JP2015073749A - Apparatus and method for monitoring oral or pharyngeal pressure - Google Patents
Apparatus and method for monitoring oral or pharyngeal pressure Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2015073749A JP2015073749A JP2013212282A JP2013212282A JP2015073749A JP 2015073749 A JP2015073749 A JP 2015073749A JP 2013212282 A JP2013212282 A JP 2013212282A JP 2013212282 A JP2013212282 A JP 2013212282A JP 2015073749 A JP2015073749 A JP 2015073749A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- pressure sensor
- oral cavity
- attached
- pharynx
- atmospheric pressure
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 13
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 10
- 210000000214 mouth Anatomy 0.000 claims abstract description 46
- 210000003800 pharynx Anatomy 0.000 claims abstract description 36
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 18
- 230000010365 information processing Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 14
- 210000002445 nipple Anatomy 0.000 claims description 12
- 230000009747 swallowing Effects 0.000 abstract description 23
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 abstract description 5
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 abstract description 3
- 210000003254 palate Anatomy 0.000 abstract description 3
- 238000003745 diagnosis Methods 0.000 abstract description 2
- 230000001055 chewing effect Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 238000012806 monitoring device Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000003183 myoelectrical effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000018984 mastication Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000010077 mastication Methods 0.000 description 4
- 210000003928 nasal cavity Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 description 3
- 208000035475 disorder Diseases 0.000 description 3
- 210000003205 muscle Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 3
- 208000019505 Deglutition disease Diseases 0.000 description 2
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 210000001983 hard palate Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 201000000615 hard palate cancer Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 210000001331 nose Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 2
- 210000004872 soft tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910000684 Cobalt-chrome Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 206010041235 Snoring Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000010952 cobalt-chrome Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002872 contrast media Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005260 corrosion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007797 corrosion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002594 fluoroscopy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000004283 incisor Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 208000015181 infectious disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 210000003300 oropharynx Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000004080 punching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000523 sample Substances 0.000 description 1
- 206010041232 sneezing Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000010935 stainless steel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910001220 stainless steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000004659 sterilization and disinfection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000013589 supplement Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000002396 uvula Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000009423 ventilation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000001260 vocal cord Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 208000008918 voyeurism Diseases 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Measuring And Recording Apparatus For Diagnosis (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は口腔または咽頭の気圧をモニタリングする装置および方法に関する。より詳細に、本発明は、嚥下、発声、咀嚼、吸綴などの時における口腔または咽頭の気圧を時系列でモニタリングすることができ、それによって口腔または咽頭の諸機能の評価および障害の診断に利用できる、装置および方法に関する。 The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for monitoring oral or pharyngeal air pressure. More specifically, the present invention can monitor the oral or pharyngeal air pressure during swallowing, vocalization, mastication, sucking, etc. in time series, thereby evaluating various functions of the oral cavity or pharynx and diagnosing disorders. The present invention relates to an apparatus and a method that can be used.
口腔・咽頭の機能(例えば、嚥下機能、構音機能など)は軟組織と筋とが閉鎖空間を作ることによって営まれる。具体的に、嚥下時の食塊移動は軟組織と筋で閉鎖空間に圧差を作り実行される。嚥下初期の舌による食塊の口腔から咽頭への送り込み、および鼻腔と咽頭の交通遮断(鼻咽腔閉鎖)は嚥下の重要な指標である。音声は声帯から発せられるバズ音が咽頭・口腔・鼻腔の共振により構音される。その際に、舌が口蓋の前後に接触したり離れたりすることによって口唇が口腔を閉鎖・開放することで気流に変化を与える。
従来、咽頭・口腔の機能は筋電計、歪み計、X線ビデオなどを用いて計測されてきた。しかし、筋電計では筋活動を計測することで機能を推測するに過ぎない。歪み計では接触圧を計測できるが、閉鎖空間に作られた圧変化を陽圧・陰圧として計測できない。X線ビデオは大がかりな装置が必要であり、咽頭・口腔の機能を正確に把握するには時間分解能が不足しており、さらに無侵襲とはいえない。
Oral and pharyngeal functions (for example, swallowing function, articulation function, etc.) are performed by creating a closed space between soft tissue and muscles. Specifically, bolus movement during swallowing is performed by creating a pressure difference in a closed space between soft tissue and muscle. Feeding the bolus from the oral cavity to the pharynx by the tongue in the early stages of swallowing, and blocking the nasal and pharyngeal traffic (nasopharyngeal closure) are important indicators of swallowing. The buzzing sound emitted from the vocal cords is composed by resonance of the pharynx, oral cavity and nasal cavity. At that time, the lip closes and opens the oral cavity when the tongue comes in contact with the front and back of the palate or moves away, thereby changing the airflow.
Conventionally, functions of the pharynx and oral cavity have been measured using electromyographs, strain gauges, X-ray videos, and the like. However, the electromyograph only estimates the function by measuring the muscle activity. Strain gauges can measure contact pressure, but cannot measure changes in pressure created in a closed space as positive or negative pressure. X-ray video requires a large-scale device, and lacks time resolution to accurately grasp the functions of the pharynx and oral cavity, and is not non-invasive.
また、遠位端から近位端までを連通するルーメンを有するカテーテルを咽頭に挿入し、該カテーテルの近位端にマノメータを取り付けて、ルーメンを通して伝わる咽頭の気圧変化を計測した研究の報告がある。マノメータを用いたこの装置はサイズが大きくまた正確な計測ができたかどうかは不明である。 In addition, there is a report of a study in which a catheter having a lumen communicating from the distal end to the proximal end was inserted into the pharynx, a manometer was attached to the proximal end of the catheter, and the pressure change of the pharynx transmitted through the lumen was measured. . It is unclear whether this device using a manometer is large in size and accurate.
小型の圧力センサを内視鏡に取り付けて内視鏡周囲の咽頭圧を部分的に計測することは行われている。しかし、嚥下・発声・咀嚼時の口腔・咽頭機能を定量的に計測することは困難である。また、Manofluorographyを鼻腔から挿入し嚥下時の圧力変化を測定したことが報告されている(非特許文献1〜3など)。従来のManofluorographyでは圧センサの位置が食塊の移動によって変化して、食塊の位置と嚥下圧変化との関係の判断が困難な場合があった。そのため、ManofluorographyとX線透視観察とを併用する方法が採用されている。透視のために造影剤が嚥下観察のために使用されている。 A small pressure sensor is attached to an endoscope to partially measure the pharyngeal pressure around the endoscope. However, it is difficult to quantitatively measure the oral and pharyngeal functions during swallowing, vocalization, and mastication. It has also been reported that Manofluorography was inserted from the nasal cavity and the pressure change during swallowing was measured (Non-Patent Documents 1 to 3, etc.). In conventional Manofluorography, the position of the pressure sensor changes due to movement of the bolus, and it may be difficult to determine the relationship between the bolus position and changes in swallowing pressure. For this reason, a method in which Manofluorography and X-ray fluoroscopic observation are used in combination is employed. Contrast agents are used for swallowing observation for fluoroscopy.
本発明の目的は、嚥下、発声、咀嚼、吸綴などの時における口腔または咽頭の気圧または測定部位の圧差を無侵襲でかつ時系列でモニタリングすることができ、それによって口腔または咽頭の諸機能の評価および障害の診断に利用できる、装置および方法を提供することである。 The object of the present invention is to monitor the pressure difference of the oral cavity or pharynx or the measurement site at the time of swallowing, vocalization, mastication, sucking, etc. non-invasively and in time series, thereby various functions of the oral cavity or pharynx It is an object of the present invention to provide an apparatus and a method that can be used for evaluation and diagnosis of disorders.
前記目的を達成するために鋭意検討した結果、以下の態様の本発明を完成するに至った。 As a result of intensive studies to achieve the above object, the present invention of the following aspect has been completed.
〔1〕 気圧レベルを信号に変換するための気圧センサ、
情報処理装置に接続するためのコネクタ、
支台歯に取り付けることができるクラスプ線、および
気圧センサから信号をコネクタに伝えるための伝送部を有し、
気圧センサがクラスプ線に取り付けられていて、クラスプ線に取り付けられた気圧センサが口腔または咽頭に配置されるようにクラスプ線を支台歯に取り付けて、口腔または咽頭の気圧を時系列でモニタリングすることができる装置。
〔2〕 複数の気圧センサがクラスプ線の先端および/または中間に取り付けられている、〔1〕に記載の装置。
[1] An atmospheric pressure sensor for converting an atmospheric pressure level into a signal,
A connector for connecting to an information processing device,
It has a clasp wire that can be attached to the abutment tooth, and a transmission part for transmitting the signal from the pressure sensor to the connector,
Attach the clasp wire to the abutment tooth so that the pressure sensor attached to the clasp wire is placed in the oral cavity or pharynx, and monitor the air pressure in the oral cavity or pharynx in time series A device that can.
[2] The apparatus according to [1], wherein a plurality of barometric sensors are attached to the tip and / or middle of the clasp line.
〔3〕 気圧レベルを信号に変換するための気圧センサ、
情報処理装置に接続するためのコネクタ、
義歯床、および
気圧センサから信号をコネクタに伝えるための伝送部を有し、
気圧センサが義歯床に取り付けられていて、義歯床に取り付けられた気圧センサが口腔または咽頭に配置されるように義歯床を口腔に取り付けて、口腔または咽頭の気圧を時系列でモニタリングすることができる装置。
〔4〕 複数の気圧センサが義歯床の口蓋縫線に相当する部分に配置されている、〔3〕に記載の装置。
[3] An atmospheric pressure sensor for converting the atmospheric pressure level into a signal,
A connector for connecting to an information processing device,
It has a transmission part for transmitting signals from the denture base and the pressure sensor to the connector.
A pressure sensor is attached to the denture base, and the denture base is attached to the oral cavity so that the pressure sensor attached to the denture base is placed in the oral cavity or pharynx, and the air pressure in the oral cavity or pharynx can be monitored over time. A device that can.
[4] The apparatus according to [3], wherein the plurality of barometric sensors are arranged in a portion corresponding to the palatal line of the denture base.
〔5〕 気圧レベルを信号に変換するための気圧センサ、
情報処理装置に接続するためのコネクタ、
哺乳瓶またはおしゃぶり用のニプル、および
気圧センサから信号をコネクタに伝えるための伝送部を有し、
気圧センサがニプルに取り付けられていて、ニプルを吸綴したときに、ニプルに取り付けられた気圧センサが口腔に配置され、口腔または咽頭の気圧を時系列でモニタリングすることができる装置。
[5] Barometric pressure sensor for converting the barometric pressure level into a signal,
A connector for connecting to an information processing device,
Nipple for baby bottles or pacifiers, and a transmission unit for transmitting signals from the pressure sensor to the connector,
A device in which an atmospheric pressure sensor is attached to a nipple and when the nipple is sucked, the atmospheric pressure sensor attached to the nipple is placed in the oral cavity, and the oral or pharyngeal pressure can be monitored in time series.
〔6〕 気圧センサが袋の中に密封されている、〔1〕〜〔5〕のいずれかひとつに記載の装置。
〔7〕 〔1〕〜〔6〕のいずれかひとつに記載の装置を口から口腔または咽頭に入れて口腔または咽頭の気圧を時系列でモニタリングする方法。
[6] The apparatus according to any one of [1] to [5], wherein the atmospheric pressure sensor is sealed in a bag.
[7] A method of monitoring the air pressure of the oral cavity or pharynx in time series by inserting the device according to any one of [1] to [6] from the mouth into the oral cavity or pharynx.
本発明に係る口腔または咽頭の気圧をモニタリングする装置および方法によれば、嚥下、発声、咀嚼、吸綴などの時における口腔または咽頭の気圧または測定部位の圧差を無侵襲でかつ時系列でモニタリングすることができ、それによって口腔または咽頭の諸機能の評価および障害の診断に利用できる。 According to the apparatus and method for monitoring the pressure of the oral cavity or pharynx according to the present invention, the pressure difference of the oral cavity or pharynx or the measurement site during swallowing, vocalization, mastication, sucking, etc. is monitored non-invasively and in time series Can be used to evaluate oral or pharyngeal functions and to diagnose disorders.
以下、図を参酌しつつ実施形態を挙げて本発明を更に詳しく説明するが、本発明はこれらの実施形態によって限定されるものではない。 Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail with reference to the drawings with reference to the drawings. However, the present invention is not limited to these embodiments.
本発明の第一実施形態に係る口腔または咽頭の気圧をモニタリングする装置(以下、「気圧モニタリング装置」という。)は、気圧レベルを信号に変換するための気圧センサ、情報処理装置に接続するためのコネクタ、支台歯に取り付けることができるクラスプ線、および気圧センサから信号をコネクタに伝えるための伝送部を有するものである。図1は本発明の一実施形態に係る気圧モニタリング装置を示す図である。図7および8は気圧モニタリング装置に用いられる気圧センサ7、伝送部10およびコネクタ9からなる素子を示す図である。
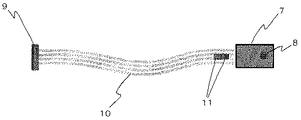
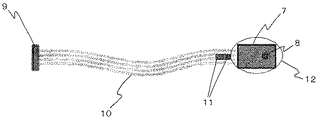
An apparatus for monitoring the pressure in the oral cavity or pharynx according to the first embodiment of the present invention (hereinafter referred to as “atmospheric pressure monitoring apparatus”) is connected to an atmospheric pressure sensor and an information processing apparatus for converting an atmospheric pressure level into a signal. Connector, a clasp wire that can be attached to the abutment tooth, and a transmission unit for transmitting a signal from the atmospheric pressure sensor to the connector. FIG. 1 is a view showing an atmospheric pressure monitoring apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention. FIGS. 7 and 8 are diagrams showing elements including the atmospheric pressure sensor 7, the
本発明に用いられる気圧センサは、気圧レベルを信号に変換することができるものであれば特に制限されない。気圧センサ7は、口腔または咽頭の内壁などの接触によって生じる圧力を感知しないようにするためにかたい覆いの中に収納されていて、その覆いの一部に通気孔8が設けられていて、気体が該通気孔8を通ってダイヤフラム(ステンレスダイヤフラム、シリコンダイヤフラムなど)に接するようになっている。そして、気圧によってダイヤフラムが変形し、その変形を感圧素子で検出し、電気信号に変換する。気圧センサとしては、半導体ピエゾ抵抗拡散圧力センサ、静電容量形圧力センサなどが挙げられる。半導体ピエゾ抵抗拡散圧力センサは、ダイヤフラムの表面に半導体ひずみゲージを有し、外部からの力(圧力)によってダイヤフラムが変形して発生するピエゾ抵抗効果による電気抵抗の変化を電気信号に変換する。静電容量形圧力センサは、ガラス固定極とシリコンダイヤフラム(可動極)を対向させて成るコンデンサを有し、外部からの力(圧力)によって可動極が変形して発生する静電容量の変化を電気信号に変換する。また、気圧センサ7は大気圧よりも高い圧力および大気圧よりも低い圧力のいずれをも測定できるものであることが好ましい。覆いは箱、網、パンチングメタル、メッシュなどのようなもので構成されていてもよい。気圧センサの大きさは、相当直径として、好ましくは数ミリ、具体的に好ましくは0.5mm〜10mmである。 The atmospheric pressure sensor used in the present invention is not particularly limited as long as it can convert the atmospheric pressure level into a signal. The air pressure sensor 7 is housed in a hard cover so as not to sense pressure caused by contact with the inner wall of the oral cavity or pharynx, and a ventilation hole 8 is provided in a part of the cover, The gas comes into contact with a diaphragm (stainless steel diaphragm, silicon diaphragm, etc.) through the vent hole 8. Then, the diaphragm is deformed by the atmospheric pressure, and the deformation is detected by the pressure sensitive element and converted into an electric signal. Examples of the atmospheric pressure sensor include a semiconductor piezoresistive diffusion pressure sensor and a capacitance type pressure sensor. The semiconductor piezoresistive diffusion pressure sensor has a semiconductor strain gauge on the surface of the diaphragm, and converts a change in electric resistance due to a piezoresistance effect generated by deformation of the diaphragm by an external force (pressure) into an electric signal. Capacitance type pressure sensors have a capacitor with a glass fixed pole and a silicon diaphragm (movable pole) facing each other, and change the capacitance that occurs when the movable pole is deformed by external force (pressure). Convert to electrical signal. Moreover, it is preferable that the atmospheric pressure sensor 7 can measure both a pressure higher than atmospheric pressure and a pressure lower than atmospheric pressure. The cover may be composed of a box, net, punched metal, mesh or the like. The size of the atmospheric pressure sensor is preferably several millimeters as an equivalent diameter, and more preferably 0.5 mm to 10 mm.
また、消毒の手順を簡素化するため、および通気孔が液体や固体などで塞がれ気圧を正確に測定できないなどの事態に備えるため、気圧センサ全体を袋(例えば、ゴム製のプローブカバー)12の中に密封してもよい。なお、袋の中には圧力を伝えるための気体や液体を封入することができる。パスカルの原理によりセンサは袋の中の閉鎖空間のいずれにあっても計測結果に大きく影響しないという特長を有する。また、口腔または咽頭の内壁などの接触によって生じる圧力を感知しないようにするために、気圧センサ全体を、網、パンチングメタル、メッシュなどからなる袋(容器)の中に入れてもよい。 Also, in order to simplify the disinfection procedure and to prepare for situations where the vent is blocked with liquid or solid, etc., and the pressure cannot be measured accurately, the entire pressure sensor is covered with a bag (for example, a rubber probe cover). 12 may be sealed. In addition, the gas and liquid for transmitting a pressure can be enclosed in a bag. Due to Pascal's principle, the sensor has a feature that it does not greatly affect the measurement result in any of the enclosed spaces in the bag. Further, in order not to sense pressure generated by contact with the inner wall of the oral cavity or pharynx, the entire barometric sensor may be placed in a bag (container) made of a net, punching metal, mesh or the like.
気圧センサの信号は、伝送部10でコネクタ9に伝えられる。図7に示す伝送部は、ケーブル、通信線などの有線式の伝送部であるが、送受信機の組み合わせからなる無線式の伝送部であってもよい。図7または8に記載の素子では、伝送部(フラットケーブル)にキャパシタ11が取り付けられている。これによって信号に入り込んだノイズを除去することができるので好ましい。コネクタは情報処理装置に接続し信号を情報処理装置に送るためのものである。情報処理装置において、信号に載せられた情報がそのままでまたは目的に応じて計算処理されて、記憶または出力される。情報処理装置としては、コンピュータ、携帯情報機器・端末、オシロスコープ、チャートレコーダーなどが挙げられる。
The signal from the atmospheric pressure sensor is transmitted to the connector 9 by the
第一実施形態に係る気圧モニタリング装置にはクラスプ線が用いられる。クラスプ線は歯の治療において使用されるものであれば特に制限されない。クラスプ線としては、弾性、粘靱性、耐蝕性などの観点から、コバルトクロム合金製のものが好ましく用いられる。 A clasp wire is used in the atmospheric pressure monitoring device according to the first embodiment. The clasp line is not particularly limited as long as it is used in dental treatment. As the clasp wire, a cobalt chrome alloy is preferably used from the viewpoint of elasticity, toughness, corrosion resistance, and the like.
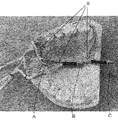
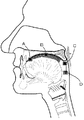
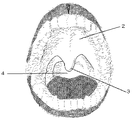
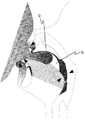
第一実施形態においては、気圧センサはクラスプ線に取り付けられている。本発明においては複数の気圧センサをクラスプ線の先端および/または中間に取り付けることが好ましい。そして、クラスプ線を支台歯に巻きつけて気圧センサを口腔または咽頭(中咽頭〜下咽頭)に配置することができる。例えば、図1に示すように、クラスプ線Sを左上顎小臼歯から左上顎大臼歯に巻きつけ、さらに硬口蓋2に接するようにして切歯乳頭辺りから口蓋縫線に沿って咽頭辺りまでにクラスプ線Sを配置することができる。このように配置すると、クラスプ線に取り付けられた気圧センサA、BおよびC、さらにDが、例えば、口蓋縫線、咽頭に沿って縦に配置される。そして、嚥下時圧変化、発音時圧変化、吸綴時圧変化などや測定部位の圧差などを時系列で測定することができる。また、クラスプ線が支台歯に固定され、気圧センサの位置が変動し難くなるので、食塊の位置と嚥下圧変化との関係が判断しやすくなる。
In the first embodiment, the atmospheric pressure sensor is attached to the clasp wire. In the present invention, it is preferable to attach a plurality of barometric sensors to the tip and / or middle of the clasp line. And a clasp line can be wound around an abutment tooth and a barometric pressure sensor can be arranged in the mouth or pharynx (oropharynx-hypopharynx). For example, as shown in FIG. 1, the clasp line S is wrapped around the left upper premolar to the left upper molar and is further in contact with the
本発明の第二実施形態に係る気圧モニタリング装置は、気圧レベルを信号に変換するための気圧センサ、情報処理装置に接続するためのコネクタ、義歯床、および気圧センサから信号をコネクタに伝えるための伝送部を有するものである。義歯床は歯の治療において用いられるものであれば特に制限されない。義歯床は口蓋に固定できるものであることが好ましい。第二実施形態は、気圧センサがクラスプ線の代わりに義歯床に取り付けられている以外は第一実施形態と同様の構造である。気圧センサは、異物感を軽減するために、義歯床に埋め込んで取り付けることができる。複数の気圧センサの義歯床に取り付ける場所はモニタリングの目的に応じて適宜設定できる。嚥下、吸綴、発音などのモニタリングにおいては、複数の気圧センサを口蓋縫線に相当する部分に沿って義歯床に取り付けることが好ましい。 A barometric pressure monitoring device according to a second embodiment of the present invention includes a barometric pressure sensor for converting a barometric pressure level into a signal, a connector for connecting to an information processing device, a denture base, and a barometer for transmitting a signal to the connector. It has a transmission part. The denture base is not particularly limited as long as it is used in the treatment of teeth. It is preferable that the denture base can be fixed to the palate. The second embodiment has the same structure as that of the first embodiment except that the atmospheric pressure sensor is attached to the denture base instead of the clasp line. The barometric sensor can be embedded and attached to the denture base in order to reduce the foreign object feeling. The place where a plurality of barometric sensors are attached to the denture base can be appropriately set according to the purpose of monitoring. In monitoring such as swallowing, sucking, and pronunciation, it is preferable to attach a plurality of barometric sensors to the denture base along a portion corresponding to the palatal line.
本発明の第三実施形態に係る気圧モニタリング装置は、気圧レベルを信号に変換するための気圧センサ、情報処理装置に接続するためのコネクタ、哺乳瓶またはおしゃぶり用のニプル、および気圧センサから信号をコネクタに伝えるための伝送部を有するものである。第三実施形態は、気圧センサがクラスプ線の代わりに哺乳瓶またはおしゃぶり用のニプルに取り付けられている以外は第一実施形態と同様の構造である。吸綴時における口腔6などの気圧を測定することができる(図9)。
A barometric pressure monitoring device according to a third embodiment of the present invention includes a barometric pressure sensor for converting a barometric pressure level into a signal, a connector for connecting to an information processing device, a nipple for a baby bottle or a pacifier, and a signal from the barometric pressure sensor. It has a transmission part for transmitting to a connector. The third embodiment has the same structure as that of the first embodiment except that the atmospheric pressure sensor is attached to a baby bottle or a nipple for pacifier instead of the clasp wire. The air pressure of the
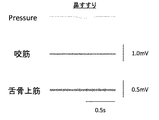
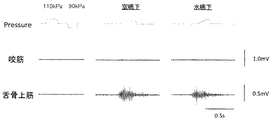
本発明に係る気圧モニタリング装置は、音声発生時の舌圧・口唇圧・口腔内圧・咽頭圧等を計測し、構音機能を定量的に評価することができる。また、構音時の舌運動は嚥下時の舌運動と類似しており、嚥下機能の評価にも応用できる。図4は、「パ」、「ガ」および「バ」と発音したときの咽頭の気圧波形および筋電波形を示す図である。筋電波形は、「パ」、「ガ」および「バ」の発音において大きな差がないが、気圧波形はその差が明瞭である。なお、図4に示す気圧波形は気圧センサDにおける測定データである。 The atmospheric pressure monitoring device according to the present invention can measure tongue pressure, lip pressure, intraoral pressure, pharyngeal pressure, etc. at the time of voice generation and quantitatively evaluate the articulation function. The tongue movement during articulation is similar to the tongue movement during swallowing, and can be applied to the evaluation of swallowing function. FIG. 4 is a diagram showing a pharyngeal air pressure waveform and a myoelectric waveform when “pa”, “ga”, and “ba” are pronounced. The myoelectric waveform has no significant difference in the pronunciation of “pa”, “ga”, and “ba”, but the difference in the atmospheric pressure waveform is clear. Note that the atmospheric pressure waveform shown in FIG.
本発明に係る気圧モニタリング装置によれば、くしゃみ、いびき、鼻すすりなどをしているときの圧変化を測定することができる。例えば、図5は鼻すすりをしたときの気圧波形および筋電波形を示す図である。なお、図5に示す気圧波形は気圧センサCにおける測定データである。 According to the atmospheric pressure monitoring device according to the present invention, it is possible to measure a change in pressure when sneezing, snoring, sniffing and the like. For example, FIG. 5 is a diagram showing an atmospheric pressure waveform and a myoelectric waveform when the nose is slipped. Note that the atmospheric pressure waveform shown in FIG.
本発明に係る気圧モニタリング装置によれば、嚥下時の圧変化を測定することができる。例えば、図6は空嚥下および水嚥下したときの気圧波形および筋電波形を示す図である。なお、図6に示す気圧波形は気圧センサCにおける測定データである。図6中の最左のデータは気圧センサを110kPaおよび90kPaで校正したときの信号波形である。 With the atmospheric pressure monitoring device according to the present invention, it is possible to measure a pressure change during swallowing. For example, FIG. 6 is a diagram showing a pressure waveform and an electromyogram when swallowing and swallowing. Note that the atmospheric pressure waveform shown in FIG. The leftmost data in FIG. 6 is a signal waveform when the pressure sensor is calibrated at 110 kPa and 90 kPa.
2:硬口蓋; 3:口蓋垂; 4:中咽頭; S:クラスプ線;
A、B、C、D:気圧センサ; 5:ニプル(哺乳瓶またはおしゃぶりの乳首);
6:口腔
2: hard palate; 3: uvula; 4: oropharynx; S: clasp line;
A, B, C, D: barometric pressure sensor; 5: Nipple (feeding bottle or pacifier nipple);
6: Oral cavity
Claims (7)
情報処理装置に接続するためのコネクタ、
支台歯に取り付けることができるクラスプ線、および
気圧センサから信号をコネクタに伝えるための伝送部を有し、
気圧センサがクラスプ線に取り付けられていて、クラスプ線に取り付けられた気圧センサが口腔または咽頭に配置されるようにクラスプ線を支台歯に取り付けて、口腔または咽頭の気圧を時系列でモニタリングすることができる装置。 An atmospheric pressure sensor to convert the atmospheric pressure level into a signal,
A connector for connecting to an information processing device,
It has a clasp wire that can be attached to the abutment tooth, and a transmission part for transmitting the signal from the pressure sensor to the connector,
Attach the clasp wire to the abutment tooth so that the pressure sensor attached to the clasp wire is placed in the oral cavity or pharynx, and monitor the air pressure in the oral cavity or pharynx in time series A device that can.
情報処理装置に接続するためのコネクタ、
義歯床、および
気圧センサから信号をコネクタに伝えるための伝送部を有し、
気圧センサが義歯床に取り付けられていて、義歯床に取り付けられた気圧センサが口腔または咽頭に配置されるように義歯床を口腔に取り付けて、口腔または咽頭の気圧を時系列でモニタリングすることができる装置。 An atmospheric pressure sensor to convert the atmospheric pressure level into a signal,
A connector for connecting to an information processing device,
It has a transmission part for transmitting signals from the denture base and the pressure sensor to the connector.
A pressure sensor is attached to the denture base, and the denture base is attached to the oral cavity so that the pressure sensor attached to the denture base is placed in the oral cavity or pharynx, and the air pressure in the oral cavity or pharynx can be monitored over time. A device that can.
情報処理装置に接続するためのコネクタ、
哺乳瓶またはおしゃぶり用のニプル、および
気圧センサから信号をコネクタに伝えるための伝送部を有し、
気圧センサがニプルに取り付けられていて、ニプルを吸綴したときに、ニプルに取り付けられた気圧センサが口腔に配置され、口腔または咽頭の気圧を時系列でモニタリングすることができる装置。 An atmospheric pressure sensor to convert the atmospheric pressure level into a signal,
A connector for connecting to an information processing device,
Nipple for baby bottles or pacifiers, and a transmission unit for transmitting signals from the pressure sensor to the connector,
A device in which an atmospheric pressure sensor is attached to a nipple and when the nipple is sucked, the atmospheric pressure sensor attached to the nipple is placed in the oral cavity, and the oral or pharyngeal pressure can be monitored in time series.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013212282A JP6174965B2 (en) | 2013-10-09 | 2013-10-09 | A device for monitoring the pressure in the oral cavity or pharynx |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013212282A JP6174965B2 (en) | 2013-10-09 | 2013-10-09 | A device for monitoring the pressure in the oral cavity or pharynx |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2015073749A true JP2015073749A (en) | 2015-04-20 |
| JP6174965B2 JP6174965B2 (en) | 2017-08-02 |
Family
ID=52999074
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013212282A Active JP6174965B2 (en) | 2013-10-09 | 2013-10-09 | A device for monitoring the pressure in the oral cavity or pharynx |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6174965B2 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019013698A (en) * | 2017-07-10 | 2019-01-31 | 株式会社東京技研 | Oral care assistance tool |
| CN112135564A (en) * | 2018-05-23 | 2020-12-25 | 松下知识产权经营株式会社 | Method, program, device and system for evaluating ingestion swallowing function |
| CN112790941A (en) * | 2021-01-28 | 2021-05-14 | 广州龙之杰科技有限公司 | A wireless intelligent therapeutic device for swallowing disorders |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS56133803U (en) * | 1980-03-10 | 1981-10-09 | ||
| JPS6221301U (en) * | 1985-07-24 | 1987-02-09 | ||
| JPH07140024A (en) * | 1993-11-18 | 1995-06-02 | Masafumi Matsumura | Vertical-stress-distribution measuring device for tongue-palate contact surface |
| JPH07265272A (en) * | 1994-04-01 | 1995-10-17 | Itec Kk | Nursing/monitoring system |
| WO2013085038A1 (en) * | 2011-12-09 | 2013-06-13 | 国立大学法人東京大学 | Oral cavity sensor |
-
2013
- 2013-10-09 JP JP2013212282A patent/JP6174965B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS56133803U (en) * | 1980-03-10 | 1981-10-09 | ||
| JPS6221301U (en) * | 1985-07-24 | 1987-02-09 | ||
| JPH07140024A (en) * | 1993-11-18 | 1995-06-02 | Masafumi Matsumura | Vertical-stress-distribution measuring device for tongue-palate contact surface |
| JPH07265272A (en) * | 1994-04-01 | 1995-10-17 | Itec Kk | Nursing/monitoring system |
| WO2013085038A1 (en) * | 2011-12-09 | 2013-06-13 | 国立大学法人東京大学 | Oral cavity sensor |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019013698A (en) * | 2017-07-10 | 2019-01-31 | 株式会社東京技研 | Oral care assistance tool |
| CN112135564A (en) * | 2018-05-23 | 2020-12-25 | 松下知识产权经营株式会社 | Method, program, device and system for evaluating ingestion swallowing function |
| CN112135564B (en) * | 2018-05-23 | 2024-04-02 | 松下知识产权经营株式会社 | Method, recording medium, evaluation device, and evaluation system for ingestion swallowing function |
| CN112790941A (en) * | 2021-01-28 | 2021-05-14 | 广州龙之杰科技有限公司 | A wireless intelligent therapeutic device for swallowing disorders |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP6174965B2 (en) | 2017-08-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US20220401256A1 (en) | Systems and methods for obstructive sleep apnea detection and monitoring | |
| Bredenoord et al. | Technical aspects of clinical high‐resolution manometry studies | |
| KR101558625B1 (en) | Breastfeeding quantification | |
| DK2667777T3 (en) | APPARATUS FOR DIAGNOSIS OF SAG dysfunction | |
| JP5022782B2 (en) | Biopsy device | |
| JP3801837B2 (en) | Oral pressure measuring device and oral pressure measuring probe | |
| US9974473B2 (en) | Swallowing assessment and improvement systems and methods | |
| KR101456695B1 (en) | Bite force measurement system | |
| JP2015144695A (en) | Device for measuring oral cavity-related pressure | |
| CN111407451A (en) | Dental occlusion force measuring device and oral cavity wearing device | |
| US20180242900A1 (en) | Swallowing movement monitoring sensor | |
| JP2019111267A (en) | Aid for improving symptom of sleep apnea syndrome | |
| JP6174965B2 (en) | A device for monitoring the pressure in the oral cavity or pharynx | |
| KR102455072B1 (en) | Malocclusion monitoring system using an electronic articulator inserted into the oral cavity and method thereof | |
| KR20160052995A (en) | functional malocclusion diagnostic system | |
| KR101642462B1 (en) | functional malocclusion diagnostic system | |
| JP2022057573A (en) | Biological monitoring device | |
| JP2022057599A (en) | Biological monitoring device | |
| JP2006204940A (en) | Oral pressure measuring device and oral pressure measuring probe | |
| Jacobs et al. | Tonic and contractile components of the oral vestibular forces in young subjects with normal occlusion | |
| CN212699215U (en) | Dental occlusion force measuring device and oral cavity wearing device | |
| JP2019013698A (en) | Oral care assistance tool | |
| JP6979553B2 (en) | Swallowing ability test device | |
| JP6444357B2 (en) | Tongue pressure measurement method | |
| JP7251804B2 (en) | Wearing device around the ear |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20160824 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20170418 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20170428 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20170426 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20170627 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20170707 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6174965 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |