JP2011069811A - Rotation angle sensor - Google Patents
Rotation angle sensor Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2011069811A JP2011069811A JP2010156427A JP2010156427A JP2011069811A JP 2011069811 A JP2011069811 A JP 2011069811A JP 2010156427 A JP2010156427 A JP 2010156427A JP 2010156427 A JP2010156427 A JP 2010156427A JP 2011069811 A JP2011069811 A JP 2011069811A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- coil
- output
- rotation angle
- magnetic pole
- angle sensor
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01D—MEASURING NOT SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR A SPECIFIC VARIABLE; ARRANGEMENTS FOR MEASURING TWO OR MORE VARIABLES NOT COVERED IN A SINGLE OTHER SUBCLASS; TARIFF METERING APPARATUS; MEASURING OR TESTING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G01D5/00—Mechanical means for transferring the output of a sensing member; Means for converting the output of a sensing member to another variable where the form or nature of the sensing member does not constrain the means for converting; Transducers not specially adapted for a specific variable
- G01D5/12—Mechanical means for transferring the output of a sensing member; Means for converting the output of a sensing member to another variable where the form or nature of the sensing member does not constrain the means for converting; Transducers not specially adapted for a specific variable using electric or magnetic means
- G01D5/14—Mechanical means for transferring the output of a sensing member; Means for converting the output of a sensing member to another variable where the form or nature of the sensing member does not constrain the means for converting; Transducers not specially adapted for a specific variable using electric or magnetic means influencing the magnitude of a current or voltage
- G01D5/20—Mechanical means for transferring the output of a sensing member; Means for converting the output of a sensing member to another variable where the form or nature of the sensing member does not constrain the means for converting; Transducers not specially adapted for a specific variable using electric or magnetic means influencing the magnitude of a current or voltage by varying inductance, e.g. by a movable armature
- G01D5/204—Mechanical means for transferring the output of a sensing member; Means for converting the output of a sensing member to another variable where the form or nature of the sensing member does not constrain the means for converting; Transducers not specially adapted for a specific variable using electric or magnetic means influencing the magnitude of a current or voltage by varying inductance, e.g. by a movable armature by influencing the mutual induction between two or more coils
- G01D5/2046—Mechanical means for transferring the output of a sensing member; Means for converting the output of a sensing member to another variable where the form or nature of the sensing member does not constrain the means for converting; Transducers not specially adapted for a specific variable using electric or magnetic means influencing the magnitude of a current or voltage by varying inductance, e.g. by a movable armature by influencing the mutual induction between two or more coils by a movable ferromagnetic element, e.g. a core
Abstract
Description
本発明は回転角度センサに関する。 The present invention relates to a rotation angle sensor.
磁性体ロータの外周を囲むように内側向きに3種類の巻き線が重ね巻きされた複数個のコイルを有するセンサを配置し、ロータ回転によるローターコイル間ギャップの変化をSIN状の電圧出力に変換するセンサにおいて、固定子に巻くコイル巻き数をSIN分布上に配するとともに、機械巻きを可能にした技術が開示されている(例えば、特許文献1参照。)。 A sensor having a plurality of coils in which three types of windings are wound inward so as to surround the outer periphery of the magnetic rotor is arranged, and the change in the gap between the rotor coils due to the rotation of the rotor is converted into a SIN voltage output. In this sensor, a technique is disclosed in which the number of coil turns wound around the stator is arranged on the SIN distribution and mechanical winding is enabled (for example, see Patent Document 1).
また、特許文献1に対し、出力コイルの巻き数を同じにすることにより、巻線工程を単純化した技術が開示されている(例えば、特許文献2参照。)。 Further, a technique is disclosed in which the winding process is simplified by making the number of turns of the output coil the same as in Patent Document 1 (see, for example, Patent Document 2).
しかしながら、従来技術の特許文献1と特許文献2では、1枚の電磁鋼板からプレスにより成形した固定子を複数枚重ねることにより、磁極ユニットを含む固定子を成形するため、ロータを配置する内周部の電磁鋼板は使用されず、歩留まりが低い問題があった。また、固定子の内周に位置する複数の突起に対し、それぞれコイルを巻かなければならないため、特殊な巻線機が必要になると同時に、複雑な巻線工程が必要なため、タクトタイムが長くなる問題があった。また、ロータの外側にある固定子が磁気的に結合するため、隣り合うコイル同士による磁場干渉が発生し、出力に誤差が生じる問題があった。
However, in
本発明は、上記問題に鑑みてなされたものであり電磁鋼板の歩留まりが高く、タクトタイムの短縮が可能で、磁場干渉を低減した回転角度センサを提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above problems, and an object of the present invention is to provide a rotation angle sensor in which the yield of electromagnetic steel sheets is high, tact time can be shortened, and magnetic field interference is reduced.
上述の課題を解決するために講じた第一の課題解決手段は、N個の突極又はNサイクルの正弦波状ギャップパーミアンスを有し、磁性体で構成されるロータと、励磁コイルとCOS出力を得る第一出力コイルおよびSIN出力を得る第二出力コイルの少なくともいずれか一方とを直接的または間接的にヨークに巻き付け、前記ロータの周囲に複数個配置される磁極ユニットと、を備える回転角度センサであって、前記磁極ユニットは、独立した閉磁路を形成していることである。 The first problem-solving means taken in order to solve the above-mentioned problems is that there are N salient poles or N cycles of sinusoidal gap permeance, a rotor made of a magnetic material, an excitation coil, and a COS output. A rotation angle sensor comprising: a first output coil to be obtained and at least one of a second output coil to obtain a SIN output directly or indirectly wound around a yoke, and a plurality of magnetic pole units arranged around the rotor The magnetic pole unit forms an independent closed magnetic circuit.
第二の課題解決手段は、N個の突極又はNサイクルの正弦波状ギャップパーミアンスを有し、磁性体で構成されるロータと、励磁コイルとCOS出力を得る第一出力コイルおよびSIN出力を得る第二出力コイルの少なくともいずれか一方とを直接的または間接的にヨークに巻き付け、前記ロータの周囲に複数個配置される磁極ユニットと、を備える回転角度センサであって、前記磁極ユニットは、非磁性体に固定されることである。 The second problem solving means has N salient poles or N cycles of sinusoidal gap permeance, obtains a rotor made of a magnetic material, an excitation coil, a first output coil for obtaining COS output, and a SIN output. A rotation angle sensor including a plurality of magnetic pole units that are wound around the yoke directly or indirectly around at least one of the second output coils, and the magnetic pole unit is a non-rotating sensor. It is fixed to a magnetic body.
また、第三の課題解決手段は、前記ヨークは、U字型形状を呈することである。 A third problem solving means is that the yoke has a U-shape.
また、第四の課題解決手段は、前記磁極ユニットは、前記ヨークのU字型形状の開口部が前記ロータと対向するように配置されることである。 A fourth problem solving means is that the magnetic pole unit is arranged so that the U-shaped opening of the yoke faces the rotor.
また、第五の課題解決手段は、前記励磁コイルと前記第一出力コイルと前記第二出力コイルとは、前記ヨークのU字型形状の屈曲部に巻き付けられることである。 A fifth problem solving means is that the exciting coil, the first output coil, and the second output coil are wound around a U-shaped bent portion of the yoke.
また、第六の課題解決手段は、前記第一出力コイルおよび前記第二出力コイルの巻き数とが同数であることである。 The sixth problem solving means is that the number of turns of the first output coil and the second output coil is the same.
また、第七の課題解決手段は、前記磁極ユニットは、前記ロータの回転軸から一定の距離に配置されることである。 A seventh problem solving means is that the magnetic pole unit is arranged at a constant distance from the rotation axis of the rotor.
また、第八の課題解決手段は、前記ロータは、巻き線を持たない構成であり、前記磁極ユニットは、(N×Y)個配置されることである。 The eighth problem-solving means is that the rotor does not have a winding, and (N × Y) magnetic pole units are arranged.
本発明によれば、本発明の回転角度センサは複数の個別の磁極ユニットから構成されているため、この磁極ユニットを構成するヨークが構成される電磁鋼板の歩留まりを高めることができる。また、磁極ユニットが独立することで、各磁極ユニットが独立した閉磁路を形成し、隣り合う磁極ユニットへの磁場干渉が低減して、回転角度の検出精度が向上する。 According to the present invention, since the rotation angle sensor of the present invention is composed of a plurality of individual magnetic pole units, it is possible to increase the yield of the electrical steel sheet that constitutes the yoke that constitutes the magnetic pole unit. In addition, since the magnetic pole units are independent, each magnetic pole unit forms an independent closed magnetic path, magnetic field interference to adjacent magnetic pole units is reduced, and the rotation angle detection accuracy is improved.
また、複数の磁極ユニットを独立して設けることで、ヨークを構成する電磁鋼板の歩留まりを高めることができる。そして、磁極ユニットは、非磁性体に固定されるため、各磁極ユニットが独立した閉磁路を形成し、隣り合う磁極ユニットへの磁場干渉が低減して、回転角度の検出精度が向上する。 Moreover, the yield of the electromagnetic steel plate which comprises a yoke can be improved by providing several magnetic pole unit independently. Since the magnetic pole unit is fixed to the non-magnetic material, each magnetic pole unit forms an independent closed magnetic path, magnetic field interference to the adjacent magnetic pole unit is reduced, and the rotation angle detection accuracy is improved.
また、ヨークはU字型形状を呈するため、特殊な巻き線機を用いず、ヨークを回転して、励磁コイルと出力コイルを巻き取ることができる。また、巻線時のコイル線の供給テンションと軸方向の送りピッチを正確にでき、コイル占積率が安定する整列巻きが可能になる。そのため、コイル占積率のばらつきに起因する出力変動が低減し、回転角度の検出精度が向上する。 Further, since the yoke has a U-shape, the exciting coil and the output coil can be wound up by rotating the yoke without using a special winding machine. In addition, the coil wire supply tension and the feed pitch in the axial direction can be accurately set during winding, and aligned winding with stable coil space factor is possible. As a result, output fluctuations due to variations in the coil space factor are reduced, and the rotation angle detection accuracy is improved.
また、磁極ユニットは、ヨークのU字型形状の開口部がロータと対向するように配置されるため、U字型形状のヨークの両端部とロータとの間のギャップが変化して、第一出力コイルと第二出力コイルに発生するCOS波形とSIN波形の2出力を比較することで、ロータの角度の検出が可能になる。 Further, since the magnetic pole unit is disposed so that the U-shaped opening of the yoke faces the rotor, the gap between the both ends of the U-shaped yoke and the rotor changes, and the first The rotor angle can be detected by comparing the two outputs of the COS waveform and the SIN waveform generated in the output coil and the second output coil.
また、励磁コイルと第一出力コイルと第二出力コイルとは、ヨークのU字型形状の屈曲部に巻き付けられるため、特殊な巻き線機を用いず、ヨークを回転して、励磁コイルと第一出力コイルと第二出力コイルとを巻き取ることができる。また、巻線時のコイル線の供給テンションと軸方向の送りピッチを正確にでき、コイル占積率が安定する整列巻きが可能になる。そのため、回転角度センサの駆動時にコイルから発生するインピーダンスが低減して、出力が向上する。 Further, since the exciting coil, the first output coil, and the second output coil are wound around the U-shaped bent portion of the yoke, the yoke is rotated without using a special winding machine. One output coil and the second output coil can be wound up. In addition, the coil wire supply tension and the feed pitch in the axial direction can be accurately set during winding, and aligned winding with stable coil space factor is possible. Therefore, the impedance generated from the coil when the rotation angle sensor is driven is reduced, and the output is improved.
また、第一出力コイルおよび第二出力コイルの巻き数とが同数であるため、第一出力コイルが巻かれるヨークと第二出力コイルが巻かれるヨークとに対し同時に出力コイルを巻くことが可能で、タクトタイムが低減する。 In addition, since the number of turns of the first output coil and the second output coil is the same, it is possible to simultaneously wind the output coil around the yoke around which the first output coil is wound and the yoke around which the second output coil is wound. , Tact time is reduced.
また、ロータの回転軸から一定の距離に独立した磁極ユニットを複数個配置するため、電磁鋼板の歩留まりを高めることができる。また、磁極ユニットが独立することで、各磁極ユニットが独立した閉磁路を形成し、隣り合う磁極ユニットへの磁場干渉が低減して、回転角度の検出精度が向上する。 In addition, since a plurality of independent magnetic pole units are arranged at a certain distance from the rotation axis of the rotor, the yield of electromagnetic steel sheets can be increased. In addition, since the magnetic pole units are independent, each magnetic pole unit forms an independent closed magnetic path, magnetic field interference to adjacent magnetic pole units is reduced, and the rotation angle detection accuracy is improved.
また、前記ロータは、巻き線を持たない構成であり、前記磁極ユニットは、(N×Y)個配置されることで、電磁鋼板の歩留まりを高めることができる。また、磁極ユニットが独立することで、各磁極ユニットが独立した閉磁路を形成し、隣り合う磁極ユニットへの磁場干渉が低減して、回転角度の検出精度が向上する。 In addition, the rotor has no winding, and (N × Y) magnetic pole units are arranged to increase the yield of the electromagnetic steel sheet. In addition, since the magnetic pole units are independent, each magnetic pole unit forms an independent closed magnetic path, magnetic field interference to adjacent magnetic pole units is reduced, and the rotation angle detection accuracy is improved.
以下、本実施の形態について図面を参照しつつ詳細に説明する。 Hereinafter, the present embodiment will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
図1は、本発明における回転角度センサ1の構成図である。本実施例にかかる回転角度センサ1は、N個の突極又は、Nサイクルの正弦波状ギャップパーミアンスを有し、磁性体で構成される楕円形状のロータ10と、励磁コイル23とCOS出力を得る第一出力コイル24aまたはSIN出力を得る第二出力コイル24bの少なくともいずれか一方のコイル22とをヨーク21に巻き付け、ロータ10の回転軸から一定の距離に(N×Y)個(Yは4以上の整数)配置される磁極ユニット20とを備えている。すなわち、磁極ユニット20はロータ10の周囲(ロータ10の外周外側)に配置されている。
FIG. 1 is a configuration diagram of a
本実施例では、N=2、Y=4としたため、配置する磁極ユニット20の数は8個となるが、NとYの数を変えることで、ロータ10の形状と磁極ユニット20の数を変えて設計することが可能である。また、Yの値が増加すれば磁極ユニットの数が増加するため、出力精度も向上する。また、ヨーク21に対し、巻き線を直接的に巻く場合でも、ヨーク21を樹脂材によるボビンで被ってボビンの外周に間接的に巻き線を巻く場合でも同様の効果が得られる。また、ヨーク21と励磁コイル23に対し、第一出力コイル24aと第二出力コイル24bとを両方巻回した場合、第一出力コイル24aのみを巻回した場合、第二出力コイル24bのみを巻回した場合でも同様の効果を得ることが可能である。なお、複数の磁極ユニット20は、ロータ10の円周外側であって、ロータ10の回転軸から一定の距離に着脱可能に配置されてもよいし、それぞれが固定した状態で配置されてもよい。また、止め具25の固定方法としては、穴部を用いてネジやナットを用いて固定する方法、固定する部材に止め具25をはめ込み固定する方法などが、用いられる。
In this embodiment, since N = 2 and Y = 4, the number of
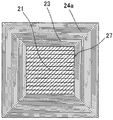
図2は、本発明における磁極ユニット20の構成図である。本発明で用いる磁極ユニット20は、U字型形状をしたヨーク21と、ヨーク21の屈曲部27に巻回されるコイル22(励磁コイル23と第一出力コイル24a(または第二出力コイル24b))と、ヨーク21の端部に止め具25とを備えている。磁極ユニット20は、上述した止め具25の固定方法により、図4に示されるように、開口部26がロータ10と対向するように配置される。本実施例のヨーク21はプレスした電磁鋼板を12枚重ね、溶接などにより一体化した構成である。なお、本実施例ではヨーク21の形状をU字型形状と表現しているが、U字型形状にはC字型、コ字型、馬蹄形型などの形状を含む。
FIG. 2 is a configuration diagram of the
図3は、本発明における磁極ユニット20のA−A断面図である。まず、ヨーク21の屈曲部27に励磁コイル23を巻き、その上に第一出力コイル24a(または第二出力コイル24b)が巻回される構造になっている。また、各ヨーク21に巻かれた励磁コイル23および第一出力コイル24a(または第二出力コイル24b)の巻き数、巻き方の例を表1に示す。
FIG. 3 is an AA cross-sectional view of the
表1において、ヨーク名の(A)〜(H)については後述する図4における(A)〜(H)と対応する。表1におけるマイナス表記は、マイナス表記をしていない巻き数におけるコイルの巻き方向に対して逆巻きを意味している。表1における「出力コイル巻き数」の「COS」、「SIN」は、それぞれいわゆる「COS巻線」、「SIN巻線」を意味し、本実施形態においてはそれぞれ、COS出力を得る第一出力コイル24a、SIN出力を得る第二出力コイル24bに対応する。
In Table 1, the yoke names (A) to (H) correspond to (A) to (H) in FIG. The minus notation in Table 1 means reverse winding with respect to the winding direction of the coil at the number of turns not represented by minus. “COS” and “SIN” of “number of output coil turns” in Table 1 mean so-called “COS winding” and “SIN winding”, respectively. In this embodiment, the first output for obtaining COS output, respectively. The
なお、コイルの巻き数を、誘導起電圧分布が各々正弦波分布となるような分布巻き(そのコイルの巻き数も正弦波分布状となる)としてもよく、このような分布巻きにおいても、本実施例と同様の効果が得られる。
図4は、本発明における励磁コイル23と第一出力コイル24aと第二出力コイル24bの配線図である。励磁コイル23は電気的に直列に接続されている。また、図4における複数の磁極ユニット20及びヨーク21のそれぞれに対して、図4に示すように(A)〜(H)の符号を付して説明する。ヨーク21(C)とヨーク21(E)とヨーク21(G)とヨーク21(A)のそれぞれに巻かれる第一出力コイル24aは、図4に示すように電気的に直列に接続される。同様に、ヨーク21(B)とヨーク21(D)とヨーク21(F)とヨーク21(H)のそれぞれに巻かれる第二出力コイル24bも図4に示すように電気的に直列に接続される。
FIG. 4 is a wiring diagram of the
図5は本発明における回転角度センサの出力結果の一例である。図5(I)は第一出力コイル24aによる出力結果の一例、図5(II)は第二出力コイル24bによる出力結果の一例である。横軸は、ロータ10の回転角度θを表し、縦軸は第一出力コイル24aと第二出力コイル24bから得られる電圧値Vを示す。
FIG. 5 is an example of the output result of the rotation angle sensor in the present invention. FIG. 5 (I) shows an example of the output result by the
次に本発明の動作について説明を行う。 Next, the operation of the present invention will be described.
上記の構成において、励磁コイル23には、例えば10kHz、10Vの正弦波電圧が励磁される。ロータ10が回転することで、ロータ10と、ロータ10の回転軸から一定の距離に配置されている磁極ユニット20のヨーク21と、の間のギャップが変化する。そうすると、ヨーク21の磁気抵抗が変化し、第一出力コイル24aと第二出力コイル24bに発生する出力電圧が正弦波状に変化する。第一出力コイル24aと第二出力コイル24bは、機械角で45°変化させて配置しているため、軸倍角2Xである本構造は、図5のように位相が90°変化して出力する。それにより、得られるCOS波形とSIN波形の2出力を比較することで、ロータ10の角度を検出が可能となる。
In the above configuration, a sine wave voltage of 10 kHz, 10 V, for example, is excited in the
ここで、従来構造と本発明の磁場解析結果について説明する。 Here, the conventional structure and the magnetic field analysis result of the present invention will be described.
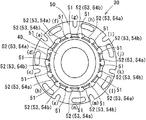
図6は、従来構造の回転角度センサ30である。ロータ40と固定子50と固定子50の内周に突起した14個の磁極ユニット51を備えている。それぞれの位置には(a)〜(n)の符号を付して説明する。また、磁極ユニット51は、励磁コイル53と第一出力コイル54aおよび第二出力コイル54bの少なくともいずれか一方とであるコイル52を備えている。
FIG. 6 shows a
図7は、図6の従来構造における回転角度センサ30に対し、磁場解析を行った結果のグラフである。解析は磁極ユニット51(g)にのみコイル52を巻いて実施した。横軸は磁極ユニット、縦軸は鎖交磁場を示す。磁極ユニット51は固定子50と磁気的に繋がっているため、磁極ユニット51(g)と隣り合う磁極ユニット51(f)と磁極ユニット51(h)に対し、それぞれ8%程度の磁束漏れがあった。また、磁極ユニット51(a)〜(n)全体では52.4%程度の磁束漏れがあった。
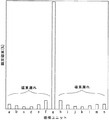
FIG. 7 is a graph showing a result of magnetic field analysis performed on the
図8は、本発明における回転角度センサ1に対し、磁場解析を行った結果のグラフである。解析は図4における磁極ユニット20(D)にのみコイル22を巻いて実施した。横軸は磁極ユニット、縦軸は鎖交磁場を示す。磁極ユニット20は磁気的に独立しているため、磁極ユニット20(D)と隣り合う磁極ユニット20(C)と磁極ユニット20(E)に対し、それぞれ0.3%程度に磁束漏れを抑えることができた。また、磁極ユニット20(A)〜(H)全体では0.65%程度に磁束漏れを抑えることができた。
FIG. 8 is a graph showing a result of magnetic field analysis performed on the
本実施例のように磁極ユニット20を独立させて成形することで、電磁鋼板の歩留まりが高まり、コスト低減が可能になる。また、ヨーク21はU字型形状を呈しているため、ヨーク21を回転させることでコイル22を巻くことができる。また、巻線時のコイル線の供給テンションと軸方向の送りピッチを正確にでき、コイル占積率が安定する整列巻きが可能になる。そのため、コイル占積率のばらつきに起因する出力変動が低減し、回転角度の検出精度が向上する。また、コイル22の巻き方は順方向と逆方向の2種類、巻き数が等しいことから、励磁コイル23と第一出力コイル24aまたは第二出力コイル24bの少なくともいずれか一方を複数のヨーク21に対して、同種の巻き方のコイルを同時に巻くことができるため、タクトタイムを短縮することが可能になる。
By forming the
また、複数ある磁極ユニット20を固定する部材として、アルミなどの非磁性体金属、または樹脂などの非磁性体の部材を用いることが可能である。上記のような非磁性体の部材に固定することにより、磁束の漏れを抑えることができ、磁極ユニット20はそれぞれが磁気的に独立するため、回転角度センサ1駆動時に発生する磁束漏れによる誤差を防止することが可能になる。
In addition, as a member for fixing the plurality of
また、磁極ユニット20は、ヨーク21のU字型形状の開口部26がロータ10と対向するように配置されており、U字型形状のヨーク21の両端部とロータ10との間のギャップが変化して、第一出力コイル24aと第二出力コイル24bとにそれぞれCOS波形とSIN波形との2出力が発生する。このCOS波形の信号とSIN波形の信号とを比較・処理等することで、ロータ10の回転角度の検出が可能になる。
In addition, the
また、励磁コイル23、第一出力コイル24a、第二出力コイル24bは、上述したようにヨーク21のU字型形状の屈曲部27に巻き付けられるため、特殊な巻き線機を用いず、ヨーク21を回転させて励磁コイル23と第一出力コイル24aと第二出力コイル24bとを巻き取ることで、励磁コイル23、第一出力コイル24a、第二出力コイル24bをヨーク21へ巻回させることができる。
Further, since the
1・・・回転角度センサ
10・・・ロータ
20・・・磁極ユニット
21・・・ヨーク
23・・・励磁コイル
24a・・・第一出力コイル
24b・・・第二出力コイル
26・・・開口部
27・・・屈曲部
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (8)
励磁コイルとCOS出力を得る第一出力コイルおよびSIN出力を得る第二出力コイルの少なくともいずれか一方とを直接的または間接的にヨークに巻き付け、前記ロータの周囲に複数個配置される磁極ユニットと、
を備える回転角度センサであって、
前記磁極ユニットは、独立した閉磁路を形成することを特徴とする回転角度センサ。 A rotor having N salient poles or N cycles of sinusoidal gap permeance and made of a magnetic material;
A magnetic pole unit that is arranged around the rotor, wherein the exciting coil and at least one of the first output coil that obtains the COS output and the second output coil that obtains the SIN output are directly or indirectly wound around the yoke; ,
A rotation angle sensor comprising:
The rotation angle sensor, wherein the magnetic pole unit forms an independent closed magnetic path.
励磁コイルとCOS出力を得る第一出力コイルおよびSIN出力を得る第二出力コイルの少なくともいずれか一方とを直接的または間接的にヨークに巻き付け、前記ロータの周囲に複数個配置される磁極ユニットと、
を備える回転角度センサであって、
前記磁極ユニットは、非磁性体に固定されることを特徴とする回転角度センサ。 A rotor having N salient poles or N cycles of sinusoidal gap permeance and made of a magnetic material;
A magnetic pole unit that is arranged around the rotor, wherein the exciting coil and at least one of the first output coil that obtains the COS output and the second output coil that obtains the SIN output are directly or indirectly wound around the yoke; ,
A rotation angle sensor comprising:
The rotation angle sensor, wherein the magnetic pole unit is fixed to a non-magnetic material.
前記磁極ユニットは、(N×Y)個配置されることを特徴とする請求項1乃至7のいずれか一項に記載の回転角度センサ。 The rotor has a configuration without windings,
The rotation angle sensor according to claim 1, wherein (N × Y) magnetic pole units are arranged.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010156427A JP2011069811A (en) | 2009-08-31 | 2010-07-09 | Rotation angle sensor |
| PCT/JP2010/063902 WO2011024678A1 (en) | 2009-08-31 | 2010-08-18 | Rotational angle sensor |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009200210 | 2009-08-31 | ||
| JP2010156427A JP2011069811A (en) | 2009-08-31 | 2010-07-09 | Rotation angle sensor |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2011069811A true JP2011069811A (en) | 2011-04-07 |
| JP2011069811A5 JP2011069811A5 (en) | 2012-01-19 |
Family
ID=43627783
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010156427A Pending JP2011069811A (en) | 2009-08-31 | 2010-07-09 | Rotation angle sensor |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2011069811A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2011024678A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021060263A (en) * | 2019-10-07 | 2021-04-15 | 多摩川精機株式会社 | Double redundant system resolver |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6153503A (en) * | 1984-08-23 | 1986-03-17 | S G:Kk | Induction type position detector having separated stator core |
| JP2006023146A (en) * | 2004-07-07 | 2006-01-26 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Rotational position detector |
| JP2008175553A (en) * | 2007-01-16 | 2008-07-31 | Tamagawa Seiki Co Ltd | Angle detector |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3877594B2 (en) * | 2002-01-11 | 2007-02-07 | オークマ株式会社 | Reluctance type resolver |
| JP3911670B2 (en) * | 2002-03-27 | 2007-05-09 | ミネベア株式会社 | Rotation position detector |
| JP2007285774A (en) * | 2006-04-13 | 2007-11-01 | Toyota Motor Corp | Magnetic resolver and its manufacturing method |
| JP5098087B2 (en) * | 2008-01-22 | 2012-12-12 | 多摩川精機株式会社 | Rotation angle detector |
-
2010
- 2010-07-09 JP JP2010156427A patent/JP2011069811A/en active Pending
- 2010-08-18 WO PCT/JP2010/063902 patent/WO2011024678A1/en active Application Filing
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6153503A (en) * | 1984-08-23 | 1986-03-17 | S G:Kk | Induction type position detector having separated stator core |
| JP2006023146A (en) * | 2004-07-07 | 2006-01-26 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Rotational position detector |
| JP2008175553A (en) * | 2007-01-16 | 2008-07-31 | Tamagawa Seiki Co Ltd | Angle detector |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021060263A (en) * | 2019-10-07 | 2021-04-15 | 多摩川精機株式会社 | Double redundant system resolver |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2011024678A1 (en) | 2011-03-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4775294B2 (en) | Resolver | |
| JP6448810B2 (en) | Rotor, permanent magnet synchronous motor, method for manufacturing permanent magnet synchronous motor, and air conditioner | |
| US20110018384A1 (en) | Motor | |
| JP2011043378A (en) | Sheet coil type resolver | |
| KR101271340B1 (en) | Winding method for stator of rotation detector, winding structure therefor, and electric motor using rotation detector | |
| US11152875B2 (en) | Multigroup-multiphase rotary electrical machine control device and multigroup-multiphase rotary electrical machine drive device | |
| KR101964371B1 (en) | Resolver and manufacturing manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP6504261B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for manufacturing rotor of motor | |
| JP2006125995A (en) | Angle of rotation detector | |
| JP2008263738A (en) | Rotary electric machine | |
| JP4652382B2 (en) | Permanent magnet type brushless motor for electric power steering system | |
| JP2011030378A (en) | Stator and electrical apparatus | |
| JP2010259267A (en) | Rotation angle detection device | |
| JP2007306798A (en) | Permanent magnet type brushless motor for electric power-steering system | |
| JP2011069811A (en) | Rotation angle sensor | |
| JP5314115B2 (en) | Resolver | |
| US20210119497A1 (en) | Electric motor | |
| JP5075022B2 (en) | Variable reluctance resolver | |
| JP2010187491A (en) | Brushless motor | |
| JP2007285856A (en) | Rotation angle detecting apparatus | |
| CN112368921B (en) | Resolver device and rotary electric machine with resolver device | |
| JP5024893B2 (en) | Variable reluctance resolver | |
| JP2011047672A (en) | Sheet coil type resolver | |
| JP2013027130A (en) | Resolver | |
| JP4896910B2 (en) | Arc type angle sensor |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20111125 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Effective date: 20111130 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20121211 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Effective date: 20130409 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 |