JP2015173291A - semiconductor device - Google Patents
semiconductor device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2015173291A JP2015173291A JP2015112383A JP2015112383A JP2015173291A JP 2015173291 A JP2015173291 A JP 2015173291A JP 2015112383 A JP2015112383 A JP 2015112383A JP 2015112383 A JP2015112383 A JP 2015112383A JP 2015173291 A JP2015173291 A JP 2015173291A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- region
- electrode
- source
- mosfet
- semiconductor
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Electrodes Of Semiconductors (AREA)
- Insulated Gate Type Field-Effect Transistor (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、半導体装置に関し、例えば、IGBT(Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor)、IEGT(Injection Enhanced Gate Transistor)、MOSFET(Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor)、スーパージャンクション型MOSFET、サイリスタ、GTO(Gate Turn Off)サイリスタなど電力制御用の半導体装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a semiconductor device, for example, an IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor), an IEGT (Injection Enhanced Gate Transistor), a MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor), a super junction MOSFET, a thyristor, a GTO (Gate Turn Off). ) It relates to a power control semiconductor device such as a thyristor.
電力制御用の半導体装置には、電力損失を少なくするためにスイッチング動作時のON抵抗が小さいことが求められる。このため、MOSFETやIGBTなどのパワーデバイスでは、ゲート電極をトレンチに埋め込んだトレンチゲート構造が採用されている。 A semiconductor device for power control is required to have a low ON resistance during a switching operation in order to reduce power loss. For this reason, power devices such as MOSFETs and IGBTs employ a trench gate structure in which a gate electrode is embedded in a trench.
トレンチゲート構造では、基板に垂直な縦方向に電流チャネルが形成されるため、横方向のゲート間隔を狭くすることができる。これにより、デバイス構造を微細化して実質的なチャネル幅を広くすることが可能となり、横方向にチャネルが形成されるゲート構造よりもON抵抗を小さくすることができる。また、デバイスサイズを小さくできることから、スイッチング速度を上げて高性能化する点でも有利である。 In the trench gate structure, since the current channel is formed in the vertical direction perpendicular to the substrate, the gate interval in the horizontal direction can be reduced. Thereby, the device structure can be miniaturized and the substantial channel width can be widened, and the ON resistance can be made smaller than that of the gate structure in which the channel is formed in the lateral direction. Further, since the device size can be reduced, it is advantageous in that the switching speed is increased and the performance is improved.
一方、ゲート間隔を狭めてデバイス構造の微細化を進めると、アバランシェ耐量が低下し、また短絡電流が増加する問題がある。これに対し、例えば、特許文献1に開示された技術では、ゲート電極間にベース層へのトレンチコンタクトを形成することにより、ドレイン−ソース間耐圧を維持したままON抵抗を低減することができる。しかしながら、トレンチコンタクトを形成するスペースを要するため、微細化が制限されるという課題も含んでいる。 On the other hand, when the gate interval is narrowed and the device structure is further miniaturized, there is a problem that the avalanche resistance decreases and the short-circuit current increases. In contrast, for example, in the technique disclosed in Patent Document 1, by forming a trench contact to the base layer between the gate electrodes, the ON resistance can be reduced while maintaining the drain-source breakdown voltage. However, since a space for forming a trench contact is required, there is a problem that miniaturization is limited.
ゲート構造を微細化してON抵抗を低減しても、アバランシェ耐量を高く維持できる半導体装置を提供する。 Provided is a semiconductor device capable of maintaining a high avalanche resistance even if the gate structure is miniaturized to reduce the ON resistance.
半導体装置は、第1電極と、前記第1電極上に設けられた第1導電型の第1半導体領域と、前記第1半導体領域上に設けられた第2導電型の第2半導体領域と、前記第1半導体領域上に位置し、前記第1電極から前記第1半導体領域に向かう第1方向に直交する第2方向において複数設けられた第2電極と、前記第1半導体領域上に位置し、前記第2方向において前記第2電極間に設けられた第3電極と、を有し、前記第1方向における前記第2電極の上面から前記第1電極までの長さが、前記第1方向における前記第3電極の上面から前記第1電極までの長さよりも大きい。 The semiconductor device includes: a first electrode; a first conductivity type first semiconductor region provided on the first electrode; a second conductivity type second semiconductor region provided on the first semiconductor region; A plurality of second electrodes provided on the first semiconductor region and provided in a second direction orthogonal to the first direction from the first electrode toward the first semiconductor region; and located on the first semiconductor region. A third electrode provided between the second electrodes in the second direction, and a length from the upper surface of the second electrode to the first electrode in the first direction is the first direction. Is longer than the length from the upper surface of the third electrode to the first electrode.
ゲート構造を微細化してON抵抗を低減しても、アバランシェ耐量を高く維持できる半導体装置を実現することができる。 Even if the gate structure is miniaturized to reduce the ON resistance, a semiconductor device capable of maintaining a high avalanche resistance can be realized.
以下、本発明の実施の形態について図面を参照しながら説明する。なお、以下の実施形態では、図面中の同一部分には同一番号を付してその詳しい説明は適宜省略し、異なる部分について適宜説明する。また、以下の説明において、第1導電型はP型、第2導電型はN型をそれぞれ意味する。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. In the following embodiments, the same parts in the drawings are denoted by the same reference numerals, detailed description thereof will be omitted as appropriate, and different parts will be described as appropriate. In the following description, the first conductivity type means P type, and the second conductivity type means N type.
[第1実施形態]
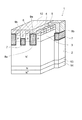
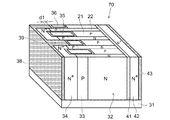
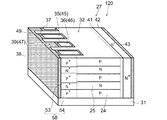
図1は、第1実施形態に係る半導体装置の構造を模式的に示す部分断面図である。ここでは、半導体装置の例としてMOSFET1を取り上げて説明するが、IGBTおよびIEGT等、他の半導体装置にも適用可能である。
[First Embodiment]
FIG. 1 is a partial cross-sectional view schematically showing the structure of the semiconductor device according to the first embodiment. Here, MOSFET 1 will be described as an example of a semiconductor device, but the present invention can also be applied to other semiconductor devices such as IGBT and IEGT.
図1に示すように、本実施形態に係る半導体装置は、N型のドリフト領域2と、ドリフト領域2に接して設けられたP型の第1半導体領域であるベース領域3と、を備えている。また、ベース領域3を挟んでドリフト領域2に対向する主電極であるソース電極12が設けられ、ベース領域3に電気的に接続される。一方、ドリフト領域2とベース領域3との境界には、トレンチ構造の複数の第1ゲート電極であるゲート電極6が境界に沿って設けられる。第1ゲート電極は、ドリフト領域2とベース領域3とに第1のゲート絶縁膜であるゲート絶縁膜8aを介して接している。 As shown in FIG. 1, the semiconductor device according to the present embodiment includes an N-type drift region 2 and a base region 3 that is a P-type first semiconductor region provided in contact with the drift region 2. Yes. A source electrode 12 that is a main electrode facing the drift region 2 with the base region 3 interposed therebetween is provided and is electrically connected to the base region 3. On the other hand, at the boundary between the drift region 2 and the base region 3, a plurality of gate electrodes 6 that are first gate electrodes having a trench structure are provided along the boundary. The first gate electrode is in contact with the drift region 2 and the base region 3 via a gate insulating film 8a that is a first gate insulating film.
さらに、2つのゲート電極6の間において、トレンチ構造の第2ゲート電極であるゲート電極7が、ドリフト領域2とベース領域3との境界に沿って、ドリフト領域2とベース領域3とに第2のゲート絶縁膜であるゲート絶縁膜8bを介して接するように設けられている。ゲート電極7は、ドリフト領域2とベース領域3との間の境界からソース電極12に向かう方向において、ベース領域3に接する長さがゲート電極6よりも短く設けられている。 Furthermore, between the two gate electrodes 6, the gate electrode 7, which is the second gate electrode of the trench structure, extends along the boundary between the drift region 2 and the base region 3 to the drift region 2 and the base region 3. The gate insulating film 8b, which is a gate insulating film, is provided so as to be in contact therewith. The gate electrode 7 has a length shorter than the gate electrode 6 in contact with the base region 3 in the direction from the boundary between the drift region 2 and the base region 3 toward the source electrode 12.
また、ソース電極12は、2つのゲート電極6の間において、ソース電極からゲート電極7に向かう方向に設けられたトレンチ9bの中に、ゲート電極7に近接した位置まで延在している。さらに、ソース電極12は、ゲート電極6のソース電極12側の端と、ゲート電極7のソース電極12側の端と、の間において、トレンチ9bの内壁面に露出したベース領域3に接している。 The source electrode 12 extends between the two gate electrodes 6 in a trench 9 b provided in a direction from the source electrode toward the gate electrode 7 to a position close to the gate electrode 7. Further, the source electrode 12 is in contact with the base region 3 exposed on the inner wall surface of the trench 9b between the end of the gate electrode 6 on the source electrode 12 side and the end of the gate electrode 7 on the source electrode 12 side. .
さらに、図1のソース電極12を除いた部分に示すように、本実施形態に係るMOSFET1では、ベース領域3とソース電極12との間に、N型の第2半導体領域であるソース領域4とP型のコンタクト領域5とが、選択的に設けられている。トレンチ9aの中に設けられたゲート電極6は、ゲート絶縁膜8aを介してドリフト領域2、ベース領域3およびソース領域4に接しており、ベース領域3とゲート絶縁膜8aとの界面に形成されるチャネルを制御する。一方、トレンチ9bでは、ソース電極12がゲート電極7に向かって延在し、トレンチ9bの内壁面に露出した、ソース領域4とドリフト領域2との間のベース領域3に接している。 Further, as shown in the portion excluding the source electrode 12 in FIG. 1, in the MOSFET 1 according to the present embodiment, the source region 4 that is an N-type second semiconductor region is provided between the base region 3 and the source electrode 12. A P-type contact region 5 is selectively provided. The gate electrode 6 provided in the trench 9a is in contact with the drift region 2, the base region 3 and the source region 4 through the gate insulating film 8a, and is formed at the interface between the base region 3 and the gate insulating film 8a. Control the channel. On the other hand, in the trench 9b, the source electrode 12 extends toward the gate electrode 7 and is in contact with the base region 3 between the source region 4 and the drift region 2 exposed on the inner wall surface of the trench 9b.
例えば、図16に示す従来のMOSFETでは、トレンチ内に設けられた全てのゲート電極6が、ゲート絶縁膜8を介してドレイン領域2、ベース領域3およびソース領域4に接している。したがって、例えば、ドリフト領域2からベース領域3に注入される正孔は、ベース領域3の上に選択的に設けられたコンタクト領域5を介してソース電極12に排出される。これに対し、本実施形態に係るMOSFET1では、ゲート電極7を設けることにより、トレンチ9bの内壁面に露出したベース領域3から直接ソース電極12へ正孔を排出できる構成となっている。 For example, in the conventional MOSFET shown in FIG. 16, all the gate electrodes 6 provided in the trench are in contact with the drain region 2, the base region 3 and the source region 4 through the gate insulating film 8. Therefore, for example, holes injected from the drift region 2 into the base region 3 are discharged to the source electrode 12 through the contact region 5 selectively provided on the base region 3. On the other hand, in the MOSFET 1 according to the present embodiment, by providing the gate electrode 7, holes can be directly discharged from the base region 3 exposed on the inner wall surface of the trench 9b to the source electrode 12.
また、ドリフト領域2のベース領域3に接する面の反対側には、ドリフト領域2よりもN型不純物の濃度が高いN型半導体領域13とN型のドレイン領域14が設けられている。さらに、図示しないドレイン電極が、ドレイン領域14に電気的に接続されて設けられている。ここで、例えば、ドレイン領域14をP型不純物がドープされた半導体領域とすれば、図1は、IGBTまたはIEGTの構造となる。 An N-type semiconductor region 13 and an N-type drain region 14 having a higher concentration of N-type impurities than the drift region 2 are provided on the opposite side of the surface of the drift region 2 that contacts the base region 3. Further, a drain electrode (not shown) is provided so as to be electrically connected to the drain region 14. Here, for example, if the drain region 14 is a semiconductor region doped with a P-type impurity, FIG. 1 has an IGBT or IEGT structure.
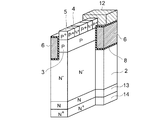
図2は、第1実施形態に係るMOSFET1の動作を説明する模式図である。図2(a)は、MOSFET1の断面構造の一部を模式的に示している。図2(b)および(c)は、MOSFETの動作を示す断面図である。 FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram for explaining the operation of the MOSFET 1 according to the first embodiment. FIG. 2A schematically shows a part of the cross-sectional structure of the MOSFET 1. 2B and 2C are cross-sectional views showing the operation of the MOSFET.
MOSFET1のON抵抗を小さくするためには、図2(a)に示すゲート電極6およびゲート電極7の間のベース領域3の幅WCを狭くして、MOSFET1に含まれるゲート電極6の数を増やすことができる。これにより、ゲート絶縁膜8とベース領域3との界面に形成される電流チャネルの数を増やすことができ、ON抵抗を低減することが可能となる。 To reduce the ON resistance of MOSFET1 is to reduce the width W C of the base region 3 between the gate electrode 6 and the gate electrode 7 shown in FIG. 2 (a), the number of gate electrodes 6 included in MOSFET1 Can be increased. Thereby, the number of current channels formed at the interface between the gate insulating film 8 and the base region 3 can be increased, and the ON resistance can be reduced.
一方、ベース領域3の幅WCが狭くなると、ベース領域3に含まれるP型不純物の量が少なくなる。例えば、200nm以下まで微細化すると、ベース領域3に含まれるP型不純物の量に対して、ドリフト領域2からベース領域3に注入される正孔の量が無視できなくなる。すなわち、ベース領域3とゲート絶縁膜8との界面に形成される電流チャネルが影響を受けるという問題が生じる。例えば、プラスチャージを持つ正孔が注入されると、ベース領域3のP型のキャリア濃度が実質的に変化し閾値電圧VTHが変動する。このため、ゲート電極に印加するゲート電圧によってソース−ドレイン間に流れる電流を制御できなくなることがある。 On the other hand, if the width W C of the base region 3 is narrowed, the amount of P-type impurity contained in the base region 3 is reduced. For example, when miniaturization to 200 nm or less, the amount of holes injected from the drift region 2 into the base region 3 cannot be ignored with respect to the amount of P-type impurities contained in the base region 3. That is, there arises a problem that a current channel formed at the interface between the base region 3 and the gate insulating film 8 is affected. For example, when positively charged holes are injected, the P-type carrier concentration in the base region 3 substantially changes, and the threshold voltage V TH varies. For this reason, the current flowing between the source and the drain may not be controlled by the gate voltage applied to the gate electrode.
したがって、ベース領域3の幅WCを狭く形成する場合には、ベース領域3に正孔が蓄積されないように、P型のコンタクト領域5を介してソース電極12へ正孔をスムーズに排出させる必要がある。例えば、図16に示す従来のMOSFETのように、ゲート電極6がソース領域4およびコンタクト領域5に隣接し、ベース領域3を挟んでゲート電極6と左右対称に設けられているような構造では、ベース領域3に注入された正孔は、コンタクト領域5を介してソース電極12に移動する。このため、コンタクト領域5の幅WPを広く設ける必要があるが、そうするとソース領域4の幅WNが相対的に狭くなりON抵抗が増加してしまう。 Therefore, in the case of narrower width W C of the base region 3, as a hole in the base region 3 is not accumulated, it must be discharged smoothly holes to the source electrode 12 through the contact region 5 of the P-type There is. For example, as in the conventional MOSFET shown in FIG. 16, the gate electrode 6 is adjacent to the source region 4 and the contact region 5, and is provided symmetrically with the gate electrode 6 with the base region 3 interposed therebetween. The holes injected into the base region 3 move to the source electrode 12 through the contact region 5. Therefore, it is necessary to provide wider W P of the contact region 5, but then the width W N of the source region 4 is relatively narrow and becomes ON resistance increases.
そこで、本実施形態に係るMOSFETでは、ゲート電極7がベース領域3に隣接する長さが、ゲート電極6がベース領域3に隣接する長さよりも短くなるように、ゲート電極7がゲート絶縁膜8bを介してドリフト領域2とベース領域3の一部に隣接するように設ける。これにより、ソース電極12がゲート電極7とソース領域4との間に露出したベース領域3の一部に接する構造としている。 Therefore, in the MOSFET according to the present embodiment, the gate electrode 7 is formed in the gate insulating film 8b so that the length of the gate electrode 7 adjacent to the base region 3 is shorter than the length of the gate electrode 6 adjacent to the base region 3. Are provided adjacent to part of the drift region 2 and the base region 3. Thus, the source electrode 12 is in contact with a part of the base region 3 exposed between the gate electrode 7 and the source region 4.
図2(b)に示すように、ドリフト領域2からベース領域3に注入された正孔は、ゲート電極7とソース領域4との間のベース領域3と、ソース電極12と、がコンタクトする部分からソース電極12へと排出される。したがって、ソース電極12がベース領域3にコンタクトする部分の、ソース領域4からドリフト領域2へ向かう方向の幅d1を広くした方が、正孔の排出がよりスムーズになる。例えば、d1>0.05μmとすることができる。 As shown in FIG. 2B, the holes injected from the drift region 2 into the base region 3 are portions where the base region 3 between the gate electrode 7 and the source region 4 and the source electrode 12 are in contact with each other. To the source electrode 12. Therefore, when the width d 1 in the direction from the source region 4 to the drift region 2 at the portion where the source electrode 12 is in contact with the base region 3 is widened, holes are discharged more smoothly. For example, d 1 > 0.05 μm can be set.
これにより、正孔がベース領域3に蓄積されることがなく、VTHの変動を抑えることが可能となる。また、ドリフト領域2からベース領域3を介してソース電極12へ排出される正孔の排出抵抗が小さくなることから、ドリフト領域2で発生する正孔をスムーズに排出してアバランシェ耐量を向上させる効果も得られる。 This prevents the holes are accumulated in the base region 3, it is possible to suppress variation in V TH. In addition, since the discharge resistance of holes discharged from the drift region 2 to the source electrode 12 via the base region 3 is reduced, the holes generated in the drift region 2 can be discharged smoothly and the avalanche resistance can be improved. Can also be obtained.
一方、本実施形態に係るMOSFETでは、ゲート電極7がソース領域4から離間するため、ゲート電極7とベース領域3の間に形成されるチャネルを介してソース領域4からドリフト層2へ直接流れる電流パスが無くなるという不利な効果も生じる。しかしながら、ベース領域3の幅WCを狭くした場合には、図2(b)中に示すように、ゲート電極7側のチャネルを介して流れる電流IN2も、ゲート電極6側の電流チャネルを流れる電流IN1に合流して寄与するので、チャネル抵抗が低くなりON抵抗を低減する効果が得られるようになる。 On the other hand, in the MOSFET according to the present embodiment, since the gate electrode 7 is separated from the source region 4, the current that flows directly from the source region 4 to the drift layer 2 through the channel formed between the gate electrode 7 and the base region 3. There is also the detrimental effect of having no pass. However, when decreasing the width W C of the base region 3, as shown in FIG. 2 (b), the current I N2 flowing through the channel of the gate electrode 7 side, the current channel of the gate electrode 6 side Since it joins and contributes to the flowing current I N1 , the channel resistance is lowered and the effect of reducing the ON resistance can be obtained.
上記の本実施態様に係るMOSFETの効果を別の観点から見れば、次のように捉えることができる。すなわち、コンタクト領域5とベース領域3とを合わせたP型領域にソース電極12が接触する面積を比較した場合、ゲート電極6が埋め込まれたトレンチ9aよりも、ゲート電極7が埋め込まれたトレンチ9bのほうが、ソース電極12が広い面積でP型領域に接触する。したがって、ソース電極12がP型領域に接触する面積を相対的に広くすることが可能となり、ベース領域3からソース電極12へ正孔を効率良く排出することができる。 If the effect of the MOSFET according to the present embodiment is viewed from another viewpoint, it can be grasped as follows. That is, when comparing the area where the source electrode 12 is in contact with the P-type region including the contact region 5 and the base region 3, the trench 9b in which the gate electrode 7 is embedded rather than the trench 9a in which the gate electrode 6 is embedded. In this case, the source electrode 12 is in contact with the P-type region over a larger area. Therefore, the area where the source electrode 12 contacts the P-type region can be relatively widened, and holes can be efficiently discharged from the base region 3 to the source electrode 12.
図2(c)は、ゲート電極7とベース領域3との間に形成されるNチャネル16を示す模式図である。ゲート電極7にプラスのゲート電圧が印加されると、ゲート絶縁膜8とベース領域3との界面に電子が引き寄せられた反転層が形成される。同図中に示すように、この反転層は、ゲート電極7のソース領域側の端部でソース電極12方向に広がって形成される。このチャネル端部16aがソース電極12につながると、ソース電極12からドリフト層2に電流パスが形成され、過剰電流が流れてしまう恐れがある。そこで、トレンチ9bの内壁面側のゲート電極7の端部とソース電極との間の間隔d2を、ある程度広くしておくと良い。例えば、d2>0.05μmとすることができる。 FIG. 2C is a schematic diagram showing an N channel 16 formed between the gate electrode 7 and the base region 3. When a positive gate voltage is applied to the gate electrode 7, an inversion layer in which electrons are attracted to the interface between the gate insulating film 8 and the base region 3 is formed. As shown in the figure, the inversion layer is formed to extend in the direction of the source electrode 12 at the end of the gate electrode 7 on the source region side. When the channel end portion 16a is connected to the source electrode 12, a current path is formed from the source electrode 12 to the drift layer 2, and there is a possibility that an excessive current flows. Therefore, the distance d 2 between the end and the source electrode of the gate electrode 7 of the inner wall surface of the trench 9b, it is advisable to some extent widened. For example, d 2 > 0.05 μm can be set.
例えば、ゲート電極7の端部とソース電極12との間にd2>0.05μmとなるような厚さのゲート絶縁膜8を形成することもできるし、また、ゲート電極7の端部とソース電極12との間に空隙を設けても良い。 For example, a gate insulating film 8 having a thickness such that d 2 > 0.05 μm can be formed between the end of the gate electrode 7 and the source electrode 12, and the end of the gate electrode 7 A gap may be provided between the source electrode 12 and the source electrode 12.
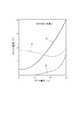
図3は、第1実施形態に係るMOSFET1の特性を示すグラフである。縦軸にソース−ドレイン間に流れるドレイン電流を示し、横軸にゲート電圧を示している。同図中に示すグラフAは、本実施形態に係るMOSFET1の特性を示している。また、グラフBは、ゲート電極7とソース領域4との間でソース電極12がベース領域3と接する部分の幅d1が0.05μmよりも狭い場合のドレイン電流を示している。一方、グラフCは、図16に示す従来のMOSFETの特性を示している。 FIG. 3 is a graph showing the characteristics of the MOSFET 1 according to the first embodiment. The vertical axis represents the drain current flowing between the source and the drain, and the horizontal axis represents the gate voltage. A graph A shown in the figure shows the characteristics of the MOSFET 1 according to the present embodiment. Graph B shows the drain current when the width d1 of the portion where the source electrode 12 is in contact with the base region 3 between the gate electrode 7 and the source region 4 is narrower than 0.05 μm. On the other hand, graph C shows the characteristics of the conventional MOSFET shown in FIG.
図3中に示すように、ソース−ドレイン間のバイアス電圧Vdを44V印加しても、ゲート電圧が0Vであれば、グラフAに示す本実施形態に係るMOSFET1ではドレイン電流は流れない。一方、グラフBおよびCに示すMOSFETではドレイン電流が流れる。すなわち、d1<0.05μmとしたグラフBに示すMOSFET、およびグラフCに示す従来のMOSFETでは、ゲート制御が不能となる場合があることを示している。したがって、d1>0.05μmとして、ベース領域3から直接ソース電極12へ正孔を排出する構造とした、本実施形態に係るMOSFET1の方が有利であることがわかる。 As shown in FIG. 3, the source - even when the bias voltage V d between the drain and 44V is applied, when the gate voltage is 0V, MOSFET 1 in the drain current according to the present embodiment shown in graph A does not flow. On the other hand, a drain current flows in the MOSFETs shown in graphs B and C. That is, in the MOSFET shown in the graph B in which d1 <0.05 μm and the conventional MOSFET shown in the graph C, gate control may be disabled. Therefore, it can be seen that the MOSFET 1 according to this embodiment is more advantageous in that d1> 0.05 μm and holes are discharged directly from the base region 3 to the source electrode 12.
図4は、第1実施形態の変形例に係るMOSFET10の構造を模式的に示す部分断面図である。ソース領域4とゲート電極7との間に露出したベース領域3と、ソース電極12と、が接する部分に、P型不純物濃度がベース領域3よりも高い第3の半導体領域であるP+領域18を設けている点において、図1に示すMOSFET1と異なる。このP+領域18を設けることにより、ソース−ドレイン間に流れる過剰なドレイン電流を抑制することができる。 FIG. 4 is a partial cross-sectional view schematically showing the structure of the MOSFET 10 according to a modification of the first embodiment. In a portion where the base region 3 exposed between the source region 4 and the gate electrode 7 and the source electrode 12 are in contact with each other, a P + region 18 which is a third semiconductor region having a P-type impurity concentration higher than that of the base region 3. Is different from MOSFET 1 shown in FIG. By providing the P + region 18, an excessive drain current flowing between the source and the drain can be suppressed.
図5および図6は、第1実施形態に係るMOSFET1およびMOSFET10の特性を示すグラフである。縦軸にソース−ドレイン間の負荷がショートした時に流れる短絡電流を示し、横軸にドレイン電圧を示している。同図中のグラフAは、MOSFET1の短絡電流を示し、グラフDは、MOSFET10の短絡電流を示している。また、グラフCは、図16に示す従来のMOSFETの短絡電流を示している。 5 and 6 are graphs showing the characteristics of the MOSFET 1 and the MOSFET 10 according to the first embodiment. The vertical axis represents the short-circuit current that flows when the load between the source and drain is short-circuited, and the horizontal axis represents the drain voltage. Graph A in the figure shows the short-circuit current of MOSFET 1, and graph D shows the short-circuit current of MOSFET 10. Graph C shows the short-circuit current of the conventional MOSFET shown in FIG.
グラフAに示すMOSFET1では、ゲート電極7側に形成されるチャネル16が直接ソース領域4につながっていないため、短絡電流は、ゲート電極6側の電流チャネルに流れる電流と合流してソース領域2に集中して流れる。したがって、ゲート電極7側のチャネルにも電流が流れる従来のMOSFETに比べて、過剰に流れる短絡電流に対する抵抗が大きくなる。その結果、グラフCに示す従来のMOSFETに比べて、短絡電流が約1/2に制限される。これにより、ゲート電極6および7に印加するゲート電圧を0Vとして、短絡電流を遮断することが可能になる。 In the MOSFET 1 shown in the graph A, since the channel 16 formed on the gate electrode 7 side is not directly connected to the source region 4, the short-circuit current merges with the current flowing in the current channel on the gate electrode 6 side to the source region 2. Concentrate and flow. Therefore, the resistance to the short-circuit current that flows excessively increases as compared with the conventional MOSFET in which current also flows in the channel on the gate electrode 7 side. As a result, compared to the conventional MOSFET shown in graph C, the short circuit current is limited to about ½. As a result, the gate voltage applied to the gate electrodes 6 and 7 can be set to 0 V to cut off the short-circuit current.
一方、グラフDに示すMOSFET10では、さらに短絡電流が減少し、従来のMOSFETに比べて約1/5、グラフAに示すMOSFET1の約1/3になっている。これは、ベース領域3に設けられたP+領域18が、電流パスを狭めて短絡電流を制限しているためと考えられる。これにより、ソース−ドレイン間につながれた負荷が短絡したとしても、ゲート電圧によって短絡電流を制御することが容易となる。 On the other hand, in the MOSFET 10 shown in the graph D, the short-circuit current is further reduced to about 1/5 of the conventional MOSFET and about 1/3 of the MOSFET 1 shown in the graph A. This is presumably because the P + region 18 provided in the base region 3 narrows the current path and limits the short-circuit current. Thereby, even if the load connected between the source and the drain is short-circuited, it becomes easy to control the short-circuit current by the gate voltage.
図6は、短絡電流とドレイン電圧と関係を示す図5のグラフの低電圧部を拡大して示している。同図中に示すように、短絡電流が0.12A程度までは、従来のMOSFETの特性を示すグラフCとMOSFET1の特性を示すグラフAとは、ほぼ一致している。すなわち、0.12A程度までのドレイン電流に対しては、ゲート電極7側のチャネルをソース領域4から離間して設けたMOSFET1でも、チャネル抵抗は高くならず低いON抵抗を維持できることを示している。 FIG. 6 is an enlarged view of the low voltage portion of the graph of FIG. 5 showing the relationship between the short-circuit current and the drain voltage. As shown in the figure, until the short-circuit current is about 0.12 A, the graph C showing the characteristics of the conventional MOSFET and the graph A showing the characteristics of the MOSFET 1 are substantially the same. In other words, for the drain current up to about 0.12 A, the MOSFET 1 in which the channel on the gate electrode 7 side is separated from the source region 4 can maintain a low ON resistance without increasing the channel resistance. .
一方、グラフDに示すMOSFET10では、ベース領域3にP+領域18を設けたことにより、チャネル抵抗がやや高くなっているが、短絡電流の抑制効果が高いことがわかる。 On the other hand, in the MOSFET 10 shown in the graph D, the channel resistance is slightly increased by providing the P + region 18 in the base region 3, but it can be seen that the short-circuit current suppressing effect is high.
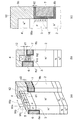
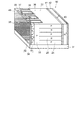
図7は、第1実施形態の変形例に係るMOSFET20および30の構造を模式的に示す部分断面図である。 FIG. 7 is a partial cross-sectional view schematically showing the structure of MOSFETs 20 and 30 according to a modification of the first embodiment.
図7(a)に示すMOSFET20では、ベース領域3の方向にコンタクト領域5をソース領域4よりも深く形成している。これにより、ドリフト層2からベース領域3に注入された正孔をP型のコンタクト領域5を介して排出する経路の排出抵抗を下げることができる。その結果、ベース領域のP型キャリアの濃度変動を抑制して、ゲート電圧によるドレイン電流の制御性を改善することができ、また、ベース領域3とドリフト層2との間のアバランシェ耐量を向上させることもできる。 In the MOSFET 20 shown in FIG. 7A, the contact region 5 is formed deeper than the source region 4 in the direction of the base region 3. As a result, the discharge resistance of the path through which holes injected from the drift layer 2 into the base region 3 are discharged through the P-type contact region 5 can be lowered. As a result, the concentration fluctuation of the P-type carrier in the base region can be suppressed, the controllability of the drain current by the gate voltage can be improved, and the avalanche resistance between the base region 3 and the drift layer 2 can be improved. You can also
図7(b)に示すMOSFET30では、図7(a)に示すMOSFET20のベース領域3に、P+領域18をさらに設けた構造となっている。これにより、短絡電流を抑制して短絡耐量を向上させることができる。 The MOSFET 30 shown in FIG. 7B has a structure in which a P + region 18 is further provided in the base region 3 of the MOSFET 20 shown in FIG. Thereby, a short circuit current can be suppressed and a short circuit tolerance can be improved.
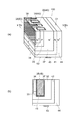
図8は、第1実施形態の変形例に係るMOSFET40および50の構造を模式的に示す部分断面図である。 FIG. 8 is a partial cross-sectional view schematically showing the structure of MOSFETs 40 and 50 according to a modification of the first embodiment.
図8(a)に示すMOSFET30では、ソース領域4は、ゲート電極6に沿ってベース領域3の表面に設けられている。これにより、ゲート電極6とベース領域3との間に形成される電流チャネルの全てにソース領域4を接続することができ、チャネル抵抗を下げてON抵抗を低減することができる。 In the MOSFET 30 shown in FIG. 8A, the source region 4 is provided on the surface of the base region 3 along the gate electrode 6. As a result, the source region 4 can be connected to all the current channels formed between the gate electrode 6 and the base region 3, and the channel resistance can be lowered to reduce the ON resistance.
一方、コンタクト領域5は、ソース領域4と並列にゲート電極7の側に形成されている。これにより、ベース領域3から排出される正孔のパスは、ゲート電極7の側でコンタクトするソース電極のみとなるが、コンタクト面積を広くして正孔の排出抵抗を低減することができる。 On the other hand, the contact region 5 is formed on the gate electrode 7 side in parallel with the source region 4. Thereby, the path of holes discharged from the base region 3 is only the source electrode that contacts on the gate electrode 7 side, but the contact area can be increased to reduce the hole discharge resistance.
図8(b)に示すMOSFET50では、ベース領域3との間の境界に沿って第5半導体領域であるP型ピラー21と第4半導体領域であるN型ピラー22が交互に配置されたスーパージャンクション構造のドリフト領域2が設けられている。スーパージャンクション構造を用いることにより、N型ピラー22の濃度を上げてON抵抗を低減することが可能となる。 In the MOSFET 50 shown in FIG. 8B, a super junction in which P-type pillars 21 as fifth semiconductor regions and N-type pillars 22 as fourth semiconductor regions are alternately arranged along the boundary with the base region 3. A drift region 2 of the structure is provided. By using the super junction structure, it is possible to increase the concentration of the N-type pillar 22 and reduce the ON resistance.
[第2実施形態]
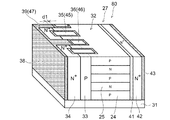
図9は、第2実施形態に係る半導体装置の構造を模式的に示す部分断面図である。本実施形態に係るMOSFET60は、絶縁層31の主面上に設けられた横型構造を有している。なお、絶縁層31は、例えば、基板上に設けられたSiO2等の絶縁膜でも良いし、半絶縁性を有する半導体層であっても良い。
[Second Embodiment]
FIG. 9 is a partial cross-sectional view schematically showing the structure of the semiconductor device according to the second embodiment. The MOSFET 60 according to the present embodiment has a lateral structure provided on the main surface of the insulating layer 31. The insulating layer 31 may be, for example, an insulating film such as SiO 2 provided on the substrate, or a semi-insulating semiconductor layer.
図9(a)に示すように、MOSFET60は、絶縁層31(または半絶縁層)の主面上に設けられたN型の半導体を含むドリフト領域32と、主面に平行な横方向にドリフト領域32に隣接して設けられたP型の第1半導体領域であるベース領域33と、ベース領域33の横方向に隣接して設けられたN型の第2半導体領域であるソース領域34と、を備えている。また、ソース領域34のベース領域33に接する側面の反対側の側面に接して主電極であるソース電極38が設けられている。 As shown in FIG. 9A, the MOSFET 60 includes a drift region 32 including an N-type semiconductor provided on the main surface of the insulating layer 31 (or a semi-insulating layer) and a lateral drift parallel to the main surface. A base region 33 that is a P-type first semiconductor region provided adjacent to the region 32; a source region 34 that is an N-type second semiconductor region provided adjacent to the base region 33 in the lateral direction; It has. Further, a source electrode 38 as a main electrode is provided in contact with the side surface opposite to the side surface in contact with the base region 33 of the source region 34.
また、ドリフト領域32とベース領域33とソース領域34とに跨った表面から絶縁層31方向に、ドリフト領域32とベース領域33との境界に沿って、複数のトレンチ45が形成されている。トレンチ45の中には、第1ゲート電極であるゲート電極35が設けられている。さらに、2つのゲート電極35の間には、ドリフト領域32とベース領域33の一部とに跨った表面から、ドリフト領域32とベース領域33との境界に沿って、絶縁層31の方向にトレンチ46が形成されている。トレンチ46の中には、第2ゲート電極であるゲート電極36が設けられている。したがって、ドリフト領域32とベース領域33との境界からソース電極38に向かう方向において、ゲート電極36がゲート絶縁膜37bを介してベース領域33に接する長さは、ゲート電極35がゲート絶縁膜37aを介してベース領域33に接する長さよりも短く設けられている。 A plurality of trenches 45 are formed along the boundary between the drift region 32 and the base region 33 in the direction from the surface straddling the drift region 32, the base region 33, and the source region 34 toward the insulating layer 31. A gate electrode 35 that is a first gate electrode is provided in the trench 45. Further, a trench is formed between the two gate electrodes 35 from the surface straddling the drift region 32 and a part of the base region 33 in the direction of the insulating layer 31 along the boundary between the drift region 32 and the base region 33. 46 is formed. A gate electrode 36 that is a second gate electrode is provided in the trench 46. Accordingly, in the direction from the boundary between the drift region 32 and the base region 33 toward the source electrode 38, the gate electrode 35 has a length that contacts the base region 33 via the gate insulating film 37b. And a length shorter than the length in contact with the base region 33.
さらに、ソース電極38の一部は、2つのゲート電極35の間で、ソース電極38からゲート電極46に向かう方向に形成されたトレンチ47の中に延在して設けられている。トレンチ47は、ソース領域34とベース領域33の一部とに跨る表面から絶縁層31の方向に形成されている。また、ソース電極38は、トレンチ47の中に、ゲート電極35のソース電極38側の端の位置を超えてゲート電極46に近接した位置まで延在し、ゲート電極36とソース領域34との間のトレンチ47の内壁面に露出したベース領域33に電気的に接続している。 Further, a part of the source electrode 38 is provided between the two gate electrodes 35 so as to extend in a trench 47 formed in a direction from the source electrode 38 to the gate electrode 46. The trench 47 is formed from the surface straddling the source region 34 and a part of the base region 33 in the direction of the insulating layer 31. The source electrode 38 extends in the trench 47 beyond the end of the gate electrode 35 on the source electrode 38 side to a position close to the gate electrode 46, and between the gate electrode 36 and the source region 34. The base region 33 exposed on the inner wall surface of the trench 47 is electrically connected.
また、ドリフト領域32に隣接して、ドリフト領域32よりもN型不純物濃度の高いN型半導体領域41と、N型半導体領域41に隣接してドレイン領域42と、が設けられている。さらに、ドレイン領域42に電気的に接続するドレイン電極43が設けられている。 An N-type semiconductor region 41 having an N-type impurity concentration higher than that of the drift region 32 and a drain region 42 are provided adjacent to the drift region 32 and adjacent to the drift region 32. Further, a drain electrode 43 that is electrically connected to the drain region 42 is provided.
また、図9(b)は、図9(a)中に示すIXb−IXb断面を示す模式図である。同図中に示すように、トレンチ45は、絶縁層31に連通して設けることができる。また、トレンチ45の内面にはゲート絶縁膜37aが形成され、さらに、トレンチ45の内部は、例えば、導電性のポリシリコンからなるゲート電極35で埋められている。トレンチ46に形成されるゲート電極36も、同様に形成することができる。また、以下、図12までに示す実施形態に係るMOSFETにおいても同様である。 Moreover, FIG.9 (b) is a schematic diagram which shows the IXb-IXb cross section shown in Fig.9 (a). As shown in the figure, the trench 45 can be provided in communication with the insulating layer 31. A gate insulating film 37a is formed on the inner surface of the trench 45, and the inside of the trench 45 is filled with a gate electrode 35 made of, for example, conductive polysilicon. The gate electrode 36 formed in the trench 46 can be formed similarly. The same applies to the MOSFETs according to the embodiments shown up to FIG.
本実施形態に係るMOSFET60では、ソース電極38の延在部39が、ソース領域34の表面からベース領域33の表面の一部に跨る表面から絶縁層31に連通するトレンチ47の中に設けられている。これにより、ソース電極38は、ゲート電極36とソース領域34との間のトレンチ47の内面に露出したベース領域33に接触して、ドリフト領域32からベース領域33に注入される正孔を排出することができる。 In the MOSFET 60 according to the present embodiment, the extending portion 39 of the source electrode 38 is provided in a trench 47 that communicates with the insulating layer 31 from the surface extending from the surface of the source region 34 to a part of the surface of the base region 33. Yes. As a result, the source electrode 38 contacts the base region 33 exposed on the inner surface of the trench 47 between the gate electrode 36 and the source region 34, and discharges holes injected from the drift region 32 into the base region 33. be able to.
また、延在部39がベース領域33に接触するコンタクト部分の幅d1を0.05μm以上として、ソース−ドレイン間に流れるドレイン電流がゲート電圧で制御不能となる不具合を防止することが可能である。 Further, the width d1 of the contact portion where the extended portion 39 contacts the base region 33 is set to 0.05 μm or more, so that it is possible to prevent a problem that the drain current flowing between the source and the drain becomes uncontrollable by the gate voltage. .
本実施形態に係るMOSFET60は、絶縁層31の上に形成されるドリフト領域32およびベース領域33、ソース領域34等の厚さが薄い場合には、例えば、絶縁層31の上に設けられた半導体層に、N型およびP型の不純物をイオン注入して形成することができる。また、各半導体領域を厚く設ける場合には、複数回のエピタキシャル成長とイオン注入を組み合わせることにより形成することができる。また、図10に説明する横型のMOSFETにおいても同様である。なお、ここで厚さとは、絶縁層31から各半導体領域の表面方向への層厚を意味するものとする。 The MOSFET 60 according to the present embodiment has, for example, a semiconductor provided on the insulating layer 31 when the drift region 32, the base region 33, the source region 34, and the like formed on the insulating layer 31 are thin. The layer can be formed by ion implantation of N-type and P-type impurities. Moreover, when each semiconductor region is provided thick, it can be formed by combining a plurality of times of epitaxial growth and ion implantation. The same applies to the lateral MOSFET described in FIG. Here, the thickness means a layer thickness from the insulating layer 31 to the surface direction of each semiconductor region.
また、本実施形態においても、例えば、ドレイン領域42をP型不純物がドープされたP型半導体領域とすれば、図9は、IGBTまたはIEGTの構造を示している。以下、図12までに示す実施形態についても同様である。 Also in this embodiment, for example, if the drain region 42 is a P-type semiconductor region doped with a P-type impurity, FIG. 9 shows an IGBT or IEGT structure. The same applies to the embodiments shown up to FIG.
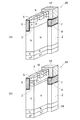
図10は、第2実施形態の変形例に係るMOSFET70の構造を模式的に示す部分断面図である。MOSFET70は、ドリフト領域32において、ドリフト領域32とベース領域33との間の境界に沿って第5の半導体領域であるP型ピラー21と第4の半導体領域であるN型ピラー22とを交互に配置したスーパージャンクション構造を有している。 FIG. 10 is a partial cross-sectional view schematically showing the structure of a MOSFET 70 according to a modification of the second embodiment. In the drift region 32, the MOSFET 70 alternates between the P-type pillar 21 that is the fifth semiconductor region and the N-type pillar 22 that is the fourth semiconductor region along the boundary between the drift region 32 and the base region 33. It has a super junction structure.
図9に示すMOSFET60と同様に、本変形例に係るMOSFET70においても、ソース電極38の延在部36がベース領域33に接触するゲート電極36とソース領域34との間のコンタクト部分からベース領域33の正孔をソース電極38に排出することができる。これにより、閾値電圧VTHを安定させることができるので、ゲート電極35とゲート電極36との間のベース領域33の幅を狭くすることが可能となる。したがって、MOSFETのチャネル数を増やしてチャネル抵抗を低減することができる。さらに、スーパージャンクション構造を用いることにより、ベース領域33につながるN型ピラー22の濃度を高くしてドリフト領域の抵抗を低減することができる。これにより、MOSFET70のON抵抗を低減することが可能である。 Similarly to the MOSFET 60 shown in FIG. 9, also in the MOSFET 70 according to this modification, the base region 33 is formed from the contact portion between the gate electrode 36 and the source region 34 where the extended portion 36 of the source electrode 38 contacts the base region 33. Holes can be discharged to the source electrode 38. Thereby, the threshold voltage VTH can be stabilized, so that the width of the base region 33 between the gate electrode 35 and the gate electrode 36 can be reduced. Therefore, the channel resistance can be reduced by increasing the number of MOSFET channels. Further, by using the super junction structure, the concentration of the N-type pillar 22 connected to the base region 33 can be increased and the resistance of the drift region can be reduced. Thereby, the ON resistance of the MOSFET 70 can be reduced.
図11は、第2実施形態の変形例に係るMOSFET80の構造を模式的に示す部分断面図である。同図中に示すように、MOSFET80のドリフト領域32は、絶縁層31から上部方向へPピラーとNピラーが交互に積層されたスーパージャンクション構造を有している。 FIG. 11 is a partial cross-sectional view schematically showing the structure of a MOSFET 80 according to a modification of the second embodiment. As shown in the figure, the drift region 32 of the MOSFET 80 has a super junction structure in which P pillars and N pillars are alternately stacked upward from the insulating layer 31.
本変形例に係るMOSFET80は、絶縁層31(または半絶縁層)の主面上に、N型の第1半導体層であるN型半導体層24と、P型の第2半導体層であるP型半導体層25と、が交互に設けられた積層体27を備え、ドリフト領域32をスーパージャンクション構造としている。また、積層体27の一方の側面には、第1の主電極であるソース電極38が電気的に接続して設けられ、他方の側面には、第2の主電極であるドレイン電極43が電気的に接続して設けられている。 The MOSFET 80 according to this modification has an N-type semiconductor layer 24 that is an N-type first semiconductor layer and a P-type that is a P-type second semiconductor layer on the main surface of the insulating layer 31 (or a semi-insulating layer). The stacked body 27 in which the semiconductor layers 25 are alternately provided is provided, and the drift region 32 has a super junction structure. Further, a source electrode 38 that is a first main electrode is electrically connected to one side surface of the stacked body 27, and a drain electrode 43 that is a second main electrode is electrically connected to the other side surface. Connected to each other.
さらに、積層体27は、ソース電極38とドレイン電極43との間に、積層体27の表面から絶縁層31の主面に連通して設けられたP型の第1半導体領域であるベース領域33を有している。さらに、ソース電極38とベース領域33とに挟まれたN型の第2半導体領域であるソース領域34と、ベース領域33とドレイン電極43との間にドリフト領域32と、を有している。 Further, the multilayer body 27 is a base region 33 that is a P-type first semiconductor region provided between the source electrode 38 and the drain electrode 43 so as to communicate with the main surface of the insulating layer 31 from the surface of the multilayer body 27. have. Further, a source region 34 which is an N-type second semiconductor region sandwiched between the source electrode 38 and the base region 33, and a drift region 32 is provided between the base region 33 and the drain electrode 43.
また、積層体27には、ソース領域34と、ベース領域33と、ドリフト領域32と、に跨った表面から、絶縁層31の主面に向かってトレンチ45が形成されている。さらに、トレンチ45の中には、第1のゲート電極であるゲート電極35が設けられている。また、ベース領域33の一部と、ドリフト領域32と、に跨った表面から、絶縁層31の主面に向かってトレンチ46が設けられ、トレンチ46の中には、第2のゲート電極であるゲート電極36が設けられている。 In the stacked body 27, a trench 45 is formed from the surface straddling the source region 34, the base region 33, and the drift region 32 toward the main surface of the insulating layer 31. Further, a gate electrode 35 which is a first gate electrode is provided in the trench 45. Further, a trench 46 is provided from a surface straddling a part of the base region 33 and the drift region 32 toward the main surface of the insulating layer 31, and the trench 46 is a second gate electrode. A gate electrode 36 is provided.
2つのゲート電極35の間には、ソース領域34とベース領域33の一部とに跨る表面から絶縁層31主面に向かってトレンチ47が形成されており、トレンチ47の中には、ソース電極38が延在している。延在39は、ソース領域34とゲート電極36との間のトレンチ47の内壁面に露出したベース領域33に接するように設けられている。 A trench 47 is formed between the two gate electrodes 35 from the surface straddling the source region 34 and a part of the base region 33 toward the main surface of the insulating layer 31. 38 extends. The extension 39 is provided in contact with the base region 33 exposed on the inner wall surface of the trench 47 between the source region 34 and the gate electrode 36.
これにより、ドリフト領域32からベース領域33へ注入される正孔がソース電極38へ排出されるので、閾値電圧VTHが安定する。また、アバランシェ耐量および短絡耐量を向上させることができる。 Thereby, the holes injected from the drift region 32 to the base region 33 are discharged to the source electrode 38, so that the threshold voltage VTH is stabilized. Further, the avalanche resistance and the short-circuit resistance can be improved.
一方、ドリフト領域32とドレイン電極43との間には、積層体27の表面から絶縁層31に連通して、N型半導体領域41とドレイン領域42とが設けられている。ドレイン領域42は、N型不純物が高濃度にドープされたN+領域である。本変形例においても、ドレイン領域42にP型不純物をドープしてP+領域とし、IGBTまたはIEGTとすることができる。 On the other hand, an N-type semiconductor region 41 and a drain region 42 are provided between the drift region 32 and the drain electrode 43 so as to communicate with the insulating layer 31 from the surface of the stacked body 27. The drain region 42 is an N + region in which an N-type impurity is doped at a high concentration. Also in this modification, the drain region 42 can be doped with a P-type impurity to form a P + region, which can be an IGBT or an IEGT.
積層体27は、複数回のエピタキシャル成長により絶縁層31の上に複数の半導体層を設け、さらに、各エピタキシャル成長の間に、P型およびN型の不純物を、選択的に所定の場所にイオン注入することにより形成することができる。 In the stacked body 27, a plurality of semiconductor layers are provided on the insulating layer 31 by a plurality of epitaxial growths, and further, P-type and N-type impurities are selectively ion-implanted into a predetermined place during each epitaxial growth. Can be formed.
図12は、第2実施形態の変形例に係るMOSFET90の構造を模式的に示す部分断面図である。MOSFET90は、図11に示すMOSFET80のソース領域34が、P+コンタクト領域51とN+ソース領域52の積層構造に置き換えられた構成となっている。これにより、ベース領域33の正孔をP+コンタクト領域51を介してソース電極38に排出することができる。P+コンタクト領域51とN+ソース領域52は、ぞれぞれイオン注入によって形成することができる。 FIG. 12 is a partial cross-sectional view schematically showing the structure of a MOSFET 90 according to a modification of the second embodiment. The MOSFET 90 has a configuration in which the source region 34 of the MOSFET 80 shown in FIG. 11 is replaced with a stacked structure of a P + contact region 51 and an N + source region 52. Thereby, holes in the base region 33 can be discharged to the source electrode 38 through the P + contact region 51. The P + contact region 51 and the N + source region 52 can be formed by ion implantation, respectively.
また、P+コンタクト領域51とN+ソース領域52の積層方向の厚さは、イオン注入する不純物のドーズ量により変えることができる。例えば、P+コンタクト領域51に注入するP型不純物のドーズ量をN+ソース領域52に注入するN型不純物のドーズ量よりも多くすると、図12中に示すように、P+コンタクト領域51をN+ソース領域52よりも厚くすることができる。これにより、ベース領域33からソース電極38への正孔の排出抵抗を小さくすることができる。また、N+ソース領域52に注入するN型不純物のドーズ量を増やせば、N+ソース領域52を厚くしてON抵抗を低減することもできる。 Further, the thickness in the stacking direction of the P + contact region 51 and the N + source region 52 can be changed depending on the dose amount of the impurity to be ion-implanted. For example, when the dose amount of the P-type impurity implanted into the P + contact region 51 is made larger than the dose amount of the N-type impurity implanted into the N + source region 52, the P + contact region 51 is formed as shown in FIG. It can be made thicker than the N + source region 52. Thereby, the discharge resistance of holes from the base region 33 to the source electrode 38 can be reduced. Further, if the dose of the N-type impurity implanted into the N + source region 52 is increased, the ON resistance can be reduced by increasing the thickness of the N + source region 52.
また、MOSFET90では、ゲート絶縁膜37を介してゲート電極35に隣接してソース電極38の延在部49が設けられているが、図10に示すMOSFET70のように、延在部49を設けないで、ゲート電極35とソース電極38との間にP+コンタクト領域51とN+ソース領域52を介在させても良い。 In the MOSFET 90, the extended portion 49 of the source electrode 38 is provided adjacent to the gate electrode 35 through the gate insulating film 37, but the extended portion 49 is not provided as in the MOSFET 70 shown in FIG. Thus, the P + contact region 51 and the N + source region 52 may be interposed between the gate electrode 35 and the source electrode 38.
[第3実施形態]
図13は、第3実施形態に係るMOSFET100の構造を模式的に示す部分断面図である。
[Third Embodiment]
FIG. 13 is a partial cross-sectional view schematically showing the structure of the MOSFET 100 according to the third embodiment.
MOSFET100は、N型不純物が高濃度にドープされた半導体層であるドレイン層44の第1の主面61に設けられたN型のドリフト領域32と、ドリフト領域32の中に設けられたP型の第1半導体領域であるベース領域33と、ベース領域33の中に設けられたN型の第2半導体領域であるソース領域34と、を備えている。 MOSFET 100 includes an N-type drift region 32 provided on first main surface 61 of drain layer 44, which is a semiconductor layer doped with N-type impurities at a high concentration, and a P-type provided in drift region 32. A base region 33 which is the first semiconductor region, and a source region 34 which is an N-type second semiconductor region provided in the base region 33.
ここでドレイン層44として、例えば、シリコン基板上に形成されたN型半導体層を用いることもできるし、N型不純物が高濃度にドープされたシリコン基板を用いても良い。また、ドレイン層44に代えてP型半導体層を用いると、IGBTまたはIEGTとすることができる。 Here, as the drain layer 44, for example, an N-type semiconductor layer formed on a silicon substrate can be used, or a silicon substrate doped with a high concentration of N-type impurities may be used. Further, when a P-type semiconductor layer is used instead of the drain layer 44, IGBT or IEGT can be obtained.
図13に示す半導体領域の構成は、例えば、所定の凹部が設けられたドレイン層44の第1の主面61に、N型半導体領域41となる半導体層、およびドリフト領域32となる半導体層、ベース領域33となる半導体層、ソース領域34となる半導体層を順次エピタキシャル成長し、さらに、各半導体層が設けられたドレイン層44の第1の主面61をCMP(Chemical Mechanical Polish)を用いて平坦化することにより形成することができる。 The configuration of the semiconductor region shown in FIG. 13 includes, for example, a semiconductor layer that becomes the N-type semiconductor region 41 and a semiconductor layer that becomes the drift region 32 on the first main surface 61 of the drain layer 44 provided with a predetermined recess. A semiconductor layer to be the base region 33 and a semiconductor layer to be the source region 34 are sequentially epitaxially grown, and the first main surface 61 of the drain layer 44 provided with each semiconductor layer is planarized using CMP (Chemical Mechanical Polish). Can be formed.
複数のトレンチ45が、ドリフト領域32とベース領域33との境界に沿ってドレイン層44の第2の主面62に向けて形成されている。また、トレンチ45の中には、第1のゲート電極であるゲート電極35が設けられている。一方、2つのゲート電極35の間には、第トレンチ46が、ドリフト領域32とベース領域33の境界に沿ってドレイン層44の第2の主面62に向けて設けられている。さらに、トレンチ46の中には、第2のゲート電極であるゲート電極36が設けられている。 A plurality of trenches 45 are formed toward the second main surface 62 of the drain layer 44 along the boundary between the drift region 32 and the base region 33. In the trench 45, a gate electrode 35 which is a first gate electrode is provided. On the other hand, a second trench 46 is provided between the two gate electrodes 35 toward the second main surface 62 of the drain layer 44 along the boundary between the drift region 32 and the base region 33. Further, a gate electrode 36 which is a second gate electrode is provided in the trench 46.
また、主電極であるソース電極38が、ソース領域34に接して設けられている。ソース電極38は、例えば、ゲート電極35の配列に沿ってソース領域34の表面からベース領域33に連通するトレンチ55の中に設けることができる。さらに、2つのゲート電極35の間に、ソース領域34とベース領域33の一部とに跨る表面からソース領域34とベース領域62の境界に沿ってトレンチ55の拡張部分が設けられている。ソース電極38は、ゲート電極36に向かってトレンチ55の拡張部分に延在して設けられている。延在部39は、ソース領域34とゲート電極36との間のトレンチ55の張り出し部の内壁面に露出した、ベース領域33に接して設けられている。 A source electrode 38 which is a main electrode is provided in contact with the source region 34. The source electrode 38 can be provided, for example, in a trench 55 that communicates with the base region 33 from the surface of the source region 34 along the arrangement of the gate electrodes 35. Further, an extended portion of the trench 55 is provided between the two gate electrodes 35 along the boundary between the source region 34 and the base region 62 from the surface straddling the source region 34 and a part of the base region 33. The source electrode 38 is provided to extend to the extended portion of the trench 55 toward the gate electrode 36. The extending portion 39 is provided in contact with the base region 33 exposed on the inner wall surface of the protruding portion of the trench 55 between the source region 34 and the gate electrode 36.
図13(b)は、図13(a)中に示されたXIIIb−XIIIb断面の構造を示す模式図である。トレンチ45は、表面からドリフト領域32とベース領域33の境界に沿ってベース領域33およびソース領域34を貫通し、下方のドリフト領域32に達するように形成されている。また、トレンチ45の内面にはゲート絶縁膜37が形成され、ゲート電極35となる、例えば、導電性のポリシリコンが埋め込まれている。 FIG. 13B is a schematic diagram showing the structure of the XIIIb-XIIIb cross section shown in FIG. The trench 45 is formed so as to penetrate the base region 33 and the source region 34 along the boundary between the drift region 32 and the base region 33 from the surface and reach the lower drift region 32. In addition, a gate insulating film 37 is formed on the inner surface of the trench 45, and, for example, conductive polysilicon that becomes the gate electrode 35 is buried.
本実施形態に係るMOSFET100においても、ソース電極38の延在部39が、ゲート電極36とソース領域34との間のトレンチ55の拡張部の内面に露出したベース領域33に接触しており、ドリフト領域32からベース領域33に注入される正孔をソース電極38へ排出することができる。 Also in the MOSFET 100 according to the present embodiment, the extended portion 39 of the source electrode 38 is in contact with the base region 33 exposed on the inner surface of the extended portion of the trench 55 between the gate electrode 36 and the source region 34, and drift. Holes injected from the region 32 into the base region 33 can be discharged to the source electrode 38.
図14(a)は、第3実施形態の変形例に係るMOSFET110の構造を模式的に示す部分断面図である。また、図14(b)は、図14(a)中に示したXIVb−XIVb断面の構造を示す模式図である。 FIG. 14A is a partial cross-sectional view schematically showing the structure of a MOSFET 110 according to a modification of the third embodiment. Moreover, FIG.14 (b) is a schematic diagram which shows the structure of the XIVb-XIVb cross section shown in Fig.14 (a).
MOSFET110は、トレンチ45およびトレンチ46がドレイン層44に達するように設けられ、ゲート電極35およびゲート電極36が埋め込まれている点で、図13に示すMOSFET100と異なる。 MOSFET 110 is different from MOSFET 100 shown in FIG. 13 in that trench 45 and trench 46 are provided to reach drain layer 44 and gate electrode 35 and gate electrode 36 are embedded.
すなわち、図14(a)に示すように、トレンチ45は、ソース領域34およびベース領域33、ドリフト領域32、N型半導体領域41、ドレイン層44に跨ったドレイン層44の第1の主面61側の表面から、第2の主面62方向に設けられている。また、図14(b)に示すように、トレンチ45は、ソース領域34およびベース領域33、ドリフト領域32、N型半導体領域41、を貫通してドレイン層44に達するように設けられている。さらに、トレンチ45の内面には、ゲート絶縁膜37が形成され、ゲート電極35となる、例えば、導電性のポリシリコンが埋め込まれている。 That is, as shown in FIG. 14A, the trench 45 has a first main surface 61 of the drain layer 44 straddling the source region 34 and the base region 33, the drift region 32, the N-type semiconductor region 41, and the drain layer 44. It is provided in the direction of the second main surface 62 from the surface on the side. Further, as shown in FIG. 14B, the trench 45 is provided so as to penetrate the source region 34 and the base region 33, the drift region 32, and the N-type semiconductor region 41 and reach the drain layer 44. Further, a gate insulating film 37 is formed on the inner surface of the trench 45, and, for example, conductive polysilicon that becomes the gate electrode 35 is buried.
一方、ゲート電極36が設けられているトレンチ46も、ベース領域33およびドリフト領域32、N型半導体領域41、ドレイン層44に跨ったドレイン層44の第1の主面61側の表面から、第2の主面62側のドレイン層44に達するように設けられている。 On the other hand, the trench 46 provided with the gate electrode 36 also has the first main surface 61 side surface of the drain layer 44 straddling the base region 33, the drift region 32, the N-type semiconductor region 41, and the drain layer 44. 2 to reach the drain layer 44 on the main surface 62 side.
MOSFET110では、ゲート電極35および36にプラスのゲート電圧が印加されると、ドリフト領域32と、ゲート絶縁膜37との界面に電子が蓄積したチャネルが形成される。これにより、ドリフト領域32の抵抗が下がり、ON抵抗を低減することができる。 In MOSFET 110, when a positive gate voltage is applied to gate electrodes 35 and 36, a channel in which electrons are accumulated is formed at the interface between drift region 32 and gate insulating film 37. Thereby, the resistance of the drift region 32 is lowered, and the ON resistance can be reduced.
[第4実施形態]
図15は、第4実施形態に係る半導体装置120の構造を模式的に示す部分断面図である。半導体装置120は、絶縁層31の主面に交互に積層された複数のP型半導体領域24およびN型半導体領域25からなるスーパージャンクション構造を有する電力制御用半導体装置である。
[Fourth Embodiment]
FIG. 15 is a partial cross-sectional view schematically showing the structure of the semiconductor device 120 according to the fourth embodiment. The semiconductor device 120 is a power control semiconductor device having a super junction structure including a plurality of P-type semiconductor regions 24 and N-type semiconductor regions 25 that are alternately stacked on the main surface of the insulating layer 31.
半導体装置120は、絶縁層31(または半絶縁層)の主面上に、N型半導体領域25と、P型半導体領域24と、が交互に設けられた積層体27を有している。積層体27の一方の側面には、第1の主電極であるソース電極38が電気的に接続して設けられている。また、積層体27の他方の側面には、第2の主電極であるドレイン電極43が電気的に接続して設けられている。 The semiconductor device 120 has a stacked body 27 in which N-type semiconductor regions 25 and P-type semiconductor regions 24 are alternately provided on the main surface of the insulating layer 31 (or semi-insulating layer). On one side surface of the stacked body 27, a source electrode 38 which is a first main electrode is provided in an electrically connected state. In addition, a drain electrode 43 that is a second main electrode is provided on the other side surface of the stacked body 27 in an electrically connected manner.
さらに、ソース電極38とドレイン電極43との間に、P型半導体領域24とN型半導体領域25とが交互に積層されたスーパージャンクション構造のドリフト領域32が設けられている。ドリフト領域32とソース電極38との間には、P型の不純物がP型半導体領域24よりも高濃度にドープされた第2半導体領域であるP+領域54と、N型の不純物がN型半導体領域25よりも高濃度にドープされたN+領域53と、を積層したコンタクト領域58が設けられている。 Furthermore, a drift region 32 having a super junction structure in which P-type semiconductor regions 24 and N-type semiconductor regions 25 are alternately stacked is provided between the source electrode 38 and the drain electrode 43. Between the drift region 32 and the source electrode 38, a P + region 54, which is a second semiconductor region doped with a P-type impurity at a higher concentration than the P-type semiconductor region 24, and an N-type impurity is an N-type impurity. A contact region 58 is provided in which an N + region 53 doped more heavily than the semiconductor region 25 is stacked.
また、コンタクト領域58とドリフト領域32とに跨った表面から、コンタクト領域58とドリフト領域32との境界に沿って、トレンチ45が形成されている。トレンチ45の中には、第1のゲート電極であるゲート電極35が設けられている。さらに、コンタクト領域51の一部と、ドリフト領域32と、に跨った表面から、コンタクト領域58とドリフト領域32との境界に沿ってトレンチ46が形成されている。トレンチ46の中には、第2のゲート電極であるゲート電極36が設けられている。 A trench 45 is formed along the boundary between the contact region 58 and the drift region 32 from the surface straddling the contact region 58 and the drift region 32. In the trench 45, a gate electrode 35 which is a first gate electrode is provided. Furthermore, a trench 46 is formed along the boundary between the contact region 58 and the drift region 32 from the surface straddling a part of the contact region 51 and the drift region 32. A gate electrode 36 that is a second gate electrode is provided in the trench 46.
半導体装置120のソース電極38は、コンタクト領域58のP+領域54とN+領域53に電気的に接続されている。ソース電極38の一部である延在部39は、2つのゲート電極35の間で、ソース電極38からゲート電極36の近傍に至るP+領域54の表面から、絶縁層31の主面に向かって形成されたトレンチ47の中に延在して設けられている。また、延在部39は、トレンチ47の内壁面に露出したコンタクト領域58に電気的に接続されている。また、ゲート電極35にゲート絶縁膜37を介して隣接する延在部49も設けられている。 The source electrode 38 of the semiconductor device 120 is electrically connected to the P + region 54 and the N + region 53 of the contact region 58. The extending portion 39 which is a part of the source electrode 38 extends from the surface of the P + region 54 between the two gate electrodes 35 and from the source electrode 38 to the vicinity of the gate electrode 36 toward the main surface of the insulating layer 31. The trench 47 is formed so as to extend. The extension 39 is electrically connected to the contact region 58 exposed on the inner wall surface of the trench 47. Further, an extending portion 49 adjacent to the gate electrode 35 via the gate insulating film 37 is also provided.
一方、ドリフト領域32とドレイン電極43との間には、N型半導体領域41とドレイン領域42とが、表面から絶縁層31の主面に連通して設けられている。本実施態様に係る半導体装置120では、ドレイン領域42は、N型不純物が高濃度にドープされたN+領域であるが、P型不純物をドープしてP+領域としても良い。その場合には、半導体装置120は、バイポーラ素子として動作する。 On the other hand, an N-type semiconductor region 41 and a drain region 42 are provided between the drift region 32 and the drain electrode 43 so as to communicate with the main surface of the insulating layer 31 from the surface. In the semiconductor device 120 according to this embodiment, the drain region 42 is an N + region doped with an N-type impurity at a high concentration, but may be doped with a P-type impurity to form a P + region. In that case, the semiconductor device 120 operates as a bipolar element.
また、積層体27は、絶縁層31の主面に複数回のエピタキシャル成長により、N型半導体領域25とP型半導体領域24とを積層することによって形成することができる。また、各半導体領域のエピタキシャル成長の間に、イオン注入を用いて選択的にP型およびN型の不純物を注入することによって、上記の積層構造とすることができる。 The stacked body 27 can be formed by stacking the N-type semiconductor region 25 and the P-type semiconductor region 24 on the main surface of the insulating layer 31 by epitaxial growth a plurality of times. Further, by selectively implanting P-type and N-type impurities using ion implantation during the epitaxial growth of each semiconductor region, the above stacked structure can be obtained.
次に、半導体装置120の動作について説明する。半導体装置120では、コンタクト領域58において、N+領域53の積層方向の幅は、P+領域54よりも狭く設ける。さらに、P+領域54とN+領域53との間のPN接合のビルトインポテンシャルにより、N+領域53を空乏化させる。これにより、ドレイン電極43とソース電極38との間にドレイン側がプラスとなるドレイン電圧を印加しても、ゲート電極35および36にゲート電圧が印加されない状態では、ドレイン電流は流れない。 Next, the operation of the semiconductor device 120 will be described. In the semiconductor device 120, the contact region 58 is provided so that the width in the stacking direction of the N + region 53 is narrower than that of the P + region 54. Further, the N + region 53 is depleted by the built-in potential of the PN junction between the P + region 54 and the N + region 53. Thus, even if a drain voltage having a positive drain side is applied between the drain electrode 43 and the source electrode 38, no drain current flows when no gate voltage is applied to the gate electrodes 35 and 36.
次に、ゲート電極35および36にプラスのゲート電圧を印加すると、N+領域53とゲート絶縁膜37との間に電子が蓄積されて電流チャネルが形成される。これにより、ドレイン電極43とソース電極38との間に電流がながれON状態となる。 Next, when a positive gate voltage is applied to the gate electrodes 35 and 36, electrons are accumulated between the N + region 53 and the gate insulating film 37 to form a current channel. As a result, a current flows between the drain electrode 43 and the source electrode 38 to be turned on.
この際、N+領域53にドリフト領域32のN型半導体層25から正孔が注入されると、N+領域53の実効的な濃度が変化してチャネル抵抗が高くなりON抵抗が上昇してしまう場合がある。 In this case, the positive holes from the N-type semiconductor layer 25 of the drift region 32 to the N + region 53 is implanted, the effective concentration is higher channel resistance changes the ON resistance of the N + region 53 rises May end up.
これに対し半導体装置120では、ソース電極38がトレンチ47の内壁面に露出したコンタクト領域58のN+領域53に電気的に接続されているので、N+領域53に注入された正孔をソース電極38へスムーズに排出することができる。これにより、N+領域53の実効的なキャリア濃度の変動を抑制して、半導体装置120を安定に動作させることができる。また、アバランシェ耐量を向上させることができる。 In contrast, in the semiconductor device 120, the source electrode 38 is electrically connected to the N + region 53 of the contact region 58 exposed on the inner wall surface of the trench 47, so that holes injected into the N + region 53 are sourced. The electrode 38 can be discharged smoothly. As a result, the fluctuation of the effective carrier concentration in the N + region 53 can be suppressed and the semiconductor device 120 can be operated stably. In addition, the avalanche resistance can be improved.
以上、本発明に係る第1〜第4の実施形態を参照して本発明を説明したが、本発明はこれらの実施形態に限定されるものではない。例えば、出願時の技術水準に基づいて、当業者がなし得る設計変更や、材料の変更等、本発明と技術的思想を同じとする実施態様も本発明の技術的範囲に含有される。 Although the present invention has been described with reference to the first to fourth embodiments according to the present invention, the present invention is not limited to these embodiments. For example, embodiments that have the same technical idea as the present invention, such as design changes and material changes that can be made by those skilled in the art based on the technical level at the time of filing, are also included in the technical scope of the present invention.
2 ドリフト領域
3、33 ベース領域
4、34、52 ソース領域
5、51、58 コンタクト領域
6、7、35、36 ゲート電極
8、8a、8b、37、37a、37b ゲート絶縁膜
9a、9b トレンチ
12、38 ソース電極
13 N型半導体層
14 ドレイン層
18、54 P+領域
21 P型ピラー
22 N型ピラー
24 P型半導体領域
25 N型半導体領域
27 積層体
31 絶縁層
32 ドリフト領域
39、49 張り出し部
41 N型半導体領域
42 ドレイン領域
43 ドレイン電極
44 ドレイン層
45、46、47、55 トレンチ
53 N+領域
61 第1の主面
62 第2の主面
1、10、20、30、40,50,60,70,80、90 MOSFET
100、110、MOSFET
120 半導体装置
2 Drift region 3, 33 Base region 4, 34, 52 Source region 5, 51, 58 Contact region 6, 7, 35, 36 Gate electrode 8, 8a, 8b, 37, 37a, 37b Gate insulating film 9a, 9b Trench 12 38 Source electrode 13 N-type semiconductor layer 14 Drain layer 18, 54 P + region 21 P-type pillar 22 N-type pillar 24 P-type semiconductor region 25 N-type semiconductor region 27 Stack 31 Insulating layer 32 Drift region 39, 49 Overhang 41 N-type semiconductor region 42 Drain region 43 Drain electrode 44 Drain layer 45, 46, 47, 55 Trench 53 N + region 61 First main surface 62 Second main surface 1, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90 MOSFET
100, 110, MOSFET
120 Semiconductor device
Claims (7)
前記第1電極上に設けられた第1導電型の第1半導体領域と、
前記第1半導体領域上に設けられた第2導電型の第2半導体領域と、
前記第1半導体領域上に位置し、前記第1電極から前記第1半導体領域に向かう第1方向に直交する第2方向において複数設けられた第2電極と、
前記第1半導体領域上に位置し、前記第2方向において前記第2電極間に設けられた第3電極と、
を有し、前記第1方向における前記第2電極の上面から前記第1電極までの長さが、前記第1方向における前記第3電極の上面から前記第1電極までの長さよりも大きい半導体装置。 A first electrode;
A first semiconductor region of a first conductivity type provided on the first electrode;
A second semiconductor region of a second conductivity type provided on the first semiconductor region;
A plurality of second electrodes located on the first semiconductor region and provided in a second direction orthogonal to the first direction from the first electrode toward the first semiconductor region;
A third electrode located on the first semiconductor region and provided between the second electrodes in the second direction;
And a length from the upper surface of the second electrode to the first electrode in the first direction is larger than a length from the upper surface of the third electrode to the first electrode in the first direction. .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015112383A JP6089070B2 (en) | 2015-06-02 | 2015-06-02 | Semiconductor device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015112383A JP6089070B2 (en) | 2015-06-02 | 2015-06-02 | Semiconductor device |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010042235A Division JP5762689B2 (en) | 2010-02-26 | 2010-02-26 | Semiconductor device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2015173291A true JP2015173291A (en) | 2015-10-01 |
| JP6089070B2 JP6089070B2 (en) | 2017-03-01 |
Family
ID=54260394
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015112383A Expired - Fee Related JP6089070B2 (en) | 2015-06-02 | 2015-06-02 | Semiconductor device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6089070B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020025050A (en) * | 2018-08-08 | 2020-02-13 | 株式会社東芝 | Semiconductor device |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009038214A (en) * | 2007-08-01 | 2009-02-19 | Toshiba Corp | Semiconductor device |
| JP2010505270A (en) * | 2006-09-27 | 2010-02-18 | マックスパワー・セミコンダクター・インコーポレイテッド | Power MOSFET with recessed field plate |
| JP2011165928A (en) * | 2010-02-10 | 2011-08-25 | Toyota Central R&D Labs Inc | Insulated gate bipolar transistor |
-
2015
- 2015-06-02 JP JP2015112383A patent/JP6089070B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010505270A (en) * | 2006-09-27 | 2010-02-18 | マックスパワー・セミコンダクター・インコーポレイテッド | Power MOSFET with recessed field plate |
| JP2009038214A (en) * | 2007-08-01 | 2009-02-19 | Toshiba Corp | Semiconductor device |
| JP2011165928A (en) * | 2010-02-10 | 2011-08-25 | Toyota Central R&D Labs Inc | Insulated gate bipolar transistor |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020025050A (en) * | 2018-08-08 | 2020-02-13 | 株式会社東芝 | Semiconductor device |
| JP7005453B2 (en) | 2018-08-08 | 2022-01-21 | 株式会社東芝 | Semiconductor device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP6089070B2 (en) | 2017-03-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5762689B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| US9362393B2 (en) | Vertical semiconductor device including element active portion and voltage withstanding structure portion, and method of manufacturing the vertical semiconductor device | |
| US9276076B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP2016167519A (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP5480084B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP6356803B2 (en) | Insulated gate bipolar transistor | |
| JP2013258333A (en) | Power semiconductor device | |
| JP5537359B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| US9502547B2 (en) | Charge reservoir IGBT top structure | |
| JP2014216572A (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP2011233701A (en) | Power semiconductor device | |
| JP2016115847A (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP2015201615A (en) | Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP2016058428A (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP6299658B2 (en) | Insulated gate type switching element | |
| US20120241817A1 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP2014154739A (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| US20140084334A1 (en) | Power semiconductor device | |
| JP2016062975A (en) | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP6173987B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP6089070B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP2017098385A (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP6458994B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| TW201803125A (en) | Vertical niobium metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor | |
| KR101397784B1 (en) | Insulated gate bipolar transistor |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20160727 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20160729 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20160923 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20161013 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20161208 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20170105 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20170206 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 6089070 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |