “15 coins” will be paid out when the push order notification is not performed in the bonus state, If it is set to 50%, ("12 sheets" x "8 times" = 96 sheets) + ("3 sheets" x "8 times" = 24 sheets) = "120" sheets (when the number of inserted sheets is not considered May be displayed as (15 sheets)ד8 times”=120 sheets+(“6 sheets”ד8 times”=48 sheets)=“168” sheets” as the planned acquisition number. .. That is, the expected number of coins to be notified in the "number of coins display effect" may be an expected value of the number of coins to be paid out (or a net increase in coins) in the bonus state.
図91に示すように、例えば、ボーナス役を含む所定の内部当籤役(例えば、「F_BB3+F_スイカ2」)が決定された場合であって、「枚数先表示演出」が実行されることが決定されている場合には、全てのリールの回転が停止するとき(すなわち、第3停止後)に、遊技価値表示部(VL)には獲得予定枚数「165」が表示される。これによって、遊技者に、ボーナス役(図91に示す例では、「F_BB3」又は「F_BB4」)に当籤したことが報知される。なお、本実施形態では、ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せよりも小役やリプレイ役に係る図柄の組合せが優先的に停止制御されるため、基本的に、このボーナス役に当籤した遊技(ボーナス役当籤ゲーム)では、小役やリプレイ役に係る図柄の組合せ(図91に示す例では、「C_スイカ」)が表示され、ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せ(図91に示す例では、「C_赤異色BB」)は表示されない。もっとも、ボーナス役当籤ゲームにおいて、ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せが表示され得るようにすることもできるが、この場合には、「枚数先表示演出」が実行されないようにしてもよいし、後述するように、遊技価値表示部(VL)を、ボーナス状態において払い出され得るメダルの残り枚数(あるいは、実際に払い出されたメダルの枚数そのもの)を表示するものとして、「枚数先表示演出」が実行されるようにすることもできる。
As shown in FIG. 91, for example, when a predetermined internal winning combination including a bonus combination (for example, “F_BB3+
その後、ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せが表示されるまで(ボーナス役成立まで)、この遊技価値表示部(VL)における獲得予定枚数「165」の表示は継続される。そして、ボーナス状態の作動が開始されてもこの遊技価値表示部(VL)における獲得予定枚数「165」の表示は継続し、例えば、ボーナス状態において小役に係る図柄の組合せ(図91に示す例では、「ベル+JACA:15枚」)が表示されると(ボーナス状態中入賞発生)、この遊技価値表示部(VL)において表示されている枚数が適宜減算更新されて表示されるようになる。すなわち、遊技価値表示部(VL)は、ボーナス状態が開始される前には、ボーナス状態において払い出され得るメダルの予定枚数を表示し、ボーナス状態においては、実際に払い出されたメダルの枚数に応じて、ボーナス状態において払い出され得るメダルの残り枚数(あるいは、実際に払い出されたメダルの枚数そのもの)を表示するものとなっている。 After that, until the combination of symbols related to the bonus combination is displayed (until the bonus combination is established), the display of the planned acquisition number “165” on the game value display unit (VL) is continued. Then, even when the operation of the bonus state is started, the display of the expected number of purchases “165” on the game value display portion (VL) continues, and for example, the combination of symbols relating to the small winning combination in the bonus state (the example shown in FIG. 91). Then, when "Bell+JACA: 15" is displayed (the winning in the bonus state occurs), the number displayed on the game value display unit (VL) is appropriately subtracted and updated to be displayed. That is, the game value display unit (VL) displays the expected number of medals that can be paid out in the bonus state before the bonus state is started, and in the bonus state, the number of medals actually paid out. In accordance with the above, the remaining number of medals that can be paid out in the bonus state (or the actual number of medals actually paid out) is displayed.
なお、本実施形態では、ボーナス役に当籤したときに、有利区間に移行することが決定される場合があるようになっている。したがって、例えば、ボーナス役に当籤したときに、有利区間に移行することが決定された場合には、この有利区間における獲得予定枚数(概ねの期待値であればよい。例えば、ラインバトル状態が平均40ゲーム継続するものであり、ラインバトル状態では1ゲーム平均1枚のメダルが純増するものであれば、「40」枚)をボーナス状態の獲得予定枚数に付加して(加算して)、遊技価値表示部(VL)に表示するようにしてもよい。 In the present embodiment, when the bonus combination is won, it may be decided to shift to the advantageous section. Therefore, for example, when it is determined to shift to the advantageous section when the bonus combination is won, the expected number of sheets to be acquired in this advantageous section (a general expected value is sufficient. If 40 games continue, and if one game averages 1 medals net increase in the line battle state, "40" pieces are added to the bonus number to be acquired (added), and the game is played. You may make it display on a value display part (VL).
このように、本実施形態では、有利状態(例えば、ボーナス状態)の発生を許容する権利が付与する旨が決定された(例えば、ボーナス役に当籤した)場合に、当該決定がされたことを報知する特定報知演出(例えば、「枚数先表示演出」)を実行可能であり、この特定報知演出では、付与することが決定された権利に基づいて発生する有利状態において獲得し得る遊技価値に関する所定値(例えば、獲得予定枚数としての役連終了枚数カウンタの値)を表示することが可能となっている。 As described above, in the present embodiment, when it is determined that the right to allow the generation of the advantageous state (for example, the bonus state) is given (for example, the bonus combination is won), the determination is made. It is possible to execute a specific notification effect to be notified (for example, “number-first display effect”), and in this specific notification effect, a predetermined value related to a game value that can be acquired in an advantageous state that is generated based on the right that is decided to be granted. It is possible to display the value (for example, the value of the combination end number counter as the expected acquisition number).
これにより、遊技者が得た権利(当籤内容)の価値を具体的に報知する演出を行うことができるため、演出に関する興趣を高めるとともに、遊技に関する興趣を高めることができる。 As a result, since it is possible to perform an effect that specifically notifies the value of the right (winning content) obtained by the player, it is possible to increase the interest in the effect and the interest in the game.
また、本実施形態では、特定報知演出において所定値を表示した場合、少なくともその後の有利状態の発生まで所定値の表示を継続し、有利状態において遊技価値が獲得された場合に、当該獲得された遊技価値の値に基づいて、所定値の表示を更新するようになっている。 Further, in the present embodiment, when the predetermined value is displayed in the specific notification effect, the display of the predetermined value is continued at least until the occurrence of the advantageous state thereafter, and when the game value is obtained in the advantageous state, it is acquired. The display of the predetermined value is updated based on the value of the game value.
これにより、有利状態の発生の前後において、価値を報知するための一連の演出を適切に行うことができるため、さらに演出に関する興趣を高めることができる。 With this, a series of effects for notifying the value can be appropriately performed before and after the occurrence of the advantageous state, so that interest in the effects can be further enhanced.
<変形例等>
以上、本実施形態に係る発明の遊技機の構成及び動作について、その作用効果も含めて説明した。しかしながら、本実施形態に係る発明は、上述した実施形態に限定されるものではなく、本実施形態に係る発明の要旨を逸脱しない限り、種々の変形を行うことができる。
<Modifications, etc.>
Heretofore, the configuration and operation of the gaming machine of the invention according to the present embodiment have been described, including the operational effects thereof. However, the invention according to this embodiment is not limited to the above-described embodiment, and various modifications can be made without departing from the gist of the invention according to this embodiment.
[変形例]
本実施形態では、少なくとも非有利区間において、各設定値間で異なる当籤確率となっている「F_BB3+F_スイカ2」及び「F_BB4+F_スイカ2」が当籤した場合には、有利区間に移行させるか否かを決定しない(ART抽籤を行わない)ようになっていたが、各設定値間で異なる当籤確率となっている「F_BB3+F_スイカ2」及び「F_BB4+F_スイカ2」が当籤した場合にも、各設定値間で同じ当籤確率となっているボーナス役を含むその他の内部当籤役と同様に、有利区間に移行させるか否かを決定する(ART抽籤を行う)ようにしてもよい。この場合、ART抽籤において、有利区間に移行させることが決定される確率は、各設定値間で同じ当籤確率となるようにすればよい。すなわち、各設定値間で異なる当籤確率となっているボーナス役を規定することで、各設定値間で、有利区間に移行させることが決定される確率が変動されるようにしてもよい。
[Modification]
In the present embodiment, at least in the non-advantageous section, when "F_BB3+
また、本実施形態では、通常有利区間においても遊技者に有利な停止操作の情報が報知され得るようになっているが、通常有利区間は、有利区間に移行させるか否かが決定される確率は非有利区間よりも優遇されているが、遊技者に有利な停止操作の情報は報知されない区間として構成することもできる。この場合には、非有利区間から通常有利区間に移行した場合に、状態表示器の点灯を開始させず、有利区間に移行した場合にのみ、状態表示器の点灯が開始されるようにすればよい。 Further, in the present embodiment, the information of the stop operation advantageous to the player can be notified even in the normal advantage section, but the probability that the normal advantage section is determined to shift to the advantage section is determined. Is favored over the non-advantageous section, but it may be configured as a section in which the information of the stop operation advantageous to the player is not notified. In this case, when the non-advantageous section is shifted to the normal advantageous section, the state indicator is not started to be lit, and the lighting of the state indicator is started only when it is shifted to the advantageous section. Good.
なお、遊技者に有利な停止操作の情報が報知されるか否かにかかわらず、通常有利区間は、全体として遊技者のメダルが減少する期間(すなわち、出玉率が「1」未満となる期間)であればよく、有利区間は、全体として遊技者のメダルが増加する期間(すなわち、出玉率が「1」を上回る期間)であればよい。また、有利区間において、一部遊技者のメダルが減少する期間(例えば、上述した各準備状態)があるとしても、当該期間は有利区間に含まれるようにすればよい。 It should be noted that the normal advantageous section is a period in which the player's medals are reduced as a whole (that is, the payout rate is less than “1”), regardless of whether or not the information of the advantageous stop operation is notified to the player. Period), and the advantageous section may be a period in which the medals of the player increase as a whole (that is, a period in which the payout rate exceeds "1"). Further, even if there is a period (for example, each of the above-mentioned preparation states) in which the medals of some players decrease in the advantageous section, the period may be included in the advantageous section.
すなわち、遊技の区間を、非有利区間と有利区間とに大別する場合、有利区間は、遊技者の期待感を高めるが出玉の増加は見込めない演出区間(例えば、本実施形態の「通常有利区間」)と、実際に出玉の増加が見込める増加区間(例えば、本実施形態の「有利区間」)と、を含んで構成されるようにしてもよい。 That is, when the game section is roughly divided into a non-advantageous section and an advantageous section, the advantageous section enhances the player's expectation, but cannot expect an increase in the number of balls (for example, "normal It may be configured to include an "advantageous section") and an increase section (for example, the "advantageous section" of the present embodiment) in which an increase in the number of payouts is actually expected.
また、本実施形態では、例えば、有利区間中のRT2状態において、押し順報知が行われたにもかかわらず、遊技者の押し順ミスによってRT1状態に移行(転落)してしまった場合にも、有利区間の遊技期間は進行する(更新される)ものとしているが、この場合には、RT2状態に移行(復帰)するまで、有利区間の遊技期間は進行しない(更新されない)ようにすることもできる。また、この場合、例えば、RT1状態に転落してからRT2状態に復帰するまでに要したゲーム数のうちの一部(例えば、RT1状態に転落してからRT2状態に復帰するまでに要したゲーム数が10ゲームである場合、1/2の5ゲーム分。あるいは、RT1状態に転落してからRT2状態に復帰するまでに要したゲーム数にかかわらず一律2ゲーム分)のみ、有利区間の遊技期間を進行させる(更新する)ようにしてもよい。 Further, in the present embodiment, for example, in the RT2 state during the advantageous section, even if the push order is informed, the player shifts (falls) to the RT1 state due to a mistake in the push order. , It is supposed that the game period of the advantageous section progresses (is updated), but in this case, the game period of the advantageous section does not progress (is not updated) until it shifts (returns) to the RT2 state. Can also Further, in this case, for example, a part of the number of games required from the fall to the RT1 state to the return to the RT2 state (for example, the game required to fall from the RT1 state to the RT2 state) If the number of games is 10, the game is 1/2 of 5 games, or 2 games are uniformly played regardless of the number of games required from returning to RT1 state to returning to RT2 state). The period may be advanced (updated).
また、本実施形態では、例えば、「チャンス目」が内部当籤役として決定された場合、直接的には有利区間に移行させるか否かを決定しない(ART抽籤を行わない)ようになっていたが、ART抽籤が行われる内部当籤役や条件は、適宜変形して設定することができる。例えば、「チャンス目」が内部当籤役として決定された場合、「チャンス役」が成立した場合にはART抽籤を行わず、「チャンス役」を取りこぼして「RT3移行目」が成立した場合(この場合、RT3状態に移行するか否かを問わない)にはART抽籤が行われるようにしてもよい。すなわち、特定の内部当籤役が当籤したときに、入賞が発生した場合にはART抽籤を行わず、取りこぼして入賞が発生しなかった場合にはART抽籤が行われるようにしてもよい。 Further, in the present embodiment, for example, when the “chance eye” is determined as the internal winning combination, it is not directly determined whether or not to shift to the advantageous section (the ART lottery is not performed). However, the internal winning combination and the condition for performing the ART lottery can be appropriately modified and set. For example, when the “chance eye” is determined as the internal winning combination, the ART lottery is not performed when the “chance hand” is established, but the “chance hand” is dropped and the “RT3 transition eye” is established (this In this case, ART lottery may be performed regardless of whether the RT3 state is entered or not. That is, when a specific internal winning combination is won, the ART lottery may not be performed when a winning is generated, and the ART lottery may be performed when a winning is not generated due to being missed.
また、例えば、メダルの投入枚数(例えば、3枚)以下のメダルの払い出しとなる小役が高確率で内部当籤役として決定され、フラグ間状態では原則としてボーナス役が成立しないようにし、遊技の基本的な遊技状態をフラグ間状態として遊技を行わせるような仕様を採用することもできる。また、この場合、ボーナス状態は、獲得しているメダルが減少、あるいは維持される状態として構成するようにしてもよい。 In addition, for example, a small winning combination that pays out medals equal to or less than the number of inserted medals (for example, 3) is determined as an internal winning combination with a high probability, and as a general rule, a bonus winning combination is not established in a state between flags, and It is also possible to adopt a specification in which a basic game state is set as a state between flags to allow a game to be played. Further, in this case, the bonus state may be configured such that the acquired medals are reduced or maintained.
また、本実施形態では、規制監視期間に対応する遊技回数が「1500回」に設定されていたが、規制監視期間に対応する遊技回数はそれ以下であってもよいし、それ以上であってもよい。また、遊技の状況に応じて、規制監視期間を変動させるようにしてもよい。例えば、規制監視期間をメダルの純増枚数(あるいは、払出枚数)によって定めるようにし、遊技店の所定の営業日中に、所定のパチスロ1において、純減枚数(すなわち、遊技者がメダルを投入したが、払い出しによって遊技者に還元されなかった、遊技店側の利益となるメダルの枚数)(あるいは、単に投入枚数)が「500枚」であれば、予め定められた規制監視期間に対応するメダルの枚数「1500枚」にその「500枚」を加算し、一連の有利区間において「2000枚」のメダルを獲得するまでは、当該有利区間が強制的に終了させないようにすることもできる。
Further, in the present embodiment, the number of games corresponding to the regulation monitoring period is set to "1500 times", but the number of games corresponding to the regulation monitoring period may be less than or more than that. Good. Further, the regulation monitoring period may be changed according to the game situation. For example, the regulation monitoring period is determined by the net increase number (or payout number) of medals, and the net decrease number (that is, the player inserts the medals) in a predetermined pachi-
[本実施形態で実装可能な遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例]
続いて、図92〜図120を参照して、本実施形態に係るパチスロ1において実装可能な遊技性(すなわち、遊技仕様)の他の例について説明する。本実施形態では、遊技状態として、ボーナスが作動することで遊技者に有利な遊技期間となるボーナス状態(特別遊技状態)、及び当該ボーナス状態でないことで相対的に遊技者に不利な遊技期間となる非ボーナス状態(通常遊技状態)があり、さらに、当該非ボーナス状態の中でも再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率が異なる複数のRT状態があることで遊技者の有利度合いを変動させることについて説明した(図13参照)。また、本実施形態では、遊技区間として、遊技者に停止操作の情報が報知されることで遊技者に有利な遊技区間となる有利区間(有利状態)、及び当該有利区間でないことで相対的に遊技者に不利な遊技区間となる非有利区間(通常状態)があることについて説明した(図14参照)。そして、これらの遊技状態や遊技区間の開始・継続・終了などの各種の条件やその内容については種々の変形を行うことが可能である。なお、特に示す場合を除き、以下に示す遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その1〜その13)では、本実施形態における、遊技状態、遊技区間、内部当籤役、図柄の組合せなどの遊技要素を適宜用いることができる。
[Another example of playability (game specification) mountable in the present embodiment]
Next, with reference to FIG. 92 to FIG. 120, another example of the playability (that is, game specification) that can be implemented in the pachi-
[遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その1)]
まず、図92及び図93を参照して、本実施形態に係るパチスロ1において実装可能な遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その1)について説明する。図92は、遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その1)における遊技の流れを概念的に説明する図であり、図93は、遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その1)における遊技価値の付与期待値の一例を示す図である。
[Another example of playability (game specification) (1)]
First, with reference to FIG. 92 and FIG. 93, another example (No. 1) of the playability (game specification) that can be mounted in the pachi-
図92及び図93に示すように、遊技者は通常、(A)非有利区間から遊技を開始する。(A)非有利区間では、遊技者に停止操作の情報が報知されないことに起因して遊技価値量は減少していくことになる。すなわち、有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値(傾斜値)は負の値となり、下り傾斜となる。 As shown in FIGS. 92 and 93, the player usually starts the game from the (A) non-advantageous section. (A) In the non-advantageous section, the game value amount is decreased due to the fact that the player is not notified of the stop operation information. That is, the expected value-added value (gradient value) of the game value per unit game in the advantageous state becomes a negative value and becomes a downward slope.
(A)非有利区間において、(1)有利区間の開始条件が成立すると、(A)非有利区間から(B)有利区間に移行する。(B)有利区間では、遊技者に停止操作の情報が報知されることに起因して遊技価値量は増加していく(少なくとも減少していかない)ことになる。すなわち、有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値(傾斜値)は正の値となり(少なくとも負の値とならず)、上り傾斜となる(少なくとも下り傾斜とはならない)。なお、説明の便宜上、本例では準備状態などにおける付与期待値やボーナス状態における付与期待値は考慮していない。 In the (A) non-advantageous section, when (1) the start condition of the advantageous section is satisfied, the (A) non-advantageous section is shifted to the (B) advantageous section. (B) In the advantageous section, the game value amount increases (at least does not decrease) due to the fact that the player is informed of the stop operation information. That is, the expected value (gradient value) of the gaming value per unit game in the advantageous state becomes a positive value (at least not a negative value) and becomes an upward slope (not at least a downward slope). It should be noted that, for convenience of explanation, in this example, the expected grant value in the ready state and the expected grant value in the bonus state are not considered.
なお、付与期待値は、以下のように算出(設計)することができる。例えば、押し順(例えば、5択)正解だと15枚のメダルの払い出しがあり、押し順(例えば、5択)不正解だとメダルの払い出しがない押し順小役の当籤確率が1/2(32768/65536)である場合であって、原則1回の遊技に3枚のメダルをベットすることが必要である場合、10回の遊技の間に必要なメダルは30枚となる。そして、(A)非有利区間である場合、10回の遊技の間に押し順小役に当籤したときに押し順正解となって15枚のメダルの払い出しを受けることができるのは1/10(1/2×1/5)であることから、確率通りであれば、10回の遊技の間でメダルの量が−15枚(15−30)となるため、付与期待値は1回の遊技あたり「−1.5枚」となる。一方、(B)有利区間である場合、押し順小役について全て停止操作の情報が報知されて遊技者がそれにしたがって停止操作を行えば、10回の遊技の間に押し順小役に当籤したときに押し順正解となって15枚のメダルの払い出しを受けることができるのは1/2であることから、確率通りであれば、10回の遊技の間でメダルの量が+45枚(75−30)となるため、付与期待値は1回の遊技あたり「+4.5枚」となる。もっとも、これらは説明の便宜上の一例であり、リプレイ役の当籤確率やボーナス役の当籤確率(及びボーナス状態中の付与期待値)も加味して、付与期待値を算出(設計)することも可能である。 Note that the expected value to be given can be calculated (designed) as follows. For example, if the pushing order (for example, 5 choices) is correct, 15 medals are paid out, and if the pushing order (for example, 5 choices) is incorrect, no medals are paid out. In the case of (32768/65536) and it is necessary to bet three medals for one game in principle, 30 medals are required for ten games. In the case of (A) non-advantageous section, when the player wins the push order small win during 10 games, the push order becomes the correct answer and the payout of 15 medals is 1/10. Since it is (1/2×1/5), if the probability is met, the amount of medals will be -15 (15-30) during 10 games, so the expected value of grant is 1 time. It becomes "-1.5 pieces" per game. On the other hand, in the case of (B) advantageous section, if the information of the stop operation is notified for all the push order small wins and the player performs the stop operation accordingly, the push order small win is won during 10 games. Since it is 1/2 that the player can receive the payout of 15 medals at the correct pressing order, if the probability is the same, the amount of medals will be +45 (75 Since it is -30), the expected value of grant is "+4.5" per game. However, these are examples for convenience of explanation, and it is also possible to calculate (design) the expected grant value by taking into consideration the winning probability of the replay role and the winning probability of the bonus role (and expected grant value in the bonus state). Is.
本例では、(B)有利区間において、有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値(傾斜値)が第1の期待値(期待値α)となる(B−1)有利区間1と、有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値(傾斜値)が第1の期待値(期待値α)とは異なる第2の期待値(期待値β)となる(B−2)有利区間2と、が設けられ、(2)期待値変動条件が成立すると、(B−1)有利区間1から(B−2)有利区間2に移行する。なお、本例では、(1)有利区間の開始条件が成立すると、まず(A)非有利区間から(B−1)有利区間1に移行し、(B−1)有利区間1において(2)期待値変動条件が成立すると、(B−2)有利区間2に移行するようにしているが、これに限られず、例えば、(1)有利区間の開始条件が成立すると、まず(A)非有利区間から(B−2)有利区間2に移行し、(B−2)有利区間2において(2)期待値変動条件が成立すると、(B−1)有利区間2に移行するようにしてもよい。
In this example, the expected value (gradient value) of the game value per unit game in the advantageous state becomes the first expected value (expected value α) in the advantageous section (B) (B-1)
また、例えば、(1)有利区間の開始条件が成立したときに、(B−1)有利区間1又は(B−2)有利区間2のいずれに移行させるかを決定するようにしてもよいし、(1)有利区間の開始条件について、(B−1)有利区間1の開始条件(1−1)と、(B−2)有利区間2の開始条件(1−2)とをそれぞれ定め、(A)非有利区間において、いずれの開始条件(1−1又は1−2)が成立したかに応じて、(B−1)有利区間1又は(B−2)有利区間2に移行させるようにしてもよい。
In addition, for example, when the condition for starting (1) the advantageous section is satisfied, it may be determined which of (B-1) the
そして、(B)有利区間((B−1)有利区間1及び(B−2)有利区間2)において、(3)有利区間の終了条件が成立すると、(B)有利区間から(A)非有利区間に移行する(すなわち、有利区間が終了する)。本例では、このようにして(A)非有利区間及び(B)有利区間の移行制御がなされるものとしている。
Then, in (B) the advantageous section ((B-1) the
ここで、本例では、(B−1)有利区間1中の期待値αが、(B−2)有利区間2中の期待値βよりも大きくなるように構成される(すなわち、(B−2)有利区間2中の期待値βが、(B−1)有利区間1中の期待値αよりも小さくなるように構成される)。具体的には、例えば上述の例を用いた場合、(B−1)有利区間1においては押し順小役の当籤時に停止操作の情報が報知される確率(報知確率)を100%(すなわち、5回の当籤中5回報知)とすることで、期待値αは「+4.5枚」とする一方、(B−2)有利区間2においては押し順小役の当籤時に停止操作の情報が報知される確率(報知確率)を40%(すなわち、5回の当籤中2回報知)とすることで、期待値βは「+−0枚」とする。
Here, in this example, the expected value α in the (B-1)
なお、この期待値α及び期待値βは任意に設定することができる。例えば、(B−1)有利区間1が、少なくとも(A)非有利区間よりも遊技者にとって有利な有利状態となっているのであれば、有利区間1における報知確率を1〜100%のうちの任意の報知確率に設定可能である。また、例えば、(B−2)有利区間2が、少なくとも(A)非有利区間よりも遊技者にとって有利な有利状態となっており、(B−1)有利区間1よりも低い報知確率となっているのであれば、有利区間2における報知確率を1〜100%のうちの任意の報知確率に設定可能である。
The expected value α and the expected value β can be set arbitrarily. For example, if (B-1) the
また、有利区間1における報知確率及び有利区間2における報知確率のそれぞれは、予め定められた確率であってもよいし、遊技価値の付与状況に応じて変動するものであってもよい。例えば、期待値α及び期待値βが、それぞれ「+3.0枚」及び「+1.0枚」と設定されている場合に、(B−1)有利区間1及び(B−2)有利区間2のそれぞれにおいて、所定の遊技回数(例えば、10回)ごとに付与期待値を算出し、算出された付与期待値が、それぞれの期待値α及び期待値βよりも所定の閾値(例えば、プラスマイナス1枚)を超えて乖離していた場合には、その後の遊技において適宜報知確率を変動させるようにして、(B−1)有利区間1及び(B−2)有利区間2のそれぞれの期間における最終的な付与期待値が、期待値α及び期待値βとなる(に近似する)ようにすればよい。
Further, each of the notification probability in the
また、この期待値α及び期待値βの設定手法も上述した報知確率を変動させる手法に限られない。例えば、(B−1)有利区間1をリプレイ役の当籤確率の高い状態(高RT状態)とし、(B−2)有利区間2をリプレイ役の当籤確率の低い状態(低RT状態)とし、リプレイ役の当籤確率(入賞確率)を異ならせることで、期待値βが期待値αよりも小さくなるように設定してもよい(この場合、付与期待値はリプレイ役の当籤確率が加味される。また、報知確率は変動させてもよいし、変動させなくともよい)。すなわち、(B−1)有利区間1と(B−2)有利区間2とを異なるRT状態に制御することで、期待値α及び期待値βを変動させるようにしてもよい。
Further, the method of setting the expected value α and the expected value β is not limited to the method of changing the notification probability described above. For example, (B-1)
また、例えば、(B−1)有利区間1をボーナス(ボーナス状態)が作動することを困難としない状態とし、(B−2)有利区間2をボーナスが作動することを困難とする状態とし、ボーナスの作動確率(入賞確率)を異ならせることで、期待値βが期待値αよりも小さくなるように設定してもよい(この場合、付与期待値はボーナスの作動確率及びボーナス状態中の付与期待値が加味される。また、報知確率は変動させてもよいし、変動させなくともよい)。すなわち、ボーナスの作動に関し、(B−1)有利区間1と(B−2)有利区間2とを異なる制御状態に制御することで、期待値α及び期待値βを変動させるようにしてもよい。なお、ボーナスが作動することを困難としない状態、あるいは困難とする状態は、内部当籤役(持越役を含む)の種別、遊技状態の種別、それらに応じた停止制御の制御内容、あるいは停止操作の情報の報知内容などを複合的に加味して適宜創出することができる(一例は、後述の図94〜図99の説明を参照)。
Further, for example, (B-1) the
また、例えば、上述の例の押し順小役について、所定の態様で停止操作が行われた場合には15枚のメダルが払い出され、上記所定の態様とは異なる特定の態様で停止操作が行われた場合には6枚のメダルが払い出されるものとし、(B−1)有利区間1において押し順小役が当籤したときには上記所定の態様を示す停止操作の情報が報知されるものとし、(B−2)有利区間2において押し順小役が当籤したときには上記特定の態様を示す停止操作の情報が報知されるものとし、払出枚数を異ならせることで、期待値βが期待値αよりも小さくなるように設定してもよい(この場合、報知確率は変動させてもよいし、変動させなくともよい)。
Further, for example, in the case of the pressing order small winning combination of the above example, when the stop operation is performed in a predetermined mode, 15 medals are paid out, and the stop operation is performed in a specific mode different from the predetermined mode. If it is performed, 6 medals shall be paid out, and (B-1) When the pushing order small winning combination is won in the
また、例えば、上述の例の押し順小役を複数種類(例えば、押し順小役Aと押し順小役B)設けるようにし、押し順小役Bの当籤確率は押し順小役Aの当籤確率よりも低く設定されるようにし、(B−1)有利区間1において押し順小役Aが当籤したときには停止操作の情報が報知される一方、押し順小役Bが当籤したときには停止操作の情報が報知されず(もっとも、停止操作の情報が報知されるようにしてもよい)、(B−2)有利区間2において押し順小役Bが当籤したときには停止操作の情報が報知される一方、押し順小役Aが当籤したときには停止操作の情報が報知されないようにして、期待値βが期待値αよりも小さくなるように設定してもよい。すなわち、(B−1)有利区間1と(B−2)有利区間2とで報知対象役を異ならせることで、期待値α及び期待値βを変動させるようにしてもよい。なお、押し順小役Aと押し順小役Bの当籤確率は同一(あるいは略同一)であるが、押し順正解時の払出枚数を、上述の如く15枚と6枚のように異ならせることで、期待値α及び期待値βを変動させるようにしてもよい。
Further, for example, a plurality of types of the pushing order small winning combination of the above example (for example, the pushing order small winning combination A and the pushing order small winning combination B) are provided, and the winning probability of the pushing order small winning combination B is the winning of the pushing order small winning combination A. (B-1) When the push order small winning combination A is won in the
また、例えば、内部当籤役として、押し順小役(例えば、6択)と押し順リプレイ(例えば、6択)とを有するとともに、遊技状態として、高RT状態と低RT状態とを有し、押し順リプレイに当籤したときに、押し順正解である場合には、低RT状態であれば高RT状態に移行し、高RT状態であれば高RT状態が維持される図柄の組合せが表示される一方、押し順不正解である場合には、低RT状態であれば低RT状態が維持され、高RT状態であれば低RT状態に移行するようにし(例えば、図23参照)、(B−1)有利区間1においては、押し順小役及び押し順リプレイのいずれに当籤したときにも正解となる押し順が報知されることで、押し順小役に当籤したときにはメダルが増加し、押し順リプレイに当籤したときには高RT状態に移行し、あるいは高RT状態が維持されるようにして期待値αが設定され、(B−2)有利区間2においては、これらのいずれか一方について正解となる押し順が報知されないことで、期待値βが設定されるようにしてもよい。
Further, for example, as an internal winning combination, a push order small combination (for example, 6 choices) and a push order replay (for example, 6 choices) are provided, and a high RT state and a low RT state are provided as game states, When the press order replay is won, if the press order is correct, the low RT state shifts to the high RT state, and the high RT state maintains the high RT state. A combination of symbols is displayed. On the other hand, if the pushing order is incorrect, the low RT state is maintained in the low RT state, and the low RT state is transitioned in the high RT state (see, for example, FIG. 23), (B -1) In the
この場合、(B−2)有利区間2を、押し順小役については正解となる押し順が報知され、押し順リプレイについては正解となる押し順が報知されない状態とした場合には、高RT状態に移行させ、あるいは高RT状態を維持することが困難となる(低RT状態の滞在率が高くなる)ものの、押し順小役に当籤したときにメダルを増加させることは容易となるという状態を創出することができる。また、(B−2)有利区間2を、押し順リプレイについては正解となる押し順が報知され、押し順小役については正解となる押し順が報知されない状態とした場合には、高RT状態に移行させ、あるいは高RT状態を維持することは容易となる(高RT状態の滞在率が高くなる)ものの、押し順小役に当籤したときはメダルを増加させるが困難となるという状態を創出することができる。すなわち、(B−1)有利区間1と(B−2)有利区間2とで報知対象となる内部当籤役の種別を異ならせることで、期待値α及び期待値βを変動させるようにしてもよい(この場合、報知確率は変動させてもよいし、変動させなくともよい)。なお、(B−2)有利区間2においては、押し順小役及び押し順リプレイのいずれに当籤したときにも正解となる押し順が報知されないようにすることで、期待値βが設定されるようにすることもできる。
In this case, (B-2) When the
また、例えば、押し順小役(例えば、6択)について、(B−1)有利区間1にあっては、少なくとも第1停止操作及び第2停止操作について正解となる押し順(すなわち、正解押し順の全て)が報知されることで期待値αが設定され、(B−2)有利区間2にあっては、第1停止操作のみについて正解となる押し順(すなわち、正解押し順の一部)が報知されることで期待値βが設定されるようにしてもよい。具体的には、例えば、第1停止操作が「左」、第2停止操作が「中」、第3停止操作が「右」のときに押し順正解となる押し順小役に当籤したとき、(B−1)有利区間1であれば「左→中→右」という押し順が報知されることで、報知にしたがって停止操作を行えば100%の確率でメダルを増加させることができる一方、(B−2)有利区間2であれば「左→?→?」という押し順が報知されることで、報知にしたがって停止操作を行っても、残りの2択は遊技者自身で正解する必要があるため、50%の確率でしかメダルを増加させることができなくなる。すなわち、(B−1)有利区間1と(B−2)有利区間2とで停止操作の情報の報知内容(択数)を異ならせることで、期待値α及び期待値βを変動させるようにしてもよい(この場合、報知確率は変動させてもよいし、変動させなくともよい)。
Further, for example, for the small push order combination (for example, 6 choices), in the (B-1)
また、例えば、(B)有利区間を、停止操作の情報が必ず報知され、期待値は「+10.0枚」と高純増であるが1回の継続期間は比較的短い(例えば、8ゲーム間)増加区間(特別有利区間)として構成し、(B−1)有利区間1及び(B−2)有利区間2を、停止操作の情報は報知されない(あるいは特別有利区間よりも少ない所定確率で報知されるものとしてもよい)が、上記特別有利区間への移行に関してそれぞれ期待値が異なる演出区間(通常有利区間)として構成し、特別有利区間と通常有利区間との間で相互に移行可能に構成する。そして、(B−1)有利区間1では特別有利区間への移行抽籤(AT抽籤)が行われ、当該抽籤においては、例えば、約1/5の確率で特別有利区間に移行することが決定される(AT抽籤に当籤する)ように移行確率が設定される(すなわち、増加区間における遊技媒体の増加率と当該増加区間への移行確率とによって期待値αが設定される)一方、(B−2)有利区間2でもAT抽籤が行われるが、当該抽籤においては、例えば、約1/20の確率でAT抽籤に当籤するように移行確率が設定される(すなわち、増加区間における遊技媒体の増加率と当該増加区間への移行確率とによって期待値αよりも小さい期待値βが設定される)ようにしてもよい。
Further, for example, (B) the advantageous section is informed of the stop operation without fail, and the expected value is a high net increase of “+10.0 sheets”, but the duration of one time is relatively short (for example, between 8 games). ) It is configured as an increased section (special advantageous section), and (B-1)
すなわち、(B−1)有利区間1と(B−2)有利区間2とで増加区間(特別有利区間)への移行確率を異ならせることで、期待値α及び期待値βを変動させるようにしてもよい。なお、上記で述べた移行確率は適宜設定することができる。また、(B−2)有利区間2ではAT抽籤が行われないようにしてもよく、この場合には、(B−2)有利区間2において、例えば、約1/20の確率で(B−1)有利区間1に移行させるか否かが抽籤され、当該抽籤に当籤した場合に(B−2)有利区間2から(B−1)有利区間1に移行されるものとすればよい。また、(B−1)有利区間1から(B−2)有利区間2に移行される条件も適宜設定することができる。この場合、例えば、(B−1)有利区間1において、AT抽籤に当籤することなく所定期間(例えば、5ゲームの間)遊技が行われたこと、AT抽籤が非当籤の場合に行われる転落抽籤に当籤したこと、増加区間(特別有利区間)への連続移行回数が所定回数(例えば、5回)となったこと、増加区間(特別有利区間)での獲得枚数が所定枚数(例えば、400枚を超える)となったこと、などを採用することができる。このように、(B−1)有利区間1と(B−2)有利区間2との移行仕様によって、さらに遊技性を多様化することも可能である。
That is, the expected value α and the expected value β are changed by making the transition probabilities to the increased section (special advantageous section) different between (B-1)
なお、本例では、異なる付与期待値が設定される状態として、期待値αが設定される(B−1)有利区間1、及び期待値βが設定される(B−2)有利区間2の2つの状態を有することを例に挙げて説明しているが、異なる付与期待値が設定される状態は3つ以上であってもよく、適宜設定可能である。例えば、さらに、期待値γが設定される(B−3)有利区間3を有していてもよい。この場合、付与期待値は、α≧γ≧βとなるように設定することもできるし、α≧β≧γとなるように設定することもできる。すなわち、(B−1)有利区間1と(B−2)有利区間2との間に中間の付与期待値となる(B−3)有利区間3を設定したり、(B−2)有利区間2よりも付与期待値が小さい(B−3)有利区間3を設定したりし、順次変動条件が成立するごとに段階的に付与期待値を変動させることで、より細分化した付与期待値の調整を可能とするようにしてもよい。
In this example, as a state in which different expected grant values are set, the expected value α is set (B-1)
(遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その1)における第1の態様)
続いて、上述した遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その1)を前提とした遊技仕様の第1の態様について説明する。この第1の態様では、例えば、期待値αが「+3.0枚」、期待値βが「+2.0枚」に設定される。もっとも、上述のとおり、付与期待値は任意に設定可能である。
(First Mode in Other Example (Part 1) of Gaming (Game Specifications))
Next, the first aspect of the game specification based on the other example (No. 1) of the game property (game specification) described above will be described. In the first mode, for example, the expected value α is set to “+3.0 sheets” and the expected value β is set to “+2.0 sheets”. However, as described above, the expected value of grant can be set arbitrarily.
この第1の態様では、(A)非有利区間において、(1)有利区間の開始条件が成立すると、(B−1)有利区間1に移行する。なお、(1)有利区間の開始条件については、本実施形態で説明した各種の条件(例えば、ARTに移行させることが決定される条件)を採用することができるし、また、内部当籤役の種別に基づく(あるいは基づかない専用の)移行抽籤の抽籤結果などを採用することもできる。
In the first aspect, in (A) the non-advantageous section, when (1) the condition for starting the advantageous section is satisfied, the process moves to (B-1) the
(B−1)有利区間1に移行すると、少なくとも所定期間(予め定められた任意の遊技期間とすることができる。例えば、50ゲーム間)は、付与期待値が期待値α(例えば、「+3.0枚」)となる(B−1)有利区間1が継続する。また、(B−1)有利区間1においては、有利区間を継続するか否かが決定される。有利区間を継続することが決定される条件については、本実施形態で説明した各種の条件(例えば、ARTを継続させることが決定される条件)を採用することができるし、また、内部当籤役の種別に基づく(あるいは基づかない専用の)移行抽籤の抽籤結果などを採用することもできる。
(B-1) When it shifts to the
(B−1)有利区間1において上記所定期間の遊技が行われたとき、有利区間を継続することが決定されている場合には、(2)期待値変動条件が成立し、(B−2)有利区間2に移行する。(B−2)有利区間2に移行すると、少なくとも特定期間(予め定められた任意の遊技期間とすることができる。例えば、100ゲーム間)は、付与期待値が期待値β(例えば、「+2.0枚」)となる(B−2)有利区間2が継続する。なお、(B−2)有利区間2においては、さらに、有利区間を継続するか否かは決定されない。(B−2)有利区間2において上記特定期間の遊技が行われたとき、(3)有利区間の終了条件が成立し、(A)非有利区間に移行する。
(B-1) When it is decided to continue the advantageous section when the game is played in the
一方、(B−1)有利区間1において上記所定期間の遊技が行われたとき、有利区間を継続することが決定されていない場合にも、(3)有利区間の終了条件が成立し、(A)非有利区間に移行する。
On the other hand, (B-1) when the game is played in the
なお、(B−1)有利区間1において上記所定期間の遊技が行われたとき、有利区間を継続することが決定されている場合には、(2)期待値変動条件が成立するが、この場合、一度(B−1)有利区間1から(A)非有利区間に移行させ、(A)非有利区間において所定の待機期間(例えば、4〜32ゲーム間の任意の前兆状態)が経過した後、(A)非有利区間から(B−2)有利区間2に移行させて、有利区間を継続させるようにしてもよい。
In addition, (B-1) When the game is played in the above-described predetermined period in the
また、この第1の態様では、(B−2)有利区間2が上記特定期間継続するものとしているが、この特定期間を予め定められた任意の遊技期間とせず、例えば、(B−1)有利区間1及び(B−2)有利区間2を含む(B)有利区間全体において、付与期待値が期待値β(例えば、「+2.0枚」)となるまでの期間としてもよい。すなわち、有利区間の序盤(B−1)においては期待値αによって付与期待値を大きくし、その後の有利区間(B−2)においては期待値βによって付与期待値を(小さく)調整するようにしてもよい。なお、この場合、上記所定の待機期間は、期待値βによって付与期待値が調整される上で、(B)有利区間全体に含まれるものとしてもよいし、(B)有利区間全体には含まれないものとしてもよい。
In addition, in the first aspect, (B-2) the
具体的には、例えば、(B−1)有利区間1において期待値α通りの遊技価値が付与された場合、(B−1)有利区間1における遊技価値の付与量は3枚×50ゲームで「150枚」となる。その後、(B−2)有利区間2において一定の基準(例えば、上記所定期間と同様50ゲーム間でもよいし、それより長いゲーム間、あるいはそれより短いゲーム間でもよいし、実際の遊技時間でもよい。また、その他の基準も適宜採用できる)にしたがい、(B)有利区間全体の付与期待値が期待値βとなるように適宜報知確率が調整される。例えば、(B)有利区間全体を100ゲームとした場合、(B−1)有利区間1において「150枚」の遊技価値が付与されているので、残りの有利区間である(B−2)有利区間2においては50ゲーム間で「50枚」の遊技価値が付与されるように報知確率が調整され、(B)有利区間全体で「200枚」の遊技価値が付与されるものとすればよい。
Specifically, for example, in the case where (B-1) the
この第1の態様の遊技機によれば、有利状態((B)有利区間)が開始されてから所定期間は、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に高い状態(期待値αが設定される(B−1)有利区間1)で遊技を行うことが可能となり、有利状態が継続されてから特定期間は、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に低い状態(期待値βが設定される(B−2)有利区間2)で遊技を行うことが可能となる。それゆえ、射幸性を適度なものとしつつも遊技の興趣を維持することができる。 According to the gaming machine of the first aspect, in a predetermined period after the advantageous state ((B) advantageous section) is started, the state in which the expected value of the game value is relatively high (the expected value α is set). (B-1) It becomes possible to play the game in the advantageous section 1), and the expected value of the game value is relatively low (expected value β is set for a specific period after the advantageous state is continued). B-2) It becomes possible to play a game in the advantageous section 2). Therefore, it is possible to maintain the interest of the game while maintaining the moderate gambling property.
なお、この第1の態様の遊技機において、有利状態が継続されてから特定期間((B−2)有利区間2)は、有利状態を継続させることを決定しないようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、より適切に出玉率を管理することができる。 In addition, in the gaming machine of the first aspect, it is possible not to decide to continue the advantageous state for a specific period ((B-2) advantageous section 2) after the advantageous state is continued. By doing so, the payout rate can be managed more appropriately.
また、この第1の態様の遊技機において、有利状態中に有利状態を継続させることを決定した場合であっても、当該有利状態を一旦終了させ、所定の待機期間が経過した後に、有利状態を継続させる(再開させる)ようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、より適切に出玉率を管理することができるのみならず、有利状態が継続するか否かに関し、遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。 In addition, in the gaming machine of the first aspect, even when it is decided to continue the advantageous state during the advantageous state, the advantageous state is temporarily ended, and after the predetermined waiting period has elapsed, the advantageous state May be continued (restarted). In this way, not only the payout rate can be managed more appropriately, but also the interest of the game can be improved regarding whether or not the advantageous state continues.
(遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その1)における第2の態様)
続いて、上述した遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その1)を前提とした遊技仕様の第2の態様について説明する。この第2の態様では、例えば、期待値αが「+7.5枚」、期待値βが「+−0枚」に設定される。もっとも、上述のとおり、付与期待値は任意に設定可能である。
(Second Mode in Another Example (1) of Gaming (Game Specifications))
Next, a second aspect of the game specification based on the other example (1) of the above-mentioned game property (game specification) will be described. In the second mode, for example, the expected value α is set to "+7.5 sheets" and the expected value β is set to "+-0 sheets". However, as described above, the expected value of grant can be set arbitrarily.
この第2の態様では、(A)非有利区間において、(1)有利区間の開始条件が成立すると、(B−1)有利区間1に移行する。なお、(1)有利区間の開始条件については、本実施形態で説明した各種の条件(例えば、ARTに移行させることが決定される条件)を採用することができるし、また、内部当籤役の種別に基づく(あるいは基づかない専用の)移行抽籤の抽籤結果などを採用することもできる。
In this second mode, in (A) non-advantageous section, if (1) the start condition of the advantageous section is satisfied, (B-1) the
(B−1)有利区間1に移行すると、少なくとも所定期間(予め定められた任意の遊技期間とすることができる。例えば、100ゲーム間)は、付与期待値が期待値α(例えば、「+7.5枚」)となる(B−1)有利区間1が継続する。なお、この所定期間は、例えば、(B−1)有利区間1が開始されてから付与された遊技価値が所定量(例えば、1000枚)となるまで(あるいは、超えるまで)の期間としてもよいし、(B−1)有利区間1が開始されてからの遊技時間が所定時間(例えば、0.25時間)となるまで(あるいは、超えるまで)の期間としてもよい。
(B-1) When shifting to the
(B−1)有利区間1において上記所定期間の遊技が行われたとき、(2)期待値変動条件が成立し、(B−2)有利区間2に移行する。(B−2)有利区間2に移行すると、(3)有利区間の終了条件が成立するまで、付与期待値が期待値β(例えば、「+−0枚」)となる(B−2)有利区間2が継続する。この第2の態様では、(3)有利区間の終了条件を、例えば、(B)有利区間が開始されてから特定期間(例えば、1500回の遊技の間)遊技が行われたこと、又は(B)有利区間が開始されてから付与された遊技価値が特定量(例えば、純増3000枚)となったこと、として定めることができる(有利区間のこのような終了処理は、上述あるいは後述のリミット処理参照)。さらに、このようにして定めた終了条件が成立する前(例えば、リミット処理が実行される前)であっても、ボーナス役に入賞(ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せが表示されてボーナス状態が作動)した場合には、(B−1)有利区間1であるか(B−2)有利区間2であるかにかかわらず、(B)有利区間が終了し、(B)有利区間から(A)非有利区間に移行する。すなわち、(B)有利区間において、ボーナス状態への移行を可能とするボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せが表示されることは、(3)有利区間の終了条件の1つとなる。
(B-1) When the game is played in the
なお、(3)有利区間の終了条件については、本実施形態で説明した各種の条件(例えば、ARTに終了させることが決定される条件)を採用することができるし、また、内部当籤役の種別に基づく(あるいは基づかない専用の)移行抽籤の抽籤結果などを採用することもできる。また、(B−2)有利区間2においては、例えば、(3)有利区間の終了条件が成立するまでは、所定の単位(例えば、1セットの50ゲーム)ごとに有利区間((B−2)有利区間2)を継続するか否かが決定され、有利区間を継続することが決定された場合に、この所定の単位分有利区間を継続させ、有利区間を継続することが決定されない場合には、(3)有利区間の終了条件が成立する前でも有利区間を終了させるようにしてもよい。この場合、有利区間を継続することが決定される条件については、本実施形態で説明した各種の条件(例えば、ARTを継続させることが決定される条件)を採用することができるし、また、内部当籤役の種別に基づく(あるいは基づかない専用の)移行抽籤の抽籤結果などを採用することもできる。
It should be noted that (3) as the ending condition of the advantageous section, various conditions described in the present embodiment (for example, a condition that is decided to be ended by ART) can be adopted, and the internal winning combination It is also possible to adopt the lottery result of the transfer lottery based on the type (or dedicated not based). Further, in (B-2) the
また、この第2の態様では、(B)有利区間において、例えば、表示装置11などを用いて特定報知を実行することが可能となっている。この特定報知は、ボーナス役に当籤していること(持ち越されていること)を遊技者に対して示唆するための報知演出となっている。もっとも、この第2の態様では、ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せが表示されると有利区間が終了するようになっていることから、この特定報知は、(ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せを表示させて)有利区間を終了させること、あるいは(ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せが表示されることを回避させて)有利区間を継続させること、のいずれかを遊技者が選択できるようにする情報を示唆するための報知演出であるとも言い得る。また、単に、ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せを表示させればボーナス状態に移行可能であることを示唆するための報知演出であるとしてもよいし、ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せが表示されることを回避させれば有利区間を継続可能であることを示唆するための報知演出であるとしてもよい。
Further, in the second aspect, in the (B) advantageous section, for example, the specific notification can be executed using the
例えば、この第2の態様では、(B)有利区間において、ボーナス役に当籤した場合(あるいは、持ち越されている場合)であって、ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せが表示されることが可能な遊技である場合には、上記特定報知が実行されるように構成することができる。なお、本実施形態では、ボーナス役よりもリプレイ役又は小役を優先的に成立させる停止制御が行われるため、ボーナス役とリプレイ役又は小役が重複して当籤した場合(あるいは、ボーナス役が持ち越されている場合にリプレイ役又は小役が重複して当籤した場合)には、原則としてボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せが表示されない。すなわち、「ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せが表示されることが可能な遊技」とはこのような状況でなく、遊技者の停止操作のタイミングが適切であれば、ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せが表示され得る遊技であることを意味する。 For example, in the second mode, in (B) the advantageous section, when the bonus combination is won (or when the bonus combination is carried over), the combination of symbols related to the bonus combination can be displayed. In the case of a game, the specific notification can be executed. In the present embodiment, since the stop control for establishing the replay combination or the small combination preferentially over the bonus combination is performed, when the bonus combination and the replay combination or the small combination are won in succession (or the bonus combination is In the case where the replay combination or the small combination is won in the case of being carried over), in principle, the combination of symbols related to the bonus combination is not displayed. That is, the "game in which the combination of symbols related to the bonus combination can be displayed" is not such a situation, and if the timing of the stop operation of the player is appropriate, the combination of the symbols related to the bonus combination is It means that the game can be displayed.
上述のように上記特定報知が実行されるように構成した場合、遊技者は、(3)有利区間の終了条件が成立するまで(例えば、有利区間のリミット処理が実行されるまで)の遊技期間の範囲内において、ボーナス状態への移行を回避することで有利区間を継続させることができる。なお、このような観点からは、必ずしも(B)有利区間を(B−1)有利区間1と(B−2)有利区間2とに区分けする必要はなく(すなわち、付与期待値を期待値αと期待値βとで異ならせる必要はなく)、(B)有利区間における付与期待値が一定の付与期待値(例えば、「+1.5枚」)となるようにしてもよい。
When the specific notification is configured to be executed as described above, the player plays the game period until (3) the advantageous period ending condition is satisfied (for example, the advantageous period limit process is executed). Within the range, the advantageous section can be continued by avoiding the transition to the bonus state. From this viewpoint, it is not always necessary to divide the (B) advantageous section into the (B-1)
また、例えば、この第2の態様では、(B−1)有利区間1において、ボーナス役に当籤した場合(あるいは、持ち越されている場合)に、(2)期待値変動条件が成立した場合には、(2)期待値変動条件が成立したときに上記特定報知が実行されるように構成することができる。なお、この場合、上記と同様、上記特定報知が実行可能となった以後の遊技において、「ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せが表示されることが可能な遊技」である場合に、上記特定報知が実行されるように構成してもよい。また、(2)期待値変動条件が成立した後、(3)有利区間の終了条件が成立する前に、(B−2)有利区間2において、ボーナス役に当籤した場合には、このときに上記特定報知が実行されるように構成することができる。なお、この場合、上記と同様、上記特定報知が実行可能となった以後の遊技において、「ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せが表示されることが可能な遊技」である場合に、上記特定報知が実行されるように構成してもよい。また、このように構成した上で、さらに(B−1)有利区間1において、ボーナス役に当籤した場合(あるいは、持ち越されている場合)に、「ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せが表示されることが可能な遊技」であれば、上記特定報知が実行されるように構成してもよい。
Further, for example, in the second mode, (B-1) in the
上述のように上記特定報知が実行されるように構成した場合、遊技者は、(3)有利区間の終了条件が成立するまで(例えば、有利区間のリミット処理が実行されるまで)の遊技期間の範囲内において、例えば、(B−1)有利区間1の遊技期間では、期待値αが設定されることで遊技価値が飛躍的に増加するので、ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せが表示されることを回避させて有利区間を継続させ、(B−2)有利区間2の遊技期間では、期待値βが設定されることで遊技価値が飛躍的に増加することはないので、ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せを表示させて有利区間を終了させ、その後の遊技で再度(1)有利区間の開始条件を成立させて(B−1)有利区間1に移行させようとすることを選択することもできるし、時間の余裕が無いなどの場合にはそのまま遊技を終了することを選択することもできる。一方、(B−2)有利区間2の遊技期間では、期待値βが設定されることで遊技価値が飛躍的に増加することはないが、(A)非有利区間よりも遊技者に有利であることにかわりはないため、遊技を楽しむべく、ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せが表示されることを回避させて有利区間を継続させることを選択することもできる。
When configured to execute the specific notification as described above, the player plays the game period until (3) the condition for ending the advantageous period is satisfied (for example, until the limit process for the advantageous period is executed). Within the range of (B-1), for example, in the game period of the
また、この第2の態様では、ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せを表示させて(B)有利区間を終了させた場合、例えば、表示装置11などを用いて特殊特典を付与することが可能となっている。この特殊特典は、遊技者に付与される各種特典のうち、遊技価値の付与に関連しない(すなわち、出玉率に影響を与えない)特典となっている。なお、特殊特典を、遊技価値の付与に関連する(すなわち、出玉率に影響を与える)特典(例えば、有利区間の移行条件を成立させるための権利、あるいはボーナス状態中に停止操作の情報が報知される権利など)とすることを妨げるものではないが、射幸性の適正化などの観点からは、遊技価値の付与に関連しない(すなわち、出玉率に影響を与えない)特典とすることが望ましい。
In addition, in the second aspect, when the combination of symbols relating to the bonus combination is displayed and (B) the advantageous section is ended, for example, the special privilege can be given using the
特殊特典の具体例としては、例えば、通常は実行される確率が低い特別演出(例えば、上述した各種エンディング演出やその他のプレミア演出)の実行、遊技者にとって有益な情報が報知される特別報知(例えば、設定値の示唆報知、演出内容ごとの期待度報知、ボーナス役の当籤確率や有利区間の移行確率などの履歴報知)の実行、遊技者の携帯端末を用いインターネットを介して提供される情報提供サービス上の得点付与や特定条件の解放などを挙げることができる。 As a specific example of the special privilege, for example, execution of a special effect (for example, various ending effects described above and other premier effects) that is not normally executed, and special notification that informs useful information to the player ( For example, notification of setting value suggestion, notification of expectation for each effect content, execution of history notification of winning probability of bonus combination, transition probability of advantageous zone, etc.), information provided via the Internet using the portable terminal of the player Examples include giving points on the provided services and releasing specific conditions.
上述のように上記特殊特典されるように構成した場合、遊技者は、遊技価値の付与といった直接的な特典を享受することはないものの、遊技を楽しむ上では関心度の高い間接的な特典を享受することができるため、特に、(B−2)有利区間2のように、期待値βが設定されることで遊技価値が飛躍的に増加することはない状態においては、有利区間を早期に終了させるインセンティブを与えることもできる。
In the case where the special privilege is configured as described above, the player does not enjoy a direct privilege such as giving a game value, but an indirect privilege with high interest in enjoying the game is provided. In particular, as in (B-2)
この第2の態様の遊技機によれば、有利状態((B)有利区間)は、所定の終了条件((3)有利区間の終了条件)が成立した場合、又は所定の終了条件が成立する前に特別遊技状態(ボーナス状態)に移行した場合に終了する。そして、有利状態では、特別遊技状態への移行が可能となっている場合、その旨を示す特定報知が実行される。したがって、遊技者は、規定された所定の終了条件の範囲内であれば、特別遊技状態への移行を回避することで有利状態を継続させることができる。それゆえ、射幸性を適度なものとしつつも遊技の興趣を維持することができる。 According to the gaming machine of the second aspect, the advantageous state ((B) advantageous section) is satisfied when a predetermined end condition ((3) end condition of the advantageous section) is satisfied or a predetermined end condition is satisfied. The process ends when the special game state (bonus state) is entered before. Then, in the advantageous state, when it is possible to shift to the special game state, a specific notification indicating that effect is executed. Therefore, the player can continue the advantageous state by avoiding the transition to the special game state if it is within the range of the prescribed predetermined ending condition. Therefore, it is possible to maintain the interest of the game while maintaining the moderate gambling property.
また、この第2の態様の遊技機において、所定の終了条件は、遊技者に一定の特典が付与されたとき(あるいは、付与されたと仮定されるとき)に(例えば、上述あるいは後述のリミット処理によって)終了されるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、簡易な構成でより適切に出玉率を管理することができる。 In addition, in the gaming machine of the second aspect, the predetermined ending condition is when a certain privilege is given to the player (or when it is assumed that the certain privilege is given) (for example, the limit process described above or later). May be terminated. With this configuration, it is possible to more appropriately manage the payout rate with a simple configuration.
また、この第2の態様の遊技機によれば、有利状態((B)有利区間)が開始されてから特定の変動条件((2)期待値変動条件)が成立するまでの間は、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に高い状態(期待値αが設定される(B−1)有利区間1)で遊技を行うことが可能となり、特定の変動条件が成立してから有利状態が終了されるまでの間は、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に低い状態(期待値βが設定される(B−2)有利区間2)で遊技を行うことが可能となる。また、有利状態は、所定の終了条件が成立する前であっても、特別遊技状態への移行を契機として終了させることが可能である。すなわち、遊技者は、例えば、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に低い状態で遊技を行う場合、所定の終了条件が成立するまで有利状態を継続させることもできるし、特別遊技状態に移行させて有利状態を終了させ、再度遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に高い状態で遊技を行う機会を得ようとすることもできる。それゆえ、射幸性を適度なものとしつつも遊技の興趣を維持することができる。 Further, according to the gaming machine of the second aspect, from the start of the advantageous state ((B) advantageous section) until the specific variation condition ((2) expected value variation condition) is satisfied, the game is played. It becomes possible to play a game in a state where the expected value of value addition is relatively high (expected value α is set ((B-1) advantageous section 1), and the advantageous state ends after a specific variation condition is satisfied. Until that time, the game can be played in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively low (the expected value β is set ((B-2) advantageous section 2)). Further, the advantageous state can be ended with the transition to the special game state as a trigger even before the predetermined ending condition is satisfied. That is, for example, when playing a game in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively low, the player can continue the advantageous state until a predetermined ending condition is satisfied, or shift to the special game state. It is also possible to end the advantageous state and obtain an opportunity to play the game again in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively high. Therefore, it is possible to maintain the interest of the game while maintaining the moderate gambling property.
また、この第2の態様の遊技機によれば、有利状態((B)有利区間)が開始されてから特定の変動条件((2)期待値変動条件)が成立するまでの間は、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に高い状態(期待値αが設定される(B−1)有利区間1)で遊技を行うことが可能となり、特定の変動条件が成立してから有利状態が終了されるまでの間は、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に低い状態(期待値βが設定される(B−2)有利区間2)で遊技を行うことが可能となる。また、有利状態は、所定の終了条件が成立する前であっても、特別遊技状態への移行を契機として終了させることが可能である。さらに、有利状態が特別遊技状態への移行を契機として終了した場合、遊技価値の付与に関連しない特殊特典を付与することが可能である。すなわち、遊技者は、例えば、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に低い状態で遊技を行う場合、所定の終了条件が成立するまで有利状態を継続させることもできるし、特別遊技状態に移行させて有利状態を終了させ、再度遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に高い状態で遊技を行う機会を得ようとすることもできる。また、特別遊技状態に移行させて有利状態を終了させる場合には、所定の終了条件が成立して有利状態を終了させた場合には付与されない特殊特典が付与されるため、遊技者に有利状態を早期に終了させるインセンティブを与えることもできる。それゆえ、射幸性を適度なものとしつつも遊技の興趣を維持することができる。 Further, according to the gaming machine of the second aspect, from the start of the advantageous state ((B) advantageous section) until the specific variation condition ((2) expected value variation condition) is satisfied, the game is played. It becomes possible to play a game in a state where the expected value of value addition is relatively high (expected value α is set ((B-1) advantageous section 1), and the advantageous state ends after a specific variation condition is satisfied. Until that time, the game can be played in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively low (the expected value β is set ((B-2) advantageous section 2)). Further, the advantageous state can be ended with the transition to the special game state as a trigger even before the predetermined ending condition is satisfied. Furthermore, when the advantageous state ends with the transition to the special game state, it is possible to give a special privilege that is not related to the giving of a game value. That is, for example, when playing a game in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively low, the player can continue the advantageous state until a predetermined ending condition is satisfied, or shift to the special game state. It is also possible to end the advantageous state and obtain an opportunity to play the game again in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively high. Further, in the case of shifting to the special game state and ending the advantageous state, a special privilege which is not given when the predetermined ending condition is satisfied and the advantageous state is ended, is given to the player. It is also possible to give an incentive to end the task early. Therefore, it is possible to maintain the interest of the game while maintaining the moderate gambling property.
なお、この第2の態様の遊技機において、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に低い状態で遊技を行う場合、特別遊技状態への移行が可能となっている場合には、その旨を示す特定報知が実行されるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、遊技者に、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に低い状態で遊技を継続させない選択肢があることを明示することができ、さらに遊技の興趣を維持することができる。 In the gaming machine of the second aspect, when the game is played in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively low, if the shift to the special gaming state is possible, this is indicated. The specific notification may be executed. By doing so, it is possible to clearly indicate to the player that there is an option not to continue the game when the expected value of the game value is relatively low, and it is possible to maintain the interest of the game.
また、この第2の態様の遊技機において、有利状態中の遊技価値の付与期待値は、有利状態中に遊技者の停止操作に関する情報が報知される確率(報知確率)によって調整されるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、簡易な構成でより適切に出玉率を管理することができる。 In addition, in the gaming machine of the second aspect, the expected value of the gaming value in the advantageous state is adjusted by the probability (information probability) of being notified of the information regarding the stop operation of the player in the advantageous state. May be. With this configuration, it is possible to more appropriately manage the payout rate with a simple configuration.
[遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その2)]
続いて、図94を参照して、本実施形態に係るパチスロ1において実装可能な遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その2)について説明する。図94は、遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その2)における遊技の流れを概念的に説明する図である。
[Another example of playability (game specifications) (Part 2)]
Next, with reference to FIG. 94, another example (2) of the playability (game specification) that can be mounted in the pachi-
図94に示すように、本例では、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)、(A)BB1状態、(B)BB2状態、及び(C)BB3状態の遊技状態がある。一般遊技状態(CZ状態)は、再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率も低く、有利区間への移行も発生しない遊技状態であり、この遊技状態自体は遊技者に有利な遊技状態ではないが、(B)BB2状態又は(C)BB3状態に移行可能な点において、(A)BB1状態よりも有利な遊技状態(チャンスゾーン。特賞連荘状態)として位置付けられる。また、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)、(B)BB2状態、及び(C)BB3状態は、後述の一連の増加区間として位置付けられる。なお、一般遊技状態(CZ)においても、(A)BB1状態と同様、特定の報知条件が成立した場合には有利区間が特定期間発生するように構成することもできる。 As shown in FIG. 94, in this example, there are general game state (CZ state), (A) BB1 state, (B) BB2 state, and (C) BB3 state game state. The general gaming state (CZ state) is a gaming state in which the winning probability of the replay (replay) combination is low, and the transition to the advantageous section does not occur. This gaming state itself is not a gaming state advantageous to the player, It is positioned as a gaming state (chance zone. Special prize extended state) which is more advantageous than (A) BB1 state in that it can be shifted to (B) BB2 state or (C) BB3 state. In addition, the general gaming state (CZ state), the (B)BB2 state, and the (C)BB3 state are positioned as a series of increase sections described later. Even in the general gaming state (CZ), as in the case of (A) BB1 state, the advantageous section may be configured to occur for a specific period when a specific notification condition is satisfied.
一般遊技状態(CZ状態)において、BB1(例えば、本実施形態におけるBB1及びBB2)に当籤し、BB1に係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示されると、(1)BB1開始条件が成立し、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)から(A)BB1状態に移行する。後述するように、これは、遊技者にとって相対的に不利な遊技状態の移行として位置付けられる。また、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)において、BB2(例えば、本実施形態におけるBB3)に当籤し、BB2に係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示されると、(3)BB2開始条件が成立し、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)から(B)BB2状態に移行する。また、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)において、BB3(例えば、本実施形態におけるBB4)に当籤し、BB3に係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示されると、(5)BB3開始条件が成立し、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)から(C)BB2状態に移行する。後述するように、これらは、遊技者にとって相対的に有利な遊技状態の移行として位置付けられる。 In the general gaming state (CZ state), when BB1 (for example, BB1 and BB2 in the present embodiment) is won and the combination of symbols related to BB1 is stopped and displayed on the activated line, (1) BB1 start condition is satisfied. Then, the general game state (CZ state) shifts to the (A) BB1 state. As will be described later, this is positioned as a transition of a game state that is relatively disadvantageous to the player. Further, in the general game state (CZ state), if BB2 (for example, BB3 in the present embodiment) is won and the symbol combination related to BB2 is stopped and displayed on the activated line, (3) BB2 start condition is satisfied. Then, the general game state (CZ state) shifts to the (B) BB2 state. Further, in the general game state (CZ state), if BB3 (for example, BB4 in the present embodiment) is won and the symbol combination related to BB3 is stopped and displayed on the activated line, (5) BB3 start condition is satisfied. Then, the general game state (CZ state) shifts to the (C)BB2 state. As will be described later, these are positioned as relatively advantageous game state transitions for the player.
ここで、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)において、BB1に一旦当籤すると、BB1に係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示されるまで当該BB1は持ち越される(BB1に係る図柄の組合せの表示が許可されるBB1許可状態が継続する)ため、当該一般遊技状態(CZ状態)ではBB2及びBB3に当籤することがない。また、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)において、BB2又はBB3に一旦当籤すると、BB2又はBB3に係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示されるまで当該BB2又はBB3は持ち越される(BB2又はBB3に係る図柄の組合せの表示が許可されるBB2許可状態又はBB3許可状態が継続する)ため、当該一般遊技状態(CZ状態)ではBB1に当籤することがない。すなわち、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)では、いずれかのボーナス役(BB1〜BB3)に当籤した場合、当籤したボーナス役に応じたボーナス状態が終了して再度一般遊技状態(CZ状態)に移行しない限り、他のボーナス役に当籤しないように構成される。 Here, in the general game state (CZ state), once the BB1 is won, the BB1 is carried over until the combination of symbols related to BB1 is stopped and displayed on the activated line (the display of the combination of symbols related to BB1 is permitted. Since the BB1 permission state is continued), in the general game state (CZ state), BB2 and BB3 are not won. Further, in the general game state (CZ state), once the BB2 or BB3 is won, the BB2 or BB3 is carried over until the combination of symbols related to BB2 or BB3 is stopped and displayed on the activated line (related to BB2 or BB3). Since the BB2 permission state or the BB3 permission state in which the display of the combination of symbols is permitted continues), the BB1 is never won in the general game state (CZ state). That is, in the general game state (CZ state), if any of the bonus combinations (BB1 to BB3) is won, the bonus state corresponding to the winning bonus combination is ended and the general game state (CZ state) is not returned again. As long as it does not win other bonus roles.
なお、本例において、BB2に係る図柄の組合せは、例えば「赤7−赤7−赤7」といった図柄の組合せとして構成され、BB3に係る図柄の組合せは、例えば「青7−青7−青7」といった図柄の組合せとして構成される。また、BB1に係る図柄の組合せは、例えば「赤7−赤7−チェリー1」及び「青7−青7−チェリー1」といった図柄の組合せとして構成される(図15参照)。本例では、このように構成した上で、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)においていずれかのボーナス役(BB1〜BB3)に当籤した場合に、ボーナス役に当籤した旨が示唆される当籤報知が行われるようにしてもよい。具体的には、「7を狙え!」などの表示がなされ、遊技者に「赤7」図柄あるいは「青7」図柄を狙うべきことが示されるようにすればよい。この場合、例えば、遊技者が「赤7」図柄を狙って目押ししたとき、BB2に当籤している場合には「赤7」揃いとなってBB2状態に移行し、BB3に当籤している場合には「赤7」揃いとならず、かつBB1に係る図柄の組合せも表示されず、BB3に当籤していることが認識され、BB1に当籤している場合にはBB1に係る図柄の組合せが表示されてBB1状態に移行することとなる。このようにすれば、本例の遊技性において、報知に関する興趣をさらに向上させることが可能となる。また、上記のような当籤報知は、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)においていずれかのボーナス役(BB1〜BB3)に当籤した場合には無条件で行われるようにしてもよいし、例えば、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)において有利区間を発生可能とした場合には、当該有利区間中にのみ行われるようにしてもよい。
In this example, the symbol combination related to BB2 is configured as a symbol combination such as "red 7-red 7-
(A)BB1状態は、(A−1)BB1一般中、(A−2)BB1RBフラグ間中、及び(A−3)BB1RB中から構成される。なお、(A)BB1状態においては、BB1〜BB3が新たに抽籤されることはなく、したがって、(A)BB1状態が継続する限り、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)、(B)BB2状態、及び(C)BB3状態に移行する場合はない。 The (A)BB1 state is composed of (A-1)BB1 general, (A-2)BB1RB flag in-between, and (A-3)BB1RB in-between. In addition, in the (A) BB1 state, BB1 to BB3 are not newly drawn, and so long as the (A) BB1 state continues, the general gaming state (CZ state), the (B) BB2 state, and (C) There is no case of shifting to the BB3 state.
(A−1)BB1一般中では、再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率が低く(あるいは、再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率が「0」に(すなわち、再遊技(リプレイ)が抽籤されないように))設定される。また、押し順小役(例えば、6択の押し順正解で9枚のメダル払出、押し順不正解だが停止操作のタイミングが適切なら1枚のメダル払出、押し順不正解で停止操作のタイミングも不適切ならメダル払出無し、など)、非作動状態と比べていずれかの小役の当籤確率が向上するRB状態を作動させるためのRB、及び(A)BB1状態を有利区間とするか否かの決定がなされる有利区間抽籤役などがそれぞれ任意の所定確率で当籤するように設定される。 (A-1) BB1 In general, the winning probability of the re-play (replay) combination is low (or the winning probability of the re-play (replay) combination is “0” (that is, the re-play (replay) is not randomly selected). )) is set. In addition, a small push order combination (for example, 6 correct push order correct payouts of 9 medals, incorrect push order, but one medal payout if the timing of the stop operation is appropriate, and stop operation timing due to incorrect push order. If it is inappropriate, there is no medal payout, etc.), RB for operating the RB state in which the winning probability of one of the small wins is improved compared to the non-operating state, and whether (A) BB1 state is set as an advantageous section. The advantageous section lottery combination for which the determination is made is set so as to win each with a predetermined probability.
(A−2)BB1RBフラグ間中では、再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率が低く(あるいは、再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率が「0」に(すなわち、再遊技(リプレイ)が抽籤されないように))設定される。また、上記押し順小役、及び上記有利区間抽籤役などがそれぞれ任意の所定確率で当籤するように設定される。なお、押し順小役の基本構成(1/6で押し順正解、5/6で押し順不正解)は、(A−1)BB1一般中と同様である。また、RBは持ち越されているため、新たに抽籤されることはないが、当籤状態(許可状態)は継続している。また、(A−1)BB1一般中と(A−2)BB1RBフラグ間中とでは、再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率は同じであってもよいし、異なっていてもよい。 (A-2) During the BB1RB flag, the winning probability of the re-play (replay) combination is low (or the winning probability of the re-play (replay) combination is "0" (that is, the re-play (replay) is not randomly selected). So)) set. Further, the push order small winning combination, the advantageous section lottery winning combination, and the like are set so as to be won with arbitrary predetermined probabilities. In addition, the basic configuration of the push order small winning combination (the push order is correct in 1/6 and the push order is incorrect in 5/6) is the same as in (A-1)BB1 general. Further, since the RB has been carried over, it is not newly drawn, but the winning state (permitted state) continues. Further, the winning probabilities of the replay (replay) combination may be the same or different between (A-1) BB1 general and (A-2) BB1RB flag.
(A−3)BB1RB中では、再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率が低く(あるいは、再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率が「0」に(すなわち、再遊技(リプレイ)が抽籤されないように))設定される。また、上記押し順小役、及び上記有利区間抽籤役などがそれぞれ任意の所定確率で当籤するように設定される。なお、押し順小役の基本構成(1/6で押し順正解、5/6で押し順不正解)は、(A−1)BB1一般中と同様である。また、(A−1)BB1一般中及び(A−2)BB1RBフラグ間中と(A−3)BB1RB中とでは、上記押し順小役及び上記有利区間抽籤役のそれぞれの当籤確率は同じであってもよいし、異なっていてもよい。あるいは、(A−3)BB1RB中では、上記押し順小役及び上記有利区間抽籤役とは異なる種類の内部当籤役として、それぞれ同様の役割を担う押し順小役及び有利区間抽籤役が当籤するようにしてもよい。また、(A−1)BB1一般中と(A−2)BB1RBフラグ間中と(A−3)BB1RB中とでは、それぞれ再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率は同じであってもよいし、異なっていてもよい。 (A-3) In BB1RB, the winning probability of the replay (replay) combination is low (or the winning probability of the replay (replay) combination is "0" (that is, the replay (replay) is not randomly selected). )) Set. Further, the push order small winning combination, the advantageous section lottery winning combination, and the like are set so as to be won with arbitrary predetermined probabilities. In addition, the basic configuration of the push order small winning combination (the push order is correct in 1/6 and the push order is incorrect in 5/6) is the same as in (A-1)BB1 general. In addition, in (A-1) BB1 general medium and (A-2) BB1RB flag middle and (A-3) BB1RB middle, the respective winning probabilities of the pushing order small combination and the advantageous zone lottery combination are the same. It can be different or different. Alternatively, in (A-3) BB1RB, as the internal winning combination of a type different from the above-mentioned pushing order small winning combination and the above-mentioned advantageous section lottery, the pushing order small winning combination and the advantageous section lottery winning the same role are won. You may do it. In addition, in (A-1) BB1 general middle, (A-2) BB1RB flag middle and (A-3) BB1RB middle, the winning probability of the replay (replay) combination may be the same, It may be different.
一般遊技状態(CZ状態)において、(1)BB1開始条件が成立すると、まず(A−1)BB1一般中に移行する。(A−1)BB1一般中において、上記RBが内部当籤役として決定されると、(A−2)BB1RBフラグ間中に移行し、(A−2)BB1RBフラグ間中は、RBに係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示されるまで継続する(RBに係る図柄の組合せの表示が許可される許可状態が継続する)。(A−2)BB1RBフラグ間中において、RBに係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示されると、(A−3)BB1RB中に移行する。(A−3)BB1RB中において、RB状態の終了条件(例えば、8回以下の任意の所定回数の入賞があったこと、あるいは12回以下の任意の所定回数の遊技が行われたこと)が成立すると、(A−1)BB1一般中に移行する。なお、(A−2)BB1RBフラグ間中において、ボーナス役(RB)よりもリプレイ役又は小役を優先的に成立させる停止制御が行われることで、RBに係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示されにくく(あるいは、停止表示されないように)し、結果として(A−3)BB1RB中に移行することが困難となる(あるいは、移行されない)ようにしてもよい。 In the general game state (CZ state), when (1) BB1 start condition is satisfied, first, the process shifts to (A-1) BB1 general state. (A-1) In the BB1 general, when the RB is determined as an internal winning combination, (A-2) the BB1RB flag is shifted to, and (A-2) BB1RB flag is shifted to a symbol relating to the RB. Continues until the combination is stopped and displayed on the activated line (the permitted state in which the display of the combination of symbols related to RB is permitted continues). (A-2) When the combination of symbols related to RB is stopped and displayed on the activated line during the BB1RB flag, (A-3) the process shifts to BB1RB. (A-3) In the BB1RB, an ending condition of the RB state (for example, winning a predetermined number of times less than or equal to 8 times, or playing a predetermined number of times less than or equal to 12 times) When it is established, the process shifts to (A-1)BB1 general. In addition, during the (A-2) BB1RB flag, the stop control for preferentially establishing the replay combination or the small combination rather than the bonus combination (RB) is performed, so that the combination of symbols related to RB is on the activated line. The stop display may be made difficult (or the stop display may not be made), and as a result, it may be difficult (or not) to shift to (A-3) BB1RB.
(A−1)BB1一般中、(A−2)BB1RBフラグ間中、及び(A−3)BB1RB中のいずれの状態においても、(A)BB1状態におけるメダルの払出枚数が規定数となった場合(例えば、285枚を超えた場合)、(2)BB1の終了条件が成立し、(A)BB1状態から一般遊技状態(CZ状態)に移行する。 In any of (A-1) BB1 general state, (A-2) BB1RB flag state, and (A-3) BB1RB state, the payout number of medals in the (A) BB1 state is the specified number. In the case (for example, when the number exceeds 285), the ending condition of (2) BB1 is satisfied, and the state shifts from the (A) BB1 state to the general gaming state (CZ state).
(A−1)BB1一般中、(A−2)BB1RBフラグ間中、及び(A−3)BB1RB中のいずれの状態においても、上記有利区間抽籤役に当籤した場合、非有利区間であれば有利区間に移行させるか否かが決定され、有利区間であれば当該有利区間を延長するか否かが決定される。この場合、一度の当籤で、例えば、30ゲームの有利区間が付与あるいは延長される。なお、有利区間の付与あるいは延長が決定される契機やその期間は、上述したものに限られない。例えば、有利区間抽籤役に当籤したときの当否抽籤の結果のみならず、他の内部当籤役に当籤したときの当否抽籤の結果や、内部当籤役に基づかない当否抽籤の結果などに応じて、有利区間の付与あるいは延長が決定されうるようにしてもよい。また、有利区間の付与あるいは延長が決定されるときに、有利区間の継続期間が別途抽籤などによって決定されうるようにしてもよい。また、(A)BB1状態が開始される前の任意のタイミング(例えば、BB1に当籤したとき、あるいは、BB1当籤後の一般遊技状態(CZ状態)において有利区間抽籤役に当籤したとき)において、当該BB1状態の全期間(あるいは、一部の期間)を有利区間とするか否かが決定されうるようにしてもよい。 In any state of (A-1) BB1 general, (A-2) during BB1RB flag, and (A-3) BB1RB, if the winning combination is a non-advantageous section. It is determined whether to shift to the advantageous zone, and if it is the advantageous zone, it is determined whether to extend the advantageous zone. In this case, a single winning will give or extend an advantageous section of 30 games, for example. Note that the trigger and the period for determining the grant or extension of the advantageous section are not limited to those described above. For example, according to not only the result of the lottery winning when winning the advantageous zone lottery, but also the result of the lottery winning when winning the other internal lottery, the result of the lottery not based on the internal winning, etc. It may be possible to determine whether to give or extend the advantageous section. Further, when the granting or extension of the advantageous section is determined, the duration of the advantageous section may be separately determined by lottery or the like. Further, (A) at an arbitrary timing before the BB1 state is started (for example, when winning BB1 or when winning the advantageous zone lottery in the general gaming state (CZ state) after winning BB1), It may be possible to determine whether or not the entire period (or part of the period) of the BB1 state is set as the advantageous section.
(A−1)BB1一般中、(A−2)BB1RBフラグ間中、及び(A−3)BB1RB中のいずれの状態においても、有利区間である場合には、例えば、上記押し順小役に当籤した遊技で(押し順正解となる)停止操作の情報が報知され、当該報知にしたがって停止操作が行われる結果、当該有利区間は遊技価値が増加する(あるいは、少なくとも減少しない)増加期間となる。一方、非有利区間である場合には、例えば、上記押し順小役に当籤した遊技で(押し順正解となる)停止操作の情報が報知されない結果、当該非有利区間は遊技価値が減少する減少期間となる。 In any state of (A-1) BB1 general, (A-2) BB1RB flag, and (A-3) BB1RB, in the case of an advantageous section, for example, the above-mentioned pushing order sub-role Information of the stop operation (which is the correct answer in the push order) is notified in the winning game, and as a result of the stop operation being performed according to the notification, the advantageous section becomes an increase period in which the game value increases (or at least does not decrease). .. On the other hand, if it is a non-advantageous section, for example, as a result of not being notified of the stop operation (which is the correct push order) in the game in which the above-mentioned push order small win is won, the game value of the non-advantageous section decreases. It will be a period.
上述したように、本例において、(A)BB1状態は、当該BB1状態中のメダルの払出枚数が「285枚」を超えるまで終了しないものとなっている。したがって、例えば、リプレイ役やその他の小役などに当籤した場合を考慮せず、また、上記押し順小役において1枚の払出がある場合を考慮せず、上記押し順小役の合計当籤確率を約1/2(32768/65536)とした場合、(A)BB1状態を終了させるのに必要な9枚の払出回数は「32回」(32回×9枚=288枚)となり、上記押し順小役が確率どおり当籤した場合、(A)BB1状態を終了させることができる最短の遊技回数は「64回」(32回÷1/2)となる。したがって、(A)BB1状態中が全て有利区間である場合、「64回」の遊技を行えば、その遊技期間中に遊技価値が増加しつつ、早期に(A)BB1状態を終了させて一般遊技状態(CZ状態)に移行させることができる。一方、(A)BB1状態中が全て非有利区間である場合、基本的には上記押し順小役が当籤した遊技で9枚の払出がある確率は1/6に低下するため、(A)BB1状態を終了させることができる目安の遊技回数は「384回」(64回÷1/6)となり、その遊技期間中は遊技価値も減少していくことになる。
As described above, in this example, the (A) BB1 state is not completed until the payout number of medals in the BB1 state exceeds “285 coins”. Therefore, for example, the total winning probability of the above-mentioned pushing order small wins is not taken into consideration without considering the case of winning a replay role or other small wins, or the case where there is one payout in the above-mentioned pushing order small wins. When the value is about 1/2 (32768/65536), the number of payouts of 9 sheets required to end the (A) BB1 state is “32 times” (32 times×9 sheets=288 sheets), If the small winning combination wins according to the probability, the shortest number of games that can end the (A) BB1 state is "64 times" (32
(B)BB2状態は、(B−1)BB2一般中、(B−2)BB2RBフラグ間中、及び(B−3)BB2RB中から構成される。なお、(B)BB2状態においては、BB1〜BB3が新たに抽籤されることはなく、したがって、(B)BB2状態が継続する限り、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)、(A)BB1状態、及び(C)BB3状態に移行する場合はない。 The (B)BB2 state is composed of (B-1)BB2 general, (B-2)BB2RB flag in-between, and (B-3)BB2RB in-between. In addition, in the (B)BB2 state, BB1 to BB3 are not newly drawn, and so long as the (B)BB2 state continues, the general gaming state (CZ state), the (A)BB1 state, and (C) There is no case of shifting to the BB3 state.
(B−1)BB2一般中では、再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率が低く(あるいは、再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率が相対的には高いが、(B−2)BB2RBフラグ間中よりも低く)設定される。また、押し順小役(例えば、6択の押し順正解で9枚のメダル払出、押し順不正解だが停止操作のタイミングが適切なら1枚のメダル払出、押し順不正解で停止操作のタイミングも不適切ならメダル払出無し、など)、非作動状態と比べていずれかの小役の当籤確率が向上するRB状態を作動させるためのRB、及び(B)BB2状態終了後に一般遊技状態(CZ状態)を経由して(A)BB1状態に移行した場合に、当該(A)BB1状態を有利区間とするか否かの決定がなされる有利区間抽籤役などがそれぞれ任意の所定確率で当籤するように設定される。 (B-1) BB2 In general, the winning probability of the replay (replay) combination is low (or the winning probability of the replay (replay) combination is relatively high, but (B-2) BB2RB flag Lower than). In addition, a small push order combination (for example, 6 correct push order correct payouts of 9 medals, incorrect push order, but one medal payout if the timing of the stop operation is appropriate, and stop operation timing due to incorrect push order. If it is inappropriate, there is no medal payout, etc.), RB for operating the RB state in which the winning probability of any small win is improved compared to the non-operating state, and (B) BB2 state after the general game state (CZ state) ), the (A) BB1 state is determined to be the advantageous section when the state shifts to the (A) BB1 state. Is set to.
(B−2)BB2RBフラグ間中では、再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率が高く設定される。また、上記押し順小役、及び上記有利区間抽籤役などがそれぞれ任意の所定確率で当籤するように設定される。なお、押し順小役の基本構成は、(B−1)BB2一般中とは異なり、いずれの押し順で停止操作が行われたとしても9枚の払出があるように(すなわち、不正解となる押し順が存在しないように)制御変更される。また、RBは持ち越されているため、新たに抽籤されることはないが、当籤状態(許可状態)は継続している。 (B-2) During the BB2RB flag, the winning probability of the replay (replay) combination is set to be high. Further, the push order small winning combination, the advantageous section lottery winning combination, and the like are set so as to be won with arbitrary predetermined probabilities. In addition, the basic configuration of the push-order small winning combination is different from that in (B-1) BB2 general, so that no matter which push order the stop operation is performed, nine pieces are paid out (that is, an incorrect answer is given). The control is changed so that there is no push order. Further, since the RB has been carried over, it is not newly drawn, but the winning state (permitted state) continues.
(B−3)BB2RB中では、再遊技(リプレイ)が抽籤されないように設定される。また、上記押し順小役が高確率で当籤するように設定されるとともに、上記有利区間抽籤役などがそれぞれ任意の所定確率で当籤するように設定される。なお、押し順小役の基本構成は、(B−1)BB2一般中とは異なり、いずれの押し順で停止操作が行われたとしても9枚の払出があるように(すなわち、不正解となる押し順が存在しないように)制御変更される。あるいは、(B−3)BB2RB中では、上記押し順小役及び上記有利区間抽籤役とは異なる種類の内部当籤役として、それぞれ同様の役割を担うRB中小役及び有利区間抽籤役が当籤するようにしてもよい。 (B-3) In BB2RB, replay (replay) is set so as not to be randomly selected. In addition, the push order small winning combination is set to be won with a high probability, and the advantageous zone lottery combination is set to be won with an arbitrary predetermined probability. In addition, the basic configuration of the push-order small winning combination is different from that in (B-1) BB2 general, so that no matter which push order the stop operation is performed, nine pieces are paid out (that is, an incorrect answer is given). The control is changed so that there is no push order. Alternatively, in (B-3) BB2RB, as the internal winning combination of a type different from the above-mentioned pushing order small combination and the above-mentioned advantageous section lottery, the RB medium and small combination and the advantageous section lottery which respectively play the same role are won. You may
もっとも、(B)BB2状態では、(B−2)BB2RBフラグ間中が最も有利となるように、(B−3)BB2RB中では、押し順小役の基本構成を、(B−1)BB2一般中と同様の構成(1/6で押し順正解、5/6で押し順不正解)としてもよい。すなわち、(B)BB2状態では、停止操作の情報が報知されないことを前提に、(B−1)BB2一般中及び(B−3)BB2RB中を相対的に不利な期間(減少期間)とし、(B−2)BB2RBフラグ間中を有利な期間(増加期間)として構成してもよい。このようにすれば、(B−1)BB2一般中では早期にRBを当籤させて(B−2)BB2RBフラグ間中に移行させ、その後は(B−3)BB2RB中に移行させないように停止操作を行えば(あるいは、そのような停止制御が行われることにより)、遊技者は最も有利な状態で遊技を行うことができるため、遊技者に有利な状態における遊技性をさらに多様化させ、遊技が単調となることなくその興趣を向上させることができる。また、必要以上に増加期間となる遊技状態を増やさないことで、出玉設計を簡易にし、また、射幸性を適度なものとすることもできる。 However, in the (B)BB2 state, the basic configuration of the pushing order small winning combination is (B-1)BB2 in (B-3)BB2RB so that (B-2)BB2RB flag is most advantageous. The configuration may be the same as that in the general case (1/6 is the correct pressing order and 5/6 is the incorrect pressing order). That is, in the (B) BB2 state, assuming that the information of the stop operation is not notified, (B-1) BB2 general and (B-3) BB2RB are relatively disadvantageous periods (reduction periods), (B-2) The middle of the BB2RB flag may be configured as an advantageous period (increase period). In this way, in (B-1)BB2 general, the RB is won early to shift to (B-2)BB2RB flag interval, and then to (B-3)BB2RB stop so as not to shift. By performing an operation (or by performing such a stop control), the player can play the game in the most advantageous state, and thus further diversify the playability in the state advantageous to the player, The entertainment can be improved without the game becoming monotonous. In addition, by not increasing the game state in which the increase period is longer than necessary, the payout design can be simplified and the gambling performance can be made moderate.
また、上述のように、(B)BB2状態において、(B−2)BB2RBフラグ間中が最も有利となるように構成する場合、RBが当籤した遊技、及びそれ以降でRBに係る図柄の組合せが表示可能な遊技では、RBが当籤したこと、あるいはRBに係る図柄の組合せが表示可能であることが報知されるようにしてもよい。当該報知により、遊技者はRBに係る図柄の組合せを表示させないように停止操作を行うことができるようになる。なお、当該報知は、端的にRBに係る図柄の組合せを表示させるべきでないことを指示ないし示唆するものであってもよい。 In addition, as described above, in the (B)BB2 state, (B-2)BB2 When the RB flag is configured to be the most advantageous, the game in which the RB is won, and the combination of the symbols related to the RB after that. In the game that can be displayed, it may be notified that the RB has won or that the combination of symbols related to the RB can be displayed. The notification allows the player to perform a stop operation so as not to display the symbol combination related to RB. The notification may be an instruction or suggestion that the combination of symbols related to RB should not be displayed.
このように、特別役(例えば、第一種特別役物に係る役物連続作動装置であるBB)に当籤し、当該特別役に対応する図柄の組合せの表示により作動する特別遊技状態において、特定役(例えば、第一種特別役物であるRB)の非当籤状態である第1遊技状態と、当該特定役の当籤状態(持越状態)である第2遊技状態と、当該特定役に対応する図柄の組合せの表示により作動する第3遊技状態(特定遊技状態)とを有し、第2遊技状態では、所定役(例えば、押し順小役)の停止制御が遊技者にとって有利となるように制御変更され、かつ、遊技者の停止操作あるいは内部的な制御によって第2遊技状態を維持することを可能とした仕様は、もちろん本実施形態や本例以外の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例で説明したボーナス状態(あるいは、その他の増加期間(増加区間))にも適用することができる。なお、以下では、説明の便宜上、このようなボーナス状態の仕様を「特殊ボーナス状態」と呼ぶ。 In this way, in a special game state in which a special combination (for example, BB, which is a character continuous operation device related to a first-class special combination) is won, and a special combination of symbols corresponding to the special combination is activated, Corresponding to the first gaming state, which is the non-winning state of the combination (for example, RB which is the first class special character), the second gaming state, which is the winning state (carry-over state) of the specific combination, and the specific combination. It has a third game state (specific game state) that is activated by the display of a combination of symbols, and in the second game state, the stop control of a predetermined winning combination (for example, a small pushing order combination) is advantageous for the player. The specifications that the control is changed and the second game state can be maintained by the player's stop operation or internal control are, of course, other game characteristics (game specifications) other than this embodiment and this example. It can also be applied to the bonus state described in the example (or other increase period (increase section)). In the following, for convenience of description, such a bonus state specification is referred to as a “special bonus state”.
一般遊技状態(CZ状態)において、(3)BB2開始条件が成立すると、まず(B−1)BB2一般中に移行する。(B−1)BB2一般中において、上記RBが内部当籤役として決定されると、(B−2)BB2RBフラグ間中に移行し、(B−2)BB2RBフラグ間中は、RBに係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示されるまで継続する(RBに係る図柄の組合せの表示が許可される許可状態が継続する)。(B−2)BB2RBフラグ間中において、RBに係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示されると、(B−3)BB2RB中に移行する。(B−3)BB2RB中において、RB状態の終了条件(例えば、8回以下の任意の所定回数の入賞があったこと、あるいは12回以下の任意の所定回数の遊技が行われたこと)が成立すると、(B−1)BB2一般中に移行する。なお、(B−2)BB2RBフラグ間中において、ボーナス役(RB)よりもリプレイ役又は小役を優先的に成立させる停止制御が行われることで、RBに係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示されにくく(あるいは、停止表示されないように)し、結果として(B−3)BB2RB中に移行することが困難となる(あるいは、移行されない)ようにしてもよい。 In the general game state (CZ state), if (3) BB2 start condition is satisfied, first, the state shifts to (B-1) BB2 general state. (B-1) In BB2 general, when the RB is determined as an internal winning combination, (B-2) transitions between BB2RB flags, and (B-2) during BB2RB flags, symbols related to RB Continues until the combination is stopped and displayed on the activated line (the permitted state in which the display of the combination of symbols related to RB is permitted continues). (B-2) When the symbol combination related to RB is stopped and displayed on the activated line during the BB2RB flag, the process moves to (B-3) BB2RB. (B-3) In the BB2RB, an ending condition of the RB state (for example, winning a predetermined number of times less than or equal to 8 times, or playing a predetermined number of times less than or equal to 12 times) When it is established, the state shifts to (B-1)BB2 general. In addition, during the (B-2) BB2RB flag, stop control is performed to preferentially establish the replay combination or the small combination rather than the bonus combination (RB), so that the combination of symbols related to RB is on the activated line. The stop display may be made difficult (or the stop display may not be performed), and as a result, it may be difficult (or not) to shift to (B-3)BB2RB.
(B−1)BB2一般中、(B−2)BB2RBフラグ間中、及び(B−3)BB2RB中のいずれの状態においても、(B)BB2状態におけるメダルの払出枚数が規定数となった場合(例えば、150枚を超えた場合)、(4)BB2の終了条件が成立し、(B)BB2状態から一般遊技状態(CZ状態)に移行する。 In any state of (B-1) BB2 general, (B-2) BB2RB flag, and (B-3) BB2RB, the number of medals paid out in the (B) BB2 state is the specified number. In the case (for example, when the number exceeds 150), the ending condition of (4) BB2 is satisfied, and the state shifts from the (B) BB2 state to the general gaming state (CZ state).
なお、本例では、(A−1)BB1一般中において当籤するRBと、(B−1)BB2一般中において当籤するRBと、を特に分けて説明していないが、例えば、(A−1)BB1一般中において当籤するRBを「RB1」(対応する図柄の組合せを「RB1に係る図柄の組合せ」、対応するRB状態(A−3)を「RB1状態」)とし、(B−1)BB2一般中において当籤するRBを「RB2」(対応する図柄の組合せを「RB2に係る図柄の組合せ」、対応するRB状態(B−3)を「RB2状態」)とし、異なるRB役を当籤可能に構成することで、(A−2)BB1RBフラグ間中(「RB1許可状態」)にあっては、押し順小役の基本構成が(A−1)BB1一般中と同様になるようにし、(B−2)BB2RBフラグ間中(「RB2許可状態」)にあっては、押し順小役の基本構成が(B−1)BB2一般中とは異なるように構成するようにしてもよい。 In this example, the RB that is won in the general (A-1)BB1 and the RB that is won in the general (B-1)BB2 are not separately described, but, for example, (A-1) ) In BB1 general, the RB to be won is set to "RB1" (corresponding symbol combination is "symbol combination relating to RB1", corresponding RB state (A-3) is "RB1 state"), and (B-1) In BB2 general, the RB that is won in the general is "RB2" (the corresponding symbol combination is "the symbol combination relating to RB2", the corresponding RB state (B-3) is the "RB2 state"), and different RB combinations can be won. In the middle of the (A-2) BB1RB flag (“RB1 permission state”), the basic configuration of the push-order small winning combination is the same as that of the (A-1) BB1 general medium. In the middle of the (B-2) BB2RB flag (“RB2 permission state”), the basic structure of the push-order small winning combination may be different from that of the (B-1) BB2 general medium.
(B−2)BB2RBフラグ間中、及び(B−3)BB2RB中では、上記押し順小役に当籤した遊技においていずれの押し順で停止操作が行われた場合であっても9枚の払出が行われる結果、当該期間は遊技価値が増加(あるいは、少なくとも減少しない)増加期間となる。一方、(B−1)BB2一般中では、上記押し順小役に当籤した遊技で正解となる押し順で停止操作が行われた場合には9枚の払出が行われる一方、正解とならない押し順で停止操作が行われた場合には9枚の払出が行われない結果、当該期間は遊技価値が減少する減少期間となる。もっとも、(B−1)BB2一般中から(B−2)BB2RBフラグ間中にはRBの当籤をもって移行するため、(B)BB2状態全体をみれば、当該期間は遊技価値が増加する増加期間として位置付けられる。 During (B-2) BB2RB flag interval, and (B-3) BB2RB, even if the stop operation is performed in any of the pressing orders in the game in which the above-mentioned pressing order small winning combination is won, 9 payouts are paid out. As a result, the game value is increased (or at least not decreased) during the period. On the other hand, in general (B-1) BB2, when the stop operation is performed in the push order that is the correct answer in the game in which the above-mentioned push order small combination is won, 9 pieces are paid out, while the push that is not the correct answer is pushed. When the stop operation is performed in order, as a result of not paying out 9 coins, the period becomes a reduction period in which the game value decreases. However, since the transition from (B-1) BB2 general to (B-2) BB2RB flag transition occurs with the winning of RB, if the (B) BB2 state as a whole is seen, the relevant period is an increase period in which the game value increases. Positioned as.
なお、(B)BB2状態全体を遊技者にとって有利な期間(増加期間)とする手法は、上述したものに限られない。例えば、(3)BB2開始条件が成立してから(4)BB2終了条件が成立するまで、常にRB状態に制御されるものとし、当該RB状態では、いずれの押し順で停止操作が行われたとしても9枚(あるいは、15枚までの範囲であればそれ以上であってもよい)の払出が発生するRB中小役が極めて高い確率で当籤するように構成してもよい。あるいは、押し順小役の基本構成を制御変更することなく、(3)BB2開始条件が成立してから(4)BB2終了条件が成立するまで、常に有利区間に制御されるようにし、押し順小役の当籤時には必ず、又は少なくとも付与期待値がプラスとなるような所定確率で正解の押し順が報知されることで増加期間となるように構成してもよい。 It should be noted that the method of setting the entire (B) BB2 state as an advantageous period (increase period) for the player is not limited to the above. For example, (3) BB2 start condition is satisfied until (4) BB2 end condition is satisfied, and it is assumed that the RB state is always controlled. In the RB state, the stop operation is performed in any pressing order. Also, the RB medium and small combination that pays out 9 (or more if it is up to 15) may be won with a very high probability. Alternatively, without changing the basic configuration of the push order small winning combination, the control is always performed in the advantageous section from (3) when the BB2 start condition is satisfied until (4) the BB2 end condition is satisfied, and the push order The winning period may be increased at all times when the small winning combination is won, or at least at a predetermined probability that the expected grant value becomes positive, by notifying the correct answer pushing order.
(B−1)BB2一般中、(B−2)BB2RBフラグ間中、及び(B−3)BB2RB中のいずれの状態においても、上記有利区間抽籤役に当籤した場合、(4)BB2終了条件が成立して移行した一般遊技状態(CZ状態)においてBB1に当籤し、(1)BB1開始条件が成立して移行した(A)BB1状態を有利区間とする権利(例えば、セット数やストックなど)を付与する否かが決定される。この場合、一度の当籤で、例えば、30ゲーム間を有利区間とする権利が付与される。なお、当該権利の付与が決定される契機やその期間は、上述したものに限られない。例えば、有利区間抽籤役に当籤したときの当否抽籤の結果のみならず、他の内部当籤役に当籤したときの当否抽籤の結果や、内部当籤役に基づかない当否抽籤の結果などに応じて、当該権利の付与が決定されうるようにしてもよい。また、当該権利の付与が決定されるときに、有利区間の継続期間が別途抽籤などによって決定されうるようにしてもよい。また、(3)BB2開始条件が成立するときから(4)BB2終了条件が成立するまでの間の任意のタイミング(例えば、BB2が入賞したとき、あるいは、BB2が終了したとき)において、BB1状態の全期間(あるいは、一部の期間)を有利区間とする権利を付与するか否かが決定されうるようにしてもよい。 In any of (B-1) BB2 general state, (B-2) BB2RB flag state, and (B-3) BB2RB state, when the above advantageous zone lottery combination is won, (4) BB2 end condition The right to win BB1 in the general game state (CZ state) that has been established and (1) BB1 start condition is established and transitioned to (A) BB1 state as an advantageous section (for example, the number of sets or stock) ) Is determined. In this case, with one win, for example, the right to make 30 games an advantageous section is given. The trigger and the period for which the grant of the right is determined are not limited to those described above. For example, according to not only the result of the lottery winning when winning the advantageous zone lottery, but also the result of the lottery winning when winning the other internal lottery, the result of the lottery not based on the internal winning, etc. The grant of the right may be determined. Further, when the granting of the right is determined, the duration of the advantageous section may be separately determined by lottery or the like. In addition, at any timing from (3) when the BB2 start condition is satisfied to (4) when the BB2 end condition is satisfied (for example, when BB2 wins or when BB2 ends), the BB1 state It may be possible to determine whether or not to grant the right to use the entire period (or part of the period) as the advantageous section.
(C)BB3状態は、(C−1)BB3一般中、(C−2)BB3RBフラグ間中、及び(C−3)BB3RB中から構成される。なお、(C−1)BB3一般中、(C−2)BB3RBフラグ間中、(C−3)BB3RB中、(5)BB3の開始条件のそれぞれは、BB2をBB3と置き換えれば、(B−1)BB2一般中、(B−2)BB2RBフラグ間中、(B−3)BB2RB中、(3)BB2の開始条件のそれぞれと同様となるため、ここでの説明は省略する。また、(6)BB2の終了条件は、(C)BB3状態におけるメダルの払出枚数が規定数となった場合(例えば、60枚を超えた場合)に成立する。 The (C)BB3 state is made up of (C-1)BB3 general, (C-2)BB3RB flag in-between, and (C-3)BB3RB in-between. In addition, in (C-1)BB3 general, (C-2)BB3RB flag, (C-3)BB3RB, and (5)BB3 start conditions, if BB2 is replaced with BB3, (B- The description is omitted here because it is the same as each of the start conditions of 1) BB2 general, (B-2) BB2RB flag, (B-3) BB2RB, and (3) BB2. Further, (6) the ending condition of BB2 is satisfied when the number of paid-out medals in the state of (C) BB3 becomes the specified number (for example, when the number exceeds 60).
かかる前提の下、本例における遊技の流れについて説明する。本例では、非有利区間である(A)BB1状態が遊技者にとって有利でない通常遊技中として位置付けられているため、遊技者は通常、非有利区間である(A)BB1状態から遊技を開始する。 Under such a premise, the flow of the game in this example will be described. In this example, since the (A)BB1 state, which is the non-advantageous section, is positioned as a normal game that is not advantageous to the player, the player normally starts the game from the (A)BB1 state, which is the non-advantageous section. ..
(A)BB1状態においては、(2)BB1の終了条件が成立するまで他の遊技状態に移行することがない。ここで、(A)BB1状態中が有利区間であれば、当該区間は増加期間として機能するため、遊技価値を増加させることができるのみならず、払出を受ける機会が増加することで早期に(2)BB1の終了条件を成立させることが可能となる(すなわち、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)に移行するまでの遊技期間を短縮させることができる)。一方、(A)BB1状態中が非有利区間であれば、当該区間は減少期間として機能するため、遊技価値は減少していき、また、払出を受ける機会は増加しないことで早期に(2)BB1の終了条件を成立させることは可能とならない(すなわち、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)に移行するまでの遊技期間を短縮させることはできない)。 In the (A) BB1 state, there is no transition to another gaming state until the ending condition of (2) BB1 is satisfied. Here, if the (A) BB1 state is an advantageous section, the section functions as an increase period, so that not only can the game value be increased, but also the opportunity to receive the payout increases, which leads to early ( 2) It becomes possible to satisfy the ending condition of BB1 (that is, it is possible to shorten the game period until shifting to the general game state (CZ state)). On the other hand, if the (A) BB1 state is a non-advantageous section, the section functions as a reduction period, so the game value is decreasing, and the chance of receiving the payout does not increase (2) It is not possible to satisfy the ending condition of BB1 (that is, it is not possible to shorten the game period until shifting to the general game state (CZ state)).
(A)BB1状態において、(2)BB1の終了条件が成立すると、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)に移行する。一般遊技状態(CZ状態)は、BB1に当籤する前にBB2又はBB3を当籤させることができれば、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)→(B)BB2状態(又は(C)BB3状態)→一般遊技状態(CZ状態)→(B)BB2状態(又は(C)BB3状態)・・・といったように、遊技者に有利なボーナス状態を繰り返し作動させることが可能な状態(一連の増加区間)として構成されるが、BB2又はBB3に当籤する前にBB1に当籤してしまうと、遊技者に有利なボーナス状態を繰り返し作動させることは不可能となり、一連の増加区間は終了する。再度一連の増加区間に移行させるためには、有利区間とならなければ減少期間となってしまう(A)BB1状態を終了させる必要がある。 In the (A) BB1 state, if the ending condition of (2) BB1 is satisfied, the game state shifts to the general game state (CZ state). General game state (CZ state), if you can win BB2 or BB3 before winning BB1, general game state (CZ state) → (B) BB2 state (or (C)BB3 state) → general game state (CZ state)→(B)BB2 state (or (C)BB3 state), etc., and is configured as a state (a series of increasing sections) in which a bonus state advantageous to the player can be repeatedly activated. However, if the player wins BB1 before winning BB2 or BB3, it is impossible to repeatedly activate the bonus state advantageous to the player, and the series of increase sections ends. In order to shift to a series of increasing sections again, it is necessary to end the (A) BB1 state, which is a decreasing period if it is not an advantageous section.
すなわち、遊技者は、(A)BB1状態にあっては、有利区間に移行、あるいは有利区間が継続することを望み、実際に有利区間に移行、あるいは有利区間が継続すれば、遊技価値を増加させつつ、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)に移行するまでの遊技期間を短縮することができる。また、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)にあっては、BB1に当籤する前にBB2又はBB3に当籤することを望み、実際にBB2又はBB3に当籤することができれば、(B)BB2状態又は(C)BB3状態において遊技価値を増加させることができる。これらの遊技状態が終了して再度一般遊技状態(CZ状態)に戻った場合も同様である。なお、(B)BB2状態又は(C)BB3状態にあっては、(A)BB1状態を有利区間とする権利が付与されることを望む。本例では、例えば、ボーナス役(BB1〜BB3)に当籤する合算確率において、BB1の当籤確率は50%程度、BB2の当籤確率は25%程度、BB3の当籤確率は25%程度となっていることから、一般遊技状態(CZ状態)において必ずしもBB2又はBB3が当籤し続けるわけではない。しかし、(A)BB1状態を有利区間とする権利が予め付与されていれば、BB2又はBB3に当籤する前にBB1に当籤したとしても、(A)BB1状態が増加期間となっていれば、遊技価値が増加し、しかも一般遊技状態(CZ状態)に早期に復帰させることができる。本例では、このような遊技性によって、遊技の興趣を向上させることを可能としている。 That is, in the (A) BB1 state, the player desires to shift to the advantageous zone or continue the advantageous zone, and if the player actually shifts to the advantageous zone or continues the advantageous zone, the game value increases. While doing, it is possible to shorten the game period until shifting to the general game state (CZ state). In the general game state (CZ state), if it is desired to win BB2 or BB3 before winning BB1, and if it is possible to actually win BB2 or BB3, (B) BB2 state or (C) It is possible to increase the game value in the BB3 state. The same applies when these gaming states are over and the general gaming state (CZ state) is resumed. In addition, in the (B)BB2 state or the (C)BB3 state, it is desired that the right to grant the (A)BB1 state as an advantageous section is given. In this example, for example, in the combined probability of winning the bonus combination (BB1 to BB3), the winning probability of BB1 is about 50%, the winning probability of BB2 is about 25%, and the winning probability of BB3 is about 25%. Therefore, BB2 or BB3 does not always continue to win in the normal gaming state (CZ state). However, if the right to (A) BB1 state as the advantageous section is given in advance, even if the BB1 is won before the BB2 or BB3 is won, if the (A) BB1 state is in the increasing period, The game value increases, and moreover, it is possible to return to the general game state (CZ state) at an early stage. In this example, it is possible to improve the enjoyment of the game due to such playability.
本例の遊技機によれば、通常遊技状態(一般遊技状態(CZ状態))において、第1特別役(BB1)に当籤する前に第2特別役(BB2又はBB3)に当籤した場合、第2特別遊技状態((B)BB2状態又は(C)BB3状態)に移行し、当該第2特別遊技状態は遊技価値が増加する増加期間として機能する。一方、通常遊技状態において、第2特別役に当籤する前に第1特別役に当籤した場合、第1特別遊技状態((A)BB1状態)に移行し、当該第1特別遊技状態において停止操作に関する操作情報が報知されない場合(非有利区間である場合)、当該第1特別遊技状態は遊技価値が減少する減少期間として機能する。 According to the gaming machine of this example, in the normal game state (general game state (CZ state)), if the second special combination (BB2 or BB3) is won before the first special combination (BB1) is won, The state shifts to the 2 special game state ((B)BB2 state or (C)BB3 state), and the second special game state functions as an increasing period during which the game value increases. On the other hand, in the normal gaming state, when the first special winning combination is won before the second special winning combination is won, the first special gaming state ((A)BB1 state) is entered, and the stop operation is performed in the first special gaming state. When the operation information regarding is not notified (when it is a non-advantageous section), the first special game state functions as a reduction period during which the game value decreases.
したがって、通常遊技状態においては、第1特別遊技状態に移行することなく第2特別遊技状態への移行が繰り返されることで、遊技者は有利な遊技期間を継続させることができるが、第1特別遊技状態に移行した場合には、当該第1特別遊技状態を終了させて通常遊技状態に移行させなければ、遊技者は有利な遊技期間を継続させることができない。 Therefore, in the normal game state, the player can continue an advantageous game period by repeating the shift to the second special game state without shifting to the first special game state, but the first special game state. When the game state is entered, the player cannot continue the advantageous game period unless the first special game state is ended and the normal game state is entered.
ここで、本例の遊技機によれば、特定の報知条件が成立した場合(例えば、有利区間に移行することが決定された場合、あるいは有利区間とする権利が付与されることが決定されている場合)、第1特別遊技状態において、所定役(押し順小役)に当籤した場合に所定数(例えば、9枚)の遊技価値が付与される停止操作に関する操作情報が報知されるようになる。第1特別遊技状態は、規定数(例えば、285枚超)の遊技価値が付与された場合に終了するものであるから、このような情報が報知されることで、第1特別遊技状態の終了時期を早めることができる。すなわち、第1特別遊技状態において停止操作に関する操作情報が報知される否かによって、第2特別遊技状態に移行可能な通常遊技状態となるまでの期間を変動させることができる。それゆえ、有利状態に移行な状態となるまでの期間を変動可能とすることで、遊技性を変化に富んだものとすることができる。 Here, according to the gaming machine of the present example, when a specific notification condition is satisfied (for example, when it is determined to shift to an advantageous section, or it is determined that a right to be an advantageous section is granted). In the first special game state, when the predetermined winning combination (pushing order small winning combination) is won, a predetermined number (for example, 9 pieces) of game value is given to the operation information about the stop operation. Become. Since the first special game state ends when a prescribed number (for example, more than 285) of game values are given, the first special game state ends by being notified of such information. The time can be advanced. That is, it is possible to change the period until the normal game state in which the second special game state can be entered is changed depending on whether or not the operation information regarding the stop operation is notified in the first special game state. Therefore, by making it possible to change the period until the state shifts to the advantageous state, it is possible to make the game rich in variety.
なお、本例の遊技機において、第1特別遊技状態において停止操作に関する操作情報が報知される期間も増加期間として機能させるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、有利状態に移行な状態となるまでの期間中であっても、遊技の興趣を維持させることができる。 In the gaming machine of this example, the period in which the operation information regarding the stop operation is notified in the first special game state may also be made to function as the increase period. By doing so, it is possible to maintain the interest of the game even during the period until the state shifts to the advantageous state.
また、本例の遊技機において、第1特別遊技状態では、さらに第1特定許可状態((A−2)BB1RBフラグ間中)に移行可能とし、第2特別遊技状態では、さらに第2特定許可状態((B−2)BB2RBフラグ間中又は(C−2)BB3RBフラグ間中)に移行可能とし、第1特別遊技状態では、第1特定許可状態であるか否かにかかわらず、停止操作に関する操作情報が報知されない期間を減少期間として機能させ、第2特別遊技状態では、第2特定許可状態である期間を増加期間として機能させるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、遊技性をさらに変化に富んだものとすることができ、遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。 Further, in the gaming machine of this example, in the first special game state, it is possible to further shift to the first specific permission state (during (A-2)BB1RB flag), and in the second special game state, further second specific permission. It is possible to shift to a state (between (B-2) BB2RB flag or (C-2) BB3RB flag), and in the first special game state, stop operation is performed regardless of whether or not it is the first specific permission state. You may make it function as a decrease period the period when the operation information regarding is not notified, and make it function as the increase period in the second special game state. By doing so, the playability can be further varied and the enjoyment of the game can be improved.
[遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その3)]
続いて、図95を参照して、本実施形態に係るパチスロ1において実装可能な遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その3)について説明する。図95は、遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その3)における遊技の流れを概念的に説明する図である。
[Another example of playability (game specifications) (3)]
Next, with reference to FIG. 95, another example (No. 3) of the playability (game specification) mountable in the pachi-
図95に示すように、本例では、(A)RT0状態、(B)BB状態、及び(C)RT1状態の遊技状態がある。(A)RT0状態は、再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率が(C)RT1状態よりも低く、(B)BB状態、及び(C)RT1状態のいずれにも移行可能な遊技状態である。(A)RT0状態において、有利区間に制御されていない場合には、(A−1)通常(非有利区間)となって遊技価値が減少する減少期間となり、有利区間に制御されている場合には、(A−2)有利区間となって遊技価値が増加する増加期間となる。なお、有利区間に制御されうる特定の報知条件は、本実施形態や本例以外の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例で説明した種々の条件を採用することができる。 As shown in FIG. 95, in this example, there are (A) RT0 state, (B) BB state, and (C) RT1 state game state. The (A) RT0 state is a gaming state in which the winning probability of the replay (replay) combination is lower than that of the (C) RT1 state, and it is possible to shift to any of the (B) BB state and the (C) RT1 state. (A) In the RT0 state, when not controlled to the advantageous section, (A-1) becomes a normal (non-advantageous section), which is a reduction period in which the game value decreases, and when the advantageous section is controlled. Is an (A-2) advantageous period, which is an increasing period during which the game value increases. As the specific notification conditions that can be controlled in the advantageous section, various conditions described in other examples of game characteristics (game specifications) other than this embodiment and this example can be adopted.
(A)RT0状態において、BB(ボーナス役)に当籤した場合、BBに係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示されるまでBBが持ち越されるBBフラグ間(BB許可状態)に制御される。BBフラグ間では、後述のベルこぼし目が有効ライン上に停止表示されても(C)RT1状態には移行しない。なお、本例では、BBは、いずれかの小役(例えば、いわゆるレア役と呼ばれる当籤確率が相対的に低い役。リプレイ役であってもよい)と重複当籤し、単独で当籤しないようになっており、かつ、本実施形態では、ボーナス役よりもリプレイ役又は小役を優先的に成立させる停止制御が行われるため、BBに当籤した遊技ではBBに係る図柄の組合せが表示されることがなく、BBは次回遊技以降に持ち越されることになる。そして、BBに係る図柄の組合せは、BBフラグ間において内部抽籤結果が「ハズレ」となった遊技(すなわち、他にいずれのリプレイ役及び小役にも当籤しなかった遊技)において、停止操作のタイミングが適切な場合に表示されること(入賞すること)が可能となる。本例では、(A)RT0状態における「ハズレ」確率を「1/12」程度と定める。もっとも、「ハズレ」が発生可能である限り、この「ハズレ」確率は任意の値とすることができる。また、BBが単独で当籤する場合があってもよく、この場合には、BBに当籤した遊技においてBBに係る図柄の組合せが表示可能であるものとする。 (A) When the BB (bonus combination) is won in the RT0 state, the BB flag is carried over (BB permitted state) until the BB is carried over until the symbol combination relating to the BB is stopped and displayed on the activated line. Between the BB flags, the state (C) RT1 does not shift even if a bell spilled eye, which will be described later, is stopped and displayed on the activated line. In this example, the BB is won with any of the small winning combinations (for example, a winning combination called a rare winning combination, which has a relatively low winning probability, and may be a replay winning combination), and does not win alone. In addition, in the present embodiment, since the stop control for preferentially establishing the replay combination or the small combination over the bonus combination is performed, the combination of the symbols related to the BB is displayed in the game in which the BB is won. There will be no BB, and the BB will be carried over after the next game. Then, the combination of symbols related to BB is a stop operation in a game in which the result of the internal lottery between the BB flags is “miss” (that is, a game in which no other replay and small wins are won). It is possible to display (win) if the timing is appropriate. In this example, the probability of "missing" in the (A) RT0 state is set to about "1/12". However, as long as “miss” can occur, this “miss” probability can be any value. In addition, there may be a case where the BB wins independently, and in this case, it is assumed that a combination of symbols related to the BB can be displayed in the game in which the BB is won.
(A)RT0状態において、BBフラグ間となり、内部抽籤結果が「ハズレ」となった遊技において、BBに係る図柄の組合せが表示されると、(1)BB開始条件が成立し、(A)RT0状態から(B)BB状態に移行する。(B)BB状態は、(C)RT1状態には移行しない遊技状態であり、遊技価値が増加する増加期間となる遊技状態である。なお、(B)BB状態を増加期間とする手法は、例えば、上述の「特殊ボーナス状態」など、本実施形態や本例以外の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例で説明した種々の手法を採用することができる。(B)BB状態において、規定数(例えば、140枚超)の遊技価値が付与されると、遊技価値の付与上限となり、(2)BB終了条件が成立し、(B)BB状態から(A)RT0状態に移行する。 (A) In the RT0 state, between the BB flags, and in the game in which the internal lottery result is “miss”, when a combination of symbols related to BB is displayed, (1) BB start condition is satisfied, (A) Transition from the RT0 state to the (B)BB state. (B) BB state is a gaming state that does not shift to (C) RT1 state, and is a gaming state that is an increasing period in which the gaming value increases. Note that (B) the method of setting the BB state as the increase period is, for example, the various methods described in other examples of game characteristics (game specifications) other than the present embodiment and this example, such as the above-mentioned “special bonus state”. Can be adopted. In the (B) BB state, when a prescribed number (for example, more than 140) of game values are given, the game value is given as an upper limit, (2) BB end condition is satisfied, and (B) BB state is changed to (A) ) Transition to RT0 state.
(A)RT0状態において、BBフラグ間となる前に(すなわち、BB非フラグ間である場合に)、(3)ベルこぼし目が有効ライン上に停止表示されると、(C)RT1状態に移行する。ベルこぼし目は、例えば、本実施形態における「R_RT1移行目」と同様の図柄の組合せであり、押し順小役に当籤した遊技において、押し順が不正解であり、停止操作のタイミングも適切でない場合に表示される図柄の組合せである。したがって、(A)RT0状態が、(A−2)有利区間であれば、正解となる押し順が報知されるため、当該報知にしたがって停止操作が行われる限り表示されることはないが、(A−1)通常(非有利区間)であれば、正解となる押し順が報知されないため、表示される可能性は高くなる。なお、本例では、例えば、BBの当籤確率は1/20(3276/65536)程度であるとすれば、押し順小役の合算当籤確率はそれよりも高い1/3(21845/65536)程度に設計されるものとすればよい。押し順小役については、本実施形態や本例以外の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例で説明した種々の仕様を採用することができるが、例えば、押し順(例えば、6択)に正解した場合、9枚の払出となり、ベルこぼし目は表示されず、押し順に正解しない場合、停止操作のタイミングが適切であれば1枚の払出となり、ベルこぼし目は表示されず、停止操作のタイミングが適切でなければ0枚の払出となり、ベルこぼし目が表示される仕様を採用することができる。 (A) In the RT0 state, before the BB flag is reached (that is, when it is between the BB non-flags), (3) When the bell-eye drops are stopped and displayed on the activated line, the (C) RT1 state is set. Transition. The bell spill is, for example, a combination of symbols similar to the "R_RT1 transition" in the present embodiment. In a game in which a small push order wins, the push order is incorrect and the timing of the stop operation is not appropriate. It is a combination of symbols displayed in the case. Therefore, if the (A) RT0 state is the (A-2) advantageous section, the correct pressing order is notified, so that it is not displayed as long as the stop operation is performed according to the notification, ( A-1) In the normal case (non-advantageous section), since the correct pressing order is not notified, the possibility of being displayed is high. In this example, if the winning probability of the BB is about 1/20 (3276/65536), the combined winning probability of the pushing order small win is about 1/3 (21845/65536) higher than that. Should be designed to. For the push order small winning combination, various specifications described in other examples of game characteristics (gaming specifications) other than this embodiment and this example can be adopted, for example, in the push order (for example, 6 options). If the correct answer is given, 9 pieces are paid out, and the spilled bells are not displayed. If the answer is not correct in the order of pressing, one piece is paid out if the timing of the stop operation is appropriate, the spilled bells are not displayed, and the stop operation If the timing is not appropriate, 0 sheets will be paid out, and it is possible to adopt a specification in which a bell spill is displayed.
(C)RT1状態は、再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率が(A)RT0状態よりも高く、(B)BB状態には移行しない遊技状態である。(C)RT1状態においても、(A)RT0状態と同様に、有利区間に制御されていない場合には、(C−1)通常(非有利区間)となって遊技価値が減少する減少期間となり、有利区間に制御されている場合には、(C−2)有利区間となって遊技価値が増加する増加期間となる。なお、有利区間に制御されうる特定の報知条件は、本実施形態や本例以外の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例で説明した種々の条件を採用することができる。 The (C) RT1 state is a gaming state in which the winning probability of the replay (replay) combination is higher than that of the (A) RT0 state, and (B) does not shift to the BB state. In the (C)RT1 state as well, as in the (A)RT0 state, when the advantageous period is not controlled, (C-1) becomes a normal (non-advantageous period) and the game value is reduced. If the game is controlled to the advantageous section, (C-2) it becomes the advantageous section, which is an increasing period in which the game value increases. As the specific notification conditions that can be controlled in the advantageous section, various conditions described in other examples of game characteristics (game specifications) other than this embodiment and this example can be adopted.
(C)RT1状態においても、BB(ボーナス役)に当籤した場合、(A)RT0状態と同様に、BBフラグ間(BB許可状態)に制御される。ただし、(C)RT1状態では、(A)RT0状態の「ハズレ」確率「1/12」の分だけ再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率が高まっており、「ハズレ」確率は「0」と(すなわち、「ハズレ」が発生しないように)なっている。したがって、たとえBBフラグ間であったとしても、(C)RT1状態においてBBに係る図柄の組合せが表示可能となる場合はない。もっとも、極めて低い確率(例えば、1/8192)で「ハズレ」が発生するようにし、BBフラグ間で「ハズレ」が発生した遊技では、BBに係る図柄の組合せが表示可能となるようにしてもよい(すなわち、(C)RT1状態を、(A)RT0状態よりもBBに係る図柄の組合せの表示を困難とする状態として構成してもよい)。 Even in the (C) RT1 state, when the BB (bonus combination) is won, the state is controlled between the BB flags (BB permitted state) as in the (A) RT0 state. However, in the (C) RT1 state, the winning probability of the re-play (replay) role is increased by the amount of the “miss” probability “1/12” in the (A) RT0 state, and the “miss” probability is “0”. (That is, "loss" does not occur). Therefore, even if it is between BB flags, there is no case where the combination of symbols related to BB can be displayed in the (C)RT1 state. However, even if the "miss" occurs at an extremely low probability (for example, 1/8192), and in the game where the "miss" occurs between the BB flags, it is possible to display a combination of symbols related to BB. Good (that is, the (C)RT1 state may be configured as a state in which it is more difficult to display the combination of symbols related to BB than the (A)RT0 state).
なお、(C)RT1状態においても「ハズレ」の発生を可能とした場合、「ハズレ」が発生した単位遊技でBBに係る図柄の組合せが表示できなかった場合には、(B)BB状態に移行させることができず、次ゲーム以降も(C)RT1状態が継続するため、当該「ハズレ」が発生した単位遊技でBBに係る図柄の組合せが表示できない態様で停止操作を行ってしまうと遊技者の損失は極めて大きくなってしまう。したがって、このような損失の発生を抑制するため、(C)RT1状態において「ハズレ」が発生した単位遊技では、開始操作後から停止操作が有効となるまでの間にBBに係る図柄の組合せの表示が許容された旨を示唆する演出や、BBに係る図柄の組合せを狙うべき旨を報知する演出や、開始操作後に各リールの回転開始を遅延させるフリーズ演出や停止操作有効までに要する時間を通常よりも長い時間とする停止操作無効化演出など、いずれか又は複数の演出を実行可能として、遊技者がBBに係る図柄の組合せを表示させやすいように配慮した仕様とすることが望ましい。 In addition, in the case of (C)RT1 state, if the "miss" can be generated, if the combination of symbols related to BB cannot be displayed in the unit game in which the "miss" occurs, the (B)BB state is set. Since the state cannot be changed and the (C)RT1 state continues after the next game, if the stop operation is performed in a mode in which the combination of symbols related to BB cannot be displayed in the unit game in which the “miss” has occurred, the game Person's loss will be extremely large. Therefore, in order to suppress the occurrence of such a loss, (C) in the unit game in which the "miss" has occurred in the RT1 state, after the start operation until the stop operation becomes effective, the combination of symbols related to BB The effect that suggests that the display is allowed, the effect that the combination of symbols related to BB should be aimed at, the freeze effect that delays the start of rotation of each reel after the start operation, and the time required for the stop operation to be effective It is desirable to make it possible to execute any one or a plurality of effects such as a stop operation invalidation effect that takes a longer time than usual so that the player can easily display a combination of symbols related to BB.
(C)RT1状態において、(4)規定数(例えば、500ゲーム)の遊技を消化すると、(C)RT1状態から(A)RT0状態に移行する。すなわち、(C)RT1状態が終了し、BBフラグ間である場合には「ハズレ」発生時にBBに係る図柄の組合せが表示可能となる。なお、(C)RT1状態から(A)RT0状態に移行した場合であってもBB非フラグ間であるときには、再度(C)RT1状態に転落してしまう可能性がある。したがって、このような場合には、(A)RT0状態においてBBフラグ間となるまで(すなわち、BBに当籤するまで)、(A−2)有利区間を継続させるようにし、遊技者の救済を図るようにしてもよい。 In the (C) RT1 state, when (4) a prescribed number of games (for example, 500 games) are exhausted, the (C) RT1 state is shifted to the (A) RT0 state. That is, when the (C) RT1 state is finished and the BB flag is in between, it is possible to display a combination of symbols related to BB when a "loss" occurs. Even when the state (C) RT1 is changed to the state (A) RT0, there is a possibility that the state will fall again to the state (C) RT1 while the BB is not in the flag state. Therefore, in such a case, (A) in the RT0 state, until the BB flag is reached (that is, until BB is won), (A-2) the advantageous section is continued, and the player is rescued. You may do it.
本例の遊技機によれば、特別役(BB)に当籤した場合には特別許可状態(BB許可状態)となり、通常遊技状態((A)RT0状態)であれば、特別図柄の組合せ(BBに係る図柄の組合せ)を表示させて特別遊技状態((B)BB状態)に移行させることを可能とする一方、特定遊技状態((C)RT1状態)であれば、当該特定遊技状態が終了するまで特別図柄の組合せを表示させて特別遊技状態に移行させることを可能としない。また、特定遊技状態には、特別許可状態でない通常遊技状態において特定役(押し順小役)に当籤した場合に、特定の態様(押し順正解となる態様)で停止操作が行われずに特定図柄の組合せ(ベルこぼし目)が表示されたことに基づいて移行する。そして、特定の報知条件が成立した場合、通常遊技状態及び特定遊技状態における特定期間(有利区間)では、特定役に当籤したときに特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知され、報知にしたがって停止操作が行われれば、特定図柄の組合せは表示されず、特定数(例えば、9枚)の遊技価値が付与される。 According to the gaming machine of this example, when the special combination (BB) is won, the special permission state (BB permission state) is set, and when the normal game state ((A) RT0 state), the combination of special symbols (BB) It is possible to shift to a special game state ((B)BB state) by displaying a combination of symbols related to), while the specific game state ends if the specific game state ((C)RT1 state) Until it does, it is not possible to display the combination of special symbols and shift to the special game state. In addition, in the specific game state, when the specific combination (pushing order small combination) is won in the normal game state which is not the special permission state, the specific symbol without the stop operation in a specific mode (mode in which the pressing order is the correct answer) A transition is made based on the display of the combination (bell spill). Then, when the specific notification condition is satisfied, during the specific period (advantageous section) in the normal game state and the specific game state, operation information regarding a specific aspect is notified when a specific winning combination is won, and a stop operation is performed according to the notification. If done, the combination of the specific symbols is not displayed, and a specific number (for example, 9) of game values are given.
ここで、本例の遊技機によれば、通常遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間となった場合には、特定遊技状態に移行することなく特別遊技状態への移行を繰り返す(すなわち、遊技者に有利な遊技期間を継続させる)ことが可能となるのみならず、特定役に当籤したときに付与される遊技価値も増加することになる。また、特定遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間となった場合には、特定遊技状態が終了しなければ特別遊技状態に移行させることはできないが、特定役に当籤したときに付与される遊技価値は増加することになる。また、通常遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間となっていない場合であっても、特定遊技状態に移行することなく特別遊技状態への移行を繰り返すことができる場合もある。 Here, according to the gaming machine of the present example, in the normal gaming state, when the specific period during which the operation information regarding the specific mode is notified is given, the shift to the special gaming state is performed without shifting to the specific gaming state. It is possible not only to repeat the game (that is, to continue the game period advantageous to the player), but also to increase the game value given when the specific combination is won. Also, in the specific game state, when it becomes a specific period in which operation information regarding a specific mode is notified, it is not possible to shift to the special game state unless the specific game state ends, but when a specific winning combination is won. The game value given to the player will increase. In addition, even in a case where the normal game state is not in a specific period in which operation information related to a specific mode is notified, it may be possible to repeat the transition to the special game state without shifting to the specific game state. ..
すなわち、本例の遊技機によれば、通常遊技状態若しくは特定遊技状態であるか、通常遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間であるか否か、又は特定遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間であるか否か、などに応じて遊技者の有利度合いを多彩に変動させることが可能となる。それゆえ、遊技意欲や興趣を向上させることができる。 That is, according to the gaming machine of the present example, whether it is the normal gaming state or the specific gaming state, or whether it is the specific period during which the operation information regarding the specific mode is notified in the normal gaming state, or the specific gaming state is specified. It is possible to change the advantage degree of the player in various ways in accordance with whether or not it is a specific period in which the operation information regarding the mode is notified. Therefore, it is possible to improve the game motivation and interest.
なお、本例の遊技機において、少なくとも特定遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される期間は、遊技価値が増加する増加期間として機能させるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、特定遊技状態であっても遊技価値が増加する場合があることから、特別遊技状態に移行しない特定遊技状態中であっても、遊技の興趣を維持させることができる。 In the gaming machine of this example, at least the period in which the operation information regarding the specific mode is notified in the specific game state may be made to function as an increasing period in which the game value increases. By doing so, the game value may increase even in the specific game state, so that the interest of the game can be maintained even during the specific game state in which the special game state is not entered.
(本例の変形例)
本例では、(A)RT0状態、(B)BB状態、及び(C)RT1状態の遊技状態を有し、(A)RT0状態において、特別役としてのBBが特定役としての押し順小役よりも先に当籤した場合には、(C)RT1状態に移行することなく(B)BB状態に移行し、このような移行が繰り返されることを可能とすることで、一連の増加区間を創出することを可能とした。また、(A)RT0状態において、特定役としての押し順小役が特別役としてのBBよりも先に当籤した場合に、遊技者の停止操作が適切であれば(C)RT1状態には移行しないが、遊技者の停止操作が適切でなければ(C)RT1状態に移行し、一連の増加区間が終了するものとした。そして、(C)RT1状態では、一定の移行条件(本例では、規定数の遊技の消化)が成立しなければ、(A)RT0状態に移行しないものとした。もっとも、このような一連の増加区間を開始、継続、及び終了させる手法は、さらに変形の余地があると考えられるため、以下に説明する。
(Modification of this example)
In this example, there are (A) RT0 state, (B) BB state, and (C) RT1 state game state, and in the (A) RT0 state, BB as a special role is a pressing order small win as a specific role. If the winning is made before that, (C) it shifts to the BB state without shifting to the RT1 state, and such a transition can be repeated, thereby creating a series of increase intervals. Made it possible. Further, in the (A) RT0 state, if the push order small combination as the specific combination is won before the BB as the special combination, and if the player's stop operation is appropriate, the state shifts to the (C) RT1 state. However, if the player's stop operation is not appropriate, the state shifts to (C) RT1 and the series of increase sections ends. Then, in (C) RT1 state, unless a certain transition condition (in this example, digestion of a specified number of games) is satisfied, (A) RT0 state is not transitioned. However, the method of starting, continuing, and ending such a series of increasing sections is considered to have further room for modification, and will be described below.
変形例では、(A)RT0状態、(B)BB状態、及び(C)RT1状態の遊技状態を有する点は本例と同じであるが、特定役としてMB(第二種特別役物に係る役物連続作動装置)を用い、MBに係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示された場合には(D)MB状態に移行するものとする。BBの当籤確率を1/10(6553/65536)程度とするとともに、MBの当籤確率も同程度とする。MBは、ボーナス役であり、一度当籤すると、MBに係る図柄の組合せが表示されるまで持ち越されるものとする(MBフラグ間、MB許可状態)。MBは、必ず複数の特殊小役グループ(例えば、特殊小役グループ1〜3)のうちいずれかの特殊小役グループと重複当籤し、単独では当籤しないものとする。
The modified example is the same as this example in that it has (A) RT0 state, (B) BB state, and (C) RT1 state gaming state, but MB (related to the second-class special character) as a specific role. If the combination of symbols related to MB is stopped and displayed on the activated line, the character state continuous operating device) is used to shift to (D) MB state. The winning probability of BB is set to about 1/10 (6553/65536), and the winning probability of MB is set to about the same. The MB is a bonus combination, and once it is won, it is carried over until the combination of symbols related to the MB is displayed (between MB flags, MB permitted state). It is assumed that the MB always wins the special winning combination group with any one of the special small winning groups (for example, the special
(A)RT0状態において、MB+特殊小役グループ1が重複当籤した場合、停止操作が予め定義された正解の態様(例えば、リール3Lに対する停止操作のタイミングが下記第2の範囲及び下記第3の範囲とは異なる第1の範囲である態様、あるいは左第1停止で停止操作が行われる態様など)で行われた場合には、MBに係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示され、(D)MB状態に移行する。一方、停止操作が予め定義された正解の態様で行われない場合には、MBに係る図柄の組合せは有効ライン上に停止表示されず、いずれかの特殊小役に係る図柄の組合せ(特定の図柄の組合せ)が有効ライン上に停止表示され、例えば、1枚のメダルが払い出され、MBフラグ間としての(C)RT1状態に移行する。
(A) In the RT0 state, when the MB+special
(A)RT0状態において、MB+特殊小役グループ2が重複当籤した場合、停止操作が予め定義された正解の態様(例えば、リール3Lに対する停止操作のタイミングが上記第1の範囲及び下記第3の範囲とは異なる第2の範囲である態様、あるいは中第1停止で停止操作が行われる態様など)で行われた場合には、MBに係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示され、(D)MB状態に移行する。一方、停止操作が予め定義された正解の態様で行われない場合には、MBに係る図柄の組合せは有効ライン上に停止表示されず、いずれかの特殊小役に係る図柄の組合せ(特定の図柄の組合せ)が有効ライン上に停止表示され、例えば、1枚のメダルが払い出され、MBフラグ間としての(C)RT1状態に移行する。
(A) In the RT0 state, when the MB+special
(A)RT0状態において、MB+特殊小役グループ3が重複当籤した場合、停止操作が予め定義された正解の態様(例えば、リール3Lに対する停止操作のタイミングが上記第1の範囲及び上記第2の範囲とは異なる第3の範囲である態様、あるいは右第1停止で停止操作が行われる態様など)で行われた場合には、MBに係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示され、(D)MB状態に移行する。一方、停止操作が予め定義された正解の態様で行われない場合には、MBに係る図柄の組合せは有効ライン上に停止表示されず、いずれかの特殊小役に係る図柄の組合せ(特定の図柄の組合せ)が有効ライン上に停止表示され、例えば、1枚のメダルが払い出され、MBフラグ間としての(C)RT1状態に移行する。
(A) In the RT0 state, when the MB+special small winning
なお、この変形例では、特定役として複数のMB(例えば、MB1、MB2、及びMB3)を用い、いずれかのMBに係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示された場合には(D)MB状態に移行するものとしてもよい。この場合、MBの合算当籤確率をBBの当籤確率と同程度とすればよい。また、MB1、MB2、及びMB3は、必ず特殊小役グループと重複当籤し、単独では当籤しないものとしてもよい。そして、MB1+特殊小役グループが重複当籤した場合には、MB+特殊小役グループ1と同様の制御が行われ、MB2+特殊小役グループが重複当籤した場合には、MB+特殊小役グループ2と同様の制御が行われ、MB3+特殊小役グループが重複当籤した場合には、MB+特殊小役グループ3と同様の制御が行われるものとすればよい。
In this modified example, when a plurality of MBs (for example, MB1, MB2, and MB3) are used as the specific combination, and a combination of symbols related to any of the MBs is stopped and displayed on the activated line (D). It may be possible to shift to the MB state. In this case, the total winning probability of MB may be set to be approximately the same as the winning probability of BB. In addition, MB1, MB2, and MB3 may be the same as the special winning combination group, and may be won without fail. Then, when the MB1+special small winning group is a double winning, the same control as the MB+special
すなわち、(A)RT0状態において、MBに当籤した場合、MBに当籤した遊技で停止操作の態様が適切であれば(例えば、上述した3択に正解した場合には)、(D)MB状態に移行する。(D)MB状態は、例えば、2枚ベットで必ず2枚のメダルが払い出されるボーナス状態であるものとし、規定数(2枚を超える)の遊技価値が付与されると、遊技価値の付与上限となり、MB終了条件が成立し、(D)MB状態から(A)RT0状態に移行する。ここで、(D)MB状態自体は、遊技価値が増加する増加期間ではない(ただし、減少期間でもなく無増減期間)が、終了後は(A)RT0状態に移行するため、(D)MB状態への移行は、上述した一連の増加区間への移行、あるいは一連の増加区間の継続として位置付けられる。 That is, in the (A) RT0 state, if the MB is won, if the mode of the stop operation is appropriate in the game in which the MB is won (for example, if the above three options are correctly answered), the (D) MB state Move to. (D) The MB state is, for example, a bonus state in which two medals are always paid out with two bets, and when a prescribed number (more than two) of game values are given, an upper limit of the game value is given. Then, the MB end condition is satisfied, and the state shifts from the (D) MB state to the (A) RT0 state. Here, the (D)MB state itself is not an increasing period in which the game value increases (however, it is not a decreasing period but a non-increasing period), but after the end, it shifts to the (A)RT0 state, so that (D)MB state. The transition to the state is positioned as the transition to the series of increment sections described above or the continuation of the series of increment sections.
一方、(A)RT0状態において、MBに当籤した場合、MBに当籤した遊技で停止操作の態様が適切でなければ(例えば、上述した3択に正解しなかった場合には)、(C)RT1状態に移行する。この変形例では、MBフラグ間である(C)RT1状態は、MBに係る図柄の組合せが表示されるまで終了しない。そして、(C)RT1状態における「ハズレ」確率を「1/300」程度と定める。すなわち、(C)RT1状態を終了させて(A)RT0状態に移行させるためには、(C)RT1状態において「ハズレ」が発生した遊技において、MBに係る図柄の組合せを表示させて(D)MB状態に移行させ、(D)MB状態における遊技を消化する必要がある。なお、(C)RT1状態において上述した特殊小役グループに当籤したときに、上述した3択に正解した場合にもMBに係る図柄の組合せを表示させることを可能としてもよい。 On the other hand, in the (A) RT0 state, if the MB is won, if the mode of the stop operation is not appropriate in the game in which the MB is won (for example, if the above three options are not correctly answered), (C) Transition to the RT1 state. In this modification, the (C)RT1 state, which is between the MB flags, does not end until the combination of symbols related to MB is displayed. Then, (C) the “miss” probability in the RT1 state is set to about “1/300”. That is, in order to end the (C)RT1 state and shift to the (A)RT0 state, in the game in which the "miss" has occurred in the (C)RT1 state, a combination of symbols relating to MB is displayed (D). ) It is necessary to shift to the MB state and digest the game in the (D) MB state. In addition, when the special small winning group described above is won in the (C) RT1 state, it may be possible to display the combination of symbols related to the MB even when the correct answer is given to the above-mentioned three options.
(本例の変形例の遊技の流れ)
この変形例では、MBフラグ間である(C)RT1状態が遊技者にとって有利でない通常遊技中として位置付けられているため、遊技者は通常、MBフラグ間である(C)RT1状態から遊技を開始する。
(Game flow of a modified example of this example)
In this modification, the (C)RT1 state between the MB flags is positioned as a normal game that is not advantageous to the player, so the player usually starts the game from the (C)RT1 state between the MB flags. To do.
(C)RT1状態においては、(D)MB状態への移行を介さなければ(A)RT0状態に移行することがない。遊技者は「ハズレ」が発生することを待って遊技を行う。「ハズレ」が発生した遊技でMBに係る図柄の組合せを表示させることができれば、(D)MB状態に移行し、(D)MB状態に終了後は(A)RT0状態に移行する。 In the (C) RT1 state, the transition to the (A) RT0 state does not occur unless the transition to the (D) MB state is performed. The player plays the game after waiting for the "loss" to occur. If a combination of symbols related to MB can be displayed in the game in which the "loss" has occurred, the state shifts to (D)MB state, and after finishing the (D)MB state, shifts to (A)RT0 state.
(A)RT0状態において、ボーナス役に当籤したとき、当該ボーナス役がBBである確率は1/2(50%)、MBである確率も1/2(50%)である。(C)RT1状態から(A)RT0状態に移行して最初に当籤したボーナス役がBBであった場合には、一連の増加区間が開始される。BBの当籤後はMBに当籤することはなく(すなわち、(C)RT1状態に移行することなく)、BBに係る図柄の組合せが表示されることで(B)BB状態に移行し、(B)BB状態において遊技価値を増加させることができる。なお、(B)BB状態は、例えば、上述の「特殊ボーナス状態」として構成される。(B)BB状態が終了すると再度(A)RT0状態に戻り、再度50%の確率でMBに当籤する前にBBに当籤させることができれば、一連の増加区間が継続する。すなわち、一連の増加区間は50%の確率でループ可能な(ループ率50%の)遊技区間となっている。なお、このループ率は一例であり、ボーナス役の抽籤値(当籤確率)を適宜変動させることで、任意の値に設定することができる。 (A) When the bonus combination is won in the RT0 state, the probability that the bonus combination is BB is 1/2 (50%), and the probability that it is MB is 1/2 (50%). When the bonus combination initially won after the transition from the (C) RT1 state to the (A) RT0 state is BB, a series of increasing sections is started. After winning the BB, the MB is not won (that is, without shifting to the (C)RT1 state), and the combination of symbols relating to the BB is displayed (the B) transitions to the BB state. It is possible to increase the game value in the BB state. The (B) BB state is configured as, for example, the above-mentioned “special bonus state”. (B) When the BB state is completed, the state returns to the (A) RT0 state again, and if the BB can be won before the MB is won again with a probability of 50%, a series of increment sections continues. That is, a series of increase sections are game sections that can be looped with a probability of 50% (loop rate of 50%). Note that this loop rate is an example, and can be set to an arbitrary value by appropriately changing the lottery value (winning probability) of the bonus combination.
一連の増加区間となった(A)RT0状態において、BBに当籤する前にMBに当籤した場合、MBに当籤した遊技でMBに係る図柄の組合せを表示させることができた場合には、(D)MB状態への移行を介して再度(A)RT0状態に戻ることができる。この場合にも、一連の増加区間が継続する。一方、MBに当籤した遊技でMBに係る図柄の組合せを表示させることができなかった場合には、(C)RT1状態に移行する。この場合には、一連の増加区間が終了する。 In the (A) RT0 state, which is a series of increasing sections, if the MB is won before the BB is won, the combination of the symbols related to the MB can be displayed in the game won to the MB, ( D) It is possible to return to the (A) RT0 state again through the transition to the MB state. In this case as well, a series of increasing sections continues. On the other hand, when the combination of symbols related to MB cannot be displayed in the game won to MB, (C) RT1 state is entered. In this case, a series of increasing sections ends.
また、(C)RT1状態から(A)RT0状態に移行して最初に当籤したボーナス役がMBであった場合には、一連の増加区間は開始されない。ただし、上述の如く、MBに当籤した遊技でMBに係る図柄の組合せを表示させることができた場合には、(D)MB状態への移行を介して再度(A)RT0状態に戻ることができる。この場合には、戻った(A)RT0状態にて一連の増加区間を開始できる場合がある。一方、MBに当籤した遊技でMBに係る図柄の組合せを表示させることができなかった場合には、(C)RT1状態に移行する。この場合には、一連の増加区間を開始できる場合はない。なお、上記の説明では、(C)RT1状態から(A)RT0状態に移行して最初に当籤したボーナス役がBBであったときを一連の増加区間の始期としているが、(C)RT1状態から(A)RT0状態に移行したときを一連の増加区間の始期としてもよいし、(C)RT1状態から(A)RT0状態に移行して最初に当籤したボーナス役がBBであり、当該BBに係る図柄の組合せが表示されて(B)BB状態に移行したときを一連の増加区間の始期としてもよい。 Further, when the (C)RT1 state is shifted to the (A)RT0 state and the first winning combination is MB, a series of increasing sections is not started. However, as described above, when the combination of symbols related to MB can be displayed in the game won in MB, it is possible to return to (A) RT0 state again through the transition to (D) MB state. it can. In this case, it may be possible to start a series of increasing sections in the returned (A) RT0 state. On the other hand, when the combination of symbols related to MB cannot be displayed in the game won to MB, (C) RT1 state is entered. In this case, there is no case where a series of increasing sections can be started. In addition, in the above description, the start of the series of increasing sections is the case where the first winning combination is BB after shifting from the (C)RT1 state to the (A)RT0 state, but the (C)RT1 state is set. The transition from (A) to RT0 state may be the start of a series of increasing sections, or (B) is the first bonus combination won after transition from (C) RT1 state to (A) RT0 state. The time when the combination of symbols relating to (3) is displayed and the state shifts to the (B) BB state may be the start of a series of increasing sections.
(本例の変形例における有利区間仕様の第1の態様)
続いて、これまでに説明した本例の変形例の遊技性(遊技仕様)を採用した場合の、有利区間仕様の第1の態様について説明する。この第1の態様は、有利区間を設けない仕様である。
(First Mode of Advantageous Interval Specification in Modification of this Example)
Next, the first mode of the advantageous zone specification when the game characteristic (game specification) of the modified example of the present example described so far is adopted will be described. The first mode is a specification in which no advantageous section is provided.
上述したように、本例の変形例の遊技性(遊技仕様)では、(A)RT0状態→(B)BB状態→(A)RT0状態→(B)BB状態・・・といったように、(A)RT0状態と(B)BB状態とが相互に繰り返されることで一連の増加区間を創出することができるため、遊技者に停止操作の情報が報知されなくとも、興趣の高い遊技性を具備することが可能となっている。したがって、この第1の態様のように、有利区間を設けないようにすることもできる。 As described above, in the game property (game specification) of the modified example of this example, (A) RT0 state → (B) BB state → (A) RT0 state → (B) BB state... By repeating the A) RT0 state and the (B) BB state, it is possible to create a series of increasing intervals, so that even if the player is not informed of the stop operation, the game is highly entertaining. It is possible to do. Therefore, as in the case of the first aspect, the advantageous section may not be provided.
なお、この第1の態様においても、例えば、(A)RT0状態においてBBに当籤したときには、その旨の告知ないし示唆が行われるようにすることができるし、(B)BB状態においてRBに当籤したときには、その旨の告知ないし示唆が行われるようにすることができる。一方、(A)RT0状態においてMBに当籤したとき、及び(C)RT1状態においてMBに係る図柄の組合せが表示可能であるときには、少なくともMBに係る図柄の組合せが表示される遊技方法が推測されるような告知ないし示唆は行われないようにすることが望ましい。ここで、「MBに係る図柄の組合せが表示される遊技方法が推測されるような告知ないし示唆」とは、例えば、MBに係る図柄の組合せが表示可能であることを直接的に告知ないし示唆するものに限られず、上述した特殊小役グループが当籤した旨、あるいは当籤した特殊小役グループに係る図柄の組合せを告知ないし示唆するものが含まれる。このような告知ないし示唆によって実質的に(C)RT1状態が終了する確率が高まることとなれば、遊技の射幸性が過度に高くなってしまうおそれがあるからである。もっとも、(C)RT1状態は少ないとも一連の増加区間に含まれないことから、(C)RT1状態においてMBに係る図柄の組合せが表示可能であるときには、「MBに係る図柄の組合せが表示される遊技方法が推測されるような告知ないし示唆」が行われるようにしてもよい。 Also in this first mode, for example, when (B) BB is won in the (A) RT0 state, notification or suggestion to that effect can be made, and (B) RB is won in the BB state. If you do, you can make an announcement or suggestion to that effect. On the other hand, (A) When the MB is won in the RT0 state, and (C) When the symbol combination related to the MB can be displayed in the RT1 state, at least a game method in which the symbol combination related to the MB is displayed is estimated. It is desirable not to make such announcements or suggestions. Here, "announcement or suggestion that a game method in which a combination of symbols relating to MB is displayed is inferred" is, for example, directly announcing or suggesting that a combination of symbols relating to MB can be displayed. The present invention is not limited to this, but includes a notice or suggestion that the above-mentioned special small winning group has won or a combination of symbols related to the special small winning group that has won. This is because if such a notification or suggestion substantially increases the probability that the (C)RT1 state will end, the gambling performance of the game may become excessively high. However, since the (C)RT1 state is not included in the series of increasing sections at least, when the (C)RT1 state can display the MB-related symbol combination, “the MB-related symbol combination is displayed. "Announcement or suggestion" such that the game method to be performed can be guessed.
(本例の変形例における有利区間仕様の第2の態様)
続いて、これまでに説明した本例の変形例の遊技性(遊技仕様)を採用した場合の、有利区間仕様の第2の態様について説明する。この第2の態様は、(B)BB状態中のみ有利区間に移行可能とした仕様である。
(Second Mode of Advantageous Interval Specification in Modification of this Example)
Next, a second mode of the advantageous zone specification when the game characteristic (game specification) of the modified example of the present example described so far is adopted will be described. The second mode is (B) a specification in which transition to the advantageous section is possible only during the BB state.
上述したように、本例の変形例の遊技性(遊技仕様)では、(B)BB状態においては押し順小役など、遊技者の停止操作の態様に応じて付与される遊技価値が変動可能な内部当籤役が決定されうるため、(B)BB状態中を有利区間として遊技者に停止操作の情報が報知されれば、(B)BB状態中に付与される遊技価値の付与期待値を最大とすることができ、遊技者の興趣の向上のみならず、遊技の公平性の担保や出玉率の管理しやすさにも資することになる。したがって、この第2の態様のように、(B)BB状態中のみ有利区間に移行可能とすることもできる。この場合、(B)BB状態が開始されるときに有利区間も開始され、(B)BB状態が終了されるときに有利区間も終了されるようにすればよい。 As described above, in the game property (game specification) of the modified example of the present example, in (B) BB state, the game value provided according to the mode of the stop operation of the player, such as the push order small win, can be changed. Since the internal winning combination can be determined, if the player is informed of the stop operation with the (B) BB state as an advantageous section, the (B) expected value of the game value given in the BB state is set. It can be maximized and contributes not only to the interest of the player, but also to guaranteeing the fairness of the game and the manageability of the payout rate. Therefore, as in the second mode, it is possible to shift to the advantageous section only during the (B) BB state. In this case, the advantageous section may be started when the (B)BB state is started, and the advantageous section may be ended when the (B)BB state is ended.
なお、この第2の態様においても、上記第1の態様と同様に、例えば、(A)RT0状態においてBBに当籤したときには、その旨の告知ないし示唆が行われるようにすることができるし、(B)BB状態においてRBに当籤したときには、その旨の告知ないし示唆が行われるようにすることができる。一方、(A)RT0状態においてMBに当籤したとき、及び(C)RT1状態においてMBに係る図柄の組合せが表示可能であるときには、上記第1の態様と同様に、少なくともMBに係る図柄の組合せが表示される遊技方法が推測されるような告知ないし示唆は行われないようにすることが望ましい。 In the second mode, as in the case of the first mode, for example, when (B) BB is won in the (A) RT0 state, notification or suggestion to that effect can be made. (B) When the RB is won in the BB state, a notification or suggestion to that effect can be made. On the other hand, (A) When the MB is won in the RT0 state, and (C) When the combination of symbols relating to the MB can be displayed in the RT1 state, at least the combination of symbols relating to the MB is similar to the first aspect. It is desirable not to make announcements or suggestions that would infer the game method in which is displayed.
(本例の変形例における有利区間仕様の第3の態様)
続いて、これまでに説明した本例の変形例の遊技性(遊技仕様)を採用した場合の、有利区間仕様の第3の態様について説明する。この第3の態様は、(A)RT0状態中及び(C)RT1状態中において有利区間に移行可能とした仕様である。
(Third Mode of Advantageous Interval Specification in Modification of this Example)
Next, a third mode of the advantageous zone specification when the game characteristic (game specification) of the modified example of the present example described so far is adopted will be described. The third mode is a specification in which it is possible to shift to the advantageous section during (A) RT0 state and (C) RT1 state.
この第3の態様は、基本的に本例で説明したものと同様であり、(A)RT0状態中にあっては、特定の報知条件が成立した場合に、(A−1)通常(非有利区間)から(A−2)有利区間に移行させ、当該有利区間の終了条件が成立した場合に、(A−2)有利区間から(A−1)通常(非有利区間)に移行させ、また、(C)RT1状態中にあっては、特定の報知条件が成立した場合に、(C−1)通常(非有利区間)から(C−2)有利区間に移行させ、当該有利区間の終了条件が成立した場合に、(C−2)有利区間から(C−1)通常(非有利区間)に移行させるものである。 The third mode is basically the same as that described in this example, and in the (A) RT0 state, when a specific notification condition is satisfied, (A-1) normal (non- (A-2) advantageous zone, and when the condition for ending the advantageous zone is satisfied, shift from (A-2) advantageous zone to (A-1) normal (non- advantageous zone), Further, in the (C) RT1 state, when a specific notification condition is satisfied, the (C-1) normal (non-advantageous section) is shifted to the (C-2) advantageous section, and the advantageous section When the termination condition is satisfied, the (C-2) advantageous section is shifted to the (C-1) normal (non-advantageous section).
ただし、本例では、(A)RT0状態において(A−2)有利区間となった場合には、押し順小役について正解となる押し順が報知されることで、実質的に(C)RT1状態への移行が回避可能な情報も報知されるものとなっているが、この第3の態様では、(C)RT1状態への移行が回避可能な情報は報知されないものとなっている。すなわち、(A−2)有利区間では、押し順小役に当籤した場合には、正解となる押し順が報知されることで、(A−1)通常(非有利区間)と比べて多くの遊技価値が付与されるが、MBに当籤した場合には、「MBに係る図柄の組合せが表示される遊技方法が推測されるような告知ないし示唆」は行われず、遊技者が自力でMBに係る図柄の組合せを表示することができた場合には(A)RT0状態が維持されるが、遊技者が自力でMBに係る図柄の組合せを表示することができなかった場合には(C)RT1状態に移行するようになっている。 However, in the present example, when the (A-2) advantageous section is reached in the (A) RT0 state, the pushing order that is the correct answer for the pushing order small winning combination is informed, so that (C) RT1 is substantially achieved. Although the information that can avoid the transition to the state is also notified, in the third aspect, the information that can avoid the transition to the (C)RT1 state is not notified. That is, in the (A-2) advantageous section, when a small winning combination in the pushing order is won, the pushing order that is the correct answer is notified, so that (A-1) more than in the normal (non-advantageous section). A game value is given, but if the MB is won, the "announcement or suggestion that the game method in which the combination of symbols relating to the MB is displayed is guessed" is not made, and the player voluntarily changes to the MB. When the combination of such symbols can be displayed (A), the RT0 state is maintained, but when the player cannot display the combination of symbols relating to MB by himself/herself (C). It is adapted to shift to the RT1 state.
もっとも、例えば、(A)RT0状態において(A−2)有利区間となり、有利区間の継続期間として50ゲームが付与された場合、10ゲーム後(すなわち、有利区間の継続期間が残り40ゲーム)にMBに当籤し、MBに係る図柄の組合せが表示されずに(C)RT1状態に移行した場合には、継続期間を40ゲームとする(C−2)有利区間に移行するようにしてもよい。すなわち、付与された有利区間の継続期間が、(A)RT0状態から(C)RT1状態、あるいは(C)RT1状態から(A)RT0状態に引き継がれるようにしてもよい(なお、後者の場合には、(D)MB状態の遊技期間は有利区間中に含まれるものとしてもよいし、含まれないものとしてもよい)。 However, for example, in the case of (A) RT0 state, the advantageous section becomes (A-2), and when 50 games are given as the duration of the advantageous section, 10 games later (that is, the remaining 40 games of the advantage section remain). In the case where the MB is won and the combination of symbols related to the MB is not displayed (C) and the state is shifted to the RT1 state, the duration may be set to 40 games (C-2), and it may be shifted to the advantageous section. .. That is, the duration of the given advantageous section may be taken over from the (A) RT0 state to the (C) RT1 state or from the (C) RT1 state to the (A) RT0 state (note that in the latter case, In (D) MB, the game period may or may not be included in the advantageous period).
また、(A)RT0状態は、一連の増加区間に含まれる遊技期間であることから、(A)RT0状態では(A−2)有利区間を設けることなく、一連の増加区間に含まれない遊技期間であり、遊技者にとって相対的に不利な(C)RT1状態でのみ(C−2)有利区間を設けるようにしてもよい。すなわち、この第3の態様では、遊技者にとって相対的に不利な遊技期間((C)RT1状態)で遊技を行う遊技者を救済し、遊技の興趣の低下を防止することを目的として、有利区間((C−2)有利区間)を設けるようにしてもよい。 In addition, (A) RT0 state is a game period included in a series of increase sections, so (A) RT0 state does not include (A-2) advantageous section, and is not included in a series of increase sections. It is a period, and the (C-2) advantageous section may be provided only in the (C) RT1 state, which is relatively disadvantageous to the player. That is, in the third mode, it is advantageous for the purpose of relieving the player who plays the game in the game period ((C)RT1 state) relatively disadvantageous to the player and preventing a decrease in the interest of the game. A section ((C-2) advantageous section) may be provided.
なお、この第3の態様においても、上記第1の態様と同様に、例えば、(A)RT0状態においてBBに当籤したときには、その旨の告知ないし示唆が行われるようにすることができるし、(B)BB状態においてRBに当籤したときには、その旨の告知ないし示唆が行われるようにすることができる。もっとも、この第3の態様のように、有利区間があくまでも入賞に係る内部当籤役(例えば、小役)について入賞を容易とする遊技区間として位置付けられる場合には、(A)RT0状態においてBBに当籤したときに、BBに係る図柄の組合せが表示されることを容易にする停止操作の態様(押し順や停止操作のタイミング)がある場合に、有利区間であることに基づいて当該停止操作の態様が直接的に報知されることは望ましくないが、このような報知が行われるものとしてもよい。 In the third mode, as in the first mode, for example, when (A) RT0 is won, BB can be notified or suggested. (B) When the RB is won in the BB state, a notification or suggestion to that effect can be made. However, as in the case of the third mode, when the advantageous section is positioned as a game section that facilitates winning of the internal winning combination (eg, small winning combination) related to the winning, (A) RT0 state is changed to BB. When there is a mode of the stop operation (pushing order or timing of the stop operation) that facilitates the display of the symbol combination related to BB when the winning is won, the stop operation of the stop operation is performed based on the advantageous section. Although it is not desirable to directly notify the mode, such notification may be performed.
この変形例では、上記第2の態様と上記第3の態様とを別の態様として説明しているが、上記第2の態様と上記第3の態様とを組み合わせた有利区間の態様を採用することもできる。この場合、BBに当籤した(A)RT0状態が、(A−2)有利区間であれば、(B)BB状態においても停止操作の情報が報知され、(A−1)通常(非有利区間)であれば、(B)BB状態においても停止操作の情報が報知されないようにしてもよい。また、この場合、(A−2)有利区間から移行した(B)BB状態では、有利区間の継続期間が遊技の進行にしたがって順次更新される(すなわち、付与されている有利区間の継続期間が減っていく)ようにしてもよいし、有利区間の継続期間が更新されない(すなわち、付与されている有利区間の継続期間が減らない)ようにしてもよい。 In this modification, the second aspect and the third aspect are described as different aspects, but an advantageous section aspect in which the second aspect and the third aspect are combined is adopted. You can also In this case, if the (A) RT0 state winning the BB is the (A-2) advantageous section, the information of the stop operation is notified even in the (B) BB state, and (A-1) the normal (non-advantageous section). In this case, the information of the stop operation may not be notified even in the (B) BB state. Further, in this case, in (B) BB state, which is shifted from (A-2) advantageous zone, the duration of the advantageous zone is sequentially updated as the game progresses (that is, the duration of the given advantageous zone is changed). The duration of the advantageous section may not be updated (that is, the duration of the given advantageous section may not be reduced).
(本例の変形例における有利区間仕様の第4の態様)
続いて、これまでに説明した本例の変形例の遊技性(遊技仕様)を採用した場合の、有利区間仕様の第4の態様について説明する。この第4の態様は、(A)RT0状態中において有利区間に移行可能とした仕様である。
(Fourth Mode of Advantageous Interval Specification in Modification of this Example)
Next, a fourth mode of the advantageous zone specification when the game characteristic (game specification) of the modified example of the present example described so far is adopted will be described. The fourth mode is a specification in which (A) the RT0 state can be shifted to the advantageous section.
この第4の態様では、上述の第3の態様とは逆で、(A)RT0状態において(A−2)有利区間となっている場合、MBに当籤したときには「MBに係る図柄の組合せが表示される遊技方法が推測されるような告知ないし示唆」が行われることで、(C)RT1状態への移行が回避可能な情報が報知されるが、押し順小役に当籤したときには正解となる押し順は報知されないものである。また、(C)RT1状態において(C−2)有利区間となっている場合、MBに係る図柄の組合せが表示可能であるときには「MBに係る図柄の組合せが表示される遊技方法が推測されるような告知ないし示唆」が行われることで、(A)RT0状態への移行を可能とする情報が報知されるが、押し順小役に当籤した場合には、正解となる押し順は報知されないものである。 In the fourth aspect, contrary to the above-described third aspect, (A) in the RT0 state (A-2) in the advantageous section, when the MB is won, “a combination of symbols related to MB is By making an announcement or suggestion that the displayed game method is guessed, (C) information that avoids the transition to the RT1 state is informed, but when the push order small win is won, it is a correct answer. The pushing order is not notified. Further, in the case of (C-2) advantageous section in the (C) RT1 state, when a combination of symbols related to MB can be displayed, "a game method in which a combination of symbols related to MB is displayed is inferred. "Announcement or suggestion" is performed, but (A) the information that enables the transition to the RT0 state is notified, but when the winning order is a small winning combination, the correct pressing order is not notified. It is a thing.
なお、この第4の態様では、例えば、有利区間は、(A−2)有利区間のみが設けられ、(C−2)有利区間は設けられないようにしてもよい。すなわち、有利区間を、一連の増加区間を継続させる((A)RT0状態を継続させる)ための機能を担うものとして構成し、(C)RT1状態を終了させるための機能を担わないものとして構成してもよい。 In the fourth aspect, for example, only the advantageous section (A-2) is provided as the advantageous section, and the (C-2) advantageous section may not be provided. That is, the advantageous section is configured to have a function of continuing a series of increasing sections ((A) continuing the RT0 state), and (C) not having a function of ending the RT1 state. You may.
また、この第4の態様では、有利区間を、「MBに係る図柄の組合せが表示される遊技方法が推測されるような告知ないし示唆」が行われた回数(ナビ回数)によって管理する手法とすることが好適である。例えば、(C)RT1状態においてMBに係る図柄の組合せが表示され、(D)MB状態に移行し、(D)MB状態が終了して(A)RT0状態に移行するまでの間のいずれか任意のタイミングで、有利区間に移行させるか否かの決定を行い、有利区間に移行させることを決定した場合には、付与するナビ回数を決定する。そして、移行した(A)RT0状態((A−2)有利区間)では、決定されたナビ回数分、「MBに係る図柄の組合せが表示される遊技方法が推測されるような告知ないし示唆」が行われるようにすればよい。もっとも、(A)RT0状態では、例えば、BBに当籤し、BBに係る図柄の組合せが表示されて(B)BB状態に移行し、(B)BB状態が終了して(A)RT0状態に移行のいずれか任意のタイミングで、有利区間に移行させる(延長させる)か否かの決定を行い、有利区間に移行させる(延長させる)ことを決定した場合には、付与するナビ回数を決定してもよい。なお、ナビ回数による管理を好適として説明したが、その他の管理手法(例えば、ゲーム数による管理など)を採用することを妨げるものではない。 Further, in the fourth aspect, a method of managing the advantageous section by the number of times (the number of times of navigation) the "announcement or suggestion that the game method in which the combination of symbols related to MB is displayed is estimated" is performed. Is preferred. For example, in (C) RT1 state, a combination of symbols relating to MBs is displayed, (D) transitions to MB state, and (D) MB state ends and (A) transitions to RT0 state. At any timing, it is determined whether or not to shift to the advantageous section, and when it is determined to shift to the advantageous section, the number of times of navigation to be given is determined. Then, in the transitioned (A) RT0 state ((A-2) advantageous section), the number of times of navigation determined is "notification or suggestion such that a game method in which a combination of symbols related to MB is displayed is inferred". Should be done. However, in the (A) RT0 state, for example, a winning combination for BB is displayed, a combination of symbols relating to BB is displayed, and the state shifts to (B) BB state, and (B) BB state ends and (A) RT0 state. At any one of the transition timings, it is decided whether or not to shift (extend) to the advantageous zone, and when it is decided to shift (extend) to the advantageous zone, the number of times of navigation to be given is determined. May be. Although the management based on the number of times of navigation has been described as preferable, it does not prevent the adoption of other management methods (for example, management based on the number of games).
なお、この第4の態様においても、上記第1の態様と同様に、例えば、(A)RT0状態においてBBに当籤したときには、その旨の告知ないし示唆が行われるようにすることができるし、(B)BB状態においてRBに当籤したときには、その旨の告知ないし示唆が行われるようにすることができる。もっとも、この第4の態様のように、有利区間があくまでも一連の増加区間の継続を容易とする遊技区間として位置付けられる場合には、(A)RT0状態においてBBに当籤したときに、BBに係る図柄の組合せが表示されることを容易にする停止操作の態様(押し順や停止操作のタイミング)がある場合に、有利区間であることに基づいて当該停止操作の態様が直接的に報知されることは望ましくないが、このような報知が行われるものとしてもよい。 In the fourth mode, as in the case of the first mode, for example, when (B) BB is won in the (A) RT0 state, notification or suggestion to that effect can be made. (B) When the RB is won in the BB state, a notification or suggestion to that effect can be made. However, in the case where the advantageous section is positioned as the game section for facilitating the continuation of the series of increasing sections as in the case of the fourth mode, (A) when the BB is won in the RT0 state, the BB is related. When there is a mode of the stop operation (pushing order or timing of the stop operation) that facilitates the display of the symbol combination, the mode of the stop operation is directly notified based on the advantageous section. This is not desirable, but such notification may be performed.
この変形例では、上記第3の態様と上記第4の態様とを別の態様として説明しているが、上記第3の態様と上記第4の態様とを組み合わせた有利区間の態様を採用することもできる。この場合、(A−2)有利区間であれば、押し順小役に当籤したときには正解となる押し順が報知されることで、(A−1)通常(非有利区間)と比べて多くの遊技価値が付与され、MBに当籤したときには「MBに係る図柄の組合せが表示される遊技方法が推測されるような告知ないし示唆」が行われることで、(C)RT1状態への移行が回避可能な情報が報知されるようにすればよい。また、(C−2)有利区間であれば、押し順小役に当籤したときには正解となる押し順が報知されることで、(C−1)通常(非有利区間)と比べて多くの遊技価値が付与され、MBに係る図柄の組合せが表示可能であるときには「MBに係る図柄の組合せが表示される遊技方法が推測されるような告知ないし示唆」が行われることで、(A)RT0状態への移行を可能とする情報が報知されるようにすればよい。なお、上述のように、(C−2)有利区間であっても、MBに係る図柄の組合せが表示可能であるときに「MBに係る図柄の組合せが表示される遊技方法が推測されるような告知ないし示唆」は行われないようにしてもよい。 In this modification, the third aspect and the fourth aspect are described as different aspects, but an advantageous section aspect in which the third aspect and the fourth aspect are combined is adopted. You can also In this case, in the case of (A-2) the advantageous section, since the pushing order that is the correct answer when the small winning combination of the pushing order is won is informed, (A-1) more than the normal (non-advantageous section) When the gaming value is given and the MB is won, the "Announcement or suggestion that the gaming method in which the combination of symbols relating to the MB is displayed is inferred" is performed, and (C) the transition to the RT1 state is avoided. All that is necessary is to be notified of possible information. In addition, (C-2) If it is an advantageous section, the pushing order that will be the correct answer when the winning combination is won is notified, so that (C-1) more games than normal (non-advantageous section). When a value is added and the symbol combination relating to MB can be displayed, "Announcement or suggestion that the game method in which the symbol combination relating to MB is displayed is inferred" is performed, and (A) RT0 Information that enables the transition to the state may be notified. As described above, even in the (C-2) advantageous section, when the combination of symbols related to MB can be displayed, "a game method in which a combination of symbols related to MB is displayed is inferred. "No announcement or suggestion" may be prohibited.
(本例の変形例における有利区間リミッタ)
続いて、これまでに説明した本例の変形例の遊技性(遊技仕様)を採用し、また、有利区間仕様として、少なくとも上記第3の態様又は上記第4の態様が含まれる有利区間の態様を採用した場合における、有利区間のリミット処理について説明する。
(Advantageous section limiter in the modification of this example)
Subsequently, the game characteristic (game specification) of the modified example of the present embodiment described so far is adopted, and the advantageous section specification includes at least the third aspect or the fourth aspect as the advantageous section specification. A description will be given of the limit processing of the advantageous section in the case of adopting.
本実施形態では、有利区間が長く継続し過ぎることに起因して射幸性が過度に高くなってしまうことを抑制するため、上述のあるいは後述のリミット処理を行うことが可能となっている。例えば、「ゲーム数リミッタ」であれば有利区間が「1500ゲーム」継続した場合、また、「枚数リミッタ」であれば有利区間において「2400枚」のメダルを獲得した場合には、未だ有利区間のゲーム数、セット数、ストック、ナビ回数、差枚数などが残存している場合であっても、リミット処理の実行により強制的に有利区間が終了され非有利区間に移行される。 In the present embodiment, it is possible to perform the above-described or later-described limit processing in order to prevent the gambling property from becoming excessively high due to the advantageous section continuing for too long. For example, if the number of games limiter is 1,500 advantageous games continue in the advantageous section, and if the number of games limiter is 2400 medal in the advantageous section, the advantageous section is still in the advantageous section. Even if the number of games, the number of sets, the number of stocks, the number of times of navigation, the number of differences, etc. remain, the limit processing is forcibly ended and the advantageous section is shifted to the non-advantageous section.
しかしながら、本例の変形例の遊技性(遊技仕様)によれば、このようなリミット処理の実行によって有利区間が終了した後も、一連の増加区間が継続する場合も生じうる。すなわち、一連の増加区間により、遊技者に有利となる有利区間の継続に関し一定の制限を設けた意義が失われるおそれがあるという問題がある。そこで、一連の増加区間を設ける場合に、それを考慮した有利区間の制限を行うことができる遊技機を提供するため、以下のような工夫をなすことが望ましい。 However, according to the game characteristic (game specification) of the modified example of the present example, a series of increasing sections may continue even after the advantageous section ends by the execution of such limit processing. That is, there is a problem in that a series of increasing sections may lose the significance of providing a certain limitation on the continuation of the advantageous section that is advantageous to the player. Therefore, in order to provide a gaming machine capable of limiting an advantageous section in consideration of a series of increasing sections, it is desirable to take the following measures.
例えば、本例の変形例の遊技性(遊技仕様)においては、一連の増加区間が開始するのと同時に、あるいは、一連の増加区間が開始する前に有利区間を開始させる。一の具体例として、一連の増加区間が(A)RT0状態においてBBに当籤したときに開始すると定めた場合には、(A)RT0状態においてBBに当籤したのと同時、あるいは、(A)RT0状態に移行したときなどに有利区間を開始させる。また、他の具体例として、一連の増加区間が(A)RT0状態に移行したときに開始すると定めた場合には、(A)RT0状態に移行したのと同時、あるいは、(D)MB状態に移行したときなどに有利区間を開始させる。なお、ここでいう有利区間の開始とは、リミット処理上(制御上)の有利区間の開始を意味し、必ずしも当該開始時点で有利区間の実質的な継続期間(ゲーム数、セット数、ストック、ナビ回数、差枚数など)が付与されることを意味するものではない。したがって、有利区間の継続期間については、例えば、本実施形態や本例以外の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例で説明した種々の条件を採用して、各遊技状態で付与(あるいは延長)の当否決定を行い、当該決定結果に応じて付与(あるいは延長)されるものとすればよい。もっとも、上記開始時点においても有利区間の継続期間付与(あるいは延長)の当否決定が行われるものとしてもよい。 For example, in the game characteristic (game specification) of the modified example of the present example, the advantageous section is started at the same time as the series of increasing sections starts or before the series of increasing sections starts. As one specific example, when it is determined that a series of increasing intervals starts when (A) RT0 state wins BB, (A) at the same time when winning BB in RT0 state, or (A) The advantageous section is started when the RT0 state is entered. Further, as another specific example, when it is determined that the series of increase intervals starts when the state shifts to the (A) RT0 state, the (A) RT0 state shifts at the same time, or the (D) MB state shifts. The advantageous section is started when, for example, shifting to. It should be noted that the start of the advantageous section here means the start of the advantageous section on the limit process (for control), and is not necessarily the substantial duration of the advantageous section (the number of games, the number of sets, the stock, It does not mean that the number of navigations, the number of differences, etc.) is added. Therefore, for the duration of the advantageous section, for example, various conditions explained in other examples of the game property (game specification) other than this embodiment and this example are adopted, and granted (or extended) in each game state. It is only necessary to decide whether or not to be given, and to give (or extend) according to the result of the decision. However, whether or not to grant (or extend) the duration of the advantageous section may be determined at the start point.
ここで、「ゲーム数リミッタ」の場合、上限の遊技数は例えば「1500ゲーム」となるが、この「1500」から、一連の増加区間において作動するボーナス状態(例えば、(B)BB状態。複数のボーナス状態がある場合には、そのうちでもっとも長い遊技数の間継続する可能性があるもの)の期待遊技数(平均遊技数)に、ループ率に応じた閾値(ループ率を遊技数に換算するための掛け率として定めた変数)を乗じた値を減じ、それを指示停止遊技数として算出する(あるいは、予め規定する)。例えば、本例の変形例において、ボーナス状態の期待遊技数を「20ゲーム」とし、ループ率50%に応じた閾値を「6」とした場合、指示停止遊技数は、「1500ゲーム−20ゲーム×6=1380ゲーム」となる。 Here, in the case of the "game number limiter", the upper limit number of games is, for example, "1500 games", but from "1500", a bonus state (for example, (B) BB state. If there is a bonus state, the expected number of games (which may continue for the longest number of them) (average number of games), the threshold according to the loop rate (convert the loop rate to the number of games The value multiplied by the variable defined as the multiplication rate for doing) is subtracted, and it is calculated as the instruction stop game number (or is defined in advance). For example, in the modified example of this example, when the expected number of games in the bonus state is "20 games" and the threshold value corresponding to the loop rate of 50% is "6", the number of instruction stop games is "1500 games-20 games". ×6=1380 games”.
ここで、「枚数リミッタ」の場合、上限の獲得枚数は例えば「2400枚」となるが、この「2400」から、一連の増加区間において作動するボーナス状態(例えば、(B)BB状態。複数のボーナス状態がある場合には、そのうちでもっとも多くのメダルが付与される可能性があるもの)の期待獲得枚数(平均獲得枚数)に、ループ率に応じた閾値(ループ率を獲得枚数に換算するための掛け率として定めた変数)を乗じた値を減じ、それを指示停止獲得枚数として算出する(あるいは、予め規定する)。例えば、本例の変形例において、ボーナス状態の期待獲得枚数を「120枚」とし、ループ率50%に応じた閾値を「6」とした場合、指示停止獲得枚数は、「2400枚−120枚×6=1680枚」となる。 Here, in the case of the “number of sheets limiter”, the upper limit of the number of sheets to be acquired is, for example, “2400 sheets”, but from this “2400”, a bonus state (for example, (B) BB state. If there is a bonus status, the expected acquisition number (average acquisition number) of the ones that may be awarded the most medals among them is converted into a threshold value corresponding to the loop rate (the loop rate is converted to the acquisition number). The value multiplied by a variable defined as a multiplication factor) is subtracted, and the value is calculated as an instruction stop acquisition number (or specified in advance). For example, in the modified example of this example, when the expected number of bonuses to be acquired is "120" and the threshold value corresponding to the loop rate of 50% is "6", the number of instruction stop acquisitions is "2400-120". ×6=1680 sheets”.
そして、「ゲーム数リミッタ」によってリミット処理が行われるように構成した場合、上記開始時点において開始された有利区間がそのまま継続して遊技数が「1380ゲーム」(指示停止遊技数)に到達した際には、有利区間の継続期間が残存していれば(制御上は)有利区間は継続するものの、以降の遊技においては、停止操作の情報が報知されないようになる(すなわち、指示機能が停止する)。 When the limit process is performed by the "game number limiter", when the advantageous period started at the start point continues and the number of games reaches "1380 games" (number of instructions stop games) , If the duration of the advantageous section remains (in terms of control), the advantageous section will continue, but in subsequent games, the information of the stop operation will not be notified (that is, the instruction function will stop). ).
また、「枚数リミッタ」によってリミット処理が行われるように構成した場合、上記開始時点において開始された有利区間がそのまま継続して獲得枚数が「1680枚」(指示停止獲得枚数)に到達した際には、有利区間の継続期間が残存していれば(制御上は)有利区間は継続するものの、以降の遊技においては、停止操作の情報が報知されないようになる(すなわち、指示機能が停止する)。 Further, in the case where the limit process is performed by the “number limiter”, when the advantageous period started at the start time is continued as it is and the acquired number reaches “1680” (instruction stop acquisition number) , If the duration of the advantageous section remains (in terms of control), the advantageous section will continue, but in subsequent games, the information of the stop operation will not be notified (that is, the instruction function will stop) ..
また、指示停止遊技数又は指示停止獲得枚数に到達したことに基づいて指示機能が停止した後の処理であるが、リミット処理が実行される前に、一連の増加区間が終了した場合には、それと同時に、あるいは、その終了後に有利区間を終了させる。一の具体例として、一連の増加区間が(A)RT0状態においてMBに当籤し、MBに係る図柄の組合せが表示されずに(C)RT1状態に移行したときに終了すると定めた場合には、(C)RT1状態に移行したのと同時、あるいは、(C)RT1状態に移行した遊技の次回遊技が開始されるときなどに有利区間を終了させる。なお、(A)RT0状態や(B)BB状態では、一連の増加区間が未だ継続する可能性があることから、(制御上)有利区間を終了させる処理を行うのは、少なくとも(C)RT1状態中とすることが望ましい。もっとも、リミット処理の実行によって有利区間を終了させる場合には、この限りではない。すなわち、(A)RT0状態や(B)BB状態において、「ゲーム数リミッタ」の場合には「1500ゲーム」に到達したとき、「枚数リミッタ」の場合には「2400枚」に到達したときには、リミット処理の実行によって有利区間を終了させることを可能としてもよい。 In addition, it is the processing after the instruction function is stopped based on reaching the instruction stop game number or the instruction stop acquisition number, but if a series of increase sections are finished before the limit processing is executed, At the same time or after that, the advantageous section is ended. As one specific example, when it is determined that a series of increase sections wins the MB in the (A) RT0 state, and ends when the (C) RT1 state shifts without the combination of symbols related to the MB being displayed, , (C) The transition to the RT1 state is performed at the same time, or the advantageous section is ended when the next game of the game that has transitioned to the (C) RT1 state is started. In addition, in the (A) RT0 state and the (B) BB state, a series of increasing sections may still continue. Therefore, at least (C) RT1 is the process of terminating the advantageous section (for control). It is desirable to be in the state. However, this is not the case when the advantageous section is ended by executing the limit process. That is, in (A) RT0 state and (B) BB state, when "1500 games" is reached in the case of "game number limiter" and "2400 sheets" is reached in the case of "number of sheets limiter", It may be possible to end the advantageous section by executing the limit process.
なお、有利区間が継続して指示停止遊技数又は指示停止獲得枚数に到達したときには、指示機能が停止するため、実質的には有利区間が終了するのと同義である。したがって、上述した「ゲーム数リミッタ」の「1500ゲーム」や、「枚数リミッタ」の「2400枚」は、あくまでも遊技店に設置可能な遊技機の規制値として定められる値とし、本例の変形例の遊技性(遊技仕様)のような一連の増加区間が搭載される遊技機にあっては、当該規制値から上述したように指示停止遊技数又は指示停止獲得枚数を算出し、算出した指示停止遊技数や指示停止獲得枚数の値を、「ゲーム数リミッタ」や「枚数リミッタ」の値として予め定め、リミット処理が実行されるようにしてもよい。すなわち、一連の増加区間が搭載されることにより、遊技価値が増加する増加期間が、予定した出玉設計や予め定められた規制値の範囲から大きくはみ出てしまう可能性がある場合に、このはみ出てしまう部分を加味した上で、(前倒しで)有利区間の規制することができる手法であれば、どのような手法を採用することもできる。 It should be noted that when the advantageous section continues to reach the instruction stop game number or the instruction stop acquisition number, the instruction function is stopped, which is substantially synonymous with the end of the advantageous section. Therefore, the “1500 games” of the “game number limiter” and the “2400 sheets” of the “number of sheets limiter” are set to the values set as the regulation values of the gaming machines that can be installed in the game store, and the modification example of this example In a gaming machine equipped with a series of increased intervals such as the game playability (gaming specification), the instruction stop game number or the instruction stop acquisition number is calculated from the regulation value as described above, and the calculated instruction stop is calculated. The value of the number of games or the number of instructions stop acquisition number may be determined in advance as the value of the “game number limiter” or the “number limiter”, and the limit process may be executed. In other words, when a series of increase sections are installed, the increase period in which the game value increases may greatly exceed the planned payout design or the range of the predetermined regulation value. Any method can be adopted as long as it is possible to regulate the advantageous section (forwardly) after taking into consideration the portion that is lost.
また、本例の変形例で説明した遊技性(遊技仕様)、本例の変形例における有利区間仕様の第1〜第4の態様、本例の変形例における有利区間リミッタに関する技術思想は、本例の変形例に係る遊技機を一例として説明したものであり、本例の変形例に係る遊技機に限って適用されるものではない。すなわち、本実施形態、本例、及び本例以外の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例で説明した遊技機においても適宜変形して適用可能である。 Further, the game characteristics (game specifications) described in the modified example of the present example, the first to fourth aspects of the advantageous interval specification in the modified example of the present example, and the technical idea regarding the advantageous interval limiter in the modified example of the present example are The game machine according to the modified example is described as an example, and the present invention is not limited to the game machine according to the modified example of this example. That is, the game machine described in this embodiment, this example, and other examples of game play (game specification) other than this example can be appropriately modified and applied.
[遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その4)]
続いて、図96を参照して、本実施形態に係るパチスロ1において実装可能な遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その4)について説明する。図96は、遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その4)における遊技の流れを概念的に説明する図である。
[Another example of playability (game specifications) (Part 4)]
Next, with reference to FIG. 96, another example (No. 4) of the playability (game specification) mountable in the pachi-
図96に示すように、本例では、(A)RT0状態、(B)RT1状態非フラグ間、(C)RT1状態MBフラグ間、(D)RT2状態BBフラグ間、(E)BB状態、及び(F)MB状態の遊技状態がある。なお、(A)RT0状態及び(E)BB状態は、上述の一連の増加区間として位置付けられる。 As shown in FIG. 96, in this example, (A) RT0 state, (B) RT1 state non-flag, (C) RT1 state MB flag, (D) RT2 state BB flag, (E) BB state, And (F) There is a game state of MB state. The (A) RT0 state and the (E) BB state are positioned as the above-described series of increasing sections.
(A)RT0状態は、再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率が少なくとも(B)(C)RT1状態よりも低く、(B)RT1状態非フラグ間、(D)RT2状態BBフラグ間、及び(F)MB状態に移行可能な遊技状態である。なお、BB、MB、押し順小役、ベルこぼし目などについては、遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その3)(変形例を含む)などにおいて説明したものと同様であるため、ここでの説明は省略する。もっとも、本例では、MBは、いずれかの小役又はリプレイ役(例えば、上述のレア役)と重複当籤し、単独で当籤しないようにし、MBに当籤した遊技ではMBに係る図柄の組合せが表示されることがなく、MBフラグ間において内部抽籤結果が「ハズレ」となった遊技においては、押し順や停止操作のタイミング(すなわち、停止操作の態様)にかかわらず、必ずMBに係る図柄の組合せが表示されるように構成されるが、遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その3)の変形例で説明したのと同様に、遊技者の停止操作の態様などに応じて、MBに当籤した遊技でMBに係る図柄の組合せが表示される場合があるように構成することもできる。 In (A) RT0 state, the winning probability of the replay (replay) combination is at least lower than (B) (C) RT1 state, (B) RT1 state non-flag, (D) RT2 state BB flag, and ( F) It is a game state in which it is possible to shift to the MB state. In addition, since BB, MB, push order small win, bell spill, etc. are the same as those described in the other example (part 3) (including modified examples) of the game property (game specification), here. The description of is omitted. However, in this example, MB is a small winning combination or replay winning combination (for example, the above-mentioned rare winning combination), so as not to win alone, in the game in which MB is won, the combination of symbols related to MB is In the game where the internal lottery result is “missed” between the MB flags without being displayed, the MB related symbol is always displayed regardless of the pushing order or the timing of the stop operation (that is, the mode of the stop operation). Although the combination is configured to be displayed, in the same manner as described in the modified example of the other example (3) of the game property (game specification), the MB is changed according to the mode of the stop operation of the player. It is also possible to configure so that a combination of symbols related to MB may be displayed in the game that is won.
(A)RT0状態において、有利区間に制御されていない場合には、(A−1)通常(非有利区間)となって遊技価値が減少する減少期間となり、有利区間に制御されている場合には、(A−2)有利区間となって遊技価値が増加する増加期間となる。なお、有利区間に制御されうる特定の報知条件は、本実施形態や本例以外の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例で説明した種々の条件を採用することができる。 (A) In the RT0 state, when not controlled to the advantageous section, (A-1) becomes a normal (non-advantageous section), which is a reduction period in which the game value decreases, and when the advantageous section is controlled. Is an (A-2) advantageous period, which is an increasing period during which the game value increases. As the specific notification conditions that can be controlled in the advantageous section, various conditions described in other examples of game characteristics (game specifications) other than this embodiment and this example can be adopted.
(A)RT0状態において、(1)BBに当籤した場合、BB許可状態としての(D)RT2状態BBフラグ間に移行する。また、(A)RT0状態において、MBに当籤した場合、MB許可状態としてのMBフラグ間に移行するが、RT状態は変動しない。また、(A)RT0状態のMBフラグ間では、ベルこぼし目が有効ライン上に停止表示されても(C)RT1状態MBフラグ間には移行しない。また、(A)RT0状態では、「ハズレ」確率が少なくとも(B)(C)RT1状態よりも高く(例えば、「1/6」に)設定されているため、MBに係る図柄の組合せが表示されて、(4)MB開始条件が成立することが容易となっている。また、(A)RT0状態において、(D)RT2状態BBフラグ間に移行する前、あるいはMBフラグ間となる前に(すなわち、非フラグ間である場合に)、(5)ベルこぼし目が有効ライン上に停止表示されると、(C)RT1状態非フラグ間に移行する。 When (1) BB is won in the (A) RT0 state, the state shifts between the (D) RT2 state BB flags as the BB permission state. Further, in (A) RT0 state, if the MB is won, the state shifts between the MB flags as the MB permitted state, but the RT state does not change. Further, between the (A) RT0 state MB flags, even if the bell-eye drops are stopped and displayed on the activated line, the (C) RT1 state MB flags do not shift. Further, in (A) RT0 state, the "miss" probability is set to be higher than at least (B) (C) RT1 state (for example, to "1/6"), so the symbol combination related to MB is displayed. As a result, the condition (4) MB start condition is easily established. Further, in (A) RT0 state, before (D) RT2 state before transition between BB flags or before between MB flags (that is, when between non-flags), (5) Bell spill is effective. When the display is stopped on the line, the state shifts to (C) RT1 state non-flag.
(B)RT1状態非フラグ間は、再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率が少なくとも(A)RT0状態よりも高く、(A)RT0状態、(C)RT1状態MBフラグ間、及び(D)RT2状態BBフラグ間に移行可能な遊技状態である。(B)RT1状態非フラグ間において、有利区間に制御されていない場合には、(B−1)通常(非有利区間)となって遊技価値が減少する減少期間となり、有利区間に制御されている場合には、(B−2)有利区間となって遊技価値が増加する増加期間となる。なお、有利区間に制御されうる特定の報知条件は、本実施形態や本例以外の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例で説明した種々の条件を採用することができる。 During (B) RT1 state non-flag, the winning probability of the re-play (replay) combination is higher than at least (A) RT0 state, (A) RT0 state, (C) RT1 state between MB flags, and (D) RT2. It is a game state that can be transferred between state BB flags. (B) Between the RT1 state non-flags, when not controlled in the advantageous section, (B-1) becomes a normal (non-advantageous section), which is a reduction period in which the game value decreases, and is controlled in the advantageous section. If so, (B-2) it becomes an advantageous section, which is an increase period during which the game value increases. As the specific notification conditions that can be controlled in the advantageous section, various conditions described in other examples of game characteristics (game specifications) other than this embodiment and this example can be adopted.
(B)RT1状態非フラグ間において、(1)BBに当籤した場合、BB許可状態としての(D)RT2状態BBフラグ間に移行する。また、(B)RT1状態非フラグ間において、(6)MBに当籤した場合、MB許可状態としての(C)RT1状態MBフラグ間に移行する(RT状態は変動しない)。なお、本例では、MBに当籤した遊技ではMBに係る図柄の組合せが表示されることがないように構成しているため、(B)RT1状態非フラグ間から(F)MB状態に移行しないものとなっているが、上述のように、(B)RT1状態非フラグ間から(F)MB状態に移行する場合があるように構成することもできる。なお、(B)RT1状態非フラグ間と(C)RT1状態MBフラグ間とは、基本的に同じRT状態(RT1状態)であり、(B)(C)いずれのRT1状態であっても、(9)RT1状態中の遊技数が規定ゲーム数(例えば、1500ゲーム)となった場合(すなわち、1500ゲームを消化した場合)、(A)RT0状態に移行する。このとき、(B)RT1状態非フラグ間であれば(A)RT0状態の非フラグ間に移行し、(C)RT1状態MBフラグ間であれば(A)RT0状態のMBフラグ間に移行する。 When (1) BB is won during the (B) RT1 state non-flag, the state shifts to the (D) RT2 state BB flag as the BB permission state. In addition, when (6) MB is won while (B) RT1 state non-flag, the state shifts to (C) RT1 state MB flag as the MB permitted state (RT state does not change). In this example, since the combination of symbols related to MB is not displayed in the game won in MB, (B) RT1 state does not shift from the non-flag state to (F) MB state However, as described above, it may be configured such that there is a case where the transition is made between the (B) RT1 state non-flag and the (F) MB state. The (B) RT1 state non-flag state and the (C) RT1 state MB flag state are basically the same RT state (RT1 state), and (B) (C) any RT1 state, (9) When the number of games in the RT1 state reaches the specified number of games (for example, 1500 games) (that is, when 1500 games are exhausted), the state shifts to (A) RT0. At this time, if it is between (B) RT1 state non-flag, it shifts between (A) RT0 state non-flags, and if it is between (C) RT1 state MB flag, it shifts between (A) RT0 state MB flags. ..
(C)RT1状態MBフラグ間は、再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率が少なくとも(A)RT0状態よりも高く、(A)RT0状態、及び(F)MB状態に移行可能な遊技状態である。(C)RT1状態MBフラグ間において、有利区間に制御されていない場合には、(C−1)通常(非有利区間)となって遊技価値が減少する減少期間となり、有利区間に制御されている場合には、(C−2)有利区間となって遊技価値が増加する増加期間となる。なお、有利区間に制御されうる特定の報知条件は、本実施形態や本例以外の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例で説明した種々の条件を採用することができる。 Between the (C) RT1 state MB flags, the winning probability of the replay (replay) combination is higher than at least the (A) RT0 state, and it is a gaming state in which the state can shift to the (A) RT0 state and (F) MB state. .. (C) Between the RT1 state MB flags, when not controlled to the advantageous section, (C-1) becomes a normal (non-advantageous section), which is a decrease period in which the game value decreases, and is controlled to the advantageous section. If there is, (C-2) it becomes an advantageous section, which is an increase period during which the game value increases. As the specific notification conditions that can be controlled in the advantageous section, various conditions described in other examples of game characteristics (game specifications) other than this embodiment and this example can be adopted.
(C)RT1状態MBフラグ間では、「ハズレ」確率が少なくとも(A)RT0状態よりも極めて低く(例えば、「1/8192」に)設定されているため、MBに係る図柄の組合せが表示されて、(7)MB開始条件が成立することが困難となっている。なお、(C)RT1状態MBフラグ間は、MB許可状態であることから、新たにMBに当籤したり、BBに当籤したりする場合はない。 (C) Between the RT1 state MB flags, the "miss" probability is set to be extremely lower than at least the (A) RT0 state (for example, to "1/8192"), so that the symbol combination related to MB is displayed. Therefore, it is difficult to satisfy the condition (7) MB start. During the (C) RT1 state MB flag, since the MB is in the MB permitted state, there is no case of newly winning the MB or winning the BB.
(D)RT2状態BBフラグ間は、再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率が少なくとも(B)(C)RT1状態よりも低く、(E)BB状態に移行可能な遊技状態である。(D)RT2状態BBフラグ間において、BBに係る図柄の組合せが表示されると、(2)BB開始条件が成立し、(E)BB状態に移行する。また、(D)RT2状態BBフラグ間では、「ハズレ」確率が少なくとも(B)(C)RT1状態よりも高く(例えば、「1/12」に)設定されているため、BBに係る図柄の組合せが表示されて、(2)BB開始条件が成立することが容易となっている。なお、(C)RT2状態BBフラグ間は、BB許可状態であることから、新たにBBに当籤したり、MBに当籤したりする場合はない。 Between the (D) RT2 state BB flags, the winning probability of the replay (replay) combination is at least lower than that of the (B) (C) RT1 state, and the (E) BB state is a gaming state in which the winning probability can be shifted. (D) When a combination of symbols related to BB is displayed between the RT2 state BB flags, (2) BB start condition is satisfied, and the state shifts to (E) BB state. In addition, between the (D)RT2 state BB flags, the "miss" probability is set to be higher than at least the (B)(C)RT1 state (for example, to "1/12"), so that the symbol relating to BB It is easy for the combination to be displayed and (2) BB start condition to be satisfied. During the (C) RT2 state BB flag, since the BB is in the permitted state, there is no case of newly winning the BB or winning the MB.
(E)BB状態は、例えば、上述した「特殊ボーナス状態」で構成され、遊技価値が増加する増加期間となる遊技状態である。(E)BB状態において、規定数(例えば、140枚超)の遊技価値が付与されると、遊技価値の付与上限となり、(3)BB終了条件が成立し、(B)BB状態から(A)RT0状態に移行する。 The (E)BB state is, for example, a gaming state that is configured by the above-mentioned “special bonus state” and has an increasing period in which the gaming value increases. In the (E)BB state, when a prescribed number of game values (for example, more than 140) are given, the game value is given as an upper limit, and the (3)BB end condition is satisfied, and the (B)BB state is changed to (A). ) Transition to RT0 state.
(F)MB状態は、通常のボーナス状態として構成され、遊技価値が増加する増加期間となる遊技状態である。なお、遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その3)の変形例で説明したのと同様に、無増減期間として構成することもできる。(F)MB状態において、規定数(例えば、13枚超)の遊技価値が付与されると、遊技価値の付与上限となり、(8)MB終了条件が成立し、(A)RT0状態から移行していた場合には(F)MB状態から(A)RT0状態に移行し、(C)RT1状態MBフラグ間から移行していた場合には(F)MB状態から(B)RT1状態非フラグ間に移行する。 The (F) MB state is a gaming state that is configured as a normal bonus state and has an increasing period in which the gaming value increases. It should be noted that, as in the case of the modified example of the other example (3) of the game property (game specification), it may be configured as a no increase/decrease period. (F) In the MB state, when a prescribed number (for example, more than 13) of game values are given, the game value is given as an upper limit, (8) MB end condition is satisfied, and (A) RT0 state is entered. If (F)MB state is changed to (A)RT0 state, (C)RT1 state is between MB flags, (F)MB state is (B)RT1 state is between non-flags Move to.
すなわち、(F)MB状態は、その作動あるいは終了によってRT状態が変動しない(より詳細には、(B)(C)RT1状態が、(F)MB状態を貫通して作動する)ものとなっている。ここで、(B)(C)RT1状態は、開始されてから規定ゲーム数(例えば、1500ゲーム)の間は終了しないものとなっている。したがって、(F)MB状態の作動あるいは終了は、この規定ゲーム数にも影響を与えないものとなっている。もっとも、(F)MB状態中の期間は、その規定ゲーム数の計数対象として算入されてもよいし、その規定ゲーム数の計数が中断される(算入されない)ものとしてもよい。 That is, in the (F)MB state, the RT state does not change due to its operation or termination (more specifically, the (B)(C)RT1 state operates through the (F)MB state). ing. Here, the (B) and (C) RT1 states do not end for a prescribed number of games (for example, 1500 games) from the start. Therefore, the operation or termination of the (F)MB state does not affect the specified number of games. However, the period in the (F)MB state may be included in the counting target of the specified number of games, or the counting of the specified number of games may be interrupted (not included).
なお、(F)MB状態と(B)(C)RT1状態の間の移行制御は、上述したものに限られない。例えば、(F)MB状態が終了した場合、それが(C)RT1状態MBフラグ間から移行していたものであっても、(A)RT0状態に移行させるようにしてもよい。すなわち、MB状態が作動したこと、あるいは終了したことを契機として、RT1状態を終了させるようにしてもよい。本例では、(C)RT1状態MBフラグ間に移行した場合、規定ゲーム数を消化して(A)RT0状態のMBフラグ間に移行させ、(F)MB状態を作動させて(A)RT0状態の非フラグ間に移行させるか、あるいは(F)MB状態を作動させて(B)RT1状態非フラグ間に移行させ、そこでBBを当籤させなければ、一連の増加区間には移行しないものなっているため、(F)MB状態が終了した場合に(A)RT0状態の非フラグ間に移行させるようにすれば、一連の増加区間に移行する頻度を高めることができる。これは、意図する出玉率やその内容などに応じて適宜選択されるものとすればよい。 The transition control between the (F)MB state and the (B)(C)RT1 state is not limited to that described above. For example, when the (F)MB state is ended, even if the state has been changed between the (C)RT1 state MB flags, the state may be changed to the (A)RT0 state. That is, the RT1 state may be ended when the MB state is activated or ended. In this example, when the state shifts to the (C) RT1 state MB flag, the specified number of games is consumed to shift to the (A) RT0 state MB flag, and the (F) MB state is activated to (A) RT0. If the state is shifted between non-flags, or (F) MB state is activated to shift between (B) RT1 state non-flags, and BB is not won there, the series of increase intervals does not occur. Therefore, when the (F)MB state is completed, if the transition is made between the non-flags of the (A)RT0 state, the frequency of transition to a series of increase sections can be increased. This may be appropriately selected according to the intended payout rate and its content.
本例の遊技機によれば、特別役(BB)に当籤した場合には特別許可状態(BB許可状態)となって第2特定遊技状態((D)RT2状態)に移行し、特別図柄の組合せ(BBに係る図柄の組合せ)を表示させて特別遊技状態((E)BB状態)に移行させることを困難としない一方、特殊役(MB)に当籤した場合には特殊許可状態(MB許可状態)となるが遊技状態は移行せず、第1特定遊技状態((C)RT1状態MBフラグ間)であれば、当該第1特定遊技状態が終了するまで特殊図柄の組合せ(MBに係る図柄の組合せ)を表示させて特殊遊技状態((F)MB状態)に移行させることを困難とし、その結果として通常遊技状態((A)RT0状態)に移行させることを困難とする。また、第1特定遊技状態には、特別許可状態及び特殊許可状態でない通常遊技状態において特定役(押し順小役)に当籤した場合に、特定の態様(押し順正解となる態様)で停止操作が行われずに特定図柄の組合せ(ベルこぼし目)が表示されたことに基づいて移行する。そして、特定の報知条件が成立した場合、通常遊技状態及び第1特定遊技状態における特定期間(有利区間)では、特定役に当籤したときに特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知され、報知にしたがって停止操作が行われれば、特定図柄の組合せは表示されず、特定数(例えば、9枚)の遊技価値が付与される。 According to the gaming machine of this example, when the special combination (BB) is won, the special permission state (BB permission state) is entered and the second specific game state ((D)RT2 state) is entered, and the special symbol While it is not difficult to display the combination (combination of symbols related to BB) and shift to the special game state ((E)BB state), if the special combination (MB) is won, the special permission state (MB permission) State) but the game state does not shift, if the first specific game state (between (C) RT1 state MB flag), the combination of special symbols (symbols related to MB) until the first specific game state ends It is difficult to shift to the special game state ((F)MB state) by displaying the combination), and as a result, it is difficult to shift to the normal game state ((A)RT0 state). In addition, in the first specific game state, when the special combination (push order small combination) is won in the special permission state and the normal game state that is not the special permission state, the stop operation is performed in a specific mode (a mode in which the press order is the correct answer). Is performed and a transition is made based on the display of a combination of specific symbols (bell-shaped eyes). Then, when the specific notification condition is satisfied, during the specific period (advantageous section) in the normal game state and the first specific game state, operation information regarding a specific mode is notified when a specific winning combination is won, and the operation is stopped according to the notification. If the operation is performed, the combination of the specific symbols is not displayed, and a specific number (for example, 9) of game values are given.
ここで、本例の遊技機によれば、通常遊技状態において、特定役に当籤したときに特定図柄の組合せが表示されて第1特定遊技状態に移行する前に、特別役又は特殊役に当籤して特別許可状態(第2特定遊技状態)又は特殊許可状態となれば、特別遊技状態又は特殊遊技状態を経由して再度通常遊技状態において遊技を行うことができる。また、第1特定遊技状態であっても、特別役に当籤して特別許可状態(第2特定遊技状態)となれば、特別遊技状態を経由して再度通常遊技状態において遊技を行うことができる。一方、第1特定遊技状態において、特殊役に当籤して特殊許可状態となると、特殊遊技状態を経由して再度通常遊技状態において遊技を行うことが困難となる。 Here, according to the gaming machine of the present example, in the normal game state, when a specific combination is won, a combination of specific symbols is displayed and the special combination or the special combination is won before the first specific game state. Then, when the special permission state (second specific game state) or the special permission state is reached, the game can be played again in the normal game state via the special game state or the special game state. Further, even in the first specific game state, if the special combination is won and the special permission state (second specific game state) is reached, the game can be played again in the normal game state via the special game state. .. On the other hand, in the first specific game state, if the special combination is won and the special permitted state is reached, it becomes difficult to play the game in the normal game state again via the special game state.
また、本例の遊技機によれば、特別役(BB)に当籤した場合には特別許可状態(BB許可状態)となって第2特定遊技状態((D)RT2状態)に移行し、特別図柄の組合せ(BBに係る図柄の組合せ)を表示させて特別遊技状態((E)BB状態)に移行させることを困難としない一方、特殊役(MB)に当籤した場合には特殊許可状態(MB許可状態)となるが遊技状態は移行せず、第1特定遊技状態((C)RT1状態MBフラグ間)であれば、規定数(例えば、1500ゲーム)の遊技が行われて当該第1特定遊技状態が終了するまで特殊図柄の組合せ(MBに係る図柄の組合せ)を表示させて特殊遊技状態((F)MB状態)に移行させることを困難とし、その結果として通常遊技状態((A)RT0状態)に移行させることを困難とする。また、第1特定遊技状態には、特別許可状態及び特殊許可状態でない通常遊技状態において特定役(押し順小役)に当籤した場合に、特定の態様(押し順正解となる態様)で停止操作が行われずに特定図柄の組合せ(ベルこぼし目)が表示されたことに基づいて移行する。そして、特定の報知条件が成立した場合、通常遊技状態及び第1特定遊技状態における特定期間(有利区間)では、特定役に当籤したときに特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知され、報知にしたがって停止操作が行われれば、特定図柄の組合せは表示されず、特定数(例えば、9枚)の遊技価値が付与される。 Further, according to the gaming machine of this example, when a special combination (BB) is won, a special permission state (BB permission state) is set and a transition is made to a second specific game state ((D)RT2 state). While it is not difficult to display a combination of symbols (combination of symbols related to BB) and shift to the special game state ((E)BB state), when the special combination (MB) is won, the special permission state ( If the first specific game state (between (C) RT1 state MB flag), the game state does not shift but becomes a prescribed number (for example, 1500 games) of the game and the first It is difficult to display a special symbol combination (combination of symbols relating to MB) and move to the special gaming state ((F)MB state) until the specific gaming state ends, and as a result, the normal gaming state ((A ) It is difficult to shift to the RT0 state). In addition, in the first specific game state, when the special combination (push order small combination) is won in the special permission state and the normal game state that is not the special permission state, the stop operation is performed in a specific mode (a mode in which the press order is the correct answer). Is performed and a transition is made based on the display of a combination of specific symbols (bell-shaped eyes). Then, when the specific notification condition is satisfied, during the specific period (advantageous section) in the normal game state and the first specific game state, operation information regarding a specific mode is notified when a specific winning combination is won, and the operation is stopped according to the notification. If the operation is performed, the combination of the specific symbols is not displayed, and a specific number (for example, 9) of game values are given.
ここで、本例の遊技機によれば、通常遊技状態において、特定役に当籤したときに特定図柄の組合せが表示されて第1特定遊技状態に移行する前に、特別役又は特殊役に当籤して特別許可状態(第2特定遊技状態)又は特殊許可状態となれば、特別遊技状態又は特殊遊技状態を経由して再度通常遊技状態において遊技を行うことができる。また、第1特定遊技状態であっても、特別役に当籤して特別許可状態(第2特定遊技状態)となれば、特別遊技状態を経由して再度通常遊技状態において遊技を行うことができる。一方、第1特定遊技状態において、特殊役に当籤して特殊許可状態となると、規定数の遊技が行われるまで特殊遊技状態を経由して再度通常遊技状態において遊技を行うことが困難となる。 Here, according to the gaming machine of the present example, in the normal game state, when a specific combination is won, a combination of specific symbols is displayed and the special combination or the special combination is won before the first specific game state. Then, when the special permission state (second specific game state) or the special permission state is reached, the game can be played again in the normal game state via the special game state or the special game state. Further, even in the first specific game state, if the special combination is won and the special permission state (second specific game state) is reached, the game can be played again in the normal game state via the special game state. .. On the other hand, in the first specific game state, if the special combination is won and the special permission state is reached, it becomes difficult to play the game in the normal game state again via the special game state until the specified number of games are played.
かかる遊技性の下、通常遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間となった場合には、第1特定遊技状態に移行することなく特別遊技状態(あるいは特殊遊技状態)への移行を繰り返す(すなわち、遊技者に有利な遊技期間を継続させる)ことが可能となるのみならず、特定役に当籤したときに付与される遊技価値も増加することになる。また、第1特定遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間となった場合には、例えば、特殊許可状態であれば特殊遊技状態を経由して通常遊技状態に移行させることは困難であるものの、特定役に当籤したときに付与される遊技価値は増加することになる。また、通常遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間となっていない場合であっても、第1特定遊技状態に移行することなく特別遊技状態(あるいは特殊遊技状態)への移行を繰り返すことができる場合もある。 Under such a game property, in the normal game state, when a specific period during which operation information related to a specific mode is notified is given, the special game state (or the special game state) is entered without shifting to the first specific game state. It is possible not only to repeat the shift (that is, to continue the game period that is advantageous to the player), but also to increase the game value given when the specific combination is won. Further, in the first specific game state, when the specific period during which the operation information regarding the specific mode is notified is given, for example, in the case of the special permission state, it is possible to shift to the normal game state via the special game state. Although difficult, the game value given when a specific combination is won is increased. In addition, even in the normal game state, even if it is not a specific period in which operation information related to a specific mode is notified, a transition to the special game state (or a special game state) without transition to the first specific game state May be repeated.
すなわち、本例の遊技機によれば、通常遊技状態若しくは第1特定遊技状態であるか、通常遊技状態において特別役、特殊役若しくは特定役がどのような順番で当籤するか、第1特定遊技状態において特別役若しくは特殊役がどのような順番で当籤するか、通常遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間であるか否か、又は第1特定遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間であるか否か、などに応じて遊技者の有利度合いを多彩に変動させることが可能となる。それゆえ、遊技意欲や興趣を向上させることができる。 That is, according to the gaming machine of this example, it is in the normal game state or the first specific game state, in which order the special combination, the special combination or the specific combination is won in the normal game state, the first specific game. In a state in which the special combination or special combination is won, whether or not it is a specific period during which operation information regarding a specific mode is notified in the normal game state, or related to a specific mode in the first specific game state It is possible to variably change the degree of advantage of the player according to whether or not it is a specific period in which the operation information is notified. Therefore, it is possible to improve the game motivation and interest.
なお、本例の遊技機において、少なくとも第1特定遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される期間は、遊技価値が増加する増加期間として機能させるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、第1特定遊技状態であっても遊技価値が増加する場合があることから、通常遊技状態に移行することが困難な特定遊技状態中であっても、遊技の興趣を維持させることができる。 In the gaming machine of this example, at least the period in which the operation information regarding the specific mode is notified in the first specific game state may be made to function as an increase period in which the game value increases. By doing so, the game value may increase even in the first specific game state, so that the interest of the game is maintained even during the specific game state in which it is difficult to shift to the normal game state. Can be made
[遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その5)]
続いて、図97を参照して、本実施形態に係るパチスロ1において実装可能な遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その5)について説明する。図97は、遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その5)における遊技の流れを概念的に説明する図である。
[Another example of playability (game specifications) (Part 5)]
Next, with reference to FIG. 97, another example (No. 5) of the playability (game specification) that can be mounted in the pachi-
図97に示すように、本例では、(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)、(B)BB1状態、(C)BB1フラグ間、(D)BB2状態、(E)BB2フラグ間、(F)BB3状態、及び(G)BB3フラグ間の遊技状態がある。本例は、一般遊技状態(通常遊技状態)で当籤したボーナス役の種別、及びボーナス役に当籤した遊技で対応する図柄の組合せが表示されたか否かで遊技性を異ならせようとするものである。 As shown in FIG. 97, in this example, (A) general gaming state (non-bonus state), (B) BB1 state, (C) BB1 flag interval, (D) BB2 state, (E) BB2 flag interval, ( There is a game state between F)BB3 state and (G)BB3 flag. In this example, the type of bonus combination won in the normal game state (normal game state), and whether or not the combination of symbols corresponding to the winning game in the bonus combination is displayed, is made to have different playability. is there.
BB1に係る図柄の組合せは、例えば本実施形態の「C_赤同色BB」(図20参照)と同様に構成される。BB2に係る図柄の組合せは、例えば本実施形態の「C_青同色BB」(図20参照)と同様に構成される。BB3に係る図柄の組合せは、例えば「BAR−BAR−BAR」(図15参照)として構成される。このとき、「赤7」図柄、「青7」図柄、及び「BAR」図柄が、少なくとも一のリール(全てのリールであってもよい)において等間隔(あるいは略等間隔)に配置され、当該リールに対して停止操作を行う場合には、「赤7」図柄が表示されるタイミングと、「青7」図柄が表示されるタイミングと、「BAR」図柄が表示されているタイミングと、が重複しないように構成する。すなわち、「赤7」図柄を狙って目押しした場合には、「青7」及び「BAR」図柄が表示される場合がなく、「青7」図柄を狙って目押しした場合には、「赤7」及び「BAR」図柄が表示される場合がなく、「BAR」図柄を狙って目押しした場合には、「赤7」及び「青7」図柄が表示される場合がないように構成する。なお、BB3に係る図柄の組合せは、例えば本実施形態の「C_赤異色BB」若しくは「C_青異色BB」(図20参照)と同様に構成されるようにしてもよい。 The combination of symbols related to BB1 is configured in the same manner as, for example, “C_red same color BB” (see FIG. 20) of the present embodiment. The combination of symbols related to BB2 is configured in the same manner as, for example, “C_blue same color BB” (see FIG. 20) of the present embodiment. The symbol combination related to BB3 is configured as, for example, "BAR-BAR-BAR" (see FIG. 15). At this time, the "red 7" symbol, the "blue 7" symbol, and the "BAR" symbol are arranged at equal intervals (or substantially equal intervals) on at least one reel (all reels may be), When the stop operation is performed on the reel, the timing at which the "red 7" symbol is displayed, the timing at which the "blue 7" symbol is displayed, and the timing at which the "BAR" symbol is displayed overlap. Configure not to. That is, when the "red 7" symbol is aimed and pressed, the "blue 7" and "BAR" symbols are not displayed, and when the "blue 7" symbol is aimed and pressed, " There is no case where the "red 7" and "BAR" symbols are displayed, and when the "BAR" symbol is pressed to aim, the "red 7" and "blue 7" symbols are not displayed To do. The combination of symbols related to BB3 may be configured in the same manner as, for example, the “C_red different color BB” or the “C_blue different color BB” (see FIG. 20) of the present embodiment.
(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)において、例えばボーナス役(BB1〜BB3のいずれか)を所定確率(例えば、合算で1/45)で当籤可能とした場合、当籤したボーナス役がBB1である確率は「45%」(当籤確率としては「1/100」)であり、当籤したボーナス役がBB2である確率は「45%」(当籤確率としては「1/100」)であり、当籤したボーナス役がBB3である確率は「10%」(当籤確率としては「1/450」)である。なお、このボーナス当籤比率は、一例を示したものであり、BB1〜BB3を同じ当籤確率(当籤比率)で当籤させてもよいし、上記とは異なる比率で当籤させてもよい。また、(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)において、BB1、BB2、及びBB3は、他のリプレイ役や小役と重複として当籤せず、それぞれ単独で当籤するように構成される。なお、当籤した遊技で対応する図柄の組合せが表示可能である限り、他の小役などと重複して当籤するように構成してもよい。 (A) In the general game state (non-bonus state), for example, when a bonus combination (one of BB1 to BB3) can be won with a predetermined probability (for example, 1/45 in total), the winning bonus combination is BB1. A certain probability is “45%” (the winning probability is “1/100”), and the probability that the winning bonus combination is BB2 is “45%” (the winning probability is “1/100”). The probability that the bonus combination is BB3 is “10%” (the winning probability is “1/450”). The bonus winning ratio is an example, and BB1 to BB3 may be won with the same winning probability (winning ratio), or may be won with a ratio different from the above. Further, in the (A) general game state (non-bonus state), BB1, BB2, and BB3 are not won as overlapping with other replay combinations and small combinations, and are individually won. It should be noted that, as long as a combination of corresponding symbols can be displayed in the winning game, it may be configured to win the winning overlapping with other small winning combinations.
(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)において、(1−1)BB1に当籤した場合、(2−1)BB2に当籤した場合、(3−1)BB3に当籤した場合、いずれの場合にも当籤した遊技でボーナス当籤報知が行われる。このボーナス当籤報知は、BB1〜BB3のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された旨は報知可能とするが、その種別を報知可能としない所定報知として構成される。この所定報知は、例えば、「大当り!」などの文字を表示したり、WINランプを点灯させたりしてボーナス役に当籤したことは報知されるが、BB1に当籤したのか、BB2に当籤したのか、あるいはBB3に当籤したのかは感得されないものとなっている。 (A) In the general game state (non-bonus state), if (1-1) BB1 is won, (2-1) BB2 is won, or (3-1) BB3 is won Also, the bonus winning notification is given in the game that has been won. This bonus winning notification can be configured to notify that any one of BB1 to BB3 is determined as the internal winning combination, but is configured as a predetermined notification that does not allow the type to be notified. The predetermined notification is, for example, that a character such as "big hit!" is displayed, or that the win lamp is turned on to win the bonus combination. However, whether BB1 is won or BB2 is won. It is not possible to feel whether or not BB3 is won.
(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)において、(1−1)BB1に当籤した場合、遊技者が「赤7」図柄の目押しを成功し(停止操作のタイミングが適切であり)、BB1に係る図柄の組合せを有効ライン上に停止表示できた場合には、(1−2)BB1成立となり、(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)から(B)BB1状態に移行する。(B)BB1状態では、他の例と同様、遊技価値が増加する増加期間となり、(B)BB1状態において、規定数(例えば、140枚超)の遊技価値が付与されると、遊技価値の付与上限となり、(1−4)BB1終了となって、(B)BB1状態から(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)に移行する。 (A) In the general game state (non-bonus state), if (1-1) BB1 is won, the player succeeds in pushing the "red 7" symbol (the timing of the stop operation is appropriate), and BB1 When the symbol combination related to (1) can be stopped and displayed on the activated line, (1-2) BB1 is established, and (A) general game state (non-bonus state) shifts to (B) BB1 state. (B) In the BB1 state, as in the other examples, the game value increases for an increasing period, and in the (B) BB1 state, when a prescribed number (for example, more than 140) of game values are given, It becomes the upper limit of grant, and (1-4) BB1 ends, and the state shifts from (B) BB1 state to (A) general game state (non-bonus state).
一方、遊技者が「赤7」図柄の目押しを失敗し(停止操作のタイミングが適切でなく)、BB1に係る図柄の組合せを有効ライン上に停止表示できなかった場合には、(1−3)BB1不成立となり、(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)から(C)BB1フラグ間に移行する。 On the other hand, if the player fails to press the "red 7" symbol (the timing of the stop operation is not appropriate) and the symbol combination related to BB1 cannot be stopped and displayed on the activated line, (1- 3) BB1 is not established and the state shifts from (A) the general game state (non-bonus state) to (C) the BB1 flag.
本例では、本実施形態や他の例と同様、押し順小役があり、これを、6択の押し順小役1〜6として説明する。通常の停止制御では、押し順小役1は、左中右が押し順正解で停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず9枚払出、その他の押し順が押し順不正解で、停止操作のタイミングが適切なら1枚払出、適切でなければ取りこぼし(払出なし)、押し順小役2は、左右中が押し順正解で停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず9枚払出、その他の押し順が押し順不正解で、停止操作のタイミングが適切なら1枚払出、適切でなければ取りこぼし(払出なし)、押し順小役3は、中左右が押し順正解で停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず9枚払出、その他の押し順が押し順不正解で、停止操作のタイミングが適切なら1枚払出、適切でなければ取りこぼし(払出なし)、押し順小役4は、中右左が押し順正解で停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず9枚払出、その他の押し順が押し順不正解で、停止操作のタイミングが適切なら1枚払出、適切でなければ取りこぼし(払出なし)、押し順小役5は、右左中が押し順正解で停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず9枚払出、その他の押し順が押し順不正解で、停止操作のタイミングが適切なら1枚払出、適切でなければ取りこぼし(払出なし)、押し順小役6は、右中左が押し順正解で停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず9枚払出、その他の押し順が押し順不正解で、停止操作のタイミングが適切なら1枚払出、適切でなければ取りこぼし(払出なし)となる。
In this example, similar to the present embodiment and other examples, there are push order small wins, which will be described as 6 choices of push order
(C)BB1フラグ間では、(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)よりも再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率が高く、「ハズレ」確率が例えば「1/4000」程度に設定される。他の例で説明したのと同様、本例でも(C)BB1フラグ間においては「ハズレ」となった遊技でのみBB1に係る図柄の組合せが表示可能となる。「ハズレ」となった遊技でBB1に係る図柄の組合せを表示させることができれば、(1−2)BB1成立となり、(C)BB1フラグ間から(B)BB1状態に移行する。また、(C)BB1フラグ間では、当籤していたボーナス役がBB1であったこと(すなわち、ボーナス役の種別)が報知されるボーナス種別報知が行われる。このボーナス種別報知は、BB1フラグ間において、BB1に当籤していること(BB1に係る図柄の組合せの表示が許可されていること)を報知する特定報知として構成される。この特定報知は、例えば、「赤7内部当たり中」など文字を表示したり、「赤7」に対応するランプを点灯させたりしてBB1に当籤していることが感得されうるものとなっている。なお、この特定報知は、(C)BB1フラグ間である間は常に行われるようにすることもできるし、(C)BB1フラグ間においてBB1に係る図柄の組合せが表示可能となった遊技で行われるようにすることもできる。 (C) Between the BB1 flags, the winning probability of the replay (replay) hand is higher than that of the (A) general game state (non-bonus state), and the “miss” probability is set to, for example, about “1/4000”. As described in other examples, also in this example, between the (C) BB1 flags, it is possible to display the combination of symbols related to BB1 only in the game in which "miss". If the combination of symbols related to BB1 can be displayed in the game that is "missed", (1-2) BB1 is established, and the state shifts from (C) BB1 flags to (B) BB1 state. Further, between (C) BB1 flags, a bonus type notification is made to notify that the winning combination that was won is BB1 (that is, the type of bonus combination). This bonus type notification is configured as a specific notification for notifying that BB1 has been won (displaying of a combination of symbols related to BB1 is permitted) between BB1 flags. This specific notification can be felt to indicate that the BB1 has been won by, for example, displaying a character such as “red 7 inside hit” or lighting a lamp corresponding to “red 7”. ing. It should be noted that this specific notification can be made to be always performed during the period between the (C)BB1 flags, or in the game in which the combination of symbols related to the BB1 can be displayed between the (C)BB1 flags. You can choose to be invited.
また、(C)BB1フラグ間では、押し順小役1〜6について、停止制御が変更される。具体的には、押し順小役1、押し順小役3、押し順小役5に当籤した場合には、押し順や停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず(これらの要因を不問として)9枚払出となり、押し順小役2、押し順小役4、押し順小役6に当籤した場合には、押し順や停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず(これらの要因を不問として)1枚払出となるように停止制御が変更される。ここで、押し順小役1〜6についてはそれぞれ同じ当籤確率となっていることから、押し順の報知が行われないことを前提とすれば、通常の停止制御が行われる(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)や後述の(G)BB3フラグ間よりも当該(C)BB1フラグ間のほうが遊技者に対する還元率が高く構成される。なお、(C)BB1フラグ間は、減少期間(ただし、(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)や後述の(G−1)非有利区間からみると減少率が低い)として構成してもよいし、増加期間(ただし、後述の(G−2)有利区間からみると増加率が低い)として構成してもよい。また、付与期待値上は、無増減期間として構成してもよい。また、付与期待値にはほとんど影響を与えないが、(C)BB1フラグ間においても、特定の報知条件にしたがって、例えば(C−1)非有利区間と(C−2)有利区間との間で移行制御が行われるようにしてもよい。
Further, between the (C) BB1 flags, the stop control is changed for the push order
(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)において、(2−1)BB2に当籤した場合、遊技者が「青7」図柄の目押しを成功し(停止操作のタイミングが適切であり)、BB2に係る図柄の組合せを有効ライン上に停止表示できた場合には、(2−2)BB2成立となり、(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)から(D)BB2状態に移行する。(D)BB2状態では、他の例と同様、遊技価値が増加する増加期間となり、(D)BB2状態において、規定数(例えば、140枚超)の遊技価値が付与されると、遊技価値の付与上限となり、(2−4)BB2終了となって、(D)BB2状態から(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)に移行する。 (A) In the general gaming state (non-bonus state), if the player wins (2-1) BB2, the player succeeds in pushing the "blue 7" symbol (the timing of the stop operation is appropriate), and BB2 When the symbol combination related to (1) can be stopped and displayed on the activated line, (2-2) BB2 is established, and (A) general game state (non-bonus state) shifts to (D) BB2 state. In the (D)BB2 state, as in other examples, the game value increases for an increasing period, and in the (D)BB2 state, when a prescribed number of game values (for example, more than 140) are given, the game value becomes It becomes the upper limit of grant, and (2-4) BB2 ends, and the state shifts from the (D) BB2 state to the (A) general game state (non-bonus state).
一方、遊技者が「青7」図柄の目押しを失敗し(停止操作のタイミングが適切でなく)、BB2に係る図柄の組合せを有効ライン上に停止表示できなかった場合には、(2−3)BB2不成立となり、(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)から(E)BB2フラグ間に移行する。なお、(E)BB2フラグ間は、BB1をBB2と置き換え、「赤7」を「青7」と置き換えれば、基本的に(C)BB1フラグ間と同様となるため、ここでの説明は省略する。また、ボーナス種別報知なども同様である。 On the other hand, if the player fails to push the "blue 7" symbol (the timing of the stop operation is not appropriate) and the symbol combination related to BB2 cannot be stopped and displayed on the activated line, (2- 3) BB2 is not established and the state shifts from (A) the general game state (non-bonus state) to (E) the BB2 flag. In addition, if (BB)1 is replaced with BB2 and “red 7” is replaced with “blue 7” between (E)BB2 flags, the description is basically the same as between (C)BB1 flags. To do. The same applies to bonus type notification and the like.
(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)において、(3−1)BB3に当籤した場合、遊技者が「BAR」図柄の目押しを成功し(停止操作のタイミングが適切であり)、BB3に係る図柄の組合せを有効ライン上に停止表示できた場合には、(3−2)BB3成立となり、(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)から(F)BB3状態に移行する。(F)BB3状態では、他の例と同様、遊技価値が増加する増加期間となり、(F)BB3状態において、規定数(例えば、140枚超)の遊技価値が付与されると、遊技価値の付与上限となり、(3−4)BB3終了となって、(F)BB3状態から(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)に移行する。なお、(F)BB3状態を、減少期間や無増減期間として構成することもできる。 (A) In the general game state (non-bonus state), if (3-1) BB3 is won, the player successfully pushes the "BAR" symbol (the timing of the stop operation is appropriate), and BB3 When the combination of such symbols can be stopped and displayed on the activated line, (3-2) BB3 is established, and (A) general gaming state (non-bonus state) shifts to (F) BB3 state. In the (F)BB3 state, as in other examples, the game value increases for an increasing period, and in the (F)BB3 state, when a prescribed number of game values (for example, more than 140) are given, the game value becomes It becomes the upper limit of grant, and (3-4) BB3 ends, and the state shifts from (F) BB3 state to (A) general game state (non-bonus state). Note that the (F)BB3 state can be configured as a decreasing period or a non-increasing period.
一方、遊技者が「BAR」図柄の目押しを失敗し(停止操作のタイミングが適切でなく)、BB3に係る図柄の組合せを有効ライン上に停止表示できなかった場合には、(3−3)BB3不成立となり、(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)から(G)BB3フラグ間に移行する。 On the other hand, if the player fails to push the "BAR" symbol (the timing of the stop operation is not appropriate) and the symbol combination related to BB3 cannot be stopped and displayed on the activated line, (3-3 ) BB3 is not established, and the state shifts from the (A) general game state (non-bonus state) to the (G) BB3 flag.
(G)BB3フラグ間では、(C)BB1フラグ間及び(E)BB2フラグ間よりも再遊技(リプレイ)役の当籤確率が高く、「ハズレ」確率が例えば「1/65536」程度やあるいは「0」に設定される。すなわち、(G)BB3フラグ間では、BB3に係る図柄の組合せが表示される確率が極めて低いか、あるいはBB3に係る図柄の組合せが表示されないように構成される。なお、「ハズレ」確率の設定はこれに限られず、(C)BB1フラグ間及び(E)BB2フラグ間と同程度に設定してもよいし、これらよりも高い確率に設定してもよい。これは、意図する出玉率やその内容などに応じて適宜選択されるものとすればよい。(G)BB3フラグ間においても同様、「ハズレ」となった遊技でのみBB3に係る図柄の組合せが表示可能となる。「ハズレ」となった遊技でBB3に係る図柄の組合せを表示させることができれば、(3−2)BB3成立となり、(G)BB3フラグ間から(F)BB3状態に移行する。なお、ボーナス種別報知は、「赤7」を「BAR」と置き換えれば、基本的に(C)BB1フラグ間と同様となるため、ここでの説明は省略する。 The (G)BB3 flags have a higher winning probability of the replay (replay) role than the (C)BB1 flags and the (E)BB2 flags, and the "miss" probability is, for example, about "1/65536" or " It is set to "0". That is, between the (G)BB3 flags, the probability that the symbol combination related to BB3 is displayed is extremely low, or the symbol combination related to BB3 is not displayed. The setting of the “miss” probability is not limited to this, and may be set to the same level as between the (C) BB1 flags and between the (E) BB2 flags, or may be set to a higher probability than these. This may be appropriately selected according to the intended payout rate and its content. (G) Similarly between the BB3 flags, the combination of symbols related to BB3 can be displayed only in the game in which "missing". If the combination of symbols related to BB3 can be displayed in the game that is "missed", (3-2) BB3 is established, and the state shifts from (G) BB3 flags to (F) BB3 state. Note that the bonus type notification is basically the same as between the (C) BB1 flags if “red 7” is replaced with “BAR”, and therefore the description thereof is omitted here.
また、(G)BB3フラグ間では、押し順小役1〜6について、停止制御が変更されず、通常の停止制御となる。したがって、押し順の報知が行われないことを前提とすれば、(C)BB1フラグ間及び(E)BB2フラグ間のほうが遊技者に対する還元率が高くなるが、(G)BB3フラグ間では、有利区間に制御されていない場合には、(G−1)非有利区間となって遊技価値が減少する減少期間となるものの、有利区間に制御されている場合には、(G−2)有利区間となって遊技価値が増加する増加期間となり、(G−2)有利区間では、少なくとも押し順小役1〜6の当籤時に正解となる押し順が報知される結果、(C)BB1フラグ間及び(E)BB2フラグ間よりも遊技者に対する還元率が高く(付与期待値が高く)構成される。なお、有利区間に制御されうる特定の報知条件は、本実施形態や本例以外の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例で説明した種々の条件を採用することができる。
Further, between the (G)BB3 flags, the stop control is not changed for the push order small winning
すなわち、(1−1)BB1に当籤し、(1−2)BB1成立の場合には、(B)BB1状態となって遊技価値が増加し、(1−3)BB1不成立の場合には、(C)BB1フラグ間となって、遊技価値が緩やかに増加し、あるいは緩やかに減少する。(C)BB1フラグ間は、(1−2)BB1が成立するまで継続するように構成される。また、(2−1)BB2に当籤し、(2−2)BB2成立の場合には、(D)BB2状態となって遊技価値が増加し、(2−3)BB2不成立の場合には、(E)BB2フラグ間となって、遊技価値が緩やかに増加し、あるいは緩やかに減少する。(E)BB2フラグ間は、(2−2)BB2が成立するまで継続するように構成される。 That is, if (1-1) BB1 is won and (1-2) BB1 is established, the game value is increased to (B) BB1 state, and if (1-3) BB1 is not established, (C) Between the BB1 flags, the game value gradually increases or gradually decreases. Between (C) BB1 flags, it is configured to continue until (1-2) BB1 is established. If (2-1) BB2 is won and (2-2) BB2 is established, the game value is increased to (D) BB2 state, and if (2-3) BB2 is not established, (E) Between the BB2 flags, the game value gradually increases or gradually decreases. Between (E)BB2 flags, it is configured to continue until (2-2)BB2 is established.
また、(3−1)BB3に当籤し、(3−2)BB3成立の場合には、(F)BB3状態となって遊技価値が増加し、(3−3)BB3不成立の場合には、(G)BB3フラグ間となって、(G−1)非有利区間であれば遊技価値が急激に減少する一方で、(G−2)有利区間であれば遊技価値が急激に増加する。(G)BB3フラグ間は、極めて低い確率で(3−2)BB3が成立するまで継続するか、あるいは一旦移行すると基本的には終了しないように構成される。なお、BB1及びBB2のほうがBB3よりも当籤確率が高いため、射幸性を抑制できる期間を十分に確保できる。また、通常は、遊技店に設置された当初は前者の遊技性が提供され、それからしばらく経過したときに後者の遊技性が提供される可能性が高い。もっとも、以下に示すような初期化操作によって遊技性を変動可能とすることが担保されるようにすることもできる。 Also, if (3-1) BB3 is won, and (3-2) BB3 is established, the state becomes (F) BB3 state and the game value increases, and if (3-3) BB3 is not established, (G) Between BB3 flags, the game value sharply decreases in the (G-1) non-advantageous section, while the game value sharply increases in the (G-2) advantageous section. The (G) BB3 flag is configured to continue with an extremely low probability until (3-2) BB3 is satisfied, or basically not to end once the transition is made. Since BB1 and BB2 have a higher winning probability than BB3, it is possible to sufficiently secure a period in which the gambling property can be suppressed. In addition, usually, when the game machine is installed in a game store, the former game property is provided, and after a while, the latter game property is likely to be provided. However, it is possible to ensure that the game playability can be changed by the following initialization operation.
例えば、(C)BB1フラグ間、(E)BB2フラグ間、又は(G)BB3フラグ間にあるとき、設定変更操作(遊技状態を初期化するための初期化操作)が行われると、持越役としてのBB1、BB2、又はBB3がクリアされることで、(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)に移行する。すなわち、(G)BB3フラグ間を終了しないように構成する場合、設定変更操作が行われたことに基づいて、持越役としてのBB3がクリアされることで(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)に移行するようにしてもよい。もっとも、設定変更操作が行われると、(C)BB1フラグ間又は(E)BB2フラグ間であれば、持越役としてのBB1又はBB2がクリアされることで(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)に移行するが、(G)BB3フラグ間であれば、持越役としてのBB3がクリアされず(A)一般遊技状態(非ボーナス状態)に移行しないようにしてもよい。また、設定変更操作が行われても、持越役としてのBB1、BB2又はBB3のいずれもがクリアされないように構成することもできる。 For example, when the setting change operation (initialization operation for initializing the game state) is performed when the flag is between (C)BB1 flag, between (E)BB2 flag, or between (G)BB3 flag, carryover combination By clearing BB1, BB2, or BB3 as (1), (A) the normal game state (non-bonus state) is entered. That is, when the (G) BB3 flags are not ended, the BB3 as the carryover combination is cleared based on the setting change operation being performed (A) the general gaming state (non-bonus state) ). However, when the setting change operation is performed, if (C) between BB1 flags or between (E) BB2 flags, BB1 or BB2 as a carryover combination is cleared (A) general gaming state (non-bonus state). ), but if it is between (G) BB3 flags, BB3 as the carryover combination is not cleared and (A) the normal gaming state (non-bonus state) may not be shifted. Further, it is also possible to configure such that none of BB1, BB2 or BB3 as the carryover combination is cleared even if the setting change operation is performed.
本例の遊技機によれば、第1特別役(BB1)又は第2特別役(BB3)に当籤した場合、当該遊技か、あるいは当籤後の第1特別許可状態(BB1フラグ間)又は第2特別許可状態(BB3フラグ間)において他の内部当籤役が決定されなかった(いわゆる、ハズレとなった)遊技でなければ第1特別図柄の組合せ(BB1に係る図柄の組合せ)又は第2特別図柄の組合せ(BB3に係る図柄の組合せ)を表示できない。また、第1特別許可状態では、第1所定役(押し順小役1,3,5)に当籤した場合、押し順不問で所定数(例えば、9枚)の遊技価値が付与され、第2所定役(押し順小役2,4,6)に当籤した場合、押し順不問で所定数の遊技価値が付与されない。一方、第2特別許可状態では、第1所定役又は第2所定役に当籤した場合に、押し順正解であれば所定数の遊技価値が付与され、押し順不正解であれば所定数の遊技価値は付与されない。そして、少なくとも第2特別許可状態の特定期間では、遊技者の停止操作の情報が報知される有利状態((G−2)有利区間)に制御されることが可能である。
According to the gaming machine of this example, when the first special winning combination (BB1) or the second special winning combination (BB3) is won, the game concerned, or the first special permission state (between BB1 flags) or the second winning combination is won. Other internal winning combination has not been determined in the special permission state (BB3 flag) (so-called, lost) If it is not a game, the combination of the first special symbol (the combination of symbols related to BB1) or the second special symbol Cannot be displayed (combination of symbols relating to BB3). Further, in the first special permission state, when the first predetermined winning combination (pushing order small winning
すなわち、第1特別役に当籤し、当該遊技で第1特別図柄の組合せが表示されなかった場合には、その後第1特別許可状態が終了するまで第1所定役及び第2所定役は押し順によって利益が変動しないものとなり、遊技者は一定の利益を受けることができる反面、その利益が飛躍的に増加することもないため、たとえ有利状態となったとしてもその遊技価値の増加量を示す傾斜値は相対的に低いものとなる。一方、第2特別役に当籤し、当該遊技で第2特別図柄の組合せが表示されなかった場合には、その後第2特別許可状態が終了するまで第1所定役及び第2所定役は押し順によって利益が変動するものとなり、遊技者は第1特別許可状態よりも不利益を被る可能性がある反面、有利状態となればその利益が飛躍的に増加するようになるため、有利状態における遊技価値の増加量を示す傾斜値は相対的に高いものとなる。それゆえ、有利状態中の遊技価値の増加量を示す傾斜値を変動可能とすることで、遊技性を変化に富んだものとすることができる。 That is, if the first special combination is won and the combination of the first special symbols is not displayed in the game, the first predetermined combination and the second predetermined combination are pushed in order until the first special permission state is finished. The profits do not fluctuate due to this, and the player can receive a certain amount of profits, but the profits do not increase dramatically, so even if it becomes advantageous, it shows the amount of increase in the game value. The slope value will be relatively low. On the other hand, if the second special combination is won, and the combination of the second special symbols is not displayed in the game, then the first predetermined combination and the second predetermined combination are pushed in order until the second special permission state ends. As a result, profits fluctuate, and the player may suffer a disadvantage more than in the first special permission state, but when the advantageous state is reached, the profit is dramatically increased. The slope value indicating the increase in value is relatively high. Therefore, by making it possible to change the inclination value indicating the amount of increase in the game value during the advantageous state, it is possible to make the game play rich in variety.
なお、本例の遊技機において、第1特別役の当籤確率を第2特別役の当籤確率よりも高くするとともに、第1特別許可状態において第1特別図柄の組合せが表示可能な確率を第2特別許可状態において第2特別図柄の組合せが表示可能な確率よりも高くするようにしてもよい。すなわち、第1特別許可状態を、第2特別許可状態よりも移行しやすく終了しやすい状態とし、第2特別許可状態を、第1特別許可状態よりも移行しにくく終了しにくい状態としてもよい。このようにすれば、射幸性を適度なものとしつつも遊技の興趣を維持することができる。 In the gaming machine of this example, the winning probability of the first special combination is made higher than the winning probability of the second special combination, and the probability that the combination of the first special symbols can be displayed in the first special permission state is the second. In the special permission state, the combination of the second special symbols may be set higher than the displayable probability. That is, the first special permission state may be set to a state in which it is easier to transition than the second special permission state and to be finished, and the second special permission state may be set to a state in which transition is less likely to occur and termination is more difficult than in the first special permission state. In this way, the enjoyment of the game can be maintained while the gambling property is moderate.
また、本例の遊技機において、第1特別役に係る第1特別図柄の組合せと第2特別役に係る第2特別図柄の組合せは、遊技者が目押しをする場合に、同時には狙えない間隔で配置されるように構成してもよい。このようにすれば、遊技性をさらに変化に富んだものとすることができ、遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。 Further, in the gaming machine of this example, the combination of the first special symbol relating to the first special combination and the second special symbol relating to the second special symbol cannot be aimed at the same time when the player makes a push. You may comprise so that it may be arrange|positioned at intervals. By doing so, the playability can be further varied and the enjoyment of the game can be improved.
また、本例の遊技機において、第1特別役又は第2特別役に当籤した場合には、いずれかに当籤した旨は報知するが、その種別までは報知せず(ボーナス当籤報知)、第1特別許可状態及び第2特別許可状態においては、その種別が報知される(ボーナス種別報知)ようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、遊技性をさらに変化に富んだものとしつつ、遊技者の所望する情報を報知することができる。 Further, in the gaming machine of the present example, when the first special winning combination or the second special winning combination is won, the fact that the winning is won is notified to one of them, but the type is not notified (bonus winning notification), In the first special permission state and the second special permission state, the type thereof may be notified (bonus type notification). By doing so, it is possible to notify the information desired by the player while further enhancing the playability.
[遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その6)]
続いて、図98及び図99を参照して、本実施形態に係るパチスロ1において実装可能な遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その6)について説明する。図98は、遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その6)における遊技の流れを概念的に説明する図であり、図99は、遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その6)において用いられる内部抽籤テーブルの一例を示した図である。
[Another example of playability (game specifications) (6)]
Next, with reference to FIGS. 98 and 99, another example (No. 6) of the playability (game specification) that can be implemented in the pachi-
図98及び図99に示すように、本例では、大別して、一般遊技状態(通常遊技状態)、及びBB状態の遊技状態があり、一般遊技状態(通常遊技状態)において、BB1及びBB2のいずれのボーナス役にも当籤していない状態を(A)一般遊技状態(非フラグ間)と定義し、BB1に当籤している状態(BB1が持ち越されているBB1許可状態)であって、3枚のメダルがベットされて(掛けられて)遊技が行われる状態を(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態と定義し、BB2に当籤している状態(BB2が持ち越されているBB2許可状態)であって、3枚のメダルがベットされて遊技が行われる状態を(C)BB2フラグ間3枚ベット状態と定義し、BB1許可状態であって、2枚のメダルがベットされて遊技が行われる状態を(D)BB1フラグ間2枚ベット状態と定義し、BB2許可状態であって、2枚のメダルがベットされて遊技が行われる状態を(E)BB2フラグ間2枚ベット状態と定義する。また、BB1に係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示されて開始されるボーナス状態を(F)BB1状態と定義し、BB2に係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示されて開始されるボーナス状態を(G)BB2状態と定義する。すなわち、一般遊技状態(通常遊技状態)で当籤する(当籤した)ボーナス役の種別、及びベット枚数(遊技価値の掛け数)に応じて遊技性を異ならせようとするものである。 As shown in FIG. 98 and FIG. 99, in this example, there are roughly classified a gaming state of a general gaming state (normal gaming state) and a BB state, and in the general gaming state (normal gaming state), either BB1 or BB2. The state in which the bonus combination is not won is defined as (A) general gaming state (between non-flags), and the state in which BB1 is won (BB1 allowed state where BB1 is carried over) is 3 pieces. The state in which the medals are bet (hanged) and the game is played is defined as (B) three-bet state between BB1 flags, and in the state where BB2 is won (BB2 permission state where BB2 is carried over). Therefore, the state in which three medals are bet and the game is played is defined as (C) three-bet state between BB2 flags. In the BB1 permitted state, two medals are bet and the game is played. The state is defined as a (D) two-bet state between BB1 flags, and the BB2 permitted state where two medals are bet and a game is played is defined as (E) two-bet state between BB2 flags. .. Further, a bonus state in which the symbol combination related to BB1 is stopped and displayed on the activated line is defined as (F)BB1 state, and the symbol combination related to BB2 is stopped and displayed on the activated line to be started. The bonus state is defined as the (G)BB2 state. That is, it is intended to make the game play different according to the type of bonus combination that is won (or won) in the normal game state (normal game state) and the number of bets (multiplying the game value).
なお、図99に示す内部抽籤テーブルでは、説明の便宜上、(A)一般遊技状態(非フラグ間)の3枚ベット状態において用いられる各抽籤値(「非フラグ間3枚ベット」の列参照)、(A)一般遊技状態(非フラグ間)の2枚ベット状態において用いられる各抽籤値(「非フラグ間2枚ベット」の列参照)、(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態及び(C)BB2フラグ間3枚ベット状態において用いられる各抽籤値(「フラグ間3枚ベット」の列参照)、及び(D)BB1フラグ間2枚ベット状態及び(E)BB2フラグ間2枚ベット状態において用いられる各抽籤値(「フラグ間2枚ベット」の列参照)を各列に表記しているが、これは遊技状態(RT状態)が異なることを意味するものではない。すなわち、RT状態としては共通のRT状態として制御することが可能である。もっとも、別のRT状態として制御することもできる。また、少なくとも後述の有利区間付与決定の対象となる内部当籤役ついては、各設定値間で共通の抽籤値となっているものとする。 In the internal lottery table shown in FIG. 99, for convenience of explanation, each lottery value used in the (A) three-bet state of the normal gaming state (between non-flags) (see the column of "three bets between non-flags"). , (A) each lottery value used in the two-bet state of the normal gaming state (between non-flags) (see the column of “two bets between non-flags”), (B) three-bet state between BB1 flags, and (C ) In each lottery value used in the three-bet state between BB2 flags (see the column “3 bets between flags”), and in (D) two-bet state between BB1 flags and (E) two-bet state between BB2 flags Each lottery value used (see the column of "two bets between flags") is described in each column, but this does not mean that the gaming state (RT state) is different. That is, the RT state can be controlled as a common RT state. However, it can also be controlled as another RT state. In addition, at least the internal winning combination that is the target of the determination of the advantageous section grant, which will be described later, has a common lottery value among the set values.
(A)一般遊技状態(非フラグ間)において、3枚ベットのとき、BB1の当籤を可能とし、BB2の当籤を可能としない(図99の「非フラグ間3枚ベット」の列参照)。一方、2ベットのとき、BB2の当籤を可能とし、BB1の当籤を可能としない(図99の「非フラグ間2枚ベット」の列参照)ように構成される。なお、本例では、遊技者は2枚のメダルをベットした場合、及び3枚のメダルをベットした場合のいずれの場合にも遊技を開始させること(開始操作を行うこと)が可能となっている。また、「ベット」とは、遊技に供するため、遊技者が2枚又は3枚のメダルをメダル投入口14に対して投入すること、遊技者がベットボタンを操作してクレジットから2枚又は3枚分のメダルを掛けること、及びリプレイ役の入賞によって自動的に2枚又は3枚分のメダルが掛けられること、のいずれをも含む。
(A) In the normal game state (between non-flags), when three bets are made, winning of BB1 is possible, and winning of BB2 is not possible (see the column of “3 bets between non-flags” in FIG. 99). On the other hand, in the case of 2 bets, the winning of BB2 is possible, and the winning of BB1 is not possible (see the column of “2 bets between non-flags” in FIG. 99). In this example, the player can start the game (perform a start operation) in the case of betting two medals and in the case of betting three medals. There is. The term "bet" means that the player inserts two or three medals into the
(A)一般遊技状態(非フラグ間)において、3枚ベットのとき、BB1に当籤した場合(当籤した遊技でBB1に係る図柄の組合せが表示されずに持ち越された場合であってもよい)には、BB1フラグ間に移行する。(1−1)BB1フラグ間において3枚ベットで遊技が行われるとき、(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態となる(図99の「フラグ間3枚ベット」の列参照)。一方、(2)BB1フラグ間において2枚ベットで遊技が行われるとき、(D)BB1フラグ間2枚ベット状態となる(図99の「フラグ間2枚ベット」の列参照)。 (A) In the normal gaming state (between non-flags), when three bets are won, if BB1 is won (may be a case where the winning game is carried over without displaying the combination of symbols relating to BB1) Shifts between BB1 flags. (1-1) When a game is played with 3 bets between BB1 flags, the state becomes (3) bet between BB1 flags (see the column of "3 bets between flags" in FIG. 99). On the other hand, when a game is played with two bets between (2) BB1 flags, a (2) bet between two flags between BB1 flags state (see the column "2 bets between flags" in FIG. 99).
(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態では、他の例ですでに説明したのと同様、「ハズレ」となった遊技でBB1に係る図柄の組合せが表示可能となっている(BB1成立可)。なお、「ハズレ」確率が適宜設定可能であるが、例えば、「1/8.5」程度に設定されるものとする。また、当該状態は、BB1許可状態であり、BB1が新たに当籤したり、BB2に当籤したりすることはない(BB1・BB2当籤不可)。また、押し順ベルA(図99のNo.「20」〜「31」の内部当籤役を参照)に当籤したとき、押し順正解(それぞれ「略称」で表示された押し順)であれば9枚払出となり、押し順不正解であって停止操作のタイミングが適切であれば(「○」)1枚払出となり、押し順不正解であって停止操作のタイミングが適切でなければ(「×」)0枚払出となる。また、押し順ベルB(図99のNo.「21」〜「43」の内部当籤役を参照)に当籤したとき、押し順や停止操作のタイミングにかかわらず9枚払出となる。すなわち、(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態は、押し順ベルBの押し順が不問となる分、有利区間を考慮しなければ、(A)一般遊技状態(非フラグ間)の3枚ベット状態や(C)BB2フラグ間3枚ベット状態よりも還元率が高く、遊技者に有利な状態となる。 (B) In the three-bet state between BB1 flags, a combination of symbols related to BB1 can be displayed in the game that has "missed", as has already been described in another example (BB1 can be established). .. The “miss” probability can be set as appropriate, but is set to, for example, about “1/8.5”. In addition, the state is a BB1 permission state, and BB1 does not newly win or wins BB2 (BB1 and BB2 cannot win). Further, when the push order bell A (refer to the internal winning combination of No. “20” to “31” in FIG. 99) is won, if the push order is correct (the push order displayed by “abbreviation” respectively), it is 9 If one sheet is paid out, the pressing order is incorrect, and the timing of the stop operation is appropriate (“○”), one sheet is paid out, the pressing order is incorrect, and the timing of the stop operation is not appropriate (“×”). ) 0 cards will be paid out. Further, when the push order bell B (refer to the internal winning combination of No. “21” to “43” in FIG. 99) is won, 9 coins are paid out regardless of the push order or the timing of the stop operation. That is, (B) BB1 three-bet state between flags, since the pressing order of the pushing order bell B is irrelevant, unless considering the advantageous section, (A) three-bet state in the normal gaming state (between non-flags) The return rate is higher than the state or the three bet state between the (C)BB2 flags, which is a state advantageous to the player.
また、(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態では、チャンス目(図99のNo.「7」〜「16」の内部当籤役を参照)に当籤したとき(あるいは、チャンス目係る図柄の組合せが表示されたときであってもよい)、強ベル(図99のNo.「17」及び「18」の内部当籤役を参照)に当籤したとき、確定役(図99のNo.「19」の内部当籤役を参照)に当籤したとき、チェリー(図99のNo.「44」の内部当籤役を参照)に当籤したとき、及びスイカ(図99のNo.「45」の内部当籤役を参照)に当籤したときには、それぞれ内部当籤役に応じた確率(確定役については100%の確率)で、有利区間付与決定(有利区間付与抽籤)が行われる。有利区間付与決定の結果、付与されることが決定されると、例えば、1セット50ゲームの有利区間が付与される(すでに有利区間中であれば、1セット50ゲーム分延長される)。なお、有利区間付与の態様は一例であり、本実施形態や本例以外の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例で説明した種々の態様を採用することができる。 Further, in the (B) three bet state between the BB1 flags, when the winning is achieved at the chance (see the internal winning combination of No. “7” to “16” in FIG. 99) (or the combination of the symbols related to the chance is It may be displayed), or when the strong bell (see the internal winning combination of No. “17” and “18” in FIG. 99) is won, the fixed winning combination (No. “19” of FIG. 99) is displayed. When the internal winning combination is won, when the cherry (see No. “44” internal winning combination in FIG. 99) is won and when the watermelon (No. “45” internal winning combination in FIG. 99 is referred to) ), the advantageous section grant determination (beneficial section grant lottery) is performed with a probability (100% probability for a fixed winning combination) corresponding to each internal winning combination. If it is determined as a result of the advantageous section grant determination, for example, one set of 50 games is provided with an advantage section (if one advantage section is already in use, one set is extended by 50 games). It should be noted that the mode of giving the advantageous section is an example, and various modes described in the present embodiment and other examples of game characteristics (game specifications) other than this example can be adopted.
また、(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態において、BB1に係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示されると、(1−2)BB1成立となり、(F)BB1状態に移行する。(F)BB1状態は、例えば、「特殊ボーナス状態」として構成され、遊技価値が増加する増加期間となる遊技状態であり、他の例ですでに説明したのと同様、任意の規定数(例えば、140枚)の遊技価値が付与されると、(1−3)BB1終了となり、(F)BB1状態から(A)一般遊技状態(非フラグ間)に移行する。 Further, in the (3) bet state between (B) BB1 flags, when the symbol combination related to BB1 is stopped and displayed on the activated line, (1-2) BB1 is established and the state shifts to (F) BB1. (F) The BB1 state is, for example, a gaming state that is configured as a "special bonus state" and has an increasing period in which the gaming value increases, and an arbitrary prescribed number (for example, the same as already described in another example. , 140 pieces) of game value is given, (1-3) BB1 ends, and the state shifts from (F) BB1 state to (A) general gaming state (between non-flags).
(D)BB1フラグ間2枚ベット状態では、BB1フラグ間ではあるものの、BB1が当籤した遊技とはベット数が異なるため、たとえ「ハズレ」となった遊技であってもBB1に係る図柄の組合せは表示不可能となっている(BB1成立不可)。また、当該状態は、BB1許可状態であり、BB1が新たに当籤したり、BB2に当籤したりすることはない(BB1・BB2当籤不可)。すなわち、当該状態は、ボーナス役に当籤することも入賞することもない遊技状態として構成される。もっとも、BB1フラグ間であることに鑑み、「ハズレ」となった遊技においてはBB1に係る図柄の組合せが表示可能となるように構成することもできる。 (D) In the two-bet state between BB1 flags, although it is between BB1 flags, the number of bets is different from the game in which BB1 is won, so even if the game is "missed", the combination of symbols related to BB1 Cannot be displayed (BB1 cannot be established). In addition, the state is a BB1 permission state, and BB1 does not newly win or wins BB2 (BB1 and BB2 cannot win). That is, the state is configured as a gaming state in which neither a winning combination nor a winning combination is won. However, in view of the fact that it is between the BB1 flags, a combination of symbols related to BB1 can be displayed in the game in which the game is “missed”.
また、(D)BB1フラグ間2枚ベット状態では、押し順ベルA及び押し順ベルBのいずれかに当籤したとき、押し順正解であれば2枚払出となり、押し順不正解であって停止操作のタイミングが適切であれば1枚払出となり、押し順不正解であって停止操作のタイミングが適切でなければ0枚払出となる。もっとも、押し順ベルA及び押し順ベルBのいずれか、あるいは双方について、押し順不問で2枚払出となるように構成することもできるし、付与期待値が(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態と同様となるように適宜抽籤値を減らした上で、(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態と同様の払出が行われるようにすることもできる。なお、(D)BB1フラグ間2枚ベット状態では、上述した有利区間付与決定は行われない。 Further, in the (D) 2 bet state between the BB1 flags, when either the pushing order bell A or the pushing order bell B is won, if the pushing order is correct, 2 pieces are paid out, and the pushing order is incorrect and the operation is stopped. If the operation timing is appropriate, 1 sheet is paid out, and if the pressing order is incorrect and the stop operation timing is not appropriate, 0 sheet is paid out. However, either or both of the pushing order bell A and the pushing order bell B can be configured so that two pieces are paid out regardless of the pushing order, and the expected expected value is (B) three bets between BB1 flags. The lottery value may be appropriately reduced so as to be similar to the state, and the same payout as in the (B) BB1 flag three-bet state may be performed. In the two-bet state of (D) BB1 flag, the above-described advantageous section grant determination is not performed.
(A)一般遊技状態(非フラグ間)において、2枚ベットのとき、BB2に当籤した場合(当籤した遊技でBB2に係る図柄の組合せが表示されずに持ち越された場合であってもよい)には、BB2フラグ間に移行する。(2)BB2フラグ間において3枚ベットで遊技が行われるとき、(C)BB2フラグ間3枚ベット状態となる(図99の「フラグ間3枚ベット」の列参照)。一方、(4−1)BB2フラグ間において2枚ベットで遊技が行われるとき、(E)BB2フラグ間2枚ベット状態となる(図99の「フラグ間2枚ベット」の列参照)。 (A) In the general game state (between non-flags), when two bets are won, if BB2 is won (may be a case where a combination of symbols related to BB2 is carried over without being displayed in the winning game) Shifts between BB2 flags. (2) When a game is played with 3 bets between BB2 flags, (C) 3 bets between BB2 flags are entered (see the "3 bets between flags" column in FIG. 99). On the other hand, when a game is played with two bets between (4-1) BB2 flags, a (2) bet state between (E) BB2 flags is entered (see the column "2 bets between flags" in FIG. 99).
(C)BB2フラグ間3枚ベット状態では、BB2フラグ間ではあるものの、BB2が当籤した遊技とはベット数が異なるため、たとえ「ハズレ」となった遊技であってもBB2に係る図柄の組合せは表示不可能となっている(BB2成立不可)。また、当該状態は、BB2許可状態であり、BB2が新たに当籤したり、BB1に当籤したりすることはない(BB1・BB2当籤不可)。すなわち、当該状態は、ボーナス役に当籤することも入賞することもない遊技状態として構成される。もっとも、BB2フラグ間であることに鑑み、「ハズレ」となった遊技においてはBB2に係る図柄の組合せが表示可能となるように構成することもできる。 (C) In the three-bet state between BB2 flags, although it is between BB2 flags, the number of bets is different from the game that BB2 wins, so even if the game is a "miss" game, a combination of symbols related to BB2 Cannot be displayed (BB2 cannot be established). Further, the state is a BB2 permission state, and BB2 does not newly win or wins BB1 (BB1 and BB2 cannot win). That is, the state is configured as a gaming state in which neither a winning combination nor a winning combination is won. However, in view of the fact that it is between the BB2 flags, a combination of symbols related to BB2 can be displayed in the game that is "missed".
また、(C)BB2フラグ間3枚ベット状態では、押し順ベルA及び押し順ベルBのいずれかに当籤したとき、押し順正解であれば9枚払出となり、押し順不正解であって停止操作のタイミングが適切であれば1枚払出となり、押し順不正解であって停止操作のタイミングが適切でなければ0枚払出となる。すなわち、(C)BB2フラグ間3枚ベット状態は、押し順ベルBの押し順が不問とならない分、有利区間を考慮しなければ、(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態よりも還元率が低く、遊技者に不利な状態となる。 Further, in the (C) BB2 flag three-bet state, when either the push order bell A or the push order bell B is won, 9 pieces are paid out if the push order is correct and the push order is incorrect and the operation is stopped. If the operation timing is appropriate, 1 sheet is paid out, and if the pressing order is incorrect and the stop operation timing is not appropriate, 0 sheet is paid out. That is, (C) the three-bet state between the BB2 flags does not matter as long as the pushing order of the pushing order bell B does not matter. It is low and disadvantageous to the player.
また、(C)BB2フラグ間3枚ベット状態では、(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態と同様、有利区間付与決定(有利区間付与抽籤)が行われる。ここで、No.「4」の「F_リプB」に着目すると、(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態では、停止操作の態様にかかわらず「通常リプ」が入賞して有利区間付与決定は行われない一方、(C)BB2フラグ間3枚ベット状態では、停止操作の態様にかかわらず「チャンス目」が入賞して有利区間付与決定が行われるものとなっている。すなわち、(C)BB2フラグ間3枚ベット状態は、「F_リプB」の内部当籤役が「チャンス目」の内部当籤役に昇格する(変換される)ため、有利区間付与決定の機会を多く得ることができることから、有利区間を考慮すれば、(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態よりも有利区間付与確率が高く、遊技者に有利な状態となる。 In the (C) BB2 flag three-bet state, as in the case of (B) BB1 flag three-bet state, the advantageous section grant determination (beneficial section grant lottery) is performed. Here, No. Focusing on “F_REP B” of “4”, in the (B) three-bet state between BB1 flags, “normal lip” is won regardless of the mode of the stop operation, and the advantageous section award is not made. (C) In the three-bet state between the BB2 flags, the "probability of chance" is won and the advantageous section award determination is made regardless of the mode of the stop operation. That is, in the (C) three-bet state between the BB2 flags, the internal winning combination of “F_REP B” is promoted (converted) to the internal winning combination of “chance eye”, so there are many opportunities to determine the advantageous section award. Since it can be obtained, if the advantageous section is taken into consideration, the probability of giving the advantageous section is higher than that in the (B) BB1 flag three-bet state, and the player is in an advantageous state.
(E)BB2フラグ間2枚ベット状態では、他の例ですでに説明したのと同様、「ハズレ」となった遊技でBB2に係る図柄の組合せが表示可能となっている(BB2成立可)。なお、「ハズレ」確率が適宜設定可能であるが、例えば、「1/8.5」程度に設定されるものとする。また、当該状態は、BB2許可状態であり、BB2が新たに当籤したり、BB1に当籤したりすることはない(BB1・BB2当籤不可)。 (E) In the two-bet state between the BB2 flags, the combination of symbols related to BB2 can be displayed in the game which has been "missed", as has already been described in the other examples (BB2 can be established). .. The “miss” probability can be set as appropriate, but is set to, for example, about “1/8.5”. Further, the state is a BB2 permission state, and BB2 does not newly win or wins BB1 (BB1 and BB2 cannot win).
また、(E)BB2フラグ間2枚ベット状態では、押し順ベルA及び押し順ベルBのいずれかに当籤したとき、押し順正解であれば2枚払出となり、押し順不正解であって停止操作のタイミングが適切であれば1枚払出となり、押し順不正解であって停止操作のタイミングが適切でなければ0枚払出となる。もっとも、押し順ベルA及び押し順ベルBのいずれか、あるいは双方について、押し順不問で2枚払出となるように構成することもできるし、付与期待値が(C)BB2フラグ間3枚ベット状態と同様となるように適宜抽籤値を減らした上で、(C)BB2フラグ間3枚ベット状態と同様の払出が行われるようにすることもできる。なお、(E)BB2フラグ間2枚ベット状態では、上述した有利区間付与決定は行われない。 Also, in the (E) BB2 flag two bet state, when the push order bell A or the push order bell B is won, if the push order is correct, 2 pieces are paid out, and the push order is incorrect and the operation is stopped. If the operation timing is appropriate, 1 sheet is paid out, and if the pressing order is incorrect and the stop operation timing is not appropriate, 0 sheet is paid out. However, either or both of the pushing order bell A and the pushing order bell B may be configured to be paid out in two ways regardless of the pushing order, and the expected payout value is (C) 3 bets between BB2 flags. The lottery value may be appropriately reduced so as to be the same as the state, and then the same payout as in the (C) BB2 flag three bet state may be performed. In the (2) bet state between (E) BB2 flags, the above-described advantageous section grant determination is not performed.
また、(E)BB2フラグ間2枚ベット状態において、BB2に係る図柄の組合せが有効ライン上に停止表示されると、(4−2)BB2成立となり、(G)BB2状態に移行する。(F)BB2状態は、例えば、「特殊ボーナス状態」として構成され、遊技価値が増加する増加期間となる遊技状態であり、他の例ですでに説明したのと同様、任意の規定数(例えば、60枚)の遊技価値が付与されると、(4−3)BB1終了となり、(G)BB2状態から(A)一般遊技状態(非フラグ間)に移行する。なお、(F)BB2状態を無増減期間として構成することもできる。 Further, in the two bet state between (E)BB2 flags, when the symbol combination related to BB2 is stopped and displayed on the activated line, (4-2)BB2 is established and the state shifts to (G)BB2. (F) The BB2 state is, for example, a gaming state that is configured as a "special bonus state" and has an increasing period in which the gaming value increases, and is an arbitrary prescribed number (for example, the same as already described in another example. , 60 cards), the game is finished (4-3) BB1 and the state changes from the (G) BB2 state to the (A) general game state (between non-flags). Note that the (F)BB2 state may be configured as a non-increasing/decreasing period.
本例では、(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態と(C)BB2フラグ間3枚ベット状態とを対比すると、(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態では、押し順ベルBについての押し順が不問となり、また、(F)BB1状態への移行が可能である分、基本的には(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態のほうが、還元率(ベース値、出玉率と換言してもよい)が高くなるように構成される。一方で、(C)BB2フラグ間3枚ベット状態では、有利区間付与決定の機会を多く得ることができ、また、有利区間となったときの付与期待値も高くなることから、「F_リプB」の内部当籤役の当籤確率、チャンス目入賞時の有利区間付与決定確率、及び有利区間付与決定がなされたときに付与される有利区間の継続期間などを適宜調整すれば、(C)BB2フラグ間3枚ベット状態の還元率を、(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態における還元率と同程度、あるいはそれ以上となるように構成することも可能となる。 In this example, when the (B) three-bet state between the BB1 flags and the (C) three-bet state between the BB2 flags are compared, in the (B) three-bet state between the BB1 flags, the pressing order for the pressing order bell B is In addition, since it is possible to shift to the (F)BB1 state, basically, the (B)BB3 three-bet flag state is the return rate (in other words, the base value and the payout rate). Is good). On the other hand, in the (C) three-bet state between the BB2 flags, there are many opportunities to decide the advantageous section award, and the expected expected value at the time of the advantageous section also becomes high. By appropriately adjusting the winning probability of the internal winning combination of “”, the probability of determining the advantageous section when the chance is won, and the duration of the advantageous section that is awarded when the advantageous section is determined, the (C) BB2 flag It is also possible to configure the return rate in the three-bet state with the three-bet state to be about the same as or higher than the return rate in the three-bet state with the (B) BB1 flag.
また、本例では、(E)BB2フラグ間2枚ベット状態と(D)BB1フラグ間2枚ベット状態とを対比すると、(E)BB2フラグ間2枚ベット状態では、(G)BB2状態への移行が可能である分、基本的には(E)BB2フラグ間2枚ベット状態のほうが、還元率が高くなるように構成される。なお、(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態と同様、(E)BB2フラグ間2枚ベット状態においても押し順ベルBについての押し順を不問とする制御が行われることで、還元率が高くなるように構成されるようにしてもよい。 Further, in this example, when the (E)BB2 flag two bet state and the (D)BB1 flag two bet state are compared, the (E)BB2 flag two bet state changes to the (G)BB2 state. As a result, the return rate is basically higher in the two bet state between the (E)BB2 flags as much as the change is possible. As in the case of (B) three-bet between BB1 flags state, the control of making the pushing order of the pushing-order bell B unquestionable is performed also in the (B) two-bet state between BB2 flags state, so that the return rate is high. You may make it comprised so that it may become.
遊技者が、例えば、(A)一般遊技状態(非フラグ間)から遊技を開始するとした場合、遊技者はまず3枚ベットとするか2枚ベットとするかを選択することができる。3枚ベットとしてBB1に当籤し、当籤した遊技で(F)BB1状態に移行しない場合、(D)BB1状態2枚ベット状態はメリットがないため、そのまま(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態で遊技を進行させる。(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態では、相対的に還元率が高いため、遊技者はさほど急激に遊技価値を減少させることなく、(F)BB1状態へ移行させて遊技価値を増加させるか、あるいは有利区間付与決定の機会を得て有利区間に移行させて(押し順ベルAについて正解となる押し順が報知される結果)遊技価値を増加させるかを選択することができる。なお、(B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態では、(C)BB2フラグ間3枚ベット状態と比較すれば、有利区間に移行したとしてもさほど急激に遊技価値が増加するわけではない。
For example, when the player starts the game from (A) the normal game state (between non-flags), the player can first select whether to make a three bet or a two bet. If you win BB1 as a 3 bet and do not shift to (F) BB1 state in the winning game, (D)
一方、2枚ベットとしてBB2に当籤し、当籤した遊技で(G)BB2状態に移行しない場合、遊技者は(C)BB2フラグ間3枚ベット状態で遊技を進行させるか、あるいは(E)BB2フラグ間2枚ベット状態で遊技を進行させるかを選択することができる。(C)BB2フラグ間3枚ベット状態では、相対的に還元率が低く、ボーナス状態には移行しないため、急激に遊技価値が減少してしまう可能性はあるものの、有利区間付与決定の機会を得る確率が上昇しており、さらに有利区間に移行させた場合には(押し順ベルA及び押し順ベルBについて正解となる押し順が報知される結果)急激に遊技価値を増加させることができる可能性がある。また、(E)BB2フラグ間2枚ベット状態では、小役での遊技価値の増加は見込めないものの、相対的には還元率が高く、また、(G)BB2状態へ移行させて遊技価値を増加させることができる。本例では、このような遊技性(遊技仕様)を提供することができる。 On the other hand, when the player wins BB2 as a two-bet and does not shift to the (G)BB2 state in the winning game, the player advances the game in a three-bet state between (C)BB2 flags or (E)BB2. It is possible to select whether to proceed with the game in the two-bet state between flags. (C) In the three-bet state between the BB2 flags, the return rate is relatively low and the bonus state is not entered, so there is a possibility that the game value will suddenly decrease, but there is an opportunity to decide the advantageous section award. The probability of gaining is increasing, and if it is further shifted to the advantageous section (the result of being notified of the correct push order for push order bell A and push order bell B), the game value can be rapidly increased. there is a possibility. Further, in the (2) bet state between the (E) BB2 flag, although the increase in the game value in the small win cannot be expected, the return rate is relatively high, and the game value is shifted to the (G) BB2 state. Can be increased. In this example, it is possible to provide such a game property (game specification).
本例の遊技機によれば、ベットされた遊技価値が第1の量(3枚)である場合、第1特別役(BB1)に当籤可能とする一方、第2特別役(BB2)に当籤可能としない。また、ベットされた遊技価値が第2の量(2枚)である場合、第2特別役に当籤可能とする一方、第1特別役に当籤可能としない。また、特定役(「F_リプB」)に当籤した場合、第1特別許可状態(BB1フラグ間)であれば特定図柄の組合せ(チャンス目)を表示可能とせず、第2特別許可状態(BB2フラグ間)であれば特定図柄の組合せを表示可能とする。そして、ベットされた遊技価値が第1の量であるとき、特定役が内部当籤役として決定された場合であって特定図柄の組合せが表示される場合には、有利状態(有利区間)を付与するか否かを決定可能とし(有利区間付与決定)、ベットされた遊技価値が第2の量であるとき、有利状態を付与するか否かを決定可能としない。 According to the gaming machine of this example, when the bet game value is the first amount (3 pieces), the first special combination (BB1) can be won, while the second special combination (BB2) is won. Not possible. When the bet game value is the second amount (2 pieces), the second special combination can be won, while the first special combination cannot be won. In addition, when the specific combination (“F_REP B”) is won, if the first special permission state (between BB1 flags), the combination of specific symbols (the chance eye) cannot be displayed, and the second special permission state (BB2). (Between flags) makes it possible to display a combination of specific symbols. Then, when the bet game value is the first amount, when the specific combination is determined as the internal winning combination and the combination of the specific symbols is displayed, an advantageous state (advantageous section) is given. It is possible to determine whether or not to perform (advantageous section grant determination), and when the bet game value is the second amount, it is not possible to determine whether or not to grant an advantageous state.
また、本例の遊技機によれば、ベットされた遊技価値が第1の量である場合、第1特別図柄の組合せ(BB1に係る図柄の組合せ)を表示可能とする一方、第2特別図柄の組合せ(BB2に係る図柄の組合せ)を表示可能としない。また、ベットされた遊技価値が第2の量である場合、第2特別図柄の組合せを表示可能とする一方、第1特別図柄の組合せを表示可能としないようにしてもよい。 Further, according to the gaming machine of this example, when the bet game value is the first amount, the first special symbol combination (the symbol combination relating to BB1) can be displayed, while the second special symbol is displayed. The combination (the combination of symbols relating to BB2) cannot be displayed. Further, when the bet game value is the second amount, the combination of the second special symbols may be displayed, while the combination of the first special symbols may not be displayed.
すなわち、本例の遊技機によれば、遊技が行われる状態として、例えば、第1特別許可状態であって第1の量の遊技価値がベットされて遊技が行われる状態((B)BB1フラグ間3枚ベット状態)、第2特別許可状態であって第1の量の遊技価値がベットされて遊技が行われる状態((C)BB2フラグ間3枚ベット状態)、第1特別許可状態であって第2の量の遊技価値がベットされて遊技が行われる状態((D)BB1フラグ間2枚ベット状態)、及び第2特別許可状態であって第2の量の遊技価値がベットされて遊技が行われる状態((E)BB2フラグ間2枚ベット状態)、という複数の状態を創出することができる。
That is, according to the gaming machine of the present example, as a state in which the game is played, for example, a state in which the game value is bet with a first amount of gaming value in the first special permission state ((B) BB1 flag) 3 bet state), a second special permission state in which a first amount of game value is bet and a game is played ((C)
そして、本例の遊技機によれば、例えば、第2特別許可状態であって第1の量の遊技価値がベットされて遊技が行われる状態を有利状態の付与が優遇される状態とし、第2の量の遊技価値がベットされて遊技が行われる状態を有利状態の付与が行われない状態としている。すなわち、有利状態の付与に関し、いずれの量の遊技価値がベットされるか、及びいずれの特別役が当籤しているか、などによって遊技者の有利度合いを変動させることを可能としている。それゆえ、有利状態中の遊技価値の増加量を示す傾斜値を変動可能とすることで、遊技性を変化に富んだものとすることができる。 Then, according to the gaming machine of the present example, for example, a state in which the game is played by betting the first amount of the game value in the second special permission state is a state in which the giving of the advantageous state is preferentially treated, and A state where the game value of 2 is bet and the game is played is a state where the advantageous state is not given. That is, regarding the provision of the advantageous state, it is possible to change the degree of advantage of the player depending on which amount of game value is bet, which special combination is won, and the like. Therefore, by making it possible to change the inclination value indicating the amount of increase in the game value during the advantageous state, it is possible to make the game play rich in variety.
なお、本例の遊技機において、第1所定役(押し順ベルA)に当籤した場合には、いずれの状態であるかにかかわらず、例えば、押し順正解であれば所定数(例えば、9枚)の遊技価値が付与され、押し順不正解であれば所定数の遊技価値は付与されないし、第2所定役(押し順ベルB)に当籤した場合には、第1特別許可状態であって第1の量の遊技価値がベットされて遊技が行われる状態にあっては、例えば、押し順不問で所定数の遊技価値が付与される一方、その他の状態にあっては、第1所定役と同様の制御が行われるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、第1特別許可状態であって第1の量の遊技価値がベットされて遊技が行われる状態を所定役当籤時において遊技価値の付与が優遇される状態とすることができるため、遊技性をより変化に富んだものとすることができる。 In the gaming machine of the present example, when the first predetermined winning combination (pushing order bell A) is won, regardless of which state, for example, a predetermined number of hitting correct answers (for example, 9 (2) a game value is given, and a predetermined number of game values are not given if the pushing order is an incorrect answer. If the second predetermined hand (the pushing order bell B) is won, it is in the first special permission state. In the state where the first amount of game value is bet and the game is played, for example, a predetermined number of game values are given regardless of the pushing order, while in other states, the first predetermined value is given. The same control as that of the winning combination may be performed. In this way, the state in which the first amount of game value is bet and the game is played in the first special permission state can be set to the state where the giving of the game value is preferentially given in the predetermined winning combination. Therefore, the game play can be made more varied.
以上、図92〜図99を参照して、本実施形態に係るパチスロ1において実装可能な遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例について説明したが、これらにおいては遊技性(遊技仕様)の要点を主として説明しており、これらにおいて説明が省略され、あるいは簡潔に説明されている点については、本実施形態、当該他の例のそれぞれ、及び変形例で説明した構成を適宜補って適用可能である。また、本実施形態、当該他の例のそれぞれ、及び変形例で説明した構成の一部又は全部を組み合わせて本発明とすることも可能である。
As described above, with reference to FIGS. 92 to 99, other examples of the playability (game specification) that can be mounted in the pachi-
[有利区間リミッタの別例(枚数リミッタ)]
続いて、図100〜図102を参照して、有利区間のリミット処理に用いるリミッタの別例について説明する。これまで、有利区間のリミッタとして、有利区間中に消化したゲーム数を用いたリミッタ(以下、「ゲーム数リミッタ」)について説明したが、有利区間のリミッタの種類は、ゲーム数リミッタに限るものではない。具体的には、主制御基板71は、有利区間中に払い出されたメダルの枚数が所定枚数(例えば、2400枚)以上に達するとリミット処理を行うこととしてもよい。なお、このような有利区間中に払い出されたメダルの枚数を用いたリミッタを、以下では「枚数リミッタ」と呼ぶ。
[Another example of an advantageous interval limiter (sheet limiter)]
Subsequently, another example of the limiter used for the limit process of the advantageous section will be described with reference to FIGS. Up to now, the limiter of the advantageous section has been described as a limiter using the number of games consumed in the advantageous section (hereinafter, “game number limiter”), but the type of the limiter of the advantageous section is not limited to the number-of-games limiter. Absent. Specifically, the
図100(A)は、枚数リミッタの概要を示す図である。同図において、縦軸は差枚数(=払出枚数−投入枚数)であり、純増枚数ともいう。差枚数のプラス及びマイナスは、遊技者から見た値であり、遊技者に対して払い出されたメダルの方が投入されたメダルよりも多い場合(遊技者側のプラス)にはプラス、逆の場合にはマイナスになる。また、横軸はゲーム数であり、右に行くほど有利区間の開始から多くのゲームが消化されたことを意味する。枚数リミッタは、遊技者が一度に極端に多くのメダルを獲得しないように最もメダルが減った時点を起点して、2400枚のプラスの差枚数が得られたときに有利区間を強制的に終了させるものである。 FIG. 100(A) is a diagram showing an outline of the number limiter. In the figure, the vertical axis is the difference number (=payout number-inserted number), which is also called a net increase number. The plus and minus of the difference number are the values seen by the player, and when there are more medals paid out to the player than the inserted medals (plus on the player's side), the reverse In the case of, it becomes negative. Further, the horizontal axis represents the number of games, and the more to the right, the more games have been consumed since the start of the advantageous section. The number limiter forcibly ends the advantageous section when a positive difference of 2400 is obtained, starting from the point when the number of medals decreases the most so that the player does not win an extremely large number of medals at one time. It is what makes me.
同図では、有利区間開始後、100枚ほどメダルが減っている。これは、例えば、当該有利区間開始を上述した通常有利区間の開始としたならばその遊技期間や、あるいは上述した有利区間中の準備状態などでメダルが減ったものである。そして有利区間開始から−100枚となった時点からメダルは増加しつづけ、最終的に+2300枚ほどまでメダルが増加している。この時点で、遊技者目線では、少なくとも2400枚のメダルが手元にあることとなる。そこで、主制御基板71は、枚数リミッタを発動し、有利区間を強制的に終了させる。これにより、射幸性を適切に抑制することができる。
In the figure, after the start of the advantageous section, about 100 medals have been reduced. This means that, for example, if the start of the advantageous zone is the start of the normal advantageous zone described above, the number of medals is reduced during the game period or in the preparation state during the advantageous zone described above. The number of medals continues to increase from the start of the advantageous zone to -100, and finally the number of medals increases to about +2300. At this point, at least 2400 medals are at hand from the player's point of view. Therefore, the
なお、主制御基板71は、ゲーム数リミッタのみを用いて有利区間のリミット処理を行うこととしてもよく、枚数リミッタのみを用いて有利区間のリミット処理を行うこととしてもよく、ゲーム数リミッタと枚数リミッタとの双方を用いて有利区間のリミット処理を行うこととしてもよい。なお、双方のリミッタを用いる場合、主制御基板71は、有利区間が開始してから何れか一方のリミッタ発動条件を満たした場合に、有利区間を終了させることが望ましい。なお、本説明においては、ゲーム数リミッタを1500ゲーム、枚数リミッタを2400枚として説明したが、これは一例であり、これより少ない値又は多い値を遊技仕様に応じて採用して射幸性を適切に制御するものとしてもよい。
The
ここで、ゲーム数リミッタと枚数リミッタとの双方を用いる場合について説明する。より具体的には、有利区間(ART、ATなど)におけるメダル増加の傾斜値A(1ゲームあたりの純増期待値、ボーナス作動による増加を含む純増期待値)と、ゲーム数リミッタの発動条件となるゲーム数Bと、枚数リミッタの発動条件となる差枚数Cとの関係について説明する。
なお、以下では、説明の便宜上、有利区間におけるメダル増加の傾斜値Aが「3枚」、ゲーム数リミッタの発動条件となるゲーム数Bが「100ゲーム」であるものとする。
Here, a case where both the game number limiter and the game number limiter are used will be described. More specifically, the gradient value A of the medal increase in the advantageous section (ART, AT, etc.) (expected net increase value per game, expected net increase value including increase by bonus operation) and the condition for activating the game number limiter are set. The relationship between the number of games B and the difference number C which is the condition for activating the number limiter will be described.
In the following, for convenience of explanation, it is assumed that the inclination value A for increasing medals in the advantageous section is "3" and the number of games B which is a condition for activating the number of games limiter is "100 games".
第1の仕様では、傾斜値A×ゲーム数リミッタのゲーム数B=枚数リミッタの差枚数Cという関係の仕様(例:A(3枚)×B(100ゲーム)=C(300枚))が考えられる。このような仕様は最も基本的な仕様であり、有利区間を安定的に制御することができ、射幸性を適切に抑制することができる。 In the first specification, the specification of the relationship of the inclination value A×the number of games of the number-of-games limiter B=the difference number C of the number of limiters (eg: A (3 pieces)×B (100 games)=C (300 pieces)) is Conceivable. Such specifications are the most basic specifications, and the advantageous section can be stably controlled, and the gambling property can be appropriately suppressed.
第2の仕様では、傾斜値A×ゲーム数リミッタのゲーム数B<枚数リミッタの差枚数Cという関係の仕様(例:A(3枚)×B(100ゲーム)<C(400枚))が考えられる。このような仕様の場合、リミッタが発動するケースを考慮すると以下の通りである。 In the second specification, the specification of the relationship of the inclination value A×the number of games B of the number-of-games limiter<the difference number C of the number of limiters (eg: A (3 pieces)×B (100 games)<C (400 pieces)) is Conceivable. In the case of such specifications, the case where the limiter is activated is as follows.
100ゲーム消化するよりも前に400枚を超えるメダルが払い出された場合に、枚数リミッタが発動し、400枚を超えるメダルが払い出されるよりも前に100ゲームを消化した場合には、ゲーム数リミッタが発動する。ボーナスを期待値よりも多く引くか、純増枚数の多い押し順役を期待値よりも極端に多く引いた場合に枚数リミッタが作動し、期待値に近い値で遊技が進行した場合は、ゲーム数リミッタが発動する可能性が高くなる。傾斜値が「3枚」であるため、結果として、リミッタが発動する場合は、100G到達によるゲーム数リミッタの方が、枚数リミッタよりも発動しやすくなり、遊技者の意識は差枚数よりもゲーム数に傾くこととなる。 When more than 400 medals are paid out before 100 games are exhausted, the number limiter is activated, and when 100 games are exhausted before more than 400 medals are paid out, the number of games The limiter is activated. If the bonus is pulled more than the expected value, or if the number of push forwards with a large number of net additions is much more than the expected value, the number limiter operates and the game progresses at a value close to the expected value. The limiter is more likely to be activated. Since the inclination value is "3", as a result, when the limiter is activated, the number-of-games limiter for reaching 100G is easier to activate than the number-of-games limiter, and the player's consciousness is that the game is more important than the difference number of games. It will be inclined to the number.
すなわち、傾斜値が「3枚」であるため、平均して133.3ゲームで400枚のメダルが払い出されることになり、その前にゲーム数リミッタに到達する可能性が高い。したがって、発動のし易さは、ゲーム数リミッタ>枚数リミッタ、となる。差枚数による枚数リミッタの発動をあまり気にさせたくない場合は、このような仕様とすると良い。例えば、ARTを1セット100枚の純増で終了など終了条件(リミッタではない)を差枚数で管理とするタイプの場合はこのようなリミッタ仕様とすると、リミッタの発動頻度を抑制でき、遊技者がリミッタにより有利区間が打ち切られる頻度を低下でき、遊技の興趣の低下を抑制できる。 That is, since the inclination value is "3", 400 medals are paid out in 133.3 games on average, and there is a high possibility that the number-of-games limiter will be reached before that. Therefore, the ease of activation is as follows: game number limiter> number of sheets limiter. If you do not want to worry about the activation of the number limiter due to the difference in number of sheets, it is recommended to use such a specification. For example, in the case of a type in which the termination condition (not the limiter) is managed by the difference number, such as ending the ART with a net increase of 100 sheets, if such a limiter specification is used, the frequency of activation of the limiter can be suppressed, and the player can It is possible to reduce the frequency at which the advantageous section is discontinued by the limiter, and it is possible to suppress a decrease in interest in the game.
第3の仕様では、傾斜値A×ゲーム数リミッタのゲーム数B>枚数リミッタの差枚数Cという関係の仕様(例:A(3枚)×B(100ゲーム)>C(200枚))が考えられる。このような仕様の場合、リミッタが発動するケースを考慮すると以下の通りである。 In the third specification, the specification of the relationship of the inclination value A×the number of games B of the number-of-games limiter>the difference number C of the number of limiters (eg: A (3 pieces)×B (100 games)>C (200 pieces)) is Conceivable. In the case of such specifications, the case where the limiter is activated is as follows.
100ゲーム消化するよりも前に200枚を超えるメダルが払い出された場合に、枚数リミッタが発動し、200枚を超えるメダルが払い出されるよりも前に100ゲームを消化した場合には、ゲーム数リミッタが発動する。傾斜値が「3枚」であるため、平均して66.6ゲームほどで200枚のメダルが払い出されることになり、100ゲーム消化の前に枚数リミッタに到達する可能性が高い。したがって、発動のし易さは、ゲーム数リミッタ<枚数リミッタ、となる。ゲーム数消化によるゲーム数リミッタの発動をあまり気にさせたくない場合は、このような仕様とすると良い。例えば、1ゲームあたりの純増枚数0.1〜1枚などと比較的低いが長いゲーム数継続するような仕様については、このような仕様とすると、リミッタの発動頻度を抑制でき、遊技者がリミッタにより有利区間が打ち切られる頻度を低下でき、遊技の興趣の低下を抑制できる。 If more than 200 medals are paid out before 100 games are exhausted, the number limiter is activated, and if 100 games are exhausted before more than 200 medals are paid out, the number of games The limiter is activated. Since the inclination value is “3”, 200 medals are paid out in about 66.6 games on average, and there is a high possibility that the number limiter will be reached before 100 games are exhausted. Therefore, the ease of activation is game number limiter<number limiter. If you do not want to worry about the activation of the game number limiter due to the consumption of the number of games, it is recommended to use such a specification. For example, if the specification is such that the number of games to be played is relatively low, such as a net increase of 0.1 to 1 per game, but the number of games continues for a long time, the frequency of activation of the limiter can be suppressed, and the player can limit the frequency. As a result, it is possible to reduce the frequency at which the advantageous section is terminated, and to suppress the decline in the interest of the game.
なお、何れの仕様にしても、リミッタ到達により終了する割合よりも、リミッタ以外の有利区間の終了条件(例えば、ARTの継続可能期間(ARTゲーム数)、セット数やストックがゼロになるなど)によることにより、有利区間が終了する割合が高い出玉設計として、有利区間を消化できる権利がリミッタ発動により消去される事象の発生を抑制することが望ましい。 Regardless of the specifications, the end condition of the advantageous section other than the limiter rather than the ratio of the limiter reaching the end (for example, ART continuable period (the number of ART games), the number of sets and the stock become zero, etc.) Therefore, it is desirable to suppress the occurrence of an event in which the right to consume the advantageous section is erased by the limiter activation, as a payout design in which the ratio of the advantageous section ending is high.
続いて、複数のリミッタを設ける場合に実現可能な遊技性について説明する。 Next, the playability that can be realized when a plurality of limiters are provided will be described.
(リミッタの種別に応じた有利区間終了時演出)
枚数リミッタの発動時と、ゲーム数リミッタの発動時とで、副制御基板72は、表示装置11などを用いて異なる有利区間終了時演出を実行可能としても良い。それぞれを専用の演出とした場合には、それぞれの演出を一度は見てみようという遊技動機につながる。また、副制御基板72は、リミッタの種別に応じて有利区間終了時に行う演出の振り分けを異ならせるものとしても良い。例えば、枚数リミッタだとゲーム数リミッタ発動時よりも、設定示唆の精度が高い(設定ごとの係数の差が大きい、または特定の設定が確定する演出が出やすいなど)としてもよい。設定示唆など特定の情報が得られる又は専用演出が見られることで、リミッタにより有利区間が打ち切りとなる不快感を低減できる。また、有利区間終了時に行う演出の振り分けを、上述のリミッタの仕様に基づき設定することとしてもよい。例えば、仕様上、発動し易いリミッタよりも、発動し難いリミッタが発動した場合の方が、副制御基板72は、遊技者にとって好ましい(例えば、設定示唆の精度が高い)演出を決定し易いとしてもよい。
(Direction at the end of the advantageous section according to the type of limiter)
The
(リミッタの種別に応じたエンディング演出)
また、副制御基板72は、枚数リミッタの発動が濃厚になった状況となった場合は、エンディング演出Aを、ゲーム数リミッタの発動が濃厚になった状況の場合は、エンディング演出Bを、どちらが発生するか割合に大きな差がないが、少なくともどちらかが発生することが濃厚になった場合には、エンディング演出C(エンディング演出A又はBへの分岐を持つ演出としてもよい)を行うなど、有利区間の終了時にいきなり打ち切りになって違和感を遊技者に与えないように、リミッタ発動前から有利区間終了示唆演出期間(エンディング)を設けることとしてもよい。なお、「枚数リミッタの発動が濃厚になった状況」とは、例えば、ARTを差枚数以外の情報に基づき管理する場合には、これまでの差枚数と、残りのART期間から算出される差枚数(例えば、ゲーム数管理のARTの場合には「残りゲーム数×傾斜値」)との和が、閾値(例えば、枚数リミッタが発動する差枚数や、当該差枚数よりも若干少ない値)に達したときであり、また、例えば、ARTを差枚数に基づき管理する場合は、これまでの差枚数と、残り枚数との和が、閾値に達したときである。また、「ゲーム数リミッタの発動が濃厚になった状況」とは、例えば、ARTをゲーム数以外の情報に基づき管理する場合には、これまでに経過したゲーム数と、残りのART期間から算出されるゲーム数(例えば、差枚数管理のARTの場合には「残り差枚数/傾斜値」)との和が、閾値(例えば、ゲーム数リミッタが発動するゲーム数や、当該ゲーム数よりも若干少ない値)に達したときであり、また、例えば、ARTをゲーム数に基づき管理する場合は、これまでに経過したゲーム数と、残りゲーム数との和が、閾値に達したときである。
(Ending effect according to the type of limiter)
Further, the
(発動したリミッタの種別を履歴画面において報知ないし示唆)
また、副制御基板72は、発動したリミッタの種別ないしリミッタ種別に対応して発生する演出(上記エンディング演出の種類など)について、遊技者がメニュー画面にて閲覧可能な遊技履歴画面に表示しても良い。この場合は、そもそも多くの出玉を獲得できているため、高設定に期待できるとの遊技意欲を喚起させることができる。
(Notification or suggestion on the history screen of the type of limiter that was activated)
Further, the
(リミッタの種別に応じた外部信号を出力)
また、枚数リミッタと、ゲーム数リミッタのどちらが発動したか、ホール側がホールコンピュータなどで把握できるように、主制御基板71は、発動したリミッタに応じた種類の外部信号を出力するとよい。このとき、主制御基板71は、外部端子板の異なるピンからリミッタ発動の外部信号を出力するものとしてもよい。例えば、本来の出玉仕様であれば主にゲーム数リミッタが発動し、枚数リミッタはあまり発動しない機種において、頻繁に枚数リミッタが発動している場合は、何らかのゴト行為が行われているか、遊技機とホールコンピュータとの接続ミスの可能性をホール店員は察知することができる。
(Outputs an external signal according to the limiter type)
Further, the
なお、同じ遊技においてで枚数リミッタの発動条件とゲーム数リミッタの発動条件を満たした場合は、主制御基板71は、予め定めたどちらか一方の信号を出力してもよいし、2種類の信号を所定の順番で出力してもよい。順番に出力する場合は、確実に受信できるように先に出力する信号の出力完了から、次の信号出力まで所定時間の間を空けるとよい。また、同じ遊技において枚数リミッタの発動条件とゲーム数リミッタの発動条件とを満たした場合は、どちらか一方のリミット処理のみを行い、他方の処理は行わないものとして、メイン(主制御基板71)において余計な処理を発生させないものとしてもよく、この場合には、主制御基板71は、行われた種別のリミッタに応じた外部信号を出力する。
In the same game, when the number limiter activation condition and the game number limiter activation condition are satisfied, the
(リミッタの種別を問わず一の外部信号を出力)
また、メイン(主制御基板71)の容量や、外部信号出力用の端子板のピン数に余裕がある場合は、上述のように異ならせても良いが、リミッタの種別に関わらず同じ外部信号を出力するものとしてもよい。メイン(主制御基板71)の容量を節約することができる。
(Outputs one external signal regardless of limiter type)
If the capacity of the main (main control board 71) and the number of pins of the terminal board for external signal output have a margin, they may be different as described above, but the same external signal may be used regardless of the type of the limiter. May be output. The capacity of the main (main control board 71) can be saved.
(リミッタ以外の有利区間終了とリミッタによる終了で同じ外部信号を出力)
また、主制御基板71は、リミッタ以外の有利区間終了とリミッタによる終了とで同じ外部信号を出力し、有利区間が終了した旨をホールコンピュータなどで察知できるものとしてもよい。この場合は、さらにメイン(主制御基板71)の容量を節約できる。
(The same external signal is output at the end of the advantageous section other than the limiter and the end by the limiter)
Further, the
(ボーナス作動中にリミッタが発動した場合の外部信号出力例(すぐに出力))
また、ボーナス作動中にリミッタが発動した場合は、主制御基板71は、外部信号の出力を当該遊技又は当該遊技の終了直後に開始してもよい。このようにすることで、例えば一撃の獲得枚数が枚数リミッタの枚数を超えたとしてもリミッタ機能に不備があったわけではなく、偶然枚数リミッタ到達付近でボーナスが作動して出玉を獲得したということをホール側は確認できる。
(Example of external signal output when the limiter is activated during bonus operation (output immediately))
Further, when the limiter is activated during the bonus operation, the
(ボーナス作動中にリミッタが発動した場合の外部信号出力(ボーナス終了時))
また、ボーナス作動中にリミッタが発動した場合は、主制御基板71は、外部信号の出力をボーナス終了時ないし終了直後に開始してもよい。実質的に出玉増加する遊技状態の終了を正確に把握させたい場合はこのような仕様としてもよい。
(External signal output when limiter is activated during bonus operation (at end of bonus))
In addition, when the limiter is activated during the bonus operation, the
(枚数リミッタ発動の可能性がある遊技で遊技者が小役を取りこぼした場合の演出)
例えば、枚数リミッタが発動するまでの残り枚数が6枚の3枚掛け遊技で、正解時に9枚のメダルが払い出される押し順小役に当籤し、正解の押し順の報知が行われたにも関わらず遊技者が押し順をミスした場合、遊技開始時の状況を見て当該ゲームで枚数リミッタが発動すると想定して、当該遊技の開始時から枚数リミッタ発動時の演出を始めていることがある。このようなケースでは、押し順を間違えた結果、枚数リミッタは発動しないものの、副制御基板72は、当該遊技の開始時から始めていた枚数リミッタ発動時の演出(例えば、枚数リミッタの発動が予定されている旨の演出)をそのまま継続して実行することとしてもよく、また、枚数リミッタが発動しないと判断したことにより、当該演出を一旦終了ないし中断することとしてもよい。
(Direction when a player drops a small role in a game in which the number limiter may be activated)
For example, in a game of playing 3 cards with a remaining number of 6 until the number limiter is activated, you win a push order small win in which 9 medals are paid out at the time of correct answer, and the notification of the push order of the correct answer is also given. Regardless, if the player makes a mistake in the pressing order, assuming that the number limiter is activated in the game by looking at the situation at the start of the game, the production at the time the number limiter is activated may be started from the start of the game. .. In such a case, although the number limiter is not activated as a result of the wrong pressing order, the
(発動するリミッタが遊技者の操作により変更される場合の演出)
また、遊技者の操作ミスなどにより発動するリミッタの種類が異なる場合がある。例えば、枚数リミッタが発動するまでの残り枚数が6枚、かつ、ゲーム数リミッタが発動するまでの残りゲーム数が2ゲームの状況において、3枚掛け遊技で正解時に9枚のメダルが払い出される押し順小役に当籤し、正解の押し順の報知が行われたケースが該当する。このようなケースでは、遊技者が報知に従い停止操作を行った場合には当該遊技において枚数リミッタが発動するが、報知に従わずに押し順にミスした場合には次遊技においてゲーム数リミッタが発動する(なお、次遊技で枚数リミッタが発動する可能性もあるが、ここでは、複数のリミッタ発動条件が成立した場合にゲーム数リミッタが優先して発動するものとする)。
(Direction when the limiter to be activated is changed by the player's operation)
Also, the type of limiter activated may be different due to a player's operation error or the like. For example, in a situation in which the number of remaining games until the number of games limiter is activated is 6 and the number of games remaining until the number of games limiter is activated is 2 games, 9 medals are paid out when the correct answer is given in a game of 3 games. The case where the winning combination is won and the pushing order of the correct answer is notified is applicable. In such a case, when the player performs a stop operation according to the notification, the number-of-games limiter is activated in the game, but when the player makes a mistake in the pushing order without following the notification, the number-of-games limiter is activated in the next game. (Note that the number of games limiter may be activated in the next game, but here, it is assumed that the number of games limiter is activated when a plurality of limiter activation conditions are satisfied).
このような場合、副制御基板72は、押し順小役に当籤した遊技において枚数リミッタ発動時の演出を開始して、枚数リミッタの非発動が確定した移行の任意のタイミング(第1停止操作〜全リール停止時のうち、取りこぼし乃至少ない枚数の図柄組合せの表示が確定した以降の任意のタイミング)で、ゲーム数リミッタ発動時の演出に切り替えるか、いずれかのリミッタ発動示唆にも対応しない演出に一旦戻すような処理を行って、発動するリミッタと演出との矛盾を回避するように制御することが好ましい。
In such a case, the
(ボーナス作動中、内部中のリミッタ発動による終了時演出の遅延及びエンディング演出の延長)
なお、ここまで説明したリミット処理に関連して行われる演出及び制御についても、前述したボーナス作動中にリミット処理が行われる場合は、リミット処理による有利区間終了に応じた演出の発生タイミングをボーナス終了時又は終了直後まで遅らせる、かつ、エンディング演出などの有利区間中演出をそれまで延長するという手法を用いることで、遊技者の違和感を軽減することができる。
(During the bonus operation, delaying the end effect due to the activation of the limiter inside and extending the ending effect)
As for the effects and control performed in connection with the limit process described above, if the limit process is performed during the bonus operation described above, the bonus generation ends with the timing of the effect according to the end of the advantageous section due to the limit process. It is possible to reduce the player's discomfort by using a method of delaying the time or immediately after the end and extending the effect during the advantageous section such as the ending effect until then.
[枚数リミッタの制御方法]
続いて、図101(B)を参照して、枚数リミッタの制御方法について説明する。枚数リミッタでは、有利区間の開始時から最もメダルの絶対値が減った地点を最下点(起点)として、直近の最下点からのプラス分を、枚数リミッタの発動契機となる差枚数として用いる。同図では、有利区間開始を1ゲーム目として遊技が進行していきメダルの増減を1〜8ゲームで繰り返した後に、増加していき枚数リミッタに到達する例を示している(なお、押し順小役は「打順ベル」と表記している)。
[How to control the number of sheets limiter]
Subsequently, a method for controlling the number limiter will be described with reference to FIG. In the number-of-sheets limiter, the point where the absolute value of medals has decreased most from the start of the advantageous zone is set as the lowest point (starting point), and the positive amount from the latest lowest point is used as the difference number of sheets which triggers the number of sheets limiter. .. The figure shows an example in which the game progresses with the start of the advantageous section as the first game, and the number of medals is repeatedly increased and decreased in 1 to 8 games, and then increases to reach the number limiter (the pushing order Small roles are described as "Battle Order Bell").
同図では、有利区間の開始時から最もメダルの絶対値が減った地点が「−9枚」であるため、Nゲーム目に差枚数が「+2391枚」となったタイミングで枚数リミッタが発動している。なお、枚数リミッタの発動に伴い、リミッタ用のカウンタは0にリセットされている。その後N+2ゲーム目に押し順に正解してベルが揃った結果、起点からの差枚数が「+2400枚」を超えているものの、既に枚数リミッタが発動し、有利区間(ART)は終了しているため、一時的なものに過ぎず、問題はない。 In the figure, since the point where the absolute value of the medal has decreased the most since the start of the advantageous section is "-9", the number limiter is activated at the timing when the difference number is "+2391" in the Nth game. ing. The counter for the limiter is reset to 0 with the activation of the number limiter. After that, as a result of the correct answers being pressed in the N+2th game and the bells being aligned, the difference from the starting point exceeds "+2400", but the number limiter has already been activated and the advantage section (ART) has ended. , It's only temporary and there is no problem.
なお、同図では、当該ゲームの払出終了時点の有利区間開始時からの絶対的差枚数を示しているが、説明用の値であり、該当するカウンタは遊技機に搭載する必要がない。もちろん、該当するカウンタを搭載して遊技者に獲得枚数を示すために用いることとしてもよい。 Although the figure shows the absolute difference number from the start of the advantageous section at the end of payout of the game, it is a value for explanation, and the corresponding counter does not need to be mounted on the gaming machine. Of course, a corresponding counter may be mounted and used to show the player the number of coins acquired.
また、起点フラグは、現時点の遊技の状況が有利区間開始後の最下点であることを示す情報である。起点フラグを持たずに、単にリミッタに用いるカウンタ(枚数カウンタ)の値が0であることを持って最下点と認識しても良いが、枚数リミッタ発動までの差枚数減算が始まったか否かをサブ(副制御基板72)側で演出する場合など、ON/OFF判定のみで行える起点フラグを参照して、枚数カウンタの値をサブ側に送信せずに演出させることでメイン(主制御基板71)の処理負荷を軽減することができる。なお、その場合は、サブ側はメインから送信される投入枚数、払出枚数の情報を受けて枚数カウンタと同様の処理をサブ側で行い、枚数カウンタの状況として演出(枚数リミッタ発動までの枚数報知など)を行っても良い。 The starting point flag is information indicating that the current game situation is the lowest point after the start of the advantageous section. It may be recognized as the lowest point by simply having the value of the counter (number of sheets counter) used for the limiter as 0 without having the starting point flag, but whether or not subtraction of the number of difference sheets before the activation of the number of limiters has started In the case of producing on the sub (sub control board 72) side, the main (main control board 72) is produced by referring to the starting point flag that can be determined only by ON/OFF judgment and not transmitting the value of the number counter to the sub side. The processing load of 71) can be reduced. In that case, the sub-side receives the information about the number of inserted sheets and the number of paid-out sheets transmitted from the main, performs the same process as the number of sheets counter on the side of the sub-side, and produces the status as the number of sheets counter (notification of the number of sheets until the number of sheets limiter is activated). Etc.) may be performed.
最下点(起点)は、直近の最下点と同じ値又はより少ない値となった場合のいずれかで更新すれば良い。有利区間開始後の1ゲーム目終了時に絶対的差枚数が「−3枚」となった後一度増加し、4ゲーム目終了時に再び絶対的差枚数が「−3枚」となっている。そのため、主制御基板71は、4ゲーム目終了時に再び起点フラグを設定している。実際には、その後もメダルが減ったため、有利区間開始後の8ゲーム目終了時の絶対的差枚数が「−9枚」が枚数リミッタにおける起点となっている。
The lowest point (starting point) may be updated with either the same value as the latest lowest point or a smaller value. The absolute difference number becomes "-3" at the end of the first game after the start of the advantageous section, and then increases once, and becomes "-3" again at the end of the fourth game. Therefore, the
なお、同図では、第1最下点を、有利区間開始後の1ゲーム目終了時としているが、有利区間開始時点の1ゲーム消化より前の時点(絶対的差枚数が0枚時点)を第1最下点として設定し、1ゲーム終了時を第2最下点、マイナス9枚となった時点を第3最下点として第3最下点から2400枚増加すると枚数リミッタを発動するものとしてもよい。また、同図では、リプレイの入賞時には投入枚数0枚、払出枚数0枚として枚数カウンタを更新している。これにより再遊技時の差枚数を更新する必要がなくなり処理負荷を軽減することができる。一方で、リプレイの入賞時に投入枚数分の払出枚数を行い、次ゲームにおいて投入枚数が3枚として枚数カウンタを更新することとしてもよい。このようにすることで、リプレイが入賞してから次ゲームの開始操作が行われるまでの間の枚数カウンタの値を現実の差枚数挙動と一致させることができ、枚数カウンタの値を実増減枚数として参照して、演出用の枚数表示などに流用し易くなる。 In the figure, the first lowest point is the end time of the first game after the start of the advantageous section, but the time before the end of one game at the start of the advantageous section (the absolute difference number is 0) Set as the first lowest point, the second lowest point at the end of one game, the third lowest point when the number of games becomes -9, and the number limiter is activated when 2400 more points are added from the third lowest point. May be Further, in the figure, when the replay is won, the number counter is updated so that the inserted number is 0 and the paid out number is 0. As a result, it is not necessary to update the difference in the number of replays, and the processing load can be reduced. On the other hand, the payout number corresponding to the inserted number may be performed at the time of winning the replay, and the number counter may be updated with the inserted number being 3 in the next game. By doing this, it is possible to match the value of the number counter from the time the replay is won until the next game start operation is performed with the actual difference behaviour. With reference to FIG.
なお、副制御基板72は、枚数カウンタの値を表示装置11(液晶画面)などで報知して、枚数リミッタ発動までの残り枚数を遊技者に把握可能ないし示唆してもよい。また、副制御基板72は、枚数リミッタ発動までの残り枚数を直接的に表示せず、枚数リミッタ発動まで残り2000枚以上なら第1演出ステージ、残り1000〜1999枚なら第2演出ステージ、残り999枚以下なら第3演出ステージのように、背景などの演出ステージを枚数リミッタ発動までの枚数範囲に応じて異ならせて示唆しても良い。
The
また、主制御基板71は、枚数カウンタの値を外部信号として出力して、ホールコンピュータやパチスロの上部などに設置される遊技データ閲覧用のデータ表示器などで表示可能としてもよい。なお、主制御基板71は、起点フラグ及び枚数カウンタの値を、電断時でも消去せず維持することが好ましい。一方で、主制御基板71は、設定変更時には、起点フラグ及び枚数カウンタの値を消去することとしてもよい。
Further, the
[枚数リミッタの調整打法]
続いて、図102(C)を参照して、枚数リミッタの調整打法について説明する。枚数リミッタを用いて有利区間を強制的に終了させる仕様では、枚数リミッタの発動直前にメダルの増減を調整することで、枚数リミッタの発動を介する方法も考えられる。例えば、押し順小役が内部当籤役として決定された場合に、正解の押し順で停止操作が行われると「9枚」のメダルが払い出され、不正解の押し順で停止操作が行われるとメダルの払い出しが「0枚」である仕様では、1回の遊技において3枚のメダルが必要であるため、押し順役の当籤時に正解の押し順で停止操作が行われると、枚数カウンタは「+6枚」され、押し順役の当籤時に不正解の押し順で停止操作が行われると、枚数カウンタは「−3枚」される。そのため、例えば、押し順役に3回当籤した場合に、押し順に2回不正解し、1回正解すると、枚数カウンタの値は維持され、結果、枚数リミッタが発動することがない。
[Adjusting the number of sheets limiter]
Next, with reference to FIG. 102(C), an adjustment hitting method of the number limiter will be described. In the specification in which the advantageous period is forcibly ended by using the number limiter, a method in which the number limiter is activated by adjusting the increase/decrease of medals immediately before the number limiter is activated can also be considered. For example, when the pressing order small winning combination is determined as the internal winning combination, if the stop operation is performed in the correct pressing order, "9 coins" are paid out, and the stopping operation is performed in the incorrect pressing order. With the specification that the payout of medals is "0", three medals are required for one game, so if the stop operation is performed in the correct push order when the push order wins, the number counter If "+6" is given and the stop operation is performed in the wrong order of pushing at the time of winning the push order, the number counter is set to "-3". For this reason, for example, when the player presses the push combination combination three times, if the answer is incorrect twice in the pressing order and correct once, the value of the number counter is maintained, and as a result, the number limiter is not activated.
このように枚数リミッタを調整することで、枚数リミッタの発動直前にART(有利区間)のままボーナスの当籤を待つことなどができる。同図に示す例では、Mゲーム目からこのような調整打法が始まっており、BB(ボーナス)に当籤するXゲーム目まで調整打法が行われている。その結果、X+10ゲーム目には、枚数リミッタが発動する+2400枚を超える+2512枚のメダルが獲得できている(なお、BB中の小役(15枚)を「BB中ベル」と表記している)。 By adjusting the number limiter in this way, it is possible to wait for a bonus winning as an ART (advantageous section) immediately before the number limiter is activated. In the example shown in the figure, such an adjustment batting method starts from the M-th game, and the adjustment batting method is performed until the X-th game which wins the BB (bonus). As a result, in the X+10th game, +2512 medals, which exceeds +2400 for which the number limiter is activated, have been obtained (note that the small win in BB (15) is described as "BB in bell"). ).
なお、パチスロ1では、意図的に押し順の報知に逆らった方が有利である旨を示唆ないし報知する演出を行って遊技者に最大の利益を得ることのできる打ち方(打順ナビと異なる停止操作)を促しても良い。なお、このような演出は、副制御基板72が表示装置11などを介して行うこととしてもよく、また、主制御基板71が行うこととしてもよい。
In the pachi-
なお、純増15枚程度かつ比較的当籤確率の高いミニボーナス(ボーナス作動中の15枚役は取りこぼし不能ないし困難)と、純増120枚のボーナスなど複数種類のボーナス役が存在する場合は、枚数リミッタ到達までの残り差枚数がミニボーナスにおける純増枚数よりも多い枚数のラインで上記調整打法を推奨する演出を行ってもよい。また、押し順役以外の小役については、払出枚数が3枚を超える増加役とせずに、枚数調整がしやすいもの(例えば、払出枚数が3枚)としてもよい。このように打ち方の工夫で出玉率を向上できる遊技性とすることで遊技の興趣が高まる。 In addition, if there are multiple types of bonus combinations, such as a mini bonus with a net increase of about 15 and a relatively high winning probability (15 bonus roles during bonus operation cannot be missed or difficult), and a bonus limit of 120 additional bonus, there is a limiter. The above-described adjustment batting method may be recommended on a line in which the remaining difference until reaching the maximum bonus is larger than the net increase in the mini bonus. In addition, for small wins other than the push forward win, the payout numbers may be easily adjusted (for example, the payout number is 3) without increasing the payout number to be more than 3. In this way, the interest of the game is enhanced by making it possible to improve the payout rate by devising the way of hitting.
なお、こうした遊技性の複雑さが初心者に敬遠されるなどのデメリットを重視する場合は、枚数カウンタを実際の純増枚数分だけ加算するのではなく、指示通りに遊技した場合の純増枚数分だけ加算することとしてもよい。例えば、3枚掛け遊技で、正解時に9枚のメダルが払い出される押し順小役に当籤した場合、主制御基板71は、正解の押し順を報知したことを条件に、遊技者の操作態様や入賞結果を問わずに枚数カウンタに+6とする処理を行う。このような仕様として、こうした調整打法を封じる仕様としてもよい。
In addition, when placing importance on the disadvantages such as the complexity of game play being shunned by beginners, instead of adding only the actual net additional number to the number counter, adding only the net additional number when playing as instructed It may be done. For example, in a three-seat game, when a winning combination of the pushing order in which nine medals are paid out at the time of a correct answer is won, the
[調整打法を封じる仕様の遊技性]
続いて、このような調整打法を封じる仕様おいて実現可能な遊技性について説明する。
[Gameplay with specifications that regulate the adjustment method]
Next, the playability that can be realized with the specifications that enclose such an adjustment hitting method will be described.
(ボーナス非搭載)
そもそもボーナス役を搭載せずに、小役と再遊技のみで内部当籤役を構成すると上記のような複雑な打法を遊技者に求めることがなくなり、遊技性が分かりやすくなる。
(Without bonus)
In the first place, if the internal winning combination is constituted only by the small winning combination and the re-play without mounting the bonus combination, the player will not be required to perform the complicated batting method as described above, and the playability will be easy to understand.
(無増減又は減るボーナス搭載)
また、上記の打法を抑制する別の仕様例として、ボーナスは作動中に投入枚数と同枚数の払出が行われる小役しか入賞しない無増減ボーナスとしてもよく、また、ボーナスは作動中に投入枚数よりも少ない枚数の払出が行われる小役しか入賞しない減るボーナスとしてもよい。この場合、ボーナスはメダルが増加しないかわりに有利区間の抽籤において有利な処理をボーナス作動時またはボーナス作動中に行うこととしてもよく、また、有利な処理を行わないものの、遊技店において遊技者が通常の遊技を行う限りリール制御でボーナスの入賞が阻害され、ボーナスが入賞困難な仕様としても良い。
(Bonus with no increase or decrease)
Also, as another example of the specification that suppresses the above batting method, the bonus may be a non-increased/decreased bonus in which only a small role in which the same number of coins as the number of coins inserted during operation is paid is awarded. The bonus may be reduced so that only a small role in which a smaller number of coins than the number of coins is paid out is won. In this case, the bonus may be such that advantageous processing in lottery of the advantageous section may be performed during the bonus operation or during the bonus operation instead of increasing the number of medals. As long as a normal game is played, the bonus winning may be hindered by the reel control, and the bonus may be difficult to win.
(ボーナス作動中の純増枚数が3枚以下)
3枚掛け遊技を前提として、ボーナス入賞時には払出がないため、ボーナス入賞ゲームでの差枚数はマイナス3枚となる。ボーナスは3枚掛け1ゲームで終了するとして、ボーナス作動中に発生する最大枚数の入賞は6枚役以下とする。このようにすることで、ボーナス作動時からボーナス終了時までの差枚数がプラスの値になることがないため、枚数カウンタの値がボーナス作動により増加することがなくなり、前述のような複雑な打法を遊技者は行わずに済む。
(The number of net additions during bonus operation is 3 or less)
Since there is no payout at the time of bonus winning, assuming a three-player game, the difference in the bonus winning game is minus three. Assuming that the bonus ends in one game with three cards, the maximum number of prizes that can be generated during bonus operation is six or less. By doing this, the difference number of sheets from the bonus operation to the end of the bonus does not become a positive value, so that the value of the number counter does not increase due to the bonus operation, and the complicated striking as described above is performed. The player does not have to practice the law.
[調整打法を認める仕様の遊技性]
続いて、このような調整打法を認める仕様おいて実現可能な遊技性について説明する。
[Gameplay with specifications that allow adjustment batting]
Next, the playability that can be realized with the specifications that allow such an adjustment batting method will be described.
(ボーナス作動中の小役はずし又は獲得枚数低減)
前述の打法を行える仕様に加えて、ボーナス作動中に枚数リミッタが発動してしまう場合は、あえてボーナスの獲得枚数を減らして、当該ボーナスを終わらせて、ボーナス後は、上述の打法により有利区間を延命しつつ、次回のボーナスを待つのが最も有利という場合がある。そこで、ボーナス作動中に、小役を目押しタイミングや押し順で取りこぼせる又は払出枚数の少ない役を入賞させることができるものとする。この場合、払出枚数の少ない役は、ボーナス作動中の投入枚数よりも少ない枚数であることが望ましいが、例えば特定ポイントを目押しすると14枚、それ以外のポイントを目押しすると15枚の払出が受けられるなど、微調整を行うことができる役を設けるというものでも一定の効果を奏することができる。
(Remove a small role during bonus operation or reduce the number of acquisitions)
In addition to the above-mentioned batting method specifications, if the number limiter is activated during bonus operation, dare to reduce the number of bonuses acquired, end the bonus, and after the bonus, use the above batting method. Sometimes it is most advantageous to wait for the next bonus while extending the life of the advantage section. Therefore, during the bonus operation, it is possible to lose the small winning combination at the timing of pressing and the order of pressing, or to make the winning combination with a small payout number. In this case, it is desirable that the combination with a small number of payouts is smaller than the number of inserted coins during the bonus operation. A certain effect can be obtained even by providing a role that allows fine adjustment, such as reception.
(押し順役以外の通常時の役は再遊技又は投入枚数以下の役のみ)
例えば、ボーナス非作動中3枚掛けと仮定する。押し順小役は9枚とするが、いわゆるスイカ、チェリー、押し順の概念なしのベルなど他の役は再遊技役、又は、払出枚数3枚以下の役として構成する。こうすることで、残り数枚の純増で枚数リミッタが作動する状況で他の小役を引いた場合でも枚数リミッタが作動することなく攻略打法の難易度が低下して遊技しやすくなる。
(Only normal re-plays or combinations with less than the number of cards inserted are normal combinations other than the push order combination)
For example, it is assumed that the bonus is not activated and the number of coins is three. The number of push-order small wins is 9, but other wins, such as so-called watermelon, cherry, and bell without the concept of push-order, are configured as re-playing wins or payouts of 3 or less. By doing so, even if another small win is drawn in a situation where the number limiter is activated by a net increase of the remaining number, the number limiter does not operate and the difficulty level of the percussion batting is reduced, making it easier to play.
(押し順役のナビと異なる停止操作をした場合に、特定枚数(1〜2枚役)が入賞する頻度に遊技者が介入できる)
押し順役のナビと異なる停止操作をした場合は、1枚払出又はとりこぼしとなる仕様がある。この場合、当該ゲームの増減がマイナス2枚、マイナス3枚の2通り生じるため、計算しにくく、遊技していて混乱することがある。そのような仕様と比べて、ナビ無視時は、必ず1〜2枚が揃うなど枚数が固定される場合は、ギリギリの枚数の状態でのナビ無視時のマイナス値が例えばマイナス2枚に固定されるため、計算しやすく、遊技者が計算をミスしてあと1回ナビ無視すべきところをナビ通りに打ってしまい打順ベルをとってしまうというケアレスミスが低減する。
(If you perform a stop operation different from the push-and-play combination navigation, the player can intervene at the frequency of winning a specific number (1 to 2 combinations))
If the stop operation is different from the push-and-play navigation, there is a specification that one piece is paid out or dropped. In this case, there are two types of increase/decrease of the game, that is, minus two and minus three, so it is difficult to calculate and may be confused when playing. Compared to such specifications, if the number of sheets is fixed, such as when 1 to 2 sheets are always aligned when ignoring navigation, the negative value when ignoring navigation when the number of sheets is barely fixed is fixed to, for example, minus 2. Therefore, the calculation is easy, and the careless mistake that the player misses the calculation and hits the place where the navigation should be ignored once more as the navigation and takes the batting order bell is reduced.
なお、必ずではなく高い頻度で1枚払出となる又は取りこぼしとなるなど、おおむね安定させるものとしてもある程度の効果は発揮できる。また、ナビ無視のパターンにより、払出枚数が安定するものでもよい。例えば、「1・2・3」(左・中・右が正解打順)の打順ナビ発生時に、1枚役入賞率は“中1st”>“右1st”という関係性を持たせて、3枚減らしたい場合は、右第1停止、2枚減らしたい場合は中第一停止と遊技者が選択できるものでもよい。また、当該ゲームで第1停止正解後に第2停止をミスした場合「1・3・2」の順に停止した場合は、他のナビ無視打順よりも高い確率で又は必ず1枚役が入賞するなど、遊技者が減らし方を打法で選択できるものとするとよい。 It should be noted that some effects can be exhibited even if it is made to be stable, for example, one sheet is dispensed at a high frequency, or it is missed at a high frequency. Further, the payout number may be stable depending on the pattern of ignoring navigation. For example, when a batting order navigation occurs for "1, 2, 3" (correct batting order for left, middle, and right), the winning ratio for one player is 3 for the relationship of "medium 1st"> "right 1st". If the player wants to reduce the number, the player can select the right first stop and the player can select the middle first stop if the player wants to reduce the number of cards. Also, if you miss the second stop after the correct answer in the first stop in the game, if you stop in the order of "1.3.2", there is a higher probability than other navigation neglected batting order, or one winning role is always won It is recommended that the player be able to select the reduction method by the batting method.
(ナビ無視すべき場合にナビ態様変化)
ナビにしたがって遊技するのが最適な場合は、副制御基板72は、押し順表示を第1態様(青数字など)で行い、ナビに逆らって遊技するのが最適な場合は、副制御基板72は、押し順表示を第2態様(赤数字など)で行う。
(Change navigation mode when navigation should be ignored)
When it is optimal to play according to the navigation, the
(ナビ無視すべき状況か演出で変化)
主制御基板71又は副制御基板72は、BGMや映像、ランプなどの態様をナビ従う状況と、ナビに逆らう状況とで異ならせてもよい。ナビ発生よりも前の時点で、次ゲームでナビが発生したらナビに逆らうべき状況か否かを事前に把握できるようにすることが望ましい。
(Navi changes depending on the situation or performance)
The
(ナビ無視すべき場合にロックやリールフリーズ)
主制御基板71は、レバーオン直後、リール回転開始後などにリールの回転開始遅延(フリーズやリールアクション)や、ストップボタンの一時操作受付無効化期間を設けることとしてもよい。これにより、遊技者に注意喚起をすることができ、有利区間を誤って終わらせてしまうケースを防止できる。また、主制御基板71又は副制御基板72は、合わせて音声や映像などでも注意喚起することが望ましい。
(Lock and reel freeze when navigation should be ignored)
The
[有利区間リミッタの別例(払出枚数リミッタ)]
ここで、上述の枚数リミッタでは、差枚数(=払出枚数−投入枚数)、すなわち、遊技者に対して払い出されたメダルの枚数から当該遊技において用いられたメダルの枚数を減算した値に基づき、リミット処理を行うこととしているが、これに限られるものではない。主制御基板71は、遊技者に対して払い出されたメダルの枚数を用いてリミット処理を行うこととしてもよく、このようなリミッタを払出枚数リミッタと呼ぶ。具体的には、主制御基板71は、有利区間中に所定枚数(例えば、2400枚など)のメダルを払い出したことを契機として、有利区間を終了するリミット処理を行うこととしてもよい。
[Another example of advantageous zone limiter (Payout amount limiter)]
Here, in the above-described number limiter, based on the difference number (=payout number-insertion number), that is, a value obtained by subtracting the number of medals used in the game from the number of medals paid out to the player. The limit process is to be performed, but not limited to this. The
上述の枚数リミッタでは、払出枚数から投入枚数を差し引いた差枚数を基準としてリミット処理を行っているが、払出枚数リミッタでは、払出枚数から投入枚数を差し引くことなく、払出枚数をそのまま参照して、払出枚数が規定値に達した場合にリミット処理を行う。このような払出枚数リミッタでは、主制御基板71は、有利区間(この場合、例えば上述した「通常有利区間」を含む)又は増加区間(すなわち、実際にメダルが増加する遊技区間。この場合、例えば上述した「通常有利区間」を含まない)の開始時に払出枚数カウンタを初期化して、小役の入賞により払出が発生するたびに当該払出枚数カウンタを更新する。そして、主制御基板71は、払出枚数カウンタの値がリミット処理を行う規定値に達すると、有利区間を終了し、また、有利区間に関する各種の処理や値を初期化するというリミット処理を行う。
In the above-mentioned number limiter, limit processing is performed based on the difference number obtained by subtracting the inserted number from the paid number, but in the paid number limiter, without subtracting the inserted number from the paid number, the payout number is directly referred to. Limit processing is performed when the number of paid-out sheets reaches the specified value. In such a payout number limiter, the
このような払出枚数リミッタにおいても、リプレイに係る役が入賞した場合の払出枚数カウンタの更新方法は任意であり、3枚の払い出しとしてカウントすることとしてもよく、また、0枚の払い出しとしてカウントすることとしてもよいが、主制御基板71は、リプレイに係る役が入賞した場合には0枚の払い出しとしてカウントすることが望ましい。このようにすることで、例えば、3BETの遊技において3枚役(入賞したときに3枚のメダルが払い出される役)が入賞した場合と、リプレイに係る役が入賞した場合とで、払出枚数カウンタの値の変化を異ならせることができる。すなわち、3枚役が入賞した場合よりも、リプレイに係る役が入賞した場合の方が払出枚数カウンタのカウントが進まない分、遊技者にお得感を感じさせることができ、実質的に同価値である3枚役とリプレイに係る役との価値に差を持たせることができる。
Also in such a payout number limiter, the method of updating the payout number counter when a winning combination relating to replay is won is arbitrary, and may be counted as three payouts, or may be counted as zero payout. However, it is preferable that the
[有利区間リミッタの別例(ナビ回数リミッタ)]
また、有利区間のリミット処理に用いるリミッタの種類としては、以下に説明するナビ回数リミッタも用いることができる。ナビ回数リミッタを用いる場合、主制御基板71は、有利区間中に遊技者に対して所定回数(例えば、400回など)の報知(ナビ)を行ったことを契機(すなわち、ナビ回数が規定値に達したことを契機)として、有利区間のリミット処理を行う。ここで、ARTなどの有利区間中に遊技者に対して行うナビの中には、有利区間中にメダルを増加させるためのナビの他、有利区間中にメダルを維持又はメダルの減少を通常区間中に比べて抑制するためのナビがある。前者のナビは、例えば、3BET遊技において正解の停止操作の態様である場合(例えば、押し順正解時)に3枚よりも多いメダル(例えば、9枚など)が払い出される役の当籤時に正解の停止操作の態様を報知することをいい、後者のナビは、例えば、RT状態を高RTのまま維持するためのナビや、3BET遊技において正解の停止操作の態様である場合に3枚、又は、正解の停止操作の態様である場合に3枚よりも少ないが不正解の停止操作の態様である場合(例えば、押し順不正解時)よりも多いメダルが払い出される役の当籤時に正解の停止操作の態様を報知することをいう。なお、前者のナビの対象となる役は、その役割から有利区間(ART)中にメダルを増加させる増加役と呼ぶことができる。パチスロにおいて、複数の役のうちのどの役を増加役とするかは、遊技仕様の観点から任意に設計することができる。
[Another example of an advantageous interval limiter (navigation limiter)]
Further, as the type of limiter used for limit processing of the advantageous section, a navigation number limiter described below can also be used. In the case of using the navigation frequency limiter, the
ナビ回数リミッタを用いる場合、主制御基板71は、増加役の当籤時に行ったナビの回数については、ナビ回数リミッタによるリミット処理の発生条件となるナビ回数のカウント対象とする一方で、非増加役の当籤時に行ったナビの回数については、当該ナビ回数のカウント対象から除外することとしてもよく、また、非増加役の当籤時に行ったナビ回数についても、当該ナビ回数のカウント対象に含めることとしてもよい。非増加役の当籤時に行ったナビの回数をカウント対象から除外することで、偶然、非増加役が有利区間(ART)の開始後に多く成立してしまったケースのように、メダルがあまり増えていない場合に、過度な出玉を抑制するというリミッタの趣旨とは関係ない事象で有利区間が終了してしまうことを防止でき、遊技者に不満を与えることがない。
When using the navigation frequency limiter, the
このようなナビ回数リミッタでは、主制御基板71は、有利区間又は増加区間の開始時にリミット処理の発生条件となるナビ回数のカウンタ(ナビ回数カウンタ)を初期化して、カウント対象となるナビが発生するたびに当該ナビ回数カウンタの値を更新する。そして、主制御基板71は、ナビ回数カウンタの値がリミット処理を行う規定値に達すると、有利区間を終了し、また、有利区間に関する各種の処理や値を初期化するというリミット処理を行う。なお、これまでに説明した各種のリミッタにおいてカウンタの更新方法は、加算式であってもよく、また、減算式であってもよい。
In such a navigation frequency limiter, the
[リミッタ期間の別例]
また、上述の説明では、ゲーム数リミッタ、枚数リミッタ、払出枚数リミッタ、ナビ回数リミッタなどのリミッタを有利区間中にのみ利用する例について説明したが、このようなリミッタは、有利区間中ではなく、任意の期間に採用することができる。例えば、偶発的に有利区間に当たり続けた場合、一回一回の有利区間においては最大でも枚数リミッタ分しかメダルの払い出しが行われないものの、有利区間への移行が複数回行われた結果、総合すると多くのメダルの払い出しが行われてしまう場合があり、射幸心を過度に煽ってしまう恐れがある。そこで、有利区間中のリミッタとは別に、直近の所定ゲーム数分の期間(例えば、直近の6000ゲーム)の増加状況を示す値(例えば、出玉率や差枚数)が予め定められた規定値(例えば、170%又は遊技者から見て+10000枚)を超えた場合に有利区間を終了させる特別リミッタを設けることとしてもよい。このような特別リミッタによれば、主制御基板71は、有利区間中に特別リミッタの発動条件が満たされたときには、たとえ当該有利区間が開始したばかりであり、ゲーム数リミッタや枚数リミッタが全く発動し得る状況でなかったとしても、当該有利区間を強制的に終了する。
[Another example of limiter period]
Further, in the above description, an example of using the limiters such as the game number limiter, the number limiter, the payout number limiter, and the navigation number limiter only during the advantageous section has been described, but such a limiter is not in the advantageous section, It can be adopted in any period. For example, if you continue to hit the advantageous zone by accident, the maximum number of coins will be paid out at most once in the advantageous zone, but as a result of multiple transitions to the advantageous zone, In that case, many medals may be paid out, and there is a risk that the euphoria will be excessively fueled. Therefore, apart from the limiter in the advantageous zone, a value (for example, a payout rate or a difference number) indicating the increase status of a period for the latest predetermined number of games (for example, the latest 6000 games) is a predetermined value set in advance. A special limiter may be provided to end the advantageous section when exceeding (for example, 170% or +10,000 sheets from the player's perspective). According to such a special limiter, when the condition for activating the special limiter is satisfied during the advantageous section, the
なお、主制御基板71における有利区間の制御において、現時点で獲得されている有利区間に関する権利(例えば、ARTの継続可能期間(ARTゲーム数)、セット数やストック、獲得可能差枚数など)と出玉率とを参照して、特別リミッタが発動するおそれがある場合に、主制御基板71は、当該規定値に到達するよりも前に上乗せの発生率を低下させるなど特別リミッタの発動可能性を低下させる、又は、特別リミッタ発動時に消去させる増加区間(ART)の権利が低減するように制御することとしてもよい。
In the control of the advantageous section on the
また、メダルの増加状況を示す値(例えば、出玉率や差枚数)による特別リミッタ発動の判定に用いられる所定期間は、ゲーム数以外を基準としてもよく、例えば、所定の時間(例えば、10時間など)や、所定の投入枚数(例えば、投入枚数18000枚)など、遊技者が遊技を所定期間にわたって行ったことを判断し得る情報に用いて、特別リミッタを発動する所定期間を決定することとしてもよい。 Further, the predetermined period used for determining the activation of the special limiter based on the value indicating the increase status of medals (for example, the payout rate or the number of remaining coins) may be based on a value other than the number of games, for example, for a predetermined time (for example, 10 Determining a predetermined period for activating the special limiter by using information such as a time) or a predetermined number of inserted coins (eg, 18,000 inserted coins) that can be used to determine that the player has played a game for a predetermined period. May be
このような特別リミッタを用いるパチスロの構成を以下に示す。
遊技価値を用いて遊技可能な遊技機であって、
遊技状態を遊技者にとって有利な有利遊技状態(例えば、パチスロにおける有利区間、増加区間(AT、ART)であってもよく、パチンコにおける確変状態や時短状態であってもよい)とする権利(パチスロでのATストック、ATゲーム数などであってもよく、また、パチンコにおける確変状態、時短状態などへの移行権利であってもよい)を付与可能な権利付与手段(例えば、主制御基板71)と、
当該権利に基づいて終了条件の成立まで遊技状態を前記有利遊技状態に制御する遊技状態制御手段(例えば、主制御基板71)と、
前記権利がある場合に前記有利遊技状態を継続させる有利遊技状態継続手段(例えば、主制御基板71(パチスロでのATストック数がある場合にAT状態を継続などであってもよく、また、パチンコでの確変状態や時短状態の継続であってもよい))、
所定の単位遊技を起点として所定期間の経過までの遊技価値の増加状況を示す値を記憶する増加状況記憶手段(例えば、主制御基板71が特別リミッタの発動条件を判定するために用いる差枚数や出玉率監視用のカウンタ)と、
前記増加状況記憶手段の値が予め定められた規定値となったときに、前記権利がある場合であっても前記有利状態を終了させる特別終了手段(特別リミッタ)と、を備える遊技機。
The structure of a pachi-slot using such a special limiter is shown below.
A gaming machine that can be played using a gaming value,
The right to set the gaming state as an advantageous gaming state that is advantageous for the player (for example, it may be an advantageous section in a pachi-slot, an increase section (AT, ART), or a probability change state or a shortened state in a pachinko). AT stock, the number of AT games, etc., and may be a right to shift to a pachinko machine's probability change state, time saving state, etc.) (right control means 71, for example) When,
Based on the right, game state control means (for example, main control board 71) for controlling the game state to the advantageous game state until the end condition is satisfied,
Advantageous game state continuation means for continuing the advantageous game state when there is the right (for example, the main control board 71 (the AT state may be continued when there is the AT stock number on the pachislot, etc., and pachinko It may be a continuation of a sudden change state or a shortened state in))),
Increasing status storage means (for example, the
A gaming machine comprising: a special ending means (special limiter) for ending the advantageous state even when the right is granted when the value of the increase status storage means reaches a predetermined specified value.
また、上述の特別リミッタは、直近の所定期間に限らず、例えば、一日単位のリミッタとしてもよく、また、両者を併用して用いることとしてもよい。なお、主制御基板71が一日単位を把握する方法は任意である。一例として、主制御基板71は、所定時間(2時間、4時間など営業時の一時的な電断と区別でき、営業終了に伴う閉店中の電断と推認できる時間値)以上の電断時、又は所定時間以上の電断後の電源投入時を一日の開始時(起点)として、当該起点から(すなわち、前日分の情報をリセットして)、メダルの増加状況を示す値(例えば、出玉率や差枚数)を監視して特別リミッタを制御する。また、主制御基板71は、電源投入状態で所定時間(1時間など)以上が経過した時を、一日の開始時(起点)として、当該起点から(すなわち、前日分の情報をリセットして)、メダルの増加状況を示す値(例えば、出玉率や差枚数)を監視して特別リミッタを制御することとしてもよい。なお、何れの場合であっても、計時方法は、主制御基板71にRTCなどの計時手段を搭載することで実現することができる。
Further, the above-mentioned special limiter is not limited to the latest predetermined period, but may be, for example, a limiter for each day, or both may be used in combination. The method by which the
[ナビミス時のペナルティ]
また、パチスロ1では、有利区間中に遊技者に対して行った報知に従わずに停止操作を行った場合に、主制御基板71は、所定のペナルティを付すこととしてもよい。例えば、ART準備中(上述した各準備状態)のように高RTへの移行待ちをしている状態において、ARTの上乗せ抽籤を行う仕様の場合、高RTへの移行を回避しART準備中を引き延ばすことでART準備中の上乗せ抽籤を多く受けることができる。そこで、主制御基板71は、遊技者に対して行った報知に従わずに停止操作が行われた場合に、このようなARTの上乗せ抽籤を行わないこととしてもよい。なお、偶然のミスであるか意図的なミスであるか判別することができないため、例えば、主制御基板71は、報知に従わない停止操作を行った回数に応じて、ペナルティの度合いを変えることとしてもよい。
[Penalty for Navimis]
Further, in the pachi-
[遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その7)]
まず、図103〜図108を参照して、本実施形態に係るパチスロ1において実装可能な遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その7)について説明する。図103は、遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その7)における遊技の流れを概念的に示す図であり、図104〜図106は、遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その7)において用いる各種のテーブルを概念的に示す図であり、図107は、遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その7)と従来の遊技性との比較例を示す図であり、図108は、遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その7)を実現可能な他の仕様例を概念的に示す図である。
[Another example of playability (game specifications) (Part 7)]
First, with reference to FIGS. 103 to 108, another example (No. 7) of the game playability (game specification) that can be mounted in the pachi-
(遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その7)の概要)
以下説明する遊技性(その7)は、有利区間の天井制御に関するものである。有利区間と非有利区間(通常区間)とを有するパチスロでは、有利区間として、遊技者にとって有利なARTなどの有利状態と、この有利状態への移行期待度が非有利区間とは異なるCZ(チャンスゾーン)などの遊技状態(通常有利区間)とを有することがある。このようなパチスロでは、非有利区間から有利区間のうちの通常有利区間(CZ)に移行したものの、有利区間のうちの有利状態(ART)に移行できないまま、非有利区間に移行してしまうことがある。
(Outline of other examples of game play (game specifications) (No. 7))
The playability (No. 7) described below relates to the ceiling control of the advantageous section. In a pachi-slot having an advantageous section and a non-advantageous section (normal section), as an advantageous section, an advantageous state such as ART, which is advantageous to the player, and a CZ (chance that is different in the degree of expectation of transition to this advantageous state from the non- advantageous zone) It may have a game state (normal zone) such as a zone). In such a pachi-slot, although it shifts from the non-advantageous zone to the normal advantageous zone (CZ) of the advantageous zones, it shifts to the non-advantageous zone without being able to shift to the advantageous state (ART) of the advantageous zones. There is.
ここで、従来、CZのスルー回数に天井を設け、CZに所定回数連続して失敗した場合にARTなどの有利状態に移行可能にするといった特典を付与する天井制御を有するパチスロが知られている。この点、有利区間と非有利区間とを有する近年のパチスロでは、有利区間を終了させる場合に、有利区間に関する全ての情報をリセット(初期化)しなければならないため、有利状態(ART)に移行できなまま終了した有利区間の回数(スルー回数)をカウントすることができなず、従来の天井制御のように有利区間のスルー回数に基づく天井制御を行うことが困難になっている。 Here, conventionally, there is known a pachi-slot having a ceiling control in which a ceiling is provided for the number of times of through the CZ and the privilege is given to enable transition to an advantageous state such as ART when the CZ fails a predetermined number of times in succession. .. In this respect, in a recent pachi-slot having an advantageous section and a non-advantageous section, all information regarding the advantageous section must be reset (initialized) when the advantageous section is ended, and therefore the state shifts to the advantageous state (ART). Since it is not possible to count the number of advantageous sections (thru numbers) that have been completed without completion, it is difficult to perform ceiling control based on the number of through sections of the advantageous section unlike the conventional ceiling control.
そこで、遊技性(その7)では、有利区間のスルー回数(有利状態に移行できなまま終了した有利区間の回数)を、RT状態に基づき把握することで、有利区間のスルー回数に基づく天井制御を実現可能にしている。
なお、以下の説明では、CZのスルー回数に対して天井を持たせる例について説明するが、遊技性(その7)は、有利区間へのスルー回数に対する天井制御に関するものであり、有利状態に移行しないまま終了した有利区間はCZに限るものではない。また、以下の説明では、天井による恩恵を、ARTへの移行としているが、遊技性(その7)は、有利区間へのスルー回数に基づき天井制御が可能であればよく、天井による恩恵もARTへの移行に限るものではない。
Therefore, in the game (No. 7), the ceiling control based on the slew number of the advantageous section is obtained by grasping the number of slews of the advantageous section (the number of the advantageous sections terminated without being able to shift to the advantageous state) based on the RT state. Is possible.
In the following description, an example in which a ceiling is provided for the number of times of CZ through is described, but the game property (No. 7) relates to ceiling control for the number of times of through to an advantageous section, and shifts to an advantageous state. The advantageous zone that ends without doing so is not limited to CZ. Further, in the following description, the benefit of the ceiling is assumed to be shifted to the ART, but the playability (No. 7) is only required to be able to control the ceiling based on the number of throughs to the advantageous section, and the benefit of the ceiling is also ART. It is not limited to the transition to.
<遊技状態の遷移フロー>
まず、図103を参照しながら、パチスロ1の主制御回路90(メインCPU101)により管理される各種遊技状態及びその遷移フローについて説明する。図103(A)は、本仕様例のパチスロ1における基本的な遊技状態の遷移フローであり、図103(B)は、本仕様例のパチスロ1における報知の有無を考慮した遊技状態の遷移フローである。
<Game state transition flow>
First, various game states managed by the main control circuit 90 (main CPU 101) of the pachi-
(基本的な遊技状態の遷移フロー)
図103(A)に示すように、本仕様例のパチスロ1では、リプレイに係る役の種類及びその当籤確率が互いに異なるRT状態として複数段階のRT状態を有する。なお、本仕様例では、複数段階のRT状態として、RT1〜RT6という6段階のRT状態を有することとしているが、RT状態の数は6つに限るものではなく、任意である。RT1〜RT6のうち少なくともRT6は、リプレイに係る役が内部当籤役として決定される確率が高確率となる高RTである。なお、RT1〜RT5におけるリプレイに係る役が内部当籤役として決定される確率は任意であるが、本仕様例では、RT1〜RT5は、当該確率が低確率となる低RTとしている。
(Basic game state transition flow)
As shown in FIG. 103A, in the pachi-
主制御回路90は、非ボーナス状態においてボーナス状態が開始されると、非ボーナス状態からボーナス状態に遊技状態を移行する。また、主制御回路90は、ボーナス状態が終了すると、非ボーナス状態に遊技状態を移行するとともに、RT状態としてRT1をセットする。
When the bonus state is started in the non-bonus state, the
そして、主制御回路90は、RT1においてRT2移行リプに係る図柄の組合せが表示されると、RT状態をRT2に移行し、RT2においてRT3移行リプに係る図柄の組合せが表示されると、RT状態をRT3に移行し、RT3においてRT4移行リプに係る図柄の組合せが表示されると、RT状態をRT4に移行し、RT4においてRT5移行リプに係る図柄の組合せが表示されると、RT状態をRT5に移行し、RT5においてRT6移行リプに係る図柄の組合せが表示されると、RT状態をRT6に移行し、RT6においてRT1移行リプに係る図柄の組合せが表示されると、RT状態をRT1に移行する。
Then, the
なお、図105において後述するように、RT2移行リプは、RT1中リプ(「RT1中リプ_123」〜「RT1中リプ_321」)が内部当籤役として決定された場合に、特定の操作態様で停止操作が行われることで表示される図柄の組合せである。また、RT3移行リプ〜RT6移行リプ及びRT1移行リプも同様であり、RT2中リプ〜RT6中リプが内部当籤役として決定された場合に、特定の操作態様で停止操作が行われることで表示される図柄の組合せである。 As will be described later with reference to FIG. 105, the RT2 transition lip is stopped in a specific operation mode when the RT1 middle lip (“RT1 middle lip_123” to “RT1 middle lip_321”) is determined as an internal winning combination. It is a combination of symbols displayed by an operation being performed. The same applies to RT3 transition lip to RT6 transition lip and RT1 transition lip, and when RT2 middle lip to RT6 middle lip is determined as the internal winning combination, it is displayed by performing a stop operation in a specific operation mode. It is a combination of symbols.
このように本仕様例のパチスロ1では、複数段階のRT状態は、RT1から1つずつ順にRT6まで移行する。なお、遊技性(その7)は、複数段階のRT状態を有していれば実現可能であり、RT状態は必ずしも1つずつ順に移行するものに限るものではなく、1つ又は複数のRT状態を飛ばして移行可能にしてもよく、また、RT状態が戻るようにRT状態を移行(例えば、RT3からRT2に移行)可能にしてもよい。
In this way, in the pachi-
(報知の有無を考慮した遊技状態の遷移フロー)
図103(B)に示すように、本仕様例のパチスロ1において主制御回路90は、報知の有無に基づいて通常区間(非有利区間)と有利区間とを区別する。通常区間は、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知しない(又は報知する頻度が低い)遊技状態であり、基本的には、遊技者にとって不利な遊技状態である。有利区間には、CZ(チャンスゾーン)とARTとが含まれ、CZは、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知しない(又は報知する頻度が低い)遊技状態であり、ARTは、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知する(又は報知する頻度が高い)遊技状態である。
(Transition flow of game state considering presence or absence of notification)
As shown in FIG. 103(B), in the pachi-
本仕様例において主制御回路90は、通常区間において有利区間への移行抽籤を行っており、この移行抽籤に当籤すると、通常区間から有利区間のCZに遊技状態を移行する。なお、主制御回路90は、有利区間への移行抽籤に当籤した場合に、移行先の有利区間の種別を決定するなどして通常区間からARTに直接移行可能にしてもよいが、遊技性(その7)の説明においては関係がないため、通常区間からARTへの移行に関しては省略する。
In the present specification example, the
また、主制御回路90は、CZ中にARTに移行するか否かの決定を行っており、ARTに移行すると決定すると、CZからARTに遊技状態を移行する。一方で、主制御回路90は、ARTに移行すると決定しないままCZが終了すると、有利区間を終了して、CZから通常区間に遊技状態を移行する。
Further, the
ここで、本仕様例のパチスロ1では、遊技性(その7)を実現するために、遊技状態がCZに移行すると、RT状態を現在のRT状態よりも先の段階のRT状態に移行させる。具体的には、主制御回路90は、RT1〜RT4において遊技状態が通常区間からCZに移行すると、RT1中リプ〜RT4中リプが内部当籤役として決定された場合に特定の操作態様を遊技者に対して報知することで、RT状態をRT2〜RT5に移行させる。
Here, in the pachi-
なお、CZからARTへの移行条件は、任意の条件を採用することができ、一例として本仕様例では、主制御回路90は、CZ中に行うARTへの移行抽籤に当籤した場合に、移行条件を満たしたとして、CZからARTに遊技状態を移行する。また、CZの終了条件も任意であり、一例として本仕様例では、主制御回路90は、ARTへの移行抽籤に当籤しないまま、CZにおいて実行された遊技回数が規定数に達した場合に、終了条件が満たされたとして、有利区間を終了して、CZから通常区間に遊技状態を移行する。このとき、CZにおいて実行された遊技回数の計数開始タイミングは任意であり、例えば、RT状態を現在のRT状態よりも先の段階のRT状態に移行させてから当該遊技回数を計数し始めることとしてもよく、また、CZに移行したときから当該遊技回数を計数し始めることとしてもよい。
Any condition can be adopted as the transition condition from CZ to ART. As an example, in the present specification example, the
後者のケースでは、先の段階のRT状態に移行させる前に、遊技回数が規定数を超えてしまう場合があるが、本仕様例では、先の段階のRT状態に移行させる前に終了条件が満たされることはない。すなわち、このような場合には、主制御回路90は、遊技回数が規定数を超えてしまった後に、先の段階のRT状態に移行したことをもって、CZを終了する。言い換えると、主制御回路90は、RT1〜RT4において遊技状態が通常区間からCZに移行した場合、RT2〜RT5に移行した後に所定期間が経過すると(CZ中の遊技回数が規定数を超えると)、有利区間を終了して、CZから通常区間に遊技状態を移行する。
In the latter case, the number of games may exceed the specified number before shifting to the RT state of the previous stage, but in this specification example, the ending condition is set before shifting to the RT state of the previous stage. It will never be met. That is, in such a case, the
なお、RT状態を先の段階のRT状態に移行させるために、特定の操作態様を遊技者に対して報知したにもかかわらず、遊技者が当該報知に従わずに停止操作を行った場合、RT状態は先の段階に移行しないが、このような場合にCZを終了するか否かは任意である。すなわち、主制御回路90は、RT1〜RT4において遊技状態が通常区間からCZに移行した場合、RT状態を先の段階のRT状態に移行させた後に終了条件を満たすと(CZ中の遊技回数が規定数を超えると)、有利区間を終了して、CZから通常区間に遊技状態を移行することとしてもよく、また、RT状態を先の段階のRT状態に移行させるための報知を行った後に終了条件を満たすと(CZ中の遊技回数が規定数を超えると)、有利区間を終了して、CZから通常区間に遊技状態を移行することとしてもよい。
In addition, in order to shift the RT state to the RT state of the previous stage, when the player performs a stop operation without following the notification, although the player is informed of a specific operation mode, Although the RT state does not shift to the previous stage, whether or not to terminate the CZ in such a case is arbitrary. That is, when the game state in RT1 to RT4 shifts from the normal section to CZ, the
また、主制御回路90は、RT5において遊技状態が通常区間からCZに移行した場合、ARTへの移行抽籤に当籤しないまま遊技回数が規定数を超えると、CZからARTに遊技状態を移行する。すなわち、本仕様例では主制御回路90は、通常区間から有利区間(CZ)に移行する度にRT状態を1段階ずつ進めていき、RT5まで移行した場合には、CZのスルー回数が天井に到達したとして、RT5において移行したCZが失敗したとしても遊技状態をARTに移行する。
Further, the
なお、CZの終了条件である遊技回数の規定数は、任意の回数であってよく、例えば、全てのRT状態において共通の値であってもよく、また、個々のRT状態毎に異なる値であってもよい。この点、本仕様例では、RT1〜RT4において遊技状態が通常区間からCZに移行した場合の規定数を100回としている。また、RT5において遊技状態が通常区間からCZに移行した場合の規定数は、RT1〜RT4において遊技状態が通常区間からCZに移行した場合の規定数と同じ100回であってもよく、RT1〜RT4において遊技状態が通常区間からCZに移行した場合の規定数よりも少ない値であってもよく、本仕様例では、30回としている。すなわち、本仕様例では、RT1〜RT4において遊技状態が通常区間からCZに移行した場合、ARTへの移行条件を満たすことなく100回の遊技が行われると、CZが終了する一方で、RT5において遊技状態が通常区間からCZに移行した場合、ARTへの移行条件を満たすことなく30回の遊技が行われると、CZが終了する。 It should be noted that the prescribed number of games, which is the ending condition of CZ, may be an arbitrary number, for example, a common value in all RT states, or a different value for each RT state. It may be. In this respect, in this specification example, the specified number when the game state shifts from the normal section to CZ in RT1 to RT4 is 100 times. Further, the specified number when the game state shifts from the normal section to CZ in RT5 may be 100 times, which is the same as the specified number when the game state shifts from the normal section to CZ in RT1 to RT4. At RT4, the game state may be a value smaller than the prescribed number when the game is transferred from the normal section to CZ, and in this specification example, it is set to 30 times. That is, in this specification example, when the game state shifts from the normal section to CZ in RT1 to RT4, if the game is played 100 times without satisfying the transition condition to ART, CZ ends, while at RT5. When the game state shifts from the normal section to CZ, the CZ ends when the game is played 30 times without satisfying the condition for shifting to ART.
また、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をARTに移行した場合、ART中に応じた所定の制御を行う。遊技性(その7)の説明においてART中の制御は関係がないため説明を省略するが、主制御回路90は、遊技状態をARTに移行した場合、RT状態を高RT状態に移行させるための報知、及び、RT状態を高RT状態のまま維持するための報知を行うとともに、ART中に押し順役が内部当籤役として決定されると、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知する。また、主制御回路90は、ART中にARTの終了条件を満たした場合に、有利区間を終了して、ARTから通常区間に遊技状態を移行する。
Further, the
(有利区間の天井制御)
続いて、図103(C)を参照して、本仕様例のパチスロ1における遊技の流れを説明することで、遊技性(その7)による有利区間の天井制御について説明する。
図103(C)に示す例では、初期の遊技状態として、通常区間のRT1が設定されている。通常区間のRT1では、通常区間であるため有利区間への移行抽籤が行われ、この移行抽籤に当籤すると、通常区間から有利区間のCZに移行する結果、通常区間のRT1からCZ(有利区間)のRT1に移行する。
(Ceiling control for advantageous sections)
Subsequently, with reference to FIG. 103C, the flow of the game in the pachi-
In the example shown in FIG. 103(C), RT1 of the normal section is set as the initial game state. In RT1 of the normal section, a transition lottery to the advantageous section is performed because it is the normal section, and if the transition lottery is won, as a result of shifting from the normal section to the CZ of the advantageous section, RT1 to CZ of the normal section (advantageous section) To RT1.
CZでは、RT状態を現在のRT状態よりも先の段階のRT状態に移行させるため、RT状態がRT1からRT2に移行する結果、CZ(有利区間)のRT1からCZ(有利区間)のRT2に移行する。このCZがARTに移行することなく終了すると(CZに失敗すると)、有利区間が終了し通常区間に移行する結果、CZのRT2から通常区間のRT2に移行する。 In the CZ, since the RT state is changed to the RT state at a stage earlier than the current RT state, the RT state is changed from RT1 to RT2, and as a result, from RT1 of CZ (advantageous section) to RT2 of CZ (advantageous section). Transition. If this CZ ends without moving to ART (fails in CZ), the advantageous zone ends and shifts to the normal zone. As a result, RT2 of the CZ shifts to RT2 of the normal zone.
ここで、有利区間の終了に伴い、主制御回路90は、有利区間に関する全ての情報をリセット(初期化)するため、通常区間に移行してしまうとCZに失敗したことを把握することができず、CZのスルー回数を計数することができない。この点、本仕様例のパチスロ1では、有利区間(CZ)の移行前後においてRT状態を異ならせることで、CZのスルー回数を間接的に計数することができる。すなわち、主制御回路90は、通常区間のRT1をCZのスルー回数が「0回」の状態であり、通常区間のRT2をCZのスルー回数が「1回」の状態であると把握する。言い換えると、主制御回路90は、通常区間のRT1から移行したCZのRT1を、「1回目」のCZであると把握する。
Here, since the
なお、CZに成功し、CZからARTに移行した場合の遊技の流れについては、詳細な説明を省略するが、主制御回路90は、高RTであるRT6に移行させるための報知、及び、RT状態をRT6のまま維持するための報知を行うとともに、ARTが終了すると、当該報知を行わなくなる結果、RT状態がRT6からRT1に移行することになる。
Although detailed description will be omitted regarding the flow of the game when the CZ succeeds and the CZ shifts to the ART, the
通常区間のRT2(スルー回数「1回」)に移行した後は同様に、有利区間への移行抽籤に当籤すると、通常区間のRT2からCZのRT2に移行する。そして、CZでは、RT状態を現在のRT状態よりも先の段階のRT状態に移行させるため、CZのRT2からCZのRT3に移行する。このCZがARTに移行することなく終了すると(CZに失敗すると)、有利区間が終了し通常区間に移行する結果、CZのRT3から通常区間のRT3に移行する。このとき、主制御回路90は、通常区間のRT2から移行したCZのRT2を「2回目」のCZであると把握し、また、CZが終了した後の通常区間のRT3をCZのスルー回数が「2回」の状態であると把握する。
After the shift to the normal section RT2 (the number of times of through is “1”), similarly, if the shift lottery to the advantageous section is won, the shift from the normal section RT2 to the CZ RT2 is performed. Then, in the CZ, in order to shift the RT state to the RT state at a stage earlier than the current RT state, the RTZ of the CZ shifts to the RT3 of the CZ. If the CZ ends without shifting to ART (fails in CZ), the advantageous zone ends and shifts to the normal zone. As a result, RT3 of the CZ shifts to RT3 of the normal zone. At this time, the
その後も同様であり、通常区間のRT3(スルー回数「2回」)において有利区間への移行抽籤に当籤すると、通常区間のRT3からCZのRT3(「3回目」のCZ)に移行し、続いて、先の段階のRT状態に移行させた結果、CZのRT3からCZのRT4に移行する。その後、CZがARTに移行することなく終了すると(CZに失敗すると)、有利区間が終了し通常区間に移行する結果、CZのRT4から通常区間のRT4(スルー回数「3回」)に移行する。 After that, the same applies, and if the lottery for the transition to the advantageous section is won in RT3 of the normal section (through number "2 times"), it shifts from RT3 of the normal section to RT3 of CZ (CZ of "third time"), As a result of shifting to the RT state of the previous stage, the shift from RT3 of CZ to RT4 of CZ. After that, when the CZ ends without shifting to ART (when CZ fails), the advantageous section ends and the section shifts to the normal section. As a result, the RT4 of the CZ shifts to RT4 of the normal section (through number "3 times"). ..
また、通常区間のRT4(スルー回数「3回」)において有利区間への移行抽籤に当籤すると、通常区間のRT4からCZのRT4(「4回目」のCZ)に移行し、続いて、先の段階のRT状態に移行させた結果、CZのRT4からCZのRT5に移行する。その後、CZがARTに移行することなく終了すると(CZに失敗すると)、有利区間が終了し通常区間に移行する結果、CZのRT5から通常区間のRT5(スルー回数「4回」)に移行する。 If the lottery for the transition to the advantageous zone is won in RT4 of the normal zone (the number of times of through is “3 times”), the RT4 of the normal zone is shifted to the RT4 of the CZ (the CZ of the “fourth time”), and then As a result of the shift to the RT state of the stage, the shift from RT4 of CZ to RT5 of CZ. After that, when the CZ ends without shifting to ART (when CZ fails), the advantageous zone ends and shifts to the normal zone. As a result, the RTZ of the CZ shifts to RT5 of the normal zone (through number "4 times"). ..
続いて、通常区間のRT5(スルー回数「4回」)において有利区間への移行抽籤に当籤すると、通常区間のRT5からCZのRT5(「5回目」のCZ)に移行する。この「5回目」のCZでは、主制御回路90は、CZ中にRT状態を移行することなくRT5のまま維持する。また、この「5回目」のCZでは、主制御回路90は、CZがARTに移行することなく終了した場合であっても(CZに失敗した場合であっても)、有利区間が終了することなく、CZからARTに遊技状態を移行する。すなわち、本仕様例のパチスロ1では、「5回目」のCZ(スルー回数「4回」)を天井として、当該CZに失敗した場合であっても、天井到達に伴う特典(ARTへの移行)を付与する。
Then, when the lottery for shifting to the advantageous section is won in RT5 of the normal section (the number of times of through "4 times"), the RT5 of the normal section is shifted to RT5 of the CZ (CZ of the "fifth time"). In this "fifth" CZ, the
<各種データテーブル>
続いて、図104〜図106を参照して、遊技性(その7)を実現するために用いる各種のデータテーブルについて説明する。
<Various data tables>
Subsequently, various data tables used to realize the game characteristic (No. 7) will be described with reference to FIGS. 104 to 106.
[内部抽籤テーブル]
図104(A)は、非ボーナス状態において参照される内部抽籤テーブルである。内部抽籤テーブルは、遊技状態毎に設けられ、複数の役のそれぞれに対して、当該役が内部当籤役として決定されるときの抽籤値を規定する。なお、RT1中は「RT1」欄が参照され、RT2中は「RT2」欄が参照され、RT3中は「RT3」欄が参照され、RT4中は「RT4」欄が参照され、RT5中は「RT5」欄が参照され、RT6中は「RT6」欄が参照される。
[Internal lottery table]
FIG. 104(A) is an internal lottery table referred to in the non-bonus state. The internal lottery table is provided for each gaming state, and defines a lottery value for each of a plurality of winning combinations when the winning combination is determined as an internal winning combination. Note that during RT1, the "RT1" column is referenced, during RT2 the "RT2" column is referenced, during RT3 the "RT3" column is referenced, during RT4 the "RT4" column is referenced, and during RT5, the "RT4" column is referenced. The “RT5” column is referred to, and the RT6 column is referred to during RT6.
同図では、夫々のRT状態毎にリプレイに係る役に関する抽籤値を示し、その他の役に関する抽籤値については省略している。また、同図の「対応する図柄組合せ」欄には、内部当籤役として決定された場合に入賞が許可される図柄の組合せが規定されている。このように夫々の役に対して入賞が許可される図柄の組合せ(表示役)を規定することで、夫々の役と表示役との間に後述の図105に示す対応関係を持たせることができる。なお、本仕様例において必要なことは、図105に示す対応関係を実現可能にすることであり、図104(A)の「対応する図柄組合せ」欄の規定は一例に過ぎず、その他の方法により図105に示す対応関係を実現可能にしてもよい。 In the same figure, the lottery values for the winning combinations related to the replay are shown for each RT state, and the lottery values for the other winning combinations are omitted. Further, in the "corresponding symbol combination" column of the figure, a symbol combination in which a winning is permitted when it is determined as an internal winning combination is defined. In this way, by defining the symbol combination (display combination) in which winning is permitted for each combination, it is possible to provide the correspondence relationship shown in FIG. 105 described later between each combination and the display combination. it can. It is to be noted that what is required in this specification example is that the correspondence relationship shown in FIG. 105 can be realized, and the definition of the “corresponding symbol combination” column in FIG. 104A is merely an example, and other methods The correspondence relationship shown in FIG. 105 may be realized by.
また、本仕様例において「RT1中リプ(「RT1中リプ_123」〜「RT1中リプ_321」)」とはRT1中に内部当籤役として決定され得るリプレイに係る役をいい、同様に「RT2中リプ(「RT2中リプ_123」〜「RT2中リプ_321」)」〜「RT6中リプ(「RT6中リプ_123」〜「RT6中リプ_321」)」とはRT2〜RT6中に内部当籤役として決定され得るリプレイに係る役をいう。 In addition, in this specification example, “RT1 middle lip (“RT1 middle lip_123” to “RT1 middle lip_321”)” refers to a role related to replay that can be determined as an internal winning combination during RT1, and similarly “RT2 middle lip”. Lip (“RT2 Middle Lip_123” to “RT2 Middle Lip_321”)” to “RT6 Middle Lip (“RT6 Middle Lip_123” to “RT6 Middle Lip_321”)” is determined as an internal winning combination during RT2 to RT6. Refers to the possible replay role.
[図柄組合せテーブル]
続いて、図104(B)を参照して、本仕様例のパチスロ1における入賞等に係る図柄の組合せを規定する図柄組合せテーブルについて説明する。なお、本仕様例のパチスロ1の遊技性の説明において、図柄の組合せを構成する図柄の種類は必要がないため、説明及び図示を省略する。図柄組合せテーブルは、複数の図柄の組合せを予め規定しており、これらの図柄の組合せの種別を示すデータを、表示役(入賞作動フラグ)として規定している。
[Design combination table]
Next, with reference to FIG. 104(B), a symbol combination table that defines a symbol combination relating to winning or the like in the pachi-
「図柄組合せA(名称「C_リプレイ」)」は、有効ラインに沿って表示されると、再遊技(リプレイ)の作動が行われる図柄の組合せである。また、「図柄組合せB(名称「C_RT2移行リプ」)」は、有効ラインに沿って表示されると、再遊技(リプレイ)の作動が行われるとともに、RT状態がRT2に移行する図柄の組合せである。また、「図柄組合せC(名称「C_RT3移行リプ」)」は、有効ラインに沿って表示されると、再遊技(リプレイ)の作動が行われるとともに、RT状態がRT3に移行する図柄の組合せである。また、「図柄組合せD(名称「C_RT4移行リプ」)」は、有効ラインに沿って表示されると、再遊技(リプレイ)の作動が行われるとともに、RT状態がRT4に移行する図柄の組合せである。また、「図柄組合せE(名称「C_RT5移行リプ」)」は、有効ラインに沿って表示されると、再遊技(リプレイ)の作動が行われるとともに、RT状態がRT5に移行する図柄の組合せである。また、「図柄組合せF(名称「C_RT6移行リプ」)」は、有効ラインに沿って表示されると、再遊技(リプレイ)の作動が行われるとともに、RT状態がRT6に移行する図柄の組合せである。また、「図柄組合せG(名称「C_RT1移行リプ」)」は、有効ラインに沿って表示されると、再遊技(リプレイ)の作動が行われるとともに、RT状態がRT1に移行する図柄の組合せである。 The "symbol combination A (name "C_replay")" is a combination of symbols for which the replay (replay) operation is performed when displayed along the activated line. In addition, "symbol combination B (name "C_RT2 transition rip")" is a combination of symbols in which, when displayed along the activated line, the replay (replay) operation is performed and the RT state shifts to RT2. is there. In addition, "symbol combination C (name "C_RT3 transition rip")" is a combination of symbols in which, when displayed along the activated line, the replay (replay) operation is performed and the RT state shifts to RT3. is there. In addition, "symbol combination D (name "C_RT4 transition rep")" is a combination of symbols in which the RT state transitions to RT4 while the replay (replay) operation is performed when displayed along the activated line. is there. In addition, "symbol combination E (name "C_RT5 transition rip")" is a combination of symbols in which, when displayed along the activated line, the replay (replay) operation is performed and the RT state shifts to RT5. is there. Further, "symbol combination F (name "C_RT6 transition rip")" is a combination of symbols in which, when displayed along the activated line, the replay (replay) operation is performed and the RT state shifts to RT6. is there. In addition, "symbol combination G (name "C_RT1 transition rep")" is a combination of symbols in which the RT state is shifted to RT1 while the replay (replay) operation is performed when displayed along the activated line. is there.
[内部当籤役と停止操作順序(押し順)と表示役との対応関係]
次に、図105は、本仕様例のパチスロ1における内部当籤役と停止操作順序(打順)と表示役との対応関係を示す表である。同図では、リプレイに係る役に関する内部当籤役と停止操作順序(押し順)と表示役との対応関係を示し、その他の役に関する対応関係については省略している。
[Correspondence between internal winning combination, stop operation sequence (pushing order), and display combination]
Next, FIG. 105 is a table showing a correspondence relationship between an internal winning combination, a stop operation sequence (a batting order), and a display combination in the pachi-
同図に示すように、「RT1中リプ」は、押し順に応じて表示される図柄の組合せが異なり、6択の押し順のうちの特定の押し順で停止操作が行われた場合に「C_RT2移行リプ」に係る図柄の組合せが表示され、6択の押し順のうちの特定の押し順以外の押し順で停止操作が行われた場合に「C_リプレイ」に係る図柄の組合せが表示される。なお、「C_RT2移行リプ」に係る図柄の組合せが表示された場合、RT状態がRT2に移行するため、「RT1中リプ」は、6択の押し順のうちの特定の押し順で停止操作が行われた場合にRT状態がRT1からRT2に移行し、特定の押し順以外の押し順で停止操作が行われた場合にRT状態がRT1のまま維持される。 As shown in the figure, "RT1 middle lip" has a different combination of symbols to be displayed according to the pressing order, and "C_RT2" when the stop operation is performed in a specific pressing order out of the 6 selecting pressing orders. The combination of symbols related to "Transition rip" is displayed, and the combination of symbols related to "C_Replay" is displayed when the stop operation is performed in a pressing order other than the specific pressing order of the six selection pressing orders. .. In addition, when a combination of symbols related to “C_RT2 shift lip” is displayed, the RT state shifts to RT2, and thus, “RT1 middle lip” is a stop operation in a specific push order out of the six selection push orders. When it is performed, the RT state shifts from RT1 to RT2, and when the stop operation is performed in a pushing order other than the specific pushing order, the RT state is maintained at RT1.
「RT2中リプ」〜「RT5中リプ」も同様であり、6択の押し順のうちの特定の押し順で停止操作が行われた場合に「C_RT3移行リプ」〜「C_RT6移行リプ」に係る図柄の組合せが表示され、6択の押し順のうちの特定の押し順以外の押し順で停止操作が行われた場合に「C_リプレイ」に係る図柄の組合せが表示される。すなわち、「RT2中リプ」〜「RT5中リプ」は、6択の押し順のうちの特定の押し順で停止操作が行われた場合にRT状態がRT2〜RT6に移行し、特定の押し順以外の押し順で停止操作が行われた場合にRT状態が現在のRT状態のまま維持される。 The same applies to “RT2 middle lip” to “RT5 middle lip”, and relates to “C_RT3 shift lip” to “C_RT6 shift lip” when the stop operation is performed in a specific push order of the six selection push orders. A combination of symbols is displayed, and a combination of symbols related to “C_Replay” is displayed when a stop operation is performed in a pressing order other than a specific pressing order out of the 6 selection pressing orders. That is, "RT2 middle lip" to "RT5 middle lip" shifts the RT state from RT2 to RT6 when the stop operation is performed in a specific pushing order of the six selection pushing orders, and the specific pushing order When the stop operation is performed in a pressing order other than, the RT state is maintained as the current RT state.
同様に「RT6中リプ」は、6択の押し順のうちの特定の押し順で停止操作が行われた場合に「C_RT1移行リプ」に係る図柄の組合せが表示され、6択の押し順のうちの特定の押し順以外の押し順で停止操作が行われた場合に「C_リプレイ」に係る図柄の組合せが表示される。すなわち、「RT6中リプ」は、6択の押し順のうちの特定の押し順で停止操作が行われた場合にRT状態がRT1に移行し、特定の押し順以外の押し順で停止操作が行われた場合にRT状態が現在のRT状態のまま維持される。なお、「RT6中リプ」は、6択の押し順のうちの特定の押し順で停止操作が行われた場合に「C_リプレイ」に係る図柄の組合せが表示され、6択の押し順のうちの特定の押し順以外の押し順で停止操作が行われた場合に「C_RT1移行リプ」に係る図柄の組合せが表示されることとしてもよい。 Similarly, “RT6 middle rep” displays a combination of symbols relating to “C_RT1 transition rep” when a stop operation is performed in a specific pressing order out of the 6-option pressing order, and the 6-option pressing order is displayed. A combination of symbols related to “C_replay” is displayed when the stop operation is performed in a pressing order other than the specific pressing order. In other words, “RT6 middle rep” means that the RT state shifts to RT1 when the stop operation is performed in a specific pressing order out of the six selection pressing orders, and the stop operation is performed in a pressing order other than the specific pressing order. If so, the RT state remains the current RT state. In addition, "RT6 middle lip" displays a combination of symbols related to "C_Replay" when a stop operation is performed in a specific pressing order among the 6-selecting pressing orders, and the 6-selecting pressing order is included. The combination of symbols related to “C_RT1 transition rep” may be displayed when the stop operation is performed in a pressing order other than the specific pressing order.
このように本仕様例のパチスロ1では、6択に正解した場合にRT状態が他のRT状態に移行することとしているが、RT状態を移行するための択数は6択に限るものではない。すなわち、6択の押し順では、報知が行われない場合であっても偶然に正解することがあり、このような場合には、CZへの移行に関係なくRT状態が先の段階のRT状態に移行してしまう。この点、遊技性(その7)は、CZのスルー回数をRT状態から間接的に把握することで天井制御を実現するものであるが、CZへの移行に関係なくRT状態が進んでしまうと、スルー回数とRT状態とがずれてしまう。なお、スルー回数とRT状態とのずれを許容することで、天井到達時期を変動させることができ好適であるが、以下では、このようなずれを抑制する方法について説明する。
As described above, in the pachi-
一例として、RT状態を移行するための択数を6択以上の択数にしてもよい。択数を調整する方法としては、本仕様例のように押し順に基づき択数を調整する方法に加え、1又は全てのリールに対して特定の位置で停止操作を行うこと(目押し)を要求することで択数を調整することもでき、また、これら押し順と目押しとを組み合わせることで択数を調整することができる。 As an example, the number of choices for shifting the RT state may be six or more. As a method of adjusting the number of choices, in addition to the method of adjusting the number of choices based on the pressing order as in this specification example, it is necessary to perform a stop operation at one or all reels at a specific position (pushing). By doing so, the number of choices can be adjusted, and the number of choices can be adjusted by combining the pressing order and the press.
また、RT状態を移行可能なリプレイに係る役の当籤確率を調整することで、CZへの移行に関係なくRT状態が先の段階のRT状態に移行してしまうことを軽減することとしてもよい。すなわち、本仕様例のパチスロ1では、例えば、RT1中に内部当籤役として決定され得るリプレイに係る役として、RT2に移行可能な「RT1中リプ」のみを設けているが(図104参照)、RT2に移行することのない「通常リプ」も内部当籤役として決定され得るように設定することとしてもよい。このように先の段階のRT状態に移行可能なリプレイに係る役(「RT1中リプ」〜「RT6中リプ」)の当籤確率を下げることで、CZへの移行に関係なくRT状態が先の段階のRT状態に移行してしまうことを軽減することができる。
Further, by adjusting the winning probability of the winning combination relating to the replay that can shift the RT state, it is possible to reduce the shift of the RT state to the RT state of the previous stage regardless of the shift to CZ. .. That is, in the pachi-
また、択数と、先の段階のRT状態に移行可能なリプレイに係る役の当籤確率と、の双方を調整することで、CZへの移行に関係なくRT状態が先の段階のRT状態に移行してしまうこと、すなわち、RT状態が偶然に先の段階に移行してしまうことを軽減することができる。 In addition, by adjusting both the number of choices and the winning probability of the replay that can shift to the RT state of the previous stage, the RT state becomes the RT state of the previous stage regardless of the transition to CZ. It is possible to reduce the transition, that is, the RT state is accidentally transitioned to the previous stage.
[通常区間中有利区間移行抽籤テーブル]
続いて、図106(A)を参照して、通常区間中に行う有利区間への移行抽籤に用いる通常区間中有利区間移行抽籤テーブルについて説明する。通常区間中有利区間移行抽籤テーブルは、有利区間への移行抽籤の抽籤結果(非当籤/当籤)についての抽籤値の情報を規定する。主制御回路90は、通常区間中の各遊技において通常区間中有利区間移行抽籤テーブルを用いて有利区間への移行抽籤を行い、この移行抽籤に当籤すると、通常区間から有利区間に遊技状態を移行する。
なお、同図では、内部当籤役に関わらず一律の抽籤を行うこととしているが、本仕様例において通常区間から有利区間への移行方法は特に問うものではなく、例えば、内部当籤役毎に有利区間への移行抽籤の抽籤結果についての抽籤値の情報を規定することとしてもよい。また、有利区間への移行抽籤の抽籤結果として、非当籤と当籤だけでなく、非当籤、CZへの移行、ARTへの移行などのように移行先の有利区間の種別を規定することとしてもよい。
[Rottery table for shifting to advantageous section during normal section]
Next, with reference to FIG. 106(A), description will be given of the during-normal-interval advantageous-section-shift lottery table used for the lottery during the normal section. The advantageous section transition lottery table in the normal section defines the lottery value information about the lottery result (non-win/win) of the transition lottery to the advantageous section. The
It should be noted that, in the figure, it is assumed that the random lottery is performed regardless of the internal winning combination, but in this specification example, the method of transition from the normal section to the advantageous section does not particularly matter, and for example, it is advantageous for each internal winning combination. The lottery value information about the lottery result of the transfer lottery to the section may be defined. In addition, as the lottery result of the transition lottery to the advantageous zone, not only the non-win and the lottery but also the type of the advantageous zone of the transition destination such as non-win, transition to CZ, transition to ART, etc. may be specified. Good.
[CZ中ART移行抽籤テーブル]
続いて、図106(B)を参照して、CZ中に行うARTへの移行抽籤に用いるCZ中ART移行抽籤テーブルについて説明する。CZ中ART移行抽籤テーブルは、ARTへの移行抽籤の抽籤結果(非当籤/当籤)についての抽籤値の情報を規定する。主制御回路90は、CZ中の各遊技においてCZ中ART移行抽籤テーブルを用いてARTへの移行抽籤を行い、この移行抽籤に当籤すると、CZからARTに遊技状態を移行する。また、主制御回路90は、この移行抽籤に当籤しないままCZの終了条件を満たした場合には、有利区間を終了して、CZから通常区間に遊技状態を移行する。
なお、同図では、内部当籤役に関わらず一律の抽籤を行うこととしているが、本仕様例においてCZからARTへの移行方法は特に問うものではなく、例えば、内部当籤役毎にARTへの移行抽籤の抽籤結果についての抽籤値の情報を規定することとしてもよい。また、ARTへの移行抽籤の抽籤結果として、非当籤と当籤だけでなく、非当籤、初期ゲーム数50のART、初期ゲーム100ゲームのARTなどのように当籤時のARTの種別を規定することとしてもよい。
[ART transfer lottery table during CZ]
Next, with reference to FIG. 106(B), a CZ in-art ART transfer lottery table used in the transfer lottery to ART during CZ will be described. The CZ-art ART transfer lottery table defines lottery value information about the lottery result (non-win/win) of the transfer lottery to ART. The
It should be noted that, in the same figure, the random lottery is performed regardless of the internal winning combination, but the method of transition from CZ to ART is not particularly questioned in this specification example. The lottery value information about the lottery result of the transfer lottery may be defined. Also, as the lottery result of the transition lottery to the ART, not only the non-winning and the winning, but also the non-winning, the ART of the
<本仕様例の制御と別制御との比較>
続いて、図107を参照して、本仕様例の制御と別制御とを比較することで、遊技性(その7)の天井制御について説明する。
<Comparison between control of this specification example and other control>
Subsequently, with reference to FIG. 107, the ceiling control of the game property (No. 7) will be described by comparing the control of this specification example with another control.
同図の比較例1は、CZ終了時に有利区間を終了してしまう場合の制御例である。比較例1では、一般遊技(通常区間)においてCZに当籤すると、通常区間から有利区間(CZ)に遊技状態が移行するが、このCZに失敗すると、CZの終了に伴い、有利区間(CZ)から通常区間(一般)に遊技状態が移行してしまう。このような制御の場合、有利区間(CZ)から通常区間(一般)への移行時に、有利区間に関する情報が全てリセットされてしまう結果、主制御回路90は、この有利区間においてCZに失敗したか否かを把握することができない。
そのため、主制御回路90は、通常区間から有利区間(CZ)に移行する場合、常に、このCZが一回目のCZであるとしか把握することができず、遊技性(その7)のようにCZのスルー回数に基づく天井制御を行うことができない。
Comparative Example 1 in the figure is a control example in the case where the advantageous zone is ended at the end of CZ. In Comparative Example 1, if the CZ is won in the general game (normal zone), the game state shifts from the normal zone to the advantageous zone (CZ). The game state shifts to the normal section (general) from. In the case of such control, when the transition from the advantageous zone (CZ) to the normal zone (general) is performed, all the information about the advantageous zone is reset, so that the
Therefore, when the
続いて、同図の比較例2は、CZ終了時に有利区間を終了することなく、有利区間において一般遊技を行う場合の制御例である。すなわち、比較例2では、有利区間の種別として、一般遊技とCZとARTとを有している。 Subsequently, a comparative example 2 in the figure is a control example in the case where a general game is played in the advantageous section without ending the advantageous section at the end of CZ. That is, in Comparative Example 2, as the types of advantageous sections, there are a general game, CZ, and ART.
比較例2では、一般遊技(通常区間)においてCZに当籤すると、通常区間から有利区間(CZ)に遊技状態を移行し、その後、このCZに失敗すると、CZを終了する一方で遊技状態は有利区間のまま維持する結果、有利区間(CZ)から有利区間(一般)に移行する。このとき、有利区間は終了していないため情報のリセットが行われない結果、主制御回路90は、CZのスルー回数が「1回」である一般遊技(有利区間)であることを把握することができる。続いて、CZのスルー回数が「1回」である一般遊技(有利区間)においてCZに当籤すると、一般遊技(有利区間)からCZ(有利区間)に遊技状態が移行する。このとき、主制御回路90は、「2回目」のCZであることを把握することができる。
In Comparative Example 2, if the CZ is won in the general game (normal zone), the game state is shifted from the normal zone to the advantageous zone (CZ), and if this CZ fails thereafter, the CZ is ended while the game state is advantageous. As a result of maintaining the section as it is, the advantageous section (CZ) shifts to the advantageous section (general). At this time, because the advantageous section has not ended, the information is not reset, and as a result, the
比較例2のように、CZ終了時に有利区間を終了することなく、有利区間において一般遊技を行うことで、CZのスルー回数を把握することができるため、遊技性(その7)のようにCZのスルー回数に基づく天井制御を行うことができる。 As in Comparative Example 2, it is possible to know the number of times the CZ has passed by performing a general game in the advantageous zone without ending the advantageous zone at the end of the CZ. It is possible to perform ceiling control based on the number of through times.
しかしながら、比較例2では、CZ終了後の一般遊技中も有利区間になってしまうため、天井到達に伴うARTの開始時において有利区間が既に長期間にわたり継続してしまっている。ここで、有利区間にはリミッタ(ゲーム数リミッタ)が設けられていることから、ARTの開始時において有利区間が長期間にわたり継続してしまっている場合、天井到達後のARTの開始直後にリミッタが発動してしまう可能性があり、ARTの期間を十分に確保することができない。また、比較例2では、CZ中に加え、CZ終了後の一般遊技中も有利区間になってしまうため、有利区間比率が著しく高くなってしまい、有利区間比率を閾値未満に抑えなければならないというパチスロ機の仕様を満たすことが困難になってしまう。 However, in Comparative Example 2, the advantageous section becomes an advantageous section even during the general game after the end of CZ, so that the advantageous section has already continued for a long time at the start of ART accompanying the ceiling arrival. Here, since the limiter (the number-of-games limiter) is provided in the advantageous section, if the advantageous section has continued for a long time at the start of ART, the limiter is set immediately after the start of ART after reaching the ceiling. May be activated, and it is not possible to secure a sufficient ART period. In addition, in Comparative Example 2, in addition to the CZ, the advantageous section becomes the advantageous section during the general game after the end of the CZ, so that the advantageous section ratio becomes extremely high, and the advantageous section ratio must be kept below the threshold value. It becomes difficult to meet the specifications of the pachi-slot machine.
これに対して、本仕様例の制御(本制御)では、CZ終了時に有利区間を終了するものの、CZの前後においてRT状態を異ならせることでCZのスルー回数を把握可能にして、CZのスルー回数に基づく天井制御を行う。具体的には、本制御では、一般遊技(通常区間)においてCZに当籤すると、通常区間から有利区間(CZ)に遊技状態が移行するが、このCZ中にRT状態を先の段階のRT状態に移行させる。その後、CZに失敗すると、CZの終了に伴い、有利区間(CZ)から通常区間(一般)に遊技状態が移行し、有利区間に関する情報が全てリセットされてしまうが、CZの前後においてRT状態が異なるため、主制御回路90は、CZのスルー回数を把握することができる。
On the other hand, in the control of the present specification example (main control), the advantageous section is ended when the CZ ends, but the RT state is made different before and after the CZ to make it possible to grasp the number of times of the CZ through, and thus the CZ through Performs ceiling control based on the number of times. Specifically, in this control, when the CZ is won in the general game (normal zone), the game state shifts from the normal zone to the advantageous zone (CZ), but during this CZ, the RT state is the RT state of the previous stage. Move to. After that, if the CZ fails, the game state shifts from the advantageous zone (CZ) to the normal zone (general) with the end of the CZ, and all the information regarding the advantageous zone is reset, but the RT state before and after the CZ Since they are different, the
一例として、主制御回路90は、RT1の一般遊技(通常区間)をCZのスルー回数が「0回」の状態であると把握し、RT2の一般遊技(通常区間)をCZのスルー回数が「1回」の状態であると把握する。このようにすることで、その後、CZのスルー回数が天井に到達している状態で、通常区間から有利区間(CZ)に遊技状態が移行すると、CZの成否に関係なくARTに移行可能にするなどの天井到達に伴う特典を付与することができる。言い換えると、本制御では、複数段階のRT状態のうちの所定段階目のRT状態(RT1〜RT4)において有利区間(CZ)に移行した場合、CZに失敗すると、有利区間を終了し通常区間に移行する一方で、複数段階のRT状態のうちの所定段階目よりも先の特定段階目(RT5)において有利区間(CZ)に移行した場合、CZに失敗しても、有利区間を終了することなく、ARTに移行可能にするなどの天井到達に伴う特典を付与することができる。
As an example, the
また、本制御では、CZ終了時に有利区間を終了するため、有利区間の継続期間はCZが終了するたびにリセットされる。その結果、天井到達に伴うARTの開始時において有利区間の継続期間は比較的短期間であり、有利区間のリミッタ(ゲーム数リミッタ)の発動まで十分な期間を確保することができ、天井制御によるARTの期間を十分に確保することができる。 Further, in the present control, the advantageous section is ended when the CZ ends, so the duration of the advantageous section is reset every time the CZ ends. As a result, the duration of the advantageous section is comparatively short at the start of ART accompanying the ceiling arrival, and it is possible to secure a sufficient period until the activation of the limiter (the number of games limiter) of the advantageous section. A sufficient ART period can be secured.
また、本制御では、CZ終了時に有利区間を終了するとともに、通常区間(一般)において所定の確率で当籤する有利区間への移行抽籤に当籤した場合に、通常区間(一般)から有利区間(CZ)に遊技状態を移行する。これにより、天井制御によるARTが開始されるまでに、通常区間(非有利区間)の期間を十分に確保することができ、有利区間比率を下げることができる。すなわち、「5回目」のCZを天井とする場合、通常区間(一般)から有利区間(CZ)への移行が「5回」行われる必要があるが、有利区間への移行抽籤に当籤する確率が、例えば本仕様例のように約1/80の確率(図106(A)参照)である場合、通常区間(一般)の期間として約400ゲーム(=80×5)を確保することができる。その結果、天井到達までの通常区間(非有利区間)の期間を十分に確保することができ、有利区間比率を下げることができる。 Further, in the present control, when the advantageous zone is ended at the end of CZ, and when the lottery for the transition to the advantageous zone in which the regular zone (general) is won with a predetermined probability is won, the normal zone (general) is shifted to the advantageous zone (CZ). ) To the game state. As a result, it is possible to sufficiently secure the period of the normal section (non-advantageous section) and to reduce the advantageous section ratio before the ART by the ceiling control is started. That is, when the “fifth” CZ is used as the ceiling, the transition from the normal section (general) to the advantageous section (CZ) needs to be performed “5 times”, but the probability of winning the lottery for transition to the advantageous section However, for example, when the probability is about 1/80 (see FIG. 106A) as in this specification example, about 400 games (=80×5) can be secured as the period of the normal section (general). .. As a result, the period of the normal section (non-advantageous section) until the ceiling is reached can be sufficiently secured, and the ratio of the advantageous section can be reduced.
すなわち、本制御では、天井到達の直前の有利区間の継続期間を短くすることができ、結果、天井到達の直後にリミッタ(ゲーム数リミッタ)が発動してしまうことを防止できる。また、本制御では、天井到達までの有利区間の総期間を短くすること(天井到達までの非有利区間の総期間を長くすること)ができ、結果、有利区間比率を下げることができる。 That is, with this control, the duration of the advantageous section immediately before the ceiling is reached can be shortened, and as a result, it is possible to prevent the limiter (game number limiter) from being activated immediately after the ceiling is reached. Further, in this control, it is possible to shorten the total period of the advantageous section until reaching the ceiling (longer the total period of the non-advantageous section until reaching the ceiling), and as a result, it is possible to reduce the advantageous section ratio.
また、本制御では、天井到達までの遊技回数も十分に確保することができ、早期に天井に到達してしまうことを防止できる。具体的には、CZは、CZ中の遊技回数が規定数(例えば、100ゲーム)を超えると終了するため、天井到達までのCZの期間として一定量(例えば、500ゲーム(=100×5))を確保することができる。また、上述のように、通常区間(一般)の期間として約400ゲームを確保することができるため、天井到達までの遊技回数として約900ゲームを確保することができる。なお、遊技者によっては、有利区間への移行抽籤に想定以上の確率で当籤してしまうことがあり、この場合には天井到達までの通常区間(一般)の期間を十分に確保することができないものの、この場合においても天井到達までに少なくともCZ中の期間は確保することができるため、必要以上に早期に天井到達になってしまうことを防止でき、遊技者の利益/不利益のバランスを調整することができる。 In addition, with this control, it is possible to secure a sufficient number of games until reaching the ceiling, and it is possible to prevent reaching the ceiling early. Specifically, the CZ ends when the number of games played in the CZ exceeds a prescribed number (for example, 100 games), so a certain amount (for example, 500 games (=100×5)) of the CZ until the ceiling is reached. ) Can be secured. Further, as described above, since it is possible to secure about 400 games as the period of the normal section (general), it is possible to secure about 900 games as the number of games to reach the ceiling. Note that some players may win the transition lottery to the advantageous section with a probability higher than expected, and in this case, it is not possible to sufficiently secure the period of the normal section (general) until the ceiling is reached. However, even in this case, it is possible to secure at least the period during the CZ until the ceiling is reached, so it is possible to prevent the ceiling from reaching the ceiling more quickly than necessary, and adjust the balance of the profit/disadvantage of the player. can do.
(天井短縮制御)
続いて、遊技性(その7)における天井短縮制御の方法について説明する。本仕様例では、CZに移行するとRT状態を1つ先の段階に進めることとしているが、2つ先などのようにRT状態を複数段階の進めることとしてもよい。以下、図108を参照して、CZ移行に伴い、RT状態を複数先の段階まで進めることが可能な制御の一例について説明する。
(Ceiling shortening control)
Subsequently, a method of ceiling shortening control in the game property (No. 7) will be described. In this specification example, the RT state is advanced to the next stage when the CZ is entered, but the RT state may be advanced to multiple stages such as two stages. Hereinafter, with reference to FIG. 108, an example of control capable of advancing the RT state to a plurality of stages ahead with the CZ transition will be described.
図108(A)は、天井短縮制御の例1を説明するための図である。上述のように本仕様例では、「RT1中リプ」〜「RT5中リプ」を、遊技者の停止操作の態様が特定の態様である場合にRT状態を1つ先のRT状態に移行させる図柄の組合せ(「C_RT2移行リプ」〜「C_RT6移行リプ」)を表示可能にしている。これに対して、例1では、「RT1中リプ」〜「RT5中リプ」として複数種類設けることで、天井短縮制御を実現する。なお、図108(A)では、「RT1中リプ」についてのみ示しているが、その他のリプレイに係る役についても同様である。 FIG. 108(A) is a diagram for explaining Example 1 of ceiling shortening control. As described above, in this specification example, "RT1 middle rep" to "RT5 middle rep", the pattern to shift the RT state to the next RT state when the player's stop operation mode is the specific mode The combinations (“C_RT2 transition rep” to “C_RT6 transition rep”) can be displayed. On the other hand, in Example 1, the ceiling shortening control is realized by providing a plurality of types of “RT1 middle rep” to “RT5 middle rep”. Note that, in FIG. 108(A), only the "repeat during RT1" is shown, but the same applies to other combinations relating to replay.
同図に示すように、例1では、「RT1中リプ」として、A系統(「RT1中リプA_123」〜「RT1中リプA_321」)と、B系統(「RT1中リプB_123」〜「RT1中リプB_321」)とを有し、A系統の「RT1中リプ」は、遊技者の停止操作の態様が特定の態様である場合にRT状態を1つ先のRT状態に移行させる図柄の組合せを表示可能とし、B系統の「RT1中リプ」は、遊技者の停止操作の態様が特定の態様である場合にRT状態を2つ先のRT状態に移行させる図柄の組合せを表示可能としている。すなわち、A系統の「RT1中リプ」が内部当籤役として決定され、遊技者の停止操作の態様が特定の態様である場合、「C_RT2移行リプ」に係る図柄の組合せが表示され、RT状態がRT1からRT2に移行する。また、B系統の「RT1中リプ」が内部当籤役として決定され、遊技者の停止操作の態様が特定の態様である場合、「C_RT3移行リプ」に係る図柄の組合せが表示され、RT状態がRT1からRT3に移行する。 As shown in the figure, in Example 1, as the “RT1 middle lip”, the A line (“RT1 middle lip A_123” to “RT1 middle lip A_321”) and the B line (“RT1 middle lip B_123” to “RT1 middle lip”). Lip B_321"), and "RT1 middle lip" of the A system is a combination of symbols for shifting the RT state to the next RT state when the player's stop operation mode is a specific mode. It is possible to display, and the “RT1 middle rep” of the B system can display a combination of symbols for shifting the RT state to the RT state which is two ahead in the case where the mode of the stop operation by the player is a specific mode. That is, if the "RT1 middle lip" of the A system is determined as the internal winning combination and the aspect of the player's stop operation is a specific aspect, the combination of symbols relating to the "C_RT2 transition lip" is displayed, and the RT state is Transition from RT1 to RT2. In addition, when the “RT1 middle lip” of the B system is determined as the internal winning combination, and the mode of the stop operation of the player is a specific mode, the combination of symbols related to the “C_RT3 shift lip” is displayed, and the RT state is Transition from RT1 to RT3.
このような構成において、主制御回路90は、CZにおいて「RT1中リプ」が内部当籤役として決定された場合に、一度だけ特定の停止操作の態様を報知する。その結果、A系統の「RT1中リプ」が内部当籤役として決定された場合には、RT状態が1つ先のRT状態に移行(RT1からRT2に移行)するだけだが、B系統の「RT1中リプ」が内部当籤役として決定された場合には、RT状態が2つ先のRT状態に移行(RT1からRT3に移行)し、天井到達までの期間を短縮することができる。
In such a configuration, the
続いて、図108(B)は、天井短縮制御の例2を説明するための図である。上述のように本仕様例では、通常区間において行う有利区間への移行抽籤において当籤すると、CZに移行し、このCZにおいてRT状態を1つ先の段階に移行する。ここで、例2では、通常区間において行う有利区間への移行抽籤の抽籤結果として、RT移行ナビが1回のCZと、RT移行ナビが2回のCZとを有することとしている。なお、天井短縮制御を実現するためには、RT移行ナビが複数回のCZを有していればよく、例2において2回としているのは一例に過ぎず、3回以上の任意の回数のCZであってもよい。 Subsequently, FIG. 108B is a diagram for explaining a second example of the ceiling shortening control. As described above, in the present specification example, when the lottery for the transition to the advantageous zone performed in the normal zone is won, the state shifts to CZ, and the RT state shifts to the next stage in this CZ. Here, in Example 2, it is assumed that the RT transition navigation has one CZ and the RT transition navigation has two CZ as the lottery result of the lottery for transition to the advantageous section performed in the normal section. In order to realize the ceiling shortening control, it is sufficient that the RT transition navigation has a plurality of CZs, and in Example 2, the number of CZs is two. It may be CZ.
このような構成において、主制御回路90は、通常区間において行う有利区間への移行抽籤において、RT移行ナビが1回のCZに当籤した場合、CZにおいてRT状態を移行するためのナビ(報知)を1回のみ行う。例えば、RT1において、RT移行ナビが1回のCZに当籤した場合、通常区間(RT1)からCZ(RT1)に移行した後、RT状態を移行するためのナビ(報知)を1回行う結果、RT状態が1つ先のRT状態に移行(RT1からRT2に移行)する。
In such a configuration, the
また、主制御回路90は、通常区間において行う有利区間への移行抽籤において、RT移行ナビが2回のCZに当籤した場合、CZにおいてRT状態を移行するためのナビ(報知)を2回行う。例えば、RT1において、RT移行ナビが2回のCZに当籤した場合、通常区間(RT1)からCZ(RT1)に移行した後、RT状態を移行するためのナビ(報知)を2回行う結果、RT状態が2つ先のRT状態に移行(RT1からRT2に移行した後更にRT2からRT3に移行)し、天井到達までの期間を短縮することができる。
In addition, in the lottery for transition to the advantageous section performed in the normal section, the
(その他の遊技性)
以上説明したように、遊技性(その7)では、通常区間から有利区間(CZ)に移行すると、RT状態を1つ先の段階に進めることで、有利区間への移行回数(CZのスルー回数)に基づく天井制御を実現可能にしている。この点、通常区間から有利区間(CZ)に移行した場合にRT状態を1つ先の段階に進めることで、遊技性(その7)に加え、更に以下のような遊技性を実現可能である。
(Other playability)
As described above, in the game (No. 7), when the normal section shifts to the advantageous section (CZ), the RT state is advanced to the next stage, so that the number of transitions to the advantageous section (the number of CZ throughs) is increased. ) Based ceiling control. In this regard, by advancing the RT state to the next stage when the normal section is shifted to the advantageous section (CZ), in addition to the game characteristic (No. 7), the following game characteristic can be realized. ..
上述した仕様例では、RT1〜RT5においてリプレイに係る役の当籤確率を略同一の確率としているが、それぞれのRT状態において当該当籤確率を異ならせることで、通常区間から有利区間(CZ)に移行するまでの期間の遊技の遊技性を多様化することができる。一例として、RT状態の段階が進むごとにリプレイに係る役の当籤確率を高くすることで、RT状態が進み天井に近づくほどメダルを投入することなく有利区間に移行させることができ、また、特定のRT状態においてリプレイに係る役の当籤確率を高くすることで、天井到達までの期間のうちの特定の段階においてメダルを投入することなく有利区間に移行させることができる。
ここで、通常区間における遊技を「周期中の遊技」とし、通常区間から有利区間(CZ)に移行した回数を「周期回数」として捉えた場合、RT状態毎にリプレイに係る役の当籤確率を異ならせることで、周期回数に応じて周期中の遊技の遊技性を異ならせることができる。
In the above-described specification example, the winning probabilities of the replay related roles are set to be substantially the same in RT1 to RT5, but by changing the winning probabilities in each RT state, the normal section is shifted to the advantageous section (CZ). It is possible to diversify the game playability of the game up to. As an example, by increasing the winning probability of the role relating to the replay as the stage of the RT state progresses, it is possible to shift to the advantageous section without throwing medals as the RT state progresses and closer to the ceiling, and In the RT state, by increasing the winning probability of the combination relating to the replay, it is possible to shift to the advantageous section without inserting a medal at a specific stage during the period until the ceiling is reached.
Here, when the game in the normal section is referred to as a "game during a cycle" and the number of times of transition from the normal section to the advantageous section (CZ) is taken as a "cycle number", the winning probability of the winning combination of the replay for each RT state is calculated. By making them different, it is possible to make the amusement of the game during the cycle different according to the number of cycles.
また、上述した仕様例では、CZ中に行うARTへの移行抽籤について特に規定していないが、CZ中に行うARTへの移行抽籤を、RT状態を参照して行うことで、遊技性を多様化することができる。一例として、RT状態の段階が進むごとにARTへの移行抽籤に当籤する確率を高くすることで、RT状態が進み天井に近づくほどメダルを投入することなくARTに移行し易くすることができ、また、特定のRT状態においてARTへの移行抽籤に当籤する確率を高くすることで、天井到達までの期間のうちの特定の段階においてARTに移行し易くすることができる。
このようにすることで、周期回数に応じて、周期到達後のCZの遊技性を異ならせることができる。
In addition, in the above-mentioned specification example, the lottery for the transition to the ART performed during the CZ is not particularly specified, but the lottery for the transition to the ART performed during the CZ is performed with reference to the RT state, so that the game is diversified. Can be transformed. As an example, by increasing the probability of winning the lottery for transitioning to ART each time the stage in the RT state progresses, it is possible to facilitate the transition to ART without throwing a medal as the RT state progresses and approaches the ceiling, Further, by increasing the probability of winning the lottery for transition to ART in a specific RT state, it is possible to facilitate the transition to ART at a specific stage in the period until reaching the ceiling.
By doing so, the playability of the CZ after the arrival of the cycle can be changed according to the number of cycles.
また、上述した仕様例では、CZに成功した場合の恩恵について特に規定していないが、CZに成功した場合の恩恵を、RT状態を参照して決定することで、遊技性を多様化することができる。一例として、RT状態の段階が進むごとに恩恵を大きくすることで、RT状態が進み天井に近づくほどCZ成功時の恩恵を大きくすることができ、また、特定のRT状態において恩恵を大きくすることで、天井到達までの期間のうちの特定の段階においてCZに成功した場合、大きな恩恵を付与することができる。
このようにすることで、周期回数に応じて、周期的に行うCZの恩恵を異ならせることができる。
In addition, in the above-mentioned specification example, although the benefit in the case of succeeding in CZ is not particularly specified, the benefit in the case of succeeding in CZ is determined by referring to the RT state, thereby diversifying the game playability. You can As an example, by increasing the benefit as the RT state progresses, the benefit at the time of CZ success can be increased as the RT state progresses and the ceiling is approached, and the benefit can be increased in a specific RT state. Then, if the CZ is successful at a specific stage of the period until the ceiling is reached, a great benefit can be given.
By doing so, it is possible to vary the benefit of CZ that is periodically performed according to the number of cycles.
[主制御基板及び副制御基板が有する各種機能]
以上、本仕様例のパチスロ1の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その7)について説明した。続いて、パチスロ1の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その7)を発揮する際の主制御回路90及び副制御回路200が有する各種機能について説明する。
[Various functions of the main control board and the sub control board]
Heretofore, another example (No. 7) of the playability (game specification) of the pachi-
主制御回路90は、スタートスイッチ6Sやストップスイッチ7Sと接続され、図1に示す遊技の進行を制御するため、遊技制御手段として機能する。また、リール3L、3C、3R及び表示窓4は、可変表示手段として機能する。
The
また、主制御回路90は、現在のRT状態から他のRT状態にRT状態を移行可能であり、また、CZ中にRT状態を移行させるために必要な情報、具体的には、RT状態を現在のRT状態よりも先の段階のRT状態に移行させるために必要な情報を報知可能であるため、主制御回路90は、RT制御手段及び報知手段として機能する。
Further, the
また、主制御回路90は、通常区間において有利区間への移行抽籤に当籤すると、有利区間のCZに遊技状態を移行可能であり、また、CZにおいてARTへの移行抽籤に当籤すると、有利区間のARTに遊技状態を移行可能、かつ、CZにおいて現在のRT状態よりも先の段階のRT状態に移行させた後(又は現在のRT状態よりも先の段階のRT状態に移行させるための報知がされた後)にCZの終了条件が満たされると、有利区間を終了して、CZから通常区間に遊技状態を移行するため、主制御回路90は、第1状態制御手段及び第2状態制御手段として機能する。このとき、主制御回路90は、CZ移行時のRT状態がRT1〜RT4である場合には(所定段階目のRT状態におけるCZでは)、ARTへの移行条件を満たすことなく終了条件が満たされると、CZから通常区間に遊技状態を移行する一方で、CZ移行時のRT状態がRT5である場合には(特定段階目のRT状態におけるCZでは)、ARTへの移行条件が満たされない場合であっても、天井制御によりCZからARTに遊技状態を移行する。
Further, the
なお、主制御回路90は、CZ移行時のRT状態がRT1〜RT4である場合には(所定段階目のRT状態におけるCZでは)、CZにおいて現在のRT状態よりも先の段階のRT状態に移行させた後(又は現在のRT状態よりも先の段階のRT状態に移行させるための報知がされた後)に所定期間(100ゲーム)が経過すると、CZから通常区間に遊技状態を移行する一方で、CZ移行時のRT状態がRT5である場合には(特定段階目のRT状態におけるCZでは)、ARTへの移行条件が満たされることなく所定期間(100ゲーム)又は特定期間(30ゲーム)が経過すると、CZからARTに遊技状態を移行する。
When the RT state at the time of CZ transition is RT1 to RT4 (in the CZ in the RT state of the predetermined stage), the
また、パチスロ1は、全遊技期間における有利区間の期間(有利区間比率)が所定割合になるように遊技状態が制御され、主制御回路90は、所定確率で当籤する有利区間への移行抽籤に当籤すると、有利区間のCZに遊技状態を移行する。
Further, the pachi-
[遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その8)]
続いて、図109を参照して、本実施形態に係るパチスロ1において実装可能な遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その8)について説明する。図109は、遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その8)における制御の概要を示す図である。
[Another example of playability (game specifications) (Part 8)]
Next, with reference to FIG. 109, another example (No. 8) of the playability (game specification) that can be mounted in the pachi-
(パチスロの仕様例)
遊技性(その8)を実現可能なパチスロの仕様例では、パチスロ1は、遊技者にとって相対的に不利な通常遊技と遊技者にとって相対的に有利な有利状態とを有する。なお、有利状態の種別は任意であり、例えば、ATやARTなどを用いることができる。主制御回路90は、一般状態において有利状態への移行条件を満たすと、遊技状態を一般状態から有利状態に移行する、通常制御による有利状態への移行が可能であるとともに、一般状態において天井に到達した場合に遊技状態を一般状態から有利状態に移行する、天井制御による有利状態への移行が可能である。
(Example of pachislot specifications)
In the specification example of the pachi-slot capable of realizing the game property (No. 8), the pachi-
なお、本仕様例において通常制御による有利状態への移行方法は任意であり、主制御回路90は、例えば、一般状態において決定された内部当籤役に基づき有利状態への移行抽籤を行い、この移行抽籤に当籤した場合に、通常制御による有利状態への移行を行うこととしてもよい。また、本仕様例において天井制御による有利状態への移行方法も任意であり、主制御回路90は、例えば、上述の遊技性(その7)のようにCZのスルー回数に基づき天井制御による有利状態への移行を行うこととしてもよく、また、有利状態に移行することなく一般状態のまま行われた遊技回数が所定回数に達した場合に天井制御による有利状態への移行を行うこととしてもよい。すなわち、主制御回路90は、一般状態に関連して計数される数値情報(例えば、スルー回数やゲーム数)が天井閾値に達すると、遊技状態を有利状態に移行する天井制御を行うことができる。
In this specification example, the method of shifting to the advantageous state by the normal control is arbitrary, and the
また、主制御回路90は、有利状態において有利状態の終了条件を満たすと、有利状態を終了して、遊技状態を有利状態から一般状態に移行する。なお、本仕様例において有利状態の終了条件、言い換えると、有利状態の継続期間を管理する方法は任意であり、例えば、ゲーム数により有利状態の継続期間を管理することとしてもよく、また、ナビ回数や差枚数等により有利状態の継続期間を管理することとしてもよい。すなわち、主制御回路90は、有利状態の継続期間を定める数値情報(例えば、ゲーム数やナビ回数や差枚数)を計数可能なカウンタを有し、有利状態中の遊技の結果に応じてこの数値情報を更新(例えば、1ゲーム毎にゲーム数を1更新)する。そして、主制御回路90は、更新の結果、この数値情報が終了閾値(例えば、残りゲーム数が0)に達すると、有利状態の終了条件を満たしたとして、有利状態を終了して、遊技状態を有利状態から一般状態に移行する。
Further, the
(遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その8)の概要)
このような仕様例のパチスロ1において、遊技性(その8)は、天井到達時の恩恵に関するものである。従来のパチスロでは、天井到達時に付与する恩恵を通常時よりも大きくしていたが、天井到達時の恩恵が大きすぎると遊技者が遊技に過度にのめり込んでしまう恐れがあるため、好ましくない。一方で、天井に到達するには、遊技者にとって不利な一般状態において長い期間の遊技を行わなければならないため、せっかく天井まで到達したにもかかわらず早期に有利状態が終了してしまったのでは、遊技者の遊技意欲が削がれてしまう。そこで、遊技性(その8)では、通常制御により移行した有利状態と天井制御におり移行した有利状態との間で、有利状態1回当たりの遊技者の利益の期待値は同一(又は略同一)にしつつも、天井到達に伴い大きな恩恵が付与されたと遊技者が感じるように制御する。
(Outline of other examples of game play (game specifications) (part 8))
In the pachi-
ここで、有利状態1回当たりの遊技者の利益の期待値は、有利状態中の単位遊技当たりの利益の期待値(メダル増加の傾斜値)と、有利状態1回当たりの有利状態の継続期間の期待値と、から求めることができる。
有利状態1回当たりの利益の期待値=単位遊技当たりの利益×継続期間の期待値
遊技性(その8)では、有利状態1回当たりの有利状態の継続期間の期待値に着目して以下の制御を行う。なお、以下では、有利状態の継続期間としてゲーム数を用いて説明する。
Here, the expected value of the profit of the player per advantageous state is the expected value of the profit per unit game during the advantageous state (the inclination value of the medal increase) and the duration of the advantageous state per advantageous state once. It can be calculated from the expected value of.
Expected value of profit per advantageous state = profit per unit game × expected value of duration In the game (No. 8), pay attention to the expected value of duration of advantageous state per advantageous state Take control. In the following description, the number of games is used as the duration of the advantageous state.
ゲーム数を有利状態の継続期間として用いる場合、有利状態の継続期間は、有利状態の開始時に決定される初期ゲーム数と、有利状態中に上乗せされる上乗せゲーム数(言い換えると、有利状態中の上乗せ期待度)とにより決まる。なお、上乗せとは、有利状態の継続期間が延長されるように制御することであり、主制御回路90は、有利状態において上乗せ条件を満たした場合に、有利状態の継続期間が延長されるように有利状態の継続期間を定める数値情報を更新する。
When the number of games is used as the duration of the advantageous state, the duration of the advantageous state includes the initial number of games determined at the start of the advantageous state and the number of additional games to be added during the advantageous state (in other words, during the advantageous state. Expected to be added) and It should be noted that the addition is to control so that the duration of the advantageous state is extended, and the
図109(A)に示すように、遊技性(その8)では、主制御回路90は、通常制御により有利状態(例えば、ART)に移行した場合、同図の「通常ART」に示すように初期ゲーム数として少ないゲーム数を設定する一方で、有利状態中の上乗せ期待度を高くし、反対に、天井制御により有利状態に移行した場合、同図の「天井ART」に示すように初期ゲーム数として多いゲーム数を設定する一方で、有利状態中の上乗せ期待度を低くする。このとき、主制御回路90は、有利状態1回当たりの遊技者の利益の期待値が、通常制御により移行した有利状態と天井制御により移行した有利状態とで同一(又は略同一)となるように、初期ゲーム数の設定及び(又は)上乗せ期待度を制御する。なお、有利状態中の単位遊技当たりの利益の期待値は、通常制御により移行した有利状態と天井制御により移行した有利状態とで同一であるため、有利状態1回当たりの遊技者の利益の期待値が同一(又は略同一)とは、通常制御により移行した有利状態の継続期間の期待値と、天井制御により移行した有利状態の継続期間の期待値とが同一(又は略同一)であることと同じである。
As shown in FIG. 109(A), in the game property (No. 8), when the
このようにすることで、有利状態1回当たりの遊技者の利益の期待値を通常制御により移行した有利状態と天井制御により移行した有利状態とで略同一としつつも、両者の遊技性を異ならせることができる。例えば、通常制御により移行した有利状態は、初期ゲーム数が少ないため開始後すぐに終了してしまう可能性があるものの、上乗せ期待度が高いため有利状態の継続期間にわたり継続する可能性もある。一方で、天井制御により移行した有利状態は、初期ゲーム数が多いため開始後すぐには終了しないものの、上乗せ期待度が低いため有利状態の継続期間の上振れも小さい。すなわち、通常制御により移行した有利状態は、継続期間の振れ幅が大きく、天井制御により移行した有利状態は反対に、継続期間の振れ幅が小さく、継続期間の長さが安定する。 By doing this, the expected value of the player's profit per advantageous state is almost the same in the advantageous state shifted by the normal control and the advantageous state shifted by the ceiling control, but if the game characteristics of the two are different. Can be made. For example, the advantageous state transitioned by the normal control may end immediately after the start because the number of initial games is small, but there is a possibility that the advantageous state may continue for the duration of the advantageous state because of high expectation of addition. On the other hand, the advantageous state transitioned by the ceiling control does not end immediately after the start because the number of initial games is large, but since the degree of expectation of addition is low, the upward swing of the advantageous state is small. That is, the advantageous state transitioned by the normal control has a large swing width of the continuation period, while the advantageous state transitioned by the ceiling control has a small swing width of the continuation period and the length of the continuation period is stable.
続いて、図109(B)は、遊技性(その8)の制御例を示す。図109(B)では、有利状態中の単位遊技当たりの利益の期待値、言い換えると、有利状態中の1ゲーム当たりの純増枚数を「2枚」としている。本制御例において、通常制御により移行した有利状態は、初期ゲーム数の平均が50ゲームであり、かつ、有利状態1回当たりの遊技者の利益の期待値が約500枚になるように有利状態中の上乗せ期待度が設定されている。 Subsequently, FIG. 109(B) shows an example of control of game characteristic (No. 8). In FIG. 109(B), the expected value of profit per unit game in the advantageous state, in other words, the net additional number per game in the advantageous state is “2”. In this control example, the advantageous state transitioned by the normal control is such that the average number of initial games is 50 and the expected value of the player's profit per advantageous state is about 500. The degree of expectation for addition to the inside is set.
このように遊技性(その8)では、天井制御により有利状態に移行した場合、初期ゲーム数を多くする一方で、上乗せ期待度を下げることで、有利状態1回当たりの遊技者の利益の期待値を通常制御により移行した有利状態と同一(又は略同一)にする。遊技者にとってみれば、付与される利益の期待値は変わらないものの、天井到達時には安定して一定期間の有利状態を行うことができ、早期に有利状態が終了してしまうことがないため、遊技者の遊技意欲の低下を抑制することができる。一方で、天井制御により移行した有利状態では上乗せ性能が低下するため、遊技者は敢えて天井を目指す必要はなく、遊技者が遊技に過度にのめり込んでしまうことを防止することができる。すなわち、遊技性(その8)では、天井到達時にあたかも大きな恩恵があるように感じさせることができる一方で、継続期間の初期値に対して上乗せ性能を調整することで、有利状態1回当たりの遊技者の利益の期待値を天井時と通常時とで合わせることができ、過度なのめり込みを防止できる。 As described above, in the playability (No. 8), when the state is shifted to the advantageous state by the ceiling control, the number of initial games is increased, while the expectation of addition is lowered to expect the profit of the player per advantageous state. The value is made the same (or almost the same) as the advantageous state shifted by the normal control. For the player, although the expected value of the profit to be given does not change, the advantage state can be stably performed for a certain period when the ceiling is reached, and the advantage state does not end early, so the game It is possible to suppress a decrease in the player's willingness to play. On the other hand, in the advantageous state transitioned by the ceiling control, the addition performance deteriorates, so that it is not necessary for the player to aim for the ceiling, and it is possible to prevent the player from being overly absorbed in the game. That is, in the playability (No. 8), it is possible to feel as if there is a great benefit when the ceiling is reached, but by adjusting the additional performance with respect to the initial value of the duration, the advantageous state per It is possible to match the expected value of the player's profit between the time of the ceiling and the time of the normal time, and it is possible to prevent the excessive depression.
[主制御基板及び副制御基板が有する各種機能]
以上、本仕様例のパチスロ1の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その8)について説明した。続いて、パチスロ1の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その8)を発揮する際の主制御回路90及び副制御回路200が有する各種機能について説明する。
[Various functions of the main control board and the sub control board]
Heretofore, another example (No. 8) of the playability (game specification) of the pachi-
主制御回路90は、スタートスイッチ6Sやストップスイッチ7Sと接続され、図1に示す遊技の進行を制御するため、遊技制御手段として機能する。また、リール3L、3C、3R及び表示窓4は、可変表示手段として機能する。
The
また、主制御回路90は、一般状態において通常制御又は天井制御による有利状態への移行が可能であるため、主制御回路90は、状態制御手段として機能する。また、主制御回路90は、有利状態の継続期間を定める数値情報を計数可能であるとともに、この数値情報を有利状態中の遊技の結果に応じて更新し、更新の結果、この数値情報が終了閾値に達すると、有利状態を終了可能であるため、主制御回路90は、継続期間計数手段及び終了制御手段として機能する。
Further, since the
また、主制御回路90は、有利状態に移行する場合に、有利状態の継続期間の初期値を設定可能であるとともに、有利状態中に有利状態の継続期間が延長されるように上乗せ制御が可能であるため、主制御回路90は、初期期間設定手段及び上乗せ制御手段として機能する。このとき、主制御回路90は、通常制御により移行した有利状態では、継続期間の初期値を低く設定するとともに、上乗せ期待度が高くなるように制御する一方で、天井制御により移行した有利状態では、継続期間の初期値を高く設定するとともに、上乗せ期待度が低くなるように制御する。特に、主制御回路90は、通常制御により移行した有利状態1回当たりの継続期間の期待値と、天井制御により移行した有利状態1回当たりの継続期間の期待値とが同一(又は略同一)になるように、継続期間の初期値及び上乗せ期待度を制御する。
Further, the
[遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その9)]
続いて、図110を参照して、本実施形態に係るパチスロ1において実装可能な遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その9)について説明する。図110は、遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その9)における制御の概要を示す図である。
[Another example of playability (game specification) (9)]
Next, with reference to FIG. 110, another example (No. 9) of the playability (game specification) that can be mounted in the pachi-
(遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その9)の概要)
遊技性(その9)は、MB状態を貫通するMB貫通型RTとMB状態とを用いた遊技性に関するものである。本仕様例では、MB状態中の表示役(すなわち、MB状態において表示される図柄の組合せ)として、3枚のメダルの払い出しが行われる表示役Aと、9枚のメダルの払い出しが行われる表示役Bとを有し、MB状態中のRT状態に応じて表示結果を異ならせることで、MB状態の有利度合いをRT状態に応じて異ならせる。なお、本仕様例においてMB貫通型RTとは、MB状態の前後及びMB状態中にRT状態を移行させることなく現在のRT状態のまま維持するRT制御をいう。
(Outline of other examples of playability (game specifications) (Part 9))
The game play (No. 9) relates to the game play using the MB penetration type RT penetrating the MB status and the MB status. In this specification example, as a display combination during the MB state (that is, a combination of symbols displayed in the MB state), a display combination A in which three medals are paid out and a display in which nine medals are paid out By having the combination B and changing the display result according to the RT state in the MB state, the advantage degree of the MB state is changed according to the RT state. In this specification example, the MB penetration type RT refers to RT control that maintains the current RT state without shifting the RT state before and after the MB state and during the MB state.
図110(A)は、本仕様例のパチスロ1における遊技状態の遷移フローである。図110(A)に示すように、本仕様例では、主制御回路90は、非MB状態においてMBに入賞すると、MBの作動を開始し、MB状態に遊技状態を移行する(言い換えると、主制御回路90は、停止制御の結果、MB役に応じた結果表示が導出されると、ボーナス遊技を開始する)。また、主制御回路90は、MB状態において終了条件を満たすと、MBの作動を終了して、非MB状態に遊技状態を移行する(言い換えると、主制御回路90は、ボーナス遊技の終了条件を満たすと、ボーナス遊技を終了する)。なお、MB状態の終了条件は、規定枚数を超えるメダルが払い出されることである。
FIG. 110(A) is a game state transition flow in the pachi-
また、本仕様例のパチスロ1では、リプレイに係る役が内部当籤役として決定される確率が異なるRT状態として、複数のRT状態を有する。ここで、遊技性(その9)では、複数のRT状態として、特定のリプレイ役(後述のリプレイA又はリプレイB)の当籤確率が異なる複数のRT状態を有していれば足りるものの、本仕様例では、複数のRT状態として低RTと高RTとを有するものとする。
In addition, the pachi-
図110(B)に示すように、低RTは、リプレイに係る役が内部当籤役として決定される確率が高RTに比較して低いRT状態であり、かつ、リプレイAが内部当籤役として決定される確率が高RTに比較して高く、リプレイBが内部当籤役として決定される確率が高RTに対して低いRT状態である。また、高RTは、リプレイに係る役が内部当籤役として決定される確率が低RTに比較して高いRT状態であり、かつ、リプレイAが内部当籤役として決定される確率が低RTに比較して低く、リプレイBが内部当籤役として決定される確率が低RTに対して高いRT状態である。なお、図110(B)に示す例では、低RTではリプレイAにのみ当籤し、リプレイBに当籤しないこととしているが、これに限るものではなく、低RTにおいてリプレイBに所定確率で当籤することとしてもよい。同様に、高RTではリプレイBにのみ当籤し、リプレイAに当籤しないこととしているが、これに限るものではなく、低RTにおいてリプレイAに所定確率で当籤することとしてもよい。 As shown in FIG. 110(B), a low RT is an RT state in which the probability of a winning combination relating to replay being determined as an internal winning combination is lower than that of a high RT, and Replay A is determined as an internal winning combination. The probability of being played is higher than that of high RT, and the probability that replay B is determined as an internal winning combination is low with respect to high RT. In addition, a high RT is an RT state in which the probability of a replay combination being determined as an internal winning combination is higher than that of a low RT, and a probability of Replay A being determined as an internal winning combination is low. Therefore, the probability that Replay B will be determined as the internal winning combination is high with respect to low RT. In the example shown in FIG. 110(B), only the replay A is won and the replay B is not won in the low RT, but the present invention is not limited to this, and the replay B is won with a predetermined probability in the low RT. It may be that. Similarly, in the high RT, only the replay B is won and the replay A is not won, but the present invention is not limited to this, and the replay A may be won with a predetermined probability at the low RT.
図110(A)に戻り、主制御回路90は、非MB状態においてRT状態の移行条件を満たすと、RT状態を低RTから高RT(又は高RTから低RT)に移行する。なお、本仕様例においてRT状態の移行条件は任意であり、例えば、停止制御の結果としてRT状態を移行する移行図柄が表示されることを移行条件としてもよく、また、RT状態において所定回数の遊技が行われることを移行条件としてもよい。また、これら移行条件は、複数のRT状態のそれぞれにおいて異ならせることとしてもよく、また、同一の移行条件としてもよい。ただし、主制御回路90は、非MB状態においてMBに入賞しMBの作動を開始した場合、MB状態において終了条件を満たしMBの作動を終了した場合、及びMB状態の最中は、RT状態を移行させることなく現在のRT状態のまま維持する(言い換えると、主制御回路90は、ボーナス遊技の前後、及びボーナス遊技の最中はRT状態を移行させることなく現在のRT状態を維持する一方で、非ボーナス遊技において特定の移行条件を満たした場合に現在のRT状態から他のRT状態にRT状態を移行する)。
Returning to FIG. 110A, when the transition condition of the RT state is satisfied in the non-MB state, the
(MB状態中の当籤役と停止制御)
続いて、図110(B)(C)を参照して、MB状態中の当籤役と停止制御について説明する。本仕様例において、主制御回路90は、MB状態中は、全ての小役を内部当籤役として決定するとともに、リプレイに係る役に関してのみ個別に抽籤しておき、全ての小役を内部当籤役として決定する際に個別に抽籤しておいたリプレイの種別に応じて停止制御を異ならせる。一例として、図110(B)に示すように、リプレイに係る役として、リプレイA及びリプレイBのみを有しているとすると、MB状態中は、リプレイA及びリプレイBの何れも内部当籤役として決定されない場合の内部当籤役が「全ての小役」となり、リプレイAが内部当籤役として決定された場合の内部当籤役が「全ての小役+リプレイA」となり、リプレイBが内部当籤役として決定された場合の内部当籤役が「全ての小役+リプレイB」となる。
(Winning combination and stop control in MB state)
Subsequently, a winning combination and stop control in the MB state will be described with reference to FIGS. In the present specification example, the
そして、主制御回路90は、MB状態中の内部当籤役が「全ての小役+リプレイB」である場合(リプレイBに当籤の場合)には多くのメダルが払い出されることになる図柄の組合せ(表示役B)が導出されるようにリールの停止制御を行い、MB状態中の内部当籤役が「全ての小役」である場合(リプレイA及びリプレイBの何れも非当籤の場合)及びMB状態中の内部当籤役が「全ての小役+リプレイA」である場合(リプレイAに当籤の場合)には、少ないメダルが払い出されることになる図柄の組合せ(表示役A)が導出されるようにリールの停止制御を行う。
And the
このようにすることで、図110(D)に示すように、低RT中のMB状態を現状維持のMBとしつつも、高RT中のMB状態をメダルが増加するMBとすることができる。例えば、高RT中に遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知するART機の場合、非ART中のMBを現状維持のMBとしつつも、ART中のMBをメダルが増加するMBとすることができる。すなわち、遊技性(その9)では、MB状態中のメダル増加の傾斜値をRT状態に応じて異ならせることができる。 By doing so, as shown in FIG. 110(D), it is possible to set the MB state during the low RT to the MB that maintains the current state, while changing the MB state during the high RT to the MB in which medals increase. For example, in the case of an ART machine which informs a player of advantageous stop operation information during a high RT, while the non-ART MB is the current state MB, the ART MB is the MB whose medal increases. You can That is, in the playability (No. 9), it is possible to make the inclination value of the medal increase in the MB state different depending on the RT state.
なお、遊技性(その9)は、MB状態中のメダル増加の傾斜値をRT状態に応じて異ならせることができればよく、低RT中のMB状態を現状維持のMB、高RT中のMB状態をメダルが増加するMBとすることに限るものではない。例えば、低RT中のMB状態をメダルが第1量増加するMBとし、高RT中のMB状態をメダルが第1量よりも多い第2量増加するMBとするものであってもよく、また、例えば、低RT中のMB状態をメダルが第3量減少するMBとし、高RT中のMB状態をメダルが第3量よりも少ない多い第4量減少するMB(又は現状維持のMB)とするものであってもよく、任意である。このような制御は、表示役A及び表示役Bが導出された場合に払い出すメダルの枚数と、MB状態中の単位遊技に用いるメダルの枚数との関係により任意に設計することができる。 It should be noted that the playability (No. 9) only needs to be able to change the inclination value of the medal increase in the MB state according to the RT state, the MB state in the low RT is the current state MB, and the MB state in the high RT is the MB state. Is not limited to the MB in which medals increase. For example, the MB state during the low RT may be the MB in which the medal increases the first amount, and the MB state during the high RT may be the MB in which the medal increases by the second amount larger than the first amount. For example, the MB state during low RT is defined as an MB in which medals are reduced by a third amount, and the MB state during high RT is defined as an MB in which medals are reduced by a fourth amount that is less than the third amount (or a current state MB). However, it is optional. Such control can be arbitrarily designed according to the relationship between the number of medals to be paid out when the display combination A and the display combination B are derived, and the number of medals used for the unit game in the MB state.
そのため、遊技性(その9)では、主制御回路90が、MB状態中の内部当籤役が「全ての小役」である場合(リプレイA及びリプレイBの何れも非当籤の場合)に、今回の遊技に用いたメダルと同数のメダル、又は今回の遊技に用いたメダルよりも少ないメダルが払い出される表示役Aを導出可能であり、MB状態中の内部当籤役が「全ての小役+リプレイA」である場合(リプレイAに当籤の場合)に、今回の遊技に用いたメダルと同数のメダル、又は今回の遊技に用いたメダルよりも少ないメダルが払い出される表示役Aを導出可能であり、MB状態中の内部当籤役が「全ての小役+リプレイB」である場合(リプレイBに当籤の場合)に、今回の遊技に用いたメダルよりも多いメダルが払い出される表示役Bを導出可能であることを含むものである。
Therefore, in the playability (No. 9), when the
また、遊技性(その9)は、MB状態中のリプレイに係る役の当籤確率をRT状態に応じて異ならせるとともに、MB状態中のリプレイに係る役の当否に応じて、リール制御(表示役)及びメダルの払出枚数を異ならせることで、MB状態中のメダル増加の傾斜値をRT状態に応じて異ならせるものであり、上述のリール制御とメダルの払い出し枚数との関係も任意である。すなわち、遊技性(その9)は、もっとも単純には、MB状態中の内部当籤役が「全ての小役」である場合と、MB状態中の内部当籤役が「全ての小役+リプレイに係る役」である場合とで、導出される表示役(結果表示)を異ならせ、結果、メダルの払い出し枚数(すなわち、付与する遊技用価値の数量)を異ならせることとすればよい。このような制御においても、RT状態に応じてリプレイに係る役の当籤確率が異なるため、MB状態中のメダル増加の傾斜値をRT状態に応じて異ならせることができる。 In addition, the playability (No. 9) is such that the winning probability of the winning combination related to the replay in the MB state is changed according to the RT status, and the reel control (display winning combination is performed depending on whether the winning combination related to the replay in the MB state is valid or not. ) And the payout number of medals are made different so that the inclination value of the medal increase in the MB state is made different according to the RT state, and the relationship between the reel control and the payout number of medals is arbitrary. That is, the simplest playability (No. 9) is when the internal winning combination in the MB state is "all small wins" and when the internal winning combination in the MB state is "all small wins + replays". The derived display combination (result display) may be made different depending on the case of “related combination”, and as a result, the payout number of medals (that is, the number of gaming values to be given) may be different. Even in such control, since the winning probability of the winning combination relating to the replay varies depending on the RT state, it is possible to change the inclination value of the medal increase during the MB state depending on the RT state.
また、上述の例では、主制御回路90は、MB状態中の内部当籤役が「全ての小役」である場合と、「全ての小役+リプレイA」である場合とで同じ表示役Aを導出可能に制御することとしているが、これに限るものではない。すなわち、主制御回路90は、MB状態中の内部当籤役が「全ての小役」である場合に、表示役Bを導出可能に制御し、MB状態中の内部当籤役が「全ての小役+リプレイA」である場合に、表示役Aを導出可能に制御することとしてもよく、反対に、MB状態中の内部当籤役が「全ての小役」である場合に、表示役Aを導出可能に制御し、MB状態中の内部当籤役が「全ての小役+リプレイA」である場合に、表示役Bを導出可能に制御することとしてもよい。また、MB状態中の内部当籤役が「全ての小役」である場合と、「全ての小役+リプレイA」である場合とで異なる表示役とする場合の表示役も、MB状態中の内部当籤役が「全ての小役+リプレイB」である場合の表示役Bに限られるものではなく、メダルの払い出し枚数が異なる他の表示役を導出可能に制御することとしてもよい。すなわち、遊技性(その9)のその他制御例として、主制御回路90は、MB状態中の内部当籤役が「全ての小役」である場合と、「全ての小役+リプレイA」である場合と、「全ての小役+リプレイB」である場合とで、導出される表示役(結果表示)を異ならせ、結果、メダルの払い出し枚数(すなわち、付与する遊技用価値の数量)を異ならせることとしてもよい。この場合において、MB状態中のメダル増加の傾斜値のパターン数は、2種類又は3種類に限るものではなく、リプレイに係る役として更に多くの種類の役を設けることで、MB状態中のメダル増加の傾斜値のパターン数も更に増やすことができる。
Further, in the above example, the
また、本仕様例では、低RTと高RTとでMB状態中のメダル増加の傾斜値を異ならせる例について説明したが、遊技性(その9)は、RT状態に応じてMB状態中のメダル増加の傾斜値が異なればよいのであり、比較対象のRT状態は低RTと高RTとに限られない。一例として、図110(E)に示すように、高RT1と高RT2とでMB状態中のメダル増加の傾斜値を異ならせることとしてもよい。すなわち、高RT1と高RT2との間で、リプレイA及びリプレイBの当籤確率を異ならせることで、MB状態中のメダル増加の傾斜値を異ならせることができる。そして、高RT1と高RT2とを行き来するように制御することで、例えば、現状維持のMBが行われるART(高RT1中のART)と、メダルが増加するMBが行われるART(高RT2中のART)とを、ART中に行き来することができ、ART中の遊技性が多様化する。 Further, in this specification example, the example in which the inclination value of the medal increase in the MB state is made different between the low RT and the high RT has been described, but the game play (No. 9) is the medal in the MB state according to the RT state. It suffices that the increase gradient values are different, and the RT state to be compared is not limited to low RT and high RT. As an example, as shown in FIG. 110(E), the high RT1 and the high RT2 may have different inclination values for increasing medals in the MB state. That is, by changing the winning probabilities of the replay A and the replay B between the high RT1 and the high RT2, the inclination value of the medal increase in the MB state can be made different. Then, by controlling the high RT1 and the high RT2 to be switched back and forth, for example, the ART in which the MB for maintaining the current state is performed (the ART in the high RT1) and the ART in which the MB for increasing the medals is performed (the high RT2 is in effect). It is possible to go back and forth during the ART, and the playability during the ART is diversified.
同様に低RT1と低RT2とでMB状態中のメダル増加の傾斜値を異ならせることとしてもよい。すなわち、低RT1と低RT2との間で、リプレイA及びリプレイBの当籤確率を異ならせる(又は表示役A及び表示役Bが導出された場合に払い出すメダルの枚数を調整する)ことで、MB状態中のメダル増加の傾斜値を異ならせることができる。そして、低RT1と低RT2とを行き来するように制御することで、例えば、現状維持のMBが行われる一般状態(低RT1中の一般状態)と、メダルが増加するMBが行われる一般状態(高RT2中の一般状態)とを、一般状態中に行き来することができ、一般状態中の遊技性が多様化する。 Similarly, the low RT1 and the low RT2 may have different inclination values for increasing medals in the MB state. That is, by changing the winning probabilities of Replay A and Replay B between low RT1 and low RT2 (or adjusting the number of medals to be paid out when the display combination A and the display combination B are derived), It is possible to make the gradient value of the medal increase in the MB state different. Then, by controlling to move back and forth between the low RT1 and the low RT2, for example, a general state in which the MB for maintaining the current state is performed (a general state in the low RT1) and a general state in which the MB for increasing medals is performed ( The general state during high RT2) can be switched to and from the general state, and the playability in the general state is diversified.
また、本仕様例では、低RTを現状維持のMBが行われるRT状態とし、高RTをメダルが増加するMBが行われるRT状態としているが、これに限るものではなく、低RTをメダルが増加するMBが行われるRT状態とし、高RTを現状維持のMBが行われるRT状態としてもよい。
なお、リプレイA及びリプレイBの当籤確率を調整することで、低RTをメダルが増加するMBが行われるRT状態とすることとしてもよく、また、表示役A及び表示役Bが導出された場合に払い出すメダルの枚数を調整することで、低RTをメダルが増加するMBが行われるRT状態とすることとしてもよい。
Further, in this specification example, the low RT is set to the RT state in which the MB for the current state is performed and the high RT is set to the RT state in which the MB for increasing the medals is performed. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and the low RT is set to The RT state in which the increasing MB is performed may be set, and the high RT may be set in the RT state in which the MB maintaining the current state is performed.
It should be noted that by adjusting the winning probabilities of Replay A and Replay B, it is possible to set the low RT to the RT state in which the MB in which medals increase is performed, and when the display combination A and the display combination B are derived. By adjusting the number of medals to be paid out, the low RT may be set to the RT state in which the MB in which medals increase is performed.
[主制御基板及び副制御基板が有する各種機能]
以上、本仕様例のパチスロ1の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その9)について説明した。続いて、パチスロ1の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その9)を発揮する際の主制御回路90及び副制御回路200が有する各種機能について説明する。
[Various functions of the main control board and the sub control board]
Heretofore, another example (No. 9) of the playability (game specification) of the pachi-
主制御回路90は、スタートスイッチ6Sやストップスイッチ7Sと接続され、図1に示す遊技の進行を制御するため、停止制御手段及び利益付与手段として機能する。なお、主制御回路90は、MB状態においてリプレイA及びリプレイBの何れも内部当籤役として決定されない場合、及びリプレイAが内部当籤役として決定された場合には、表示役Aの結果表示が導出されるように停止制御を行う結果、今回の遊技に用いたメダルと同数又は今回の遊技に用いたメダルよりも少ないメダルを付与し、MB状態においてリプレイBが内部当籤役として決定された場合には、表示役Bの結果表示が導出されるように停止制御を行う結果、今回の遊技に用いたメダルよりも多いメダルを付与する。また、リール3L、3C、3R及び表示窓4は、可変表示手段として機能する。
The
また、主制御回路90は、リール停止制御の結果として、MB役に応じた結果表示が導出されると、MB状態を開始し、MB状態の終了条件を満たすと、MB状態を終了するため、主制御回路90は、遊技制御手段として機能する。また、主制御回路90は、MB状態の前後、及びMB状態の最中はRT状態を移行させることがなく現在のRT状態を維持する一方で、RT状態の移行条件を満たした場合に現在のRT状態から他のRT状態にRT状態を移行するため、主制御回路90は、RT制御手段として機能する。
Further, the
[遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その10)]
続いて、図111を参照して、本実施形態に係るパチスロ1において実装可能な遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その10)について説明する。図111は、遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その10)における制御の概要を示す図である。
[Another example of playability (game specifications) (10)]
Next, with reference to FIG. 111, another example (No. 10) of the playability (game specification) that can be mounted in the pachi-
(パチスロの仕様例)
遊技性(その10)を実現可能なパチスロの仕様例では、パチスロ1は、報知状態と非報知状態とを有する。報知状態は、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知する(又は報知する頻度が高い)遊技状態であり、例えば、有利区間中のATやARTといった遊技状態が該当する。非報知状態は、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知しない(又は報知する頻度が低い)遊技状態であり、報知状態以外の遊技状態が該当する。
(Example of pachislot specifications)
In the specification example of the pachi-slot capable of realizing the game play (No. 10), the pachi-
また、パチスロ1は、内部当籤役として決定された場合に遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知する対象の役である報知対象役を有する。報知対象役は、所定の操作態様で停止操作が行われると、所定の結果表示が導出可能であり(所定の図柄の組合せが表示可能であり)、所定の操作態様とは異なる操作態様で停止操作が行われると、所定の結果表示とは異なる結果表示が導出可能な(所定の図柄の組合せとは異なる図柄の組合せが表示可能な)役であり、例えば、上記実施形態における押し順小役(押し順役)である。なお、パチスロ1では、主制御回路90は、報知対象役の当籤時に所定の結果表示が導出可能された場合には、所定の結果表示以外の結果表示が導出された場合よりも多くのメダルを払い出す。以下に示す例では、所定の結果表示が導出可能された場合には「9枚」のメダルを払い出し、所定の結果表示以外の結果表示が導出された場合には「0枚」のメダルを払い出す。なお、所定の結果表示以外の結果表示が導出された場合に払い出すメダルの枚数は、「9枚」よりも少なければよく、「0枚」であることに限られない。そのため、報知対象役は、所定の操作態様で停止操作が行われると多くのメダルが払い出され、所定の操作態様以外の操作態様で停止操作が行われると少ないメダル(又は0枚)が払い出される役であるといえる。主制御回路90は、報知状態において報知対象役が内部当籤役として決定されると、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報である所定の操作態様を遊技者に対して報知する。
In addition, the pachi-
また、主制御回路90は、非報知状態において報知状態への移行条件を満たすと、遊技状態を非報知状態から報知状態に移行する。なお、本仕様例において報知状態への移行条件は任意である。そして、主制御回路90は、報知状態において報知状態の終了条件を満たすと、遊技状態を報知状態から非報知状態に移行する。
Further, the
ここで、本仕様例において報知状態の終了条件は、報知状態中に払い出されたメダルの枚数に関連するものであり、例えば、報知状態中に払い出されたメダルの枚数が規定値に達すること、又は報知状態中の差枚数(=払出枚数−投入枚数)が規定値に達することであってよい。なお、本仕様例では、報知状態中に払い出されたメダルの枚数が規定値に達することを終了条件として用いる。そのため、主制御回路90は、報知状態の継続期間を定める数値情報として、報知状態において払い出されたメダルの総数を計数可能なカウンタを有し、報知状態中に払い出されたメダルの枚数に応じてカウンタを更新し、カウンタの値が規定値に達すると、報知状態を終了する。また、主制御回路90は、報知状態中に上乗せ条件を満たすと、報知状態の継続期間が延長されるように、このカウンタの値を更新する。なお、本仕様例において、上乗せ条件は任意である。
Here, the termination condition of the notification state in this specification example is related to the number of medals paid out during the notification state, for example, the number of medals paid out during the notification state reaches a specified value. Alternatively, it may be that the difference sheet number (=dispensed sheet number-inserted sheet number) in the notification state reaches a specified value. In this specification example, the condition that the number of medals paid out during the notification state reaches a specified value is used as the ending condition. Therefore, the
(遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その10)の概要)
このような仕様例のパチスロ1において、遊技性(その10)は、報知状態の終了時期を遊技者が調整可能にする制御に関するものである。具体的には、遊技性(その10)では、報知状態の終了条件である、報知状態中に払い出されたメダルの枚数の計数方法に特徴を有しており、以下説明する計数方法により、遊技者は、報知状態の終了時期を調整することができる。
(Outline of another example of playability (game specification) (10))
In the pachi-
遊技性(その10)では、主制御回路90は、報知状態中に内部当籤役として決定されただけでは払出枚数を更新することなく、メダルの払い出しが実際に行われた場合に、実際に払い出したメダルの枚数に応じて、払出枚数を更新する。すなわち、報知状態中は、基本的には、報知に従い停止操作を行うことで最大の利益を得ることができるため、メダルの払い出しを行う前に払い出されるであろうメダルの枚数を把握することができる。そのため、AT機やART機では、報知状態中に報知対象役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、当該遊技において遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知したことをもって、払出枚数を更新することがある。
In the playability (No. 10), the
これに対して、本仕様例のパチスロ1では、主制御回路90は、報知状態中に報知対象役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、当該遊技において遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知しただけでは払出枚数を更新することなく、遊技者の停止操作の結果として導出された結果表示に伴い払い出されたメダルの枚数に応じて払出枚数を更新する。すなわち、遊技者が報知に従い停止操作を行った場合には、報知状態中に払い出されたメダルの枚数を「9枚」加算し、遊技者が報知に従わずに停止操作を行った場合には、報知状態中に払い出されたメダルの枚数を「0枚」加算する。
On the other hand, in the pachi-
(遊技性(その10)の制御例)
ここで、図111(A)は、遊技性(その10)の制御例を示す。同図(a)において、報知状態の残り払出枚数は「9枚」であり、当該遊技において報知対象役が内部当籤役として決定された結果、主制御回路90は、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報として「左中右」の押し順を報知している。遊技者が報知に従い停止操作を行うと、同図(b)に示すように、ベルが入賞し「9枚」のメダルが払い出される結果、報知状態の残り払出枚数が「0枚」に更新され、報知状態(ART)が終了してしまう。一方で、遊技者が報知に従わずに停止操作を行うと、同図(c)に示すように、ベルが入賞しないためメダルの払い出しも行われない結果、報知状態の残り払出枚数が「9枚」のまま維持され、報知状態(ART)は終了せずに、次遊技の遊技状態も報知状態(ART)となる。
(Game example (10) control example)
Here, FIG. 111(A) shows an example of control of playability (No. 10). In the figure (a), the remaining payout number in the notification state is “9”, and as a result of the notification target combination being determined as an internal winning combination in the game, the
このように本仕様例のパチスロ1では、遊技者が報知に従い停止操作を行った場合には、遊技者は多くのメダルを獲得できる一方で、報知状態の終了が早まってしまい、反対に、遊技者が報知に従わずに停止操作を行った場合には、遊技者は当該遊技において用いた分のメダルを減少させてしまうものの、報知状態の終了時期を先延ばしすることができる。なお、主制御回路90は、報知状態中に上乗せ制御が可能であるため、報知に逆らって伸ばした期間において上乗せ制御を受けることにより、最終的には多くのメダルの払い出しを受けることができる可能性もあるため、報知に従うか否かについて戦略性を持った遊技性とすることができる。また、報知に逆らって停止操作を行った場合には、遊技者は当該遊技において損をしてしまうため、損した分の利益を他の部分に振り分けることができる。
As described above, in the pachi-
(上乗せ制御例)
続いて、図111(B)は、主制御回路90による上乗せ制御の例を示す図である。同図に示すように、遊技性(その10)では、報知状態の経過ゲーム数に応じて上乗せ期待度を異ならせることで(所謂、上乗せ期待度が高いゲーム数ゾーンを設けることで)、更に戦略性を高めることができる。一例として、報知状態が開始してから「77ゲーム目」の遊技が上乗せ期待度が高い遊技である場合について考える。「77ゲーム目」の1ゲーム前の「76ゲーム目」において、報知状態の残り払出枚数が「9枚」であり、かつ、報知対象役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、当該遊技において報知に従い停止操作を行うと、次ゲームが上乗せ期待度が高い遊技であるにも関わらず、当該遊技で報知状態が終了してしまう。これに対して、当該遊技において報知に従わないことで、上乗せ期待度が高い「77ゲーム目」の遊技を行うことができ、次遊技において継続期間の上乗せが行われた場合には、終了してしまった場合よりも遊技者にとって有利になる可能性がある。
(Example of additional control)
Subsequently, FIG. 111B is a diagram showing an example of the addition control by the
このように報知状態の終了条件を払出枚数により管理しつつ、報知状態の経過ゲーム数に応じて上乗せ期待度を異ならせることで、戦略性を高めることができ、遊技性が多様化する。なお、上乗せ期待度とは、上乗せ抽籤に当籤する確率(すなわち、上乗せが行われ易いか否か)であってもよく、また、上乗せが行われる場合の上乗せの大きさであってもよく、両者を組み合わせたものであってもよい。一例として、図111(B)に示す例において、報知状態が開始してから「51〜53ゲーム目」の遊技を上乗せ抽籤に当籤する確率が高く、かつ、上乗せが行われる場合の上乗せの大きさが通常の遊技とし、報知状態が開始してから「77ゲーム目」の遊技を上乗せ抽籤に当籤する確率が高く、かつ、上乗せが行われる場合の上乗せの大きさも大きい遊技とし、報知状態が開始してから「99〜100ゲーム目」の遊技を上乗せ抽籤に当籤する確率が通常、かつ、上乗せが行われる場合の上乗せの大きさが大きい遊技としてもよい。このようにすることで、更に戦略性を高めることができ、遊技性が多様化する。 In this way, by controlling the termination condition of the notification state by the number of payouts, and by changing the expected degree of addition according to the number of elapsed games in the notification state, it is possible to enhance the strategic characteristic and diversify the game characteristic. Note that the expected degree of addition may be the probability of winning the additional lottery (that is, whether or not the addition is easy to perform), or may be the size of the addition when the addition is performed, It may be a combination of both. As an example, in the example shown in FIG. 111(B), there is a high probability that the game of “51st to 53rd games” will be added to the lottery after the notification state is started, and the amount of addition when the addition is performed. Is a normal game, the probability of winning the "77th game" game after winning the notification state is high, and the amount of addition when the addition is performed is also large, and the notification state is It is also possible that the probability of winning the "99th to 100th game" games from the start and winning the lottery is normal, and the amount of the addition is large when the addition is performed. By doing so, it is possible to further enhance the strategy and diversify the game.
なお、遊技性(その10)では、報知状態中に払い出されたメダルの枚数(又は報知状態中の差枚数)が規定値に達することを終了条件として用いることとしている。ここで、主制御回路90は、複数の役のうちの一部の役が内部当籤役として決定された遊技においてのみ、終了条件として用いるメダルの枚数(又は差枚数、以下省略)を更新し、他の役が内部当籤役として決定された遊技では、メダルの払い出しがあったか否かに関係なく、終了条件として用いるメダルの枚数を更新しないこととしてもよい。例えば、内部当籤役として決定されると、遊技者の停止操作に関わらず必ず入賞し(すなわち、停止操作の態様に関わらず必ず所定の結果表示が導出され移され)、特定枚数のメダルが付与される引込1の役を有する仕様の場合、このような引込1の役に応じて終了条件として用いるメダルの枚数を更新してしまったのでは、遊技者が報知状態の終了時期を調整することができなくなってしまう。この点、このような引込1の役を、内部当籤役として決定された場合に終了条件として用いるメダルの枚数を更新しない役とすることで、遊技者は、報知状態の終了時期を調整することができる。なお、終了条件として用いるメダルの枚数を更新する役と、更新しない役とは任意に設定することができるが、報知対象役については、終了条件として用いるメダルの枚数を更新する役とすることが好ましく、また、引込1の役は、終了条件として用いるメダルの枚数を更新しない役とすることが好ましい。また、引込1ではない役、すなわち、内部当籤役として決定された場合に遊技者の停止操作に応じて入賞することもあれば、入賞しないこともある役(取りこぼすことがある役)は、終了条件として用いるメダルの枚数を更新する役としてもよく、また、更新しない役としてもよい。
In the game property (No. 10), the end condition is that the number of medals paid out in the notification state (or the difference number in the notification state) reaches a specified value. Here, the
[主制御基板及び副制御基板が有する各種機能]
以上、本仕様例のパチスロ1の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その10)について説明した。続いて、パチスロ1の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その10)を発揮する際の主制御回路90及び副制御回路200が有する各種機能について説明する。
[Various functions of the main control board and the sub control board]
Heretofore, another example (No. 10) of the playability (game specification) of the pachi-
主制御回路90は、スタートスイッチ6Sやストップスイッチ7Sと接続され、図1に示す遊技の進行を制御するため、遊技制御手段及び利益付与手段として機能する。また、リール3L、3C、3R及び表示窓4は、可変表示手段及び変動表示手段として機能する。
The
また、主制御回路90は、非報知状態において報知状態への移行条件を満たすと、遊技状態を報知状態に移行可能であるため、主制御回路90は、状態制御手段として機能する。また、主制御回路90は、報知状態において報知対象役が内部当籤役として決定されると、指示モニタを介して遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知するため、主制御回路90は、報知手段として機能する。
Further, the
また、主制御回路90は、報知状態の継続期間を定める払出枚数などの数値情報を計数可能であるとともに、報知状態中の上乗せ制御により、報知状態の継続期間が延長されるようにこの数値情報を更新可能であるため、主制御回路90は、継続期間計数手段及び上乗せ制御手段として機能する。また、主制御回路90は、報知状態中に払い出されたメダルの枚数に応じてこの数値情報を更新可能であり、この数値情報が終了閾値に達すると、報知状態を終了可能であるため、主制御回路90は、継続期間管理手段として機能する。
Also, the
[遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その11)]
続いて、図112を参照して、本実施形態に係るパチスロ1において実装可能な遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その11)について説明する。図112は、遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その11)における制御の概要を示す図である。
[Another example of playability (game specifications) (Part 11)]
Next, with reference to FIG. 112, another example (No. 11) of the playability (game specification) that can be mounted in the pachi-
(パチスロの仕様例)
図112(A)に示すように、遊技性(その11)を実現可能なパチスロの仕様例では、パチスロ1は、通常区間(一般状態)と有利区間とを有し、有利区間には、非報知状態と非報知状態よりも遊技者にとって有利な報知状態とが含まれる。有利区間の報知状態は、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知する(又は報知する頻度が高い)遊技状態であり、本仕様例においてはARTである。また、有利区間の非報知状態は、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知しない(又は報知する頻度が低い)遊技状態であり、本仕様例においてはCZ(チャンスゾーン)である。
(Example of pachislot specifications)
As shown in FIG. 112(A), in the specification example of the pachi-slot capable of realizing the game characteristic (11), the pachi-
主制御回路90は、通常区間において有利区間への移行抽籤を行っており、この移行抽籤に当籤すると、通常区間から有利区間のCZに遊技状態を移行する。なお、主制御回路90は、有利区間への移行抽籤に当籤した場合に、移行先の有利区間の種別を決定するなどして通常区間からARTに直接移行可能にしてもよいが、遊技性(その11)の説明においては関係がないため、通常区間からARTへの移行に関しては省略する。
The
また、主制御回路90は、CZ中にARTへの移行条件を満たすと、CZからARTに遊技状態を移行する。なお、CZからARTへの移行条件は任意であるが、本仕様例では、CZの1/2では、終了条件を満たすことなく10ゲーム間継続した場合にARTに移行し、残り1/2のCZでは、終了条件を満たすことなく20ゲーム間継続した場合にARTに移行する。具体的には、主制御回路90は、有利区間への移行抽籤において「10ゲーム間のCZ」と「20ゲーム間のCZ」との何れかを決定し、「10ゲーム間のCZ」を決定した場合には、終了条件を満たすことなく10ゲーム間継続した場合にARTに移行し、「20ゲーム間のCZ」を決定した場合には、終了条件を満たすことなく20ゲーム間継続した場合にARTに移行する。
なお、本仕様例において、「10ゲーム間のCZ」と「20ゲーム間のCZ」との当籤確率には、設定差がないものとする。すなわち、低設定においても高設定においても、「10ゲーム間のCZ」と「20ゲーム間のCZ」との振分確率は同一であるとする。
Further, the
In this specification example, it is assumed that there is no setting difference in the winning probabilities of “CZ for 10 games” and “CZ for 20 games”. That is, it is assumed that the distribution probabilities of "CZ between 10 games" and "CZ between 20 games" are the same in both the low setting and the high setting.
また、主制御回路90は、CZ中にCZの終了条件を満たすと、CZから通常区間に遊技状態を移行する。ここで、本仕様例においてCZの終了条件は、CZ中に特定の役が内部当籤役として決定されること、より具体的には、CZ中にMBが内部当籤役として決定されると、CZの終了条件を満たしたとして、CZから通常区間に遊技状態を移行する。
Further, the
このとき、本仕様例では、複数の設定値の少なくとも一部において他の設定値とは異なる確率で、MBを内部当籤役として決定する。ここで、図112(B)は、非ボーナス状態中に内部当籤役を決定するために用いる一般遊技中内部抽籤テーブルである。同図に示すように、本仕様例では、MBを内部当籤役として決定する確率は、低設定であるほど高く、高設定であるほど低い。 At this time, in this specification example, MB is determined as an internal winning combination with a probability that at least a part of the plurality of setting values is different from the other setting values. Here, FIG. 112(B) is a general game internal lottery table used for determining an internal winning combination during the non-bonus state. As shown in the figure, in this specification example, the probability of determining the MB as the internal winning combination is higher as the setting is low, and is lower as the setting is high.
(遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その11)の概要)
このようにARTへの移行契機となるCZの終了条件であるMBの当籤確率を設定値に応じて異ならせることで、遊技性(その11)では、ARTへの移行期待度に対して設定差を持たせることができる。すなわち、図112(C)に示すように、MBの当籤確率が高い場合、MBの当籤を終了条件とするCZの期間は短くなる結果、ARTへの移行期待度は低くなる。反対に、MBの当籤確率が低い場合、MBの当籤を終了条件とするCZの期間は長くなる結果、ARTへの移行期待度は高くなる。そのため、本仕様例のパチスロ1では、ARTへの移行期待度は、低設定であるほど低くなり、高設定であるほど高くなる。このように遊技性(その11)では、ARTへの移行抽籤に当籤する確率に設定差を直接設けるのではなく、ARTへの移行が期待できるCZの終了確率に設定差を設けることで、ARTへの移行期待度に設定差を設けることができ、ARTへの移行に関して従来にない新たな制御が可能になる。
(Outline of another example (11) of playability (game specification))
In this way, by setting the winning probability of MB, which is the ending condition of CZ that triggers the transition to ART, according to the set value, in the game (11), the setting difference with respect to the transition expectation to ART is set. Can have That is, as shown in FIG. 112(C), when the winning probability of MB is high, the period of CZ in which the winning condition of MB is a termination condition is short, and as a result, the degree of expectation of transition to ART is low. On the other hand, when the winning probability of MB is low, the period of CZ with the winning condition of MB as the end condition becomes long, and as a result, the expectation of transition to ART becomes high. Therefore, in the pachi-
なお、本仕様例では、CZの終了条件をMBに当籤することとしているため、CZが終了してしまいARTに移行できなかった場合であっても、その後、MBに応じた結果表示が導出されてMBが入賞することで、MB状態(ボーナス状態)に移行可能である。すなわち、主制御回路90は、MBに応じた結果表示が導出されると、遊技状態をMB状態(ボーナス状態)に移行可能である。これにより、ARTへの移行期待度が低い低設定であっても、高設定よりも多くのMB状態(ボーナス状態)を行うことができるため、遊技者が感じる不満を軽減することができる。
In addition, in this specification example, since the termination condition of CZ is to win the MB, even if the CZ is terminated and it is not possible to shift to ART, the result display corresponding to the MB is derived thereafter. By winning the MB as a prize, it is possible to shift to the MB state (bonus state). That is, the
[主制御基板及び副制御基板が有する各種機能]
以上、本仕様例のパチスロ1の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その11)について説明した。続いて、パチスロ1の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その11)を発揮する際の主制御回路90及び副制御回路200が有する各種機能について説明する。
[Various functions of the main control board and the sub control board]
Heretofore, another example (11) of the playability (game specification) of the pachi-
主制御回路90は、スタートスイッチ6Sやストップスイッチ7Sと接続され、図1に示す遊技の進行を制御するため、遊技制御手段として機能する。また、リール3L、3C、3R及び表示窓4は、可変表示手段として機能する。
The
また、主制御回路90は、通常区間において有利区間への移行条件を満たすと、遊技状態を有利区間のCZに移行可能であり、CZにおいてARTへの移行条件を満たすと、遊技状態をARTに移行可能であり、また、CZにおいてMBが内部当籤役として決定されると、遊技状態を通常区間に移行可能であるため、主制御回路90は、第1状態制御手段及び第2状態制御手段として機能する。また、主制御回路90は、MBに応じた結果表示が導出されてMBが入賞すると、MB状態というボーナス遊技を開始可能であるため、主制御回路90は、ボーナス開始手段として機能する。
In addition, the
[遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その12)]
続いて、図113及び図114を参照して、本実施形態に係るパチスロ1において実装可能な遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その12)について説明する。図113及び図114は、遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その12)における制御の概要を示す図である。
[Another example of playability (game specifications) (12)]
Next, with reference to FIG. 113 and FIG. 114, another example (No. 12) of the playability (game specification) that can be mounted in the pachi-
(パチスロの仕様例)
遊技性(その12)を実現可能なパチスロの仕様例では、パチスロ1は、非ボーナス状態とボーナス状態とを有し、主制御回路90は、非ボーナス状態においてボーナスの開始条件を満たすと、非ボーナス状態からボーナス状態に遊技状態を移行し、ボーナス状態においてボーナスの終了条件を満たすと、ボーナス状態から非ボーナス状態に遊技状態を移行する。なお、ボーナス状態の開始条件は、ボーナスに係る役が入賞することである。また、ボーナス状態の終了条件は、ボーナス状態中に払い出されたメダルの枚数が規定値に達することであり、詳しくは後述する。
(Example of pachislot specifications)
In the specification example of the pachi-slot capable of realizing the game play (part 12), the pachi-
また、パチスロ1は、リプレイに係る役の種類及びその当籤確率が互いに異なるRT状態として複数段階のRT状態を有する。一例として、本仕様例のパチスロ1では、RT状態として低RTと高RTとを有する。なお、低RT及び高RTとしてそれぞれ1つのRT状態を有するものであってもよく、また、複数のRT状態を有するものであってもよい(例えば、低RT1、低RT2、高RT1、高RT2など)。主制御回路90は、非ボーナス状態の低RTにおいて高RTへの移行条件を満たすと、RT状態を低RTから高RTに移行し、非ボーナス状態の高RTにおいて低RTへの移行条件を満たすと、RT状態を高RTから低RTに移行する。なお、非ボーナス状態におけるRT状態の移行条件は任意である。また、ボーナス状態におけるRT状態の移行条件については後述する。また、主制御回路90は、ボーナス状態が終了し非ボーナス状態に移行した場合、ボーナス状態終了時のRT状態を維持したまま、非ボーナス状態に移行する。一例として、低RTの状態でボーナス状態が終了した場合、ボーナス終了後の非ボーナス状態におけるRT状態は低RTのまま維持され、高RTの状態でボーナス状態が終了した場合、ボーナス終了後の非ボーナス状態におけるRT状態は高RTのまま維持される。
Further, the pachi-
また、パチスロ1は、非ボーナス状態中の遊技状態として報知状態と非報知状態とを有する。報知状態は、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知する(又は報知する頻度が高い)遊技状態であり、本仕様例では、有利区間中のARTが該当する。非報知状態は、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知しない(又は報知する頻度が低い)遊技状態であり、報知状態以外の遊技状態が該当する。
Further, the pachi-
主制御回路90は、非報知状態において報知状態への移行条件を満たすと、遊技状態を非報知状態から報知状態に移行する。そして、主制御回路90は、報知状態において報知状態の終了条件を満たすと、遊技状態を報知状態から非報知状態に移行する。なお、本仕様例において報知状態への移行条件及び報知状態の終了条件は任意であるが、報知状態への移行条件については、その一例を後述する。
The
(遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その12)の概要)
このような仕様例のパチスロ1において、遊技性(その12)は、ボーナス状態中の特典付与に関するものである。なお、遊技性(その12)は、ボーナス状態中に以下に説明する制御により何らかの特典を付与可能なものであり、特典の種別については規定するものではないが、本仕様例のパチスロ1では、ボーナス状態中に報知状態(ART)に関する特典を付与するものとして、遊技性(その12)について説明する。
(Outline of another example (No. 12) of playability (game specification))
In the pachi-
図113(A)は、ボーナス状態中の遊技状態の遷移フローを示す図である。本仕様例のパチスロ1では、ボーナス状態として、第一種特別役物と呼ばれるレギュラーボーナス(以下、「RB」と記す)に係る役物連続作動装置であるBBを採用している。同図に示すように、ボーナス状態(BB)は、BB中一般、BB中RB持越及びBB中RBにより構成される。
FIG. 113(A) is a diagram showing a transition flow of the gaming state during the bonus state. In the pachi-
主制御回路90は、ボーナスに係る役(BB)に入賞しボーナス状態が開始されると、まず、BB中一般に遊技状態を移行する。主制御回路90は、BB中一般において内部当籤役としてRBが決定されると、BB中RB持越に遊技状態を移行する。なお、主制御回路90は、BB中一般において内部当籤役としてRBが決定される前にボーナス状態の終了条件を満たした場合には、ボーナス状態を終了し非ボーナス状態に遊技状態を移行するため、このボーナス状態の終了に伴いBB中一般も終了する。
When the winning combination (BB) is won and the bonus state is started, the
主制御回路90は、ボーナス状態中にRBを内部当籤役として決定した遊技においてRBに応じた結果表示が導出されない場合(RBが入賞しない場合)、RBに応じた結果表示が導出されるまでRBを内部当籤役として持ち越す。すなわち、ボーナス状態中にRBが内部当籤役として決定されると、RBが入賞するまでボーナス状態中の遊技状態はBB中RB持越となる。なお、RBは、入賞可能な遊技において停止操作のタイミングが適切である場合に入賞し、入賞可能な遊技であっても停止操作のタイミングが適切ではない場合には入賞しない。すなわち、RBを入賞させるか否かは、遊技者がRBを入賞させるように停止操作を行うか否かにより決まり、遊技者はRBを入賞させるか否かを選択することができる。また、主制御回路90は、BB中RB持越において内部当籤役として持ち越しているRBに応じた結果表示が導出されると(RBが入賞すると)、BB中RBに遊技状態を移行する。なお、主制御回路90は、RBが入賞する前にボーナス状態の終了条件を満たした場合には、ボーナス状態を終了し非ボーナス状態に遊技状態を移行するため、このボーナス状態の終了に伴いBB中RB持越も終了する。
When the result display corresponding to the RB is not derived in the game in which the RB is determined as the internal winning combination during the bonus state (when the RB does not win), the
また、主制御回路90は、BB中RBにおいて、RBの終了条件(例えば、8回以下の任意の所定回数の入賞があったこと、あるいは12回以下の任意の所定回数の遊技が行われたこと)を満たすと、BB中一般に遊技状態を移行する。なお、主制御回路90は、RBの終了条件を満たす前に、ボーナス状態(BB)の終了条件を満たした場合には、ボーナス状態を終了し非ボーナス状態に遊技状態を移行するため、このボーナス状態の終了に伴いBB中RBも終了する。
Further, the
また、主制御回路90は、ボーナス状態中にRT状態を移行可能に制御する。具体的には、主制御回路90は、ボーナスに係る役(BB)に入賞しボーナス状態が開始されると、RT状態を低RTに移行し、その後、ボーナス状態においてRBが内部当籤役として決定されると、RT状態を高RTに移行し、その後、内部当籤役として決定された(持ち越されている)RBが入賞すると、RT状態を低RTに移行する。すなわち、同図に示すように、主制御回路90は、ボーナス状態のBB中一般においてはRT状態を低RTとし、ボーナス状態のBB中RB持越においてはRT状態を高RTとし、ボーナス状態のBB中RBにおいてはRT状態を低RTとする。なお、上述したように、主制御回路90は、ボーナス状態が終了した場合、ボーナス状態終了時のRT状態を維持したまま、非ボーナス状態に移行するため、BB中一般又はBB中RBにおいてボーナス状態が終了した場合には、非ボーナス状態のRT状態は低RTとなり、BB中RB持越においてボーナス状態が終了した場合には、非ボーナス状態のRT状態は高RTとなる。
Further, the
続いて、図113(B)は、ボーナス状態中に内部当籤役を決定するために用いる内部抽籤テーブルである。なお、同図の「対応する図柄組合せ」欄には、内部当籤役として決定された場合に入賞が許可される図柄の組合せが規定されているが一例に過ぎず、以下説明するように、「押し順ベル_1st」〜「押し順ベル_3rd」が押し順小役(押し順役)として機能し、「RB中ベル」が押し順を要求しない役として機能すればよい。 Subsequently, FIG. 113(B) is an internal lottery table used for determining an internal winning combination during the bonus state. In the "corresponding symbol combination" column of the same figure, the symbol combinations that are allowed to win when determined as an internal winning combination are stipulated only as an example. The pressing order bell_1st” to “pressing order bell_3rd” may function as a small pressing order combination (pushing order combination), and the “RB middle bell” may function as a combination that does not require a pressing order.
同図において、「押し順ベル_1st」〜「押し順ベル_3rd」は、押し順小役(押し順役)であり、3択の押し順に正解した場合にベルが入賞して「9枚」のメダルが払い出され、3択の押し順に不正解した場合にベルが入賞せずにベル入賞時よりも少ないメダル(又は0枚のメダル)が払い出される。また、「RB中ベル」とは、停止操作の態様が不問のベル(共通ベル)であり、停止操作の態様に関係なく必ずベルが入賞して「9枚」のメダルが払い出される。 In the figure, "push order bell_1st" to "push order bell_3rd" are push order small wins (push win wins), and when the correct answer is given in three choices, Bell wins and "9 pieces" When the medals are paid out and the wrong answer is given in the order of three choices, the bell does not win, and fewer medals (or 0 medals) are paid out than when the bell wins. The "RB middle bell" is a bell (common bell) in which the mode of the stop operation does not matter, and the bell is always won and "9" medals are paid out regardless of the mode of the stop operation.
同図に示すように、BB中一般及びBB中RB持越においては、「押し順ベル_1st」〜「押し順ベル_3rd」が当籤し、ベルの入賞に3択の押し順が要求される。一方で、BB中RBにおいては、「RB中ベル」が当籤し、ベルの入賞に押し順が要求されない。なお、主制御回路90は、BB中一般及びBB中RB持越において、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報(すなわち、正解の押し順)を報知することとしてもよく、また、報知しないこととしてもよい。また、主制御回路90は、報知状態中のBB中一般及びBB中RB持越については、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知し、非報知状態中のBB中一般及びBB中RB持越については、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知しないこととしてもよい。なお、本仕様例においては、主制御回路90は、報知状態か否かに関係なく、BB中一般及びBB中RB持越において遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知する。
As shown in the figure, in the BB general and the BB middle RB carryover, "push order bell_1st" to "push order bell_3rd" are won, and three push orders are required for winning the bell. On the other hand, in RB in BB, “RB in bell” is won, and the pushing order is not required to win the bell. It should be noted that the
また、同図において「通常リプ」は、リプレイに係る役である。また、同図において「一般中強レア役」は、BB中一般及びBB中RB持越における強レア役であり、「一般中弱レア役」は、BB中一般及びBB中RB持越における弱レア役である。同様に、「RB中強レア役」は、BB中RBにおける強レア役であり、「RB中弱レア役」は、BB中RBにおける弱レア役である。 Further, in the figure, "normal rep" is a role related to replay. Further, in the figure, "general medium strong rare role" is a strong rare role in BB medium general and BB medium RB carryover, and "general medium weak rare role" is a weak rare role in BB medium general and BB medium RB carryover. Is. Similarly, the "RB medium strong rare combination" is a strong rare combination in the BB medium RB, and the "RB medium weak rare combination" is a weak rare combination in the BB medium RB.
BB中一般(低RT)、BB中RB持越(高RT)、及びBB中RB(低RT)では、RT状態が異なるため、「通常リプ」の当籤確率が異なり、BB中RB持越は「通常リプ」の当籤確率が高く、BB中一般及びBB中RBは「通常リプ」の当籤確率が低い。また、BB中一般、BB中RB持越、及びBB中RBでは、RB(第一種特別役物)の作動の有無によりメダルの払い出しに係る役(小役)の当籤確率が異なり、BB中一般及びBB中RB持越と、BB中RBとでは、ベル(「BEL_01」〜「BEL_09」)の当籤確率が異なる。なお、本仕様例では、RBの作動の有無に応じてベルの当籤確率を異ならせる一方で、レア役の当籤確率については同一としているが、レア役の当籤確率についてもRBの作動の有無に応じて異ならせることとしてもよい。 Since the RT status is different for BB Medium General (Low RT), BB Medium RB Carryover (High RT), and BB Medium RB (Low RT), the winning probability of "Normal Lip" is different, and BB Medium RB Carryover is "Normal". The winning probability of “lip” is high, and the winning probability of “normal lip” is low for general BB and RB in BB. In addition, in the BB medium general, the BB medium RB carryover, and the BB medium RB, the winning probability of the combination (small combination) relating to the payout of the medals is different depending on whether or not the RB (first-class special character) is activated. And the winning probability of the bell (“BEL_01” to “BEL_09”) is different between the RB in BB carryover and the RB in BB. In this specification example, while the winning probability of the bell is made different depending on whether or not the RB is activated, the winning probability of the rare combination is the same, but the winning probability of the rare combination is also determined by whether or not the RB is activated. It may be different depending on the situation.
ここで、本仕様例のパチスロ1では、BB中一般及びBB中RBは、低RTでありリプレイに係る役の当籤確率が低いため、はずれの当籤確率が高く、結果、メダルの払出期待値(すなわち、単位遊技当たりに付与されるメダルの期待値)がBB中RB持越に比べて低い低ベースの遊技状態である。また、BB中RB持越は、高RTでありリプレイに係る役の当籤確率が高いため、はずれの当籤確率が低く、結果、メダルの払出期待値がBB中一般及びBB中RBに比べて高い高ベースの遊技状態である。すなわち、メダルの払出期待値という観点から見ると、BB中RB持越は、BB中一般及びBB中RBよりも有利な遊技状態である。
Here, in the pachi-
続いて、図113(C)及び図114(D)は、ボーナス状態中に行うART抽籤に用いる抽籤テーブルであり、図113(C)は、非報知状態においてARTの初当たり抽籤に用いるBB中ART初当たり抽籤テーブルであり、図114(D)は、報知状態においてARTの上乗せ抽籤に用いるBB中ART上乗せ抽籤テーブルである。また、図114(E)は、ボーナス状態中に行うART抽籤の抽籤概要を示す図であり、遊技性(その12)の概要を示すものである。 Subsequently, FIG. 113(C) and FIG. 114(D) are lottery tables used for the ART lottery performed in the bonus state, and FIG. 113(C) is the BB used for ART first win lottery in the non-notification state. FIG. 114D is an ART initial lottery table, and FIG. 114D is a BB ART additional lottery table used in the ART additional lottery in the notification state. Further, FIG. 114(E) is a diagram showing an outline of the lottery of the ART lottery performed during the bonus state, showing an outline of the game characteristic (No. 12).
図113(C)及び図114(D)に示すように、ART抽籤に用いる抽籤テーブルは、遊技状態及び内部当籤役毎にART抽籤の抽籤結果についての抽籤値の情報を規定する。なお、本仕様例では、レア役の当籤時にARTの初当たり抽籤や上乗せ抽籤を行うこととしているが、他の役の当籤時においても当該抽籤を行うこととしてもよい。 As shown in FIGS. 113(C) and 114(D), the lottery table used for the ART lottery defines the lottery value information about the lottery result of the ART lottery for each gaming state and internal winning combination. In addition, in the present specification example, the initial win lottery and the additional lottery of the ART are performed when the rare combination is won, but the lottery may be performed when the other combination is won.
ここで、図114(E)に示す表は、本仕様例のパチスロ1におけるART抽籤の抽籤概要を示す。同図に示すように、本仕様例のパチスロ1では、BB中一般及びBB中RB持越では、特典付与確率が高いものの、特典を付与する場合に付与する特典の大きさが小さい。例えば、図113(C)のBB中ART初当たり抽籤テーブルを参照すると、BB中一般及びBB中RB持越では、レア役に応じてARTの初当たり抽籤に当籤する確率は高いものの、当籤した場合のARTの初期ゲーム数は「50ゲーム」と少ない。同様に図114(D)のBB中ART上乗せ抽籤テーブルを参照すると、BB中一般及びBB中RB持越では、レア役に応じて必ずARTの上乗せ抽籤に当籤するものの、当籤した場合の上乗せゲーム数は「10ゲーム」〜「50ゲーム」と少ない。
Here, the table shown in FIG. 114E shows the outline of the lottery of the ART lottery in the pachi-
一方で、BB中RBでは、特典付与確率が低いものの、特典を付与する場合に付与する特典の大きさが大きい。例えば、図113(C)のBB中ART初当たり抽籤テーブルを参照すると、BB中RBでは、レア役に応じてARTの初当たり抽籤に当籤する確率は低いものの、当籤した場合のARTの初期ゲーム数として「50ゲーム」だけでなく「100ゲーム」や「200ゲーム」が決定されることがある。同様に図114(D)のBB中ART上乗せ抽籤テーブルを参照すると、BB中一般及びBB中RB持越では、レア役に応じてARTの上乗せ抽籤に当籤する確率は低いものの、当籤した場合の上乗せゲーム数は「50ゲーム」〜「200ゲーム」と多い。 On the other hand, in the BB in BB, although the privilege granting probability is low, the size of the privilege granted when granting the privilege is large. For example, referring to the ART in BB first win lottery table of FIG. 113(C), in the RB in BB, although the probability of winning the first win lottery of ART according to the rare combination is low, the initial game of the ART in the case of winning. As the number, not only “50 games” but also “100 games” and “200 games” may be determined. Similarly, referring to the BB in-art lottery lottery table of FIG. 114D, in the BB in general and in the BB in RB carryover, although the probability of winning the ART in the lottery according to the rare hand is low, the additional in the case of winning is won. The number of games is often "50 games" to "200 games".
このように遊技性(その12)では、特典付与の確率と付与する特典の大きさとをクロスすることで、ボーナス状態中の遊技性を多様化することができる。例えば、図114(E)に示すように、ボーナス状態(BB)の開始直後であるBB中一般は、特典付与の振れ幅が小さい安定的な状態となる。また、その後RBに当籤しBB中RB持越に移行した場合も、特典付与の振れ幅が小さい安定的な状態となる。一方で、その後RBに入賞しBB中RBに移行した場合、特典付与の振れ幅が大きい暴れ状態となる。RBを入賞させるか否かは、遊技者が選択することができるため、遊技性(その12)では、RBの入賞を回避することで特典付与の振れ幅を安定的な状態とするか、RBを入賞させることで特典付与の振れ幅を暴れ状態とするか、遊技者が選択することができる。なお、遊技性(その12)は、ボーナス状態中の遊技状態間で特典付与の確率と付与する特典の大きさとをクロスすることで実現可能なものであり、どの遊技状態を特典付与の振れ幅が小さい安定的な状態とするか、また、どの遊技状態を特典付与の振れ幅が大きい暴れ状態とするかは任意である。また、特典付与の確率と付与する特典の大きさとをクロスした遊技状態間において、特典付与の総合的な期待度は同一(又は略同一)となるように、特典付与の確率と付与する特典の大きさとが設定されていることが好ましい。 As described above, in the game property (12), the game property in the bonus state can be diversified by crossing the probability of granting the privilege and the size of the privilege to be granted. For example, as shown in FIG. 114(E), the general state of BB immediately after the start of the bonus state (BB) is in a stable state in which the swing of privilege grant is small. Further, even if the player subsequently wins the RB and shifts to the RB carryover in the BB, the amount of swing of privilege grant is small and stable. On the other hand, when the player subsequently wins the RB and shifts to the RB during the BB, the swing range of the award is large, which is a violent state. Since it is possible for the player to select whether or not to win the RB, in the playability (No. 12), it is possible to avoid the winning of the RB to make the swing of the privilege grant stable. It is possible for the player to select whether or not the swing range of the privilege grant is in a rampage state by winning the prize. The game property (No. 12) can be realized by crossing the probability of award and the size of the award to be given between the game states in the bonus state. Is a small and stable state, and which gaming state is a rampage state in which the swing of privilege grant is large is arbitrary. In addition, between the gaming states in which the probability of awarding the privilege and the size of the awarding privilege are crossed, the probability of awarding the privilege and the awarding privilege are set so that the overall degree of expectation of the awarding is the same (or substantially the same). The size is preferably set.
(遊技例)
続いて、図114(F)は、ボーナス状態中の遊技例を示す図であり、遊技例1は、特典付与の振れ幅を安定的な状態とする場合の遊技例であり、遊技例2は、特典付与の振れ幅を暴れ状態とする場合の遊技例である。
(Game example)
Subsequently, FIG. 114(F) is a diagram showing a game example during the bonus state, game example 1 is a game example in which the swing range of the privilege grant is stable, and game example 2 is , Is a game example in the case where the swing of privilege grant is in a rampage state.
遊技例1では、ボーナス状態中にRBに当籤した場合、RBを入賞させることなくBB中RB持越のままボーナス状態中の遊技を行う。RBに当籤するまで(BB中一般)及びRBを持ち越している間(BB中RB持越)は、特典付与確率が高いものの、特典を付与する場合に付与する特典の大きさが小さいため、特典付与の振れ幅が小さく安定する。 In the game example 1, when an RB is won in the bonus state, the game in the bonus state is carried out while the RB in the BB is carried over without winning the RB. Until the RB is won (general in BB) and while the RB is carried over (RB in BB carryover), the privilege grant probability is high, but the size of the privilege granted when granting the privilege is small, so the privilege grant The fluctuation range is small and stable.
一方、遊技例2では、ボーナス状態中にRBに当籤した場合、RBを入賞させてBB中RBにおいてボーナス状態中の遊技を行う。BB中RBは、特典付与確率が低いものの、特典を付与する場合に付与する特典の大きさが大きいため、特典付与の振れ幅が大きく暴れる。 On the other hand, in the game example 2, when the RB is won in the bonus state, the RB is won and the game in the bonus state is performed in the BB in the BB. Although the RB in the BB has a low privilege granting probability, the size of the privilege granted when granting the privilege is large, and thus the swing of privilege granting is greatly violent.
また、本仕様例では、ボーナス状態が終了し非ボーナス状態に移行した場合、ボーナス状態終了時のRT状態を維持したまま、非ボーナス状態に移行する。ここで、報知状態(ART)中にボーナス状態に移行した場合、ボーナス状態の終了後に再びARTを行うことになるが、ボーナス状態が高RTのまま終了した場合には、ボーナス状態の終了後にRT状態を高RTへ移行することなくそのままARTを開始することができ、ボーナス状態が低RTのまま終了した場合には、ボーナス状態の終了後にRT状態を高RTへ移行させた後にARTを開始することになる。そのため、遊技例1のようにRBを入賞させることなくBB中RB持越(高RT)のままボーナス状態中の遊技を行った場合には、ボーナス状態の終了直後からARTを開始することができ、遊技例2のようにBB中RB(低RT)においてボーナス状態を終了した場合には、ボーナス状態の終了後にRT状態を高RTへ移行させるための準備期間を経由して、ARTを開始することになる。 Further, in the present specification example, when the bonus state ends and the non-bonus state is entered, the non-bonus state is entered while maintaining the RT state at the end of the bonus state. Here, if the bonus state is entered during the notification state (ART), ART will be performed again after the bonus state ends. ART can be started as it is without shifting the state to high RT, and if the bonus state ends with low RT, the RT state is shifted to high RT after the bonus state ends and then ART is started. It will be. Therefore, if you play a game in the bonus state with RB carryover in BB (high RT) without winning the RB as in the game example 1, you can start ART immediately after the bonus state ends, When the bonus state is ended in RB during BB (low RT) as in the game example 2, after starting the bonus state, the ART is started via the preparation period for shifting the RT state to the high RT. become.
また、上述したようにRBの入賞を回避しているBB中RB持越は、RBを入賞させた場合のBB中RBよりもメダルの払出期待値が高い高ベースの遊技状態である。そのため、特典付与の振れ幅が大きいBB中RBでは、特典付与の確率低下分だけでなく、ボーナス状態終了後の準備期間分、及び出玉のベース低下分も、付与する特典の大きさに振り分けることができる。そのため、遊技者にとってみれば、ボーナス状態中に特典が付与され易いが小さな特典しか付与されないように遊技を行うか(BB中RB持越)、特典が付与され難いが大きな特典が付与されるよう遊技を行う(BB中RB)か、選択することができ、戦略性を持った新たな遊技性を実現することができる。 Further, as described above, the RB carryover in BB avoiding the winning of the RB is a high base game state in which the expected payout value of the medal is higher than that of the RB in the BB when the RB is won. Therefore, in the BB in BB in which the swing of the bonus grant is large, not only the probability reduction of the bonus grant but also the preparation period after the end of the bonus state and the bonus drop base are distributed to the bonus size to be granted. be able to. Therefore, for the player, the game is performed so that the privilege is easily awarded in the bonus state but only the small privilege is provided (RB carryover in BB), or the game is provided so that the privilege is difficult to be provided but the large privilege is provided. Can be selected (RB in BB) or can be selected, and a new game property with a strategic characteristic can be realized.
(遊技性(その12)の別例)
以上説明した仕様例のパチスロ1では、特典付与の確率と付与する特典の大きさとをクロスすることで、ボーナス状態中の遊技性を多様化しているが、遊技性(その12)は、これに限るものではなく、以下のような仕様も含むものである。具体的には、上述のように本仕様例のパチスロ1では、BB中RB持越と、BB中RBとでは、メダルの払出期待値(すなわち、単位遊技当たりに付与されるメダルの期待値)が異なる。遊技性(その12)は、メダルの払出期待値と、特典の期待値とをクロスさせる仕様を含む。
(Another example of playability (12))
In the pachi-
ここで、上述の説明では、BB中RB持越のメダルの払出期待値と、BB中RBのメダルの払出期待値とを、リプレイに係る役の当籤確率(言い換えると、はずれの当籤確率)に応じて異なる点について説明した。この点、BB中RB持越のメダルの払出期待値と、BB中RBのメダルの払出期待値とは、ベルの当籤確率に応じても異なるため、以下説明する。 Here, in the above description, the expected payout value of the medal of the RB in BB carryover and the expected payout value of the medal of the RB in BB are determined according to the winning probability (in other words, the winning probability of failure) of the hand related to the replay. Different points were explained. In this respect, the expected payout value of the BB in-RB carryover medal and the expected payout value of the BB in RB medal are different depending on the winning probability of the bell, and will be described below.
図113(B)に示すように、BB中RB持越と、BB中RBとでは、ベル(「BEL_01」〜「BEL_09」)の当籤確率が異なる。具体的には、ベルのうちの「BEL_01」〜「BEL_09」の夫々が内部当籤役として決定される個々の当籤確率が、BB中RB持越と、BB中RBとで異なるとともに、ベルのうちの「BEL_01」〜「BEL_09」の少なくとも何れかが内部当籤役として決定される当籤確率も、BB中RB持越と、BB中RBとで異なる。 As shown in FIG. 113(B), the winning probability of the bell (“BEL_01” to “BEL_09”) is different between the RB carry-over in the BB and the RB carry out in the BB. Specifically, the individual winning probabilities that "BEL_01" to "BEL_09" of the bells are determined as the internal winning combinations are different between the RB in BB carryover and the RB in BB, and The winning probability that at least one of “BEL_01” to “BEL_09” is determined as the internal winning combination is different between the RB in BB carryover and the RB in BB.
より具体的には、BB中RB持越では、「押し順ベル1st」〜「押し順ベル3rd」に対して「3000」の抽籤値が設定されている結果、「BEL_01」〜「BEL_09」の夫々に対して「3000」の抽籤値が設定されている。これに対して、BB中RBでは、「RB中ベル」に対して「3100」の抽籤値が設定されている結果、「BEL_01」〜「BEL_09」の夫々に対して「3100」の抽籤値が設定されている。そのため、BB中RB持越と、BB中RBとでは、ベルのうちの「BEL_01」〜「BEL_09」の夫々が内部当籤役として決定される個々の当籤確率は、BB中RBの方が高い(3100>3000)。一方で、BB中RB持越では、夫々「3000」の抽籤値が設定された3種類のベル(「押し順ベル1st」〜「押し順ベル3rd」)が当籤するのに対して、BB中RBでは、「3000」の抽籤値が設定された「RB中ベル」の1種類のみが当籤する。そのため、BB中RB持越と、BB中RBとでは、ベルのうちの「BEL_01」〜「BEL_09」の少なくとも何れかが当籤役として決定される当籤確率は、BB中RB持越の方が高い(9000>3100)。 More specifically, in the RB carryover during BB, as a result of the lottery value of “3000” being set for “push order bell 1st” to “push order bell 3rd”, each of “BEL_01” to “BEL_09” is set. A lottery value of “3000” is set for. On the other hand, in the RB in BB, the lottery value of “3100” is set for the “bell in RB”, and as a result, the lottery value of “3100” is set for each of “BEL_01” to “BEL_09”. It is set. Therefore, in the RB in BB carryover and the RB in BB, the individual winning probabilities in which each of “BEL_01” to “BEL_09” of the bell is determined as the internal winning combination are higher in the RB in BB (3100). >3000). On the other hand, in the BB middle RB carryover, while three types of bells (“push order bell 1st” to “push order bell 3rd”), each of which has a lottery value of “3000”, win the RB middle RB. Then, only one kind of "RB middle bell" for which the lottery value of "3000" is set is won. Therefore, in the RB in BB carryover and in the RB in BB, the winning probability that at least one of "BEL_01" to "BEL_09" of the bell is determined as the winning combination is higher in the RB in BB carryover (9000). >3100).
そのため、本仕様例では、「BEL_01」〜「BEL_09」の個々の当籤確率を単独で見ると、BB中RBの方が当籤確率が高いものの、「BEL_01」〜「BEL_09」の全体の当籤確率を総合的に見ると、BB中RB持越の方が高くなる。そして、上述したように、主制御回路90は、BB中RB持越において遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知するため、ベルの当籤確率という観点からも、BB中RBと、BB中RB持越とでは、前者の方がメダルの払出期待値が高いことになる。
Therefore, in the present specification example, when the individual winning probabilities of “BEL_01” to “BEL_09” are individually viewed, the winning probability of the RB in the BB is higher, but the overall winning probability of “BEL_01” to “BEL_09” is determined. Overall, RB carryover is higher than BB carryover. Then, as described above, since the
続いて、メダルの払出期待値とクロスする特典の期待値について説明する。特典の期待値には、特典付与の確率と付与する特典の大きさとが含まれ、これらを任意に設定することができる。なお、上述の仕様例では、特典付与の総合的な期待度が同一(又は略同一)となるように、特典付与の確率と付与する特典の大きさとを設定することとしているが、別例のように、メダルの払出期待値と特典の期待値とをクロスする場合には、特典の期待値が必ずしも同一になる必要はなく、メダルの払出期待値の大小と特典の期待値の大小とを総合した遊技者の有利度合いが同一(又は略同一)となればよい。 Next, the expected value of the benefit that crosses the expected payout value of the medal will be described. The expected value of the privilege includes the probability of granting the privilege and the size of the privilege to be granted, and these can be set arbitrarily. In the above-mentioned specification example, the probability of awarding and the size of the awarding are set so that the overall degree of expectation of awarding is the same (or substantially the same). As described above, when the expected value of the medal payout and the expected value of the benefit are crossed, the expected value of the benefit does not necessarily have to be the same, and the expected value of the medal payout is different from the expected value of the benefit. It is only necessary that the overall degree of advantage of the player is the same (or substantially the same).
具体的には、別例では、BB中RBと、BB中RB持越とでは、メダルの払出期待値が低いBB中RBの方が、メダルの払出期待値が高いBB中RB持越よりも、特典の期待値が遊技者にとって有利となるように設定することで、メダルの払出期待値と特典の期待値とをクロスする。一例として、BB中RBでは、BB中RB持越よりも、特典付与の確率を高くするとともに、付与する特典の大きさも大きくすることで、メダルの払出期待値と特典の期待値とをクロスすることとしてもよく、また、BB中RBでは、BB中RB持越よりも、特典付与の確率を低くする一方で(又は同一の確率とする一方で)、付与する特典の大きさを大きくすることで、メダルの払出期待値と特典の期待値とをクロスすることとしてもよく、また、BB中RBでは、BB中RB持越よりも、特典付与の確率を高くする一方で、付与する特典の大きさを小さくする(又は同一にする)ことで、メダルの払出期待値と特典の期待値とをクロスすることとしてもよい。 Specifically, in another example, in BB in BB and in BB in BB carryover, BB in RB with a lower expected payout value of medals is more advantageous than in BB in RB carryover with a higher expected medal payout value. By setting so that the expected value of is advantageous to the player, the expected value of payout of medals and the expected value of privilege are crossed. As an example, in the RB in the BB, the probability of granting the privilege is made higher and the size of the privilege to be granted is made larger than that in the carryover in the RB in the BB to cross the expected payout value of the medal and the expected value of the benefit. Also, in the RB in the BB, the probability of granting the privilege is lower than that in the carryover in the RB in the BB (or the same probability), and the size of the privilege to be granted is increased, The expected payout value of the medal may be crossed with the expected value of the privilege, and in the RB in the BB, the probability of granting the privilege is higher than in the carryover in the RB in the BB, while the size of the privilege to be granted is increased. The payout expected value of the medal and the expected value of the privilege may be crossed by reducing (or making the same).
[主制御基板及び副制御基板が有する各種機能]
以上、本仕様例のパチスロ1の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その11)について説明した。続いて、パチスロ1の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その11)を発揮する際の主制御回路90及び副制御回路200が有する各種機能について説明する。
[Various functions of the main control board and the sub control board]
Heretofore, another example (11) of the playability (game specification) of the pachi-
主制御回路90は、スタートスイッチ6Sやストップスイッチ7Sと接続され、図1に示す遊技の進行を制御するため、遊技制御手段として機能する。また、リール3L、3C、3R及び表示窓4は、可変表示手段として機能する。
The
また、主制御回路90は、非ボーナス状態においてBBの開始条件を満たすと、ボーナス状態(BB)を開始可能であり、ボーナス状態においてBBの終了条件を満たすと、ボーナス状態を終了可能であるため、主制御回路90は、状態制御手段として機能する。
Further, the
また、主制御回路90は、ボーナス状態においてRBに対応する結果表示が導出されると、ボーナス状態中の遊技状態をBB中RBに移行可能であり、BB中RBにおいてBBの終了条件、又はRBの終了条件を満たすと、BB中RBを終了可能である。また、主制御回路90は、ボーナス状態において、RBが内部当籤役として決定された遊技においてRBが入賞しない場合に、ボーナス状態の間、RBを内部当籤役として持ち越し可能であるとともに、RBを内部当籤役として持ち越している間のボーナス状態中の遊技状態をBB中RB持越とする。そのため、主制御回路90は、特定状態制御手段、第1特定状態制御手段、第2特定状態制御手段及び持越手段として機能する。
Further, when the result display corresponding to the RB in the bonus state is derived, the
また、主制御回路90は、ボーナス状態中に報知状態(ART)に関する特典を付与可能であり、特に、BB中RB持越とBB中RBとで、特典付与の確率と付与する特典の大きさとをクロスするため、主制御回路90は、特典付与手段として機能する。このとき、主制御回路90は、BB中RB持越とBB中RBとで、特典付与の確率と付与する特典の大きさとをクロスするのではなく、BB中RB持越とBB中RBとで、メダルの払出期待値と特典の期待値とをクロスすることとしてもよい。
In addition, the
また、主制御回路90は、ボーナス状態中のBB中RB持越が高RTとなるようにRT状態を制御し、BB中RBが低RTとなるようにRT状態を制御するため、主制御回路90は、RT制御手段として機能する。
Further, the
[遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その13)]
続いて、図115〜図119を参照して、本実施形態に係るパチスロ1において実装可能な遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その13)について説明する。
[Another example of playability (game specification) (13)]
Next, with reference to FIGS. 115 to 119, another example (No. 13) of the playability (game specification) that can be mounted in the pachi-
(遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その13)の概要)
初めに、図115を参照して、遊技性(その13)の概要について説明する。遊技性(その13)では、色択小役と押し順小役とを重複して内部当籤役として決定することで、従来にない新たな遊技性を実現する。上述のように、択数を調整する方法としては、押し順に基づき択数を調整する方法に加え、1又は全てのリールに対して特定の位置で停止操作を行うこと(目押し)を要求することで択数を調整する方法がある。本仕様例において、色択小役とは、全てのリールに対して特定の位置で停止操作を行うこと(目押し)で入賞する択数小役であり、押し順小役とは、特定の押し順で停止操作を行うことで入賞する択数小役をいう。
(Outline of another example of playability (game specification) (13))
First, with reference to FIG. 115, an outline of the game characteristic (13) will be described. In the playability (13), the color selection small combination and the push order small combination are overlapped and determined as the internal winning combination, thereby realizing a new gameplay which has never existed before. As described above, as a method of adjusting the number of choices, in addition to the method of adjusting the number of choices based on the pressing order, one or all reels are required to perform a stop operation at a specific position (pushing). There is a way to adjust the number of choices. In this specification example, the color selection small win is a small number of small wins that are won by performing a stop operation (pushing) on all reels at a specific position. It refers to a small number of small wins that are won by performing stop operations in the pressing order.
本仕様例のパチスロ1では、リール3L,3C,3Rのそれぞれを、大きさが同一(又は略同一)の赤領域、青領域及び黄領域の3つの領域に分ける。リール配列については省略するが、例えば、各リールに図柄位置「0」〜「20」の21個の図柄が配置されている場合、各リールの図柄位置「0」〜「6」を赤領域とし、図柄位置「7」〜「13」を青領域とし、図柄位置「14」〜「20」を黄領域とすることで実現することができる。
In the pachi-
色択小役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、3つのリール3L,3C,3Rのそれぞれにおいて、3つの領域のうちの正解の領域において停止操作が行われると、全てのリールに対して特定の位置で停止操作が行われたとして、色択小役が入賞する。すなわち、色択小役は、27択(=3×3×3)に正解した場合に入賞する。なお、詳しくは後述するが、本仕様例においては、色択小役と押し順小役とを重複させるとともに、色択小役よりも押し順小役を優先して引き込む制御としているため、色択小役は、色択小役と押し順小役とが重複して当籤した場合の40.5択に正解した場合に入賞する。
When the color selection small winning combination is determined as the internal winning combination, when the stop operation is performed in the correct answer area of the three areas in each of the three
また、以下の説明において、色択小役の名称には「色択_」に続いて3つの色の名称を付す。これら3つの色の名称が3つのリール3L,3C,3Rのそれぞれにおいて正解の領域(目押しタイミング)を意味する。例えば、「色択_赤青黄」は、左リール3Lにおいて正解の領域が赤領域であり、中リール3Cにおいて正解の領域が青領域であり、右リール3Rにおいて正解の領域が黄領域の色択小役である。また、押し順小役の名称には「押し順ベル_」に続いて正解の押し順として「1st」〜「3rd」を付す。正解の押し順「1st」は、第1停止操作が左のリール3Lに対するものであり、正解の押し順「2nd」は、第1停止操作が中のリール3Cに対するものであり、正解の押し順「3rd」は、第1停止操作が右のリール3Rに対するものであることを意味する。すなわち、本仕様例においては、押し順小役は、3択の押し順に正解した場合に入賞する。そして、色択小役と押し順ベルとが重複している役の名称を、例えば「色択_赤青黄+押し順ベル_1st」のように表記する。
In addition, in the following description, the names of the color selection subcommittees are given the names of three colors after “color selection_”. The names of these three colors mean the correct areas (pushing timing) on each of the three
図115(A)(B)に示すように、色択小役と押し順小役とが重複して当籤した場合(「色択小役+押し順小役」が内部当籤役として決定された場合)に色択に正解すると色択小役が入賞し、押し順に正解すると押し順小役(ベル)が入賞し、色択及び押し順の何れにも不正解すると、はずれとなる。そして、主制御回路90は、色択小役又は押し順小役が入賞した場合、「色択小役+押し順小役」の当籤時に払い出され得る最大の枚数のメダル(例えば、6枚)を払い出し、はずれの場合、当該最大の枚数よりも少ない枚数のメダル(例えば、1枚又は2枚)又は0枚のメダルを払い出す。また、色択小役が入賞した場合には、主制御回路90は、当該最大の払出枚数のメダルの払い出しに加えて、押し順小役が入賞した場合及びはずれの場合には付与されることのない特典を付与する可能性がある。
As shown in FIGS. 115(A) and 115(B), when the winning combination of the color-selecting small combination and the pressing-order small winning is overlapped (“color-selecting small combination + pressing-order small winning combination” is determined as an internal winning combination). If the correct answer to the color choice in the case) wins the color choice small win, if the correct answer in the press order wins the push order small win (bell), if you answer incorrectly in both the color choice and the press order, you will be out of touch. Then, the
すなわち、押し順よりも正解が困難な色択に正解した場合には、最大のメダルの払出を受けることができるとともに、特典付与を受けることができる一方で、色択よりも正解が容易な押し順に正解した場合には、最大のメダルの払出を受けることができるものの、特典付与を受けることはできない。なお、色択正解時に付与可能な特典の種類は任意であるが、以下においては、報知状態(ATやART)に関する特典を付与するものとする。一例として、主制御回路90は、非報知状態において色択小役が入賞すると、50%の確率で報知状態に関する特典(例えば、ATのストック)を付与する。そして、主制御回路90は、非報知状態において報知状態に関する特典を付与した場合、その後、遊技状態を報知状態に移行する(例えば、50ゲーム間の間ATを行う)。
That is, if you answer correctly to a color choice that is harder to answer than the press order, you can get the maximum medal payout and receive a privilege, but you can get the correct answer more easily than color choice. If the answers are correct in order, the maximum medal can be paid out, but the privilege cannot be granted. It should be noted that the type of privilege that can be granted at the time of correct answer of color selection is arbitrary, but in the following, it is assumed that the privilege related to the notification state (AT or ART) is granted. As an example, the
続いて、図115(C)に本仕様例のパチスロ1における遊技例を示す。同図(a)に示すように、主制御回路90は、「色択小役+押し順小役」が内部当籤役として決定された場合であっても、非報知状態では停止操作の情報を何も報知しない(すなわち、正解の目押しタイミングも正解の押し順も報知せず、また、はずれとなる停止操作の情報も報知しない)ため、遊技者は、報知状態に移行させるために色択の自力正解を目指して遊技を行う。ここで、色択小役は、択数が多いため入賞させることが困難であるため、「色択小役+押し順小役」の当籤確率は高くすることができる。以下に示すように、本仕様例のパチスロ1では、「色択小役+押し順小役」の当籤確率を約1/5(=(162×81)/65536)となるように設定している。そのため、遊技性(その13)では、非報知状態において5ゲームに1回の割合で、報知状態に関する特典付与のチャンスが訪れるという遊技性を実現することができる。
Subsequently, FIG. 115C shows a game example in the pachi-
なお、色択小役の択数は、40.5択(3択の押し順に不正解の場合の27択正解(=2/3×1/27))であるため、色択小役の入賞確率は、約1/202.5(=1/5×1/40.5)であり、色択小役の入賞に伴う特典付与の確率は、約1/405(1/202.5×50%)である。すなわち、遊技性(その13)では、非報知状態において5ゲームに1回という比較的高い割合で遊技者に対してチャンスを与えることができるものの、実際に報知状態に関する特典が付与される割合は、約405ゲームに1回とすることができるため、遊技者に対して特典付与の機会を多く与えつつも、遊技者に過度な利益与えてしまうことがない。 It should be noted that the number of choices for the color-selecting small winning combination is 40.5 choices (27 correct answers in the case of incorrect answers in the order of pressing 3 selections (= 2/3 x 1/27)), so the winning of the color-selecting small winning combination is The probability is about 1/202.5 (=1/5×1/40.5), and the probability of awarding a prize associated with a winning of a color-selecting small winning combination is about 1/405 (1/202.5×50). %). That is, in the playability (13), although the opportunity can be given to the player at a relatively high rate of once in five games in the non-notification state, the rate at which the privilege related to the notification state is actually given is Since it can be performed once per about 405 games, it does not give an excessive profit to the player while giving the player many opportunities to give a privilege.
また、同図(b)に示すように、主制御回路90は、報知状態において「色択小役+押し順小役」が内部当籤役として決定されると、押し順小役を入賞させるために必要な停止操作の情報(3択の正解の押し順)を報知する。すなわち、本仕様例のパチスロ1では、報知状態中に「色択小役+押し順小役」が内部当籤役として決定された場合、色択小役ではなく押し順小役の入賞を促す報知を行う。上述したように、色択小役が入賞した場合に払い出されるメダルの枚数と押し順小役が入賞した場合に払い出されるメダルの枚数は同一であるため、「色択小役+押し順小役」の当籤時に押し順小役を入賞させたとしても、払い出されるメダルの枚数に差はない。報知状態中にも色択小役を入賞させるための目押しを必要としたのでは、遊技者にとって煩わしく、所謂取りこぼしが発生してしまう可能性もあるが、押し順に従うだけで最大の枚数の払い出しを受けることができるように制御することで、遊技者は煩わしさを感じることもなく、また、取りこぼしの発生も抑えることができる。
Further, as shown in FIG. 7B, the
このように遊技性(その13)では、非報知状態中は、択数が多く入賞が困難な色択小役に基づき特典を付与することで、遊技者に対して特典付与の機会を多く与えるとともに、遊技者が特典付与の決定結果に関して関与可能な遊技性を実現することができる。また、遊技性(その13)では、報知状態中は、押し順のみで入賞する押し順小役の入賞を促す報知を行うことで、報知状態中は目押しよりも簡易な押し順が正解するように遊技を行えば足りるため、報知状態中の遊技をスムーズに行うことができるという遊技性を実現することができる。 As described above, in the playability (part 13), in the non-notification state, the privilege is given based on the color selection small combination that has a large number of choices and is difficult to win, thereby giving the player many opportunities to give the privilege. At the same time, it is possible to realize a game property in which the player can be involved in the determination result of the privilege grant. In addition, in the playability (part 13), during the notification state, the notification that prompts the winning of the push order small winning combination that wins only in the push order is performed, so that the pressing order that is simpler than the pressing is correct during the notification state. Since it is sufficient to play the game as described above, it is possible to realize the game property that the game in the notification state can be played smoothly.
(パチスロの仕様例)
続いて、遊技性(その13)を実現可能なパチスロの仕様例について説明する。パチスロ1は、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知する(又は報知する頻度が高い)報知状態と遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知する(又は報知する頻度が高い)非報知状態とを有する。主制御回路90は、非報知状態において報知状態への移行条件を満たすと、遊技状態を非報知状態から報知状態に移行する。具体的には、主制御回路90は、非報知状態において色択小役に応じた結果表示が導出されると(色択小役が入賞すると)、所定の確率(50%)で報知状態に移行すると決定する。また、主制御回路90は、報知状態において報知状態の終了条件を満たすと、遊技状態を報知状態から非報知状態に移行する。なお、本仕様例において報知状態の終了条件は任意である。
(Example of pachislot specifications)
Next, a specification example of a pachi-slot that can achieve the game play (13) will be described. The pachi-
ここで、図116及び図117は、内部当籤役を決定するために用いる一般遊技中内部抽籤テーブルである。同図では、「色択小役+押し順小役」に関する抽籤値を示し、その他の役に関する抽籤値については省略している。また、同図では、「対応する図柄組合せ」欄の表示は省略しているが、本仕様例では、図119に示す対応関係を実現可能になるように内部当籤役として決定された場合に入賞が許可される図柄の組合せが対応付けられている。 Here, FIG. 116 and FIG. 117 are internal lottery tables during normal game used for determining an internal winning combination. In the figure, the lottery values for "color selection small combination + push order small combination" are shown, and the lottery values for other combinations are omitted. Further, in the same figure, the display of the "corresponding symbol combination" column is omitted, but in this specification example, a prize is awarded when the internal winning combination is determined so that the correspondence shown in FIG. 119 can be realized. The combinations of symbols that are permitted are associated with each other.
同図に示すように、本仕様例のパチスロ1では、81種類の「色択小役+押し順小役」を有し、夫々に対して抽籤値「162」を規定している。そのため、81種類の「色択小役+押し順小役」の総抽籤値は「13122(=162×81)」であり、「色択小役+押し順小役」の何れかは、約1/5(=13122/65536)の確率で当籤する。
As shown in the figure, in the pachi-
続いて、図118は、本仕様例のパチスロ1における入賞等に係る図柄の組合せを規定する図柄組合せテーブルである。なお、本仕様例のパチスロ1の遊技性の説明において、図柄の組合せを構成する図柄の種類は必要がないため、説明及び図示を省略する。また、同図では、「色択小役+押し順小役」に関する図柄の組合せについてのみ示し、その他の図柄の組合せについては省略している。図柄組合せテーブルは、複数の図柄の組合せを予め規定しており、これらの図柄の組合せの種別を示すデータを、表示役(入賞作動フラグ)として規定している。
Next, FIG. 118 is a symbol combination table that defines symbol combinations relating to winning and the like in the pachi-
同図において、「図柄組合せ1−1」〜「図柄組合せ1−n」は、「C_色択_赤赤赤」に係る図柄の組合せであり、内部当籤役として「色択_赤赤赤」が決定され、かつ、色択に正解した場合に表示される可能性のある図柄の組合せである。同様に、「図柄組合せ2−1」〜「図柄組合せ2−n」乃至「図柄組合せ27−1」〜「図柄組合せ27−n」は、「C_色択_赤赤青」乃至「C_色択_黄黄黄」に係る図柄の組合せであり、内部当籤役として「色択_赤赤赤」乃至「色択_黄黄黄」が決定され、かつ、色択に正解した場合に表示される可能性のある図柄の組合せである。 In the figure, "symbol combination 1-1" to "symbol combination 1-n" are combinations of symbols relating to "C_color selection_red red red", and "color selection_red red red" as an internal winning combination. Is the combination of the symbols that may be displayed when the answer is correct for the color selection. Similarly, “symbol combination 2-1” to “symbol combination 2-n” to “symbol combination 27-1” to “symbol combination 27-n” are “C_color selection_red/red/blue” to “C_color selection”. It is a combination of symbols related to "_YellowYellow", and is displayed when "Choice_Red_Red_Red" to "Choice_Yellow-Yellow" are determined as the internal winning combination and the correct answer is given to the color choice It is a possible combination of symbols.
また、「図柄組合せ28−1」〜「図柄組合せ28−n」は、「C_ベル」に係る図柄の組合せであり、内部当籤役として押し順小役の何れかが決定され、かつ、当該押し順小役における正解の押し順で停止操作が行われた場合に表示される可能性のある図柄の組合せである。また、「図柄組合せ29−1」〜「図柄組合せ29−n」は、「C_こぼし目」に係る図柄の組合せであり、内部当籤役として「色択小役+押し順小役」の何れかが決定され、かつ、色択及び押し順に不正解した場合に表示される可能性のある図柄の組合せである。 In addition, “symbol combination 28-1” to “symbol combination 28-n” are combinations of symbols related to “C_bell”, and one of the push order small winning combinations is determined as the internal winning combination, and the pressing is performed. It is a combination of symbols that may be displayed when the stop operation is performed in the order of pressing the correct answer in the forward small win. In addition, "symbol combination 29-1" to "symbol combination 29-n" is a combination of symbols relating to "C_ Kobo eyes", and any one of "color selection small combination + push order small combination" as an internal winning combination. Is a combination of symbols that may be displayed when the color selection and the pressing order are incorrect.
「色択小役+押し順小役」の夫々には、「図柄組合せ1−1」〜「図柄組合せ29−n」のうちの複数の図柄の組合せが対応する図柄の組合せとして規定されている結果、本仕様例のパチスロ1では、主制御回路90は、「色択小役+押し順小役」が内部当籤役として決定された場合に、図119に示す対応関係を有する図柄の組合せが表示されるように、リール制御が可能になる。
In each of the "color selection small combination + push order small combination", a combination of a plurality of symbols of "symbol combination 1-1" to "symbol combination 29-n" is defined as a corresponding symbol combination. As a result, in the pachi-
続いて、図119は、本仕様例のパチスロ1における内部当籤役と停止操作(押し順/目押し)と表示役との対応関係を示す表である。同図では、「色択小役+押し順小役」が内部当籤役として決定された場合の停止操作毎の表示役の対応関係を示し、その他の役に関する対応関係については省略している。
Next, FIG. 119 is a table showing a correspondence relationship between an internal winning combination, a stop operation (pushing order/pressing) and a display combination in the pachi-
同図に示すように「色択_赤赤赤+押し順ベル_1st」が内部当籤役として決定された場合、主制御回路90は、第1停止操作として左のリール3Lに対する停止操作が行われると(左1st)、「C_ベル」に係る図柄の組合せが表示されるように(押し順小役が入賞するように)リールの停止制御を行う。また、第1停止操作として左のリール3L以外のリールに対する停止操作が行われると、主制御回路90は、色択に正解している場合には、「C_色択_赤赤赤」に係る図柄の組合せが表示されるように(色択小役が入賞するように)リールの停止制御を行い、色択に正解していない場合には、「C_こぼし目」に係る図柄の組合せが表示されるように、又は、はずれとなるようにリールの停止制御を行う。
As shown in the figure, when "color selection_red red red+push order bell_1st" is determined as the internal winning combination, the
なお、他の「色択小役+押し順小役」における対応関係は省略しているが、主制御回路90は、他の「色択小役+押し順小役」においても、押し順に正解している場合に押し順小役が入賞するようにリールの停止制御を行い、押し順に不正解で色択に正解している場合に色択小役が入賞するようにリールの停止制御を行い、押し順及び色択の双方に不正解している場合に、「C_こぼし目」に係る図柄の組合せが表示されるように、又は、はずれとなるようにリールの停止制御を行う。そのため、「色択小役+押し順小役」の当籤時には、押し順及び色択の組合せである81通りの停止操作の態様のうち、2通りの態様で色択小役が入賞し、27通りの態様で押し順小役が入賞し、52通りの態様でこぼし目又ははずれとなる。
Although the corresponding relationship in the other "color selection small combination + push order small combination" is omitted, the
このような仕様例のパチスロ1において、遊技性(その13)では、非報知状態中に択数が多く入賞が困難な色択小役の入賞に基づき特典を付与する。ここで、本仕様例においては、色択小役は1/5の確率で内部当籤役として決定されるため、非報知状態では5ゲームに1回の割合で報知状態に関する特典付与のチャンスが訪れるという遊技性を実現することができる。なお、色択小役の当籤確率は、択数を増やすほど増やすことができるため、択数を調整することで、特典付与のチャンスが訪れる頻度も調整することができる。例えば、色択小役が入賞する条件として、6択の停止操作の順序を更に追加することで、色択小役の択数を増やすことができ、また、色択小役が入賞する条件として、全てのリールに対する目押しを要求するのではなく、一部のリールに対する目押しを要求するようにすることで、色択小役の択数を少なくすることができる。
In the pachi-
一方で、択数を増やすと、報知状態中に要求される停止操作が複雑になり煩わしいが、遊技性(その13)では、色択小役と押し順小役とを重複させておき、報知状態中は押し順を報知して押し順小役の入賞を促すため、遊技者は煩わしさを感じることもなく、また、取りこぼしの発生も抑えることができる。 On the other hand, if the number of choices is increased, the stop operation required during the notification state becomes complicated and annoying, but in game play (No. 13), the color selection small combination and the pushing order small combination are overlapped and the notification is made. During the state, since the pushing order is notified and the winning of the pushing order small winning combination is promoted, the player does not feel bothered and the occurrence of omission can be suppressed.
なお、本仕様例のパチスロ1では、色択及び押し順不正解時のこぼし目を表示させるために、「C_ベル」に係る図柄の組合せとは別に、「C_こぼし目」に係る図柄の組合せを設けることとしているが、これに限られるものではない。例えば、有効ラインを、センターライン、トップライン、クロスダウンライン及びクロスアップラインの4本(ボトムラインを除く)とし、有効ラインに沿って表示された場合に「2枚」のメダルが払い出される図柄の組合せとして「ANY−ベル−ANY」を設ける。そして、主制御回路90は、「色択小役+押し順小役」が内部当籤役として決定された遊技において、押し順に正解しているときは、中のリール3Cの中段に図柄「ベル」を停止表示し、色択及び押し順の双方に不正解しているときは、中のリール3Cの上段に図柄「ベル」を停止表示するようにリールの停止制御を行うこととしてもよい。押し順正解に伴い中のリール3Cの中段に図柄「ベル」を停止表示されると、センターライン、クロスダウンライン及びクロスアップラインの3本の有効ラインに沿って「ANY−ベル−ANY」が表示される結果、「6枚(=2×3)」のメダルが払い出される。そして、色択及び押し順不正解に伴いリール3Cの上段に図柄「ベル」を停止表示されると、トップラインの1本の有効ラインに沿って「ANY−ベル−ANY」が表示される結果、「2枚(=2×1)」のメダルが払い出される。このようにすることで、リールの図柄配列や役構成の設計が容易になる。
In addition, in Pachi-
また、本仕様例のパチスロ1では、「色択小役+押し順小役」の当籤時に、色択に正解した場合と、押し順に正解した場合との双方において、「色択小役+押し順小役」の当籤時に払い出され得る最大の枚数のメダルを払い出し、色択及び押し順の何れにも不正解の場合に、当該最大の枚数よりも少ない枚数のメダルを払い出すこととしているが、これに限られるものではない。遊技性(その13)においては、報知状態中の報知対象である押し順に正解した場合に最大の枚数のメダルを払い出しが可能であればよく、色択の正解時に払い出す枚数については任意である。一例として、主制御回路90は、「色択小役+押し順小役」の当籤時に、押し順に正解した場合には最大の枚数のメダルを払い出し、色択に正解した場合と色択及び押し順の何れにも不正解の場合との双方において、当該最大の枚数よりも少ない枚数のメダル(双方において同一の枚数のメダル)を払い出すこととしてもよい。また、主制御回路90は、色択に正解した場合には、当該最大の枚数よりも少ない第1の枚数のメダルを払い出し、色択及び押し順の何れにも不正解の場合には、当該最大の枚数よりも少なく、かつ、第1の枚数とは異なる(少なくてもよく、また、多くてもよい)第2の枚数のメダルを払い出すこととしてもよい。
In addition, in Pachi-
[主制御基板及び副制御基板が有する各種機能]
以上、本仕様例のパチスロ1の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その13)について説明した。続いて、パチスロ1の遊技性(遊技仕様)の他の例(その13)を発揮する際の主制御回路90及び副制御回路200が有する各種機能について説明する。
[Various functions of the main control board and the sub control board]
Heretofore, another example (13) of the playability (game specification) of the pachi-
主制御回路90は、スタートスイッチ6Sやストップスイッチ7Sと接続され、図1に示す遊技の進行を制御するため、遊技制御手段として機能する。また、リール3L、3C、3R及び表示窓4は、可変表示手段として機能する。
The
また、パチスロ1は、報知状態と非報知状態とを有するとともに、押し順正解時に(第2の操作態様で停止操作が行われると)押し順小役が入賞し、押し順不正解かつ色択正解時(第1の操作態様で停止操作が行われると)色択小役が入賞し、押し順及び色択の双方ともに不正解時に(第3の操作態様で停止操作が行われると)こぼし目又ははずれとなる「色択小役+押し順小役」を有する。
In addition, the pachi-
そして、パチスロ1の主制御回路90は、色択小役の入賞時及び押し順小役の入賞時には「6枚」のメダルを払い出し、こぼし目又ははずれの場合には「6枚」よりも少ないメダル又は0枚のメダルを払い出すため、主制御回路90は、利益付与手段として機能する。また、主制御回路90は、非報知状態中の色択小役の入賞時にはメダルの払い出しに加えて、50%の確率で報知状態に関する特典を付与するため、主制御回路90は、報知特典付与手段として機能する。
Then, the
また、主制御回路90は、色択小役の入賞に基づき報知状態に関する特典が付与されると、非報知状態から報知状態に遊技状態を遷移可能であるため、主制御回路90は、報知制御手段として機能する。そして、主制御回路90は、非報知状態において「色択小役+押し順小役」が内部当籤役として決定されても何らの停止操作の情報も報知しない一方で、報知状態において「色択小役+押し順小役」が内部当籤役として決定されると、押し順小役に正解の押し順を報知するため、主制御回路90は、報知手段として機能する。
Further, since the
なお、主制御回路90は、「色択小役+押し順小役」が内部当籤役として決定された遊技において、回転しているリールに対する停止操作のタイミングが適切なタイミングで行われた場合に、言い換えると、回転しているリールにおいて、色択小役に正解の領域が表示されているタイミングで、当該リールに対する停止操作が行われた場合に、色択に正解したとして色択小役を入賞可能にリールの停止制御を行い、回転しているリールに対する停止操作が押し順小役において正解の押し順で行われた場合に、押し順に正解したとして押し順小役を入賞可能にリールの停止制御を行う。
Incidentally, the
[その他の変形例]
上述したように、ART(有利区間)の継続期間の管理方法は任意である。例えば、ゲーム数により継続期間を管理することとしてもよく、また、セット数により継続期間を管理することとしてもよく、また、ART中に払い出されるメダルの枚数や差枚数により継続期間を管理することとしてもよく、また、ART中にメダルの払い出しに影響を与える報知を行った回数(ナビ回数)により継続期間を管理することとしてもよく、また、ART中の任意のタイミングで行う継続判定により継続期間を管理することとしてもよく、また、ART中に特定の図柄組合せが表示されるとARTを終了させることとしてもよい。
この場合、上乗せの対象は、ゲーム数、セット数、ナビ回数、差枚数などのようにARTの継続期間の管理方法によって適宜調整される。
[Other modifications]
As described above, the method of managing the duration of the ART (advantageous section) is arbitrary. For example, the duration may be managed by the number of games, the duration may be managed by the number of sets, or the duration may be managed by the number of medals paid out during ART or the difference. Also, the duration may be managed by the number of times of notifications (number of times of navigation) that influence the payout of medals during ART, and the continuation may be performed by the continuation determination performed at any timing during ART. The period may be managed, or ART may be terminated when a specific symbol combination is displayed during ART.
In this case, the target of addition is appropriately adjusted according to the management method of the duration of the ART such as the number of games, the number of sets, the number of times of navigation, the number of differences, and the like.
また、上述のパチスロ1では、報知(ART)機能の作動を、メイン(主制御基板71)側の制御の下に行うこととしているが、これに限られるものではなく、サブ(副制御基板72)側の制御により報知(ART)機能の作動を行うこととしてもよい。
Further, in the above-described pachi-
また、設定値は1段階のみとしてもよい。このとき、設定変更処理をのこしても良いし、無くしてしまってもよい。設定変更処理を残す場合には、同一設定への打ち直しのみが可能となるため、実質的にはRAMクリアするための処理となる。設定値を1段階のみとする場合であっても、有利状態(ART状態など)の抽籤(初当り及び/又は上乗せなど)に関するモードを設け、所定確率で当籤する所定役が当籤した回数を計数し、その回数が規定値に達したときに、このモードを切り替わるようにすることで、出玉に起伏を生じさせることができる。 Further, the set value may be only one step. At this time, the setting change process may be added or may be omitted. When the setting change process is left, only the same setting can be reset, so that the RAM is substantially cleared. Even when the setting value is only one level, a mode for lottery (first hit and/or addition, etc.) in an advantageous state (ART state, etc.) is provided, and the number of times a predetermined winning combination is won with a certain probability is counted. However, when the number of times reaches a specified value, by switching this mode, it is possible to cause undulation in the payout.
この場合、所定確率の分母と規定値とを掛けた値が一つの出玉の波となる。その値を1日に相当する遊技回数で切り替わるように規定すれば、設定値が1段階であっても、複数設けた遊技機と遜色のないものとすることが出来る。例えば、1日の営業時間を11時間とした場合、11h=39600secであるため、1遊技にかかる最短時間を規則に則り4.1秒とすると、1日当たりの最大遊技回数は、39600/4.1=約9659回となる。なお、休憩(食事やトイレ)を一切挟まないというのは現実的ではないため、1日当たりの遊技回数を概ね8000回程度と考える。所定確率を1/32、規定値を256とすることで、32×256=8192となるため、概ね1日で出玉の波が切り替わるようにすることができる。 In this case, a value obtained by multiplying the denominator of a predetermined probability by a specified value becomes one output ball. If the value is regulated to be switched at the number of games corresponding to one day, even if the set value is one stage, it can be compared with a plurality of gaming machines. For example, if the business hours of one day is 11 hours, then 11h=39600 sec. Therefore, if the minimum time required for one game is 4.1 seconds according to the rule, the maximum number of games per day is 39600/4. 1=about 9659 times. Since it is not realistic that no break (meal or toilet) is sandwiched, the number of games played per day is considered to be about 8,000. By setting the predetermined probability to 1/32 and the specified value to 256, 32×256=8192, so that the output wave can be switched in approximately one day.
さらに、所定役が当籤した回数が規定値に達するたびに、遊技者に有利なモードと不利なモードとが交互に切り替わるようにすれば、二日間サイクルで収益が安定するようになるため、遊技店の営業に資することができる。なお、設定値を1段階にした場合の説明を行ったが、1段階には限られず転用が可能である。より具体的には、設定値の数を変えずに採用すれば、設定値の数を増やさずに、出玉の波をより複雑にすることが可能となる。また、設定値の数を減らせば、設定値が減って単調になるところを補うことができる。 Further, if the number of times the predetermined winning combination reaches the specified value, the mode that is advantageous to the player and the mode that is unfavorable to the player are alternately switched. Can contribute to the business of the store. Although the case where the setting value is set to one step has been described, the setting value is not limited to one step and can be diverted. More specifically, if it is adopted without changing the number of set values, it is possible to make the wave of payout balls more complicated without increasing the number of set values. Further, by reducing the number of set values, it is possible to compensate for the fact that the set values decrease and become monotonous.
また、設定値の数を減らすことができた場合、その分のデータ容量を削減することができる。仮に6段階の設定値を1段階の設定値にすることができれば、データを1/6にまで削減することができる。また、各段階で望む出玉率に設計するための開発コストも1/6となる。さらに言えば、遊技機は試験に適合したもののみが、営業に用いることが許可されるものであるところ、試験に要する時間も短縮することが可能となる。 If the number of set values can be reduced, the data capacity can be reduced accordingly. If the setting value of 6 steps can be changed to the setting value of 1 step, the data can be reduced to 1/6. Also, the development cost for designing the desired payout rate at each stage is 1/6. Furthermore, only the gaming machines that are suitable for the test are permitted to be used for sales, and thus the time required for the test can be shortened.
[その他の遊技機への適用]
また、本実施形態では、遊技機としてパチスロ1を例に挙げて説明したが、本実施形態に係る発明が適用可能な遊技機はこれに限定されない。例えば、停止操作に基づくリール停止制御に係る特徴などのパチスロに特有の特徴以外の特徴は、「パチンコ」と呼ばれる遊技機にも適用可能であり、同様の効果が得られる。すなわち、遊技者の遊技動作(操作)に応じて遊技を行う(遊技制御を行う)ことが可能な遊技機であれば、本実施形態に係る発明を適用することができる。
[Application to other game machines]
Further, in the present embodiment, the pachi-
[その他の本実施形態に係る遊技機の拡張性]
本実施形態のパチスロ1では、遊技者のメダルの投入操作(すなわち、手持ちのメダルをメダル投入口14に対して投入する操作、あるいは、クレジットされたメダルをMAXベットボタン15a、若しくは1ベットボタン15bを操作して投入する操作)により遊技が開始され、遊技が終了したときにメダルの払い出しがある場合には、ホッパー装置51が駆動してメダル払出口24からメダルが払い出され、あるいは、クレジットされる形態について説明したが、これに限られるものではない。
[Other expandability of gaming machine according to the present embodiment]
In the pachi-
例えば、遊技者によって遊技に必要な遊技媒体が投入され、それに基づいて遊技が行われ、その遊技の結果に基づいて特典が付与(例えば、メダルが払い出される)形態全てについて、本発明を適用することができる。すなわち、物理的な遊技者の動作によって遊技媒体が投入され(掛けられ)、遊技媒体が払い出される形態のみならず、主制御回路90(主制御基板71)自体が、遊技者が保有する遊技媒体を電磁的に管理し、メダルレスで遊技を可能とするものであってもよい。また、遊技者が保有する遊技媒体を電磁的に管理するのは、主制御回路90(主制御基板71)に装着され(接続され)、遊技媒体を管理する遊技媒体管理装置であってもよい。 For example, the present invention is applied to all modes in which a player inserts a game medium required for a game, a game is performed based on the game medium, and a privilege is provided (for example, a medal is paid out) based on the result of the game. be able to. That is, not only the game medium is thrown in (played) by the physical action of the player and the game medium is paid out, but the main control circuit 90 (main control board 71) itself has the game medium owned by the player. May be managed electromagnetically to enable games without medals. Further, the game medium managed by the player may be electromagnetically managed by a game medium management device mounted (connected) to the main control circuit 90 (main control board 71) and managing the game medium. ..
この場合、遊技媒体管理装置は、ROM及びRWM(あるいは、RAM)を有して、遊技機に設けられる装置であって、図示しない外部の遊技媒体取扱装置と所定のインターフェースを介して双方向通信可能に接続されるものであり、遊技媒体の貸出動作(すなわち、遊技者が遊技媒体の投入操作を行う上で、必要な遊技媒体を提供する動作)若しくは遊技媒体の払出に係る役に入賞(当該役が成立)した場合の、遊技媒体の払出動作(すなわち、遊技者に対して遊技媒体の払出を行う上で、必要な遊技媒体を獲得させる動作)、又は遊技の用に供する遊技媒体を電磁的に記録する動作を行い得るものとすればよい。また、遊技媒体管理装置は、これら実際の遊技媒体数の管理のみならず、例えば、その遊技媒体数の管理結果に基づいて、パチスロ1の前面に、保有する遊技媒体数を表示する保有遊技媒体数表示装置(不図示)を設けることとし、この保有遊技媒体数表示装置に表示される遊技媒体数を管理するものであってもよい。すなわち、遊技媒体管理装置は、遊技者が遊技の用に供することができる遊技媒体の総数を電磁的方法により記録し、表示することができるものとすればよい。
In this case, the game medium management device has a ROM and an RWM (or RAM), is a device provided in the game machine, and is a two-way communication with an external game medium handling device (not shown) through a predetermined interface. It is connected as much as possible and wins a role relating to the lending operation of the game medium (that is, the operation of providing the necessary game medium when the player performs the operation of inserting the game medium) or the payout of the game medium ( The payout operation of the game medium (that is, the operation of acquiring the necessary game medium for paying out the game medium to the player) when the combination is established), or the game medium used for the game It suffices if it is possible to perform the operation of recording electromagnetically. In addition, the game medium management device not only manages the actual number of game media, but also holds the number of game media held on the front of the pachi-
また、この場合、遊技媒体管理装置は、遊技者が、記録された遊技媒体数を示す信号を、外部の遊技媒体取扱装置に対して自由に送信させることできる性能を有し、また、遊技者が直接操作する場合のほか、記録された遊技媒体数を減ずることができない性能を有し、また、外部の遊技媒体取扱装置との間に外部接続端子板(不図示)が設けられる場合には、その外部接続端子板を介してでなければ、遊技者が、記録された遊技媒体数を示す信号を送信できない性能を有することが望ましい。 Further, in this case, the game medium management device has the capability of allowing the player to freely transmit a signal indicating the recorded number of game media to an external game medium handling device, and In addition to the case where the player directly operates, the number of recorded game media cannot be reduced, and when an external connection terminal board (not shown) is provided between the game machine handling device and an external game media handling device. It is desirable that the player has the ability to transmit a signal indicating the number of recorded game media only through the external connection terminal board.
遊技機には上記の他、遊技者が操作可能な貸出操作手段、返却(精算)操作手段、外部接続端子板が設けられ、遊技媒体取扱装置には紙幣等の有価価値の投入口、記録媒体(例えばICカード)の挿入口、携帯端末から電子マネー等の入金を行うための非接触通信アンテナ等、その他貸出操作手段、返却操作手段等各種操作手段、遊技媒体取扱装置側外部接続端子板が設けられるようにしてもよい(いずれも不図示)。 In addition to the above, the game machine is provided with a lending operation means, a return (settlement) operation means, and an external connection terminal board that can be operated by the player. (For example, an IC card), a non-contact communication antenna for depositing electronic money or the like from a mobile terminal, various lending operation means, various operation means such as return operation means, and a game medium handling device-side external connection terminal board It may be provided (all are not shown).
その際の遊技の流れとしては、例えば、遊技者が遊技媒体取扱装置に対しいずれかの方法で有価価値を入金し、上記いずれかの貸出操作手段の操作に基づいて所定数の有価価値を減算し、遊技媒体取扱装置から遊技媒体管理装置に対し減算した有価価値に対応する遊技媒体を増加させる。そして遊技者は遊技を行い、さらに遊技媒体が必要な場合には上記操作を繰り返し行う。その後遊技の結果所定数の遊技媒体を獲得し、遊技を終了する際にはいずれかの返却操作手段を操作することにより遊技媒体管理装置から遊技媒体取扱装置に対し遊技媒体数を送信し、遊技媒体取扱装置はその遊技媒体数を記録した記録媒体を排出する。遊技媒体管理装置は遊技媒体数を送信したときに自身が記憶する遊技媒体数をクリアする。遊技者は排出された記録媒体を景品交換するために景品カウンター等に持っていくか、又は他の台で記録された遊技媒体に基づいて遊技を行うために遊技台を移動する。 As the flow of the game at that time, for example, the player deposits a valuable value into the game medium handling device by any method, and subtracts a predetermined number of valuable values based on the operation of any one of the above lending operation means. Then, the game media corresponding to the subtracted valuable value from the game media handling device to the game media management device is increased. Then, the player plays the game and repeats the above operation when a game medium is required. After that, a predetermined number of game media are obtained as a result of the game, and when the game is finished, one of the return operation means is operated to transmit the number of game media from the game medium management device to the game medium handling device, thereby playing the game. The medium handling device ejects the recording medium on which the number of game media is recorded. The game medium management device clears the number of game media stored therein when transmitting the number of game media. The player brings the discharged recording medium to a prize counter or the like to exchange the prize, or moves the game table to play a game based on the game medium recorded on another table.
なお、上記例では全遊技媒体を遊技媒体取扱装置に対して送信したが、遊技機又は遊技媒体取扱装置側で遊技者が所望する遊技媒体数のみを送信し、遊技者が所持する遊技媒体を分割して処理することとしてもよい。また、記録媒体を排出するだけに限らず、現金又は現金等価物を排出するようにしてもよいし、携帯端末等に記憶させるようにしもよい。また、遊技媒体取扱装置は遊技店の会員記録媒体を挿入可能とし、会員記録媒体に貯留して後日再遊技可能とするようにしてもよい。 In the above example, all the game media are transmitted to the game medium handling device, but only the number of game media desired by the player on the game machine or the game medium handling device side is transmitted, and the game medium possessed by the player is transmitted. It may be divided and processed. Further, not only the recording medium is ejected, but cash or a cash equivalent may be ejected, or it may be stored in a mobile terminal or the like. Further, the game medium handling device may be configured so that a member recording medium of a game store can be inserted and stored in the member recording medium so that the game can be played again later.
また、遊技機又は遊技媒体取扱装置において、図示しない所定の操作手段を操作することにより遊技媒体取扱装置又は遊技媒体管理装置に対し遊技媒体又は有価価値のデータ通信をロックするロック操作を実行可能としてもよい。その際にはワンタイムパスワード等遊技者にしか知りえない情報を設定することや遊技機又は遊技媒体取扱装置に設けられた撮像手段により遊技者を記憶するようにしてもよい。 Further, in the game machine or the game medium handling device, it is possible to execute a lock operation for locking the data communication of the game medium or the valuable value to the game medium handling device or the game medium management device by operating a predetermined operation means (not shown). Good. In that case, information such as a one-time password that is only known to the player may be set, or the player may be stored by the image pickup means provided in the game machine or the game medium handling device.
なお、この遊技媒体管理装置は、上述のように、メダルレスでのみ遊技を可能とするものであってもよいし、物理的な遊技者の動作によって遊技媒体が投入され(掛けられ)、遊技媒体が払い出される形態、及びメダルレスで遊技を可能とする形態、双方の形態で遊技を可能とするものであってもよい。この場合には、遊技媒体管理装置が、上述のセレクタ66やホッパー装置51を直接的に制御する方式を採用することもできるし、これらが主制御回路90(主制御基板71)によって制御され、その制御結果が送信されること基づいて、遊技者が遊技の用に供することができる遊技媒体の総数を電磁的方法により記録し、表示する制御を行い得る制御を可能とする方式を採用することもできる。
It should be noted that this game medium management device may be one that allows a game only without medals, as described above, or the game medium is loaded (hanged) by a physical player operation, It may be possible to play the game in both modes, that is, the mode in which the game is paid out, and the mode in which the game can be played without medals. In this case, the game medium management device may employ a method of directly controlling the
また、上記では、遊技媒体管理装置を、パチスロ1に適用する場合について説明しているが、上述した遊技球を用いるスロットマシンや封入式遊技機においても同様に遊技媒体管理装置を設け、遊技者の遊技媒体が管理されるようにすることもできる。
Further, in the above description, the case where the game medium management device is applied to the pachi-
このように、上述した遊技媒体管理装置を設けることにより、遊技媒体が物理的に遊技に供される場合と比べて、遊技機内部のセレクタ66やホッパー装置51等を減らすことができ、遊技機の原価及び製造コストを削減できるのみならず、遊技者が直接遊技媒体に接触しないようにすることもでき、遊技環境が改善し、騒音も減らすことができるとともに、装置を減らしたことにより遊技機の消費電力を減らすことにもなる。また、遊技媒体や遊技媒体の投入口や払出口を介した不正行為を防止することができる。すなわち、遊技機をとりまく種々の環境を改善することができる遊技機を提供することが可能となる。
As described above, by providing the above-mentioned game medium management device, it is possible to reduce the
<付記(本発明のまとめ)>
[第1〜第4の構成の遊技機]
従来の遊技機において、遊技者に有利な有利状態(例えば、ART状態)でない場合に、当該有利状態に移行するか否かの抽籤を行うとともに、当該有利状態である場合に、当該有利状態を継続するか否かの抽籤を行うことを可能にしたものが知られている(例えば、特開2010−240017号公報参照)。
<Appendix (Summary of the Invention)>
[Game machines having first to fourth configurations]
In a conventional gaming machine, when the advantageous state is not advantageous to the player (for example, ART state), the lottery is performed to determine whether or not to shift to the advantageous state, and when the advantageous state is set, the advantageous state is set to It is known that lottery can be performed to determine whether or not to continue (for example, see Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 2010-240017).
しかしながら、上記に示す遊技機では、当該有利状態を継続するか否かの決定に関して、バリエーションが乏しい点もあり、さらに興趣を高めるための工夫をなすことが求められている。 However, in the above-mentioned gaming machine, there is little variation in determining whether or not to continue the advantageous state, and it is required to devise a device for further enhancing the interest.
本発明は、このような点に鑑みてなされたものであり、遊技者に有利な状態の継続に関する興趣の向上を図ることができる遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and an object of the present invention is to provide a gaming machine capable of improving the interest in continuing a state advantageous to a player.
上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような第1の構成の遊技機を提供することができる。 In order to achieve the above object, the gaming machine of the present embodiment can provide a gaming machine having the following first configuration.
複数の図柄を複数列に変動表示し、複数の有効ラインが設定された図柄表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R及び図柄表示領域4)と、
遊技者の開始操作に基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を開始する図柄変動手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール回転開始処理)と、
前記開始操作に基づいて、内部当籤役を決定する内部当籤役決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による内部抽籤処理)と、
前記内部当籤役決定手段により決定された内部当籤役と遊技者の停止操作とに基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を停止する停止制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール停止制御処理)と、
前記停止制御手段により前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示が停止されたときに、前記有効ライン上に表示された図柄の組合せに応じた利益を付与する利益付与手段(メインCPU101による入賞チェック・メダル払出処理)と、を備えた遊技機であって、
所定の有利条件が成立した場合(例えば、ART抽籤に当籤した場合)に、所定期間、遊技者に有利な有利状態(例えば、ラインバトル状態)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記有利状態において、前記有利状態を継続させるか否かを決定可能な有利状態継続決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、を備え、
前記有利状態継続決定手段は、
前記有利状態において、複数の前記有効ラインのうち、一又は複数のいずれかの前記有効ラインを前記有利状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインとするかを決定可能な判定ライン決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による味方種別の決定)と、
前記有利状態において、前記判定ライン決定手段により決定された前記判定ラインに特定の図柄の組合せが表示される場合に、前記継続度合いを遊技者に有利な度合いに変動させることが可能な継続度合決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による敵ステータスの決定)と、を含み、
前記所定期間が経過するときに、前記継続度合決定手段により決定された前記継続度合いに基づいて前記有利状態を継続させるか否かを決定する、ことを特徴とする遊技機。
A plurality of symbols are variably displayed in a plurality of columns, and a symbol display means (for example,
On the basis of the player's start operation, a symbol changing means for starting variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol displaying means (for example, reel rotation start processing by the main CPU 101),
An internal winning combination determination means (for example, an internal lottery process by the main CPU 101) that determines an internal winning combination based on the start operation.
Based on the internal winning combination determined by the internal winning combination determining means and the player's stop operation, stop control means for stopping variable display of symbols displayed on the symbol display means (for example, reel stop by the main CPU 101) Control processing),
When the variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit is stopped by the stop control unit, a profit giving unit for giving a profit according to the combination of the symbols displayed on the activated line (the winning by the main CPU 101) A check/medal payout process),
Advantageous state control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of controlling to an advantageous state (for example, a line battle state) advantageous to the player for a predetermined period when a predetermined advantageous condition is satisfied (for example, when the ART lottery is won). )When,
In the advantageous state, an advantageous state continuation determining unit (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of determining whether to continue the advantageous state,
The advantageous state continuation determination means,
In the advantageous state, a determination line determining means (for example, a main line, which can determine whether one or a plurality of the effective lines among the plurality of effective lines is to be the determination line regarding the variation of the continuation degree of the advantageous state Determination of ally type by CPU 101),
In the advantageous state, when a combination of specific symbols is displayed on the determination line determined by the determination line determination means, the continuation degree determination capable of varying the continuation degree to an advantageous degree for the player Means (for example, determination of enemy status by the main CPU 101),
When the predetermined time period has elapsed, it is determined whether or not to continue the advantageous state, based on the continuation degree determined by the continuation degree determination means.
複数の図柄を複数列に変動表示する図柄表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、
前記図柄表示手段について所定領域を視認可能とし、当該所定領域において一又は複数の有効ラインが設定された図柄表示領域(例えば、図柄表示領域4)と、
遊技者の開始操作に基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を開始する図柄変動手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール回転開始処理)と、
前記開始操作に基づいて、内部当籤役を決定する内部当籤役決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による内部抽籤処理)と、
前記内部当籤役決定手段により決定された内部当籤役と遊技者の停止操作とに基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を停止する停止制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール停止制御処理)と、
前記停止制御手段により前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示が停止されたときに、前記有効ライン上に表示された図柄の組合せに応じた利益を付与する利益付与手段(メインCPU101による入賞チェック・メダル払出処理)と、を備えた遊技機であって、
所定の有利条件が成立した場合(例えば、ART抽籤に当籤した場合)に、所定期間、遊技者に有利な有利状態(例えば、ラインバトル状態)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記有利状態において、前記有利状態を継続させるか否かを決定可能な有利状態継続決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、を備え、
前記有利状態継続決定手段は、
前記図柄表示領域に表示される図柄のうち、各列ごとのいずれかの一の図柄を通るように、直線又は折れ線で結んで構成される一又は複数の特別ラインを設定可能な特別ライン設定手段と、
前記有利状態において、前記特別ラインのうち、一又は複数のいずれかの前記特別ラインを前記有利状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインとするかを決定可能な判定ライン決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による味方種別の決定)と、
前記有利状態において、前記判定ライン決定手段により決定された前記判定ラインに特定の図柄の組合せが表示される場合に、前記継続度合いを遊技者に有利な度合いに変動させることが可能な継続度合決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による敵ステータスの決定)と、を含み、
前記所定期間が経過するときに、前記継続度合決定手段により決定された前記継続度合いに基づいて前記有利状態を継続させるか否かを決定する、ことを特徴とする遊技機。
Symbol display means (for example,
A predetermined area of the symbol display means is made visible, and a symbol display area (for example, symbol display area 4) in which one or a plurality of effective lines are set in the predetermined area,
On the basis of the player's start operation, a symbol changing means for starting variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol displaying means (for example, reel rotation start processing by the main CPU 101),
An internal winning combination determination means (for example, an internal lottery process by the main CPU 101) that determines an internal winning combination based on the start operation.
Based on the internal winning combination determined by the internal winning combination determining means and the player's stop operation, stop control means for stopping variable display of symbols displayed on the symbol display means (for example, reel stop by the main CPU 101) Control processing),
When the variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit is stopped by the stop control unit, a profit giving unit for giving a profit according to the combination of the symbols displayed on the activated line (the winning by the main CPU 101) A check/medal payout process),
Advantageous state control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of controlling to an advantageous state (for example, a line battle state) advantageous to the player for a predetermined period when a predetermined advantageous condition is satisfied (for example, when the ART lottery is won). )When,
In the advantageous state, an advantageous state continuation determining unit (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of determining whether to continue the advantageous state,
The advantageous state continuation determination means,
Of the symbols displayed in the symbol display area, special line setting means capable of setting one or more special lines configured by connecting straight lines or polygonal lines so as to pass through any one symbol for each column When,
In the advantageous state, a determination line determination unit (for example, by the main CPU 101) capable of determining whether one or more of the special lines among the special lines is to be the determination line regarding the variation of the continuation degree of the advantageous state. Determination of ally type)
In the advantageous state, when a combination of specific symbols is displayed on the determination line determined by the determination line determination means, the continuation degree determination capable of varying the continuation degree to an advantageous degree for the player Means (for example, determination of enemy status by the main CPU 101),
When the predetermined time period has elapsed, it is determined whether or not to continue the advantageous state, based on the continuation degree determined by the continuation degree determination means.
前記継続度合決定手段は、前記有利状態において、前記判定ライン決定手段により決定された前記判定ラインに所定の図柄の組合せが表示される場合に、前記継続度合いを遊技者に不利な度合いに変動させることが可能であることを特徴とする上記に記載の遊技機。 In the advantageous state, the continuation degree determining means changes the continuation degree to a degree unfavorable to the player when a combination of predetermined symbols is displayed on the determination line determined by the determination line determining means. It is possible that the gaming machine described above.
また、上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような第2の構成の遊技機を提供することができる。 Further, in order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a gaming machine having the following second configuration.
複数の図柄を複数列に変動表示し、複数の有効ラインが設定された図柄表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R及び図柄表示領域4)と、
遊技者の開始操作に基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を開始する図柄変動手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール回転開始処理)と、
前記開始操作に基づいて、内部当籤役を決定する内部当籤役決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による内部抽籤処理)と、
前記内部当籤役決定手段により決定された内部当籤役と遊技者の停止操作とに基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を停止する停止制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール停止制御処理)と、
前記停止制御手段により前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示が停止されたときに、前記有効ライン上に表示された図柄の組合せに応じた利益を付与する利益付与手段(例えば、メインCPU101による入賞チェック・メダル払出処理)と、を備えた遊技機であって、
所定の有利条件が成立した場合(例えば、ART抽籤に当籤した場合)に、所定期間、遊技者に有利な有利状態(例えば、ラインバトル状態)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記有利状態において、特定の有利条件が成立した場合(例えば、ラインバトル状態において権利獲得抽籤状態に移行することが決定され、権利獲得抽籤状態において権利獲得状態移行抽籤に当籤した場合)に、特定期間、遊技者に有利な特定状態(例えば、権利獲得状態)に制御可能な特定状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記有利状態において、前記有利状態を継続させるか否かを決定可能な有利状態継続決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、を備え、
前記有利状態継続決定手段は、
前記有利状態において、複数の前記有効ラインのうち、一又は複数のいずれかの前記有効ラインを前記有利状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインとするかを決定可能な判定ライン決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による味方種別の決定)と、
前記有利状態において、前記判定ライン決定手段により決定された前記判定ラインに特定の図柄の組合せが表示される場合に、前記継続度合いを遊技者に有利な度合いに変動させることが可能な継続度合決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による敵ステータスの決定)と、を含み、
前記所定期間が経過するときに、前記継続度合決定手段により決定された前記継続度合いに基づいて前記有利状態を継続させるか否かを決定し、
前記特定状態は、特定権利(例えば、永続権利又は限定的権利)が付与されるか否かを決定可能な状態であり、
前記判定ライン決定手段は、付与された前記特定権利に基づいて前記判定ラインを決定することを特徴とする遊技機。
A plurality of symbols are variably displayed in a plurality of columns, and a symbol display means (for example,
On the basis of the player's start operation, a symbol changing means for starting variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol displaying means (for example, reel rotation start processing by the main CPU 101),
An internal winning combination determination means (for example, an internal lottery process by the main CPU 101) that determines an internal winning combination based on the start operation.
Based on the internal winning combination determined by the internal winning combination determining means and the player's stop operation, stop control means for stopping variable display of symbols displayed on the symbol display means (for example, reel stop by the main CPU 101) Control processing),
When the variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit is stopped by the stop control unit, a profit giving unit (for example, the main CPU 101) that gives a profit according to the combination of the symbols displayed on the activated line. A prize check/medal payout process by),
Advantageous state control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of controlling to an advantageous state (for example, a line battle state) advantageous to the player for a predetermined period when a predetermined advantageous condition is satisfied (for example, when the ART lottery is won). )When,
In the advantageous state, when a specific advantageous condition is satisfied (for example, when it is decided to shift to the right acquisition lottery state in the line battle state and the right acquisition state transition lottery is won in the right acquisition lottery state) A specific state control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of controlling to a specific state advantageous for the player (for example, a right acquisition state) for a period of time;
In the advantageous state, an advantageous state continuation determining unit (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of determining whether to continue the advantageous state,
The advantageous state continuation determination means,
In the advantageous state, a determination line determining means (for example, a main line, which can determine whether one or a plurality of the effective lines among the plurality of effective lines is to be the determination line regarding the variation of the continuation degree of the advantageous state Determination of ally type by CPU 101),
In the advantageous state, when a combination of specific symbols is displayed on the determination line determined by the determination line determination means, the continuation degree determination capable of varying the continuation degree to an advantageous degree for the player Means (for example, determination of enemy status by the main CPU 101),
When the predetermined period of time elapses, it is determined whether or not to continue the advantageous state based on the continuation degree determined by the continuation degree determination means,
The specific state is a state in which it is possible to determine whether a specific right (for example, a permanent right or a limited right) is granted,
The gaming machine, wherein the determination line determining means determines the determination line based on the given specific right.
複数の図柄を複数列に変動表示する図柄表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、
前記図柄表示手段について所定領域を視認可能とし、当該所定領域において一又は複数の有効ラインが設定された図柄表示領域(例えば、図柄表示領域4)と、
遊技者の開始操作に基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を開始する図柄変動手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール回転開始処理)と、
前記開始操作に基づいて、内部当籤役を決定する内部当籤役決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による内部抽籤処理)と、
前記内部当籤役決定手段により決定された内部当籤役と遊技者の停止操作とに基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を停止する停止制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール停止制御処理)と、
前記停止制御手段により前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示が停止されたときに、前記有効ライン上に表示された図柄の組合せに応じた利益を付与する利益付与手段(メインCPU101による入賞チェック・メダル払出処理)と、を備えた遊技機であって、
所定の有利条件が成立した場合(例えば、ART抽籤に当籤した場合)に、所定期間、遊技者に有利な有利状態(例えば、ラインバトル状態)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記有利状態において、特定の有利条件が成立した場合(例えば、ラインバトル状態において権利獲得抽籤状態に移行することが決定され、権利獲得抽籤状態において権利獲得状態移行抽籤に当籤した場合)に、特定期間、遊技者に有利な特定状態(例えば、権利獲得状態)に制御可能な特定状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記有利状態において、前記有利状態を継続させるか否かを決定可能な有利状態継続決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、を備え、
前記有利状態継続決定手段は、
前記図柄表示領域に表示される図柄のうち、各列ごとのいずれかの一の図柄を通るように、直線又は折れ線で結んで構成される一又は複数の特別ラインを設定可能な特別ライン設定手段と、
前記有利状態において、前記特別ラインのうち、一又は複数のいずれかの前記特別ラインを前記有利状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインとするかを決定可能な判定ライン決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による味方種別の決定)と、
前記有利状態において、前記判定ライン決定手段により決定された前記判定ラインに特定の図柄の組合せが表示される場合に、前記継続度合いを遊技者に有利な度合いに変動させることが可能な継続度合決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による敵ステータスの決定)と、を含み、
前記所定期間が経過するときに、前記継続度合決定手段により決定された前記継続度合いに基づいて前記有利状態を継続させるか否かを決定し、
前記特定状態は、特定権利(例えば、永続権利又は限定的権利)が付与されるか否かを決定可能な状態であり、
前記判定ライン決定手段は、付与された前記特定権利に基づいて前記判定ラインを決定することを特徴とする遊技機。
Symbol display means (for example,
A predetermined area of the symbol display means is made visible, and a symbol display area (for example, symbol display area 4) in which one or a plurality of effective lines are set in the predetermined area,
On the basis of the player's start operation, a symbol changing means for starting variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol displaying means (for example, reel rotation start processing by the main CPU 101),
An internal winning combination determination means (for example, an internal lottery process by the main CPU 101) that determines an internal winning combination based on the start operation.
Based on the internal winning combination determined by the internal winning combination determining means and the player's stop operation, stop control means for stopping variable display of symbols displayed on the symbol display means (for example, reel stop by the main CPU 101) Control processing),
When the variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit is stopped by the stop control unit, a profit giving unit for giving a profit according to the combination of the symbols displayed on the activated line (the winning by the main CPU 101) A check/medal payout process),
Advantageous state control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of controlling to an advantageous state (for example, a line battle state) advantageous to the player for a predetermined period when a predetermined advantageous condition is satisfied (for example, when the ART lottery is won). )When,
In the advantageous state, when a specific advantageous condition is satisfied (for example, when it is decided to shift to the right acquisition lottery state in the line battle state and the right acquisition state transition lottery is won in the right acquisition lottery state) A specific state control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of controlling to a specific state advantageous for the player (for example, a right acquisition state) for a period of time;
In the advantageous state, an advantageous state continuation determining unit (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of determining whether to continue the advantageous state,
The advantageous state continuation determination means,
Of the symbols displayed in the symbol display area, special line setting means capable of setting one or more special lines configured by connecting straight lines or polygonal lines so as to pass through any one symbol for each column When,
In the advantageous state, a determination line determination unit (for example, by the main CPU 101) capable of determining whether one or more of the special lines among the special lines is to be the determination line regarding the variation of the continuation degree of the advantageous state. Determination of ally type)
In the advantageous state, when a combination of specific symbols is displayed on the determination line determined by the determination line determination means, the continuation degree determination capable of varying the continuation degree to an advantageous degree for the player Means (for example, determination of enemy status by the main CPU 101),
When the predetermined period of time elapses, it is determined whether or not to continue the advantageous state based on the continuation degree determined by the continuation degree determination means,
The specific state is a state in which it is possible to determine whether a specific right (for example, a permanent right or a limited right) is granted,
The gaming machine, wherein the determination line determining means determines the determination line based on the given specific right.
前記特定状態は、前記判定ライン決定手段により前記判定ラインとして決定可能な上限数(例えば、2)を超える数の前記特定権利を付与可能な状態であり、
前記判定ライン決定手段は、前記判定ラインとして決定可能な上限数以上の前記特定権利が付与された場合、当該上限数分の前記特定権利を用いて当該上限数分の前記判定ラインを決定し、
前記継続度合決定手段は、前記有利状態において、前記判定ライン決定手段により決定された前記判定ラインに所定の図柄の組合せが表示される場合に、前記特定権利が残存していなければ、前記継続度合いを遊技者に不利な度合いに変動させ、前記特定権利が残存していれば、前記継続度合いを遊技者に不利な度合いに変動させないことが可能であることを特徴とする上記に記載の遊技機。
The specific state is a state in which the number of the specific rights exceeding the upper limit number (for example, 2) that can be determined as the determination line by the determination line determination unit can be given,
The determination line determination means, when the specific rights of the upper limit number or more that can be determined as the determination line is granted, determines the determination line of the upper limit number by using the specific right of the upper limit number,
The continuation degree determining means, in the advantageous state, when a predetermined symbol combination is displayed on the determination line determined by the determination line determining means, if the specific right does not remain, the continuation degree is determined. To a degree unfavorable to the player, and if the specific right remains, it is possible to not change the continuation degree to a degree unfavorable to the player. ..
また、上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような第3の構成の遊技機を提供することができる。 Further, in order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a gaming machine having the following third configuration.
複数の図柄を複数列に変動表示し、複数の有効ラインが設定された図柄表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R及び図柄表示領域4)と、
遊技者の開始操作に基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を開始する図柄変動手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール回転開始処理)と、
前記開始操作に基づいて、内部当籤役を決定する内部当籤役決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による内部抽籤処理)と、
前記内部当籤役決定手段により決定された内部当籤役と遊技者の停止操作とに基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を停止する停止制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール停止制御処理)と、
前記停止制御手段により前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示が停止されたときに、前記有効ライン上に表示された図柄の組合せに応じた利益を付与する利益付与手段(例えば、メインCPU101による入賞チェック・メダル払出処理)と、を備えた遊技機であって、
所定の有利条件が成立した場合(例えば、ART抽籤に当籤した場合)に、所定期間、遊技者に有利な有利状態(例えば、ラインバトル状態)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記有利状態において、前記有利状態を継続させるか否かを決定可能な有利状態継続決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、を備え、
前記有利状態継続決定手段は、
前記有利状態において、複数の前記有効ラインのうち、一又は複数のいずれかの前記有効ラインを前記有利状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインとするかを決定可能な判定ライン決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による味方種別の決定)と、
前記有利状態において、前記判定ライン決定手段により決定された前記判定ラインに特定の図柄の組合せが表示される場合に、前記継続度合いを遊技者に有利な度合いに変動させることが可能な継続度合決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による敵ステータスの決定)と、を含み、
前記所定期間が経過するときに、前記継続度合決定手段により決定された前記継続度合いに基づいて前記有利状態を継続させるか否かを決定し、
特別の有利条件が成立した場合(例えば、永続権利獲得抽籤に当籤した場合)に、特別権利(例えば、永続権利)を付与することを決定可能な特別権利付与手段(例えば、メインCPU101)をさらに備え、
前記判定ライン決定手段は、
前記特別権利付与手段により前記特別権利が付与されている場合には、複数の前記有効ラインのうち、いずれかの複数の前記有効ラインを前記判定ラインとして必ず決定し、
前記特別権利付与手段により前記特別権利が付与されていない場合には、前記判定ラインを決定するときに、複数の前記有効ラインのうち、一又は複数のいずれかの前記有効ラインを前記判定ラインとするかを決定可能である、ことを特徴とする遊技機。
A plurality of symbols are variably displayed in a plurality of columns, and a symbol display means (for example,
On the basis of the player's start operation, a symbol changing means for starting variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol displaying means (for example, reel rotation start processing by the main CPU 101),
An internal winning combination determination means (for example, an internal lottery process by the main CPU 101) that determines an internal winning combination based on the start operation.
Based on the internal winning combination determined by the internal winning combination determining means and the player's stop operation, stop control means for stopping variable display of symbols displayed on the symbol display means (for example, reel stop by the main CPU 101) Control processing),
When the variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit is stopped by the stop control unit, a profit giving unit (for example, the main CPU 101) that gives a profit according to the combination of the symbols displayed on the activated line. A prize check/medal payout process by),
Advantageous state control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of controlling to an advantageous state (for example, a line battle state) advantageous to the player for a predetermined period when a predetermined advantageous condition is satisfied (for example, when the ART lottery is won). )When,
In the advantageous state, an advantageous state continuation determining unit (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of determining whether to continue the advantageous state,
The advantageous state continuation determination means,
In the advantageous state, a determination line determining means (for example, a main line, which can determine whether one or a plurality of the effective lines among the plurality of effective lines is to be the determination line regarding the variation of the continuation degree of the advantageous state Determination of ally type by CPU 101),
In the advantageous state, when a combination of specific symbols is displayed on the determination line determined by the determination line determination means, the continuation degree determination capable of varying the continuation degree to an advantageous degree for the player Means (for example, determination of enemy status by the main CPU 101),
When the predetermined period of time elapses, it is determined whether or not to continue the advantageous state based on the continuation degree determined by the continuation degree determination means,
When a special advantageous condition is established (for example, when the permanent right acquisition lottery is won), a special right granting means (for example, the main CPU 101) that can decide to grant the special right (for example, the permanent right) is further provided. Prepare,
The determination line determining means,
When the special right has been granted by the special right granting means, any of the plurality of valid lines is necessarily determined as the determination line,
When the special right is not granted by the special right granting means, when determining the determination line, one or a plurality of the effective lines of the plurality of the effective lines is referred to as the determination line. A gaming machine characterized by being able to decide whether or not to play.
複数の図柄を複数列に変動表示する図柄表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、
前記図柄表示手段について所定領域を視認可能とし、当該所定領域において一又は複数の有効ラインが設定された図柄表示領域(例えば、図柄表示領域4)と、
遊技者の開始操作に基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を開始する図柄変動手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール回転開始処理)と、
前記開始操作に基づいて、内部当籤役を決定する内部当籤役決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による内部抽籤処理)と、
前記内部当籤役決定手段により決定された内部当籤役と遊技者の停止操作とに基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を停止する停止制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール停止制御処理)と、
前記停止制御手段により前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示が停止されたときに、前記有効ライン上に表示された図柄の組合せに応じた利益を付与する利益付与手段(メインCPU101による入賞チェック・メダル払出処理)と、を備えた遊技機であって、
所定の有利条件が成立した場合(例えば、ART抽籤に当籤した場合)に、所定期間、遊技者に有利な有利状態(例えば、ラインバトル状態)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記有利状態において、前記有利状態を継続させるか否かを決定可能な有利状態継続決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、を備え、
前記有利状態継続決定手段は、
前記図柄表示領域に表示される図柄のうち、各列ごとのいずれかの一の図柄を通るように、直線又は折れ線で結んで構成される一又は複数の特別ラインを設定可能な特別ライン設定手段と、
前記有利状態において、前記特別ラインのうち、一又は複数のいずれかの前記特別ラインを前記有利状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインとするかを決定可能な判定ライン決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による味方種別の決定)と、
前記有利状態において、前記判定ライン決定手段により決定された前記判定ラインに特定の図柄の組合せが表示される場合に、前記継続度合いを遊技者に有利な度合いに変動させることが可能な継続度合決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による敵ステータスの決定)と、を含み、
前記所定期間が経過するときに、前記継続度合決定手段により決定された前記継続度合いに基づいて前記有利状態を継続させるか否かを決定し、
特別の有利条件が成立した場合(例えば、永続権利獲得抽籤に当籤した場合)に、特別権利(例えば、永続権利)を付与することを決定可能な特別権利付与手段(例えば、メインCPU101)をさらに備え、
前記判定ライン決定手段は、
前記特別権利付与手段により前記特別権利が付与されている場合には、複数の前記特別ラインのうち、いずれかの複数の前記特別ラインを前記判定ラインとして必ず決定し、
前記特別権利付与手段により前記特別権利が付与されていない場合には、前記判定ラインを決定するときに、複数の前記特別ラインのうち、一又は複数のいずれかの前記特別ラインを前記判定ラインとするかを決定可能である、ことを特徴とする遊技機。
Symbol display means (for example,
A predetermined area of the symbol display means is made visible, and a symbol display area (for example, symbol display area 4) in which one or a plurality of effective lines are set in the predetermined area,
On the basis of the player's start operation, a symbol changing means for starting variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol displaying means (for example, reel rotation start processing by the main CPU 101),
An internal winning combination determination means (for example, an internal lottery process by the main CPU 101) that determines an internal winning combination based on the start operation.
Based on the internal winning combination determined by the internal winning combination determining means and the player's stop operation, stop control means for stopping variable display of symbols displayed on the symbol display means (for example, reel stop by the main CPU 101) Control processing),
When the variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit is stopped by the stop control unit, a profit giving unit for giving a profit according to the combination of the symbols displayed on the activated line (the winning by the main CPU 101) A check/medal payout process),
Advantageous state control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of controlling to an advantageous state (for example, a line battle state) advantageous to the player for a predetermined period when a predetermined advantageous condition is satisfied (for example, when the ART lottery is won). )When,
In the advantageous state, an advantageous state continuation determining unit (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of determining whether to continue the advantageous state,
The advantageous state continuation determination means,
Of the symbols displayed in the symbol display area, special line setting means capable of setting one or more special lines configured by connecting straight lines or polygonal lines so as to pass through any one symbol for each column When,
In the advantageous state, a determination line determination unit (for example, by the main CPU 101) capable of determining whether one or more of the special lines among the special lines is to be the determination line regarding the variation of the continuation degree of the advantageous state. Determination of ally type)
In the advantageous state, when a combination of specific symbols is displayed on the determination line determined by the determination line determination means, the continuation degree determination capable of varying the continuation degree to an advantageous degree for the player Means (for example, determination of enemy status by the main CPU 101),
When the predetermined period of time elapses, it is determined whether or not to continue the advantageous state based on the continuation degree determined by the continuation degree determination means,
When a special advantageous condition is established (for example, when the permanent right acquisition lottery is won), a special right granting means (for example, the main CPU 101) that can decide to grant the special right (for example, the permanent right) is further provided. Prepare,
The determination line determining means,
When the special right has been granted by the special right granting means, any of the plurality of special lines is definitely determined as the determination line,
When the special right is not granted by the special right granting means, when determining the determination line, one or more of the special lines among the plurality of special lines is referred to as the determination line. A gaming machine characterized in that it can be decided whether or not to do it.
前記継続度合決定手段は、前記有利状態において、前記判定ライン決定手段により決定された前記判定ラインに所定の図柄の組合せが表示される場合に、前記継続度合いを遊技者に不利な度合いに変動させることが可能であることを特徴とする上記に記載の遊技機。 In the advantageous state, the continuation degree determining means changes the continuation degree to a degree unfavorable to the player when a combination of predetermined symbols is displayed on the determination line determined by the determination line determining means. It is possible that the gaming machine described above.
また、上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような第4の構成の遊技機を提供することができる。 Further, in order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a gaming machine having the following fourth configuration.
複数の図柄を複数列に変動表示する図柄表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、
遊技者の開始操作に基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を開始する図柄変動手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール回転開始処理)と、
前記開始操作に基づいて、内部当籤役を決定する内部当籤役決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による内部抽籤処理)と、
前記内部当籤役決定手段により決定された内部当籤役と遊技者の停止操作とに基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を停止する停止制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール停止制御処理)と、
前記停止制御手段により前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示が停止されたときに、前記図柄表示手段に表示された図柄の組合せに応じた利益を付与する利益付与手段(例えば、メインCPU101による入賞チェック・メダル払出処理)と、を備えた遊技機であって、
所定の有利条件が成立した場合(例えば、ART抽籤に当籤した場合)に、所定期間、遊技者に有利な有利状態(例えば、ラインバトル状態)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記有利状態において、前記有利状態を継続させるか否かを決定可能な有利状態継続決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記所定の有利条件が成立したことに基づいて、前記有利状態における遊技状態を第1遊技状態(例えば、RT2状態)に変移させることが可能であるとともに、前記有利状態において特別の図柄の組合せ(例えば、RT3移行目)が表示された場合に、前記有利状態における遊技状態を第2遊技状態(例えば、RT3状態)に変移させることが可能な遊技状態変移制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるRTチェック処理)と、を備え、
前記有利状態継続決定手段は、
前記有利状態において特定の図柄の組合せが表示される場合に、前記有利状態の継続度合いを遊技者に有利な度合いに変動させることが可能な継続度合決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による敵ステータスの決定)を含み、
前記内部当籤役決定手段が前記特定の図柄の組合せが表示され得る特定の内部当籤役を決定する確率は、前記第1遊技状態よりも前記第2遊技状態のほうが高いことを特徴とする遊技機。
Symbol display means (for example,
On the basis of the player's start operation, a symbol changing means for starting variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol displaying means (for example, reel rotation start processing by the main CPU 101),
An internal winning combination determination means (for example, an internal lottery process by the main CPU 101) that determines an internal winning combination based on the start operation.
Based on the internal winning combination determined by the internal winning combination determining means and the player's stop operation, stop control means for stopping variable display of symbols displayed on the symbol display means (for example, reel stop by the main CPU 101) Control processing),
When the variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit is stopped by the stop control unit, a profit giving unit (for example, the main CPU 101) that gives a profit according to the combination of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit. A prize check/medal payout process by),
Advantageous state control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of controlling to an advantageous state (for example, a line battle state) advantageous to the player for a predetermined period when a predetermined advantageous condition is satisfied (for example, when the ART lottery is won). )When,
In the advantageous state, advantageous state continuation determining means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of determining whether or not to continue the advantageous state,
Based on the satisfaction of the predetermined advantageous condition, it is possible to change the game state in the advantageous state to the first game state (for example, RT2 state), and a special symbol combination in the advantageous state ( For example, when RT3 transition) is displayed, a gaming state transition control means (for example, RT check by the main CPU 101) capable of shifting the gaming state in the advantageous state to a second gaming state (for example, RT3 state). Processing) and
The advantageous state continuation determination means,
When a combination of specific symbols is displayed in the advantageous state, a continuation degree determining means capable of varying the degree of continuation of the advantageous state to a degree advantageous to the player (for example, determination of enemy status by the main CPU 101) ) Is included,
A probability that the internal winning combination determination means determines a specific internal winning combination in which the combination of the specific symbols can be displayed is higher in the second gaming state than in the first gaming state. ..
前記継続度合決定手段は、前記有利状態において所定の図柄の組合せが表示される場合に、前記継続度合いを遊技者に不利な度合いに変動させることが可能であり、
前記内部当籤役決定手段は、前記第1遊技状態において前記所定の図柄の組合せが表示され得る所定の内部当籤役を決定可能とし、前記第2遊技状態において前記所定の内部当籤役を決定可能としないことを特徴とする上記に記載の遊技機。
The continuation degree determining means is capable of varying the continuation degree to a disadvantageous degree to the player when a predetermined symbol combination is displayed in the advantageous state,
The internal winning combination determination means can determine a predetermined internal winning combination in which the combination of the predetermined symbols can be displayed in the first gaming state, and can determine the predetermined internal winning combination in the second gaming state. The gaming machine described above, characterized in that it does not.
上記構成の遊技機によれば、有利状態(例えば、有利区間のラインバトル状態)において、一又は複数のいずれかのライン(有効ラインであるかを問わない)を有利状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインとするかを決定可能とし、有利状態において、決定された判定ラインに特定の図柄の組合せ(例えば、「リプレイ」又は「ベル」の図柄揃い)表示される場合に、有利状態の継続度合いを遊技者に有利な度合いに変動させることを可能とし、決定された継続度合いに基づいて有利状態を継続させるか否かを決定することが可能となっている。 According to the gaming machine having the above configuration, in the advantageous state (for example, the line battle state of the advantageous section), one or a plurality of lines (regardless of whether the line is an effective line) is related to the variation of the continuation degree of the advantageous state. It is possible to decide whether or not to use the judgment line, and in the advantageous state, when a specific combination of symbols is displayed on the determined judgment line (for example, "Replay" or "bell" symbol alignment), the degree of continuation of the advantageous state Can be changed to a degree advantageous to the player, and it is possible to determine whether or not to continue the advantageous state based on the determined degree of continuation.
これにより、判定ラインの決定結果に応じて有利状態の継続度合いを変動させることができるため、遊技者に有利な状態の継続に関する興趣の向上を図ることができる。 As a result, the degree of continuation of the advantageous state can be changed according to the determination result of the determination line, so that the interest in continuing the advantageous state for the player can be improved.
また、上記構成の遊技機によれば、有利状態において、決定された判定ラインに所定の図柄の組合せ(例えば、「被弾リプ」の図柄の組合せ)が表示される場合に、有利状態の継続度合いを遊技者に不利な度合いに変動させることが可能となっている。 Further, according to the gaming machine having the above-described configuration, in the advantageous state, when a predetermined combination of symbols (for example, a combination of symbols of “shot bullets”) is displayed on the determined determination line, the degree of continuation of the advantageous state Can be changed to a degree that is disadvantageous to the player.
これにより、有利状態中における緊張感を高めることができ、有利状態中の遊技が単調とならず、さらに遊技者に有利な状態の継続に関する興趣の向上を図ることができる。 As a result, it is possible to increase the tension in the advantageous state, the game in the advantageous state is not monotonous, and it is possible to improve the interest in continuing the advantageous state for the player.
また、上記構成の遊技機によれば、有利状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインついての決定結果は、特定状態(例えば、権利獲得状態)において権利が付与されたか否かによって変動するようになっている。すなわち、特定状態において付与された権利に基づいて判定ラインを決定することが可能となっている。 Further, according to the gaming machine having the above configuration, the determination result regarding the determination line regarding the variation of the continuation degree of the advantageous state varies depending on whether or not the right is granted in the specific state (for example, the right acquisition state). ing. That is, it is possible to determine the determination line based on the right granted in the specific state.
また、上記構成の遊技機によれば、特定状態において判定ラインの上限数以上の権利が付与された場合には、まず、上限数分の権利を用いて上限数の判定ラインが決定される。そして、有利状態において、決定された判定ラインに、所定の図柄の組合せ(例えば、「被弾リプ」の図柄の組合せ)が表示される場合に、付与された権利が残存していなければ、有利状態の継続度合いを遊技者に不利な度合いに変動させ、付与された権利が残存していれば、有利状態の継続度合いを遊技者に不利な度合いに変動させないことが可能となっている。 Further, according to the gaming machine having the above configuration, when the right of the upper limit number or more of the determination lines is given in the specific state, first, the upper limit number of the determination lines is determined by using the right of the upper limit number. Then, in the advantageous state, when a predetermined combination of symbols (for example, a combination of symbols of "bulleted lip") is displayed on the determined determination line, if the granted right does not remain, the advantageous state It is possible to change the degree of continuation of the above to a degree unfavorable to the player, and if the granted right remains, to change the degree of continuation of the advantageous state to a degree unfavorable to the player.
また、上記構成の遊技機によれば、特別権利(例えば、永続権利)が付与されている場合には、複数の判定ラインが必ず決定され、特別権利が付与されていない場合には、判定ラインを決定するときに、一又は複数のいずれかのラインが判定ラインとして決定されるようになっている。 Further, according to the gaming machine having the above configuration, a plurality of determination lines are always determined when a special right (for example, a permanent right) is granted, and a determination line is determined when the special right is not granted. When determining, one or a plurality of lines are determined as the determination line.
これにより、有利状態中の各遊技状態の役割を多様化させ、また、有利状態が継続する継続度合いを多様に変動させることができるため、遊技者に有利な状態の継続に関する興趣の向上を図ることができる。 As a result, the role of each gaming state in the advantageous state can be diversified, and the degree of continuation of the advantageous state can be varied in various ways, so that the interest in continuing the advantageous state for the player can be improved. be able to.
また、上記構成の遊技機によれば、有利状態(例えば、有利区間のラインバトル状態)における遊技状態を第1遊技状態(例えば、RT2状態)に変移させることが可能であるとともに、特別の図柄の組合せ(例えば、「RT3移行目」)が表示された場合に、有利状態における遊技状態を第2遊技状態(例えば、RT3状態)に変移させることが可能となっており、有利状態の継続度合いを遊技者に有利な度合いに変動させる特定の図柄の組合せ(例えば、「中段リプ」の図柄の組合せ)が表示され得る特定の内部当籤役(例えば、「F_中段リプ1」及び「F_中段リプ2」のいずれか)を決定する確率は、RT2状態よりもRT3状態のほうが高くなっている。
Further, according to the gaming machine having the above configuration, it is possible to change the gaming state in the advantageous state (for example, the line battle state of the advantageous section) to the first gaming state (for example, the RT2 state), and a special symbol. When a combination (for example, "RT3 transition eye") is displayed, it is possible to change the gaming state in the advantageous state to the second gaming state (for example, RT3 state), and the degree of continuation of the advantageous state. A specific internal winning combination (for example, “
また、上記構成の遊技機によれば、第1遊技状態においては、有利状態の継続度合いを遊技者に有利な度合いに変動させる所定の図柄の組合せ(例えば、「被弾リプ」の図柄の組合せ)が表示され得る所定の内部当籤役(例えば、「F_被弾リプ」)を決定可能とし、第2遊技状態においては、この所定の内部当籤役を決定可能としないようになっている。 Further, according to the gaming machine having the above configuration, in the first gaming state, a predetermined symbol combination that changes the degree of continuation of the advantageous state to an advantageous degree for the player (for example, a combination of the symbols of "hit replies") It is possible to determine a predetermined internal winning combination (for example, “F_bulleted lip”) that can be displayed. In the second gaming state, the predetermined internal winning combination cannot be determined.
これにより、有利状態においては、いずれの遊技状態であるかによって遊技者の有利さの度合いがさらに変動するようになるため、有利状態中の遊技をより多彩なものとし、さらに遊技者に有利な状態の継続に関する興趣の向上を図ることができる。 As a result, in the advantageous state, the degree of the advantage of the player is further changed depending on which game state, so that the game in the advantageous state can be made more diversified and further advantageous to the player. It is possible to improve the interest in maintaining the state.
[第5の構成の遊技機]
従来の遊技機において、停止操作の手順によって遊技者の有利の度合いが変化する所定の内部当籤役に当籤した場合に、遊技制御回路が、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の手順が報知される有利状態にあっては、停止操作の手順の報知を可能とする報知可能情報を演出制御回路に対して送信し、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の手順が報知されない通常遊技にあっては、停止操作の手順の報知を不能とする報知不能情報を演出制御回路に対して送信することを可能にしたものが知られている(例えば、特開2016−144568号公報参照)。
[Gaming machine with fifth configuration]
In a conventional gaming machine, when a predetermined internal winning combination in which the degree of advantage of the player changes depending on the procedure of the stop operation is won, the game control circuit notifies the procedure of the stop operation advantageous to the player. In the state, informing information that enables the notification of the stop operation procedure is transmitted to the effect control circuit, and in the normal game in which the advantageous stop operation procedure is not notified to the player, the stop operation is performed. It is known that notification information that disables notification of the procedure can be transmitted to the effect control circuit (for example, see JP-A-2016-144568).
しかしながら、上記に示す遊技機では、例えば、所定の内部当籤役が、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の手順は同じであっても表示される図柄の組合せが異なるといったような複数の内部当籤役を含む場合に、停止操作の手順を報知する演出は行えるものの、表示される図柄の組合せに関連した演出は行えないという問題があった。 However, in the gaming machine shown above, for example, a plurality of internal winning combinations such as a predetermined internal winning combination having different combinations of symbols displayed even if the procedure of the stop operation advantageous to the player is the same. In the case where it is included, there is a problem that the effect of notifying the procedure of the stop operation can be performed, but the effect related to the combination of the displayed symbols cannot be performed.
ここで、遊技制御回路が、内部当籤役の種別を詳細に演出制御回路に送信することも考えられるが、このようにすると、遊技制御回路の制御負担が増大してしまうという問題が生じることとなる。 Here, it is conceivable that the game control circuit transmits the type of the internal winning combination in detail to the effect control circuit, but in this case, there is a problem that the control load of the game control circuit increases. Become.
本発明は、このような点に鑑みてなされたものであり、制御負担を増大させることなく、より適切な演出を行うことができる遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and an object of the present invention is to provide a gaming machine that can perform more appropriate effects without increasing the control load.
上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような第5の構成の遊技機を提供することができる。 In order to achieve the above object, the gaming machine of the present embodiment can provide a gaming machine having the following fifth configuration.
複数の図柄を複数列に変動表示する図柄表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、
遊技者の開始操作に基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を開始する図柄変動手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール回転開始処理)と、
前記開始操作に基づいて、内部当籤役を決定する内部当籤役決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による内部抽籤処理)と、
前記内部当籤役決定手段により決定された内部当籤役と遊技者の停止操作とに基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を停止する停止制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール停止制御処理)と、
前記停止制御手段により前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示が停止されたときに、前記図柄表示手段に表示された図柄の組合せに応じた利益を付与する利益付与手段(例えば、メインCPU101による入賞チェック・メダル払出処理)と、
演出を実行する演出実行手段(例えば、サブCPU201によって制御される表示装置11)と、を備えた遊技機であって、
前記演出実行手段に対して前記内部当籤役決定手段により決定された内部当籤役に関する所定の情報(例えば、当籤役番号)を送信可能な情報送信手段(例えば、メインCPU101による通信データ送信処理)と、
所定の有利条件が成立した場合(例えば、ART抽籤に当籤した場合)に、所定期間、遊技者に有利な停止操作の手順が報知され得る有利状態(例えば、ラインバトル状態)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、を備え、
前記内部当籤役決定手段は、
第1の停止操作の手順(例えば、「打順1」)で停止操作が行われた場合に、前記図柄表示手段における第1のライン(例えば、トップライン)上に特定の図柄の組合せが表示される第1の内部当籤役(例えば、「F_上段左ベル1」)と、
前記第1の停止操作の手順で停止操作が行われた場合に、前記図柄表示手段における第2のライン(例えば、センターライン)上に前記特定の図柄の組合せが表示される第2の内部当籤役(例えば、「F_中段左ベル1」)と、
第2の停止操作の手順(例えば、「打順3」)で停止操作が行われた場合に、前記図柄表示手段における前記第1のライン上に前記特定の図柄の組合せが表示される第3の内部当籤役(例えば、「F_上段中ベル1」)と、
前記第2の停止操作の手順で停止操作が行われた場合に、前記図柄表示手段における前記第2のライン上に前記特定の図柄の組合せが表示される第4の内部当籤役(例えば、「F_中段中ベル1」)と、を内部当籤役として決定可能であり、
前記情報送信手段は、
前記有利状態において、前記内部当籤役決定手段が前記第1の内部当籤役又は前記第3の内部当籤役を決定した場合、前記所定の情報として第1の情報(例えば、当籤役番号として「23」)を送信し、
前記有利状態において、前記内部当籤役決定手段が前記第2の内部当籤役又は前記第4の内部当籤役を決定した場合、前記所定の情報として第2の情報(例えば、当籤役番号として「24」)を送信し、
前記演出実行手段は、前記第1の情報が送信されたときと、前記第2の情報が送信されたときと、で異なる演出を実行可能であることを特徴とする遊技機。
Symbol display means (for example,
On the basis of the player's start operation, a symbol changing means for starting variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol displaying means (for example, reel rotation start processing by the main CPU 101),
An internal winning combination determination means (for example, an internal lottery process by the main CPU 101) that determines an internal winning combination based on the start operation.
Based on the internal winning combination determined by the internal winning combination determining means and the player's stop operation, stop control means for stopping variable display of symbols displayed on the symbol display means (for example, reel stop by the main CPU 101) Control processing),
When the variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit is stopped by the stop control unit, a profit giving unit (for example, the main CPU 101) that gives a profit according to the combination of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit. Prize check/medal payout processing by
A gaming machine provided with a performance executing means (for example, a
An information transmitting unit (for example, a communication data transmitting process by the main CPU 101) capable of transmitting predetermined information (for example, a winning combination number) regarding the internal winning combination determined by the internal winning combination determining unit to the effect executing unit; ,
When a predetermined advantageous condition is established (for example, when the lottery is won in the ART), it is possible to control to an advantageous state (for example, a line battle state) in which the procedure of the stop operation advantageous to the player can be notified for a predetermined period. A state control means (for example, the main CPU 101),
The internal winning combination determination means,
A combination of specific symbols is displayed on the first line (for example, the top line) of the symbol display means when the stopping operation is performed in the first stop operation procedure (for example, "
When a stop operation is performed in the procedure of the first stop operation, a second internal winning combination in which the specific symbol combination is displayed on the second line (for example, the center line) of the symbol display means. A role (for example, "F_Middle stage
A third combination in which the specific symbol combination is displayed on the first line in the symbol display means when the stopping operation is performed in the second stopping operation procedure (for example, “
A fourth internal winning combination (for example, “the combination of the specific symbols is displayed on the second line of the symbol display means when the stopping operation is performed in the procedure of the second stopping operation” F_Middle-stage
The information transmitting means,
In the advantageous state, when the internal winning combination determination means determines the first internal winning combination or the third internal winning combination, first information as the predetermined information (for example, “23 as a winning combination number”). ))
In the advantageous state, when the internal winning combination determination means determines the second internal winning combination or the fourth internal winning combination, the second information as the predetermined information (for example, “24 as the winning combination number”). ))
A game machine characterized in that the effect executing means can execute different effects depending on when the first information is transmitted and when the second information is transmitted.
前記有利状態において、前記第1のライン及び前記第2のラインを含む複数のラインのうち、一又は複数のいずれかのラインを前記有利状態の継続度合いの変動に関する判定ラインとするかを決定可能な判定ライン決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による味方種別の決定)と、
前記有利状態において、前記判定ライン決定手段により決定された前記判定ラインに前記特定の図柄の組合せが表示される場合に、前記継続度合いを遊技者に有利な度合いに変動させることが可能な継続度合決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による敵ステータスの決定)と、
前記所定期間が経過するときに、前記継続度合決定手段により決定された前記継続度合いに基づいて前記有利状態を継続させるか否かを決定する有利状態継続決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による継続抽籤)と、を備えたことを特徴とする上記に記載の遊技機。
In the advantageous state, it is possible to determine whether one or a plurality of lines among the plurality of lines including the first line and the second line are set as the determination line regarding the variation in the degree of continuation of the advantageous state. A determination line determining means (for example, the
In the advantageous state, when a combination of the specific symbols is displayed on the determination line determined by the determination line determination means, the continuation degree capable of varying the continuation degree to an advantageous degree for the player. Determining means (for example, determining the enemy status by the main CPU 101),
Advantageous state continuation determination means (for example, continuous lottery by the main CPU 101) that determines whether or not to continue the advantageous state based on the continuation degree determined by the continuation degree determination means when the predetermined period elapses. And the gaming machine described above.
上記構成の遊技機によれば、例えば、「打順1」で停止操作が行われた場合に、トップラインで「ベル」の図柄の組合せが表示される「F_上段左ベル1」と、「打順1」で停止操作が行われた場合に、センターラインで「ベル」の図柄の組合せが表示される「F_中段左ベル1」と、「打順3」で停止操作が行われた場合に、トップラインで「ベル」の図柄の組合せが表示される「F_上段中ベル1」と、「打順3」で停止操作が行われた場合に、センターラインで「ベル」の図柄の組合せが表示される「F_中段中ベル1」と、を少なくとも内部当籤役として決定可能であり、有利状態において、例えば、「F_上段左ベル1」又は「F_上段中ベル1」が決定された場合には、当籤役番号として「23」を送信し、「F_中段左ベル1」又は「F_中段中ベル1」が決定された場合には、当籤役番号として「24」を送信するようになっている。そして、本実施形態では、送信された当籤役番号に応じて異なる演出を実行することが可能となっている。
According to the gaming machine having the above configuration, for example, when the stop operation is performed at "
これにより、例えば、有利状態(例えば、有利区間のラインバトル状態)において、図柄が表示されるラインによって遊技者の有利さの度合いが変動するような遊技性を有する場合に、表示される図柄の組合せに関連した演出を行うことができるため、制御負担を増大させることなく、より適切な演出を行うことができる。 Thereby, for example, in the advantageous state (for example, the line battle state of the advantageous section), in the case where the game has such a playability that the degree of advantage of the player varies depending on the line on which the symbol is displayed, Since effects related to the combination can be performed, more appropriate effects can be performed without increasing the control load.
[第6の構成の遊技機]
従来の遊技機において、遊技者に有利な特定遊技状態中に、遊技者に有利な特別遊技状態に移行した回数に応じて実行されるストーリー演出のストーリーを進行させる、すなわち、遊技者に有利な状態が継続した期間に応じて演出内容を変化させることを可能にしたものが知られている(例えば、特開2016−187467号公報参照)。
[Amusement machine with sixth configuration]
In a conventional gaming machine, during a specific game state that is advantageous to a player, a story production story that is executed according to the number of transitions to a special game state that is advantageous to the player is advanced, that is, it is advantageous to the player. It is known that the effect contents can be changed according to the period in which the state continues (for example, see JP-A-2016-187467).
ここで、上記に示すような遊技機では、例えば、遊技者に有利な状態が所定期間継続した場合、通常では見ることのできない特別の演出(例えば、エンディング演出など)を行うことも可能である。 Here, in the gaming machine as shown above, for example, when a state advantageous to the player continues for a predetermined period, it is possible to perform a special effect (for example, ending effect) that cannot be normally seen. ..
ところで、このような特別の演出は、例えば、遊技者への追加的な特典の付与として実行されるものであるが、遊技者の遊技意欲をさらに高め、演出の興趣を向上させるための工夫をなし得る余地があるものと考えられる。 By the way, such a special effect is executed, for example, as giving an additional privilege to the player, but a device for further increasing the player's motivation for playing and improving the interest of the effect is provided. It seems that there is room to do.
本発明は、このような点に鑑みてなされたものであり、遊技者の遊技意欲を高め、演出の興趣を向上させることができる遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and an object of the present invention is to provide a gaming machine that can increase a player's motivation for a game and enhance the enjoyment of production.
上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような第6の構成の遊技機を提供することができる。 In order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a gaming machine having the following sixth configuration.
遊技者の開始操作に基づいて図柄を変動表示し、遊技者の停止操作に基づいて図柄を停止表示することで遊技を行う遊技機(例えば、パチスロ1)であって、
所定の有利条件が成立した場合(例えば、ART抽籤に当籤した場合)に、遊技者に有利な有利状態(例えば、有利区間)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
演出を実行する演出実行手段(例えば、表示装置11)と、を備え、
前記演出実行手段は、
前記有利状態制御手段により前記有利状態に制御されている期間が特別期間(例えば、有利区間の遊技期間が「1200」回以上)となったときに、特別演出(例えば、エンディング2状態におけるエンディング演出)を実行可能であり、
前記所定の有利条件が成立した場合に、所定の実行条件が成立した場合(例えば、エンディング1状態に移行させることが決定された場合)には、前記特別演出の一部の演出が実行される特殊演出(例えば、エンディング1状態におけるエンディング演出)を実行可能である、ことを特徴とする遊技機。
A gaming machine (for example, a pachi-slot 1) that variably displays a symbol based on a player's start operation, and stops and displays a symbol based on a player's stop operation,
Advantageous state control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of controlling to an advantageous state (for example, advantageous zone) advantageous to the player when a predetermined advantageous condition is satisfied (for example, when the ART lottery is won).
And a performance executing means (for example, the display device 11) for executing a performance,
The effect execution means,
When the period controlled by the advantageous state control unit to the advantageous state becomes a special period (for example, the game period of the advantageous section is “1200” times or more), special effect (for example, ending effect in ending 2 state) ) Is possible,
When the predetermined advantageous condition is satisfied and when the predetermined execution condition is satisfied (for example, when it is determined to shift to the ending 1 state), a part of the special effect is executed. A gaming machine characterized by being capable of executing a special effect (for example, an ending effect in the ending 1 state).
前記有利状態において、前記有利状態を継続させるか否かを決定可能な有利状態継続決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による継続抽籤)と、
前記有利状態継続決定手段により前記有利状態を継続させることが決定されない場合に、前記有利状態を終了させる通常終了手段と、
前記有利状態継続決定手段により前記有利状態を継続させることが決定された場合であっても、前記有利状態制御手段により前記有利状態に制御されている期間が前記特別期間を越える特定期間(例えば、規制監視期間が「1500」回)となったときに、前記有利状態を終了させる特定終了手段と、をさらに備え、
前記演出実行手段は、前記有利状態制御手段により前記有利状態に制御されている期間が前記特別期間となったときから前記特定期間となるまで、前記特別演出を実行可能であることを特徴とする上記に記載の遊技機。
In the advantageous state, advantageous state continuation determination means (for example, continuous lottery by the main CPU 101) capable of determining whether or not to continue the advantageous state,
Normal ending means for ending the advantageous state when it is not determined by the advantageous state continuation determining means to continue the advantageous state,
Even when the advantageous state continuation determination unit determines to continue the advantageous state, the period during which the advantageous state control unit controls the advantageous state exceeds the special period (for example, a specific period). And a specific ending means for ending the advantageous state when the regulation monitoring period becomes “1500” times),
The effect execution means is capable of executing the special effect from the time when the period controlled by the advantageous state control means to the advantageous state becomes the special period to the specific period. The gaming machine described above.
前記演出実行手段は、前記有利状態制御手段により前記有利状態に制御されている期間が前記特定期間となるまで、前記有利状態継続決定手段により前記有利状態を継続させることが決定される度に、前記有利状態制御手段により前記有利状態に制御されている期間の目安を示唆する示唆演出を実行可能であることを特徴とする上記に記載の遊技機。 The effect execution means, until the period during which the advantageous state control means is controlled to the advantageous state becomes the specific period, every time the advantageous state continuation determining means determines to continue the advantageous state, The gaming machine described above, characterized in that it is possible to execute a suggestion effect that suggests a guideline of a period during which the advantageous state control means controls the advantageous state.
上記構成の遊技機によれば、有利状態に制御されている期間が特別期間となったとき(例えば、エンディング2状態となったとき)に、特別演出が実行されることを可能とするとともに、有利状態に制御されることが決定された場合に、所定の実行条件が成立した場合(例えば、エンディング1状態に移行させることが決定された場合)には、特別演出の一部が実行される特殊演出が実行されることを可能としている。 According to the gaming machine having the above configuration, when the period controlled in the advantageous state becomes the special period (for example, when the ending 2 state is set), the special effect can be executed, and When it is determined to be controlled to the advantageous state and a predetermined execution condition is satisfied (for example, when it is determined to shift to the ending 1 state), a part of the special effect is executed. It is possible to execute special effects.
すなわち、上記構成の遊技機によれば、通常、遊技者に有利な状態中の遊技の終盤に実行され得るようになっている特別演出の一部である特殊演出が、所定の実行条件が成立した場合には、遊技者に有利な状態中の遊技の序盤において実行され得るようになっている。これにより、遊技者は特別演出を全て見たいと望みながら遊技を行うようになるため、遊技者の遊技意欲を高め、演出の興趣を向上させることができる。 That is, according to the gaming machine having the above-described configuration, the special effect, which is a part of the special effect that can be normally executed at the end of the game in the advantageous state for the player, satisfies the predetermined execution condition. In this case, the game can be executed in the early stage of the game in a state advantageous to the player. As a result, the player comes to play the game while wanting to see all the special effects, so that the player's motivation for the game can be increased and the interest of the effect can be improved.
また、上記構成の遊技機によれば、有利状態に制御されている期間が特別期間となったときから、有利状態に制御されている期間が特定期間となって、有利状態が終了されるまで、特別演出が実行されることを可能としている。これにより、遊技媒体の獲得を規制する場合であっても、遊技者の興趣が低下してしまうことを軽減することができる。 Further, according to the gaming machine having the above configuration, from the time when the period controlled to the advantageous state becomes the special period to the period when the period controlled to the advantageous state becomes the specific period, until the advantageous state ends , Special effects can be executed. As a result, even if the acquisition of the game medium is restricted, it is possible to reduce the decrease in the interest of the player.
また、上記構成の遊技機によれば、有利状態に制御されている期間が特別期間となるまでは、有利状態を継続させることが決定される度に、有利状態に制御されている期間の目安を示唆する示唆演出を実行可能としている。これにより、特別演出の実行が開始される時期や有利状態が終了する時期などを遊技者が概ね把握できるようになるため、遊技の興趣を高めつつ、遊技者に適切な情報を提供することができる。 Further, according to the gaming machine having the above-described configuration, until the period in which the advantageous state is controlled becomes a special period, each time it is decided to continue the advantageous state, a guideline of the period in which the advantageous state is controlled is obtained. It is possible to execute suggestive production that suggests. This makes it possible for the player to generally understand the time when the execution of the special effect is started, the time when the advantageous state is ended, etc. Therefore, it is possible to provide the player with appropriate information while enhancing the interest of the game. it can.
[第7〜第12の構成の遊技機]
従来の遊技機において、遊技者に有利な状態(例えば、ボーナス状態)への移行を可能とする特別役(例えば、ボーナス役)が内部当籤役として決定されたか否かを報知するための連続演出を行うことを可能にしたものが知られている(例えば、特開2008−79697号公報参照)。
[Game machines having seventh to twelfth configurations]
In a conventional gaming machine, a continuous effect for notifying whether or not a special winning combination (for example, a bonus winning combination) that allows a player to shift to a more advantageous condition (for example, a bonus winning combination) is determined as an internal winning combination. It is known that the above can be performed (see, for example, Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 2008-79697).
しかしながら、特別役が内部当籤役として決定された否かは、連続演出の演出内容のみならず、表示される図柄の組合せなどによっても推測できてしまう場合も少なくないことから、有利な状態に移行するか否かに関する報知や有利な状態の移行態様自体などにはさらに工夫をなし得る余地があるものと考えられる。 However, whether or not the special combination is decided as the internal winning combination can be guessed not only by the effect contents of the continuous effect but also by the combination of the symbols displayed, etc., so it shifts to an advantageous state. It is considered that there is room for further devising the notification regarding whether or not to do it, the transition state of the advantageous state itself, and the like.
本発明は、このような点に鑑みてなされたものであり、遊技者に有利な状態の移行に関する興趣の向上を図ることができる遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and an object of the present invention is to provide a gaming machine capable of improving the interest in transition of a state advantageous to a player.
上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような第7の構成の遊技機を提供することができる。 In order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a gaming machine having the following seventh configuration.
複数の図柄を複数列に変動表示する図柄表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、
遊技者の開始操作に基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を開始する図柄変動手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール回転開始処理)と、
前記開始操作に基づいて、内部当籤役を決定する内部当籤役決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による内部抽籤処理)と、
前記内部当籤役決定手段により決定された内部当籤役と遊技者の停止操作とに基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を停止する停止制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール停止制御処理)と、
前記停止制御手段により前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示が停止されたときに、前記図柄表示手段に表示された図柄の組合せに応じた利益を付与する利益付与手段(例えば、メインCPU101による入賞チェック・メダル払出処理)と、を備えた遊技機であって、
特定役(例えば、「チャンス目」)が内部当籤役として決定された場合に、所定期間、遊技者に有利な第1有利状態(例えば、通常有利区間)に制御可能であるとともに、所定の有利条件が成立した場合(例えば、ART抽籤に当籤した場合)に、前記第1有利状態よりも遊技者に有利な第2有利状態(例えば、有利区間)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記特定役に対応する特定の図柄の組合せ(例えば、「RT3移行目」)が表示された場合に、遊技状態を第1通常遊技状態(例えば、RT3状態)に変移させることが可能であるとともに、特別役(例えば、ボーナス役)が内部当籤役として決定された場合に、遊技状態を第2通常遊技状態(例えば、RT5状態)に変移させることが可能な通常遊技状態変移制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記特別役に対応する特別の図柄の組合せ(例えば、ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せ)が表示される場合に、遊技状態を特別遊技状態(例えば、ボーナス状態)に変移させることが可能な特別遊技状態変移制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
演出を実行する演出実行手段(例えば、表示装置11)と、を備え、
前記内部当籤役決定手段は、
前記停止操作の手順によって遊技者の有利の度合いが変化する複数の所定役(例えば、押し順小役)と、前記特定役と、前記特別役と、を内部当籤役として決定可能であるとともに、前記特別役を内部当籤役として決定した場合、前記特別の図柄の組合せが表示されるまで前記特別役の当籤を持ち越すことが可能であり、
前記特別役の当籤が持ち越されていない場合、前記特定役と前記特別役とを同時に内部当籤役として決定可能であり、
前記演出実行手段は、
前記第1有利状態であって前記第1通常遊技状態である場合に、複数の前記所定役のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合、遊技者に有利な前記停止操作の手順を報知可能な演出を実行し、前記第1有利状態であって前記第2通常遊技状態である場合に、複数の前記所定役のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合、遊技者に有利な前記停止操作の手順を報知可能な演出を実行する、ことを特徴とする遊技機。
Symbol display means (for example,
On the basis of the player's start operation, a symbol changing means for starting variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol displaying means (for example, reel rotation start processing by the main CPU 101),
An internal winning combination determination means (for example, an internal lottery process by the main CPU 101) that determines an internal winning combination based on the start operation.
Based on the internal winning combination determined by the internal winning combination determining means and the player's stop operation, stop control means for stopping variable display of symbols displayed on the symbol display means (for example, reel stop by the main CPU 101) Control processing),
When the variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit is stopped by the stop control unit, a profit giving unit (for example, the main CPU 101) that gives a profit according to the combination of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit. A prize check/medal payout process by),
When a specific winning combination (for example, a “chance eye”) is determined as an internal winning combination, it is possible to control the player in a first advantageous state (for example, a normal advantageous zone) that is advantageous to the player for a predetermined period of time, and a predetermined advantage. When the condition is satisfied (for example, when the lottery is won in the ART lottery), the advantageous state control means (for example, the advantageous period control means) that can be controlled to the second advantageous state (for example, the advantageous zone) that is more advantageous to the player than the first advantageous state. Main CPU 101),
When a combination of specific symbols corresponding to the specific combination (for example, "RT3 transition eye") is displayed, it is possible to change the game state to the first normal game state (for example, RT3 state). , If a special combination (for example, a bonus combination) is determined as an internal winning combination, a normal game state transition control unit (for example, a game state transition control unit that can change the game state to a second normal game state (for example, RT5 state)) Main CPU 101),
When a combination of special symbols corresponding to the special combination (for example, a combination of symbols related to a bonus combination) is displayed, a special game capable of shifting the game state to a special game state (for example, bonus state) A state transition control means (for example, the main CPU 101),
And a performance executing means (for example, the display device 11) for executing a performance,
The internal winning combination determination means,
While it is possible to determine a plurality of predetermined winning combinations (for example, small pressing order winning combinations) in which the degree of advantage of the player changes according to the procedure of the stop operation, the specific winning combination, and the special winning combination, as internal winning combinations, When the special combination is determined as the internal winning combination, it is possible to carry over the winning of the special combination until the combination of the special symbols is displayed,
If the winning of the special combination has not been carried over, it is possible to determine the specific combination and the special combination at the same time as an internal winning combination,
The effect execution means,
In the case of the first advantageous state and the first normal game state, if any one of the plurality of predetermined winning combinations is determined as the internal winning combination, it is possible to inform the player of the procedure of the stop operation that is advantageous. In the case of being in the first advantageous state and the second normal game state, if any one of the plurality of predetermined winning combinations is determined as an internal winning combination, the stop advantageous to the player is executed. A gaming machine characterized by executing an effect capable of notifying an operation procedure.
また、上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような第8の構成の遊技機を提供することができる。 Further, in order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a gaming machine having the following eighth configuration.
複数の図柄を複数列に変動表示する図柄表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、
遊技者の開始操作に基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を開始する図柄変動手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール回転開始処理)と、
前記開始操作に基づいて、内部当籤役を決定する内部当籤役決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による内部抽籤処理)と、
前記内部当籤役決定手段により決定された内部当籤役と遊技者の停止操作とに基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を停止する停止制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール停止制御処理)と、
前記停止制御手段により前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示が停止されたときに、前記図柄表示手段に表示された図柄の組合せに応じた利益を付与する利益付与手段(例えば、メインCPU101による入賞チェック・メダル払出処理)と、を備えた遊技機であって、
特定役(例えば、「チャンス目」)が内部当籤役として決定された場合に、所定期間、遊技者に有利な第1有利状態(例えば、通常有利区間)に制御可能であるとともに、所定の有利条件が成立した場合(例えば、ART抽籤に当籤した場合)に、前記第1有利状態よりも遊技者に有利な第2有利状態(例えば、有利区間)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記特定役に対応する特定の図柄の組合せ(例えば、「RT3移行目」)が表示された場合に、遊技状態を第1通常遊技状態(例えば、RT3状態)に変移させることが可能であるとともに、特別役(例えば、ボーナス役)が内部当籤役として決定された場合に、遊技状態を第2通常遊技状態(例えば、RT5状態)に変移させることが可能な通常遊技状態変移制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記特別役に対応する特別の図柄の組合せ(例えば、ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せ)が表示される場合に、遊技状態を特別遊技状態(例えば、ボーナス状態)に変移させることが可能な特別遊技状態変移制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
演出を実行する演出実行手段(例えば、表示装置11)と、を備え、
前記特定役は、前記停止操作が特定の態様であった場合に前記特定の図柄の組合せが表示され、前記停止操作が前記特定の態様でなかった場合に前記特定の図柄の組合せが表示されない内部当籤役であり、
前記内部当籤役決定手段は、
前記停止操作の手順によって遊技者の有利の度合いが変化する複数の所定役(例えば、押し順小役)と、前記特定役と、前記特別役と、を内部当籤役として決定可能であるとともに、前記特別役を内部当籤役として決定した場合、前記特別の図柄の組合せが表示されるまで前記特別役の当籤を持ち越すことが可能であり、
前記特別役の当籤が持ち越されていない場合、前記特定役と前記特別役とを同時に内部当籤役として決定可能であり、
前記演出実行手段は、
前記第1有利状態であって前記第1通常遊技状態である場合に、複数の前記所定役のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合、前記第1有利状態が終了するまで、遊技者に有利な前記停止操作の手順を報知可能な演出を実行可能とし、前記第1有利状態であって前記第2通常遊技状態である場合に、複数の前記所定役のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合、前記第1有利状態が終了するまで、遊技者に有利な前記停止操作の手順を報知可能な演出を実行可能とし、
前記第1有利状態であって前記第1通常遊技状態及び前記第2通常遊技状態のいずれの遊技状態でもない場合に、複数の前記所定役のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合、所定回数(例えば、1回)に限り、遊技者に有利な前記停止操作の手順を報知可能な演出を実行可能とする、ことを特徴とする遊技機。
Symbol display means (for example,
On the basis of the player's start operation, a symbol changing means for starting variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol displaying means (for example, reel rotation start processing by the main CPU 101),
An internal winning combination determination means (for example, an internal lottery process by the main CPU 101) that determines an internal winning combination based on the start operation.
Based on the internal winning combination determined by the internal winning combination determining means and the player's stop operation, stop control means for stopping variable display of symbols displayed on the symbol display means (for example, reel stop by the main CPU 101) Control processing),
When the variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit is stopped by the stop control unit, a profit giving unit (for example, the main CPU 101) that gives a profit according to the combination of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit. A prize check/medal payout process by),
When a specific winning combination (for example, a “chance eye”) is determined as an internal winning combination, it is possible to control the player in a first advantageous state (for example, a normal advantageous zone) that is advantageous to the player for a predetermined period of time, and a predetermined advantage. When the condition is satisfied (for example, when the lottery is won in the ART lottery), the advantageous state control means (for example, the advantageous period control means) that can be controlled to the second advantageous state (for example, the advantageous zone) that is more advantageous to the player than the first advantageous state. Main CPU 101),
When a combination of specific symbols corresponding to the specific combination (for example, "RT3 transition eye") is displayed, it is possible to change the game state to the first normal game state (for example, RT3 state). , If a special combination (for example, a bonus combination) is determined as an internal winning combination, a normal game state transition control unit (for example, a game state transition control unit that can change the game state to a second normal game state (for example, RT5 state)) Main CPU 101),
When a combination of special symbols corresponding to the special combination (for example, a combination of symbols related to a bonus combination) is displayed, a special game capable of shifting the game state to a special game state (for example, bonus state) A state transition control means (for example, the main CPU 101),
And a performance executing means (for example, the display device 11) for executing a performance,
The specific combination, the combination of the specific symbol is displayed when the stop operation is a specific mode, the combination of the specific symbol is not displayed when the stop operation is not the specific mode Internal The winning role,
The internal winning combination determination means,
While it is possible to determine a plurality of predetermined winning combinations (for example, small pressing order winning combinations) in which the degree of advantage of the player changes according to the procedure of the stop operation, the specific winning combination, and the special winning combination, as internal winning combinations, When the special combination is determined as the internal winning combination, it is possible to carry over the winning of the special combination until the combination of the special symbols is displayed,
If the winning of the special combination has not been carried over, it is possible to determine the specific combination and the special combination at the same time as an internal winning combination,
The effect execution means,
In the case of the first advantageous state and the first normal game state, if any of the plurality of predetermined winning combinations is determined as an internal winning combination, the player is given a game until the first advantageous state ends. It is possible to execute an effect capable of informing the advantageous procedure of the stop operation, and in the case of the first advantageous state and the second normal gaming state, any one of the plurality of predetermined combinations is determined as an internal winning combination. When it is done, until the first advantageous state ends, it is possible to execute an effect that can inform the player of the procedure of the stop operation, which is advantageous.
When the first advantageous state is not the gaming state of the first normal gaming state and the second normal gaming state, and one of the plurality of predetermined winning combinations is determined as an internal winning combination, a predetermined A game machine characterized in that it is possible to execute an effect that can inform the player of the procedure of the stop operation, which is advantageous to the player, only once (for example, once).
また、上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような第9の構成の遊技機を提供することができる。 Further, in order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a gaming machine having the following ninth configuration.
複数の図柄を複数列に変動表示する図柄表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、
遊技者の開始操作に基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を開始する図柄変動手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール回転開始処理)と、
前記開始操作に基づいて、内部当籤役を決定する内部当籤役決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による内部抽籤処理)と、
前記内部当籤役決定手段により決定された内部当籤役と遊技者の停止操作とに基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を停止する停止制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール停止制御処理)と、
前記停止制御手段により前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示が停止されたときに、前記図柄表示手段に表示された図柄の組合せに応じた利益を付与する利益付与手段(例えば、メインCPU101による入賞チェック・メダル払出処理)と、を備えた遊技機であって、
特定役(例えば、「チャンス目」)が内部当籤役として決定された場合に、所定期間(例えば、9ゲーム間)、遊技者に有利な第1有利状態(例えば、通常有利区間の高確2状態)に制御可能であるとともに、所定の有利条件が成立した場合(例えば、ART抽籤に当籤した場合)に、前記第1有利状態よりも遊技者に有利な第2有利状態(例えば、有利区間)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記特定役に対応する特定の図柄の組合せ(例えば、「RT3移行目」)が表示された場合に、遊技状態を第1通常遊技状態(例えば、RT3状態)に変移させることが可能であるとともに、特別役(例えば、ボーナス役)が内部当籤役として決定された場合に、遊技状態を第2通常遊技状態(例えば、RT5状態)に変移させることが可能な通常遊技状態変移制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記特別役に対応する特別の図柄の組合せ(例えば、ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せ)が表示される場合に、遊技状態を特別遊技状態(例えば、ボーナス状態)に変移させることが可能な特別遊技状態変移制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
演出を実行する演出実行手段(例えば、表示装置11)と、を備え、
前記内部当籤役決定手段は、
前記停止操作の手順によって遊技者の有利の度合いが変化する複数の所定役(例えば、押し順小役)と、前記特定役と、前記特別役と、を内部当籤役として決定可能であるとともに、前記特別役を内部当籤役として決定した場合、前記特別の図柄の組合せが表示されるまで前記特別役の当籤を持ち越すことが可能であり、
前記特別役の当籤が持ち越されていない場合、前記特定役と前記特別役とを同時に内部当籤役として決定可能であり、
前記演出実行手段は、
前記第1有利状態であって前記第1通常遊技状態である場合に、複数の前記所定役のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合、遊技者に有利な前記停止操作の手順を報知可能な演出を実行可能とし、前記第1有利状態であって前記第2通常遊技状態である場合に、複数の前記所定役のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合、遊技者に有利な前記停止操作の手順を報知可能な演出を実行可能とし、
前記有利状態制御手段は、前記特別遊技状態が終了した場合に、
前記所定の有利条件が成立している場合には、前記第2有利状態に制御し、
前記所定の有利条件が成立していない場合には、特定期間(例えば、32ゲーム間)、第3有利状態(例えば、通常有利区間の高確4状態)に制御する、ことを特徴とする遊技機。
Symbol display means (for example,
On the basis of the player's start operation, a symbol changing means for starting variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol displaying means (for example, reel rotation start processing by the main CPU 101),
An internal winning combination determination means (for example, an internal lottery process by the main CPU 101) that determines an internal winning combination based on the start operation.
Based on the internal winning combination determined by the internal winning combination determining means and the player's stop operation, stop control means for stopping variable display of symbols displayed on the symbol display means (for example, reel stop by the main CPU 101) Control processing),
When the variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit is stopped by the stop control unit, a profit giving unit (for example, the main CPU 101) that gives a profit according to the combination of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit. A prize check/medal payout process by),
When a specific winning combination (for example, a “chance eye”) is determined as an internal winning combination, a first advantageous state advantageous to the player for a predetermined period (for example, 9 games) (for example, a high-
When a combination of specific symbols corresponding to the specific combination (for example, "RT3 transition eye") is displayed, it is possible to change the game state to the first normal game state (for example, RT3 state). , If a special combination (for example, a bonus combination) is determined as an internal winning combination, a normal game state transition control unit (for example, a game state transition control unit that can change the game state to a second normal game state (for example, RT5 state)) Main CPU 101),
When a combination of special symbols corresponding to the special combination (for example, a combination of symbols related to a bonus combination) is displayed, a special game capable of shifting the game state to a special game state (for example, bonus state) A state transition control means (for example, the main CPU 101),
And a performance executing means (for example, the display device 11) for executing a performance,
The internal winning combination determination means,
While it is possible to determine a plurality of predetermined winning combinations (for example, small pressing order winning combinations) in which the degree of advantage of the player changes according to the procedure of the stop operation, the specific winning combination, and the special winning combination, as internal winning combinations, When the special combination is determined as the internal winning combination, it is possible to carry over the winning of the special combination until the combination of the special symbols is displayed,
If the winning of the special combination has not been carried over, it is possible to determine the specific combination and the special combination at the same time as an internal winning combination,
The effect execution means,
In the case of the first advantageous state and the first normal game state, if any one of the plurality of predetermined winning combinations is determined as the internal winning combination, it is possible to inform the player of the procedure of the stop operation that is advantageous. In the case of the first advantageous state and the second normal game state, if any one of the plurality of predetermined winning combinations is determined as an internal winning combination, It is possible to execute an effect that can notify the procedure of the stop operation,
The advantageous state control means, when the special game state is over,
When the predetermined advantageous condition is satisfied, the second advantageous state is controlled,
When the predetermined advantageous condition is not established, the game is characterized by controlling to a third advantageous state (for example, high-
遊技者の有利の度合いを異ならせるための複数の設定値(例えば、設定1〜6)のうち、いずれかの設定値を設定可能であり、
前記特別役は、前記複数の設定値間で当籤確率が異なる第1の特別役と、前記複数の設定値間で当籤確率が同じである第2の特別役と、を含み、
前記所定の有利条件は、
前記第1有利状態及び第3有利状態のいずれかの有利状態であるとき、前記第1の特別役及び前記第2の特別役のいずれの特別役が内部当籤役として決定された場合であっても成立するか否かが決定され、
前記第1有利状態及び第3有利状態のいずれの有利状態でもないとき、前記第1の特別役が内部当籤役として決定された場合には成立するか否かが決定されない、ことを特徴とする上記に記載の遊技機。
It is possible to set one of a plurality of setting values (for example,
The special winning combination includes a first special winning combination having a different winning probability between the plurality of setting values, and a second special winning combination having a same winning probability between the plurality of setting values,
The predetermined advantageous condition is
In the case where any one of the first special combination and the second special combination is determined as an internal winning combination when the first advantageous state or the third advantageous state is one of the advantageous states, Is also determined,
When neither the first advantageous state nor the third advantageous state is an advantageous state, it is not determined whether or not to be established when the first special combination is determined as an internal winning combination. The gaming machine described above.
また、上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような第10の構成の遊技機を提供することができる。 Further, in order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a gaming machine having the following tenth configuration.
複数の図柄を複数列に変動表示する図柄表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、
遊技者の開始操作に基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を開始する図柄変動手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール回転開始処理)と、
前記開始操作に基づいて、内部当籤役を決定する内部当籤役決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による内部抽籤処理)と、
前記内部当籤役決定手段により決定された内部当籤役と遊技者の停止操作とに基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を停止する停止制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール停止制御処理)と、
前記停止制御手段により前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示が停止されたときに、前記図柄表示手段に表示された図柄の組合せに応じた利益を付与する利益付与手段(例えば、メインCPU101による入賞チェック・メダル払出処理)と、を備えた遊技機であって、
特定役(例えば、「チャンス目」)が内部当籤役として決定された場合に、所定期間、遊技者に有利な第1有利状態(例えば、通常有利区間)に制御可能であるとともに、所定の有利条件が成立した場合(例えば、ART抽籤に当籤した場合)に、前記第1有利状態よりも遊技者に有利な第2有利状態(例えば、有利区間)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記特定役に対応する特定の図柄の組合せ(例えば、「RT3移行目」)が表示された場合に、遊技状態を第1通常遊技状態(例えば、RT3状態)に変移させることが可能であるとともに、特別役(例えば、ボーナス役)が内部当籤役として決定された場合に、遊技状態を第2通常遊技状態(例えば、RT5状態)に変移させることが可能な通常遊技状態変移制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記特別役に対応する特別の図柄の組合せ(例えば、ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せ)が表示される場合に、遊技状態を特別遊技状態(例えば、ボーナス状態)に変移させることが可能な特別遊技状態変移制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
演出を実行する演出実行手段(例えば、表示装置11)と、を備え、
前記内部当籤役決定手段は、
前記停止操作の手順によって遊技者の有利の度合いが変化する複数の所定役(例えば、押し順小役)と、前記特定役と、前記特別役と、を内部当籤役として決定可能であるとともに、前記特別役を内部当籤役として決定した場合、前記特別の図柄の組合せが表示されるまで前記特別役の当籤を持ち越すことが可能であり、
前記特別役の当籤が持ち越されていない場合、前記特定役と前記特別役とを同時に内部当籤役として決定可能であり、
前記有利状態制御手段は、前記第1有利状態において、前記所定の有利条件を成立させるか否かを決定可能であり、
前記演出実行手段は、
前記第1有利状態であって前記第1通常遊技状態及び前記第2通常遊技状態である場合に、複数の前記所定役のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合、遊技者に有利な前記停止操作の手順を報知可能な演出を実行可能とし、
前記第2有利状態において前記特別遊技状態に制御された場合に、当該特別遊技状態において複数の前記所定役のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合、遊技者に有利な前記停止操作の手順を報知可能な演出を実行可能とし、
前記第1有利状態において前記特別遊技状態に制御された場合に、当該特別遊技状態において複数の前記所定役のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合、遊技者に有利な前記停止操作の手順を報知可能な演出を実行可能としない、ことを特徴とする遊技機。
Symbol display means (for example,
On the basis of the player's start operation, a symbol changing means for starting variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol displaying means (for example, reel rotation start processing by the main CPU 101),
An internal winning combination determination means (for example, an internal lottery process by the main CPU 101) that determines an internal winning combination based on the start operation.
Based on the internal winning combination determined by the internal winning combination determining means and the player's stop operation, stop control means for stopping variable display of symbols displayed on the symbol display means (for example, reel stop by the main CPU 101) Control processing),
When the variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit is stopped by the stop control unit, a profit giving unit (for example, the main CPU 101) that gives a profit according to the combination of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit. A prize check/medal payout process by),
When a specific winning combination (for example, a “chance eye”) is determined as an internal winning combination, it is possible to control the player in a first advantageous state (for example, a normal advantageous zone) that is advantageous to the player for a predetermined period of time, and a predetermined advantage. When the condition is satisfied (for example, when the lottery is won in the ART lottery), the advantageous state control means (for example, the advantageous period control means) that can be controlled to the second advantageous state (for example, the advantageous zone) that is more advantageous to the player than the first advantageous state. Main CPU 101),
When a combination of specific symbols corresponding to the specific combination (for example, "RT3 transition eye") is displayed, it is possible to change the game state to the first normal game state (for example, RT3 state). , If a special combination (for example, a bonus combination) is determined as an internal winning combination, a normal game state transition control unit (for example, a game state transition control unit that can change the game state to a second normal game state (for example, RT5 state)) Main CPU 101),
When a combination of special symbols corresponding to the special combination (for example, a combination of symbols related to a bonus combination) is displayed, a special game capable of shifting the game state to a special game state (for example, bonus state) A state transition control means (for example, the main CPU 101),
And a performance executing means (for example, the display device 11) for executing a performance,
The internal winning combination determination means,
While it is possible to determine a plurality of predetermined winning combinations (for example, small pressing order winning combinations) in which the degree of advantage of the player changes according to the procedure of the stop operation, the specific winning combination, and the special winning combination, as internal winning combinations, When the special combination is determined as the internal winning combination, it is possible to carry over the winning of the special combination until the combination of the special symbols is displayed,
If the winning of the special combination has not been carried over, it is possible to determine the specific combination and the special combination at the same time as an internal winning combination,
The advantageous state control means can determine whether or not the predetermined advantageous condition is satisfied in the first advantageous state,
The effect execution means,
In the case of the first advantageous state and the first normal game state and the second normal game state, if any one of the plurality of predetermined combinations is determined as an internal winning combination, the game is advantageous to the player. It is possible to execute an effect that can notify the procedure of the stop operation,
When the special game state is controlled in the second advantageous state, and when any one of the plurality of predetermined combinations is determined as an internal winning combination in the special game state, the procedure of the stop operation advantageous to the player It is possible to execute the production that can inform
When the special game state is controlled in the first advantageous state, and when any one of the plurality of predetermined combinations is determined as an internal winning combination in the special game state, the procedure of the stop operation advantageous to the player A game machine characterized by not being able to execute an effect capable of informing.
上記構成の遊技機によれば、特定役(例えば、「チャンス目」)が内部当籤役として決定された場合に、第1有利状態(例えば、通常有利区間)に制御可能であるとともに、所定の有利条件が成立した場合(例えば、ART抽籤に当籤した場合)に、第2有利状態(例えば、有利区間)に制御可能であり、特定の図柄の組合せ(例えば、「RT3移行目」)が表示された場合に、遊技状態を第1通常遊技状態(例えば、RT3状態)に変移させることが可能であるとともに、特別役(例えば、ボーナス役)が内部当籤役として決定された場合に、遊技状態を第2通常遊技状態(例えば、RT5状態)に変移させることが可能となっている。また、特定役と特別役とを同時に内部当籤役として決定可能となっている。そして、第1有利状態であって第1通常遊技状態及び第2通常遊技状態である場合には、所定役(例えば、押し順小役)について、遊技者に有利な停止操作の手順が報知されるようになっている。 According to the gaming machine configured as described above, when the specific winning combination (for example, “chance eye”) is determined as the internal winning combination, the gaming machine can be controlled to the first advantageous state (for example, the normal advantageous zone) and the predetermined winning combination can be performed. When the advantageous condition is established (for example, when the lottery is won in the ART lottery), it is possible to control in the second advantageous state (for example, the advantageous zone), and a specific symbol combination (for example, “RT3 transition eye”) is displayed. In the case of being played, it is possible to change the game state to the first normal game state (for example, RT3 state), and when the special combination (for example, bonus combination) is determined as the internal winning combination, the game state Can be changed to the second normal game state (for example, RT5 state). In addition, it is possible to simultaneously determine a specific winning combination and a special winning combination as an internal winning combination. Then, in the case of the first advantageous state and the first normal game state and the second normal game state, the procedure of the stop operation advantageous to the player is informed regarding the predetermined combination (for example, the small pushing order combination). It has become so.
これにより、第1有利状態では、通常遊技であるときよりも付与される遊技媒体数が増加する可能性が高まるとともに、特別遊技状態に遷移するか否かの期待感も高まることから、遊技者に有利な状態の移行に関する興趣の向上を図ることができる。 As a result, in the first advantageous state, the possibility that the number of game media to be provided will increase more than that in the normal game and the expectation of whether or not to transition to the special game state also increases. It is possible to improve the interest in the transition of the state that is advantageous to.
また、上記構成の遊技機によれば、特定役は、停止操作が特定の態様(例えば、適切なタイミング)で行われた場合に特定の図柄の組合せが表示され、特定の態様で行われなかった場合に特定の図柄の組合せが表示されない内部当籤役であり、第1有利状態であってRT3状態及びRT5状態である場合には、当該第1有利状態が終了するまで、所定役について遊技者に有利な停止操作の手順が報知され、第1有利状態であって第1通常遊技及び第2通常遊技状態でない場合には、所定回数(例えば、1回)に限り、所定役について遊技者に有利な停止操作の手順が報知されるようになっている。 Further, according to the gaming machine configured as described above, the specific winning combination is displayed in a specific combination when the stop operation is performed in a specific mode (for example, at an appropriate timing), and is not performed in the specific mode. In the case of an internal winning combination in which a specific combination of symbols is not displayed, and in the first advantageous state and the RT3 state and the RT5 state, the player with respect to the predetermined combination until the first advantageous state ends. In the case where the procedure of the stop operation advantageous to is notified, and the first advantageous state is not the first normal game state and the second normal game state, the player is given a predetermined combination only for a predetermined number of times (for example, once). An advantageous stop operation procedure is notified.
これにより、特定役が当籤したときに、特別役も同時に内部当籤役として決定されているか否かと、特定の図柄の組合せが表示されたか否かと、によって第1有利状態の有利度合いや内容を変動させることができるため、さらに遊技者に有利な状態の移行に関する興趣の向上を図ることができる。 Thereby, when the specific winning combination is won, whether the special winning combination is also determined as an internal winning combination at the same time, and whether or not a specific symbol combination is displayed, the advantageous degree and content of the first advantageous state are changed. As a result, it is possible to further improve the interest of the player regarding the transition to a more advantageous state.
また、上記構成の遊技機では、特別遊技状態(例えば、ボーナス状態)が終了した場合に、所定の有利条件が成立している場合には第2有利状態に移行させ、所定の有利条件が成立していない場合には、特定期間(例えば、32ゲーム間)、第3有利状態(例えば、通常有利区間の高確4状態)に移行させるようになっている。
Further, in the gaming machine having the above-mentioned configuration, when the special gaming state (for example, the bonus state) is finished, if the predetermined advantageous condition is satisfied, the state is shifted to the second advantageous state, and the predetermined advantageous condition is satisfied. If not, the game is shifted to the third advantageous state (for example, the high-
また、上記構成の遊技機では、第1有利状態及び第3有利状態のいずれかの遊技状態であるとき、複数の設定値間で当籤確率が同じである第2特別役(例えば、「F_BB3+F_スイカ2」及び「F_BB4+F_スイカ2」以外のボーナス役を含む内部当籤役)、及び複数の設定値間で当籤確率が異なる第1特別役(例えば、「F_BB3+F_スイカ2」及び「F_BB4+F_スイカ2」)のいずれに当籤した場合であっても、第2有利状態に移行させるか否かが決定されるが、第1有利状態及び第3有利状態のいずれの遊技状態でもないときに、第1特別役に当籤した場合には、第2有利状態に移行させるか否かが決定されないようになっている。
Further, in the gaming machine having the above-described configuration, when the gaming state is one of the first advantageous state and the third advantageous state, the second special combination (eg, “F_BB3+F_watermelon”) having the same winning probability among a plurality of setting values. 2” and an internal winning combination including a bonus combination other than “F_BB4+
これにより、特別役に当籤したときの遊技状態やその種別によって、その後の遊技状態(有利状態)の遷移をより多様なものとすることができるため、さらに遊技者に有利な状態の移行に関する興趣の向上を図ることができる。 As a result, the transition of the subsequent game state (advantageous state) can be made more diverse depending on the game state when the special combination is won and the type thereof, and therefore the interest regarding the transition of the state more advantageous to the player Can be improved.
また、上記構成の遊技機では、第2有利状態に移行させるか否かを決定可能な第1有利状態の通常遊技状態では、所定役について遊技者に有利な停止操作の手順を報知可能であり、第2有利状態において特別遊技状態(例えば、ボーナス状態)に制御された場合にも所定役について遊技者に有利な停止操作の手順を報知可能であるが、第1有利状態において特別遊技状態に制御された場合には所定役について遊技者に有利な停止操作の手順を報知可能としないようになっている。 Further, in the gaming machine having the above configuration, in the normal gaming state of the first advantageous state in which it is possible to determine whether or not to shift to the second advantageous state, it is possible to inform the player of an advantageous stop operation procedure for a predetermined winning combination. Although it is possible to inform the player of the advantageous stop operation procedure for the predetermined combination even when the special game state (for example, the bonus state) is controlled in the second advantageous state, the special game state is set in the first advantageous state. When controlled, it is not possible to inform the player of the procedure of the stop operation advantageous for the predetermined winning combination.
これにより、第2有利状態に移行する期待度が高まるとともに、付与される遊技媒体数が増加する可能性も高まる遊技区間である第1有利状態を設けることができるため、遊技者に有利な状態の移行に関する興趣の向上を図ることができるとともに、このような遊技区間を設ける場合であっても、遊技者に付与される利益が過度となってしまうことを抑制し、遊技者の射幸心が過度に煽られることを抑制することもできる。 As a result, it is possible to provide the first advantageous state, which is a game section, in which the degree of expectation of shifting to the second advantageous state is increased and the possibility that the number of game media to be provided is also increased. It is possible to improve the interest in the transition of the game, and even when such a game section is provided, it is possible to prevent the profit given to the player from becoming excessive, and to increase the player's ambition. It is also possible to suppress excessive fanning.
また、上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような第11の構成の遊技機を提供することができる。 Further, in order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a gaming machine having the following eleventh configuration.
複数の図柄を複数列に変動表示する図柄表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、
遊技者の開始操作に基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を開始する図柄変動手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール回転開始処理)と、
前記開始操作に基づいて、内部当籤役を決定する内部当籤役決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101による内部抽籤処理)と、
前記内部当籤役決定手段により決定された内部当籤役と遊技者の停止操作とに基づいて、前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示を停止する停止制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101によるリール停止制御処理)と、
前記停止制御手段により前記図柄表示手段に表示される図柄の変動表示が停止されたときに、前記図柄表示手段に表示された図柄の組合せに応じた利益を付与する利益付与手段(例えば、メインCPU101による入賞チェック・メダル払出処理)と、を備えた遊技機であって、
特定役(例えば、「チャンス目」)が内部当籤役として決定された場合に、所定期間、遊技者に有利な有利状態(例えば、通常有利区間の高確2状態)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記特定役に対応する特定の図柄の組合せ(例えば、「RT3移行目」)が表示された場合に、遊技状態を第1通常遊技状態(例えば、RT3状態)に変移させることが可能であるとともに、特別役(例えば、ボーナス役)が内部当籤役として決定された場合に、遊技状態を第2通常遊技状態(例えば、RT5状態)に変移させることが可能な通常遊技状態変移制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記特別役に対応する特別の図柄の組合せ(例えば、ボーナス役に係る図柄の組合せ)が表示される場合に、遊技状態を特別遊技状態(例えば、ボーナス状態)に変移させることが可能な特別遊技状態変移制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
演出を実行する演出実行手段(例えば、表示装置11)と、を備え、
前記内部当籤役決定手段は、
前記停止操作の手順によって遊技者の有利の度合いが変化する複数の所定役(例えば、押し順小役)と、前記特定役と、前記特別役と、を内部当籤役として決定可能であるとともに、前記特別役を内部当籤役として決定した場合、前記特別の図柄の組合せが表示されるまで前記特別役の当籤を持ち越すことが可能であり、
前記特別役の当籤が持ち越されていない場合、前記特定役と前記特別役とを同時に内部当籤役として決定可能であり、
前記演出実行手段は、
前記有利状態であって前記第1通常遊技状態である場合に、複数の前記所定役のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合、遊技者に有利な前記停止操作の手順を報知可能な演出を実行可能とし、
前記有利状態であって前記第2通常遊技状態である場合に、複数の前記所定役のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合、遊技者に有利な前記停止操作の手順を報知可能な演出を実行可能とし、
前記通常遊技状態変移制御手段は、前記特定役が前記特別役と同時に内部当籤役として決定されなかった場合であって、前記特定の図柄の組合せが表示された場合に、特定期間(例えば、8ゲーム間)、遊技状態を前記第1通常遊技状態に変移させ、
前記所定期間は、前記特定期間よりも長い期間(例えば、9ゲーム間)に設定されていることを特徴とする遊技機。
Symbol display means (for example,
On the basis of the player's start operation, a symbol changing means for starting variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol displaying means (for example, reel rotation start processing by the main CPU 101),
An internal winning combination determination means (for example, an internal lottery process by the main CPU 101) that determines an internal winning combination based on the start operation.
Based on the internal winning combination determined by the internal winning combination determining means and the player's stop operation, stop control means for stopping variable display of symbols displayed on the symbol display means (for example, reel stop by the main CPU 101) Control processing),
When the variable display of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit is stopped by the stop control unit, a profit giving unit (for example, the main CPU 101) that gives a profit according to the combination of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit. A prize check/medal payout process by),
When a specific winning combination (for example, a "chance eye") is determined as an internal winning combination, an advantageous state control capable of controlling to an advantageous state advantageous to the player for a predetermined period (for example, two highly accurate states of a normal advantageous section) Means (for example, the main CPU 101),
When a combination of specific symbols corresponding to the specific combination (for example, "RT3 transition eye") is displayed, it is possible to change the game state to the first normal game state (for example, RT3 state). , If a special combination (for example, a bonus combination) is determined as an internal winning combination, a normal game state transition control unit (for example, a game state transition control unit that can change the game state to a second normal game state (for example, RT5 state)) Main CPU 101),
When a combination of special symbols corresponding to the special combination (for example, a combination of symbols related to a bonus combination) is displayed, a special game capable of shifting the game state to a special game state (for example, bonus state) A state transition control means (for example, the main CPU 101),
And a performance executing means (for example, the display device 11) for executing a performance,
The internal winning combination determination means,
While it is possible to determine a plurality of predetermined winning combinations (for example, small pressing order winning combinations) in which the degree of advantage of the player changes according to the procedure of the stop operation, the specific winning combination, and the special winning combination, as internal winning combinations, When the special combination is determined as the internal winning combination, it is possible to carry over the winning of the special combination until the combination of the special symbols is displayed,
If the winning of the special combination has not been carried over, it is possible to determine the specific combination and the special combination at the same time as an internal winning combination,
The effect execution means,
In the advantageous state and in the first normal game state, if any of the plurality of predetermined winning combinations is determined as an internal winning combination, it is possible to inform the player of the procedure of the stop operation which is advantageous. And then
In the advantageous state and in the second normal game state, if any of the plurality of predetermined winning combinations is determined as an internal winning combination, the player can be notified of the procedure of the stop operation that is advantageous. And then
The normal game state transition control means, when the specific combination is not determined as an internal winning combination at the same time as the special combination, and the combination of the specific symbols is displayed, a specific period (for example, 8 Between games), the game state is changed to the first normal game state,
The gaming machine, wherein the predetermined period is set to a period longer than the specific period (for example, 9 games).
上記構成の遊技機によれば、特定役(例えば、「チャンス目」)が内部当籤役として決定された場合に、有利状態(例えば、通常有利区間の高確2状態)に制御可能であり、特定の図柄の組合せ(例えば、「RT3移行目」)が表示された場合に、遊技状態を第1通常遊技状態(例えば、RT3状態)に変移させることが可能であるとともに、特別役(例えば、ボーナス役)が内部当籤役として決定された場合に、遊技状態を第2通常遊技状態(例えば、RT5状態)に変移させることが可能となっている。また、特定役と特別役とを同時に内部当籤役として決定可能となっている。そして、有利状態であって第1通常遊技状態及び第2通常遊技状態である場合には、所定役(例えば、押し順小役)について、遊技者に有利な停止操作の手順が報知可能であり、有利状態が継続可能な期間(例えば、9ゲーム間)が、第1通常遊技状態が継続可能な期間(例えば、8ゲーム間)よりも長い期間に設定されている。 According to the gaming machine having the above configuration, when the specific winning combination (for example, the "chance eye") is determined as the internal winning combination, it is possible to control to the advantageous state (for example, the two highly accurate states of the normal advantageous section). When a combination of specific symbols (for example, "RT3 transition eye") is displayed, it is possible to change the game state to the first normal game state (for example, RT3 state), and a special character (for example, When the bonus combination) is determined as the internal winning combination, it is possible to change the game state to the second normal game state (for example, RT5 state). In addition, it is possible to simultaneously determine a specific winning combination and a special winning combination as an internal winning combination. Then, in the advantageous state and in the first normal game state and the second normal game state, it is possible to inform the player of the advantageous stop operation procedure for the predetermined combination (for example, the small pushing order combination). The period during which the advantageous state can be continued (for example, between 9 games) is set to be longer than the period during which the first normal gaming state can be continued (for example, 8 games).
これにより、特定の遊技状態(第1通常遊技状態)が終了するか否かにかかわらず、遊技者の期待感を維持させることが可能となるため、遊技者に有利な状態の移行に関する興趣の向上を図ることができる。 This makes it possible to maintain the player's sense of expectation regardless of whether or not the particular game state (first normal game state) ends, which is of interest for the player in transition to a state. It is possible to improve.
また、上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような第12の構成の遊技機を提供することができる。 Further, in order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a gaming machine having a twelfth configuration as described below.
所定の有利条件が成立した場合(例えば、ボーナス役に当籤した場合)に、遊技者に有利な有利状態(例えば、ボーナス状態)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段と、
画像を表示可能な表示手段(例えば、表示装置11)と、
遊技者の操作を検出可能な検出手段(例えば、タッチセンサ19)と、を備えた遊技機であって、
前記表示手段は、前記所定の有利条件が成立したか否かを報知するための特定画像を表示可能であり、
前記特定画像は、前記所定の有利条件が成立している場合に表示される第1特定画像(例えば、ベース画像と一部が異なる画像)と、前記所定の有利条件が成立していない場合に表示される第2特定画像(例えば、ベース画像と同じ画像)と、を含み、
前記第1特定画像と前記第2特定画像とは、特定部分において異なり、前記特定部分以外の他の部分において共通する画像であり、
前記第1特定画像が表示された場合に、遊技者が前記特定部分を指定する操作を行ったことを前記検出手段が検出した場合には、前記所定の有利条件が成立していることを報知する特別画像(例えば、「ボーナス確定!」のメッセージ)が前記表示手段に表示されることを特徴とする遊技機。
Advantageous state control means capable of controlling to an advantageous state (for example, bonus state) advantageous to the player when a predetermined advantageous condition is satisfied (for example, when a bonus hand is won),
Display means capable of displaying an image (for example, the display device 11),
A gaming machine provided with a detection unit (for example, a touch sensor 19) capable of detecting a player's operation,
The display means is capable of displaying a specific image for informing whether or not the predetermined advantageous condition is satisfied,
The specific image includes a first specific image (for example, an image partially different from the base image) displayed when the predetermined advantageous condition is satisfied, and a specific image when the predetermined advantageous condition is not satisfied. A second specific image to be displayed (for example, the same image as the base image),
The first specific image and the second specific image are images that are different in a specific portion and are common in other portions than the specific portion,
When the detection means detects that the player has performed an operation of designating the specific portion when the first specific image is displayed, the fact that the predetermined advantageous condition is satisfied is notified. A game machine characterized in that a special image (for example, a message of "bonus confirmed!") to be displayed is displayed on the display means.
前記第2特定画像は、前記遊技機のモチーフとして使用された原作品における所定の画像と同一又は近似の画像であることを特徴とする上記に記載の遊技機。 The gaming machine according to the above, wherein the second specific image is an image which is the same as or similar to a predetermined image in an original work used as a motif of the gaming machine.
上記構成の遊技機によれば、遊技者に有利な有利状態(例えば、ボーナス状態)に制御可能となる所定の有利条件(例えば、ボーナス役に当籤したこと)が成立したか否かを報知するため、所定の有利条件が成立している場合には、第1特定画像(例えば、ベース画像と一部が異なる画像)が表示され、所定の有利条件が成立していない場合には第2特定画像(例えば、ベース画像と同じ画像)が表示されることが可能となっており、第1特定画像が表示された場合に、遊技者が第2特定画像と異なる部分を指定する操作を行った場合には、所定の有利条件が成立していることを報知する特別画像(例えば、「ボーナス確定!」のメッセージ)が表示されることが可能となっている。 According to the gaming machine configured as described above, it is notified whether or not a predetermined advantageous condition (for example, winning of a bonus combination) that enables control to an advantageous condition for advantageous to a player (for example, a bonus state) is established. Therefore, the first specific image (for example, an image partially different from the base image) is displayed when the predetermined advantageous condition is established, and the second specific image is displayed when the predetermined advantageous condition is not established. An image (for example, the same image as the base image) can be displayed, and when the first specific image is displayed, the player performs an operation of designating a part different from the second specific image. In this case, it is possible to display a special image (for example, a message of "bonus confirmed!") that notifies that a predetermined advantageous condition is established.
これにより、遊技者の所定の操作も関与させた新規な演出態様によって、所定の有利条件が成立したか否かを報知することができるため、遊技者に有利な状態の移行に関する興趣の向上を図ることができる。 With this, it is possible to inform whether or not the predetermined advantageous condition is satisfied by the new effect mode in which the predetermined operation of the player is also involved, so that the interest for the transition to the advantageous state for the player is improved. Can be planned.
また、上記構成の遊技機によれば、第2特定画像が、遊技機のモチーフとして使用された原作品における所定の画像と同一又は近似の画像となっている。これにより、原作品に愛着のある遊技者は、所定の有利条件が成立したか否かを認識しやすくなるため、遊技意欲を高めることができるとともに、演出に関する興趣をより高めることができる。 Further, according to the gaming machine configured as described above, the second specific image is an image that is the same as or similar to the predetermined image in the original work used as the motif of the gaming machine. As a result, a player who is attached to the original work can easily recognize whether or not a predetermined advantageous condition is established, and thus, it is possible to increase the motivation for the game and further increase the interest in the production.
[第13の構成の遊技機]
従来の遊技機において、遊技制御装置側で特定の操作手段(例えば、ストップボタン)が押されている時間(オンエッジタイマが計数する時間)を監視し、その時間が演出制御回路側に送られることで、演出内容を変化させることを可能にしたものが知られている(例えば、特開2009−233278号公報参照)。
[Game machine with 13th configuration]
In a conventional gaming machine, a game control device monitors the time (a time counted by an on-edge timer) that a specific operation means (for example, a stop button) is pressed, and the time is sent to the effect control circuit side. Therefore, it is known that the effect contents can be changed (see, for example, Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 2009-233278).
しかしながら、演出の多彩化が求められる昨今の遊技機では多くの演出を搭載する必要があるため、演出の制御負荷を軽減するための工夫をなすことが求められている。 However, in recent game machines that require a variety of effects, it is necessary to mount many effects, and therefore it is required to devise a method for reducing the control load of effects.
本発明は、このような点に鑑みてなされたものであり、特定の操作手段の操作態様によって演出を変化させる場合であっても、当該演出に関する制御負荷の軽減を図ることができる遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and provides a gaming machine capable of reducing the control load related to the effect even when the effect is changed depending on the operation mode of a specific operation means. The purpose is to provide.
上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような第13の構成の遊技機を提供することができる。 In order to achieve the above object, the gaming machine of the present embodiment can provide a gaming machine having the following thirteenth configuration.
遊技者が操作可能な操作手段(例えば、ストップボタン)と、
前記操作手段の操作を検出可能な操作検出手段(例えば、ストップスイッチ)と、
演出を制御する演出制御手段(例えば、サブCPU201)と、を備え、
前記演出制御手段は、
前記操作検出手段が前記操作手段の操作(例えば、オンエッジ)を検出したときに、計時を開始し、当該計時の開始から所定時間(例えば、3秒)が経過した場合に第1演出(例えば、「演出1」)を発生させる制御を行い、
所定条件が成立したときに、第2演出(例えば、「演出2」)を発生させる制御を行い、
前記計時の開始から前記所定時間が経過するよりも前に前記所定条件が成立した場合は、前記第1演出を発生させる制御を行わない、ことを特徴とする遊技機。
An operation means that can be operated by the player (for example, a stop button),
Operation detecting means (for example, a stop switch) capable of detecting the operation of the operating means,
And a production control means (for example, the sub CPU 201) for controlling the production,
The effect control means,
When the operation detecting unit detects an operation of the operating unit (for example, on-edge), the time measurement is started, and when a predetermined time (for example, 3 seconds) has elapsed from the start of the time measurement, the first effect (for example, "
When a predetermined condition is satisfied, control is performed to generate a second effect (for example, "
A game machine characterized in that, if the predetermined condition is satisfied before the predetermined time has elapsed from the start of the time counting, the control for generating the first effect is not performed.
前記所定条件は、前記操作検出手段が前記操作手段の操作が終了したことを検出したとき(例えば、オフエッジを検出したとき)に成立することを特徴とする上記に記載の遊技機。 The gaming machine according to the above, wherein the predetermined condition is satisfied when the operation detecting means detects that the operation of the operating means is completed (for example, when an off edge is detected).
上記構成の遊技機によれば、特定の操作手段の操作(例えば、オンエッジ)を検出したときに、計時を開始し、当該計時の開始から所定時間(例えば、3秒)が経過した場合に第1演出(例えば、「演出1」)を実行する制御を行い、所定条件が成立したとき(例えば、オフエッジを検出したとき)に、第2演出(例えば、「演出2」)を実行する制御を行い、計時の開始から所定時間が経過するよりも前に所定条件が成立した場合は、第1演出を実行する制御を行わないことが可能となっている。
According to the gaming machine having the above configuration, when the operation (for example, on-edge) of the specific operation means is detected, the time counting is started, and when a predetermined time (for example, 3 seconds) has elapsed from the start of the time counting, The control for executing the first effect (for example, "
これにより、特定の操作手段の操作態様によって演出を変化させる場合であっても、当該演出に関する制御負荷の軽減を図ることができる。 Accordingly, even when the effect is changed according to the operation mode of the specific operation means, it is possible to reduce the control load related to the effect.
[第14の構成の遊技機]
従来の遊技機において、特定の操作手段(例えば、ストップボタン)の発光態様によって内部当籤役を報知するなどの演出を行うことを可能にしたものが知られている(例えば、2010−82034号公報参照)。
[Gaming machine with fourteenth configuration]
In the conventional gaming machine, it is known that it is possible to perform an effect such as notifying an internal winning combination by a light emitting mode of a specific operating means (for example, a stop button) (for example, 2010-82034). reference).
しかしながら、このような演出については、さらに工夫をなし得る余地があるものと考えられる。 However, it is considered that there is room for further improvement in such an effect.
本発明は、このような点に鑑みてなされたものであり、演出に関する興趣を高めるとともに、遊技に関する興趣を高めることができる遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and an object of the present invention is to provide a gaming machine that can enhance the interest in production and the enjoyment in games.
上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような第14の構成の遊技機を提供することができる。 To achieve the above object, the gaming machine of the present embodiment can provide a gaming machine having the following fourteenth configuration.
所定条件の成立に基づいて有利状態(例えば、ボーナス状態)を発生させる状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記有利状態の発生より前に、前記有利状態の発生を許容する権利(例えば、ボーナス役の当籤)を付与するか決定可能な事前決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
所定の演出を実行可能な演出実行手段(例えば、遊技価値表示部(VL))と、を備えた遊技機であって、
前記演出実行手段は、前記事前決定手段により前記有利状態の発生を許容する権利が付与する旨が決定された場合に、当該決定がされたことを報知する特定報知演出(例えば、「枚数先表示演出」)を実行可能であり、当該特定報知演出において当該決定により付与される権利に基づいて発生する前記有利状態において獲得し得る遊技価値に関する所定値(例えば、獲得予定枚数としての役連終了枚数カウンタの値)を表示することを特徴とする遊技機。
State control means (for example, the main CPU 101) for generating an advantageous state (for example, a bonus state) based on the establishment of a predetermined condition,
Prior to the occurrence of the advantageous state, a pre-determination unit (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of determining whether to grant a right to allow the occurrence of the advantageous state (for example, a winning of a bonus combination),
A game machine provided with a performance executing means (for example, a game value display unit (VL)) capable of executing a predetermined performance,
When the pre-determination unit determines that the right to permit the occurrence of the advantageous state is given, the production execution unit gives a specific notification production (for example, “number of sheets ahead”). Display effect") can be executed, and a predetermined value (eg, end of winning combination as a planned acquisition number) related to a game value that can be acquired in the advantageous state generated based on the right granted by the determination in the specific notification effect. A gaming machine characterized by displaying a value of a number counter).
前記特定報知演出において前記演出実行手段が前記所定値を表示した場合、少なくともその後の前記有利状態の発生まで前記所定値の表示を継続し、前記有利状態において遊技価値が獲得された場合に、当該獲得された遊技価値の値に基づいて、前記所定値の表示を更新することを特徴とする上記に記載の遊技機。 When the effect executing means displays the predetermined value in the specific notification effect, the display of the predetermined value is continued at least until the subsequent occurrence of the advantageous state, and when the game value is acquired in the advantageous state, The gaming machine described above, characterized in that the display of the predetermined value is updated based on the value of the acquired gaming value.
上記構成の遊技機によれば、有利状態(例えば、ボーナス状態)の発生を許容する権利が付与する旨が決定された(例えば、ボーナス役に当籤した)場合に、当該決定がされたことを報知する特定報知演出(例えば、「枚数先表示演出」)を実行可能であり、この特定報知演出では、付与することが決定された権利に基づいて発生する有利状態において獲得し得る遊技価値に関する所定値(例えば、獲得予定枚数としての役連終了枚数カウンタの値)を表示することが可能となっている。 According to the gaming machine having the above configuration, when it is determined that the right to allow the generation of the advantageous state (for example, the bonus state) is given (for example, the bonus combination is won), the decision is made. It is possible to execute a specific notification effect to be notified (for example, “number-first display effect”), and in this specific notification effect, a predetermined value related to a game value that can be acquired in an advantageous state that is generated based on the right that is decided to be granted It is possible to display the value (for example, the value of the combination end number counter as the expected acquisition number).
これにより、遊技者が得た権利(当籤内容)の価値を具体的に報知する演出を行うことができるため、演出に関する興趣を高めるとともに、遊技に関する興趣を高めることができる。 As a result, since it is possible to perform an effect that specifically notifies the value of the right (winning content) obtained by the player, it is possible to increase the interest in the effect and the interest in the game.
また、上記構成の遊技機によれば、特定報知演出において所定値を表示した場合、少なくともその後の有利状態の発生まで所定値の表示を継続し、有利状態において遊技価値が獲得された場合に、当該獲得された遊技価値の値に基づいて、所定値の表示を更新するようになっている。 Further, according to the gaming machine having the above configuration, when the predetermined value is displayed in the specific notification effect, the display of the predetermined value is continued at least until the occurrence of the advantageous state thereafter, and when the game value is obtained in the advantageous state, The display of the predetermined value is updated based on the acquired value of the game value.
これにより、有利状態の発生の前後において、価値を報知するための一連の演出を適切に行うことができるため、さらに演出に関する興趣を高めることができる。 With this, a series of effects for notifying the value can be appropriately performed before and after the occurrence of the advantageous state, so that interest in the effects can be further enhanced.
[第15〜第18の構成の遊技機]
従来の遊技機において、遊技者にとって有利な遊技期間(有利区間)である有利状態(例えば、ART状態)でない場合に、当該有利状態に移行するか否かの抽籤を行うとともに、当該有利状態である場合に、当該有利状態を継続するか否かの抽籤を行うことを可能にしたものが知られている(例えば、特開2010−240017号公報参照)。
[Game machines having 15th to 18th configurations]
In a conventional gaming machine, when the player is not in an advantageous state (for example, ART state), which is a game period (advantageous section) advantageous to the player, lottery is performed to determine whether or not to shift to the advantageous state, and in the advantageous state. In some cases, it is known that lottery can be performed to determine whether or not to continue the advantageous state (see, for example, JP 2010-240017 A).
このような遊技機によれば、有利状態の移行確率や継続確率の高低などの設定条件によって有利区間となる遊技期間も変動するため、このような設定条件は、遊技の興趣を左右する事象となっている。 According to such a gaming machine, the game period that is an advantageous section also changes depending on the setting conditions such as the transition probability of the advantageous state and the continuity probability. Therefore, such a setting condition is an event that influences the interest of the game. Has become.
ところで、このような遊技機では、所定期間における遊技価値の付与量を所定の出玉率の範囲内とするため、有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与量(遊技価値の増加量を示す傾斜値)が一定の値となるように設計される。 By the way, in such a gaming machine, in order to keep the amount of game value given within a predetermined payout rate within a predetermined period, the amount of game value given per unit game in the advantageous state (the amount of increase in game value is The slope value shown) is designed to be a constant value.
それゆえ、有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与量が比較的高い値に設定された場合に、上記のような設定条件も遊技者に有利となるように設定されてしまうと、遊技の射幸性が過度に高くなってしまうという問題がある。 Therefore, when the amount of game value given per unit game in the advantageous state is set to a relatively high value, if the above setting conditions are also set to be advantageous to the player, There is a problem that the gambling property of is too high.
一方、遊技の射幸性を抑制するため、有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与量を比較的低い値に設定することや、上記のような設定条件を遊技者に不利となるように設定することも考えられるが、この場合には、遊技の興趣が著しく低下してしまうという問題がある。 On the other hand, in order to suppress the gambling of the game, set the amount of game value per unit game in the advantageous state to a relatively low value, and make the above setting conditions disadvantageous to the player. It may be set, but in this case, there is a problem that the interest of the game is significantly reduced.
本発明は、このような点に鑑みてなされたものであり、射幸性を適度なものとしつつも遊技の興趣を維持することができる遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and an object of the present invention is to provide a gaming machine that can maintain the interest of a game while maintaining an appropriate gambling property.
上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような第15の構成の遊技機を提供することができる。 In order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a gaming machine having the following fifteenth configuration.
遊技者の開始操作に基づいて図柄の変動表示を開始し、遊技者の停止操作に基づいて図柄の変動表示を停止することで遊技を行う遊技機であって、
遊技者の停止操作に関する情報が報知される有利状態(例えば、有利区間)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値を第1の期待値(例えば、期待値α)に制御可能な第1期待値制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値を前記第1の期待値よりも小さい第2の期待値(例えば、期待値β)に制御可能な第2期待値制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、を備え、
前記有利状態制御手段は、
前記有利状態でない場合に、前記有利状態を開始させるか否かを決定可能な有利状態開始決定手段と、
前記有利状態である場合に、前記有利状態を継続させるか否かを決定可能な有利状態継続決定手段と、を含み、
前記第1期待値制御手段は、少なくとも前記有利状態が開始されてから所定期間、前記有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値が前記第1の期待値となるように制御し、
前記第2期待値制御手段は、少なくとも前記有利状態が継続されてから特定期間、前記所定期間を含む前記有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値が前記第2の期待値となるように制御することを特徴とする遊技機。
A gaming machine that starts a variable display of symbols based on a start operation of a player and stops the variable display of symbols based on a stop operation of the player to perform a game,
Advantageous state control means (for example, main CPU 101) capable of controlling to an advantageous state (for example, advantageous zone) in which information regarding the stop operation of the player is notified,
First expected value control means (for example, main CPU 101) capable of controlling the expected value of the game value per unit game in the advantageous state to a first expected value (for example, expected value α),
Second expected value control means capable of controlling the expected expected value of the game value per unit game in the advantageous state to the second expected value (for example, expected value β) smaller than the first expected value (for example, And a main CPU 101),
The advantageous state control means,
Advantageous state start determining means capable of determining whether to start the advantageous state when the advantageous state is not present,
When the advantageous state, it is possible to determine whether to continue the advantageous state, advantageous state continuation determining means, including,
The first expected value control means controls the expected expected value of the game value per unit game in the advantageous state to be the first expected value for at least a predetermined period after the advantageous state is started,
In the second expected value control means, an expected value of a game value per unit game in the advantageous state including the predetermined period for at least a specific period after the advantageous state is continued becomes the second expected value. A gaming machine characterized by being controlled as follows.
前記有利状態継続決定手段は、少なくとも前記有利状態が継続されてから前記特定期間、前記有利状態を継続させることを決定しないことを特徴とする遊技機。 The gaming machine characterized in that the advantageous state continuation determining means does not decide to continue the advantageous state for the specific period at least after the advantageous state is continued.
前記有利状態継続決定手段が前記有利状態を継続させることを決定した場合、前記有利状態開始決定手段が前記有利状態を開始させることを決定したことに基づいて開始された前記有利状態が終了してから所定の待機期間が経過した後、前記有利状態を継続させることを特徴とする遊技機。 When the advantageous state continuation determining means determines to continue the advantageous state, the advantageous state started based on the advantageous state start determining means having decided to start the advantageous state has ended. After a lapse of a predetermined waiting period from the above, the gaming machine is characterized by continuing the advantageous state.
上記構成の遊技機によれば、有利状態が開始されてから所定期間は、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に高い状態で遊技を行うことが可能となり、有利状態が継続されてから特定期間は、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に低い状態で遊技を行うことが可能となる。それゆえ、射幸性を適度なものとしつつも遊技の興趣を維持することができる。 According to the gaming machine configured as described above, it becomes possible to play the game in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively high for a predetermined period after the advantageous state is started, and a specific period after the advantageous state is continued. Allows a game to be played in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively low. Therefore, it is possible to maintain the interest of the game while maintaining the moderate gambling property.
なお、上記構成の遊技機において、有利状態が継続されてから特定期間は、有利状態を継続させることを決定しないようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、より適切に出玉率を管理することができる。 It should be noted that, in the gaming machine having the above-described configuration, it may not be decided to continue the advantageous state for a specific period after the advantageous state is continued. By doing so, the payout rate can be managed more appropriately.
また、上記構成の遊技機において、有利状態中に有利状態を継続させることを決定した場合であっても、当該有利状態を一旦終了させ、所定の待機期間が経過した後に、有利状態を継続させる(再開させる)ようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、より適切に出玉率を管理することができるのみならず、有利状態が継続するか否かに関し、遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。 Further, in the gaming machine having the above configuration, even when it is decided to continue the advantageous state during the advantageous state, the advantageous state is once ended and the advantageous state is continued after a predetermined waiting period has elapsed. (Restart) may be performed. In this way, not only the payout rate can be managed more appropriately, but also the interest of the game can be improved regarding whether or not the advantageous state continues.
また、上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような第16の構成の遊技機を提供することができる。 Further, in order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a gaming machine having the following sixteenth configuration.
遊技者の開始操作に基づいて図柄の変動表示を開始し、遊技者の停止操作に基づいて図柄の変動表示を停止することで遊技を行う遊技機であって、
遊技者の停止操作に関する情報が報知される有利状態(例えば、有利区間)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
特別遊技状態への移行を可能とする特別図柄の組合せが表示されることを許可するか否かを決定可能な事前決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記事前決定手段により前記特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可されている旨を報知する特定報知を実行可能な特定報知実行手段(例えば、表示装置11)と、を備え、
前記有利状態制御手段は、
所定の開始条件が成立した場合に、前記有利状態を開始させ、
所定の終了条件が成立した場合に、前記有利状態を終了させ、
前記所定の終了条件が成立する前に、前記特別図柄の組合せが表示された場合に、前記有利状態を終了させることが可能であり、
前記特定報知実行手段は、前記有利状態において、前記事前決定手段により前記特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可されている場合、当該遊技において前記特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが可能な場合には、前記特定報知を実行可能であることを特徴とする遊技機。
A gaming machine that starts a variable display of symbols based on a start operation of a player and stops the variable display of symbols based on a stop operation of the player to perform a game,
Advantageous state control means (for example, main CPU 101) capable of controlling to an advantageous state (for example, advantageous zone) in which information regarding the stop operation of the player is notified,
Predetermination means (for example, the main CPU 101) that can determine whether or not to permit the display of a combination of special symbols that enables the transition to the special gaming state,
Specific notification execution means (for example, display device 11) capable of executing a specific notification for notifying that the combination of the special symbols is allowed to be displayed by the pre-determination means,
The advantageous state control means,
When the predetermined start condition is satisfied, the advantageous state is started,
When a predetermined termination condition is satisfied, the advantageous state is terminated,
It is possible to end the advantageous state when a combination of the special symbols is displayed before the predetermined end condition is satisfied,
The specific notification execution means, in the advantageous state, if the combination of the special symbol is allowed to be displayed by the pre-determination means, the combination of the special symbol can be displayed in the game. In this case, the gaming machine is characterized in that the specific notification can be executed.
前記有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値を第1の期待値(例えば、期待値α)に制御可能な第1期待値制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値を前記第1の期待値よりも低い第2の期待値(例えば、期待値β)に制御可能な第2期待値制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、をさらに備え、
前記第1期待値制御手段は、前記有利状態が開始されてから特定の変動条件が成立するまで、前記有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値が前記第1の期待値となるように制御し、
前記第2期待値制御手段は、前記特定の変動条件が成立してから前記有利状態が終了されるまで、前記有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値が前記第2の期待値となるように制御することを特徴とする遊技機。
First expected value control means (for example, main CPU 101) capable of controlling the expected value of the game value per unit game in the advantageous state to a first expected value (for example, expected value α),
Second expected value control means capable of controlling the expected expected value of the game value per unit game in the advantageous state to a second expected value (for example, expected value β) lower than the first expected value (for example, A main CPU 101),
In the first expected value control means, the expected expected value of the game value per unit game in the advantageous state becomes the first expected value from the start of the advantageous state until the specific variation condition is satisfied. Control as
The second expected value control means, the expected value of the game value per unit game in the advantageous state is the second expected value until the advantageous state is ended after the specific variation condition is satisfied. A gaming machine characterized by being controlled so that
前記所定の終了条件は、前記有利状態が開始されてから所定期間遊技が行われたこと、又は前記有利状態が開始されてから付与された遊技価値が所定量となったこと、に基づいて成立することを特徴とする遊技機。 The predetermined ending condition is established based on that the game is played for a predetermined period after the advantageous state is started, or that the game value provided since the advantageous state is started becomes a predetermined amount. A gaming machine characterized by being.
上記構成の遊技機によれば、有利状態は、所定の終了条件が成立した場合、又は所定の終了条件が成立する前に特別遊技状態に移行した場合に終了する。そして、有利状態では、特別遊技状態への移行が可能となっている場合、その旨を示す特定報知が実行される。したがって、遊技者は、規定された所定の終了条件の範囲内であれば、特別遊技状態への移行を回避することで有利状態を継続させることができる。それゆえ、射幸性を適度なものとしつつも遊技の興趣を維持することができる。 According to the gaming machine configured as described above, the advantageous state ends when a predetermined ending condition is satisfied or when a special game state is entered before the predetermined ending condition is satisfied. Then, in the advantageous state, when it is possible to shift to the special game state, a specific notification indicating that effect is executed. Therefore, the player can continue the advantageous state by avoiding the transition to the special game state if it is within the range of the prescribed predetermined ending condition. Therefore, it is possible to maintain the interest of the game while maintaining the moderate gambling property.
なお、上記構成の遊技機において、有利状態が開始されてから特定の変動条件が成立するまでの間は、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に高い状態で遊技を行うことが可能となり、特定の変動条件が成立してから有利状態が終了されるまでの間は、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に低い状態で遊技を行うことが可能となるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、遊技者は、例えば、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に低い状態で遊技を行う場合、所定の終了条件が成立するまで有利状態を継続させることもできるし、特別遊技状態に移行させて有利状態を終了させ、再度遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に高い状態で遊技を行う機会を得ようとすることもできるため、射幸性をより適度なものとしつつも遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。 In the gaming machine with the above configuration, it is possible to play the game in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively high from the start of the advantageous state to the establishment of the specific variation condition. During the period from the satisfaction of the variable condition of 1 to the end of the advantageous state, it may be possible to play the game in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively low. In this way, the player can continue the advantageous state until a predetermined ending condition is satisfied, for example, when the game is played in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively low, or the special game. It is possible to shift to the state, end the advantageous state, and try to have the opportunity to play the game again in the state where the expected value of the game value is relatively high. The interest of can be improved.
また、上記構成の遊技機において、所定の終了条件は、遊技者に一定の特典が付与されたとき(あるいは、付与されたと仮定されるとき)に終了されるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、簡易な構成でより適切に出玉率を管理することができる。 Further, in the gaming machine having the above configuration, the predetermined termination condition may be terminated when a certain privilege is given to the player (or when it is assumed that the privilege is given). With this configuration, it is possible to more appropriately manage the payout rate with a simple configuration.
また、上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような第17の構成の遊技機を提供することができる。 Further, in order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a gaming machine having the following seventeenth configuration.
遊技者の開始操作に基づいて図柄の変動表示を開始し、遊技者の停止操作に基づいて図柄の変動表示を停止することで遊技を行う遊技機であって、
遊技者の停止操作に関する情報が報知される有利状態(例えば、有利区間)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値を第1の期待値(例えば、期待値α)に制御可能な第1期待値制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値を前記第1の期待値よりも低い第2の期待値(例えば、期待値β)に制御可能な第2期待値制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、を備え、
前記有利状態制御手段は、
所定の開始条件が成立した場合に、前記有利状態を開始させ、
所定の終了条件が成立した場合に、前記有利状態を終了させ、
前記所定の終了条件が成立する前に、特別遊技状態への移行を可能とする特別図柄の組合せが表示された場合に、前記有利状態を終了させることが可能であり、
前記第1期待値制御手段は、前記有利状態が開始されてから特定の変動条件が成立するまで、前記有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値が前記第1の期待値となるように制御し、
前記第2期待値制御手段は、前記特定の変動条件が成立してから前記有利状態が終了されるまで、前記有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値が前記第2の期待値となるように制御することを特徴とする遊技機。
A gaming machine that starts a variable display of symbols based on a start operation of a player and stops the variable display of symbols based on a stop operation of the player to perform a game,
Advantageous state control means (for example, main CPU 101) capable of controlling to an advantageous state (for example, advantageous zone) in which information regarding the stop operation of the player is notified,
First expected value control means (for example, main CPU 101) capable of controlling the expected value of the game value per unit game in the advantageous state to a first expected value (for example, expected value α),
Second expected value control means capable of controlling the expected expected value of the game value per unit game in the advantageous state to a second expected value (for example, expected value β) lower than the first expected value (for example, And a main CPU 101),
The advantageous state control means,
When the predetermined start condition is satisfied, the advantageous state is started,
When a predetermined termination condition is satisfied, the advantageous state is terminated,
Before the predetermined ending condition is satisfied, it is possible to end the advantageous state when a combination of special symbols that enables the transition to the special gaming state is displayed.
In the first expected value control means, the expected expected value of the game value per unit game in the advantageous state becomes the first expected value from the start of the advantageous state until the specific variation condition is satisfied. Control as
The second expected value control means, the expected value of the game value per unit game in the advantageous state is the second expected value until the advantageous state is ended after the specific variation condition is satisfied. A gaming machine characterized by being controlled so that
前記特別図柄の組合せが表示されることを許可するか否かを決定可能な事前決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記事前決定手段により前記特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可されている旨を報知する特定報知を実行可能な特定報知実行手段(例えば、表示装置11)と、をさらに備え、
前記特定報知実行手段は、
前記有利状態において、前記有利状態が開始されてから前記特定の変動条件が成立するまでの間に、前記事前決定手段により前記特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可されている場合には、前記特定の変動条件が成立したときに前記特定報知を実行可能であり、
前記有利状態において、前記特定の変動条件が成立してから前記有利状態が終了されるまでの間に、前記事前決定手段により前記特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可された場合には、前記事前決定手段により前記特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可されたときに前記特定報知を実行可能であることを特徴とする遊技機。
Predetermination means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of determining whether or not to allow the combination of the special symbols to be displayed,
A specific notification execution unit (for example, the display device 11) capable of executing a specific notification to notify that the combination of the special symbols is permitted to be displayed by the pre-determination unit,
The specific notification execution means,
In the advantageous state, when the combination of the special symbols is permitted to be displayed by the pre-determination means from the start of the advantageous state to the establishment of the specific variation condition, The specific notification can be executed when the specific variation condition is satisfied,
In the advantageous state, when the combination of the special symbols is permitted to be displayed by the pre-determination means during the period from the satisfaction of the specific variation condition to the end of the advantageous state, The gaming machine, wherein the specific notification can be executed when the combination of the special symbols is permitted to be displayed by the pre-determination means.
前記第1期待値制御手段は、前記有利状態における遊技者の停止操作に関する情報が報知される確率を第1の確率とすることで、前記有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値が前記第1の期待値となるように制御し、
前記第2期待値制御手段は、前記有利状態における遊技者の停止操作に関する情報が報知される確率を前記第1の確率よりも低い第2の確率とすることで、前記有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値が前記第2の期待値となるように制御することを特徴とする遊技機。
The first expected value control means sets the probability that the information regarding the stop operation of the player in the advantageous state is notified as the first probability, so that the expected value of the gaming value per unit game in the advantageous state is given. Is controlled to be the first expected value,
The second expected value control means sets the probability that the information regarding the stop operation of the player in the advantageous state is notified to be the second probability lower than the first probability, so that the unit game in the advantageous state. A gaming machine, characterized in that the expected value of per game value is controlled to be the second expected value.
上記構成の遊技機によれば、有利状態が開始されてから特定の変動条件が成立するまでの間は、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に高い状態で遊技を行うことが可能となり、特定の変動条件が成立してから有利状態が終了されるまでの間は、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に低い状態で遊技を行うことが可能となる。また、有利状態は、所定の終了条件が成立する前であっても、特別遊技状態への移行を契機として終了させることが可能である。すなわち、遊技者は、例えば、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に低い状態で遊技を行う場合、所定の終了条件が成立するまで有利状態を継続させることもできるし、特別遊技状態に移行させて有利状態を終了させ、再度遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に高い状態で遊技を行う機会を得ようとすることもできる。それゆえ、射幸性を適度なものとしつつも遊技の興趣を維持することができる。 According to the gaming machine having the above configuration, it is possible to play the game in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively high from the start of the advantageous state to the establishment of the specific variation condition. From the time the variable condition is satisfied until the advantageous state is ended, it is possible to play the game in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively low. Further, the advantageous state can be ended with the transition to the special game state as a trigger even before the predetermined ending condition is satisfied. That is, for example, when playing a game in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively low, the player can continue the advantageous state until a predetermined ending condition is satisfied, or shift to the special game state. It is also possible to end the advantageous state and obtain an opportunity to play the game again in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively high. Therefore, it is possible to maintain the interest of the game while maintaining the moderate gambling property.
なお、上記構成の遊技機において、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に低い状態で遊技を行う場合、特別遊技状態への移行が可能となっている場合には、その旨を示す特定報知が実行されるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、遊技者に、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に低い状態で遊技を継続させない選択肢があることを明示することができ、さらに遊技の興趣を維持することができる。 In the gaming machine having the above configuration, when a game is played in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively low, if a special game state can be entered, a specific notification to that effect is issued. It may be executed. By doing so, it is possible to clearly indicate to the player that there is an option not to continue the game when the expected value of the game value is relatively low, and it is possible to maintain the interest of the game.
また、上記構成の遊技機において、有利状態中の遊技価値の付与期待値は、有利状態中に遊技者の停止操作に関する情報が報知される確率によって調整されるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、簡易な構成でより適切に出玉率を管理することができる。 Further, in the gaming machine having the above-described configuration, the expected value-added game value in the advantageous state may be adjusted according to the probability of being notified of the information regarding the stop operation of the player in the advantageous state. With this configuration, it is possible to more appropriately manage the payout rate with a simple configuration.
また、上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような第18の構成の遊技機を提供することができる。 Further, in order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a gaming machine having the following eighteenth configuration.
遊技者の開始操作に基づいて図柄の変動表示を開始し、遊技者の停止操作に基づいて図柄の変動表示を停止することで遊技を行う遊技機であって、
遊技者の停止操作に関する情報が報知される有利状態(例えば、有利区間)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値を第1の期待値(例えば、期待値α)に制御可能な第1期待値制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値を前記第1の期待値よりも低い第2の期待値(例えば、期待値β)に制御可能な第2期待値制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、を備え、
前記有利状態制御手段は、
所定の開始条件が成立した場合に、前記有利状態を開始させ、
所定の終了条件が成立した場合に、前記有利状態を終了させ、
前記所定の終了条件が成立する前に、特別遊技状態への移行を可能とする特別図柄の組合せが表示された場合に、前記有利状態を終了させることが可能であり、
前記第1期待値制御手段は、前記有利状態が開始されてから特定の変動条件が成立するまで、前記有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値が前記第1の期待値となるように制御し、
前記第2期待値制御手段は、前記特定の変動条件が成立してから前記有利状態が終了されるまで、前記有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値が前記第2の期待値となるように制御し、
前記有利状態が前記特別図柄の組合せが表示されたことに応じて終了した場合に、遊技価値の付与に関連しない特殊特典を付与可能な特殊特典付与手段(例えば、サブCPU201)をさらに備えたことを特徴とする遊技機。
A gaming machine that starts a variable display of symbols based on a start operation of a player and stops the variable display of symbols based on a stop operation of the player to perform a game,
Advantageous state control means (for example, main CPU 101) capable of controlling to an advantageous state (for example, advantageous zone) in which information regarding the stop operation of the player is notified,
First expected value control means (for example, main CPU 101) capable of controlling the expected value of the game value per unit game in the advantageous state to a first expected value (for example, expected value α),
Second expected value control means capable of controlling the expected expected value of the game value per unit game in the advantageous state to a second expected value (for example, expected value β) lower than the first expected value (for example, And a main CPU 101),
The advantageous state control means,
When the predetermined start condition is satisfied, the advantageous state is started,
When a predetermined termination condition is satisfied, the advantageous state is terminated,
Before the predetermined ending condition is satisfied, it is possible to end the advantageous state when a combination of special symbols that enables the transition to the special gaming state is displayed.
In the first expected value control means, the expected expected value of the game value per unit game in the advantageous state becomes the first expected value from the start of the advantageous state until the specific variation condition is satisfied. Control as
The second expected value control means, the expected value of the game value per unit game in the advantageous state is the second expected value until the advantageous state is ended after the specific variation condition is satisfied. Control so that
When the advantageous state is ended in response to the combination of the special symbols being displayed, a special privilege granting means (for example, a sub CPU 201) capable of granting a special privilege not related to granting a game value is further provided. A gaming machine characterized by.
前記特別図柄の組合せが表示されることを許可するか否かを決定可能な事前決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記事前決定手段により前記特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可されている旨を報知する特定報知を実行可能な特定報知実行手段(例えば、表示装置11)と、をさらに備え、
前記特定報知実行手段は、
前記有利状態において、前記有利状態が開始されてから前記特定の変動条件が成立するまでの間に、前記事前決定手段により前記特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可されている場合には、前記特定の変動条件が成立したときに前記特定報知を実行可能であり、
前記有利状態において、前記特定の変動条件が成立してから前記有利状態が終了されるまでの間に、前記事前決定手段により前記特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可された場合には、前記事前決定手段により前記特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可されたときに前記特定報知を実行可能であることを特徴とする遊技機。
Predetermination means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of determining whether or not to allow the combination of the special symbols to be displayed,
A specific notification execution unit (for example, the display device 11) capable of executing a specific notification to notify that the combination of the special symbols is permitted to be displayed by the pre-determination unit,
The specific notification execution means,
In the advantageous state, when the combination of the special symbols is permitted to be displayed by the pre-determination means from the start of the advantageous state to the establishment of the specific variation condition, The specific notification can be executed when the specific variation condition is satisfied,
In the advantageous state, when the combination of the special symbols is permitted to be displayed by the pre-determination means during the period from the satisfaction of the specific variation condition to the end of the advantageous state, The gaming machine, wherein the specific notification can be executed when the combination of the special symbols is permitted to be displayed by the pre-determination means.
前記第1期待値制御手段は、前記有利状態における遊技者の停止操作に関する情報が報知される確率を第1の確率とすることで、前記有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値が前記第1の期待値となるように制御し、
前記第2期待値制御手段は、前記有利状態における遊技者の停止操作に関する情報が報知される確率を前記第1の確率よりも低い第2の確率とすることで、前記有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与期待値が前記第2の期待値となるように制御することを特徴とする遊技機。
The first expected value control means sets the probability that the information regarding the stop operation of the player in the advantageous state is notified as the first probability, so that the expected value of the gaming value per unit game in the advantageous state is given. Is controlled to be the first expected value,
The second expected value control means sets the probability that the information regarding the stop operation of the player in the advantageous state is notified to be the second probability lower than the first probability, so that the unit game in the advantageous state. A gaming machine, characterized in that the expected value of per game value is controlled to be the second expected value.
上記構成の遊技機によれば、有利状態が開始されてから特定の変動条件が成立するまでの間は、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に高い状態で遊技を行うことが可能となり、特定の変動条件が成立してから有利状態が終了されるまでの間は、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に低い状態で遊技を行うことが可能となる。また、有利状態は、所定の終了条件が成立する前であっても、特別遊技状態への移行を契機として終了させることが可能である。さらに、有利状態が特別遊技状態への移行を契機として終了した場合、遊技価値の付与に関連しない特殊特典を付与することが可能である。すなわち、遊技者は、例えば、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に低い状態で遊技を行う場合、所定の終了条件が成立するまで有利状態を継続させることもできるし、特別遊技状態に移行させて有利状態を終了させ、再度遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に高い状態で遊技を行う機会を得ようとすることもできる。また、特別遊技状態に移行させて有利状態を終了させる場合には、所定の終了条件が成立して有利状態を終了させた場合には付与されない特殊特典が付与されるため、遊技者に有利状態を早期に終了させるインセンティブを与えることもできる。それゆえ、射幸性を適度なものとしつつも遊技の興趣を維持することができる。 According to the gaming machine having the above configuration, it is possible to play the game in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively high from the start of the advantageous state to the establishment of the specific variation condition. From the time the variable condition is satisfied until the advantageous state is ended, it is possible to play the game in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively low. Further, the advantageous state can be ended with the transition to the special game state as a trigger even before the predetermined ending condition is satisfied. Furthermore, when the advantageous state ends with the transition to the special game state, it is possible to give a special privilege that is not related to the giving of a game value. That is, for example, when playing a game in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively low, the player can continue the advantageous state until a predetermined ending condition is satisfied, or shift to the special game state. It is also possible to end the advantageous state and obtain an opportunity to play the game again in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively high. Further, in the case of shifting to the special game state and ending the advantageous state, a special privilege which is not given when the predetermined ending condition is satisfied and the advantageous state is ended, is given to the player. It is also possible to give an incentive to end the task early. Therefore, it is possible to maintain the interest of the game while maintaining the moderate gambling property.
なお、上記構成の遊技機において、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に低い状態で遊技を行う場合、特別遊技状態への移行が可能となっている場合には、その旨を示す特定報知が実行されるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、遊技者に、遊技価値の付与期待値が相対的に低い状態で遊技を継続させない選択肢があることを明示することができ、さらに遊技の興趣を維持することができる。 In the gaming machine having the above configuration, when a game is played in a state where the expected value of the game value is relatively low, if a special game state can be entered, a specific notification to that effect is issued. It may be executed. By doing so, it is possible to clearly indicate to the player that there is an option not to continue the game when the expected value of the game value is relatively low, and it is possible to maintain the interest of the game.
また、上記構成の遊技機において、有利状態中の遊技価値の付与期待値は、有利状態中に遊技者の停止操作に関する情報が報知される確率によって調整されるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、簡易な構成でより適切に出玉率を管理することができる。 Further, in the gaming machine having the above-described configuration, the expected value-added game value in the advantageous state may be adjusted according to the probability of being notified of the information regarding the stop operation of the player in the advantageous state. With this configuration, it is possible to more appropriately manage the payout rate with a simple configuration.
[第19の構成の遊技機]
従来の遊技機において、所定の遊技回数毎(すなわち、所定の周期毎)に、遊技者に有利な有利状態(例えば、ART状態)に移行可能な状態となるようにしたものが知られている(例えば、特開2010−167197号公報参照)。
[Game machine with nineteenth configuration]
It is known that a conventional gaming machine is set such that it can be shifted to an advantageous state (for example, an ART state) advantageous to a player every predetermined number of games (that is, every predetermined cycle). (See, for example, JP 2010-167197A).
このような遊技機によれば、所定の周期毎に有利状態移行の期待感を高めることができるため、遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。 According to such a gaming machine, it is possible to increase the expectation of the transition to the advantageous state every predetermined period, so that the interest of the game can be improved.
しかしながら、このような遊技機では、有利状態に移行な状態となるまでの期間は一定であり、遊技性の変化に乏しいという問題があった。 However, in such a gaming machine, there is a problem that the period until the state transitions to the advantageous state is constant and there is little change in game performance.
本発明は、このような点に鑑みてなされたものであり、有利状態に移行可能な状態となるまでの期間を変動可能とすることで、遊技性を変化に富んだものとすることができる遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of such a point, and by making it possible to change the period until it becomes a state in which it is possible to shift to an advantageous state, it is possible to make game play rich in variation. An object is to provide a game machine.
上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような構成第19の遊技機を提供することができる。 In order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a gaming machine with the following configuration 19th.
複数の図柄を複数列に変動表示可能な図柄表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R及び図柄表示領域4)と、
第1特別役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その2)におけるBB1)、第2特別役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その2)におけるBB2)、及び所定役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その2)における押し順小役)を含む複数の役の中から内部当籤役を決定可能な内部当籤役決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記内部当籤役決定手段により決定された内部当籤役と遊技者の停止操作とに基づいて、図柄の変動表示を停止可能な停止制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記停止制御手段により図柄の変動表示が停止された場合に、前記図柄表示手段に表示された図柄の組合せに応じた特典を付与可能な特典付与手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、を備えた遊技機であって、
前記図柄表示手段に第1特別図柄の組合せ(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その2)におけるBB1に係る図柄の組合せ)が表示された場合に第1特別遊技状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その2)におけるBB1状態)を開始させ、第1特別終了条件が成立した場合に当該第1特別遊技状態を終了させる制御が可能な第1特別遊技状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記図柄表示手段に第2特別図柄の組合せ(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その2)におけるBB2に係る図柄の組合せ)が表示された場合に第2特別遊技状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その2)におけるBB2状態)を開始させ、第2特別終了条件が成立した場合に当該第2特別遊技状態を終了させる制御が可能な第2特別遊技状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
遊技者の停止操作に関する操作情報を報知可能な報知手段(例えば、指示モニタ)と、を備え、
前記第1特別役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、前記図柄表示手段に前記第1特別図柄の組合せが表示されるまで、前記図柄表示手段に前記第1特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可される第1特別許可状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その2)におけるBB1許可状態)を継続させ、
前記第2特別役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、前記図柄表示手段に前記第2特別図柄の組合せが表示されるまで、前記図柄表示手段に前記第2特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可される第2特別許可状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その2)におけるBB2許可状態)を継続させ、
前記内部当籤役決定手段は、
前記第1特別許可状態において、前記第2特別役を内部当籤役として決定可能とせず、
前記第2特別許可状態において、前記第1特別役を内部当籤役として決定可能とせず、
前記第1特別許可状態及び前記第2特別許可状態のいずれでもない通常遊技状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その2)における一般遊技状態(CZ状態))において、前記第1特別役又は前記第2特別役を内部当籤役として決定可能とし、
前記第1特別終了条件は、前記第1特別遊技状態において規定数(例えば、285枚を超える)の遊技価値が付与された場合に成立し、
前記第1特別遊技状態においては、前記所定役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、特定の態様で停止操作が行われた場合には所定数(例えば、9枚)の遊技価値が付与される一方、前記特定の態様で停止操作が行われなかった場合には前記所定数の遊技価値が付与されず、
少なくとも前記第1特別遊技状態において前記報知手段により前記特定の態様に関する前記操作情報が報知されない期間は、遊技価値が減少する減少期間として機能し、
前記第2特別遊技状態は、遊技価値が増加する増加期間として機能し、
特定の報知条件が成立した場合、前記第1特別遊技状態における特定期間を、前記報知手段により前記特定の態様に関する前記操作情報が報知される期間(例えば、有利区間)とすることが可能であることを特徴とする遊技機。
Symbol display means (for example,
A first special combination (for example, BB1 in another example (2) of game property), a second special combination (for example, BB2 in another example (2) of game property), and a predetermined combination (for example, game property) An internal winning combination determining means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of determining an internal winning combination from a plurality of combinations including another example (
Based on the internal winning combination determined by the internal winning combination determining means and the player's stop operation, stop control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of stopping variable display of symbols,
When the variable display of symbols is stopped by the stop control unit, a privilege providing unit (for example, the main CPU 101) that can provide a privilege according to the combination of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit, and a game including Machine,
When a combination of first special symbols (for example, a combination of symbols related to BB1 in another example (2) of game property) is displayed on the symbol display means, a first special game state (for example, other game property) (BB1 state in the example (2)) is started, and the first special game state control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of controlling to end the first special game state when the first special end condition is satisfied When,
A second special game state (for example, other game property) when a combination of second special symbols (for example, a combination of symbols relating to BB2 in another example (2) of game property) is displayed on the symbol display means. BB2 state in the example (part 2)) is started, and the second special game state control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of controlling to end the second special game state when the second special end condition is satisfied When,
And a notifying unit (for example, an instruction monitor) capable of notifying operation information regarding the stop operation of the player,
When the first special combination is determined as an internal winning combination, the combination of the first special symbol is displayed on the symbol display unit until the combination of the first special symbol is displayed on the symbol display unit. Is allowed to continue the first special permission state (for example, BB1 permission state in another example (2) of game nature),
When the second special combination is determined as an internal winning combination, the combination of the second special symbols is displayed on the symbol display unit until the combination of the second special symbols is displayed on the symbol display unit. The second special permission state (for example, the BB2 permission state in another example (2) of game nature) is allowed to continue,
The internal winning combination determination means,
In the first special permission state, it is not possible to determine the second special combination as an internal winning combination,
In the second special permission state, it is not possible to determine the first special combination as an internal winning combination,
In the normal game state that is neither the first special permission state nor the second special permission state (for example, a general game state (CZ state) in another example (2) of playability), the first special role or The second special combination can be determined as an internal winning combination,
The first special end condition is met when a prescribed number (for example, over 285) of game values are given in the first special game state,
In the first special game state, when the predetermined winning combination is determined as an internal winning combination, and when a stop operation is performed in a specific mode, a predetermined number (for example, 9) of game values are given. On the other hand, when the stop operation is not performed in the specific mode, the predetermined number of game values are not given,
At least a period in which the operation information regarding the specific mode is not notified by the notification means in the first special game state functions as a decrease period in which the game value decreases,
The second special game state functions as an increasing period in which the game value increases,
When the specific notification condition is satisfied, the specific period in the first special game state can be set as a period (for example, an advantageous section) in which the operation information regarding the specific mode is notified by the notification unit. A gaming machine characterized by that.
前記第1特別遊技状態において前記報知手段により前記特定の態様に関する前記操作情報が報知される期間は、前記増加期間として機能することを特徴とする遊技機。 A game machine characterized in that a period during which the notification information is notified by the notification means in the first special game state functions as the increase period.
前記第1特別遊技状態において、前記図柄表示手段に第1特定図柄の組合せ(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その2)におけるRB1に係る図柄の組合せ)が表示された場合に第1特定遊技状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その2)におけるRB1状態)を開始させ、第1特定終了条件が成立した場合に当該第1特定遊技状態を終了させる制御が可能な第1特定遊技状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記第2特別遊技状態において、前記図柄表示手段に第2特定図柄の組合せ(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その2)におけるRB2に係る図柄の組合せ)が表示された場合に第2特定遊技状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その2)におけるRB2状態)を開始させ、第2特定終了条件が成立した場合に当該第2特定遊技状態を終了させる制御が可能な第2特定遊技状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、をさらに備え、
前記内部当籤役決定手段は、
前記第1特別遊技状態において、第1特定役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その2)におけるRB1)を内部当籤役として決定可能であり、
前記第2特別遊技状態において、第2特定役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その2)におけるRB2)を内部当籤役として決定可能であり、
前記第1特別遊技状態において前記第1特定役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、前記図柄表示手段に前記第1特定図柄の組合せが表示されるまで、前記図柄表示手段に前記第1特定図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可される第1特定許可状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その2)におけるRB1許可状態)を継続させ、
前記第2特別遊技状態において前記第2特定役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、前記図柄表示手段に前記第2特定図柄の組合せが表示されるまで、前記図柄表示手段に前記第2特定図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可される第2特定許可状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その2)におけるRB2許可状態)を継続させ、
前記第1特別遊技状態では、前記第1特定許可状態であるか否かにかかわらず、前記報知手段により前記特定の態様に関する前記操作情報が報知されない期間が前記減少期間として機能し、
前記第2特別遊技状態では、前記第2特定許可状態である期間が前記増加期間として機能することを特徴とする遊技機。
In the first special game state, the first specific game when a combination of first specific symbols (for example, a combination of symbols related to RB1 in another example (2) of game property) is displayed on the symbol display means. A first specific game state in which control is possible to start a state (for example, RB1 state in another example (2) of game nature) and end the first specific game state when a first specific end condition is satisfied. Control means (for example, the main CPU 101),
In the second special game state, the second specific game when a combination of second specific symbols (for example, a combination of symbols related to RB2 in another example (2) of game property) is displayed on the symbol display means. A second specific game state in which control is possible to start a state (for example, RB2 state in another example (2) of game nature) and end the second specific game state when the second specific end condition is satisfied. A control unit (for example, the main CPU 101),
The internal winning combination determination means,
In the first special game state, it is possible to determine a first specific winning combination (for example, RB1 in another example (2) of game play) as an internal winning combination,
In the second special game state, it is possible to determine a second specific winning combination (for example, RB2 in another example (2) of game play) as an internal winning combination,
When the first specific winning combination is determined as an internal winning combination in the first special game state, the first specific symbol is displayed on the symbol displaying module until a combination of the first specific symbols is displayed on the symbol displaying module. The first specific permission state (for example, the RB1 permission state in another example (2) of game nature) in which the combination of is permitted to be displayed is continued,
When the second specific combination is determined as an internal winning combination in the second special game state, the second specific symbol is displayed on the symbol display unit until a combination of the second specific symbols is displayed on the symbol display unit. The second specific permission state (for example, the RB2 permission state in another example (2) of game nature) in which the combination of is permitted to be displayed is continued,
In the first special gaming state, a period in which the operation information regarding the specific aspect is not notified by the notification means functions as the decrease period regardless of whether or not it is the first specific permission state,
In the second special game state, a period of the second specific permission state functions as the increase period, the gaming machine.
上記構成の遊技機によれば、通常遊技状態において、第1特別役に当籤する前に第2特別役に当籤した場合、第2特別遊技状態に移行し、当該第2特別遊技状態は遊技価値が増加する増加期間として機能する。一方、通常遊技状態において、第2特別役に当籤する前に第1特別役に当籤した場合、第1特別遊技状態に移行し、当該第1特別遊技状態において停止操作に関する操作情報が報知されない場合、当該第1特別遊技状態は遊技価値が減少する減少期間として機能する。 According to the gaming machine configured as described above, in the normal game state, if the second special combination is won before the first special combination is won, the second special game state is entered, and the second special game state is the game value. Function as an increasing period. On the other hand, in the normal gaming state, when the first special winning combination is won before the second special winning combination is won, the first special gaming state is transitioned to, and operation information related to the stop operation is not notified in the first special gaming state. , The first special game state functions as a reduction period during which the game value decreases.
したがって、通常遊技状態においては、第1特別遊技状態に移行することなく第2特別遊技状態への移行が繰り返されることで、遊技者は有利な遊技期間を継続させることができるが、第1特別遊技状態に移行した場合には、当該第1特別遊技状態を終了させて通常遊技状態に移行させなければ、遊技者は有利な遊技期間を継続させることができない。 Therefore, in the normal game state, the player can continue an advantageous game period by repeating the shift to the second special game state without shifting to the first special game state, but the first special game state. When the game state is entered, the player cannot continue the advantageous game period unless the first special game state is ended and the normal game state is entered.
ここで、上記構成の遊技機によれば、特定の報知条件が成立した場合、第1特別遊技状態において、所定役に当籤した場合に所定数の遊技価値が付与される停止操作に関する操作情報が報知されるようになる。第1特別遊技状態は、規定数の遊技価値が付与された場合に終了するものであるから、このような情報が報知されることで、第1特別遊技状態の終了時期を早めることができる。すなわち、第1特別遊技状態において停止操作に関する操作情報が報知される否かによって、第2特別遊技状態に移行可能な通常遊技状態となるまでの期間を変動させることができる。それゆえ、有利状態に移行な状態となるまでの期間を変動可能とすることで、遊技性を変化に富んだものとすることができる。 Here, according to the gaming machine having the above-mentioned configuration, when the specific notification condition is satisfied, in the first special gaming state, operation information regarding a stop operation in which a predetermined number of game values are awarded when a predetermined winning combination is won is provided. Be notified. Since the first special game state ends when a prescribed number of game values are given, the end timing of the first special game state can be advanced by notifying such information. That is, it is possible to change the period until the normal game state in which the second special game state can be entered is changed depending on whether or not the operation information regarding the stop operation is notified in the first special game state. Therefore, by making it possible to change the period until the state shifts to the advantageous state, it is possible to make the game rich in variety.
なお、上記構成の遊技機において、第1特別遊技状態において停止操作に関する操作情報が報知される期間も増加期間として機能させるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、有利状態に移行な状態となるまでの期間中であっても、遊技の興趣を維持させることができる。 In the gaming machine having the above-described configuration, the period in which the operation information regarding the stop operation is notified in the first special game state may also function as the increase period. By doing so, it is possible to maintain the interest of the game even during the period until the state shifts to the advantageous state.
また、上記構成の遊技機において、第1特別遊技状態では、さらに第1特定許可状態に移行可能とし、第2特別遊技状態では、さらに第2特定許可状態に移行可能とし、第1特別遊技状態では、第1特定許可状態であるか否かにかかわらず、停止操作に関する操作情報が報知されない期間を減少期間として機能させ、第2特別遊技状態では、第2特定許可状態である期間を増加期間として機能させるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、遊技性をさらに変化に富んだものとすることができ、遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。 Further, in the gaming machine having the above configuration, in the first special game state, it is possible to further shift to the first specific permission state, and in the second special game state, it is possible to further shift to the second specific permission state, and the first special game state. Then, regardless of whether it is in the first specific permission state, the period in which the operation information regarding the stop operation is not notified is made to function as the reduction period, and in the second special game state, the period in the second specific permission state is increased. You may make it function as. By doing so, the playability can be further varied and the enjoyment of the game can be improved.
[第20〜第22の構成の遊技機]
従来の遊技機において、所定の有利条件が成立すると遊技者に有利な有利状態に移行する一方、所定の不利条件が成立すると遊技者に不利な不利状態に移行する所定状態を有し、不利状態へ移行することなく所定状態から有利状態への移行が繰り返されることで、遊技者にとって有利な状態が継続することを可能としたものが知られている(例えば、特開2010−167197号公報参照)。
[A game machine having 20th to 22nd configurations]
In a conventional gaming machine, when a predetermined advantageous condition is established, it shifts to an advantageous state that is advantageous to the player, while when a predetermined disadvantageous condition is established, it has a certain state in which it shifts to a disadvantageous state that is disadvantageous to the player. It is known that the advantageous state for the player can be continued by repeating the transition from the predetermined state to the advantageous state without shifting to (see, for example, JP 2010-167197 A). ).
しかしながら、このような遊技機では、所定状態から不利状態に移行した場合、再度所定状態に移行するまで遊技者にとって有利な状態とはならないため、特に、不利状態における遊技意欲や興趣が低下してしまうという問題があった。 However, in such a gaming machine, when the state shifts from the predetermined state to the disadvantageous state, the state does not become advantageous to the player until the state shifts to the predetermined state again. There was a problem that it would end up.
本発明は、このような点に鑑みてなされたものであり、遊技意欲や興趣を向上させることができる遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above points, and an object of the present invention is to provide a gaming machine capable of improving a game motivation and interest.
上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような構成の第20の遊技機を提供することができる。 To achieve the above object, the gaming machine of the present embodiment can provide a twentieth gaming machine having the following configuration.
複数の図柄を複数列に変動表示可能な図柄表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R及び図柄表示領域4)と、
特別役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その3)におけるBB)及び特定役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その3)における押し順小役)を含む複数の役の中から内部当籤役を決定可能な内部当籤役決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記内部当籤役決定手段により決定された内部当籤役と遊技者の停止操作とに基づいて、図柄の変動表示を停止可能な停止制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記停止制御手段により図柄の変動表示が停止された場合に、前記図柄表示手段に表示された図柄の組合せに応じた特典を付与可能な特典付与手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、を備えた遊技機であって、
遊技状態として、通常遊技状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その3)におけるRT0状態)、特別遊技状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その3)におけるBB状態)及び特定遊技状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その3)におけるRT1状態)を有し、
前記図柄表示手段に特別図柄の組合せ(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その3)におけるBBに係る図柄の組合せ)が表示された場合に前記特別遊技状態を開始させ、特別終了条件が成立した場合に前記特別遊技状態を終了させる制御が可能な特別遊技状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記図柄表示手段に特定図柄の組合せ(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その3)におけるベルこぼし目)が表示された場合に前記特定遊技状態を開始させ、特定終了条件が成立した場合に前記特定遊技状態を終了させる制御が可能な特定遊技状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
遊技者の停止操作に関する操作情報を報知可能な報知手段(例えば、指示モニタ)と、を備え、
前記特別役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、前記図柄表示手段に前記特別図柄の組合せが表示されるまで、前記図柄表示手段に前記特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可される特別許可状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その3)におけるBB許可状態)を継続させ、
前記特定遊技状態制御手段は、前記特別許可状態でない前記通常遊技状態において、前記図柄表示手段に前記特定図柄の組合せが表示された場合に、前記特定遊技状態を開始させ、
前記特定終了条件は、規定数(例えば、500ゲーム)の遊技が行われた場合に成立し、
前記停止制御手段は、
前記特別許可状態である前記特定遊技状態においては前記図柄表示手段に前記特別図柄の組合せを表示させることを可能とせず、
前記特定役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、特定の態様で停止操作が行われた場合には前記図柄表示手段に前記特定図柄の組合せを表示させることを可能とせず、前記特定の態様で停止操作が行われなかった場合には前記図柄表示手段に前記特定図柄の組合せを表示させることを可能とし、
前記特典付与手段は、前記特定役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、前記特定の態様で停止操作が行われた場合には特定数の遊技価値の付与を可能とし、前記特定の態様で停止操作が行われなかった場合には前記特定数の遊技価値の付与を可能とせず、
特定の報知条件が成立した場合、前記通常遊技状態及び前記特定遊技状態における特定期間を、前記報知手段により前記特定の態様に関する前記操作情報が報知される期間(例えば、有利区間)とすることが可能であることを特徴とする遊技機。
Symbol display means (for example,
Internal winning from a plurality of combinations including a special combination (for example, BB in another example (3) of game play) and a specific combination (for example, small push order combination in another example (3) of game play) An internal winning combination determination means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of determining a combination,
Based on the internal winning combination determined by the internal winning combination determining means and the player's stop operation, stop control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of stopping variable display of symbols,
When the variable display of symbols is stopped by the stop control unit, a privilege providing unit (for example, the main CPU 101) that can provide a privilege according to the combination of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit, and a game including Machine,
As the gaming state, a normal gaming state (for example, RT0 state in another example (3) of gaming nature), a special gaming state (for example, BB state in other example (3) of gaming nature) and a specific gaming state ( For example, having another example of playability (RT1 state in Part 3),
When the combination of special symbols (for example, the combination of symbols relating to BB in another example (3) of game property) is displayed on the symbol display means, the special game state is started, and the special end condition is satisfied. Special game state control means (for example, main CPU 101) capable of controlling to end the special game state,
The specific game state is started when a combination of specific symbols (for example, a bell-shaped eye in another example (3) of playability) is displayed on the symbol display means, and when a specific end condition is satisfied, Specific game state control means (for example, main CPU 101) capable of controlling to end the specific game state,
And a notifying unit (for example, an instruction monitor) capable of notifying operation information regarding the stop operation of the player,
When the special combination is determined as an internal winning combination, a special permission that allows the combination of the special symbols to be displayed on the symbol display unit until the combination of the special symbols is displayed on the symbol display unit. Continue the state (for example, the BB permission state in another example (3) of game play),
The specific game state control means, in the normal game state which is not the special permission state, when the combination of the specific symbol is displayed on the symbol display means, start the specific game state,
The specific ending condition is met when a prescribed number of games (for example, 500 games) are played,
The stop control means,
In the specific game state, which is the special permission state, it is not possible to display the combination of the special symbols on the symbol display means,
If the specific winning combination is determined as an internal winning combination, it is not possible to display the combination of the specific symbols on the symbol display means when a stop operation is performed in a specific aspect, and in the specific aspect. When the stop operation is not performed, it is possible to display the combination of the specific symbol on the symbol display means,
When the specific winning combination is determined as an internal winning combination, the privilege granting means makes it possible to grant a specific number of game values when a stop operation is performed in the specific winning combination, and the special winning combination is stopped in the specific winning combination. If the operation is not performed, it is not possible to give the specified number of game values,
When the specific notification condition is satisfied, the specific period in the normal game state and the specific game state may be set as a period (for example, an advantageous section) in which the notification information is notified by the notification unit. A gaming machine characterized by being possible.
少なくとも前記特定遊技状態において前記報知手段により前記特定の態様に関する前記操作情報が報知される期間は、遊技価値が増加する増加期間として機能することを特徴とする遊技機。 A gaming machine characterized in that at least the period in which the operation information related to the specific mode is notified by the notification means in the specific game state functions as an increase period in which the game value increases.
上記構成の遊技機によれば、特別役に当籤した場合には特別許可状態となり、通常遊技状態であれば、特別図柄の組合せを表示させて特別遊技状態に移行させることを可能とする一方、特定遊技状態であれば、当該特定遊技状態が終了するまで特別図柄の組合せを表示させて特別遊技状態に移行させることを可能としない。また、特定遊技状態には、特別許可状態でない通常遊技状態において特定役に当籤した場合に、特定の態様で停止操作が行われずに特定図柄の組合せが表示されたことに基づいて移行する。そして、特定の報知条件が成立した場合、通常遊技状態及び特定遊技状態における特定期間では、特定役に当籤したときに特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知され、報知にしたがって停止操作が行われれば、特定図柄の組合せは表示されず、特定数の遊技価値が付与される。 According to the gaming machine having the above configuration, when a special combination is won, a special permission state is entered, and in the normal gaming state, it is possible to display a combination of special symbols and shift to a special gaming state, If it is a specific game state, it is not possible to display a combination of special symbols and shift to the special game state until the specific game state ends. Further, the specific game state, based on the combination of specific symbols is displayed without a stop operation in a specific mode when a specific winning combination is won in a normal game state that is not the special permission state. Then, when the specific notification condition is satisfied, during the specific period in the normal game state and the specific game state, operation information regarding a specific aspect is notified when a specific winning combination is won, and if a stop operation is performed according to the notification, A combination of specific symbols is not displayed, and a specific number of game values are given.
ここで、上記構成の遊技機によれば、通常遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間となった場合には、特定遊技状態に移行することなく特別遊技状態への移行を繰り返す(すなわち、遊技者に有利な遊技期間を継続させる)ことが可能となるのみならず、特定役に当籤したときに付与される遊技価値も増加することになる。また、特定遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間となった場合には、特定遊技状態が終了しなければ特別遊技状態に移行させることはできないが、特定役に当籤したときに付与される遊技価値は増加することになる。また、通常遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間となっていない場合であっても、特定遊技状態に移行することなく特別遊技状態への移行を繰り返すことができる場合もある。 Here, according to the gaming machine having the above-described configuration, in the normal gaming state, when a specific period during which operation information regarding a specific aspect is notified is given, the shift to the special gaming state is performed without shifting to the specific gaming state. It is possible not only to repeat the game (that is, to continue the game period advantageous to the player), but also to increase the game value given when the specific combination is won. Also, in the specific game state, when it becomes a specific period in which operation information regarding a specific mode is notified, it is not possible to shift to the special game state unless the specific game state ends, but when a specific winning combination is won. The game value given to the player will increase. In addition, even in a case where the normal game state is not in a specific period in which operation information related to a specific mode is notified, it may be possible to repeat the transition to the special game state without shifting to the specific game state. ..
すなわち、上記構成の遊技機によれば、通常遊技状態若しくは特定遊技状態であるか、通常遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間であるか否か、又は特定遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間であるか否か、などに応じて遊技者の有利度合いを多彩に変動させることが可能となる。それゆえ、遊技意欲や興趣を向上させることができる。 That is, according to the gaming machine having the above configuration, whether the game is in the normal game state or the specific game state, whether or not it is the specific period during which the operation information regarding the specific mode is notified in the normal game state, or the specific game state is specified. It is possible to variably change the degree of advantage of the player depending on whether or not it is a specific period in which the operation information regarding the mode is notified. Therefore, it is possible to improve the game motivation and interest.
なお、上記構成の遊技機において、少なくとも特定遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される期間は、遊技価値が増加する増加期間として機能させるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、特定遊技状態であっても遊技価値が増加する場合があることから、特別遊技状態に移行しない特定遊技状態中であっても、遊技の興趣を維持させることができる。 In the gaming machine configured as described above, at least the period in which the operation information related to the specific mode is notified in the specific game state may be made to function as an increasing period in which the game value increases. By doing so, the game value may increase even in the specific game state, so that the interest of the game can be maintained even during the specific game state in which the special game state is not entered.
また、上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような構成の第21の遊技機を提供することができる。 Further, in order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a twenty-first gaming machine having the following configuration.
複数の図柄を複数列に変動表示可能な図柄表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R及び図柄表示領域4)と、
特別役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるBB)、特殊役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるMB)及び特定役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)における押し順小役)を含む複数の役の中から内部当籤役を決定可能な内部当籤役決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記内部当籤役決定手段により決定された内部当籤役と遊技者の停止操作とに基づいて、図柄の変動表示を停止可能な停止制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記停止制御手段により図柄の変動表示が停止された場合に、前記図柄表示手段に表示された図柄の組合せに応じた特典を付与可能な特典付与手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、を備えた遊技機であって、
遊技状態として、通常遊技状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるRT0状態)、特別遊技状態、特殊遊技状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるBB状態)、第1特定遊技状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるRT1状態)及び第2特定遊技状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるRT2状態)を有し、
前記図柄表示手段に特別図柄の組合せ(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるBBに係る図柄の組合せ)が表示された場合に前記特別遊技状態を開始させ、特別終了条件が成立した場合に前記特別遊技状態を終了させる制御が可能な特別遊技状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記図柄表示手段に特殊図柄の組合せ(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるMBに係る図柄の組合せ)が表示された場合に前記特殊遊技状態を開始させ、特殊終了条件が成立した場合に前記特殊遊技状態を終了させる制御が可能な特殊遊技状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記図柄表示手段に特定図柄の組合せ(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるベルこぼし目)が表示された場合に前記第1特定遊技状態を開始させ、特定終了条件が成立した場合に前記第1特定遊技状態を終了させる制御が可能な第1特定遊技状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記特別役が内部当籤役として決定された場合に前記第2特定遊技状態を開始させ、前記特別遊技状態が開始される場合に前記第2特定遊技状態を終了させる制御が可能な第2特定遊技状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
遊技者の停止操作に関する操作情報を報知可能な報知手段(例えば、指示モニタ)と、を備え、
前記特別役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、前記図柄表示手段に前記特別図柄の組合せが表示されるまで、前記図柄表示手段に前記特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可される特別許可状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるBB許可状態)を継続させ、
前記特殊役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、前記図柄表示手段に前記特殊図柄の組合せが表示されるまで、前記図柄表示手段に前記特殊図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可される特殊許可状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるMB許可状態)を継続させ、
前記内部当籤役決定手段は、
前記特別許可状態において、前記特殊役を内部当籤役として決定可能とせず、
前記特殊許可状態において、前記特別役を内部当籤役として決定可能とせず、
前記特別許可状態及び前記特殊許可状態のいずれでもない前記通常遊技状態及び前記第1特定遊技状態において、前記特別役又は前記特殊役を内部当籤役として決定可能とし、
前記第1特定遊技状態制御手段は、前記特別許可状態及び前記特殊許可状態でない前記通常遊技状態において、前記図柄表示手段に前記特定図柄の組合せが表示された場合に、前記第1特定遊技状態を開始させ、
前記停止制御手段は、
前記特別許可状態である前記第2特定遊技状態においては前記図柄表示手段に前記特別図柄の組合せを表示させることを困難とせず、
前記特殊許可状態である前記第1特定遊技状態においては前記図柄表示手段に前記特殊図柄の組合せを表示させることを困難とし、
前記特定役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、特定の態様で停止操作が行われた場合には前記図柄表示手段に前記特定図柄の組合せを表示させることを可能とせず、前記特定の態様で停止操作が行われなかった場合には前記図柄表示手段に前記特定図柄の組合せを表示させることを可能とし、
前記特典付与手段は、前記特定役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、前記特定の態様で停止操作が行われた場合には特定数の遊技価値の付与を可能とし、前記特定の態様で停止操作が行われなかった場合には前記特定数の遊技価値の付与を可能とせず、
特定の報知条件が成立した場合、前記通常遊技状態及び前記第1特定遊技状態における特定期間を、前記報知手段により前記特定の態様に関する前記操作情報が報知される期間(例えば、有利区間)とすることが可能であることを特徴とする遊技機。
Symbol display means (for example,
Special combination (for example, BB in another example of playability (4)), special combination (for example, MB in another example of playability (4)) and specific combination (for example, other example of playability ( Internal winning combination determination means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of determining an internal winning combination from a plurality of combinations including the pressing order small combination in 4).
Based on the internal winning combination determined by the internal winning combination determining means and the player's stop operation, stop control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of stopping variable display of symbols,
When the variable display of symbols is stopped by the stop control unit, a privilege providing unit (for example, the main CPU 101) that can provide a privilege according to the combination of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit, and a game including Machine,
As the gaming state, a normal gaming state (for example, RT0 state in another example of gaming property (4)), a special gaming state, a special gaming state (for example, BB state in another example of gaming property (4)), Having a first specific game state (for example, RT1 state in another example of playability (4)) and a second specific game state (for example, RT2 state in other example of playability (fourth)),
When the combination of special symbols (for example, the combination of symbols related to BB in another example (4) of game property) is displayed on the symbol display means, the special game state is started, and the special ending condition is satisfied. Special game state control means (for example, main CPU 101) capable of controlling to end the special game state,
When the combination of special symbols (for example, the combination of symbols relating to MB in another example (4) of game property) is displayed on the symbol display means, the special game state is started and the special end condition is satisfied. Special game state control means (for example, main CPU 101) capable of controlling to end the special game state in the case,
When the first specific game state is started when a combination of specific symbols (for example, a bell-shaped eye in another example (4) of game nature) is displayed on the symbol display means, and a specific end condition is satisfied First specific game state control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of controlling to end the first specific game state,
A second specific game capable of controlling to start the second specific game state when the special combination is determined as an internal winning combination and to end the second specific game state when the special game state is started. A state control means (for example, the main CPU 101),
And a notifying unit (for example, an instruction monitor) capable of notifying operation information regarding the stop operation of the player,
When the special combination is determined as an internal winning combination, a special permission that allows the combination of the special symbols to be displayed on the symbol display unit until the combination of the special symbols is displayed on the symbol display unit. The state (for example, the BB permission state in another example (4) of game play) is continued,
When the special winning combination is determined as an internal winning combination, a special permission that allows the combination of the special symbols to be displayed on the symbol displaying unit until the combination of the special symbols is displayed on the symbol displaying unit. Continue the state (for example, MB permission state in another example of playability (4)),
The internal winning combination determination means,
In the special permission state, it is not possible to determine the special winning combination as an internal winning combination,
In the special permission state, it is not possible to determine the special winning combination as an internal winning combination,
In the normal game state and the first specific game state, which is neither the special permission state nor the special permission state, the special combination or the special combination can be determined as an internal winning combination,
The first specific game state control means, in the special permission state and the normal game state is not the special permission state, when the combination of the specific symbol is displayed on the symbol display means, the first specific game state, Let it start,
The stop control means,
In the second specific game state, which is the special permission state, without making it difficult to display the combination of the special symbols on the symbol display means,
In the first specific game state, which is the special permission state, it is difficult to display the combination of the special symbols on the symbol display means,
If the specific winning combination is determined as an internal winning combination, it is not possible to display the combination of the specific symbols on the symbol display means when a stop operation is performed in a specific aspect, and in the specific aspect. When the stop operation is not performed, it is possible to display the combination of the specific symbol on the symbol display means,
When the specific winning combination is determined as an internal winning combination, the privilege granting means makes it possible to grant a specific number of game values when a stop operation is performed in the specific winning combination, and the special winning combination is stopped in the specific winning combination. If the operation is not performed, it is not possible to give the specified number of game values,
When the specific notification condition is satisfied, the specific period in the normal game state and the first specific game state is set as a period (for example, an advantageous section) in which the notification information notifies the operation information related to the specific mode. A gaming machine characterized in that it is possible.
少なくとも前記第1特定遊技状態において前記報知手段により前記特定の態様に関する前記操作情報が報知される期間は、遊技価値が増加する増加期間として機能することを特徴とする遊技機。 A gaming machine characterized in that at least a period in which the operation information related to the specific mode is notified by the notification means in the first specific game state functions as an increase period in which a game value increases.
上記構成の遊技機によれば、特別役に当籤した場合には特別許可状態となって第2特定遊技状態に移行し、特別図柄の組合せを表示させて特別遊技状態に移行させることを困難としない一方、特殊役に当籤した場合には特殊許可状態となるが遊技状態は移行せず、第1特定遊技状態であれば、当該第1特定遊技状態が終了するまで特殊図柄の組合せを表示させて特殊遊技状態に移行させることを困難とし、その結果として通常遊技状態に移行させることを困難とする。また、第1特定遊技状態には、特別許可状態及び特殊許可状態でない通常遊技状態において特定役に当籤した場合に、特定の態様で停止操作が行われずに特定図柄の組合せが表示されたことに基づいて移行する。そして、特定の報知条件が成立した場合、通常遊技状態及び第1特定遊技状態における特定期間では、特定役に当籤したときに特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知され、報知にしたがって停止操作が行われれば、特定図柄の組合せは表示されず、特定数の遊技価値が付与される。 According to the gaming machine having the above-mentioned configuration, when a special winning is won, it becomes a special permission state and shifts to the second specific game state, and it is difficult to display a combination of special symbols and shift to the special game state. On the other hand, if you win the special combination, you will be in a special permission state, but the game state will not shift, and if it is the first specific game state, the combination of special symbols will be displayed until the first specific game state ends. Therefore, it is difficult to shift to the special game state, and as a result, it is difficult to shift to the normal game state. Further, in the first specific game state, when the special combination is won in the special permission state and the normal game state which is not the special permission state, the combination of the specific symbols is displayed without performing the stop operation in the specific mode. Based on the transition. Then, when the specific notification condition is satisfied, during the specific period in the normal game state and the first specific game state, operation information regarding a specific mode is notified when a specific winning combination is won, and a stop operation is performed according to the notification. For example, a combination of specific symbols is not displayed, and a specific number of game values are given.
ここで、上記構成の遊技機によれば、通常遊技状態において、特定役に当籤したときに特定図柄の組合せが表示されて第1特定遊技状態に移行する前に、特別役又は特殊役に当籤して特別許可状態(第2特定遊技状態)又は特殊許可状態となれば、特別遊技状態又は特殊遊技状態を経由して再度通常遊技状態において遊技を行うことができる。また、第1特定遊技状態であっても、特別役に当籤して特別許可状態(第2特定遊技状態)となれば、特別遊技状態を経由して再度通常遊技状態において遊技を行うことができる。一方、第1特定遊技状態において、特殊役に当籤して特殊許可状態となると、特殊遊技状態を経由して再度通常遊技状態において遊技を行うことが困難となる。 Here, according to the gaming machine having the above-mentioned configuration, in the normal game state, when a specific combination is won, a combination of specific symbols is displayed and a special combination or a special combination is won before the first specific game state is entered. If the special permission state (second specific game state) or the special permission state is reached, the game can be played again in the normal game state via the special game state or the special game state. Further, even in the first specific game state, if the special combination is won and the special permission state (second specific game state) is reached, the game can be played again in the normal game state via the special game state. .. On the other hand, in the first specific game state, if the special combination is won and the special permitted state is reached, it becomes difficult to play the game in the normal game state again via the special game state.
かかる遊技性の下、通常遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間となった場合には、第1特定遊技状態に移行することなく特別遊技状態(あるいは特殊遊技状態)への移行を繰り返す(すなわち、遊技者に有利な遊技期間を継続させる)ことが可能となるのみならず、特定役に当籤したときに付与される遊技価値も増加することになる。また、第1特定遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間となった場合には、例えば、特殊許可状態であれば特殊遊技状態を経由して通常遊技状態に移行させることは困難であるものの、特定役に当籤したときに付与される遊技価値は増加することになる。また、通常遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間となっていない場合であっても、第1特定遊技状態に移行することなく特別遊技状態(あるいは特殊遊技状態)への移行を繰り返すことができる場合もある。 Under such a game property, in the normal game state, when a specific period during which operation information related to a specific mode is notified is given, the special game state (or the special game state) is entered without shifting to the first specific game state. It is possible not only to repeat the shift (that is, to continue the game period that is advantageous to the player), but also to increase the game value given when the specific combination is won. Further, in the first specific game state, when the specific period during which the operation information regarding the specific mode is notified is given, for example, in the case of the special permission state, it is possible to shift to the normal game state via the special game state. Although difficult, the game value given when a specific combination is won is increased. In addition, even in the normal game state, even if it is not a specific period in which operation information related to a specific mode is notified, a transition to the special game state (or a special game state) without transition to the first specific game state May be repeated.
すなわち、上記構成の遊技機によれば、通常遊技状態若しくは第1特定遊技状態であるか、通常遊技状態において特別役、特殊役若しくは特定役がどのような順番で当籤するか、第1特定遊技状態において特別役若しくは特殊役がどのような順番で当籤するか、通常遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間であるか否か、又は第1特定遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間であるか否か、などに応じて遊技者の有利度合いを多彩に変動させることが可能となる。それゆえ、遊技意欲や興趣を向上させることができる。 That is, according to the gaming machine having the above-described configuration, whether the game is in the normal game state or the first specific game state, in what order the special combination, the special combination, or the specific combination is won in the normal game state, the first specific game. In a state, a special combination or a special combination is won in an order, whether or not it is a specific period in which operation information related to a specific mode is notified in the normal gaming state, or a specific mode in the first specific gaming state It is possible to variably change the degree of advantage of the player according to whether or not it is a specific period in which the operation information is notified. Therefore, it is possible to improve the game motivation and interest.
なお、上記構成の遊技機において、少なくとも第1特定遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される期間は、遊技価値が増加する増加期間として機能させるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、第1特定遊技状態であっても遊技価値が増加する場合があることから、通常遊技状態に移行することが困難な特定遊技状態中であっても、遊技の興趣を維持させることができる。 In the gaming machine configured as described above, at least the period in which the operation information related to the specific mode is notified in the first specific game state may function as an increase period in which the game value increases. By doing so, the game value may increase even in the first specific game state, so that the interest of the game is maintained even during the specific game state in which it is difficult to shift to the normal game state. Can be made
また、上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような構成の第22の遊技機を提供することができる。 Further, in order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a twenty-second gaming machine having the following configuration.
複数の図柄を複数列に変動表示可能な図柄表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R及び図柄表示領域4)と、
特別役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるBB)、特殊役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるMB)及び特定役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)における押し順小役)を含む複数の役の中から内部当籤役を決定可能な内部当籤役決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記内部当籤役決定手段により決定された内部当籤役と遊技者の停止操作とに基づいて、図柄の変動表示を停止可能な停止制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記停止制御手段により図柄の変動表示が停止された場合に、前記図柄表示手段に表示された図柄の組合せに応じた特典を付与可能な特典付与手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、を備えた遊技機であって、
遊技状態として、通常遊技状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるRT0状態)、特別遊技状態、特殊遊技状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるBB状態)、第1特定遊技状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるRT1状態)及び第2特定遊技状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるRT2状態)を有し、
前記図柄表示手段に特別図柄の組合せ(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるBBに係る図柄の組合せ)が表示された場合に前記特別遊技状態を開始させ、特別終了条件が成立した場合に前記特別遊技状態を終了させる制御が可能な特別遊技状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記図柄表示手段に特殊図柄の組合せ(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるMBに係る図柄の組合せ)が表示された場合に前記特殊遊技状態を開始させ、特殊終了条件が成立した場合に前記特殊遊技状態を終了させる制御が可能な特殊遊技状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記図柄表示手段に特定図柄の組合せ(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるベルこぼし目)が表示された場合に前記第1特定遊技状態を開始させ、特定終了条件が成立した場合に前記第1特定遊技状態を終了させる制御が可能な第1特定遊技状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記特別役が内部当籤役として決定された場合に前記第2特定遊技状態を開始させ、前記特別遊技状態が開始される場合に前記第2特定遊技状態を終了させる制御が可能な第2特定遊技状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
遊技者の停止操作に関する操作情報を報知可能な報知手段(例えば、指示モニタ)と、を備え、
前記特別役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、前記図柄表示手段に前記特別図柄の組合せが表示されるまで、前記図柄表示手段に前記特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可される特別許可状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるBB許可状態)を継続させ、
前記特殊役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、前記図柄表示手段に前記特殊図柄の組合せが表示されるまで、前記図柄表示手段に前記特殊図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可される特殊許可状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その4)におけるMB許可状態)を継続させ、
前記内部当籤役決定手段は、
前記特別許可状態において、前記特殊役を内部当籤役として決定可能とせず、
前記特殊許可状態において、前記特別役を内部当籤役として決定可能とせず、
前記特別許可状態及び前記特殊許可状態のいずれでもない前記通常遊技状態及び前記第1特定遊技状態において、前記特別役又は前記特殊役を内部当籤役として決定可能とし、
前記第1特定遊技状態制御手段は、前記特別許可状態及び前記特殊許可状態でない前記通常遊技状態において、前記図柄表示手段に前記特定図柄の組合せが表示された場合に、前記第1特定遊技状態を開始させ、
前記特定終了条件は、規定数(例えば、1500ゲーム)の遊技が行われた場合に成立し、前記特殊遊技状態が開始される場合には成立せず、
前記停止制御手段は、
前記特別許可状態である前記第2特定遊技状態においては前記図柄表示手段に前記特別図柄の組合せを表示させることを困難とせず、
前記特殊許可状態である前記第1特定遊技状態においては前記図柄表示手段に前記特殊図柄の組合せを表示させることを困難とし、
前記特定役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、特定の態様で停止操作が行われた場合には前記図柄表示手段に前記特定図柄の組合せを表示させることを可能とせず、前記特定の態様で停止操作が行われなかった場合には前記図柄表示手段に前記特定図柄の組合せを表示させることを可能とし、
前記特典付与手段は、前記特定役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、前記特定の態様で停止操作が行われた場合には特定数の遊技価値の付与を可能とし、前記特定の態様で停止操作が行われなかった場合には前記特定数の遊技価値の付与を可能とせず、
特定の報知条件が成立した場合、前記通常遊技状態及び前記第1特定遊技状態における特定期間を、前記報知手段により前記特定の態様に関する前記操作情報が報知される期間(例えば、有利区間)とすることが可能であることを特徴とする遊技機。
Symbol display means (for example,
Special combination (for example, BB in another example of playability (4)), special combination (for example, MB in another example of playability (4)) and specific combination (for example, other example of playability ( Internal winning combination determination means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of determining an internal winning combination from a plurality of combinations including the pressing order small combination in 4).
Based on the internal winning combination determined by the internal winning combination determining means and the player's stop operation, stop control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of stopping variable display of symbols,
When the variable display of symbols is stopped by the stop control unit, a privilege providing unit (for example, the main CPU 101) that can provide a privilege according to the combination of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit, and a game including Machine,
As the gaming state, a normal gaming state (for example, RT0 state in another example of gaming property (4)), a special gaming state, a special gaming state (for example, BB state in another example of gaming property (4)), Having a first specific game state (for example, RT1 state in another example of playability (4)) and a second specific game state (for example, RT2 state in other example of playability (fourth)),
When the combination of special symbols (for example, the combination of symbols related to BB in another example (4) of game property) is displayed on the symbol display means, the special game state is started, and the special ending condition is satisfied. Special game state control means (for example, main CPU 101) capable of controlling to end the special game state,
When the combination of special symbols (for example, the combination of symbols relating to MB in another example (4) of game property) is displayed on the symbol display means, the special game state is started and the special end condition is satisfied. Special game state control means (for example, main CPU 101) capable of controlling to end the special game state in the case,
When the first specific game state is started when a combination of specific symbols (for example, a bell-shaped eye in another example (4) of game nature) is displayed on the symbol display means, and a specific end condition is satisfied First specific game state control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of controlling to end the first specific game state,
A second specific game capable of controlling to start the second specific game state when the special combination is determined as an internal winning combination and to end the second specific game state when the special game state is started. A state control means (for example, the main CPU 101),
And a notifying unit (for example, an instruction monitor) capable of notifying operation information regarding the stop operation of the player,
When the special combination is determined as an internal winning combination, a special permission that allows the combination of the special symbols to be displayed on the symbol display unit until the combination of the special symbols is displayed on the symbol display unit. The state (for example, the BB permission state in another example (4) of game play) is continued,
When the special winning combination is determined as an internal winning combination, a special permission that allows the combination of the special symbols to be displayed on the symbol displaying unit until the combination of the special symbols is displayed on the symbol displaying unit. Continue the state (for example, MB permission state in another example of playability (4)),
The internal winning combination determination means,
In the special permission state, it is not possible to determine the special winning combination as an internal winning combination,
In the special permission state, it is not possible to determine the special winning combination as an internal winning combination,
In the normal game state and the first specific game state, which is neither the special permission state nor the special permission state, the special combination or the special combination can be determined as an internal winning combination,
The first specific game state control means, in the special permission state and the normal game state is not the special permission state, when the combination of the specific symbol is displayed on the symbol display means, the first specific game state, Let it start,
The specific ending condition is satisfied when a specified number of games (for example, 1500 games) are played, and is not satisfied when the special game state is started,
The stop control means,
In the second specific game state, which is the special permission state, without making it difficult to display the combination of the special symbols on the symbol display means,
In the first specific game state, which is the special permission state, it is difficult to display the combination of the special symbols on the symbol display means,
If the specific winning combination is determined as an internal winning combination, it is not possible to display the combination of the specific symbols on the symbol display means when a stop operation is performed in a specific aspect, and in the specific aspect. When the stop operation is not performed, it is possible to display the combination of the specific symbol on the symbol display means,
When the specific winning combination is determined as an internal winning combination, the privilege granting means makes it possible to grant a specific number of game values when a stop operation is performed in the specific winning combination, and the special winning combination is stopped in the specific winning combination. If the operation is not performed, it is not possible to give the specified number of game values,
When the specific notification condition is satisfied, the specific period in the normal game state and the first specific game state is set as a period (for example, an advantageous section) in which the notification information notifies the operation information related to the specific mode. A gaming machine characterized in that it is possible.
少なくとも前記第1特定遊技状態において前記報知手段により前記特定の態様に関する前記操作情報が報知される期間は、遊技価値が増加する増加期間として機能することを特徴とする遊技機。 A gaming machine characterized in that at least a period in which the operation information related to the specific mode is notified by the notification means in the first specific game state functions as an increase period in which a game value increases.
上記構成の遊技機によれば、特別役に当籤した場合には特別許可状態となって第2特定遊技状態に移行し、特別図柄の組合せを表示させて特別遊技状態に移行させることを困難としない一方、特殊役に当籤した場合には特殊許可状態となるが遊技状態は移行せず、第1特定遊技状態であれば、規定数の遊技が行われて当該第1特定遊技状態が終了するまで特殊図柄の組合せを表示させて特殊遊技状態に移行させることを困難とし、その結果として通常遊技状態に移行させることを困難とする。また、第1特定遊技状態には、特別許可状態及び特殊許可状態でない通常遊技状態において特定役に当籤した場合に、特定の態様で停止操作が行われずに特定図柄の組合せが表示されたことに基づいて移行する。そして、特定の報知条件が成立した場合、通常遊技状態及び第1特定遊技状態における特定期間では、特定役に当籤したときに特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知され、報知にしたがって停止操作が行われれば、特定図柄の組合せは表示されず、特定数の遊技価値が付与される。 According to the gaming machine having the above-mentioned configuration, when a special winning is won, it becomes a special permission state and shifts to the second specific game state, and it is difficult to display a combination of special symbols and shift to the special game state. On the other hand, if the special combination is won, the special permission state is entered, but the game state does not shift, and if the first specific game state, a prescribed number of games are played and the first specific game state ends. Until it is difficult to display the combination of special symbols and shift to the special game state, and as a result, it is difficult to shift to the normal game state. Further, in the first specific game state, when the special combination is won in the special permission state and the normal game state which is not the special permission state, the combination of the specific symbols is displayed without performing the stop operation in the specific mode. Based on the transition. Then, when the specific notification condition is satisfied, during the specific period in the normal game state and the first specific game state, operation information regarding a specific mode is notified when a specific winning combination is won, and a stop operation is performed according to the notification. For example, a combination of specific symbols is not displayed, and a specific number of game values are given.
ここで、上記構成の遊技機によれば、通常遊技状態において、特定役に当籤したときに特定図柄の組合せが表示されて第1特定遊技状態に移行する前に、特別役又は特殊役に当籤して特別許可状態(第2特定遊技状態)又は特殊許可状態となれば、特別遊技状態又は特殊遊技状態を経由して再度通常遊技状態において遊技を行うことができる。また、第1特定遊技状態であっても、特別役に当籤して特別許可状態(第2特定遊技状態)となれば、特別遊技状態を経由して再度通常遊技状態において遊技を行うことができる。一方、第1特定遊技状態において、特殊役に当籤して特殊許可状態となると、規定数の遊技が行われるまで再度通常遊技状態において遊技を行うことが困難となる。 Here, according to the gaming machine having the above-mentioned configuration, in the normal game state, when a specific combination is won, a combination of specific symbols is displayed and a special combination or a special combination is won before the first specific game state is entered. If the special permission state (second specific game state) or the special permission state is reached, the game can be played again in the normal game state via the special game state or the special game state. Further, even in the first specific game state, if the special combination is won and the special permission state (second specific game state) is reached, the game can be played again in the normal game state via the special game state. .. On the other hand, in the first specific game state, if the special combination is won and the special permitted state is achieved, it becomes difficult to play the game in the normal game state again until the specified number of games have been played.
かかる遊技性の下、通常遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間となった場合には、第1特定遊技状態に移行することなく特別遊技状態(あるいは特殊遊技状態)への移行を繰り返す(すなわち、遊技者に有利な遊技期間を継続させる)ことが可能となるのみならず、特定役に当籤したときに付与される遊技価値も増加することになる。また、第1特定遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間となった場合には、例えば、特殊許可状態であれば特殊遊技状態を経由して通常遊技状態に移行させることは困難であるものの、特定役に当籤したときに付与される遊技価値は増加することになる。また、通常遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間となっていない場合であっても、第1特定遊技状態に移行することなく特別遊技状態(あるいは特殊遊技状態)への移行を繰り返すことができる場合もある。 Under such a game property, in the normal game state, when a specific period during which operation information related to a specific mode is notified is given, the special game state (or the special game state) is entered without shifting to the first specific game state. It is possible not only to repeat the shift (that is, to continue the game period that is advantageous to the player), but also to increase the game value given when the specific combination is won. Further, in the first specific game state, when the specific period during which the operation information regarding the specific mode is notified is given, for example, in the case of the special permission state, it is possible to shift to the normal game state via the special game state. Although difficult, the game value given when a specific combination is won is increased. In addition, even in the normal game state, even if it is not a specific period in which operation information related to a specific mode is notified, a transition to the special game state (or a special game state) without transition to the first specific game state May be repeated.
すなわち、上記構成の遊技機によれば、通常遊技状態若しくは第1特定遊技状態であるか、通常遊技状態において特別役、特殊役若しくは特定役がどのような順番で当籤するか、第1特定遊技状態において特別役若しくは特殊役がどのような順番で当籤するか、通常遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間であるか否か、又は第1特定遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される特定期間であるか否か、などに応じて遊技者の有利度合いを多彩に変動させることが可能となる。それゆえ、遊技意欲や興趣を向上させることができる。 That is, according to the gaming machine having the above-described configuration, whether the game is in the normal game state or the first specific game state, in what order the special combination, the special combination, or the specific combination is won in the normal game state, the first specific game. In a state, a special combination or a special combination is won in an order, whether or not it is a specific period in which operation information related to a specific mode is notified in the normal gaming state, or a specific mode in the first specific gaming state It is possible to variably change the degree of advantage of the player according to whether or not it is a specific period in which the operation information is notified. Therefore, it is possible to improve the game motivation and interest.
なお、上記構成の遊技機において、少なくとも第1特定遊技状態において特定の態様に関する操作情報が報知される期間は、遊技価値が増加する増加期間として機能させるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、第1特定遊技状態であっても遊技価値が増加する場合があることから、通常遊技状態に移行することが困難な特定遊技状態中であっても、遊技の興趣を維持させることができる。 In the gaming machine configured as described above, at least the period in which the operation information related to the specific mode is notified in the first specific game state may function as an increase period in which the game value increases. By doing so, the game value may increase even in the first specific game state, so that the interest of the game is maintained even during the specific game state in which it is difficult to shift to the normal game state. Can be made
[第23及び第24の構成の遊技機]
従来の遊技機において、特別役(例えば、ボーナス役)の持ち越し状態中において、特定の条件が満たされた場合に、遊技者に有利な有利状態(例えば、ART状態)に移行させることを可能にしたものが知られている(例えば、特開2015−73810号公報参照)。
[Game Machines of 23rd and 24th Configurations]
In a conventional gaming machine, it is possible to shift to an advantageous state (eg, ART state) advantageous to a player when a specific condition is satisfied while a special combination (eg, bonus role) is being carried over. There are known ones (see, for example, JP-A-2015-73810).
ところで、このような遊技機では、有利状態中の単位遊技あたりの遊技価値の付与量(遊技価値の増加量を示す傾斜値)は一定の値となるように設計される。このため、遊技性の変化に乏しいという問題があった。 By the way, in such a gaming machine, the amount of game value given per unit game in the advantageous state (gradient value indicating the amount of increase in game value) is designed to be a constant value. Therefore, there is a problem that the change in game playability is poor.
本発明は、このような点に鑑みてなされたものであり、有利状態中の遊技価値の増加量を示す傾斜値を変動可能とすることで、遊技性を変化に富んだものとすることができる遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of such a point, and by making it possible to change the inclination value indicating the increase amount of the game value in the advantageous state, it is possible to make the game property rich in change. An object is to provide a game machine that can be used.
上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような構成の第23の遊技機を提供することができる。 In order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a 23rd gaming machine having the following configuration.
複数の図柄を複数列に変動表示可能な図柄表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R及び図柄表示領域4)と、
第1特別役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その5)におけるBB1)、第2特別役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その5)におけるBB3)、第1所定役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その5)における押し順小役1,3,5)及び第2所定役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その5)における押し順小役2,4,6)を含む複数の役の中から内部当籤役を決定可能な内部当籤役決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記内部当籤役決定手段により決定された内部当籤役と遊技者の停止操作とに基づいて、図柄の変動表示を停止可能な停止制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記停止制御手段により図柄の変動表示が停止された場合に、前記図柄表示手段に表示された図柄の組合せに応じた特典を付与可能な特典付与手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、を備えた遊技機であって、
前記図柄表示手段に第1特別図柄の組合せ(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その5)におけるBB1に係る図柄の組合せ)が表示された場合に第1特別遊技状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その5)におけるBB1状態)を開始させる制御が可能な第1特別遊技状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記図柄表示手段に第2特別図柄の組合せ(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その5)におけるBB3に係る図柄の組合せ)が表示された場合に第2特別遊技状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その5)におけるBB3状態)を開始させる制御が可能な第2特別遊技状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
遊技者の停止操作に関する情報が報知される有利状態(例えば、有利区間)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、を備え、
前記第1特別役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、前記図柄表示手段に前記第1特別図柄の組合せが表示されるまで、前記図柄表示手段に前記第1特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可される第1特別許可状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その5)におけるBB1フラグ間)を継続させ、
前記第2特別役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、前記図柄表示手段に前記第2特別図柄の組合せが表示されるまで、前記図柄表示手段に前記第2特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可される第2特別許可状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その5)におけるBB3フラグ間)を継続させ、
前記内部当籤役決定手段は、前記第1特別許可状態及び前記第2特別許可状態のいずれでもない場合に、前記第1特別役及び前記第2特別役のそれぞれを、他の内部当籤役と重複することなく内部当籤役として決定可能であり、
前記停止制御手段は、
前記第1特別役が内部当籤役として決定された遊技、及び前記第1特別許可状態において他の内部当籤役が決定されなかった遊技において、遊技者の停止操作のタイミングが適切である場合に、前記図柄表示手段に前記第1特別図柄の組合せを表示させることを可能とし、
前記第2特別役が内部当籤役として決定された遊技、及び前記第2特別許可状態において他の内部当籤役が決定されなかった遊技において、遊技者の停止操作のタイミングが適切である場合に、前記図柄表示手段に前記第2特別図柄の組合せを表示させることを可能とし、
前記第1特別許可状態において、前記第1所定役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、遊技者の停止操作の順序にかかわらず、前記図柄表示手段に所定数(例えば、9枚)の遊技価値が付与される所定図柄の組合せを表示させ、
前記第1特別許可状態において、前記第2所定役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、遊技者の停止操作の順序にかかわらず、前記図柄表示手段に前記所定図柄の組合せを表示させず、
前記第2特別許可状態において、前記第1所定役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、遊技者の停止操作の順序が適切である場合に、前記図柄表示手段に前記所定図柄の組合せを表示させる一方、遊技者の停止操作の順序が適切でない場合には、前記図柄表示手段に前記所定図柄の組合せを表示させず、
前記第2特別許可状態において、前記第2所定役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、遊技者の停止操作の順序が適切である場合に、前記図柄表示手段に前記所定図柄の組合せを表示させる一方、遊技者の停止操作の順序が適切でない場合には、前記図柄表示手段に前記所定図柄の組合せを表示させず、
前記有利状態制御手段は、特定の有利条件が成立した場合、少なくとも前記第2特別許可状態における特定期間を、前記有利状態とすることが可能であり、
前記有利状態において、前記第1所定役及び前記第2所定役のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された場合、前記図柄表示手段に前記所定図柄の組合せを表示させるための遊技者の停止操作の順序が報知されることを特徴とする遊技機。
Symbol display means (for example,
A first special combination (for example, BB1 in another example of playability (5)), a second special combination (for example, BB3 in another example of playability (5)), a first predetermined combination (for example, game) Of the small push order wins 1, 3, 5 in other examples of sex (No. 5) and the second predetermined winning role (for example, the
Based on the internal winning combination determined by the internal winning combination determining means and the player's stop operation, stop control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of stopping variable display of symbols,
When the variable display of symbols is stopped by the stop control unit, a privilege providing unit (for example, the main CPU 101) that can provide a privilege according to the combination of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit, and a game including Machine,
When a combination of first special symbols (for example, a combination of symbols related to BB1 in another example (5) of game property) is displayed on the symbol display means, a first special game state (for example, other game property) The first special game state control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of controlling to start the BB1 state in the example (5)
A second special game state (for example, other game property) when a combination of second special symbols (for example, a combination of symbols related to BB3 in another example (5) of game property) is displayed on the symbol display means. Second special game state control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of controlling to start the BB3 state in the example (No. 5),
An advantageous state control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of controlling in an advantageous state (for example, an advantageous zone) in which information regarding a stop operation of the player is notified,
When the first special combination is determined as an internal winning combination, the combination of the first special symbol is displayed on the symbol display unit until the combination of the first special symbol is displayed on the symbol display unit. The first special permission state (for example, between BB1 flags in another example (5) of game nature) in which is permitted is continued,
When the second special combination is determined as an internal winning combination, the combination of the second special symbols is displayed on the symbol display unit until the combination of the second special symbols is displayed on the symbol display unit. The second special permission state (for example, between BB3 flags in another example (5) of game nature) in which is permitted is continued,
The internal winning combination determination means overlaps each of the first special winning combination and the second special winning combination with another internal winning combination when neither the first special permission state nor the second special permission state is present. Can be decided as an internal winning combination without
The stop control means,
In a game in which the first special winning combination is determined as an internal winning combination, and in a game in which no other internal winning combination is determined in the first special permission state, when the timing of the stop operation of the player is appropriate, It is possible to display the combination of the first special symbol on the symbol display means,
In the game in which the second special combination is determined as an internal winning combination, and in the game in which no other internal winning combination is determined in the second special permission state, when the timing of the stop operation of the player is appropriate, It is possible to display a combination of the second special symbols on the symbol display means,
In the first special permission state, when the first predetermined winning combination is determined as an internal winning combination, a predetermined number (for example, 9) of game values are displayed on the symbol display means regardless of the order of stop operations by the player. Display the combination of predetermined symbols to be given,
In the first special permission state, when the second predetermined combination is determined as an internal winning combination, the combination of the predetermined symbols is not displayed on the symbol display means regardless of the order of the stop operation by the player,
In the second special permission state, when the first predetermined winning combination is determined as an internal winning combination, the combination of the predetermined symbols is displayed on the symbol display means when the order of the stop operation of the player is appropriate. On the other hand, when the order of the stop operation by the player is not appropriate, the symbol display means does not display the combination of the predetermined symbols,
In the second special permission state, if the second predetermined combination is determined as an internal winning combination, and if the order of the stop operation of the player is appropriate, the combination of the predetermined symbols is displayed on the pattern display means. On the other hand, when the order of the stop operation by the player is not appropriate, the symbol display means does not display the combination of the predetermined symbols,
The advantageous state control means can set at least a specific period in the second special permission state to the advantageous state when a specific advantageous condition is satisfied,
In the advantageous state, when any one of the first predetermined combination and the second predetermined combination is determined as an internal winning combination, the player's stop operation for displaying the combination of the predetermined symbols on the symbol display means. A gaming machine characterized by being informed of the order.
前記内部当籤役決定手段は、
前記第1特別役を第1の確率(例えば、1/100)で内部当籤役として決定し、
前記第2特別役を前記第1の確率よりも低い第2の確率(例えば、1/450)で内部当籤役として決定し、
前記第1特別許可状態において他の内部当籤役が決定されない確率(例えば、1/4000)は、前記第2特別許可状態において他の内部当籤役が決定されない確率(例えば、1/65536)よりも高いことを特徴とする遊技機。
The internal winning combination determination means,
The first special winning combination is determined as an internal winning combination with a first probability (for example, 1/100),
The second special combination is determined as an internal winning combination with a second probability (for example, 1/450) lower than the first probability,
The probability that no other internal winning combination is determined in the first special permission state (for example, 1/4000) is more than the probability that no other internal winning combination is determined in the second special permission state (for example, 1/65536). A gaming machine characterized by high price.
前記図柄表示手段に前記第1特別図柄の組合せを表示させることが可能な遊技者の停止操作のタイミングは、前記図柄表示手段に前記第2特別図柄の組合せを表示させることが可能な遊技者の停止操作のタイミングと重複しないことを特徴とする遊技機。 The timing of the stop operation of the player capable of displaying the combination of the first special symbols on the symbol display means is the timing of the player capable of displaying the combination of the second special symbols on the symbol display means. A game machine characterized by not overlapping the timing of the stop operation.
前記第1特別役又は前記第2特別役が内部当籤役として決定された遊技において、前記第1特別役又は前記第2特別役のいずれかが内部当籤役として決定された旨は報知可能とするが、その種別を報知可能としない所定報知(例えば、ボーナス当籤報知)を実行可能な所定報知実行手段(例えば、表示装置11)と、
前記第1特別許可状態において、前記図柄表示手段に前記第1特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可されている旨を報知可能とし、前記第2特別許可状態において、前記図柄表示手段に前記第2特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可されている旨を報知可能とする特定報知(例えば、ボーナス種別報知)を実行可能な特定報知実行手段(例えば、表示装置11)と、をさらに備えたことを特徴とする遊技機。
In the game in which the first special combination or the second special combination is determined as the internal winning combination, it is possible to inform that either the first special combination or the second special combination is determined as the internal winning combination. However, a predetermined notification execution means (for example, the display device 11) capable of executing a predetermined notification (for example, bonus winning notification) that does not allow the type to be notified,
In the first special permission state, it is possible to notify that the combination of the first special symbols is permitted to be displayed on the symbol display means, and in the second special permission state, the symbol display means Further, a specific notification executing means (for example, the display device 11) capable of executing a specific notification (for example, bonus type notification) that can notify that the combination of the second special symbols is permitted to be displayed. A game machine characterized by having it.
上記構成の遊技機によれば、第1特別役又は第2特別役に当籤した場合、当該遊技か、あるいは当籤後の第1特別許可状態又は第2特別許可状態において他の内部当籤役が決定されなかった(いわゆる、ハズレとなった)遊技でなければ第1特別図柄の組合せ又は第2特別図柄の組合せを表示できない。また、第1特別許可状態では、第1所定役に当籤した場合、押し順不問で所定数の遊技価値が付与され、第2所定役に当籤した場合、押し順不問で所定数の遊技価値が付与されない。一方、第2特別許可状態では、第1所定役又は第2所定役に当籤した場合に、押し順正解であれば所定数の遊技価値が付与され、押し順不正解であれば所定数の遊技価値は付与されない。そして、少なくとも第2特別許可状態の特定期間では、遊技者の停止操作の情報が報知される有利状態に制御されることが可能である。 According to the gaming machine having the above configuration, when the first special winning combination or the second special winning combination is won, another internal winning combination is determined in the game concerned or in the first special permission state or the second special permission state after winning. Unless the game is not played (so-called, lost), the combination of the first special symbol or the combination of the second special symbol cannot be displayed. Further, in the first special permission state, when the first predetermined winning combination is won, a predetermined number of game values are given regardless of the pushing order, and when the second predetermined winning combination is won, the predetermined number of gaming values is obtained regardless of the pushing order. Not granted. On the other hand, in the second special permission state, when the first predetermined combination or the second predetermined combination is won, a predetermined number of game values are given if the pushing order is correct and a predetermined number of games are given if the pushing order is incorrect. No value is given. Then, at least during the specific period of the second special permission state, it is possible to control to an advantageous state in which the information of the stop operation of the player is notified.
すなわち、第1特別役に当籤し、当該遊技で第1特別図柄の組合せが表示されなかった場合には、その後第1特別許可状態が終了するまで第1所定役及び第2所定役は押し順によって利益が変動しないものとなり、遊技者は一定の利益を受けることができる反面、その利益が飛躍的に増加することもないため、たとえ有利状態となったとしてもその遊技価値の増加量を示す傾斜値は相対的に低いものとなる。一方、第2特別役に当籤し、当該遊技で第2特別図柄の組合せが表示されなかった場合には、その後第2特別許可状態が終了するまで第1所定役及び第2所定役は押し順によって利益が変動するものとなり、遊技者は第1特別許可状態よりも不利益を被る可能性がある反面、有利状態となればその利益が飛躍的に増加するようになるため、有利状態における遊技価値の増加量を示す傾斜値は相対的に高いものとなる。それゆえ、有利状態中の遊技価値の増加量を示す傾斜値を変動可能とすることで、遊技性を変化に富んだものとすることができる。 That is, if the first special combination is won and the combination of the first special symbols is not displayed in the game, the first predetermined combination and the second predetermined combination are pushed in order until the first special permission state is finished. The profits do not fluctuate due to this, and the player can receive a certain amount of profits, but the profits do not increase dramatically, so even if it becomes advantageous, it shows the amount of increase in the game value. The slope value will be relatively low. On the other hand, if the second special combination is won, and the combination of the second special symbols is not displayed in the game, then the first predetermined combination and the second predetermined combination are pushed in order until the second special permission state ends. As a result, profits fluctuate, and the player may suffer a disadvantage more than in the first special permission state, but when the advantageous state is reached, the profit is dramatically increased. The slope value indicating the increase in value is relatively high. Therefore, by making it possible to change the inclination value indicating the amount of increase in the game value during the advantageous state, it is possible to make the game play rich in variety.
なお、上記構成の遊技機において、第1特別役の当籤確率を第2特別役の当籤確率よりも高くするとともに、第1特別許可状態において第1特別図柄の組合せが表示可能な確率を第2特別許可状態において第2特別図柄の組合せが表示可能な確率よりも高くするようにしてもよい。すなわち、第1特別許可状態を、第2特別許可状態よりも移行しやすく終了しやすい状態とし、第2特別許可状態を、第1特別許可状態よりも移行しにくく終了しにくい状態としてもよい。このようにすれば、射幸性を適度なものとしつつも遊技の興趣を維持することができる。 In the gaming machine having the above configuration, the winning probability of the first special combination is made higher than the winning probability of the second special combination, and the probability that the combination of the first special symbols can be displayed in the first special permission state is the second. In the special permission state, the combination of the second special symbols may be set higher than the displayable probability. That is, the first special permission state may be set to a state in which it is easier to transition than the second special permission state and to be finished, and the second special permission state may be set to a state in which transition is less likely to occur and termination is more difficult than in the first special permission state. In this way, the enjoyment of the game can be maintained while the gambling property is moderate.
また、上記構成の遊技機において、第1特別役に係る第1特別図柄の組合せと第2特別役に係る第2特別図柄の組合せは、遊技者が目押しをする場合に、同時には狙えない間隔で配置されるように構成してもよい。このようにすれば、遊技性をさらに変化に富んだものとすることができ、遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。 Further, in the gaming machine having the above-mentioned configuration, the combination of the first special symbol relating to the first special combination and the second special symbol relating to the second special symbol cannot be aimed at simultaneously when the player makes a detent. You may comprise so that it may be arrange|positioned at intervals. By doing so, the playability can be further varied and the enjoyment of the game can be improved.
また、上記構成の遊技機において、第1特別役又は第2特別役に当籤した場合には、いずれかに当籤した旨は報知するが、その種別までは報知せず、第1特別許可状態及び第2特別許可状態においては、その種別が報知されるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、遊技性をさらに変化に富んだものとしつつ、遊技者の所望する情報を報知することができる。 Further, in the gaming machine having the above-mentioned configuration, when the first special combination or the second special combination is won, the fact that the one is won is notified, but the type is not notified, and the first special permission state and The type may be notified in the second special permission state. By doing so, it is possible to notify the information desired by the player while further enhancing the playability.
また、上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような構成の第24の遊技機を提供することができる。 Further, in order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a twenty-fourth gaming machine having the following configuration.
複数の図柄を複数列に変動表示可能な図柄表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R及び図柄表示領域4)と、
第1特別役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その6)におけるBB1)、第2特別役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その6)におけるBB2)、及び特定役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その6)における「F_リプB」)を含む複数の役の中から内部当籤役を決定可能な内部当籤役決定手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記内部当籤役決定手段により決定された内部当籤役と遊技者の停止操作とに基づいて、図柄の変動表示を停止可能な停止制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記停止制御手段により図柄の変動表示が停止された場合に、前記図柄表示手段に表示された図柄の組合せに応じた特典を付与可能な特典付与手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、を備えた遊技機であって、
前記図柄表示手段に第1特別図柄の組合せ(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その6)におけるBB1に係る図柄の組合せ)が表示された場合に第1特別遊技状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その6)におけるBB1状態)を開始させる制御が可能な第1特別遊技状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
前記図柄表示手段に第2特別図柄の組合せ(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その6)におけるBB2に係る図柄の組合せ)が表示された場合に第2特別遊技状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その6)におけるBB2状態)を開始させる制御が可能な第2特別遊技状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、
遊技者の停止操作に関する情報が報知される有利状態(例えば、有利区間)に制御可能な有利状態制御手段(例えば、メインCPU101)と、を備え、
前記第1特別役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、前記図柄表示手段に前記第1特別図柄の組合せが表示されるまで、前記図柄表示手段に前記第1特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可される第1特別許可状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その6)におけるBB1フラグ間)を継続させ、
前記第2特別役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、前記図柄表示手段に前記第2特別図柄の組合せが表示されるまで、前記図柄表示手段に前記第2特別図柄の組合せが表示されることが許可される第2特別許可状態(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その6)におけるBB2フラグ間)を継続させ、
前記内部当籤役決定手段は、
前記第1特別許可状態及び前記第2特別許可状態のいずれでもない場合であって、ベットされた遊技価値が第1の量(例えば、3枚)であるとき、前記第1特別役を内部当籤役として決定可能とし、ベットされた遊技価値が第2の量(例えば、2枚)であるとき、前記第1特別役を内部当籤役として決定可能とせず、
前記第1特別許可状態及び前記第2特別許可状態のいずれでもない場合であって、ベットされた遊技価値が前記第2の量であるとき、前記第2特別役を内部当籤役として決定可能とし、ベットされた遊技価値が前記第1の量であるとき、前記第2特別役を内部当籤役として決定可能とせず、
前記停止制御手段は、
前記特定役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、前記第1特別許可状態である場合には、前記図柄表示手段に特定図柄の組合せ(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その6)におけるチャンス目)を表示させることを可能とせず、前記第2特別許可状態である場合には、前記図柄表示手段に前記特定図柄の組合せを表示させることを可能とし、
前記有利状態制御手段は、
ベットされた遊技価値が前記第1の量であるとき、少なくとも前記特定役が内部当籤役として決定された場合であって前記図柄表示手段に前記特定図柄の組合せが表示される場合に、前記有利状態を付与するか否かを決定可能とし、
ベットされた遊技価値が前記第2の量であるとき、前記有利状態を付与するか否かを決定可能としないことを特徴とする遊技機。
Symbol display means (for example,
A first special combination (for example, BB1 in another example of playability (6)), a second special combination (for example, BB2 in another example of playability (6)), and a specific combination (for example, playability) An internal winning combination determining means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of determining an internal winning combination from a plurality of combinations including “F_REP B” in another example (6).
Based on the internal winning combination determined by the internal winning combination determining means and the player's stop operation, stop control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of stopping variable display of symbols,
When the variable display of symbols is stopped by the stop control unit, a privilege providing unit (for example, the main CPU 101) that can provide a privilege according to the combination of the symbols displayed on the symbol display unit, and a game including Machine,
When a combination of first special symbols (for example, a combination of symbols related to BB1 in another example of game property (6)) is displayed on the symbol display means, a first special game state (for example, other game property) The first special game state control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of controlling to start the BB1 state in the example (6)
A second special game state (for example, other game property) when a combination of second special symbols (for example, a combination of symbols related to BB2 in another example (6) of game property) is displayed on the symbol display means. Second special game state control means (for example, main CPU 101) capable of controlling to start the BB2 state in the example (6)
An advantageous state control means (for example, the main CPU 101) capable of controlling in an advantageous state (for example, an advantageous zone) in which information regarding a stop operation of the player is notified,
When the first special combination is determined as an internal winning combination, the combination of the first special symbol is displayed on the symbol display unit until the combination of the first special symbol is displayed on the symbol display unit. The first special permission state (for example, between the BB1 flags in another example (6) of game nature) that is permitted is continued,
When the second special combination is determined as an internal winning combination, the combination of the second special symbols is displayed on the symbol display unit until the combination of the second special symbols is displayed on the symbol display unit. The second special permission state (for example, between the BB2 flags in another example (6) of game nature) in which is permitted is continued,
The internal winning combination determination means,
In a case where neither the first special permission state nor the second special permission state is set and the game value bet is the first amount (for example, 3), the first special combination is internally won. When the bet game value is the second amount (for example, 2 cards), it is not possible to determine the first special combination as an internal winning combination,
When neither the first special permission state nor the second special permission state, and the bet game value is the second amount, it is possible to determine the second special combination as an internal winning combination. When the bet game value is the first amount, the second special combination cannot be determined as an internal winning combination,
The stop control means,
When the specific combination is determined as an internal winning combination, in the case of the first special permission state, a combination of specific symbols on the symbol display means (for example, chance of another example (6) of game nature) ) Is not possible, and in the case of the second special permission state, it is possible to display the combination of the specific symbols on the symbol display means,
The advantageous state control means,
When the game value bet is the first amount, at least when the specific combination is determined as an internal winning combination, and when the combination of the specific symbols is displayed on the symbol display means, the advantage It is possible to decide whether to add a state,
A gaming machine characterized in that when the bet game value is the second amount, it is not possible to decide whether or not to give the advantageous state.
前記停止制御手段は、
ベットされた遊技価値が前記第1の量であるとき、前記第1特別許可状態である場合には、前記図柄表示手段に前記第1特別図柄の組合せを表示させることを可能とし、前記第2特別許可状態である場合には、前記図柄表示手段に前記第2特別図柄の組合せを表示させることを可能とせず、
ベットされた遊技価値が前記第2の量であるとき、前記第2特別許可状態である場合には、前記図柄表示手段に前記第2特別図柄の組合せを表示させることを可能とし、前記第1特別許可状態である場合には、前記図柄表示手段に前記第1特別図柄の組合せを表示させることを可能としないことを特徴とする遊技機。
The stop control means,
When the game value bet is the first amount, in the case of the first special permission state, it is possible to display the combination of the first special symbol on the symbol display means, the second In the special permission state, it is not possible to display the combination of the second special symbols on the symbol display means,
When the game value bet is the second amount, in the case of the second special permission state, it is possible to display the combination of the second special symbols on the symbol display means, the first In the special permission state, it is not possible to display the combination of the first special symbol on the symbol display means, a gaming machine.
前記内部当籤役決定手段は、さらに第1所定役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その6)における押し順ベルA)及び第2所定役(例えば、遊技性の他の例(その6)における押し順ベルB)を内部当籤役として決定可能であり、
前記停止制御手段は、
前記第1所定役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、遊技者の停止操作の態様が適切であれば、前記図柄表示手段に所定数の遊技価値が付与される所定図柄の組合せを表示させる一方、遊技者の停止操作の態様が適切でなければ、前記図柄表示手段に前記所定図柄の組合せを表示させず、
前記第2所定役が内部当籤役として決定された場合、ベットされた遊技価値が前記第1の量であって前記第1特別許可状態である場合には、遊技者の停止操作の態様にかかわらず、前記図柄表示手段に前記所定図柄の組合せを表示させ、ベットされた遊技価値が前記第1の量であって前記第2特別許可状態である場合、及びベットされた遊技価値が前記第2の量である場合には、遊技者の停止操作の態様が適切であれば、前記所定図柄の組合せを表示させる一方、遊技者の停止操作の態様が適切でなければ、前記図柄表示手段に前記所定図柄の組合せを表示させず、
前記有利状態においては、前記図柄表示手段に前記所定図柄の組合せを表示させるための遊技者の停止操作の態様を示す情報が報知されることを特徴とする遊技機。
The internal winning combination determination means further includes a first predetermined combination (for example, the pushing order bell A in another example of playability (6)) and a second predetermined combination (for example, another example of playability (6)). It is possible to decide the push order bell B) as an internal winning combination,
The stop control means,
When the first predetermined winning combination is determined as the internal winning combination, and if the mode of the stop operation of the player is appropriate, one of the predetermined symbol combinations to which a predetermined number of game values are given is displayed on the symbol display means. If the mode of the player's stop operation is not appropriate, the symbol display means does not display the combination of the predetermined symbols,
When the second predetermined winning combination is determined as an internal winning combination, the bet game value is the first amount and the first special permission state is set, regardless of the mode of the stop operation of the player. Instead, the combination of the predetermined symbols is displayed on the symbol display means, the bet game value is the first amount and the second special permission state, and the bet game value is the second. If the mode of the stop operation of the player is appropriate, the combination of the predetermined symbols is displayed, while if the mode of the stop operation of the player is not appropriate, the symbol display means Without displaying the combination of predetermined symbols,
In the advantageous state, a game machine characterized in that information indicating a mode of a stop operation of a player for displaying a combination of the predetermined symbols on the symbol display means is notified.
上記構成の遊技機によれば、ベットされた遊技価値が第1の量である場合、第1特別役に当籤可能とする一方、第2特別役に当籤可能としない。また、ベットされた遊技価値が第2の量である場合、第2特別役に当籤可能とする一方、第1特別役に当籤可能としない。また、特定役に当籤した場合、第1特別許可状態であれば特定図柄の組合せを表示可能とせず、第2特別許可状態であれば特定図柄の組合せを表示可能とする。そして、ベットされた遊技価値が第1の量であるとき、特定役が内部当籤役として決定された場合であって特定図柄の組合せが表示される場合には、有利状態を付与するか否かを決定可能とし、ベットされた遊技価値が第2の量であるとき、有利状態を付与するか否かを決定可能としない。 According to the gaming machine configured as described above, when the bet game value is the first amount, the first special combination can be won, while the second special combination cannot be won. When the bet game value is the second amount, the second special combination can be won, but the first special combination cannot be won. When the winning combination is won, the combination of specific symbols cannot be displayed in the first special permission state, and the combination of specific symbols can be displayed in the second special permission state. Then, when the bet game value is the first amount, when the specific combination is determined as the internal winning combination and the combination of the specific symbols is displayed, whether or not the advantageous state is given When the bet gaming value is the second amount, it is not possible to decide whether or not to give the advantageous state.
また、上記構成の遊技機によれば、ベットされた遊技価値が第1の量である場合、第1特別図柄の組合せを表示可能とする一方、第2特別図柄の組合せを表示可能としない。また、ベットされた遊技価値が第2の量である場合、第2特別図柄の組合せを表示可能とする一方、第1特別図柄の組合せを表示可能としないようにしてもよい。 Further, according to the gaming machine having the above configuration, when the bet game value is the first amount, the combination of the first special symbols can be displayed, while the combination of the second special symbols cannot be displayed. Further, when the bet game value is the second amount, the combination of the second special symbols may be displayed, while the combination of the first special symbols may not be displayed.
すなわち、上記構成の遊技機によれば、遊技が行われる状態として、例えば、第1特別許可状態であって第1の量の遊技価値がベットされて遊技が行われる状態、第2特別許可状態であって第1の量の遊技価値がベットされて遊技が行われる状態、第1特別許可状態であって第2の量の遊技価値がベットされて遊技が行われる状態、及び第2特別許可状態であって第2の量の遊技価値がベットされて遊技が行われる状態、という複数の状態を創出することができる。 That is, according to the gaming machine having the above-described configuration, as a state in which the game is played, for example, a state in which the game value is bet with a first amount of game value being bet, and a second special permission state. And a state in which a first amount of game value is bet and a game is performed, a state in which a first amount of game value is bet and a game is performed, and a second special permission It is possible to create a plurality of states such as a state in which the second amount of game value is bet and the game is played.
そして、上記構成の遊技機によれば、例えば、第2特別許可状態であって第1の量の遊技価値がベットされて遊技が行われる状態を有利状態の付与が優遇される状態とし、第2の量の遊技価値がベットされて遊技が行われる状態を有利状態の付与が行われない状態としている。すなわち、有利状態の付与に関し、いずれの量の遊技価値がベットされるか、及びいずれの特別役が当籤しているか、などによって遊技者の有利度合いを変動させることを可能としている。それゆえ、有利状態中の遊技価値の増加量を示す傾斜値を変動可能とすることで、遊技性を変化に富んだものとすることができる。 According to the gaming machine having the above configuration, for example, a state in which the game is played by betting the first amount of the game value in the second special permission state is defined as a state in which the giving of the advantageous state is favored, A state in which a game value of 2 is bet and a game is played is a state in which an advantageous state is not given. That is, regarding the provision of the advantageous state, it is possible to change the degree of advantage of the player depending on which amount of game value is bet, which special combination is won, and the like. Therefore, by making it possible to change the inclination value indicating the amount of increase in the game value during the advantageous state, it is possible to make the game play rich in variety.
なお、上記構成の遊技機において、第1所定役に当籤した場合には、いずれの状態であるかにかかわらず、例えば、押し順正解であれば所定数の遊技価値が付与され、押し順不正解であれば所定数の遊技価値は付与されないし、第2所定役に当籤した場合には、第1特別許可状態であって第1の量の遊技価値がベットされて遊技が行われる状態にあっては、例えば、押し順不問で所定数の遊技価値が付与される一方、その他の状態にあっては、第1所定役と同様の制御が行われるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、第1特別許可状態であって第1の量の遊技価値がベットされて遊技が行われる状態を所定役当籤時において遊技価値の付与が優遇される状態とすることができるため、遊技性をより変化に富んだものとすることができる。 In the gaming machine having the above-mentioned configuration, when the first predetermined winning combination is won, regardless of which state it is, for example, if the correct pushing order is given, a predetermined number of gaming values are given and the pushing order is improper. If the answer is correct, a predetermined number of game values will not be given, and if the second predetermined combination is won, it will be in a state where the first amount of game value is bet and the game is performed with the first amount of game value being bet. Then, for example, while a predetermined number of game values are given regardless of the pressing order, in other states, the same control as the first predetermined winning combination may be performed. In this way, the state in which the first amount of game value is bet and the game is played in the first special permission state can be set to the state where the giving of the game value is preferentially given in the predetermined winning combination. Therefore, the game play can be made more varied.
[第25の構成の遊技機]
AT機能を有する遊技機において、長期間にわたってAT機能が発動しない場合には、遊技者は著しく不利な状況に陥り、遊技に対する興味を失ってしまう。そこで、AT機能が発動しないまま一定期間が経過した場合に、救済措置としてAT抽籤の結果に関係なくAT機能を発動する遊技機(所謂、天井)が知られており、例えば、特開2017−064539号公報には、天井に到達するまでの期間を固定せず変化をつけることで、稼動の向上を狙った遊技機が記載されている。
[Gaming machine with 25th configuration]
In a gaming machine having an AT function, if the AT function is not activated for a long period of time, the player falls into a significantly disadvantageous state and loses interest in the game. Therefore, a game machine (so-called ceiling) that activates the AT function regardless of the result of the AT lottery is known as a relief measure when a certain period of time has passed without activating the AT function. Japanese Patent No. 064539 describes a gaming machine aiming to improve the operation by fixing the period until reaching the ceiling without changing the period.
このような救済措置としての天井を発動させる場合、天井に到達するまでの期間は任意に設定することができ、例えば、所定回数の遊技が行われた場合に天井を発動させるゲーム数天井や、AT抽籤が優遇されるチャンスゾーン(CZ)を所定回数行ったにもかかわらずAT機能が発動しない場合に天井を発動させるスルー回数天井といった方法などが知られている。 When activating the ceiling as such a remedy, the period until reaching the ceiling can be set arbitrarily, and for example, the number of games ceiling that activates the ceiling when a predetermined number of games have been played, There is known a method such as a through-time ceiling method in which the ceiling is activated when the AT function is not activated even though the chance zone (CZ) in which the AT lottery is preferentially performed is performed a predetermined number of times.
ところで、近年の遊技機では、通常区間よりも遊技者にとって有利な状態(所謂、有利区間)を終了させる場合、終了させる有利な状態に関する全ての情報をリセット(初期化)しなければならず、このような遊技機では、有利区間(CZ)をスルーした回数を把握することができず、従来のスルー回数天井のような有利区間のスルー回数に基づく天井制御が困難になってしまうという問題があった。 By the way, in recent game machines, when ending a state that is more advantageous to the player than the normal section (so-called advantageous section), all information regarding the advantageous state to be ended must be reset (initialized), In such a gaming machine, it is not possible to grasp the number of times through the advantageous zone (CZ), and it is difficult to control the ceiling based on the number of times of through the advantageous zone like the conventional ceiling of the number of times of through. there were.
本発明はこのような問題に鑑みてなされたものであり、終了時に関連する情報がリセットされてしまう状態が複数回終了した場合に救済措置としての天井を発動可能な遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of such a problem, and provides a gaming machine capable of activating a ceiling as a relief measure when a state in which related information is reset at the time of ending ends a plurality of times. To aim.
上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような構成の第25の遊技機を提供することができる。 In order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a twenty-fifth gaming machine having the following configuration.
本発明に係る遊技機は、複数の識別表示を変動表示可能な可変表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、複数の役の中から決定された当籤役に応じて前記可変表示手段を用いた遊技の進行を制御する遊技制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を備える遊技機であって、再遊技役が当籤役として決定される確率が異なるRT状態として複数段階のRT状態(例えば、RT1〜RT6)を有するとともに、遊技に関する遊技状態として、通常状態(例えば、通常区間)と、第1所定状態(例えば、有利区間中のCZ)及び当該第1所定状態よりも遊技者にとって有利な第2所定状態(例えば、有利区間中のART)とを少なくとも含む所定状態(例えば、有利区間)と、を有し、現在のRT状態から他のRT状態にRT状態を移行可能なRT制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、RT状態を移行させるために必要な情報を報知可能な報知手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記通常状態において第1条件(例えば、有利区間への移行抽籤に当籤)が満たされると、前記第1所定状態に遊技状態を移行可能な第1状態制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を更に備え、前記報知手段は、前記第1状態制御手段により前記遊技状態が前記第1所定状態に移行すると、RT状態を現在のRT状態よりも先の段階のRT状態に移行させるために必要な情報を報知可能であり、前記第1所定状態において第2条件(例えば、ARTへの移行抽籤に当籤)が満たされると、前記第2所定状態に遊技状態を移行可能、かつ、前記第1所定状態において前記報知手段により現在のRT状態よりも先の段階のRT状態に移行させるために必要な前記情報が報知された後に終了条件が満たされると、前記通常状態に遊技状態を移行可能な第2状態制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)、を更に備え、前記第2状態制御手段は、所定段階目のRT状態(例えば、RT1〜RT4)における前記第1所定状態では、前記第2条件が満たされることなく前記終了条件が満たされると、前記通常状態に遊技状態を移行する一方で、所定段階目よりも先の特定段階目のRT状態(例えば、RT5)における前記第1所定状態では、前記第2条件が満たされない場合であっても、前記通常状態に遊技状態を移行することなく、前記第2所定状態に遊技状態を移行することを特徴とする。
The gaming machine according to the present invention includes a variable display means (for example,
このような遊技機によれば、通常状態から第1所定状態(例えば、CZ)に移行すると、RT状態が先の段階に進むため、第2所定状態への移行条件(第2条件)を満たすことなく第1所定状態が終了した場合であっても、第1所定状態の前後においてRT状態が異なる(先の段階に進む)ことになる。ここで通常の遊技機では、第1所定状態の終了時に、所定状態に関する情報を初期化した場合、第2所定状態に移行することなく終了した第1所定状態の回数(スルー回数)を把握することができないものの、本発明に係る遊技機では、第1所定状態の前後においてRT状態を異ならせることで、所定状態とは別のRT状態に関する情報(RT状態の段階)から第1所定状態のスルー回数を把握することができる。そして、本発明に係る遊技機では、特定段階目のRT状態において第1所定状態に移行した場合には、第2所定条件への移行条件(第2条件)の成立の有無に関係なく、遊技状態を第2所定状態(例えば、ART)へ移行することで、第1所定状態のスルー回数に基づき、第2所定状態の天井を発動することができる。 According to such a gaming machine, when the normal state shifts to the first predetermined state (for example, CZ), the RT state advances to the previous stage, so the shift condition (second condition) to the second predetermined state is satisfied. Even if the first predetermined state ends without any action, the RT state is different before and after the first predetermined state (goes to the previous stage). Here, in a normal gaming machine, when the information about the predetermined state is initialized at the end of the first predetermined state, the number of times (the number of times of through) of the first predetermined state that has ended without shifting to the second predetermined state is grasped. Although not possible, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, by changing the RT state before and after the first predetermined state, information about the RT state different from the predetermined state (RT state stage) indicates the first predetermined state. You can grasp the number of throughs. Then, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, when the state shifts to the first predetermined state in the RT state of the specific stage, the game is played regardless of whether or not the transition condition (second condition) to the second predetermined condition is satisfied. By shifting the state to the second predetermined state (for example, ART), it is possible to activate the ceiling in the second predetermined state based on the number of throughs in the first predetermined state.
また、本発明に係る遊技機において、前記第2状態制御手段は、前記所定段階目のRT状態における前記第1所定状態では、前記第1所定状態において前記報知手段により現在のRT状態よりも先の段階のRT状態に移行させるために必要な前記情報が報知された後に所定期間(例えば、100回の遊技)が経過すると、前記終了条件が満たされたとして、前記通常状態に遊技状態を移行し、前記特定段階目のRT状態における前記第1所定状態では、前記第2条件が満たされることなく前記所定期間又は前記所定期間よりも短い特定期間(例えば、30回の遊技)が経過すると、前記第2所定状態に遊技状態を移行することを特徴とする。 Further, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, the second state control means may set the first predetermined state in the RT state of the predetermined stage to be earlier than the current RT state by the notification means in the first predetermined state. When a predetermined period (for example, 100 games) has passed after the information necessary to shift to the RT state at the stage is notified, it is determined that the ending condition is satisfied, and the game state is shifted to the normal state. However, in the first predetermined state in the RT state of the specific stage, when the predetermined period or a specific period shorter than the predetermined period (for example, 30 games) has passed without the second condition being satisfied, The game state is shifted to the second predetermined state.
このような遊技機によれば、天井到達前の第1所定状態では、第1所定状態を所定期間継続させた後に通常状態に遊技状態を移行させるため、天井到達までに要する遊技期間を一定量(=所定期間×スルー回数(RT状態の段階数))確保することができる。その結果、通常状態から第1所定状態への移行が運良く高頻度で行われてしまった場合であっても、天井到達までには必ず一定期間以上の遊技が行われることになるため、必要以上に早期に天井到達になってしまうことを防止でき、遊技者の利益/不利益のバランスを調整することができる。 According to such a gaming machine, in the first predetermined state before reaching the ceiling, the game state is shifted to the normal state after the first predetermined state is continued for a predetermined period, so that the game period required to reach the ceiling is fixed. (=predetermined period×number of times of through (number of stages in RT state)) can be secured. As a result, even if the transition from the normal state to the first predetermined state is carried out with good fortune, the game will always be played for a certain period or longer until the ceiling is reached, so it is necessary. As described above, it is possible to prevent the ceiling from reaching the ceiling early, and it is possible to adjust the balance of the profit/disadvantage of the player.
また、本発明に係る遊技機は、全遊技期間における前記所定状態中の期間が所定割合になるように遊技状態が制御される遊技機であって、前記第1状態制御手段は、前記通常状態において、遊技状態を前記第1所定状態に移行すると所定の確率で決定すると、前記第1条件が満たされたとして、前記第1所定状態に遊技状態を移行することを特徴とする。 Further, the gaming machine according to the present invention is a gaming machine in which a gaming state is controlled so that a period in the prescribed state in a whole gaming period becomes a prescribed ratio, and the first state control means is the normal state. In the above, when the gaming state is determined with a predetermined probability to shift to the first predetermined state, it is determined that the first condition is satisfied, and the game state is shifted to the first predetermined state.
近年の遊技機では、遊技者に過度な利益を付与してしまうことを防止するため、全遊技期間における所定状態中の期間が所定割合になるように遊技状態を制御することが求められている。この点、本発明に係る遊技機では、天井到達までに要する所定状態以外(通常状態)の遊技期間を一定量(=所定の確率に当籤するまでに要する期間×スルー回数(RT状態の段階数))確保することができる。その結果、天井到達後に継続可能な第2所定状態の期間を十分に確保しつつ、全遊技期間における所定状態中の期間を所定割合に収めることができる。 In recent years, game machines are required to control the game state so that the period of the predetermined state in the entire game period becomes a predetermined ratio in order to prevent excessive profits from being given to the player. .. In this respect, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, the game period other than the predetermined state required to reach the ceiling (normal state) is a fixed amount (=period required to win a predetermined probability x number of slews (number of steps in RT state) )) Can be secured. As a result, it is possible to keep the period in the predetermined state in the entire game period within a predetermined ratio while sufficiently securing the period of the second predetermined state that can be continued after reaching the ceiling.
[第26の構成の遊技機]
AT機能を有する遊技機において、長期間にわたってAT機能が発動しない場合には、遊技者は著しく不利な状況に陥り、遊技に対する興味を失ってしまう。そこで、AT機能が発動しないまま一定期間が経過した場合に、救済措置としてAT抽籤の結果に関係なくAT機能を発動する遊技機(所謂、天井)が知られており、例えば、特開2017−064539号公報には、天井に到達するまでの期間を固定せず変化をつけることで、稼動の向上を狙った遊技機が記載されている。
[Amusement machine with 26th configuration]
In a gaming machine having an AT function, if the AT function is not activated for a long period of time, the player falls into a significantly disadvantageous state and loses interest in the game. Therefore, a game machine (so-called ceiling) that activates the AT function regardless of the result of the AT lottery is known as a relief measure when a certain period of time has passed without activating the AT function. Japanese Patent No. 064539 describes a gaming machine aiming to improve the operation by fixing the period until reaching the ceiling without changing the period.
ところで、このような天井機能を有する遊技機として、天井到達時に付与する特典を、通常時の特典よりも大きくする遊技機も知られているが、天井到達時の特典が大きすぎると遊技者が遊技に過度にのめり込んでしまう恐れがあるため、好ましくない。一方で、せっかく天井まで到達したにもかかわらず早期にATが終了してしまったのでは、遊技者の遊技意欲が削がれてしまい、稼動の低下を招いてしまう。 By the way, as a gaming machine having such a ceiling function, there is also known a gaming machine in which the privilege given when the ceiling is reached is made larger than the privilege when the ceiling is reached. It is not preferable because there is a risk of being overly absorbed in the game. On the other hand, if AT ends early even though the ceiling has been reached, the player's willingness to play will be discouraged and the operation will be reduced.
本発明はこのような問題に鑑みてなされたものであり、過度なのめり込みを防止しつつ、遊技意欲の低下を抑制可能な遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of such a problem, and an object of the present invention is to provide a gaming machine capable of suppressing a decrease in game motivation while preventing excessive depression.
上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような構成の第26の遊技機を提供することができる。 To achieve the above object, the gaming machine of the present embodiment can provide a twenty-sixth gaming machine having the following configuration.
本発明に係る遊技機は、複数の識別表示を変動表示可能な可変表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、複数の役の中から決定された当籤役に応じて前記可変表示手段を用いた遊技の進行を制御する遊技制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を備える遊技機であって、遊技に関する遊技状態として、第1状態(例えば、一般状態)と第2状態(例えば、有利状態)とを有し、前記第1状態において所定条件を満たすと、遊技状態を前記第2状態に移行する通常移行制御を実行可能であるとともに、前記第1状態に関連して計数される第1数値情報が天井閾値に達すると、遊技状態を前記第2状態に移行する天井移行制御を実行可能な状態制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記第2状態の継続期間を定める第2数値情報を計数可能な継続期間計数手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記第2状態における遊技の結果に応じて、前記継続期間計数手段が計数する前記第2数値情報を更新可能であるとともに、更新の結果、前記第2数値情報が終了閾値に達すると、前記第2状態を終了可能な終了制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記状態制御手段が遊技状態を前記第2状態に移行する場合に、移行する前記第2状態の継続期間を定める前記第2数値情報の初期値を設定可能な初期期間設定手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記第2状態において、前記第2状態の継続期間が延長されるように前記第2数値情報を更新する上乗せ制御を実行可能な上乗せ制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を更に備え、前記初期期間設定手段は、前記通常移行制御により前記第2状態に移行した場合、第1初期値を設定する一方で、前記天井移行制御により前記第2状態に移行した場合、前記第1初期値よりも前記第2状態の継続期間が長い第2初期値を設定し、前記上乗せ制御手段は、前記通常移行制御により移行した前記第2状態においては、前記第2状態の継続期間の延長に関する期待度が第1期待度の前記上乗せ制御を実行し、前記天井移行制御により移行した前記第2状態においては、前記第1期待度よりも前記第2状態の継続期間の延長に関する期待度が低い第2期待度の前記上乗せ制御を実行することを特徴とする。
The gaming machine according to the present invention includes a variable display means (for example,
このような遊技機によれば、通常移行制御により移行した第2状態は、継続期間の初期値が少ない一方で、継続期間の上乗せ期待度が高く、反対に、天井移行制御により移行した第2状態は、続期間の初期値が多い一方で、継続期間の上乗せ期待度が低い。このように継続期間の初期値を、天井移行制御により移行した第2状態において多くすることで、天井到達時に早期に第2状態が終了してしまうことがなく、遊技者の遊技意欲の低下を抑制することができる。一方で、天井移行制御により移行した第2状態では上乗せ性能が低下するため、遊技者は敢えて天井を目指す必要はなく、遊技者が遊技に過度にのめり込んでしまうことを防止することができる。すなわち、本発明に係る遊技機では、天井到達時にあたかも大きな恩恵があるように感じさせることができる一方で、継続期間の初期値に対して上乗せ性能を調整することで、第2状態の1回あたりの期待値を天井時と通常時とで合わせることができ、過度なのめり込みを防止できる。 According to such a gaming machine, the second state transitioned by the normal transition control has a small initial value of the continuation period, but the expectation of adding the continuation period is high, and conversely, the second state transitioned by the ceiling transition control. As for the state, the initial value of the continuation period is large, but the degree of expectation of addition of the continuation period is low. In this way, by increasing the initial value of the duration in the second state transitioned by the ceiling transition control, the second state does not end early when the ceiling is reached, and the player's willingness to play is reduced. Can be suppressed. On the other hand, in the second state transitioned by the ceiling transition control, the ride-on performance deteriorates, so that it is not necessary for the player to aim for the ceiling, and it is possible to prevent the player from being overly absorbed in the game. That is, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, it is possible to make the user feel as if he/she has a great benefit when the ceiling is reached. It is possible to match the expected value per hit at the time of the ceiling and at the time of normal, and prevent excessive depression.
また、本発明に係る遊技機において、前記初期期間設定手段、及び/又は前記上乗せ制御手段は、前記通常移行制御により移行した前記第2状態の継続期間の期待値と、前記天井移行制御により移行した前記第2状態の継続期間の期待値とが略同一となるように、前記初期値の設定、及び/又は前記上乗せ制御を実行することを特徴とする。 Further, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, the initial period setting means and/or the addition control means shifts by the expected value of the duration of the second state shifted by the normal shift control and the ceiling shift control. The setting of the initial value and/or the addition control are executed so that the expected value of the duration of the second state is substantially the same.
このような遊技機によっても、上述の遊技機と同様に過度なのめり込みを防止しつつ、遊技意欲の低下を抑制することができる。 With such a gaming machine as well, it is possible to prevent a decrease in the gaming motivation while preventing excessive intrusion as in the above gaming machine.
[第27の構成の遊技機]
AT機能を有する遊技機では、遊技者に付与する利益が過度になり過ぎてしまうことを防止するための工夫が様々なされており、例えば、特開2017−153724号公報には、報知期間(AT)が長期間にわたり継続すると(例えば、1500回)、残りのゲーム数に関わらず強制的に報知期間を終了させるリミット処理を行う遊技機が開示されている。
[Amusement machine with 27th configuration]
In a game machine having an AT function, various measures are taken to prevent the profit to be given to a player from becoming excessive. For example, Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 2017-153724 discloses a notification period (AT ) Is continued for a long time (for example, 1500 times), a gaming machine is disclosed which performs a limit process for forcibly ending the notification period regardless of the number of remaining games.
ところで、従来の遊技機では、遊技者に付与する利益を抑えることで、のめり込みを防止することとしているが、射幸性を適切に抑制するためには、遊技者に付与する利益だけでなく、遊技者が受ける不利益も適切に調整し、利益/不利益のバランスを図る必要がある。 By the way, in the conventional game machine, it is supposed that the profit given to the player is suppressed to prevent the intrusion, but in order to appropriately suppress the gambling property, not only the profit given to the player but also the game It is necessary to appropriately adjust the disadvantages of the person to balance the profit/disadvantage.
本発明はこのような問題に鑑みてなされたものであり、遊技者が受ける利益/不利益のバランスを適切に調整可能な遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of such a problem, and an object of the present invention is to provide a gaming machine capable of appropriately adjusting a balance of profit/disadvantage received by a player.
上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような構成の第27の遊技機を提供することができる。 In order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a 27th gaming machine having the following configuration.
本発明に係る遊技機は、複数の識別表示を変動表示可能な可変表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、複数の役の中から決定された当籤役に応じて前記可変表示手段の変動表示を停止させることで結果表示を導出可能な停止制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、導出された結果表示に応じて利益を付与する利益付与手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を備える遊技機であって、再遊技役が当籤役として決定される確率が異なるRT状態として、第1RT状態と第2RT状態とを有し、前記停止制御手段により前記可変表示手段の変動表示が停止された結果、特定役(例えば、MB役)に応じた結果表示が導出されると、ボーナス遊技(例えば、MB状態)を開始し、前記ボーナス遊技の終了条件を満たすと、前記ボーナス遊技を終了する遊技制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記ボーナス遊技の前後、及び前記ボーナス遊技の最中はRT状態を移行させることなく現在のRT状態を維持する一方で、特定の移行条件を満たした場合に現在のRT状態から他のRT状態にRT状態を移行するRT制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を更に備え、前記停止制御手段は、前記ボーナス遊技において前記再遊技役が当籤役として決定されない場合(例えば、「全ての小役」に当籤)には、第1の結果表示を導出可能であり、前記ボーナス遊技において前記再遊技役が当籤役として決定された場合(例えば、「全ての小役+リプレイ」に当籤)には、前記第1の結果表示とは異なる第2の結果表示を導出可能であり、前記利益付与手段は、前記第1の結果表示が導出された場合と、前記第2の結果表示が導出された場合とで、異なる数量の遊技用価値を付与可能であることを特徴とする遊技機。
The gaming machine according to the present invention includes a variable display means (for example,
このような遊技機によれば、ボーナス遊技では、再遊技役の当籤の有無に応じて導出される結果表示が異なり、結果、付与される遊技用価値の数量が異なる。ここで、再遊技役は、当籤役として決定される確率がRT状態に応じて異なり、また、RT状態は、ボーナス遊技の前後及び最中には移行することがない。そのため、再遊技役が当籤役として決定される確率が高いRT状態中にボーナス遊技が開始された場合と、再遊技役が当籤役として決定される確率が低いRT状態中にボーナス遊技が開始された場合とで、そのボーナス遊技の有利度合いを異ならせることができる。これにより、本発明に係る遊技機では、遊技者が受ける利益/不利益のバランスを適切に調整することができる。 According to such a gaming machine, in the bonus game, the result display derived depending on whether or not the re-play combination is won is different, and as a result, the number of game values to be given is different. Here, the re-game combination has a different probability of being determined as a winning combination depending on the RT state, and the RT state does not shift before, during, and after the bonus game. Therefore, the bonus game is started when the bonus game is started during the RT state where the probability that the re-gaming combination is determined as the winning combination is high, and when the bonus game is started during the RT state where the probability that the re-gaming combination is determined as the winning combination is low. The advantage degree of the bonus game can be made different depending on the case. Thereby, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, it is possible to appropriately adjust the balance of profit/disadvantage received by the player.
また、本発明に係る遊技機は、複数の識別表示を変動表示可能な可変表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、複数の役の中から決定された当籤役に応じて前記可変表示手段の変動表示を停止させることで結果表示を導出可能な停止制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、導出された結果表示に応じて利益を付与する利益付与手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を備える遊技機であって、再遊技役が当籤役として決定される確率が異なるRT状態として、第1再遊技役(例えば、リプレイA)が当籤役として決定される確率が高く、第2再遊技役(例えば、リプレイB)が当籤役として決定される確率が低い第1RT状態と、前記第1再遊技役が当籤役として決定される確率が低く、前記第2再遊技役が当籤役として決定される確率が高い第2RT状態とを有し、前記停止制御手段により前記可変表示手段の変動表示が停止された結果、特定役(例えば、MB役)に応じた結果表示が導出されると、ボーナス遊技(例えば、MB状態)を開始し、前記ボーナス遊技の終了条件を満たすと、前記ボーナス遊技を終了する遊技制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記ボーナス遊技の前後、及び前記ボーナス遊技の最中はRT状態を移行させることなく現在のRT状態を維持する一方で、特定の移行条件を満たした場合に現在のRT状態から他のRT状態にRT状態を移行するRT制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を更に備え、前記停止制御手段は、前記ボーナス遊技において前記第1再遊技役及び前記第2再遊技役の何れも当籤役として決定されない場合(例えば、「全ての小役」に当籤)には、第1の結果表示(例えば、表示役A)を導出可能であり、また、前記ボーナス遊技において前記第1再遊技役が当籤役として決定された場合(例えば、「全ての小役+リプレイA」に当籤)には、前記第1の結果表示を導出可能であり、また、前記ボーナス遊技において前記第1再遊技役が当籤役として決定された場合(例えば、「全ての小役+リプレイB」に当籤)には、前記第1の結果表示とは異なる第2の結果表示(例えば、表示役B)を導出可能であり、前記利益付与手段は、前記第1の結果表示が導出された場合には、今回の遊技に用いた遊技用価値以下の数量の遊技用価値を付与可能であり、前記第2の結果表示が導出された場合には、今回の遊技に用いた遊技用価値よりも多い数量の遊技用価値を付与可能であることを特徴とする。
Further, the gaming machine according to the present invention, the variable display means (eg,
このような遊技機によれば、ボーナス遊技において第2再遊技役が当籤役として決定された場合には、今回の遊技に用いた遊技用価値よりも多くの遊技用価値が付与される一方で、ボーナス遊技において第2再遊技役が当籤役として決定されない場合には、今回の遊技に用いた遊技用価値以下の遊技用価値が付与される。そして、第2再遊技役は、当籤役として決定される確率がRT状態に応じて異なり、また、RT状態は、ボーナス遊技の前後及び最中には移行することがない。そのため、第2再遊技役が当籤役として決定される確率が高い第2RT状態中にボーナス遊技が開始された場合には、そのボーナス遊技を遊技者にとって有利な状態とすることができ、反対に、第2再遊技役が当籤役として決定される確率が低い第1RT状態中にボーナス遊技が開始された場合には、そのボーナス遊技を遊技者にとって現状維持又は不利な状態とすることができる。このようにボーナス遊技の有利度合いをRT状態に応じて異ならせることで、ボーナス遊技中に遊技者に付与する利益を抑えることができる。一方で、第1RT状態中のボーナス遊技であっても、遊技者には、一定量の遊技用価値が付与されるため、相対的に不利なボーナス遊技であったとしても遊技者が受ける不利益を抑えることができる。そのため、本発明に係る遊技機では、遊技者が受ける利益/不利益のバランスを適切に調整することができる。 According to such a gaming machine, when the second re-game combination is determined as the winning combination in the bonus game, more game value than the game value used in the current game is given. In the bonus game, when the second re-game combination is not determined as a winning combination, the game value equal to or lower than the game value used for the current game is given. Then, the second re-game combination has a different probability of being determined as a winning combination depending on the RT state, and the RT state does not shift before, during, and after the bonus game. Therefore, when the bonus game is started during the second RT state in which the probability that the second re-game combination is determined as the winning combination is high, the bonus game can be made advantageous to the player, and conversely. If the bonus game is started during the first RT state in which the probability that the second re-gaming combination is determined as a winning combination is low, the bonus game can be maintained or disadvantageous to the player. In this way, by varying the advantage degree of the bonus game depending on the RT state, it is possible to suppress the profit given to the player during the bonus game. On the other hand, even if the bonus game is in the first RT state, a certain amount of game value is given to the player, so that the player receives a disadvantage even if the bonus game is relatively disadvantageous. Can be suppressed. Therefore, with the gaming machine according to the present invention, it is possible to appropriately adjust the balance of profit/disadvantage received by the player.
また、本発明に係る遊技機において、前記第1RT状態は、前記再遊技役が当籤役として決定される確率が低い低RT状態であり、前記第2RT状態は、前記再遊技役が当籤役として決定される確率が高い高RT状態であることを特徴とする。 Further, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, the first RT state is a low RT state in which the probability that the re-gaming combination is determined as a winning combination is low, and the second RT state is the re-gaming combination as a winning combination. It is characterized by a high RT state with a high probability of being determined.
このようにすることで、高RT状態中のボーナス遊技を遊技者にとって有利な状態とすることができ、また、低RT状態中のボーナス遊技を遊技者にとって現状維持又は不利な状態とすることができる。 By doing so, the bonus game in the high RT state can be made advantageous for the player, and the bonus game in the low RT state can be maintained or disadvantageous for the player. it can.
[第28の構成の遊技機]
AT機能を搭載した遊技機によれば、ナビを行うか否かを制御することで遊技者に払い出す遊技媒体の数が制御されるため、遊技者は、ATを継続するATゲーム数(ナビゲーム数)が増加することを望むことになる。ATゲーム数を増加させるための工夫はこれまで様々な観点からなされてきており、例えば、特開2010−057732号公報には、内部当籤役としてスイカやチェリーなどの特定の役が決定されるとATゲーム数を増加させる(ATゲーム数を上乗せさせる)遊技機が開示されている。
[28th Configuration Gaming Machine]
According to the gaming machine equipped with the AT function, the number of game media to be paid out to the player is controlled by controlling whether or not to perform the navigation. We hope that the number of games) will increase. Various measures have been taken so far to increase the number of AT games. For example, in Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 2010-057732, a specific combination such as watermelon or cherry is determined as an internal winning combination. A gaming machine that increases the number of AT games (adds the number of AT games) is disclosed.
ところで、従来の遊技機では、今回の遊技において決定された当籤役に応じてATなどの有利な状態の継続期間を延長させるだけであり、有利な状態の継続期間の長さに関して遊技者が介入する余地が少なかった。 By the way, in the conventional gaming machine, only the duration of the advantageous state such as AT is extended according to the winning combination determined in this game, and the player intervenes with respect to the duration of the advantageous state. There was little room to do it.
本発明はこのような問題に鑑みてなされたものであり、有利な状態の継続期間の長さに関して遊技者が介入可能な遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of such a problem, and an object of the present invention is to provide a gaming machine in which a player can intervene regarding the length of an advantageous state duration.
上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような構成の第28の遊技機を提供することができる。 To achieve the above object, the gaming machine of the present embodiment can provide a twenty-eighth gaming machine having the following configuration.
本発明に係る遊技機は、複数の識別表示を変動表示可能な可変表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、複数の役の中から決定された当籤役に応じて前記可変表示手段を用いた遊技の進行を制御する遊技制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を備える遊技機であって、当籤役として決定された場合に、所定の操作態様で停止操作が行われると第1の結果表示を導出可能、かつ、前記所定の操作態様とは異なる操作態様で停止操作が行われると第2の結果表示を導出可能な報知対象役を有し、遊技に関する遊技状態として、第1状態(例えば、非報知状態)と第2状態(例えば、報知状態)とを有し、前記第1状態において所定条件を満たすと、遊技状態を前記第2状態に移行可能な状態制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記報知対象役が当籤役として決定された遊技において前記第1の結果表示が導出されると、所定数量の遊技用価値を付与可能である一方で、当該遊技において前記第2の結果表示が導出されると、前記所定数量よりも少ない遊技用価値を付与可能な利益付与手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記第2状態において前記報知対象役が当籤役として決定されると、前記第1の結果表示を導出するために必要な前記所定の操作態様を報知可能な報知手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記第2状態の継続期間を定める数値情報である、前記第2状態において前記利益付与手段により付与された遊技用価値の総数を計数可能な継続期間計数手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記第2状態において前記利益付与手段により付与された遊技用価値の数量に応じて前記数値情報を更新可能であるとともに、更新の結果、前記数値情報が終了閾値に達すると、前記第2状態を終了可能な継続期間管理手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記第2状態において、前記第2状態の継続期間が延長されるように前記数値情報を更新する上乗せ制御を実行可能な上乗せ制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を更に備え、前記継続期間管理手段は、前記第2状態の前記報知対象役が当籤役として決定された遊技において前記報知手段が前記所定の操作態様を報知した場合であっても、遊技者の停止操作の結果として前記第2の結果表示が導出された場合には、導出された前記第2の結果表示に応じて付与される遊技用価値の数量に応じて、前記数値情報を更新することを特徴とする。
The gaming machine according to the present invention includes a variable display means (for example,
このような遊技機によれば、報知対象役が当籤役として決定された際に所定の操作態様を報知可能な第2状態(有利な状態)は、第2状態において付与された遊技用価値の総数(数値情報)が終了閾値に達すると終了するため、所謂、有利な状態を当該状態中の差枚数又は獲得枚数により管理することができる。このとき、本発明に係る遊技機では、第2状態中に報知対象役に応じた報知を行っただけでは、数値情報(差枚数や獲得枚数)を更新せず、停止操作の結果として停止した結果表示に伴い実際に付与された遊技用価値の数量に応じて数値情報を更新する。遊技者にとってみれば、報知に従い停止操作を行うことで、多くの遊技用価値を獲得できる一方で有利な状態(第2状態)の終了が早まってしまい、反対に、報知に逆らって停止操作を行うことで、遊技用価値の獲得は減るものの有利な状態を継続させることができるため、有利な状態の継続期間の長さに関して遊技者が介入することができる。また、本発明に係る遊技機では、第2状態において、継続期間を延長する上乗せ制御を実行可能であるため、報知に逆らい有利な状態を継続させることで、一時的には遊技用価値の獲得を減らしてしまうものの、報知に逆らって伸ばした期間において上乗せ制御を受けることにより、最終的には多くの遊技用価値を獲得する可能性もあるため、従来にない戦略性を持った遊技性を実現することができる。 According to such a gaming machine, the second state (advantageous state) in which the predetermined operation mode can be notified when the notification target combination is determined as the winning combination is the gaming value given in the second state. Since the process ends when the total number (numerical value information) reaches the end threshold, a so-called advantageous state can be managed by the difference number or the acquired number in the state. At this time, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, the numerical information (the difference number or the acquired number) is not updated only by performing the notification according to the notification target combination during the second state, and the game is stopped as a result of the stop operation. Numerical information is updated according to the quantity of the gaming value actually given along with the result display. For the player, by performing the stop operation according to the notification, a lot of gaming value can be obtained, but the advantageous state (second state) ends earlier, and conversely, the stop operation is performed against the notification. By doing so, it is possible to continue the advantageous state although the acquisition of the gaming value is reduced, so that the player can intervene regarding the length of the duration of the advantageous state. Further, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, in the second state, it is possible to execute additional control for extending the duration, so by continuing the advantageous state against the notification, the gaming value is temporarily obtained. However, it is possible to eventually gain a lot of gaming value by receiving additional control during the extended period against the notification, so a gameplay with a strategy that has never existed is possible. Can be realized.
また、本発明に係る遊技機において、当籤役として決定されると、停止操作の態様に関わらず前記利益付与手段により特定数量の遊技用価値が付与される第3の結果表示を導出可能な特定役(例えば、引込1の役)を更に有し、継続期間管理手段は、複数の役のうちの前記特定役が当籤役として決定されたことに応じて前記利益付与手段により遊技用価値が付与された場合には、前記数値情報を更新しないことを特徴とする。 Further, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, when it is determined as a winning combination, a third result display in which a specific amount of gaming value is given by the profit giving means regardless of the mode of the stop operation can be derived. It further has a winning combination (for example, a winning combination 1), and the continuation period management means gives the gaming value by the profit giving means in response to the specific winning combination of a plurality of winning combinations being determined as a winning combination. In the case of being performed, the numerical information is not updated.
このような遊技機によれば、上述と同様に、報知に逆らい有利な状態を継続させることで、一時的には遊技用価値の獲得を減らしてしまうものの、報知に逆らって伸ばした期間において上乗せ制御を受けることにより、最終的には多くの遊技用価値を獲得する可能性もあるため、従来にない戦略性を持った遊技性を実現することができる。 According to such a gaming machine, similarly to the above, by continuing the advantageous state against the notification, although it temporarily reduces the acquisition of the gaming value, the addition in the period extended against the notification By receiving the control, there is a possibility that a large amount of gaming value will eventually be obtained, so that it is possible to realize a gaming property with a strategy that has never been seen before.
[第29の構成の遊技機]
特開2016−104425号公報には、内部当籤役に決定された役を取りこぼすことがないように、内部当籤役を成立させるための情報など、遊技者にとって有利な情報を、遊技者に対して報知する遊技機が開示されている。なお、このように遊技者が有利となるような情報を報知することを、一般にナビする(ナビを行う)などといい、ナビが行われる期間をAT(assist time)といい、AT機能を備える遊技機をAT機やART機と呼ぶ。AT(ART)機によると、内部当籤役の抽籤確率だけでなく、報知の有無に応じて利益に差が生じることになるため、遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。
[Amusement machine with 29th configuration]
Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 2016-104425 discloses information useful for a player, such as information for establishing an internal winning combination, so that a winning combination determined as an internal winning combination is not lost. There is disclosed a gaming machine that informs by means of this. It should be noted that such notification of information that is advantageous to the player is generally referred to as navigating (navigating), the period during which navigating is performed is called AT (assist time), and the AT function is provided. Gaming machines are called AT machines and ART machines. According to the AT (ART) machine, not only the lottery probability of the internal winning combination, but also the profit varies depending on the presence or absence of the notification, so that the interest of the game can be improved.
このようなAT機能を備える遊技機では、通常の状態から有利な状態(AT)に移行させるまでの制御に様々な工夫がなされており、例えば、有利な状態への移行確率を定めるモードを複数備え、現在のモード毎に移行期待度を異ならせる制御も知られているが、このような制御は多くの遊技機において採用されており、単にモードを設けるだけでは遊技が単調になり、有利な状態への移行に関して更なる改善が求められている。 In a gaming machine equipped with such an AT function, various measures have been taken to control the transition from a normal state to an advantageous state (AT). For example, there are a plurality of modes that determine the transition probability to the advantageous state. Although it is known that there is a control that changes the degree of transition expectation for each current mode, such control is adopted in many gaming machines, and simply providing a mode makes the game monotonous, which is advantageous. Further improvement is required for the transition to the state.
本発明はこのような問題に鑑みてなされたものであり、有利な状態への移行に関して従来にない新たな制御が可能な遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of such a problem, and an object of the present invention is to provide a gaming machine capable of new control that has not existed in the past regarding transition to an advantageous state.
上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような構成の第29の遊技機を提供することができる。 To achieve the above object, the gaming machine of the present embodiment can provide a twenty-ninth gaming machine having the following configuration.
本発明に係る遊技機は、複数の識別表示を変動表示可能な可変表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、複数の役の中から決定された当籤役に応じて前記可変表示手段を用いた遊技の進行を制御する遊技制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を備える遊技機であって、遊技に関する遊技状態として、通常状態(例えば、通常区間)と、第1所定状態(例えば、CZ)及び当該第1所定状態よりも遊技者にとって有利な第2所定状態(例えば、ART)とを少なくとも含む所定状態(例えば、有利区間)と、を有し、前記通常状態において第1条件が満たされると、前記第1所定状態に遊技状態を移行可能な第1状態制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記第1所定状態において第2条件が満たされると、前記第2所定状態に遊技状態を移行可能、かつ、前記第1所定状態において特定役(例えば、MB)が当籤役として決定されると、前記通常状態に遊技状態を移行可能な第2状態制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を更に備え、前記遊技制御手段は、複数の設定値の少なくとも一部において他の設定値とは異なる確率で、前記特定役を当籤役として決定することを特徴とする。
The gaming machine according to the present invention includes a variable display means (for example,
このような遊技機によれば、第1所定状態において第2条件が満たされると、有利な状態である第2所定状態に移行可能である一方で、第1所定状態において特定役が当籤役として決定されると、通常状態に移行してしまう。すなわち、遊技者は、第1所定状態において、特定役に当籤する前に(第1所定状態が終了する前に)、第2所定状態への移行条件(第2条件)が満たされることを望んで遊技を行うことになる。このとき、第1所定状態の終了条件である特定役は、設定値に応じて当籤確率が異なるため、第2所定状態(有利な状態)への移行が期待できる第1所定状態も、設定値に応じて終了確率が異なることになる。このように本発明に係る遊技機では、例えば、有利な状態(第2所定状態)への移行抽籤に当籤する確率に設定差を直接設けるのではなく、有利な状態への移行が期待できる第1所定状態の終了確率に設定差を設けることで、有利な状態への移行確率に設定差を設けるため、有利な状態への移行に関して従来にない新たな制御が可能になる。 According to such a gaming machine, when the second condition is satisfied in the first predetermined state, it is possible to shift to the advantageous second predetermined state, while the specific combination is a winning combination in the first predetermined state. If it is decided, it will shift to the normal state. That is, in the first predetermined state, the player desires that the condition for transitioning to the second predetermined state (second condition) is satisfied before winning the specific combination (before the first predetermined state ends). You will play a game. At this time, since the winning combination of the specific winning combination, which is the ending condition of the first predetermined state, differs depending on the set value, the first predetermined state that can be expected to shift to the second predetermined state (advantageous state) also has the set value. The end probability varies depending on. As described above, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, for example, a transition to an advantageous state (second predetermined state) is not directly provided with a setting difference in the probability of winning the lottery, but a transition to an advantageous state can be expected. By providing a setting difference in the completion probability of the 1 predetermined state, a setting difference is provided in the transition probability to the advantageous state, and thus it becomes possible to perform a new control which is not related to the transition to the advantageous state.
また、本発明に係る遊技機において、前記所定状態は、遊技者にとって有利な停止操作の情報を報知可能な報知状態であり、遊技の結果として前記特定役に応じた結果表示が導出されると、ボーナス遊技を開始するボーナス開始手段(例えば、主制御回路90)を更に備えることを特徴とする。 Further, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, the predetermined state is a notification state capable of notifying information of a stop operation that is advantageous for a player, and a result display corresponding to the specific combination is derived as a result of the game. A bonus start means (for example, a main control circuit 90) for starting a bonus game is further provided.
このような遊技機によれば、第1所定状態において特定役に当籤することなく第2条件を満たすことができた場合には、遊技者にとって有利な報知状態(第2所定状態)に移行することができる一方で、第2条件を満たすことなく特定役に当籤してしまった場合であっても、ボーナス遊技が開始されるため、遊技者が感じる不満を軽減することができる。 According to such a gaming machine, when the second condition can be satisfied without winning the specific winning combination in the first predetermined state, a transition is made to a notification state (second predetermined state) advantageous to the player. On the other hand, even if the specific combination is won without satisfying the second condition, the bonus game is started, so that the dissatisfaction felt by the player can be reduced.
また、本発明に係る遊技機において、前記遊技制御手段は、複数の設定値のうち遊技者にとって不利な設定値である低設定値である場合ほど高い確率で前記特定役を当籤役として決定することを特徴とする。 Further, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, the game control means determines the specific winning combination as a winning combination with a higher probability as a lower setting value that is a disadvantageous setting value to the player among the plurality of setting values. It is characterized by
このような遊技機によれば、遊技者にとって不利な低設定であるほど、特定役が当籤役として決定され易いため、低設定であるほど、報知状態(第2所定状態)への移行が期待できる第1所定状態も終了し易く、結果、報知状態に移行し難い。しかしながら、遊技の結果として特定役に応じた結果表示が導出された場合には、ボーナス遊技が開始されるため、有利な状態に移行し難い低設定である場合には、高設定よりも多くのボーナス遊技を行うことができ、遊技者が感じる不満を軽減することができる。 According to such a gaming machine, the lower the setting that is disadvantageous to the player, the easier it is to determine the specific winning combination as the winning combination. Therefore, the lower the setting, the higher the transition to the notification state (second predetermined state) is expected. The possible first predetermined state is also easily finished, and as a result, it is difficult to shift to the notification state. However, when the result display according to the specific combination is derived as a result of the game, the bonus game is started, so if the low setting is difficult to shift to the advantageous state, the number of the high setting is more than that of the high setting. A bonus game can be played, and dissatisfaction felt by the player can be reduced.
[第30の構成の遊技機]
AT機能を搭載した遊技機によれば、ナビを行うか否かを制御することで遊技者に払い出す遊技媒体の数が制御されるため、遊技者は、ATを継続するATゲーム数(ナビゲーム数)が増加することを望むことになる。ATゲーム数を増加させるための工夫はこれまで様々な観点からなされてきており、例えば、特開2010−057732号公報には、内部当籤役としてスイカやチェリーなどの特定の役が決定されるとATゲーム数を増加させる(ATゲーム数を上乗せさせる)遊技機が開示されている。
[Gaming machine with 30th configuration]
According to the gaming machine equipped with the AT function, the number of game media to be paid out to the player is controlled by controlling whether or not to perform the navigation. We hope that the number of games) will increase. Various measures have been taken so far to increase the number of AT games. For example, in Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 2010-057732, a specific combination such as watermelon or cherry is determined as an internal winning combination. A gaming machine that increases the number of AT games (adds the number of AT games) is disclosed.
しかしながら、上述の遊技機では、AT期間に関する特典が付与されるか否か、及び付与される特典の大きさが、予め役毎に対応付けられているため、遊技者からすると当籤役として決定された役の種別から、特典が付与されるか否か、及び付与される特典の大きさを把握できてしまい、遊技が単調になってしまう可能性があった。 However, in the above-mentioned gaming machine, whether or not the privilege regarding the AT period is granted and the size of the privilege to be granted are associated with each winning combination in advance, so that the player determines the winning combination. Whether or not the privilege is granted and the size of the privilege to be granted can be grasped from the type of winning combination, and the game may be monotonous.
本発明はこのような問題に鑑みてなされたものであり、特典付与の決定結果に関して従来にない遊技性を有する遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of such a problem, and an object of the present invention is to provide a gaming machine having an unprecedented game playability with respect to the determination result of privilege grant.
上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような構成の第30の遊技機を提供することができる。 In order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a thirtieth gaming machine having the following configuration.
本発明に係る遊技機は、複数の識別表示を変動表示可能な可変表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、複数の役の中から決定された当籤役に応じて前記可変表示手段を用いた遊技の進行を制御する遊技制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を備える遊技機であって、停止操作の態様を報知可能な報知状態を有するとともに、遊技に関する遊技状態として、所定状態(例えば、非ボーナス状態)と、第1特定状態(例えば、BB中RB)及び第2特定状態(例えば、BB中RB持越)を含む特定状態(例えば、ボーナス状態)と、を有し、前記所定状態において開始条件(例えば、ボーナス状態の開始条件)を満たすと、前記特定状態を開始可能であり、前記特定状態において終了条件(例えば、ボーナス状態の終了条件)を満たすと、前記特定状態を終了可能な状態制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記特定状態において第1の条件(例えば、RBの入賞)を満たすと、前記第1特定状態に遊技状態を制御可能であり、前記特定状態において第2の条件(例えば、RBを当籤役として持ち越す)を満たすと、前記第2特定状態に遊技状態を制御可能な特定状態制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記特定状態において、前記報知状態に関する特典を付与可能な特典付与手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を更に備え、前記特典付与手段は、前記特定状態の前記第1特定状態と、前記特定状態の前記第2特定状態とにおいて、前記報知状態に関する特典を異なる確率で付与可能である一方で、前記報知状態に関する特典を付与する場合、前記特定状態の前記第1特定状態と、前記特定状態の前記第2特定状態とのうち、前記確率が低い状態の方が大きな特典を付与可能であることを特徴とする。
The gaming machine according to the present invention includes a variable display means (for example,
このような遊技機によれば、第1特定状態と第2特定状態とでは、報知状態に関する特典を異なる確率が異なるとともに、特典を付与する場合に付与する特典の大きさが、特典を付与する確率が低いほど大きな特典を付与する。すなわち、本発明に係る遊技機では、特定状態中の第1特定状態と第2特定状態とで、報知状態に関する特典を付与する確率と大きさとがクロスする。遊技者にとってみれば、特定状態中に特典が付与され易いが小さな特典しか付与されないように遊技を行うか、特典が付与され難いが大きな特典が付与されるよう遊技を行うか、選択することができるため、本発明に係る遊技機によれば、特典付与の決定結果に関して戦略性を持った新たな遊技性を実現することができる。 According to such a gaming machine, the first specific state and the second specific state have different probabilities of different benefits relating to the notification state, and the size of the privilege granted when the privilege is granted gives the privilege. The lower the probability, the greater the benefit. That is, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, the probability and the size of giving the privilege related to the notification state are crossed between the first specific state and the second specific state in the specific state. From the perspective of the player, it is possible to select whether to perform the game so that the privilege is easily granted but only a small privilege is given during the specific state, or the game is performed so that the privilege is hard to be granted but the large privilege is granted. Therefore, according to the gaming machine of the present invention, it is possible to realize a new gaming property having a strategic characteristic with respect to the determination result of the privilege grant.
また、本発明に係る遊技機において、再遊技役が当籤役として決定される確率が異なるRT状態として、当該確率が低い低RT状態と、高RT状態とを有し、前記特定状態制御手段は、前記特定状態において特定役(例えば、RB)に対応する特定の結果表示が導出されると、前記第1の条件を満たしたとして、前記特定状態の前記第1特定状態を開始可能な第1特定状態制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記特定状態において前記特定役が当籤役として決定されると、前記第2の条件を満たしたとして、前記特定状態の前記第2特定状態を開始可能であり、前記特定の結果表示が導出されると、前記第2特定状態を終了可能な第2特定状態制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記特定状態の前記特定役が当籤役として決定された単位遊技において前記特定の結果表示が導出されない場合に、前記特定の結果表示が導出されるまで、前記特定役を当籤役として持ち越し可能な持越手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を備え、前記特定状態において前記特定役が当籤役として決定されると、RT状態を前記高RT状態に移行し、前記特定状態において前記特定役に対応する前記特定の結果表示が導出されると、RT状態を前記低RT状態に移行するRT制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)、を更に備え、前記特典付与手段は、前記特定状態の前記第1特定状態では、前記特定状態の前記第2特定状態に比べて低い確率で、前記報知状態に関する特典を付与可能である一方で、前記特定状態の前記第1特定状態において前記報知状態に関する特典を付与する場合、前記特定状態の前記第2特定状態において前記報知状態に関する特典を付与する場合に比べて大きな特典を付与することを特徴とする。 Further, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, the RT state having different probabilities that a re-gaming combination is determined as a winning combination has a low RT state and a high RT state with low probability, and the specific state control means When a specific result display corresponding to a specific combination (for example, RB) is derived in the specific state, it is determined that the first condition is satisfied, and the first specific state of the specific state can be started. When the specific state control means (for example, the main control circuit 90) determines that the specific combination is a winning combination in the specific state, it is determined that the second condition is satisfied and the second specific state of the specific state is set. When it is possible to start and the specific result display is derived, the second specific state control means (for example, the main control circuit 90) capable of ending the second specific state and the specific combination in the specific state are won. When the specific result display is not derived in the unit game determined as the combination, the specific combination display can be carried over as the winning combination until the specific result display is derived (for example, the main control circuit 90). And, when the specific combination is determined as a winning combination in the specific state, the RT state is shifted to the high RT state, and the specific result display corresponding to the specific combination is derived in the specific state. Then, an RT control unit (for example, a main control circuit 90) that shifts the RT state to the low RT state is further provided, and the privilege granting unit is configured to change the specific state from the first specific state to the specific state. While the privilege related to the notification state can be granted with a lower probability than the second specific state, when the privilege related to the notification state is granted in the first specific state of the specific state, the privilege of the specific state is It is characterized in that a larger privilege is given in comparison with a case where the privilege related to the notification state is given in the second specific state.
このような遊技機によれば、特定役に応じた結果表示の導出を避けて、特定役を持ち越した状態(第2特定状態)で遊技を行うことで、付与される特典は小さいものの、特典が付与され易い状態で遊技を行うことができる。このとき、特定状態において特定役が持ち越されている間は高RT状態であるため、その後、報知状態(所謂、ART)に移行するとき、RT状態を高RT状態に移行させるための準備期間を持たせる必要がない。そのため、第2特定状態で遊技を行うことで、報知状態に移行し易く、かつ、準備期間を経ることなく直ちに報知状態を開始可能になる。一方で、特定役に応じた結果表示が導出された状態(第1特定状態)で遊技を行うことで、特典が付与され難いものの、付与される特典が大きい状態で遊技を行うことができる。このとき、特定状態において特定役に応じた結果表示が導出されると低RT状態に移行するため、高RT状態である場合に比べて出玉率のベースが下がることになる。その結果、第1特定状態中は、特典付与の確率低下分だけでなく、低RT状態による出玉率のベース低下分も、付与する特典の大きさに振り分けることができる。そのため、遊技者にとってみれば、特定状態中に特典が付与され易いが小さな特典しか付与されないように遊技を行うか(特定役を入賞又は持ち越す)、特典が付与され難いが大きな特典が付与されるよう遊技を行うか、選択することができ、戦略性を持った新たな遊技性を実現することができる。 According to such a gaming machine, by avoiding the derivation of the result display according to the specific combination and playing the game in the state in which the specific combination is carried over (second specific state), the privilege is given, but the privilege is small. The game can be played in a state where is easily given. At this time, since the high RT state is maintained while the specific combination is carried over in the specific state, when the state is subsequently shifted to the notification state (so-called ART), the preparation period for shifting the RT state to the high RT state is set. You don't have to have it. Therefore, by playing the game in the second specific state, it is easy to shift to the notification state, and the notification state can be started immediately without the preparation period. On the other hand, by performing the game in a state where the result display corresponding to the specific combination is derived (first specific state), it is possible to perform the game in a state where the privilege is hard to be granted but the privilege is large. At this time, when the result display corresponding to the specific winning combination is derived in the specific state, the state shifts to the low RT state, so that the base of the payout rate is lower than that in the high RT state. As a result, during the first specific state, not only the amount of decrease in the probability of awarding but also the amount of base decrease in the payout rate due to the low RT state can be allocated to the amount of the awarding privilege. Therefore, for the player, the game is performed so that the privilege is easily granted in the specific state but only the small privilege is granted (the specific role is won or carried over), or the privilege is hard to be granted but the large privilege is granted. It is possible to perform or select a game so that a new game property having a strategic characteristic can be realized.
また、本発明に係る遊技機は、複数の識別表示を変動表示可能な可変表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、複数の役の中から決定された当籤役に応じて前記可変表示手段を用いた遊技の進行を制御する遊技制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を備える遊技機であって、停止操作の態様を報知可能な報知状態を有するとともに、遊技に関する遊技状態として、所定状態(例えば、非ボーナス状態)と、第1特定状態(例えば、BB中RB)及び第2特定状態(例えば、BB中RB持越)を含む特定状態(例えば、ボーナス状態)と、を有し、前記所定状態において開始条件(例えば、ボーナス状態の開始条件)を満たすと、前記特定状態を開始可能であり、前記特定状態において終了条件(例えば、ボーナス状態の終了条件)を満たすと、前記特定状態を終了可能な状態制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記特定状態において第1の条件(例えば、RBの入賞)を満たすと、前記第1特定状態に遊技状態を制御可能であり、前記特定状態において第2の条件(例えば、RBを当籤役として持ち越す)を満たすと、前記第2特定状態に遊技状態を制御可能な特定状態制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記特定状態において、前記報知状態に関する特典を付与可能な特典付与手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を更に備え、前記特定状態の前記第1特定状態の単位遊技当たりに付与される遊技用価値の期待値と、前記特定状態の前記第2特定状態の単位遊技当たりに付与される遊技用価値の期待値とでは、前記特定状態の前記第2特定状態の単位遊技当たりに付与される遊技用価値の期待値の方が高く、前記特定状態の前記第1特定状態における特典の期待値と、前記特定状態の前記第2特定状態における特典の期待値とでは、単位遊技当たりに付与される遊技用価値の期待値が低い前記特定状態の前記第1特定状態の方が特典の期待値が高いことを特徴とする。
Further, the gaming machine according to the present invention, the variable display means (eg,
このような遊技機によれば、第1特定状態と第2特定状態とでは、単位遊技当たりに付与される遊技用価値の期待値が異なるとともに、単位遊技当たりに付与される遊技用価値の期待値が低いほど、報知状態に関する特典の期待値が高い。すなわち、本発明に係る遊技機では、特定状態中の第1特定状態と第2特定状態とで、単位遊技当たりに付与される遊技用価値の期待値と、報知状態に関する特典の期待値とがクロスする。遊技者にとってみれば、特典が付与され難いが遊技用価値の付与を多く受けるように遊技を行うか、特典が付与され易いが遊技用価値の付与が少ない遊技を行うかを選択することができるため、本発明に係る遊技機によれば、特典付与に関して戦略性を持った新たな遊技性を実現することができる。 According to such a gaming machine, the expected value of the game value given per unit game is different between the first specific state and the second specific state, and the expected value of the game value given per unit game is different. The lower the value, the higher the expected value of the privilege related to the notification state. That is, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, the expected value of the gaming value given per unit game and the expected value of the privilege related to the notification state are in the first specific state and the second specific state in the specific state. Cross. From the perspective of the player, it is possible to select whether to perform the game so that the privilege is hard to be granted but receive a large amount of the game value, or to perform the game in which the privilege is easily provided but the game value is less likely to be granted. Therefore, according to the gaming machine according to the present invention, it is possible to realize a new gaming property having a strategic characteristic with respect to granting a privilege.
また、本発明に係る遊技機において、前記複数の役には、入賞すると所定数の遊技用価値が付与される所定役が複数種類(例えば、BEL_01〜09)含まれ、前記特定状態の前記第1特定状態と、前記特定状態の前記第2特定状態とでは、複数種類の前記所定役のうちの夫々が当籤役として決定される複数種類の前記所定役の個々の当籤確率は、前記第1特定状態の方が高いものの、複数種類の前記所定役の少なくとも何れかが当籤役として決定される当籤確率は、前記第2特定状態の方が高いことを特徴とする。 Further, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, the plurality of winning combinations include a plurality of types (for example, BEL_01 to 09) of predetermined winning combinations to which a predetermined number of gaming values are awarded when a prize is won. In the one specific state and the second specific state of the specific state, the individual winning probabilities of a plurality of types of the predetermined winning combinations in which each of the plurality of types of the predetermined winning combinations is determined as a winning combination are Although the specific state is higher, the winning probability that at least one of the plurality of predetermined combinations is determined as the winning combination is higher in the second specific state.
このような遊技機によれば、第1特定状態では、複数種類の所定役の個々の当籤確率は上げつつも、複数種類の所定役の少なくとも何れかが当籤役として決定される確率は下がるため、単位遊技当たりに付与される遊技用価値の期待値を、第2特定状態よりも低くすることができる。そのため、上述と同様に、単位遊技当たりに付与される遊技用価値の期待値と、報知状態に関する特典の期待値とをクロスすることができる。 According to such a gaming machine, in the first specific state, the probability of individual winning combinations of a plurality of types of predetermined winning combinations increasing, but the probability of at least one of the plurality of types of predetermined winning combinations being determined as a winning combination decreases. The expected value of the gaming value given per unit game can be set lower than that in the second specific state. Therefore, similarly to the above, it is possible to cross the expected value of the game value given per unit game and the expected value of the privilege related to the notification state.
[第31の構成の遊技機]
こうしたAT機能を搭載した遊技機によれば、ナビを行うか否かを制御することで遊技者に払い出す遊技媒体の数が制御されるため、遊技者は、ATを継続するATゲーム数(ナビゲーム数)が増加することを望むことになる。ATゲーム数を増加させるための工夫はこれまで様々な観点からなされてきており、例えば、特開2010−057732号公報には、内部当籤役としてスイカやチェリーなどの特定の役が決定されるとATゲーム数を増加させる(ATゲーム数を上乗せさせる)遊技機が開示されている。
[Gaming machine with 31st configuration]
According to the gaming machine equipped with such an AT function, the number of gaming media to be paid out to the player is controlled by controlling whether or not to perform the navigation. We hope that the number of navigation games) will increase. Various measures have been taken so far to increase the number of AT games. For example, in Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 2010-057732, a specific combination such as watermelon or cherry is determined as an internal winning combination. A gaming machine that increases the number of AT games (adds the number of AT games) is disclosed.
しかしながら、上述の遊技機では、AT期間に関する特典が付与されるか否か、及び付与される特典の大きさが、予め役毎に対応付けられているため、遊技者からすると当籤役として決定された役の種別から、特典が付与されるか否か、及び付与される特典の大きさを把握できてしまい、遊技が単調になってしまう可能性があった。 However, in the above-mentioned gaming machine, whether or not the privilege regarding the AT period is granted and the size of the privilege to be granted are associated with each winning combination in advance, so that the player determines the winning combination. Whether or not the privilege is granted and the size of the privilege to be granted can be grasped from the type of winning combination, and the game may be monotonous.
本発明はこのような問題に鑑みてなされたものであり、特典付与の決定結果に関して従来にない遊技性を有する遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of such a problem, and an object of the present invention is to provide a gaming machine having an unprecedented game playability with respect to the determination result of privilege grant.
上記目的を達成するために、本実施形態の遊技機によれば、以下のような構成の第31の遊技機を提供することができる。 In order to achieve the above object, according to the gaming machine of the present embodiment, it is possible to provide a 31st gaming machine having the following configuration.
本発明に係る遊技機は、複数の識別表示を変動表示可能な複数の可変表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、複数の役の中から決定された当籤役に応じて前記可変表示手段を用いた遊技の進行を制御する遊技制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を備える遊技機であって、停止操作の態様を報知可能な報知状態を有するとともに、当籤役として決定された場合に、第1の操作態様で停止操作(例えば、色択に正解の停止操作)が行われると第1の結果表示(例えば、色択小役の入賞)を導出可能、第2の操作態様で停止操作(例えば、押し順に正解の停止操作)が行われると第2の結果表示(例えば、押し順小役の入賞)を導出可能、かつ、前記第1の操作態様及び前記第2の操作態様の何れでもない第3の操作態様で停止操作が行われると第3の結果表示(例えば、こぼし目又ははずれ)を導出可能な特定役(例えば、「色択小役+押し順小役」)を有し、前記第1の結果表示又は前記第2の結果表示が導出されると、所定量の遊技用価値を付与可能、かつ、前記第3の結果表示が導出されると、前記所定量よりも少ない量の遊技用価値を付与可能な利益付与手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、非報知状態において前記第1の結果表示が導出されると、前記報知状態に関する特典を付与可能な報知特典付与手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記報知特典付与手段により前記特典が付与されたことに応じて、前記報知状態に遷移可能な報知制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、遊技者に対して所定の操作態様を報知可能な報知手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を更に備え、前記報知手段は、非報知状態において前記特定役が当籤役として決定されると、前記第1の操作態様、前記第2の操作態様及び前記第3の操作態様の何れも報知することなく、前記報知状態において前記特定役が当籤役として決定されると、前記第2の操作態様を報知可能であることを特徴とする。
The gaming machine according to the present invention, the variable display means (eg,
このような遊技機によれば、非報知状態において特定役が当籤役として決定された場合に、第1の操作態様で停止操作を行い第1の結果表示が導出されると、報知状態に関する特典が付与される。一方で、第2の操作態様で停止操作を行い第2の結果表示が導出された場合には、第1の結果表示が導出された場合と同量の所定量の遊技用価値が付与されるものの、報知状態に関する特典は付与されず、また、第3の操作態様で停止操作を行った場合には、所定量よりも少ない量の遊技用価値しか付与されず、かつ、報知状態に関する特典も付与されない。このように本発明に係る遊技機によれば、特典付与の決定結果に関して、遊技者が関与可能な遊技性を実現することができる。
また、本発明に係る遊技機では、報知状態中に報知対象となる役を、操作態様の種別に応じて特典を付与可能な特定役として用いている。ここで、利益バランスを考慮すると、複数の操作態様のうち最も利益が大きい第1の操作態様は、成立し難い操作態様であることが好ましいが、報知状態中に遊技用価値を付与するために報知する操作態様を第1の操作態様としてしまったのでは、特定役(報知対象役)の当籤時に成立し難い第1の操作態様を要求することになり、遊技者の停止操作が煩雑になってしまう。そこで、本発明に係る遊技機では、報知状態中は、報知状態に関する特典を付与可能な第1の操作態様と同量の遊技用価値が付与される第2の操作態様を報知し、第1の操作態様は報知しない。これにより、利益バランスを考慮して第1の操作態様を煩雑な操作態様とした場合であっても、報知状態中はより簡易な第2の操作態様で遊技を行えば足りるため、報知状態中の遊技をスムーズに行うことができる。
According to such a gaming machine, when the specific combination is determined as the winning combination in the non-notification state, the stop operation is performed in the first operation mode and the first result display is derived, and the privilege related to the notification state is obtained. Is given. On the other hand, when the second result display is derived by performing the stop operation in the second operation mode, a predetermined amount of gaming value that is the same as when the first result display is derived is given. However, the privilege related to the notification state is not given, and when the stop operation is performed in the third operation mode, only the game value less than the predetermined amount is added, and the privilege related to the notification state is also given. Not granted. As described above, according to the gaming machine of the present invention, it is possible to realize a gaming property in which the player can participate in the determination result of the privilege grant.
Further, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, the winning combination to be notified during the notification state is used as a specific winning combination to which a privilege can be given according to the type of operation mode. Here, considering the profit balance, it is preferable that the first operation mode having the largest profit among the plurality of operation modes is an operation mode that is difficult to be established, but in order to give a gaming value in the notification state. If the operation mode to be notified is set as the first operation mode, the first operation mode that is difficult to be established at the time of winning the specific winning combination (notification target winning combination) is requested, and the stopping operation of the player becomes complicated. Will end up. Therefore, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, during the notification state, the second operation mode in which the same amount of gaming value is given as the first operation mode in which the privilege relating to the notification state can be given is notified, and the first operation mode is given. The operation mode is not notified. With this, even when the first operation mode is a complicated operation mode in consideration of the profit balance, it is sufficient to play the game in the simpler second operation mode during the notification state. Can be played smoothly.
また、本発明に係る遊技機において、前記遊技制御手段は、前記特定役が当籤役として決定された遊技において、変動表示している前記可変表示手段に対する停止操作が所定のタイミングで行われた場合に、前記第1の操作態様で停止操作が行われたとして、前記第1の結果表示を導出し、当該遊技において、変動表示している複数の前記可変表示手段に対する停止操作が所定の順序で行われた場合に、前記第2の操作態様で停止操作が行われたとして、前記第2の結果表示を導出することを特徴とする。 Further, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, the game control means, in a game in which the specific winning combination is determined as a winning combination, when a stop operation for the variable display means that is variably displayed is performed at a predetermined timing. In addition, assuming that the stop operation is performed in the first operation mode, the first result display is derived, and in the game, the stop operation for the plurality of variable display means that are variably displayed is in a predetermined order. If the stop operation is performed in the second operation mode, the second result display is derived.
このような遊技機によれば、報知状態に関する特典を受けるためには、遊技者は適切なタイミングで停止操作を行う必要があるが、単に所定量の遊技用価値を得るだけであれば、遊技者は適切な順序で停止操作を行えば足りる。その結果、非報知状態中に報知状態に関する特典を受けるための第1の操作態様は成立困難にしつつも、報知状態中は煩雑な操作態様を必要とすることなく、スムーズに遊技を行うことができる。 According to such a gaming machine, the player needs to perform a stop operation at an appropriate timing in order to receive the privilege related to the notification state, but if only a predetermined amount of gaming value is obtained, the game is played. The person only needs to perform the stop operation in an appropriate order. As a result, it is difficult to establish the first operation mode for receiving the privilege related to the notification state during the non-notification state, but it is possible to smoothly play the game during the notification state without requiring a complicated operation mode. it can.
また、本発明に係る遊技機において、複数の識別表示を変動表示可能な複数の可変表示手段(例えば、リール3L,3C,3R)と、複数の役の中から決定された当籤役に応じて前記可変表示手段を用いた遊技の進行を制御する遊技制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を備える遊技機であって、停止操作の態様を報知可能な報知状態を有するとともに、当籤役として決定された場合に、第1の操作態様で停止操作(例えば、色択に正解の停止操作)が行われると第1の結果表示(例えば、色択小役の入賞)を導出可能、第2の操作態様で停止操作(例えば、押し順に正解の停止操作)が行われると第2の結果表示(例えば、押し順小役の入賞)を導出可能、かつ、前記第1の操作態様及び前記第2の操作態様の何れでもない第3の操作態様で停止操作が行われると第3の結果表示(例えば、こぼし目又ははずれ)を導出可能な特定役(例えば、「色択小役+押し順小役」)を有し、前記第1の結果表示又は前記第2の結果表示の何れかが導出されると、所定量の遊技用価値を付与可能な利益付与手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、非報知状態において前記第1の結果表示が導出されると、前記報知状態に関する特典を付与可能な報知特典付与手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、前記報知特典付与手段により前記特典が付与されたことに応じて、前記報知状態に遷移可能な報知制御手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、遊技者に対して所定の操作態様を報知可能な報知手段(例えば、主制御回路90)と、を更に備え、前記報知手段は、非報知状態において前記特定役が当籤役として決定されると、前記第1の操作態様、前記第2の操作態様及び前記第3の操作態様の何れも報知することなく、前記報知状態において前記特定役が当籤役として決定されると、前記第2の操作態様を報知可能であり、前記遊技制御手段は、前記特定役が当籤役として決定された遊技において、変動表示している複数の前記可変表示手段に対する停止操作が所定の順序で行われた場合に、前記第2の操作態様で停止操作が行われたとして、前記第2の結果表示を導出し、変動表示している複数の前記可変表示手段に対する停止操作が前記所定の順序ではない特定の順序で行われた場合であって、停止操作が所定のタイミングで行われた場合に、前記第1の操作態様で停止操作が行われたとして、前記第1の結果表示を導出し、変動表示している複数の前記可変表示手段に対する停止操作が前記特定の順序で行われた場合であって、停止操作が前記所定のタイミングではない特定のタイミングで行われた場合に、前記第3の操作態様で停止操作が行われたとして、前記第3の結果表示を導出することを特徴とする。
Further, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, a plurality of variable display means (for example,
このような遊技機によれば、上述と同様に、特典付与の決定結果に関して、遊技者が関与可能な遊技性を実現することができるとともに、報知状態中の遊技をスムーズに行うことができる。 According to such a gaming machine, similarly to the above, regarding the determination result of the privilege granting, it is possible to realize the gaming property in which the player can be involved and to smoothly play the game in the notification state.
また、本発明に係る遊技機において、前記特定役が当籤役として決定された遊技において遊技者が無作為に停止操作を行った場合、前記第1の操作態様、前記第2の操作態様及び前記第3の操作態様のうち、前記第1の操作態様が成立する割合が最も低いことを特徴とする。 Further, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, when the player randomly performs a stop operation in a game in which the specific combination is determined as a winning combination, the first operation mode, the second operation mode, and the Among the third operation modes, the ratio of the first operation mode being established is the lowest.
このような遊技機によれば、利益バランスを考慮して第1の操作態様を煩雑な操作態様としつつも、報知状態中の遊技をスムーズに行うことができる。また、第1の操作態様は成立し難い操作態様であるため、特定役の当籤確率を高めたとしても、遊技者に過度な利益(報知状態に関する特典)を付与してしまうことがない。そのため、本発明に係る遊技機では、特定役の当籤確率を高めることができ、結果、遊技者に対して、報知状態に関する特典が付与される機会を多く与えることができる。 According to such a gaming machine, it is possible to smoothly play the game in the notification state while making the first operation mode a complicated operation mode in consideration of the profit balance. Further, since the first operation mode is a difficult operation mode, even if the winning probability of the specific combination is increased, the player is not provided with an excessive profit (a privilege related to the notification state). Therefore, in the gaming machine according to the present invention, it is possible to increase the winning probability of the specific combination, and as a result, it is possible to give the player many opportunities to be given a privilege related to the notification state.
1…パチスロ、3L,3C,3R…リール、4…リール表示窓、6…情報表示器、11…表示装置、17L,17C,17R…ストップボタン、18…サブ表示装置、71…主制御基板、72…副制御基板、90…主制御回路、91…マイクロプロセッサ、101…メインCPU、102…メインROM、103…メインRAM、107…演算回路、114…第1シリアル通信回路、115…第2シリアル通信回路、200…副制御回路、201…サブCPU201、301…第1インターフェースボード、302…第2インターフェースボード
1... Pachi-slot, 3L, 3C, 3R... Reel, 4... Reel display window, 6... Information display, 11... Display device, 17L, 17C, 17R... Stop button, 18... Sub display device, 71... Main control board, 72... Sub control board, 90... Main control circuit, 91... Microprocessor, 101... Main CPU, 102... Main ROM, 103... Main RAM, 107... Arithmetic circuit, 114... First serial communication circuit, 115... Second serial Communication circuit, 200... Sub control circuit, 201...
Claims (2)
当籤役として決定された場合に、所定の操作態様で停止操作が行われると第1の結果表示を導出可能、かつ、前記所定の操作態様とは異なる操作態様で停止操作が行われると第2の結果表示を導出可能な報知対象役を有し、
遊技に関する遊技状態として、第1状態と第2状態とを有し、
前記第1状態において所定条件を満たすと、遊技状態を前記第2状態に移行可能な状態制御手段と、
前記報知対象役が当籤役として決定された遊技において前記第1の結果表示が導出されると、所定数量の遊技用価値を付与可能である一方で、当該遊技において前記第2の結果表示が導出されると、前記所定数量よりも少ない遊技用価値を付与可能な利益付与手段と、
前記第2状態において前記報知対象役が当籤役として決定されると、前記第1の結果表示を導出するために必要な前記所定の操作態様を報知可能な報知手段と、
前記第2状態の継続期間を定める数値情報である、前記第2状態において前記利益付与手段により付与された遊技用価値の総数を計数可能な継続期間計数手段と、
前記第2状態において前記利益付与手段により付与された遊技用価値の数量に応じて前記数値情報を更新可能であるとともに、更新の結果、前記数値情報が終了閾値に達すると、前記第2状態を終了可能な継続期間管理手段と、
前記第2状態において、前記第2状態の継続期間が延長されるように前記数値情報を更新する上乗せ制御を実行可能な上乗せ制御手段と、
を更に備え、
前記継続期間管理手段は、前記第2状態の前記報知対象役が当籤役として決定された遊技において前記報知手段が前記所定の操作態様を報知した場合であっても、遊技者の停止操作の結果として前記第2の結果表示が導出された場合には、導出された前記第2の結果表示に応じて付与される遊技用価値の数量に応じて、前記数値情報を更新する、
ことを特徴とする遊技機。 A gaming machine provided with variable display means capable of variably displaying a plurality of identification displays, and game control means for controlling the progress of a game using the variable display means in accordance with a winning combination determined from a plurality of winning combinations. And
When the winning combination is determined, the first result display can be derived when the stop operation is performed in the predetermined operation mode, and the second result is displayed when the stop operation is performed in the operation mode different from the predetermined operation mode. Has a notification target role that can derive the result display of
As a game state related to the game, it has a first state and a second state,
When a predetermined condition is satisfied in the first state, state control means capable of shifting the game state to the second state,
When the first result display is derived in the game in which the notification target combination is determined as the winning combination, a predetermined amount of game value can be given, while the second result display is derived in the game. Then, a profit giving means capable of giving a gaming value less than the predetermined amount,
When the notification target combination is determined as a winning combination in the second state, a notification unit capable of notifying the predetermined operation mode necessary for deriving the first result display,
Continuation period counting means capable of counting the total number of gaming values given by the profit giving means in the second state, which is numerical information defining the continuation period of the second state,
In the second state, the numerical value information can be updated according to the amount of the gaming value given by the profit giving means, and as a result of the update, when the numerical value information reaches the end threshold value, the second state is set. Term management method that can be terminated,
In the second state, an addition control means capable of executing addition control for updating the numerical information so that the duration of the second state is extended,
Further equipped with,
Even if the notification means notifies the predetermined operation mode in the game in which the notification target combination in the second state is determined as the winning combination, the continuation period management means results in the stop operation of the player. When the second result display is derived as, the numerical value information is updated according to the quantity of the gaming value given according to the derived second result display.
A gaming machine characterized by that.
継続期間管理手段は、複数の役のうちの前記特定役が当籤役として決定されたことに応じて前記利益付与手段により遊技用価値が付与された場合には、前記数値情報を更新しない
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の遊技機。
If the winning combination is determined, the winning combination further includes a specific winning combination that can derive a third result display in which a specified amount of gaming value is added by the profit giving means, regardless of the mode of the stop operation.
The continuation period management means does not update the numerical information when the gaming value is given by the profit giving means in response to the specific winning combination of a plurality of winning combinations being determined as a winning combination. The gaming machine according to claim 1, wherein the gaming machine is a gaming machine.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019000413A JP2020108661A (en) | 2019-01-07 | 2019-01-07 | Game machine |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019000413A JP2020108661A (en) | 2019-01-07 | 2019-01-07 | Game machine |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2020108661A true JP2020108661A (en) | 2020-07-16 |
| JP2020108661A5 JP2020108661A5 (en) | 2021-05-06 |
Family
ID=71570254
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019000413A Pending JP2020108661A (en) | 2019-01-07 | 2019-01-07 | Game machine |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2020108661A (en) |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017202204A (en) * | 2016-05-12 | 2017-11-16 | サミー株式会社 | Slot machine |
| JP2018023426A (en) * | 2016-08-08 | 2018-02-15 | 株式会社ユニバーサルエンターテインメント | Game machine |
| JP2018175562A (en) * | 2017-04-18 | 2018-11-15 | 株式会社ユニバーサルエンターテインメント | Device for games |
| JP2018198668A (en) * | 2017-05-25 | 2018-12-20 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
-
2019
- 2019-01-07 JP JP2019000413A patent/JP2020108661A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017202204A (en) * | 2016-05-12 | 2017-11-16 | サミー株式会社 | Slot machine |
| JP2018023426A (en) * | 2016-08-08 | 2018-02-15 | 株式会社ユニバーサルエンターテインメント | Game machine |
| JP2018175562A (en) * | 2017-04-18 | 2018-11-15 | 株式会社ユニバーサルエンターテインメント | Device for games |
| JP2018198668A (en) * | 2017-05-25 | 2018-12-20 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7133677B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP2020108608A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2020108620A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2020108664A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2020108611A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2020108618A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2020108609A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6999494B2 (en) | Pachinko machine | |
| JP2020108615A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2020108610A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2020108623A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2020108601A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2020062095A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2019201969A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP7046717B2 (en) | Pachinko machine | |
| JP7046714B2 (en) | Pachinko machine | |
| JP7046715B2 (en) | Pachinko machine | |
| JP6999496B2 (en) | Pachinko machine | |
| JP7046716B2 (en) | Pachinko machine | |
| JP2020108661A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2020108660A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2020108659A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2020108663A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2020108662A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2020108658A (en) | Game machine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20210212 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20210323 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20211228 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20220111 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20220705 |