JP2012228966A - In-wheel motor - Google Patents
In-wheel motor Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2012228966A JP2012228966A JP2011098672A JP2011098672A JP2012228966A JP 2012228966 A JP2012228966 A JP 2012228966A JP 2011098672 A JP2011098672 A JP 2011098672A JP 2011098672 A JP2011098672 A JP 2011098672A JP 2012228966 A JP2012228966 A JP 2012228966A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- fixed shaft
- shaft member
- hub
- gear
- wheel motor
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Abstract
Description
本発明は、インホイールモータ、特にインホイールモータの振動特性や騒音特性を改善するための技術に関する。 The present invention relates to a technique for improving vibration characteristics and noise characteristics of an in-wheel motor, particularly an in-wheel motor.
従来、車両を走行させるための駆動源の1つとしてインホイールモータが利用されている。例えば、電動二輪車、電動車椅子、モータ付きスクータ、電動台車、ゴルフカート、電動自転車等がある。インホイールモータは、例えば、特許文献1に記載されるように、車輪のハブの内部に収納されたモータのロータがギア列を介してハブの内壁面に固定されたリング状の内歯ギアに接続され、ロータの回転力をハブに伝達する構造になっている。 Conventionally, an in-wheel motor has been used as one of driving sources for running a vehicle. For example, there are an electric motorcycle, an electric wheelchair, a motorized scooter, an electric cart, a golf cart, an electric bicycle, and the like. An in-wheel motor is, for example, as described in Patent Document 1, a ring-shaped internal gear in which a rotor of a motor housed in a wheel hub is fixed to an inner wall surface of a hub via a gear train. The rotor is connected and transmits the rotational force of the rotor to the hub.
上述した特許文献1に示されるように、電動二輪車等にインホイールモータを利用する場合、インホイールモータは、ハブの左右から突出させた一対の固定軸を車両のフレームの一部となるフォークで支持する構造が一般的となる。このときハブから左右に突出させた一対の固定軸は同軸精度が高いことが必要となる。もし、同軸精度が低い場合、車両のフォークの支持中心に対してハブ、すなわちインホイールモータの回転中心が傾いて固定されることになる。その結果、車輪回転時に車両を上下左右に振動させたり、その振動に伴う異音や騒音の発生を招く原因になる。この振動、異音、騒音等の発生は、乗り心地低下の原因にもなる。 As shown in Patent Document 1 described above, when an in-wheel motor is used in an electric motorcycle or the like, the in-wheel motor is a fork that is a pair of fixed shafts that protrude from the left and right sides of the hub and that is a part of the vehicle frame. Supporting structures are common. At this time, the pair of fixed shafts protruding left and right from the hub needs to have high coaxial accuracy. If the coaxial accuracy is low, the hub, that is, the center of rotation of the in-wheel motor is inclined and fixed with respect to the support center of the fork of the vehicle. As a result, the vehicle is caused to vibrate up and down and left and right when the wheels rotate, and it may cause abnormal noise and noise due to the vibration. The occurrence of vibration, abnormal noise, noise, and the like also causes a decrease in riding comfort.
特許文献1の構造の場合、ハブの左右から突出する固定軸は、ロータやステータ、減速機等を収納するハブに設けられたベアリングよって支持されている。この場合、ハブの左右から突出する固定軸に加わる力、例えば車両の自重や搭乗者や搭載物の重みによる力は、それぞれの固定軸に加わる。左右から突出する固定軸は、ベアリングを介してハブによって個別に支持されているため、力が加わると左側に突出する固定軸は左下がりに傾き、右側に突出する固定軸は右下がりに傾く。つまり、左右の固定軸の同軸精度の維持が困難になるという問題がある。また、ベアリングには、内輪と外輪の間でガタつきが存在し、そのガタつきが左右の固定軸の同軸精度の低下の原因になっていた。また、特許文献1の構造の場合、ロータを介して左右の固定軸を間接的に接続しているが、固定軸に対してロータを回転させる必要があるため複数のベアリングを介在させる必要がある。その結果、前述と同様にベアリングのガタつきに起因して左右の固定軸の同軸精度の低下を招いていた。 In the case of the structure of Patent Document 1, the fixed shaft protruding from the left and right sides of the hub is supported by a bearing provided on the hub that houses a rotor, a stator, a speed reducer, and the like. In this case, the force applied to the fixed shaft protruding from the left and right of the hub, for example, the force due to the weight of the vehicle or the weight of the passenger or the load is applied to each fixed shaft. Since the fixed shafts protruding from the left and right are individually supported by the hub via bearings, when a force is applied, the fixed shaft protruding to the left side tilts to the left and the fixed shaft protruding to the right side tilts to the right. That is, there is a problem that it is difficult to maintain the coaxial accuracy of the left and right fixed shafts. Further, the bearing has a backlash between the inner ring and the outer ring, and this backlash has caused a decrease in the coaxial accuracy of the left and right fixed shafts. In the case of the structure of Patent Document 1, the left and right fixed shafts are indirectly connected via the rotor. However, since it is necessary to rotate the rotor with respect to the fixed shaft, it is necessary to interpose a plurality of bearings. . As a result, the coaxial accuracy of the left and right fixed shafts is reduced due to the backlash of the bearing as described above.
本発明はこうした状況に鑑みてなされたものであり、その目的は、ハブの左右から突出する一対の固定軸の同軸精度を向上させ、振動、異音、騒音の発生を抑制し乗り心地の改善に寄与できるインホイールモータを提供することにある。 The present invention has been made in view of such circumstances, and its purpose is to improve the coaxial accuracy of a pair of fixed shafts protruding from the left and right sides of the hub, and to suppress the generation of vibration, abnormal noise and noise, and to improve the riding comfort. It is providing the in-wheel motor which can contribute to.
上記課題を解決するために、本発明のある態様のインホイールモータは、外周に車輪が結合されるべき円筒形状のハブと、ハブの一面側を貫通し当該ハブを回転自在に支持する第1固定軸部材と、第1固定軸部材と同軸でハブの他面側を貫通し当該ハブを回転自在に支持する第2固定軸部材と、ハブの内部に配置され、第1固定軸部材が貫通すると共に第1固定軸部材に固定されたモータベースと、モータベースに固定されたステータと、ステータの内周領域に配置され、第1固定軸部材に回転自在に支持されたロータと、第2固定軸部材と同軸となる貫通口を有すると共にロータから回転力が入力されて当該ロータの回転速度を減速する減速機構と、ハブの内周面に固定され、減速機構の出力側ギアが接続されたリング状の内歯ギアと、貫通口を介して第1固定軸部材と第2固定軸部材とをそれらの軸線上で連結する第3固定軸部材と、を含む。 In order to solve the above-described problems, an in-wheel motor according to an aspect of the present invention includes a cylindrical hub to which a wheel is to be coupled to the outer periphery, and a first that penetrates one surface of the hub and rotatably supports the hub. A fixed shaft member, a second fixed shaft member that is coaxial with the first fixed shaft member, passes through the other surface side of the hub and rotatably supports the hub, and is disposed inside the hub, and the first fixed shaft member passes through the first fixed shaft member. And a motor base fixed to the first fixed shaft member, a stator fixed to the motor base, a rotor disposed in an inner peripheral region of the stator and rotatably supported by the first fixed shaft member, a second A reduction mechanism that has a through-hole that is coaxial with the fixed shaft member and that receives a rotational force from the rotor to reduce the rotational speed of the rotor, is fixed to the inner peripheral surface of the hub, and is connected to the output side gear of the reduction mechanism. Ring-shaped internal gear And a third fixed shaft member for connecting the first fixed shaft member and the second fixing shaft member through the mouth with them on the axis, a.
この態様によると、ハブの内部で減速機構に形成された貫通口を貫通する第3固定軸部材が第1固定軸部材と第2固定軸部材とをその軸線上で直接連結させるため、第1固定軸部材と第2固定軸部材の同軸精度を向上できる。また、第3固定軸部材によって第1固定軸部材と第2固定軸部材とを直結することで軸剛性を向上できると共に同軸精度の維持ができる。その結果、インホイールモータの振動、異音、騒音の発生を抑制できる。 According to this aspect, the third fixed shaft member that penetrates the through hole formed in the speed reduction mechanism inside the hub directly connects the first fixed shaft member and the second fixed shaft member on the axis thereof. The coaxial accuracy of the fixed shaft member and the second fixed shaft member can be improved. Further, by directly connecting the first fixed shaft member and the second fixed shaft member by the third fixed shaft member, the shaft rigidity can be improved and the coaxial accuracy can be maintained. As a result, it is possible to suppress the occurrence of vibration, abnormal noise, and noise of the in-wheel motor.
本発明によれば、ハブの左右から突出する一対の固定軸部材の同軸精度を向上させ、振動、異音、騒音の発生を抑制して、乗り心地の改善に寄与できるインホイールモータが提供できる。 ADVANTAGE OF THE INVENTION According to this invention, the in-wheel motor which improves the coaxial precision of a pair of fixed shaft member which protrudes from the right and left of a hub, suppresses generation | occurrence | production of a vibration, abnormal noise, and noise, and can contribute to improvement of riding comfort can be provided. .
以下、本発明の好適な実施の形態(以下実施形態という)を図面に基づいて説明する。各図面に示される同一または同等の構成要素、部材には、同一の符号を付するものとし、適宜重複した説明は省略する。また、各図面における部材の寸法は、理解を容易にするために適宜拡大、縮小して示される。また、各図面において実施形態を説明する上で重要ではない部材の一部は省略して表示する。 DESCRIPTION OF EXEMPLARY EMBODIMENTS Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the invention (hereinafter referred to as embodiments) will be described with reference to the drawings. The same or equivalent components and members shown in the drawings are denoted by the same reference numerals, and repeated descriptions are appropriately omitted. In addition, the dimensions of the members in each drawing are appropriately enlarged or reduced for easy understanding. In addition, in the drawings, some of the members that are not important for describing the embodiment are omitted.
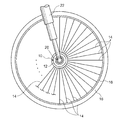
図1は、本実施形態のインホイールモータを適用した車両の車輪部分の拡大図である。インホイールモータ10は、円筒状のハブ12の内部にモータを内蔵するもので、ハブ12の外周部には放射線状に延びる複数のスポーク14の一端側が固定されている。また、スポーク14の他端側は、タイヤ部16を支持するリム18に固定されている。リム18は、ハブ12とスポーク14で結合されて車輪の骨格を形成する。また、ハブ12から突出する第1固定軸部材20(図1の場合、ハブ12の片側から突出する第1固定軸部材20のみを図示)が車両のフレームの一部であるフォーク22に固定支持されている。したがって、ハブ12、スポーク14、タイヤ部16、リム18からなる車輪は第1固定軸部材20および第1固定軸部材20と対をなす第2固定軸部材を中心に回転するように構成されている。
FIG. 1 is an enlarged view of a wheel portion of a vehicle to which the in-wheel motor of the present embodiment is applied. The in-
なお、図1の場合、車輪は、ハブ12、スポーク14、タイヤ部16、リム18を含む、いわゆるスポークホイールを示しているが、スポーク14の代わりに円板を用いた、いわゆるディスクホイールでもよい。
In the case of FIG. 1, the wheel is a so-called spoke wheel including the
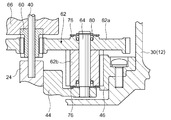
図2は、インホイールモータ10の内部構造を説明するための断面図である。インホイールモータ10は大別して、ハブ12と、このハブ12の左右から突出する第1固定軸部材20と第2固定軸部材24と、ハブ12の内部に収納されたモータ部26、減速機構28とで構成されている。
FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view for explaining the internal structure of the in-
ハブ12は、外周に車輪が結合されるべき円筒形状の部品で、本実施形態の場合、ハブ12は、一方面に開口部30aを有するカップ形状の第1部材30と、開口部30aを封止する円板形状または蓋形状の第2部材32とで構成される。ハブ12は鉄や鋳物、ステンレス鋼等で形成することができる。なお、図2の場合、第1部材30は円筒状の胴部と、その胴部を塞ぐ底部とからなるカップ形状の一体部品としているが、これに限られない。例えば、胴部と底部とを別々に形成して結合するようにしてもよい。胴部と底部との結合方法としては溶接やネジ結合等既知の結合方法を用いることができる。このように、ハブ12が蓋形状の第2部材32を含むことにより、第2部材32の着脱により内部の露出が容易になり、組立性の向上やメンテナンス時の作業性の向上に寄与できる。なお、ハブ12の完全な内部気密は必要ないが、水等が浸入しない程度の防水レベルを実現しておくことが好ましい。例えば、第1部材30と第2部材32との接合部分にOリング等を介在させて防水シール機能を持たせることが好ましい。また、回転側である第2部材32と固定側である第1固定軸部材20との間や、回転側である第1部材30と固定側である第2固定軸部材24との間にラビリンスを設け、液体の浸入を抑制するようにしてもよい。
The
ハブ12を構成する蓋形状の第2部材32は、当該ハブ12の回転中心と同軸となる中央部に第1固定軸部材20を貫通可能とする貫通口32aを有する。また第2部材32の貫通口32aに対応する部分には、第1固定軸部材20を軸として第2部材32、つまりハブ12を回転自在に支持する第1ベアリング34が固定されている。また、第2部材32の内部側、つまり、ハブ12の内部には、モータ部26の基台となるモータベース36が、第1固定軸部材20に固定されて配置される。図2に示すように、モータベース36には、第1固定軸部材20が貫通する軸受孔36aが形成され、第1固定軸部材20が、圧入や溶接、またはその複合処理により固着されている。したがって、モータベース36は第1固定軸部材20と一体化され、その周囲を第2部材32、すなわちハブ12が回転するように構成される。
The lid-shaped
第1固定軸部材20は、例えば鉄やステンレス鋼で形成され、図2に示すように内部にモータ部26を駆動するための信号線や電力線等の駆動ライン38を通すライン孔20aが形成されている。図2の場合、ライン孔20aは説明のため比較的大径で描いているが、駆動ライン38の配索作業ができる程度の直径があればよい。したがって、第1固定軸部材20の直径やライン孔20aの直径は、インホイールモータ10を組み付ける車両の自重やその車両の積載重量等を考慮して定められる付加加重に耐え得る剛性が得られるように適宜選択することが望ましい。また、第1固定軸部材20のハブ12内部側の端部には、後述する第3固定軸部材40を連結するための連結孔20bが形成されている。
The first fixed
同様に、ハブ12を構成するカップ形状の第1部材30は、当該ハブ12の回転中心と同軸となる中央部に第2固定軸部材24を貫通可能とする貫通口30bを有する。また第1部材30の貫通口30bに対応する部分には、第2固定軸部材24を軸として第1部材30、つまりハブ12を回転自在に支持する第2ベアリング42が固定されている。また、第1部材30の内部側、つまり、ハブ12の内部には、モータ部26の回転数を減速する減速機構28の一部を構成するギアケース44が、第2固定軸部材24に固定されて配置される。図2に示すように、ギアケース44には、第2固定軸部材24が貫通する軸受孔44aが形成され、第2固定軸部材24が、圧入や溶接、またはその複合処理により固着されている。第2固定軸部材24は、例えば鉄やステンレス鋼で形成され、ハブ12の内部側の端部には、後述する第3固定軸部材40を連結するための連結孔24aが形成されている。第1部材30のカップ形状の内周面には減速機構28の出力側ギア、つまり後述する遊星ギアと噛合するリング状の内歯ギア46が固定されている。前述のようにギアケース44は第2固定軸部材24に固着され一体化されているので、減速機構28の出力側ギアの回転により内歯ギア46が回転させられると、第2固定軸部材24および減速機構28の周囲を第1部材30、すなわちハブ12が回転する。なお、上述したように、ギアケース44は、第2固定軸部材24に固定されているため、遊星ギア62は第2固定軸部材24または第1固定軸部材20に対して公転を制限されるようにギアケース44に支持されることになる。
Similarly, the cup-shaped
モータ部26は、モータベース36、ステータコア48、コイル50、ロータコア52、マグネット54等を含んで構成されている。
本実施形態の場合、モータベース36はカップ形状であり、金属や樹脂またはその複合により形成されている。カップ形状のモータベース36は、コイル50が巻回されたステータコア48と、リング状のマグネット54が固定されたロータコア52を内部に収納する。
The
In the case of this embodiment, the
ステータコア48は、ケイ素鋼板等の磁性材を積層した後に、表面に電着塗装や粉体塗装等による絶縁コーディングを施して形成される。ステータコア48は複数のネジ56等の締結手段によってモータベース36に固定されている。また、ステータコア48は、内方向に突出する複数の突極(図示せず)を有するリング状であり、各突極にはコイル50が巻回されている。コイル50の巻き線端末は、モータベース36の底面から引き込まれている駆動ライン38とコネクタ等を介して接続され、コイル50は磁界の発生に必要な電力の供給を受ける。
The
ロータコア52は、ステータコア48およびコイル50を含むステータの内周領域に配置されている。ロータコア52は、鉄を切削加工などによりリング形状に加工して、外周面側にリング状のマグネット54を固定している。内周面側は、第1固定軸部材20に内輪側が圧入固定された第3ベアリング58の外輪が圧入固定されている。所定の駆動回路により3相の略正弦波状の電流がコイル50に通電されると、コイル50はステータコア48の突極に回転磁界を発生する。そして、マグネット54の駆動用磁極と回転磁界との相互作用により回転駆動力が生じて、ロータコア52が第1固定軸部材20の周囲を電流量に応じた速度で回転可能となる。
The rotor core 52 is disposed in the inner peripheral region of the stator including the
なお、本実施形態の場合、モータベース36をカップ形状とすることで、ステータコア48およびコイル50、すなわちステータの少なくとも一部をハブ12内部に露出させるように露出口36bを形成している。モータ部26の駆動時にはコイル50で発熱する。コイル50で発生した熱はステータコア48を介してモータベース36に伝わり放熱されるが、本実施形態に場合、モータベース36が露出口36bを有しコイル50を含むステータの一方面をハブ12内部に露出させることで、放熱効果を高めている。このように、露出口36bを形成することで、モータ部26全体をケーシングで覆う場合に比べて放熱効率が高まり、発熱によるモータ性能の低下が抑制できる。また、露出口36bはモータ駆動時に回転駆動している減速機構28側に開口しているので、減速機構28の回転駆動による熱の拡散や冷却が可能になり、放熱効率をさらに高めることができる。
In the present embodiment, the
減速機構28は、ギアケース44、太陽ギア60、複数の遊星ギア62、内歯ギア46等を含んで構成される。
第2固定軸部材24に固定されたギアケース44には、遊星ギア62を支持するギア固定軸64が複数植設されている。このギア固定軸64は遊星ギア62を回転自在に支持する。遊星ギア62は、第1固定軸部材20および第2固定軸部材24と同軸上に配置された太陽ギア60を中心として等間隔で配置され、相互の遊星ギア62の位置が偏らないようにしている。このように配置することで、各遊星ギア62に均等にトルクがかかるようにしている。つまり、特定の遊星ギア62に偏ったストレスがかからないようして遊星ギア62のスムーズな回転や破損抑制を実現している。そのため、遊星ギア62は最低2以上配置する必要がある。なお、遊星ギア62の数は、数が多くなれば個々の遊星ギア62にかかる負荷を低下させることができるので、インホイールモータ10を適用する車両で求められるトルクに応じて適宜選択することが望ましい。つまり、遊星ギア62は2個以上であり、内歯ギア46の内周側に収納できる数から適宜選択することができる。ただし、遊星ギア62の数が増えるほど部品点数が増えると共に製造工数がかかる。本出願人は、シミュレーションの結果、遊星ギア62の数が5以下であれば、製造工数は実用上で障害とならないことを確認した。したがって、遊星ギア62の個数は2〜5個とすることが望ましく、個々の遊星ギア62の負荷軽減と製造工数のバランスから本実施形態においては、遊星ギア62の数の最適値は3個としている。なお、図2においては遊星ギア62が2個見えている状態を図示している。
The
A plurality of gear fixed
前述したように、第1固定軸部材20には連結孔20bが形成され、第2固定軸部材24には連結孔24aが形成されている。そして、第3固定軸部材40が連結孔20bおよび連結孔24aに挿入され第1固定軸部材20と第2固定軸部材24とをそれらの軸線上で連結している。第1固定軸部材20と第2固定軸部材24を第3固定軸部材40によって軸線上で直結することによって、第1固定軸部材20と第2固定軸部材24との同軸精度を向上させることができる。つまり、ハブ12が回転したときの同軸性能に起因する振動を抑制できると共に、振動に伴う異音や騒音の発生も抑制できる。また、第1固定軸部材20と第2固定軸部材24を第3固定軸部材40によって直結することにより、第1固定軸部材20と第2固定軸部材24を1本の固定軸として構成している場合と等価となり、固定軸全体としての軸剛性が向上できる。その結果、車両自重や搭載重量に起因する部材の歪みを抑制すると共に同軸精度の維持が可能となり、振動、異音、騒音の抑制に寄与できる。第1固定軸部材20および第2固定軸部材24と第3固定軸部材40との接合は、圧入、溶接、接着等が利用可能であり、それらを単独で利用したり組み合わせて利用することができる。また、第1固定軸部材20、第2固定軸部材24、第3固定軸部材40を接続した場合の同軸精度の許容範囲内であれば、第1固定軸部材20および第2固定軸部材24と第3固定軸部材40を隙間嵌めによって接合してもよい。この場合、メンテナンス時の分解が容易になり作業性を向上できる。
As described above, the first fixed
第3固定軸部材40は、第1固定軸部材20や第2固定軸部材24と同様に鉄やステンレス鋼で形成することができる。この第3固定軸部材40は、リング状のロータコア52の内周側と第3ベアリング58の外輪とを跨ぐように固定されたギアホルダ66を回転自在に支持している。このギアホルダ66には第3固定軸部材40を回転中心とする太陽ギア60が固定されている。つまり、ロータコア52が回転することにより太陽ギア60が回転する。前述したように、太陽ギア60には、複数の遊星ギア62が噛合している。遊星ギア62は、太陽ギア60と噛合する第1遊星ギア62aと、内歯ギア46と噛合する第2遊星ギア62bとで構成されている。第1遊星ギア62aと第2遊星ギア62bは、いずれもギア固定軸64を中心軸として回転する。第1遊星ギア62aと第2遊星ギア62bは別々に形成されてギア固定軸64に固定されてもよいし、第1遊星ギア62aと第2遊星ギア62bを一体で形成してギア固定軸64に固定してもよい。
Similar to the first fixed
本発明者らは、各種シミュレーションにより、減速機構28の減速比は例えば6〜21が本実施形態のインホイールモータ10において好適であることを確認した。
減速比は、太陽ギア60の歯数をZa、内歯ギア46の歯数をZc、第1遊星ギア62aの歯数をZ1、第2遊星ギア62bの歯数をZ2とした場合、以下のようになる。
減速比≒(Z1/Za)×(Zc/Z2)
ここで、噛み合うギアの歯の大きさ、つまり太陽ギア60と第1遊星ギア62a及び第2遊星ギア62bと内歯ギア46の歯の大きさは一致させることが一般的であるので、各ギアの歯数は対応するギアの円周の長さに比例すると見なせる。したがって、ギアの基準ピッチ円直径を用いた以下の計算式で減速比を簡易的に表現できる。つまり、太陽ギア60の基準ピッチ円直径をDa、内歯ギア46の基準ピッチ円直径をDc、第1遊星ギア62aの基準ピッチ円直径をD1、第2遊星ギア62bの基準ピッチ円直径をD2とした場合、以下のようになる。
減速比≒(D1/Da)×(Dc/D2)
ここで、発明者らは本実施形態のインホイールモータ10の構成における太陽ギア60基準ピッチ円直径の下限値について、太陽ギア60の必要軸強度やインホイールモータ10全体の組み立て作業性等を考慮して検討した。その結果、Da=11.0mmを下限値として、D1=50.0mm、D2=16.2mm、Dc=77.2mmに設定することで、インホイールモータ10に要求される性能を維持できることを確認した。この場合の減速比は、21.7になった。
The present inventors have confirmed through various simulations that the reduction ratio of the
The reduction ratio is as follows when the number of teeth of the
Reduction ratio ≒ (Z1 / Za) x (Zc / Z2)
Here, since the sizes of the teeth of the meshing gears, that is, the sizes of the teeth of the
Reduction ratio ≒ (D1 / Da) x (Dc / D2)
Here, the inventors consider the required shaft strength of the
また、発明者らは本実施形態のインホイールモータ10の構成における太陽ギア60基準ピッチ円直径の上限値について、インホイールモータ10のサイズや重量、ハブ12の内部スペースの制限、インホイールモータ10全体の組み立て作業性等を考慮して検討した。その結果、Da=27.6mmを上限値として、D1=33.4mm、D2=16.2mm、Dc=77.2mmに設定することで、インホイールモータ10に要求されるサイズや重量の制限を満たすことを確認した。この場合の減速比は、5.77になった。
Further, the inventors set the size and weight of the in-
また、発明者らは、Da=13.2mm、D1=47.8mm、D2=16.2mm、Dc=77.2mmが、太陽ギア60の軸強度やインホイールモータ10全体としての組み立て作業性、サイズや重量の制限をバランスよく満たす最適値であることを確認した。そして、この場合の減速比は17.3になった。このように、減速比については、減速比6〜21の範囲で、インホイールモータ10を搭載する車両の種類や用途により太陽ギア60、第1遊星ギア62a、第2遊星ギア62b、内歯ギア46の基準ピッチ円直径や歯数を適宜選択して決定することが望ましい。
In addition, the inventors have Da = 13.2 mm, D1 = 47.8 mm, D2 = 16.2 mm, and Dc = 77.2 mm, the shaft strength of the
ところで、図2に示すように、本実施形態のインホイールモータ10は、減速機構28を構成する太陽ギア60の中央部に貫通口66aを有し、この貫通口66aを第3固定軸部材40が貫通して第1固定軸部材20と第2固定軸部材24とを軸線上で連結している。その結果、他の構成部品の干渉を受けることなく、また、ハブ12内部の構造の複雑化を招くことなく、第1固定軸部材20と第2固定軸部材24を直結して、第1固定軸部材20と第2固定軸部材24との同軸精度を向上させると共に、軸剛性を向上させている。
By the way, as shown in FIG. 2, the in-
このように構成されるインホイールモータ10の動作を説明する。
図示しない車両に設けられたアクセル装置の開度を調整することにより、駆動回路(不図示)から3相の略正弦波状の電流が駆動ライン38を介してコイル50に通電される。その結果、コイル50はステータコア48の突極に回転磁界を発生する。そして、マグネット54の駆動用磁極と回転磁界との相互作用により回転駆動力が生じて、ロータコア52を回転させる。ロータコア52は、ギアホルダ66を介して太陽ギア60に接続されているので、ロータコア52と太陽ギア60は同速で回転する。太陽ギア60は、遊星ギア62の第1遊星ギア62aと噛合し、第1遊星ギア62aは、第2遊星ギア62bと同軸に接合され、この第2遊星ギア62bが内歯ギア46と噛合している。したがって、ロータコア52の回転により内歯ギア46が固定された第1部材30が回転する。第1部材30と第2部材32は、ネジ68等の締結部材によってハブ12として一体化されていて、第1固定軸部材20および第2固定軸部材24を固定の回転軸として回転する。つまり、第1固定軸部材20と第2固定軸部材24とが固定された車体に対して、ハブ12、つまり車輪が回転して車両の走行を実現する。
The operation of the in-
By adjusting the opening of an accelerator device provided in a vehicle (not shown), a three-phase substantially sinusoidal current is passed through the
図3(a)〜(c)は、第1固定軸部材20と第2固定軸部材24と第3固定軸部材40の連結構造の他の構造例を説明する説明図である。図2の場合、第1固定軸部材20と第2固定軸部材24と第3固定軸部材40とは、それぞれ別部品として形成して、圧入や溶接、接着等の接合方法を単独または組み合わせて用いて直結した例を示した。図3(a)の例は、第1固定軸部材20と第3固定軸部材40を一体形成して固定軸70とした例である。固定軸70の第3固定軸部材40側は、第2固定軸部材24の連結孔24aに圧入や溶接、接着等の接合方法を単独または組み合わせて用いて直結する。
FIGS. 3A to 3C are explanatory views for explaining another structural example of the connection structure of the first fixed
同様に、図3(b)の例は、第2固定軸部材24と第3固定軸部材40を一体形成して固定軸72とした例である。固定軸72の第3固定軸部材40側は、第1固定軸部材20の連結孔20bに圧入や溶接、接着等の接合方法を単独または組み合わせて用いて直結する。このように、第1固定軸部材20と第2固定軸部材24のいずれか一方に第3固定軸部材40を一体的に形成することにより、各固定軸を別部品とする場合に比べて部品点数や製造工数の低減、および軸剛性の向上等を図ることができる。
Similarly, the example of FIG. 3B is an example in which the second fixed
図3(c)は、第1固定軸部材20、第2固定軸部材24、第3固定軸部材40を一体として固定軸74とした例である。この場合、図3(a)、図3(b)の例よりさらに部品点数や製造工数の低減、および軸剛性の向上等を図ることができる。ただし、図3(c)の場合、第3固定軸部材40に相当する部分でギアホルダ66および太陽ギア60を回転自在に軸支する必要がある。そのような構造の場合の組立を可能にするため、第3固定軸部材40に相当する部分を第1固定軸部材20および第2固定軸部材24と同径またはそれより大径にする必要がある。第3固定軸部材40相当部分の直径を大きくすることにより、太陽ギア60の基準ピッチ円直径を大きくし、遊星ギア62の基準ピッチ円直径を小さくする必要が生じるため、減速比とのバランスを考慮して固定軸74の採用を決定することが好ましい。
FIG. 3C is an example in which the first fixed
ところで、図2に示すインホイールモータ10の構造において、遊星ギア62はギア固定軸64の周囲をベアリング等を介することなく回転する構造を採用している。そのため、62の上下の支持端面が被支持面と摺動する。その結果、回転時にギア固定軸64に支持される遊星ギア62の支持端面が早期に摩耗する場合がある。本実施形態では、図4に示すように、第2固定軸部材24に固定されたギアケース44に植設されたギア固定軸64に、当該ギア固定軸64の軸方向に遊星ギア62が移動することを規制するリング状の一対のワッシャ76を設け、遊星ギア62を挟み位置決めしている。そして、このワッシャ76は、遊星ギア62と共に回転するように構成している。例えば、ワッシャ76に形成した係合爪を遊星ギア62の端面と係合させるようにしている。その結果、遊星ギア62の回転時に、ワッシャ76がギアケース44やギア固定軸64の固定部と接触させて、ワッシャ76が先に摩耗するように構成している。したがって、インホイールモータ10のメンテナンスはワッシャ76の摩耗に基づいて実施すると共に、交換部品はワッシャ76のみにできるように構成している。その結果、インホイールモータ10のメンテナンスコストの低減ができる。
In the structure of the in-
このワッシャ76は、例えばステンレス鋼、鉄、銅材等の金属を用いて形成することができる。また、ワッシャ76は、自己潤滑性のある材料で形成してもよい。例えば、ワッシャ76をPEEK(ポリエーテル・エーテル・ケトン)で形成してもよい。PEEKは、熱可塑性の超耐熱高分子樹脂であり、耐疲労性・耐衝撃性・耐クリープ性に優れ、耐薬品性では濃硫酸以外は使用可能であり、ガス・金属イオンの溶出が少ない材料であり、耐発熱性、耐衝撃性、耐腐食性等が要求されるインホイールモータ10への使用に適している。ワッシャ76は、その厚みを調整したり、積層したりして耐久性を調整してもよい。
The
また、図5(a)は、遊星ギア62の支持安定性を向上させるための弾性ブラケット78の一例を示す斜視図である。弾性ブラケット78は、ギアケース44と遊星ギア62との間に弾性力を付与する弾性部材として機能し、遊星ギア62を所定方向、例えば、ギアケース44から離間する方向に付勢するような付勢力を発生する。弾性ブラケット78は例えば板状のバネ鋼をプレス加工等で打ち抜きおよび変形させることで形成することができる。図5(b)は、弾性ブラケット78をギアケース44と遊星ギア62の間に介在させた状態を説明する説明図である。弾性ブラケット78により遊星ギア62を一定方向(図中矢印A方向)に付勢しておくことにより、遊星ギア62をギア固定軸64の先端に装着された固定リング80等の固定部材に付勢して、遊星ギア62が回転するときのギア固定軸64の軸方向へ振動(ばたつき)を抑制する。このように遊星ギア62のギア固定軸64の軸方向への振動を抑制することにより、インホイールモータ10全体の振動抑制、異音抑制、遊星ギア62の摩耗軽減等を実現できる。
FIG. 5A is a perspective view showing an example of an
なお、図5(b)の場合、弾性ブラケット78の上面にワッシャ76を介在させている例を示している。この場合、弾性ブラケット78は、ワッシャ76と共に遊星ギア62を付勢し、ワッシャ76と遊星ギア62が、弾性ブラケット78上で回転することになる。また。弾性ブラケット78上のワッシャ76を省略して弾性ブラケット78のみで遊星ギア62を付勢支持するようにしてもよい。この場合、弾性ブラケット78は遊星ギア62と共に回転しない。そのため、弾性ブラケット78を自己潤滑性のある材料で構成するか、弾性ブラケット78の上面に潤滑層をコーティングして、遊星ギア62の摩耗を軽減するようにしてもよい。
In the case of FIG. 5B, an example in which a
なお、図5(a)では、弾性ブラケット78はギア固定軸64が挿通できる円形の開口を有する例を示しているが、その形状は遊星ギア62に対して付勢力を発生できればよい。例えば、ギア固定軸64の挿通部をU字形状にして、ギア固定軸64の横方向から装着できるようにしてもよい。また、弾性ブラケット78を遊星ギア62の上下位置に配置してもよい。この場合、一対の弾性ブラケット78の付勢力を同じにして遊星ギア62をギア固定軸64の中央に位置させてもよい。また、付勢力を異ならせて一方側に付勢するようにしてもよい。
5A shows an example in which the
本実施形態は、車両が停止状態から最大速度までモータ部26の制御により完全カバーする電動車両に適用するインホイールモータ10の例を示した。変形例においては、例えば、ハブ12内部にクラッチ機構を設け、電動アシスト仕様にしてもよい。例えば、電動アシスト自転車の駆動部としてインホイールモータ10を利用する場合、発進時にクラッチ機構をインホイールモータ10に接続して、モータ部26によるモータアシストを行う。そして、所定の速度を超えた場合や運転者の要求があった場合にクラッチ機構を離脱させ、ペダル回転力のみで自転車を走行させるようにしてもよい。また、自転車を漕ぐ力(トルク)の検出器を回路に組み込むことによって、トルクに応じたレベルのアシストをインホイールモータ10で行うようにしてもよい。さらに、本実施形態のインホイールモータ10と他の駆動源を組み合わせて、インホイールモータ10を含む複数の駆動源を同時使用モードで使用したり、選択使用モードで使用するようにしてもよい。
In the present embodiment, an example of the in-
なお、上述の実施形態では、インホイールモータ10を搭載する車両を特定することなく構造や効果を説明したが、このようなインホイールモータ10を適用する車両の例としては、例えば、電動二輪車、電動車椅子、モータ付きスクータ、電動台車、ゴルフカート、電動自転車等がある。このように、本実施形態のインホイールモータ10は自走タイプの車輪またはトルクアシストタイプ車輪を構成可能であり、上述した例と同様の効果を得ることができる。
In the above-described embodiment, the structure and effect have been described without specifying the vehicle on which the in-
以上、実施の形態に係るインホイールモータの構成について説明した。これらの実施の形態は例示であり、本発明の原理、応用を示しているにすぎないことはいうまでもない。実施の形態には、請求の範囲に規定された本発明の思想を逸脱しない範囲において、多くの変形例や配置の変更が可能であり、またそうした変形例も本発明の範囲にあることは当業者に理解されるところである。 The configuration of the in-wheel motor according to the embodiment has been described above. These embodiments are merely examples, and it is needless to say that they merely illustrate the principles and applications of the present invention. In the embodiment, many modifications and arrangements can be made without departing from the spirit of the present invention defined in the claims, and such modifications are also within the scope of the present invention. That is understood by the contractor.
10 インホイールモータ、 12 ハブ、 20 第1固定軸部材、 24 第2固定軸部材、 28 減速機構、 30a 開口部、 30 第1部材、 30b 貫通口、 32 第2部材、 32a 貫通口、 36 モータベース、 36b 露出口、 40 第3固定軸部材、 44 ギアケース、 48 ステータコア、 52 ロータコア、 60 太陽ギア、 62 遊星ギア、 64 ギア固定軸、 66a 貫通口、 70,72,74 固定軸、 76 ワッシャ。 10 in-wheel motor, 12 hub, 20 first fixed shaft member, 24 second fixed shaft member, 28 speed reduction mechanism, 30a opening, 30 first member, 30b through port, 32 second member, 32a through port, 36 motor Base, 36b Exposed port, 40 Third fixed shaft member, 44 Gear case, 48 Stator core, 52 Rotor core, 60 Sun gear, 62 Planetary gear, 64 Gear fixed shaft, 66a Through port, 70, 72, 74 Fixed shaft, 76 Washer .
Claims (9)
前記ハブの一面側を貫通し当該ハブを回転自在に支持する第1固定軸部材と、
前記第1固定軸部材と同軸で前記ハブの他面側を貫通し当該ハブを回転自在に支持する第2固定軸部材と、
前記ハブの内部に配置され、前記第1固定軸部材が貫通すると共に前記第1固定軸部材に固定されたモータベースと、
前記モータベースに固定されたステータと、
前記ステータの内周領域に配置され、前記第1固定軸部材に回転自在に支持されたロータと、
前記第2固定軸部材と同軸となる貫通口を有すると共に前記ロータから回転力が入力されて当該ロータの回転速度を減速する減速機構と、
前記ハブの内周面に固定され、前記減速機構の出力側ギアが接続されたリング状の内歯ギアと、
前記貫通口を介して前記第1固定軸部材と前記第2固定軸部材とをそれらの軸線上で連結する第3固定軸部材と、
を含むことを特徴とするインホイールモータ。 A cylindrical hub to which a wheel should be coupled to the outer periphery;
A first fixed shaft member that passes through one side of the hub and rotatably supports the hub;
A second fixed shaft member that is coaxial with the first fixed shaft member and penetrates the other surface side of the hub and rotatably supports the hub;
A motor base disposed inside the hub, through which the first fixed shaft member passes and fixed to the first fixed shaft member;
A stator fixed to the motor base;
A rotor disposed in an inner peripheral region of the stator and rotatably supported by the first fixed shaft member;
A speed reduction mechanism that has a through-hole that is coaxial with the second fixed shaft member and receives a rotational force from the rotor to reduce the rotational speed of the rotor;
A ring-shaped internal gear fixed to the inner peripheral surface of the hub and connected to the output side gear of the speed reduction mechanism;
A third fixed shaft member for connecting the first fixed shaft member and the second fixed shaft member on their axes via the through hole;
An in-wheel motor comprising:
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011098672A JP2012228966A (en) | 2011-04-26 | 2011-04-26 | In-wheel motor |
| CN2012101202463A CN102756640A (en) | 2011-04-26 | 2012-04-18 | Wheel driving apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011098672A JP2012228966A (en) | 2011-04-26 | 2011-04-26 | In-wheel motor |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2012228966A true JP2012228966A (en) | 2012-11-22 |
| JP2012228966A5 JP2012228966A5 (en) | 2014-04-24 |
Family
ID=47430911
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011098672A Ceased JP2012228966A (en) | 2011-04-26 | 2011-04-26 | In-wheel motor |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2012228966A (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103707757A (en) * | 2013-12-30 | 2014-04-09 | 绍兴金道齿轮箱有限公司 | Dynamic drive pallet truck and dynamic drive wheel thereof |
| CN103738155A (en) * | 2013-12-30 | 2014-04-23 | 绍兴金道齿轮箱有限公司 | Electric horizontal driving wheel assembly |
| KR101488507B1 (en) | 2012-05-21 | 2015-02-02 | 씨스톤 테크놀로지스(주) | Hub Drive Mechanism |
| JP2016016718A (en) * | 2014-07-07 | 2016-02-01 | ブリヂストンサイクル株式会社 | Hub structure with built-in motor, and bicycle |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS61189752U (en) * | 1985-05-18 | 1986-11-26 | ||
| US5581136A (en) * | 1994-12-20 | 1996-12-03 | Li; I-Ho | Auxiliary magnetic motor (AMM) |
| JP2003191882A (en) * | 2001-10-19 | 2003-07-09 | Yamaha Motor Co Ltd | Braking device for motor-driven two-wheeled vehicle |
| JP2005214393A (en) * | 2004-02-02 | 2005-08-11 | Nsk Ltd | Planetary gear mechanism |
| JP2005335536A (en) * | 2004-05-27 | 2005-12-08 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Hub unit for electromotive vehicle wheel, and vehicle with the hub unit |
| US6974399B2 (en) * | 2004-02-11 | 2005-12-13 | Chiu-Hsiang Lo | Hub motor mechanism |
| JP2009008127A (en) * | 2007-06-26 | 2009-01-15 | Toyota Motor Corp | Planetary gear device |
-
2011
- 2011-04-26 JP JP2011098672A patent/JP2012228966A/en not_active Ceased
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS61189752U (en) * | 1985-05-18 | 1986-11-26 | ||
| US5581136A (en) * | 1994-12-20 | 1996-12-03 | Li; I-Ho | Auxiliary magnetic motor (AMM) |
| JP2003191882A (en) * | 2001-10-19 | 2003-07-09 | Yamaha Motor Co Ltd | Braking device for motor-driven two-wheeled vehicle |
| JP2005214393A (en) * | 2004-02-02 | 2005-08-11 | Nsk Ltd | Planetary gear mechanism |
| US6974399B2 (en) * | 2004-02-11 | 2005-12-13 | Chiu-Hsiang Lo | Hub motor mechanism |
| JP2005335536A (en) * | 2004-05-27 | 2005-12-08 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Hub unit for electromotive vehicle wheel, and vehicle with the hub unit |
| JP2009008127A (en) * | 2007-06-26 | 2009-01-15 | Toyota Motor Corp | Planetary gear device |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101488507B1 (en) | 2012-05-21 | 2015-02-02 | 씨스톤 테크놀로지스(주) | Hub Drive Mechanism |
| CN103707757A (en) * | 2013-12-30 | 2014-04-09 | 绍兴金道齿轮箱有限公司 | Dynamic drive pallet truck and dynamic drive wheel thereof |
| CN103738155A (en) * | 2013-12-30 | 2014-04-23 | 绍兴金道齿轮箱有限公司 | Electric horizontal driving wheel assembly |
| JP2016016718A (en) * | 2014-07-07 | 2016-02-01 | ブリヂストンサイクル株式会社 | Hub structure with built-in motor, and bicycle |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6753752B2 (en) | Support structure of electric motor for bicycle and drive unit for bicycle including this | |
| US7375450B2 (en) | Hub unit for use in electrically movable wheels and vehicle comprising the hub unit | |
| US8939871B2 (en) | Acceleration mechanism for exercise equipment | |
| US8674573B2 (en) | Direct-current motor and hub unit | |
| JP2005335536A (en) | Hub unit for electromotive vehicle wheel, and vehicle with the hub unit | |
| JP2007269129A (en) | Wheel rotating device of in-wheel motor vehicle | |
| JP2004175175A (en) | Mounting structure of rotary electric machine for wheels | |
| JP2006062476A (en) | Housing structure of in-wheel motor | |
| JP6865699B2 (en) | Drive systems for electric vehicles and electric vehicles | |
| JP6169531B2 (en) | Bicycle drive unit | |
| JP2005186667A (en) | Electrically driven wheel driving device | |
| JP2012228966A (en) | In-wheel motor | |
| JP2012244810A (en) | In-wheel motor | |
| US10155565B2 (en) | Construction of motorized wheel for vehicle motorization | |
| JP2013032094A (en) | Hub bearing, speed reduction mechanism, and in-wheel motor | |
| JP2012214203A (en) | In-wheel motor driving device | |
| JP2013166437A (en) | Wheel drive device | |
| JP2014065396A (en) | Wheel driving device | |
| WO2019124242A1 (en) | In-wheel motor | |
| JPWO2012014969A1 (en) | Molded motor and moving body equipped with the same | |
| CN102756640A (en) | Wheel driving apparatus | |
| JP2005212657A (en) | Motorized wheel driving device | |
| JP2013032095A (en) | Hub bearing, speed reduction mechanism, and in-wheel motor | |
| JP5378114B2 (en) | Differential device with motor | |
| JP6100354B1 (en) | In-wheel motor drive device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140307 |
|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20140307 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20140414 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20150129 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20150203 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150212 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20150311 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150420 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20150804 |
|
| A045 | Written measure of dismissal of application |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A045 Effective date: 20151222 |