JP2010245905A - Transmission apparatus and communication system - Google Patents
Transmission apparatus and communication system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2010245905A JP2010245905A JP2009093444A JP2009093444A JP2010245905A JP 2010245905 A JP2010245905 A JP 2010245905A JP 2009093444 A JP2009093444 A JP 2009093444A JP 2009093444 A JP2009093444 A JP 2009093444A JP 2010245905 A JP2010245905 A JP 2010245905A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- signal
- transmission
- phase
- input point
- unit
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01P—WAVEGUIDES; RESONATORS, LINES, OR OTHER DEVICES OF THE WAVEGUIDE TYPE
- H01P1/00—Auxiliary devices
- H01P1/18—Phase-shifters
- H01P1/182—Waveguide phase-shifters
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L27/00—Modulated-carrier systems
- H04L27/32—Carrier systems characterised by combinations of two or more of the types covered by groups H04L27/02, H04L27/10, H04L27/18 or H04L27/26
- H04L27/34—Amplitude- and phase-modulated carrier systems, e.g. quadrature-amplitude modulated carrier systems
- H04L27/36—Modulator circuits; Transmitter circuits
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Transmitters (AREA)
- Digital Transmission Methods That Use Modulated Carrier Waves (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、送信装置および通信システムに関する。詳しくは、第1の送信信号を導波路に入力する第1の入力点と第2の送信信号を導波路に入力する第2の入力点とを、第1の送信信号と第2の送信信号との間に所定の位相差を与える距離だけずらすことにより、IQ直交軸による高速伝送を実現するものである。 The present invention relates to a transmission device and a communication system. Specifically, a first input point for inputting the first transmission signal to the waveguide and a second input point for inputting the second transmission signal to the waveguide are referred to as the first transmission signal and the second transmission signal. Is shifted by a distance that gives a predetermined phase difference between the two and the high-speed transmission by the IQ orthogonal axis.
近年、CMOS技術を利用することにより低消費電力かつ低コスト(小回路規模)な信号伝送を目指した、ミリ波などの高周波帯を利用した高速伝送技術が盛んに研究されている。これは、量産に適したCMOSプロセスを用いることにより、デジタル回路モジュールとミリ波RFフロントエンドモジュールを1チップで構成することで実現の可能性があるからである。従来の高速ベースバンド信号伝送装置は、誘電体損失の少ない基板と、この基板上に実装された第1および第2の部品と、第1および第2の部品間を結合する導波路とで構成されている。お互いの干渉を低減させることで、基板上での第1および第2の部品間での高速信号伝送を実現している。 In recent years, high-speed transmission technology using a high-frequency band such as millimeter waves has been actively studied aiming at low-power consumption and low-cost (small circuit scale) signal transmission by using CMOS technology. This is because a digital circuit module and a millimeter-wave RF front-end module can be realized on a single chip by using a CMOS process suitable for mass production. A conventional high-speed baseband signal transmission device includes a substrate with a small dielectric loss, first and second components mounted on the substrate, and a waveguide that couples the first and second components. Has been. By reducing mutual interference, high-speed signal transmission between the first and second components on the substrate is realized.
ところで、上述した高速ベースバンド信号伝送装置等においては、さらなる伝送速度の高速化を目指して直交するIQ軸を使った位相変調が従来から広く利用されている。位相変調とは、例えばデジタル伝送においてはデジタル符号に応じて搬送波の位相を離散的に変化させる変調方式であり、下記(1)で与えられる位相成分θに対してデジタル符号のマッピングを行うものである。
S(t)=A(t)cos(2πfc+θ(t))・・・(1)
ここで、A(t)は振幅であり、θ(t)は位相である。
By the way, in the above-described high-speed baseband signal transmission apparatus and the like, phase modulation using orthogonal IQ axes has been widely used for the purpose of further increasing the transmission speed. Phase modulation is a modulation method in which the phase of a carrier wave is discretely changed according to a digital code in digital transmission, for example, and performs mapping of a digital code with respect to a phase component θ given in (1) below. is there.
S (t) = A (t) cos (2πfc + θ (t)) (1)
Here, A (t) is the amplitude and θ (t) is the phase.
例えば位相変調の一種であるQPSK変調を考えた場合、2ビットのデジタル符号を1つの位相で表現することで実現できる。デジタル符号と位相θのマッピングの一例を図16に示し、各デジタル符号が複素ベースバンド信号上でマッピングされている様子を図17に示す。このように、1つの位相情報に多ビットの情報を載せることで高速化が可能になる技術は古くから行われてきている。多ビットを伝送する他の技術としては、振幅と位相の両方を用いたQAM(Quadrature Amplitude Modulation)伝送等が近年盛んに行われている。 For example, when QPSK modulation which is a kind of phase modulation is considered, it can be realized by expressing a 2-bit digital code with one phase. An example of the mapping between the digital code and the phase θ is shown in FIG. 16, and how each digital code is mapped on the complex baseband signal is shown in FIG. As described above, a technique that can increase the speed by placing multi-bit information on one phase information has been performed for a long time. As other techniques for transmitting multiple bits, QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) transmission using both amplitude and phase has been actively performed in recent years.
しかし、これらの伝送を行うには、複素平面でいうところのI軸とQ軸を直交させる90°移相器(Phase Shifter)等が必要になり、多ビットの伝送を試みようとすると高い精度で実現することが要求されている。そのため、これまでにも様々な精度補償方法が考えられてきた。 However, in order to perform these transmissions, a 90 ° phase shifter or the like that makes the I axis and Q axis orthogonal to each other in the complex plane is required. It is required to be realized with. Therefore, various accuracy compensation methods have been considered so far.
例えば、特許文献1に記載される発明には、直交変調回路の精度を懸念し、検波器により生じた検波電圧が所定値以下になるように直流バイアスを増減させることにより、搬送波リークを所望の値以下に抑圧制御する補償回路を備えた送信機が開示されている。
For example, the invention described in
また、特許文献2に記載される発明には、精度が悪くかつIQ直交性が不要なときにはBPSK方式に切り替え、精度が良好なときにはQPSK方式に切り替えることで、IQの直交精度の維持よりも伝送チャネルの維持を確保する無線通信装置が開示されている。 Further, in the invention described in Patent Document 2, when accuracy is poor and IQ orthogonality is unnecessary, switching to the BPSK system is performed, and switching to the QPSK system is performed when accuracy is good, so that transmission can be performed rather than maintaining the orthogonal accuracy of IQ. A wireless communication device that ensures channel maintenance is disclosed.
しかしながら、上記特許文献1および2に開示される発明において、90°移相器等を用いてIQ直交軸による高速伝送を実現させようとした場合には以下のような問題がある。すなわち、特許文献1に記載される発明では、本来の信号の変調部やミキサ等を含む伝達経路に加えて、演算部や検波部等を含む補償回路を別途設ける必要がある。そのため、送信機の回路の小型化に支障をきたし、ひいてはコストアップにつながるという問題がある。また、特許文献2に記載される発明では、BPSK変調適用時に伝送レートが低下してしまうのが明らかであり、安定した高速伝送は期待できない。
However, in the inventions disclosed in
そこで、本発明は、上記課題に鑑みてなされたものであり、I軸とQ軸を直交させる90°移相器や直交発振器等を削減して回路の簡略化を図りつつも高精度かつ高速伝送を実現する、導波路を用いた送信装置および通信システムを提供することを目的とする。 Therefore, the present invention has been made in view of the above-described problems, and has achieved high accuracy and high speed while simplifying the circuit by reducing a 90 ° phase shifter, a quadrature oscillator, or the like that makes the I axis and Q axis orthogonal. An object of the present invention is to provide a transmission device and a communication system using a waveguide that realize transmission.
本発明に係る送信装置は、所定周波数の搬送波信号を入力される第1の信号に基づいて変調して第1の送信信号を出力する第1の送信部と、所定周波数の搬送波信号を入力される第2の信号に基づいて変調して第2の送信信号を出力する第2の送信部とを備え、第1の送信部により出力された第1の送信信号を導波路に入力する第1の入力点と第2の送信部により出力された第2の送信信号を導波路に入力する第2の入力点とが、第1の送信信号と第2の送信信号との間に所定の位相差を与える距離だけずれているものである。 A transmission apparatus according to the present invention receives a first transmission unit that modulates a carrier signal having a predetermined frequency based on a first signal input thereto and outputs the first transmission signal, and a carrier signal having a predetermined frequency. And a second transmission unit that modulates based on the second signal and outputs a second transmission signal, and inputs the first transmission signal output from the first transmission unit to the waveguide. And a second input point for inputting the second transmission signal output from the second transmission unit to the waveguide is a predetermined position between the first transmission signal and the second transmission signal. It is shifted by a distance that gives a phase difference.
また本発明に係る通信システムは、所定周波数の搬送波信号を入力される第1の信号に基づいて変調して第1の送信信号を出力する第1の送信部と、所定周波数の搬送波信号を入力される第2の信号に基づいて変調して第2の送信信号を出力する第2の送信部とを有する送信装置と、第1の送信部から出力された第1の送信信号および第2の送信部から出力された第2の送信信号が入力される導波路と、導波路を介して送信された第1および第2の送信信号を受信し、当該第1および第2の送信信号を所定周波数の搬送波信号に基づいて復調して受信信号を得る受信部を有する受信装置とを備え、第1の送信部により出力された第1の送信信号を導波路に入力する第1の入力点と第2の送信部により出力された第2の送信信号を導波路に入力する第2の入力点とが、第1の送信信号と第2の送信信号との間に所定の位相差を与える距離だけずれているものである。 The communication system according to the present invention also includes a first transmitter that modulates a carrier signal having a predetermined frequency based on a first signal input thereto and outputs a first transmission signal, and a carrier signal having a predetermined frequency. A second transmission unit that modulates the second transmission signal and outputs a second transmission signal, a first transmission signal output from the first transmission unit, and a second transmission unit A waveguide to which the second transmission signal output from the transmission unit is input, and the first and second transmission signals transmitted through the waveguide are received, and the first and second transmission signals are determined in advance. A receiving device having a receiving unit that demodulates based on a frequency carrier signal to obtain a received signal, and a first input point that inputs the first transmission signal output by the first transmitting unit to the waveguide; The second transmission signal output from the second transmitter is input to the waveguide. That a second input point, in which are shifted by a distance that gives a predetermined phase difference between the first transmission signal and the second transmit signal.
本発明において、所定周波数の搬送波信号は、入力される第1の信号に基づいて第1の送信部により変調されて第1の送信信号として出力される。所定周波数の搬送波信号は、入力される第2の信号に基づいて第2の送信部により変調されて第2の送信信号として出力される。変調方式としては、例えば、位相変調や振幅変調等が挙げられ、より具体的にはBPSK,QPSK,8相PSK,QAM等の変調方式が挙げられる。 In the present invention, a carrier wave signal having a predetermined frequency is modulated by the first transmission unit based on the input first signal and is output as the first transmission signal. A carrier wave signal having a predetermined frequency is modulated by the second transmitter based on the input second signal and is output as a second transmission signal. Examples of the modulation method include phase modulation and amplitude modulation, and more specifically, modulation methods such as BPSK, QPSK, 8-phase PSK, and QAM.
信号処理された第1の送信信号は第1の入力点を介して導波路に入力され、第2の送信信号は第2の入力点を介して導波路に入力される。本発明において第1の入力点と第2の入力点とは、第1の送信信号と第2の送信信号との間に所定の位相差を与える距離だけずれている。そのため、例えば、第1および第2の入力点間の距離を、(1/4+N)λ波長分ずらした場合には、第1の送信信号と第2の送信信号との位相差を90°に制御することができるので、IQ直交軸を用いることにより高速伝送を実現することができる。ここでNは整数、λは搬送波信号の波長である。また、複雑なシステムを用いることなく、精度の高いIQ直交軸を実現できるので、多値変調などの高次の変調方式を実現できる。 The signal-processed first transmission signal is input to the waveguide via the first input point, and the second transmission signal is input to the waveguide via the second input point. In the present invention, the first input point and the second input point are shifted by a distance that gives a predetermined phase difference between the first transmission signal and the second transmission signal. Therefore, for example, when the distance between the first and second input points is shifted by (1/4 + N) λ wavelengths, the phase difference between the first transmission signal and the second transmission signal is set to 90 °. Since it can be controlled, high-speed transmission can be realized by using the IQ orthogonal axis. Here, N is an integer, and λ is the wavelength of the carrier signal. In addition, since a highly accurate IQ orthogonal axis can be realized without using a complicated system, a high-order modulation method such as multi-level modulation can be realized.
本発明によれば、第1の入力点と第2の入力点とを第1の送信信号と第2の送信信号との間に位相差を与える距離だけずらした状態で導波路に設けるため、直交発振器や90°位相器を用いることなくIQ直交伝送を実現できる。その結果、送信装置の回路規模の削減、ひいてはコスト削減を図ることができる。 According to the present invention, the first input point and the second input point are provided in the waveguide while being shifted by a distance that gives a phase difference between the first transmission signal and the second transmission signal. IQ quadrature transmission can be realized without using a quadrature oscillator or a 90 ° phase shifter. As a result, it is possible to reduce the circuit scale of the transmission device and thus reduce the cost.
以下、発明を実施するための最良の形態(以下実施の形態とする)について説明する。なお、説明は以下の順序で行う。
1.第1の実施の形態(高周波伝送システムにおいてIQ直交軸を実現する例)
2.第1の実施の形態の変形例
3.第2の実施の形態(アンテナ部材によりキャリブレーションを行う例)
4.第2の実施の形態の変形例
5.第3の実施の形態(振幅のキャリブレーションを行う例)
6.第4の実施の形態(液晶層を用いてキャリブレーションを行う例)
7.第5の実施の形態(遅延素子を用いてキャリブレーションを行う例)
8.第6の実施の形態(移相素子を用いてキャリブレーションを行う例)
9.第7の実施の形態(送信装置および受信装置で連動してキャリブレーションを行う例)
10.第8の実施の形態(送信装置および受信装置で連動してキャリブレーションを行う例)
Hereinafter, the best mode for carrying out the invention (hereinafter referred to as an embodiment) will be described. The description will be given in the following order.
1. 1st Embodiment (example which implement | achieves IQ orthogonal axis in a high frequency transmission system)
2. 2. Modification of first embodiment Second Embodiment (Example in which calibration is performed using an antenna member)
4). 4. Modification of second embodiment Third Embodiment (Example of performing amplitude calibration)
6). Fourth Embodiment (Example of performing calibration using a liquid crystal layer)
7). Fifth Embodiment (Example of performing calibration using a delay element)
8). Sixth Embodiment (Example of performing calibration using a phase shift element)
9. Seventh Embodiment (Example in which calibration is performed in conjunction with a transmission device and a reception device)
10. Eighth Embodiment (Example in which calibration is performed in conjunction with a transmission device and a reception device)
<1.第1の実施の形態>
[高周波システムの構成例]
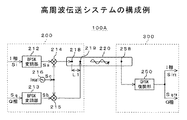
図1に示すように、本発明に係る高周波伝送システム100Aは、通信システムの一例であり、例えば、伝送する信号の周波数が30GHz〜300GHzのミリ波の信号を高速伝送することが可能である。この高周波伝送システム100Aは、基板40上に実装された、部品A,部品B,部品C,部品Dと、これらの部品A,B,C,Dを結合する導波路20とから構成されている。
<1. First Embodiment>
[Configuration example of high-frequency system]
As shown in FIG. 1, the high-
部品A〜部品Dのそれぞれはミリ波送受信モジュールを内蔵しており、この例では部品A,Cが送信装置として構成され、部品B,Dが受信装置として構成されている。部品Aと部品Bとは導波路20を介して接続されており、部品A,B間において画像信号や音声信号等の高速信号伝送を行う。部品Cと部品Dとは導波路20を介して接続されており、部品C,D間において画像信号や音声信号等の高速信号伝送を行う。以下では部品A(送信装置200),部品B(受信装置300)間における信号伝送を例に挙げる。
Each of the parts A to D has a built-in millimeter-wave transmission / reception module. In this example, the parts A and C are configured as a transmitting apparatus, and the parts B and D are configured as a receiving apparatus. The component A and the component B are connected via the
[高周波システムのブロック構成例]
図2に示すように、高周波伝送システム100Aは、送信装置200と受信装置300とこれらを結合する導波路20とを備えている。送信装置200は、信号入力部10と変調回路12と周波数変換回路14と増幅器16と基板との結合回路18とを有している。受信装置300は、基板との結合回路22と増幅器24と周波数変換回路26と復調回路28と信号出力部30とを有している。
[Example of block configuration of high-frequency system]
As shown in FIG. 2, the high-
信号入力部10には送信装置200内において生成された所定の信号が入力される。信号入力部10に入力された信号は変調回路12に供給される。変調回路12は、供給された信号を変調して周波数変換回路14に供給する。周波数変換回路14は、変調された信号を所望の周波数帯(ミリ波)までアップコンバートして増幅器16に供給する。増幅器16は、アップコンバートされた信号を増幅して結合回路18に供給する。結合回路18は、増幅された信号を導波路20を介して受信装置300に送信する。
A predetermined signal generated in the
受信装置300の結合回路22は、送信装置200側から導波路20を介して送信された信号を受信して増幅器24に供給する。増幅器24は、受信された信号の減衰を補うために増幅して、増幅後の信号を周波数変換回路26に供給する。周波数変換回路26は、増幅された信号をダウンコンバートして復調回路28に供給する。復調回路28は、ダウンコンバートされた信号を復調してベースバンド信号を得る。最後に、信号出力部30は、復調されたベースバンド信号に基づくデータ列を出力することで、送信装置200から受信装置300での信号伝送が完了することになる。なお、通信を行う送信装置200,受信装置300間が近い場合は送信側、受信側の増幅器16,24を省略しても良い。
The coupling circuit 22 of the receiving
[高周波伝送システムの回路構成例]
次に、上述した高周波伝送システム100Aの回路構成例について説明する。なお、図3においてBPSK変調部212,213は図2に示した変調回路12に対応し、搬送波信号生成部216およびミキサ214,215は図2に示した周波数変換回路14に対応し、入力点218,219は図2に示した結合回路18に対応している。また、図3において出力点258は図2に示した結合回路22に対応し、QPSK復調部250は図2に示した復調回路28等に対応している。
[Circuit configuration example of high-frequency transmission system]
Next, a circuit configuration example of the above-described high-
図3に示すように、受信装置300に伝送したい信号のそれぞれは、I相とQ相に割り当てられる。I相に割り当てられたベースバンド信号Siは、BPSK変調部212に供給される。BPSK変調部212は、割り当てられたビットに従ってBPSK変調(マッピング)を施すことにより変調信号Saを生成してミキサ214に供給する。搬送波信号生成部216は、所定周波数の搬送波信号Scを生成してミキサ214に供給する。ミキサ214は、BPSK変調部212により生成された変調信号Saと搬送波信号生成部216により生成された搬送波信号Scとを乗算して変調信号Saを周波数変換(アップコンバート)し、周波数変換された変調信号Saを入力点218に供給する。なお、ベースバンド信号Siは第1の信号の一例であり、変調信号Saは第1の送信信号の一例である。入力点218は第1の入力点の一例であり、BPSK変調部212およびミキサ214は第1の送信部の一例を構成している。
As shown in FIG. 3, each signal to be transmitted to receiving
Q相に割り当てられたベースバンド信号Sqは、BPSK変調部213に供給される。BPSK変調部213は、割り当てられたビットに従ってBPSK変調(マッピング)を施すことにより変調信号Sbを生成してミキサ215に供給する。搬送波信号生成部216は、所定周波数の搬送波信号Scを生成してミキサ215に供給する。ミキサ215は、BPSK変調部213により生成された変調信号Sbと搬送波信号Scとを乗算して変調信号Sbを周波数変換(アップコンバート)し、周波数変換された変調信号Sbを入力点219に供給する。なお、ベースバンド信号Sqは第2の信号の一例であり、変調信号Sbは第2の送信信号の一例である。入力点219は第2の入力点の一例であり、BPSK変調部213およびミキサ215は第2の送信部の一例を構成している。
The baseband signal Sq assigned to the Q phase is supplied to the
入力点218,219は導波路220の一端側に設けられ、入力点218,219のそれぞれには後述するようにダイポールアンテナ、ループアンテナまたは小型アパーチャ結合素子(スリットアンテナ)等が設けられている。入力点218と入力点219とは、導波路220の搬送方向において、変調信号Saと変調信号Sbとの間に所定の位相差を与える、下記(2)式の関係を満たす距離L1だけずれている。
L1=(1/4+N)λ・・・(2)
ここで、λ=c/√εrf、Cは真空中の高速であり、fは搬送波信号の周波数であり、εrは導波路の比誘電率であり、Nは整数である。
The input points 218 and 219 are provided on one end side of the
L1 = (1/4 + N) λ (2)
Here, λ = c / √ε r f, C is the high speed in vacuum, f is the frequency of the carrier signal, εr is the relative dielectric constant of the waveguide, and N is an integer.
これにより、図4(B)に示すように、入力点218から送信される変調信号Saと入力点219から送信される変調信号Sbとが、複素平面上で位相が少なくとも90°ずれることになる。つまり、入力点218と入力点219との距離L1を(1/4+N)λずらすことにより、従来のように90°移相器を用いることなく、変調信号Sa,Sbの位相を直交させることができるようになる。この状態は、導波路220上の一点(例えば出力点258)で観測するとsin波とcos波の関係に等しく、あたかもQPSK変調された信号が到来して来ているのと同じことになる。なお、図4(A)は位相をずらす前の変調信号Sa,Sbの位相関係を示している。
As a result, as shown in FIG. 4B, the phase of the modulated signal Sa transmitted from the
図3に戻り、導波路220は、導電部材によって区画された細長の筐体を有し、基板40上に実装された送信装置200と受信装置300との間に実装されている。導波路220の筐体内部には、例えば空気やエポキシ樹脂(基板40と同一材料)などの所定の比誘電率を有した誘電体が封入されている。なお、基板40としては、例えばガラスエポキシ樹脂を絶縁ベースとした両面に銅箔が貼り付けられた、例えば誘電正接(tanδ)が0.01以上で、従来、ミリ波帯では伝送損失が大きく、ミリ波伝送に適していないとされていた損失の大きい基板が用いられる。
Returning to FIG. 3, the
出力点258は導波路220の他端側に設けられ、この出力点258には後述するようにダイポールアンテナ、ループアンテナまたは小型アパーチャ結合素子(スリットアンテナ)等が設けられている。出力点258は、導波路220を介して送信される変調信号Sa,Sbを受信してQPSK復調部250に供給する。
The
QPSK復調部250は、出力点258により受信された互いに直交する変調信号Sa,SbにQPSK変調を施すことにより、変調信号Saに基づくベースバンド信号Sirxと、変調信号Sbに基づくベースバンド信号Sqrxとを得る。
The QPSK demodulator 250 performs QPSK modulation on the orthogonally-modulated modulation signals Sa and Sb received by the
以上説明したように、本実施の形態では、入力点218と入力点219との間の距離L1を(1/4+N)λに設定して導波路220に結合させている。これにより、第1の変調信号Saと第2の変調信号Sbとの位相差を90°に設定することができ、直交発振器や90°位相器を用いることなく、IQ直交伝送を実現できるようになる。その結果、送信装置200の回路規模の削減、ひいてはコスト削減を図ることができる。さらに、導波路220を用いた高周波伝送システム100Aにおいて、上述したIQ直交軸を用いることにより高速伝送を実現することができる。
As described above, in the present embodiment, the distance L1 between the
<2.第1の実施の形態の変形例>
第1の実施の形態の変形例では、高周波伝送システム100Bの受信装置300を、上記第1の実施の形態で説明した高周波伝送システム100Aの受信装置300とは異なる構成を採用している。なお、上述した第1の実施の形態の高周波伝送システム100Aと共通する構成要素には同一の符号を付し、詳細な説明は省略する。
<2. Modification of First Embodiment>
In the modification of the first embodiment, the receiving
図5に示すように、受信装置300は、出力点260,261とミキサ254,255とBPSK復調部252,253とを備えている。出力点261は導波路220の他端側に設けられ、この出力点261には例えばダイポールアンテナ等が設けられている。出力点261は、導波路220を介して送信される変調信号Saを受信してミキサ254に供給する。搬送波信号生成部256は、搬送波信号Scrxを生成してミキサ254に供給する。ミキサ254は、変調信号Saと搬送波信号Scrxとを乗算することにより変調信号Saを周波数変換(ダウンコンバート)し、周波数変換された変調信号SaをBPSK復調部252に供給する。BPSK復調部252は、変調信号Saを復調(マッピング)してベースバンド信号Sirxを得る。
As illustrated in FIG. 5, the
出力点260は導波路220の他端側に設けられ、この出力点260には例えばダイポールアンテナ等が設けられている。また、出力点260は、出力点261と上記(2)式の関係を満たす距離L1だけずれた位置に設けられている。そのため、導波路220を介して送信される変調信号Sbを変調信号Saと(1/4+N)λ波長だけずれた状態で受信することができる。受信された変調信号Saはミキサ255に供給される。ミキサ255は、導波路220を介して受信された変調信号Sbと搬送波信号Scrxとを乗算して変調信号Sbを周波数変換(ダウンコンバート)し、周波数変換された変調信号SaをBPSK復調部253に供給する。BPSK復調部253は、変調信号Sbを復調(マッピング)してベースバンド信号Sqrxを得る。
The
本変形例のように、受信装置300を送信装置200と同様に構成しても、上記第1の実施の形態と同様の作用効果を得ることができる。例えば、第1の変調信号Saと第2の変調信号Sbとの位相差を90°に設定することができ、直交発振器や90°位相器を用いることなく、IQ直交伝送を実現でき、その結果、送信装置200の回路規模の削減、ひいてはコスト削減を図ることができる。
Even if the receiving
<3.第2の実施の形態>
[位相のキャリブレーション機能を備えた高周波伝送システムの例]
第2の実施の形態では、I相の変調信号SaとQ相の変調信号Sbとの位相差を90°に調整するキャリブレーション機能を備えた高周波伝送システム100Cについて説明する。なお、高周波伝送システム100Cは、上述した高周波伝送システム100Aにキャリブレーション機能を持たせたものであるので、共通する構成要素および動作については説明を省略する。
<3. Second Embodiment>
[Example of high-frequency transmission system with phase calibration function]
In the second embodiment, a high-
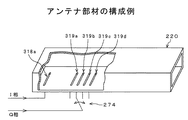
(アンテナ部材の構成例)
まず、キャリブレーション機能を備えた高周波伝送システム100Cのアンテナ部材の構成例について説明する。図6および図8に示すように、I相の入力点218には、例えばミリ波の信号の波長λに基づく所定の長さを有したダイポール型等のアンテナ部材218aが設けられている。このアンテナ部材218aは、導波路220の一端側に結合され、ミキサ254から出力されたテスト用の変調信号Satを導波路220の内部に放射する。
(Configuration example of antenna member)
First, a configuration example of the antenna member of the high-
Q相の入力点219には、例えばミリ波の信号の波長λに基づく所定の長さを有したダイポール型等の4本のアンテナ部材219a〜219dが設けられ、それぞれが所定間隔を隔てて導波路220の一端側に結合されている。アンテナ部材219a〜219dの何れかは、切り替えに応じてスイッチ部274に電気的に接続され、キャリブレーションモード時にアンテナ部材218aから放射されたテスト用の変調信号Satを受信する。なお、上述した例では4本のアンテナ部材219a〜219dにより構成したが、2本であっても良いし、5本以上であっても良い。アンテナ部材の本数を増やすことにより、より細かい位相差の微調整が可能となる。
The Q-
ここで、アンテナ部材219a〜219dのうち、例えばアンテナ部材219bはI相用のアンテナ部材218aと(1/4+N)λずれた位置に結合され、他のアンテナ部材219a,219c,219dはアンテナ部材413の近傍位置に結合される。アンテナ部材219a〜219dの位置(移相)情報は、後述する位置回転量計算部270に格納されており、算出したずれ量とアンテナ部材219a〜219dの位置情報に基づいて最適なアンテナ部材219a〜219dを選択できるようになっている。
Here, of the antenna members 219a to 219d, for example, the
(アンテナ部材の他の構成例)
なお、上述した例では、アンテナ部材218a〜218dをダイポール型のアンテナにより構成したが、これに代えてスリット状のアンテナにより構成することもできる。図7に示すように、スリットアンテナ318aは、導波路220の一端側の底面部であってその短手方向に沿って形成されている。スリットアンテナ319a〜319dは、導波路220の一端側の底面部であってその短手方向に沿って所定間隔を隔てて形成されている。
(Another configuration example of the antenna member)
In the above-described example, the antenna members 218a to 218d are configured by dipole antennas, but may be configured by slit-shaped antennas instead. As shown in FIG. 7, the slit antenna 318 a is a bottom surface portion on one end side of the
スリットアンテナ319a〜319dの何れか(例えばスリットアンテナ319b)はスリットアンテナ318aと(1/4+N)λずれた位置に形成される。他のスリットアンテナ319a,319c,319dは、スリットアンテナ319bの近傍位置に形成される。このような構成によっても、変調信号Sa,Sb間の位相差の微調整を行うことができる。
Any of the
(高周波伝送システムの構成例)
次に、上述したアンテナ部材218a,219a〜219dを備えた高周波伝送システム100Cについて説明する。高周波伝送システム100Cは、位相制御を行うキャリブレーションモードと通常の通信を行う通信モードとを有している。これらのモードの切り替えは、ユーザが任意に設定したり、図示しない制御部により自動的に設定することが可能となっている。高周波伝送システム100Cは、キャリブレーションモードが設定されると、図8に示すように、入力点218から送信されるテスト用の変調信号Satを入力点219により受信する、ループLpを形成することによりキャリブレーションを実行する。つまり、送信装置200側だけで位相のキャリブレーションを行う。
(Configuration example of high-frequency transmission system)
Next, the high-
I相側のBPSK変調部212は、割り当てられたテスト用のベースバンド信号Sit(ビット)に従ってBPSK変調を施すことによりテスト用の変調信号Satを生成してミキサ214に供給する。搬送波信号生成部216は、搬送波信号Sctを生成してミキサ214に供給する。ミキサ214は、BPSK変調部212により生成された変調信号Satに搬送波信号Sctを乗算して変調信号Satを周波数変換(アップコンバート)し、周波数変換された変調信号Satを入力点218に供給する。入力点218に供給された変調信号Satは、アンテナ部材を介して導波路220の内部に送信される。
The
入力点219に設けられたアンテナ部材219a〜219dの何れかは、キャリブレーションモード時にはテスト用の変調信号Satを受信するアンテナ部材としても機能し、入力点218から送信された変調信号Satを受信してミキサ215に供給する。ここで、入力点218,219間の距離L1は、上述したように、(1/4+N)λに設定されているものとする。ミキサ215は、入力点219のアンテナ部材により受信された変調信号Satに、搬送波信号生成部216により生成された搬送波信号Sctを乗算することにより変調信号Satを周波数変換(ダウンコンバート)して受信信号Sarxを得る。周波数変換された受信信号Sarxはスイッチ部272を介して位置回転量計算部270に供給される。キャリブレーションモードにおいてスイッチ部272は、位置回転量計算部270や図示しない制御部により端子b側に切り替えられる。
Any of the antenna members 219a to 219d provided at the
位置回転量計算部270は、制御部の一例であり、ミキサ215から出力されたテスト用の受信信号Sarxと基準信号Stとの位相差が90°(1/4+N)λであるか否かを判断する。これは、入力点218,219間の位相差が(1/4+N)λに設定されているので、理論上、基準信号Stと受信信号Sarxとの位相差は90°となるからである。基準信号Stとしては、搬送波信号生成部216から供給される搬送波信号Sctや、BPSK変調部212により変調されて入力点218から送信される前の変調信号Satを予めメモリしたものが用いられる。位置回転量計算部270は、位相差が90°でないと判断した場合には、位相の回転量、具体的には90°を基準とした場合にどの程度、受信信号Sarxの位相がずれているかのずれ量を計算する。そして、位置回転量計算部270は、計算したずれ量に基づくアンテナ部材219a〜219dの何れかを選択し、選択に応じた切替信号を生成してスイッチ部274に供給する。
The position rotation
スイッチ部274は、位置回転量計算部270から供給される切替信号に基づいて、切替信号に対応したアンテナ部材219a〜219dに切り替える(図6参照)。これにより、キャリブレーションモードにおいて入力点218,219間が(1/4+N)λに微調整されるので、通信モードにおいてはI相の変調信号SaとQ相の変調信号Sbとの位相差を90°に設定することが可能となる。その結果、高精度なIQ直交軸によって高速伝送を実現することができる。
The
<4.第2の実施の形態の変形例>
[位相のキャリブレーション機能を備えた高周波伝送システムの例]
第2の実施の形態の変形例では、テスト用の搬送波信号Sciを用いてアンテナ部材219a〜219dのキャリブレーションを行う場合について説明する。なお、図9においてBPSK変調部212,213等の構成については便宜上省略している。
<4. Modification of Second Embodiment>
[Example of high-frequency transmission system with phase calibration function]
In the modification of the second embodiment, a case where the antenna members 219a to 219d are calibrated using the test carrier signal Sci will be described. In FIG. 9, the configuration of the
図9に示すように、高周波伝送システム100Dの搬送波信号生成部216は、所定周波数のテスト用の搬送波信号Sciを生成する。搬送波信号生成部216により生成されたテスト用の搬送波信号Sciは、入力点218のアンテナ部材218aから導波路220の内部に放射される。
As shown in FIG. 9, the carrier
入力点219のアンテナ部材219Aは、入力点218のアンテナ部材218aから放射されたテスト用の搬送波信号Sciを受信してミキサ215に供給する。なお、以下の説明において、アンテナ部材219a〜219dのうち何れかのアンテナ部材を指す場合にはアンテナ部材219Aと称する(図6参照)。搬送波信号生成部216は、所定周波数のテスト用の搬送波信号Scqを生成してミキサ215に供給する。なお、テスト用の搬送波信号Sciと搬送波信号Scqとは同一の周波数に設定されているものとする。ミキサ215は、テスト用の搬送波信号Sciと搬送波信号Scqとを乗算し、乗算により得られた出力信号Smxを周波数解析部280に供給する。
The antenna member 219A at the
周波数解析部280は、ミキサ215から出力されて周波数解析部280により観測される出力信号Smxの周波数が、搬送波信号生成部216により生成されたテスト用の搬送波信号Sci,Scqの周波数の2倍であるか否かを判断する(図9(B)参照)。これは、入力点218,219間の距離L1が(1/4+N)λ、つまりテスト用の搬送波信号Sci,Scqの位相差が90°であれば、ミキサ215の乗算により搬送波信号Sci,Scqの2倍の周波数成分が得られるからである。なお、周波数解析部280は制御部の一例を構成している。
In the
周波数解析部280は、出力信号Smxの周波数が2倍であると判断した場合には、入力点218,219間の距離L1が(1/4+N)λであると判断して、現在設定されているアンテナ部材219a〜219dに維持する。一方、出力信号Smxの周波数が2倍でないと判断した場合には、入力点218,219間の距離L1が(1/4+N)λでないと判断して、図6で示したアンテナ部材219a〜219dの何れかにスイッチ部587を切り替える。このような操作を繰り返しながら、搬送波信号Sci,Scqの2倍の周波数成分となるようなアンテナ部材219a〜219dの何れかを選択し、入力点218,219間の距離L1を(1/4+N)λに設定する。これにより、入力点218のアンテナ部材218aから送信される変調信号Saと、入力点219のアンテナ部材219Aから送信される変調信号Sbの位相を直交させることができる。
When the
<5.第3の実施の形態>
[振幅のキャリブレーション機能を備えた高周波伝送システムの例]
第3の実施の形態では、キャリブレーションモードにおいて、入力点218,219のアンテナ部材218a,219Aから送信される信号の位相差に加えて振幅値を調整する手法について説明する。なお、I相側の入力点218から変調信号が送信されるまでの動作は、上記第2の実施の形態と同様であるため、説明を省略する。
<5. Third Embodiment>
[Example of high-frequency transmission system with amplitude calibration function]
In the third embodiment, a method of adjusting the amplitude value in addition to the phase difference between signals transmitted from the antenna members 218a and 219A at the input points 218 and 219 in the calibration mode will be described. The operation until the modulation signal is transmitted from the
図10に示すように、高周波伝送システム100Eの入力点219のアンテナ部材219Aは、キャリブレーションモード時に変調信号Satを受信するアンテナ部材としても機能し、入力点218のアンテナ部材218aから送信された変調信号Satを受信する。アンテナ部材218aにより受信された変調信号Satはミキサ215に供給される。ここで、入力点218,219間の距離L1は、上述したように、(1/4+N)λに設定されているものとする。
As shown in FIG. 10, the antenna member 219A of the
ミキサ215は、入力点219のアンテナ部材219Aにより受信された変調信号Satと、搬送波信号生成部216により生成された搬送波信号Scと乗算することにより変調信号Satを周波数変換して受信信号Sarxを得る。周波数変換された受信信号Sarxは、端子d側に設定されたスイッチ部276を介して振幅値測定部370に供給される。
The
振幅値測定部370は、ミキサ215から出力された受信信号Sarxの振幅値を測定し、測定した受信信号Sarxの振幅値と搬送波信号生成部216から供給される搬送波信号Sctや予めメモリに保持される減衰前の変調信号Satの振幅値との差分を算出する。そして、振幅値測定部370は、この差分に基づく制御信号を生成して振幅値制御部378に供給する。
The amplitude
振幅値制御部378は、振幅値測定部370からの制御信号に基づいて、入力点219のアンテナ部材219Aで受信された変調信号Satの振幅値を減衰前の変調信号Satや搬送波信号Sctの振幅値と一致するように振幅制御を行う。例えば、受信された変調信号Satが減衰している場合には、その振幅値を上げるような振幅制御を行う。振幅制御されたテスト用の受信信号Sarxは、端子b側に設定されたスイッチ部276を介して位置回転量計算部270に供給される。
Based on the control signal from the amplitude
位置回転量計算部270は、導波路220による減衰が修正されたテスト用の受信信号Sarxに基づいて、上述したような位相のキャリブレーションを行い、最適なアンテナ部材219a〜219dを選択する。なお、I相側の振幅値制御部380およびQ相側の振幅値制御部378は、通常の通信モード時に、変調信号Sa,Sbを増幅する増幅器としても用いられる。
The position rotation
以上説明したように、本実施の形態では、キャリブレーションモード時に、テスト用の受信信号Sarxの振幅値を計測することにより、入力点218,219間の導波路220の影響による変調信号Satの振幅値の減衰率を算出することができる。これにより、振幅方向の誤差を補正することができ、より正確な位相のキャリブレーションを行うことができる。
As described above, in the present embodiment, the amplitude of the modulation signal Sat due to the influence of the
<6.第4の実施の形態>
[位相のキャリブレーション機能を備えた高周波伝送システムの例]
第4の実施の形態では、位相のキャリブレーションを上述した複数のアンテナ部材219a〜219dを切り替えて行うのではなく、電気や光学エネルギーを加えると誘電率が可変する誘電体を用いることによりI相およびQ相の信号間の位相差を調整する。以下の例では、誘電率が可変な誘電体として液晶を用いた場合について説明する。
<6. Fourth Embodiment>
[Example of high-frequency transmission system with phase calibration function]
In the fourth embodiment, the phase calibration is not performed by switching the plurality of antenna members 219a to 219d described above, but by using a dielectric whose dielectric constant is variable when electric or optical energy is applied, the I-phase is obtained. And adjust the phase difference between the Q-phase signals. In the following example, a case where liquid crystal is used as a dielectric having a variable dielectric constant will be described.
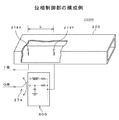
図11(A)および図11(B)に示すように、導波路220の送信側端部には、入力点218,219間の距離Lを調整して2つの信号の位相差を制御するための位相制御部400が設けられている。位相制御部400は、筐体402と、筐体402の内部に封入された液晶層406と、筐体402の上面および下面のそれぞれに設けられた電極410,412と、電極410,412に所定の電圧を印加するための電圧制御部414とを有している。
As shown in FIGS. 11A and 11B, the transmission side end of the
液晶層406としては、例えばネマチィック方式等の液晶が好適に用いられる。ネマチィック型の液晶の比誘電率εは、60GHzなどのミリ波帯においても、印加電圧に応じて3.0から3.5まで変化することが明らかにされている。そのため、このような液晶層406を導波路220内に封入することで、電圧を加えながらの波長の微調節が可能となる。
As the
電圧制御部414は、図8に示した位置回転量計算部270に接続され、位置回転量計算部270により算出された回転量(ずれ量)に基づいて印加電圧を算出し、算出した印加電圧を電極410,412に印加する。これにより、印加された電圧値に応じて液晶層406を通過する信号の透過率が調整される。
The
入力点218のアンテナ部材218Xは、筐体402内部であって導波路220と反対側の端部に結合され、変調信号Saを液晶層406を介して導波路220に放射する。入力点219のアンテナ部材219Yは、筐体402の外部であって導波路220内の位相制御部400側の端部に結合され、変調信号Sbを導波路220に放射する。本例では、入力点218X,219Y間の距離Lは(1/4+N)λから若干ずれているものとする。
The
このように構成された高周波伝送システム100Fにおいて、I相に割り当てられた信号は、入力点218のアンテナ部材218Xから比誘電率εで与えられる液晶層406中に放射される。本例では、電圧制御部414により印加電圧を電気的に制御することにより、液晶層406の誘電率を変化させて、液晶層406を通過する信号の透過率を変化させる。これにより、入力点218,219間の距離Lに依存することなく、I相側のアンテナ部材218Xから放射される変調信号Saと、Q相側のアンテナ部材219Yから放射される変調信号Sbとの位相差を90°に設定することができる。
In the high-
なお、誘電率が変化する物質としては、液晶層406の他にも磁気エネルギーや光エネルギーを用いるもの、熱エネルギーや力学的エネルギーを用いるものもあるので、それらを本発明で示すシステムに適用することは容易に想像できる。磁気エネルギーや光エネルギーを用いて誘電率を変化させる一例としては、特開2003−209266号公報に記載されているように、例えば量子常誘電体(SrTiO3,CaTiO3,KTaO3など)で構成される物質が挙げられる。また、熱エネルギーの一例としては、例えばフッ素系強誘電性高分子などが挙げられる。この場合には、フッ素系強誘電性高分子をヒートシンクによって温度を変化等させることによって、誘電率を変化させることができる。さらに、力学的エネルギーの一例としては、例えばニオブ酸リチウムなどが挙げられる。この場合にはニオブ酸リチウムに対してネジ等の締結部材により締めるなどの方法で圧力を加えることによって、誘電率を変化させることができる。
In addition to the
<7.第5の実施の形態>
[位相のキャリブレーション機能を備えた高周波伝送システムの例]
第5の実施の形態では、位相のキャリブレーションを上述した複数のアンテナ部材219a〜219dを切り替えて行うのではなく、遅延素子を用いることによりI相およびQ相の信号間の位相差を調整する。
<7. Fifth embodiment>
[Example of high-frequency transmission system with phase calibration function]
In the fifth embodiment, phase calibration is not performed by switching the plurality of antenna members 219a to 219d described above, but the phase difference between the I-phase and Q-phase signals is adjusted by using a delay element. .
図12に示すように、位相制御部500は、例えばバッファ等の遅延素子郡により構成され、スイッチ部274と入力点219との間に設けられている。この位相制御部500は、例えば、複数段(n段)で構成され、各段には段数に応じて直列に接続されたn個の遅延素子が配設されている。例えば、1段目には1個の遅延素子が設けられ、2段目には2個の遅延素子が直列に接続されて設けられ、n段目にはn個の遅延素子が直列に接続されて設けられる。各段の一端側に配設された遅延素子は、スイッチ部274の切り替えに応じてスイッチ部274に電気的に接続される。
As shown in FIG. 12, the
このように構成された高周波伝送システム100Gでは、図8に示した位置回転量計算部270は、例えば、キャリブレーションモードにおいてテスト用の変調信号Satに基づいて信号間の位相差が90°となるような遅延素子を選択する。そして、位置回転量計算部270は、選択した遅延素子に対応した切替信号を生成してスイッチ部274に供給する。スイッチ部274は、位置回転量計算部270から供給された切替信号に基づいて、信号間の位相差が90°となる最適な遅延素子に切り替える。
In the high-
以上説明したように、本実施の形態によれば、位相制御部500を設けることで、Q相の変調信号Sbの位相を複数段階で遅らせることができる。これにより、I相側の入力点218のアンテナ部材218Xから放射される変調信号SaとQ相側の入力点219のアンテナ部材219Yから放射される変調信号Sbとの位相差を高精度に調整することができ、IQ直交軸を用いた高速伝送を実現できる。なお、位相制御部500は、Q相側ではなくI相側に設けることもできるし、I相およびQ相の双方に設けることもできる。
As described above, according to the present embodiment, by providing
<8.第6の実施の形態>
[位相のキャリブレーション機能を備えた高周波伝送システムの例]
第6の実施の形態では、位相のキャリブレーションを上述した複数のアンテナ部材219a〜219dを切り替えて行うのではなく、移相素子を用いることにより、I相およびQ相の信号間の位相差を調整する。
<8. Sixth Embodiment>
[Example of high-frequency transmission system with phase calibration function]
In the sixth embodiment, the phase calibration is not performed by switching the plurality of antenna members 219a to 219d described above, but the phase difference between the I-phase and Q-phase signals is obtained by using a phase shift element. adjust.
図13に示すように、位相制御部600は、例えば抵抗(R)、インダクタ(L)、キャパシタ(C)等から構成され、スイッチ部274と入力点219との間に設けられている。この位相制御部600は、例えば、複数段(n段)で構成され、各段には段数に応じて直列または並列に接続されたn個の移相素子が配設されている。例えば、1段目にはインダクタと抵抗とが直列に接続されて設けられ、2段目にはキャパシタと抵抗とが並列に接続されて設けられている。
As illustrated in FIG. 13, the
このように構成された高周波伝送システム100Hでは、図8に示した位置回転量計算部270は、例えば、キャリブレーションモードにおいてテスト用の変調信号Satに基づいて信号間の位相差が90°となるような移相素子を選択する。そして、位置回転量計算部270は、選択した移相素子に対応した切替信号を生成してスイッチ部274に供給する。スイッチ部274は、位置回転量計算部270から供給された切替信号に基づいて、信号間の位相差が90°となる最適な遅延素子に切り替える。
In the high-
以上説明したように、本実施の形態によれば、位相制御部600を設けることで、Q相の変調信号Sbの位相を複数段階で遅らせることができる。これにより、I相側の入力点218のアンテナ部材218Xから放射される変調信号SaとQ相側の入力点219のアンテナ部材219Yから放射される変調信号Sbとの位相差を高精度に調整することができ、IQ直交軸を用いた高速伝送を実現できる。なお、位相制御部600は、Q相側ではなくI相側に設けることもできるし、I相およびQ相の双方に設けることもできる。
As described above, according to the present embodiment, by providing
<9.第7の実施の形態>
[位相のキャリブレーション機能を備えた高周波伝送システムの例]
第7の実施の形態では、送信装置200と受信装置300との間において連動してキャリブレーションを行う。本実施の形態に係る高周波伝送システム100Iは、図3に示した高周波伝送システム100Aの通信機能を備えると共に、受信装置300は受信機能に加えて送信機能も兼ね備えている。以下では、図6に示した複数のアンテナ部材219a〜219dのそれぞれをNo.1〜No.4と称する。
<9. Seventh Embodiment>
[Example of high-frequency transmission system with phase calibration function]
In the seventh embodiment, calibration is performed in conjunction between the
図14に示すように、ステップS100で受信装置300は、高周波伝送システム100Iがキャリブレーションモードに設定されると、出力点258のアンテナ部材からテスト用のIQ信号を導波路220を介して送信装置200に送信する。
As shown in FIG. 14, when the high-frequency transmission system 100I is set to the calibration mode in step S100, the receiving
次に、ステップS102で送信装置200は、キャリブレーションモードに設定されると、スイッチ部274をアンテナ部材219a〜219dのうちアンテナ部材219a(No.1)に設定する。
Next, in step S102, when the
ステップS104でアンテナ部材219aは、受信装置300から送信されたテスト用のIQ信号を受信して位置回転量計算部270に供給する。また、アンテナ部材218aは、受信装置300から送信されたテスト用のIQ信号を受信して位置回転量計算部270に供給する。位置回転量計算部270は、それぞれのテスト用のIQ信号から信号点情報を取得して図示しないメモリ部に記憶する。
In step S <b> 104, the antenna member 219 a receives the test IQ signal transmitted from the receiving
アンテナ部材219aにおける信号点情報を取得したら、続けて、ステップS106で受信装置300は、出力点258のアンテナ部材からテスト用のIQ信号を導波路220を介して再度送信装置200に送信する。次に、ステップS108で送信装置200は、スイッチ部274をアンテナ部材219aからアンテナ部材219bに切り替える。
After acquiring the signal point information in the antenna member 219a, the receiving
ステップS110でアンテナ部材419bは、受信装置300から送信されたテスト用のIQ信号を受信して位置回転量計算部270に供給する。また、アンテナ部材218aは、受信装置300から送信されたテスト用のIQ信号を受信して位置回転量計算部270に供給する。位置回転量計算部270は、それぞれのテスト用のIQ信号から信号点情報を取得して図示しないメモリ部に記憶する。
In step S <b> 110, the antenna member 419 b receives the test IQ signal transmitted from the receiving
このようなキャリブレーション動作をアンテナ部材219c,219dのそれぞれに対しても行い、アンテナ部材219c,219dのそれぞれにより受信したテスト用のIQ信号における信号点情報を取得してメモリ部に記憶する。
Such a calibration operation is performed for each of the
ステップS112で位置回転量計算部270は、メモリ部に記憶されたアンテナ部材219a〜219dのそれぞれのテスト用のIQ信号における信号点情報に基づいて、変調信号Sa,Sbの位相差が90°となるようなアンテナ部材219a〜219dを決定する。そして、位置回転量計算部270は、決定したアンテナ部材219a〜219dに対応した切替信号を生成してスイッチ部274に供給する。
In step S112, the position rotation
ステップS114でスイッチ部274は、位置回転量計算部270から供給される切替信号に基づいて、変調信号Sa,Sbの位相差が90°となる最適なアンテナ部材219a〜219dに切り替える。このような一連のキャリブレーション動作により、変調信号Sa,Sbの位相差を高精度に調整することができ、IQ直交軸を用いた高速伝送を実現できる。なお、上述した信号点情報以外にも例えばIQ信号に付加したエラービット情報(エラー訂正信号)などで実現することも容易に考えられる。
In step S114, the
<10.第8の実施の形態>
[位相のキャリブレーション機能を備えた高周波伝送システムの例]
第8の実施の形態では、上記第7の実施の形態と同様に、送信装置200と受信装置300との間において連動してキャリブレーションを行う。図15に示すように、ステップS200で高周波伝送システム100Jの送信装置200は、スイッチ部274をアンテナ部材219a〜219dのうちアンテナ部材219a(No.1)に設定する。そして、ステップS202で送信装置200は、アンテナ部材218a,219aのそれぞれから導波路220を介して受信装置300にテスト用のIQ信号を送信する。
<10. Eighth Embodiment>
[Example of high-frequency transmission system with phase calibration function]
In the eighth embodiment, as in the seventh embodiment, calibration is performed in conjunction between the
ステップS204で受信装置300は、図3に示す出力点258のアンテナ部材を介してテスト用のIQ信号のそれぞれを受信する。受信装置300には図8で示した位置回転量計算部270が設けられており、位置回転量計算部270はそれぞれのテスト用のIQ信号から信号点情報(IQ信号の位相の回転量)を取得して図示しないメモリ部に記憶する。
In step S204, the receiving
次に、ステップS206で送信装置200は、スイッチ部274をアンテナ部材219a(No.1)からアンテナ部材219b(No.2)に切り替える。そして、ステップS208において、アンテナ部材218a,219aのそれぞれから導波路220を介して受信装置300にテスト用のIQ信号を送信する。
Next, in step S206, the
ステップS210で受信装置300は、出力点258のアンテナ部材を介してテスト用のIQ信号のそれぞれを受信する。位置回転量計算部270は、それぞれのテスト用のIQ信号から信号点情報(IQ信号の位相の回転量)を取得して図示しないメモリ部に記憶する。
In step S <b> 210, receiving
このようなキャリブレーション動作を、アンテナ部材219c,219dのそれぞれに対しても行い、アンテナ部材219c,219dのそれぞれにより受信したテスト用のIQ信号における信号点情報を取得してメモリ部に記憶する。
Such a calibration operation is also performed on each of the
そして、ステップS212で受信装置300は、メモリ部に記憶されたアンテナ部材219a〜219dのそれぞれのテスト用のIQ信号における信号点情報に基づいて、変調信号Sa,Sbの位相差が90°となるアンテナ部材219a〜219dを決定する。
In step S212, the receiving
ステップS214で受信装置300は、最適なアンテナ部材219a〜219dを決定したら、位置回転量計算部270により決定されたアンテナ部材219a〜219dに基づく切替信号を送信装置200にフィードバックする。送信装置200は、入力点218のアンテナ部材218aおよび入力点219のアンテナ部材219a〜219dの何れかを介して切替信号を受信する。
When the optimal antenna members 219a to 219d are determined in step S214, the
ステップS216で送信装置200は、受信装置300から供給される切替信号に基づいて、変調信号Sa,Sbの位相差が90°となる最適なアンテナ部材219a〜219dに切り替える。このような一連のキャリブレーション動作により、変調信号Sa,Sbの位相差を高精度に調整することができ、IQ直交軸を用いた高速伝送を実現できる。
In step S216, based on the switching signal supplied from the
なお、本発明の技術範囲は、上述した実施形態に限定されるものではなく、本発明の趣旨を逸脱しない範囲において、上述した実施形態に種々の変更を加えたものを含む。 It should be noted that the technical scope of the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiments, and includes those in which various modifications are made to the above-described embodiments without departing from the spirit of the present invention.
例えば、上述した実施の形態では、BPSK変調について説明したが、これに限定されることはなく、QPSK(4相PSK)変調方式や8相PSK変調方式等にも本発明を適用することができる。さらに、上述したBPSK変調部212,213の前後に振幅制御装置を加えることで、振幅方向にもデジタル符号を重畳するQAM方式に応用可能であることは自明である。QAM伝送によれば、IQ軸の直交性が伝送特性に大きな影響を与えるので、本高周波伝送システムの特徴を活かして精度の高いIQ直交軸伝送を行うことができる。
For example, in the above-described embodiments, BPSK modulation has been described. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and the present invention can also be applied to a QPSK (4-phase PSK) modulation system, an 8-phase PSK modulation system, and the like. . Further, it is obvious that an amplitude control device is added before and after the above-described
100A,100B,100C,100D,100E,100F,100G,100H,00I,100J・・・高周波伝送システム、200・・・送信装置、212,213・・・BPSK変調部、214,215・・・ミキサ、216,256・・・搬送波信号生成部、218,219・・・入力点、218a,218X,219a〜219d,219Y・・・アンテナ部材、220・・・導波路、250・・・QPSK復調部、252,253・・・BPSK変調部、254,255・・・ミキサ、258,260・・・出力点、270・・・位置回転量計算部、280・・・周波数解析部、370・・・振幅値測定部、376・・・スイッチ部、378・・・振幅値制御部、300・・・受信装置、400,500,600・・・位相制御部 100A, 100B, 100C, 100D, 100E, 100F, 100G, 100H, 00I, 100J ... high frequency transmission system, 200 ... transmission device, 212, 213 ... BPSK modulator, 214, 215 ... mixer , 216, 256... Carrier wave signal generation unit, 218, 219... Input point, 218 a, 218 X, 219 a to 219 d, 219 Y... Antenna member, 220. , 252 ... 253 ... BPSK modulator, 254,255 ... mixer, 258,260 ... output point, 270 ... position rotation amount calculator, 280 ... frequency analyzer, 370 ... Amplitude value measuring unit, 376... Switch unit, 378... Amplitude value control unit, 300... Receiving device, 400, 500, 600. Control unit
Claims (14)
所定周波数の搬送波信号を入力される第2の信号に基づいて変調して第2の送信信号を出力する第2の送信部とを備え、
前記第1の送信部により出力された前記第1の送信信号を導波路に入力する第1の入力点と前記第2の送信部により出力された前記第2の送信信号を前記導波路に入力する第2の入力点とが、前記第1の送信信号と前記第2の送信信号との間に所定の位相差を与える距離だけずれている送信装置。 A first transmitter that modulates a carrier signal of a predetermined frequency based on an input first signal and outputs a first transmission signal;
A second transmission unit that modulates a carrier signal of a predetermined frequency based on an input second signal and outputs a second transmission signal;
A first input point for inputting the first transmission signal output from the first transmission unit to the waveguide, and a second input signal output from the second transmission unit to the waveguide. And a second input point that is shifted by a distance that gives a predetermined phase difference between the first transmission signal and the second transmission signal.
前記搬送波信号の位相と、前記第1の入力点から送信されて前記第2の入力点により受信された前記第1の送信信号の位相を比較し、当該比較結果により算出された前記第1の送信信号の位相のずれ量に基づいて前記複数のアンテナのうち何れかの前記アンテナを選択する制御部をさらに備える請求項1に記載の送信装置。 The second input point is provided with a plurality of antennas for receiving the first transmission signal,
The phase of the carrier wave signal is compared with the phase of the first transmission signal transmitted from the first input point and received by the second input point, and the first calculated by the comparison result is compared. The transmission apparatus according to claim 1, further comprising a control unit that selects any one of the plurality of antennas based on a phase shift amount of a transmission signal.
前記第2の送信部には、前記第2の信号を増幅する第2の増幅部が設けられ、
前記第1の入力点から送信されて前記第2の入力点により受信された前記第1の送信信号の振幅値を測定し、当該測定結果に基づいて前記第2の増幅部から出力される前記第2の信号の振幅値を調整する振幅値測定部をさらに備える請求項6に記載の送信装置。 The first transmitter is provided with a first amplifier for amplifying the first signal,
The second transmission unit includes a second amplification unit that amplifies the second signal,
The amplitude value of the first transmission signal transmitted from the first input point and received by the second input point is measured, and the amplitude value output from the second amplification unit based on the measurement result The transmission apparatus according to claim 6, further comprising an amplitude value measurement unit that adjusts an amplitude value of the second signal.
前記制御部により計算された前記ずれ量に基づいて前記第1および第2の送信信号の少なくとも一方の位相を調整する位相調整部とをさらに備える請求項1に記載の送信装置。 Comparing the phase of the carrier wave signal with the phase of the first transmission signal transmitted from the first input point and received by the second input point, and based on the comparison result, A control unit for calculating a phase shift amount of the transmission signal;
The transmission apparatus according to claim 1, further comprising a phase adjustment unit that adjusts a phase of at least one of the first and second transmission signals based on the shift amount calculated by the control unit.
前記導波路の一端部に設けられ、電気、光学、磁気あるいは熱エネルギーにより誘電率が変化する物質から構成される請求項8に記載の送信装置。 The phase adjusting unit is
The transmission device according to claim 8, wherein the transmission device is formed of a substance that is provided at one end of the waveguide and whose dielectric constant changes due to electric, optical, magnetic, or thermal energy.
前記導波路の外部に設けられ、遅延素子、抵抗、インダクタおよびキャパシタのうち少なくとも1以上の素子から構成される請求項8に記載の送信装置。 The phase adjusting unit is
The transmission device according to claim 8, wherein the transmission device is provided outside the waveguide and includes at least one of a delay element, a resistor, an inductor, and a capacitor.
前記位相変調に加えて前記第1および第2の信号の振幅変調を行う請求項1に記載の送信装置。 The signal processing is phase modulation for modulating the phase of the first and second signals;
The transmission apparatus according to claim 1, wherein amplitude modulation of the first and second signals is performed in addition to the phase modulation.
所定周波数の搬送波信号を入力される第2の信号に基づいて変調して第2の送信信号を出力する第2の送信部とを有する送信装置と、
前記第1の送信部から出力された前記第1の送信信号および前記第2の送信部から出力された前記第2の送信信号が入力される導波路と、
前記導波路を介して送信された前記第1および第2の送信信号を受信し、当該第1および第2の送信信号を所定周波数の搬送波信号に基づいて復調して受信信号を得る受信部を有する受信装置とを備え、
前記第1の送信部により出力された前記第1の送信信号を前記導波路に入力する第1の入力点と前記第2の送信部により出力された前記第2の送信信号を前記導波路に入力する第2の入力点とが、前記第1の送信信号と前記第2の送信信号との間に所定の位相差を与える距離だけずれている通信システム。 A first transmitter that modulates a carrier signal of a predetermined frequency based on an input first signal and outputs a first transmission signal;
A transmission device having a second transmission unit that modulates a carrier wave signal of a predetermined frequency based on an input second signal and outputs a second transmission signal;
A waveguide to which the first transmission signal output from the first transmission unit and the second transmission signal output from the second transmission unit are input;
A receiving unit that receives the first and second transmission signals transmitted through the waveguide, demodulates the first and second transmission signals based on a carrier signal of a predetermined frequency, and obtains a reception signal; And a receiving device having
A first input point for inputting the first transmission signal output from the first transmission unit to the waveguide and a second transmission signal output from the second transmission unit to the waveguide. A communication system in which an input second input point is shifted by a distance that gives a predetermined phase difference between the first transmission signal and the second transmission signal.
前記第1および第2の送信部から出力された前記第1および第2の送信信号を前記導波路を介して前記受信装置に送信し、
前記受信装置は、
前記送信装置から送信された前記第1および第2の送信信号を受信し、受信した前記第1および第2の送信信号に基づいて前記第1の入力点と前記第2の入力点とが前記所定の位相差ずれているか否かを判断し、当該判断結果を前記送信装置にフィードバックする請求項12に記載の通信システム。 The transmitter is
Transmitting the first and second transmission signals output from the first and second transmission units to the reception device via the waveguide;
The receiving device is:
The first input point and the second input point are received based on the received first and second transmission signals, the first and second transmission signals transmitted from the transmission device are received. The communication system according to claim 12, wherein it is determined whether or not a predetermined phase difference is shifted, and the determination result is fed back to the transmission device.
前記第1および第2の送信信号を前記導波路を介して前記送信装置に送信し、
前記送信装置は、
前記受信装置から送信された前記第1および第2の送信信号を受信し、受信した前記第1および第2の送信信号に基づいて前記第1の入力点と前記第2の入力点とが前記所定の位相差ずれているか否かを判断する請求項12に記載の通信システム。 The receiving device is:
Transmitting the first and second transmission signals to the transmission device via the waveguide;
The transmitter is
The first input point and the second input point are received based on the received first and second transmission signals, the first and second transmission signals transmitted from the receiving device are received. The communication system according to claim 12, wherein it is determined whether or not a predetermined phase difference is shifted.
Priority Applications (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009093444A JP2010245905A (en) | 2009-04-07 | 2009-04-07 | Transmission apparatus and communication system |
| AT10002629T ATE523919T1 (en) | 2009-04-07 | 2010-03-12 | TRANSMISSION DEVICE AND COMMUNICATION SYSTEM |
| EP10002629A EP2239812B1 (en) | 2009-04-07 | 2010-03-12 | Transmission apparatus and communication system |
| US12/731,425 US8213534B2 (en) | 2009-04-07 | 2010-03-25 | Transmission apparatus and communication system |
| CN201010151434A CN101860506A (en) | 2009-04-07 | 2010-03-31 | Dispensing device and communication system |
| BRPI1000681-8A BRPI1000681A2 (en) | 2009-04-07 | 2010-03-31 | transmission apparatus and communication system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009093444A JP2010245905A (en) | 2009-04-07 | 2009-04-07 | Transmission apparatus and communication system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010245905A true JP2010245905A (en) | 2010-10-28 |
| JP2010245905A5 JP2010245905A5 (en) | 2012-05-10 |
Family
ID=42340877
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009093444A Ceased JP2010245905A (en) | 2009-04-07 | 2009-04-07 | Transmission apparatus and communication system |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8213534B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP2239812B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP2010245905A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN101860506A (en) |
| AT (1) | ATE523919T1 (en) |
| BR (1) | BRPI1000681A2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015130570A (en) * | 2014-01-07 | 2015-07-16 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | Transmission system and method, and receiver |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SG188012A1 (en) * | 2011-08-26 | 2013-03-28 | Sony Corp | An on pcb dielectric waveguide |
| CN103645380A (en) * | 2013-12-04 | 2014-03-19 | 北京无线电计量测试研究所 | Design method of waveguide-type phase standard selector used for millimeter waves |
| US10338873B2 (en) * | 2015-02-27 | 2019-07-02 | Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. | Waveguides in a computing device |
| DE102019133684A1 (en) * | 2019-12-10 | 2021-06-10 | Sennheiser Electronic Gmbh & Co. Kg | Device for configuring a wireless radio link and method for configuring a wireless radio link |
| CN110879387B (en) * | 2019-12-17 | 2021-10-15 | 成都华创电科信息技术有限公司 | Based on radio broadband signal distancer |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS63175557A (en) * | 1986-12-30 | 1988-07-19 | トムソン−セエスエフ | Apparatus and method for amplitude-phase modulation by using a plurality of transmitters |
| JP2000209162A (en) * | 1999-01-12 | 2000-07-28 | Hitachi Cable Ltd | Light source for optical wavelength multiplex |
| WO2002031965A1 (en) * | 2000-10-12 | 2002-04-18 | Sony Corporation | Demodulator and receiver |
| JP2004516743A (en) * | 2000-12-21 | 2004-06-03 | ブッカム・テクノロジー・ピーエルシー | Improvements in or related to optical communications |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB1507147A (en) * | 1974-09-25 | 1978-04-12 | Marconi Co Ltd | Multiplexing arrangements |
| IT1277256B1 (en) * | 1995-10-13 | 1997-11-05 | Pirelli Cavi S P A Ora Pirelli | TUNABLE ACOUSTIC OPTICAL SWITCH IN WAVE GUIDE, WITH BALANCED OPTICAL PATHS |
| JP2885713B2 (en) | 1996-08-27 | 1999-04-26 | 埼玉日本電気株式会社 | Transmitter |
| CA2403689A1 (en) * | 1999-11-23 | 2001-05-31 | Nanovation Technologies, Inc. | Waveguide optical phase shifter |
| JP2003209266A (en) | 2001-08-31 | 2003-07-25 | Kanagawa Acad Of Sci & Technol | Method for changing permittivity, optical variable condensor, ultraviolet sensor and magnetic sensor |
| US6657510B2 (en) * | 2001-11-27 | 2003-12-02 | Harris Corporation | Corrective phase quadrature modulator system and method |
| US7583897B2 (en) * | 2002-01-08 | 2009-09-01 | Enablence Usa Fttx Networks Inc. | Optical network system and method for supporting upstream signals propagated according to a cable modem protocol |
| GB0305619D0 (en) * | 2003-03-12 | 2003-04-16 | Qinetiq Ltd | Phase shifter device |
| KR100703410B1 (en) * | 2005-01-19 | 2007-04-03 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Offset quadrature phase-shift-keying method and optical transmitter using the same |
| JP4760333B2 (en) | 2005-11-28 | 2011-08-31 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Wireless communication apparatus and wireless communication method |
| CN100464191C (en) * | 2007-05-18 | 2009-02-25 | 东南大学 | Microelectronic machinery microwave frequency detector and its preparation method |
| JP4986800B2 (en) | 2007-10-10 | 2012-07-25 | 双葉電子工業株式会社 | A hub device having a reference voltage generation circuit and a reference voltage generation circuit used in a robot and a transmission line for the robot. |
-
2009
- 2009-04-07 JP JP2009093444A patent/JP2010245905A/en not_active Ceased
-
2010
- 2010-03-12 EP EP10002629A patent/EP2239812B1/en not_active Not-in-force
- 2010-03-12 AT AT10002629T patent/ATE523919T1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2010-03-25 US US12/731,425 patent/US8213534B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2010-03-31 BR BRPI1000681-8A patent/BRPI1000681A2/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2010-03-31 CN CN201010151434A patent/CN101860506A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS63175557A (en) * | 1986-12-30 | 1988-07-19 | トムソン−セエスエフ | Apparatus and method for amplitude-phase modulation by using a plurality of transmitters |
| JP2000209162A (en) * | 1999-01-12 | 2000-07-28 | Hitachi Cable Ltd | Light source for optical wavelength multiplex |
| WO2002031965A1 (en) * | 2000-10-12 | 2002-04-18 | Sony Corporation | Demodulator and receiver |
| JP2004516743A (en) * | 2000-12-21 | 2004-06-03 | ブッカム・テクノロジー・ピーエルシー | Improvements in or related to optical communications |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015130570A (en) * | 2014-01-07 | 2015-07-16 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | Transmission system and method, and receiver |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2239812A1 (en) | 2010-10-13 |
| BRPI1000681A2 (en) | 2011-03-22 |
| EP2239812B1 (en) | 2011-09-07 |
| US8213534B2 (en) | 2012-07-03 |
| CN101860506A (en) | 2010-10-13 |
| US20100254477A1 (en) | 2010-10-07 |
| ATE523919T1 (en) | 2011-09-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| De Wit et al. | Analysis and design of a foam-cladded PMF link with phase tuning in 28-nm CMOS | |
| Tatu et al. | A new direct millimeter-wave six-port receiver | |
| Fritsche et al. | A low-power SiGe BiCMOS 190-GHz transceiver chipset with demonstrated data rates up to 50 Gbit/s using on-chip antennas | |
| CN107037282B (en) | System and method for measuring multiple RF signal paths | |
| Van Thienen et al. | A multi-gigabit CPFSK polymer microwave fiber communication link in 40 nm CMOS | |
| Tatu et al. | Ka-band analog front-end for software-defined direct conversion receiver | |
| JP2010245905A (en) | Transmission apparatus and communication system | |
| Tatu et al. | Ka-band direct digital receiver | |
| KR101716546B1 (en) | System and method for a radio frequency system | |
| Karakuzulu et al. | A four-channel bidirectional D-band phased-array transceiver for 200 Gb/s 6G wireless communications in a 130-nm BiCMOS technology | |
| US20150043623A1 (en) | Wireless transmission system, wireless communication device, and wireless communication method | |
| US6260406B1 (en) | Densitometer using microwaves | |
| Sawaby et al. | A fully packaged 130-GHz QPSK transmitter with an integrated PRBS generator | |
| Lee et al. | Multi-mode 60-GHz radar transmitter SoC in 45-nm SOI CMOS | |
| Ardakani et al. | V-band six-port interferometer receiver: High data-rate wireless applications, BER and EVM analysis, and CFO compensation | |
| Antes et al. | System concept and implementation of a mmW wireless link providing data rates up to 25 Gbit/s | |
| Standaert et al. | A 410 GHz OOK transmitter in 28 nm CMOS for short distance chip-to-chip communications | |
| Standaert et al. | A 390-GHz outphasing transmitter in 28-nm CMOS | |
| US20070286190A1 (en) | Transmitter-receiver crossbar for a packet switch | |
| CN101552754B (en) | Carrier leakage corrective system for radio frequency transceiver | |
| Hagiwara et al. | A 258-GHz CMOS transmitter with phase-shifting architecture for phased-array systems | |
| Chen et al. | Generation of high data rate MSK-modulated 180-GHz signals | |
| Afzal et al. | A highly efficient 165-GHz 4FSK 17-Gb/s transceiver system with frequency overlapping architecture in 65-nm CMOS | |
| WO2022016110A1 (en) | Optically synchronized phased array | |
| Voinigescu et al. | Silicon D-band wireless transceivers and applications |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120321 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20120321 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20130118 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130205 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130325 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130528 |
|
| A045 | Written measure of dismissal of application [lapsed due to lack of payment] |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A045 Effective date: 20130924 |