JP2012015577A - Optical transmission system - Google Patents
Optical transmission system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2012015577A JP2012015577A JP2010147140A JP2010147140A JP2012015577A JP 2012015577 A JP2012015577 A JP 2012015577A JP 2010147140 A JP2010147140 A JP 2010147140A JP 2010147140 A JP2010147140 A JP 2010147140A JP 2012015577 A JP2012015577 A JP 2012015577A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- wavelength
- light
- optical
- transmission
- awg
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Optical Communication System (AREA)
- Small-Scale Networks (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、WDM−PON(Wavelength Division Multiplexing Passive Optical Network)システムのような、波長分割多重(Wavelength Division Multiplexing)を利用する光伝送システムに関する。 The present invention relates to an optical transmission system that uses wavelength division multiplexing, such as a WDM-PON (Wavelength Division Multiplexing Passive Optical Network) system.
FTTH(Fiber To The Home)等の光アクセス分野において、伝送トラフィック容量の増加に伴う将来の高速化伝送技術として、WDM−PONが注目されている。WDM−PONでは、上り通信、下り通信又はその両方で各ユーザに異なった光波長を割り当てて通信を行うので、各ユーザは通信帯域を占有できる。 In the field of optical access such as FTTH (Fiber To The Home), WDM-PON has attracted attention as a future high-speed transmission technology accompanying an increase in transmission traffic capacity. In WDM-PON, communication is performed by assigning different optical wavelengths to each user in uplink communication, downlink communication, or both, so that each user can occupy a communication band.
特許文献1には、波長分割多重光伝送システムとして、光ファイバ伝送路の両側に波長多重分離素子、例えば、アレイ導波路格子(AWG)を配置するWDM−PONシステムが記載されている。波長多重分離素子としてAWGを使用する場合、光伝送路の両側に位置する光送受信装置(PONの場合には、センター局に配置されるOLT(Optical Line Terminal)と、各ユーザ宅に配置されるONU(Optical Network Unit))の信号光源は、AWGで多重及び分離可能な波長に調整されている必要がある。
AWGの透過波長の経時変化及び交換用ONUの汎用性、いわゆるカラーレス可を考慮すると、各ONUに装備される信号光源には波長可変のレーザダイオード(TLD:Tunable Laser Diode)を用い、必要な波長に設定又は調整できるのが好ましい。特許文献2,3には、波長可変レーザダイオードを信号光源に用い、その波長を調節する技術が記載されている。 Considering the aging of the transmission wavelength of the AWG and the versatility of the ONU for replacement, the so-called colorless capability, a variable wavelength laser diode (TLD: Tunable Laser Diode) is used as the signal light source installed in each ONU. Preferably, the wavelength can be set or adjusted. Patent Documents 2 and 3 describe techniques for adjusting the wavelength by using a wavelength tunable laser diode as a signal light source.
また、非特許文献1には、ONUでTLDの波長を変化させながら光出力し、AWGを透過して光ファイバ伝送中に生じるレイリー散乱による戻り受光パワーをONU側でモニタし、最大の受光レベルが得られた波長を伝送チャネルとして設定することが記載されている。
In
特許文献2に記載の技術では、光伝送路上の合波器装置に、TLDが、波長多重分離素子で適切に分離されうる波長の光を出力するときに発光するLEDを配置する必要があり、コストを増加させ、また、保守管理の手間とコストが増加する。 In the technique described in Patent Document 2, it is necessary to dispose an LED that emits light when the TLD outputs light having a wavelength that can be appropriately separated by the wavelength demultiplexing element in the multiplexer device on the optical transmission line. The cost is increased, and maintenance labor and cost are increased.
特許文献3に記載の技術では、一方の光送受信装置が、他方の光送受信装置からの信号光を受信できる場合に、その波長を他方の光送受信装置に通知する必要があり、往復遅延により信号光波長の決定に時間がかかるという問題がある。 In the technique described in Patent Document 3, when one optical transmission / reception device can receive signal light from the other optical transmission / reception device, it is necessary to notify the wavelength to the other optical transmission / reception device. There is a problem that it takes time to determine the optical wavelength.
非特許文献1に記載の技術では、レイリー散乱による戻り光をモニタしているが、通常、レイリー散乱による散乱光レベルは非常に小さく、またその影響は伝送路条件にも依存するので、実用的ではない。下り信号光が存在する場合、ONUには、下り信号光とレイリー散乱光を区別するため光フィルタを設ける必要があり、装置コストの増大も招く。
In the technique described in
本発明は、安価な構成で信号光源の波長を適切に調節又は設定できる光伝送システムを提示することを目的とする。 An object of the present invention is to provide an optical transmission system that can appropriately adjust or set the wavelength of a signal light source with an inexpensive configuration.
本発明に係る光伝送システムは、光伝送路と、互いに異なる上り波長及び下り波長を使用する複数の第1の光送受信装置と、当該複数の第1の光送受信装置と通信する複数の第2の光送受信装置と、当該複数の第1の光送受信装置が出力する下り光を波長多重し、光伝送路からの多重化された上り光を当該複数の第1の送受信装置のそれぞれに向かう上り光に波長分離する第1の波長多重分離手段とを具備し、当該光伝送路が、当該複数の第2の光送受信装置が出力する上り光を波長多重し、当該第1の波長多重分離手段で多重された当該下り光を、当該複数の第2の送受信装置のそれぞれに向かう下り光に波長分離する第2の波長多重分離手段と、当該第1の波長多重分離手段と当該第2の波長多重分離手段との間に配置される反射器とを具備し、当該第1の光送受信装置が、当該複数の第1の光送受信装置が使用する全部の下り波長と、当該複数の第1の光送受信装置が使用する全部の上り波長とを多重分離する第1のWDMカプラと、信号光源となる第1の波長可変光源を具備する第1の送信装置と、第1の受信装置と、当該第1の送信装置の出力する下り光の、当該反射器による第1の反射光を受光する第1の受光器と、当該第1の送信装置の出力する下り光を当該第1のWDMカプラに供給し、当該第1のWDMカプラからの、当該第1の反射光を当該第1の受光器に供給する第1の光カプラと、当該第1の受光器により受光される当該反射光のレベルに応じて、当該第1の反射光のレベルが所定値以上になるように当該第1の波長可変光源の波長を制御する第1の制御装置とを具備することを特徴とする。
An optical transmission system according to the present invention includes an optical transmission line, a plurality of first optical transmission / reception devices that use different upstream and downstream wavelengths, and a plurality of second optical communication devices that communicate with the plurality of first optical transmission / reception devices. And the downstream light output from the plurality of first optical transmission / reception devices are wavelength-multiplexed, and the upstream light multiplexed from the optical transmission path is directed to each of the plurality of first transmission / reception devices. First wavelength demultiplexing means for wavelength-separating light, and the optical transmission line wavelength-multiplexes upstream light output from the plurality of second optical transmission / reception devices, and the first wavelength demultiplexing means A second wavelength multiplexing / separating unit for wavelength-separating the downstream light multiplexed in
本発明によれば、波長多重分離手段を通過した光を反射する反射器を設けることで、信号光源となる波長可変光源の波長を、波長多重分離手段を透過する波長に容易に調整することができる。また、データ伝送を実行しながら、波長を調整できる。 According to the present invention, by providing a reflector that reflects the light that has passed through the wavelength demultiplexing means, it is possible to easily adjust the wavelength of the wavelength variable light source serving as the signal light source to a wavelength that is transmitted through the wavelength demultiplexing means. it can. In addition, the wavelength can be adjusted while executing data transmission.
以下、図面を参照して、本発明の実施例を詳細に説明する。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
図1は、本発明の一実施例の概略構成ブロック図を示す。図1に示すWDM−PONシステムでは、センター局に配置されるOLT(Optical Line Terminal)10は、光伝送路40を介してn台のONU(Optical Network Unit)50−1〜50−nに光学的に接続する。
FIG. 1 shows a schematic block diagram of an embodiment of the present invention. In the WDM-PON system shown in FIG. 1, an OLT (Optical Line Terminal) 10 disposed in a center station is optically connected to n ONUs (Optical Network Units) 50-1 to 50-n via an
OLT10は、それぞれ異なるONU50−1〜50−nと通信する光送受信装置12−1〜12−nと、光送受信装置12−1〜12−nからの出力信号光を波長多重して光伝送路40に出力し、光伝送路40からの光信号を個々の波長光に分離する波長多重分離手段としてのAWG(Arrayed Waveguide Grating)14を具備する。光送受信装置12−1〜12−nは同じ構成からなるが、上り信号光波長及び下り信号光波長が異なる。
The
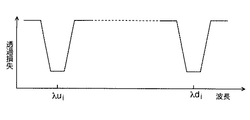
AWG14は、n個の入出力ポート#1〜#nの入力光をその波長に応じて多重して多重光入出力ポート#Mから出力し、多重光入出力ポート#Mの入力光をその波長に応じて分離して入出力ポート#1〜#nから出力する光学素子であり、周知の通り周期的な波長透過特性を具備する。図2は、AWG14の1つの入出力ポート#iと多重光入出力ポート#M間の透過特性例を示し、図3は、AWG14の入出力ポート#1〜#nと多重光入出力ポート#Mとの間の透過特性例を示す。図2及び図3で、横軸は波長を示し、縦軸は透過損失を示す。
The AWG 14 multiplexes the input light of the n input /
詳細は後述するが、OLT10の光送受信装置12−iは、下り信号光波長λdiと上り信号光波長λuiを使って、ONU50−iと通信する。ただし、i=1〜nである。下り信号光波長λd1〜λdnは互いに異なり、上り信号光波長λu1〜λunは、互いに異なり、且つ、どの下り信号光波長λd1〜λdnとも異なる。
Although details will be described later, the optical transceiver 12-i of the
AWG14は、光送受信装置12−1〜12−nからそれぞれONU50−1〜50−nへの下り信号光(波長λd1〜λdn)を多重し、ONU50−1〜50−nからそれぞれ光送受信装置12−1〜12−nへの上り信号光(波長λu1〜λun)を分離する。下り信号光波長λd1〜λdnと上り信号光波長λu1〜λunは、AWG14の異なるバンドに位置する。例えば、下り信号光波長λd1〜λdnは、AWG14のLバンドに属し、上り信号光波長λu1〜λunはAWG14のCバンドに属する。 The AWG 14 multiplexes downstream signal lights (wavelengths λd 1 to λd n ) from the optical transmission / reception apparatuses 12-1 to 12 -n to the ONUs 50-1 to 50 -n, respectively, and transmits and receives optical signals from the ONUs 50-1 to 50 -n. The upstream signal light (wavelengths λu 1 to λu n ) to the devices 12-1 to 12-n is separated. Downstream signal light wavelength λd 1 ~λd n and an uplink signal wavelength λu 1 ~λu n are located in a different band of AWG14. For example, the downstream signal wavelength λd 1 ~λd n belong to the L-band of AWG14, upstream signal wavelength λu 1 ~λu n belongs to C-band of AWG14.
光伝送路40は、シングルモード光ファイバ42、反射器44、AWG46、及び分岐光ファイバ48−1〜48−nからなる。光ファイバ42が、OLT10とAWG46の多重光入出力ポート#Mを接続し、光ファイバ42上の反射器44が配置される。分岐光ファイバ48−1〜48−nは、AWG46の入出力ポート#1〜#nをそれぞれONU50−1〜50−nに接続する。反射器44及びAWG46は、いわゆるリモートノードである。本実施例では、反射器44は、波長λd1〜λdn,λu1〜λunを、約4%(−14dB相当)、好ましくは1〜10%程度の反射率で反射する。反射器44は、光ファイバ42とOLT10の間に配置してもよい。
The
反射器44は、例えば、光ファイバ42とAWGを接続する光コネクタ部のフェルール部分形状を意図的に加工して形成してよい。また、OLT側の信号光源の波長を調整する必要が無い場合には、反射器44として、ONU50−1〜50−nからの上り信号光を反射し、OLT10からの下り信号光を無反射で透過する構成としてもよい。そのような反射器44は、例えば、1:2分岐光カプラを使い、AWG46からOLT10に向かう上り信号光を2分割して、一方を光ファイバ42に入力し、他方を光学ミラーに入射して反射させ、反射光をAWG46に戻すような構成で実現できる。
The reflector 44 may be formed, for example, by intentionally processing the ferrule part shape of the optical connector part that connects the
AWG46は、AWG14と同じ波長多重分離特性を具備する。ただし、各入出力ポート#1〜#nの透過波長(中心波長)が一致していれば良く、個々の入出力ポート#1〜#nの透過波長特性の特性曲線が同じである必要はない。すなわち、一般にAWGの各入出力ポートの波長透過特性にはフラットトップ型とガウシアン型の2タイプがあるが、AWG14(又は46)がフラットトップ型で、AWG46(又は14)がガウシアン方であってもよい。AWG46は、OLT10からの波長多重された下り信号光をONU50−1〜50−nへの下り信号光(波長λd1〜λdn)に波長分離し、ONU50−1〜50−nからの上り信号光(波長λu1〜λun)を波長多重する。
The AWG 46 has the same wavelength demultiplexing characteristics as the
光送受信装置12−1の構成と基本的な信号の流れを説明する。光送受信装置12−1の送信装置22は、信号光源としてのTLD(Tunable Laser Diode)24を具備する。TLD24はLバンド内の任意の波長のレーザ光を出力可能であり、制御装置34は、TLD24の波長を、後述する方法でAWG14のポート#1の透過波長である下り信号光波長λd1に調整する。レーザダイオードの波長を変更する方法には、レーザダイオードの温度を制御する方法、注入電流を制御する方法、レーザ共振器を構成する反射器の反射波長特性を変更する方法等がある。
The configuration and basic signal flow of the optical transceiver 12-1 will be described. The
光カプラ26は、送信装置22の出力光を波長分割多重(WDM: Wavelength Division Multiplexing)カプラ28に供給する。WDMカプラ28は、Cバンドの光とLバンドの光を多重し分離する光素子であり、光カプラ26からのLバンドの光をAWG14のポート#1に供給する。WDMカプラ28にはまた、AWG14のポート#1からCバンドの光(波長λu1の信号光)とLバンドの光(後述するが、波長λd1の反射光)が入射し、WDMカプラ28は、前者を受信装置30に供給し、後者を光カプラ26に供給する。受信装置30は、波長λu1の信号光を光電変換し、データDu1を復調して出力する。
The
光カプラ26は、WDMカプラ28からの光、すなわち、AWG14のポート#1からのLバンドの光(後述するが、波長λd1の反射光)を受光器32に供給する。WDMカプラ28からの光の一部がTLD24に入射して問題が発生する場合には、光カプラ26とTLD24の間に光アイソレータを配置すれば良い。このような機能から、光カプラ26を光サーキュレータで代替できることは明らかである。
The
受光器32は、光カプラ26から入力する光を電気信号に変換する。制御装置34は、受光器32の出力信号に従い、受光器32の出力信号振幅が大きくなるように、TLD24の波長を制御する。
The
ONU50−1〜50−nは同じ構成からなり、図1では、ONU50−1の構成を詳細に図示してある。ONU50−1の構成と基本的な信号の流れを説明する。送信装置52は、信号光源としてのTLD54を具備する。TLD54はCバンド内の任意の波長のレーザ光を出力可能であり、制御装置64は、TLD54の波長を、後述する方法でAWG46(及び14)のポート#1の透過波長である上り信号光波長λu1に調整する。光カプラ56は、送信装置52の出力光をWDMカプラ58に供給する。WDMカプラ58は、Cバンドの光とLバンドの光を多重し分離する光素子であり、光カプラ56からのCバンドの光を分岐光ファイバ48−1を介してAWG46のポート#1に供給する。WDMカプラ58にはまた、分岐光ファイバ48−1を介してAWG46のポート#1からLバンドの光(波長λd1の信号光)とCバンドの光(後述するが、波長λu1の反射光)が入射し、WDMカプラ58は、前者を受信装置60に供給し、後者を光カプラ56に供給する。受信装置60は、波長λd1の信号光を光電変換し、データDd1を復調して出力する。
The ONUs 50-1 to 50-n have the same configuration, and FIG. 1 illustrates the configuration of the ONU 50-1 in detail. The configuration of the ONU 50-1 and the basic signal flow will be described. The
光カプラ56は、WDMカプラ58からの光、すなわち、AWG46の入出力ポート#1からのCバンドの光(後述するが、波長λu1の反射光)を受光器62に供給する。WDMカプラ58からの光の一部がTLD54に入射して問題が発生する場合には、光カプラ56とTLD54の間に光アイソレータを配置すれば良い。このような機能から、光カプラ56を光サーキュレータで代替できることは明らかである。
The
受光器62は、光カプラ56から入力する光を電気信号に変換する。制御装置64は、受光器62の出力信号に従い、受光器62の出力信号振幅が大きくなるように、TLD54の波長を制御する。
The
まず、TLD24の波長調整動作を説明する。制御装置34は、Lバンドの一端(例えば、長波長側)から他端(例えば、短波長側)に向かい、TLD24の発光波長を連続的又は離散的に掃引する。先に説明したように、TLD24の出力光は、光カプラ26及びWDMカプラ28を介してAWG14のポート#1に入射する。TLD24の出力光の波長が、AWG14のポート#1の透過範囲に入らない間は、反射器44による反射は発生しない。従って、受光器32には反射器44による反射光が入射せず、受光器32の出力レベルは低いままとなる。
First, the wavelength adjustment operation of the
TLD24の出力波長がAWG14のポート#1の透過範囲に入ると、TLD24の出力光が、AWG14のポート#1の透過特性に応じた減衰を受けつつもAWG14を透過し、光ファイバ42を介して反射器44に到達し、反射器44によりその一部が反射される。反射器44による反射光は、光ファイバ42を伝搬してAWG14の多重光入出力ポート#Mに入射する。AWG14は、多重光入出力ポート#Mに入射する反射光を入出力ポート#1からWDMカプラ28に出力する。WDMカプラ28は反射光を光カプラ26に供給し、光カプラ26はWDMカプラ28からの反射光を受光器32に入射する。これにより、受光器32の出力信号レベルが、受光器32に入射する反射光強度に応じた量だけ増大する。制御装置34は、受光器32の出力信号レベルの増大により、TLD24の出力波長がAWG14の入出力ポート#1の透過波長λd1に近づいたことを知ることができる。
When the output wavelength of the
制御装置34が更にTLD24の出力波長を掃引していくと、受光器32の出力信号レベルが増加し、次に低下に転ずる。その時点で、制御装置34は、AWG14の入出力ポート#1の透過帯域を通り過ぎつつあることを知ることができる。制御装置34は、掃引で得られた受光器32の出力信号レベル変化から、受光器32の出力信号レベルが最大になる波長にTLD24の出力波長を調整する。以後、制御装置34は、受光器32の出力信号レベルが一定以上になるように、又は、ピーク値を取り続けるように、AWG14の入出力ポート#1の透過帯域幅の範囲内で、TLD24の出力波長を変動させる。このような波長の微調整は、データ伝送中にも実行可能である。これにより、TLD24の駆動信号対波長特性及び周囲温度による波長変化、並びにAWG14の透過特性の経時変化等に関わらず、TLD24の波長をAWG14の入出力ポート#1を通過できる波長に維持できる。
As the
初期的にTLD24の出力波長を調整する方法として、まず、AWG14の入出力ポート#1の透過帯域幅の半分程度のステップ幅でTLD24の出力波長を掃引し、反射器44による反射光が受光器32に入射するようになったら、より細かいステップでTLD24の出力波長を掃引するようにしてもよい。換言すると、TLD24の波長を粗調整し、透過帯域内に入るか近づいたら、波長を微調整する。最初から最後まで細かい一定のステップで波長を掃引する方法又は連続的に波長を掃引する方法に比べ、波長を決定するまでに要する時間が短縮できる。
As a method of initially adjusting the output wavelength of the
AWG14の透過特性がガウシアンタイプの場合、所定間隔離れた3つの波長の反射光レベルから、最大透過率(最低透過損失)の波長を近似的に決定可能である。この場合、制御装置34は、透過特性のガウシアン波形内にその3波長が入るような波長間隔でTLD24の波長を離散的に掃引し、その波長掃引で得られる隣接する3波長の反射光レベルを演算すれば良い。
When the transmission characteristic of the
AWG14の透過特性が、図2及び図3に示すようなフラットトップタイプの場合は、その透過特性の、短波長側エッジと長波長側エッジを検出することで、中心波長を決定できる。この場合は、これらのエッジを検出できる程度に細かく又は連続的にTLD24の波長を掃引する必要がある。片方のエッジを検出し、透過波長幅の半分相当、波長をシフトする方法でもよい。
When the transmission characteristic of the
なお、受光器32で受光する反射光の強度を比較する場合、TLD24の出力光パワーが一定に制御されていることが前提となる。例えば、TLD24の出力光パワーが変動する場合でも、TLD24の出力パワーのモニタ結果で反射光強度を規格化することで、反射光強度を比較でき、従って、WAWG14の透過波長を検出できる。
When comparing the intensity of the reflected light received by the
ONU50−1〜50−nの信号光源であるTLD54の波長調整方法は、基本的に、TLD24のそれと同じである。ONU50−1のTLD54の波長調整動作を説明する。
The wavelength adjustment method of the
制御装置64は、Cバンドの一端(例えば、長波長側)から他端(例えば、短波長側)に向かい、TLD54の発光波長を掃引する。先に説明したように、TLD54の出力光は、光カプラ56及びWDMカプラ58を介してAWG46のポート#1に入射する。TLD54の出力光の波長が、AWG46のポート#1の透過範囲に入らない間は、反射器44による反射は発生しない。従って、受光器62には反射器44による反射光が入射せず、受光器62の出力レベルは低いままとなる。
The
TLD54の出力波長がAWG46のポート#1の透過範囲に入ると、TLD54の出力光が、AWG46のポート#1の透過特性に応じた減衰を受けつつもAWG46を透過して反射器44に入射し、反射器44によりその一部が反射される。反射器44による反射光は、AWG46の多重光入出力ポート#M及び入出力ポート#1、WDMカプラ58並びに光カプラ56を介して受光器62に入射する。これにより、受光器62の出力信号レベルが、受光器62に入射する反射光強度に応じた量だけ増大する。制御装置64は、受光器62の出力信号レベルの増大により、TLD54の出力波長がAWG46の入出力ポート#1の透過波長λu1に近づいたことを知ることができる。
When the output wavelength of the
制御装置64が更にTLD54の出力波長を掃引していくと、受光器62の出力信号レベルが増加し、次に低下に転ずる。その時点で、制御装置64は、AWG46の入出力ポート#1の透過帯域を通り過ぎつつあることを知ることができる。制御装置64は、掃引で得られた受光器62の出力信号レベル変化から、受光器62の出力信号レベルが最大になる波長にTLD54の出力波長を調整する。以後、制御装置64は、受光器62の出力信号レベルが一定以上になるように、又は、ピーク値を取り続けるように、AWG46の入出力ポート#1の透過帯域幅の範囲内で、TLD54の出力波長を変動させる。このような波長の微調整は、データ伝送中にも実行可能である。これにより、TLD54の駆動信号対波長特性及び周囲温度による波長変化、並びにAWG46の透過特性の経時変化等に関わらず、TLD54の波長をAWG46の入出力ポート#1を通過できる波長に維持できる。
When the
初期的にTLD54の出力波長を調整する方法として、まず、AWG46の入出力ポート#1の透過帯域幅の半分程度のステップ幅でTLD54の出力波長を掃引し、反射器44による反射光が受光器62に入射するようになったら、より細かいステップでTLD54の出力波長を掃引するようにしてもよい。換言すると、TLD54の波長を粗調整し、透過帯域内に入るか近づいたら、波長を微調整する。最初から最後まで細かい一定のステップで波長を掃引する方法に比べ、波長を決定するまでに要する時間が短縮できる。
As a method of initially adjusting the output wavelength of the
このようにOLT10の光送受信装置12−1〜12−nの各TLD24と、ONU50−1〜50−nのTLD54の波長が調整されると、互いに対応する光送受信装置12−1〜12−nとONU50−1〜50−nとの間でデータ通信が可能になる。
Thus, when the wavelengths of the
光送受信装置12−1からONU50−1への下りデータ伝送の動作を簡単に説明する。光送受信装置12−1の送信装置22は、TLD24を使って、下りデータDd1を搬送する下り信号光(波長λd1)を生成し、光カプラ26に出力する。下り信号光(波長λd1)は、光カプラ26、WDMカプラ28、AWG14及び光ファイバ42を通過して、反射器44に入射する。反射器44は、入射する下り信号光(波長λd1)のほとんどを透過し、ごく一部を反射する。反射器44で反射した成分は、先に説明したように、光送受信装置12−1のTLD24の波長を調整するのに使用される。
An operation of downlink data transmission from the optical transceiver 12-1 to the ONU 50-1 will be briefly described. The
反射器44を透過した下り信号光(波長λd1)は、AWG46の多重光入出力ポート#Mに入射し、入出力ポート#1から分岐光ファイバ48−1に出力されて、ONU50−1に入射する。ONU50−1では、WDMカプラ58は、光ファイバ48−1からの下り信号光(波長λd1)を受信装置60に供給する。受信装置60は、WDMカプラ58からの下り信号光(波長λd1)を光電変換し、データDd1を復調して出力する。このようにして、OLT10からONU50−1に下りデータDd1が伝送される。
Downstream signal light (wavelength λd 1 ) transmitted through the reflector 44 enters the multiplexed optical input / output port #M of the
ONU50−1から光送受信装置12−1への上りデータ伝送の動作を簡単に説明する。ONU50−1の送信装置52は、TLD54を使って、上りデータDu1を搬送する上り信号光(波長λu1)を生成し、光カプラ56に出力する。上り信号光(波長λu1)は、光カプラ56、WDMカプラ58、分岐光ファイバ48−1、並びにAWG46の入出力ポート#1及び多重光入出力ポート#Mを通過して、反射器44に入射する。反射器44は、入射する上り信号光(波長λu1)のほとんどを透過し、ごく一部を反射する。反射器44で反射した成分は、先に説明したように、ONU50−1のTLD54の波長を調整するのに使用される。
The operation of uplink data transmission from the ONU 50-1 to the optical transceiver 12-1 will be briefly described. The
反射器44を透過した上り信号光(波長λu1)は、光ファイバ42、AWG14の多重光入出力ポート#M及び入出力ポート#1を介してWDMカプラ28に入射する。WDMカプラ28は、AWG14の入出力ポート#1からの上り信号光(波長λu1)を受信装置30に供給する。受信装置30は、WDMカプラ28からの上り信号光(波長λu1)を光電変換し、データDu1を復調して出力する。このようにして、ONU50−1からOLT10に上りデータDu1が伝送される。
The upstream signal light (wavelength λu 1 ) transmitted through the reflector 44 enters the
ONU50−1〜50−nのTLD54の場合、個々のONU50−1〜50−nで使用するAWG14,46の波長チャネルをディップスイッチ等で設定できるようにしておいてもよい。例えば、ユーザ又はONU設置作業者が、そのディップスイッチで、予め指定される波長チャネルを設定する。制御装置64は、ディップスイッチで設定される波長チャネルを目標に、上述の波長調整を実行する。
In the case of the
上記実施例は、より一般的にはWDM光伝送システムであり、その場合、ONU50−1〜50−nはいわゆる光送受信装置と呼ぶことができ、それぞれ、光送受信装置12−1〜12−nと1対1で通信する。 The above embodiment is more generally a WDM optical transmission system, in which case the ONUs 50-1 to 50-n can be referred to as so-called optical transmission / reception devices, and the optical transmission / reception devices 12-1 to 12-n, respectively. 1-to-1 communication.
特定の説明用の実施例を参照して本発明を説明したが、特許請求の範囲に規定される本発明の技術的範囲を逸脱しないで、上述の実施例に種々の変更・修整を施しうることは、本発明の属する分野の技術者にとって自明であり、このような変更・修整も本発明の技術的範囲に含まれる。 Although the invention has been described with reference to specific illustrative embodiments, various modifications and alterations may be made to the above-described embodiments without departing from the scope of the invention as defined in the claims. This is obvious to an engineer in the field to which the present invention belongs, and such changes and modifications are also included in the technical scope of the present invention.
10:OLT
12−1〜12−n:光送受信装置
14:AWG
22:送信装置
24:TLD
26:光カプラ
28:WDMカプラ
30:受信装置
32:受光器
34:制御装置
40:光伝送路
42:シングルモード光ファイバ
44:反射器
46:AWG
48−1〜48−n:分岐光ファイバ
50−1〜50−n:ONU
52:送信装置
54:TLD
56:光カプラ
58:WDMカプラ
60:受信装置
62:受光器
64:制御装置
10: OLT
12-1 to 12-n: Optical transceiver 14: AWG
22: Transmitter 24: TLD
26: Optical coupler 28: WDM coupler 30: Receiver 32: Light receiver 34: Controller 40: Optical transmission line 42: Single mode optical fiber 44: Reflector 46: AWG
48-1 to 48-n: Branched optical fibers 50-1 to 50-n: ONU
52: Transmitter 54: TLD
56: Optical coupler 58: WDM coupler 60: Receiver 62: Light receiver 64: Controller
Claims (2)
互いに異なる上り波長及び下り波長を使用する複数の第1の光送受信装置(12−1〜12−n)と、
当該複数の第1の光送受信装置と通信する複数の第2の光送受信装置(50−1〜50−n)と、
当該複数の第1の光送受信装置が出力する下り光を波長多重し、光伝送路からの多重化された上り光を当該複数の第1の送受信装置のそれぞれに向かう上り光に波長分離する第1の波長多重分離手段(14)
とを具備し、
当該光伝送路が、
当該複数の第2の光送受信装置が出力する上り光を波長多重し、当該第1の波長多重分離手段で多重された当該下り光を、当該複数の第2の送受信装置のそれぞれに向かう下り光に波長分離する第2の波長多重分離手段(40)と、
当該第1の波長多重分離手段と当該第2の波長多重分離手段との間に配置される反射器(44)
とを具備し、
当該第1の光送受信装置が、当該複数の第1の光送受信装置が使用する全部の下り波長と、当該複数の第1の光送受信装置が使用する全部の上り波長とを多重分離する第1のWDMカプラ(28)と、信号光源となる第1の波長可変光源(24)を具備する第1の送信装置(22)と、第1の受信装置(30)と、当該第1の送信装置(22)の出力する下り光の、当該反射器(44)による第1の反射光を受光する第1の受光器(32)と、当該第1の送信装置(22)の出力する下り光を当該第1のWDMカプラ(28)に供給し、当該第1のWDMカプラ(28)からの、当該第1の反射光を当該第1の受光器(32)に供給する第1の光カプラ(26)と、当該第1の受光器(32)により受光される当該反射光のレベルに応じて、当該第1の反射光のレベルが所定値以上になるように当該第1の波長可変光源の波長を制御する第1の制御装置(34)とを具備する
ことを特徴とする光伝送システム。 An optical transmission line (40);
A plurality of first optical transceivers (12-1 to 12-n) that use different upstream and downstream wavelengths;
A plurality of second optical transceivers (50-1 to 50-n) communicating with the plurality of first optical transceivers;
First, the downstream light output from the plurality of first optical transmission / reception devices is wavelength-multiplexed, and the multiplexed upstream light from the optical transmission path is wavelength-separated into upstream light directed to each of the plurality of first transmission / reception devices. 1 wavelength demultiplexing means (14)
And
The optical transmission line is
Downlink light that wavelength-multiplexes upstream light output from the plurality of second optical transmission / reception devices, and that transmits the downstream light multiplexed by the first wavelength demultiplexing means to each of the plurality of second transmission / reception devices. Second wavelength demultiplexing means (40) for wavelength separation into
Reflector (44) disposed between the first wavelength demultiplexing means and the second wavelength demultiplexing means
And
The first optical transmission / reception device demultiplexes all the downstream wavelengths used by the plurality of first optical transmission / reception devices and all the upstream wavelengths used by the plurality of first optical transmission / reception devices. WDM coupler (28), a first transmission device (22) including a first variable wavelength light source (24) serving as a signal light source, a first reception device (30), and the first transmission device The downstream light output from the first transmitter (22) and the first light receiver (32) that receives the first reflected light from the reflector (44) of the downstream light output from (22). A first optical coupler (supplied to the first WDM coupler (28) and supplying the first reflected light from the first WDM coupler (28) to the first light receiver (32). 26) and the level of the reflected light received by the first light receiver (32), An optical transmission system, wherein a level of the reflected light of said 1 comprises a first control unit (34) and controlling the wavelength of the first wavelength-tunable light source to be equal to or greater than the predetermined value.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010147140A JP2012015577A (en) | 2010-06-29 | 2010-06-29 | Optical transmission system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010147140A JP2012015577A (en) | 2010-06-29 | 2010-06-29 | Optical transmission system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2012015577A true JP2012015577A (en) | 2012-01-19 |
| JP2012015577A5 JP2012015577A5 (en) | 2013-04-18 |
Family
ID=45601547
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010147140A Pending JP2012015577A (en) | 2010-06-29 | 2010-06-29 | Optical transmission system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2012015577A (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016225923A (en) * | 2015-06-02 | 2016-12-28 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | Optical transmission and reception system |
| JP2020098987A (en) * | 2018-12-17 | 2020-06-25 | 富士通株式会社 | Optical transmission device, wavelength setting method, and optical transceiver |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005033802A (en) * | 2003-07-07 | 2005-02-03 | Samsung Electronics Co Ltd | Self-recovering wavelength division multiplexing,passive optical subscriber network |
| JP2005277686A (en) * | 2004-03-24 | 2005-10-06 | Fujitsu Ltd | Wavelength multiplex optical transmission system and transmission wavelength control method in it |
-
2010
- 2010-06-29 JP JP2010147140A patent/JP2012015577A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005033802A (en) * | 2003-07-07 | 2005-02-03 | Samsung Electronics Co Ltd | Self-recovering wavelength division multiplexing,passive optical subscriber network |
| JP2005277686A (en) * | 2004-03-24 | 2005-10-06 | Fujitsu Ltd | Wavelength multiplex optical transmission system and transmission wavelength control method in it |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016225923A (en) * | 2015-06-02 | 2016-12-28 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | Optical transmission and reception system |
| JP2020098987A (en) * | 2018-12-17 | 2020-06-25 | 富士通株式会社 | Optical transmission device, wavelength setting method, and optical transceiver |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101855716B1 (en) | Optical line terminal for a passive optical wavelength division multiplex network | |
| US9455782B2 (en) | Monitoring a multiplexed laser array in an optical communication system | |
| US10038946B2 (en) | Optical network and method for processing data in an optical network | |
| EP2020767B1 (en) | Optical relay device and optical relay transmission system | |
| KR100608946B1 (en) | Wdm-pon by using self-injection locked fabry-perot laser diode, remote node, and control method therefor | |
| KR100711201B1 (en) | The long-reach wavelength division multiplexing passive optical networks by using the position adjustment of broadband light source | |
| KR100734873B1 (en) | Wavelength tracking apparatus and method in WDM-PON system | |
| EP3119015B1 (en) | Optical time domain reflectometer implementation apparatus and system | |
| CN103634066B (en) | Optical line terminal and optical network unit | |
| WO2012062119A1 (en) | Passive optical network and signal transmission method of passive optical network | |
| US9531155B2 (en) | Switched radio frequency (RF) driver for tunable laser with multiple in-line sections | |
| KR20140076112A (en) | Optical line terminal for monitoring and controlling of upstream/downstream optical signals | |
| US9166691B2 (en) | Method for coupling an emitting device to a frequency splitter in an optical passive network | |
| US20090304388A1 (en) | Optical Branching Apparatus and Passive Optical Network System | |
| KR100711352B1 (en) | Wavelength-division-multiplexed passive optical network using wavelength-locked optical transmitter | |
| Chowdhury et al. | A survivable protection and restoration scheme using wavelength switching of integrated tunable optical transmitter for high throughput WDM-PON system | |
| JP2012015577A (en) | Optical transmission system | |
| Lee et al. | First commercial service of a colorless gigabit WDM/TDM hybrid PON system | |
| EP2408125B1 (en) | Optical transmitter for wdm passive optical network | |
| US20150372758A1 (en) | Transmitting and receiving apparatus using wavelength-tunable filter and method thereof | |
| CN102098106A (en) | Optical line terminal for wavelength division multiplexing-time division multiplexing passive optical network | |
| KR101325858B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for adaptive optical power controlling, optical communication system and for the same | |
| KR20130101961A (en) | Optical line terminal for controlling and monitoring optical power and wavelength of downstream wdm optical signals in bidirectional wavelength-division-multiplexing optical network | |
| JP2010193181A (en) | Optical transmission system, wavelength router, subscriber terminal device, and optical transmission method | |
| Lee et al. | A linear bus wavelength-reuse WDM-PON with simple add/drop nodes |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130301 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20130301 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20140115 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20140121 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20140617 |