JP2012037726A - Voice synthesizer and computer program - Google Patents
Voice synthesizer and computer program Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2012037726A JP2012037726A JP2010177776A JP2010177776A JP2012037726A JP 2012037726 A JP2012037726 A JP 2012037726A JP 2010177776 A JP2010177776 A JP 2010177776A JP 2010177776 A JP2010177776 A JP 2010177776A JP 2012037726 A JP2012037726 A JP 2012037726A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- control
- fundamental frequency
- speech speed
- speech
- unit
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- User Interface Of Digital Computer (AREA)
Abstract
【課題】容易に且つ効率的に音声データを補正する。
【解決手段】制御情報テーブルを記憶する制御情報テーブル記憶部51と、音声データの基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成する基本周波数分析部31と、話速値を計算する話速計算部32と、制御方法の種別と話速の制御量または基本周波数の変化幅の制御量を指定するキー情報とを設定する制御条件設定部52と、制御方法の種別に関連付けられた制御情報テーブルを読み込み、キー情報と話速値と基本周波数の時間変化情報とに基づいて話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを取得する制御情報取得部53と、基本周波数の変化幅の制御量に基づいて基本周波数の時間変化情報から目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成する目標基本周波数生成部54と、話速の制御量と目標基本周波数の時間変化情報とに基づいて音声データを補正する音声データ補正部80とを備えた。
【選択図】図1Sound data is corrected easily and efficiently.
A control information table storage unit 51 that stores a control information table, a fundamental frequency analysis unit 31 that generates time change information of a fundamental frequency of voice data, a speech rate calculation unit 32 that calculates a speech rate value, The control condition setting unit 52 for setting the control method type and the key information for specifying the control amount of the speech speed or the change amount of the fundamental frequency, and the control information table associated with the control method type are read A control information acquisition unit 53 that acquires the control amount of the speech speed and the control amount of the change width of the fundamental frequency based on the information, the speech speed value, and the time change information of the fundamental frequency; Based on the target basic frequency generation unit 54 for generating the time change information of the target basic frequency from the time change information of the basic frequency based on the control amount of the speech speed and the time change information of the target basic frequency. And a voice data correction unit 80 to which a positive to.
[Selection] Figure 1
Description
本発明は、入力音声の韻律を補正する音声合成装置およびコンピュータプログラムに関する。 The present invention relates to a speech synthesizer and a computer program that correct prosody of input speech.
合成音声等の音声データを聴き易い音声データに変換するために、韻律に関する音響特徴量を変更することは有効である。そして、韻律に関する音響特徴量として例えばピッチ、パワー、および継続長を制御対象とし、ピッチもしくはパワー、またはピッチパターンの時間変動のダイナミックレンジを変更したりポーズ長を変えたりして、音声の音質を変化させる技術が知られている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。 In order to convert voice data such as synthesized voice into voice data that is easy to listen to, it is effective to change the acoustic feature quantity related to prosody. Then, for example, pitch, power, and duration are controlled as acoustic features related to the prosody, and the sound quality is improved by changing the dynamic range of the time variation of the pitch or power or pitch pattern or changing the pause length. A technique for changing is known (see, for example, Patent Document 1).
音声データの音声を聴き易い音声に変換するためには、音声データの韻律に関する複数種類の音響特徴量を補正することが有効である。しかしながら、複数種類の音響特徴量を調整して所望の韻律の音声に近づけるには、音響特徴量相互の関係や音響特徴量と聴き易さとの関係等の音響に関する専門知識や豊かな調整経験が必要である。また、このような調整作業を、人手を伴って行うことは非常に複雑でかつ煩雑である。
そこで、本発明は上記事情に鑑みてなされたものであり、音響に関する専門知識や豊かな調整経験がなくとも音声データを補正でき、聴き易い音声データを容易に且つ効果的に得ることができる、音声合成装置およびコンピュータプログラムを提供することを目的とする。
In order to convert the sound of the sound data into a sound that is easy to hear, it is effective to correct a plurality of types of acoustic feature values related to the prosody of the sound data. However, in order to adjust multiple types of acoustic features and bring them closer to the desired prosody, you need extensive expertise in sound and rich adjustment experience, such as the relationship between acoustic features and the relationship between acoustic features and ease of listening. is necessary. In addition, it is very complicated and complicated to perform such adjustment work with human hands.
Therefore, the present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, it is possible to correct the audio data without having specialized knowledge and rich adjustment experience, and it is possible to easily and effectively obtain easy-to-listen audio data. An object is to provide a speech synthesizer and a computer program.
[1]上記の課題を解決するため、本発明の一態様である音声合成装置は、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを対応付けた制御情報テーブルを、制御方法の種別に関連付けて記憶する制御情報テーブル記憶部と、音声データを取得する音声データ取得部と、前記音声データ取得部が取得した前記音声データに基づいて基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成する基本周波数分析部と、前記音声データに基づいて話速値を計算する話速計算部と、所望の制御方法の種別と制御情報テーブルにおける話速の制御量または基本周波数の変化幅の制御量を指定するキー情報とを設定する制御条件設定部と、前記制御条件設定部が設定した前記制御方法の種別に関連付けられた制御情報テーブルを前記制御情報テーブル記憶部から読み込み、前記制御条件設定部が設定した前記キー情報と前記話速計算部が計算した前記話速値と前記基本周波数分析部が生成した前記基本周波数の時間変化情報とに基づいて、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを取得する制御情報取得部と、前記制御情報取得部が取得した前記基本周波数の変化幅の制御量に基づいて、前記基本周波数の時間変化情報から目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成する目標基本周波数生成部と、前記制御情報取得部が取得した前記話速の制御量と、前記目標基本周波数生成部が生成した前記目標基本周波数の時間変化情報とに基づいて、前記音声データを補正して補正後音声データを出力する音声データ補正部と、を備えることを特徴とする。
ここで、話速の制御量は、音声データ補正部が韻律の音響特徴量である話速を補正するための補正データまたは補正量を表すデータである。また、基本周波数の変化幅の制御量は、音声データ補正部が韻律の音響特徴量である基本周波数の変化幅、言い換えると音域を補正するための補正データまたは補正量を表すデータである。
この構成によれば、本発明の一態様である音声合成装置は、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とのいずれか一方を指定することにより、この一方の制御量に対応する他方の制御量を制御情報テーブル記憶部から取得する。そして、この音声合成装置は、取得した基本周波数の変化幅の制御量に基づいて目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成し、取得した話速の制御量と生成した目標基本周波数の時間変化情報とに基づいて、音声データの話速および基本周波数の変化幅に関する韻律を補正する。
よって、本発明の一態様である音声合成装置によれば、音声データが容易に且つ効率的に補正後音声データに補正される。
[1] In order to solve the above-described problem, a speech synthesizer according to an aspect of the present invention provides a control information table in which a control amount of speech speed and a control amount of a change amount of a fundamental frequency are associated with each other in a control method. Basic frequency analysis that generates time change information of a fundamental frequency based on the audio data acquired by the audio data acquisition unit, a control information table storage unit that stores the data in association with a type, an audio data acquisition unit , A speech speed calculation unit for calculating a speech speed value based on the voice data, and a key for designating a desired control method type and a control amount of a speech speed or a change amount of a fundamental frequency in a control information table A control condition setting unit for setting information, and a control information table associated with the type of the control method set by the control condition setting unit is read from the control information table storage unit, Based on the key information set by the control condition setting unit, the speech speed value calculated by the speech speed calculation unit, and the time change information of the fundamental frequency generated by the fundamental frequency analysis unit, A control information acquisition unit that acquires a control amount of a change width of the fundamental frequency, and a target basic frequency from the time change information of the fundamental frequency based on the control amount of the change width of the fundamental frequency acquired by the control information acquisition unit. Based on the target fundamental frequency generation unit that generates the time change information of the target, the control amount of the speech speed acquired by the control information acquisition unit, and the time change information of the target basic frequency generated by the target basic frequency generation unit An audio data correction unit that corrects the audio data and outputs the corrected audio data.
Here, the speech speed control amount is correction data or data representing a correction amount for the speech data correction unit to correct the speech speed, which is the prosody acoustic feature amount. Further, the control amount of the change width of the fundamental frequency is data representing the correction data or the correction amount for correcting the change width of the fundamental frequency, which is the acoustic feature quantity of the prosody, in other words, correcting the sound range.
According to this configuration, the speech synthesizer according to one aspect of the present invention can handle either one of the control amounts by designating either the control amount of the speech speed or the control amount of the change width of the fundamental frequency. The other control amount to be acquired is acquired from the control information table storage unit. Then, the speech synthesizer generates time change information of the target basic frequency based on the acquired control amount of the change width of the basic frequency, and the acquired control amount of the speech speed and the generated time change information of the target basic frequency, Based on the above, the prosody related to the speech speed and the change width of the fundamental frequency of the voice data is corrected.
Therefore, according to the speech synthesizer which is an aspect of the present invention, speech data is easily and efficiently corrected into corrected speech data.
[2]上記[1]記載の音声合成装置において、話速の絶対値を話速の制御量とし、基本周波数の変化幅の絶対値を基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とし、前記制御情報テーブル記憶部は、複数の話速値の絶対値それぞれに基本周波数の変化幅の絶対値を対応付けた制御情報テーブルを制御方法の種別に関連付けて記憶することを特徴とする。
[3]上記[1]記載の音声合成装置において、話速の倍率を話速の制御量とし、基本周波数の変化幅の倍率を基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とし、前記制御情報テーブル記憶部は、複数の話速の倍率それぞれに基本周波数の変化幅の倍率を対応付けた制御情報テーブルを制御方法の種別に関連付けて記憶し、前記制御条件設定部は、前記キー情報についての所望の倍率をさらに設定し、前記制御情報取得部は、前記制御条件設定部が設定した前記キー情報と前記倍率と前記話速計算部が計算した前記話速値と前記基本周波数分析部が生成した前記基本周波数の時間変化情報とに基づいて、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを取得することを特徴とする。
[4]上記[3]記載の音声合成装置において、前記制御情報テーブル記憶部は、複数の指定話速値それぞれに対応して、複数の話速の倍率それぞれに基本周波数の変化幅の倍率を対応付けた制御情報テーブルを制御方法の種別に関連付けて記憶し、前記制御情報取得部は、前記制御条件設定部が設定した前記制御方法の種別に関連し且つ前記話速計算部が計算した前記話速値と同一である指定話速値に対応する制御情報テーブルを前記制御情報テーブル記憶部から読み込み、前記制御条件設定部が設定した前記キー情報と前記倍率と前記話速値と前記基本周波数分析部が生成した前記基本周波数の時間変化情報とに基づいて、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを取得することを特徴とする。
[5]上記[1]記載の音声合成装置において、前記制御情報テーブル記憶部は、話速の制御量である話速の倍率に基本周波数の変化幅の制御量である基本周波数の変化幅の倍率を対応付けた制御情報テーブルを、制御方法の種別に関連付けて記憶し、前記制御条件設定部は、所望の制御方法の種別を設定し、前記制御情報取得部は、前記制御条件設定部が設定した前記制御方法の種別に関連付けられた制御情報テーブルを前記制御情報テーブル記憶部から読み込み、前記制御情報テーブルから話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを取得することを特徴とする。
[2] In the speech synthesizer according to [1], the absolute value of the speech speed is set as a control amount of the speech speed, the absolute value of the change width of the basic frequency is set as a control amount of the change width of the basic frequency, and the control information table The storage unit stores a control information table in which an absolute value of a change frequency of a fundamental frequency is associated with each absolute value of a plurality of speech speed values in association with a type of control method.
[3] In the speech synthesizer described in [1] above, the control information table storage unit includes a speech speed magnification as a speech speed control amount, a fundamental frequency change width as a fundamental frequency change amount control amount, and Stores a control information table in which a magnification of a change rate of a fundamental frequency is associated with each of a plurality of speech speed magnifications in association with a type of control method, and the control condition setting unit is configured to store a desired magnification for the key information. The control information acquisition unit further includes the key information set by the control condition setting unit, the magnification, the speech speed value calculated by the speech speed calculation unit, and the basic frequency generated by the fundamental frequency analysis unit. Based on the time change information of the frequency, the control amount of the speech speed and the control amount of the change width of the fundamental frequency are acquired.
[4] In the speech synthesizer according to [3] above, the control information table storage unit may multiply the multiples of the plurality of speech speeds by the multiples of the basic frequency corresponding to the plurality of designated speech speed values. The associated control information table is stored in association with the type of control method, and the control information acquisition unit is related to the type of control method set by the control condition setting unit and calculated by the speech speed calculation unit. A control information table corresponding to a designated speech speed value that is the same as the speech speed value is read from the control information table storage unit, and the key information, the magnification, the speech speed value, and the fundamental frequency set by the control condition setting unit Based on the time change information of the fundamental frequency generated by the analysis unit, the control amount of the speech speed and the control amount of the change width of the fundamental frequency are acquired.
[5] In the speech synthesizer described in [1] above, the control information table storage unit may calculate a basic frequency change width that is a control amount of a basic frequency change amount to a speech speed magnification that is a control amount of the speech speed. A control information table in which magnifications are associated is stored in association with a control method type, the control condition setting unit sets a desired control method type, and the control information acquisition unit is stored in the control condition setting unit. A control information table associated with the set type of the control method is read from the control information table storage unit, and a control amount of speech speed and a control amount of a change width of a fundamental frequency are acquired from the control information table. And
[6]上記の課題を解決するため、本発明の一態様であるコンピュータプログラムは、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを対応付けた制御情報テーブルを、制御方法の種別に関連付けて記憶する制御情報テーブル記憶部を備えるコンピュータを、音声データを取得する音声データ取得手段と、前記音声データ取得手段が取得した前記音声データに基づいて基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成する基本周波数分析手段と、前記音声データに基づいて話速値を計算する話速計算手段と、所望の制御方法の種別と制御情報テーブルにおける話速の制御量または基本周波数の変化幅の制御量を示すキー情報とを設定する制御条件設定手段と、前記制御条件設定手段が設定した前記制御方法の種別に関連付けられた制御情報テーブルを前記制御情報テーブル記憶部から読み込み、前記制御条件設定手段が設定した前記キー情報と前記話速計算手段が計算した前記話速値と前記基本周波数分析手段が生成した前記基本周波数の時間変化情報とに基づいて、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを取得する制御情報取得手段と、前記制御情報取得手段が取得した前記基本周波数の変化幅の制御量に基づいて、前記基本周波数の時間変化情報から目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成する目標基本周波数生成手段と、前記制御情報取得手段が取得した前記話速の制御量と、前記目標基本周波数生成手段が生成した前記目標基本周波数の時間変化情報とに基づいて、前記音声データを補正して補正後音声データを出力する音声データ補正手段と、として機能させる。 [6] In order to solve the above-described problem, the computer program according to one aspect of the present invention provides a control information table in which a control amount of speech speed and a control amount of a change width of a fundamental frequency are associated with each other by a control method type A computer having a control information table storage unit stored in association with audio data acquisition means for acquiring audio data, and basic for generating time change information of a fundamental frequency based on the audio data acquired by the audio data acquisition means A frequency analysis means, a speech speed calculation means for calculating a speech speed value based on the voice data, a type of a desired control method, and a control amount of a speech speed or a control amount of a change amount of a fundamental frequency in a control information table Control condition setting means for setting key information, and a control information table associated with the type of control method set by the control condition setting means. Based on the key information set by the control condition setting means, the speech speed value calculated by the speech speed calculation means, and time change information of the fundamental frequency generated by the fundamental frequency analysis means, read from the information table storage unit Control information acquisition means for acquiring the control amount of the speech speed and the control amount of the change width of the fundamental frequency, and the basic frequency based on the control amount of the change width of the fundamental frequency acquired by the control information acquisition means Target fundamental frequency generating means for generating time change information of the target fundamental frequency from the time change information of the above, the control amount of the speech speed acquired by the control information acquiring means, and the target basic frequency generated by the target basic frequency generating means Based on the time change information of the frequency, the sound data is corrected and the sound data correcting means for outputting the corrected sound data is made to function.
本発明によれば、音響に関する専門知識や豊かな調整経験がなくとも音声データを補正でき、聴き易い音声データを容易且つ効率的に得ることができる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to correct audio data without having specialized knowledge about sound and rich adjustment experience, and it is possible to easily and efficiently obtain audio data that is easy to listen to.
以下、本発明を実施するための形態について、図面を参照して詳細に説明する。
[第1の実施の形態]
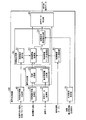
図1は、本発明の第1実施形態である音声合成装置の機能構成を示すブロック図である。同図に示すように、音声合成装置100は、音声データ取得部10と、音声属性情報取得部20と、音声分析部30と、制御条件情報生成部40と、目標値生成部50と、制御情報テーブル更新部60と、生成条件取得部70と、音声データ補正部80とを備える。
Hereinafter, embodiments for carrying out the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
[First Embodiment]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a functional configuration of a speech synthesizer according to the first embodiment of the present invention. As shown in the figure, the
音声データ取得部10は、外部から供給される音声データを取得し、この取得した音声データを音声分析部30に供給する。音声データは、アナログ音声信号を標本化周波数で標本化し量子化して得られるデジタル音声データであり、例えば不図示の録音装置によって録音されて得られた録音音声データや不図示の音声合成装置によって音声合成処理された合成音声データである。音声データは、例えばPCM(Pulse Code Modulation)データであり、フォーマットは、例えばWAVEである。
The voice
音声属性情報取得部20は、音声データ取得部10に供給される音声データに関連する音声属性情報の供給を受けて取得し、その音声属性情報を音声分析部30に供給する。音声属性情報は、音声データの発話内容を文章化したテキスト情報、または音声データの音素区切時間情報である。
音声データの発話内容が「おはようございます(空白)ごきげんいかがですか(空白)」である場合、テキスト情報は、例えば“おはようございます。ごきげんいかがですか。”である。なお、“(空白)”は、その前後の音声の間に、発声されない区間があることを表す。また、テキスト情報に含まれる文章は、ひらがな表記の他、カタカナ表記、ローマ字表記、または漢字混じり表記のいずれであってもよい。また、本実施形態では、音声データの発話内容が日本語である場合について説明するが、本実施形態は外国語についても適用可能である。
音素区切時間情報は、音声データの音声の先頭に対応する時点を基準時としたときの、当該音声データの各音素の発声時間を示す情報である。音素とは、音韻論上の音の最小単位であり、母音および子音それぞれが1音素に対応する。また、撥音、長音、および促音それぞれも1音素に対応する。この音素区切時間情報の具体例については後述する。
The voice attribute
When the utterance content of the voice data is “Good morning (blank) how are you? (Blank)”, the text information is, for example, “Good morning. How are you?” Note that “(blank)” indicates that there is a section that is not uttered between the preceding and following sounds. In addition to the hiragana notation, the sentence included in the text information may be any katakana notation, romaji notation, or kanji mixed notation. Further, in the present embodiment, a case where the utterance content of the voice data is Japanese will be described, but the present embodiment can also be applied to a foreign language.
The phoneme separation time information is information indicating the utterance time of each phoneme of the voice data when the time corresponding to the head of the voice of the voice data is set as the reference time. A phoneme is a minimum unit of sound in phonology, and each vowel and consonant corresponds to one phoneme. In addition, each of the repellent sound, the long sound, and the prompt sound corresponds to one phoneme. A specific example of the phoneme separation time information will be described later.
音声分析部30は、音声データ取得部10から供給される音声データと音声属性情報取得部20から供給される音声属性情報とをそれぞれ取り込み、これら音声データと音声属性情報とを分析して音声の基本周波数(以下、単に「基本周波数」と呼ぶ。)の時間変化情報と話速値とをそれぞれ求めて目標値生成部50に供給する。
The
音声分析部30は、その機能構成として基本周波数分析部31と、話速計算部32とを含んで構成される。
基本周波数分析部31は、音声データに基づいて、基本周波数の時間変化情報を有声区間(声帯の振動を伴う音声である有声音声の区間)において生成し、その生成した基本周波数の値に対し、有声区間の分析値を用いてスプライン関数等によりスムージング処理を行うことによって、変化が滑らかな基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成する。このとき、基本周波数分析部31は、基本周波数を抽出できない無声区間(声帯の振動を伴わない音声である無声音声の区間)については、この無声区間の前後の有声区間における基本周波数の値から内挿した値を用いて、無声区間における基本周波数の値を補間する。
なお、基本周波数分析部31は、スムージング処理を行わずに、生成した基本周波数の値そのものを基本周波数の時間変化情報としてもよい。
The
The fundamental
The fundamental
音声属性情報がテキスト情報である場合、話速計算部32は、次の二通りの方法のいずれかによって音声データの話速値を計算する。
第1の話速値を計算する方法は、音声データとテキスト情報とに基づいて音素区切時間情報を生成し、生成した音素区切時間情報に基づいて話速を計算する方法である。具体的には、話速計算部32は、音声データから音声区間の総時間長を求め、この総時間長とテキスト情報とに基づき公知の音声認識処理技術によって音素区切時間情報を生成する。そして、話速計算部32は、音素区切時間情報から単位時間当たりのモーラ(Mora)数を求めることによって話速値(単位は、「モーラ/秒」)を得る。モーラとは、音の長さについての音韻論上の単位である。日本語では、おおむね拗音については仮名二文字が1モーラに対応し、直音については仮名一文字が1モーラに対応する。そして、1モーラは、一つまたは複数の音素により構成される。
第2の話速値を計算する方法は、音声データから音声区間の総時間長を求めるとともにテキスト情報からモーラ数を求めて、これら音声区間の総時間長とモーラ数とに基づいて話速値を計算する方法である。
When the speech attribute information is text information, the speech
The method for calculating the first speech speed value is a method for generating phoneme segmentation time information based on speech data and text information and calculating the speech rate based on the generated phoneme segmentation time information. Specifically, the speech
The method for calculating the second speech speed value is to obtain the total time length of the speech section from the speech data and the number of mora from the text information, and based on the total time length of the speech section and the number of mora. Is a method of calculating
また、音声属性情報が音素区切時間情報である場合、話速計算部32は、その音素区切時間情報から単位時間当たりのモーラ数を求めることによって話速値を得る。
When the speech attribute information is phoneme break time information, the speech
制御条件情報生成部40は、ユーザによるキーボードやマウス等の入力装置の操作によって所望の制御方法の種別と所望の制御パラメータと所望の補正目的の種別との供給を受け、これら制御方法の種別と制御パラメータと補正目的の種別とを含めた制御条件情報を生成して目標値生成部50に供給する。
制御方法の種別は、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量との制御方法を区別するデータである。話速の制御量は、音声データ補正部80が韻律の第1の音響特徴量である話速を補正するための補正データまたは補正量を表すデータであり、目標となる話速値の絶対値、または話速の倍率で表される。基本周波数の変化幅の制御量は、音声データ補正部80が韻律の第2の音響特徴量である基本周波数の変化幅、言い換えると音域を補正するための補正データまたは補正量を表すデータであり、基本周波数の変化幅の絶対値、または基本周波数の変化幅の倍率で表される。
制御方法の種別について具体的に説明する。本実施形態における制御方法の種別は定量的に制御量を指定する制御方法であり、下記の表1のように分類される。
The control condition
The type of the control method is data that distinguishes the control method between the control amount of the speech speed and the control amount of the change width of the fundamental frequency. The speech speed control amount is correction data for the speech
The type of control method will be specifically described. The type of control method in the present embodiment is a control method for quantitatively specifying a control amount, and is classified as shown in Table 1 below.
表1において、制御方法1は、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを数値の絶対値で指定する方法である。制御方法2は、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを倍率で指定する方法である。制御方法3は、音声分析部30から供給される話速値(指定話速値)に対応して、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを倍率で指定する方法である。制御方法の種別は、制御方法1〜制御方法3それぞれに対応付けられたデータである。
In Table 1, the
制御パラメータは、目標値生成部50が話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを取得するために用いられるキー情報であり、具体的には次のとおりである。制御方法1に対応する制御パラメータは、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とのいずれかを指定する情報である。制御方法2および制御方法3に対応する制御パラメータは、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とのいずれかを指定する情報と所望の倍率とである。
The control parameter is key information used by the target
補正目的の種別は、韻律制御の目的を指定する情報、言い換えると、目標値生成部50が取得する話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量との補正傾向を指定する情報である。具体的には、補正目的の種別は、例えば、「難聴者向け」、「速聴向け」、「早口向け」を指定する情報である。
The type of correction purpose is information that specifies the purpose of prosody control, in other words, information that specifies the correction tendency between the control amount of the speech speed and the control amount of the change amount of the fundamental frequency acquired by the target
目標値生成部50は、音声分析部30から供給される話速値と基本周波数の時間変化情報とを取り込み、制御条件情報生成部40から供給される制御条件情報にしたがって、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを求める。さらに、目標値生成部50は、基本周波数の変化幅の制御量に基づいて目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成する。そして、目標値生成部50は、話速の制御量と目標基本周波数の時間変化情報とを音声データ補正部80に供給する。
The target
次に、詳細に目標値生成部50を説明する。目標値生成部50は、その機能構成として、制御情報テーブル記憶部51と、制御条件設定部52と、制御情報取得部53と、目標基本周波数生成部54とを含んで構成される。
Next, the target
制御情報テーブル記憶部51は、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを対応付けた複数の制御情報テーブルを、制御方法の種別と補正目的の種別とに関連付けて記憶する。制御情報テーブルは、話速値の絶対値に基本周波数の変化幅の絶対値を対応付けたテーブルと、複数の話速の倍率それぞれに基本周波数の変化幅の倍率を対応付けたテーブルと、複数の指定話速値それぞれに対応して、複数の話速の倍率それぞれに基本周波数の変化幅の倍率を対応付けたテーブルとの3種類である。各種制御情報テーブルの具体例については後述する。
制御情報テーブル記憶部51は、読み出しおよび書き込み可能な記憶装置であり、例えば、磁気ハードディスク装置、半導体記憶装置等である。また、制御情報テーブル記憶部51は、光磁気ディスク等の可搬型記録媒体であってもよい。
The control information
The control information
制御条件設定部52は、制御条件情報生成部40から供給される制御条件情報を取り込み、その制御条件情報に含まれる制御方法の種別と制御パラメータと補正目的の種別とを制御情報取得部53に設定する。
The control
制御情報取得部53は、制御条件設定部52により設定された制御方法の種別と補正目的の種別とに対応付けられた制御情報テーブルを制御情報テーブル記憶部51から読み込む。そして、制御情報取得部53は、読み込んだ制御情報テーブルと、制御条件設定部52により設定された制御パラメータと、音声分析部30からそれぞれ供給された話速値および基本周波数の時間変化情報とに基づいて、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを求める。さらに、制御情報取得部53は、話速の制御量を音声データ補正部80に供給するとともに、基本周波数の変化幅の制御量を目標基本周波数生成部54に供給する。
The control
具体的には、制御条件設定部52により制御方法の種別(例えば、制御方法1)と制御パラメータ(例えば、キー情報は話速の制御量を指定する情報である。)と補正目的の種別(例えば、難聴者向け)とが設定された場合、制御情報取得部53は、制御方法1と難聴者向けとに対応付けられた制御情報テーブル(話速値の絶対値に基本周波数の変化幅の絶対値を対応付けた難聴者向けテーブル)を制御情報テーブル記憶部51から読み込む。そして、制御情報取得部53は、制御パラメータにしたがい、音声分析部30から供給された話速値の絶対値をキーとして、そのキーに対応付けられた制御量である基本周波数の変化幅の絶対値を制御情報テーブルから抽出する。そして、制御情報取得部53は、キーである話速値の絶対値を話速の制御量とし、制御情報テーブルから抽出した基本周波数の変化幅の絶対値を基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とする。
Specifically, the control
また、制御条件設定部52により制御方法の種別(例えば、制御方法1)と制御パラメータ(例えば、キー情報は基本周波数の変化幅の制御量を指定する情報である。)と補正目的の種別(例えば、難聴者向け)とが設定された場合、制御情報取得部53は、制御方法1と難聴者向けとに対応付けられた制御情報テーブル(話速値の絶対値に基本周波数の変化幅の絶対値を対応付けた難聴者向けテーブル)を制御情報テーブル記憶部51から読み込む。そして、制御情報取得部53は、制御パラメータにしたがい、音声分析部30から供給された基本周波数の時間変化情報に基づき得られる基本周波数の変化幅の絶対値をキーとして、そのキーに対応付けられた制御量である話速値の絶対値を制御情報テーブルから抽出する。そして、制御情報取得部53は、キーである基本周波数の変化幅の絶対値を基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とし、制御情報テーブルから抽出した話速値の絶対値を話速の制御量とする。
In addition, the control
また、制御条件設定部52により制御方法の種別(例えば、制御方法2)と制御パラメータ(例えば、キー情報は話速の制御量を指定する情報であり、倍率も指定されている。)と補正目的の種別(例えば、速聴向け)とが設定された場合、制御情報取得部53は、制御方法2と速聴向けとに対応付けられた制御情報テーブル(複数の話速の倍率それぞれに基本周波数の変化幅の倍率を対応付けた速聴向けテーブル)を制御情報テーブル記憶部51から読み込む。そして、制御情報取得部53は、制御パラメータによる話速の倍率をキーとして、そのキーに対応付けられた制御量である基本周波数の変化幅の倍率を制御情報テーブルから抽出する。そして、制御情報取得部53は、制御パラメータによる話速の倍率を話速の制御量とし、制御情報テーブルから抽出した基本周波数の変化幅の倍率を基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とする。
Further, the control
また、制御条件設定部52により制御方法の種別(例えば、制御方法2)と制御パラメータ(例えば、キー情報は基本周波数の変化幅の制御量を指定する情報であり、倍率も指定されている。)と補正目的の種別(例えば、速聴向け)とが設定された場合、制御情報取得部53は、制御方法2と速聴向けとに対応付けられた制御情報テーブル(複数の話速の倍率それぞれに基本周波数の変化幅の倍率を対応付けた速聴向けテーブル)を制御情報テーブル記憶部51から読み込む。そして、制御情報取得部53は、制御パラメータによる基本周波数の変化幅の倍率をキーとして、そのキーに対応付けられた制御量である話速の倍率を制御情報テーブルから抽出する。そして、制御情報取得部53は、制御パラメータによる基本周波数の変化幅の倍率を基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とし、制御情報テーブルから抽出した話速の倍率を話速の制御量とする。
Further, the control
また、制御条件設定部52により制御方法の種別(例えば、制御方法3)と制御パラメータ(例えば、キー情報は話速の制御量を指定する情報であり、倍率も指定されている。)と補正目的の種別(例えば、早口向け)とが設定された場合、制御情報取得部53は、制御方法3と早口向けとに対応付けられて且つ音声分析部30から供給された話速値と同一である指定話速値の制御情報テーブル(指定話速値に対応して、複数の話速の倍率それぞれに基本周波数の変化幅の倍率を対応付けた早口向けテーブル)を、制御情報テーブル記憶部51から読み込む。そして、制御情報取得部53は、制御パラメータによる話速の倍率をキーとして、そのキーに対応付けられた制御量である基本周波数の変化幅の倍率を制御情報テーブルから抽出する。そして、制御情報取得部53は、制御パラメータによる話速の倍率を話速の制御量とし、制御情報テーブルから抽出した基本周波数の変化幅の倍率を基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とする。
Further, the control
また、制御条件設定部52により制御方法の種別(例えば、制御方法3)と制御パラメータ(例えば、キー情報は基本周波数の変化幅の制御量を指定する情報であり、倍率も指定されている。)と補正目的の種別(例えば、早口向け)とが設定された場合、制御情報取得部53は、制御方法3と早口向けとに対応付けられて且つ音声分析部30から供給された話速値と同一である指定話速値の制御情報テーブル(指定話速値に対応して、複数の話速の倍率それぞれに基本周波数の変化幅の倍率を対応付けた早口向けテーブル)を、制御情報テーブル記憶部51から読み込む。そして、制御情報取得部53は、制御パラメータによる基本周波数の変化幅の倍率をキーとして、そのキーに対応付けられた制御量である話速値の倍率を制御情報テーブルから抽出する。そして、制御情報取得部53は、制御パラメータによる基本周波数の変化幅の倍率を基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とし、制御情報テーブルから抽出した話速の倍率を話速の制御量とする。
Further, the control
目標基本周波数生成部54は、制御情報取得部53から供給された基本周波数の変化幅の制御量に基づいて、基本周波数分析部31で生成された基本周波数の時間変化情報から目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成して音声データ補正部80に供給する。このとき、目標基本周波数生成部54は、内部に記憶している生成条件情報にしたがって目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成する。
生成条件情報は、目標基本周波数生成部54が目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成するときの条件を指定する情報であり、平均値固定指定と、最小値固定指定と、指定値固定指定とのいずれかが指定される。
The target fundamental
The generation condition information is information for specifying a condition when the target fundamental
平均値固定指定は、基本周波数分析部31が生成した基本周波数の時間変化情報の所定区間における周波数値の平均値と同一の平均値となるようにして、当該区間における目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成することを指定するものである。
最小値固定指定は、基本周波数分析部31が生成した基本周波数の時間変化情報の所定区間における周波数値の最小値を基準とし、その最小値以上の周波数値となるように、当該区間における目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成することを指定するものである。
指定値固定指定には次の二通りの指定がある。第1の指定値固定指定は、基本周波数分析部31が生成した基本周波数の時間変化情報の所定区間における任意の一つの周波数値を基準として、当該区間における目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成することを指定するものである。
また、第2の指定値固定指定は、所定区間の始点と終点とのそれぞれに対応する二つの周波数値を基準として、当該区間における目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成することを指定するものである。
The average value fixed designation is such that the average value is the same as the average value of the frequency values in the predetermined section of the time change information of the fundamental frequency generated by the fundamental
The minimum value fixed designation is based on the minimum value of the frequency value in the predetermined section of the time change information of the basic frequency generated by the basic
There are the following two types of fixed value specification. The first specified value fixed designation generates time change information of the target fundamental frequency in the section based on any one frequency value in the predetermined section of the time change information of the fundamental frequency generated by the fundamental
In addition, the second specified value fixed designation designates that time change information of the target fundamental frequency in the section is generated with reference to two frequency values corresponding to the start point and the end point of the predetermined section, respectively. is there.
目標基本周波数生成部54は、生成条件取得部70から生成条件情報の供給を受けると、その生成条件情報で内部に記憶した生成条件情報を書き換える。
When receiving the generation condition information from the generation
目標基本周波数生成部54は、制御情報取得部53から供給される基本周波数の変化幅の制御量が「基本周波数の変化幅の数値の絶対値」である場合、生成条件取得部70から供給される生成条件情報にしたがって、周波数の変化幅が「基本周波数の変化幅の数値の絶対値」に合致する目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成する。
また、目標基本周波数生成部54は、制御情報取得部53から供給される基本周波数の変化幅の制御量が「基本周波数の変化幅の倍率」である場合、生成条件取得部70から供給される生成条件情報にしたがって、周波数の変化幅が「基本周波数の変化幅の倍率」に適合する目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成する。
The target fundamental
Further, the target fundamental
制御情報テーブル更新部60は、ユーザによるキーボードやマウス等の入力装置の操作によって制御情報テーブルの供給を受け、その制御情報テーブルを制御情報テーブル記憶部51に新規に書き込んだり、その制御情報テーブルで、既に記憶されている制御情報テーブルを書き換えたりする。
生成条件取得部70は、ユーザによるキーボードやマウス等の入力装置の操作によって平均値固定指定と最小値固定指定と第1の指定値固定指定と第2の指定値固定指定とのいずれかの指定を受け、その指定を示す生成条件情報を生成して目標基本周波数生成部54に供給する。
The control information
The generation
音声データ補正部80は、制御情報取得部53から供給される話速の制御量と、目標基本周波数生成部54から供給される目標基本周波数の時間変化情報とをそれぞれ取り込み、音声データ取得部10が取得した音声データの韻律を補正して補正後音声データを出力する。
具体的には、例えば、音声データ補正部80は、音声データに目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を適用して基本周波数の時間変化情報を補正する。そして、音声データ補正部80は、話速の制御量(話速値の絶対値または話速の倍率)に基づいて話速計算部32が算出した話速値を補正し、音声データの音素区切時間情報をその補正した話速値に基づいて補正する。そして、音声データ補正部80は、基本周波数の時間変化情報が補正された音声データに、補正後の音素区切時間情報を適用して時間軸方向を補正した補正後音声データを生成する。
The audio
Specifically, for example, the audio
図2は、音素区切時間情報を表すテキストデータの例を示す図である。同図に示すように、音素区切時間情報は複数の行からなるテキストデータであり、各行が音素に対応している。この音素区切時間情報の1行目から17行目までのデータは、音声データにおける“(空白)おはようございます(空白)”の部分についての音素の区切りを示す時間情報である。
また、音素区切時間情報の各行は、区切り文字(例えば、スペースやタブ等)で区切られた3つの列を有している。一列目は、音声データの先頭に対応する時点を基準時として各音素の開始時点までの時間を1万分の1秒単位で表し、二列目は上記基準時から各音素の終了時点までの時間を1万分の1秒単位で表し、三列目は音素の音素ラベルを表す。例えば、同図において、“0 2740 sil”は、基準時から0.274秒経過するまでの間が無声区間であることを表す。また、“2740 3168 o(お)”は、基準時から0.274秒経過した時点から、基準時から0.3168秒経過するまでの間の音素が“o(お)”であることを表す。なお、音素ラベル“sil”は音素がないことを表す。
なお、ここでは、時刻が1万分の1秒単位である場合を一例として説明したが、1千分の1秒単位(ミリ秒)等、他の単位で表すようにしてもよい。
FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating an example of text data representing phoneme segmentation time information. As shown in the figure, the phoneme break time information is text data composed of a plurality of lines, and each line corresponds to a phoneme. The data from the first line to the 17th line of the phoneme separation time information is time information indicating the phoneme breakage for the “(blank) good morning (blank)” portion in the voice data.
Each row of phoneme separation time information has three columns separated by a delimiter (for example, a space or a tab). The first column shows the time from the reference time to the end point of each phoneme, with the time from the reference time to the end point of each phoneme. Is expressed in units of 1 / 10,000 second, and the third column indicates phoneme labels of phonemes. For example, in the figure, “0 2740 sil” indicates that the period from the reference time until 0.274 seconds elapses is a silent section. Further, “2740 3168 o (o)” represents that the phoneme from the time point when 0.274 seconds have elapsed from the reference time to the point when 0.3168 seconds have elapsed from the reference time is “o (o)”. . Note that the phoneme label “sil” indicates that there is no phoneme.
Here, the case where the time is in units of 1 / 10,000 seconds has been described as an example. However, the time may be expressed in other units such as 1 / 1000th of a second (millisecond).
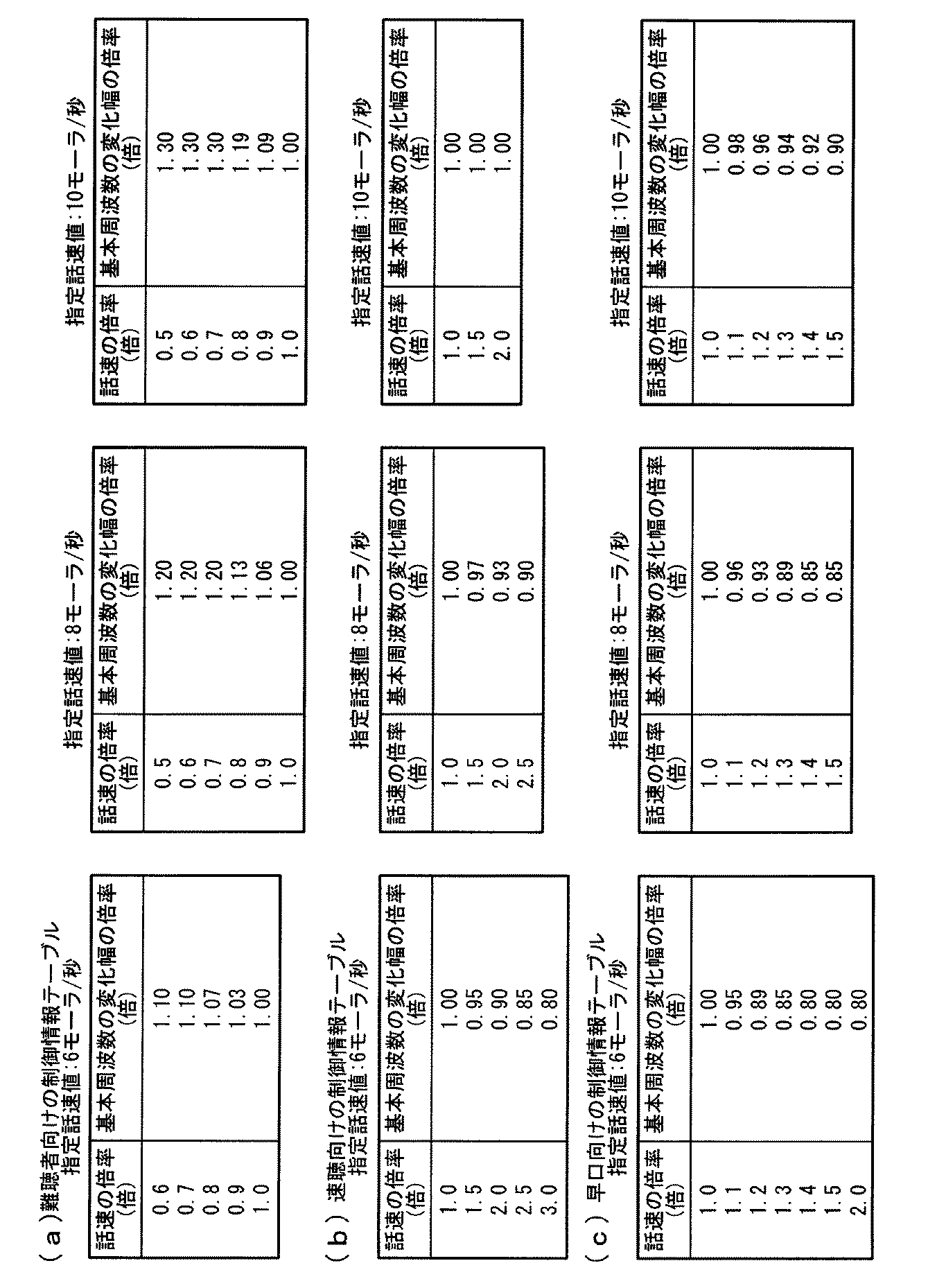
図3(a)〜(c)のそれぞれは、話速値の絶対値に基本周波数の変化幅の絶対値を対応付けた制御情報テーブルの例を示す図である。同図(a)〜(c)それぞれの制御情報テーブルは、制御方法1を示す制御方法の種別に関連付けられている。これら制御情報テーブルにおいて、話速値の絶対値は話速の制御量であり、基本周波数の変化幅の絶対値は基本周波数の変化幅の制御量である。同図(a)は難聴者向けテーブルであり、「難聴者向け」を示す補正目的の種別に関係付けられている。また、同図(b)は速聴向けテーブルであり、「速聴向け」を示す補正目的の種別に関係付けられている。また、同図(c)は早口向けテーブルであり、「早口向け」を示す補正目的の種別に関係付けられている。
Each of FIGS. 3A to 3C is a diagram illustrating an example of a control information table in which the absolute value of the fundamental frequency is associated with the absolute value of the speech speed value. Each of the control information tables in FIGS. 9A to 9C is associated with a control method type indicating the
図4(a)〜(c)のそれぞれは、複数の話速の倍率それぞれに基本周波数の変化幅の倍率を対応付けた制御情報テーブルの例を示す図である。同図(a)〜(c)それぞれの制御情報テーブルは、制御方法2を示す制御方法の種別に関連付けられている。これら制御情報テーブルにおいて、話速値の倍率は話速の制御量であり、基本周波数の変化幅の倍率は基本周波数の変化幅の制御量である。同図(a)は難聴者向けテーブルであり、「難聴者向け」を示す補正目的の種別に関係付けられている。また、同図(b)は速聴向けテーブルであり、「速聴向け」を示す補正目的の種別に関係付けられている。また、同図(c)は早口向けテーブルであり、「早口向け」を示す補正目的の種別に関係付けられている。
Each of FIGS. 4A to 4C is a diagram illustrating an example of a control information table in which a magnification of a change width of a fundamental frequency is associated with each of a plurality of magnifications of speech speed. Each of the control information tables in FIGS. 9A to 9C is associated with a control method type indicating the
図5(a)〜(c)のそれぞれは、三つの指定話速値それぞれに対応して、複数の話速の倍率それぞれに基本周波数の変化幅の倍率を対応付けた制御情報テーブルの例を示す図である。同図(a)〜(c)それぞれの制御情報テーブルは、制御方法3を示す制御方法の種別に関連付けられている。これら制御情報テーブルにおいて、話速値の倍率は話速の制御量であり、基本周波数の変化幅の倍率は基本周波数の変化幅の制御量である。同図(a)は難聴者向けテーブルであり、「難聴者向け」を示す補正目的の種別に関係付けられている。また、同図(b)は速聴向けテーブルであり、「速聴向け」を示す補正目的の種別に関係付けられている。また、同図(c)は早口向けテーブルであり、「早口向け」を示す補正目的の種別に関係付けられている。同図(a),(b),(c)とも、指定話速値が6,8,10(モーラ/秒)である例を表す。 Each of FIGS. 5A to 5C is an example of a control information table in which the magnification of the change frequency of the fundamental frequency is associated with each of a plurality of magnifications of the speech speed corresponding to each of the three designated speech speed values. FIG. Each of the control information tables in FIGS. 9A to 9C is associated with a control method type indicating the control method 3. In these control information tables, the magnification of the speech speed value is a control amount of the speech speed, and the magnification of the change width of the fundamental frequency is a control amount of the change width of the fundamental frequency. FIG. 6A shows a table for the hearing impaired person, and is associated with the type of correction purpose indicating “for the hearing impaired”. FIG. 5B is a table for quick listening, and is related to the type of correction purpose indicating “for quick listening”. FIG. 6C is a quick mouth table, which is related to the type of correction purpose indicating “for fast mouth”. FIGS. 9A, 9B, and 9C show examples in which the designated speech speed values are 6, 8, and 10 (mora / second).
なお、図3から図5までの制御情報テーブルの例は、話速計算部32から供給される音声データの話速値が7モーラ/秒から8モーラ/秒程度である場合の例である。
The example of the control information table from FIG. 3 to FIG. 5 is an example in the case where the speech speed value of the voice data supplied from the speech
図6は、目標基本周波数生成部54が、制御情報取得部53から供給される基本周波数の変化幅の制御量に基づいて生成する目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を模式的に示す図である。
同図(a)は、生成条件情報が平均値固定指定を示す情報である場合に、目標基本周波数生成部54が生成した目標基本周波数の時間変化情報の例である。同図(a)は、時刻t1から時刻t2まで(t1<t2)の時間における音声データの基本周波数の時間変化情報1と、この基本周波数の時間変化情報1を基本周波数の変化幅の制御量に基づいて、拡大した基本周波数の時間変化情報1aと、縮小した基本周波数の時間変化情報1rとを示す。同図(a)において、基本周波数の時間変化情報1の時刻t1から時刻t2までにおける周波数値の平均値は平均値faveである。同図(a)に示すように、目標基本周波数生成部54は、時刻t1から時刻t2までの基本周波数の時間変化情報の平均値が平均値faveになるように、基本周波数の時間変化情報2を拡大したり縮小したりする。
FIG. 6 is a diagram schematically illustrating the time change information of the target fundamental frequency generated by the target fundamental
FIG. 6A shows an example of time change information of the target fundamental frequency generated by the target fundamental
図6(b)は、生成条件情報が最小値固定指定を示す情報である場合に、目標基本周波数生成部54が生成した目標基本周波数の時間変化情報の例である。同図(b)は、時刻t1から時刻t2まで(t1<t2)の時間における音声データの基本周波数の時間変化情報2と、この基本周波数の時間変化情報2を基本周波数の変化幅の制御量に基づいて、拡大した基本周波数の時間変化情報2aと、縮小した基本周波数の時間変化情報2rとを示す。同図(b)において、基本周波数の時間変化情報2の時刻t1から時刻t2までにおける周波数値の最小値は最小値fminである。同図(b)に示すように、目標基本周波数生成部54は、時刻t1から時刻t2までの基本周波数の時間変化情報2を周波数値の最小値fminを基準として拡大したり縮小したりする。
FIG. 6B is an example of the time change information of the target fundamental frequency generated by the target fundamental
図6(c)は、生成条件情報が第1の指定値固定指定を示す情報である場合に、目標基本周波数生成部54が生成した目標基本周波数の時間変化情報の例である。同図(c)は、時刻t1から時刻t2まで(t1<t2)の時間における音声データの基本周波数の時間変化情報3と、この基本周波数の時間変化情報3を基本周波数の変化幅の制御量に基づいて、拡大した基本周波数の時間変化情報3aと、縮小した基本周波数の時間変化情報3rとを示す。同図(c)に示すように、目標基本周波数生成部54は、時刻t1から時刻t2までの基本周波数の時間変化情報3を、任意の周波数値fsを基準として拡大したり縮小したりする。
FIG. 6C is an example of the time change information of the target fundamental frequency generated by the target
図6(d)は、生成条件情報が第2の指定値固定指定を示す情報である場合に、目標基本周波数生成部54が生成した目標基本周波数の時間変化情報の例である。同図(d)は、時刻t1から時刻t2まで(t1<t2)の時間における音声データの基本周波数の時間変化情報4と、この基本周波数の時間変化情報4を基本周波数の変化幅の制御量に基づいて、拡大した基本周波数の時間変化情報4aと、縮小した基本周波数の時間変化情報4rとを示す。同図(d)に示すように、目標基本周波数生成部54は、時刻t1における周波数値fs1と時刻t2(t1<t2)における周波数値fs2とを基準として、時刻t1から時刻t2までの基本周波数の時間変化情報4を拡大したり縮小したりする。
FIG. 6D is an example of the time change information of the target fundamental frequency generated by the target
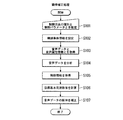
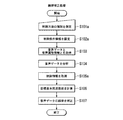
次に、第1実施形態である音声合成装置100の動作について説明する。図7は、音声合成装置100の韻律補正処理の処理手順を示すフローチャートである。
まず、ステップS101において、制御条件情報生成部40は、ユーザによるキーボードやマウス等の入力装置の操作によって所望の制御方法の種別と所望の制御パラメータと補正目的の種別との供給を受けると、これら制御方法の種別と制御パラメータと補正目的の種別とを含めた制御条件情報を生成して目標値生成部50に供給する。
次に、ステップS102において、目標値生成部50の制御条件設定部52は、制御条件情報生成部40から供給される制御条件情報を取り込み、その制御条件情報に含まれる制御方法の種別と制御パラメータと補正目的の種別とを制御情報取得部53に設定する。
次に、ステップS103において、音声データ取得部10は、音声データの供給を受けると、その音声データを取り込んで音声分析部30に供給する。さらに、音声属性情報取得部20は、音声データ取得部10に供給される音声データに関連する音声属性情報の供給を受けると、その音声属性情報を取り込んで音声分析部30に供給する。
Next, the operation of the
First, in step S101, when the control condition
Next, in step S102, the control
Next, in step S <b> 103, when the audio
次に、ステップS104において、音声分析部30は、音声データ取得部10から供給される音声データと音声属性情報取得部20から供給される音声属性情報とをそれぞれ取り込むと、これら音声データと音声属性情報とを分析し、音声の基本周波数の時間変化情報と話速値とをそれぞれ求めて目標値生成部50に供給する。詳細には、音声分析部30の基本周波数分析部31は、音声データに基づいて基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成して目標値生成部52に供給する。また、音声属性情報がテキスト情報である場合、音声分析部30の話速計算部32は、音声データとテキスト情報とに基づいて音素区切時間情報を生成し、生成した音素区切時間情報に基づいて話速を計算する(第1の話速値を計算する方法)か、音声データから音声区間の総時間長を求めるとともにテキスト情報からモーラ数を求めて、これら音声区間の総時間長とモーラ数とに基づいて話速値を計算する(第2の話速値を計算する方法)。また、音声属性情報が音素区切時間情報である場合、話速計算部32は、その音素区切時間情報から単位時間当たりのモーラ数を求めることによって話速値を得る。
Next, in step S104, the
次に、ステップS105において、制御情報取得部53は、制御条件設定部52により設定された制御方法の種別と補正目的の種別とに対応付けられた制御情報テーブルを制御情報テーブル記憶部51から読み込む。次に、制御情報取得部53は、読み込んだ制御情報テーブルと、制御条件設定部52により設定された制御パラメータと、音声分析部30からそれぞれ供給された話速値および基本周波数の時間変化情報とに基づいて、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを求める。次に、制御情報取得部53は、話速の制御量を音声データ補正部80に供給し、基本周波数の変化幅の制御量を目標基本周波数生成部54に供給する。
Next, in step S <b> 105, the control
次に、ステップS106において、目標基本周波数生成部54は、制御情報取得部53から供給された基本周波数の変化幅の制御量に基づいて、基本周波数分析部31で生成された基本周波数の時間変化情報から目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成して音声データ補正部80に供給する。このとき、目標基本周波数生成部54は、内部に記憶している生成条件情報にしたがって目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成する。
次に、ステップS107において、音声データ補正部80は、制御情報取得部53から供給された話速の制御量と、目標基本周波数生成部54から供給された目標基本周波数の時間変化情報とをそれぞれ取り込むと、音声データ取得部10が取得した音声データの韻律を補正して補正後音声データを出力する。
Next, in step S <b> 106, the target fundamental
Next, in step S107, the audio
以上説明したように、第1実施形態である音声合成装置100は、ユーザによる入力装置の操作により話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とのいずれか一方と補正目的とを指定することによって、補正目的に応じて、指定した一方の制御量に対応する他方の制御量を容易に且つ効率的に取得することができる。そして、音声合成装置100は、それぞれ取得した話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とに基づいて、音声データの話速および基本周波数の変化幅に関する韻律をユーザの補正目的に沿って補正することができる。
したがって、本実施形態である音声合成装置100によれば、音響に関する専門知識や豊かな調整経験を必要とせず、容易に且つ効率的に音声データを聴き易い補正後音声データに補正することができる。
As described above, the
Therefore, according to the
[第2の実施の形態]
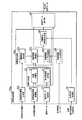
図8は、本発明の第2実施形態である音声合成装置の機能構成を示すブロック図である。なお、本実施形態において、第1実施形態である音声合成装置100の構成と同一の構成については、同一の符号を付してその説明を省略する。同図に示す音声合成装置100aは、音声合成装置100の構成における制御条件情報生成部40と目標値生成部50とを、それぞれ、制御条件情報生成部40aと目標値生成部50aとに変更したものである。
[Second Embodiment]
FIG. 8 is a block diagram showing a functional configuration of the speech synthesizer according to the second embodiment of the present invention. In the present embodiment, the same components as those of the
制御条件情報生成部40aは、ユーザによるキーボードやマウス等の入力装置の操作によって所望の制御方法の種別の供給を受け、この制御方法の種別を含めた制御条件情報を生成して目標値生成部50aに供給する。
本実施形態における制御方法の種別について具体的に説明する。本実施形態における制御方法の種別は定性的に制御量を指定する制御方法であり、下記の表2のように分類される。
The control condition
The type of control method in this embodiment will be specifically described. The type of control method in the present embodiment is a control method for qualitatively specifying a control amount, and is classified as shown in Table 2 below.
表2において、制御方法Aは、音声データの話速を「遅く」するよう指定するとともに、音声データの基本周波数の変化幅を「拡大」するよう指定する方法である。具体的には、例えば、制御方法Aは、音声分析部30から供給される話速値を約0.5倍から約0.9倍までの間にするよう指定するとともに、音声分析部30から供給される基本周波数の時間変化情報に基づき得られる基本周波数の変化幅を約1.15倍から約1.05倍までの間にするよう指定する方法である。
この制御方法Aは、老人性難聴の症状を有する高齢者や他の難聴者等に、ゆっくりとした速度で且つ音域を拡張した聴き取り易い音声を提供する場合に好適な制御方法である。
In Table 2, the control method A is a method for designating “slow” for the speech speed of the speech data and for “enlarging” the change width of the fundamental frequency of the speech data. Specifically, for example, the control method A specifies that the speech speed value supplied from the
This control method A is a control method suitable for providing an easy-to-listen sound with a slow speed and an extended sound range to an elderly person with senile deafness or another deaf person.
また、表2において、制御方法Bは、音声データの話速を「速く」するよう指定するとともに、音声データの基本周波数の変化幅を「少し縮小」するよう指定する方法である。具体的には、例えば、制御方法Bは、音声分析部30から供給される話速値を約1.5倍から約2.5倍までの間にするよう指定するとともに、音声分析部30から供給される基本周波数の時間変化情報に基づき得られる基本周波数の変化幅を約0.97倍から約0.9倍までの間にするよう指定する方法である。
この制御方法Bは、聴き取り可能な程度の速い速度で且つ音域を少し狭めた速聴向けの音声を提供する場合に好適な制御方法である。
In Table 2, the control method B is a method of designating that the speech speed of the voice data is “fast” and that the change width of the fundamental frequency of the voice data is “slightly reduced”. Specifically, for example, the control method B specifies that the speech speed value supplied from the
This control method B is a control method suitable for providing sound for quick listening with a speed that is high enough to be heard and with a slightly narrower sound range.
また、表2において、制御方法Cは、音声データの話速を「少し速く」するよう指定するとともに、音声データの基本周波数の変化幅を「縮小」するよう指定する方法である。具体的には、例えば、制御方法Cは、音声分析部30から供給される話速値を約1.1倍から約1.5倍までの間にするよう指定するとともに、音声分析部30から供給される基本周波数の時間変化情報に基づき得られる基本周波数の変化幅を約0.96倍から約0.8倍までの間にするよう指定する方法である。
この制御方法Cは、違和感を与えない程度の速い速度で且つ音域を狭めた早口音声を提供する場合に好適な制御方法である。
In Table 2, the control method C is a method of designating that the speech speed of the voice data is “slightly faster” and that the change width of the fundamental frequency of the voice data is “reduced”. Specifically, for example, the control method C specifies that the speech speed value supplied from the
This control method C is a control method suitable for providing a fast-speech voice with a narrow speed range that does not give a sense of incongruity.
表2において、制御方法Dは、音声データの話速を「固定」するよう指定するとともに、音声データの基本周波数の変化幅を「拡大」するよう指定する方法である。具体的には、例えば、制御方法Dは、音声分析部30から供給される話速値を変更しないよう指定するとともに、音声分析部30から供給される基本周波数の時間変化情報に基づき得られる基本周波数の変化幅を約1.1倍から約1.2倍までの間にするよう指定する方法である。
この制御方法Dは、話速を変えることなく且つ音域を拡張して、例えば騒音・雑音環境下において聴き取り易い音声を提供する場合に好適な制御方法である。
In Table 2, the control method D is a method of designating to “fix” the speech speed of the audio data and to “enlarge” the change width of the fundamental frequency of the audio data. Specifically, for example, the control method D specifies that the speech speed value supplied from the
This control method D is a control method suitable for expanding the sound range without changing the speech speed and providing a voice that can be easily heard in a noise / noise environment, for example.
目標値生成部50aは、音声分析部30から供給される話速値と基本周波数の時間変化情報とを取り込み、制御条件情報生成部40aから供給される制御条件情報にしたがって、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを求める。さらに、目標値生成部50aは、基本周波数の変化幅の制御量に基づいて目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成する。そして、目標値生成部50aは、話速の制御量と目標基本周波数の時間変化情報とを音声データ補正部80に供給する。
The target
次に、詳細に目標値生成部50aを説明する。目標値生成部50aは、音声合成装置100の目標値生成部50における制御情報テーブル記憶部51と制御条件設定部52と制御情報取得部53とを、制御情報テーブル記憶部51aと制御条件設定部52aと制御情報取得部53aとに変更したものである。
Next, the target
制御情報テーブル記憶部51aは、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを対応付けた複数の制御情報テーブルを、制御方法の種別に対応付けて記憶する。制御情報テーブルは、補正目的(例えば、難聴者向け、速聴、早口、雑音環境下)ごとに、話速の倍率に基本周波数の変化幅の倍率を対応付けたテーブルである。補正目的ごとの種制御情報テーブルの具体例については後述する。
制御情報テーブル記憶部51aは、読み出しおよび書き込み可能な記憶装置であり、例えば、磁気ハードディスク装置、半導体記憶装置等である。また、制御情報テーブル記憶部51aは、光磁気ディスク等の可搬型記録媒体であってもよい。
The control information
The control information
制御条件設定部52aは、制御条件情報生成部40aから供給される制御条件情報を取り込み、その制御条件情報に含まれる制御方法の種別を制御情報取得部53aに設定する。
The control
制御情報取得部53aは、制御条件設定部52aにより設定された制御方法の種別に対応付けられた制御情報テーブルを制御情報テーブル記憶部51aから読み込む。そして、制御情報取得部53aは、読み込んだ制御情報テーブルに格納された話速の制御量を音声データ補正部80に供給するとともに、制御情報テーブルに格納された基本周波数の変化幅の制御量を目標基本周波数生成部54に供給する。
The control
具体的には、例えば、制御条件設定部52aにより制御方法の種別(制御方法A)が設定された場合、制御情報取得部53aは、制御方法Aに関係付けられた制御情報テーブル(難聴者向けの制御情報が格納されたテーブル)を制御情報テーブル記憶部51aから読み込む。そして、制御情報取得部53aは、読み込んだ制御情報テーブルに格納された話速の倍率と基本周波数の変化幅の倍率とを、それぞれ話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とする。
Specifically, for example, when the type of control method (control method A) is set by the control
また、例えば、制御条件設定部52aにより制御方法(制御方法B)が設定された場合、制御情報取得部53aは、制御方法Bに関連付けられた制御情報テーブル(速聴向けの制御情報が格納されたテーブル)を制御情報テーブル記憶部51aから読み込む。そして、制御情報取得部53aは、読み込んだ制御情報テーブルに格納された話速の倍率と基本周波数の変化幅の倍率とを、それぞれ話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とする。
For example, when a control method (control method B) is set by the control
また、例えば、制御条件設定部52aにより制御方法(制御方法C)が設定された場合、制御情報取得部53aは、制御方法Cに関連付けられた制御情報テーブル(早口向けの制御情報が格納されたテーブル)を制御情報テーブル記憶部51aから読み込む。そして、制御情報取得部53aは、読み込んだ制御情報テーブルに格納された話速の倍率と基本周波数の変化幅の倍率とを、それぞれ話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とする。
For example, when the control method (control method C) is set by the control
また、例えば、制御条件設定部52aにより制御方法(制御方法D)が設定された場合、制御情報取得部53aは、制御方法Dに関連付けられた制御情報テーブル(雑音環境下向けのテーブル)を制御情報テーブル記憶部51aから読み込む。そして、制御情報取得部53aは、話速の倍率を1倍として話速の制御量とし、読み込んだ制御情報テーブルに格納された基本周波数の変化幅の倍率を基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とする。
For example, when the control method (control method D) is set by the control
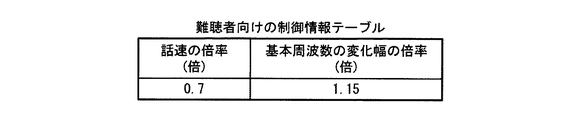
図9は、難聴者向けの制御情報が格納された制御情報テーブルの例を示す図である。同図に示す難聴者向けの制御情報テーブルは、音声データの話速を0.7倍する指定と、音声データの基本周波数の変化幅を1.15倍する指定とを含んでいる。
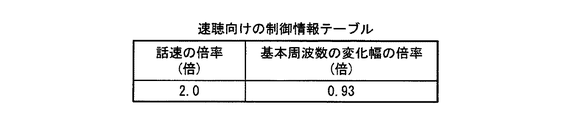
図10は、速聴向けの制御情報が格納された制御情報テーブルの例を示す図である。同図に示す速聴向けの制御情報テーブルは、音声データの話速を2.0倍する指定と、音声データの基本周波数の変化幅を0.93倍する指定とを含んでいる。
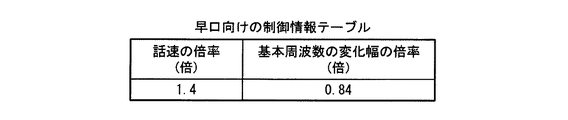
図11は、早口向けの制御情報が格納された制御情報テーブルの例を示す図である。同図に示す早口向けの制御情報テーブルは、音声データの話速を1.4倍する指定と、音声データの基本周波数の変化幅を0.84倍する指定とを含んでいる。
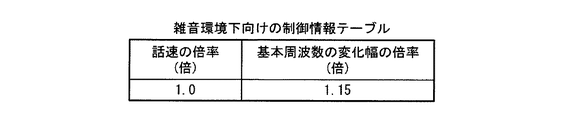
図12は、雑音環境下向けの制御情報テーブルの例を示す図である。同図に示す雑音環境下向けの制御情報テーブルは、音声データの話速を固定(1.0倍)する指定と、音声データの基本周波数の変化幅を1.15倍する指定とを含んでいる。
なお、図9から図12までの制御情報テーブルの例は、話速計算部32から供給される音声データの話速値が7モーラ/秒から8モーラ/秒程度である場合の例である。
FIG. 9 is a diagram illustrating an example of a control information table in which control information for the hearing impaired person is stored. The control information table for the hearing-impaired person shown in the figure includes designation for increasing the speech speed of voice data by 0.7 and designation for increasing the change width of the fundamental frequency of voice data by 1.15.
FIG. 10 is a diagram illustrating an example of a control information table in which control information for quick listening is stored. The control information table for quick listening shown in the figure includes a designation for multiplying the speech speed of voice data by 2.0 and a designation for multiplying the change width of the fundamental frequency of voice data by 0.93.
FIG. 11 is a diagram illustrating an example of a control information table in which control information for a quick mouth is stored. The control information table for the quick mouth shown in the figure includes a designation for multiplying the speech speed of voice data by 1.4 and a designation for multiplying the change width of the fundamental frequency of voice data by 0.84.
FIG. 12 is a diagram illustrating an example of a control information table for a noisy environment. The control information table for a noisy environment shown in the figure includes a designation for fixing the speech speed of voice data (1.0 times) and a designation for multiplying the change width of the fundamental frequency of voice data by 1.15. Yes.
Note that the control information tables in FIGS. 9 to 12 are examples in which the speech speed value of the voice data supplied from the speech
次に、第2実施形態である音声合成装置100aの動作について説明する。図13は、音声合成装置100aの韻律補正処理の処理手順を示すフローチャートである。なお、本実施形態において、第1実施形態である音声合成装置100の処理手順と同一の処理については、同一の符号を付してその説明を省略する。
まず、ステップS101aにおいて、制御条件情報生成部40aは、ユーザによるキーボードやマウス等の入力装置の操作によって所望の制御方法の種別の供給を受けると、この制御方法の種別を含めた制御条件情報を生成して目標値生成部50aに供給する。
次に、ステップS102aにおいて、目標値生成部50aの制御条件設定部52aは、制御条件情報生成部40aから供給される制御条件情報を取り込み、その制御条件情報に含まれる制御方法の種別を制御情報取得部53aに設定する。
Next, the operation of the
First, in step S101a, when the control condition
Next, in step S102a, the control
ステップS105aにおいて、制御情報取得部53aは、制御条件設定部52aにより設定された制御方法の種別に関連付けられた制御情報テーブルを制御情報テーブル記憶部51aから読み込む。次に、制御情報取得部53aは、読み込んだ制御情報テーブルに格納された話速の制御量を音声データ補正部80に供給し、制御情報テーブルに格納された基本周波数の変化幅の制御量を目標基本周波数生成部54に供給する。
In step S105a, the control
以上説明したように、第2実施形態である音声合成装置100aは、ユーザによる入力装置の操作により補正目的に応じた制御方法の種別を指定することによって、その補正目的に対応した話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを容易に且つ効率的に取得することができる。そして、音声合成装置100aは、それぞれ取得した話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とに基づいて、音声データの話速および基本周波数の変化幅に関する韻律をユーザの補正目的に沿って補正することができる。
したがって、本実施形態である音声合成装置100aによれば、音響に関する専門知識や豊かな調整経験を必要とせず、容易に且つ効率的に音声データを聴き易い補正後音声データに補正することができる。
As described above, the
Therefore, according to the
なお、第1実施形態である音声合成装置100と第2実施形態である音声合成装置100aとのそれぞれは、音声属性情報取得部20を搭載しない構成としてもよい。その場合、音声分析部30の話速計算部32は、以下の処理を行って音声データの話速値を計算する。つまり、話速計算部32は、音声データから公知の音声認識処理を適用してテキスト情報を生成するか、または音声データから音素区切時間情報を生成する。そして、話速計算部32は、第1実施形態に詳述したように、音声データとテキスト情報とに基づいて音素区切時間情報を生成し、生成した音素区切時間情報に基づいて話速を計算する(第1の話速値を計算する方法)か、音声データから音声区間の総時間長を求めるとともにテキスト情報からモーラ数を求めて、これら音声区間の総時間長とモーラ数とに基づいて話速値を計算する(第2の話速値を計算する方法)。または、話速計算部32は、音素区切時間情報から単位時間当たりのモーラ数を求めることによって話速値を得る。
Each of the
また、第2実施形態である音声合成装置100aの制御情報テーブル記憶部51aは、話速の倍率と基本周波数の変化幅の倍率とを対応付けた複数の制御情報テーブルを、制御方法の種別に対応付けて記憶するものであった。これ以外にも、制御情報テーブル記憶部51aは、話速値の絶対値と基本周波数の変化幅の絶対値とを対応付けた複数の制御情報テーブルを、制御方法の種別に対応付けて記憶するようにしてもよい。
In addition, the control information
また、音声合成装置100,100aの一部の機能をコンピュータで実現するようにしてもよい。この場合、その機能を実現するためのプログラムをコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体に記録して、この記録媒体に記録されたプログラムをコンピュータシステムに読み込ませ、実行することによって実現してもよい。なお、ここでいう「コンピュータシステム」とは、OS(Operating System)や周辺機器のハードウェアを含むものとする。また、「コンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体」とは、フレキシブルディスク、光磁気ディスク、光ディスク、メモリカード等の可搬型記録媒体、コンピュータシステムに内蔵されるハードディスク等の記憶装置のことをいう。さらに「コンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体」とは、インターネット等のネットワークや電話回線等の通信回線を介してプログラムを送信する場合の通信線のように、短時間の間、動的にプログラムを保持するもの、その場合のサーバやクライアントとなるコンピュータシステム内部の揮発性メモリのように、一定時間プログラムを保持するものを含んでもよい。また上記のプログラムは、前述した機能の一部を実現するためのものであってもよく、さらに前述した機能をコンピュータシステムにすでに記録されているプログラムとの組み合わせにより実現するものであってもよい。
Further, some functions of the
以上、本発明の実施形態について図面を参照して詳述したが、具体的な構成はこの実施形態に限られるものではなく、本発明の要旨を逸脱しない範囲の設計等も含まれる。 As mentioned above, although embodiment of this invention was explained in full detail with reference to drawings, the concrete structure is not restricted to this embodiment, The design etc. of the range which does not deviate from the summary of this invention are included.
10 音声データ取得部
20 音声属性情報取得部
30 音声分析部
31 基本周波数分析部
32 話速計算部
40,40a 制御条件情報生成部
50,50a 目標値生成部
51,51a 制御情報テーブル記憶部
52,52a 制御条件設定部
53,53a 制御情報取得部
54 目標基本周波数生成部
60 制御情報テーブル更新部
70 生成条件取得部
80 音声データ補正部
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (6)
音声データを取得する音声データ取得部と、
前記音声データ取得部が取得した前記音声データに基づいて基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成する基本周波数分析部と、
前記音声データに基づいて話速値を計算する話速計算部と、
所望の制御方法の種別と制御情報テーブルにおける話速の制御量または基本周波数の変化幅の制御量を指定するキー情報とを設定する制御条件設定部と、
前記制御条件設定部が設定した前記制御方法の種別に関連付けられた制御情報テーブルを前記制御情報テーブル記憶部から読み込み、前記制御条件設定部が設定した前記キー情報と前記話速計算部が計算した前記話速値と前記基本周波数分析部が生成した前記基本周波数の時間変化情報とに基づいて、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを取得する制御情報取得部と、
前記制御情報取得部が取得した前記基本周波数の変化幅の制御量に基づいて、前記基本周波数の時間変化情報から目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成する目標基本周波数生成部と、
前記制御情報取得部が取得した前記話速の制御量と、前記目標基本周波数生成部が生成した前記目標基本周波数の時間変化情報とに基づいて、前記音声データを補正して補正後音声データを出力する音声データ補正部と、
を備えることを特徴とする音声合成装置。 A control information table storage unit that stores a control information table in which a control amount of speech speed is associated with a control amount of a change width of a fundamental frequency in association with a type of control method;
An audio data acquisition unit for acquiring audio data;
A fundamental frequency analysis unit that generates time change information of a fundamental frequency based on the speech data acquired by the speech data acquisition unit;
A speech speed calculator that calculates a speech speed value based on the voice data;
A control condition setting unit that sets a type of a desired control method and key information that specifies a control amount of a speech speed or a control amount of a change width of a fundamental frequency in a control information table;
A control information table associated with the type of control method set by the control condition setting unit is read from the control information table storage unit, and the key information set by the control condition setting unit and the speech speed calculation unit are calculated. Based on the speech speed value and the time variation information of the fundamental frequency generated by the fundamental frequency analysis unit, a control information acquisition unit that acquires a control amount of the speech speed and a control amount of the variation range of the fundamental frequency;
A target fundamental frequency generation unit that generates time change information of a target fundamental frequency from time change information of the fundamental frequency based on a control amount of a change width of the fundamental frequency acquired by the control information acquisition unit;
Based on the control amount of the speech speed acquired by the control information acquisition unit and the time change information of the target basic frequency generated by the target basic frequency generation unit, the audio data is corrected and corrected audio data is obtained. An audio data correction unit to output;
A speech synthesizer comprising:
ことを特徴とする請求項1記載の音声合成装置。 The absolute value of the speech speed is set as the control amount of the speech speed, the absolute value of the change width of the basic frequency is set as the control amount of the change width of the basic frequency, and the control information table storage unit stores each of the absolute values of the plurality of speech speed values. The speech synthesizer according to claim 1, wherein a control information table in which absolute values of change widths of fundamental frequencies are associated is stored in association with the type of control method.
前記制御条件設定部は、前記キー情報についての所望の倍率をさらに設定し、
前記制御情報取得部は、前記制御条件設定部が設定した前記キー情報と前記倍率と前記話速計算部が計算した前記話速値と前記基本周波数分析部が生成した前記基本周波数の時間変化情報とに基づいて、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを取得する
ことを特徴とする請求項1記載の音声合成装置。 The rate of speech speed is defined as the amount of control of speech rate, the rate of change in the basic frequency is defined as the control amount of the rate of change in basic frequency, and the control information table storage unit changes the fundamental frequency for each of multiple rates of speech speed. A control information table in which the magnification of the width is associated is stored in association with the type of control method,
The control condition setting unit further sets a desired magnification for the key information,
The control information acquisition unit includes the key information set by the control condition setting unit, the magnification, the speech speed value calculated by the speech speed calculation unit, and time change information of the fundamental frequency generated by the fundamental frequency analysis unit. The speech synthesizer according to claim 1, further comprising: acquiring a control amount of a speech speed and a control amount of a change width of a fundamental frequency based on
前記制御情報取得部は、前記制御条件設定部が設定した前記制御方法の種別に関連し且つ前記話速計算部が計算した前記話速値と同一である指定話速値に対応する制御情報テーブルを前記制御情報テーブル記憶部から読み込み、前記制御条件設定部が設定した前記キー情報と前記倍率と前記話速値と前記基本周波数分析部が生成した前記基本周波数の時間変化情報とに基づいて、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを取得する
ことを特徴とする請求項3記載の音声合成装置。 The control information table storage unit associates a control information table in which a multiple of a plurality of speech speeds is associated with a magnification of a change width of a fundamental frequency in association with each of a plurality of designated speech speed values, and is associated with a type of control method. Remember,
The control information acquisition unit is a control information table corresponding to a designated speech speed value related to the type of the control method set by the control condition setting unit and the same as the speech speed value calculated by the speech speed calculation unit From the control information table storage unit, based on the key information set by the control condition setting unit, the magnification, the speech speed value, and the time change information of the fundamental frequency generated by the fundamental frequency analysis unit, The speech synthesizer according to claim 3, wherein a speech rate control amount and a control amount of a fundamental frequency change width are acquired.
前記制御条件設定部は、所望の制御方法の種別を設定し、
前記制御情報取得部は、前記制御条件設定部が設定した前記制御方法の種別に関連付けられた制御情報テーブルを前記制御情報テーブル記憶部から読み込み、前記制御情報テーブルから話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを取得する
ことを特徴とする請求項1記載の音声合成装置。 The control information table storage unit includes a control information table in which a magnification of the basic frequency that is the control amount of the fundamental frequency is associated with a magnification of the speech speed that is the control amount of the speech speed, and a type of control method Remember and associate with
The control condition setting unit sets a type of a desired control method,
The control information acquisition unit reads a control information table associated with the type of the control method set by the control condition setting unit from the control information table storage unit, and controls a speech rate control amount and a basic frequency from the control information table. The speech synthesizer according to claim 1, further comprising: obtaining a control amount of a change width of
音声データを取得する音声データ取得手段と、
前記音声データ取得手段が取得した前記音声データに基づいて基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成する基本周波数分析手段と、
前記音声データに基づいて話速値を計算する話速計算手段と、
所望の制御方法の種別と制御情報テーブルにおける話速の制御量または基本周波数の変化幅の制御量を示すキー情報とを設定する制御条件設定手段と、
前記制御条件設定手段が設定した前記制御方法の種別に関連付けられた制御情報テーブルを前記制御情報テーブル記憶部から読み込み、前記制御条件設定手段が設定した前記キー情報と前記話速計算手段が計算した前記話速値と前記基本周波数分析手段が生成した前記基本周波数の時間変化情報とに基づいて、話速の制御量と基本周波数の変化幅の制御量とを取得する制御情報取得手段と、
前記制御情報取得手段が取得した前記基本周波数の変化幅の制御量に基づいて、前記基本周波数の時間変化情報から目標基本周波数の時間変化情報を生成する目標基本周波数生成手段と、
前記制御情報取得手段が取得した前記話速の制御量と、前記目標基本周波数生成手段が生成した前記目標基本周波数の時間変化情報とに基づいて、前記音声データを補正して補正後音声データを出力する音声データ補正手段と、
として機能させるためのコンピュータプログラム。 A computer including a control information table storage unit that stores a control information table in which a control amount of a speech speed and a control amount of a change width of a fundamental frequency are associated with each other,
Audio data acquisition means for acquiring audio data;
Fundamental frequency analysis means for generating time change information of the fundamental frequency based on the voice data acquired by the voice data acquisition means;
Speaking speed calculation means for calculating a speaking speed value based on the voice data;
A control condition setting means for setting a type of a desired control method and key information indicating a control amount of speech speed or a control amount of a change width of a fundamental frequency in the control information table;
The control information table associated with the type of the control method set by the control condition setting means is read from the control information table storage unit, and the key information set by the control condition setting means and the speech speed calculation means are calculated. Control information acquisition means for acquiring the control amount of the speech speed and the control amount of the change width of the fundamental frequency based on the speech speed value and the time change information of the fundamental frequency generated by the fundamental frequency analysis means;
Target basic frequency generation means for generating time change information of the target fundamental frequency from time change information of the fundamental frequency based on a control amount of the change width of the fundamental frequency acquired by the control information acquisition means;
Based on the control amount of the speech speed acquired by the control information acquisition unit and the time change information of the target basic frequency generated by the target basic frequency generation unit, the audio data is corrected and corrected audio data is obtained. Audio data correction means for outputting;
Computer program to function as.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010177776A JP5518621B2 (en) | 2010-08-06 | 2010-08-06 | Speech synthesizer and computer program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010177776A JP5518621B2 (en) | 2010-08-06 | 2010-08-06 | Speech synthesizer and computer program |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2012037726A true JP2012037726A (en) | 2012-02-23 |
| JP5518621B2 JP5518621B2 (en) | 2014-06-11 |
Family
ID=45849776
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010177776A Expired - Fee Related JP5518621B2 (en) | 2010-08-06 | 2010-08-06 | Speech synthesizer and computer program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5518621B2 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015141294A (en) * | 2014-01-28 | 2015-08-03 | 富士通株式会社 | Communication device |
| CN105765654A (en) * | 2013-11-28 | 2016-07-13 | 弗劳恩霍夫应用研究促进协会 | Hearing device with base frequency modification |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH08171395A (en) * | 1994-12-19 | 1996-07-02 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Speech synthesizer |
| JP2002268700A (en) * | 2001-03-09 | 2002-09-20 | Canon Inc | Acoustic information encoding device and decoding device and method, computer program and storage medium |
-
2010
- 2010-08-06 JP JP2010177776A patent/JP5518621B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH08171395A (en) * | 1994-12-19 | 1996-07-02 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Speech synthesizer |
| JP2002268700A (en) * | 2001-03-09 | 2002-09-20 | Canon Inc | Acoustic information encoding device and decoding device and method, computer program and storage medium |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| CSNG199801269010; '放送における話速変換:話者や音環境の多様性への対応' 日本音響学会誌 54巻7号, 19980701, pp.533-538, 都木 徹 * |
| JPN6013061530; '放送における話速変換:話者や音環境の多様性への対応' 日本音響学会誌 54巻7号, 19980701, pp.533-538, 都木 徹 * |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105765654A (en) * | 2013-11-28 | 2016-07-13 | 弗劳恩霍夫应用研究促进协会 | Hearing device with base frequency modification |
| JP2016540432A (en) * | 2013-11-28 | 2016-12-22 | フラウンホーファー−ゲゼルシャフト・ツール・フェルデルング・デル・アンゲヴァンテン・フォルシュング・アインゲトラーゲネル・フェライン | Hearing aid using fundamental frequency correction |
| US9936308B2 (en) | 2013-11-28 | 2018-04-03 | Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft Zur Foerderung Der Angewandten Forschung E.V. | Hearing aid apparatus with fundamental frequency modification |
| JP2015141294A (en) * | 2014-01-28 | 2015-08-03 | 富士通株式会社 | Communication device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5518621B2 (en) | 2014-06-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7228998B2 (en) | speech synthesizer and program | |
| US7739113B2 (en) | Voice synthesizer, voice synthesizing method, and computer program | |
| JP5029168B2 (en) | Apparatus, program and method for reading aloud | |
| US20080319755A1 (en) | Text-to-speech apparatus | |
| US20090006098A1 (en) | Text-to-speech apparatus | |
| JP2008545995A (en) | Hybrid speech synthesizer, method and application | |
| EP3065130A1 (en) | Voice synthesis | |
| JP2023007405A (en) | Voice conversion device, voice conversion method, program, and storage medium | |
| JP5518621B2 (en) | Speech synthesizer and computer program | |
| CN113255313B (en) | Music generation method, device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| JP2007140200A (en) | Language learning device and program | |
| JP6314879B2 (en) | Reading aloud evaluation device, reading aloud evaluation method, and program | |
| JP4744338B2 (en) | Synthetic speech generator | |
| JP4953767B2 (en) | Speech generator | |
| JP4260071B2 (en) | Speech synthesis method, speech synthesis program, and speech synthesis apparatus | |
| JPH07140996A (en) | Speech rule synthesizer | |
| KR20040015605A (en) | Method and apparatus for synthesizing virtual song | |
| JP2010224392A (en) | Utterance support device, method, and program | |
| JP3575919B2 (en) | Text-to-speech converter | |
| JP3113101B2 (en) | Speech synthesizer | |
| JP2004004952A (en) | Voice synthesis device and voice synthesis method | |
| JP2000310995A (en) | Device and method for synthesizing speech and telephone set provided therewith | |
| JP5677137B2 (en) | Prosody conversion device and program | |
| JP2003005774A (en) | Speech synthesizer | |
| JP2001265374A (en) | Voice synthesizing device and recording medium |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20130225 |
|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A711 Effective date: 20130225 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A821 Effective date: 20130225 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20131024 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20131205 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20131217 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140214 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20140304 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20140402 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5518621 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |