JP2011107343A - Optical sheet, surface light source device, transmission type display device and method of manufacturing the optical sheet - Google Patents
Optical sheet, surface light source device, transmission type display device and method of manufacturing the optical sheet Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2011107343A JP2011107343A JP2009261288A JP2009261288A JP2011107343A JP 2011107343 A JP2011107343 A JP 2011107343A JP 2009261288 A JP2009261288 A JP 2009261288A JP 2009261288 A JP2009261288 A JP 2009261288A JP 2011107343 A JP2011107343 A JP 2011107343A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- sheet
- optical
- optical sheet
- prism
- unit
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Optical Elements Other Than Lenses (AREA)
- Liquid Crystal (AREA)
- Planar Illumination Modules (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、少なくとも一方の面に単位光学形状が複数配列された光学シート、これを備える面光源装置,透過型表示装置、及び、光学シートの製造方法に関するものである。 The present invention relates to an optical sheet having a plurality of unit optical shapes arranged on at least one surface, a surface light source device including the optical sheet, a transmissive display device, and an optical sheet manufacturing method.
従来、少なくとも一方の面にレンズ形状やプリズム形状等が形成された光学シートは、面光源装置やスクリーン等に広く使用されている。
このような光学シートは、一般には、基材シートに紫外線硬化型樹脂を塗布し、金型に押圧して紫外線を照射することによって硬化させてレンズ形状等を転写する紫外線成形や、熱可塑性樹脂を用いた押し出し成形等によって形成されている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。
Conventionally, an optical sheet having a lens shape, a prism shape, or the like formed on at least one surface is widely used for a surface light source device, a screen, or the like.
Such an optical sheet is generally formed by applying an ultraviolet curable resin to a base sheet, curing it by irradiating the mold with ultraviolet rays and transferring the lens shape or the like, or a thermoplastic resin. (For example, refer patent document 1).
このような光学シートを押し出し成形によって作製する際、一般的には、ダイからシート状に押し出された樹脂材料を、金型となる成形ロールと加圧ロールとの間を加圧しながら通すことによってレンズ形状等を賦形する。しかし、このような方法では、その成形ロールに樹脂材料が加圧される面積が狭く、加圧字の金型とシート状の樹脂材料とは略線接触に近い状態であり、また、加圧の時間も短い。そのため、金型の凹形状の部分には、版深方向に凹形状の奥まで十分に樹脂材料が充填され難いという問題や、樹脂そのものの弾性によって版深方向に入った樹脂が戻されるという問題を有している。
特に、レンズ形状等のピッチが小さい場合には、従来の押し出し成形では、樹脂材料の版深方向への充填が不十分となり易く、レンズ形状等の賦形性が低下し、集光性や拡散性等の所望する光学性能が得られないという問題があった。
そこで、一般的に、押し出し成形では、レンズ形状等のピッチを、紫外線成形のものに比べて大きくすることにより、レンズ形状等の賦形性を向上させ、所望する光学性能が得られるようにしている。
When producing such an optical sheet by extrusion molding, generally, a resin material extruded into a sheet shape from a die is passed while being pressed between a molding roll serving as a mold and a pressure roll. Shape the lens shape. However, in such a method, the area where the resin material is pressed onto the molding roll is narrow, and the press-shaped mold and the sheet-shaped resin material are in a state of nearly line contact, The time is short. Therefore, it is difficult to fill the concave part of the mold sufficiently with the resin material to the depth of the concave part in the plate depth direction, and the problem that the resin that entered the plate depth direction is returned by the elasticity of the resin itself. have.
In particular, when the pitch of the lens shape or the like is small, the conventional extrusion molding tends to cause insufficient filling of the resin material in the plate depth direction, and the shapeability of the lens shape and the like is reduced, and the light collecting property and diffusion are reduced. There is a problem that desired optical performance such as property cannot be obtained.
Therefore, in general, in extrusion molding, by increasing the pitch of the lens shape, etc., compared to that of ultraviolet molding, the shapeability of the lens shape etc. is improved and the desired optical performance is obtained. Yes.
透過型表示装置や面光源装置等では、薄型化が求められており、用いられる光学シートの厚さをそれほど厚くできない。そこで、光学シートの総厚を変えないまま、単純にレンズ形状等のピッチを大きくすると、その形状の高さも比例して大きくなり、光学シートの総厚に対して、レンズ形状部分の厚みが占める割合が大きくなる。そのため、レンズ形状部分以外の連続した領域の厚みが薄くなって、結果として光学シートの剛性が低下する。そして、剛性の低下により、透過型表示装置の使用状態において、自重等により光学シートの撓みが生じ易くなる。
また、レンズ形状等のピッチが大きくなると、光学シートの表裏面での表面積の差が大きくなり、表裏面での吸水量等に差が生じ、温度や湿度の変化による撓みや反り等の変形が生じ易くなる。
このような撓み等の変形は、輝度ムラ等の画質の低下を生じさせる。
前述の特許文献1では、厚みムラや外観不良に関する対策はなされているが、賦形性向上に関する対策はなんら開示されていない。
A transmissive display device, a surface light source device, and the like are required to be thin, and the thickness of an optical sheet to be used cannot be increased so much. Therefore, if the pitch of the lens shape or the like is simply increased without changing the total thickness of the optical sheet, the height of the shape also increases proportionally, and the thickness of the lens shape portion occupies the total thickness of the optical sheet. The proportion increases. Therefore, the thickness of the continuous area other than the lens-shaped portion is reduced, and as a result, the rigidity of the optical sheet is lowered. Due to the decrease in rigidity, the optical sheet is likely to be bent due to its own weight or the like when the transmission type display device is in use.
In addition, when the pitch of the lens shape, etc. increases, the difference in surface area between the front and back surfaces of the optical sheet increases, resulting in a difference in water absorption on the front and back surfaces, and deformation such as bending and warping due to changes in temperature and humidity. It tends to occur.
Such deformation such as bending causes deterioration in image quality such as luminance unevenness.
In the above-mentioned Patent Document 1, measures for thickness unevenness and appearance defects are taken, but no measures for improving the formability are disclosed.
本発明の課題は、押し出し成形可能であり、高い賦形性を有する光学シート、これを備える面光源装置、透過型表示装置、及び、光学シートの製造方法を提供することである。 An object of the present invention is to provide an optical sheet that can be extruded and has high formability, a surface light source device including the optical sheet, a transmissive display device, and a method for manufacturing the optical sheet.
本発明は、以下のような解決手段により、前記課題を解決する。なお、理解を容易にするために、本発明の実施形態に対応する符号を付して説明するが、これに限定されるものではない。
請求項1の発明は、少なくとも一方の面に、単位光学形状(161)が複数配列された光学形状部を有する光学シートであって、少なくとも前記光学形状部は、ポリカーボネート樹脂により形成され、前記ポリカーボネート樹脂は、その重量平均分子量が18000〜22000であり、前記ポリカーボネート樹脂に含有される分子量1000以下の成分が前記ポリカーボネート樹脂全体の重量に対して占める割合が2.0〜4.0重量%であり、150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´が3.0×107〜2.0×108Paであること、を特徴とする光学シート(16)である。
The present invention solves the above problems by the following means. In addition, in order to make an understanding easy, although the code | symbol corresponding to embodiment of this invention is attached | subjected and demonstrated, it is not limited to this.
The invention according to claim 1 is an optical sheet having an optical shape portion in which a plurality of unit optical shapes (161) are arranged on at least one surface, wherein at least the optical shape portion is formed of a polycarbonate resin. The resin has a weight average molecular weight of 18000 to 22000, and a ratio of the component having a molecular weight of 1000 or less contained in the polycarbonate resin to the weight of the whole polycarbonate resin is 2.0 to 4.0% by weight. The optical modulus (16) is characterized in that the storage elastic modulus G ′ at 150 ° C. is 3.0 × 10 7 to 2.0 × 10 8 Pa.
請求項2の発明は、請求項1に記載の光学シートであって、前記単位光学形状(161)は、凸形状であり、シート面に沿って一次元方向に規則的に複数配列されていること、を特徴とする光学シート(16)である。
請求項3の発明は、請求項2に記載の光学シートにおいて、前記単位光学形状(161)は、その配列方向に平行であって厚み方向に平行な断面での断面形状が略三角形形状であること、を特徴とする光学シート(16)である。
Invention of Claim 2 is the optical sheet of Claim 1, Comprising: The said unit optical shape (161) is convex shape, and it is regularly arranged in multiple numbers by the one-dimensional direction along the sheet | seat surface. This is an optical sheet (16).
According to a third aspect of the present invention, in the optical sheet according to the second aspect, the unit optical shape (161) is substantially triangular in cross section in a cross section parallel to the arrangement direction and parallel to the thickness direction. This is an optical sheet (16).
請求項4の発明は、請求項1から請求項3までのいずれか1項に記載の光学シート(16)と、前記光学シートに光を照射する光源部(12,13)と、を備える面光源装置(12,13,14,15,16,17)である。
請求項5の発明は、請求項4に記載の面光源装置(12,13,14,15,16,17)と、前記面光源装置によって背面から照明される透過型表示部(11)と、を備える透過型表示装置(10)である。
Invention of Claim 4 is a surface provided with the optical sheet (16) of any one of Claim 1 to Claim 3, and the light source part (12, 13) which irradiates light to the said optical sheet. It is a light source device (12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17).
Invention of Claim 5 is the surface light source device (12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17) of Claim 4, and the transmission type display part (11) illuminated from the back surface by the said surface light source device, Is a transmissive display device (10).
請求項6の発明は、請求項1から請求項3までのいずれか1項に記載の光学シートを製造する光学シートの製造方法において、前記ポリカーボネート樹脂をシート状に押し出し成形し、少なくとも一方が前記単位光学形状を賦形する金型となる成形ロール(24)である一対のロール(23,24)の間隙を加圧しながら通過させることにより、前記単位光学形状(161)を賦形すること、を特徴とする光学シートの製造方法である。 The invention of claim 6 is an optical sheet manufacturing method for manufacturing an optical sheet according to any one of claims 1 to 3, wherein the polycarbonate resin is extruded into a sheet shape, at least one of which is the Shaping the unit optical shape (161) by passing through a gap between a pair of rolls (23, 24), which is a molding roll (24) serving as a mold for shaping the unit optical shape, An optical sheet manufacturing method characterized by the above.
本発明によれば、以下の効果を奏することができる。
(1)本発明による光学シートは、少なくとも一方の面に単位光学形状が複数配列された光学形状部を有し、光学形状部は、ポリカーボネート樹脂により形成され、このポリカーボネート樹脂は、その重量平均分子量が18000〜22000であり、ポリカーボネート樹脂に含有される分子量1000以下の成分が、ポリカーボネート樹脂全体の重量に対して占める割合が2.0〜4.0重量%であり、150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´が3.0×107〜2.0×108Paであるものとした。
従って、光学シートは、光学形状部がポリカーボネート樹脂により形成されるので、光透過性を有し、屈折率が高く、光学シートとして良好な剛性及び靭性を有する。よって、光学シートとして良好な光学特性を有し、かつ、製造時や運搬時等での取り扱いも容易である。また、押し出し成形可能であるので、製造も容易に行える。
さらに、樹脂材料の重量平均分子量、ポリカーボネート樹脂に含有される分子量1000以下の成分が占める割合、150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´が、上記の範囲を満たしているので、賦形性が高く、単位光学形状による集光や拡散等の光学性能を良好に発揮することができる。
According to the present invention, the following effects can be obtained.
(1) The optical sheet according to the present invention has an optical shape portion in which a plurality of unit optical shapes are arranged on at least one surface, and the optical shape portion is formed of a polycarbonate resin, and the polycarbonate resin has a weight average molecular weight. Is 18000 to 22000, the proportion of the component having a molecular weight of 1000 or less contained in the polycarbonate resin is 2.0 to 4.0% by weight with respect to the total weight of the polycarbonate resin, and the storage elastic modulus at 150 ° C. G 'shall be 3.0 * 10 < 7 > -2.0 * 10 < 8 > Pa.
Therefore, since the optical shape portion of the optical sheet is formed of a polycarbonate resin, it has optical transparency, a high refractive index, and good rigidity and toughness as an optical sheet. Therefore, it has good optical properties as an optical sheet, and is easy to handle during production and transportation. Moreover, since extrusion molding is possible, manufacture can also be performed easily.
Furthermore, since the weight average molecular weight of the resin material, the proportion of the component having a molecular weight of 1000 or less contained in the polycarbonate resin, and the storage elastic modulus G ′ at 150 ° C. satisfy the above range, the shapeability is high, Optical performance such as light collection and diffusion due to the unit optical shape can be exhibited well.
(2)単位光学形状は、凸形状であり、シート面に沿って一次元方向に規則的に複数配列されているので、その配列方向における光線制御を容易に行うことができる。 (2) The unit optical shape is a convex shape, and a plurality of unit optical shapes are regularly arranged in a one-dimensional direction along the sheet surface, so that light control in the arrangement direction can be easily performed.
(3)単位光学形状は、その配列方向に平行であって厚み方向に平行な断面での断面形状が略三角形形状であるので、高い集光性を有し、輝度を上げることができる。 (3) The unit optical shape is parallel to the arrangement direction and the cross-sectional shape in the cross-section parallel to the thickness direction is a substantially triangular shape, so that it has high light collecting properties and can increase the luminance.
(4)本発明による光学シートと、光学シートに光を照射する光源部とを備える面光源装置であるので、優れた光学特性を有する面光源装置とすることができる。 (4) Since the surface light source device includes the optical sheet according to the present invention and a light source unit that irradiates light to the optical sheet, the surface light source device having excellent optical characteristics can be obtained.
(5)本発明による面光源装置と、この面光源装置によって背面から照明される透過型表示部とを備える透過型表示装置であるので、良好な映像を表示することができる。 (5) Since the transmissive display device includes the surface light source device according to the present invention and the transmissive display unit illuminated from the back by the surface light source device, a good image can be displayed.
(6)本発明による光学シートの製造方法は、ポリカーボネート樹脂をシート状に押し出し成形し、少なくとも一方が単位光学形状を賦形する金型となる成形ロールである一対のロールの間隙を加圧しながら通過させることにより、単位光学形状を賦形するので、大幅な設備投資を行うことなく、従来の押し出し成形装置を用いて光学シートを作製することができる。従って、光学性能の優れた光学シートを安価に提供できる。 (6) In the method for producing an optical sheet according to the present invention, a polycarbonate resin is extruded into a sheet shape, and at least one of them is pressed while a gap between a pair of rolls is a molding roll that forms a unit optical shape. By passing, the unit optical shape is shaped, so that an optical sheet can be produced using a conventional extrusion molding apparatus without making a large capital investment. Therefore, an optical sheet with excellent optical performance can be provided at low cost.
以下、図面等を参照して、本発明の実施形態について説明する。
なお、図1を含め、以下に示す各図は、模式的に示した図であり、各部の大きさ、形状は、理解を容易にするために、適宜誇張している。
また、板、シート、フィルム等の言葉を使用しているが、これらは、一般的な使い方として、厚さの厚い順に、板、シート、フィルムの順で使用されており、本明細書中でもそれに倣って使用している。しかし、このような使い分けには、技術的な意味は無いので、特許請求の範囲の記載は、シートという記載で統一して使用した。従って、シート、板、フィルムの文言は、適宜置き換えることができるものとする。例えば、光学シートは、光学フィルムとしてもよいし、光学板としてもよい。
さらに、本明細書中に記載する各部材の寸法等の数値及び材料名等は、実施形態としての一例であり、これに限定されるものではなく、適宜選択して使用してよい。
Embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings.
In addition, each figure shown below including FIG. 1 is the figure shown typically, and the magnitude | size and shape of each part are exaggerated suitably for easy understanding.
In addition, the terms “plate”, “sheet”, “film” and the like are used, but these are generally used in the order of thickness, “plate”, “sheet”, “film”. I am using it. However, since there is no technical meaning in such proper use, the description in the claims is used in the unified description of the sheet. Accordingly, the terms “sheet”, “plate”, and “film” can be appropriately replaced. For example, the optical sheet may be an optical film or an optical plate.
Furthermore, numerical values such as dimensions and material names of each member described in the present specification are examples of the embodiment, and the present invention is not limited thereto, and may be appropriately selected and used.
(実施形態)
図1は、本実施形態の透過型表示装置10を説明する図である。
本実施形態における透過型表示装置10は、LCD(Liquid Crystal Display)パネル11,反射板12,発光管13,乳白板14,第1拡散シート15,プリズムシート16,第2拡散シート17等を備え、LCDパネル11に形成される映像情報を背面から照明して表示する透過型液晶表示装置である。なお、LCDパネル11を背面から照明する面光源装置としては、反射板12,発光管13,乳白板14,第1拡散シート15,プリズムシート16,第2拡散シート17が該当している。
(Embodiment)
FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating a
The
LCDパネル11は、透過型の液晶表示素子により形成されており、対角32インチ(740mm×420mm)、解像度1280×768ドットの表示を行うことができる。
発光管13は、面光源装置の光源部を構成し、光を発する線光源である。本実施形態では、発光管13として冷陰極管を用いている。図1では、発光管13は、模式的に6本配列されている様子を示しているが、実際には、略20mm間隔で等間隔に18本が並列に並べられている。発光管13の背面には、反射板12が設けられている。
発光管13の長手方向に平行な方向は、面光源装置の使用状態における水平方向となっており、また、発光管13が並ぶ方向は、面光源装置の使用状態における垂直方向となっている。なお、以下の説明において、特に明記しない限り、垂直方向、水平方向とは、面光源装置及び透過型表示装置10の使用状態における垂直方向、水平方向であるとする。
反射板12は、発光管13の背面側(乳白板14とは反対側)の全面にわたって設けられており、背面側へ進む照明光を拡散反射して乳白板14方向(出射方向)へ向かわせ、入射光照度を均一に近付ける働きを持つ。
The
The
The direction parallel to the longitudinal direction of the
The
乳白板14は、無指向性の光拡散特性を有した拡散板であり、発光管13のLCDパネル11側(第1拡散シート15の光源側)に配置されている。
第1拡散シート15は、乳白板14とプリズムシート16との間に配置され、光を拡散する作用を有するシートである。本実施形態の第1拡散シート15は、光透過性を有する樹脂に、拡散材として微小ビーズが練り込まれて形成されている。
The milky
The
プリズムシート16は、発光管13から出射した光を、所定の視野角範囲内に集光、拡散する作用を有する光学シートである。プリズムシート16の出射側(観察面側)には、凸形状の単位プリズム161がシート面に沿って一方向(一次元方向)に規則的に複数配列された光学形状部を有する。また、プリズムシート16の入射側(発光管13側)の面162は、本実施形態では略平面状となっている。プリズムシート16の詳細に関しては後述する。
ここで、シート面とは、各光学シートにおいて、その光学シート全体として見たときにおけるその光学シートの平面方向となる面を示すものであり、本明細書中、及び、特許請求の範囲においても同一の定義として用いている。例えば、プリズムシート16のシート面は、プリズムシート16全体として見たときにおける、プリズムシート16の平面方向となる面であり、プリズムシート16の入射側の面162と平行な面である。
本実施形態の単位プリズム161は、水平方向に延在する略三角柱形状であり、シート面に沿って垂直方向に複数配列されている。
The
Here, the sheet surface refers to a surface which is a planar direction of the optical sheet when viewed as the entire optical sheet in each optical sheet, and also in the present specification and claims. They are used as the same definition. For example, the sheet surface of the
The unit prisms 161 of the present embodiment have a substantially triangular prism shape extending in the horizontal direction, and a plurality of
第2拡散シート17は、プリズムシート16とLCDパネル11との間に配置され、観察面側に微細凸形状が形成された光拡散作用を有するシート状の部材である。第2拡散シート17は、透明基材フィルムの一方の面の表面に、バインダ中に拡散材として微小ビーズを混練した拡散層をコートして形成される。この拡散層は、微小ビーズがバインダ部分よりも突出しており、これにより、第2拡散シート17の表面に微細凸形状が形成されている。
この第2拡散シート17では、微小ビーズのトップの丸い部分が突出しており、レンズ効果を発揮する。そのため、第2拡散シート17のシート面の法線方向(正面方向)に対して大きな角度をなす拡散光(視野角の広い拡散光)が入射した場合には、集光効果を発揮し、小さな角度をなす拡散光(視野角の狭い拡散光)が入射した場合には、拡散効果を発揮する。また、この第2拡散シート17は、拡散材を分散させてコーティングしているので、周期構造を持たず、モアレが発生することがない。
The
In the
なお、第2拡散シート17は、光透過性を有する樹脂に微小ビーズ等の拡散材を練り込んだ、第1拡散シート15と同様の形態のものや、表面に微細凹凸を形成したものや、これらを組み合わせた形態のものとしてもよい。また、第2拡散シート17ではなく、マイクロレンズシートをプリズムシート16とLCDパネル11との間に配置してもよい。
第1拡散シート15に関しても、例えば、表面に微細凹凸が形成された形態のものを用いてもよいし、第2拡散シート17と同様に、表面に拡散材を分散させてコーティングした形態としてもよいし、所望する光学性能等に合わせて適宜選択して用いてよい。
In addition, the
Regarding the
図2は、単位プリズムの形状を説明する図である。図2は、プリズムシート16のシート面に垂直であって単位プリズム161の配列方向(垂直方向)に平行な断面の一部を拡大して示している。
単位プリズム161の断面形状は、図2に示すように、頂点tを有し、出射側(LCDパネル11側)が凸となる略直角二等辺三角形状である。単位プリズム161の頂角αは、90°であり、単位プリズム161の頂点tを含む頂部は、曲面となっている。
単位プリズム161が配列されるピッチPは、P=138μmであり、その高さ(プリズムシート16の厚み方向における、単位プリズム161間の谷底となる点vから頂点tまでの寸法)hは、h=65.5μm(賦形率95%)であり、このプリズムシート16の厚さ(プリズムシート16の厚み方向における、入射側の面162から頂点tまでの寸法)は、280μmである。
本実施形態のプリズムシート16は、ポリカーボネート樹脂(PC樹脂)を単層押し出し成形により形成されており、その屈折率は、1.585である。
FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating the shape of the unit prism. FIG. 2 shows an enlarged part of a cross section perpendicular to the sheet surface of the
As shown in FIG. 2, the cross-sectional shape of the
The pitch P at which the
The
また、このプリズムシート16の材料となるPC樹脂は、その重量平均分子量が20000であり、PC樹脂に含まれる分子量1000以下の成分がPC樹脂全体の重量に対して占める割合(即ち、PC樹脂に含まれる分子量1000以下の成分の重量比率)が2.0重量%であり、150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´が1.0×108Paである。また、このプリズムシート16の材料となるPC樹脂の分子量分布(重量平均分子量(Mw)を数平均分子量(Mv)で割った値)は、2.6である。
なお、PC樹脂は、2,2−ビス(4−ヒドロキシフェニル)プロパン(ビスフェノールA)から製造する等、公知の製造法で得られるものであれば、特に制限はない。
Further, the PC resin used as the material of the
The PC resin is not particularly limited as long as it is obtained by a known production method such as production from 2,2-bis (4-hydroxyphenyl) propane (bisphenol A).
図3は、プリズムシート16の製造方法を説明する図である。
図3(a)は、プリズムシート16を製造する押出成形装置20を示し、図3(b)は、単位プリズム161の形状が賦形される部分を拡大して示している。
このプリズムシート16は、PC樹脂を押し出し成形することにより作製される。図3に示す、プリズムシート16を作製する押出成形装置20は、押出機21、ダイ22、第1ロール23、第2ロール24、第3ロール25、不図示の切断部等を有する。
押出機21は、不図示のホッパーから供給された熱可塑性樹脂を加熱、溶融する部分である。本実施形態では、プリズムシート16の材料はPC樹脂であり、そのガラス転移点が約145℃であるため、押出機21は、約280℃まで樹脂材料(PC樹脂)を加熱する。ダイ22は、押出機21から供給された樹脂材料を吐出する開口部であり、その開口の断面形状が略直線状(フラット状)である。このダイ22は、樹脂材料Rを成形しようとするシート幅まで広げて吐出する。
FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating a method for manufacturing the
3A shows the
This
The
第1ロール23、第2ロール24、第3ロール25は、略円柱形状であり、その中心軸を回転軸として回転駆動可能となっている。
第1ロール23は、その表面が金属製であり、その表面は平滑面となっている。なお、第1ロール23は、その表面をゴム製としてもよいし、金属とゴムの複合材を用いて形成してもよい。
第2ロール24は、その表面に単位プリズム161の形状を賦形するための金型となる凹凸形状が形成された成形ロールである。単位プリズム161の形状を賦形するための凹凸形状は、その長手方向が第2ロール24の周方向となるように形成されていてもよいし、軸方向に平行な方向となるように形成されていてもよい。
第1ロール23,第2ロール24は、これらのロールの間隙に加圧されながら樹脂材料Rが通ることによって、樹脂材料Rに単位プリズム161の形状を賦形する一対のロールである。また、第1ロール23,第2ロール24はいずれも不図示の温度調節部を備えており、ロール芯での温度が所定の温度となるように調整されている。
第3ロール25は、不図示の温度調節部等を備えた冷却ロールであり、単位プリズム161の形状が賦形されたシート状の樹脂材料Rを冷却する機能を有する。
The
The surface of the
The
The
The
押出機21によってガラス転移点を越える温度(約280℃)にまで加熱され、流動性を有した樹脂材料Rは、ダイ22からシート状に吐出される。本実施形態の樹脂材料R(PC樹脂)のMFRは、22である。シート状に吐出された樹脂材料Rは、第1ロール23と第2ロール24との間隙部分に毎分15mの速度で進み、第1ロール23によって第2ロール24の外周面に形成された凹凸形状に圧着される。
このとき、第1ロール23と第2ロール24とは、樹脂材料Rを介して略線接触している状態であり、図3(b)に示すように、ロールの回転軸に垂直な方向の断面では、直線A上で略点接触している。また、このとき、第1ロール23のロール芯での温度が約110℃、第2ロール24のロール芯での温度が130℃であり、第1ロール23と第2ロール24との間隙部分における樹脂材料Rの温度(バンク部bにおいて測定)は、約150℃となっている。
このように第1ロール23と第2ロール24との間で挟まれて加圧されることにより、シート状の樹脂材料Rは、第2ロール24に圧着し、樹脂が金型の凹凸形状部分に十分に流れ込んで充填され、一方の面に単位プリズム161の形状が賦形される。また、シート状の樹脂材料Rの他方の面は、第1ロール23の外周面と接触しており、略平面状となる。
The resin material R that is heated to a temperature exceeding the glass transition point (about 280 ° C.) by the
At this time, the
Thus, the sheet-like resin material R is pressure-bonded to the
第1ロール23と第2ロール24との間隙通過後、シート状の樹脂材料Rは、第2ロール24に外接したまま移動する。ロール芯での温度がPC樹脂のガラス転移点以下の温度に設定された第1ロール23,第2ロール24との接触や外気等によりシート状の樹脂材料Rは、冷却され、シート状の樹脂材料Rの表面温度がPC樹脂のガラス転移点以下になり、その表面がわずかに硬化する。そして、シート状の樹脂材料Rは、第2ロール24と第3ロール25との間隙で第3ロール25へ移動し、第3ロール25の回転によって、シート状の樹脂材料Rは、第2ロール24から剥離する。第3ロール25に外接することによりシート状の樹脂材料Rが冷却されてさらに硬化する。
次いで、シート状の樹脂材料Rは、第3ロール25のから不図示の引き取りロールや調整ロール等へ移動して、不図示の切断部等によって所望する大きさや形状に加工され、プリズムシート16が形成される。
After passing through the gap between the
Next, the sheet-like resin material R is moved from the
ここで、プリズムシート16の材料となるPC樹脂は、以下の条件を全て満たすことが好ましい。
(条件1)重量平均分子量(Mw)が、18000以上、22000以下である。
(条件2)PC樹脂全体の重量に対して、PC樹脂に含まれる分子量1000以下の成分が占める割合(即ち、PC樹脂に含まれる分子量1000以下の成分の重量比率)が、2.0重量%以上、4.0重量%以下である。
(条件3)150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´(JIS K7244−6に準拠)が、3.0×107Pa以上、2.0×108Pa以下である。
これらの条件は、上述のような製造方法を用いた場合に、樹脂材料Rが、金型の版深方向に十分流れ込む流動性や加圧して賦形する際に必要な弾性を有し、賦形性を向上させるためのものである。
Here, it is preferable that the PC resin used as the material of the
(Condition 1) The weight average molecular weight (Mw) is 18000 or more and 22000 or less.
(Condition 2) The ratio of the component having a molecular weight of 1000 or less contained in the PC resin to the total weight of the PC resin (that is, the weight ratio of the component having a molecular weight of 1000 or less contained in the PC resin) is 2.0% by weight. The content is 4.0% by weight or less.
(Condition 3) The storage elastic modulus G ′ (conforming to JIS K7244-6) at 150 ° C. is 3.0 × 10 7 Pa or more and 2.0 × 10 8 Pa or less.
These conditions are such that when the manufacturing method as described above is used, the resin material R has sufficient fluidity to flow in the plate depth direction of the mold and elasticity necessary for shaping by pressurization. This is to improve the formability.
重量平均分子量(Mw)は、その樹脂材料の流動性との関連が大きく、重量平均分子量が22000より大きいと、製品として十分な剛性及び靭性を有するが、流動性が小さくなり、型入りが低下し、賦形性が低下する。一方、重量平均分子量が18000より小さいと、流動性が大きくなり、賦形性は向上するが、ガラス転移点の低下を招き、また、靭性が低下して製品として脆いものとなる。
従って、材料となるPC樹脂の重量平均分子量(Mw)は、18000〜22000の範囲内であることが好ましい。
The weight average molecular weight (Mw) is strongly related to the fluidity of the resin material. If the weight average molecular weight is larger than 22000, the product has sufficient rigidity and toughness, but the fluidity becomes small and the mold entry decreases. However, the formability decreases. On the other hand, when the weight average molecular weight is less than 18000, the fluidity increases and the formability is improved, but the glass transition point is lowered, and the toughness is lowered to make the product brittle.
Therefore, it is preferable that the weight average molecular weight (Mw) of PC resin used as a material exists in the range of 18000-22000.
分子量1000以下の成分(化合物)は、所謂、可塑剤のような機能を有し、金型の凹形状の表面に樹脂材料が流れ込み易くする機能を有している。PC樹脂に含まれる分子量1000以下の成分としては、精製したPC樹脂に含まれる不純物(低分子化合物)を利用することができる。精製されたPC樹脂には、不純物として、モノマーやオリゴマーは少なからず残存しており、それらの割合を上記(条件2)の範囲内とすることにより、上述のような可塑剤としての効果を期待できる。このようなモノマーとしては、ビスフェノールA、オリゴマーとしては、数平均重合度nが2〜6程度の直鎖状や環状のビスフェノールAを用いることができる。なお、このように分子量1000以下の成分として不純物を利用する場合、精製されているため、一般にその割合が4.0重量%を越えることはない。 The component (compound) having a molecular weight of 1000 or less has a function like a so-called plasticizer, and has a function of facilitating the flow of the resin material into the concave surface of the mold. As a component having a molecular weight of 1000 or less contained in the PC resin, impurities (low molecular weight compounds) contained in the purified PC resin can be used. In the purified PC resin, not a few monomers and oligomers remain as impurities, and by setting the ratio thereof within the above range (Condition 2), the effect as a plasticizer as described above is expected. it can. As such a monomer, bisphenol A can be used, and as the oligomer, linear or cyclic bisphenol A having a number average polymerization degree n of about 2 to 6 can be used. In addition, when using impurities as a component having a molecular weight of 1000 or less as described above, since the impurities are purified, the ratio generally does not exceed 4.0% by weight.
また、必要であれば、分子量1000以下の成分が樹脂材料R(PC樹脂)に対して2.0〜4.0重量%の割合なるように、添加剤を適宜樹脂材料に添加してもよい。このような添加剤としては、熱安定剤や離形剤等として用いられるものが好ましく、一般的にはフェノール系やリン系のものを用いる。
熱安定剤としては、2,6−ジ−t−ブチル−4−メチルフェノール、2−(1−メチルシクロヘキシル)−4,6−ジメチルフェノール、2,2−メチレンビス−(4−エチル−6−t−メチルフェノール)、4,4´−チオビス−(6−t−ブチル−3−メチルフェノール)、ジラウリルチオジプロピオネート、トリス(ジ−ノニルフェニル)ホスファイト等を用いることができる。
離型剤としては、パラフィンワックス、ステアリン酸、硬化油、ステアロアミド、メチレンビスステアロアミド、エチレンビスステアロアミド、n−ブチルステアレート、ケトンワックス、オクチルアルコール、ラウリルアルコール、ヒドロキシステアリン酸トリグリセリド等を用いることができる。
Further, if necessary, an additive may be appropriately added to the resin material so that the component having a molecular weight of 1000 or less is 2.0 to 4.0% by weight with respect to the resin material R (PC resin). . As such an additive, what is used as a heat stabilizer, a mold release agent, etc. is preferable, and generally a phenol type or phosphorus type is used.
Examples of the heat stabilizer include 2,6-di-t-butyl-4-methylphenol, 2- (1-methylcyclohexyl) -4,6-dimethylphenol, 2,2-methylenebis- (4-ethyl-6- t-methylphenol), 4,4′-thiobis- (6-tert-butyl-3-methylphenol), dilaurylthiodipropionate, tris (di-nonylphenyl) phosphite, and the like can be used.
Examples of mold release agents include paraffin wax, stearic acid, hydrogenated oil, stearamide, methylene bisstearamide, ethylene bisstearamide, n-butyl stearate, ketone wax, octyl alcohol, lauryl alcohol, hydroxystearic acid triglyceride, etc. Can be used.
また、他にも、トリフェニルホスフェート等の流動性改良剤を添加してもよいし、PC樹脂に対する分解防止剤、離型剤として用いられる、天然蜜蝋、合成蜜蝋、一価アルコールと一価の脂肪酸エステル(例えば、ステアリルステアレート)、多価アルコールの部分エステル(例えば、グリセロールモノエステル、グリセロールジエステル)、多価アルコールの飽和エステル(例えば、グリセロールトリエステル、ペンタエリスリトールテトラステアレート)、ポリエチレン系ワックス(低分子量のポリエチレン或いは部分親水化処理されたポリエチレン系ワックス)等を添加剤として用いることができる。
さらに、上述した各種の離型剤や熱安定剤等を適宜組み合わせて用いてもよい。
In addition, fluidity improvers such as triphenyl phosphate may be added, natural beeswax, synthetic beeswax, monohydric alcohols and monovalent alcohols used as decomposition inhibitors and release agents for PC resins. Fatty acid ester (for example, stearyl stearate), partial ester of polyhydric alcohol (for example, glycerol monoester, glycerol diester), saturated ester of polyhydric alcohol (for example, glycerol triester, pentaerythritol tetrastearate), polyethylene wax (Low molecular weight polyethylene or partially hydrophilized polyethylene wax) or the like can be used as an additive.
Furthermore, you may use suitably combining various mold release agents, a heat stabilizer, etc. which were mentioned above.
分子量1000以下の成分が占める割合が4.0重量%より大きいと、賦形性が向上するが、プリズムシートの透明度の低下や加水分解が生じ易くなるといった問題や、成形ロールの汚染が生じ易くなり、このような汚染による製品としての外観不良や金型離型性(成型性)が不安定となるといった問題がある。
一方、分子量1000以下の成分が占める割合が2.0重量%より小さいと、樹脂材料Rが金型の版深方向に十分に入らず賦形性が低下する。
従って、分子量1000以下の成分がPC樹脂全体に対して占める割合は、2.0〜4.0重量%であることが好ましい。
また、重量平均分子量と分子量1000以下の成分が占める割合との関係から、分子量分布(重量平均分子量/数平均分子量)が大きい方が、賦形性が良好であり、小さいと腑形性が低下する。従って、分子量分布は、2.6以上であることが、賦形性を高める観点から好ましい。
When the proportion of the component having a molecular weight of 1000 or less is larger than 4.0% by weight, the formability is improved, but the problem that the transparency of the prism sheet is lowered and the hydrolysis tends to occur, and the contamination of the molding roll is likely to occur. Thus, there are problems such as poor appearance as a product due to such contamination and mold releasability (moldability) becoming unstable.
On the other hand, if the proportion of the component having a molecular weight of 1000 or less is less than 2.0% by weight, the resin material R does not sufficiently enter the plate depth direction of the mold and the formability is lowered.
Therefore, the ratio of the component having a molecular weight of 1000 or less to the whole PC resin is preferably 2.0 to 4.0% by weight.
In addition, from the relationship between the weight average molecular weight and the proportion of the component having a molecular weight of 1000 or less, the larger the molecular weight distribution (weight average molecular weight / number average molecular weight), the better the shapeability, and the smaller the lower the shapeability. To do. Therefore, the molecular weight distribution is preferably 2.6 or more from the viewpoint of enhancing the formability.
貯蔵弾性率G´は、単位プリズム161の形状の賦形時の加圧に対して影響を有している。150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´は、JIS K7244−6に準拠し、動的粘弾性測定装置(レオメトリック社製 RDA−III)を用いて、以下の条件(モード)で測定した。
試験方法:動的温度傾斜試験(Dynamic temperature ramp test)
測定冶具:直径8mmの円形のパラレルプレート(Parallel Plate,Dia.=8mm)
測定周波数:10Hz(Freq.=10Hz)
温度範囲:240〜140℃(Initial Temp.=240deg,Final Temp.=140deg)
降温速度:2℃/分(Ramp rate=2deg/min,Cooling scan)
歪み:5%、自動歪みモード(strain=5%,autostrain)
The storage elastic modulus G ′ has an influence on the pressurization at the time of shaping the shape of the
Test method: Dynamic temperature ramp test
Measuring jig: Circular parallel plate with a diameter of 8 mm (Parallel Plate, Dia. = 8 mm)
Measurement frequency: 10 Hz (Freq. = 10 Hz)
Temperature range: 240-140 ° C. (Initial Temp. = 240 deg, Final Temp. = 140 deg)
Temperature decrease rate: 2 ° C./min (Ramp rate = 2 deg / min, Cooling scan)
Distortion: 5%, automatic distortion mode (strain = 5%, autostrain)
150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´が2.0×108Paより大きくなると、粘度が上がり、第1ロール23と第2ロール24とでシート状の樹脂材料Rを挟んで加圧して、単位プリズム161を賦形する際に、樹脂材料R自体の弾性による、賦形された形状から戻ろうとする力によって型入れが不十分になり、賦形性が低下する。また、150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´が3.0×107Paより小さくなると、樹脂材料Rの流動性が高まり、第1ロール23と第2ロール24とでシート状の樹脂材料Rを挟んで加圧する際に、樹脂材料Rに加圧された力が緩和される圧力逃げが生じ、樹脂材料Rに版深方向への加圧力が十分伝わらず、賦形性が低下する。
When the storage elastic modulus G ′ at 150 ° C. is larger than 2.0 × 10 8 Pa, the viscosity increases, and the
なお、本実施形態では、PC樹脂のガラス転移点が約145℃であるため、樹脂材料Rの貯蔵弾性率G´は150℃のものとした。これは、上述のような押し出し成形を用いた製造方法によってプリズムシートを成形する際に、PC樹脂のガラス転移点(約145℃)よりやや高温となる温度(150℃)は、樹脂材料Rの流動性と硬化とが混在する状態であって、ロールによる加圧時の樹脂層(シート状の樹脂材料R)での圧力逃げ防止と版深への樹脂流動の両方の効果を期待できる温度領域であるからである。実際に、本実施形態では、第1ロール23と第2ロール24との間(バンク部)における樹脂材料Rの温度は、150℃程度となっている。
以上のことから、プリズムシート16を形成する樹脂材料は、上記条件を満たすことが好ましい。
In this embodiment, since the glass transition point of the PC resin is about 145 ° C., the storage elastic modulus G ′ of the resin material R is 150 ° C. This is because when the prism sheet is formed by the manufacturing method using extrusion molding as described above, the temperature (150 ° C.) slightly higher than the glass transition point (about 145 ° C.) of the PC resin is A temperature range in which fluidity and curing are mixed, and the effects of both prevention of pressure escape in the resin layer (sheet-like resin material R) when pressed by a roll and resin flow to the plate depth can be expected. Because. Actually, in the present embodiment, the temperature of the resin material R between the
From the above, the resin material forming the
ここで、重量平均分子量(Mw)や分子量1000以下の成分が占める割合が異なるPC樹脂を用意し、これらを用いてプリズムシートを成形した場合の賦形性や正面輝度に関して調べた。
用意されたPC樹脂は、それぞれ、重量平均分子量(Mw)や分子量1000以下の成分が占める割合、150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´が異なる以外は、本実施形態で用いるPC樹脂と同様であり、測定例のプリズムシートは、本実施形態のプリズムシートと同様の製造方法によって作製されており、略直角二等辺三角形形状の単位プリズムの配列ピッチPは、P=138μmである。
測定例1のプリズムシートは、重量平均分子量(Mw)が20000、分子量1000以下の成分が占める割合が2.0重量%、150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´が2.0×108PaであるPC樹脂により形成されており、これは、本実施形態のプリズムシート16に相当する。
測定例2のプリズムシートは、重量平均分子量(Mw)が22000、分子量1000以下の成分が占める割合が2.0重量%、150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´が3.0×108PaであるPC樹脂により形成されている。
測定例3のプリズムシートは、重量平均分子量(Mw)が20000、分子量1000以下の成分が占める割合が2.0重量%、150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´が8.0×106PaであるPC樹脂を材料としている。
Here, PC resins having different ratios of components having a weight average molecular weight (Mw) and a molecular weight of 1000 or less were prepared, and the shapeability and front luminance when a prism sheet was formed using these were examined.
The prepared PC resin is the same as the PC resin used in the present embodiment except that the weight average molecular weight (Mw), the proportion of components having a molecular weight of 1000 or less, and the storage elastic modulus G ′ at 150 ° C. are different. The prism sheet of the measurement example is manufactured by the same manufacturing method as the prism sheet of this embodiment, and the arrangement pitch P of the unit prisms having a substantially right isosceles triangle shape is P = 138 μm.
The prism sheet of Measurement Example 1 has a weight average molecular weight (Mw) of 20000, a ratio of components having a molecular weight of 1000 or less is 2.0% by weight, and a storage elastic modulus G ′ at 150 ° C. is 2.0 × 10 8 Pa. It is formed of a certain PC resin, and this corresponds to the
The prism sheet of Measurement Example 2 has a weight average molecular weight (Mw) of 22,000, a ratio of components having a molecular weight of 1000 or less is 2.0% by weight, and a storage elastic modulus G ′ at 150 ° C. is 3.0 × 10 8 Pa. It is made of a certain PC resin.
The prism sheet of Measurement Example 3 has a weight average molecular weight (Mw) of 20000, a proportion of components having a molecular weight of 1000 or less is 2.0% by weight, and a storage elastic modulus G ′ at 150 ° C. is 8.0 × 10 6 Pa. A certain PC resin is used as a material.
測定例4のプリズムシートは、重量平均分子量(Mw)が23000、分子量1000以下の成分が占める割合が2.0重量%、150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´が3.0×107PaであるPC樹脂により形成されている。
測定例5のプリズムシートは、重量平均分子量(Mw)が22000、分子量1000以下の成分が占める割合が1.0重量%、150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´が9.0×107PaであるPC樹脂により形成されている。
測定例6のプリズムシートは、重量平均分子量(Mw)が25000、分子量1000以下の成分が占める割合が2.0重量%、150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´が3.0×108PaであるPC樹脂により形成されている。
The prism sheet of Measurement Example 4 has a weight average molecular weight (Mw) of 23000, a ratio of components having a molecular weight of 1000 or less is 2.0% by weight, and a storage elastic modulus G ′ at 150 ° C. is 3.0 × 10 7 Pa. It is made of a certain PC resin.
The prism sheet of Measurement Example 5 has a weight average molecular weight (Mw) of 22,000, a ratio of components having a molecular weight of 1000 or less is 1.0% by weight, and a storage elastic modulus G ′ at 150 ° C. is 9.0 × 10 7 Pa. It is made of a certain PC resin.
The prism sheet of Measurement Example 6 has a weight average molecular weight (Mw) of 25,000, a ratio of components having a molecular weight of 1000 or less is 2.0% by weight, and a storage elastic modulus G ′ at 150 ° C. is 3.0 × 10 8 Pa. It is made of a certain PC resin.
測定例7のプリズムシートは、重量平均分子量(Mw)が20000、分子量1000以下の成分が占める割合が1.0重量%、150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´が2.0×107PaであるPC樹脂により形成されている。
測定例8のプリズムシートは、重量平均分子量(Mw)が25000、分子量1000以下の成分が占める割合が1.0重量%、150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´が2.0×108PaであるPC樹脂により形成されている。
測定例9のプリズムシートは、重量平均分子量(Mw)が25000、分子量1000以下の成分が占める割合が1.0重量%、150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´が3.0×108PaであるPC樹脂により形成されている。
The prism sheet of Measurement Example 7 has a weight average molecular weight (Mw) of 20000, a proportion of components having a molecular weight of 1000 or less is 1.0% by weight, and a storage elastic modulus G ′ at 150 ° C. is 2.0 × 10 7 Pa. It is made of a certain PC resin.
The prism sheet of Measurement Example 8 has a weight average molecular weight (Mw) of 25,000, a ratio of components having a molecular weight of 1000 or less is 1.0% by weight, and a storage elastic modulus G ′ at 150 ° C. is 2.0 × 10 8 Pa. It is made of a certain PC resin.
The prism sheet of Measurement Example 9 has a weight average molecular weight (Mw) of 25,000, a ratio of components having a molecular weight of 1000 or less is 1.0% by weight, and a storage elastic modulus G ′ at 150 ° C. is 3.0 × 10 8 Pa. It is made of a certain PC resin.
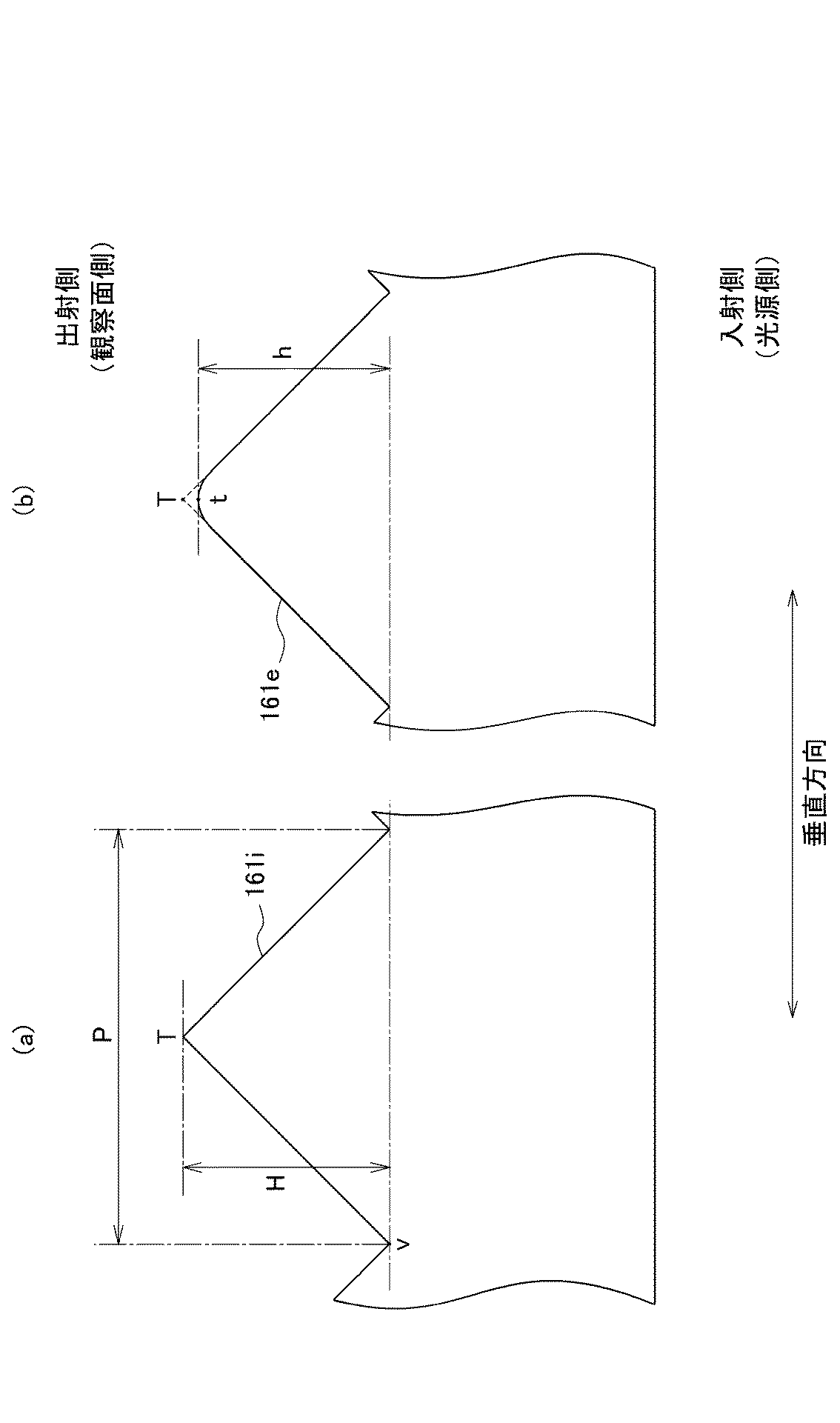
図4は、賦形率の測定方法を説明する図である。図4(a)は、理論上の単位プリズム161iの断面図であり、図4(b)は、任意の測定例の単位プリズム161eの断面図である。
樹脂材料Rに対する単位プリズム161の形状の賦形性は、賦形率によって評価する。
賦形率は、金型に樹脂が隙間無く充填された場合の理論上の単位プリズム161iの高さ(厚さ方向における理論上の頂点Tから谷底となる点vまでの寸法)Hに対して、実際形成された単位プリズム161eの高さ(厚さ方向における賦形された頂点tから谷底vまでの寸法)hが占める割合である。すなわち、賦形率A%は、A=(h/H)×100として示される。
FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating a method for measuring the shaping rate. 4A is a cross-sectional view of a
The formability of the shape of the
The shaping rate is relative to the height (the dimension from the theoretical vertex T to the valley bottom point v in the thickness direction) H of the
この賦形率は100%に近いほど好ましく、賦形率が高いほど単位プリズムによる集光効果が高く、面光源装置等にその光学シートを用いた場合に光の正面輝度が高くなる。これは、賦形率が上がることによって、単位プリズム161の出射側表面のうち平面部分(曲面である頂部以外の部分)が占める割合が大きくなることに起因する。これにより、頂部の曲面によって光源側に戻される等する光の量が低下するからである。なお、この測定では、理論上の単位プリズム161iの高さHは、69μmである。
賦形性に関する評価は、上述の方法により求めた賦形率92%以上を良好であるとし、賦形率が87%以上92%未満であるものを可とし、賦形率が87%未満であるものを不可であるとした。
The shaping rate is preferably closer to 100%, and the higher the shaping rate, the higher the light condensing effect by the unit prism, and the higher the front luminance of light when the optical sheet is used for a surface light source device or the like. This is because the proportion of the flat surface portion (portion other than the top portion that is a curved surface) of the exit side surface of the
The evaluation regarding the formability is good when the shaping rate obtained by the above-mentioned method is 92% or more, and the shaping rate is 87% or more and less than 92%, and the shaping rate is less than 87%. Some things were considered impossible.
また、これらの各測定例のプリズムシートを実際に本実施形態の透過型表示装置と略同様の透過型表示装置(観察面側から順に、LCDパネル11、第2拡散シート17,測定例のプリズムシート,第1拡散シート15,乳白板14,発光管13,反射板12という構成)に組みこんでその透過型表示装置の正面輝度を、輝度計(トプコン社製 BM−8)を用いて測定し、正面輝度を評価した。
正面輝度の評価方法は、紫外線成形によって単位プリズムの形状が賦形された不図示のプリズムシート(住友スリーエム株式会社製、BEF−III)の正面方向における輝度を基準(100%)とし、この基準に対する測定された正面輝度の比率(%)で評価した。測定された正面輝度が基準のプリズムシートの正面輝度に対して、102%以上であれば高輝度であり良好とし、97%以上、102%未満である場合には、使用可能であるとして可とし、97%未満である場合には、不可として評価した。
In addition, the prism sheet of each of these measurement examples is actually the same transmission type display device as the transmission type display device of this embodiment (in order from the observation surface side, the
The evaluation method of the front luminance is based on the luminance in the front direction of a prism sheet (not shown) (BEF-III, manufactured by Sumitomo 3M Ltd.) in which the shape of the unit prism is formed by ultraviolet molding, and this standard is used. It was evaluated by the ratio (%) of the measured front luminance with respect to. If the measured front brightness is 102% or more of the front brightness of the reference prism sheet, the brightness is high and good, and if it is 97% or more and less than 102%, it can be used. When it was less than 97%, it was evaluated as impossible.
表1は、各測定例のプリズムシートとその賦形性に関する検証結果を示している。
測定例1〜9のプリズムシートにおける単位プリズムの賦形性を検討すると、(条件1)〜(条件3)を全て満たす測定例1のプリズムシートは、賦形率が95%であり、良好な賦形率を有していた。
また、(条件1)〜(条件3)のいずれか2つを満たすが1つを満たしていない測定例2〜5のプリズムシートでは、賦形率がいずれも87%〜92%の範囲内であり、使用可能な範囲であった。
しかし、(条件1)〜(条件3)のいずれか1つを満たすが2つを満たしていない測定例6〜8のプリズムシート、及び(条件1)〜(条件3)を満たしていない測定例9のプリズムシートでは、いずれも賦形率が87%未満であり、低い賦形率を示した。
Table 1 shows the prism sheet of each measurement example and the verification result regarding its shaping property.
When the shaping property of the unit prism in the prism sheets of Measurement Examples 1 to 9 is examined, the prism sheet of Measurement Example 1 that satisfies all of (Condition 1) to (Condition 3) has a good shaping rate of 95%. It had a shaping rate.
Moreover, in the prism sheets of Measurement Examples 2 to 5 that satisfy any two of (Condition 1) to (Condition 3) but do not satisfy one, the shaping rate is within the range of 87% to 92%. There was a usable range.
However, the prism sheet of measurement examples 6 to 8 that satisfies any one of (condition 1) to (condition 3) but does not satisfy two, and the measurement example that does not satisfy (condition 1) to (condition 3) In all 9 prism sheets, the forming rate was less than 87%, indicating a low forming rate.
また、表1の結果から、各条件と賦形率との関係を調べた。
測定例1〜3のプリズムシートは、いずれも(条件1)及び(条件2)を満たしている。しかし、(条件3)の150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´に関しては、測定例1のプリズムシートのみが(条件3)を満たし、測定例2のプリズムシートは(条件3)に規定する範囲よりも大きく、測定例3のプリズムシートは(条件3)に規定する範囲よりも小さく、(条件3)を満たしていない。
その結果、表1に示すように、賦形率は、(条件3)を満たす測定例1のプリズムシートが良好であったが、(条件3)を満たさない測定例2,3のプリズムシートは、測定例1に比べて賦形率は低下していた。
Further, from the results in Table 1, the relationship between each condition and the shaping rate was examined.
The prism sheets of Measurement Examples 1 to 3 all satisfy (Condition 1) and (Condition 2). However, regarding the storage elastic modulus G ′ at 150 ° C. of (Condition 3), only the prism sheet of Measurement Example 1 satisfies (Condition 3), and the prism sheet of Measurement Example 2 is within the range specified in (Condition 3). The prism sheet of Measurement Example 3 is smaller than the range defined in (Condition 3) and does not satisfy (Condition 3).
As a result, as shown in Table 1, the shaping rate was good for the prism sheet of Measurement Example 1 that satisfies (Condition 3), but the prism sheets of Measurement Examples 2 and 3 that did not satisfy (Condition 3) Compared to measurement example 1, the shaping rate was reduced.
また、測定例1,4のプリズムシートは、いずれも(条件2)及び(条件3)を満たしている。しかし、(条件1)の重量平均分子量(Mw)に関しては、測定例1のプリズムシートは(条件1)を満たしているが、測定例4のプリズムシートは(条件1)を満たしていない。
その結果、表1に示すように、(条件1)を満たさない測定例4のプリズムシートの賦形率は、(条件1)を満たす測定例1のプリズムシートと比べて低下していた。
The prism sheets of Measurement Examples 1 and 4 both satisfy (Condition 2) and (Condition 3). However, regarding the weight average molecular weight (Mw) of (Condition 1), the prism sheet of Measurement Example 1 satisfies (Condition 1), but the prism sheet of Measurement Example 4 does not satisfy (Condition 1).
As a result, as shown in Table 1, the shaping rate of the prism sheet of Measurement Example 4 that does not satisfy (Condition 1) was lower than that of the prism sheet of Measurement Example 1 that satisfies (Condition 1).
さらに、測定例1,5のプリズムシートは、いずれも(条件1)及び(条件3)を満たしている。しかし、(条件2)の分子量1000以下の成分(化合物)が占める割合に関しては、測定例1のプリズムシートは(条件2)を満たしているが、測定例5のプリズムシートは(条件2)を満たしていない。
その結果、表1に示すように、(条件2)を満たさない測定例5のプリズムシートの賦形率は、(条件2)を満たす測定例1のプリズムシートと比べて低下していた。
以上のことから、高い賦形率を実現するためには、(条件1)〜(条件3)を全て満たすことが必要である。
Further, the prism sheets of Measurement Examples 1 and 5 both satisfy (Condition 1) and (Condition 3). However, regarding the ratio of the component (compound) having a molecular weight of 1000 or less in (Condition 2), the prism sheet of Measurement Example 1 satisfies (Condition 2), but the prism sheet of Measurement Example 5 satisfies (Condition 2). not filled.
As a result, as shown in Table 1, the shaping rate of the prism sheet of Measurement Example 5 that does not satisfy (Condition 2) was lower than that of the prism sheet of Measurement Example 1 that satisfies (Condition 2).
From the above, in order to realize a high shaping rate, it is necessary to satisfy all of (Condition 1) to (Condition 3).
次に、正面輝度に関して、(条件1)〜(条件3)を満たす測定例1のプリズムシート(本実施形態のプリズムシート16に相当)を用いたものが最も正面輝度が高く、良好であった。次いで、(条件1)〜(条件3)のうちいずれか2つを満たす測定例2〜5のプリズムシートを用いたものが高く、面光源装置の集光性に寄与する光学シートとして使用可能な範囲内であった。(条件1)〜(条件3)のうちいずれか1つを満たす、又は、いずれも満たさない測定例6〜9のプリズムシートでは、使用に適さないほど正面輝度が低下しており、不可であった。
従って、正面輝度の向上には、単位プリズム161の賦形率が大きく寄与しており、上述の(条件1)〜(条件3)を満たすことが好ましい。
Next, regarding the front luminance, the one using the prism sheet of Measurement Example 1 (corresponding to the
Therefore, the shaping ratio of the
ここで、さらに、本実施形態のプリズムシート16と同様のPC樹脂(すなわち、本実施形態のプリズムシート16重量平均分子量(Mw)、分子量100以下の成分の占める割合、150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´が同じPC樹脂)を用いて、断面形状が略直角二等辺三角形形状であり、本実施形態のプリズムシート16とは配列ピッチPが異なる不図示の測定例10,11のプリズムシートを本実施形態と同様の製造方法により製造し、その単位プリズムの賦形性や正面輝度に関して、前述の方法により評価した。
Here, further, the same PC resin as the
表2は、測定例10,11のプリズムシート及び測定例1のプリズムシート(本実施形態のプリズムシート16に相当)の賦形性及び正面輝度の評価を示す表である。
測定例10のプリズムシートは、単位プリズムの配列ピッチPが93μmであり、理論上のレンズ高さHが46.5μmである。この測定例10のプリズムシートは、実際に形成された単位プリズムのレンズ高さhが約44μmであり、その単位プリズムの賦形率が約95%であり、賦形性が良好であった。
測定例1のプリズムシートは、単位プリズムの配列ピッチPが138μmであり、理論上のレンズ高さHが69μmである。この測定例10のプリズムシートは、実際に形成された単位プリズムのレンズ高さhが65.5μmであり、その単位プリズムの賦形率が約95%であり、賦形性が良好であった。
測定例11のプリズムシートは、単位プリズムの配列ピッチPが148μmであり、理論上のレンズ高さHが74μmである。この測定例11のプリズムシートは、実際に形成された単位プリズムのレンズ高さhが約70μmであり、その単位プリズムの賦形率が約95%であり、賦形性が良好であった。
測定例1,10,11のプリズムシートを、本実施形態と同様の透過型表示装置に用いてその正面輝度を測定したところ、いずれも高輝度であり、良好であった。
Table 2 is a table showing the evaluation of the formability and front luminance of the prism sheets of Measurement Examples 10 and 11 and the prism sheet of Measurement Example 1 (corresponding to the
In the prism sheet of Measurement Example 10, the arrangement pitch P of unit prisms is 93 μm, and the theoretical lens height H is 46.5 μm. In the prism sheet of Measurement Example 10, the lens height h of the actually formed unit prism was about 44 μm, the forming rate of the unit prism was about 95%, and the forming property was good.
The prism sheet of Measurement Example 1 has a unit prism arrangement pitch P of 138 μm and a theoretical lens height H of 69 μm. In the prism sheet of Measurement Example 10, the lens height h of the actually formed unit prism was 65.5 μm, the forming rate of the unit prism was about 95%, and the forming property was good. .
In the prism sheet of measurement example 11, the unit prism arrangement pitch P is 148 μm, and the theoretical lens height H is 74 μm. In the prism sheet of Measurement Example 11, the lens height h of the actually formed unit prism was about 70 μm, the forming rate of the unit prism was about 95%, and the forming property was good.
When the front luminance was measured using the prism sheets of Measurement Examples 1, 10, and 11 in the same transmissive display device as in this embodiment, all were high and good.
従って、重量平均分子量(Mw)が、18000〜22000であり(条件1)、PC樹脂全体の重量に対して、PC樹脂に含まれる分子量1000以下の成分が占める割合が、2.0〜4.0重量%であり(条件2)、150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´が、3.0×107〜2.0×108Paである(条件3)という条件を満たすPC樹脂を用いることにより、従来の押し出し成形では製造が困難な配列ピッチ150μm以下の単位プリズムであっても、高い賦形率で形成することができ、高い正面輝度を実現できる。 Therefore, the weight average molecular weight (Mw) is 18000 to 22000 (Condition 1), and the ratio of the component having a molecular weight of 1000 or less contained in the PC resin to the weight of the entire PC resin is 2.0 to 4. Use a PC resin that satisfies the condition of 0% by weight (condition 2) and a storage elastic modulus G ′ at 150 ° C. of 3.0 × 10 7 to 2.0 × 10 8 Pa (condition 3). Therefore, even unit prisms having an arrangement pitch of 150 μm or less, which are difficult to manufacture by conventional extrusion molding, can be formed with a high shaping rate, and high front luminance can be realized.
本実施形態のプリズムシート16は、重量平均分子量が20000であり、分子量1000以下の成分の含有率が2.0重量%であり、150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´が2.0×108PaであるPC樹脂を材料とするので、(条件1)〜(条件3)を全て満たしている。本実施形態のプリズムシート16は、上記条件を満たしていることから、その単位プリズム161の賦形率は、95%であり、賦形性の高い単位プリズム161を有している。また、本実施形態のプリズムシート16を形成するPC樹脂の分子量分布は、2.6であり、分子量分布の好ましい範囲も満たしている。
従って、本実施形態によれば、面光源装置等に用いられる光学シートとして適当な靭性を有し、かつ、賦形性が高く、集光作用等の光学性能が良好なプリズムシートとすることができ、正面輝度の高い面光源装置及び透過型表示装置とすることができる。
また、プリズムシート16の材料であるPC樹脂は、熱可塑性樹脂であり、上述の(条件1)〜(条件3)を満たすので、一般的な押出成形機によって高い賦形率を有するプリズム形状を賦形することができる。従って、新たに大規模な設備投資等を行うことなく、正面輝度等の光学特性の優れたプリズムシートを安価に作製することができる。
The
Therefore, according to the present embodiment, a prism sheet having an appropriate toughness as an optical sheet used in a surface light source device and the like, a high formability, and a good optical performance such as a light collecting function can be obtained. In addition, a surface light source device and a transmissive display device with high front luminance can be obtained.
Further, the PC resin that is the material of the
さらに、一般的な押し出し成形では、本実施形態の単位プリズム161等のような単位光学形状は、高い賦形率を確保するためには、150〜200μm程度の配列ピッチが最小であった。しかし、プリズムシート16の材料であるPC樹脂は、上述の(条件1)〜(条件3)を満たすので、単位プリズム161の配列ピッチPを本実施形態のように138μmとしたり、例えば、測定例10のプリズムシートのように、より小さい90μm程度としたりする等、従来の配列ピッチと比べて小さくした場合であっても、高い賦形率を維持することができる。従って、単位プリズム161の配列ピッチPを従来のものに比べて小さくできるので、同じ総厚で、よりピッチが大きなプリズムシートに比べて、入射面162から谷底vまでの厚さを大きくすることができ、製品として十分な剛性を有し、製造中や搬送中での扱いも容易であり、自重等による撓みも低減できる。
また、ピッチPを小さくできるので、プリズムシート16の表裏面での表面積差が小さくなり、面光源装置等に組み込んだ場合に、発光管13からの熱によって表裏面での吸水量の差等による撓みや反り等を防止することができる。従って、正面輝度が高く、高精細であって、十分な剛性有し、温度や湿度の差によって撓みにくい光学シートとすることができる。
Further, in general extrusion molding, the unit optical shape such as the
Further, since the pitch P can be reduced, the surface area difference between the front and back surfaces of the
(変形形態)
以上説明した実施形態に限定されることなく、種々の変形や変更が可能であって、それらも本発明の範囲内である。
(1)本実施形態では、単位光学形状は、シート面の法線方向に平行であり、配列方向に平行な断面形状が、頂角90°である略二等辺三角形形状である単位プリズム161である例を示したが、これに限らず、例えば、他の略三角形形状や、略半球形状、略楕円形形状の一部形状であってもよい。例えば、単位光学形状の断面形状が略楕円形形状の一部形状である場合には、単位光学形状は、光の集光作用に加えて光拡散作用も有するので、面光源装置の発光管等の光源の位置に起因した光源ムラ等の輝度ムラを解消することができる。なお、単位光学形状の断面形状を略楕円形形状の一部とする場合には、長軸がシート面に直交する楕円形形状の一部とすることが、光拡散性と高い集光性とを両立する観点から好ましい。
また、本実施形態では、単位プリズム161は、シート面に沿って垂直方向に配列される例を示したが、これに限らず、例えば、水平方向に配列してもよい。
さらに、本実施形態では、単位プリズム161は、長手方向を水平方向とする略三角柱形状であり、シート面に沿って一次元方向に配列される例を示したが、これに限らず、例えば、略半球形状や略四角錐形状とし、シート面に沿って二方向(例えば、垂直方向及び水平方向)に配列してもよい。
(Deformation)
The present invention is not limited to the embodiment described above, and various modifications and changes are possible, and these are also within the scope of the present invention.
(1) In the present embodiment, the unit optical shape is a
In the present embodiment, the
Furthermore, in the present embodiment, the
(2)本実施形態では、プリズムシート16は、単層である例を示したが、これに限らず、例えば、多層押出成形等による2層以上の多層形状としてもよい。ただし、賦形性を高める観点から、単位プリズム161が形成される側の表面となる層は、(条件1)〜(条件3)を満たすPC樹脂とすることが好ましい。
(2) In the present embodiment, the
(3)本実施形態では、プリズムシート16は、拡散材等を含有していない例を示したが、これに限らず、例えば、樹脂材料(PC樹脂)にスチレンビーズ等の拡散材を混錬したものを用いてもよい。また、例えば、拡散材を含有する樹脂材料と拡散材を有しない樹脂材料とを用いて2層押し出し成形等により形成してもよい。
(3) In the present embodiment, the
(4)本実施形態では、プリズムシート16は、面光源装置に用いられる例を示したが、これに限らず、例えば、透過型スクリーン等に使用してもよい。
(4) In the present embodiment, the
(5)本実施形態では、面光源装置の光源部を構成する発光源として、線光源である発光管を用いる例を示したが、これに限らず、例えば、LED(Light Emitting Diode)等の点光源を用いてもよいし、有機EL(Electro Luminescence)や無機ELのような面光源を用いてもよい。 (5) In the present embodiment, an example in which an arc tube that is a linear light source is used as the light source constituting the light source unit of the surface light source device is shown. However, the present invention is not limited thereto, and for example, an LED (Light Emitting Diode) or the like. A point light source may be used, or a surface light source such as an organic EL (Electro Luminescence) or an inorganic EL may be used.
なお、本実施形態及び変形形態は、適宜組み合わせて用いることもできるが、詳細な説明は省略する。また、本発明は以上説明した実施形態によって限定されることはない。 In addition, although this embodiment and modification can also be used in combination as appropriate, detailed description is abbreviate | omitted. Further, the present invention is not limited to the embodiment described above.
10 透過型表示装置
11 LCDパネル
12 反射板
13 発光管
14 乳白板
15 第1拡散シート
16 プリズムシート
161 単位プリズム
17 第2拡散シート
20 光学シートの製造装置
21 押出機
22 ダイ
23 第1ロール
24 第2ロール
25 第3ロール
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (6)
少なくとも前記光学形状部は、ポリカーボネート樹脂により形成され、
前記ポリカーボネート樹脂は、
その重量平均分子量が18000〜22000であり、
前記ポリカーボネート樹脂に含有される分子量1000以下の成分が前記ポリカーボネート樹脂全体の重量に対して占める割合が2.0〜4.0重量%であり、
150℃での貯蔵弾性率G´が3.0×107〜2.0×108Paであること、
を特徴とする光学シート。 An optical sheet having an optical shape portion in which a plurality of unit optical shapes are arranged on at least one surface,
At least the optical shape portion is formed of a polycarbonate resin,
The polycarbonate resin is
Its weight average molecular weight is 18000-22000,
The proportion of the component having a molecular weight of 1000 or less contained in the polycarbonate resin is 2.0 to 4.0% by weight with respect to the total weight of the polycarbonate resin,
The storage elastic modulus G ′ at 150 ° C. is 3.0 × 10 7 to 2.0 × 10 8 Pa,
An optical sheet characterized by
前記単位光学形状は、凸形状であり、シート面に沿って一次元方向に規則的に複数配列されていること、
を特徴とする光学シート。 The optical sheet according to claim 1,
The unit optical shape is a convex shape, and a plurality of unit optical shapes are regularly arranged in a one-dimensional direction along the sheet surface,
An optical sheet characterized by
前記単位光学形状は、その配列方向に平行であって厚み方向に平行な断面での断面形状が略三角形形状であること、
を特徴とする光学シート。 The optical sheet according to claim 2,
The unit optical shape is substantially triangular in cross section in a cross section parallel to the arrangement direction and parallel to the thickness direction,
An optical sheet characterized by
前記光学シートに光を照射する光源部と、
を備える面光源装置。 The optical sheet according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
A light source unit that emits light to the optical sheet;
A surface light source device comprising:
前記面光源装置によって背面から照明される透過型表示部と、
を備える透過型表示装置。 A surface light source device according to claim 4,
A transmissive display unit illuminated from the back by the surface light source device;
A transmissive display device.
前記ポリカーボネート樹脂をシート状に押し出し成形し、
少なくとも一方が前記単位光学形状を賦形する金型となる成形ロールである一対のロールの間隙を加圧しながら通過させることにより、前記単位光学形状を賦形すること、
を特徴とする光学シートの製造方法。 In the manufacturing method of the optical sheet which manufactures the optical sheet of any one of Claim 1- Claim 3,
Extruding the polycarbonate resin into a sheet,
Shaping the unit optical shape by passing through a gap between a pair of rolls, which is a molding roll that is a mold for shaping the unit optical shape,
An optical sheet manufacturing method characterized by the above.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009261288A JP2011107343A (en) | 2009-11-16 | 2009-11-16 | Optical sheet, surface light source device, transmission type display device and method of manufacturing the optical sheet |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009261288A JP2011107343A (en) | 2009-11-16 | 2009-11-16 | Optical sheet, surface light source device, transmission type display device and method of manufacturing the optical sheet |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2011107343A true JP2011107343A (en) | 2011-06-02 |
Family
ID=44230890
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009261288A Pending JP2011107343A (en) | 2009-11-16 | 2009-11-16 | Optical sheet, surface light source device, transmission type display device and method of manufacturing the optical sheet |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2011107343A (en) |
-
2009
- 2009-11-16 JP JP2009261288A patent/JP2011107343A/en active Pending
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR100977321B1 (en) | Light transmissive resin plate | |
| CN102033253B (en) | Optical unit and backlight unit using the same | |
| KR100894778B1 (en) | Liquid crystal display, method for producing optical sheet and optical sheet | |
| KR101441714B1 (en) | Polymer film | |
| JPWO2009028439A1 (en) | Prism sheet, backlight unit using the same, and liquid crystal display device | |
| JP5330457B2 (en) | Surface light source device and liquid crystal display device | |
| KR102472940B1 (en) | Light diffusion plate and backlight unit | |
| KR20060129051A (en) | Light diffusing screen | |
| JP2010211027A (en) | Moire fringe suppression film and prism sheet with moire fringe suppression function | |
| JP2009075266A (en) | Optical sheet | |
| JP2012234117A (en) | Prism sheet, surface light source device, and liquid crystal display | |
| JP5957865B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of molding sheet, manufacturing method of resin-coated molding sheet, and manufacturing method of optical sheet | |
| JP2011123131A (en) | Optical sheet, surface light source apparatus, transmission-type display apparatus and method for manufacturing the optical sheet | |
| JP2011033643A (en) | Optical path changing sheet, backlight unit and display device | |
| JP2012069355A (en) | Optical sheet, plane light source device, and transmission type display device | |
| JP2011107343A (en) | Optical sheet, surface light source device, transmission type display device and method of manufacturing the optical sheet | |
| JP2006292857A (en) | Scratch resistant lens film and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP2014093193A (en) | Light guide plate, backlight unit including light guide plate and display device | |
| JP5757378B2 (en) | Optical sheet, optical member, surface light source device, transmissive display device, and light emitting device | |
| JP2011090104A (en) | Optical sheet, surface light source device, and transmission type display device | |
| JP4730339B2 (en) | Surface light source device, transmissive display device | |
| JP5621321B2 (en) | Optical sheet, surface light source device, display device | |
| JP2011206934A (en) | Roll die for processing plastic sheet including optical function, method of manufacturing optical sheet using the roll die, the optical sheet obtained in the manufacturing method, backlight unit for liquid crystal display device using the optical sheet and the liquid crystal display device | |
| JP2011064744A (en) | Optical sheet, backlight unit, and display device | |
| JP5097153B2 (en) | Diffusion sheet |