JP2010000528A - Spot welding method - Google Patents
Spot welding method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2010000528A JP2010000528A JP2008162522A JP2008162522A JP2010000528A JP 2010000528 A JP2010000528 A JP 2010000528A JP 2008162522 A JP2008162522 A JP 2008162522A JP 2008162522 A JP2008162522 A JP 2008162522A JP 2010000528 A JP2010000528 A JP 2010000528A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- value
- spot welding
- servo motor
- pressure
- command value
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Resistance Welding (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、スポット溶接方法に関し、特に、スポット溶接ガンを構成する電極チップをサーボモータで駆動して電極チップ間でワーク(被溶接物)を加圧しながら溶接するスポット溶接方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a spot welding method, and more particularly, to a spot welding method in which an electrode tip constituting a spot welding gun is driven by a servo motor and a workpiece (workpiece) is welded while being pressed between the electrode tips.
スポット溶接においては、スポット溶接ガンによるワークの加圧力が不足すると溶接不良やスパッタの発生が引き起こされる。これを防止するために、スポット溶接時の加圧力を所定の範囲内に維持する種々の方策が提案されている。 In spot welding, if the workpiece pressure by the spot welding gun is insufficient, poor welding and spatter are caused. In order to prevent this, various measures for maintaining the applied pressure during spot welding within a predetermined range have been proposed.
特許文献1に開示された方法では、スポット溶接ガンを駆動してワークを加圧するサーボモータの電流値を溶接中に監視している。そして、サーボモータの電流値が基準値を下回った場合に、加圧力が低下したと判定してサーボモータの電流指令値の補正を行い、加圧力を調整している。
In the method disclosed in
しかしながら実際には、スポット溶接ガンの経年変化による機構部の摩擦増加等の要因によって、サーボモータの電流指令値、すなわち加圧力指令値と実際に発生する把持加圧力の値との関係には変化が生じる。このため、人手により、スポット溶接のシステムの休止時に定期的にスポット溶接ガンの把持加圧力を測定し、この測定結果に基づいて、加圧力指令値と実際に発生する把持加圧力の値との関係式の補正を行う再調整作業が一般的に行なわれている。 In reality, however, the relationship between the servo motor current command value, that is, the force command value and the actual gripping force value, changes due to factors such as increased friction in the mechanism due to aging of the spot welding gun. Occurs. For this reason, the grip welding force of the spot welding gun is periodically measured manually when the spot welding system is stopped, and based on the measurement result, the force command value and the actually generated gripping force value are A readjustment operation for correcting the relational expression is generally performed.
これに対して、特許文献2に開示された方法では、スポット溶接ガンを移動させる多関節ロボットの動作範囲内に圧力検出器を配置している。そして、この圧力検出器によりスポット溶接ガンの実際に発生する加圧力を定期的に測定し、その時のサーボモータの電流指令値との関係から、サーボモータの電流指令値、すなわち加圧力指令値と、実際の加圧力との関係式を自動的に補正している。
On the other hand, in the method disclosed in
また、特許文献3に開示された方法では、スポット溶接ガンを微速度で移動させた時にサーボモータに流れる電流値を測定している。そして、測定された電流値を、スポット溶接ガンの姿勢の変化などによる把持加圧力の変化を抑制するのに利用している。 In the method disclosed in Patent Document 3, the value of the current flowing through the servo motor when the spot welding gun is moved at a slow speed is measured. The measured current value is used to suppress a change in gripping pressure due to a change in the position of the spot welding gun.
本発明の目的は、機構部などに経年変化が生じても、適切な加圧力でワークを把持して溶接を行うことができる新規なスポット溶接方法を提供することにある。 An object of the present invention is to provide a novel spot welding method capable of gripping and welding a workpiece with an appropriate pressurizing force even when a mechanical part or the like undergoes secular change.
上述の目的を達成するため、本発明のスポット溶接方法は、設定値に応じた加圧力指令値にしたがってサーボモータによって対の電極チップを駆動することにより、電極チップの間にワークを挟み込み加圧した状態で、電極チップ間に通電することによってワークをスポット溶接するスポット溶接方法において、サーボモータを動作させて外乱トルク値を求め、求められた外乱トルク値を基準値として記録する第1のステップと、第1のステップから任意の時間経過後に、サーボモータを動作させて外乱トルク値を求める第2のステップと、第2のステップで求めた外乱トルク値と基準値との差から加圧力補正値を求める第3のステップと、スポット溶接時の電極チップによるワークの加圧力の指令値を、前記設定値から加圧力補正値だけずれた値に補正する第4のステップと、を有することを特徴とする。 In order to achieve the above-described object, the spot welding method of the present invention uses a servo motor to drive a pair of electrode tips in accordance with a pressure command value corresponding to a set value, thereby sandwiching a workpiece between the electrode tips and applying pressure. In the spot welding method in which the workpiece is spot-welded by energizing between the electrode tips in a state of being performed, a first step of obtaining a disturbance torque value by operating a servo motor and recording the obtained disturbance torque value as a reference value Then, after an arbitrary time has elapsed from the first step, the second step of calculating the disturbance torque value by operating the servo motor and the correction of the applied pressure from the difference between the disturbance torque value obtained in the second step and the reference value The third step of obtaining the value and the command value of the workpiece pressing force by the electrode tip at the time of spot welding, not only the pressing force correction value from the set value, A fourth step of correcting the value obtained, characterized by having a.
この構成によれば、外乱トルク値の変化によって、機構部の摩擦増加などの経年変化を評価し、スポット溶接時のワークの加圧力の、経年変化に起因する変動を低減するように、加圧力指令値の補正を行うことができる。この際、外乱トルク値は、サーボモータに通常備わっている検出部を用いて求めることができるので、専用の検出装置を新たに設置する必要がない。 According to this configuration, the change in the disturbance torque value is used to evaluate the secular change such as an increase in the friction of the mechanical part, and the pressurization force is reduced so as to reduce the fluctuation due to the secular change of the work force during spot welding. The command value can be corrected. At this time, the disturbance torque value can be obtained by using a detection unit usually provided in the servo motor, so that it is not necessary to newly install a dedicated detection device.
本発明のスポット溶接方法は、第1のステップに続いて、予め定められた加圧力指令値にしたがってサーボモータを駆動し、電極チップ同士が、間にワークを挟むことなく押し付けられて加圧力指令値が満足された状態の時のサーボモータの位置を検出し、基準位置として記録する第5のステップと、第3のステップに続いて、第5のステップにおける加圧力指令値に、第3のステップで求められた加圧力補正値を加算した新たな加圧力指令値にしたがってサーボモータを駆動し、電極チップ同士が、間にワークを挟むことなく押し付けられて加圧力指令値が満足された状態の時のサーボモータの位置を検出する第6のステップと、第6のステップで検出したサーボモータの位置と基準位置との差が所定の閾値を越えている場合に警告を発する第7のステップと、をさらに有するのが好ましい。 In the spot welding method of the present invention, following the first step, the servomotor is driven in accordance with a predetermined pressure command value, and the electrode tips are pressed against each other without interposing a workpiece therebetween. After the fifth step of detecting the position of the servo motor when the value is satisfied and recording it as the reference position, and the third step, the pressure command value in the fifth step is changed to the third step. The servo motor is driven according to the new pressure command value obtained by adding the pressure correction value obtained in the step, and the pressure command value is satisfied when the electrode tips are pressed without interposing a workpiece between them. When the difference between the servo motor position detected in the sixth step and the reference position exceeds a predetermined threshold, a warning is issued. Preferably further comprising the steps of the seventh, the.
第5のステップと第6のステップとで実際に電極チップにかかる加圧力に差が生じれば、電極チップの保持部材の撓み量に差が生じ、第5のステップと第6のステップとで、検出されるサーボモータの位置に差が生じる。したがって、この差を評価することによって、加圧力補正値の妥当性を評価することができる。 If there is a difference in the pressure applied to the electrode tip between the fifth step and the sixth step, there will be a difference in the amount of deflection of the holding member of the electrode tip, and the difference between the fifth step and the sixth step. A difference occurs in the position of the detected servo motor. Therefore, the validity of the pressure correction value can be evaluated by evaluating this difference.
第6のステップで検出したサーボモータの位置と基準位置との差が所定の閾値を越えている場合には、スポット溶接工程を実行しないようにしてもよい。それによって、加圧力補正値が妥当でない状態で、スポット溶接工程が実行されるのを回避することができる。 If the difference between the position of the servo motor detected in the sixth step and the reference position exceeds a predetermined threshold value, the spot welding process may not be executed. Thereby, it is possible to avoid the spot welding process being executed in a state where the pressure correction value is not valid.
サーボモータのトルク特性などは、モータの温度によってある程度変化する。そこで、サーボモータに付属する温度検出器によって検出された温度値によって、サーボモータの外乱トルク値に補正を加えることによって、加圧力補正値の精度を高めることができる。 The torque characteristics of the servo motor change to some extent depending on the motor temperature. Therefore, the accuracy of the applied pressure correction value can be increased by correcting the disturbance torque value of the servo motor based on the temperature value detected by the temperature detector attached to the servo motor.
加圧力補正値の算出には、外乱トルク値の変化の代わりに、サーボモータのモータ電流値の変化を用いてもよい。 In calculating the pressure correction value, a change in the motor current value of the servo motor may be used instead of the change in the disturbance torque value.
本発明のスポット溶接方法によれば、スポット溶接時のワークの加圧力の、経年変化に起因する変動を、加圧力補正値により加圧指令値を補正することによって低減することができる。それによって、機構部などに経年変化が生じても、適切な加圧力でワークを把持して溶接を行うことができるスポット溶接方法が提供される。 According to the spot welding method of the present invention, it is possible to reduce the fluctuation caused by the secular change of the workpiece pressing force during spot welding by correcting the pressurization command value with the pressing force correction value. As a result, a spot welding method is provided in which a workpiece can be gripped and welded with an appropriate applied pressure even when a mechanical part or the like undergoes secular change.
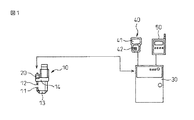
以下、図面を参照して本発明の実施形態について説明する。図1は、本発明の一実施形態に係るスポット溶接ガンシステムの模式的な構成図である。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. FIG. 1 is a schematic configuration diagram of a spot welding gun system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
このスポット溶接ガンシステムには、スポット溶接ガン10が備えられている。スポット溶接ガン10は、固定側電極チップ11が先端に取り付けられたアーム13と、可動側電極チップ12が先端に取り付けられたアーム14を有している。アーム14は、固定側電極チップ11と可動側電極チップ12とを互いに対向して位置した状態に保ったまま互いの距離を変化させることができるように、アーム13に、それに対して移動できるように連結されている。アーム14には、それをアーム13に対して移動させるための駆動力を発生するサーボモータ20が、不図示のギヤ機構などの機構部を介して接続されている。固定側電極チップ11と可動側電極チップ12とは、両者間に把持した不図示のワークを溶接するための所定の電力を両者間に通電できるように構成されている。
The spot welding gun system is provided with a
可動側電極チップ12の駆動のための機構部や、固定側電極チップ11と可動側電極チップ12との間の通電装置などには、公知のものを用いることができ、これらは、本発明に直接関わるものではないので、詳細な説明は省略する。スポット溶接ガンシステムには、ワークを固定側電極チップ11と可動側電極チップ12との間に位置させるための搬送機構や、スポット溶接ガン10の位置や姿勢を制御するための機構などが通常備えられるが、これらについても詳細な説明を省略する。また、電極チップは、複数対備えられていてもよく、それらを共通のサーボモータで駆動しても、別々のサーボモータで駆動してもよいが、ここでは説明を分かりやすくするため、1つのサーボモータ20と1対の電極チップを用いた構成について説明する。
Well-known devices can be used for the mechanism for driving the
サーボモータ20には制御装置30が接続されている。制御装置30は、サーボモータ20の他、前述の電極チップ間の通電装置、ワークの搬送機構、スポット溶接ガン10に付属するアーム機構などの制御を行うものであってよい。また、図1に示すスポット溶接ガンシステムは、ワークに対して、スポット溶接以外の種々の処理を施す生産ラインの一構成要素であってもよく、制御装置30は、スポット溶接以外の他の工程を実行する機構の制御機能を有していてもよい。
A
制御装置30には教示操作盤40が接続され、教示操作盤40には、操作員が、制御装置30内の情報の閲覧などを行うための画像表示部41と、制御装置30の操作や設定などを行うための入力部42とが備えられている。さらに、制御装置30に備えられた通信用インターフェイスを介して制御装置30と通信を行い、専用処理を行う周辺機器50が設けられていてもよい。周辺機器50には、例えば、前述のような生産ラインの各種機構を制御するための制御装置群の管理を行い、制御装置の起動や制御装置の状態監視を行うライン制御盤が含まれていてよく、あるいは、ワークの位置の検出・監視機構などが含まれてもよい。
A
図2は、本実施形態のスポット溶接ガンシステムの制御系の、主に、本発明に関わる部分のブロック図である。同図に示すように、制御装置30は、サーボモータ20の制御を行うためのサーボCPU31を有している。サーボモータ20には、回転機構部21に加え、その位置、速度などを検出して外部に出力するための検出部が備えられており、図2には、特に、位置検出部22を示している。サーボCPU31は、検出部からの受信信号に応じ、サーボアンプ32を介して回転機構部21への供給電力を制御する。それによって、サーボCPU31は、サーボモータ20の位置制御とトルク制御を実行可能であり、また速度制御を実行可能なものであってもよい。サーボCPU31によるサーボモータ20のこのような制御は、サーボモータ20の検出部の信号や、サーボモータ20の電流値をフィードバック信号とした制御などによって実現され、これには、公知のどのような構成を用いてもよい。また、特に、本実施形態において、サーボCPU31は、トルク指令値と、検出部からの信号によって求められる実速度値との比較などによって、種々の機構部の摩擦などによって発生する外乱トルクを予測、検出する機能を有している。
FIG. 2 is a block diagram of a part mainly related to the present invention of the control system of the spot welding gun system of the present embodiment. As shown in the figure, the
制御装置30は、さらに、教示操作盤40や周辺機器50との情報交換などを含む種々の統括制御を行うメインCPU35を有している。メインCPU35は、種々の演算処理を行う演算部36と、種々の設定などの情報や、スポット溶接工程を実行するためのプログラムなどを保存しておくための記憶部37を有している。なお、図示していないが、サーボCPU31も、必要に応じて、記憶部などを有していてよい。また、サーボCPU31とメインCPU35とは、別々のハードウェアによって構成されるものでなくてもよく、同一のハードウェアが実行する別々のソフトウェアによってそれぞれの機能が実現されるものであってもよい。
The
サーボCPU31は、前述のように、サーボモータ20の位置制御およびトルク制御を実行可能であり、これらの制御指令がメインCPU35から与えられる。メインCPU35は、位置指令によって、サーボモータ20の回転機構21を、したがって可動側電極チップ12を所定の位置に移動させることができる。また、加圧力指令によって、サーボモータ20の発生トルクを、したがって、固定側電極チップ11と可動側電極チップ12とによる加圧力が所定の値になるようにすることができる。
As described above, the
次に、動作について説明する。スポット溶接工程は、制御装置30のメインCPU35が、記憶部37に記憶されたプログラムにしたがって動作することによって実行される。この際、制御装置30は、ワークの搬送機構などの制御を行う他の制御装置と協働したり、ワークの位置検出機構などからの情報に応答したりするものであってよいが、これらの動作は、本発明に直接関わるものではないので、詳細な説明は省略する。
Next, the operation will be described. The spot welding process is executed by the
最初に、可動側電極チップ12が、固定側電極チップ11から十分に離れた所定の位置に配置された状態で、可動側電極チップ12と固定側電極チップ11との間にワークが位置決めされる。この状態から、サーボモータ20によって可動側電極チップ12が、固定側電極チップ11との間にワークを挟み込む所定の位置に動かされ、さらに、ワークに対して所定の加圧力が加わるように、サーボモータ20によってトルクが発生させられる。このようにして、ワークが固定側電極チップ11と可動側電極チップ12との間に把持され、所定の加圧力を加えられた状態で、固定側電極チップ11と可動側電極チップ12との間に所定の通電が行われて、ワークがスポット溶接される。
First, the workpiece is positioned between the
上記のようにして所望のスポット溶接が良好に行われるようにするために、電極チップへの通電時の加圧力指令値pは、予め適切に設定される。この加圧力指令値pは、スポット溶接ガンシステムの設計時に、ワークの種類などに応じて適切に設定することができ、また、個々のスポット溶接ガンシステムの施工後に、さらに試験を通じて、適切に調整してもよい。 In order to perform desired spot welding satisfactorily as described above, the pressure command value p when energizing the electrode tip is appropriately set in advance. This pressure command value p can be set appropriately in accordance with the type of workpiece when designing a spot welding gun system, and is also adjusted appropriately through tests after each spot welding gun system is installed. May be.
しかしながら、スポット溶接ガンシステムにおいては、一般に、機構部の摩擦増加などの経年変化のために、同じ加圧力指令値pによって動作させた時にワークに加わる加圧力は、経年的に変化してしまう。そこで、本実施形態では、このような経年変化の影響に対する補正動作を行う。 However, in a spot welding gun system, generally, the pressure applied to the workpiece when it is operated with the same pressure command value p changes over time due to aging such as increased friction of the mechanism. Therefore, in the present embodiment, a correction operation for the influence of such aging is performed.
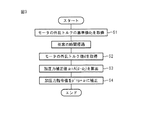
この補正動作のフローチャートを図3に示す。最初に、ステップS1(第1のステップ)において、サーボモータ20にかかる外乱トルクの基準値d0を取得する。すなわち、前述のように、サーボCPU31は、外乱トルクを予測、検出する機能を有しており、これを利用して外乱トルク値を取得し、これを基準値d0とする。より詳細に述べると、サーボCPU31は、外乱トルクの測定用に予め用意された制御プログラムを実行してサーボモータ20を所定のパターンで動作させ、その際のトルク指令値と実速度値との比較などから外乱トルク値を算出する。外乱トルク値の算出には、公知のどのような構成を用いてもよい。サーボCPU31で算出された基準値d0は、メインCPU36に送信され、記録部37に保存される。
A flowchart of this correction operation is shown in FIG. First, in step S1 (first step), a reference value d 0 of disturbance torque applied to the
この際、可動側電極チップ12が固定側電極チップ11に接触すると、接触によって発生するトルクが支配的となり、機構部の摩擦などによる、より小さな外乱トルクを精度良く測定することが困難となる。このため、外乱トルクの測定は、可動側電極チップ12が固定側電極チップ11に接触しない範囲で、可動側電極チップ12に一定の動作をさせて行うのが好ましい。
At this time, when the
次に、任意の時間経過後、ステップS2(第2のステップ)において、再度、外乱トルク値dを取得する。この際には、ステップS1で実行したものと同じ制御プログラムを実行することにより、同一条件で外乱トルク値dを取得するのが好ましい。 Next, after an arbitrary time has elapsed, in step S2 (second step), the disturbance torque value d is acquired again. In this case, it is preferable to obtain the disturbance torque value d under the same conditions by executing the same control program as that executed in step S1.
次に、ステップS3(第3のステップ)において、ステップS1で取得した基準値d0とステップS2で取得した外乱トルク値d1との差から、それに比例定数Aを乗算して加圧力補正値α=A(d−d0)を算出する。そして、ステップS4(第4のステップ)において、スポット溶接時の加圧力指令値を加圧力補正値α分だけ補正して、p’=p+αに設定し直す。 Next, in step S3 (third step), the difference between the disturbance torque value d 1 obtained in the reference value d 0 and Step S2 obtained in step S1, pressure correction value by multiplying the proportional constant A thereto α = A (d−d 0 ) is calculated. In step S4 (fourth step), the pressure command value at the time of spot welding is corrected by the pressure correction value α, and p ′ = p + α is set again.
このようにして、以降のスポット溶接時には、補正された加圧力指令値p’を用いることによって、経年変化によりワークの加圧力が変動するのを抑制し、ワークに適切な加圧力を加えた状態で、良好に溶接を行うことができる。すなわち、ステップS1の時点からステップS2の時点までの時間経過の間の、機構部の摩擦増加などの経年変化のために生じる、同一の加圧力指令値で動作させた場合のワークの加圧力の変化は、ステップS1とステップS2で測定した外乱トルク値の差に実質的に比例する。したがって、この差にしたがって、経年変化のために生じる加圧力の変化分だけ加圧指令値を補正することによって、経年変化の影響を相殺し、ワークの加圧力の、経年変化による変動を低減することができる。 Thus, at the time of subsequent spot welding, by using the corrected pressure command value p ′, it is possible to suppress the workpiece pressure from fluctuating due to secular change and to apply an appropriate pressure to the workpiece. Thus, welding can be performed satisfactorily. That is, the pressure of the workpiece when it is operated with the same pressure command value that occurs due to a secular change such as an increase in friction of the mechanism during the time elapsed from the time of step S1 to the time of step S2. The change is substantially proportional to the difference between the disturbance torque values measured in step S1 and step S2. Therefore, according to this difference, the pressurization command value is corrected by the change in the pressurizing force caused by the secular change, thereby canceling the influence of the secular change and reducing the fluctuation due to the secular change of the workpiece. be able to.
なお、ステップS1は、スポット溶接ガンシステムの施工後、早期に実行するのが好ましく、あるいは、施工後などに試験などによって加圧力指令値pの調整を行った場合、その後、なるべく近い時点でステップS1を実行するのが好ましい。それによって、ワークの加圧力が最も適切に調整された状態を基準とし、その状態を再現するように補正を行って、適切な溶接工程を実現することができる。 In addition, it is preferable to perform step S1 at an early stage after the spot welding gun system is constructed. Alternatively, when the pressure command value p is adjusted by a test or the like after the construction, the step S1 is performed at a time as close as possible thereafter. It is preferable to execute S1. Accordingly, an appropriate welding process can be realized by performing correction so as to reproduce the state based on the state in which the pressurizing force of the workpiece is most appropriately adjusted.
ステップS2およびS3は、操作員が適宜な時期に教示操作盤40を介して実行する構成にすることができ、定期的に繰り返し行われてよい。特に、制御装置30が、時間情報を自動的に取得して適切な時期に実行するように構成するのが好ましい。それによって、補正時期が遅れないように確実に適切な間隔で補正を行うことができ、それによって把持加圧力の経年変化による変動が大きくなるのを抑制することができる。
Steps S2 and S3 can be configured to be executed by the operator via the
以上説明したように、本実施形態によれば、機構部などに経年変化が生じても、それに応じて、加圧指令値に補正を加えることによって、ワークの加圧力が変化するのを抑制することができ、それによって、溶接工程を良好に実行可能とすることができる。この際、本実施形態の構成では、加圧指令値の補正処理を、制御装置30で自動的に行うことができるので、再調整作業を人手で行う場合に比べて、作業工数を減らして、システムの稼動コストを抑えることができる。また、システムを完全に休止しなくても補正を行うことができるので、適切な間隔で定期的に補正を行うことができ、それによって、把持加圧力の、経年変化に起因する変動が大きくなるのを抑制することができる。さらに、補正処理に専用の検出機構を必要とすることなく、サーボモータ20に元々備わっている検出部を利用して補正値を求めているので、システムが複雑になることもなく、低コストで実現可能である。
As described above, according to the present embodiment, even if the mechanical unit or the like undergoes secular change, the pressurization command value is corrected accordingly to suppress the change in the pressurizing force of the workpiece. Thereby making the welding process feasible. At this time, in the configuration of the present embodiment, the correction process of the pressurization command value can be automatically performed by the
なお、上述の実施形態は本発明を例示するものであり、特許請求の範囲に規定する本発明の範囲内で種々の変更が可能である。例えば、上述の実施形態では、スッテプS1の時点からステップS2の時点までの時間経過による、加圧力の経年変化による影響を評価するのに、外乱トルク値の差を用いる例を示したが、サーボモータ20のモータ電流値の差を用いてもよい。すなわち、通常、モータ電流値は、サーボモータ20の発生トルクに比例する。したがって、スッテプS1の時点とステップS2の時点とで、同一条件でサーボモータ20を駆動した時のモータ電流値の差を求めれば、この差分値は、加圧力の、経年変化値に起因する変動量に比例する。したがって、外乱トルク値の代わりにモータ電流値を用いても、加圧力の経年変化の補正を実現することができる。
The above-described embodiments are examples of the present invention, and various modifications can be made within the scope of the present invention defined in the claims. For example, in the above-described embodiment, the example in which the difference in the disturbance torque value is used to evaluate the influence of the aging of the pressurizing force due to the passage of time from the time of step S1 to the time of step S2 is shown. A difference in motor current value of the
また、サーボモータ20の位置検出部22の検出信号を利用して、加圧動作の補正の妥当性の評価をさらに行ってもよい。このような処理のフローチャートを図4に示す。図4において、図3と同様の部分には同一の符号を付し、詳細な説明は省略する。
Further, the validity of the correction of the pressing operation may be further evaluated using the detection signal of the
図4に示す処理では、ステップS1に続いて、ステップS11(第5のステップ)において、予め定められた加圧力指令値pc0をメインCPU36からサーボCPU31に出力する。それによって、可動側電極チップ12が固定側電極チップ11に、加圧力指令値に対応した加圧力で押し付けられる。この動作は、可動側電極チップ12と固定側電極チップ11との間にワークを挟まずに行う。そして、サーボCPU31において加圧力指令値pc0が満足されているのが判定された時のサーボモータ20の位置を位置検出器22によって検出して基準位置f0として記録する。
In the process shown in FIG. 4, following step S1, in step S11 (fifth step), a predetermined pressure command value pc 0 is output from the
次に、任意の時間経過後に行われるステップS2,S3に続いて、ステップS12(第6のステップ)において、ステップS11における加圧力指令値pc0を、加圧力補正値αによって補正した加圧力指令値pc=pc0+αにしたがって、ステップS11と同様に、加圧を行う。サーボCPU31において加圧力指令値pcが満足されているのが判定された時のサーボモータ20の位置fを位置検出器22によって検出する。
Next, following steps S2 and S3 performed after an arbitrary time has elapsed, in step S12 (sixth step), the pressure command value p c0 in step S11 is corrected by the pressure correction value α. In accordance with the value p c = p c0 + α, pressurization is performed as in step S11. The
この時、実際の加圧力がステップS11の時と、ステップS12の時とで異なっていれば、スポット溶接ガン10のアーム13,14などに加わる応力が異なることになり、それらの撓み量に差が生じる。その結果、位置f0とfとに差が生じることになる。そこで、ステップS13において、位置f0とfとの差が、所定の閾値fbを越えているかどうか判定する。
At this time, if the actual pressurizing force is different between step S11 and step S12, the stress applied to the
ステップS13において、位置f0とfとの差が、所定の閾値fbより小さいことが判定された場合には、ステップS4に進む。すなわち、加圧力補正値αは妥当なものと判断し、図3を用いて説明した場合と同様に、加圧力補正値αによる加圧力の補正を行う。 If it is determined in step S13 that the difference between the positions f 0 and f is smaller than the predetermined threshold f b , the process proceeds to step S4. That is, it is determined that the pressurizing force correction value α is appropriate, and the pressurizing force is corrected by the pressurizing force correction value α as in the case described with reference to FIG.
一方、位置f0とfとの差が、所定の閾値fbを越えていた場合には、加圧力補正値αが妥当なものではない可能性があることに対して、ステップS14(第7のステップ)において警告を発する。警告は、教示操作盤40の画面表示部41に表示して行うことができ、あるいは、周辺機器50として設けられた、音や光によって警報を発する警報装置を用いて行ってもよい。
On the other hand, if the difference between the positions f 0 and f exceeds the predetermined threshold value f b , the pressure correction value α may not be valid. A warning is issued in step (1). The warning can be performed by being displayed on the screen display unit 41 of the
ステップS14に続いて、ステップS15において、加圧力補正値αを0に修正した後、ステップS4に進む。すなわち、加圧力補正値αの使用を除外する。加圧力補正値αを、問題を生じないように予め定められた別の値に修正してもよい。あるいは、位置f0とfとの差が、所定の閾値fbを越えていた場合には、以降、スポット溶接工程を実行しないように構成してもよい。 Subsequent to step S14, the pressure correction value α is corrected to 0 in step S15, and then the process proceeds to step S4. That is, the use of the pressure correction value α is excluded. The pressing force correction value α may be corrected to another predetermined value so as not to cause a problem. Alternatively, when the difference between the positions f 0 and f exceeds a predetermined threshold value f b , the spot welding process may not be performed thereafter.
また、図5に示すように、サーボモータ20に、その温度を測定する温度検出器25を付属させて、その検出値をメインCPU35に取り込み、加圧力補正値αを算出するのに利用してもよい。すなわち、スポット溶接ガン10の可動部のグリスの粘性、あるいはサーボモータのトルク特性などは、通常、温度にある程度左右されるので、その影響を考慮することによって、加圧力の補正の精度を高めることができる。
Further, as shown in FIG. 5, a
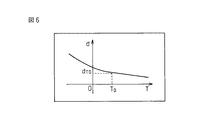
このために、モータ温度以外は同じ条件で外乱トルクを求めることによって、図6に示すように、モータ温度Tと外乱トルク値dTとの相関関係を予め求める。また、スポット溶接ガン10が通常使用される時、すなわちスポット溶接が実行される時の、サーボモータ20のモータ温度T0を予め求めておく。これらから、モータ温度がT0の時の外乱トルク値dT0と、モータ温度がTの時の外乱トルク値dTとは、一般に、関数f(T)を用いて、dT=dT0×f(T)と表すことができる。
Therefore, other than the motor temperature by calculating the disturbance torque at the same conditions, as shown in FIG. 6, we obtain the correlation between the motor temperature T and the disturbance torque value d T in advance. Further, the motor temperature T 0 of the
加圧力補正値αは、スポット溶接を実行する時の加圧力に適用されるものであるので、それを算出する際に用いる外乱トルク値dやその基準値d0は、スポット溶接を実行する時のモータ温度T0の状態で算出したものを用いるのが好ましい。一方、外乱トルク値dやその基準値d0は、スポット溶接の実行時に算出されるものではないので、算出時のモータ温度Tは、通常、モータ温度T0とは一致しない。そこで、上記の関数f(T)を用いて、モータ温度Tの状態で求めた外乱トルク値dTから、モータ温度T0の状態の時の外乱トルク値に相当する補正値dT0=dT/f(T)を求め、これを加圧力補正値αの算出に用いる。それによって、加圧力補正値αの精度を高めることができる。 Since the applied pressure correction value α is applied to the applied pressure when spot welding is performed, the disturbance torque value d and its reference value d 0 used to calculate it are determined when spot welding is performed. It is preferable to use the one calculated in the state of the motor temperature T 0 . On the other hand, since the disturbance torque value d and its reference value d 0 are not calculated at the time of spot welding, the motor temperature T at the time of calculation usually does not coincide with the motor temperature T 0 . Therefore, a correction value d T0 = dT / corresponding to the disturbance torque value in the motor temperature T 0 state from the disturbance torque value d T obtained in the motor temperature T state using the function f (T) described above. f (T) is obtained and used to calculate the pressure correction value α. Thereby, the accuracy of the pressure correction value α can be increased.
また、この場合、加圧力補正値αの妥当性を評価するための前述の加圧力指令値pc0,pcについても同様に、モータ温度による影響を考慮してもよい。すなわち、加圧力補正値αは、上述のように、スポット溶接を実行する時のモータ温度T0の状態を想定して設定される。したがって、加圧力補正値αを評価するための加圧力指令値pc0,pcも、モータ温度T0の状態での値として扱う必要がある。一方、実際に加圧力指令値pc0,pcにしたがって加圧が行われる時のモータ温度は、T0に一致しない。このため、加圧力補正値αの評価のための加圧を行う時には、加圧力指令値pc0,pcを、その時のモータ温度での値に補正した指令値を用いるのが好ましい。 In this case, the same applies to the pressure-force command value p c0, p c of the foregoing for evaluating the validity of the pressure correction value alpha, it may be considered the influence of motor temperature. That is, the pressure correction value α is set assuming the state of the motor temperature T 0 when spot welding is performed as described above. Therefore, even pressure-force command value p c0, p c for assessing pressure correction value alpha, should be treated as a value in the state of the motor temperature T 0. On the other hand, the motor temperature when the pressurization is performed actually in accordance with pressure-force command value p c0, p c does not match the T 0. Therefore, when performing the pressurization for the evaluation of pressure correction value α is a pressure-force command value p c0, p c, is preferable to use a command value corrected to a value of the motor temperature at that time.
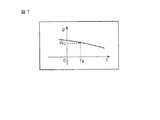
このため、モータ温度以外は同じ条件で、実際に発生する加圧力が同じになる加圧力指令値pを求めることによって、図7に示すように、モータ温度Tと加圧力指令値pTとの相関関係を予め求める。すると、この加圧力指令値pTは、一般に、モータ温度がT0の時の加圧力指令値pT0に対して、関数g(T)を用いて、pT=pT0×g(T)と表すことができる。このようにして、関数g(T)を用いて、加圧を行う時のモータ温度Tでの値に換算した加圧力指令値を求めることができ、その加圧力指令値を用いることによって、加圧力補正値αの評価の信頼性を向上させることができる。 For this reason, as shown in FIG. 7, by obtaining the pressure command value p at which the pressure force actually generated is the same under the same conditions except for the motor temperature, the motor temperature T and the pressure command value p T The correlation is obtained in advance. Then, the pressure-force command value p T is general, for pressure-force command value p T0 when the motor temperature T 0, using the function g (T), p T = p T0 × g (T) It can be expressed as. In this manner, the pressure command value converted into the value at the motor temperature T when pressurizing can be obtained using the function g (T), and by using the pressure command value, the pressure command value can be obtained. The reliability of the evaluation of the pressure correction value α can be improved.
10 スポット溶接ガン
11 固定側電極チップ
12 可動側電極チップ
20 サーボモータ
30 制御装置
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (5)
前記サーボモータを動作させて外乱トルク値を求め、求められた外乱トルク値を基準値として記録する第1のステップと、
前記第1のステップから任意の時間経過後に、前記サーボモータを動作させて外乱トルク値を求める第2のステップと、
前記第2のステップで求めた外乱トルク値と前記基準値との差から加圧力補正値を求める第3のステップと、
スポット溶接時の前記電極チップによる前記ワークの加圧力の指令値を、前記設定値から前記加圧力補正値だけずれた値に補正する第4のステップと、
を有することを特徴とするスポット溶接方法。 By driving the pair of electrode chips by a servo motor in accordance with a pressure command value corresponding to the set value, the work piece is energized between the electrode chips in a state where the work piece is sandwiched and pressed between the electrode chips. In the spot welding method of spot welding,
A first step of operating the servo motor to obtain a disturbance torque value, and recording the obtained disturbance torque value as a reference value;
A second step of determining a disturbance torque value by operating the servo motor after an arbitrary time has elapsed from the first step;
A third step of obtaining a pressure correction value from a difference between the disturbance torque value obtained in the second step and the reference value;
A fourth step of correcting a command value of the pressing force of the workpiece by the electrode tip at the time of spot welding to a value shifted from the set value by the pressing force correction value;
A spot welding method characterized by comprising:
前記第3のステップに続いて、前記第5のステップにおける前記加圧力指令値に、前記第3のステップで求められた前記加圧力補正値を加算した新たな加圧力指令値にしたがって前記サーボモータを駆動し、前記電極チップ同士が押し付けられて前記加圧力指令値が満足された状態の時の前記サーボモータの位置を検出する第6のステップと、
前記第6のステップで検出した前記サーボモータの位置と前記基準位置との差が所定の閾値を越えている場合に警告を発する第7のステップと、
をさらに有する請求項1に記載のスポット溶接方法。 Following the first step, the servo motor is driven in accordance with a predetermined pressure command value, and the servo motor is in a state where the electrode chips are pressed against each other to satisfy the pressure command value. A fifth step of detecting the position of and recording as a reference position;
Subsequent to the third step, the servo motor according to a new pressure command value obtained by adding the pressure correction value obtained in the third step to the pressure command value in the fifth step. A sixth step of detecting the position of the servo motor when the electrode tips are pressed against each other and the pressure command value is satisfied;
A seventh step of issuing a warning when a difference between the position of the servo motor detected in the sixth step and the reference position exceeds a predetermined threshold;
The spot welding method according to claim 1, further comprising:
前記サーボモータを動作させてモータ電流値を測定し、測定されたモータ電流値を基準値として記録する第1のステップと、
前記第1のステップから任意の時間経過後に、前記第1のステップと同一条件で前記サーボモータを動作させてモータ電流値を求める第2のステップと、
前記第2のステップで求めたモータ電流値と前記基準値との差から加圧力補正値を求める第3のステップと、
スポット溶接時の前記電極チップによる前記ワークの加圧力の指令値を、前記設定値から前記加圧力補正値だけずれた値に補正する第4のステップと、
を有することを特徴とするスポット溶接方法。 By driving the pair of electrode chips by a servo motor in accordance with a pressure command value corresponding to the set value, the work piece is energized between the electrode chips in a state where the work piece is sandwiched and pressed between the electrode chips. In the spot welding method of spot welding,
A first step of operating the servo motor to measure a motor current value and recording the measured motor current value as a reference value;
A second step of obtaining a motor current value by operating the servo motor under the same condition as the first step after an arbitrary time has elapsed from the first step;
A third step of obtaining a pressure correction value from a difference between the motor current value obtained in the second step and the reference value;
A fourth step of correcting a command value of the pressing force of the workpiece by the electrode tip at the time of spot welding to a value shifted from the set value by the pressing force correction value;
A spot welding method characterized by comprising:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008162522A JP5113640B2 (en) | 2008-06-20 | 2008-06-20 | Spot welding method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008162522A JP5113640B2 (en) | 2008-06-20 | 2008-06-20 | Spot welding method |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010000528A true JP2010000528A (en) | 2010-01-07 |
| JP5113640B2 JP5113640B2 (en) | 2013-01-09 |
Family
ID=41582668
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008162522A Expired - Fee Related JP5113640B2 (en) | 2008-06-20 | 2008-06-20 | Spot welding method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5113640B2 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102014004102A1 (en) | 2013-03-28 | 2014-10-02 | Fanuc Corporation | Spot welding system, including spot welding gun |
| CN108161198A (en) * | 2017-12-25 | 2018-06-15 | 中国重汽集团济南动力有限公司 | A kind of robot resistance spot welding process parameter testing and control method |
| EP4000817A1 (en) * | 2020-11-16 | 2022-05-25 | Kabushiki Kaisha Yaskawa Denki | Diagnosis of state of device |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH106026A (en) * | 1996-06-27 | 1998-01-13 | Nachi Fujikoshi Corp | Method for adjusting pressing force of servo control welding gun |
| JP2004130357A (en) * | 2002-10-11 | 2004-04-30 | Fanuc Ltd | Spot welding gun, and method for controlling pressurizing force of spot welding gun |
-
2008
- 2008-06-20 JP JP2008162522A patent/JP5113640B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH106026A (en) * | 1996-06-27 | 1998-01-13 | Nachi Fujikoshi Corp | Method for adjusting pressing force of servo control welding gun |
| JP2004130357A (en) * | 2002-10-11 | 2004-04-30 | Fanuc Ltd | Spot welding gun, and method for controlling pressurizing force of spot welding gun |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102014004102A1 (en) | 2013-03-28 | 2014-10-02 | Fanuc Corporation | Spot welding system, including spot welding gun |
| JP2014188585A (en) * | 2013-03-28 | 2014-10-06 | Fanuc Ltd | Spot weld system having spot weld gun |
| US9440306B2 (en) | 2013-03-28 | 2016-09-13 | Fanuc Corporation | Spot welding system including spot welding gun |
| DE102014004102B4 (en) | 2013-03-28 | 2019-09-05 | Fanuc Corporation | Spot welding system with a spot welding gun |
| CN108161198A (en) * | 2017-12-25 | 2018-06-15 | 中国重汽集团济南动力有限公司 | A kind of robot resistance spot welding process parameter testing and control method |
| EP4000817A1 (en) * | 2020-11-16 | 2022-05-25 | Kabushiki Kaisha Yaskawa Denki | Diagnosis of state of device |
| US11833695B2 (en) | 2020-11-16 | 2023-12-05 | Kabushiki Kaisha Yaskawa Denki | Diagnosis of state of device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5113640B2 (en) | 2013-01-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7600435B2 (en) | Method of determining deterioration of pressurizing performance of spot welding gun | |
| JP5638102B2 (en) | Spot welding system with spot welding gun | |
| US7863539B2 (en) | Positioning method of spot welding robot | |
| JP4880021B2 (en) | Welding workpiece position detection method | |
| JP2008504134A (en) | Resistance welding method monitoring method and apparatus for carrying out the method | |
| JP2016203246A (en) | Spot welding quality diagnosis system | |
| JP3629022B2 (en) | SPOT WELDING GUN AND METHOD OF CONTROLLING PRESSURE OF SPOT WELDING GUN | |
| JP2000288743A (en) | Controller for resistance welding equipment | |
| JP5113640B2 (en) | Spot welding method | |
| US9884386B2 (en) | Welding process for the Welding of Aluminum | |
| US20150336201A1 (en) | Spot welding system and spot welding method | |
| JP3864240B2 (en) | Welding method | |
| CN108136537B (en) | Friction stir spot welding apparatus and friction stir spot welding method | |
| JP4880020B2 (en) | Welding workpiece position detection method using movable electrode | |
| JPH1094882A (en) | Method and device for detecting and controlling pressure of welding gun | |
| JP4980323B2 (en) | Plant control diagnosis apparatus, method and program | |
| JP5290661B2 (en) | Electrode consumption measurement method and electrode consumption measurement device for spot welding equipment | |
| WO2004108339A1 (en) | Spot welding method, spot welding machine and spot welding robot | |
| KR101882096B1 (en) | Smart bending system | |
| JP5172278B2 (en) | Spot welding gun controller | |
| JP7335093B2 (en) | welding system | |
| KR101637654B1 (en) | Robot for inspecting vehicle avn system and method for controlling the robot | |
| JP2001009515A (en) | Hydraulic reduction diagnosis device | |
| KR100900629B1 (en) | Test method of welding part of coil | |
| JP2009082946A (en) | Spot-welding system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20101224 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20120906 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20120918 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20121012 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20151019 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |