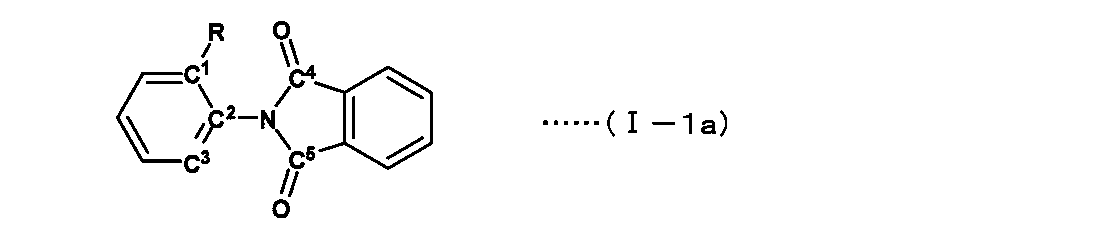JP2010053070A - Bisimide phenol compound, method for producing the same, and polymer compound - Google Patents
Bisimide phenol compound, method for producing the same, and polymer compound Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2010053070A JP2010053070A JP2008219495A JP2008219495A JP2010053070A JP 2010053070 A JP2010053070 A JP 2010053070A JP 2008219495 A JP2008219495 A JP 2008219495A JP 2008219495 A JP2008219495 A JP 2008219495A JP 2010053070 A JP2010053070 A JP 2010053070A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- amino
- group
- hydroxy
- compound
- methyl
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Landscapes
- Indole Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、新規ビスイミドフェノール化合物及びその製造方法と、このビスイミドフェノール化合物をモノマーの少なくとも一部として重合して得られる高分子化合物に関する。 The present invention relates to a novel bisimidephenol compound, a method for producing the same, and a polymer compound obtained by polymerizing the bisimidephenol compound as at least a part of a monomer.
イミド化合物は耐熱性に優れていることが知られており、イミド基を導入したイミドフェノール化合物は、耐熱性が要求される高分子材料の原料として有用である。耐熱性高分子材料の代表的なものとして、芳香族ポリイミド樹脂があるが、融点が非常に高い上、一般的な有機溶剤(例えばケトン系)に対する溶解性が非常に低く、作業性、加工性の面で問題が多い。例えば、ポリイミドを溶液として用いるには、N−メチルピロリドンのような高極性溶剤が必要であるが、N−メチルピロリドンのような高極性溶剤は沸点が非常に高いため、除去が困難であり、後工程でフクレの原因となりやすいなどの問題がある。 An imide compound is known to have excellent heat resistance, and an imide phenol compound into which an imide group has been introduced is useful as a raw material for a polymer material that requires heat resistance. A typical heat-resistant polymer material is an aromatic polyimide resin, but it has a very high melting point and very low solubility in common organic solvents (eg, ketones), making it workable and workable. There are many problems. For example, in order to use polyimide as a solution, a highly polar solvent such as N-methylpyrrolidone is required, but a highly polar solvent such as N-methylpyrrolidone has a very high boiling point and is difficult to remove. There are problems such as being likely to cause blisters in the subsequent process.
この対策として、ポリイミドの前駆体であるポリアミック酸の溶液を用い、溶剤を除去した後に加熱或いは化学的手法によってイミド環を閉環してポリイミド樹脂とする方法が知られている(非特許文献1)が、この方法では閉環時の体積収縮によって反りが起こるなどの問題がある。 As a countermeasure against this, a method is known in which a solution of polyamic acid, which is a precursor of polyimide, is used, and after removing the solvent, the imide ring is closed by heating or a chemical method to form a polyimide resin (Non-Patent Document 1). However, this method has problems such as warping due to volumetric shrinkage during ring closure.
一方で、ビスイミドフェノール化合物をモノマーとして用いる方法も開示されている(特許文献1〜4)。しかし、これまでに知られているビスイミドフェノール化合物は、一般的な有機溶剤、例えばケトン系溶剤への溶解性が十分でなかったり、また溶解性を付与するために分子構造を複雑にした結果、イミド基の濃度が低下してしまったりするものであった。 On the other hand, the method of using a bisimide phenol compound as a monomer is also disclosed (patent documents 1 to 4). However, the bisimide phenol compounds known so far are not sufficiently soluble in common organic solvents such as ketone solvents, and the molecular structure is complicated to impart solubility. The concentration of the imide group may decrease.
また、主鎖にエステル基を導入して溶解性を上げた例もあるが(特許文献5)、エステル基は加水分解の問題があるため好ましくない。
本発明はこのような状況を鑑みてなされたものであり、その課題は、樹脂の耐熱性改良が期待されるイミド基を含有し、一般的なケトン系溶剤中での反応に十分な溶解性を有し、また単純化された分子構造によって十分なイミド基含量を有する、耐熱性高分子材料の原料モノマーとして有用な芳香族ビスイミドフェノール化合物を提供することにある。 The present invention has been made in view of such circumstances, and the problem is that it contains an imide group that is expected to improve the heat resistance of the resin, and has sufficient solubility for reactions in general ketone solvents. Another object of the present invention is to provide an aromatic bisimidephenol compound useful as a raw material monomer for a heat-resistant polymer material having a sufficient imide group content due to a simplified molecular structure.
本発明者らは前記の課題を解決するため、鋭意検討の結果、特定の構造を有することで、ケトン系溶剤への十分な溶解性を発現するビスイミドフェノール化合物を見出した。また、特定のアミノフェノール化合物と芳香族カルボン酸二無水物とを反応させることにより、このビスイミドフェノール化合物を製造することができることを見出した。 As a result of intensive studies, the present inventors have found a bisimidephenol compound that exhibits a sufficient solubility in a ketone solvent by having a specific structure. Moreover, it discovered that this bisimide phenol compound could be manufactured by making a specific aminophenol compound and aromatic carboxylic dianhydride react.
即ち、本発明の要旨は、下記一般式(I)で表されるビスイミドフェノール化合物、に存する。 That is, the gist of the present invention resides in a bisimidephenol compound represented by the following general formula (I).
(一般式(I)において、R1は、以下に定義される|α|が45゜以上、90゜以下となる一価の官能基を示し、R5は、水素原子又は以下に定義される|α|が0゜以上、45゜未満となる一価の官能基を示す。
R2、R3及びR4は、各々独立に、水素原子、水酸基又は炭素数1〜10の有機基を示すが、隣接する2つの基が結合してベンゼン環に縮合する炭素数20以下の環を形成してもよい。
R6は、炭素数1〜10の有機基を示すが、隣接する2つの基が結合してベンゼン環に縮合する炭素数20以下の環を形成してもよい。
Xは、単結合、置換されていてもよい炭素数1〜20の二価の有機基、−O−又は−SO2−を示す。
nは0〜3の整数である。
複数のR1〜R6は、互いに同一であってもよく、異なっていてもよい。ただし、R1〜R6はハロゲン原子であることはなく、また、各R2〜R5のうちのいずれか一つは水酸基であることにより、化合物中には2個の水酸基を有する。)
(In general formula (I), R 1 represents a monovalent functional group in which | α | defined below is 45 ° or more and 90 ° or less, and R 5 is a hydrogen atom or defined below. | Α | represents a monovalent functional group with 0 ° or more and less than 45 °.
R 2 , R 3, and R 4 each independently represent a hydrogen atom, a hydroxyl group, or an organic group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms. A ring may be formed.
R 6 represents an organic group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms, but two adjacent groups may be bonded to form a ring having 20 or less carbon atoms condensed with a benzene ring.
X represents a single bond, an optionally substituted divalent organic group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, —O— or —SO 2 —.
n is an integer of 0-3.
The plurality of R 1 to R 6 may be the same as or different from each other. However, R 1 to R 6 are not halogen atoms, and any one of R 2 to R 5 is a hydroxyl group, so that the compound has two hydroxyl groups. )
{|α|の定義}
|α|とは、下記式(I−1)に示す構造において、理論計算に基づいた最安定構造を算出した際、2つの共役平面の成す二面角αの絶対値である。
{Definition of ||
| Α | is the absolute value of the dihedral angle α formed by two conjugate planes when the most stable structure based on theoretical calculation is calculated in the structure represented by the following formula (I-1).
ここで、二面角の理論計算は、OSとして「Microsoft社製Windows XP Professional Version 2002 Service Pack2」、ソフトに「Gaussian社製Gaussian03 x86-Win32版Rev.B.05」を用いて、AM1法(オプションとして「opt=verytight」を指定)により、最安定構造を計算して行われる。
αとしては、隣接する4つの原子、C(イミドのカルボニル炭素)−N(イミドの窒素)−C(芳香環)−C(芳香環)の成す以下の(1)〜(4)の4種の二面角の内、絶対値が最小のものとする。なお、C1〜C5は下記式(I−Ia)に示される。
(1) C1−C2−N−C4
(2) C1−C2−N−C5
(3) C3−C2−N−C4
(4) C3−C2−N−C5
Here, the theoretical calculation of the dihedral angle is performed using the AM1 method using “Microsoft Windows XP Professional Version 2002 Service Pack 2” as the OS and “Gaussian 03 x86-Win32 version Rev.B.05” as the software. This is done by calculating the most stable structure by specifying “opt = verytight” as an option).
α is the following four types (1) to (4) consisting of four adjacent atoms, C (carbonyl carbon of imide) -N (imide nitrogen) -C (aromatic ring) -C (aromatic ring) Of the dihedral angles, the absolute value is the smallest. C 1 to C 5 are represented by the following formula (I-Ia).
(1) C 1 -C 2 -N -C 4
(2) C 1 -C 2 -N-C 5
(3) C 3 -C 2 -N -C 4
(4) C 3 -C 2 -N -C 5
本発明の別の要旨は、下記一般式(II)で表されるアミノフェノールと、下記一般式(III)で表される芳香族カルボン酸二無水物とを脱水縮合させることを特徴とする、上記ビスイミドフェノール化合物の製造方法、に存する。 Another gist of the present invention is characterized by dehydrating condensation of an aminophenol represented by the following general formula (II) and an aromatic carboxylic dianhydride represented by the following general formula (III): The manufacturing method of the said bisimide phenol compound exists.
本発明の更に別の要旨は、上記ビスイミドフェノール化合物をモノマーの少なくとも一部として重合して得られる高分子化合物、に存する。 Still another subject matter of the present invention resides in a polymer compound obtained by polymerizing the bisimidephenol compound as at least a part of a monomer.
本発明によれば、樹脂の耐熱性改良が期待されるイミド基を含有するビスイミドフェノール化合物であって、一般的なケトン系溶剤中での反応に十分な溶剤溶解性を有し、また単純化された分子構造によって十分なイミド基含量を有する、耐熱性高分子材料の原料モノマーとして有用な新規芳香族ビスイミドフェノール化合物が提供される。
しかも、本発明のビスイミドフェノール化合物は、ハロゲン原子を含まない非ハロゲン系化合物であるので、近年の脱ハロゲン化の流れの中で非常に好適である。
According to the present invention, it is a bisimide phenol compound containing an imide group that is expected to improve the heat resistance of a resin, has sufficient solvent solubility for reaction in a general ketone solvent, and is simple. Provided is a novel aromatic bisimidephenol compound useful as a raw material monomer for a heat-resistant polymer material having a sufficient imide group content due to the converted molecular structure.
Moreover, since the bisimidephenol compound of the present invention is a non-halogen compound containing no halogen atom, it is very suitable in the recent dehalogenation flow.
以下に本発明の実施の形態を詳細に説明する。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail.
[ビスイミドフェノール化合物]
本発明のビスイミドフェノール化合物は、下記一般式(I)で表されるものであり、ケトン系溶剤に対する溶解度が高いために、重合反応等における取り扱い性に優れ、また、分子中のイミド基濃度が高いことから、エポキシ樹脂、ポリエステル樹脂、ポリカーボネート樹脂、フェノール樹脂等に耐熱性を付与するための原料モノマーとして有用である。
[Bisimidophenol compounds]
The bisimidophenol compound of the present invention is represented by the following general formula (I), and has high solubility in a ketone solvent, so that it is excellent in handling property in polymerization reaction and the like, and the imide group concentration in the molecule Therefore, it is useful as a raw material monomer for imparting heat resistance to epoxy resins, polyester resins, polycarbonate resins, phenol resins and the like.
(一般式(I)において、R1は、以下に定義される|α|が45゜以上、90゜以下となる一価の官能基を示し、R5は、水素原子又は以下に定義される|α|が0゜以上、45゜未満となる一価の官能基を示す。
R2、R3及びR4は、各々独立に、水素原子、水酸基又は炭素数1〜10の有機基を示すが、隣接する2つの基が結合してベンゼン環に縮合する炭素数20以下の環を形成してもよい。
R6は、炭素数1〜10の有機基を示すが、隣接する2つの基が結合してベンゼン環に縮合する炭素数20以下の環を形成してもよい。
Xは、単結合、置換されていてもよい炭素数1〜20の二価の有機基、−O−又は−SO2−を示す。
nは0〜3の整数である。
複数のR1〜R6は、互いに同一であってもよく、異なっていてもよい。ただし、R1〜R6はハロゲン原子であることはなく、また、各R2〜R5のうちのいずれか一つは水酸基であることにより、化合物中には2個の水酸基を有する。)
(In general formula (I), R 1 represents a monovalent functional group in which | α | defined below is 45 ° or more and 90 ° or less, and R 5 is a hydrogen atom or defined below. | Α | represents a monovalent functional group with 0 ° or more and less than 45 °.
R 2 , R 3, and R 4 each independently represent a hydrogen atom, a hydroxyl group, or an organic group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms. A ring may be formed.
R 6 represents an organic group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms, but two adjacent groups may be bonded to form a ring having 20 or less carbon atoms condensed with a benzene ring.
X represents a single bond, an optionally substituted divalent organic group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, —O— or —SO 2 —.
n is an integer of 0-3.
The plurality of R 1 to R 6 may be the same as or different from each other. However, R 1 to R 6 are not halogen atoms, and any one of R 2 to R 5 is a hydroxyl group, so that the compound has two hydroxyl groups. )
{|α|の定義}
|α|とは、下記式(I−1)に示す構造において、理論計算に基づいた最安定構造を算出した際、2つの共役平面の成す二面角αの絶対値である。
{Definition of ||
| Α | is the absolute value of the dihedral angle α formed by two conjugate planes when the most stable structure based on theoretical calculation is calculated in the structure represented by the following formula (I-1).
ここで、二面角の理論計算は、OSとして「Microsoft社製Windows XP Professional Version 2002 Service Pack2」、ソフトに「Gaussian社製Gaussian03 x86-Win32版Rev.B.05」を用いて、AM1法(オプションとして「opt=verytight」を指定)により、最安定構造を計算して行われる。
αとしては、隣接する4つの原子、C(イミドのカルボニル炭素)−N(イミドの窒素)−C(芳香環)−C(芳香環)の成す以下の(1)〜(4)の4種の二面角の内、絶対値が最小のものとする。なお、C1〜C5は下記式(I−Ia)に示される。
(1) C1−C2−N−C4
(2) C1−C2−N−C5
(3) C3−C2−N−C4
(4) C3−C2−N−C5
Here, the theoretical calculation of the dihedral angle is performed using the AM1 method using “Microsoft Windows XP Professional Version 2002 Service Pack 2” as the OS and “Gaussian 03 x86-Win32 version Rev.B.05” as the software. This is done by calculating the most stable structure by specifying “opt = verytight” as an option).
α is the following four types (1) to (4) consisting of four adjacent atoms, C (carbonyl carbon of imide) -N (imide nitrogen) -C (aromatic ring) -C (aromatic ring) Of the dihedral angles, the absolute value is the smallest. C 1 to C 5 are represented by the following formula (I-Ia).
(1) C 1 -C 2 -N -C 4
(2) C 1 -C 2 -N-C 5
(3) C 3 -C 2 -N -C 4
(4) C 3 -C 2 -N -C 5
なお、本発明において、「有機基」とは炭素原子を含む基であり、また、「官能基」とは有機基と水酸基などの無機基との総称である。 In the present invention, “organic group” is a group containing a carbon atom, and “functional group” is a general term for an organic group and an inorganic group such as a hydroxyl group.
<溶解性発現の説明>
イミド基含有化合物、特に芳香族イミド化合物は、イミド基を含む共役平面同士がスタッキングすることによる強い凝集力によって優れた物性を示す一方で、溶剤溶解性が非常に低く、取り扱いが困難であった。
<Explanation of solubility expression>
Imide group-containing compounds, especially aromatic imide compounds, have excellent physical properties due to strong cohesion due to stacking of conjugated planes containing imide groups, but have very low solvent solubility and are difficult to handle. .
本発明のビスイミドフェノール化合物が溶剤に対する溶解性に優れる理由の詳細は明らかではないが、以下のように推定される。
(1) イミド基のオルト位に適切な大きさの置換基R1を有することで、イミド基を含む共役平面が捻れを持ち、分子間のスタッキングが適度に阻害される。
(2) イミド基の両オルト位が非対称(R1≠R5)であることで結晶性が低下する。
Although the details of the reason why the bisimidephenol compound of the present invention is excellent in solubility in a solvent are not clear, it is estimated as follows.
(1) By having the substituent R 1 having an appropriate size at the ortho position of the imide group, the conjugate plane containing the imide group has a twist, and stacking between molecules is appropriately inhibited.
(2) Both ortho positions of the imide group are asymmetric (R 1 ≠ R 5 ), so that the crystallinity is lowered.
本発明のビスイミドフェノール化合物では、これらの要因が協奏的に作用することによって良好な溶剤溶解性が発現している。
ただし、捻れを生じさせる置換基R1が大きすぎる場合は、イミド化合物の特徴である分子間のスタッキングを完全に阻害してしまい、十分な物性が得られない可能性があるため、該置換基R1は適度な大きさに留めるのが好ましい。
In the bisimide phenol compound of the present invention, good solvent solubility is exhibited by these factors acting in concert.
However, if the substituent R 1 that causes twisting is too large, stacking between molecules, which is a feature of the imide compound, may be completely inhibited, and sufficient physical properties may not be obtained. R 1 is preferably kept at an appropriate size.
<R1>
R1は上記|α|が45゜以上、90゜以下の、ハロゲン原子以外の一価の官能基である。R1の|α|の下限は、分子間の重なりによる溶剤溶解性低下が起こりにくいことから、好ましくは48°、より好ましくは51°である。一方、|α|の上限は、置換基がイミド化合物の特徴である分子間のスタッキングの起きる適度な大きさであることから、好ましくは75°、より好ましくは60°である。
<R 1 >
R 1 is a monovalent functional group other than a halogen atom having the above | α | of 45 ° or more and 90 ° or less. Of R 1 | α | lower limit, since the overlapping solvent solubility decreases hardly occurs due to the intermolecular, preferably 48 °, more preferably 51 °. On the other hand, the upper limit of | α | is preferably 75 °, more preferably 60 °, because the substituent has an appropriate size at which stacking between molecules, which is a characteristic of an imide compound, occurs.
R1は、上記|α|を満たした上で、炭素イミドフェノール分子中のイミド基濃度、及び、イミド化合物に期待される物性が発現しやすい、即ち、分子量が過度に大きくないことにより、イミド基含量を十分なものとし、また、イミド化合物に期待される物性が、立体障害により分子間の相互作用が阻害されることにより損なわれないと思われることから、炭素数1〜10の有機基が好ましく、炭素数1〜3の有機基が更に好ましく、炭素数1〜2の有機基が特に好ましい。 R 1 satisfies the above | α | and easily develops the imide group concentration in the carbon imide phenol molecule and the physical properties expected of the imide compound, that is, the molecular weight is not excessively large. The organic group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms is considered to have sufficient group content and the physical properties expected of the imide compound are not impaired by the intermolecular interaction being inhibited by steric hindrance. Is preferable, an organic group having 1 to 3 carbon atoms is more preferable, and an organic group having 1 to 2 carbon atoms is particularly preferable.
R1の具体例は、炭化水素基、芳香族基、アシル基(アルデヒド、ケトン)、カルボキシル基、アルコキシカルボニル基(エステル)、アルコキシル基、アリ−ロキシル基、置換されていてもよいアミノ基、置換されていてもよいカルボキサミド基、メルカプト基、アルキルチオ基、アリ−ルチオ基、スルフィニル基、スルホニル基、スルホ基、トリアルキルシリル基等が挙げられる。中でも、|α|が好適範囲であることから、直鎖又は二級炭化水素基、アシル基(アルデヒド、ケトン)、カルボキシル基、アルコキシカルボニル基(エステル)、アルコキシル基、アリ−ロキシル基、置換されたアミノ基、置換されたカルボキサミド基、メルカプト基、アルキルチオ基、アリ−ルチオ基、スルフィニル基、スルホニル基、スルホ基が好ましく、とりわけ、直鎖炭化水素基、ホルミル基を除くアシル基、カルボキシル基、アルコキシカルボニル基(エステル)、置換されたアミノ基、スルホニル基、スルホ基が好ましい。 Specific examples of R 1 include a hydrocarbon group, an aromatic group, an acyl group (aldehyde, ketone), a carboxyl group, an alkoxycarbonyl group (ester), an alkoxyl group, an allyloxyl group, an optionally substituted amino group, An optionally substituted carboxamide group, mercapto group, alkylthio group, arylthio group, sulfinyl group, sulfonyl group, sulfo group, trialkylsilyl group and the like can be mentioned. Among them, since | α | is a suitable range, it is a linear or secondary hydrocarbon group, acyl group (aldehyde, ketone), carboxyl group, alkoxycarbonyl group (ester), alkoxyl group, aryloxyl group, substituted Amino group, substituted carboxamide group, mercapto group, alkylthio group, arylthio group, sulfinyl group, sulfonyl group, sulfo group are preferred, and in particular, linear hydrocarbon group, acyl group excluding formyl group, carboxyl group, Alkoxycarbonyl groups (esters), substituted amino groups, sulfonyl groups and sulfo groups are preferred.
なお、|α|が45〜90°の官能基を表1に、また、これらのうち特にR1として好適な官能基(|α|=48〜75°)について、その|α|と共に表2に示す(以下においてPhはフェニル基を、Meはメチル基を、Etはエチル基を、Prはプロピル基を、Buはブチル基を示す。)。 In addition, the functional groups having | α | of 45 to 90 ° are shown in Table 1, and among these functional groups particularly suitable as R 1 (| α | = 48 to 75 °), Table 2 together with the | α | (In the following, Ph represents a phenyl group, Me represents a methyl group, Et represents an ethyl group, Pr represents a propyl group, and Bu represents a butyl group).
表2に示す官能基のうち、R1としては特に下記表3に示すもの(|α|=51〜60°)が好ましい。 Of the functional groups shown in Table 2, R 1 is particularly preferably those shown in Table 3 below (| α | = 51-60 °).
<R5>
R5は、水素原子又は上記|α|が0°以上、45°未満のハロゲン原子以外の一価の官能基である。|α|が0°となるのは、R5がイミド基のカルボニル酸素と強く相互作用するルイス酸性を有した置換基の場合であり、こうした場合にはR1による二面角の形成をR5が阻害し、十分な溶解性を確保できない可能性があることから、|α|の下限は、好ましくは10°、より好ましくは20°である。また、大きな捻れを生じさせる置換基は、R1によって生じた二面角を更に増大し、好ましい範囲を逸脱させるおそれがあることから、|α|の上限は、好ましくは43°である。
<R 5 >
R 5 is a hydrogen atom or a monovalent functional group other than a halogen atom having the above | α | of 0 ° or more and less than 45 °. | Α | is 0 ° when R 5 is a substituent having Lewis acidity that strongly interacts with the carbonyl oxygen of the imide group. In such a case, the formation of a dihedral angle by R 1 is R 5 inhibits, since there may not be enough solubility, | alpha | lower limit is preferably 10 °, more preferably 20 °. In addition, since a substituent that causes a large twist may further increase the dihedral angle generated by R 1 and deviate from the preferred range, the upper limit of | α | is preferably 43 °.
R5の具体例としては、下記表4に|α|を示す水素原子又は官能基のような立体的に小さい水素原子又は官能基が挙げられ、この内、水素原子又は水酸基などの、立体的に小さく、ルイス酸性が小さい水素原子又は官能基が好ましい。 Specific examples of R 5 include sterically small hydrogen atoms or functional groups such as hydrogen atoms or functional groups represented by | α | in Table 4 below. Among these, steric ones such as hydrogen atoms or hydroxyl groups And a hydrogen atom or a functional group having a small Lewis acidity is preferable.
<R2〜R4>
R2〜R4は、各々独立に、水素原子、水酸基、又は炭素数1〜10のハロゲン原子以外の一価の有機基を示すが、R2〜R4のうち、隣接する2つの基が互いに結合してベンゼン環に縮合する、炭素数20以下の環を形成してもよい。
R2〜R4としての炭素数1〜10の有機基としては、特に限定されないが、各基の分子量が大きくなると相対的なイミド基含量が低下するため、炭素数3以下の有機基であることが好ましい。
<R 2 to R 4 >
R 2 to R 4 each independently represent a hydrogen atom, a hydroxyl group, or a monovalent organic group other than a halogen atom having 1 to 10 carbon atoms, but among R 2 to R 4 , two adjacent groups are A ring having 20 or less carbon atoms that is bonded to each other and condensed to a benzene ring may be formed.
The organic group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms as R 2 to R 4, is not particularly limited, since the relative imide group content the molecular weight of each group is large is reduced, is the number 3 or less organic group having a carbon It is preferable.
R2〜R4の具体例としては、各々独立に、水素原子、炭化水素基、芳香族基(複素環基を含む)、カルボニル基(アルデヒド、ケトン、エステル、アミド等)、アルコキシ基、アシロキシ基、アルキルチオ基、アリ−ロキシ基、ジアルキルアミノ基が挙げられる。R2〜R4が炭化水素基の場合、炭素数が10以下であれば置換基を有していてもよく、該置換基としては、複素環基、カルボニル基、ジアルキルアミノ基、アルコキシ基、アシロキシ基、アルキルチオ基、アリ−ロキシ基、シリル基が挙げられる。 Specific examples of R 2 to R 4 are each independently a hydrogen atom, a hydrocarbon group, an aromatic group (including a heterocyclic group), a carbonyl group (aldehyde, ketone, ester, amide, etc.), an alkoxy group, or an acyloxy group. Group, alkylthio group, aryloxy group, dialkylamino group. When R 2 to R 4 are hydrocarbon groups, they may have a substituent as long as the carbon number is 10 or less. Examples of the substituent include a heterocyclic group, a carbonyl group, a dialkylamino group, an alkoxy group, Examples include an acyloxy group, an alkylthio group, an aryloxy group, and a silyl group.
R2〜R4としては、各々独立に、水素原子、水酸基又はメチル基であることが好ましい。 R 2 to R 4 are each independently preferably a hydrogen atom, a hydroxyl group or a methyl group.
<R2〜R5の水酸基>
本発明のビスイミドフェノール化合物においては、R2〜R5のうち、いずれか一つは水酸基である必要がある。
これは、本発明のビスイミドフェノール化合物を原料モノマーとして用いて高分子量化する場合に、反応可能な置換基がないと重合できないこと、また、最も汎用性の高い反応性の置換基が水酸基であることによる。
ただし、一分子中に水酸基が3個以上あり、3官能以上になるとゲル化するので、R2〜R5のいずれか一つずつが水酸基であり、一分子中のイミド基に結合した2個のベンゼン環に各々1個ずつの水酸基が結合していればよい。
<Hydroxyl group of R 2 to R 5 >
In the bisimide phenol compound of the present invention, any one of R 2 to R 5 needs to be a hydroxyl group.
This is because, when the bisimidephenol compound of the present invention is used as a raw material monomer and polymerized, it cannot be polymerized without a reactive substituent, and the most versatile reactive substituent is a hydroxyl group. It depends.
However, there hydroxyl groups or three in one molecule, 3 since the gel becomes more than functional, a one by one either R 2 to R 5 is a hydroxyl group, two bonded to the imide groups in one molecule It is sufficient that one hydroxyl group is bonded to each benzene ring.
<R6>
R6は、各々独立に、炭素数1〜10のハロゲン原子以外の一価の有機基を示し、1つのベンゼン環上でR6が隣接する位置にある場合、隣接する2つのR6は互いに結合してベンゼン環に縮合する、炭素数20以下の環を形成していてもよい。
R6としては、炭素数1〜10のハロゲン原子以外の有機基であれば、特に限定されないが、各基の分子量が大きくなると、相対的なイミド基含量が低下するため、炭素数3以下の有機基であることが好ましい。
<R 6 >
R 6 each independently represents a monovalent organic group other than a halogen atom having 1 to 10 carbon atoms, and when R 6 is adjacent to each other on one benzene ring, the two adjacent R 6 are A ring having 20 or less carbon atoms that is bonded and condensed to a benzene ring may be formed.
R 6 is not particularly limited as long as it is an organic group other than a halogen atom having 1 to 10 carbon atoms. However, since the relative imide group content decreases as the molecular weight of each group increases, the number of carbon atoms is 3 or less. An organic group is preferred.
R6の具体例としては、各々独立に、炭化水素基、芳香族基(複素環基を含む)、カルボニル基(アルデヒド、ケトン、エステル、アミド等)、ジアルキルアミノ基が挙げられる。R6が炭化水素基の場合、炭素数が10以下であれば置換基を有していてもよく、該置換基としては、複素環基、カルボニル基、ジアルキルアミノ基、アルコキシ基、アシロキシ基、アルキルチオ基、アリ−ロキシ基、シリル基が挙げられる。 Specific examples of R 6 each independently include a hydrocarbon group, an aromatic group (including a heterocyclic group), a carbonyl group (aldehyde, ketone, ester, amide, etc.), and a dialkylamino group. When R 6 is a hydrocarbon group, it may have a substituent as long as it has 10 or less carbon atoms. Examples of the substituent include a heterocyclic group, a carbonyl group, a dialkylamino group, an alkoxy group, an acyloxy group, An alkylthio group, an aryloxy group, and a silyl group are mentioned.
<X>
Xは単結合、置換されていてもよい炭素数1〜20の二価の有機基、−O−、又は−SO2−を示す。Xが二価の有機基の場合、その分子量が大きくなると相対的にイミド基含量が低下するため、炭素数1〜10の有機基であることが好ましく、炭素数1〜3の有機基であることが好ましい。炭素数1〜3の二価の有機基としては具体的には、メチレン基、2,2−プロピリデン基、オキシメチレン基等が挙げられる。
<X>
X represents a single bond, an optionally substituted divalent organic group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, —O—, or —SO 2 —. In the case where X is a divalent organic group, the imide group content is relatively lowered when the molecular weight is increased. Therefore, an organic group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms is preferable, and an organic group having 1 to 3 carbon atoms. It is preferable. Specific examples of the divalent organic group having 1 to 3 carbon atoms include a methylene group, a 2,2-propylidene group, and an oxymethylene group.
Xとしては、特に単結合、オキシメチレン基、−O−、又は−SO2−が好ましい。 X is particularly preferably a single bond, an oxymethylene group, —O—, or —SO 2 —.
<n>
nは0〜3の整数であるが、nが大きく、ビスイミドフェノール化合物の分子量が大きくなると、相対的なイミド基含量が低下するため、nは0又は1が好ましい。
<N>
n is an integer of 0 to 3. However, when n is large and the molecular weight of the bisimidephenol compound is increased, the relative imide group content is decreased. Therefore, n is preferably 0 or 1.
<対称性>
本発明のビスイミドフェノール化合物において、連結基Xで連結される左右の環構造のベンゼン環部分に結合するR1〜R6と、R6の個数を表すnは、左右で各々同一でも異なってもよいが、同一の方が分子の対称性がよく、高分子量化した際にイミドの特徴である凝集力を損なわないことから好ましい。
<Symmetry>
In the bisimide phenol compound of the present invention, R 1 to R 6 bonded to the benzene ring portion of the left and right ring structures connected by the linking group X and n representing the number of R 6 are the same or different on the left and right. However, the same is preferable because the symmetry of the molecule is good and the cohesive force that is characteristic of the imide is not impaired when the molecular weight is increased.
<分子量>
本発明のビスイミドフェノール化合物の分子量の下限は504であるが、その上限としては、1000以下、特に800以下、とりわけ600以下であることが好ましい。
本発明のビスイミドフェノール化合物の分子量が過度に小さいと、本発明のビスイミドフェノール化合物の分子設計が不可能であり、逆に過度に大きいと、ビスイミドフェノール化合物中のイミド基含量が小さくなり、好ましくない。
<Molecular weight>
The lower limit of the molecular weight of the bisimidephenol compound of the present invention is 504, and the upper limit is preferably 1000 or less, particularly 800 or less, and particularly 600 or less.
If the molecular weight of the bisimide phenol compound of the present invention is excessively small, the molecular design of the bisimide phenol compound of the present invention is impossible, and conversely if excessively large, the imide group content in the bisimide phenol compound is small. Is not preferable.
<イミド基含量>
本発明のビスイミドフェノール化合物のイミド基含量(本発明のビスイミドフェノール化合物1g当たりのイミド基のモル量)は、イミド基含量の多い、耐熱性高分子材料の原料モノマーとして有用なビスイミドフェノール化合物となり得ることから、0.22mmol/g以上、特に1.0mmol/g以上、とりわけ2.0mmol/g以上であることが好ましい。なお、イミド基含量の最大値は、理論的には4.0mmol/gである。
<Imido group content>
The imide group content of the bisimidephenol compound of the present invention (molar amount of imide group per gram of the bisimidephenol compound of the present invention) is a bisimidephenol useful as a raw material monomer for heat-resistant polymer materials having a large imide group content. Since it can become a compound, it is preferably 0.22 mmol / g or more, particularly 1.0 mmol / g or more, particularly 2.0 mmol / g or more. The maximum value of the imide group content is theoretically 4.0 mmol / g.
イミド基含量等の本発明のビスイミドフェノール化合物の構造は、1H−NMR(核磁気共鳴スペクトル分析法:重ジメチルスルホキシド溶媒)、IR(赤外線吸収スペクトル法)、MS(質量分析法)によって確認することができる。 The structure of the bisimidephenol compound of the present invention such as imide group content is confirmed by 1 H-NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum analysis: heavy dimethyl sulfoxide solvent), IR (infrared absorption spectroscopy), MS (mass spectrometry). can do.
<溶剤に対する溶解度>
本発明のビスイミドフェノール化合物は、ケトン系溶剤に対する溶解度が高い。具体的には、本発明のビスイミドフェノール化合物の内、好ましいものは、ケトン系溶剤に対し、60℃で0.5重量%以上の溶解度を示し、更に好ましいものは1.0重量%以上の溶解度を示し、特に好ましいものは2.0重量%以上の溶解度を示し、最も好ましいものは3.0重量%以上の溶解度を示す。
<Solubility in solvents>
The bisimide phenol compound of the present invention has high solubility in ketone solvents. Specifically, among the bisimidephenol compounds of the present invention, a preferable one shows a solubility of 0.5% by weight or more at 60 ° C. in a ketone solvent, and a more preferable one is 1.0% by weight or more. In particular, the solubility is 2.0% by weight or more, and the most preferable is 3.0% by weight or more.
ここで、ケトン系溶剤とは、ケトン基を有する液体を指す。中でも、ビスイミドフェノールの反応を妨げないように非プロトン性であることが望ましく、例えばアセトン、メチルエチルケトン(MEK)、メチルイソブチルケトン(MIBK)、ジイソプロピルケトン、ジ−tert−ブチルケトン、シクロペンタノン、シクロヘキサノン、シクロヘキシルメチルケトン、アセトフェノン、アセチルアセトン等が挙げられる。 Here, the ketone solvent refers to a liquid having a ketone group. Among them, it is desirable that it is aprotic so as not to interfere with the reaction of bisimidephenol, for example, acetone, methyl ethyl ketone (MEK), methyl isobutyl ketone (MIBK), diisopropyl ketone, di-tert-butyl ketone, cyclopentanone, cyclohexanone. Cyclohexyl methyl ketone, acetophenone, acetylacetone and the like.
これらの溶剤に対する溶解度がごく僅かであっても、部分的にでも溶解していれば温度や時間をかけることで反応は進行するが、実際の作業性を考慮すると溶解度は高いことが好ましい。 Even if the solubility in these solvents is very slight, the reaction proceeds by taking time or time if it is partially dissolved, but it is preferable that the solubility is high in consideration of actual workability.
なお、本発明のビスイミドフェノール化合物の溶剤に対する溶解度の測定方法は以下の通りである。 In addition, the measuring method of the solubility with respect to the solvent of the bisimide phenol compound of this invention is as follows.
{溶解度の測定方法}
サンプル瓶に、ビスイミドフェノール化合物と溶剤を入れ、時々手で振り混ぜながら、油浴中で60℃で2時間加熱した際の溶解性を目視で確認する。高濃度から測定を開始し、溶け残りがある場合には少量ずつ溶剤を足して濃度を下げ、完全に溶解した時点の濃度を溶解度とする。
{Solubility measurement method}
A bisimidephenol compound and a solvent are put into a sample bottle, and the solubility when heated in an oil bath at 60 ° C. for 2 hours is visually confirmed while occasionally shaking by hand. Start measurement from a high concentration. If there is any undissolved material, add a small amount of solvent to lower the concentration, and use the concentration at the time of complete dissolution as solubility.
<用途>
本発明のビスイミドフェノール化合物の用途としては、例えば、耐熱性に優れたエポキシ樹脂、ポリエステル樹脂、ポリカーボート樹脂、フェノール樹脂等の製造原料モノマー等として有用である。
<Application>
As a use of the bisimide phenol compound of this invention, it is useful as a manufacturing raw material monomer etc., such as an epoxy resin excellent in heat resistance, a polyester resin, a polycarbonate resin, a phenol resin, etc., for example.
[ビスイミドフェノール化合物の製造方法]
本発明のビスイミドフェノール化合物の製造方法には特に制限はないが、例えば、下記一般式(II)で表されるアミノフェノールと、下記一般式(III)で表される芳香族カルボン酸二無水物を脱水縮合させる本発明の製造方法により製造することができる。
[Method for producing bisimidephenol compound]
The production method of the bisimidephenol compound of the present invention is not particularly limited. For example, an aminophenol represented by the following general formula (II) and an aromatic carboxylic acid dianhydride represented by the following general formula (III) It can be produced by the production method of the present invention wherein the product is dehydrated and condensed.
前記一般式(II)で表されるアミノフェノール(以下、単に「アミノフェノール」と称す。)と、前記一般式(III)で表される芳香族カルボン酸二無水物(以下単に「芳香族カルボン酸二無水物」と称す。)の脱水縮合は、フェノール性水酸基によるエステル生成の副反応を最小化する観点から、イミド閉環(脱水)が起こらない温度条件でこれらの原料をアミック酸としてから(以下「一段目反応」と称す場合がある。)、反応温度を上げてイミド環を形成させる(以下「二段目反応]と称す場合がある。)手法で行うのが好ましい。 An aminophenol represented by the general formula (II) (hereinafter simply referred to as “aminophenol”) and an aromatic carboxylic dianhydride represented by the general formula (III) (hereinafter simply referred to as “aromatic carboxylic acid”). The dehydration condensation of “acid dianhydride”) is carried out by converting these raw materials into an amic acid under a temperature condition in which imide ring closure (dehydration) does not occur from the viewpoint of minimizing a side reaction of ester formation by a phenolic hydroxyl group Hereinafter, it may be referred to as “first-stage reaction”), and the reaction temperature is preferably raised to form an imide ring (hereinafter sometimes referred to as “second-stage reaction”).
アミック酸を生成させる際に、活性プロトンが存在すると酸無水物基と副反応を起こし、アミック酸の生成を阻害することから、アミック酸の生成は非プロトン性の有機溶剤中で加熱して行うのが好ましい。
アミック酸からイミド環を形成させる脱水反応は、生成したアミック酸を更に加熱して行ってもよく、また、脱水剤を用いて行ってもよい。この脱水反応は、溶剤存在下でも不在下でも構わない。
When an amic acid is generated, if an active proton is present, a side reaction with an acid anhydride group occurs, which inhibits the formation of the amic acid. Therefore, the amic acid is generated by heating in an aprotic organic solvent. Is preferred.
The dehydration reaction for forming an imide ring from an amic acid may be carried out by further heating the produced amic acid or using a dehydrating agent. This dehydration reaction may be performed in the presence or absence of a solvent.
以下、アミノフェノールと芳香族カルボン酸二無水物との脱水縮合反応による本発明のビスイミドフェノール化合物の製造方法につき、詳細に説明する。 Hereinafter, the manufacturing method of the bisimide phenol compound of this invention by the dehydration condensation reaction of aminophenol and aromatic carboxylic dianhydride is demonstrated in detail.
<アミノフェノール>
前記一般式(II)で表されるアミノフェノールとしては、例えば、次のようなものが挙げられる。
<Aminophenol>
Examples of aminophenols represented by the general formula (II) include the following.
(|α|=51°〜60°のもの)
<安息香酸類:R1=COOH>
2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ安息香酸、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−4−メチル安息香酸、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−4−エチル安息香酸、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−4−プロピル安息香酸、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−5−メチル安息香酸、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−4−メトキシ安息香酸、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−4−エトキシ安息香酸、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−5−メトキシ安息香酸、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−4−アセチルアミノ安息香酸、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−4,5−ジメチル安息香酸、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−4,6−ジメチル安息香酸、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−4−エチルチオ安息香酸、2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシ安息香酸、5−アセチル−2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシ安息香酸、6−アセチル−2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシ安息香酸、2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシ−5−メトキシ安息香酸、2−アミノ−5−エトキシ−4−ヒドロキシ安息香酸、2−アミノ−5−ベンジロキシ−4−ヒドロキシ安息香酸、2−アミノ−5−ヒドロキシ安息香酸、2−アミノ−4−メチル−5−ヒドロキシ安息香酸、2−アミノ−4−メトキシ−5−ヒドロキシ安息香酸、2−アミノ−6−ヒドロキシ安息香酸、2−アミノ−6−ヒドロキシ−4−メチル安息香酸、6−アミノ−3−エチル−2−ヒドロキシ安息香酸
(| Α | = 51 ° -60 °)
<Benzoic acids: R 1 = COOH>
2-amino-3-hydroxybenzoic acid, 2-amino-3-hydroxy-4-methylbenzoic acid, 2-amino-3-hydroxy-4-ethylbenzoic acid, 2-amino-3-hydroxy-4-propylbenzoic acid Acid, 2-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylbenzoic acid, 2-amino-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzoic acid, 2-amino-3-hydroxy-4-ethoxybenzoic acid, 2-amino-3- Hydroxy-5-methoxybenzoic acid, 2-amino-3-hydroxy-4-acetylaminobenzoic acid, 2-amino-3-hydroxy-4,5-dimethylbenzoic acid, 2-amino-3-hydroxy-4,6 -Dimethylbenzoic acid, 2-amino-3-hydroxy-4-ethylthiobenzoic acid, 2-amino-4-hydroxybenzoic acid, 5-acetyl-2-amino-4-hydride Xylbenzoic acid, 6-acetyl-2-amino-4-hydroxybenzoic acid, 2-amino-4-hydroxy-5-methoxybenzoic acid, 2-amino-5-ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzoic acid, 2-amino- 5-benzyloxy-4-hydroxybenzoic acid, 2-amino-5-hydroxybenzoic acid, 2-amino-4-methyl-5-hydroxybenzoic acid, 2-amino-4-methoxy-5-hydroxybenzoic acid, 2- Amino-6-hydroxybenzoic acid, 2-amino-6-hydroxy-4-methylbenzoic acid, 6-amino-3-ethyl-2-hydroxybenzoic acid
<安息香酸メチル類:R1=COOMe>
2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ安息香酸メチル、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−4−メチル安息香酸メチル、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−5−メチル安息香酸メチル、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−5−メトキシ安息香酸メチル、2−アミノ−5−エトキシ−3−ヒドロキシ安息香酸メチル、3,4−メトキシカルボニル−2−アミノフェノール、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−4−アセチルアミノ安息香酸メチル、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−6−[(2−トリメチルシリルエトキシ)メトキシ]安息香酸メチル、2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシ安息香酸メチル、5−アセチル−2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシ安息香酸メチル、2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシ−5−メトキシ安息香酸メチル、2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシ−5−メトキシカルボニル安息香酸メチル、2−アミノ−5−ヒドロキシ安息香酸メチル、2−アミノ−4−メトキシカルボニル−5−ヒドロキシ安息香酸メチル、2−アミノ−4−ベンゾイルオキシ−5−ヒドロキシ安息香酸メチル、2−アミノ−4−メトキシ−5−ヒドロキシ安息香酸メチル、2−アミノ−6−ヒドロキシ安息香酸メチル、6−アミノ−3−エチル−2−ヒドロキシ安息香酸メチル
<Methyl benzoates: R 1 = COOMe>
Methyl 2-amino-3-hydroxybenzoate, methyl 2-amino-3-hydroxy-4-methylbenzoate, methyl 2-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylbenzoate, 2-amino-3-hydroxy-5 -Methyl methoxybenzoate, methyl 2-amino-5-ethoxy-3-hydroxybenzoate, 3,4-methoxycarbonyl-2-aminophenol, methyl 2-amino-3-hydroxy-4-acetylaminobenzoate, 2 -Amino-3-hydroxy-6-[(2-trimethylsilylethoxy) methoxy] methyl benzoate, methyl 2-amino-4-hydroxybenzoate, methyl 5-acetyl-2-amino-4-hydroxybenzoate, 2- Methyl amino-4-hydroxy-5-methoxybenzoate, 2-amino-4-hydroxy-5-methoxycarbo Methyl benzoate, methyl 2-amino-5-hydroxybenzoate, methyl 2-amino-4-methoxycarbonyl-5-hydroxybenzoate, methyl 2-amino-4-benzoyloxy-5-hydroxybenzoate, 2- Methyl amino-4-methoxy-5-hydroxybenzoate, methyl 2-amino-6-hydroxybenzoate, methyl 6-amino-3-ethyl-2-hydroxybenzoate
<アセトフェノン類:R1=COMe>
2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシアセトフェノン、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−5−メチルアセトフェノン、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−6−メチルアセトフェノン、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−4,6−ジメチルアセトフェノン、2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシアセトフェノン、2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシ−5−プロピルアセトフェノン、2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシ−6−フェニルアセトフェノン、2−アミノ−5−ヒドロキシアセトフェノン、2−アミノ−3−メトキシ−5−ヒドロキシアセトフェノン、2−アミノ−5−ヒドロキシ−6−メチルアセトフェノン、2−アミノ−6−ヒドロキシアセトフェノン、2−アミノ−6−ヒドロキシ−4−メチルアセトフェノン
<Acetophenones: R 1 = COMe>
2-amino-3-hydroxyacetophenone, 2-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylacetophenone, 2-amino-3-hydroxy-6-methylacetophenone, 2-amino-3-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylacetophenone, 2-amino-4-hydroxyacetophenone, 2-amino-4-hydroxy-5-propylacetophenone, 2-amino-4-hydroxy-6-phenylacetophenone, 2-amino-5-hydroxyacetophenone, 2-amino-3- Methoxy-5-hydroxyacetophenone, 2-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methylacetophenone, 2-amino-6-hydroxyacetophenone, 2-amino-6-hydroxy-4-methylacetophenone
<ジメチルアニリン類:R1=NMe2>
2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−N,N−ジメチルアニリン、2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシ−N,N−ジメチルアニリン、2−アミノ−5−ヒドロキシ−N,N−ジメチルアニリン、2−アミノ−6−ヒドロキシ−N,N−ジメチルアニリン
<Dimethylanilines: R 1 = NMe 2 >
2-amino-3-hydroxy-N, N-dimethylaniline, 2-amino-4-hydroxy-N, N-dimethylaniline, 2-amino-5-hydroxy-N, N-dimethylaniline, 2-amino-6 -Hydroxy-N, N-dimethylaniline
<アセチルアニリン類:R1=NHCOMe>
2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−N−アセチルアニリン、2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシ−N−アセチルアニリン、2−アミノ−5−ヒドロキシ−N−アセチルアニリン、2−アミノ−4−カルボキシ−5−ヒドロキシ−N−アセチルアニリン、2−アミノ−4−エトキシカルボニル−5−ヒドロキシ−N−アセチルアニリン、2−アミノ−4−アセチル−5−ヒドロキシ−N−アセチルアニリン、2−アミノ−6−ヒドロキシ−N−アセチルアニリン
<Acetylanilines: R 1 = NHCOMe>
2-amino-3-hydroxy-N-acetylaniline, 2-amino-4-hydroxy-N-acetylaniline, 2-amino-5-hydroxy-N-acetylaniline, 2-amino-4-carboxy-5-hydroxy -N-acetylaniline, 2-amino-4-ethoxycarbonyl-5-hydroxy-N-acetylaniline, 2-amino-4-acetyl-5-hydroxy-N-acetylaniline, 2-amino-6-hydroxy-N -Acetylaniline
<スルホン酸メチル類:R1=SO3Me>
2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシフェニルスルホン酸メチル、2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシフェニルスルホン酸メチル、2−アミノ−5−ヒドロキシフェニルスルホン酸メチル、2−アミノ−6−ヒドロキシフェニルスルホン酸メチル
<Methyl sulfonates: R 1 = SO 3 Me>
Methyl 2-amino-3-hydroxyphenylsulfonate, methyl 2-amino-4-hydroxyphenylsulfonate, methyl 2-amino-5-hydroxyphenylsulfonate, methyl 2-amino-6-hydroxyphenylsulfonate
<メチルスルホン類:R1=SO2Me>
(2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシフェニル)メチルスルホン、(2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシフェニル)メチルスルホン、(2−アミノ−5−ヒドロキシフェニル)メチルスルホン、(2−アミノ−6−ヒドロキシフェニル)メチルスルホン
<Methyl sulfones: R 1 = SO 2 Me>
(2-amino-3-hydroxyphenyl) methylsulfone, (2-amino-4-hydroxyphenyl) methylsulfone, (2-amino-5-hydroxyphenyl) methylsulfone, (2-amino-6-hydroxyphenyl) methyl Sulfone
<アミノフェノール類:R1=Me>
4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノール、4−アミノ−2,3−ジメチルフェノール、4−アミノ−2,5−ジメチルフェノール、4−アミノ−2,3,6−トリメチルフェノール、3−アミノ−2−メチルフェノール、3−アミノ−4−メチルフェノール、3−アミノ−2,6−ジメチルフェノール、3−アミノ−2,5−ジメチルフェノール、5−アミノ−2,4−ジメチルフェノール、5−アミノ−3,4−ジメチルフェノール、5−アミノ−2,3,4−トリメチルフェノール、5−アミノ−2,3,6−トリメチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3−メチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3,6−ジメチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3,4−ジメチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3,5−ジメチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3,4,6−トリメチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3,5,6−トリメチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3,4,5−トリメチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3,4,5,6−テトラメチルフェノール
2−アミノ−6−イソプロピル−3−メチルフェノール、2−アミノ−4,6−ジ−tert−ブチル−3−メチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3−メチル−6−(1,1,3,3−テトラメチルブチル)フェノール、2−アミノ−2,3−ジメチル−6−(1,1,3,3−テトラメチルブチル)フェノール、2−アミノ−3−メチル−5−(2−トリル)フェノール、2−(1−アダマンチル)−5−アミノ−4−メチルフェノール、4−アミノ−2−イソプロピル−5−メチルフェノール、4−アミノ−2−tert−ブチル−5−メチルフェノール、4−アミノ−2−シクロヘキシル−5−メチルフェノール、4−アミノ−2−(1,1−ジメチルプロピル)−5−メチルフェノール、4−アミノ−5−メチル−2−(1,1,3,3−テトラメチルブチル)フェノール、4−アミノ−2−(4−シクロヘキシルブチル)−5−メチルフェノール、4−アミノ−6−エチル−2,3−ジメチルフェノール、2−ヒドロキシ−6−メチル−3−アニシジン、2−ヒドロキシ−3,4−ジメチル−5−アニシジン、2−ヒドロキシ−6−メチル−4−アニシジン、3−ヒドロキシ−2−メチル−4−アニシジン、5−ヒドロキシ−3−メチル−4−アニシジン、5−ヒドロキシ−2,3−ジメチル−4−アニシジン、2−アミノ−5−ヘキサデシルオキシ−4−イソブチル−3−メチルフェノール、3−アミノ−5−ヒドロキシ−2−メチル安息香酸、3−アミノ−5−ヒドロキシ−4−メチル安息香酸、5−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−4−メチル安息香酸、5−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−3,6−ジメチル安息香酸、5−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−3−イソプロピル−6−メチル安息香酸、4−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−3−メチル安息香酸、4−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−5−メチル安息香酸、4−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−3,6−ジメチル安息香酸、3−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−4−メチル安息香酸メチル、4−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−5−メチル安息香酸メチル、4−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−3−メチルアセトフェノン、4−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−5−メチルアセトフェノン、2−アミノ−4−シアノ−3,5−ジメチルフェノール、N,N−ジメチル−3−アミノ−4,5−ジメチル−2−ヒドロキシベンズアミド、N,N−ジメチル−3−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−4−メチルベンズアミド、2−アミノ−5−(tert−ブトキシカルボニルメチル)−3−メチルフェノール、4−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−3−メチルベンゾフェノン、4−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−5−メチルベンゾフェノン、2−アセトキシ−4−アミノ−6−イソプロピル−3−メチルフェノール、2−アセチルアミノ−4−アミノ−5−メチルフェノール、4−アセチルアミノ−2−アミノ−3−メチルフェノール、6−アセチルアミノ−2−アミノ−3−メチルフェノール、N,N−ジベンジル−2−(4−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−5−メチルフェニル)プロパンアミド、2−アミノ−3−メチル−4,6−ビス(N−ピペリジニルメチル)フェノール、4−アミノ−3−メチル−2,6−ビス(N−ピペリジニルメチル)フェノール、2−アミノ−3−メチル−4,6−ビス(N−ピロリジニルメチル)フェノール、4−アミノ−3−メチル−2−(3−チオフェニル)フェノール、4−アミノ−3−メチル−6−(3−チオフェニル)フェノール、4−アミノ−3−メチル−6−(3−チオフェニルメチル)フェノール
<Aminophenols: R 1 = Me>
4-amino-3-methylphenol, 4-amino-2,3-dimethylphenol, 4-amino-2,5-dimethylphenol, 4-amino-2,3,6-trimethylphenol, 3-amino-2- Methylphenol, 3-amino-4-methylphenol, 3-amino-2,6-dimethylphenol, 3-amino-2,5-dimethylphenol, 5-amino-2,4-dimethylphenol, 5-amino-3 , 4-dimethylphenol, 5-amino-2,3,4-trimethylphenol, 5-amino-2,3,6-trimethylphenol, 2-amino-3-methylphenol, 2-amino-3,6-dimethyl Phenol, 2-amino-3,4-dimethylphenol, 2-amino-3,5-dimethylphenol, 2-amino-3,4,6-trimethyl Phenol, 2-amino-3,5,6-trimethylphenol, 2-amino-3,4,5-trimethylphenol, 2-amino-3,4,5,6-tetramethylphenol 2-amino-6-isopropyl -3-methylphenol, 2-amino-4,6-di-tert-butyl-3-methylphenol, 2-amino-3-methyl-6- (1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl) phenol, 2-amino-2,3-dimethyl-6- (1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl) phenol, 2-amino-3-methyl-5- (2-tolyl) phenol, 2- (1-adamantyl) ) -5-amino-4-methylphenol, 4-amino-2-isopropyl-5-methylphenol, 4-amino-2-tert-butyl-5-methylphenol, 4-amino 2-cyclohexyl-5-methylphenol, 4-amino-2- (1,1-dimethylpropyl) -5-methylphenol, 4-amino-5-methyl-2- (1,1,3,3-tetramethyl) Butyl) phenol, 4-amino-2- (4-cyclohexylbutyl) -5-methylphenol, 4-amino-6-ethyl-2,3-dimethylphenol, 2-hydroxy-6-methyl-3-anisidine, 2 -Hydroxy-3,4-dimethyl-5-anisidine, 2-hydroxy-6-methyl-4-anisidine, 3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4-anisidine, 5-hydroxy-3-methyl-4-anisidine, 5 -Hydroxy-2,3-dimethyl-4-anisidine, 2-amino-5-hexadecyloxy-4-isobutyl-3-methylphenol, 3-a No-5-hydroxy-2-methylbenzoic acid, 3-amino-5-hydroxy-4-methylbenzoic acid, 5-amino-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzoic acid, 5-amino-2-hydroxy-3, 6-dimethylbenzoic acid, 5-amino-2-hydroxy-3-isopropyl-6-methylbenzoic acid, 4-amino-2-hydroxy-3-methylbenzoic acid, 4-amino-2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzoic acid Acid, 4-amino-2-hydroxy-3,6-dimethylbenzoic acid, methyl 3-amino-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzoate, methyl 4-amino-2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzoate, 4- Amino-2-hydroxy-3-methylacetophenone, 4-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylacetophenone, 2-amino-4-cyano-3,5-dimethylphen Nol, N, N-dimethyl-3-amino-4,5-dimethyl-2-hydroxybenzamide, N, N-dimethyl-3-amino-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzamide, 2-amino-5- (tert -Butoxycarbonylmethyl) -3-methylphenol, 4-amino-2-hydroxy-3-methylbenzophenone, 4-amino-2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzophenone, 2-acetoxy-4-amino-6-isopropyl-3 -Methylphenol, 2-acetylamino-4-amino-5-methylphenol, 4-acetylamino-2-amino-3-methylphenol, 6-acetylamino-2-amino-3-methylphenol, N, N- Dibenzyl-2- (4-amino-2-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl) propanamide, 2-a No-3-methyl-4,6-bis (N-piperidinylmethyl) phenol, 4-amino-3-methyl-2,6-bis (N-piperidinylmethyl) phenol, 2-amino-3- Methyl-4,6-bis (N-pyrrolidinylmethyl) phenol, 4-amino-3-methyl-2- (3-thiophenyl) phenol, 4-amino-3-methyl-6- (3-thiophenyl) phenol 4-amino-3-methyl-6- (3-thiophenylmethyl) phenol
(|α|=48°〜75°のもの)
<R1=Et>
3−アミノ−2−エチルフェノール、4−アミノ−3−エチルフェノール、4−アミノ−3−エチル−2,6−ジメチルフェノール、4−アミノ−2,3−ジエチルフェノール、3−アミノ−4−エチルフェノール、5−アミノ−4−エチル−2−メトキシカルボニルフェノール、2−アミノ−3−エチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3,5−ジエチルフェノール
(| Α | = 48 ° -75 °)
<R 1 = Et>
3-amino-2-ethylphenol, 4-amino-3-ethylphenol, 4-amino-3-ethyl-2,6-dimethylphenol, 4-amino-2,3-diethylphenol, 3-amino-4- Ethylphenol, 5-amino-4-ethyl-2-methoxycarbonylphenol, 2-amino-3-ethylphenol, 2-amino-3,5-diethylphenol
<R1=iPr>
3−アミノ−2−イソプロピルフェノール、4−アミノ−3−イソプロピルフェノール、4−アミノ−3−イソプロピル−6−メチルフェノール、2−アセチル−4−アミノ−3−イソプロピル−6−メチルフェノール、4−アミノ−6−カルボキシ−3−イソプロピルフェノール、4−アミノ−2,5−ジイソプロピルフェノール、3−アミノ−4−イソプロピルフェノール、2−アミノ−3−イソプロピルフェノール、2−アミノ−3−イソプロピル−6−メチルフェノール
<R 1 = iPr>
3-amino-2-isopropylphenol, 4-amino-3-isopropylphenol, 4-amino-3-isopropyl-6-methylphenol, 2-acetyl-4-amino-3-isopropyl-6-methylphenol, 4- Amino-6-carboxy-3-isopropylphenol, 4-amino-2,5-diisopropylphenol, 3-amino-4-isopropylphenol, 2-amino-3-isopropylphenol, 2-amino-3-isopropyl-6 Methylphenol
<R1=OMe>
3−ヒドロキシ−2−アニシジン、4−ヒドロキシ−2−アニシジン、4−ヒドロキシ−5−メチル−2−アニシジン、4−ヒドロキシ−2,5−ジメトキシアニリン、5−アセチル−4−ヒドロキシ−2−アニシジン、4−ヒドロキシ−5−エトキシカルボニル−2−アニシジン、4−ヒドロキシ−3−メチル−2,5−ジメトキシアニリン、4−ヒドロキシ−5−ベンゾイル−2−アニシジン、5−アセチル−4−ヒドロキシ−3−メチル−2−アニシジン、4−アミノ−2,3−ジメトキシ−6−メチルフェノール、4−アミノ−2,3−ジメトキシフェノール、4−ヒドロキシ−5−tert−ブチル−2−アニシジン、5−ヒドロキシ−2−アニシジン、5−ヒドロキシ−4−メチル−2−アニシジン、5−ヒドロキシ−2,4−ジメトキシアニリン、5−ヒドロキシ−3−メチル−2,4−ジメトキシアニリン、5−ヒドロキシ−4−ベンゾイルアミノ−2−アニシジン、5−ヒドロキシ−4−アセチルアミノ−2−アニシジン、6−ヒドロキシ−2−アニシジン、6−ヒドロキシ−5−メチル−2−アニシジン、6−ヒドロキシ−5−アセチル−2−アニシジン、6−ヒドロキシ−5−ベンゾイル−2−アニシジン、6−ヒドロキシ−5−メトキシカルボニル−2−アニシジン、6−ヒドロキシ−5−[2−(N,N−ジプロピルアミノ)エチル]−2−アニシジン、2−ヒドロキシ−3−カルボキシメチル−4,6−ジメトキシアニリン、6−ヒドロキシ−2,4−ジメトキシアニリン、3−ヒドロキシ−2,4−ジメトキシアニリン、2,3,4−トリメトキシ−6−アミノフェノール
<R 1 = OMe>
3-hydroxy-2-anisidine, 4-hydroxy-2-anisidine, 4-hydroxy-5-methyl-2-anisidine, 4-hydroxy-2,5-dimethoxyaniline, 5-acetyl-4-hydroxy-2-anisidine 4-hydroxy-5-ethoxycarbonyl-2-anisidine, 4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2,5-dimethoxyaniline, 4-hydroxy-5-benzoyl-2-anisidine, 5-acetyl-4-hydroxy-3 -Methyl-2-anisidine, 4-amino-2,3-dimethoxy-6-methylphenol, 4-amino-2,3-dimethoxyphenol, 4-hydroxy-5-tert-butyl-2-anisidine, 5-hydroxy -2-anisidine, 5-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-anisidine, 5-hydroxy-2,4- Methoxyaniline, 5-hydroxy-3-methyl-2,4-dimethoxyaniline, 5-hydroxy-4-benzoylamino-2-anisidine, 5-hydroxy-4-acetylamino-2-anisidine, 6-hydroxy-2- Anisidine, 6-hydroxy-5-methyl-2-anisidine, 6-hydroxy-5-acetyl-2-anisidine, 6-hydroxy-5-benzoyl-2-anisidine, 6-hydroxy-5-methoxycarbonyl-2-anisidine 6-hydroxy-5- [2- (N, N-dipropylamino) ethyl] -2-anisidine, 2-hydroxy-3-carboxymethyl-4,6-dimethoxyaniline, 6-hydroxy-2,4- Dimethoxyaniline, 3-hydroxy-2,4-dimethoxyaniline, 2,3,4-trimethoxy 6-amino-phenol
<R1=SMe>
2−メチルチオ−3−アミノフェノール、3−メチルチオ−4−アミノフェノール、4−メチルチオ−3−アミノフェノール、2−メトキシ−4−メチルチオ−5−アミノフェノール、2,4−メチルチオ−5−アミノフェノール、3−メチルチオ−2−アミノフェノール
<R 1 = SMe>
2-methylthio-3-aminophenol, 3-methylthio-4-aminophenol, 4-methylthio-3-aminophenol, 2-methoxy-4-methylthio-5-aminophenol, 2,4-methylthio-5-aminophenol , 3-methylthio-2-aminophenol
<R1=CONH2>
2−アミノ−6−ヒドロキシベンズアミド、2−アミノ−5−ヒドロキシベンズアミド、2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシベンズアミド、5−アセチル−2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシベンズアミド、2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシ−5−メトキシカルボニルベンズアミド、2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシ−5−エトキシカルボニルベンズアミド、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシベンズアミド、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−4−メチルベンズアミド
<R 1 = CONH 2>
2-amino-6-hydroxybenzamide, 2-amino-5-hydroxybenzamide, 2-amino-4-hydroxybenzamide, 5-acetyl-2-amino-4-hydroxybenzamide, 2-amino-4-hydroxy-5- Methoxycarbonylbenzamide, 2-amino-4-hydroxy-5-ethoxycarbonylbenzamide, 2-amino-3-hydroxybenzamide, 2-amino-3-hydroxy-4-methylbenzamide
(|α|=45°〜90°のもの)
<R1=tBu>
3−アミノ−2−tert−ブチルフェノール、3−アミノ−2,5−ジ−tert−ブチルフェノール、3−アミノ−2,6−ジ−tert−ブチルフェノール、4−アミノ−3−tert−ブチルフェノール、4−アミノ−2,5−ジ−tert−ブチルフェノール、3−アミノ−4−tert−ブチルフェノール、5−アミノ−2,4−ジ−tert−ブチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3−tert−ブチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3,5−ジ−tert−ブチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3,6−ジ−tert−ブチルフェノール
(| Α | = 45 ° ~ 90 °)
<R 1 = tBu>
3-amino-2-tert-butylphenol, 3-amino-2,5-di-tert-butylphenol, 3-amino-2,6-di-tert-butylphenol, 4-amino-3-tert-butylphenol, 4- Amino-2,5-di-tert-butylphenol, 3-amino-4-tert-butylphenol, 5-amino-2,4-di-tert-butylphenol, 2-amino-3-tert-butylphenol, 2-amino- 3,5-di-tert-butylphenol, 2-amino-3,6-di-tert-butylphenol
<R1=Ph>
3−アミノ−2−フェニルフェノール、4−アミノ−3−フェニルフェノール、4−アミノ−2,5−ジフェニルフェノール、3−アミノ−4−フェニルフェノール、5−アミノ−2−メトキシカルボニル−4−フェニルフェノール、2−アミノ−3−フェニルフェノール
<R 1 = Ph>
3-amino-2-phenylphenol, 4-amino-3-phenylphenol, 4-amino-2,5-diphenylphenol, 3-amino-4-phenylphenol, 5-amino-2-methoxycarbonyl-4-phenyl Phenol, 2-amino-3-phenylphenol
<R1=SiMe3>
3−アミノ−2−トリメチルシリルフェノール、4−アミノ−3−トリメチルシリルフェノール、3−アミノ−4−トリメチルシリルフェノール、2−アミノ−3−トリメチルシリルフェノール
<R 1 = SiMe 3 >
3-amino-2-trimethylsilylphenol, 4-amino-3-trimethylsilylphenol, 3-amino-4-trimethylsilylphenol, 2-amino-3-trimethylsilylphenol
<R1=CONHMe>
2−アミノ−6−ヒドロキシ−N−メチルベンズアミド、2−アミノ−5−ヒドロキシ−N−メチルベンズアミド、2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシ−N−メチルベンズアミド、2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−N−メチルベンズアミド
<R 1 = CONHMe>
2-amino-6-hydroxy-N-methylbenzamide, 2-amino-5-hydroxy-N-methylbenzamide, 2-amino-4-hydroxy-N-methylbenzamide, 2-amino-3-hydroxy-N-methyl Benzamide
中でも、分子量が小さく、置換基の反応性が低いことから、以下のものが好ましい。
<R1=NMe2>
2−アミノ−3−ヒドロキシ−N,N−ジメチルアニリン、2−アミノ−4−ヒドロキシ−N,N−ジメチルアニリン、2−アミノ−5−ヒドロキシ−N,N−ジメチルアニリン、2−アミノ−6−ヒドロキシ−N,N−ジメチルアニリン
Among these, since the molecular weight is small and the reactivity of the substituent is low, the following are preferable.
<R 1 = NMe 2 >
2-amino-3-hydroxy-N, N-dimethylaniline, 2-amino-4-hydroxy-N, N-dimethylaniline, 2-amino-5-hydroxy-N, N-dimethylaniline, 2-amino-6 -Hydroxy-N, N-dimethylaniline
<R1=Me>
4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノール、4−アミノ−2,3−ジメチルフェノール、4−アミノ−2,5−ジメチルフェノール、4−アミノ−2,3,6−トリメチルフェノール、3−アミノ−2−メチルフェノール、3−アミノ−4−メチルフェノール、3−アミノ−2,6−ジメチルフェノール、3−アミノ−2,5−ジメチルフェノール、5−アミノ−2,4−ジメチルフェノール、5−アミノ−3,4−ジメチルフェノール、5−アミノ−2,3,4−トリメチルフェノール、5−アミノ−2,3,6−トリメチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3−メチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3,6−ジメチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3,4−ジメチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3,5−ジメチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3,4,6−トリメチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3,5,6−トリメチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3,4,5−トリメチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3,4,5,6−テトラメチルフェノール、2−アミノ−6−イソプロピル−3−メチルフェノール、4−アミノ−2−イソプロピル−5−メチルフェノール、4−アミノ−6−エチル−2,3−ジメチルフェノール、2−ヒドロキシ−6−メチル−3−アニシジン、2−ヒドロキシ−3,4−ジメチル−5−アニシジン、2−ヒドロキシ−6−メチル−4−アニシジン、3−ヒドロキシ−2−メチル−4−アニシジン、5−ヒドロキシ−3−メチル−4−アニシジン、5−ヒドロキシ−2,3−ジメチル−4−アニシジン、3−アミノ−5−ヒドロキシ−2−メチル安息香酸、3−アミノ−5−ヒドロキシ−4−メチル安息香酸、5−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−4−メチル安息香酸、5−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−3,6−ジメチル安息香酸、5−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−3−イソプロピル−6−メチル安息香酸、4−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−3−メチル安息香酸、4−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−5−メチル安息香酸、4−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−3,6−ジメチル安息香酸、3−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−4−メチル安息香酸メチル、4−アミノ−2−ヒドロキシ−5−メチル安息香酸メチル
<R 1 = Me>
4-amino-3-methylphenol, 4-amino-2,3-dimethylphenol, 4-amino-2,5-dimethylphenol, 4-amino-2,3,6-trimethylphenol, 3-amino-2- Methylphenol, 3-amino-4-methylphenol, 3-amino-2,6-dimethylphenol, 3-amino-2,5-dimethylphenol, 5-amino-2,4-dimethylphenol, 5-amino-3 , 4-dimethylphenol, 5-amino-2,3,4-trimethylphenol, 5-amino-2,3,6-trimethylphenol, 2-amino-3-methylphenol, 2-amino-3,6-dimethyl Phenol, 2-amino-3,4-dimethylphenol, 2-amino-3,5-dimethylphenol, 2-amino-3,4,6-trimethyl Phenol, 2-amino-3,5,6-trimethylphenol, 2-amino-3,4,5-trimethylphenol, 2-amino-3,4,5,6-tetramethylphenol, 2-amino-6- Isopropyl-3-methylphenol, 4-amino-2-isopropyl-5-methylphenol, 4-amino-6-ethyl-2,3-dimethylphenol, 2-hydroxy-6-methyl-3-anisidine, 2-hydroxy -3,4-dimethyl-5-anisidine, 2-hydroxy-6-methyl-4-anisidine, 3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4-anisidine, 5-hydroxy-3-methyl-4-anisidine, 5-hydroxy -2,3-dimethyl-4-anisidine, 3-amino-5-hydroxy-2-methylbenzoic acid, 3-amino-5-hydroxy- -Methylbenzoic acid, 5-amino-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzoic acid, 5-amino-2-hydroxy-3,6-dimethylbenzoic acid, 5-amino-2-hydroxy-3-isopropyl-6-methyl Benzoic acid, 4-amino-2-hydroxy-3-methylbenzoic acid, 4-amino-2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzoic acid, 4-amino-2-hydroxy-3,6-dimethylbenzoic acid, 3-amino Methyl 2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzoate, methyl 4-amino-2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzoate
<R1=Et>
3−アミノ−2−エチルフェノール、4−アミノ−3−エチルフェノール、4−アミノ−3−エチル−2,6−ジメチルフェノール、4−アミノ−2,3−ジエチルフェノール、3−アミノ−4−エチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3−エチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3,5−ジエチルフェノール
<R 1 = Et>
3-amino-2-ethylphenol, 4-amino-3-ethylphenol, 4-amino-3-ethyl-2,6-dimethylphenol, 4-amino-2,3-diethylphenol, 3-amino-4- Ethylphenol, 2-amino-3-ethylphenol, 2-amino-3,5-diethylphenol
<R1=iPr>
3−アミノ−2−イソプロピルフェノール、4−アミノ−3−イソプロピルフェノール、4−アミノ−3−イソプロピル−6−メチルフェノール、2−アセチル−4−アミノ−3−イソプロピル−6−メチルフェノール、4−アミノ−2,5−ジイソプロピルフェノール、3−アミノ−4−イソプロピルフェノール、2−アミノ−3−イソプロピルフェノール、2−アミノ−3−イソプロピル−6−メチルフェノール
<R 1 = iPr>
3-amino-2-isopropylphenol, 4-amino-3-isopropylphenol, 4-amino-3-isopropyl-6-methylphenol, 2-acetyl-4-amino-3-isopropyl-6-methylphenol, 4- Amino-2,5-diisopropylphenol, 3-amino-4-isopropylphenol, 2-amino-3-isopropylphenol, 2-amino-3-isopropyl-6-methylphenol
<R1=OMe>
3−ヒドロキシ−2−アニシジン、4−ヒドロキシ−2−アニシジン、4−ヒドロキシ−5−メチル−2−アニシジン、4−ヒドロキシ−5−メトキシ−2−アニシジン、5−アセチル−4−ヒドロキシ−2−アニシジン、4−ヒドロキシ−3−メチル−5−メトキシ−2−アニシジン、5−アセチル−4−ヒドロキシ−3−メチル−2−アニシジン、4−アミノ−2,3−ジメトキシ−6−メチルフェノール、4−アミノ−2,3−ジメトキシフェノール、5−ヒドロキシ−2−アニシジン、5−ヒドロキシ−4−メチル−2−アニシジン、5−ヒドロキシ−4−メトキシ−2−アニシジン、5−ヒドロキシ−4−メトキシ−3−メチル−2−アニシジン、6−ヒドロキシ−2−アニシジン、6−ヒドロキシ−5−メチル−2−アニシジン、6−ヒドロキシ−5−アセチル−2−アニシジン、6−ヒドロキシ−5−[2−(N,N−ジプロピルアミノ)エチル]−2−アニシジン、6−ヒドロキシ−2,4−ジメトキシアニリン、3−ヒドロキシ−2,4−ジメトキシアニリン、2,3,4−トリメトキシ−6−アミノフェノール
<R 1 = OMe>
3-hydroxy-2-anisidine, 4-hydroxy-2-anisidine, 4-hydroxy-5-methyl-2-anisidine, 4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-2-anisidine, 5-acetyl-4-hydroxy-2- Anisidine, 4-hydroxy-3-methyl-5-methoxy-2-anisidine, 5-acetyl-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-anisidine, 4-amino-2,3-dimethoxy-6-methylphenol, 4 -Amino-2,3-dimethoxyphenol, 5-hydroxy-2-anisidine, 5-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-anisidine, 5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-2-anisidine, 5-hydroxy-4-methoxy- 3-methyl-2-anisidine, 6-hydroxy-2-anisidine, 6-hydroxy-5-methyl-2-anisidine 6-hydroxy-5-acetyl-2-anisidine, 6-hydroxy-5- [2- (N, N-dipropylamino) ethyl] -2-anisidine, 6-hydroxy-2,4-dimethoxyaniline, 3- Hydroxy-2,4-dimethoxyaniline, 2,3,4-trimethoxy-6-aminophenol
これらのうち、特に、4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノール、4−アミノ−2,3−ジメチルフェノール、3−アミノ−2−メチルフェノール、2−アミノ−3−メチルフェノールなどが、得られるビスイミドフェノール化合物の溶解性と凝集力のバランスや、入手の容易さから好ましい。 Among these, in particular, 4-amino-3-methylphenol, 4-amino-2,3-dimethylphenol, 3-amino-2-methylphenol, 2-amino-3-methylphenol, and the like are obtained. It is preferable from the viewpoint of the balance between the solubility and cohesive force of the phenol compound and availability.
これらのアミノフェノールは1種を単独で用いてもよく、2種以上を混合して用いてもよいが、対称性のよいビスイミドフェノール化合物を製造する上で、好ましくは1種のみを用いる。 These aminophenols may be used singly or in combination of two or more, but preferably only one is used for producing a symmetric bisimidephenol compound.
<芳香族カルボン酸二無水物>
前記一般式(III)で表される芳香族カルボン酸二無水物としては、例えば、2,2’,3,3’−ビフェニルテトラカルボン酸二無水物、2,3’,3,4’−ビフェニルテトラカルボン酸二無水物(a−BPDA)、3,3’,4,4’−ビフェニルテトラカルボン酸二無水物(s−BPDA)等のテトラカルボン酸二無水物;2,2’,3,3’−ジフェニルメタンテトラカルボン酸二無水物、2,3’,3,4’−ジフェニルメタンテトラカルボン酸二無水物、3,3’,4,4’−ジフェニルメタンテトラカルボン酸二無水物等のジフェニルメタンテトラカルボン酸二無水物;2,2’,3,3’−(2,2−ジフェニルプロパン)テトラカルボン酸二無水物、2,3’,3,4’−(2,2−ジフェニルプロパン)テトラカルボン酸二無水物、3,3’,4,4’−(2,2−ジフェニルプロパン)テトラカルボン酸二無水物等の(2,2−ジフェニルプロパン)テトラカルボン酸二無水物;2,2’,3,3’−ベンゾフェノンテトラカルボン酸二無水物、2,3’,3,4’−ベンゾフェノンテトラカルボン酸二無水物、3,3’,4,4’−ベンゾフェノンテトラカルボン酸二無水物等のベンゾフェノンテトラカルボン酸二無水物;2,2’,3,3’−ジフェニルエーテルテトラカルボン酸二無水物、2,3’,3,4’−ジフェニルエーテルテトラカルボン酸二無水物、3,3’,4,4’−ジフェニルエーテルテトラカルボン酸二無水物等のジフェニルエーテルテトラカルボン酸二無水物;2,2’,3,3’−ジフェニルスルホンテトラカルボン酸二無水物、2,3’,3,4’−ジフェニルスルホンテトラカルボン酸二無水物、3,3’,4,4’−ジフェニルスルホンテトラカルボン酸二無水物等のジフェニルスルホンテトラカルボン酸二無水物などが挙げられる。中でも、それ自体の分子の対称性がよく、ビスイミドフェノール化合物全体としての対称性をよくしてイミドの性質を十分に発揮させ、前記|α|を適切に設定することで必要な溶解性を確保することができ、また、入手容易であることから、3,3’,4,4’−ビフェニルテトラカルボン酸二無水物(s−BPDA)、3,3’,4,4’−ベンゾフェノンテトラカルボン酸二無水物、3,3’,4,4’−ジフェニルエーテルテトラカルボン酸二無水物、3,3’,4,4’−ジフェニルスルホンテトラカルボン酸二無水物などが好ましい。
なお、これらは、1種を単独で用いてもよく、2種以上を混合して用いてもよい。
<Aromatic carboxylic dianhydride>
Examples of the aromatic carboxylic dianhydride represented by the general formula (III) include 2,2 ′, 3,3′-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride, 2,3 ′, 3,4′- Tetracarboxylic dianhydrides such as biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride (a-BPDA), 3,3 ′, 4,4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride (s-BPDA); 2,2 ′, 3 , 3′-diphenylmethane tetracarboxylic dianhydride, 2,3 ′, 3,4′-diphenylmethane tetracarboxylic dianhydride, 3,3 ′, 4,4′-diphenylmethane tetracarboxylic dianhydride, etc. Tetracarboxylic dianhydride; 2,2 ′, 3,3 ′-(2,2-diphenylpropane) tetracarboxylic dianhydride, 2,3 ′, 3,4 ′-(2,2-diphenylpropane) Tetracarboxylic dianhydride, 3,3 ', 4 (2,2-diphenylpropane) tetracarboxylic dianhydride such as 4 ′-(2,2-diphenylpropane) tetracarboxylic dianhydride; 2,2 ′, 3,3′-benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride 2,3 ′, 3,4′-benzophenone tetracarboxylic dianhydride, benzophenone tetracarboxylic dianhydride such as 3,3 ′, 4,4′-benzophenone tetracarboxylic dianhydride; ', 3,3'-Diphenyl ether tetracarboxylic dianhydride, 2,3', 3,4'-diphenyl ether tetracarboxylic dianhydride, 3,3 ', 4,4'-diphenyl ether tetracarboxylic dianhydride Diphenyl ether tetracarboxylic dianhydride such as 2,2 ′, 3,3′-diphenylsulfone tetracarboxylic dianhydride, 2,3 ′, 3,4′-diphenylsulfonetetra Carboxylic acid dianhydride, 3,3 ', 4,4'-diphenylsulfone tetracarboxylic dianhydride diphenyl tetracarboxylic acid dianhydride and the like. Among them, the symmetry of the molecule itself is good, the symmetry of the bisimidephenol compound as a whole is improved, the properties of the imide are fully exhibited, and the necessary solubility can be obtained by setting the above | α | appropriately. 3,3 ′, 4,4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride (s-BPDA), 3,3 ′, 4,4′-benzophenone tetra Carboxylic dianhydride, 3,3 ′, 4,4′-diphenyl ether tetracarboxylic dianhydride, 3,3 ′, 4,4′-diphenylsulfone tetracarboxylic dianhydride and the like are preferable.
In addition, these may be used individually by 1 type and may be used in mixture of 2 or more types.
<溶剤>
一段目反応に用いられる溶剤は、前述の如く、活性プロトンが存在すると酸無水物基と反応する可能性があり、アミック酸生成を妨げることから、非プロトン性有機溶剤が好ましい。二段目反応に溶剤を用いる場合、その溶剤には特に制限はない。この場合、アミック酸を生成する一段目反応とイミド環を生成する二段目反応で用いる溶剤は、同一でも異なってもよいが、簡便性の点では、溶剤交換の煩雑さを避けるために同一とするか、或いは異なる溶剤を用いる場合は二段目反応において、更に別の溶剤を追加するようにすることが好ましい。
<Solvent>
As described above, an aprotic organic solvent is preferable as the solvent used in the first-stage reaction because it may react with an acid anhydride group in the presence of active protons and hinder the formation of amic acid. When a solvent is used for the second stage reaction, the solvent is not particularly limited. In this case, the solvent used in the first-stage reaction for generating an amic acid and the second-stage reaction for generating an imide ring may be the same or different, but in terms of simplicity, the same solvent is used to avoid complication of solvent exchange. In the case of using a different solvent, it is preferable to add another solvent in the second stage reaction.
一段目のアミック酸を生成する際に用いる有機溶剤は、芳香族カルボン酸二無水物とアミノフェノールを部分的にでも溶解可能で、かつ反応条件において原料と反応しない非プロトン性有機溶剤であればよく、例えば、N−メチルピロリドン、N,N−ジメチルホルムアミド、N,N−ジメチルアセトアミド等のアミド系溶剤;アセトン、メチルエチルケトン、メチルイソブチルケトン、シクロヘキサノン等のケトン系溶剤;酢酸エチル、酢酸ブチル等のエステル系溶剤;1,4−ジオキサン、テトラヒドロフラン、ジエチルエーテル、ジブチルエーテル、メチル−t−ブチルエーテル、ジフェニルエーテル等のエーテル系溶剤;トルエン、キシレン、メシチレン、エチルベンゼン、クメン、アニソール等の芳香族系溶剤などが挙げられる。これらは1種を単独で用いてもよく、2種以上を混合して用いてもよい。混合して用いる場合は、反応初期から混合されていてもよく、また反応の途中で添加されてもよい。 The organic solvent used for producing the first stage amic acid is an aprotic organic solvent that can partially dissolve the aromatic carboxylic dianhydride and aminophenol and does not react with the raw material under the reaction conditions. Well, for example, amide solvents such as N-methylpyrrolidone, N, N-dimethylformamide, N, N-dimethylacetamide; ketone solvents such as acetone, methyl ethyl ketone, methyl isobutyl ketone, cyclohexanone; ethyl acetate, butyl acetate, etc. Ester solvents; ether solvents such as 1,4-dioxane, tetrahydrofuran, diethyl ether, dibutyl ether, methyl-t-butyl ether, diphenyl ether; aromatic solvents such as toluene, xylene, mesitylene, ethylbenzene, cumene, anisole, etc. Can be mentioned. These may be used alone or in combination of two or more. When mixed and used, it may be mixed from the beginning of the reaction or may be added during the reaction.
<原料比率・原料温度>
反応に供する芳香族カルボン酸二無水物とアミノフェノールとのモル比率は、両原料が残留しない反応当量の1:2が最も好ましい。しかしながら、除去容易なアミノフェノールが芳香族カルボン酸二無水物に対し、必要量以上(芳香族カルボン酸二無水物1モルに対し2モル以上)であっても構わない。即ち、アミノフェノールは酸処理によって水溶化するため、反応後に残留しても除去が容易である。一方、酸無水物基は、アルカリ処理によってジカルボン酸のアルカリ塩とし、水溶化することは可能であるが、生成したビスイミドフェノールもアルカリ塩となることから、アミノフェノールに比べて芳香族カルボン酸二無水物は、分離、精製しにくい。反応に供する芳香族カルボン酸二無水物とアミノフェノールのモル比率としては、芳香族カルボン酸二無水物:アミノフェノールが1:2〜1:4が好ましく、1:2〜1:3が更に好ましく、1:2が特に好ましい。
<Raw material ratio / Raw material temperature>
The molar ratio of the aromatic carboxylic dianhydride and aminophenol to be subjected to the reaction is most preferably 1: 2 of the reaction equivalent in which both raw materials do not remain. However, the aminophenol which can be easily removed may be more than the necessary amount (2 mol or more per 1 mol of the aromatic carboxylic dianhydride) relative to the aromatic carboxylic dianhydride. That is, since aminophenol is water-soluble by acid treatment, it can be easily removed even if it remains after the reaction. On the other hand, the acid anhydride group can be converted into an alkali salt of a dicarboxylic acid by alkali treatment and water-solubilized, but the bisimidephenol produced also becomes an alkali salt. The dianhydride is difficult to separate and purify. The molar ratio of the aromatic carboxylic dianhydride and aminophenol used in the reaction is preferably 1: 2 to 1: 4, more preferably 1: 2 to 1: 3 of aromatic carboxylic dianhydride: aminophenol. 1: 2 is particularly preferred.
一段目反応と二段目反応を溶剤を用いて行う場合、アミノフェノールの反応溶液中濃度としては0.2〜95重量%、特に1〜55重量%、とりわけ3〜35重量%とすることが好ましい。また、芳香族カルボン酸二無水物の反応溶液中濃度としては0.02〜88重量%、特に2〜64重量%、とりわけ、5〜50重量%とすることが好ましい。
また、反応溶液中の芳香族カルボン酸二無水物とアミノフェノールの合計濃度は特に限定されないが、作業性の問題から、アミック酸を生成する一段目反応では8〜85重量%が好ましく、イミド環を生成する二段目反応では5重量%以上が好ましい。なお、この二段目反応は無溶剤で行われても構わない。
When the first-stage reaction and the second-stage reaction are performed using a solvent, the concentration of aminophenol in the reaction solution may be 0.2 to 95% by weight, particularly 1 to 55% by weight, especially 3 to 35% by weight. preferable. The concentration of the aromatic carboxylic dianhydride in the reaction solution is preferably 0.02 to 88% by weight, particularly 2 to 64% by weight, and particularly 5 to 50% by weight.
Further, the total concentration of the aromatic carboxylic dianhydride and aminophenol in the reaction solution is not particularly limited. However, from the viewpoint of workability, it is preferably 8 to 85% by weight in the first stage reaction for generating an amic acid, and the imide ring In the second-stage reaction for producing, 5% by weight or more is preferable. Note that this second-stage reaction may be performed without a solvent.
<触媒>
一段目反応も、二段目反応も、多くの場合、無触媒でも十分に反応は進行するが、必要に応じて触媒を用いてもよい。触媒としては、例えばピリジン、N,N−ジメチルアミノピリジンのような芳香族アミン;トリエチルアミン、トリブチルアミン、トリフェニルアミン、N,N’−ジメチルベンジルアミン、N−メチルモルフォリン、N−メチルピペリジン、1,4−ジアザビシクロ[2.2.2]オクタン(DABCO)、1,8−ジアザビシクロ[5.4.0]−7−ウンデセン(DBU)、ウロトロピン、N,N,N’N’−テトラメチルエチレンジアミン、N,N,N’,N”,N”−ペンタメチルジエチレントリアミンのような3級アミン化合物;酢酸、トリフルオロ酢酸、フェノール化合物、ベンゼンスルホン酸、トルエンスルホン酸、ホウ酸、リン酸のようなブレンステッド酸性化合物;アルカリ金属、アルカリ土類金属、ホウ素、アルミニウム、ガリウム、インジウム、ケイ素、ゲルマニウム、スズ、アンチモン、ビスマス、ランタノイド類、チタン、ジルコニウム、ハフニウム、バナジウム、ニオブ、タンタル、マンガン、レニウム、鉄、コバルト、ロジウム、イリジウム、ニッケル、パラジウム、白金、銅、銀、金、亜鉛等を含むルイス酸性化合物等が挙げられ、これらは1種を単独で用いても、2種以上を併用してもよい。
<Catalyst>
In both the first-stage reaction and the second-stage reaction, the reaction proceeds satisfactorily even without a catalyst, but a catalyst may be used if necessary. Examples of the catalyst include aromatic amines such as pyridine and N, N-dimethylaminopyridine; triethylamine, tributylamine, triphenylamine, N, N′-dimethylbenzylamine, N-methylmorpholine, N-methylpiperidine, 1,4-diazabicyclo [2.2.2] octane (DABCO), 1,8-diazabicyclo [5.4.0] -7-undecene (DBU), urotropine, N, N, N′N′-tetramethyl Tertiary amine compounds such as ethylenediamine, N, N, N ′, N ″, N ″ -pentamethyldiethylenetriamine; acetic acid, trifluoroacetic acid, phenolic compounds, benzenesulfonic acid, toluenesulfonic acid, boric acid, phosphoric acid and the like Bronsted acidic compounds; alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, boron, aluminum, Gallium, indium, silicon, germanium, tin, antimony, bismuth, lanthanoids, titanium, zirconium, hafnium, vanadium, niobium, tantalum, manganese, rhenium, iron, cobalt, rhodium, iridium, nickel, palladium, platinum, copper, silver Lewis acidic compounds containing gold, zinc and the like, and these may be used alone or in combination of two or more.
触媒の使用量には特に制限はないが、反応点となる酸無水物基に対して概ね10モル%以下、例えば1〜5モル%程度とするのが好ましい。
なお、触媒の有無により、以下に記載する反応条件を変える必要はない。
Although there is no restriction | limiting in particular in the usage-amount of a catalyst, It is preferable to set it as about 10 mol% or less with respect to the acid anhydride group used as a reaction point, for example, about 1-5 mol%.
The reaction conditions described below need not be changed depending on the presence or absence of a catalyst.
<脱水剤>
二段目反応の脱水反応を脱水剤を用いる化学的手法で行う場合、その方法としては、例えば無水酢酸とピリジンのように酸無水物と塩基を併用する方法や、酸ハライドと塩基を併用する方法、またN,N’−ジシクロヘキシルカルボジイミドのようなカルボジイミド系化合物やリン酸系の脱水縮合剤を用いる方法が挙げられる。
<Dehydrating agent>
When the dehydration reaction of the second stage reaction is performed by a chemical method using a dehydrating agent, for example, a method of using an acid anhydride and a base together, such as acetic anhydride and pyridine, or an acid halide and a base are used in combination. And a method using a carbodiimide compound such as N, N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide or a phosphoric acid-based dehydration condensing agent.
これらの脱水剤の使用量としては特に制限はないが、例えば酸無水物基に対して1.0〜2.0モル当量程度とすることが好ましい。
これらの脱水剤を用いる場合、一段目反応終了後に、上記適当量の脱水剤を反応系に添加して二段目反応を行えばよい。
Although there is no restriction | limiting in particular as the usage-amount of these dehydrating agents, For example, it is preferable to set it as about 1.0-2.0 molar equivalent with respect to an acid anhydride group.
When these dehydrating agents are used, after the completion of the first stage reaction, the appropriate amount of the dehydrating agent may be added to the reaction system to carry out the second stage reaction.
<反応条件>
反応温度、反応時間などの反応条件は、イミド環が生成される条件であればよいが、作業性の観点から以下の範囲内が好ましい。
<Reaction conditions>
The reaction conditions such as reaction temperature and reaction time may be any conditions that allow an imide ring to be generated, but are preferably within the following ranges from the viewpoint of workability.
即ち、アミック酸を生成する一段目反応では、反応温度は、イミドの閉環反応(脱水)が起こらない条件が望ましいことから、上限として110℃が好ましく、100℃が更に好ましく、95℃が特に好ましく、90℃が最も好ましい。また、同下限は、低すぎると反応速度が遅くなり効率が低下することから、5℃が好ましく、40℃が更に好ましく、60℃が特に好ましい。この一段目反応のアミック酸の生成反応の反応時間は温度にもよるが、下限が通常0.5時間、好ましくは1時間、同上限が通常12時間、好ましくは6時間である。
反応圧力は、常圧または加圧が好ましく、常圧が更に好ましい。
That is, in the first-stage reaction for producing an amic acid, the reaction temperature is preferably a condition that does not cause a ring-closing reaction (dehydration) of the imide. Therefore, the upper limit is preferably 110 ° C, more preferably 100 ° C, and particularly preferably 95 ° C. 90 ° C. is most preferred. The lower limit is preferably 5 ° C., more preferably 40 ° C., and particularly preferably 60 ° C., because if it is too low, the reaction rate becomes slow and the efficiency decreases. The reaction time of the first-stage amic acid production reaction depends on the temperature, but the lower limit is usually 0.5 hours, preferably 1 hour, and the upper limit is usually 12 hours, preferably 6 hours.
The reaction pressure is preferably normal pressure or increased pressure, more preferably normal pressure.
一段目反応において、加熱時の突沸を防ぐため、反応系を撹拌することが好ましく、撹拌にはメカニカルスターラーやマグネチックスターラーを用いることができる。撹拌速度は特に限定されない。 In the first-stage reaction, it is preferable to stir the reaction system in order to prevent bumping during heating, and a mechanical stirrer or a magnetic stirrer can be used for stirring. The stirring speed is not particularly limited.
二段目反応のイミド環の生成段階で、加熱による脱水を行う場合の反応温度は、水が揮発して反応系外に除去されるに十分な温度が必要であることから、下限は好ましくは120℃、より好ましくは130℃、特に好ましくは140℃であり、同上限は、生成物の熱分解を防ぐ観点から、好ましくは250℃、より好ましくは200℃がよい。脱水反応は、除去された水の量が理論量に達するまで行われ、ほとんどの場合24時間以内である。 The reaction temperature when performing dehydration by heating in the stage of formation of the imide ring in the second stage reaction requires a sufficient temperature for water to volatilize and be removed from the reaction system, so the lower limit is preferably 120 ° C., more preferably 130 ° C., particularly preferably 140 ° C. The upper limit is preferably 250 ° C., more preferably 200 ° C. from the viewpoint of preventing thermal decomposition of the product. The dehydration reaction is carried out until the amount of water removed reaches the theoretical amount, most often within 24 hours.
脱水剤を用いる化学的手法によって脱水を行う場合の反応温度は、水を加熱留去する必要性がないことから、通常5〜100℃とする。
脱水剤を用いて脱水を行う場合、溶剤を必要とするが、加熱による脱水を行う場合は、溶剤は存在してもしなくてもよく、例えばある溶剤中でアミック酸を生成させた後に、別の高沸点の溶剤に置換して加熱脱水を行ったり、或いはアミック酸から溶剤を留去して無溶剤で加熱脱水を行ったりすることもできる。
The reaction temperature when dehydration is carried out by a chemical method using a dehydrating agent is usually 5 to 100 ° C. because it is not necessary to distill off water by heating.
When dehydrating using a dehydrating agent, a solvent is required. However, when dehydrating by heating, the solvent may or may not be present. For example, after the amic acid is generated in a certain solvent, another solvent is required. It is also possible to carry out heat dehydration by substituting with a solvent having a high boiling point, or heat dihydration without solvent by distilling off the solvent from the amic acid.
二段目反応において、溶剤を用いる場合、反応圧力は常圧でよく、溶剤を用いない場合には常圧でも減圧でもよいが、脱水をスムーズに進行させるためには減圧であることが好ましい。また、溶剤を用いる場合、一段目反応と同様に加熱時の突沸を防ぐため、反応系を撹拌することが好ましく、撹拌にはメカニカルスターラーやマグネチックスターラーを用いることができる。撹拌速度は特に限定されない。
二段目反応を無溶剤で行う場合には継続的な撹拌は不要である。
In the second stage reaction, when a solvent is used, the reaction pressure may be normal pressure, and when no solvent is used, normal pressure or reduced pressure may be used. However, in order to allow dehydration to proceed smoothly, reduced pressure is preferred. Moreover, when using a solvent, in order to prevent bumping at the time of a heating similarly to the 1st step reaction, it is preferable to stir the reaction system, and a mechanical stirrer or a magnetic stirrer can be used for stirring. The stirring speed is not particularly limited.
When the second stage reaction is carried out without solvent, continuous stirring is not necessary.
<その他の添加剤>
本発明の方法では、本発明の反応を大幅に妨げなければ、反応系に、酸化防止剤、界面活性剤等の添加剤を加えてもよいが、イミド化の反応を妨げないよう必要最低限に止めるべきであり、これらの添加剤を添加する場合、添加量は原料の5重量%以下とすることが好ましい。
これらの添加剤としては、イミド環の形成の点から、原料以外の1級アミン、2級アミン、フェノール類を除くアルコール、原料以外の酸無水物、イソシアネート化合物等以外の物質が好ましい。
<Other additives>
In the method of the present invention, an additive such as an antioxidant or a surfactant may be added to the reaction system as long as the reaction of the present invention is not significantly hindered. When these additives are added, the amount added is preferably 5% by weight or less of the raw material.
These additives are preferably substances other than primary amines other than raw materials, secondary amines, alcohols other than phenols, acid anhydrides other than raw materials, isocyanate compounds and the like from the viewpoint of imide ring formation.
<反応の進行状況の確認>
反応の進行は、薄層クロマトグラフィ(TLC)やガスクロマトグラフィ(GC)、液体クロマトグラフィ(LC)等によって原料の消費をモニターすることで確認することができる。また、加熱脱水法においてはより簡便に、除去された水の量によって反応の進行を確認することができる。例えば、溶媒を用いる方法においては、Dean−Stark管を用いることで水の量を測定することができ、溶媒を用いない方法においては、重量の減少によって除去された水の量を知ることができ、これによって反応の進行を確認することができる。
<Confirmation of reaction progress>
The progress of the reaction can be confirmed by monitoring the consumption of the raw material by thin layer chromatography (TLC), gas chromatography (GC), liquid chromatography (LC) or the like. In addition, in the heat dehydration method, the progress of the reaction can be confirmed more simply by the amount of water removed. For example, in the method using a solvent, the amount of water can be measured by using a Dean-Stark tube, and in the method using no solvent, the amount of water removed by weight reduction can be known. Thus, the progress of the reaction can be confirmed.
<生成物の回収、精製>
一段目反応及び二段目反応を経て生成したビスイミドフェノール化合物は、溶剤を用いた場合には溶液となるか、あるいは析出して分散液か沈殿物となる。溶液となっている場合には溶剤を蒸発させて除去したり、又はビスイミドフェノール化合物が溶解しない貧溶媒を混合することで析出させたりして固体として得ることができる。分散液や沈殿物となっている場合にはそのまま濾取することも可能であるし、貧溶媒と混合することでさらに濾取しやすくすることもできる。濾過は加圧、常圧、減圧濾過のいずれを用いてもよい。
<Product recovery and purification>
The bisimidophenol compound produced through the first-stage reaction and the second-stage reaction becomes a solution or precipitates to form a dispersion or a precipitate when a solvent is used. When it is in solution, it can be obtained as a solid by evaporating and removing the solvent, or by precipitating by mixing with a poor solvent in which the bisimidephenol compound does not dissolve. If it is a dispersion or a precipitate, it can be filtered as it is, or it can be further easily filtered by mixing with a poor solvent. Any one of pressurization, normal pressure, and vacuum filtration may be used for the filtration.
濾取したビスイミドフェノールは、原料の比率が適切であれば十分な純度で得られるが、残留アミノフェノールや微量の着色成分等の不純物が問題となる場合には、更に精製することもできる。 The filtered bisimidephenol can be obtained with sufficient purity if the ratio of the raw materials is appropriate, but can be further purified if impurities such as residual aminophenol or a small amount of coloring components are a problem.
精製法としては、ビスイミドフェノールが溶解せず、不純物が溶解する溶剤を用いて洗浄除去する方法が最も簡便であり、この場合、用いる溶剤としては、例えばメタノール、エタノール、イソプロパノール等のアルコール類;トルエン、キシレン等の芳香族類;ジエチルエーテル、ジブチルエーテル、テトラヒドロフラン、1,4−ジオキサン等のエーテル類等が挙げられる。どの溶剤が適切であるかは、ビスイミドフェノールによって異なる。また、塩酸、硫酸、硝酸、リン酸等の酸で洗浄することで、残留アミノフェノールをより効率的に除去することができる。 As the purification method, a method of washing and removing using a solvent in which bisimidephenol does not dissolve and impurities are dissolved is the simplest. In this case, examples of the solvent used include alcohols such as methanol, ethanol, and isopropanol; Aromatics such as toluene and xylene; ethers such as diethyl ether, dibutyl ether, tetrahydrofuran and 1,4-dioxane. Which solvent is suitable depends on the bisimide phenol. Moreover, residual aminophenol can be more efficiently removed by washing with an acid such as hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, or phosphoric acid.
不純物が結晶中に取り込まれて、洗浄では除去が困難である場合には、再結晶法が有効である。再結晶は、濾取したビスイミドフェノールを一旦溶剤に溶解し、貧溶媒を加えて再度析出させた後、濾取することにより行うことができる。ビスイミドフェノールを溶解する溶剤と貧溶媒の組み合わせとしては特に限定されないが、例えばアセトン/水、N−メチルピロリドン/水、N−メチルピロリドン/トルエン等が挙げられる。更にこれを濾取した後、前述の洗浄を行ってもよい。 The recrystallization method is effective when impurities are taken into the crystal and are difficult to remove by washing. Recrystallization can be carried out by dissolving the filtered bisimidephenol in a solvent, adding a poor solvent to precipitate again, and then filtering. The combination of the solvent for dissolving bisimidephenol and the poor solvent is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include acetone / water, N-methylpyrrolidone / water, N-methylpyrrolidone / toluene and the like. Further, the above-mentioned washing may be performed after filtering this.
ビスイミドフェノールの乾燥法は特に限定されず、加温されていてもいなくてもよく、減圧されていてもいなくてもよい。 The drying method of bisimide phenol is not particularly limited, and it may or may not be heated and may or may not be decompressed.
上記の好ましい条件で反応及び精製を行えば、収率は良好であり、通常、本発明の方法によれば、80〜100%の収率で目的とするビスイミドフェノール化合物を得ることができる。 If the reaction and purification are carried out under the above-mentioned preferable conditions, the yield is good. Usually, according to the method of the present invention, the desired bisimidephenol compound can be obtained at a yield of 80 to 100%.
なお、不純物として混入する可能性のあるものとしては、例えば、未反応の原料、アミノフェノール中に含まれる不純物のジアミンが反応してできたイミドオリゴマー、残留溶剤、アミンの酸化物等が挙げられる。 Examples of substances that may be mixed as impurities include unreacted raw materials, imide oligomers formed by reaction of impurity diamines contained in aminophenol, residual solvents, amine oxides, and the like. .
[高分子化合物]
本発明の高分子化合物は、上述の本発明のビスイミドフェノール化合物を原料モノマーの少なくとも一部として用い、これを重合するか、或いは他のモノマーと共重合してなるものであり、具体的にはエポキシ樹脂、ポリエステル樹脂、ポリカーボネート樹脂、フェノール樹脂等が挙げられる。
[Polymer compound]
The polymer compound of the present invention is obtained by polymerizing the above-described bisimide phenol compound of the present invention as at least a part of the raw material monomer, or copolymerizing it with other monomers, specifically May be an epoxy resin, a polyester resin, a polycarbonate resin, a phenol resin, or the like.
以下に実施例及び比較例を挙げて本発明をより具体的に説明するが、本発明はその要旨を超えない限り、以下の実施例に何ら限定されるものではない。 Hereinafter, the present invention will be described more specifically with reference to examples and comparative examples. However, the present invention is not limited to the following examples as long as the gist thereof is not exceeded.
なお、以下において、純度を示す「%」はすべて「重量%」である。
また、合成された化合物の1H−NMRは、Bruker AV400Mを用いて、重DMSO(ジメチルスルホキシド)溶媒中、室温で測定した。また、IRは、FT/IR−230(日本分光(株)製)を用いて、KBr錠剤を作成し、透過法で測定した。MSはPolaris Q((株)日立ハイテクノロジーズ製)を用い、イオン源温度200℃、イオン化法はEI、イオン化エネルギー70eVで、直接導入法で測定した。
In the following, all “%” indicating purity is “wt%”.
Further, 1 H-NMR of the synthesized compound was measured at room temperature in a heavy DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide) solvent using a Bruker AV400M. In addition, IR was measured by a permeation method by preparing KBr tablets using FT / IR-230 (manufactured by JASCO Corporation). MS was Polaris Q (manufactured by Hitachi High-Technologies Corporation), the ion source temperature was 200 ° C., the ionization method was EI, and the ionization energy was 70 eV.
[実施例1]
メカニカルスターラー、Dean−Stark管、及び還流冷却管を装備した2Lフラスコに、3,3’,4,4’−ビフェニルテトラカルボン酸二無水物(s−BPDA、三菱化学(株)製、純度99.8%)100g(340mmol)とN−メチルピロリドン(NMP、三菱化学(株)製、純度99.9%)300mlを加え、撹拌しながら4−アミノ−m−クレゾール(製品名)(又は4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノール(別名))(和光純薬工業(株)製、純度98%以上)84g(680mmol)を投入した。これを80℃の油浴で2時間加熱した後、トルエン150mlを加え、油浴温度を160℃に上げた。トルエンが還流開始してから3時間後、Dean−Stark管にほぼ理論量の水が留出したことを確認し、油浴を外して室温まで撹拌しながら冷却した。ここに1.5Lの蒸留水を加えると、生成物が析出した。これをブフナー漏斗で濾取し、3Lの水、1Lのエタノールで洗浄した後、135℃で減圧乾燥して溶剤を除去し、下記式(A1−1)で表される、薄黄色のN,N’−ビス(2−メチル−4−ヒドロキシフェニル)−4,4’−ジフタルイミドを得た。収量167g(332mmol、収率98%)。この化合物において、一般式(I)のR1に相当するメチル基(Me)の|α|は55.8°である。
[Example 1]
To a 2 L flask equipped with a mechanical stirrer, Dean-Stark tube, and reflux condenser, 3,3 ′, 4,4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride (s-BPDA, manufactured by Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, purity 99) .8%) 100 g (340 mmol) and N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP, Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, purity 99.9%) 300 ml were added and stirred, 4-amino-m-cresol (product name) (or 4 84 g (680 mmol) of -amino-3-methylphenol (alias)) (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., purity of 98% or more) was added. This was heated in an oil bath at 80 ° C. for 2 hours, 150 ml of toluene was added, and the oil bath temperature was raised to 160 ° C. Three hours after toluene began to reflux, it was confirmed that almost the theoretical amount of water had distilled into the Dean-Stark tube, and the oil bath was removed and the mixture was cooled to room temperature with stirring. When 1.5 L of distilled water was added thereto, the product was precipitated. This was filtered with a Buchner funnel, washed with 3 L of water and 1 L of ethanol, and then dried under reduced pressure at 135 ° C. to remove the solvent, and a pale yellow N, represented by the following formula (A1-1): N′-bis (2-methyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) -4,4′-diphthalimide was obtained. Yield 167 g (332 mmol, 98% yield). In this compound, | α | of the methyl group (Me) corresponding to R 1 of the general formula (I) is 55.8 °.
この化合物の分析結果は以下の通りである。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6):δ2.05(6H,s,-CH3),6.72(2H,dd,J=2.8,8.0Hz,Ar-H),6.79(2H,d,J=2.8Hz,Ar-H),7.15(2H,d,J=8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.09(2H,d,J=8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.38(2H,d,J=8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.41(2H,s,Ar-H),9.71(2H,s,-OH)
IR(KBr):3448,1774,1709,1618,1504,1460,1421,1383,1300,1257,1111,744,546cm-1
MS:m/z504([M+],100%),505([M+]+1,31%),506([M+]+2,6.2%)
The analysis results of this compound are as follows.
1 H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ): δ 2.05 (6H, s, —CH 3 ), 6.72 (2H, dd, J = 2.8, 8.0 Hz, Ar—H), 6.79 (2H, d, J = 2.8Hz, Ar-H), 7.15 (2H, d, J = 8.0Hz, Ar-H), 8.09 (2H, d, J = 8.0Hz, Ar-H), 8.38 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 8.41 (2H, s, Ar-H), 9.71 (2H, s, -OH)
IR (KBr): 3448,1774,1709,1618,1504,1460,1421,1383,1300,1257,1111,744,546cm -1
MS: m / z 504 ([M + ], 100%), 505 ([M + ] +1, 31%), 506 ([M + ] + 2,6.2%)
[実施例2]
4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノールを4−アミノ−2,3−キシレノール(製品名)(又は4−アミノ−2,3−ジメチルフェノール(別名))(東京化成工業(株)製、純度97%以上)93g(680mmol)に変更した以外は、実施例1と同様に行って、下記式(A1−2)で表される生成物のN,N’−ビス(2,3−ジメチル−4−ヒドロキシフェニル)−4,4’−ジフタルイミドを得た。収量169g(317mmol、収率93%)。この化合物において、一般式(I)のR1に相当するメチル基(Me)の|α|は55.8°である。
[Example 2]
4-Amino-3-methylphenol was converted to 4-amino-2,3-xylenol (product name) (or 4-amino-2,3-dimethylphenol (alias)) (Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., purity 97% N) N′-bis (2,3-dimethyl-4-) of the product represented by the following formula (A1-2), except that the amount was changed to 93 g (680 mmol). Hydroxyphenyl) -4,4′-diphthalimide was obtained. Yield 169 g (317 mmol, 93% yield). In this compound, | α | of the methyl group (Me) corresponding to R 1 of the general formula (I) is 55.8 °.
この化合物の分析結果は以下の通りである。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6):δ1.97(3H,s,-CH3),2.13(3H,s,-CH3),6.79(2H,d,J=8.4Hz,Ar-H),7.00(2H,d,J=8.4Hz,Ar-H),8.09(2H,d,J=8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.38(2H,d,J=8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.41(2H,s,Ar-H),9.64(2H,s,-OH)
IR(KBr):3417,1770,1716,11628,1591,1491,1423,1383,1284,1236,1109,814,746,548cm-1
MS:m/z532([M+],100%),533([M+]+1,39.3%),534([M+]+2,8.6%)
The analysis results of this compound are as follows.
1 H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ): δ 1.97 (3H, s, —CH 3 ), 2.13 (3H, s, —CH 3 ), 6.79 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, Ar—H) , 7.00 (2H, d, J = 8.4Hz, Ar-H), 8.09 (2H, d, J = 8.0Hz, Ar-H), 8.38 (2H, d, J = 8.0Hz, Ar-H), 8.41 (2H, s, Ar-H), 9.64 (2H, s, -OH)
IR (KBr): 3417,1770,1716,11628,1591,1491,1423,1383,1284,1236,1109,814,746,548cm -1
MS: m / z 532 ([M + ], 100%), 533 ([M + ] + 1,39.3%), 534 ([M + ] + 2,8.6%)
[実施例3]
4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノールを3−アミノ−o−クレゾール(製品名)(又は3−アミノ−2−メチルフェノール(別名))(東京化成工業(株)製、純度98%以上)84g(680mmol)に変更した以外は、実施例1と同様に行って、下記式(A2)で表されるN,N’−ビス(2−メチル−3−ヒドロキシフェニル)−4,4’−ジフタルイミドを得た。収量170g(337mmol、収率99%)。この化合物において、一般式(I)のR1に相当するメチル基(Me)の|α|は55.8°である。
[Example 3]
4-amino-3-methylphenol was converted to 3-amino-o-cresol (product name) (or 3-amino-2-methylphenol (also known as)) (manufactured by Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., purity 98% or more) 84 g ( N, N′-bis (2-methyl-3-hydroxyphenyl) -4,4′-diphthalimide represented by the following formula (A2), except that it was changed to 680 mmol). Got. Yield 170 g (337 mmol, 99% yield). In this compound, | α | of the methyl group (Me) corresponding to R 1 of the general formula (I) is 55.8 °.
この化合物の分析結果は以下の通りである。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6):δ1.94(6H,s,-CH3),6.83(2H,d,J=8.0Hz,Ar-H),6.95(2H,d,J=8.0Hz,Ar-H),7.15(2H,dd,J=8.0,8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.11(2H,d,J=8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.39(2H,d,J=8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.44(2H,s,Ar-H),9.77(2H,s,-OH)
IR(KBr):3442,1770,1718,1610,1593,1473,1423,1377,1336,1282,1228,1115,897,781,742,717cm-1
MS:m/z504([M+],100%),505([M+]+1,32.9%),506([M+]+2,7.4%)
The analysis results of this compound are as follows.
1 H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ): δ 1.94 (6H, s, —CH 3 ), 6.83 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar—H), 6.95 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.15 (2H, dd, J = 8.0,8.0Hz, Ar-H), 8.11 (2H, d, J = 8.0Hz, Ar-H), 8.39 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 8.44 (2H, s, Ar-H), 9.77 (2H, s, -OH)
IR (KBr): 3442,1770,1718,1610,1593,1473,1423,1377,1336,1282,1228,1115,897,781,742,717cm -1
MS: m / z 504 ([M + ], 100%), 505 ([M + ] +1, 32.9%), 506 ([M + ] + 2,7.4%)
[実施例4]
4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノールを2−アミノ−m−クレゾール(製品名)(又は2−アミノ−3−メチルフェノール(別名))(東京化成工業(株)製、純度95%)84g(680mmol)に変更した以外は、実施例1と同様に行って、下記式(A3)で表されるN,N’−ビス(2−メチル−6−ヒドロキシフェニル)−4,4’−ジフタルイミドを得た。収量165g(326mmol、収率96%)。この化合物において、一般式(I)のR1に相当するメチル基(Me)の|α|は55.8°であり、R5に相当する水酸基(OH)の|α|は42.3°である。
[Example 4]
4-amino-3-methylphenol was converted to 2-amino-m-cresol (product name) (or 2-amino-3-methylphenol (alias)) (manufactured by Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., purity 95%) 84 g (680 mmol) ), Except that N, N′-bis (2-methyl-6-hydroxyphenyl) -4,4′-diphthalimide represented by the following formula (A3) is used. Obtained. Yield 165 g (326 mmol, yield 96%). In this compound, | α | of the methyl group (Me) corresponding to R 1 of the general formula (I) is 55.8 °, and | α | of the hydroxyl group (OH) corresponding to R 5 is 42.3 °. It is.
この化合物の分析結果は以下の通りである。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6):δ2.10(6H,s,-CH3),6.84(2H,d,J=8.0Hz,Ar-H),7.23(2H,dd,J=8.0,8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.13(2H,d,J=8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.41(2H,d,J=8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.46(2H,s,Ar-H),9.86(2H,s,-OH)
IR(KBr):3401,3330,1772,1709,1618,1591,1508,1473,1387,1294,1209,1105,891,852,779,746,696,546cm-1
MS:m/z504([M+],100%),505([M+]+1,39.5%),506([M+]+2,6.4%)
The analysis results of this compound are as follows.
1 H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ): δ 2.10 (6H, s, —CH 3 ), 6.84 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar—H), 7.23 (2H, dd, J = 8.0 , 8.0Hz, Ar-H), 8.13 (2H, d, J = 8.0Hz, Ar-H), 8.41 (2H, d, J = 8.0Hz, Ar-H), 8.46 (2H, s, Ar-H ), 9.86 (2H, s, -OH)
IR (KBr): 3401,330,1772,1709,1618,1591,1508,1473,1387,1294,1209,1105,891,852,779,746,696,546cm -1
MS: m / z 504 ([M + ], 100%), 505 ([M + ] +1, 39.5%), 506 ([M + ] + 2,6.4%)
[実施例5]
3,3’,4,4’−ビフェニルテトラカルボン酸二無水物を4,4’−オキシジフタル酸無水物(製品名)(又は3,3’,4,4’−ジフェニルエーテルテトラカルボン酸無水物(別名))(東京化成工業(株)製、純度98%)100g(322mmol)とし、4−アミノ−m−クレゾール(製品名)(又は4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノール(別名))(和光純薬工業(株)製、純度98%以上)の量を79g(644mmol)とした以外は、実施例1と同様に行って、下記式(A4)で表されるN,N’−ビス(2−メチル−4−ヒドロキシフェニル)−4,4’−オキシジフタルイミドを得た。収量164g(316mmol、収率98%)。この化合物において、一般式(I)のR1に相当するメチル基(Me)の|α|は55.8°である。
[Example 5]
3,3 ′, 4,4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride is converted to 4,4′-oxydiphthalic anhydride (product name) (or 3,3 ′, 4,4′-diphenyl ether tetracarboxylic anhydride ( Alias)) (Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., purity 98%) 100 g (322 mmol), 4-amino-m-cresol (product name) (or 4-amino-3-methylphenol (alias)) (Wako Jun N, N′-bis (2) represented by the following formula (A4) is carried out in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the amount of Yakuhin Kogyo Co., Ltd. (purity 98% or more) is 79 g (644 mmol). -Methyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) -4,4'-oxydiphthalimide was obtained. Yield 164 g (316 mmol, 98% yield). In this compound, | α | of the methyl group (Me) corresponding to R 1 of the general formula (I) is 55.8 °.
この化合物の分析結果は以下の通りである。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6):δ2.03(6H,s,-CH3),6.70(2H,dd,J=2.4,8.4Hz,Ar-H),6.76(2H,d,J=2.4Hz,Ar-H),7.11(2H,d,J=8.4Hz,Ar-H),7.63(2H,d,J=2.4Hz,Ar-H),7.64(2H,dd,J=2.4,8.8Hz,Ar-H),8.50(2H,d,J=8.8Hz,Ar-H),9.70(2H,s,-OH)
IR(KBr):3413,1772,1716,1608,1508,1464,1437,1385,1300,1259,1201,1107,1084,852,752,553cm-1
MS:m/z520([M+],100%),521([M+]+1,36.4%),522([M+]+2,8.9%)
The analysis results of this compound are as follows.
1 H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ): δ 2.03 (6H, s, —CH 3 ), 6.70 (2H, dd, J = 2.4, 8.4 Hz, Ar—H), 6.76 (2H, d, J = 2.4Hz, Ar-H), 7.11 (2H, d, J = 8.4Hz, Ar-H), 7.63 (2H, d, J = 2.4Hz, Ar-H), 7.64 (2H, dd, J = 2.4 , 8.8Hz, Ar-H), 8.50 (2H, d, J = 8.8Hz, Ar-H), 9.70 (2H, s, -OH)
IR (KBr): 3413,1772,1716,1608,1508,1464,1437,1385,1300,1259,1201,1107,1084,852,752,553cm -1
MS: m / z 520 ([M + ], 100%), 521 ([M + ] +1, 36.4%), 522 ([M + ] + 2,8.9%)
[実施例6]
3,3’,4,4’−ビフェニルテトラカルボン酸二無水物を3,3’,4,4’−ジフェニルスルホンテトラカルボン酸二無水物(東京化成工業(株)製、純度96%以上)100g(279mmol)とし、4−アミノ−m−クレゾール(製品名)(又は4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノール(別名))(和光純薬工業(株)製、純度98%以上)の量を69g(558mmol)とした以外は、実施例1と同様に行って、下記式(A5)で表されるN,N’−ビス(2−メチル−4−ヒドロキシフェニル)−4,4’−スルホニルジフタルイミドを得た。収量136g(240mmol、収率86%)。この化合物において、一般式(I)のR1に相当するメチル基(Me)の|α|は55.8°である。
[Example 6]
3,3 ′, 4,4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride is converted to 3,3 ′, 4,4′-diphenylsulfonetetracarboxylic dianhydride (manufactured by Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., purity 96% or more). 100 g (279 mmol) and 69 g of 4-amino-m-cresol (product name) (or 4-amino-3-methylphenol (alias)) (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., purity 98% or more) (N, N′-bis (2-methyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) -4,4′-sulfonyldibenzene represented by the following formula (A5)), except that (558 mmol) was used. Phthalimide was obtained. Yield 136 g (240 mmol, 86% yield). In this compound, | α | of the methyl group (Me) corresponding to R 1 of the general formula (I) is 55.8 °.
この化合物の分析結果は以下の通りである。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6):δ2.00(6H,s,-CH3),6.70(2H,dd,J=2.4,8.8Hz,Ar-H),6.75(2H,d,J=2.4Hz,Ar-H),7.10(2H,d,J=8.8Hz,Ar-H),8.20(2H,d,J=8.8Hz,Ar-H),8.63(2H,dd,J=0.8,8.8Hz,Ar-H),8.65(2H,d,J=0.8Hz,Ar-H),9.72(2H,s,-OH)
IR(KBr):3424,1778,1718,1608,1504,1460,1431,1383,1327,1302,1259,1221,1180,1155,1107,673,638,565cm-1
MS:m/z568([M+],100%),569([M+]+1,35.6%),570([M+]+2,11.6%),571([M+]+3,3.0%)
The analysis results of this compound are as follows.
1 H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ): δ2.00 (6H, s, —CH 3 ), 6.70 (2H, dd, J = 2.4, 8.8 Hz, Ar—H), 6.75 (2H, d, J = 2.4Hz, Ar-H), 7.10 (2H, d, J = 8.8Hz, Ar-H), 8.20 (2H, d, J = 8.8Hz, Ar-H), 8.63 (2H, dd, J = 0.8 , 8.8Hz, Ar-H), 8.65 (2H, d, J = 0.8Hz, Ar-H), 9.72 (2H, s, -OH)
IR (KBr): 3424,1778,1718,1608,1504,1460,1431,1383,1327,1302,1259,1221,1180,1155,1107,673,638,565cm -1
MS: m / z 568 ([M + ], 100%), 569 ([M + ] + 1,35.6%), 570 ([M + ] + 2,11.6%), 571 ([M + ] +3, (3.0%)
[実施例7]
3,3’,4,4’−ビフェニルテトラカルボン酸二無水物を3,3’,4,4’−ベンゾフェノンテトラカルボン酸二無水物(和光純薬工業(株)製、純度96%以上)100g(310mmol)とし、4−アミノ−m−クレゾール(製品名)(又は4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノール(別名))(和光純薬工業(株)製、純度98%以上)の量を76g(620mol)とした以外は、実施例1と同様に行って、下記式(A6)で表されるN,N’−ビス(2−メチル−4−ヒドロキシフェニル)−4,4’−オキソメチレンジフタルイミドを得た。収量164g(309mmol、収率99%)。この化合物において、一般式(I)のR1に相当するメチル基(Me)の|α|は55.8°である。
[Example 7]
3,3 ′, 4,4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride is converted to 3,3 ′, 4,4′-benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., purity 96% or more) 100 g (310 mmol) and the amount of 4-amino-m-cresol (product name) (or 4-amino-3-methylphenol (alias)) (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., purity 98% or more) is 76 g. (N, N′-bis (2-methyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) -4,4′-oxomethylene represented by the following formula (A6)) except that (620 mol) was used. Diphthalimide was obtained. Yield 164 g (309 mmol, 99% yield). In this compound, | α | of the methyl group (Me) corresponding to R 1 of the general formula (I) is 55.8 °.
この化合物の分析結果は以下の通りである。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6):δ2.05(6H,s,-CH3),6.72(2H,dd,J=2.8,8.4Hz,Ar-H),6.78(2H,d,J=2.8Hz,Ar-H),7.15(2H,d,J=8.4Hz,Ar-H),8.17(2H,dd,J=0.4,8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.18(2H,dd,J=0.8,8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.27(2H,dd,J=0.8,8.0Hz,Ar-H),9.72(2H,s,-OH)
IR(KBr):3363,1772,1718,1658,1608,1508,1466,1439,1377,1290,1238,1165,1128,1103,854,725,546cm-1
MS:m/z532([M+],100%),533([M+]+1,33.8%),534([M+]+2,6.2%)
The analysis results of this compound are as follows.
1 H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ): δ 2.05 (6H, s, —CH 3 ), 6.72 (2H, dd, J = 2.8, 8.4 Hz, Ar—H), 6.78 (2H, d, J = 2.8Hz, Ar-H), 7.15 (2H, d, J = 8.4Hz, Ar-H), 8.17 (2H, dd, J = 0.4,8.0Hz, Ar-H), 8.18 (2H, dd, J = 0.8,8.0Hz, Ar-H), 8.27 (2H, dd, J = 0.8,8.0Hz, Ar-H), 9.72 (2H, s, -OH)
IR (KBr): 3363,1772,1718,1658,1608,1508,1466,1439,1377,1290,1238,1165,1128,1103,854,725,546cm -1
MS: m / z 532 ([M + ], 100%), 533 ([M + ] +1, 33.8%), 534 ([M + ] + 2,6.2%)
[比較例1]
4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノールをp−アミノフェノール(製品名)(和光純薬工業(株)製、純度98%)74g(680mmol)に変更した以外は、実施例1と同様に行って、下記式(B1−1)で表されるN,N’−ビス(4−ヒドロキシフェニル)−4,4’−ジフタルイミド(CAS No.128761−43−3)を得た。収量159g(335mmol、収率98%)。
[Comparative Example 1]
Except that 4-amino-3-methylphenol was changed to 74 g (680 mmol) of p-aminophenol (product name) (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., purity 98%), the same procedure as in Example 1 was carried out. N, N′-bis (4-hydroxyphenyl) -4,4′-diphthalimide (CAS No. 128764-43-3) represented by the following formula (B1-1) was obtained. Yield 159 g (335 mmol, 98% yield).
[比較例2]
4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノールを4−アミノ−3,5−キシレノール(東京化成工業(株)製、純度98%以上)93g(680mmol)に変更した以外は、実施例1と同様に行って、下記式(B1−2)で表されるN,N’−ビス(2,6−ジメチル−4−ヒドロキシフェニル)−4,4’−ジフタルイミドを得た。収量177g(333mmol、収率98%)。この化合物において、一般式(I)のR1,R5に相当するメチル基(Me)の|α|は55.8°である。
[Comparative Example 2]
The same procedure as in Example 1 was carried out except that 4-amino-3-methylphenol was changed to 93 g (680 mmol) of 4-amino-3,5-xylenol (manufactured by Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., purity 98% or more). N, N′-bis (2,6-dimethyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) -4,4′-diphthalimide represented by the following formula (B1-2) was obtained. Yield 177 g (333 mmol, 98% yield). In this compound, | α | of the methyl group (Me) corresponding to R 1 and R 5 in the general formula (I) is 55.8 °.
この化合物の分析結果は以下の通りである。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6):δ2.00(12H,s,-CH3),6.63(4H,s,Ar-H),8.12(2H,d,J=8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.40(2H,dd,J=0.8,8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.44(2H,d,J=0.8Hz,Ar-H),9.64(2H,s,-OH)
IR(KBr):3371,1770,1707,1597,1475,1423,1377,1321,1271,1161,1113,1028,889,847,748,692,557,538cm-1
MS:m/z532([M+],100%),533([M+]+1,38.1%),534([M+]+2,7.5%),535([M+]+3,1.0%)
The analysis results of this compound are as follows.
1 H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ): δ2.00 (12H, s, —CH 3 ), 6.63 (4H, s, Ar—H), 8.12 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar—H ), 8.40 (2H, dd, J = 0.8,8.0Hz, Ar-H), 8.44 (2H, d, J = 0.8Hz, Ar-H), 9.64 (2H, s, -OH)
IR (KBr): 3371, 1770, 1707, 1597, 1475, 1423, 1377, 1321, 1271, 1161, 1113, 1028, 889, 847, 748, 692, 557, 538cm -1
MS: m / z 532 ([M + ], 100%), 533 ([M + ] + 1,38.1%), 534 ([M + ] + 2,7.5%), 535 ([M + ] +3, 1.0%)
[比較例3]
4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノールをm−アミノフェノール(製品名)(和光純薬工業(株)製、純度98.5%)74g(680mmol)に変更した以外は、実施例1と同様に行って、下記式(B2−1)で表されるN,N’−ビス(3−ヒドロキシフェニル)−4,4’−ジフタルイミド(CAS No.295348−32−2)を得た。収量152g(319mmol、収率94%)。
[Comparative Example 3]
The same procedure as in Example 1 was conducted except that 4-amino-3-methylphenol was changed to 74 g (680 mmol) of m-aminophenol (product name) (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., purity 98.5%). Thus, N, N′-bis (3-hydroxyphenyl) -4,4′-diphthalimide (CAS No. 295348-32-2) represented by the following formula (B2-1) was obtained. Yield 152 g (319 mmol, 94% yield).
[比較例4]
4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノールを5−アミノ−o−クレゾール(和光純薬工業(株)製、純度97%以上)84g(680mmol)に変更した以外は、実施例1と同様に行って、下記式(B2−2)で表されるN,N’−ビス(4−メチル−3−ヒドロキシフェニル)−4,4’−ジフタルイミドを得た。収量151g(300mmol、収率88%)。
[Comparative Example 4]
The same procedure as in Example 1 was conducted except that 4-amino-3-methylphenol was changed to 84 g (680 mmol) of 5-amino-o-cresol (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., purity 97% or more), N, N′-bis (4-methyl-3-hydroxyphenyl) -4,4′-diphthalimide represented by the following formula (B2-2) was obtained. Yield 151 g (300 mmol, yield 88%).
この化合物の分析結果は以下の通りである。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6):δ2.19(6H,s,-CH3),6.80(2H,dd,J=2.0,8.0Hz,Ar-H),6.89(2H,d,J=2.0Hz,Ar-H),7.20(2H,d,J=8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.08(2H,d,J=7.6Hz,Ar-H),8.37(2H,dd,J=1.2,7.6Hz,Ar-H),8.41(2H,d,J=1.2Hz,Ar-H),9.67(2H,s,-OH)
IR(KBr):3471,1770,1718,1618,1599,1523,1427,1369,1281,1265,1232,1186,1128,1095,796,741,553cm-1
MS:m/z504([M+],100%),505([M+]+1,34.0%),506([M+]+2,6.9%)
The analysis results of this compound are as follows.
1 H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ): δ 2.19 (6H, s, —CH 3 ), 6.80 (2H, dd, J = 2.0, 8.0 Hz, Ar—H), 6.89 (2H, d, J = 2.0Hz, Ar-H), 7.20 (2H, d, J = 8.0Hz, Ar-H), 8.08 (2H, d, J = 7.6Hz, Ar-H), 8.37 (2H, dd, J = 1.2 , 7.6Hz, Ar-H), 8.41 (2H, d, J = 1.2Hz, Ar-H), 9.67 (2H, s, -OH)
IR (KBr): 3471,1770,1718,1618,1599,1523,1427,1369,1281,1265,1232,1186,1128,1095,796,741,553cm -1
MS: m / z 504 ([M + ], 100%), 505 ([M + ] +1, 34.0%), 506 ([M + ] + 2,6.9%)
[比較例5]
4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノールをo−アミノフェノール(製品名)(和光純薬工業(株)製、純度97%)74g(680mmol)に変更した以外は、実施例1と同様に行って、下記式(B3−1)で表されるN,N’−ビス(4−ヒドロキシフェニル)−4,4’−ジフタルイミドを得た。収量160g(337mmol、収率99%)。この化合物において、一般式(I)のR1に相当する水酸基(OH)の|α|は42.3°である。
[Comparative Example 5]
Except for changing 4-amino-3-methylphenol to 74 g (680 mmol) of o-aminophenol (product name) (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., purity 97%), the same procedure as in Example 1 was carried out. N, N′-bis (4-hydroxyphenyl) -4,4′-diphthalimide represented by the following formula (B3-1) was obtained. Yield 160 g (337 mmol, yield 99%). In this compound, | α | of the hydroxyl group (OH) corresponding to R 1 of the general formula (I) is 42.3 °.
この化合物の分析結果は以下の通りである。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6):δ6.94(2H,ddd,J=1.2,7.6,7.6Hz,Ar-H),7.01(2H,dd,J=1.2,7.6Hz,Ar-H),7.30(2H,dd,J=1.6,7.6Hz,Ar-H),7.34(2H,ddd,J=1.2,7.6,7.6Hz,Ar-H),8.01(2H,d,J=8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.44(2H,dd,J=1.6,8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.44(2H,d,J=1.6Hz,Ar-H),9.90(2H,s,-OH)
IR(KBr):3317,1768,1701,1620,1601,1512,1464,1425,1389,1300,1286,1198,1111,1090,893,872,758,744,631cm-1
MS:m/z476([M+],100%),477([M+]+1,33.0%),478([M+]+2,6.5%)
The analysis results of this compound are as follows.
1 H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ): δ 6.94 (2H, ddd, J = 1.2, 7.6, 7.6 Hz, Ar—H), 7.01 (2H, dd, J = 1.2, 7.6 Hz, Ar—H ), 7.30 (2H, dd, J = 1.6, 7.6Hz, Ar-H), 7.34 (2H, ddd, J = 1.2, 7.6, 7.6Hz, Ar-H), 8.01 (2H, d, J = 8.0Hz) , Ar-H), 8.44 (2H, dd, J = 1.6,8.0Hz, Ar-H), 8.44 (2H, d, J = 1.6Hz, Ar-H), 9.90 (2H, s, -OH)
IR (KBr): 3317,1768,1701,1620,1601,1512,1464,1425,1389,1300,1286,1198,1111,1090,893,872,758,744,631cm -1
MS: m / z 476 ([M + ], 100%), 477 ([M + ] + 1,33.0%), 478 ([M + ] + 2,6.5%)
[比較例6]
4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノールを6−アミノ−m−クレゾール(和光純薬工業(株)製、純度90%以上)84g(680mmol)に変更した以外は、実施例1と同様に行って、下記式(B3−2)で表されるN,N’−ビス(4−メチル−2−ヒドロキシフェニル)−4,4’−ジフタルイミドを得た。収量168g(333mmol、収率98%)。この化合物において、一般式(I)のR1に相当する水酸基(OH)の|α|は42.3°である。
[Comparative Example 6]
Except that 4-amino-3-methylphenol was changed to 84 g (680 mmol) of 6-amino-m-cresol (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., purity 90% or more), the same procedure as in Example 1 was carried out. N, N′-bis (4-methyl-2-hydroxyphenyl) -4,4′-diphthalimide represented by the following formula (B3-2) was obtained. Yield 168 g (333 mmol, 98% yield). In this compound, | α | of the hydroxyl group (OH) corresponding to R 1 of the general formula (I) is 42.3 °.
この化合物の分析結果は以下の通りである。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6):δ2.26(6H,s,-CH3),6.90(2H,d,J=8.4Hz,Ar-H),7.09(2H,d,J=2.4Hz,Ar-H),7.14(2H,dd,J=2.4,8.4Hz,Ar-H),8.09(2H,d,J=8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.39(2H,d,J=8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.43(2H,s,Ar-H),9.62(2H,s,-OH)
IR(KBr):3398,1774,1718,1618,1512,1425,1375,1336,1292,1277,1188,1140,1109,1088,820,768,742,557cm-1
MS:m/z504([M+],100%),505([M+]+1,34.6%),506([M+]+2,7.3%)
The analysis results of this compound are as follows.
1 H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ): δ 2.26 (6H, s, —CH 3 ), 6.90 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, Ar—H), 7.09 (2H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, Ar-H), 7.14 (2H, dd, J = 2.4, 8.4 Hz, Ar-H), 8.09 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 8.39 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 8.43 (2H, s, Ar-H), 9.62 (2H, s, -OH)
IR (KBr): 3398,1774,1718,1618,1512,1425,1375,1336,1292,1277,1188,1140,1109,1088,820,768,742,557cm -1
MS: m / z 504 ([M + ], 100%), 505 ([M + ] +1, 34.6%), 506 ([M + ] + 2,7.3%)
[比較例7]
4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノールを2−アミノ−p−クレゾール(東京化成工業(株)製、純度98%)84g(680mmol)に変更した以外は、実施例1と同様に行って、下記式(B3−3)で表されるN,N’−ビス(5−メチル−2−ヒドロキシフェニル)−4,4’−ジフタルイミドを得た。収量158g(313mmol、収率92%)。この化合物において、一般式(I)のR1に相当する水酸基(OH)の|α|は42.3°である。
[Comparative Example 7]
The same procedure as in Example 1 was carried out except that 4-amino-3-methylphenol was changed to 84 g (680 mmol) of 2-amino-p-cresol (manufactured by Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., purity 98%). N, N′-bis (5-methyl-2-hydroxyphenyl) -4,4′-diphthalimide represented by (B3-3) was obtained. Yield 158 g (313 mmol, 92% yield). In this compound, | α | of the hydroxyl group (OH) corresponding to R 1 of the general formula (I) is 42.3 °.
この化合物の分析結果は以下の通りである。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6):δ2.32(6H,s,-CH3),6.75(2H,d,J=7.6Hz,Ar-H),6.82(2H,s,Ar-H),7.15(2H,d,J=7.6Hz,Ar-H),8.08(2H,d,J=7.6Hz,Ar-H),8.38(2H,dd,J=1.6,7.6Hz,Ar-H),8.42(2H,d,J=1.6Hz,Ar-H),9.73(2H,s,-OH)
IR(KBr):3556,3473,1768,1707,1616,1527,1427,1383,1304,1279,1171,1117,891,808,746,559cm-1
MS:m/z504([M+],100%),505([M+]+1,33.9%),506([M+]+2,7.0%)
The analysis results of this compound are as follows.
1 H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ): δ 2.32 (6H, s, —CH 3 ), 6.75 (2H, d, J = 7.6 Hz, Ar—H), 6.82 (2H, s, Ar—H) ), 7.15 (2H, d, J = 7.6Hz, Ar-H), 8.08 (2H, d, J = 7.6Hz, Ar-H), 8.38 (2H, dd, J = 1.6, 7.6Hz, Ar-H) ), 8.42 (2H, d, J = 1.6Hz, Ar-H), 9.73 (2H, s, -OH)
IR (KBr): 3556,3473,1768,1707,1616,1527,1427,1383,1304,1279,1171,1117,891,808,746,559cm -1
MS: m / z 504 ([M + ], 100%), 505 ([M + ] +1, 33.9%), 506 ([M + ] + 2,7.0%)
[比較例8]
3,3’,4,4’−ビフェニルテトラカルボン酸二無水物を4,4’−オキシジフタル酸無水物(製品名)(又は3,3’,4,4’−ジフェニルエーテルテトラカルボン酸二無水物(別名))(東京化成工業(株)製、純度98%)100g(322mmol)とし、4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノールをp−アミノフェノール(製品名)(和光純薬工業(株)製、純度98%)70g(644mmol)とした以外は、実施例1と同様に行って、下記式(B4−1)で表されるN,N’−ビス(4−ヒドロキシフェニル)−4,4’−オキシジフタルイミド(CAS No.95576−73−1)を得た。収量157g(320mmol、収率99%)。
[Comparative Example 8]
3,3 ′, 4,4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride is converted to 4,4′-oxydiphthalic anhydride (product name) (or 3,3 ′, 4,4′-diphenyl ether tetracarboxylic dianhydride. (Alias)) (Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., purity 98%) 100 g (322 mmol), 4-amino-3-methylphenol was p-aminophenol (product name) (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., N, N′-bis (4-hydroxyphenyl) -4,4 ′ represented by the following formula (B4-1), except that the purity is 98 g) and 70 g (644 mmol). -Oxydiphthalimide (CAS No. 95576-73-1) was obtained. Yield 157 g (320 mmol, 99% yield).
[比較例9]
3,3’,4,4’−ビフェニルテトラカルボン酸二無水物を4,4’−オキシジフタル酸無水物(製品名)(又は3,3’,4,4’−ジフェニルエーテルテトラカルボン酸二無水物(別名))(東京化成工業(株)製、純度98%)100g(322mmol)とし、4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノールをm−アミノフェノール(製品名)(和光純薬工業(株)製、純度98.5%)70g(644mmol)とした以外は、実施例1と同様に行って、下記式(B4−2)で表されるN,N’−ビス(3−ヒドロキシフェニル)−4,4’−オキシジフタルイミド(CAS No.50444−30−9)を得た。収量157g(320mmol、収率99%)。
[Comparative Example 9]
3,3 ′, 4,4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride is converted to 4,4′-oxydiphthalic anhydride (product name) (or 3,3 ′, 4,4′-diphenyl ether tetracarboxylic dianhydride. (Alias)) (Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., purity 98%) 100 g (322 mmol), 4-amino-3-methylphenol was m-aminophenol (product name) (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., N, N′-bis (3-hydroxyphenyl) -4 represented by the following formula (B4-2), except that the purity was 98.5% and 70 g (644 mmol). 4'-oxydiphthalimide (CAS No. 50444-30-9) was obtained. Yield 157 g (320 mmol, 99% yield).
[比較例10]
3,3’,4,4’−ビフェニルテトラカルボン酸二無水物を3,3’,4,4’−ジフェニルスルホンテトラカルボン酸二無水物(東京化成工業(株)製、純度96%以上)100g(279mmol)とし、4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノールをp−アミノフェノール(製品名)(和光純薬工業(株)製、純度98%)61g(558mmol)とした以外は、実施例1と同様に行って、下記式(B5−1)で表されるN,N’−ビス(4−ヒドロキシフェニル)−4,4’−スルホニルジフタルイミドを得た。収量149g(276mmol、収率99%)。
[Comparative Example 10]
3,3 ′, 4,4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride is converted to 3,3 ′, 4,4′-diphenylsulfonetetracarboxylic dianhydride (manufactured by Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., purity 96% or more). Example 1 except that 100 g (279 mmol) and 4-amino-3-methylphenol were replaced with 61 g (558 mmol) of p-aminophenol (product name) (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., purity 98%). In the same manner, N, N′-bis (4-hydroxyphenyl) -4,4′-sulfonyldiphthalimide represented by the following formula (B5-1) was obtained. Yield 149 g (276 mmol, 99% yield).
この化合物の分析結果は以下の通りである。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6):δ6.88(4H,dd,J=2.0,6.8Hz,Ar-H),7.20(4H,dd,J=2.0,6.8Hz,Ar-H),8.17(2H,dd,J=0.8,8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.61(2H,dd,J=1.6,8.0Hz,Ar-H),8.63(2H,dd,J=0.8,1.6Hz,Ar-H),9.79(2H,s,-OH)
IR(KBr):3450,1778,1711,1599,1518,1452,1389,1319,1242,1178,1149,1119,1095,1059,837,742,675,638,598,563,526cm-1
MS:m/z540([M+],100%),541([M+]+1,31.3%),542([M+]+2,12.0%),543([M+]+3,2.6%)
The analysis results of this compound are as follows.
1 H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ): δ 6.88 (4H, dd, J = 2.0, 6.8 Hz, Ar—H), 7.20 (4H, dd, J = 2.0, 6.8 Hz, Ar—H), 8.17 (2H, dd, J = 0.8,8.0Hz, Ar-H), 8.61 (2H, dd, J = 1.6,8.0Hz, Ar-H), 8.63 (2H, dd, J = 0.8,1.6Hz, Ar -H), 9.79 (2H, s, -OH)
IR (KBr): 3450,1778,1711,1599,1518,1452,1389,1319,1242,1178,1149,1119,1095,1059,837,742,675,638,598,563,526cm -1
MS: m / z 540 ([M + ], 100%), 541 ([M + ] + 1,31.3%), 542 ([M + ] + 2,12.0%), 543 ([M + ] +3, 2.6%)
[比較例11]
3,3’,4,4’−ビフェニルテトラカルボン酸二無水物を3,3’,4,4’−ジフェニルスルホンテトラカルボン酸二無水物(東京化成工業(株)製、純度96%以上)100g(279mmol)とし、4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノールをm−アミノフェノール(製品名)(和光純薬工業(株)製、純度98.5%)61g(558mmol)とした以外は、実施例1と同様に行って、下記式(B5−2)で表されるN,N’−ビス(3−ヒドロキシフェニル)−4,4’−スルホニルジフタルイミド(CAS No.129209−40−1)を得た。収量149g(276mmol、収率99%)。
[Comparative Example 11]
3,3 ′, 4,4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride is converted to 3,3 ′, 4,4′-diphenylsulfonetetracarboxylic dianhydride (manufactured by Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., purity 96% or more). 100 g (279 mmol) and 4-amino-3-methylphenol was changed to m-aminophenol (product name) (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., purity 98.5%) 61 g (558 mmol). 1 and N, N′-bis (3-hydroxyphenyl) -4,4′-sulfonyldiphthalimide (CAS No. 129209-40-1) represented by the following formula (B5-2) Obtained. Yield 149 g (276 mmol, 99% yield).
[比較例12]
3,3’,4,4’−ビフェニルテトラカルボン酸二無水物を3,3’,4,4’−ベンゾフェノンテトラカルボン酸二無水物(和光純薬工業(株)製、純度96%以上)100g(310mmol)とし、4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノールをp−アミノフェノール(製品名)(和光純薬工業(株)製、純度98%)68g(620mol)とした以外は、実施例1と同様に行って、下記式(B6−1)で表されるN,N’−ビス(4−ヒドロキシフェニル)−4,4’−オキソメチレンジフタルイミド(CAS No.53417−18−8)を得た。収量155g(307mmol、収率99%)。
[Comparative Example 12]
3,3 ′, 4,4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride becomes 3,3 ′, 4,4′-benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., purity 96% or more) Example 1 except that 100 g (310 mmol) and 4-amino-3-methylphenol were changed to p-aminophenol (product name) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., purity 98%) 68 g (620 mol). In the same manner, N, N′-bis (4-hydroxyphenyl) -4,4′-oxomethylenediphthalimide (CAS No. 53417-18-8) represented by the following formula (B6-1) is obtained. It was. Yield 155 g (307 mmol, 99% yield).
[比較例13]
3,3’,4,4’−ビフェニルテトラカルボン酸二無水物を3,3’,4,4’−ベンゾフェノンテトラカルボン酸二無水物(和光純薬工業(株)製、純度96%以上)100g(310mmol)とし、4−アミノ−3−メチルフェノールをm−アミノフェノール(和光純薬工業(株)製、純度98.5%)68g(620mol)とした以外は、実施例1と同様に行って、下記式(B6−2)で表されるN,N’−ビス(3−ヒドロキシフェニル)−4,4’−オキソメチレンジフタルイミド(CAS No.54942−20−0)を得た。収量150g(298mmol、収率96%)。
[Comparative Example 13]
3,3 ′, 4,4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride becomes 3,3 ′, 4,4′-benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., purity 96% or more) 100 g (310 mmol), and 4-amino-3-methylphenol was m-aminophenol (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., purity 98.5%) 68 g (620 mol). And N, N′-bis (3-hydroxyphenyl) -4,4′-oxomethylenediphthalimide (CAS No. 54492-20-0) represented by the following formula (B6-2) was obtained. Yield 150 g (298 mmol, 96% yield).
[溶解性の比較]
溶剤としてシクロヘキサノン(和光純薬工業(株)製、グレードS、純度99%以上)を用い、60℃に加熱した状態での溶解度を、前述の溶解度の測定方法に従って、目視で測定した。結果を表5、表6に示した。
[Solubility comparison]
Using cyclohexanone (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., grade S, purity 99% or more) as a solvent, the solubility in a state heated to 60 ° C. was measured visually according to the above-described solubility measurement method. The results are shown in Tables 5 and 6.
以上の結果から次のことが分かる。
表5は、原料となる芳香族カルボン酸二無水物が3,3’,4,4’−ビフェニルテトラカルボン酸二無水物であるものをまとめたものである。なお、表5,6中、「メチル基の位置」と、「OH基の位置」とは、それぞれフェノール部分のベンゼン環上の位置を表し、イミド基のNに対しての位置である。
The following can be understood from the above results.
Table 5 summarizes the raw material aromatic carboxylic dianhydrides that are 3,3 ′, 4,4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydrides. In Tables 5 and 6, “position of methyl group” and “position of OH group” represent positions on the benzene ring of the phenol moiety, respectively, and are positions relative to N of the imide group.
実施例の化合物A1−1、A1−2、A2、A3はいずれも一方のオルト位の一方にメチル基を有し、1重量%以上の溶解度を示した。特に、化合物A1−1、A3はそれぞれ5重量%、10重量%と、構造が剛直なビスイミドフェノールとしては非常に高い溶解性を有していることが分かる。 The compounds A1-1, A1-2, A2, and A3 in the examples all had a methyl group at one of the ortho positions and exhibited a solubility of 1% by weight or more. In particular, the compounds A1-1 and A3 are 5% by weight and 10% by weight, respectively, and it is understood that the bisimide phenol having a rigid structure has very high solubility.
一方で、両オルト位にメチル基を有するB1−2はわずかに0.5重量%しか溶解せず、化合物A1−1と比較して非常に溶解性が悪い。また、化合物A1−2と比較すると、同様にメチル基を2つ有するにも関わらず、対称性の高い化合物B1−2は溶解性が悪かった。更に、オルト位以外にメチル基を有する化合物B2−2、B3−2、B3−3、メチル基を持たない化合物B1−1、B2−1、B3−1はいずれも溶解度0.5重量%未満であった。 On the other hand, B1-2 having a methyl group at both ortho positions dissolves only 0.5% by weight, which is very poor in solubility as compared with compound A1-1. Moreover, compared with compound A1-2, although it had two methyl groups similarly, compound B1-2 with high symmetry was bad in solubility. Further, compounds B2-2, B3-2 and B3-3 having a methyl group other than the ortho position, and compounds B1-1, B2-1 and B3-1 having no methyl group are all less than 0.5% by weight. Met.
表6はその他の芳香族カルボン酸二無水物を用いたものをまとめたものであるが、この場合も同様に、一方のオルト位のみにメチル基を有する化合物A4、A5、A6はいずれも対応する無置換ビスイミドフェノールよりも高い溶解度を示した。 Table 6 summarizes the results using other aromatic carboxylic dianhydrides, but in this case as well, all of compounds A4, A5, and A6 having a methyl group only at one ortho position correspond. It showed higher solubility than the unsubstituted bisimidephenol.
Claims (3)
R2、R3及びR4は、各々独立に、水素原子、水酸基又は炭素数1〜10の有機基を示すが、隣接する2つの基が結合してベンゼン環に縮合する炭素数20以下の環を形成してもよい。
R6は、炭素数1〜10の有機基を示すが、隣接する2つの基が結合してベンゼン環に縮合する炭素数20以下の環を形成してもよい。
Xは、単結合、置換されていてもよい炭素数1〜20の二価の有機基、−O−又は−SO2−を示す。
nは0〜3の整数である。
複数のR1〜R6は、互いに同一であってもよく、異なっていてもよい。ただし、R1〜R6はハロゲン原子であることはなく、また、各R2〜R5のうちのいずれか一つは水酸基であることにより、化合物中には2個の水酸基を有する。)
{|α|の定義}
|α|とは、下記式(I−1)に示す構造において、理論計算に基づいた最安定構造を算出した際、2つの共役平面の成す二面角αの絶対値である。
ここで、二面角の理論計算は、OSとして「Microsoft社製Windows XP Professional Version 2002 Service Pack2」、ソフトに「Gaussian社製Gaussian03 x86-Win32版Rev.B.05」を用いて、AM1法(オプションとして「opt=verytight」を指定)により、最安定構造を計算して行われる。
αとしては、隣接する4つの原子、C(イミドのカルボニル炭素)−N(イミドの窒素)−C(芳香環)−C(芳香環)の成す以下の(1)〜(4)の4種の二面角の内、絶対値が最小のものとする。なお、C1〜C5は下記式(I−Ia)に示される。
(1) C1−C2−N−C4
(2) C1−C2−N−C5
(3) C3−C2−N−C4
(4) C3−C2−N−C5
R 2 , R 3, and R 4 each independently represent a hydrogen atom, a hydroxyl group, or an organic group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms. A ring may be formed.
R 6 represents an organic group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms, but two adjacent groups may be bonded to form a ring having 20 or less carbon atoms condensed with a benzene ring.
X represents a single bond, an optionally substituted divalent organic group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, —O— or —SO 2 —.
n is an integer of 0-3.
The plurality of R 1 to R 6 may be the same as or different from each other. However, R 1 to R 6 are not halogen atoms, and any one of R 2 to R 5 is a hydroxyl group, so that the compound has two hydroxyl groups. )
{Definition of ||
| Α | is the absolute value of the dihedral angle α formed by two conjugate planes when the most stable structure based on theoretical calculation is calculated in the structure represented by the following formula (I-1).
Here, the theoretical calculation of the dihedral angle is performed using the AM1 method using “Microsoft Windows XP Professional Version 2002 Service Pack 2” as the OS and “Gaussian 03 x86-Win32 version Rev.B.05” as the software. This is done by calculating the most stable structure by specifying “opt = verytight” as an option).
α is the following four types (1) to (4) consisting of four adjacent atoms, C (carbonyl carbon of imide) -N (imide nitrogen) -C (aromatic ring) -C (aromatic ring) Of the dihedral angles, the absolute value is the smallest. C 1 to C 5 are represented by the following formula (I-Ia).
(1) C 1 -C 2 -N -C 4
(2) C 1 -C 2 -N-C 5
(3) C 3 -C 2 -N -C 4
(4) C 3 -C 2 -N -C 5
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008219495A JP5304105B2 (en) | 2008-08-28 | 2008-08-28 | Bisimide phenol compound and method for producing the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008219495A JP5304105B2 (en) | 2008-08-28 | 2008-08-28 | Bisimide phenol compound and method for producing the same |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010053070A true JP2010053070A (en) | 2010-03-11 |
| JP5304105B2 JP5304105B2 (en) | 2013-10-02 |
Family
ID=42069361
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008219495A Active JP5304105B2 (en) | 2008-08-28 | 2008-08-28 | Bisimide phenol compound and method for producing the same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5304105B2 (en) |
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010053071A (en) * | 2008-08-28 | 2010-03-11 | Japan Epoxy Resin Kk | Bisimide phenol compound, method for producing the same, and polymer compound |
| JP2011074029A (en) * | 2009-09-30 | 2011-04-14 | Mitsubishi Chemicals Corp | Bisimide alcohol compound, process for producing the same and polymer compound obtained by polymerizing the same |
| JP2011173827A (en) * | 2010-02-24 | 2011-09-08 | Mitsubishi Chemicals Corp | Bisimide phenol derivative and method for producing the same, and polymer compound |
| WO2011111847A1 (en) * | 2010-03-08 | 2011-09-15 | 味の素株式会社 | Resin composition |
| JP2011208126A (en) * | 2010-03-08 | 2011-10-20 | Mitsubishi Chemicals Corp | Curing agent for epoxy resin, curing resin composition, and cured material of the same |
| WO2016101538A1 (en) * | 2014-12-26 | 2016-06-30 | 广东生益科技股份有限公司 | Epoxy resin composition, prepreg and laminate using same |
| US9873789B2 (en) | 2014-12-26 | 2018-01-23 | Shengyi Technology Co., Ltd. | Halogen-free epoxy resin composition, prepreg and laminate using same |
| WO2018193983A1 (en) * | 2017-04-21 | 2018-10-25 | 積水化学工業株式会社 | Imide oligomer, curing agent, adhesive and method for producing imide oligomer |
| US10544255B2 (en) | 2015-12-28 | 2020-01-28 | Shengyi Technology Co., Ltd. | Epoxy resin composition, prepreg and laminate prepared therefrom |
| US10696844B2 (en) | 2014-02-25 | 2020-06-30 | Shengyi Technology Co., Ltd. | Halogen-free flame retardant type resin composition |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH03209858A (en) * | 1990-01-12 | 1991-09-12 | Nitto Denko Corp | Semiconductor device |
| JPH05257273A (en) * | 1992-03-11 | 1993-10-08 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | Positive type photoresist composition |
| JP2001253870A (en) * | 2000-03-13 | 2001-09-18 | Manac Inc | Method for producing imide compound and its new derivative |
| JP2002533324A (en) * | 1998-12-21 | 2002-10-08 | ゼネラル・エレクトリック・カンパニイ | Synthesis of phenolic monomer containing imide or diimide moiety and production of heat-resistant carbonate polymer |
| JP2006213827A (en) * | 2005-02-04 | 2006-08-17 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | Polyarylate imide, optical film, and image display device |
| JP2010053071A (en) * | 2008-08-28 | 2010-03-11 | Japan Epoxy Resin Kk | Bisimide phenol compound, method for producing the same, and polymer compound |
-
2008
- 2008-08-28 JP JP2008219495A patent/JP5304105B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH03209858A (en) * | 1990-01-12 | 1991-09-12 | Nitto Denko Corp | Semiconductor device |
| JPH05257273A (en) * | 1992-03-11 | 1993-10-08 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | Positive type photoresist composition |
| JP2002533324A (en) * | 1998-12-21 | 2002-10-08 | ゼネラル・エレクトリック・カンパニイ | Synthesis of phenolic monomer containing imide or diimide moiety and production of heat-resistant carbonate polymer |
| JP2001253870A (en) * | 2000-03-13 | 2001-09-18 | Manac Inc | Method for producing imide compound and its new derivative |
| JP2006213827A (en) * | 2005-02-04 | 2006-08-17 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | Polyarylate imide, optical film, and image display device |
| JP2010053071A (en) * | 2008-08-28 | 2010-03-11 | Japan Epoxy Resin Kk | Bisimide phenol compound, method for producing the same, and polymer compound |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| JPN7013000877; DATABASE CHEMCATS ON STN, ACCESSION NO : 2081330636, 1H-Isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione, 5,5'-oxybis[2-(4-hy * |
| JPN7013000878; DATABASE CHEMCATS ON STN, ACCESSION NO : 0090585732, 1 JAN. 2013, AMB3371580, 1H-Isoindole-1,3(2H)-d * |
Cited By (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010053071A (en) * | 2008-08-28 | 2010-03-11 | Japan Epoxy Resin Kk | Bisimide phenol compound, method for producing the same, and polymer compound |
| JP2011074029A (en) * | 2009-09-30 | 2011-04-14 | Mitsubishi Chemicals Corp | Bisimide alcohol compound, process for producing the same and polymer compound obtained by polymerizing the same |
| JP2011173827A (en) * | 2010-02-24 | 2011-09-08 | Mitsubishi Chemicals Corp | Bisimide phenol derivative and method for producing the same, and polymer compound |
| WO2011111847A1 (en) * | 2010-03-08 | 2011-09-15 | 味の素株式会社 | Resin composition |
| JP2011208126A (en) * | 2010-03-08 | 2011-10-20 | Mitsubishi Chemicals Corp | Curing agent for epoxy resin, curing resin composition, and cured material of the same |
| US10696844B2 (en) | 2014-02-25 | 2020-06-30 | Shengyi Technology Co., Ltd. | Halogen-free flame retardant type resin composition |
| US9873789B2 (en) | 2014-12-26 | 2018-01-23 | Shengyi Technology Co., Ltd. | Halogen-free epoxy resin composition, prepreg and laminate using same |
| US10208156B2 (en) | 2014-12-26 | 2019-02-19 | Shengyi Technology Co., Ltd. | Epoxy resin composition, prepreg and laminate using same |
| WO2016101538A1 (en) * | 2014-12-26 | 2016-06-30 | 广东生益科技股份有限公司 | Epoxy resin composition, prepreg and laminate using same |
| US10544255B2 (en) | 2015-12-28 | 2020-01-28 | Shengyi Technology Co., Ltd. | Epoxy resin composition, prepreg and laminate prepared therefrom |
| WO2018193983A1 (en) * | 2017-04-21 | 2018-10-25 | 積水化学工業株式会社 | Imide oligomer, curing agent, adhesive and method for producing imide oligomer |
| CN110461818A (en) * | 2017-04-21 | 2019-11-15 | 积水化学工业株式会社 | The manufacturing method of acid imide oligomer, curing agent, bonding agent and acid imide oligomer |
| CN110461818B (en) * | 2017-04-21 | 2023-11-14 | 积水化学工业株式会社 | Imide oligomer, curing agent, adhesive, and method for producing imide oligomer |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5304105B2 (en) | 2013-10-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5304105B2 (en) | Bisimide phenol compound and method for producing the same | |
| JP5304106B2 (en) | Bisimide phenol compound and method for producing the same | |
| CN106279689B (en) | Material used in polyimide precursor, polyimides and its preparation | |
| Hsiao et al. | Synthesis and characterization of novel fluorinated polyimides derived from 1, 3-bis (4-amino-2-trifluoromethylphenoxy) naphthalene and aromatic dianhydrides | |
| JP6635506B2 (en) | Diamine having fluorene skeleton, polyamic acid, and polyimide | |
| EP2558434B1 (en) | Novel cross-linker | |
| TWI284650B (en) | Novel polyimide compositions and novel acid dianhydrides to be used therein | |
| JP5047896B2 (en) | Novel bistrimellitic anhydride esters and polyesterimide precursors obtained from it and diamines | |
| JP6304494B2 (en) | Polyimide and heat-resistant material | |
| US8962890B1 (en) | Multifunctional crosslinkers for shape-memory polyimides, polyamides and poly(amide-imides) and methods of making the same | |
| JP2011173827A (en) | Bisimide phenol derivative and method for producing the same, and polymer compound | |
| WO2017189293A1 (en) | Method for isolation of a dianhydride and dianhydrides prepared by the method | |
| CN105348512B (en) | A kind of polyarylether material containing acid imide side base and preparation method thereof | |
| Qiu et al. | Synthesis and gas transport property of polyimide from 2, 2′-disubstituted biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydrides (BPDA) | |
| JP2003313180A (en) | Acid anhydride, liquid crystal-orienting film and liquid crystal-displaying element | |
| US20240239741A1 (en) | Meta-ester aromatic diamines, method for producing same, and polyimide having said meta-ester aromatic diamines as raw material | |
| JP2016210735A (en) | Asymmetric diamine having fluorene skeleton, polyamic acid, and polyimide | |
| JP6268959B2 (en) | Fluorine-containing polymerizable monomer and polymer compound using the same | |
| Ghaemy et al. | Organosoluble and thermally stable polyimides derived from a new diamine containing bulky-flexible triaryl pyridine pendent group | |
| JP2006206879A (en) | Fluorodiamine and polymer obtained using the same | |
| Hsiao et al. | Synthesis and properties of poly (ether imide) s derived from 2, 5‐bis (3, 4‐dicarboxyphenoxy) biphenyl dianhydride and aromatic ether–diamines | |
| JP5903788B2 (en) | Method for purifying 2,2 ', 3,3'-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride powder, powder, and polyimide using the same | |
| TW201105711A (en) | Liquid crystal polyimide, liquid crystal resin composite containing same, and resin film for semiconductor elements | |
| WO2020158523A1 (en) | Novel diamine, novel polyimide derived therefrom, and molded body thereof | |
| JP4698165B2 (en) | Polyamic acid and polyimide |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A712 Effective date: 20100427 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20110419 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20130305 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130312 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130508 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130528 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130610 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Ref document number: 5304105 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313111 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |