JP2010034875A - Image quality management system, method and program - Google Patents
Image quality management system, method and program Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2010034875A JP2010034875A JP2008195248A JP2008195248A JP2010034875A JP 2010034875 A JP2010034875 A JP 2010034875A JP 2008195248 A JP2008195248 A JP 2008195248A JP 2008195248 A JP2008195248 A JP 2008195248A JP 2010034875 A JP2010034875 A JP 2010034875A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- image
- image quality
- packet
- frame
- management system
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000003326 Quality management system Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 28
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 19
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 50
- 238000007726 management method Methods 0.000 claims description 36
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 32
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 abstract description 8
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 abstract description 8
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 15
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 7
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000013507 mapping Methods 0.000 description 2
- 101000969688 Homo sapiens Macrophage-expressed gene 1 protein Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100021285 Macrophage-expressed gene 1 protein Human genes 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Testing, Inspecting, Measuring Of Stereoscopic Televisions And Televisions (AREA)
- Time-Division Multiplex Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、画像品質管理システム、方法及びプログラムに関し、例えば、パケット損失による映像フレームの影響を管理する画像品質管理システム、方法及びプログラムに適用し得るものである。 The present invention relates to an image quality management system, method, and program, and can be applied to, for example, an image quality management system, method, and program for managing the influence of video frames due to packet loss.
例えば、音声、静止画、動画像などのメディア情報を通信や放送する場合に、その情報量が多いため、例えばMPEG方式などの圧縮符号化が行われるが、メディア情報の品質を維持するために、そのサービス品質を測定することが必要となる。 For example, when communicating or broadcasting media information such as audio, still images, and moving images, the amount of information is large, so compression encoding such as the MPEG method is performed. However, in order to maintain the quality of media information It is necessary to measure its service quality.
特許文献1は、ネットワーク通信や放送するメディア情報の通信品質を測定する技術が記載されている。具体的には、メディア用パケットで送受信した各フレームのうち、メディア用パケットの損失による影響を受けた無効フレームの割合に基づいて無効フレーム率を求め、この無効フレーム率をユーザが体感するサービス品質の推定値とみなす技術である。
ところで、ユーザが体感する主観的な映像品質に影響を与える要素として「ブロックノイズ」がある。このブロックノイズとは、映像フレームの一部のブロックがモザイク状態となり、映像の欠落を引き起こす現象をいい、通信又は放送されるパケットの損失が原因であると考えられる。 Incidentally, “block noise” is an element that affects the subjective video quality experienced by the user. This block noise refers to a phenomenon in which a part of a block of a video frame is in a mosaic state and causes a loss of video, and is considered to be caused by a loss of a communication or broadcast packet.
フレーム内でのTSパケット損失をエンコード側での負荷軽減を目的としてしまうと、以下のような点から実際のフレームの劣化状況を特定することが困難であり、またユーザが体感する映像品質も異なってしまうおそれもある。 If the loss of TS packets in a frame is intended to reduce the load on the encoding side, it is difficult to specify the actual frame degradation status from the following points, and the video quality experienced by the user is also different. There is also a risk.
(1)コーデックによって各フレームに対して重み付けを行なっているが、その映像フレームをパケット化する際のTSパケットの損失状況を考慮していないため、フレーム内に生じる「ブロックノイズ」そのものを検知できていない。 (1) Although each frame is weighted by the codec, the loss situation of TS packets when packetizing the video frame is not taken into account, so the “block noise” generated in the frame itself can be detected. Not.
(2)また、そのTSパケットの損失によって、ユーザに与える体感品質の影響度まで考慮していないため、実際に体感する品質との間に差異が生じる。 (2) Moreover, since the influence of the quality of experience given to the user is not considered due to the loss of the TS packet, there is a difference between the quality actually experienced.
(3)コーデックの特性上、各フレームそのものは損失していないが、各フレーム内のブロック(TSパケット)が損失するといった現象を考慮していない。 (3) Due to the characteristics of the codec, each frame itself is not lost, but the phenomenon that a block (TS packet) in each frame is lost is not considered.
そのため、実際のフレーム自体の劣化状況に応じた映像品質を求めることができる画像品質管理システム、方法及びプログラムが求められている。 Therefore, there is a need for an image quality management system, method, and program that can determine the video quality according to the actual degradation state of the frame itself.
かかる課題を解決するために、第1の本発明の画像品質管理システムは、クライアント端末に配信される画像品質を管理する画像品質管理システムにおいて、(1)クライアント端末に配信される画像データを有するパケットを受信する受信手段と、(2)受信パケットに基づいて画像の構成を示す画像構成情報を取得する画像構成情報取得手段と、(3)画像構成情報に基づく構成順にしたフレームと、シーケンス番号に基づいて時系列に並べたパケットとを対応させ、各フレームとパケットとを関連付けて画像品質を測定する画像品質測定手段と、(4)画像品質測定手段により測定された画像品質測定結果を蓄積する蓄積手段とを備えることを特徴とする。 In order to solve this problem, an image quality management system according to a first aspect of the present invention is an image quality management system for managing image quality distributed to a client terminal. (1) It has image data distributed to a client terminal. Receiving means for receiving a packet; (2) image configuration information acquiring means for acquiring image configuration information indicating an image configuration based on the received packet; (3) frames arranged in order of configuration based on the image configuration information; and a sequence number And (4) storing the image quality measurement results measured by the image quality measuring means, by associating the packets arranged in time series based on the above and associating each frame with the packet to measure the image quality. And an accumulating means.
第2の本発明の画像品質管理方法は、クライアント端末に配信される画像品質を管理する画像品質管理システムでの画像品質管理方法において、画像品質管理システムが、受信手段、画像構成情報取得手段、画像品質測定手段及び蓄積手段を備え、(1)受信手段が、クライアント端末に配信される画像データを有するパケットを受信する受信工程と、(2)画像構成情報取得手段が、受信パケットに基づいて画像の構成を示す画像構成情報を取得する画像構成情報取得工程と、(3)画像品質測定手段が、画像構成情報に基づく構成順にしたフレームと、シーケンス番号に基づいて時系列に並べたパケットとを対応させ、各フレームとパケットとを関連付けて画像品質を測定する画像品質測定工程と、(4)蓄積手段が、画像品質測定手段により測定された画像品質測定結果を蓄積する蓄積工程とを有することを特徴とする。 An image quality management method according to a second aspect of the present invention is an image quality management method in an image quality management system for managing image quality delivered to a client terminal. The image quality management system includes a receiving unit, an image configuration information acquiring unit, An image quality measuring unit and a storage unit, wherein (1) the receiving unit receives a packet having image data distributed to the client terminal; and (2) the image configuration information acquiring unit is based on the received packet. An image configuration information acquisition step for acquiring image configuration information indicating the configuration of the image, (3) frames arranged in the order of configuration based on the image configuration information by the image quality measurement means, and packets arranged in time series based on the sequence numbers An image quality measuring step for measuring the image quality by associating each frame with the packet, and (4) the storage means is the image quality measuring means And having a storage step of storing a more measured image quality measurement results.
第3の本発明の画像品質管理プログラムは、クライアント端末に配信される画像品質を管理する画像品質管理システムでの画像品質管理プログラムにおいて、コンピュータを、(1)クライアント端末に配信される画像データを有するパケットを受信する受信手段、(2)受信パケットに基づいて画像の構成を示す画像構成情報を取得する画像構成情報取得手段、(3)画像構成情報に基づく構成順にしたフレームと、シーケンス番号に基づいて時系列に並べたパケットとを対応させ、各フレームとパケットとの関連付けて画像品質を測定する画像品質測定手段、(4)画像品質測定手段により測定された画像品質測定結果を蓄積する蓄積手段として機能させることを特徴とする。 An image quality management program according to a third aspect of the present invention is an image quality management program in an image quality management system for managing image quality distributed to a client terminal. (1) Image data distributed to a client terminal Receiving means for receiving packets, (2) image configuration information acquiring means for acquiring image configuration information indicating the configuration of an image based on the received packet, (3) frames arranged in the order of configuration based on the image configuration information, and a sequence number And an image quality measuring means for measuring the image quality in association with each frame and the packet, and (4) an accumulation for storing the image quality measurement results measured by the image quality measuring means. It is made to function as a means.
本発明によれば、実際のフレーム自体の劣化状況に応じた映像品質を求めることができる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to obtain the video quality corresponding to the actual degradation state of the frame itself.
(A)第1の実施形態
以下では、本発明の画像品質管理システム、方法及びプログラムの第1の実施形態について図面を参照しながら説明する。
(A) First Embodiment Hereinafter, a first embodiment of an image quality management system, method, and program according to the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
第1の実施形態は、マルチキャストにより、配信サーバが提供する配信映像をクライアント端末に配信する映像配信システムに、本発明の画像品質管理システム、方法及びプログラムを適用する実施形態を例示して説明する。 The first embodiment will be described by exemplifying an embodiment in which the image quality management system, method, and program of the present invention are applied to a video distribution system that distributes distribution video provided by a distribution server to client terminals by multicast. .
(A−1)第1の実施形態の構成
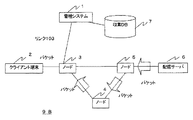
図1は、第1の実施形態のメディア情報品質管理システムの構成を示す構成図である。図1に示すように、第1の実施形態のメディア情報品質管理システム9Aは、管理システム1、クライアント端末2、ノード3〜5、配信サーバ6、収集DB7を少なくとも有して構成される。
(A-1) Configuration of the First Embodiment FIG. 1 is a configuration diagram showing the configuration of the media information quality management system of the first embodiment. As shown in FIG. 1, the media information quality management system 9A according to the first embodiment is configured to include at least a
図1において例示する映像配信システムは、配信サーバ6が、ノード5、4及び3を介して、クライアント端末2に向けて配信映像を配信するシステムである。
The video distribution system illustrated in FIG. 1 is a system in which the
この映像配信システムの配信形態としては、種々の形態を広く採用することができるが、例えば、有線回線を用いて配信する形態や、無線回線を用いて配信する形態や、有線回線と無線回線を結合させた形態や、放送により配信する形態などを適用することができる。 Various forms can be widely adopted as the distribution form of this video distribution system. For example, a form using a wired line, a form using a wireless line, a wired line and a wireless line can be used. A combined form or a form distributed by broadcasting can be applied.
また、この映像配信システムは、マルチキャストを用いて映像を配信しているため、図1では1台のクライアント端末2のみを示しているが、そのマルチキャストに参加するクライアント端末2が複数ある場合には、複数のクライアント端末2に対して映像を配信する。
Also, since this video distribution system distributes video using multicast, only one
配信サーバ6は、1又は複数種類の映像を配信する画像送信装置である。配信サーバ6は、既存の配信サーバを用いることができるので、その構成の詳細な説明は省略するが、例えば、映像ストリームデータに対して圧縮符号化処理を行なう圧縮符号化処理部(エンコーダ部)、圧縮符号化データを有するTS(Transport Stream)パケットを変調する変調部、変調したパケットを送信する送信部を少なくとも有するものである。
The
また、配信サーバ6が配信映像を符号化する圧縮符号化方式は、特に限定されず広く適用することができるが、一般にMPEG方式(MPEG1、MPEG2、MPEG4、MPEG7など)を採用する。
In addition, the compression encoding method by which the
配信サーバ6のエンコーダ部は、配信すべき入力画像データを受け取ると、GOP(Group Of Picture)構成の設定情報に従って、その画像データをMPEG符号化してES(Elementary Stream)を生成し、生成したESをパケット化してPES(Packetized Elementary Stream)パケットにする。そして、エンコーダ部は、このPESパケットを分割して、固定長のTSパケットのペイロードに挿入してTSパケットを生成して変調部に与える。
When receiving the input image data to be distributed, the encoder unit of the
ここで、GOP(Group Of Picture)構成とは、複数の画像(フレーム)を有して構成する1グループをいう。例えば、画像の種類には、Iフレーム(Intra Frame)、Pフレーム(Predictive Frame)、Bフレーム(Bi-Directional Frame)があるが、これらIフレーム、Pフレーム、Bフレームの組み合わせをGOP構成という。 Here, the GOP (Group Of Picture) configuration refers to one group configured with a plurality of images (frames). For example, image types include an I frame (Intra Frame), a P frame (Predictive Frame), and a B frame (Bi-Directional Frame). A combination of these I frame, P frame, and B frame is called a GOP configuration.
例えば、GOPの構成態様としては、(1)Iフレーム、Pフレーム、Bフレームのそれぞれを有するIPB構成、(2)IフレームとPフレームとを有するIP構成、(3)複数のIフレームを有するI構成がある。 For example, as a configuration mode of the GOP, (1) an IPB configuration having each of an I frame, a P frame, and a B frame, (2) an IP configuration having an I frame and a P frame, and (3) a plurality of I frames There is an I configuration.
また、GOPを構成するフレーム数やフレーム周期は特に制限がないので、提供する画像ストリームの種類やサービス種類に応じてフレーム数やフレーム周期は異なり得る。 In addition, since the number of frames and the frame period constituting the GOP are not particularly limited, the number of frames and the frame period may differ depending on the type of image stream to be provided and the type of service.
ノード3〜5は、配信サーバ6とクライアント端末2との間に介在する転送装置であり、配信サーバ6からの映像パケットをクライアント端末2に転送するものである。
The
クライアント端末2は、配信サーバ6からの配信映像を受信する画像受信装置を有するものであり、受信映像を出力するユーザ端末である。
The
また、クライアント端末2は、受信した映像パケットを管理システム1に送信するものである。このようにクライアント端末2が受信パケットを管理システム1に送信することにより、管理システム1による映像品質を測定管理させることができる。
The
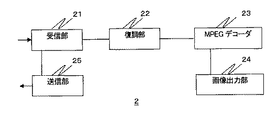
図2は、クライアント端末2の内部構成を示す内部構成図である。図2に示すように、クライアント端末2は、受信部21、復調部22、MPEGデコーダ23、画像出力部24、送信部25を少なくとも有するものである。
FIG. 2 is an internal configuration diagram showing an internal configuration of the
受信部21は、配信された映像信号を受信し、受信信号を復調部22に与えるものである。また、受信部21は、受信した映像信号を送信部25に与えるものである。これにより、管理システム1に対して、受信した配信映像のパケットを与えることができる。
The
復調部22は、受信部21が受信した受信信号を復調し、MPEGデコーダ23に与えるものである。つまり、受信した映像信号からTSパケットを復調するものである。
The
送信部25は、受信部21から受け取った映像信号を管理システム1に与えるものである。ここで、送信部25には、予め管理システム1の送信先情報(例えば、IPアドレス等)が設定されており、受信した映像信号に送信先情報を付与して送信することで、管理システム1に与えることができる。
The
MPEGデコーダ23は、復調部22により復調されたTSパケットからPESパケットを分離し、PESパケットからESパケットを復号して画像データを生成するものである。
The
画像出力部24は、MPEGデコーダ23により復元された画像データに基づいて画像を出力するものである。
The
管理システム1は、クライアント端末2から受信した映像パケットに基づいて、配信映像の品質を測定して、その測定結果を収集DB7に蓄積して管理するものである。
The
ここで、管理システム1は、GOP構成を認識した後、各フレームにシーケンス番号を割り当て、各フレームのシーケンス番号とIPパケットのシーケンス番号とを対応付けてGOP構成テーブルを作成し、各フレームとTSパケット損失との対応関係を明確にする。
Here, after recognizing the GOP configuration, the
これにより、実際のフレーム画像の劣化とTSパケット損失との関係に基づいてフレーム毎の映像品質を測定することができる。 Thereby, the video quality for each frame can be measured based on the relationship between actual frame image degradation and TS packet loss.
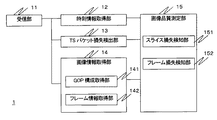
図3は、管理システム1の内部構成を示す機能ブロック図である。図3に示すように、管理システム1は、受信部11、時刻情報取得部12、TSパケット損失検出部13、画像情報取得部14、画像品質測定部15を少なくとも有するものである。
FIG. 3 is a functional block diagram showing the internal configuration of the
受信部11は、映像パケットを受信するものであり、クライアント端末2が受信した映像パケットを受信するものである。
The receiving
ここで、映像パケットは、RTPパケットである。図4は、映像信号のパケット構成を示すパケット構成図であり、映像パケットは、IPヘッダ、UDPヘッダ、RTPヘッダを有し、RTPパケットのペイロードに複数のTSパケットが含まれている。また、TSパケットは、GOP構成の順に従って、各フレームのヘッダ情報及び映像データが含まれている。 Here, the video packet is an RTP packet. FIG. 4 is a packet configuration diagram showing a packet configuration of a video signal. The video packet has an IP header, a UDP header, and an RTP header, and a plurality of TS packets are included in the payload of the RTP packet. The TS packet includes header information and video data of each frame in the order of the GOP configuration.
時刻情報取得部12は、受信パケットのIPヘッダに基づいてIPパケットの時刻情報を取得するものである。また、時刻情報取得部12は、受信したIPパケットのシーケンス番号を時刻情報に対応付けするものである。これにより、受信したIPパケットを時系列で管理するものである。
The time
TSパケット損失検出部13は、受信パケットのRTPパケットペイロードに含まれている各TSパケットのTSヘッダに基づいて、TSパケットのロス又はエラーを検出し、パケット損失数をカウントするものである。
The TS packet
TSパケット損失数のカウント方法としては、TSパケット損失検出部13は、TSヘッダに含まれているヘッダ情報に基づいてTSパケットの損失を検出し、その損失数をカウントする方法を適用できる。
As a method for counting the number of TS packet losses, the TS packet
例えば、図5及び図6は、ETSI(European Telecommunications Standards Institute)の測定ガイドラインTR 101 290を示す。TSパケット損失検出部13は、図5及び図6に示す測定パラメータを測定し、図5及び図6に示す「内容」に設定される条件に従って、TSパケットの損失をカウントする。
For example, FIGS. 5 and 6 show a measurement guideline TR 101 290 of ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute). The TS packet
画像情報取得部14は、受信パケットのRTPパケットペイロードに含まれている各TSパケットのTSペイロードをデコードして、GOP構成や各フレーム情報を取得するものである。
The image
画像情報取得部14は、図3に示すように、各TSペイロードに含まれている各ESに付与されているGOP毎のシーケンス番号に基づいて、GOP構成のパターンを取得するGOP構成取得部141と、各フレーム情報を取得するフレーム情報取得部142とを有する。
As shown in FIG. 3, the image
画像品質測定部15は、時刻情報取得部12、TSパケット損失検出部13及び画像情報取得部14により得られた各種情報に基づいて、各フレームとIPパケットとを対応付けたGOP構成テーブルを形成するものである。
The image
また、画像品質測定部15は、フレーム内でのGOP構成(Intra Period)内を割り出し、フレーム内でのスライス損失を検知するものである。
The image
画像品質測定部15は、図3に示すように、スライス損失検知部151と、フレーム損失検知部152とを有して構成される。
As shown in FIG. 3, the image
スライス損失検知部151は、I−Slice内におけるGOP(Intra Period)構成パターンを割り出し、そのGOP構成内のSlice数を出し、GOP構成(Intra Period)の長さを求めるものである。
The slice
また、スライス損失検知部151は、GOP構成の長さを測定周期とし、この測定周期内の各Sliceのロス数を求めるものである。
Further, the slice
さらに、スライス損失検知部151は、受信した画像(Picture)数、各Sliceのロス数を用いて、画像(Picture)のロス率を求める。また、スライス損失検知部151は、イントラ内(画面内)の空間圧縮(TSパケット)の損失最大値やその事象が起きた回数を求める。
Further, the slice
図7は、第1の実施形態のスライス損失検知方法を説明する説明図と各GOP構成のスライス損失の測定結果を示す図である。 FIG. 7 is an explanatory diagram for explaining a slice loss detection method according to the first embodiment and a diagram showing a measurement result of slice loss of each GOP configuration.
図7(A)は、I−Slice内のGOP(Intra Period)構成パターンを例示する図である。図7(A)に示すように、スライス損失検知部151は、I−Slice内のIntra Periodを構成するSliceに対するロスを検知する。
FIG. 7A is a diagram illustrating a GOP (Intra Period) configuration pattern in the I-Slice. As shown in FIG. 7A, the slice
ここで、スライス損失検知部151は、各フレーム情報に基づいてSlice種別を認識しており、Slice種別毎のロス数を検知する。
Here, the slice
図7(B)は、スライス損失検知部151が測定した測定結果を示すテーブルである。図7(B)に示すテーブルは、例えば、「Time Stamp」、「Intra Period Pattern」、「Intra Periodの長さ」、「I−Sliceロス数」、「P−Sliceロス数」、「B−Sliceロス数」、「Pictureロス率」、「受信Picture数」を項目にもつ。
FIG. 7B is a table showing measurement results measured by the slice
「Time Stamp」は、受信したIPパケットの時刻情報を管理する項目であり、時刻情報取得部12が取得した時刻情報に基づいて時刻を管理する。
“Time Stamp” is an item for managing time information of the received IP packet, and manages time based on the time information acquired by the time
「Intra Period Pattern」は、GOP(Intra Period)の構成パターンを管理する項目であり、画像情報取得部14から受け取ったGOP(Intra Period)構成を管理する。また、「Intra Periodの長さ」は、GOP(Intra Period)の長さを管理する項目である。
“Intra Period Pattern” is an item for managing the GOP (Intra Period) configuration pattern, and manages the GOP (Intra Period) configuration received from the image
「I−Sliceロス数」、「P−Sliceロス数」及び「B−Sliceロス数」は、測定周期内でカウントしたSliceロス数をSlice種別毎に管理する項目である。 “I-Slice loss number”, “P-Slice loss number”, and “B-Slice loss number” are items for managing the number of Slice losses counted for each slice type within the measurement period.
「受信Picture数」は、受信した画像(Picture)の総数を管理する項目である。 The “number of received pictures” is an item for managing the total number of received images (pictures).
「Pictureロス率」は、画像(Picture)の総数に対するロスした画像(Picture)の比率を管理する項目である。例えば、図7(B)の第1行目の場合、画像(Picture)総数は、282+3+5+4=294であり、総ロス数は、3+5+4=12であるから、(12/294)×100≒4となる。 “Picture loss rate” is an item for managing the ratio of lost images (pictures) to the total number of images (pictures). For example, in the case of the first row in FIG. 7B, the total number of images (Picture) is 282 + 3 + 5 + 4 = 294, and the total number of losses is 3 + 5 + 4 = 12, so (12/294) × 100≈4. Become.
フレーム損失検知部152は、パケット損失が発生した際のTSパケットのロス数及び損失したフレーム種別、並びに、パケット損失フレームのGOP内での位置関係を時系列にてテーブル化するものである。
The frame
また、フレーム損失検知部152は、スライス損失検知部151が検知した各フレームのロス数を各フレームに対応付けるようにする。
In addition, the frame
図8(A)は、GOP構成を例示する図であり、図8(B)は、フレーム損失検知部152が測定するフレーム損失の測定結果を示す図である。
FIG. 8A is a diagram illustrating a GOP configuration, and FIG. 8B is a diagram illustrating a measurement result of frame loss measured by the frame
フレーム損失検知部152は、受信パケットの時刻情報を基準にして、GOP構成、フレーム構成、TSパケット損失の位置関係を管理する。また、フレーム損失検知部152は、受信パケットの時刻情報を基にして所定の測定時間内で測定する。
The frame
フレーム損失検知部152は、測定時間内で受信した各受信パケットの各フレームのGOP構成に基づいて、図8(B)に示すようにテーブル化を行なう。
Based on the GOP configuration of each frame of each received packet received within the measurement time, the frame
このとき、フレーム損失検知部152は、GOPを構成する各フレームに対してシーケンス番号を付与する。また、フレーム損失検知部152は、各フレームのフレーム種別も認識する。
At this time, the frame
また、フレーム損失検知部152は、図8(B)に示すように、受信パケットの時刻情報に基づいて、IPパケットのシーケンス番号と各フレームのシーケンス番号とのマッピングを行なう。
Further, as shown in FIG. 8B, the frame
このように、各フレームとTSパケットとの対応付けを行なうことができるので、フレームの画像劣化とTSパケットの損失との関係を認識させることができる。 Thus, since each frame can be associated with the TS packet, the relationship between the image degradation of the frame and the loss of the TS packet can be recognized.
(A−2)第1の実施形態の動作
次に、第1の実施形態のメディア情報品質管理システム9における処理の動作を説明する。
(A-2) Operation of First Embodiment Next, the operation of processing in the media information
まず、クライアント端末2は、配信サーバ6が提供する映像配信に係るマルチキャストにJoinして配信サーバ6から映像信号を取得する。
First, the
クライアント端末2は、配信サーバ6から映像信号を受信すると、受信した映像信号をデコードして配信映像を出力すると共に、その受信した映像信号を管理システム1に向けて送信する。
When the
管理システム1において、受信部11がクライアント端末2からの映像パケットを受信すると、時刻情報取得部12が、受信パケットのIPヘッダから時刻情報を取得し、当該IPパケットのシーケンス番号と対応付けて管理する。
In the
次に、TSパケット損失検出部13は、受信パケットのRTPパケットペイロードに含まれている各TSパケットのTSヘッダに基づいて、TSパケットの損失の有無を検出し、TSパケットの損失数をカウントする。
Next, the TS
次に、画像情報取得部14は、各TSパケットのペイロードに含まれている各フレーム情報に基づいてGOP構成を認識する。また、画像情報取得部14は、各フレーム情報に基づいてフレームをデコードする。
Next, the image
このとき、画像情報取得部14は、TSペイロードに含まれているタイムスタンプ情報(DTS/PTS)に基づいて、IPパケットに含まれているTSパケット数を管理する。
At this time, the image
画像品質測定部15は、画像情報取得部14によりGOP構成が認識されると、そのGOPの構成パターンと、そのGOP構成の測定範囲内での各Sliceのロス数とを測定する。
When the GOP configuration is recognized by the image
このとき、図7(B)に示すように、画像品質測定部15は、各GOP構成内でのSlice種別毎のロス数や、画像(Picture)の総数に対するPictureロス率を求める。
At this time, as shown in FIG. 7B, the image
このようにして、各GOP(Intra Period)構成におけるSliceロスを測定することができる。 In this way, the slice loss in each GOP (Intra Period) configuration can be measured.
また、画像品質測定部15は、時刻情報取得部12からの時刻情報を用いて、所定の測定期間内に受信した受信パケットに含まれるフレームと、TSパケットの損失との対応関係をテーブル化する。
Further, the image
例えば、図8(B)では、時刻情報(Timestamp)に基づいて測定期間「12:42:00−12:42:10」での画像品質の測定結果である。 For example, FIG. 8B shows the measurement result of the image quality in the measurement period “12: 42: 00-12: 42: 10” based on the time information (Timestamp).
まず、画像品質測定部15は、この測定期間内のフレームに対してシーケンス番号を付与する。また、画像品質測定部15は、各フレームヘッダに基づいてフレーム種別を認識し、各シーケンス番号にフレーム種別を対応付ける。
First, the image
次に、画像品質測定部15は、時刻情報取得部12が管理するIPパケットの時刻情報とシーケンス番号との対応関係を利用して、IPパケットのシーケンス番号と各フレームのシーケンス番号との対応関係をとる。そして、各フレーム毎に求めたTSパケット損失数を図8(B)のテーブルに載せる。
Next, the image
画像品質測定部15は、次の測定期間内でのGOP構成及びフレーム構成とTSパケット損失情報との関連付けを継続的に行い、その測定結果を収集DB7に蓄積する。
The image
(A−3)第1の実施形態の効果
以上のように、第1の実施形態によれば、管理システム1は、各フレームとTSパケット損失情報とを対応付けた情報を収集し、これらの統計情報に基づいて、各フレームにおける画像劣化(ノイズブロック)の度合を精度良く把握することができる。
(A-3) Effect of First Embodiment As described above, according to the first embodiment, the
なお、1UDPパケット内には、最大7TSパケットが格納されているため、フレーム種別及びその時のパケット損失の位置関係が分かれば、どのフレームにおける画像劣化(ブロックノイズ)が生じているのかが分かる。 In addition, since a maximum of 7 TS packets are stored in one UDP packet, if the frame type and the positional relationship of packet loss at that time are known, it is possible to know in which frame image degradation (block noise) has occurred.
(B)第2の実施形態
次に、本発明のメディア情報品質管理システムの第2の実施形態について図面を参照しながら説明する。
(B) Second Embodiment Next, a second embodiment of the media information quality management system of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
(B−1)第2の実施形態の構成及び動作
図9は、第2の実施形態のメディア情報品質管理システムの構成を示す構成図である。図9に示すように、第2の実施形態のメディア情報品質管理システム9Bは、管理システム1、クライアント端末2、ノード3〜5、配信サーバ6、収集DB7を少なくとも有して構成される。
(B-1) Configuration and Operation of Second Embodiment FIG. 9 is a configuration diagram showing the configuration of the media information quality management system of the second embodiment. As shown in FIG. 9, the media information quality management system 9B of the second embodiment is configured to include at least a
第2の実施形態が第1の実施形態と異なる点は、管理システム1がクライアント端末2に配信される映像パケットの取得方法である。
The second embodiment is different from the first embodiment in an acquisition method of a video packet that the
つまり、第1の実施形態では、クライアント端末2が受信した配信パケットを管理システム1に向けて送信するものとした。
That is, in the first embodiment, the distribution packet received by the
これに対して、第2の実施形態は、クライアント端末2に映像パケットを転送するノードが、管理システム1に対してパケットログをアップロードするようにする。
On the other hand, in the second embodiment, a node that transfers a video packet to the
従って、以下では、管理システム1に対してパケットログをアップロードするまでの処理について説明するが、第1の実施形態で既に説明した構成の説明については省略する。
Therefore, in the following, processing until the packet log is uploaded to the
図9において、配信サーバ6は、クライアント端末2に向けて映像パケットを配信する。このとき、配信サーバ6が配信する映像パケットはノード5→ノード4→ノード3→クライアント端末2の経路で配信されるものとする。
In FIG. 9, the
クライアント端末2に映像パケットを転送するノード3は、クライアント端末2に転送するパケットのパケットログを蓄積しており、このパケットログを管理システム1に向けて送信する。
The
ここで、ノード3による管理システム1へのパケットログのアップロードの仕方としては、例えば、映像品質を管理する管理対象のクライアント端末2の識別情報を指定しておき、当該クライアント端末2の識別情報宛の映像パケットのパケット情報を蓄積するように設定しておく。また、ノード3は、クライアント端末2の識別情報宛のパケットログを周期的に管理システム1に送信する。
Here, as a method of uploading the packet log to the
管理システム1は、ノード3からクライアント端末2に転送したパケットログを受け取ると、このノード3からの情報に基づいて、各GOP構成の各フレームとIPパケットとのマッピングを行い、その結果を収集DB7に蓄積するものである。
Upon receiving the packet log transferred from the
管理システム1の内部構成は、第1の実施形態で説明した図3に示す内部構成を適用できるので、図3を参照して管理システム1の処理の動作を説明する。
Since the internal configuration shown in FIG. 3 described in the first embodiment can be applied to the internal configuration of the
つまり、管理システム1では、第1の実施形態と同様に、リンク103にて接続しているノード3からクライアント端末2宛のIPパケットを取得すると、そのIPパケットのIPヘッダに含まれるシーケンス番号及び時刻情報を取得し、IPパケットのシーケンス番号と時刻情報を対応付けて管理する。
That is, in the
次に、IPパケットに含まれているGOP構成を取得すると、図8(B)に示すように、各フレームに対してシーケンス番号を付与して、GOP構成をテーブル化する。 Next, when the GOP configuration included in the IP packet is acquired, as shown in FIG. 8B, a sequence number is assigned to each frame, and the GOP configuration is tabulated.
そして、IPパケットの時刻情報を基準にして、IPパケットのシーケンス番号と各フレームのシーケンス番号との対応付けを行い、GOP構成テーブルのマッピングを行う。 Then, based on the time information of the IP packet, the sequence number of the IP packet is associated with the sequence number of each frame, and the GOP configuration table is mapped.
管理システム1では、上記の第1の実施形態と同様の一連処理を継続的に行い、その結果を収集DB7に蓄積するという処理を繰り返し行なう。
In the
(B−2)第2の実施形態の効果
以上のように、第2の実施形態によれば、第1の実施形態と同様の効果に加えて、中継ノードが保持するクライアント端末宛のパケットログを取得して、映像パケットの品質を管理することにより、クライアント端末の受信パケットだけでなく、未受信パケットにつても各フレームに対するTSパケット(ブロックノイズの元となる)の損失状況を正確に把握すること可能となる。
(B-2) Effects of Second Embodiment As described above, according to the second embodiment, in addition to the same effects as those of the first embodiment, the packet log addressed to the client terminal held by the relay node By managing the quality of video packets, it is possible to accurately grasp the loss status of TS packets (which are the source of block noise) for each frame not only for client terminal received packets but also for unreceived packets. It becomes possible to do.
(C)他の実施形態
第1及び第2の実施形態で説明した管理システムの各種機能は、ソフトウェア処理により実現されるものである。つまり、例えば、CPU、ROM、RAM、EEPROM等のハードウェア構成を備え、CPUが、ROMに格納される処理プログラムを実行することにより実現されるものである。
(C) Other Embodiments Various functions of the management system described in the first and second embodiments are realized by software processing. That is, for example, a hardware configuration such as a CPU, ROM, RAM, and EEPROM is provided, and the CPU is realized by executing a processing program stored in the ROM.
また、第1及び第2の実施形態で説明した管理システムの各種機能部は、物理的に同一のサーバ上で実現されるものであってもよいし、分散配置されたサーバ上で分散処理により実現されるものであってよい。 In addition, the various functional units of the management system described in the first and second embodiments may be realized on the physically same server, or may be performed by distributed processing on the distributed servers. It may be realized.
1…管理システム、2…クライアント端末、3〜5…ノード、6…配信サーバ、9A及び9B…映像配信システム、11…受信部、12…時刻情報取得部、13…TSパケット損失検出部、14…画像情報取得部、141…GOP構成取得部、142…フレーム情報取得部、15…画像品質測定部、151…スライス損失検知部、152…フレーム損失検知部。
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (4)
上記クライアント端末に配信される画像データを有するパケットを受信する受信手段と、
受信パケットに基づいて画像の構成を示す画像構成情報を取得する画像構成情報取得手段と、
上記画像構成情報に基づく構成順にしたフレームと、シーケンス番号に基づいて時系列に並べた上記パケットとを対応させ、各フレームと上記パケットとを関連付けて画像品質を測定する画像品質測定手段と、
上記画像品質測定手段により測定された画像品質測定結果を蓄積する蓄積手段と
を備えることを特徴とする画像品質管理システム。 In an image quality management system for managing image quality delivered to client terminals,
Receiving means for receiving a packet having image data distributed to the client terminal;
Image configuration information acquisition means for acquiring image configuration information indicating the configuration of the image based on the received packet;
Image quality measuring means for associating frames arranged in sequence based on the image configuration information with the packets arranged in time series based on sequence numbers, and measuring the image quality by associating each frame with the packets;
An image quality management system comprising: storage means for storing the image quality measurement results measured by the image quality measurement means.
受信パケットに含まれる画像データに基づいて、各フレーム内における処理単位の構成パターンを割り出し、フレーム内での各処理単位のロス数をカウントする処理単位損失検知部と、
上記画像構成情報に基づいて各フレームに対してシーケンス番号を付与し、各フレームのシーケンス番号と上記パケットのシーケンス番号とを対応付けて画像構成テーブルを形成し、上記処理単位損失検知部が求めたロス数を上記画像構成テーブルに対応させるフレーム損失検知部と
を有することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の画像品質管理システム。 The image quality measuring means is
Based on the image data included in the received packet, a processing unit loss detection unit that calculates a configuration pattern of processing units in each frame and counts the number of losses of each processing unit in the frame;
A sequence number is assigned to each frame based on the image configuration information, and an image configuration table is formed by associating the sequence number of each frame with the sequence number of the packet. The image quality management system according to claim 1, further comprising: a frame loss detection unit that associates the number of losses with the image configuration table.
上記画像品質管理システムが、受信手段、画像構成情報取得手段、画像品質測定手段及び蓄積手段を備え、
上記受信手段が、上記クライアント端末に配信される画像データを有するパケットを受信する受信工程と、
上記画像構成情報取得手段が、受信パケットに基づいて画像の構成を示す画像構成情報を取得する画像構成情報取得工程と、
画像品質測定手段が、上記画像構成情報に基づく構成順にしたフレームと、シーケンス番号に基づいて時系列に並べた上記パケットとを対応させ、各フレームと上記パケットとを関連付けて画像品質を測定する画像品質測定工程と、
蓄積手段が、上記画像品質測定手段により測定された画像品質測定結果を蓄積する蓄積工程と
を有することを特徴とする画像品質管理方法。 In an image quality management method in an image quality management system for managing image quality delivered to a client terminal,
The image quality management system includes a receiving unit, an image configuration information acquiring unit, an image quality measuring unit, and a storage unit,
A receiving step in which the receiving means receives a packet having image data distributed to the client terminal;
The image configuration information acquisition unit acquires image configuration information indicating image configuration information based on the received packet, and
An image in which the image quality measuring unit associates the frames arranged in the configuration order based on the image configuration information with the packets arranged in time series based on the sequence number, and measures the image quality by associating each frame with the packets. Quality measurement process,
An image quality management method comprising: an accumulation step for accumulating an image quality measurement result measured by the image quality measurement means.
コンピュータを、
上記クライアント端末に配信される画像データを有するパケットを受信する受信手段、
受信パケットに基づいて画像の構成を示す画像構成情報を取得する画像構成情報取得手段、
上記画像構成情報に基づく構成順にしたフレームと、シーケンス番号に基づいて時系列に並べた上記パケットとを対応させ、各フレームと上記パケットとを関連付けて画像品質を測定する画像品質測定手段、
上記画像品質測定手段により測定された画像品質測定結果を蓄積する蓄積手段
として機能させることを特徴とする画像品質管理プログラム。 In the image quality management program in the image quality management system that manages the image quality delivered to the client terminal,
Computer
Receiving means for receiving a packet having image data distributed to the client terminal;
Image configuration information acquisition means for acquiring image configuration information indicating the configuration of an image based on a received packet;
Image quality measuring means for associating the frames arranged in the configuration order based on the image configuration information with the packets arranged in time series based on a sequence number, and measuring the image quality by associating each frame with the packets;
An image quality management program for causing an image quality measurement result measured by the image quality measurement means to function as an accumulation means for accumulating.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008195248A JP4935776B2 (en) | 2008-07-29 | 2008-07-29 | Image quality management system, method and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008195248A JP4935776B2 (en) | 2008-07-29 | 2008-07-29 | Image quality management system, method and program |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010034875A true JP2010034875A (en) | 2010-02-12 |
| JP4935776B2 JP4935776B2 (en) | 2012-05-23 |
Family
ID=41738856
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008195248A Active JP4935776B2 (en) | 2008-07-29 | 2008-07-29 | Image quality management system, method and program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4935776B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103167313A (en) * | 2011-12-08 | 2013-06-19 | 中国电信股份有限公司 | Video monitoring service quality measuring method, system and quality measuring server |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003199062A (en) * | 1997-03-17 | 2003-07-11 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Transmitting device and receiving device |
| JP2004187025A (en) * | 2002-12-04 | 2004-07-02 | Shibasoku:Kk | Signal evaluating device |
| JP2006217470A (en) * | 2005-02-07 | 2006-08-17 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Quality management method for large-scale stream distribution, viewing quality management device and viewing quality management program |
| JP2007135040A (en) * | 2005-11-11 | 2007-05-31 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | User experience quality estimation apparatus, method, and program |
-
2008
- 2008-07-29 JP JP2008195248A patent/JP4935776B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003199062A (en) * | 1997-03-17 | 2003-07-11 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Transmitting device and receiving device |
| JP2004187025A (en) * | 2002-12-04 | 2004-07-02 | Shibasoku:Kk | Signal evaluating device |
| JP2006217470A (en) * | 2005-02-07 | 2006-08-17 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Quality management method for large-scale stream distribution, viewing quality management device and viewing quality management program |
| JP2007135040A (en) * | 2005-11-11 | 2007-05-31 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | User experience quality estimation apparatus, method, and program |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103167313A (en) * | 2011-12-08 | 2013-06-19 | 中国电信股份有限公司 | Video monitoring service quality measuring method, system and quality measuring server |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP4935776B2 (en) | 2012-05-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Yang et al. | End-to-end TCP-friendly streaming protocol and bit allocation for scalable video over wireless Internet | |
| JP5996541B2 (en) | Method and system for measuring the quality of audio and video bitstream transmission over a transmission chain | |
| US8576909B2 (en) | System and method for monitoring video packets for quantifying video quality | |
| US9641588B2 (en) | Packets recovery system and method | |
| US9241197B2 (en) | System and method for video delivery over heterogeneous networks with scalable video coding for multiple subscriber tiers | |
| CN102742245A (en) | A method and apparatus for parsing a network abstraction-layer for reliable data communication | |
| Greengrass et al. | Not all packets are equal, part i: Streaming video coding and sla requirements | |
| US8782481B2 (en) | Receiving terminal and receiving method | |
| CN101632265B (en) | Method for determining space loss and time loss in a packet-based video broadcasting system | |
| JP2014535196A (en) | Apparatus and method for transmitting multimedia data in a hybrid network | |
| Usman et al. | Performance evaluation of high definition video streaming over mobile ad hoc networks | |
| EP2404451B1 (en) | Processing of multimedia data | |
| CN102333209B (en) | Data transmission method and equipment applied to video monitoring system | |
| WO2009155871A1 (en) | Method, device and system for processing data packets | |
| KR102056438B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for transceiving data packet for transmitting and receiving multimedia data | |
| EP2649794B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for managing content distribution over multiple terminal devices in collaborative media system | |
| JP5877960B2 (en) | Receiving apparatus, system, program and method for controlling video frame rate based on transmission bit rate | |
| JP4935776B2 (en) | Image quality management system, method and program | |
| JP2014093584A (en) | Transmission device, transmission method, receiving device, reception method and computer program | |
| CN103716640B (en) | Method and device for detecting frame type | |
| KR102093408B1 (en) | Method and apparatus of selective classification of packet error of multiple packet streams multiplexed in same port | |
| JP2010063004A (en) | Video data transmission apparatus, video distribution system, video quality evaluation method and program | |
| KR20200015655A (en) | Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving data packet | |
| KR102330416B1 (en) | Method and Apparatus for Detecting Packet Loss | |
| Son et al. | Fast required bandwidth estimation technique for network adaptive streaming |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20110322 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20110706 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20110809 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110930 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20120124 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20120206 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20150302 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4935776 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |