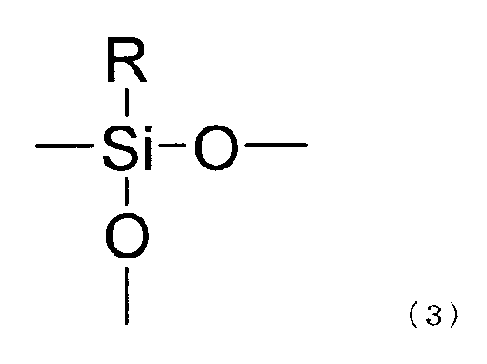JP2014123750A - Coating composition for solar cell - Google Patents
Coating composition for solar cell Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2014123750A JP2014123750A JP2014006353A JP2014006353A JP2014123750A JP 2014123750 A JP2014123750 A JP 2014123750A JP 2014006353 A JP2014006353 A JP 2014006353A JP 2014006353 A JP2014006353 A JP 2014006353A JP 2014123750 A JP2014123750 A JP 2014123750A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- component
- group
- coating composition
- solar cell
- ratio
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E10/00—Energy generation through renewable energy sources
- Y02E10/50—Photovoltaic [PV] energy
Abstract
Description
本発明は、太陽電池用コーティング組成物、積層体、太陽電池用カバー材、及び太陽電池に関する。 The present invention relates to a solar cell coating composition, a laminate, a solar cell cover material, and a solar cell.
太陽電池は、太陽の光を直接電気エネルギーに変換できる。太陽電池は、化石燃料とは異なり枯渇することのない太陽光を資源としているため半永久的に利用可能で、しかも非常にクリーンなエネルギーである。 Solar cells can directly convert sunlight into electrical energy. Unlike fossil fuels, solar cells use semi-permanent sunlight as a resource, so they can be used semipermanently and are very clean energy.
太陽電池の受光面は通常、ガラスや耐候性樹脂フィルムなどからなる保護カバーによって保護されている。ここで、当該保護カバーは長期間の使用中に煤塵で汚れるため、光透過率が低下し、太陽電池のエネルギー変換効率が低下する。特に、近年の環境汚染に伴い、カバーの汚れが早く、太陽電池の変換効率が早期に減少しやすい。太陽電池カバーを定期的に又は必要に応じて清掃するのが望ましいが、太陽電池カバーは一般に屋根や建物の外壁に設置されるのでカバーの清掃は容易でない。 The light receiving surface of the solar cell is usually protected by a protective cover made of glass, a weather resistant resin film, or the like. Here, since the protective cover is soiled with dust during long-term use, the light transmittance is lowered, and the energy conversion efficiency of the solar cell is lowered. In particular, with recent environmental pollution, the cover is quickly soiled, and the conversion efficiency of the solar cell tends to decrease early. Although it is desirable to clean a solar cell cover regularly or as needed, since a solar cell cover is generally installed in the outer wall of a roof or a building, cleaning of a cover is not easy.
このような事情のもと、特許文献1(特開平10−107303号公報)には、光触媒粒子とシリコーンと撥水性フッ素樹脂、或いは光触媒粒子と無定型シリカと撥水性フッ素樹脂とを有する表層部を備えた太陽電池カバーが提案されている。 Under such circumstances, Patent Document 1 (Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 10-107303) discloses a surface layer portion including photocatalyst particles and silicone and water repellent fluororesin, or photocatalyst particles, amorphous silica and water repellent fluororesin. A solar cell cover provided with is proposed.
また、特許文献2(特開平10−270732号公報)には、電池表面に、順次、保護カバーフィルム層、フッ素系樹脂フィルム層、及び光触媒含有表層部を設けて、表面に付着した汚染物質を分解させることを特徴とする太陽電池カバーが提案されている。
しかしながら、特許文献1に記載の方法では、表層部中の光触媒の有機物分解作用によって保護カバーフィルムの基材層が劣化し、太陽電池カバーの外観が悪くなる場合がある。
また、特許文献2に記載の方法では、表層部中の光触媒の有機物分解作用によって保護カバーフィルム層が劣化するのを防ぐため、フッ素系樹脂フィルム層を設けており、製造工程が煩雑になりやすい。また、各層の間に界面が存在するため、光触媒層の剥離等の問題が懸念される。従って、層構成がより単純な太陽電池カバーが求められていた。
更に、近年の太陽電池は低コスト、長期耐久性の要求が強いため、太陽電池カバーに用いられるガラス基材や樹脂基材への長期密着性に優れ、環境負荷の少ない水系の太陽電池用コーティング剤が望まれていた。
本発明の課題は、基材密着性、防汚染性、基材保護性が良好な太陽電池用コーティング組成物等を提供することにある。
However, in the method described in Patent Document 1, the base material layer of the protective cover film may be deteriorated by the organic substance decomposition action of the photocatalyst in the surface layer portion, and the appearance of the solar cell cover may be deteriorated.
In the method described in Patent Document 2, a fluororesin film layer is provided to prevent the protective cover film layer from deteriorating due to the organic substance decomposition action of the photocatalyst in the surface layer portion, and the manufacturing process tends to be complicated. . Moreover, since an interface exists between the layers, there is a concern about problems such as peeling of the photocatalyst layer. Therefore, a solar cell cover having a simpler layer structure has been demanded.
Furthermore, recent solar cells have a strong demand for low cost and long-term durability, so they have excellent long-term adhesion to glass substrates and resin substrates used for solar cell covers, and have a low environmental impact. An agent was desired.
The subject of this invention is providing the coating composition for solar cells etc. with favorable base-material adhesiveness, antifouling property, and base-material protection.
本発明者らは上記課題を解決すべく鋭意検討した結果、本発明に到達した。
すなわち、本発明は以下の通りである。
[1] 以下の(A)と(B)の各成分,
(A)成分:粒子径が1nm〜400nmの金属化合物粒子、
(B)成分:粒子径が10nm〜800nmの重合体エマルジョン粒子、
を含み、
前記(B)成分が、以下の(b1)〜(b4)の各成分、
(b1)成分:加水分解性珪素化合物、
(b2)成分:水酸基、カルボキシル基,アミド基、アミノ基、エーテル基よりなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1種の官能基を含有するビニル単量体、
(b3)成分:乳化剤、
(b4)成分:水、
を含む重合原液を重合して得られる重合体エマルジョン粒子であることを特徴とする太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[2] (b2)成分が、2級及び/又は3級アミド基を有するビニル単量体である上記[1]に記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[3] (b2)成分と、(B)成分との比(b2)/(B)(質量比)が、0.1/1〜0.8/1である上記[1]又は[2]に記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[4] (B)成分が、コア層と、当該コア層を被覆する1層又は2層以上のシェル層とを備えたコア/シェル構造を有する上記[1]〜[3]のいずれかに記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[5] コア層において、(b2)成分と(b1)成分との比(b2)/(b1)(質量比)が0.01/1〜1/1であり、シェル層の最外層において、(b2)成分と(b1)成分との比(b2)/(b1)(質量比)が0.1/1〜5/1である上記[4]に記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[6] (B)成分が、コア層と、当該コア層を被覆するシェル第1層とさらにその外側を被覆するシェル第2層とを備えた3層構造を有する上記[1]〜[3]のいずれかに記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[7] コア層において、(b2)成分と(b1)成分との比(b2)/(b1)(質量比)が0.01/1〜1/1であり、シェル第1層において(b2)/(b1)(質量比)が0.1/1〜1/1、シェル第2層において(b2)/(b1)(質量比)が1/1〜9/1である上記[6]に記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[8] (B)成分が、コア層を形成するシード粒子の存在下で重合原液を重合して得られ、前記シード粒子が、(b1)成分、(b2)成分、及び以下の(b5)成分、
(b5)成分:(b2)成分と共重合可能な他のビニル単量体、
よりなる群から選択される少なくとも1種以上を重合して得られる上記[4]〜[7]のいずれかに記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[9] (b1)成分が、以下の(b1−1)成分、
(b1−1)成分:ビニル重合性基を有する加水分解性珪素化合物、
を含み、
(b1−1)成分と、(B)成分との比(b1−1)/(B)(質量比)が、0.01/100〜20/100である上記[1]〜[8]のいずれかに記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[10] (b1−1)成分と、(b2)成分との比(b1−1)/(b2)(質量比)が、0.1/100〜100/100である上記[9]に記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[11] (A)成分が、二酸化珪素、光触媒活性を有する金属酸化物、又は導電性を有する金属酸化物のいずれかを用いて形成される上記[1]〜[10]のいずれかに記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[12] (A)成分の粒子長(l)と粒子直径(d)との比(l/d)が、1/1〜20/1である上記[1]〜[11]のいずれかに記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[13] (A)成分が、以下の(A’)成分、
(A’)成分:式(1)で表されるトリオルガノシラン単位、式(2)で表されるモノオキシジオルガノシラン単位、式(3)で表されるジオキシオルガノシラン単位、式(4)で表されるトリオキシシラン単位、及びジフルオロメチレン単位よりなる群から選択される少なくとも1種の構造単位を有する変性剤化合物を用いて、(A)成分の金属化合物粒子を変性処理して形成される変性金属化合物粒子、
を含む上記[1]〜[12]のいずれかに記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
R3Si− (1)
(式中、Rは各々独立に直鎖状または分岐状の炭素数1〜30個のアルキル基、炭素数5〜20のシクロアルキル基、直鎖状または分岐状の炭素数1〜30個のフルオロアルキル基、直鎖状または分岐状の炭素数2〜30個のアルケニル基、フェニル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、又は水酸基を表す。)
−(R2SiO)− (2)
(式中、Rは式(1)で定義した通りである。)
(式中、Rは式(1)で定義した通りである。)
[14] (A’)成分が、光触媒活性を有する上記[13]に記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[15] (A’)成分の粒子長(l)と粒子直径(d)の比(l/d)が、1/1から20/1である上記[13]又は[14]に記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[16] 上記[1]〜[15]のいずれかに記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物を用いて形成される塗膜と、樹脂基材とを含む積層体。
[17] 塗膜のヘイズが20以下である上記[16]に記載の積層体。
[18] 上記[16]〜[17]のいずれかに記載の積層体を用いてなる太陽電池用カバー材。
[19] 上記[1]〜[15]のいずれかに記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物を含んでなる太陽電池。
As a result of intensive studies aimed at solving the above problems, the present inventors have reached the present invention.
That is, the present invention is as follows.
[1] Each component of the following (A) and (B),
(A) component: metal compound particles having a particle diameter of 1 nm to 400 nm,
(B) component: polymer emulsion particles having a particle size of 10 nm to 800 nm,
Including
The component (B) is the following components (b1) to (b4):
(B1) component: hydrolyzable silicon compound,
(B2) component: a vinyl monomer containing at least one functional group selected from the group consisting of a hydroxyl group, a carboxyl group, an amide group, an amino group, and an ether group;
(B3) component: emulsifier,
(B4) component: water,
A coating composition for solar cells, which is polymer emulsion particles obtained by polymerizing a polymerization stock solution containing
[2] The solar cell coating composition according to [1], wherein the component (b2) is a vinyl monomer having a secondary and / or tertiary amide group.
[3] The above [1] or [2], wherein the ratio (b2) / (B) (mass ratio) between the component (b2) and the component (B) is 0.1 / 1 to 0.8 / 1. The coating composition for solar cells described in 1.
[4] In any one of the above [1] to [3], the component (B) has a core / shell structure including a core layer and one or more shell layers covering the core layer. The coating composition for solar cells described.
[5] In the core layer, the ratio (b2) / (b1) (mass ratio) of the component (b2) to the component (b1) is 0.01 / 1 to 1/1, and in the outermost layer of the shell layer, The coating composition for solar cells according to the above [4], wherein the ratio (b2) / (b1) (mass ratio) of the component (b2) to the component (b1) is 0.1 / 1 to 5/1.
[6] The above [1] to [3], wherein the component (B) has a three-layer structure including a core layer, a shell first layer that covers the core layer, and a shell second layer that covers the outer side of the core layer. ] The coating composition for solar cells in any one of.
[7] In the core layer, the ratio (b2) / (b1) (mass ratio) of the component (b2) to the component (b1) is 0.01 / 1 to 1/1, and in the shell first layer (b2 ) / (B1) (mass ratio) is 0.1 / 1 to 1/1, and (b2) / (b1) (mass ratio) is 1/1 to 9/1 in the shell second layer [6] The coating composition for solar cells described in 1.
[8] The component (B) is obtained by polymerizing the polymerization stock solution in the presence of the seed particles forming the core layer, and the seed particles include the component (b1), the component (b2), and the following (b5) component,
Component (b5): other vinyl monomer copolymerizable with component (b2),
The coating composition for solar cells according to any one of the above [4] to [7], obtained by polymerizing at least one selected from the group consisting of:
[9] The component (b1) is the following component (b1-1):
(B1-1) component: a hydrolyzable silicon compound having a vinyl polymerizable group,
Including
Of the above [1] to [8], the ratio (b1-1) / (B) (mass ratio) of the component (b1-1) to the component (B) is 0.01 / 100 to 20/100. The coating composition for solar cells in any one.
[10] The above [9], wherein the ratio (b1-1) / (b2) (mass ratio) of the component (b1-1) to the component (b2) is 0.1 / 100 to 100/100. The coating composition for solar cells.
[11] The component according to any one of [1] to [10], wherein the component (A) is formed using any one of silicon dioxide, a metal oxide having photocatalytic activity, or a metal oxide having conductivity. The coating composition for solar cells.
[12] The ratio (l / d) of the particle length (l) and the particle diameter (d) of the component (A) is any one of the above [1] to [11], which is 1/1 to 20/1. The coating composition for solar cells described.
[13] The component (A) is the following component (A ′):
(A ′) component: triorganosilane unit represented by formula (1), monooxydiorganosilane unit represented by formula (2), dioxyorganosilane unit represented by formula (3), formula ( 4) Using a modifier compound having at least one structural unit selected from the group consisting of a trioxysilane unit represented by 4) and a difluoromethylene unit, the metal compound particles of component (A) are modified. Modified metal compound particles formed,
The solar cell coating composition according to any one of the above [1] to [12].
R 3 Si- (1)
(In the formula, each R is independently a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms, a cycloalkyl group having 5 to 20 carbon atoms, or a linear or branched carbon group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms. (A fluoroalkyl group, a linear or branched alkenyl group having 2 to 30 carbon atoms, a phenyl group, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, or a hydroxyl group.)
- (R 2 SiO) - ( 2)
(In the formula, R is as defined in formula (1).)
(In the formula, R is as defined in formula (1).)
[14] The solar cell coating composition according to [13], wherein the component (A ′) has photocatalytic activity.
[15] The sun as described in [13] or [14] above, wherein the ratio (l / d) of the particle length (l) to the particle diameter (d) of the component (A ′) is from 1/1 to 20/1. Battery coating composition.
[16] A laminate comprising a coating film formed using the solar cell coating composition according to any one of [1] to [15], and a resin base material.
[17] The laminate according to [16], wherein the coating film has a haze of 20 or less.
[18] A solar cell cover material comprising the laminate according to any one of [16] to [17].
[19] A solar cell comprising the solar cell coating composition according to any one of [1] to [15].
本発明の太陽電池用コーティング組成物によって、基材密着性、防汚染性、基材保護性が良好な太陽電池用コーティング組成物を提供することができる。 The coating composition for solar cells of the present invention can provide a coating composition for solar cells with good substrate adhesion, antifouling properties, and substrate protection properties.
以下、本発明を実施するための最良の形態(以下、「実施の形態」と略記することがある。)について詳細に説明する。尚、本発明は、以下の実施の形態に限定されるものではなく、その要旨の範囲内で種々変形して実施することができる。
本実施の形態の太陽電池用コーティング組成物は、以下の(A)成分と(B)成分,
(A)成分:粒子径が1nm〜400nmの金属化合物粒子、
(B)成分:粒子径が10nm〜800nmの重合体エマルジョン粒子、
を含み、
前記(B)成分が、以下の(b1)〜(b4)の各成分、
(b1)成分:加水分解性珪素化合物、
(b2)成分:水酸基、カルボキシル基,アミド基、アミノ基、エーテル基よりなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1種の官能基を含有するビニル単量体、
(b3)成分:乳化剤、
(b4)成分:水、
を含む重合原液を重合して得られる重合体エマルジョン粒子であることを特徴とする。
前記(A)成分は、前記(B)成分と相互作用することにより、前記(B)成分の硬化剤として作用すると考えられる。当該相互作用としては、例えば、前記(A)成分が一般に有する水酸基と、前記(B)成分が有する水酸基、カルボキシル基,アミド基、アミノ基、エーテル基との水素結合や、前記(A)成分が一般に有する水酸基と、前記(B)成分を構成する前記(b1)成分の重合生成物との縮合(化学結合)等を例示することができる。
また、前記(A)成分が、前記(B)成分と相互作用しながら前記(B)成分の粒子間に連続層を形成して存在することが好ましい。この場合、得られる太陽電池用コーティング組成物の透明性がより向上し得る。
Hereinafter, the best mode for carrying out the present invention (hereinafter, sometimes abbreviated as “embodiment”) will be described in detail. In addition, this invention is not limited to the following embodiment, It can implement by changing variously within the range of the summary.
The solar cell coating composition of the present embodiment includes the following components (A) and (B):
(A) component: metal compound particles having a particle diameter of 1 nm to 400 nm,
(B) component: polymer emulsion particles having a particle size of 10 nm to 800 nm,
Including
The component (B) is the following components (b1) to (b4):
(B1) component: hydrolyzable silicon compound,
(B2) component: a vinyl monomer containing at least one functional group selected from the group consisting of a hydroxyl group, a carboxyl group, an amide group, an amino group, and an ether group;
(B3) component: emulsifier,
(B4) component: water,
It is the polymer emulsion particle | grains obtained by superposing | polymerizing the polymerization stock solution containing this.
The component (A) is considered to act as a curing agent for the component (B) by interacting with the component (B). Examples of the interaction include a hydrogen bond between the hydroxyl group that the component (A) generally has and the hydroxyl group, carboxyl group, amide group, amino group, and ether group that the component (B) has, or the component (A). Can be exemplified by the condensation (chemical bond) of the hydroxyl group generally possessed by the polymerization product of the component (b1) constituting the component (B).
Moreover, it is preferable that the component (A) exists while forming a continuous layer between the particles of the component (B) while interacting with the component (B). In this case, the transparency of the resulting solar cell coating composition can be further improved.
前記(A)成分に用いられる金属化合物としては、前記(B)成分との相互作用の観点から、例えば、二酸化珪素、酸化アルミニウム、酸化アンチモン、酸化チタン、酸化インジウム、酸化スズ、酸化ジルコニウム、酸化鉛、酸化鉄、珪酸カルシウム、酸化マグネシウム、酸化ニオブ、酸化セリウム、等を例示することができる。
中でも、相互作用の強さの観点から、表面水酸基の多い二酸化珪素(シリカ)、酸化アルミニウム(アルミナ)、酸化アンチモン、及びそれらの複合酸化物等が好ましく、これらの2種以上を併用することについては差し支えない。
Examples of the metal compound used for the component (A) include silicon dioxide, aluminum oxide, antimony oxide, titanium oxide, indium oxide, tin oxide, zirconium oxide, and oxide from the viewpoint of interaction with the component (B). Examples thereof include lead, iron oxide, calcium silicate, magnesium oxide, niobium oxide, and cerium oxide.
Among these, from the viewpoint of the strength of interaction, silicon dioxide (silica), aluminum oxide (alumina), antimony oxide, and complex oxides thereof having a large surface hydroxyl group are preferable, and these two or more are used in combination. Is fine.
前記(A)成分に用いられる金属化合物としては、防汚染性を付与する観点から、光照射により、光触媒活性及び/又は親水性を発現する化合物(以下、単に「光触媒」と略記することがある)を用いることが好適である。前記(A)成分として、光照射により光触媒活性を発現する化合物を用いた場合、得られる太陽電池用コーティング組成物の表面は優れた汚染有機物質の分解活性や耐汚染性を発現し得る。また、前記(A)成分として、光照射により親水性を発現する化合物を用いた場合、得られる太陽電池用コーティング組成物の表面は降雨等の水による自己浄化能(セルフクリーニング)を発現し得、耐汚染性を発現し得る。なお、本実施の形態において「親水性」とは、測定対象物表面に対する水(20℃)の接触角として、好ましくは60゜以下、より好ましくは30゜以下、更に好ましくは20゜以下になることを意味する。
なお、可視光(例えば約400nm〜800nmの波長)の照射により光触媒活性及び/又は親水性を発現する光触媒(可視光応答型光触媒)を選択すると、得られる太陽電池用コーティング組成物の表面は、紫外線が十分に照射されない場所(室内等)における環境浄化効果や防汚効果が非常に大きなものとなるため好ましい。
The metal compound used for the component (A) is a compound that expresses photocatalytic activity and / or hydrophilicity upon irradiation with light (hereinafter, simply referred to as “photocatalyst”) from the viewpoint of imparting antifouling properties. ) Is preferred. When a compound that expresses photocatalytic activity by light irradiation is used as the component (A), the surface of the resulting solar cell coating composition can exhibit excellent decomposition activity and contamination resistance of contaminating organic substances. Further, when a compound that exhibits hydrophilicity by light irradiation is used as the component (A), the surface of the resulting solar cell coating composition can exhibit self-cleaning ability (self-cleaning) by water such as rain. , Can exhibit stain resistance. In the present embodiment, “hydrophilic” means that the contact angle of water (20 ° C.) with respect to the surface of the measurement object is preferably 60 ° or less, more preferably 30 ° or less, and still more preferably 20 ° or less. Means that.
In addition, when a photocatalyst that exhibits photocatalytic activity and / or hydrophilicity by irradiation with visible light (for example, a wavelength of about 400 nm to 800 nm) (a visible light responsive photocatalyst) is selected, the surface of the resulting coating composition for solar cells is This is preferable because the environmental purification effect and antifouling effect in a place (such as indoors) where ultraviolet rays are not sufficiently irradiated become very large.
前記光触媒としてより具体的には、例えば、TiO2、ZnO、SrTiO3、BaTiO3、BaTiO4、BaTi4O9、K2NbO3、Nb2O5、Fe2O3、Ta2O5、K3Ta3Si2O3、WO3、SnO2、Bi2O3、BiVO4、NiO、Cu2O、RuO2、CeO2等、さらにはTi、Nb、Ta、Vから選ばれた少なくとも1種の元素を有する層状酸化物(例えば特開昭62−74452号公報、特開平2−172535号公報、特開平7−24329号公報、特開平8−89799号公報、特開平8−89800号公報、特開平8−89804号公報、特開平8−198061号公報、特開平9−248465号公報、特開平10−99694号公報、特開平10−244165号公報等参照)を挙げることができる。これらの光触媒の中でもTiO2(酸化チタン)は無害であり、化学的安定性にも優れるため好ましい。酸化チタンとしては、アナターゼ型、ルチル型、ブルッカイト型のいずれも使用できるが、紫外線吸収の観点から光触媒活性が比較的穏やかなルチル型が好ましい。
前記可視光応答型光触媒としては、例えば、TaON、LaTiO2N、CaNbO2N、LaTaON2、CaTaO2N等のオキシナイトライド化合物(例えば特開2002−66333号公報参照)、Sm2Ti2S2O7等のオキシサルファイド化合物(例えば特開2002−233770号公報参照)、CaIn2O4、SrIn2O4、ZnGa2O4、Na2Sb2O6等のd10電子状態の金属イオンを含む酸化物(例えば特開2002−59008号公報参照)、アンモニアや尿素等の窒素含有化合物存在下でチタン酸化物前駆体(オキシ硫酸チタン、塩化チタン、アルコキシチタン等)や高表面酸化チタンを焼成して得られる窒素ドープ酸化チタン(例えば特開2002−29750号公報、特開2002−87818号公報、特開2002−154823号公報、特開2001−207082号公報参照)、チオ尿素等の硫黄化合物存在下にチタン酸化物前駆体(オキシ硫酸チタン、塩化チタン、アルコキシチタン等)を焼成して得られる硫黄ドープ酸化チタン、酸化チタンを水素プラズマ処理したり真空下で加熱処理したりすることによって得られる酸素欠陥型の酸化チタン(例えば特開2001−98219号公報参照)、さらには光触媒粒子をハロゲン化白金化合物で処理したり(例えば特開2002−239353号公報参照)、タングステンアルコキシドで処理(特開2001−286755号公報参照)したりすることによって得られる表面処理光触媒、等を好適に挙げることができる。
More specifically, examples of the photocatalyst include TiO 2 , ZnO, SrTiO 3 , BaTiO 3 , BaTiO 4 , BaTi 4 O 9 , K 2 NbO 3 , Nb 2 O 5 , Fe 2 O 3 , Ta 2 O 5 , K 3 Ta 3 Si 2 O 3 , WO 3 , SnO 2 , Bi 2 O 3 , BiVO 4 , NiO, Cu 2 O, RuO 2 , CeO 2, etc., and at least selected from Ti, Nb, Ta, V Layered oxides having one element (for example, JP-A-62-274452, JP-A-2-172535, JP-A-7-24329, JP-A-8-89799, JP-A-8-89800) JP-A-8-89804, JP-A-8-198061, JP-A-9-248465, JP-A-10-99694, JP-A-10-2 It can be cited reference No. Publication 4165). Among these photocatalysts, TiO 2 (titanium oxide) is preferable because it is harmless and has excellent chemical stability. As the titanium oxide, any of anatase type, rutile type and brookite type can be used, but a rutile type having relatively mild photocatalytic activity is preferable from the viewpoint of ultraviolet absorption.
Examples of the visible light responsive photocatalyst include oxynitride compounds such as TaON, LaTiO 2 N, CaNbO 2 N, LaTaON 2 , and CaTaO 2 N (see, for example, JP-A-2002-66333), Sm 2 Ti 2 S. oxysulfide compounds such as 2 O 7 (see, for example JP 2002-233770 JP), CaIn 2 O 4, SrIn 2 O 4, ZnGa 2 O 4, Na 2 Sb 2 O 6 , etc. d 10 of electronic state metal ion Oxides (see, for example, JP-A-2002-59008), titanium oxide precursors (titanium oxysulfate, titanium chloride, alkoxy titanium, etc.) and high surface titanium oxide in the presence of nitrogen-containing compounds such as ammonia and urea. Nitrogen-doped titanium oxide obtained by firing (for example, JP 2002-29750 A, 2002-87818, JP-A-2002-154823, JP-A-2001-207082), titanium oxide precursors (titanium oxysulfate, titanium chloride, alkoxytitanium, etc.) in the presence of sulfur compounds such as thiourea. Sulfur-doped titanium oxide obtained by calcining titanium, oxygen-deficient titanium oxide obtained by subjecting titanium oxide to hydrogen plasma treatment or heat treatment under vacuum (for example, see JP-A-2001-98219), and Is a surface-treated photocatalyst obtained by treating a photocatalyst particle with a platinum halide compound (see, for example, JP-A-2002-239353) or tungsten alkoxide (see, for example, JP-A-2001-286755), etc. Can be preferably mentioned.
上記可視光応答型光触媒の中でもオキシナイトライド化合物、オキシサルファイド化合物は可視光による光触媒活性が大きく、特に好適に使用することができる。
また、前記(A)成分に用いられる金属化合物としては、得られる太陽電池用コーティング組成物の帯電防止性能等を発現する観点から、導電性を有する金属酸化物が好適に用いられる。
このような導電性を有する金属酸化物としては、例えば、錫をドープした酸化インジウム(ITO)、アンチモンをドープした酸化錫(ATO)、酸化スズ、酸化亜鉛等を挙げることができる。
なお、前記(A)成分は、上述した種々の金属化合物を用いて(好ましくは主成分として用いて)形成することができる。ここで、本実施の形態において「主成分」とは、特定成分(2種以上の特定成分を併用する場合には、それらの総量)がマトリックス成分中に占める割合が好ましくは50質量%以上、より好ましくは70質量%以上、更に好ましくは90質量%以上であり、100質量%であってもよいことを意味する。
前記(A)成分を用いる際の形態としては、例えば、粉体、分散液、ゾル等が挙げられる。
ここでいう分散液、またはゾルとは、前記(A)成分が水及び/又は親水性有機溶媒中に0.01〜80質量%、好ましくは0.1〜50質量%の濃度で、一次粒子及び/又は二次粒子として分散された状態を意味する。
Among the visible light responsive photocatalysts, oxynitride compounds and oxysulfide compounds have a large photocatalytic activity by visible light, and can be particularly preferably used.
Moreover, as a metal compound used for said (A) component, the metal oxide which has electroconductivity is used suitably from a viewpoint of expressing the antistatic performance etc. of the coating composition for solar cells obtained.
Examples of such conductive metal oxides include indium oxide (ITO) doped with tin, tin oxide (ATO) doped with antimony, tin oxide, and zinc oxide.
In addition, the said (A) component can be formed using the various metal compounds mentioned above (preferably using as a main component). Here, in the present embodiment, the “main component” means that the proportion of the specific component (the total amount thereof when two or more specific components are used in combination) in the matrix component is preferably 50% by mass or more, More preferably, it is 70 mass% or more, More preferably, it is 90 mass% or more, and it means that 100 mass% may be sufficient.
Examples of forms when the component (A) is used include powders, dispersions, and sols.
The dispersion or sol as used herein refers to primary particles in which the component (A) is in a concentration of 0.01 to 80% by mass, preferably 0.1 to 50% by mass in water and / or a hydrophilic organic solvent. And / or a state of being dispersed as secondary particles.
上記親水性有機溶媒としては、例えば、エチレングリコール、ブチルセロソルブ、n−プロパノール、イソプロパノール、n−ブタノール、エタノール、メタノール等のアルコール類、アセトン、メチルエチルケトン、メチルイソブチルケトン等のケトン類、テトラヒドロフラン、ジオキサン等のエーテル類、ジメチルアセトアミド、ジメチルホルムアミド等のアミド類、ジメチルスルホキシド、ニトロベンゼン等、さらにはこれらの2種以上の混合物が挙げられる。
上記分散液又はゾル中に観察される前記(A)成分の数平均粒子径(1次粒子と2次粒子との混合物であっても良いし、1次粒子、2次粒子何れかのみであってもよい)としては、好ましくは1nm〜400nm、より好ましくは1nm〜100nm、更に好ましくは3nm〜80nm、特に好ましくは5nm〜50nmである。前記(A)成分の数平均粒子径は、得られる太陽電池用コーティング組成物を用いて形成される積層体(太陽電池用カバー材等)の光学特性等に寄与し得る。特に、100nm以下とすることは、得られる太陽電池用カバー材の透明性を大きく向上させ得る。
なお、本実施の形態における数平均粒子径(単に、「粒子径」と略記することがある)とは、後述する実施例の方法に準じて測定された値である。
Examples of the hydrophilic organic solvent include alcohols such as ethylene glycol, butyl cellosolve, n-propanol, isopropanol, n-butanol, ethanol and methanol, ketones such as acetone, methyl ethyl ketone and methyl isobutyl ketone, tetrahydrofuran and dioxane, and the like. Examples include ethers, amides such as dimethylacetamide, dimethylformamide, dimethyl sulfoxide, nitrobenzene, and a mixture of two or more thereof.
The number average particle size of the component (A) observed in the dispersion or sol (may be a mixture of primary particles and secondary particles, or only primary particles or secondary particles). May be 1 nm to 400 nm, more preferably 1 nm to 100 nm, still more preferably 3 nm to 80 nm, and particularly preferably 5 nm to 50 nm. The number average particle diameter of the component (A) can contribute to the optical characteristics and the like of a laminate (such as a solar cell cover material) formed using the resulting solar cell coating composition. In particular, setting the thickness to 100 nm or less can greatly improve the transparency of the obtained solar cell cover material.
In addition, the number average particle diameter (simply abbreviated as “particle diameter”) in the present embodiment is a value measured according to the method of Examples described later.
前記(A)成分としては、溶媒に対する分散安定性、化学的安定性、耐久性を向上させる観点から、以下の(A’)成分、
(A’)成分:式(1)で表されるトリオルガノシラン単位、式(2)で表されるモノオキシジオルガノシラン単位、式(3)で表されるジオキシオルガノシラン単位、式(4)で表されるトリオキシシラン単位、及びジフルオロメチレン単位よりなる群から選択される少なくとも1種の構造単位を有する変性剤化合物を用いて、前記(A)成分の金属化合物粒子を変性処理して形成される変性金属化合物粒子を含むことが好ましい。なお、「変性処理」とは、上記変性剤化合物を前記金属化合物粒子の表面に固定化することを意味する。上記変性剤化合物の前記金属化合物粒子表面への固定化は、ファン・デル・ワールス力(物理吸着)または化学結合によるものと考えられる。
R3Si− (1)
(式中、Rは各々独立に直鎖状または分岐状の炭素数1〜30個のアルキル基、炭素数5〜20のシクロアルキル基、直鎖状または分岐状の炭素数1〜30個のフルオロアルキル基、直鎖状または分岐状の炭素数2〜30個のアルケニル基、フェニル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、又は水酸基を表す。)
−(R2SiO)− (2)
(式中、Rは式(1)で定義した通りである。)
As the component (A), from the viewpoint of improving dispersion stability, chemical stability and durability with respect to a solvent, the following component (A ′):
(A ′) component: triorganosilane unit represented by formula (1), monooxydiorganosilane unit represented by formula (2), dioxyorganosilane unit represented by formula (3), formula ( Using the modifier compound having at least one structural unit selected from the group consisting of a trioxysilane unit represented by 4) and a difluoromethylene unit, the metal compound particles of the component (A) are modified. It is preferable that the modified | denatured metal compound particle formed in this is included. “Modification” means immobilizing the modifier compound on the surface of the metal compound particles. The immobilization of the modifier compound on the surface of the metal compound particles is considered to be caused by van der Waals force (physical adsorption) or chemical bonding.
R 3 Si- (1)
(In the formula, each R is independently a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms, a cycloalkyl group having 5 to 20 carbon atoms, or a linear or branched carbon group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms. (A fluoroalkyl group, a linear or branched alkenyl group having 2 to 30 carbon atoms, a phenyl group, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, or a hydroxyl group.)
- (R 2 SiO) - ( 2)
(In the formula, R is as defined in formula (1).)
(式中、Rは式(1)で定義した通りである。)
(In the formula, R is as defined in formula (1).)
前記変性剤化合物としては、例えばSi−H基、加水分解性シリル基(アルコキシシリル基、ヒドロキシシリル基、ハロゲン化シリル基、アセトキシシリル基、アミノキシシリル基等)、エポキシ基、アセトアセチル基、チオール基、酸無水物基等を有することが好適である。また、前記変性剤化合物としては、ケイ素化合物、フルオロアルキル化合物、フルオロオレフィン重合体であることが好ましい。このような変性剤化合物は、前記金属化合物粒子と強固に結合し得る。
前記変性剤化合物の中でフルオロアルキル化合物の具体例を示すと、式(5)で示される化合物を挙げることができる。
CF3(CF2)g−Y−(V)w (5)
{式中、gは0〜29の整数を表す。Yは分子量14〜50000のw価の有機基を表す。wは1〜20の整数である。Vは、エポキシ基、水酸基、アセトアセチル基、チオール基、環状酸無水物基、カルボキシル基、スルホン酸基、ポリオキシアルキレン基、リン酸基、及び下式(6)で表される基からなる群から選ばれた少なくとも1つの官能基を表す。
−SiWxRy (6)
(式中、Wは炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、水酸基、炭素数1〜20のアセトキシ基、ハロゲン原子、水素原子、炭素数1〜20のオキシム基、エノキシ基、アミノキシ基、アミド基から選ばれた少なくとも1種の基を表す。Rは、直鎖状または分岐状の炭素数が1〜30個のアルキル基、炭素数5〜20のシクロアルキル基、及び置換されていないか或いは炭素数1〜20のアルキル基又は炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、又はハロゲン原子で置換されている炭素数6〜20のアリール基から選ばれる少なくとも1種の炭化水素基を表す。xは1以上3以下の整数であり、yは0以上2以下の整数である。また、x+y=3である。)}
Examples of the modifier compound include Si—H group, hydrolyzable silyl group (alkoxysilyl group, hydroxysilyl group, halogenated silyl group, acetoxysilyl group, aminoxysilyl group, etc.), epoxy group, acetoacetyl group, It preferably has a thiol group, an acid anhydride group or the like. In addition, the modifier compound is preferably a silicon compound, a fluoroalkyl compound, or a fluoroolefin polymer. Such a modifier compound can be firmly bonded to the metal compound particles.
When the specific example of a fluoroalkyl compound is shown in the said modifier compound, the compound shown by Formula (5) can be mentioned.
CF 3 (CF 2) g- Y- (V) w (5)
{In the formula, g represents an integer of 0 to 29. Y represents a w-valent organic group having a molecular weight of 14 to 50,000. w is an integer of 1-20. V is composed of an epoxy group, a hydroxyl group, an acetoacetyl group, a thiol group, a cyclic acid anhydride group, a carboxyl group, a sulfonic acid group, a polyoxyalkylene group, a phosphoric acid group, and a group represented by the following formula (6). It represents at least one functional group selected from the group.
-SiWxRy (6)
(In the formula, W represents an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, a hydroxyl group, an acetoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, a halogen atom, a hydrogen atom, an oxime group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an enoxy group, an aminoxy group, and an amide group. Represents at least one selected group, wherein R is a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms, a cycloalkyl group having 5 to 20 carbon atoms, and an unsubstituted or carbon atom. It represents at least one hydrocarbon group selected from an alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, or an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms substituted with a halogen atom, where x is 1 or more. Is an integer of 3 or less, and y is an integer of 0 or more and 2 or less, and x + y = 3.)}
また、上記変性剤化合物としては、得られる(A’)成分の表面エネルギーを小さくして自己傾斜機能を発現させる観点から、表面エネルギーの小さい化合物(例えば、上記式(1)〜(4)における置換基Rが直鎖状または分岐状の炭素数1〜30個のアルキル基、直鎖状または分岐状の炭素数1〜30個のフルオロアルキル基、直鎖状または分岐状の炭素数2〜30個のアルケニル基から選ばれる少なくとも1種である化合物、及び/又はジフルオロメチレン単位を有する化合物)を選択することが好ましい。 Moreover, as said modifier compound, from a viewpoint of making the surface energy of the (A ') component obtained small and expressing a self-inclination function (for example, in said formula (1)-(4)), a small surface energy is used. The substituent R is a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms, a linear or branched fluoroalkyl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms, a linear or branched carbon number 2 to 2. It is preferable to select a compound which is at least one selected from 30 alkenyl groups and / or a compound having a difluoromethylene unit.
ここで、上記「自己傾斜機能を発現」とは、前記(A’)成分と前記(B)成分とを含む太陽電池用コーティング組成物を基材上に積層して太陽電池用カバー材を形成する際、基材表面の性状(特に親水/疎水性)に対応して前記(A’)成分の濃度勾配(太陽電池用コーティング組成物にて形成される層中の濃度の偏り)が自立的に形成されることを意味する。
前記(A’)成分として、表面エネルギーの小さな化合物で変性された光触媒を用い、表面親水性の大きな基材を用いて太陽電池用カバー材を形成する場合、前記(A’)成分は空気と接する側に偏在して前記基材表面付近の存在量が少なくなる傾向となる。このような場合、高い光触媒活性を期待し得ると共に、基材が分解され難くなる(基材の耐久性が向上する)ため好ましい。
Here, “express self-grading function” means that a solar cell cover material is formed by laminating a solar cell coating composition containing the component (A ′) and the component (B) on a substrate. When this is done, the concentration gradient of the component (A ′) (the concentration deviation in the layer formed by the coating composition for solar cells) is self-supporting corresponding to the properties of the substrate surface (particularly hydrophilic / hydrophobic). It means that it is formed.
When the photocatalyst modified with a compound having a small surface energy is used as the component (A ′) and a solar cell cover material is formed using a substrate having a large surface hydrophilicity, the component (A ′) It tends to be unevenly distributed on the side in contact with the surface of the base material and decrease in the abundance. In such a case, high photocatalytic activity can be expected, and the substrate is hardly decomposed (durability of the substrate is improved), which is preferable.
なお、上記変性処理の方法としては、例えば、水及び/又は有機溶媒の存在下、あるいは非存在下において、前記金属化合物粒子と前記変性剤化合物とを混合し、好ましくは0〜200℃、より好ましくは10〜80℃にて加熱する方法や、混合溶媒の存在下で前記金属化合物粒子と前記変性剤化合物とを混合し、(減圧)蒸留等して混合溶媒の溶媒組成を変化させる方法、等が挙げられる。
前記(A’)成分が、前記(A)成分中に占める割合としては、好ましくは0.01〜100質量%、より好ましくは0.01〜99.99質量%、更に好ましくは0.1〜95質量%、特に好ましくは1〜90質量%である。当該割合を0.01質量%以上とすることは、自己傾斜性を付与する観点から好適である。なお、当該割合を99.99質量%以下とすることは、光触媒性能を比較的短時間で発現させる観点から好適である。
In addition, as a method for the above modification treatment, for example, the metal compound particles and the modifier compound are mixed in the presence or absence of water and / or an organic solvent, preferably 0 to 200 ° C. Preferably, a method of heating at 10 to 80 ° C., a method of mixing the metal compound particles and the modifier compound in the presence of a mixed solvent, and changing the solvent composition of the mixed solvent by (vacuum) distillation or the like, Etc.
The proportion of the component (A ′) in the component (A) is preferably 0.01 to 100% by mass, more preferably 0.01 to 99.99% by mass, and still more preferably 0.1 to 100% by mass. It is 95 mass%, Most preferably, it is 1-90 mass%. Setting the ratio to 0.01% by mass or more is preferable from the viewpoint of imparting self-tilting property. In addition, it is suitable that the said ratio shall be 99.99 mass% or less from a viewpoint of making photocatalytic performance express in a comparatively short time.
また、前記(A)成分、又は前記(A’)成分について、その粒子長(l)と粒子直径(d)の比(l/d)としては、比表面積を確保する観点、及び粒子の配向効果の観点から、好ましくは1/1〜20/1、より好ましくは1/1〜15/1、さらに好ましくは1/1〜10/1である。
なお、上記粒子長や粒子直径の測定方法としては、透過型電子顕微鏡観察する方法を用いることができる。
In addition, regarding the component (A) or the component (A ′), the ratio (l / d) of the particle length (l) to the particle diameter (d) is a viewpoint of securing a specific surface area and the orientation of the particles. From the viewpoint of the effect, it is preferably 1/1 to 20/1, more preferably 1/1 to 15/1, and further preferably 1/1 to 10/1.
As a method for measuring the particle length and particle diameter, a method of observation with a transmission electron microscope can be used.
前記(B)成分は、以下の(b1)〜(b4)の各成分、
(b1)成分:加水分解性珪素化合物、
(b2)成分:水酸基、カルボキシル基、アミド基、アミノ基、エーテル基よりなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1種の官能基を含有するビニル単量体、
(b3)成分:乳化剤、
(b4)成分:水、
を含む重合原液を重合して得られる重合体エマルジョン粒子である。このようにして得られる(B)成分としては、前記(b1)成分に由来する水酸基と、前記(b2)成分の重合生成物とが、水素結合等により複合化されたものを用いることが好適である。
The component (B) includes the following components (b1) to (b4):
(B1) component: hydrolyzable silicon compound,
(B2) component: a vinyl monomer containing at least one functional group selected from the group consisting of a hydroxyl group, a carboxyl group, an amide group, an amino group, and an ether group;
(B3) component: emulsifier,
(B4) component: water,
Polymer emulsion particles obtained by polymerizing a polymerization stock solution containing As the component (B) thus obtained, it is preferable to use a compound in which the hydroxyl group derived from the component (b1) and the polymerization product of the component (b2) are combined by hydrogen bonding or the like. It is.
前記(b1)成分としては、下記式(7)で表される化合物やその縮合生成物、シランカップリング剤を例示することができる。
SiWxRy (7)
(式中、Wは炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、水酸基、炭素数1〜20のアセトキシ基、ハロゲン原子、水素原子、炭素数1〜20のオキシム基、エノキシ基、アミノキシ基、アミド基から選ばれた少なくとも1種の基を表す。Rは、直鎖状又は分岐状の炭素数が1〜30個のアルキル基、炭素数5〜20のシクロアルキル基、及び置換されていないか又は炭素数1〜20のアルキル基若しくは炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基若しくはハロゲン原子で置換されている炭素数6〜20のアリール基から選ばれる少なくとも1種の炭化水素基を表す。xは1以上4以下の整数であり、yは0以上3以下の整数である。また、x+y=4である。)
なお、シランカップリング剤とは、ビニル重合性基、エポキシ基、アミノ基、メタクリル基、メルカプト基、イソシアネート基等の有機物と反応性を有する官能基が分子内に存在する化合物を意味する。
As said (b1) component, the compound represented by following formula (7), its condensation product, and a silane coupling agent can be illustrated.
SiWxRy (7)
(In the formula, W represents an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, a hydroxyl group, an acetoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, a halogen atom, a hydrogen atom, an oxime group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an enoxy group, an aminoxy group, and an amide group. Represents at least one selected group, wherein R represents a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms, a cycloalkyl group having 5 to 20 carbon atoms, and an unsubstituted or carbon atom. It represents at least one hydrocarbon group selected from an alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, or an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms substituted with a halogen atom, where x is 1 or more and 4; And y is an integer of 0 or more and 3 or less, and x + y = 4.)
In addition, a silane coupling agent means the compound in which the functional group which has reactivity with organic substances, such as a vinyl polymerizable group, an epoxy group, an amino group, a methacryl group, a mercapto group, an isocyanate group, exists in a molecule | numerator.
前記式(7)で表される化合物の具体例としては、例えばテトラメトキシシラン、テトラエトキシシラン、テトラ−n−プロポキシシラン、テトライソプロポキシシラン、テトラ−n−ブトキシシラン等のテトラアルコキシシラン類;メチルトリメトキシシラン、メチルトリエトキシシラン、エチルトリメトキシシラン、エチルトリエトキシシラン、n−プロピルトリメトキシシラン、n−プロピルトリエトキシシラン、イソプロピルトリメトキシシラン、イソプロピルトリエトキシシラン、n−ブチルトリメトキシシラン、n−ブチルトリエトキシシラン、n−ペンチルトリメトキシシラン、n−ヘキシルトリメトキシシラン、n−ヘプチルトリメトキシシラン、n−オクチルトリメトキシシラン、ビニルトリメトキシシラン、ビニルトリエトキシシラン、アリルトリメトキシシラン、シクロヘキシルトリメトキシシラン、シクロヘキシルトリエトキシシラン、フェニルトリメトキシシラン、フェニルトリエトキシシラン、3−クロロプロピルトリメトキシシラン、3−クロロプロピルトリエトキシシラン、3,3,3−トリフロロプロピルトリメトキシシラン、3,3,3−トリフロロプロピルトリエトキシシラン、3−アミノプロピルトリメトキシシラン、3−アミノプロピルトリエトキシシラン、2−ヒドロキシエチルトリメトキシシラン、2−ヒドロキシエチルトリエトキシシラン、2−ヒドロキシプロピルトリメトキシシラン、2−ヒドロキシプロピルトリエトキシシラン、3−ヒドロキシプロピルトリメトキシシラン、3−ヒドロキシプロピルトリエトキシシラン、3−メルカプトプロピルトリメトキシシラン、3−メルカプトプロピルトリエトキシシラン、3−イソシアナートプロピルトリメトキシシラン、3−イソシアナートプロピルトリエトキシシラン、3−グリシドキシプロピルトリメトキシシラン、3−グリシドキシプロピルトリエトキシシラン、2−(3,4−エポキシシクロヘキシル)エチルトリメトキシシラン、2−(3,4−エポキシシクロヘキシル)エチルトリエトキシシラン、3−(メタ)アクリルオキシプロピルトリメトキシシラン、3−(メタ)アタクリルオキシプロピルトリエトキシシラン、3−(メタ)アクリロイルオキシプロピルトリ−n−プロポキシシラン、3−(メタ)アクリロイルオキシプロピルトリイソプロポキシシラン、3−ウレイドプロピルトリメトキシシラン、3−ウレイドプロピルトリエトキシシラン等のトリアルコキシシラン類;ジメチルジメトキシシラン、ジメチルジエトキシシラン、ジエチルジメトキシシラン、ジエチルジエトキシシラン、ジ−n−プロピルジメトキシシラン、ジ−n−プロピルジエトキシシラン、ジイソプロピルジメトキシシラン、ジイソプロピルジエトキシシラン、ジ−n−ブチルジメトキシシラン、ジ−n−ブチルジエトキシシラン、ジ−n−ペンチルジメトキシシラン、ジ−n−ペンチルジエトキシシラン、ジ−n−ヘキシルジメトキシシラン、ジ−n−ヘキシルジエトキシシラン、ジ−n−ヘプチルジメトキシシラン、ジ−n−ヘプチルジエトキシシラン、ジ−n−オクチルジメトキシシラン、ジ−n−オクチルジエトキシシラン、ジ−n−シクロヘキシルジメトキシシラン、ジ−n−シクロヘキシルジエトキシシラン、ジフェニルジメトキシシラン、ジフェニルジエトキシシラン、3−(メタ)アクリロイルオキシプロピルメチルジメトキシシラン等のジアルコキシシラン類;トリメチルメトキシシラン、トリメチルエトキシシラン等のモノアルコキシシラン類;等を挙げることができる。また、これらは、単独で又は2種以上を混合して使用することができる。 Specific examples of the compound represented by the formula (7) include tetraalkoxysilanes such as tetramethoxysilane, tetraethoxysilane, tetra-n-propoxysilane, tetraisopropoxysilane, and tetra-n-butoxysilane; Methyltrimethoxysilane, methyltriethoxysilane, ethyltrimethoxysilane, ethyltriethoxysilane, n-propyltrimethoxysilane, n-propyltriethoxysilane, isopropyltrimethoxysilane, isopropyltriethoxysilane, n-butyltrimethoxysilane N-butyltriethoxysilane, n-pentyltrimethoxysilane, n-hexyltrimethoxysilane, n-heptyltrimethoxysilane, n-octyltrimethoxysilane, vinyltrimethoxysilane, vinyltri Toxisilane, allyltrimethoxysilane, cyclohexyltrimethoxysilane, cyclohexyltriethoxysilane, phenyltrimethoxysilane, phenyltriethoxysilane, 3-chloropropyltrimethoxysilane, 3-chloropropyltriethoxysilane, 3,3,3-tri Fluoropropyltrimethoxysilane, 3,3,3-trifluoropropyltriethoxysilane, 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane, 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane, 2-hydroxyethyltrimethoxysilane, 2-hydroxyethyltriethoxysilane 2-hydroxypropyltrimethoxysilane, 2-hydroxypropyltriethoxysilane, 3-hydroxypropyltrimethoxysilane, 3-hydroxypropyltriethoxysilane, -Mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane, 3-mercaptopropyltriethoxysilane, 3-isocyanatopropyltrimethoxysilane, 3-isocyanatopropyltriethoxysilane, 3-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane, 3-glycidoxypropyltri Ethoxysilane, 2- (3,4-epoxycyclohexyl) ethyltrimethoxysilane, 2- (3,4-epoxycyclohexyl) ethyltriethoxysilane, 3- (meth) acryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane, 3- (meth) Atacyloxypropyltriethoxysilane, 3- (meth) acryloyloxypropyltri-n-propoxysilane, 3- (meth) acryloyloxypropyltriisopropoxysilane, 3-ureidopropyltrimethoxysila , Trialkoxysilanes such as 3-ureidopropyltriethoxysilane; dimethyldimethoxysilane, dimethyldiethoxysilane, diethyldimethoxysilane, diethyldiethoxysilane, di-n-propyldimethoxysilane, di-n-propyldiethoxysilane , Diisopropyldimethoxysilane, diisopropyldiethoxysilane, di-n-butyldimethoxysilane, di-n-butyldiethoxysilane, di-n-pentyldimethoxysilane, di-n-pentyldiethoxysilane, di-n-hexyldimethoxy Silane, di-n-hexyldiethoxysilane, di-n-heptyldimethoxysilane, di-n-heptyldiethoxysilane, di-n-octyldimethoxysilane, di-n-octyldiethoxysilane, di-n-cyclohexyl The Dialkoxysilanes such as toxisilane, di-n-cyclohexyldiethoxysilane, diphenyldimethoxysilane, diphenyldiethoxysilane, 3- (meth) acryloyloxypropylmethyldimethoxysilane; monoalkoxysilanes such as trimethylmethoxysilane and trimethylethoxysilane And the like. Moreover, these can be used individually or in mixture of 2 or more types.
また、前記(b1)成分としては、フェニル基を有する珪素アルコキシド(例えばフェニルトリメトキシシラン、フェニルトリエトキシシラン、ジフェニルジメトキシシラン等)を用いることができる。フェニル基を有する珪素アルコキシドを用いた場合、水及び乳化剤の存在下における重合安定性が良好となり好適である。
更に、前記(b1)成分としては、チオール基を有するシランカップリング剤や、以下の(b1−1)成分、
(b1−1)成分:ビニル重合性基を有する加水分解性珪素化合物
を含んでもよい。これらを用いた場合、得られる太陽電池用カバー材の耐候性、防汚染性が良好となり好適である。
As the component (b1), a silicon alkoxide having a phenyl group (for example, phenyltrimethoxysilane, phenyltriethoxysilane, diphenyldimethoxysilane, etc.) can be used. When a silicon alkoxide having a phenyl group is used, the polymerization stability in the presence of water and an emulsifier is good, which is preferable.
Furthermore, as said (b1) component, the silane coupling agent which has a thiol group, the following (b1-1) component,
(B1-1) Component: A hydrolyzable silicon compound having a vinyl polymerizable group may be included. When these are used, the weather resistance and antifouling properties of the obtained solar cell cover material are favorable, which is preferable.
上記チオール基を有するシランカップリング剤としては、例えば、3−メルカプトプロピルトリメトキシシラン、3−メルカプトプロピルトリエトキシシラン等、を挙げることができる。
また、前記(b1−1)成分としては、例えば、3−(メタ)アクリルオキシプロピルトリメトキシシラン、3−(メタ)アタクリルオキシプロピルトリエトキシシラン、3−(メタ)アクリロイルオキシプロピルメチルジメトキシシラン、3−(メタ)アクリロイルオキシプロピルトリn−プロポキシシラン、3−(メタ)アクリロイルオキシプロピルトリイソプロポキシシラン、ビニルトリメトキシシラン、ビニルトリエトキシシラン、アリルトリメトキシシラン、2−トリメトキシシリルエチルビニルエーテル等のビニル重合性基を有するシランカップリング剤、等を挙げることができる。
これらシランカップリング剤は、後述する(b2)成分との共重合又は連鎖移動反応により化学結合を生成し得る。このため、ビニル重合性基やチオール基を有するシランカップリング剤を上述した前記(b1)成分と混合若しくは複合化させて用いた場合、前記(b1)の重合生成物と後述する(b2)成分の重合生成物とを化学結合により複合化し得る。
なお、(b1−1)成分にいう「ビニル重合性基」としては、例えば、ビニル基、アリル基等を挙げることができ、中でも3−(メタ)アクリルオキシプロピル基が好ましい。
Examples of the silane coupling agent having a thiol group include 3-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane and 3-mercaptopropyltriethoxysilane.
Examples of the component (b1-1) include 3- (meth) acryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane, 3- (meth) acryloxypropyltriethoxysilane, and 3- (meth) acryloyloxypropylmethyldimethoxysilane. 3- (meth) acryloyloxypropyltri-n-propoxysilane, 3- (meth) acryloyloxypropyltriisopropoxysilane, vinyltrimethoxysilane, vinyltriethoxysilane, allyltrimethoxysilane, 2-trimethoxysilylethyl vinyl ether Examples thereof include silane coupling agents having a vinyl polymerizable group.
These silane coupling agents can generate chemical bonds by copolymerization or chain transfer reaction with the component (b2) described later. For this reason, when a silane coupling agent having a vinyl polymerizable group or a thiol group is used by mixing or combining with the above-described component (b1), the polymerization product of (b1) and the component (b2) described later These polymerization products can be combined by chemical bonding.
Examples of the “vinyl polymerizable group” referred to as the component (b1-1) include a vinyl group and an allyl group. Among them, a 3- (meth) acryloxypropyl group is preferable.
また、前記(b1)成分としては、以下の(b1−2)成分、
(b1−2)成分:環状シロキサンオリゴマー
を含んでいてもよい。当該(b1−2)成分を用いた場合、得られる太陽電池用カバー材の柔軟性がより良好となり好適である。
Moreover, as said (b1) component, the following (b1-2) components,
Component (b1-2): A cyclic siloxane oligomer may be included. When the said (b1-2) component is used, the softness | flexibility of the solar cell cover material obtained becomes more favorable, and is suitable.
前記環状シロキサンオリゴマーとしては、下記式(8)で表される化合物を例示することができる。
(R’2SiO)m (8)
(式中、R’は、水素原子、直鎖状又は分岐状の炭素数が1〜30個のアルキル基、炭素数5〜20のシクロアルキル基、及び置換されていないか又は炭素数1〜20のアルキル基若しくは炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基若しくはハロゲン原子で置換されている炭素数6〜20のアリール基から選ばれる少なくとも1種を表す。mは整数であり、2≦m≦20である。)
中でも、反応性等の点からオクタメチルシクロテトラシロキサン等の環状ジメチルシロキサンオリゴマーが好ましい。
As said cyclic siloxane oligomer, the compound represented by following formula (8) can be illustrated.
(R ′ 2 SiO) m (8)
(In the formula, R ′ is a hydrogen atom, a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms, a cycloalkyl group having 5 to 20 carbon atoms, and an unsubstituted or substituted carbon atom having 1 to 30 carbon atoms. It represents at least one selected from an alkyl group having 20 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, or an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms substituted with a halogen atom, m is an integer, and 2 ≦ m ≦ 20 is there.)
Of these, cyclic dimethylsiloxane oligomers such as octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane are preferred from the viewpoint of reactivity.
なお、前記(b1)成分が縮合生成物として使用される場合、当該縮合生成物のポリスチレン換算重量平均分子量(GPC法による)は、好ましくは200〜5000、より好ましくは300〜1000である。 In addition, when the said (b1) component is used as a condensation product, the polystyrene conversion weight average molecular weight (by GPC method) of the said condensation product becomes like this. Preferably it is 200-5000, More preferably, it is 300-1000.
前記(b1)成分と、後述する(B)成分との比(b1)/(B)(質量比)としては、重合安定性の観点から、好ましくは0.01/100〜80/100、より好ましくは0.1/100〜70/100である。
一方、前記(b1−1)成分と、前記(B)成分との比(b1−1)/(B)(質量比)としては、重合安定性の観点から、好ましくは0.01/100〜20/100、より好ましくは0.5/100〜10/100である。
また、前記(b1−1)成分と、前記(b2)成分との比(b1−1)/(b2)(質量比)としては、重合安定性の観点から、好ましくは0.1/100〜100/100、より好ましくは0.5/100〜50/100である。
他方、前記(b1−2)成分と、前記(B)成分との比(b1−2)/(B)(質量比)としては、親水性の観点から、好ましくは0.01/100〜20/100、より好ましくは0.5/100〜5/100である。
また、前記(b1−2)成分と、前記(b2)成分との比(b1−2)/(b2)(質量比)としては、重合安定性の観点から、好ましくは0.5/100〜50/100、より好ましくは1.0/100〜20/100である。
The ratio (b1) / (B) (mass ratio) between the component (b1) and the component (B) described later is preferably 0.01 / 100 to 80/100, from the viewpoint of polymerization stability. Preferably it is 0.1 / 100-70 / 100.
On the other hand, the ratio (b1-1) / (B) (mass ratio) between the component (b1-1) and the component (B) is preferably 0.01 / 100 to from the viewpoint of polymerization stability. 20/100, more preferably 0.5 / 100 to 10/100.
The ratio (b1-1) / (b2) (mass ratio) between the component (b1-1) and the component (b2) is preferably 0.1 / 100 to from the viewpoint of polymerization stability. 100/100, more preferably 0.5 / 100 to 50/100.
On the other hand, the ratio (b1-2) / (B) (mass ratio) between the component (b1-2) and the component (B) is preferably 0.01 / 100 to 20 from the viewpoint of hydrophilicity. / 100, more preferably 0.5 / 100 to 5/100.
The ratio (b1-2) / (b2) (mass ratio) between the component (b1-2) and the component (b2) is preferably 0.5 / 100 to from the viewpoint of polymerization stability. 50/100, more preferably 1.0 / 100 to 20/100.
前記(b2)成分としては、例えば、水酸基含有ビニル単量体としては、2−ヒドロキシエチル(メタ)アクリレート、2−ヒドロキシプロピル(メタ)アクリレートもしくは4−ヒドロキシブチル(メタ)アクリレートの如き、各種のヒドロキシアルキル(メタ)アクリレート類;2−ヒドロキシエチルビニルエーテルもしくは4−ヒドロキシブチルビニルエーテルの如き、各種の水酸基含有ビニルエーテル類;2−ヒドロキシエチルアリルエーテルの如き、各種の水酸基含有アリルエーテル類;ポリエチレングリコールなどを以て代表されるような、種々のポリエーテルポリオールと、(メタ)アクリル酸などを以て代表されるような、種々の不飽和カルボン酸とから得られるポリオキシアルキレングリコールのモノエステル類;前掲したような各種の水酸基含有単量体類と、ε−カプロラクトンなどを以て代表されるような、種々のラクトン類との付加物;またはグリシジル(メタ)アクリレートなどを以て代表されるような、種々のエポキシ基含有不飽和単量体と、酢酸などを以て代表されるような、種々の酸類との付加物;さらには、(メタ)アクリル酸などを以て代表されるような、種々の不飽和カルボン酸類と、「カーデュラ E」(オランダ国シェル社製の商品名)などを以て代表されるような、α−オレフィンのエポキサイド以外の、種々のモノエポキシ化合物との付加物などのような種々の水酸基含有ビニル単量体類などである。
カルボキシル基含有ビニル単量体としては、(メタ)アクリル酸、2−カルボキシエチル(メタ)アクリレート、クロトン酸、イタコン酸、マレイン酸またはフマル酸の如き、各種の不飽和カルボン酸類;イタコン酸モノメチル、イタコン酸モノ−n−ブチル、マレイン酸モノメチル、マレイン酸モノ−n−ブチル、フマル酸モノメチル、フマル酸モノ−n−ブチルの如き、不飽和ジカルボン酸類と、飽和1価アルコール類とのモノエステル類(ハーフエステル類);アジピン酸モノビニルまたはコハク酸モノビニルの如き、各種の飽和ジカルボン酸のモノビニルエステル類;無水コハク酸、無水グルタル酸、無水フタル酸または無水トリメリット酸の如き、各種の飽和ポリカルボン酸の無水物類と前掲した各種の水酸基含有ビニル系単量体類との付加反応生成物;さらには、前掲したような各種のカルボキシル基含有単量体類とラクトン類を付加反応せしめて得られるような単量体類などである。
Examples of the component (b2) include various hydroxyl groups-containing vinyl monomers such as 2-hydroxyethyl (meth) acrylate, 2-hydroxypropyl (meth) acrylate and 4-hydroxybutyl (meth) acrylate. Hydroxyalkyl (meth) acrylates; various hydroxyl group-containing vinyl ethers such as 2-hydroxyethyl vinyl ether or 4-hydroxybutyl vinyl ether; various hydroxyl group-containing allyl ethers such as 2-hydroxyethyl allyl ether; polyethylene glycol, etc. Monoesters of polyoxyalkylene glycols obtained from various polyether polyols as typified and various unsaturated carboxylic acids as typified by (meth) acrylic acid and the like; Adducts of various hydroxyl group-containing monomers and lactones such as ε-caprolactone; or various epoxy groups such as glycidyl (meth) acrylate Adducts of the unsaturated monomer containing and various acids such as represented by acetic acid; and various unsaturated carboxylic acids such as represented by (meth) acrylic acid; Various hydroxyl group-containing vinyl monomers such as adducts with various monoepoxy compounds other than epoxides of α-olefins as represented by “Cardura E” (trade name of Shell, Netherlands) Etc.
As the carboxyl group-containing vinyl monomer, various unsaturated carboxylic acids such as (meth) acrylic acid, 2-carboxyethyl (meth) acrylate, crotonic acid, itaconic acid, maleic acid or fumaric acid; monomethyl itaconate, Monoesters of unsaturated dicarboxylic acids with saturated monohydric alcohols such as mono-n-butyl itaconate, monomethyl maleate, mono-n-butyl maleate, monomethyl fumarate, mono-n-butyl fumarate (Half esters); monovinyl esters of various saturated dicarboxylic acids such as monovinyl adipate or monovinyl succinate; various saturated polycarboxylic acids such as succinic anhydride, glutaric anhydride, phthalic anhydride or trimellitic anhydride Acid anhydrides and various hydroxyl-containing vinyl monomers listed above Addition reaction products of; further, and the like monomers, such as obtained allowed the addition reaction of various carboxyl group-containing monomers and lactones, such as supra.
アミノ基含有ビニル単量体としては、2−ジメチルアミノエチル(メタ)アクリレート、2−ジエチルアミノエチル(メタ)アクリレート、2−ジ−n−プロピルアミノエチル(メタ)アクリレート、3−ジメチルアミノプロピル(メタ)アクリレート、4−ジメチルアミノブチル(メタ)アクリレートまたはN−[2−(メタ)アクリロイルオキシ]エチルモルホリンの如き、各種の3級アミノ基含有(メタ)アクリル酸エステル類;ビニルピリジン、N−ビニルカルバゾールN−ビニルキノリンの如き、各種の3級アミノ基含有芳香族ビニル系単量体類;N−(2−ジメチルアミノ)エチル(メタ)アクリルアミド、N−(2−ジエチルアミノ)エチル(メタ)アクリルアミド、N−(2−ジ−n−プロピルアミノ)エチル(メタ)アクリルアミド、N−(3−ジメチルアミノ)プロピル(メタ)アクリルアミド、N−(4−ジメチルアミノ)ブチル(メタ)アクリルアミドまたはN−[2−(メタ)アクリルアミド]エチルモルホリンの如き、各種の3級アミノ基含有(メタ)アクリルアミド類;N−(2−ジメチルアミノ)エチルクロトン酸アミド、N−(2−ジエチルアミノ)エチルクロトン酸アミド、N−(2−ジ−n−プロピルアミノ)エチルクロトン酸アミド、N−(3−ジメチルアミノ)プロピルクロトン酸アミドまたはN−(4−ジメチルアミノ)ブチルクロトン酸アミドの如き、各種の3級アミノ基含有クロトン酸アミド類;2−ジメチルアミノエチルビニルエーテル、2−ジエチルアミノエチルビニルエーテル、3−ジメチルアミノプロピルビニルエーテルまたは4−ジメチルアミノブチルビニルエーテルの如き、各種の3級アミノ基含有ビニルエーテル類などである。 Examples of amino group-containing vinyl monomers include 2-dimethylaminoethyl (meth) acrylate, 2-diethylaminoethyl (meth) acrylate, 2-di-n-propylaminoethyl (meth) acrylate, 3-dimethylaminopropyl (meth) ) Various tertiary amino group-containing (meth) acrylic esters such as acrylate, 4-dimethylaminobutyl (meth) acrylate or N- [2- (meth) acryloyloxy] ethylmorpholine; vinylpyridine, N-vinyl Various tertiary amino group-containing aromatic vinyl monomers such as carbazole N-vinylquinoline; N- (2-dimethylamino) ethyl (meth) acrylamide, N- (2-diethylamino) ethyl (meth) acrylamide N- (2-di-n-propylamino) ethyl (meth) acrylate Various tertiary amino acids such as luamide, N- (3-dimethylamino) propyl (meth) acrylamide, N- (4-dimethylamino) butyl (meth) acrylamide or N- [2- (meth) acrylamide] ethylmorpholine Group-containing (meth) acrylamides; N- (2-dimethylamino) ethylcrotonamide, N- (2-diethylamino) ethylcrotonamide, N- (2-di-n-propylamino) ethylcrotonamide, Various tertiary amino group-containing crotonic acid amides such as N- (3-dimethylamino) propyl crotonic acid amide or N- (4-dimethylamino) butyl crotonic acid amide; 2-dimethylaminoethyl vinyl ether, 2-diethylamino Ethyl vinyl ether, 3-dimethylaminopropyl vinyl ether Or 4, such as dimethylamino-butyl vinyl ether, tertiary amino group-containing vinyl ethers of various or the like.
エーテル基含有ビニル単量体としては、ポリオキシエチレンアルキルエーテル、ポリオキシエチレンアルキルフェニルエーテル、ポリオキシエチレン高級脂肪酸エステル、ポリオキシエチレン-ポリオキシプロピレンブロック共重合体のような各種のポリエーテル鎖を側鎖に有するビニルエーテル類、アリルエーテル類又は(メタ)アクリル酸エステル類のビニル単量体類などが挙げられる。具体例としては、ブレンマーPE−90、PE−200、PE−350、PME−100、PME−200、PME−400、AE−350〔以上、日本油脂(株)製〕、MA−30、MA−50、MA−100、MA−150、RA−1120、RA−2614、RMA−564、RMA−568、RMA−1114、MPG130−MA〔以上、日本乳化剤(株)製〕などが挙げられる。ここで、ポリオキシエチレン鎖のオキシエチレン単位は2〜30が好ましい。2未満では、塗膜の柔軟性が不十分となり、30を超えると、塗膜が軟らかくなり、耐ブロッキング性に劣る。 Examples of ether group-containing vinyl monomers include various polyether chains such as polyoxyethylene alkyl ether, polyoxyethylene alkyl phenyl ether, polyoxyethylene higher fatty acid ester, and polyoxyethylene-polyoxypropylene block copolymer. Examples thereof include vinyl ethers, allyl ethers or vinyl monomers such as (meth) acrylic acid esters having a side chain. As specific examples, Bremer PE-90, PE-200, PE-350, PME-100, PME-200, PME-400, AE-350 [above, manufactured by NOF Corporation], MA-30, MA- 50, MA-100, MA-150, RA-1120, RA-2614, RMA-564, RMA-568, RMA-1114, MPG130-MA [above, manufactured by Nippon Emulsifier Co., Ltd.]. Here, as for the oxyethylene unit of a polyoxyethylene chain, 2-30 are preferable. If it is less than 2, the flexibility of the coating film becomes insufficient, and if it exceeds 30, the coating film becomes soft and the blocking resistance is poor.
アミド基含有ビニル単量体としては、例えば、N−アルキル又はN−アルキレン置換(メタ)アクリルアミドを例示することができる。
より具体的には、例えばN−メチルアクリルアミド、N−メチルメタアクリルアミド、N−エチルアクリルアミド、N,N−ジメチルアクリルアミド、N,N−ジメチルメタアクリルアミド、N,N−ジエチルアクリルアミド、N−エチルメタアクリルアミド、N−メチル−N−エチルアクリルアミド、N−メチル−N−エチルメタアクリルアミド、N−イソプロピルアクリルアミド、N−n−プロピルアクリルアミド、N−イソプロピルメタアクリルアミド、N−n−プロピルメタアクリルアミド、N−メチル−N−n−プロピルアクリルアミド、N−メチル−N−イソプロピルアクリルアミド、N−アクリロイルピロリジン、N−メタクリロイルピロリジン、N−アクリロイルピペリジン、N−メタクリロイルピペリジン、N−アクリロイルヘキサヒドロアゼピン、N−アクリロイルモルホリン、N−メタクリロイルモルホリン、N−ビニルピロリドン、N−ビニルカプロラクタム、N,N’−メチレンビスアクリルアミド、N,N’−メチレンビスメタクリルアミド、N−ビニルアセトアミド、ダイアセトンアクリルアミド、ダイアセトンメタアクリルアミド、N−メチロールアクリルアミド、N−メチロールメタアクリルアミド等を挙げることができる。
Examples of the amide group-containing vinyl monomer include N-alkyl or N-alkylene-substituted (meth) acrylamide.
More specifically, for example, N-methylacrylamide, N-methylmethacrylamide, N-ethylacrylamide, N, N-dimethylacrylamide, N, N-dimethylmethacrylamide, N, N-diethylacrylamide, N-ethylmethacrylamide N-methyl-N-ethylacrylamide, N-methyl-N-ethylmethacrylamide, N-isopropylacrylamide, Nn-propylacrylamide, N-isopropylmethacrylamide, Nn-propylmethacrylamide, N-methyl- Nn-propylacrylamide, N-methyl-N-isopropylacrylamide, N-acryloylpyrrolidine, N-methacryloylpyrrolidine, N-acryloylpiperidine, N-methacryloylpiperidine, N-acrylo Ruhexahydroazepine, N-acryloylmorpholine, N-methacryloylmorpholine, N-vinylpyrrolidone, N-vinylcaprolactam, N, N'-methylenebisacrylamide, N, N'-methylenebismethacrylamide, N-vinylacetamide, dye Acetone acrylamide, diacetone methacrylamide, N-methylol acrylamide, N-methylol methacrylamide, etc. can be mentioned.
前記(b2)成分としては、他成分との水素結合性をより向上させる観点から、2級及び/又は3級アミド基を有するビニル単量体を用いることが好ましい。 As said (b2) component, it is preferable to use the vinyl monomer which has a secondary and / or tertiary amide group from a viewpoint of improving a hydrogen bond property with another component more.
前記(b2)成分と、前記(B)成分との比(b2)/(B)(質量比)としては、重合安定性の観点から、好ましくは0.1/1〜0.5/1である。
また、前記(b2)成分と、前記(A)成分との比(b2)/(A)(質量比)としては、(A)成分との水素結合性や配合安定性の観点から、好ましくは0.1/1〜1.0/1である。
前記(b3)成分としては、例えば、アルキルベンゼンスルホン酸、アルキルスルホン酸、アルキルスルホコハク酸、ポリオキシエチレンアルキル硫酸、ポリオキシエチレンアルキルアリール硫酸、ポリオキシエチレンジスチリルフェニルエーテルスルホン酸等の酸性乳化剤、酸性乳化剤のアルカリ金属(Li、Na、K等)塩、酸性乳化剤のアンモニウム塩、脂肪酸石鹸等のアニオン性界面活性剤;アルキルトリメチルアンモニウムブロミド、アルキルピリジニウムブロミド、イミダゾリニウムラウレート等の四級アンモニウム塩、ピリジニウム塩、イミダゾリニウム塩型のカチオン性界面活性剤;ポリオキシエチレンアルキルアリールエーテル、ポリオキシエチレンソルビタン脂肪酸エステル、ポリオキシエチレンオキシプロピレンブロックコポリマー、ポリオキシエチレンジスチリルフェニルエーテル等のノニオン型界面活性剤;等が挙げられる。これらは1種を単独で、又は2種以上を併用することができる。
The ratio (b2) / (B) (mass ratio) between the component (b2) and the component (B) is preferably 0.1 / 1 to 0.5 / 1 from the viewpoint of polymerization stability. is there.
The ratio (b2) / (A) (mass ratio) between the component (b2) and the component (A) is preferably from the viewpoint of hydrogen bondability with the component (A) and blending stability. 0.1 / 1 to 1.0 / 1.
Examples of the component (b3) include acidic emulsifiers such as alkylbenzenesulfonic acid, alkylsulfonic acid, alkylsulfosuccinic acid, polyoxyethylene alkylsulfuric acid, polyoxyethylenealkylarylsulfuric acid, polyoxyethylene distyrylphenyl ether sulfonic acid, Anionic surfactants such as alkali metal (Li, Na, K, etc.) salts of emulsifiers, ammonium salts of acidic emulsifiers, fatty acid soaps; quaternary ammonium salts such as alkyltrimethylammonium bromide, alkylpyridinium bromide, imidazolinium laurate , Pyridinium salt, imidazolinium salt type cationic surfactants; polyoxyethylene alkyl aryl ether, polyoxyethylene sorbitan fatty acid ester, polyoxyethyleneoxypropylene bromide Kukoporima, nonionic surfactants such as polyoxyethylene distyryl phenyl ether; and the like. These can be used alone or in combination of two or more.
前記(b3)成分としては、得られる前記(B)成分の水分散安定性を向上させる観点、及び、得られる太陽電池用カバー材の耐候性、防汚染性を向上させる観点から、ラジカル重合性の二重結合を有する反応性乳化剤を用いることが好ましい。
上記反応性乳化剤としてより具体的には、例えば、スルホン酸基又はスルホネート基を有するビニル単量体、硫酸エステル基を有するビニル単量体やそれらのアルカリ金属塩、アンモニウム塩、ポリオキシエチレン等のノニオン基を有するビニル単量体、4級アンモニウム塩を有するビニル単量体等を挙げることができる。
上記スルホン酸基又はスルホネート基を有するビニル単量体としては、例えば、ラジカル重合性の二重結合を有し、且つスルホン酸基のアンモニウム塩、ナトリウム塩又はカリウム塩のような置換基により一部が置換された、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数2〜4のアルキルエーテル基、炭素数2〜4のポリアルキルエーテル基、フェニル基、ナフチル基、及びコハク酸基よりなる群から選ばれる置換基を有する化合物;スルホン酸基のアンモニウム塩、ナトリウム塩又はカリウム塩のような置換基が結合しているビニル基を有するビニルスルホネート化合物;等が挙げられる。
硫酸エステル基を有するビニル単量体としては、例えば、ラジカル重合性の二重結合を有し、かつ硫酸エステル基のアンモニウム塩、ナトリウム塩又はカリウム塩のような置換基により一部が置換された、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数2〜4のアルキルエーテル基、炭素数2〜4のポリアルキルエーテル基、フェニル基、及びナフチル基よりなる群から選ばれる置換基を有する化合物が挙げられる。
上記スルホン酸基のアンモニウム塩、ナトリウム塩又はカリウム塩のような置換基により一部が置換されたコハク酸基を有する化合物の具体例としては、アリルスルホコハク酸塩が挙げられる。より詳しくは、例えば、エレミノールJS−2(商品名)(三洋化成(株)製)、ラテムルS−120、S−180A又はS−180(商品名)(花王(株)製)等を挙げることができる。
As the component (b3), from the viewpoint of improving the water dispersion stability of the component (B) to be obtained, and from the viewpoint of improving the weather resistance and antifouling properties of the resulting solar cell cover material, radical polymerization is possible. It is preferable to use a reactive emulsifier having a double bond.
More specifically, the reactive emulsifier includes, for example, a vinyl monomer having a sulfonic acid group or a sulfonate group, a vinyl monomer having a sulfate ester group, an alkali metal salt thereof, an ammonium salt, a polyoxyethylene, etc. Examples thereof include a vinyl monomer having a nonionic group and a vinyl monomer having a quaternary ammonium salt.
Examples of the vinyl monomer having a sulfonic acid group or a sulfonate group include, for example, a radically polymerizable double bond, and partly by a substituent such as an ammonium salt, a sodium salt, or a potassium salt of the sulfonic acid group. Selected from the group consisting of an alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkyl ether group having 2 to 4 carbon atoms, a polyalkyl ether group having 2 to 4 carbon atoms, a phenyl group, a naphthyl group, and a succinic acid group. A compound having a substituent, a vinyl sulfonate compound having a vinyl group to which a substituent is bonded, such as an ammonium salt, a sodium salt, or a potassium salt of a sulfonic acid group;
As the vinyl monomer having a sulfate ester group, for example, it has a radical polymerizable double bond and is partially substituted by a substituent such as an ammonium salt, sodium salt or potassium salt of the sulfate ester group. , A compound having a substituent selected from the group consisting of an alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkyl ether group having 2 to 4 carbon atoms, a polyalkyl ether group having 2 to 4 carbon atoms, a phenyl group, and a naphthyl group. It is done.
Specific examples of the compound having a succinic acid group partially substituted with a substituent such as ammonium salt, sodium salt or potassium salt of the sulfonic acid group include allylsulfosuccinate. More specifically, for example, Eleminol JS-2 (trade name) (manufactured by Sanyo Chemical Co., Ltd.), Latemuru S-120, S-180A or S-180 (trade name) (manufactured by Kao Corporation), etc. Can do.
また、上記スルホン酸基のアンモニウム塩、ナトリウム塩又はカリウム塩である基により一部が置換された、炭素数2〜4のアルキルエーテル基又は炭素数2〜4のポリアルキルエーテル基を有する化合物の具体例としては、例えばアクアロンHS−10又はKH−1025(商品名)(第一工業製薬(株)製)、アデカリアソープSE−1025N又はSR−1025(商品名)(旭電化工業(株)製)等を挙げることができる。
また、ノニオン基を有するビニル単量体として具体的には、例えば、α−〔1−〔(アリルオキシ)メチル〕−2−(ノニルフェノキシ)エチル〕−ω−ヒドロキシポリオキシエチレン(商品名:アデカリアソープNE−20、NE−30、NE−40等、旭電化工業(株)製)、ポリオキシエチレンアルキルプロペニルフェニルエーテル(商品名:アクアロンRN−10、RN−20、RN−30、RN−50等、第一製薬工業(株)製)等を挙げることができる。
前記(b3)成分の使用量としては、重合安定性の観点から、前記(B)成分100質量部に対して、好ましくは10質量部以下、より好ましくは0.001〜5質量部である。
前記(B)成分は上述した(b1)〜(b3)の各成分、及び前記(b4)成分(即ち「水」)を含む重合原液を重合して得られる重合体エマルジョン粒子である。前記(b4)成分の使用量としては、重合安定性の観点から、重合原液中の含有率として好ましくは30〜99.9質量%である。
前記重合原液には、(b1)〜(b4)成分に加え、更に種々の成分を混合することができる。
Further, a compound having an alkyl ether group having 2 to 4 carbon atoms or a polyalkyl ether group having 2 to 4 carbon atoms, which is partially substituted by a group which is an ammonium salt, sodium salt or potassium salt of the sulfonic acid group. Specific examples include, for example, Aqualon HS-10 or KH-1025 (trade name) (Daiichi Kogyo Seiyaku Co., Ltd.), Adeka Soap SE-1025N or SR-1025 (trade name) (Asahi Denka Kogyo Co., Ltd.) Manufactured).
Specific examples of the vinyl monomer having a nonionic group include, for example, α- [1-[(allyloxy) methyl] -2- (nonylphenoxy) ethyl] -ω-hydroxypolyoxyethylene (trade name: ADEKA Rear soap NE-20, NE-30, NE-40, etc., manufactured by Asahi Denka Kogyo Co., Ltd., polyoxyethylene alkylpropenyl phenyl ether (trade names: Aqualon RN-10, RN-20, RN-30, RN- 50, manufactured by Dai-ichi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.).
The amount of the component (b3) used is preferably 10 parts by mass or less, more preferably 0.001 to 5 parts by mass with respect to 100 parts by mass of the component (B) from the viewpoint of polymerization stability.
The component (B) is polymer emulsion particles obtained by polymerizing a polymerization stock solution containing the components (b1) to (b3) described above and the component (b4) (that is, “water”). The amount of the component (b4) used is preferably 30 to 99.9% by mass as the content in the polymerization stock solution from the viewpoint of polymerization stability.
In addition to the components (b1) to (b4), various components can be further mixed in the polymerization stock solution.
まず、前記重合原液には、以下の(b5)成分、
(b5)成分:(b2)成分と共重合可能な他のビニル単量体、
を混合することができる。
このような(b5)成分を用いることは、生成する重合生成物の特性(ガラス転移温度、分子量、水素結合力、極性、分散安定性、耐候性、加水分解性珪素化合物(b1)の重合生成物との相溶性等)を制御する観点から好適である。
前記(b5)成分としては、例えば、アクリル酸エステル、メタクリル酸エステル、芳香族ビニル化合物、シアン化ビニル類の他、エポキシ基含有ビニル単量体、カルボニル基含有ビニル単量体、アニオン型ビニル単量体のような官能基を含有する単量体、等を挙げることができる。
前記(b5)成分が全ビニル単量体中に占める割合としては、好ましくは0.001〜30質量%であり、より好ましくは0.05〜10質量%の範囲である。このような使用量とすることは、ガラス転移温度、分子量、水素結合力、極性、分散安定性、耐候性、加水分解性珪素化合物(b1)の重合生成物との相溶性等を制御する観点から好適である。
また、前記重合原液には、連鎖移動剤を混合することができる。
このような連鎖移動剤としては、例えば、n−オクチルメルカプタン、n−ドデシルメルカプタン、t−ドデシルメルカプタンのようなアルキルメルカプタン類;ベンジルメルカプタン、ドデシルベンジルメルカプタンのような芳香族メルカプタン類;チオリンゴ酸のようなチオカルボン酸又はそれらの塩若しくはそれらのアルキルエステル類、又はポリチオール類、ジイソプロピルキサントゲンジスルフィド、ジ(メチレントリメチロールプロパン)キサントゲンジスルフィド及びチオグリコール、さらにはα−メチルスチレンのダイマー等のアリル化合物等を挙げることができる。
これら連鎖移動剤の使用量としては、全ビニル単量体合計量100質量部に対して、好ましくは0.001〜30質量部、より好ましくは0.05〜10質量部である。このような使用量とすることは、重合安定性の観点から好適である。
更に、前記重合原液には分散安定剤を混合することができる。
このような分散安定剤としては、例えば、ポリカルボン酸及びスルホン酸塩からなる群から選ばれる各種の水溶性オリゴマー類や、ポリビニルアルコール、ヒドロキシエチルセルロース、澱粉、マレイン化ポリブタジエン、マレイン化アルキッド樹脂、ポリアクリル酸(塩)、ポリアクリルアミド、水溶性又は水分散性アクリル樹脂などの合成又は天然の水溶性又は水分散性の各種の水溶性高分子物質が挙げられ、これらの1種又は2種以上の混合物を使用することができる。
これらの分散安定剤の使用量としては、重合体エマルジョン粒子(B)100質量部に対して、好ましくは10質量部以下であり、より好ましくは0.001〜5質量部である。
上述した重合原液の重合は、重合触媒の存在下で実施するのが好ましい。
前記(b1)成分の重合触媒としては、例えば、塩酸、フッ酸等のハロゲン化水素類、酢酸、トリクロル酢酸、トリフルオロ酢酸、乳酸等のカルボン酸類、硫酸、p−トルエンスルホン酸等のスルホン酸類、アルキルベンゼンスルホン酸、アルキルスルホン酸、アルキルスルホコハク酸、ポリオキシエチレンアルキル硫酸、ポリオキシエチレンアルキルアリール硫酸、ポリオキシエチレンジスチリルフェニルエーテルスルホン酸等の酸性乳化剤類、酸性又は弱酸性の無機塩、フタル酸、リン酸、硝酸のような酸性化合物類;水酸化ナトリウム、水酸化カリウム、ナトリウムメチラート、酢酸ナトリウム、テトラメチルアンモニウムクロリド、テトラメチルアンモニウムヒドロキシド、トリブチルアミン、ジアザビシクロウンデセン、エチレンジアミン、ジエチレントリアミン、エタノールアミン類、γ−アミノプロピルトリメトキシシラン、γ−(2−アミノエチル)−アミノプロピルトリメトキシシランのような塩基性化合物類;ジブチル錫オクチレート、ジブチル錫ジラウレートのような錫化合物等を挙げることができる。
First, the polymerization stock solution contains the following component (b5):
Component (b5): other vinyl monomer copolymerizable with component (b2),
Can be mixed.
The use of such component (b5) means that the properties of the polymerization product to be produced (glass transition temperature, molecular weight, hydrogen bonding force, polarity, dispersion stability, weather resistance, polymerization of hydrolyzable silicon compound (b1)) From the viewpoint of controlling compatibility with the product.
Examples of the component (b5) include acrylic acid esters, methacrylic acid esters, aromatic vinyl compounds, vinyl cyanides, epoxy group-containing vinyl monomers, carbonyl group-containing vinyl monomers, anionic vinyl monomers. Examples thereof include a monomer containing a functional group such as a monomer.
The proportion of the component (b5) in the total vinyl monomer is preferably 0.001 to 30% by mass, and more preferably 0.05 to 10% by mass. The use amount is such that the glass transition temperature, molecular weight, hydrogen bonding force, polarity, dispersion stability, weather resistance, compatibility with the polymerization product of the hydrolyzable silicon compound (b1), and the like are controlled. To preferred.
Further, a chain transfer agent can be mixed in the polymerization stock solution.
Examples of such chain transfer agents include alkyl mercaptans such as n-octyl mercaptan, n-dodecyl mercaptan and t-dodecyl mercaptan; aromatic mercaptans such as benzyl mercaptan and dodecyl benzyl mercaptan; thiomalic acid and the like. Thiocarboxylic acids or their salts or their alkyl esters, or polythiols, diisopropylxanthogen disulfide, di (methylenetrimethylolpropane) xanthogen disulfide and thioglycol, and allyl compounds such as dimers of α-methylstyrene be able to.
The amount of these chain transfer agents to be used is preferably 0.001 to 30 parts by mass, more preferably 0.05 to 10 parts by mass with respect to 100 parts by mass of the total amount of all vinyl monomers. Setting the amount to be used is suitable from the viewpoint of polymerization stability.
Furthermore, a dispersion stabilizer can be mixed in the polymerization stock solution.
Examples of such a dispersion stabilizer include various water-soluble oligomers selected from the group consisting of polycarboxylic acids and sulfonates, polyvinyl alcohol, hydroxyethyl cellulose, starch, maleated polybutadiene, maleated alkyd resins, poly Synthetic or natural water-soluble or water-dispersible various water-soluble polymer substances such as acrylic acid (salt), polyacrylamide, water-soluble or water-dispersible acrylic resin, and the like, one or more of these Mixtures can be used.
The amount of these dispersion stabilizers used is preferably 10 parts by mass or less, more preferably 0.001 to 5 parts by mass with respect to 100 parts by mass of the polymer emulsion particles (B).
The polymerization of the polymerization stock solution described above is preferably carried out in the presence of a polymerization catalyst.
Examples of the polymerization catalyst for the component (b1) include hydrogen halides such as hydrochloric acid and hydrofluoric acid, carboxylic acids such as acetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, trifluoroacetic acid and lactic acid, and sulfonic acids such as sulfuric acid and p-toluenesulfonic acid. Acid emulsifiers such as alkylbenzene sulfonic acid, alkyl sulfonic acid, alkyl sulfosuccinic acid, polyoxyethylene alkyl sulfuric acid, polyoxyethylene alkyl aryl sulfuric acid, polyoxyethylene distyryl phenyl ether sulfonic acid, acidic or weakly acidic inorganic salts, phthalates Acid compounds such as acid, phosphoric acid and nitric acid; sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, sodium methylate, sodium acetate, tetramethylammonium chloride, tetramethylammonium hydroxide, tributylamine, diazabicycloundecene, ethylene Basic compounds such as amines, diethylenetriamine, ethanolamines, γ-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane, γ- (2-aminoethyl) -aminopropyltrimethoxysilane; tin compounds such as dibutyltin octylate and dibutyltin dilaurate Etc.
中でも、加水分解性珪素化合物(b1)の重合触媒としては、重合触媒のみならず乳化剤としての作用を有する酸性乳化剤類、特に炭素数が5〜30のアルキルベンゼンスルホン酸(ドデシルベンゼンスルホン酸等)が非常に好ましい。
前記(b2)成分の重合触媒としては、熱又は還元性物質などによってラジカル分解してビニル単量体の付加重合を起こさせるラジカル重合触媒が好適である。水溶性又は油溶性の過硫酸塩、過酸化物、アゾビス化合物等が好ましく使用される。より具体的には、例えば、過硫酸カリウム、過硫酸ナトリウム、過硫酸アンモニウム、過酸化水素、t−ブチルヒドロパーオキシド、t−ブチルパーオキシベンゾエート、2,2−アゾビスイソブチロニトリル、2,2−アゾビス(2−ジアミノプロパン)ヒドロクロリド、2,2−アゾビス(2,4−ジメチルバレロニトリル)等が挙げられる。
Among them, as the polymerization catalyst for the hydrolyzable silicon compound (b1), not only the polymerization catalyst but also an acidic emulsifier having an action as an emulsifier, particularly an alkylbenzene sulfonic acid having 5 to 30 carbon atoms (such as dodecylbenzene sulfonic acid). Highly preferred.
The polymerization catalyst for the component (b2) is preferably a radical polymerization catalyst that undergoes radical decomposition by heat or a reducing substance to cause addition polymerization of a vinyl monomer. Water-soluble or oil-soluble persulfates, peroxides, azobis compounds and the like are preferably used. More specifically, for example, potassium persulfate, sodium persulfate, ammonium persulfate, hydrogen peroxide, t-butyl hydroperoxide, t-butyl peroxybenzoate, 2,2-azobisisobutyronitrile, 2, Examples include 2-azobis (2-diaminopropane) hydrochloride, 2,2-azobis (2,4-dimethylvaleronitrile), and the like.
なお、重合触媒の使用量としては、全ビニル単量体100質量部に対して、好ましくは0.001〜5質量部である。なお、重合速度の促進、及び70℃以下での低温の重合を望むときには、例えば重亜硫酸ナトリウム、塩化第一鉄、アスコルビン酸塩、ロンガリット等の還元剤をラジカル重合触媒と組み合わせて用いると有利である。
本実施の形態において、前記(b1)成分の重合と、前記(b2)成分との重合とは、別々に実施することも可能であるが、同時に実施すると水素結合等によるミクロな有機・無機複合化が達成できるので好ましい。
前記(B)成分を得る方法としては、乳化剤がミセルを形成するのに十分な量の水の存在下に前記(b1)成分と前記(b2)成分とを重合する、いわゆる乳化重合が適している。
乳化重合の方法としては、例えば、前記(b1)成分と前記(b2)成分、更には必要に応じて前記(b3)成分を、そのまま又は乳化した状態で、一括若しくは分割して、又は連続的に、反応容器中に滴下し、前記重合触媒の存在下、好ましくは大気圧から必要により10MPaの圧力下で、約30〜150℃の反応温度で重合させる方法が挙げられる。場合によっては、これ以上の圧力で、又はこれ以下の温度条件で重合を行っても差し支えない。
なお、重合原液の配合としては、重合安定性の観点から、最終固形分量が0.1〜70質量%、好ましくは1〜55質量%の範囲になるように前記(b1)〜(b4)の各成分を配合するのが好ましい。
更に、前記乳化重合を行なうに際しては、粒子径を適度に成長又は制御する観点から、シード重合法を用いることが好ましい。シード重合法とは、予め水相中にエマルジョン粒子(シード粒子)を存在させて重合させる方法である。シード重合法を行なう際の重合系中のpHとしては、好ましくは1.0〜10.0、より好ましくは1.0〜6.0である。pHは、燐酸二ナトリウムやボラックス、又は、炭酸水素ナトリウム、アンモニアなどのpH緩衝剤を用いて調節することが可能である。
なお、前記(B)成分を得る方法としては、前記(b1)成分を重合させるのに必要な前記(b3)成分及び前記(b4)成分の存在下、前記(b1)成分及び前記(b2)成分を、必要により溶剤存在下で重合した後、重合生成物がエマルジョンとなるまで水を添加する手法も適用できる。
In addition, as a usage-amount of a polymerization catalyst, Preferably it is 0.001-5 mass parts with respect to 100 mass parts of all the vinyl monomers. When acceleration of the polymerization rate and polymerization at a low temperature of 70 ° C. or lower are desired, it is advantageous to use a reducing agent such as sodium bisulfite, ferrous chloride, ascorbate, or longalite in combination with the radical polymerization catalyst. is there.
In the present embodiment, the polymerization of the component (b1) and the polymerization of the component (b2) can be carried out separately. This is preferable because it can be achieved.
As a method for obtaining the component (B), so-called emulsion polymerization in which the emulsifier polymerizes the component (b1) and the component (b2) in the presence of a sufficient amount of water to form micelles is suitable. Yes.
As a method of emulsion polymerization, for example, the component (b1) and the component (b2), and further, the component (b3) as necessary, as they are or in an emulsified state, are collectively or divided, or continuously. And a method of polymerizing at a reaction temperature of about 30 to 150 ° C. in the presence of the polymerization catalyst, preferably from atmospheric pressure to a pressure of 10 MPa if necessary. In some cases, the polymerization may be carried out at a higher pressure or lower temperature.
In addition, as a mixing | blending of superposition | polymerization stock solution, from a viewpoint of superposition | polymerization stability, the amount of final solid content is 0.1-70 mass%, Preferably it is 1-55 mass% of said (b1)-(b4). Each component is preferably blended.
Furthermore, when performing the emulsion polymerization, it is preferable to use a seed polymerization method from the viewpoint of appropriately growing or controlling the particle diameter. The seed polymerization method is a method in which emulsion particles (seed particles) are previously present in an aqueous phase for polymerization. The pH in the polymerization system when performing the seed polymerization method is preferably 1.0 to 10.0, more preferably 1.0 to 6.0. The pH can be adjusted using a pH buffer such as disodium phosphate, borax, sodium hydrogen carbonate, or ammonia.
In addition, as a method of obtaining the component (B), the component (b1) and the component (b2) in the presence of the component (b3) and the component (b4) necessary for polymerizing the component (b1). A method in which water is added until the polymerization product becomes an emulsion after the components are polymerized in the presence of a solvent, if necessary, can also be applied.
前記(B)成分としては、得られる太陽電池用コーティング組成物を用いて形成される塗膜の基材密着性を向上させる観点から、コア層と、当該コア層を被覆する1層又は2層以上のシェル層とを備えたコア/シェル構造を有することが好ましい。そして、当該コア/シェル構造を形成する方法としては、前記乳化重合を多段で行なう、多段乳化重合が非常に有用である。
多段乳化重合の例としてより具体的には、例えば第一段階として、前記(b3)成分及び前記(b4)成分の存在下、前記(b1)、(b2)、及び(b5)成分よりなる群から選択される少なくとも1種以上を重合してシード粒子を形成し、第二段階として、当該シード粒子の存在下、前記(b1)成分及び前記(b2)成分、更には必要に応じ前記(b5)成分を含む重合原液を添加して重合する(2段重合法)。3段以上の多段乳化重合を実施する場合は、例えば第三段階として、さらに前記(b1)成分及び前記(b2)成分、必要に応じ前記(b5)成分を含む重合原液を添加して重合することができる。このような方法は、重合安定性の観点からも好適である。
As said (B) component, from a viewpoint of improving the base-material adhesiveness of the coating film formed using the coating composition for solar cells obtained, 1 layer or 2 layers which coat | cover the said core layer It is preferable to have a core / shell structure provided with the above shell layer. As a method for forming the core / shell structure, multistage emulsion polymerization in which the emulsion polymerization is performed in multiple stages is very useful.
More specifically as an example of multi-stage emulsion polymerization, for example, as the first stage, in the presence of the component (b3) and the component (b4), a group consisting of the components (b1), (b2), and (b5) At least one selected from the above is polymerized to form seed particles, and in the second stage, in the presence of the seed particles, the component (b1) and the component (b2), and further, if necessary (b5) ) Polymerization is conducted by adding a polymerization stock solution containing the component (two-stage polymerization method). When carrying out multi-stage emulsion polymerization of three or more stages, for example, as a third stage, polymerization is carried out by adding a polymerization stock solution further containing the component (b1) and the component (b2) and, if necessary, the component (b5). be able to. Such a method is also suitable from the viewpoint of polymerization stability.
2段重合法においては、前記第一段階において用いられる重合原液中の固形分質量(M1)と、前記第二段階において添加される重合原液中の固形分質量(M2)の質量比としては、重合安定性の観点から、好ましくは(M1)/(M2)=9/1〜1/9、より好ましくは8/2〜2/8である。
3段重合法においては、前記第一段階において用いられる重合原液中の固形分質量(M1)と、前記第二段階において添加される重合原液中の固形分質量(M2)、前記第三段階において添加される重合原液中の固形分質量(M3)の質量比としては、重合安定性の観点から、好ましくは(M2+M3)/(M1)=9/1〜1/9、M3/M2=1/1〜0.1/1が好ましい。
In the two-stage polymerization method, as a mass ratio of the solid content mass (M1) in the polymerization stock solution used in the first stage and the solid content mass (M2) in the polymerization stock solution added in the second stage, From the viewpoint of polymerization stability, (M1) / (M2) = 9/1 to 1/9, more preferably 8/2 to 2/8.
In the three-stage polymerization method, the solid content mass (M1) in the polymerization stock solution used in the first stage, the solid content mass (M2) in the polymerization stock solution added in the second stage, and the third stage The mass ratio of the solid content mass (M3) in the added polymerization stock solution is preferably (M2 + M3) / (M1) = 9/1 to 1/9, M3 / M2 = 1 / from the viewpoint of polymerization stability. 1 to 0.1 / 1 is preferable.
また、前記(b1)成分と(b2)成分との比(b2)/(b1)(質量比)は、基材密着性の観点から、重合の第一段階で形成されるコア部においては(b2)/(b1)=1/1以下、第二段階において形成されるシェル層においては(b2)/(b1)=0.1/1〜1/1、第三段階において形成されるシェル層においては(b2)/(b1)=1/1〜9/1とすることがより好ましい。
また、前記コア/シェル構造としては、重合安定性の観点から、前記シード粒子の粒径分布(体積平均粒子径/数平均粒子径)が大きく変化することなく、前記第二段階の重合によって粒子径が増大した構造を有することが好ましい。なお、体積平均粒子径は、数平均粒子径と同様に測定し得る。
前記コア/シェル構造は、例えば、透過型電子顕微鏡等による形態観察や粘弾性測定による解析等により観察することができる。
前記コア/シェル構造のコア層のガラス転移温度(Tg)としては、好ましくは0℃以下である。この場合、得られる太陽電池用コーティング組成物の物性として、室温における柔軟性に優れ、割れ等が生じにくい太陽電池用カバー材を形成することが可能となり、好ましい。
なお、本実施の形態におけるTgは示差走査熱量測定装置(DSC)にて測定することができる。
前記(B)成分の粒子径としては、10nm〜800nmである。この様な粒子径の範囲に調整し、粒子径が1nm〜400nmの前記(A)成分と組み合わせて組成物を形成することにより、耐候性、防汚染性が良好であり、しかも樹脂基材に対する保護性が良好な太陽電池用コーティング組成物を実現し得る。また、前記(B)成分の粒子径を50nm〜300nmとすることは、得られる塗膜の透明性向上の観点から好適である。
前記(A)成分と前記(B)成分の比(A)/(B)(質量比)としては、好ましくは1/99〜99/1、より好ましくは5/95〜90/10、さらに好ましくは9/91〜83/17である。この範囲で配合された太陽電池用コーティング組成物からは、耐候性、防汚染性に優れた太陽電池用カバー材を実現し得るため好ましい。
Further, the ratio (b2) / (b1) (mass ratio) between the component (b1) and the component (b2) is (in the core part formed in the first stage of polymerization from the viewpoint of substrate adhesion) b2) / (b1) = 1/1 or less, (b2) / (b1) = 0.1 / 1 to 1/1 in the shell layer formed in the second stage, shell layer formed in the third stage Is more preferably (b2) / (b1) = 1/1 to 9/1.
Further, as the core / shell structure, from the viewpoint of polymerization stability, the particle size distribution (volume average particle size / number average particle size) of the seed particles does not change greatly, and the particles are obtained by the second stage polymerization. It is preferable to have a structure with an increased diameter. The volume average particle diameter can be measured in the same manner as the number average particle diameter.
The core / shell structure can be observed, for example, by morphological observation using a transmission electron microscope or the like, analysis by viscoelasticity measurement, or the like.
The glass transition temperature (Tg) of the core layer having the core / shell structure is preferably 0 ° C. or lower. In this case, as a physical property of the obtained coating composition for solar cells, it becomes possible to form a solar cell cover material that is excellent in flexibility at room temperature and is less likely to be cracked.
In addition, Tg in this Embodiment can be measured with a differential scanning calorimeter (DSC).
The particle size of the component (B) is 10 nm to 800 nm. By adjusting to such a particle diameter range and forming the composition in combination with the component (A) having a particle diameter of 1 nm to 400 nm, the weather resistance and antifouling properties are good, and the resin base material A coating composition for solar cells with good protection can be realized. Moreover, it is suitable from a viewpoint of the transparency improvement of the coating film obtained that the particle diameter of the said (B) component shall be 50 nm-300 nm.
The ratio (A) / (B) (mass ratio) of the component (A) to the component (B) is preferably 1/99 to 99/1, more preferably 5/95 to 90/10, and even more preferably. Is 9/91 to 83/17. From the coating composition for solar cells blended in this range, a solar cell cover material excellent in weather resistance and antifouling property can be realized, which is preferable.
また、前記(A)成分の表面積(SA)と前記(B)成分の表面積(SB)との比(SA)/(SB)としては、好ましくは0.001〜1000の範囲である。なお表面積は、前記(A)成分及び前記(B)成分の各々の粒子径、及び各々の配合質量数から算出することができる。
本実施の形態の太陽電池用コーティング組成物には、その用途及び使用方法などに応じて、通常、塗料や成型用樹脂に添加配合される添加剤成分、例えば、光安定剤、紫外線吸収剤、増粘剤、レベリング剤、チクソ化剤、消泡剤、凍結安定剤、艶消し剤、架橋反応触媒、顔料、硬化触媒、架橋剤、充填剤、皮張り防止剤、分散剤、湿潤剤、酸化防止剤、紫外線吸収剤、レオロジーコントロール剤、成膜助剤、防錆剤、染料、可塑剤、潤滑剤、還元剤、防腐剤、防黴剤、消臭剤、黄変防止剤、静電防止剤又は帯電調整剤等をそれぞれの目的に応じて選択したり、組み合わせたりして配合することができる。
前記光安定剤としては、例えば、ヒンダードアミン系光安定剤が好ましく用いられる。中でも、分子内にラジカル重合性の二重結合を有するラジカル重合性光安定剤が好ましい。
また、前記紫外線吸収剤としては、例えば有機系紫外線吸収剤を挙げることができる。このような有機系紫外線吸収剤としては、例えば、ベンゾフェノン系紫外線吸収剤、ベンゾトリアゾール系紫外線吸収剤、トリアジン系紫外線吸収剤が挙げられる。中でも、分子内にラジカル重合性の二重結合を有するラジカル重合性紫外線吸収剤を用いることが好ましい。また、紫外線吸収能の高いベンゾトリアゾール系紫外線吸収剤、トリアジン系紫外線吸収剤が好ましい。
なお、前記光安定剤は、前記有機系紫外線吸収剤と併用することが好ましい。両者を併用することは、得られる太陽電池用コーティング組成物の耐候性向上に寄与し得る。
The ratio (SA) / (SB) of the surface area (SA) of the component (A) and the surface area (SB) of the component (B) is preferably in the range of 0.001 to 1000. The surface area can be calculated from the particle diameter of each of the component (A) and the component (B) and the blending mass number.
In the solar cell coating composition of the present embodiment, depending on its use and usage, etc., additive components that are usually added and blended into paints and molding resins, such as light stabilizers, ultraviolet absorbers, Thickener, leveling agent, thixotropic agent, antifoaming agent, freezing stabilizer, matting agent, crosslinking reaction catalyst, pigment, curing catalyst, crosslinking agent, filler, anti-skinning agent, dispersing agent, wetting agent, oxidation Inhibitors, UV absorbers, rheology control agents, film forming aids, rust inhibitors, dyes, plasticizers, lubricants, reducing agents, antiseptics, antifungal agents, deodorants, anti-yellowing agents, antistatic An agent, a charge control agent, or the like can be selected or combined depending on the purpose.
As the light stabilizer, for example, a hindered amine light stabilizer is preferably used. Among these, a radical polymerizable light stabilizer having a radical polymerizable double bond in the molecule is preferable.
Moreover, as said ultraviolet absorber, an organic type ultraviolet absorber can be mentioned, for example. Examples of such organic ultraviolet absorbers include benzophenone ultraviolet absorbers, benzotriazole ultraviolet absorbers, and triazine ultraviolet absorbers. Among these, it is preferable to use a radical polymerizable ultraviolet absorber having a radical polymerizable double bond in the molecule. Moreover, a benzotriazole type ultraviolet absorber and a triazine type ultraviolet absorber having high ultraviolet absorbing ability are preferable.
The light stabilizer is preferably used in combination with the organic ultraviolet absorber. Using both together can contribute to improving the weather resistance of the resulting solar cell coating composition.
また、これらの有機系紫外線吸収剤や、光安定剤、各種添加剤成分は、前記(A)成分及び前記(B)成分と単に配合することも可能であるし、前記(B)成分を合成する際に共存させることも可能である。
本実施の形態の積層体は、樹脂基材と、上述した太陽電池用コーティング組成物にて形成される塗膜とを含む積層体であり、好ましくは、樹脂基材と、上述した太陽電池用コーティング組成物からなる塗膜とからなる積層体である。
また、本実施の形態の太陽電池用カバー材は、当該積層体を用いて形成され、好ましくは樹脂基材と、上述した太陽電池用コーティング組成物からなる塗膜とからなる積層体として形成される。
Moreover, these organic ultraviolet absorbers, light stabilizers, and various additive components can be simply blended with the component (A) and the component (B), or the component (B) is synthesized. It is also possible to coexist when doing so.
The laminated body of this Embodiment is a laminated body containing the resin base material and the coating film formed with the coating composition for solar cells mentioned above, Preferably, the resin base material for solar cells mentioned above is preferable. A laminate comprising a coating film made of a coating composition.
Further, the solar cell cover material of the present embodiment is formed using the laminate, and is preferably formed as a laminate comprising a resin base material and a coating film comprising the above-described solar cell coating composition. The
更に、本実施の形態の太陽電池は、当該太陽電池用カバー材を含む。
ここで、前記基材としては、例えば、合成樹脂、天然樹脂等の有機基材や、ガラス等の無機基材や、それらの組み合わせ等を挙げることができる。
上述した太陽電池用コーティング組成物は、特に限定されるものではないが、水等の溶媒等に溶解乃至分散させた状態として調製することができる。
また、前記塗膜は、例えば、水等の溶媒等に分散させた前記太陽電池用コーティング組成物(「水分散体」と略記することがある)を前記基材上に塗工し、乾燥して形成される。ここで、水分散体の固形分濃度としては、好ましくは0.01〜60質量%、より好ましくは1〜40質量%である。また、水分散体の粘度としては、好ましくは20℃において0.1〜100000mPa・s、好ましくは1〜10000mPa・sである。更に、前記塗工方法としては、例えばスプレー吹き付け法、フロー太陽電池用コーティング法、ロールコート法、刷毛塗り法、ディップ太陽電池用コーティング法、スピン太陽電池用コーティング法、スクリーン印刷法、キャスティング法、グラビア印刷法、フレキソ印刷法等が挙げられる。なお、前記積層体は、例えば、前記塗膜を前記基材上で乾燥した後、所望により好ましくは20℃〜500℃、より好ましくは40℃〜250℃での熱処理や紫外線照射等を行い、形成することも可能である。
前記塗膜の厚みとしては、好ましくは0.05〜100μm、より好ましくは0.1〜10μmである。透明性の面から、100μm以下の厚みであることが好ましく、耐候性、防汚染性等の機能を発現するためには0.05μm以上の厚みであることが好ましい。
なお、本実施の形態に言う「塗膜」は、必ずしも連続膜である必要はなく、不連続膜、島状分散膜等の態様であっても構わない。
前記塗膜のヘイズとしては、塗膜の強度や耐久性、太陽電池の変換効率の観点から総合的に選定すれば良いが、太陽電池の変換効率の観点から好ましくは20以下、より好ましくは10以下、さらに好ましくは5以下である。
Furthermore, the solar cell of the present embodiment includes the solar cell cover material.
Here, as said base material, organic base materials, such as a synthetic resin and a natural resin, inorganic base materials, such as glass, those combinations, etc. can be mentioned, for example.
The solar cell coating composition described above is not particularly limited, but can be prepared in a state dissolved or dispersed in a solvent such as water.
The coating film is, for example, coated on the substrate with the solar cell coating composition dispersed in a solvent such as water (sometimes abbreviated as “water dispersion”) and dried. Formed. Here, as solid content concentration of an aqueous dispersion, Preferably it is 0.01-60 mass%, More preferably, it is 1-40 mass%. The viscosity of the aqueous dispersion is preferably 0.1 to 100,000 mPa · s, preferably 1 to 10,000 mPa · s at 20 ° C. Furthermore, as the coating method, for example, spraying method, flow solar cell coating method, roll coating method, brush coating method, dip solar cell coating method, spin solar cell coating method, screen printing method, casting method, Examples include gravure printing and flexographic printing. The laminate is, for example, after drying the coating film on the base material, preferably subjected to heat treatment or ultraviolet irradiation at 20 ° C. to 500 ° C., more preferably 40 ° C. to 250 ° C., if desired. It is also possible to form.
The thickness of the coating film is preferably 0.05 to 100 μm, more preferably 0.1 to 10 μm. From the viewpoint of transparency, the thickness is preferably 100 μm or less, and in order to exhibit functions such as weather resistance and antifouling properties, the thickness is preferably 0.05 μm or more.
The “coating film” referred to in the present embodiment is not necessarily a continuous film, and may be a discontinuous film, an island-shaped dispersion film, or the like.
The haze of the coating film may be selected comprehensively from the viewpoint of the strength and durability of the coating film and the conversion efficiency of the solar cell, but is preferably 20 or less, more preferably 10 from the viewpoint of the conversion efficiency of the solar cell. Hereinafter, it is more preferably 5 or less.
なお、ここでいう「ヘイズ」とは、後述する実施例に準じて測定することができ、前記(A)、(B)成分の粒子径の大小により調節することが可能である。 In addition, "haze" here can be measured according to the Example mentioned later, and can be adjusted with the magnitude | size of the particle diameter of the said (A) and (B) component.
次に、実施例及び比較例を挙げて本実施の形態をより具体的に説明するが、本実施の形態はその要旨を超えない限り、以下の実施例に限定されるものではない。なお、各種物性は下記の方法で評価した。
1.数平均粒子径
試料中の固形分含有量が0.01〜20質量%となるよう適宜溶媒を加えて希釈し、湿式粒度分析計(日本国日機装製マイクロトラックUPA−9230)を用いて測定した。
2.接触角(CA)
太陽電池用カバー材の表面(太陽電池用コーティング組成物の塗工面)に脱イオン水の水滴を乗せ、20℃で1分間放置した後、接触角測定装置(日本国協和界面科学製 CA−X150型接触角計)を用いて測定した。
3.ヘイズ
濁度計(日本国日本電色工業製NDH2000)を用い、太陽電池用コーティング組成物の塗膜について、JIS−K7105に準じてヘイズ値を測定した(初期ヘイズ値)。
4.耐汚染性
太陽電池用コーティング組成物を市販の太陽電池モジュールに塗布した後一般道路に面した曝露台(南面、曝露角度30度)に1ヶ月貼り付けた後、変換効率をI−Vカーブトレーサー(英弘精機(株)製、型式MP−160)で測定し、曝露前の変換効率と比較し、低下度合いを以下の基準で評価した。
○:効率低下5%以下
△:効率低下5〜10%
×:効率低下20%以下
5.基材密着性
太陽電池用カバー材をサンシャインウェザーメーター(スガ試験器製)を使用して曝露試験(ブラックパネル温度63℃、降雨18分/2時間)を行った後に、塗工面にセロテープ(登録商標)(1cm×5cm)を貼り付け、180℃の角度でセロテープ(登録商標)を剥がし、セロテープ(登録商標)への太陽電池用コーティング組成物の塗膜の付着状況を目視で判定した。
○:付着なし
△:わずかに付着あり
×:付着あり
6.基材保護性
太陽電池用カバー材に対し、UV照射機(オーク製作所製 UV300)を使用して照度10mWで6時間、紫外光を照射した。その後、基材(PETフィルム)の黄変度を色差計(BYK Gardner製 カラーガイド45/0)を用いて評価した。UV光照射前のPETフィルムに対するΔb値を測定し、以下の基準で評価した。
○:1未満
△:1以上5未満
×:5以上
Next, the present embodiment will be described more specifically with reference to examples and comparative examples. However, the present embodiment is not limited to the following examples unless it exceeds the gist. Various physical properties were evaluated by the following methods.
1. Number average particle size The sample was diluted with a suitable solvent so that the solid content in the sample was 0.01 to 20% by mass, and measured using a wet particle size analyzer (Microtrac UPA-9230, manufactured by Nihon Kikkiso). .
2. Contact angle (CA)
A surface of the solar cell cover material (coating surface of the solar cell coating composition) was placed on a deionized water drop and allowed to stand at 20 ° C. for 1 minute, and then contact angle measuring device (CA-X150, manufactured by Kyowa Interface Science, Japan). Type contact angle meter).
3. Using a haze turbidimeter (NDH2000 manufactured by Nippon Denshoku Industries Co., Ltd., Japan), the haze value of the coating film of the solar cell coating composition was measured according to JIS-K7105 (initial haze value).
4). Contamination resistance After applying the solar cell coating composition to a commercially available solar cell module, it is attached to an exposure table facing the general road (south surface, exposure angle 30 degrees) for 1 month, and the conversion efficiency is converted to an IV curve tracer. (Measured by Eihiro Seiki Co., Ltd., model MP-160) and compared with the conversion efficiency before exposure, the degree of decrease was evaluated according to the following criteria.
○: Efficiency decrease 5% or less Δ: Efficiency decrease 5 to 10%
X: Efficiency reduction 20% or less Adhesion of base material After the exposure test (black panel temperature 63 ° C, rainfall 18 minutes / 2 hours) using a sunshine weather meter (manufactured by Suga Test Instruments Co., Ltd.), cover the solar cell cover material with cellophane (registered) Trademark) (1 cm × 5 cm) was applied, and the cellotape (registered trademark) was peeled off at an angle of 180 ° C., and the adhesion state of the coating film of the solar cell coating composition on the cellotape (registered trademark) was visually determined.
○: No adhesion Δ: Slight adhesion ×: Adhesion Substrate protection The cover material for solar cells was irradiated with ultraviolet light at an illuminance of 10 mW for 6 hours using a UV irradiator (UV300 manufactured by Oak Manufacturing Co., Ltd.). Then, the yellowing degree of the base material (PET film) was evaluated using a color difference meter (color guide 45/0 manufactured by BYK Gardner). The Δb value for the PET film before UV light irradiation was measured and evaluated according to the following criteria.
○: Less than 1 △: 1 or more and less than 5 ×: 5 or more
[製造例1]
[エマルジョン粒子B−1]
還流冷却器、滴下槽、温度計および撹拌装置を有する反応器に、イオン交換水1600g、ドデシルベンゼンスルホン酸3gを投入した後、撹拌下で温度を80℃に加温した。これに、ジメチルジメトキシシラン185g、フェニルトリメトキシシラン117gの混合液を反応容器中の温度を80℃に保った状態で約2時間かけて滴下し、その後、反応容器中の温度が80℃の状態で約1時間撹拌を続行した。次にアクリル酸ブチル86g、フェニルトリメトキシシラン133g、3−メタクリロキシプロピルトリメトキシシラン1.3gの混合液とジエチルアクリルアミド137g、アクリル酸3g、反応性乳化剤(商品名「アデカリアソープSR−1025」、旭電化(株)製、固形分25%水溶液)13g、過硫酸アンモニウムの2質量%水溶液40g、イオン交換水1900gの混合液を、反応容器中の温度を80℃に保った状態で約2時間かけて同時に滴下した。さらに反応容器中の温度が80℃の状態で約2時間撹拌を続行した後、室温まで冷却した。100メッシュの金網で濾過した後、イオン交換水で固形分を10質量%に調整し、エマルジョン粒子B−1((B)成分)の10質量%水分散体(数平均粒子径160nm)を得た。
[Production Example 1]
[Emulsion particles B-1]
Into a reactor having a reflux condenser, a dropping tank, a thermometer, and a stirring device, 1600 g of ion-exchanged water and 3 g of dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid were added, and then the temperature was heated to 80 ° C. with stirring. To this, a mixture of 185 g of dimethyldimethoxysilane and 117 g of phenyltrimethoxysilane was dropped over about 2 hours while maintaining the temperature in the reaction vessel at 80 ° C., and then the temperature in the reaction vessel was 80 ° C. And stirring was continued for about 1 hour. Next, a mixed solution of 86 g of butyl acrylate, 133 g of phenyltrimethoxysilane, 1.3 g of 3-methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane, 137 g of diethylacrylamide, 3 g of acrylic acid, a reactive emulsifier (trade name “ADEKA rear soap SR-1025” Asahi Denka Co., Ltd., 25% solid content aqueous solution) 13 g, ammonium persulfate 2 mass% aqueous solution 40 g, and ion-exchanged water 1900 g mixed solution with the temperature in the reaction vessel kept at 80 ° C. for about 2 hours It was dripped at the same time. Further, stirring was continued for about 2 hours in a state where the temperature in the reaction vessel was 80 ° C., and then cooled to room temperature. After filtration through a 100 mesh wire mesh, the solid content is adjusted to 10% by mass with ion-exchanged water to obtain a 10% by mass aqueous dispersion (number average particle size 160 nm) of emulsion particles B-1 (component (B)). It was.
[製造例2]
[エマルジョン粒子B−2]
還流冷却器、滴下槽、温度計および撹拌装置を有する反応器に、イオン交換水1600g、ドデシルベンゼンスルホン酸3gを投入した後、撹拌下で温度を80℃に加温した。これに、ジメチルジメトキシシラン185g、フェニルトリメトキシシラン117gの混合液を反応容器中の温度を80℃に保った状態で約2時間かけて滴下し、その後、反応容器中の温度が80℃の状態で約1時間撹拌を続行した。次にアクリル酸ブチル86g、フェニルトリメトキシシラン133g、3−メタクリロキシプロピルトリメトキシシラン1.3gの混合液とジエチルアクリルアミド137g、アクリル酸3g、反応性乳化剤(商品名「アデカリアソープSR−1025」、旭電化(株)製、固形分25%水溶液)13g、過硫酸アンモニウムの2質量%水溶液40g、イオン交換水1900gの混合液を、反応容器中の温度を80℃に保った状態で約2時間かけて同時に滴下した。さらに、アクリル酸ブチル5g、フェニルトリメトキシシラン5g、3−メタクリロキシプロピルトリメトキシシラン0.1gの混合液とジエチルアクリルアミド30g、アクリル酸0.1g、反応性乳化剤(商品名「アデカリアソープSR−1025」、旭電化(株)製、固形分25%水溶液)0.1g、過硫酸アンモニウムの2質量%水溶液4g、イオン交換水190gの混合液さらに反応容器中の温度が80℃の状態で約2時間撹拌を続行した後、室温まで冷却した。100メッシュの金網で濾過した後、イオン交換水で固形分を10質量%に調整し、エマルジョン粒子B−2((B)成分)の10質量%水分散体(数平均粒子径180nm)を得た。
[Production Example 2]
[Emulsion particles B-2]
Into a reactor having a reflux condenser, a dropping tank, a thermometer, and a stirring device, 1600 g of ion-exchanged water and 3 g of dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid were added, and then the temperature was heated to 80 ° C. with stirring. To this, a mixture of 185 g of dimethyldimethoxysilane and 117 g of phenyltrimethoxysilane was dropped over about 2 hours while maintaining the temperature in the reaction vessel at 80 ° C., and then the temperature in the reaction vessel was 80 ° C. And stirring was continued for about 1 hour. Next, a mixed solution of 86 g of butyl acrylate, 133 g of phenyltrimethoxysilane, 1.3 g of 3-methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane, 137 g of diethylacrylamide, 3 g of acrylic acid, a reactive emulsifier (trade name “ADEKA rear soap SR-1025” Asahi Denka Co., Ltd., 25% solid content aqueous solution) 13 g, ammonium persulfate 2 mass% aqueous solution 40 g, and ion-exchanged water 1900 g mixed solution with the temperature in the reaction vessel kept at 80 ° C. for about 2 hours It was dripped at the same time. Further, a mixed solution of 5 g of butyl acrylate, 5 g of phenyltrimethoxysilane, 0.1 g of 3-methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane, 30 g of diethylacrylamide, 0.1 g of acrylic acid, a reactive emulsifier (trade name “ADEKA rear soap SR- 1025 ", manufactured by Asahi Denka Co., Ltd., 25 g solid content aqueous solution) 0.1 g, ammonium persulfate 2 g% aqueous solution 4 g, ion-exchanged water 190 g mixed solution and about 2 at a temperature of 80 ° C in the reaction vessel Stirring was continued for an hour, and then cooled to room temperature. After filtration through a 100 mesh wire mesh, the solid content is adjusted to 10% by mass with ion-exchanged water to obtain a 10% by mass aqueous dispersion (number average particle size 180 nm) of emulsion particles B-2 (component (B)). It was.
[製造例3]
[エマルジョン粒子B−3]
還流冷却器、滴下槽、温度計および撹拌装置を有する反応器に、イオン交換水1600g、ドデシルベンゼンスルホン酸3gを投入した後、撹拌下で温度を80℃に加温した。これに、ジメチルジメトキシシラン185g、フェニルトリメトキシシラン117gの混合液を反応容器中の温度を80℃に保った状態で約2時間かけて滴下し、その後、反応容器中の温度が80℃の状態で約1時間撹拌を続行した。次にアクリル酸ブチル86g、フェニルトリメトキシシラン133g、3−メタクリロキシプロピルトリメトキシシラン1.3gの混合液とポリオキシメチレンメタクリレート(商品名「ブレンマーPE−200」、日本油脂(株)製)137g、アクリル酸3g、反応性乳化剤(商品名「アデカリアソープSR−1025」、旭電化(株)製、固形分25%水溶液)13g、過硫酸アンモニウムの2質量%水溶液40g、イオン交換水1900gの混合液を、反応容器中の温度を80℃に保った状態で約2時間かけて同時に滴下した。さらに反応容器中の温度が80℃の状態で約2時間撹拌を続行した後、室温まで冷却した。100メッシュの金網で濾過した後、イオン交換水で固形分を10質量%に調整し、エマルジョン粒子B−3((B)成分)の10質量%水分散体(数平均粒子径250nm)を得た。
[Production Example 3]
[Emulsion particles B-3]
Into a reactor having a reflux condenser, a dropping tank, a thermometer, and a stirring device, 1600 g of ion-exchanged water and 3 g of dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid were added, and then the temperature was heated to 80 ° C. with stirring. To this, a mixture of 185 g of dimethyldimethoxysilane and 117 g of phenyltrimethoxysilane was dropped over about 2 hours while maintaining the temperature in the reaction vessel at 80 ° C., and then the temperature in the reaction vessel was 80 ° C. And stirring was continued for about 1 hour. Next, a mixed solution of 86 g of butyl acrylate, 133 g of phenyltrimethoxysilane, 1.3 g of 3-methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane and polyoxymethylene methacrylate (trade name “Blenmer PE-200”, manufactured by NOF Corporation) 137 g , 3 g of acrylic acid, 13 g of reactive emulsifier (trade name “Adekaria Soap SR-1025”, manufactured by Asahi Denka Co., Ltd., 25% solid content aqueous solution), 40 g of 2 mass% aqueous solution of ammonium persulfate, and 1900 g of ion-exchanged water The liquid was simultaneously added dropwise over about 2 hours while maintaining the temperature in the reaction vessel at 80 ° C. Further, stirring was continued for about 2 hours in a state where the temperature in the reaction vessel was 80 ° C., and then cooled to room temperature. After filtration through a 100 mesh wire mesh, the solid content is adjusted to 10% by mass with ion-exchanged water to obtain a 10% by mass aqueous dispersion (number average particle size 250 nm) of emulsion particles B-3 (component (B)). It was.
[製造例4]
[エマルジョン粒子B−4]
還流冷却器、滴下槽、温度計および撹拌装置を有する反応器に、イオン交換水1600g、ドデシルベンゼンスルホン酸3gを投入した後、撹拌下で温度を80℃に加温した。これに、ジメチルジメトキシシラン185g、フェニルトリメトキシシラン117gの混合液を反応容器中の温度を80℃に保った状態で約2時間かけて滴下し、その後、反応容器中の温度が80℃の状態で約1時間撹拌を続行した。次にアクリル酸ブチル86g、フェニルトリメトキシシラン133g、3−メタクリロキシプロピルトリメトキシシラン1.3g、ジメチルジメトキシシラン137g、アクリル酸3gの混合液と反応性乳化剤(商品名「アデカリアソープSR−1025」、旭電化(株)製、固形分25%水溶液)13g、過硫酸アンモニウムの2質量%水溶液40g、イオン交換水1900gの混合液を、反応容器中の温度を80℃に保った状態で約4時間かけて同時に滴下した。さらに反応容器中の温度が80℃の状態で約2時間撹拌を続行した後、室温まで冷却した。100メッシュの金網で濾過した後、イオン交換水で固形分を10質量%に調整し、エマルジョン粒子B−4((B)成分)の10質量%水分散体(数平均粒子径160nm)を得た。
[Production Example 4]
[Emulsion particles B-4]
Into a reactor having a reflux condenser, a dropping tank, a thermometer, and a stirring device, 1600 g of ion-exchanged water and 3 g of dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid were added, and then the temperature was heated to 80 ° C. with stirring. To this, a mixture of 185 g of dimethyldimethoxysilane and 117 g of phenyltrimethoxysilane was dropped over about 2 hours while maintaining the temperature in the reaction vessel at 80 ° C., and then the temperature in the reaction vessel was 80 ° C. And stirring was continued for about 1 hour. Next, a mixed solution of 86 g of butyl acrylate, 133 g of phenyltrimethoxysilane, 1.3 g of 3-methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane, 137 g of dimethyldimethoxysilane and 3 g of acrylic acid and a reactive emulsifier (trade name “ADEKA rear soap SR-1025” "Asahi Denka Co., Ltd., 25% solid content aqueous solution) 13 g, ammonium persulfate 2 mass% aqueous solution 40 g, and ion-exchanged water 1900 g mixed solution of about 4 with the temperature in the reaction vessel maintained at 80 ℃. It was dripped simultaneously over time. Further, stirring was continued for about 2 hours in a state where the temperature in the reaction vessel was 80 ° C., and then cooled to room temperature. After filtration through a 100 mesh wire mesh, the solid content is adjusted to 10% by mass with ion-exchanged water to obtain a 10% by mass aqueous dispersion (number average particle size 160 nm) of emulsion particles B-4 (component (B)). It was.
[実施例1〜3、比較例1]
表1に示す配合にて太陽電池用コーティング組成物を得た。
[Examples 1 to 3, Comparative Example 1]
The coating composition for solar cells was obtained with the formulation shown in Table 1.
10cm×10cmのPETフィルム上に、得られた太陽電池用コーティング組成物を膜厚が0.5μmとなるようにバーコートした後、70℃、10分間乾燥して、太陽電池用カバー材を得た。これらの評価結果を表1に記載した。 The obtained solar cell coating composition is bar-coated on a 10 cm × 10 cm PET film so that the film thickness becomes 0.5 μm, and then dried at 70 ° C. for 10 minutes to obtain a solar cell cover material. It was. These evaluation results are shown in Table 1.
[コロイダルシリカの10質量%水分散体]
日産化学工業(株)製商品名「スノーテックスO」((A)成分)を水中に分散させたもの(固形分10質量%、数平均粒子径10nm)。
[10 mass% aqueous dispersion of colloidal silica]
A product name “Snowtex O” (component (A)) manufactured by Nissan Chemical Industries, Ltd. dispersed in water (solid content 10% by mass, number average particle size 10 nm).
[シリカ被覆酸化チタンの10質量%水分散体]
石原産業(株)製商品名「TSK−5」((A)成分)を水中に分散させたもの(固形分10質量%、数平均粒子径73nm)。
[10 mass% aqueous dispersion of silica-coated titanium oxide]
A product name “TSK-5” (component (A)) manufactured by Ishihara Sangyo Co., Ltd. dispersed in water (solid content 10 mass%, number average particle size 73 nm).
本発明者らは上記課題を解決すべく鋭意検討した結果、本発明に到達した。
すなわち、本発明は以下の通りである。
[1] 以下の(A)と(B)の各成分,
(A)成分:粒子径が1nm〜400nmの金属化合物粒子、
(B)成分:粒子径が10nm〜800nmの重合体エマルジョン粒子、
を含み、
前記(B)成分が、以下の(b1)〜(b4)の各成分、
(b1)成分:加水分解性珪素化合物、
(b2)成分:ポリオキシメチレンメタクリレート、
(b3)成分:乳化剤、
(b4)成分:水、
を含む重合原液を重合して得られる重合体エマルジョン粒子であることを特徴とする太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[2] (b2)成分と、(B)成分との比(b2)/(B)(質量比)が、0.1/1〜0.8/1である上記[1]に記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[3] (B)成分が、コア層と、当該コア層を被覆する1層又は2層以上のシェル層とを備えたコア/シェル構造を有する上記[1]又は[2]に記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[4] 前記シェル層の最外層において、前記(b2)成分と前記(b1)成分との比(b2)/(b1)(質量比)が0.1/1〜5/1である上記[3]に記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[5] コア層において、(b2)成分と(b1)成分との比(b2)/(b1)(質量比)が0.01/1〜1/1であり、前記シェル層の最外層において、前記(b2)成分と前記(b1)成分との比(b2)/(b1)(質量比)が0.1/1〜5/1である上記[3]に記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[6] (B)成分が、コア層と、当該コア層を被覆するシェル第1層とさらにその外側を被覆するシェル第2層とを備えた3層構造を有する上記[1]又は[2]に記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[7] コア層において、(b2)成分と(b1)成分との比(b2)/(b1)(質量比)が0.01/1〜1/1であり、シェル第1層において(b2)/(b1)(質量比)が0.1/1〜1/1、シェル第2層において(b2)/(b1)(質量比)が1/1〜9/1である上記[6]に記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[8] (B)成分が、コア層を形成するシード粒子の存在下で重合原液を重合して得られ、前記シード粒子が、(b1)成分、(b2)成分、及び以下の(b5)成分、
(b5)成分:(b2)成分と共重合可能な他のビニル単量体、
よりなる群から選択される少なくとも1種以上を重合して得られる上記[3]〜[7]のいずれかに記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[9] (b1)成分が、以下の(b1−1)成分、
(b1−1)成分:ビニル重合性基を有する加水分解性珪素化合物、
を含み、
(b1−1)成分と、(B)成分との比(b1−1)/(B)(質量比)が、0.01/100〜20/100である上記[1]〜[8]のいずれかに記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[10] (b1−1)成分と、(b2)成分との比(b1−1)/(b2)(質量比)が、0.1/100〜100/100である上記[9]に記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[11] (A)成分が、二酸化珪素、光触媒活性を有する金属酸化物、又は導電性を有する金属酸化物のいずれかを用いて形成される上記[1]〜[10]のいずれかに記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[12] (A)成分の粒子長(l)と粒子直径(d)との比(l/d)が、1/1〜20/1である上記[1]〜[11]のいずれかに記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[13] (A)成分が、以下の(A’)成分、
(A’)成分:式(1)で表されるトリオルガノシラン単位、式(2)で表されるモノオキシジオルガノシラン単位、式(3)で表されるジオキシオルガノシラン単位、式(4)で表されるトリオキシシラン単位、及びジフルオロメチレン単位よりなる群から選択される少なくとも1種の構造単位を有する変性剤化合物を用いて、(A)成分の金属化合物粒子を変性処理して形成される変性金属化合物粒子、
を含む上記[1]〜[12]のいずれかに記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
R3Si− (1)
(式中、Rは各々独立に直鎖状または分岐状の炭素数1〜30個のアルキル基、炭素数5〜20のシクロアルキル基、直鎖状または分岐状の炭素数1〜30個のフルオロアルキル基、直鎖状または分岐状の炭素数2〜30個のアルケニル基、フェニル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、又は水酸基を表す。)
−(R2SiO)− (2)
(式中、Rは式(1)で定義した通りである。)
(式中、Rは式(1)で定義した通りである。)
[14] (A’)成分が、光触媒活性を有する上記[13]に記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[15] (A’)成分の粒子長(l)と粒子直径(d)の比(l/d)が、1/1から20/1である上記[13]又は[14]に記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
[16] 上記[1]〜[15]のいずれかに記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物を用いて形成される塗膜と、樹脂基材とを含む積層体。
[17] 塗膜のヘイズが20以下である上記[16]に記載の積層体。
[18] 上記[16]〜[17]のいずれかに記載の積層体を用いてなる太陽電池用カバー材。
[19] 上記[1]〜[15]のいずれかに記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物を含んでなる太陽電池。
As a result of intensive studies aimed at solving the above problems, the present inventors have reached the present invention.
That is, the present invention is as follows.
[1] Each component of the following (A) and (B),
(A) component: metal compound particles having a particle diameter of 1 nm to 400 nm,
(B) component: polymer emulsion particles having a particle size of 10 nm to 800 nm,
Including
The component (B) is the following components (b1) to (b4):
(B1) component: hydrolyzable silicon compound,
(B2) component: polyoxymethylene methacrylate ,
(B3) component: emulsifier,
(B4) component: water,
A coating composition for solar cells, which is polymer emulsion particles obtained by polymerizing a polymerization stock solution containing
[ 2 ] The sun according to [ 1 ] above, wherein the ratio (b2) / (B) (mass ratio) of the component (b2) to the component (B) is 0.1 / 1 to 0.8 / 1. Battery coating composition.
[ 3 ] The sun according to [1] or [ 2 ], wherein the component (B) has a core / shell structure including a core layer and one or more shell layers covering the core layer. Battery coating composition.
[ 4 ] In the outermost layer of the shell layer, the ratio (b2) / (b1) (mass ratio) of the component (b2) to the component (b1) is 0.1 / 1 to 5/1. 3] The coating composition for solar cells according to [3].
[ 5 ] In the core layer, the ratio (b2) / (b1) (mass ratio) of the component (b2) to the component (b1) is 0.01 / 1 to 1/1, and in the outermost layer of the shell layer The coating composition for solar cells according to [ 3 ] above, wherein the ratio (b2) / (b1) (mass ratio) between the component (b2) and the component (b1) is 0.1 / 1 to 5/1. object.
[6] The above [1] or [2] , wherein the component (B) has a three-layer structure including a core layer, a shell first layer that covers the core layer, and a shell second layer that covers the outer side of the core layer. ] The coating composition for solar cells as described in above.
[7] In the core layer, the ratio (b2) / (b1) (mass ratio) of the component (b2) to the component (b1) is 0.01 / 1 to 1/1, and in the shell first layer (b2 ) / (B1) (mass ratio) is 0.1 / 1 to 1/1, and (b2) / (b1) (mass ratio) is 1/1 to 9/1 in the shell second layer [6] The coating composition for solar cells described in 1.
[8] The component (B) is obtained by polymerizing a polymerization stock solution in the presence of seed particles forming the core layer, and the seed particles are the component (b1), the component (b2), and the following (b5) component,
Component (b5): other vinyl monomer copolymerizable with component (b2),
The coating composition for solar cells according to any one of the above [ 3 ] to [7], which is obtained by polymerizing at least one selected from the group consisting of:
[9] The component (b1) is the following component (b1-1):
(B1-1) component: a hydrolyzable silicon compound having a vinyl polymerizable group,
Including
Of the above [1] to [8], the ratio (b1-1) / (B) (mass ratio) of the component (b1-1) to the component (B) is 0.01 / 100 to 20/100. The coating composition for solar cells in any one.
[10] The above [9], wherein the ratio (b1-1) / (b2) (mass ratio) of the component (b1-1) to the component (b2) is 0.1 / 100 to 100/100. The coating composition for solar cells.
[11] The component according to any one of [1] to [10], wherein the component (A) is formed using any one of silicon dioxide, a metal oxide having photocatalytic activity, or a metal oxide having conductivity. The coating composition for solar cells.
[12] The ratio (l / d) of the particle length (l) and the particle diameter (d) of the component (A) is any one of the above [1] to [11], which is 1/1 to 20/1. The coating composition for solar cells described.
[13] The component (A) is the following component (A ′):
(A ′) component: triorganosilane unit represented by formula (1), monooxydiorganosilane unit represented by formula (2), dioxyorganosilane unit represented by formula (3), formula ( 4) Using a modifier compound having at least one structural unit selected from the group consisting of a trioxysilane unit represented by 4) and a difluoromethylene unit, the metal compound particles of component (A) are modified. Modified metal compound particles formed,
The solar cell coating composition according to any one of the above [1] to [12].
R 3 Si- (1)
(In the formula, each R is independently a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms, a cycloalkyl group having 5 to 20 carbon atoms, or a linear or branched carbon group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms. (A fluoroalkyl group, a linear or branched alkenyl group having 2 to 30 carbon atoms, a phenyl group, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, or a hydroxyl group.)
- (R 2 SiO) - ( 2)
(In the formula, R is as defined in formula (1).)
(In the formula, R is as defined in formula (1).)
[14] The solar cell coating composition according to [13], wherein the component (A ′) has photocatalytic activity.
[15] The sun according to [13] or [14], wherein the ratio (l / d) of the particle length (l) to the particle diameter (d) of the component (A ′) is from 1/1 to 20/1. Battery coating composition.
[16] A laminate comprising a coating film formed using the coating composition for solar cells according to any one of [1] to [15], and a resin base material.
[17] The laminate according to [16], wherein the coating film has a haze of 20 or less.
[18] A solar cell cover material using the laminate according to any one of [16] to [17].
[19] A solar cell comprising the solar cell coating composition according to any one of [1] to [15].
Claims (19)
(A)成分:粒子径が1nm〜400nmの金属化合物粒子、
(B)成分:粒子径が10nm〜800nmの重合体エマルジョン粒子、
を含み、
前記(B)成分が、以下の(b1)〜(b4)の各成分、
(b1)成分:加水分解性珪素化合物、
(b2)成分:水酸基、カルボキシル基、アミド基、アミノ基、エーテル基よりなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1種の官能基を含有するビニル単量体、
(b3)成分:乳化剤、
(b4)成分:水、
を含む重合原液を重合して得られる重合体エマルジョン粒子であることを特徴とする太陽電池用コーティング組成物。 The following components (A) and (B)
(A) component: metal compound particles having a particle diameter of 1 nm to 400 nm,
(B) component: polymer emulsion particles having a particle size of 10 nm to 800 nm,
Including
The component (B) is the following components (b1) to (b4):
(B1) component: hydrolyzable silicon compound,
(B2) component: a vinyl monomer containing at least one functional group selected from the group consisting of a hydroxyl group, a carboxyl group, an amide group, an amino group, and an ether group;
(B3) component: emulsifier,
(B4) component: water,
A coating composition for solar cells, which is polymer emulsion particles obtained by polymerizing a polymerization stock solution containing
(b5)成分:(b2)成分と共重合可能な他のビニル単量体、
よりなる群から選択される少なくとも1種以上を重合して得られる請求項4〜7に記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。 Component (B) is obtained by polymerizing a polymerization stock solution in the presence of seed particles forming a core layer, and the seed particles are (b1) component, (b2) component, and the following (b5) component:
Component (b5): other vinyl monomer copolymerizable with component (b2),
The coating composition for solar cells according to claim 4, obtained by polymerizing at least one selected from the group consisting of:
(b1−1)成分:ビニル重合性基を有する加水分解性珪素化合物、
を含み、
(b1−1)成分と、(B)成分との比(b1−1)/(B)(質量比)が、0.01/100〜20/100である請求項1〜8のいずれか一項に記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。 (B1) component is the following (b1-1) component,
(B1-1) component: a hydrolyzable silicon compound having a vinyl polymerizable group,
Including
The ratio (b1-1) / (B) (mass ratio) between the component (b1-1) and the component (B) is 0.01 / 100 to 20/100. The coating composition for solar cells according to item.
(A’)成分:式(1)で表されるトリオルガノシラン単位、式(2)で表されるモノオキシジオルガノシラン単位、式(3)で表されるジオキシオルガノシラン単位、式(4)で表されるトリオキシシラン単位、及びジフルオロメチレン単位よりなる群から選択される少なくとも1種の構造単位を有する変性剤化合物を用いて、(A)成分の金属化合物粒子を変性処理して形成される変性金属化合物粒子、
を含む請求項1〜12のいずれか一項に記載の太陽電池用コーティング組成物。
R3Si− (1)
(式中、Rは各々独立に直鎖状または分岐状の炭素数1〜30個のアルキル基、炭素数5〜20のシクロアルキル基、直鎖状または分岐状の炭素数1〜30個のフルオロアルキル基、直鎖状または分岐状の炭素数2〜30個のアルケニル基、フェニル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、又は水酸基を表す。)
−(R2SiO)− (2)
(式中、Rは式(1)で定義した通りである。)
(式中、Rは式(1)で定義した通りである。)
(A ′) component: triorganosilane unit represented by formula (1), monooxydiorganosilane unit represented by formula (2), dioxyorganosilane unit represented by formula (3), formula ( 4) Using a modifier compound having at least one structural unit selected from the group consisting of a trioxysilane unit represented by 4) and a difluoromethylene unit, the metal compound particles of component (A) are modified. Modified metal compound particles formed,
The coating composition for solar cells as described in any one of Claims 1-12 containing these.
R 3 Si- (1)
(In the formula, each R is independently a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms, a cycloalkyl group having 5 to 20 carbon atoms, or a linear or branched carbon group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms. (A fluoroalkyl group, a linear or branched alkenyl group having 2 to 30 carbon atoms, a phenyl group, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, or a hydroxyl group.)
- (R 2 SiO) - ( 2)
(In the formula, R is as defined in formula (1).)
(In the formula, R is as defined in formula (1).)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014006353A JP2014123750A (en) | 2014-01-17 | 2014-01-17 | Coating composition for solar cell |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014006353A JP2014123750A (en) | 2014-01-17 | 2014-01-17 | Coating composition for solar cell |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008102473A Division JP5518299B2 (en) | 2008-04-10 | 2008-04-10 | Coating composition for solar cell |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2014123750A true JP2014123750A (en) | 2014-07-03 |
Family
ID=51403956
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014006353A Pending JP2014123750A (en) | 2014-01-17 | 2014-01-17 | Coating composition for solar cell |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2014123750A (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016037579A (en) * | 2014-08-08 | 2016-03-22 | 旭化成イーマテリアルズ株式会社 | Metal oxide transparent molding |
| CN109337486A (en) * | 2018-10-18 | 2019-02-15 | 扬州中涂科技集团有限公司 | A kind of water-based metal antirust, anti-corrosive lotion |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003313386A (en) * | 2002-04-22 | 2003-11-06 | Jsr Corp | Aqueous dispersion |
| WO2007069596A1 (en) * | 2005-12-13 | 2007-06-21 | Asahi Kasei Chemicals Corporation | Aqueous organic-inorganic hybrid composition |
-
2014
- 2014-01-17 JP JP2014006353A patent/JP2014123750A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003313386A (en) * | 2002-04-22 | 2003-11-06 | Jsr Corp | Aqueous dispersion |
| WO2007069596A1 (en) * | 2005-12-13 | 2007-06-21 | Asahi Kasei Chemicals Corporation | Aqueous organic-inorganic hybrid composition |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016037579A (en) * | 2014-08-08 | 2016-03-22 | 旭化成イーマテリアルズ株式会社 | Metal oxide transparent molding |
| CN109337486A (en) * | 2018-10-18 | 2019-02-15 | 扬州中涂科技集团有限公司 | A kind of water-based metal antirust, anti-corrosive lotion |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6863962B2 (en) | Highly durable anti-fog coating and coating composition | |
| JP2009253203A (en) | Coating composition for solar cell | |
| JP5518299B2 (en) | Coating composition for solar cell | |
| JP5415014B2 (en) | Coating composition | |
| JP5666803B2 (en) | Energy conversion device member, reflector device and solar power generation system | |
| JP5905658B2 (en) | Functional coating | |
| JP2010235676A (en) | Coating composition for hard coat | |
| JP2012219209A (en) | Composite composition, method for producing coating film using the composite composition, coating film obtained by the method, and member with the coating film | |
| JP5366440B2 (en) | Cover material for solar cells | |
| JP2011181636A (en) | Heat shielding composition, member for solar cell, and solar cell | |
| JP5368720B2 (en) | Photocatalyst coating film and photocatalyst composition | |
| JP2012170859A (en) | Method of manufacturing functional coating film | |
| JP5466868B2 (en) | Anti-reflection coating composition | |
| JP5514463B2 (en) | Heat-resistant coating composition | |
| JP2010235678A (en) | Antistatic coating composition | |
| JP2011207170A (en) | Functional laminate, and method for manufacturing the same | |
| JP5280120B2 (en) | Multilayer coating | |
| JP2014123750A (en) | Coating composition for solar cell | |
| JP7026446B2 (en) | Anti-fog coating and coating composition | |
| JP6006912B2 (en) | Coating film, manufacturing method thereof, laminate and protective member | |
| JP6105344B2 (en) | Laminate manufacturing method, laminate, solar cell cover glass, and solar power generation mirror | |
| JP2010235682A (en) | Solvent resistant coating composition | |
| JP5530725B2 (en) | Laminated body and method for producing the same | |
| JP6022663B2 (en) | Functional coating | |
| JP5409078B2 (en) | Functional composite and method for producing the same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20141022 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20141024 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20141120 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20141216 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150205 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20150303 |