JP2008169970A - Tapered roller bearings for driving automobiles - Google Patents
Tapered roller bearings for driving automobiles Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2008169970A JP2008169970A JP2007005566A JP2007005566A JP2008169970A JP 2008169970 A JP2008169970 A JP 2008169970A JP 2007005566 A JP2007005566 A JP 2007005566A JP 2007005566 A JP2007005566 A JP 2007005566A JP 2008169970 A JP2008169970 A JP 2008169970A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- cage
- tapered roller
- section
- roller bearing
- driving
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16C—SHAFTS; FLEXIBLE SHAFTS; ELEMENTS OR CRANKSHAFT MECHANISMS; ROTARY BODIES OTHER THAN GEARING ELEMENTS; BEARINGS
- F16C19/00—Bearings with rolling contact, for exclusively rotary movement
- F16C19/22—Bearings with rolling contact, for exclusively rotary movement with bearing rollers essentially of the same size in one or more circular rows, e.g. needle bearings
- F16C19/34—Bearings with rolling contact, for exclusively rotary movement with bearing rollers essentially of the same size in one or more circular rows, e.g. needle bearings for both radial and axial load
- F16C19/36—Bearings with rolling contact, for exclusively rotary movement with bearing rollers essentially of the same size in one or more circular rows, e.g. needle bearings for both radial and axial load with a single row of rollers
- F16C19/364—Bearings with rolling contact, for exclusively rotary movement with bearing rollers essentially of the same size in one or more circular rows, e.g. needle bearings for both radial and axial load with a single row of rollers with tapered rollers, i.e. rollers having essentially the shape of a truncated cone
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Rolling Contact Bearings (AREA)
Abstract
【課題】鉄製保持器に代わり、軽量化を図かりつつ、機械的強度や寸法安定性、摺動性、耐疲労性等にも優れる保持器を備える自動車駆動用円錐ころ軸受を提供する。
【解決手段】少なくとも内輪、外輪、保持器及びころを備える自動車駆動用円錐ころ軸受において、前記保持器が、異形断面を有するガラス繊維を10〜40質量%の割合で含有する合成樹脂組成物からなることを特徴とする自動車駆動用円錐ころ軸受。
【選択図】図1Provided is a tapered roller bearing for driving an automobile provided with a cage that is excellent in mechanical strength, dimensional stability, slidability, fatigue resistance, and the like while reducing the weight in place of an iron cage.
In a tapered roller bearing for driving an automobile comprising at least an inner ring, an outer ring, a cage and a roller, the cage is made of a synthetic resin composition containing 10 to 40% by mass of a glass fiber having an irregular cross section. A tapered roller bearing for driving an automobile.
[Selection] Figure 1
Description
本発明は、オートマチックトランスミッション等の自動車駆動系に使用される円錐ころ軸受に関する。 The present invention relates to a tapered roller bearing used in an automobile drive system such as an automatic transmission.
オートマチックトランスミッション、具体的にはディファレンシャル、カウンタードライブギア等には円錐ころ軸受が使用されている。これらの円錐ころ軸受では、ATF(オートマチックフルード)等の薬剤に晒され、高温になると同時に、高い信頼性が求められることから、これまでは鉄製のプレス保持器が使用されている(例えば、特許文献1〜4参照)。 Tapered roller bearings are used in automatic transmissions, specifically differentials, counter drive gears, and the like. Since these tapered roller bearings are exposed to chemicals such as ATF (automatic fluid) and become high temperature and at the same time require high reliability, iron press cages have been used so far (for example, patents) References 1-4).
しかし、近年では軽量化や低トルク化の要求が高く、構造等の見直しを行っても、鉄製保持器では対応しきれなくなっている。 However, in recent years, there is a high demand for weight reduction and torque reduction, and even with a review of the structure and the like, the iron cage can no longer handle it.
本発明はこのような状況に鑑みてなされたものであり、これまでの鉄製保持器に代わり、軽量化を図かりつつ、機械的強度や寸法安定性、摺動性、耐疲労性等にも優れる保持器を備える自動車駆動用円錐ころ軸受を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of such a situation, and instead of the conventional iron cage, while reducing the weight, the mechanical strength, dimensional stability, slidability, fatigue resistance, etc. An object of the present invention is to provide a tapered roller bearing for driving an automobile having an excellent cage.
上記目的を達成するために、本発明は、少なくとも内輪、外輪、保持器及びころを備える自動車駆動用円錐ころ軸受において、前記保持器が、異形断面を有するガラス繊維を10〜40質量%の割合で含有する合成樹脂組成物からなることを特徴とする自動車駆動用円錐ころ軸受を提供する。 In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides a tapered roller bearing for driving an automobile comprising at least an inner ring, an outer ring, a cage, and a roller, wherein the cage has a ratio of 10 to 40% by mass of glass fiber having an irregular cross section. A tapered roller bearing for driving an automobile is provided.
本発明の自動車駆動用円錐ころ軸受では、保持器を樹脂製としたため鉄製保持器に比べて大幅に軽量化できる。更に、保持器は、補強材として異形断面を有するガラス繊維を含有することから機械的強度や耐疲労性等に優れるとともに、ガラス繊維の異方性が低下して成形時のヒケの発生も無く、寸法精度も高いものとなるため、本発明の自動車用円錐こと軸受は耐久性にも優れ、信頼性の高いものとなる。 In the tapered roller bearing for driving an automobile of the present invention, since the cage is made of resin, the weight can be significantly reduced as compared with an iron cage. Furthermore, since the cage contains glass fibers having a deformed cross section as a reinforcing material, it has excellent mechanical strength, fatigue resistance, etc., and there is no occurrence of sink marks during molding due to a decrease in the anisotropy of the glass fibers. Since the dimensional accuracy is also high, the conical bearing for automobiles of the present invention has excellent durability and high reliability.
以下、本発明の実施形態について詳細に説明する。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail.
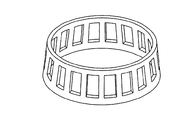
本発明において、自動車駆動用用円錐ころ軸受は、その構造には制限がなく、例えば図1に示す円錐ころ軸受を例示することができる。図示される円錐ころ軸受は、外周面に内輪軌道1を有する内輪2と、内周面に外輪軌道3を有する外輪4と、複数個の円錐ころ5と、この円錐ころ5を等配で分割して配置するための保持器6とを備える。また、図2に保持器6の斜視図を示す。
In the present invention, the structure of the tapered roller bearing for driving an automobile is not limited, and for example, the tapered roller bearing shown in FIG. 1 can be exemplified. The illustrated tapered roller bearing includes an
本発明では、上記保持器6として、異形断面を有するガラス繊維を合成樹脂に配合した合成樹脂組成物を成形したものを用いる。合成樹脂には制限はないが、耐熱性や耐疲労性等を考慮すると、ポリフェニレンサルファイド、芳香族ポリアミド、ポリアミド46、ポリアミド66等が好ましい。中でも、ポリフェニレンサルファイドは、150〜180℃の高温での使用が可能で、ATF等の耐薬品性にも優れるため最も好ましい。但し、ポリフェニレンサルファイドは脆く、衝撃等を受けて損傷するおそれがあるため、グリシジルメタクリレート等の反応性官能基を有するエチレン系共重合体からなるタフ化剤を5〜20質量%の割合で配合することが好ましい。 In this invention, what shape | molded the synthetic resin composition which mix | blended the synthetic fiber with the glass fiber which has a deformed cross section as the said holder | retainer 6 is used. Although there is no restriction | limiting in a synthetic resin, when heat resistance, fatigue resistance, etc. are considered, polyphenylene sulfide, aromatic polyamide, polyamide 46, polyamide 66, etc. are preferable. Among these, polyphenylene sulfide is most preferable because it can be used at a high temperature of 150 to 180 ° C. and has excellent chemical resistance such as ATF. However, since polyphenylene sulfide is brittle and may be damaged by impact or the like, a toughening agent composed of an ethylene-based copolymer having a reactive functional group such as glycidyl methacrylate is blended at a ratio of 5 to 20% by mass. It is preferable.
また、芳香族ポリアミドは高融点、高強度であり、130〜150℃の高温での使用が可能であり、耐薬品性にも優れることから、ポリフェニレンサルファイドに次いで好ましい。但し、ポリフェニレンサルファイドと同様に脆いため、同様にタフ化剤を配合することが好ましい。 Aromatic polyamide is preferred next to polyphenylene sulfide because it has a high melting point and high strength, can be used at a high temperature of 130 to 150 ° C., and has excellent chemical resistance. However, since it is brittle like polyphenylene sulfide, it is preferable to add a toughening agent in the same manner.
ポリアミド46も120〜140℃の耐熱性を有し、樹脂自体の衝撃強度・耐疲労性が高く、合成樹脂製保持器の破損に対して信頼性が向上するため好ましい。 Polyamide 46 is also preferable because it has a heat resistance of 120 to 140 ° C., the impact strength and fatigue resistance of the resin itself is high, and the reliability is improved against breakage of the synthetic resin cage.
ポリアミド66は、耐熱性は100〜120℃であるが、衝撃強度、耐疲労性等のバランスがよく、材料コストも低いため、低温環境で使用する場合には最も好適である。 Polyamide 66 has a heat resistance of 100 to 120 ° C., but has a good balance of impact strength, fatigue resistance and the like, and has a low material cost. Therefore, it is most suitable when used in a low temperature environment.
これら合成樹脂の分子量は、生産性を考慮して、異形断面を有するガラス繊維を含有した状態で射出成形が可能となる分子量とすることが好ましい。具体的には数平均分子量で13000〜30000が好ましく、更に衝撃強度等の機械的強度を考慮すると数平均分子量で18000〜26000がより好ましい。数平均分子量が13000未満では、分子量が低すぎて機械的強度が低く、実用性が低い。これに対して数平均分子量が30000を越える場合は、異形断面を有するガラス繊維を規定量含有した状態での溶融粘度が高すぎ、精度よく射出成形で製造することが困難になる。 The molecular weight of these synthetic resins is preferably set to a molecular weight that allows injection molding in a state of containing glass fibers having an irregular cross section in consideration of productivity. Specifically, the number average molecular weight is preferably 13,000 to 30000, and further considering the mechanical strength such as impact strength, the number average molecular weight is more preferably 18000 to 26000. When the number average molecular weight is less than 13,000, the molecular weight is too low, the mechanical strength is low, and the practicality is low. On the other hand, when the number average molecular weight exceeds 30000, the melt viscosity in a state where a prescribed amount of glass fiber having a modified cross section is contained is too high, and it becomes difficult to manufacture by injection molding with high accuracy.
異形断面を有するガラス繊維は、ぞの断面形状が円形ではないガラス繊維である。断面形状として例えばまゆ形、楕円、長円等が挙げられる。好ましくは、異形比(長径部と短径部との比率)が1.5〜5であるガラス繊維であり、2〜4であるガラス繊維がより好ましい。異形比が1.5未満では機械的強度の向上等の効果が少なく、異形比が5を越えると扁平すぎて安定して製造するのが難しくなる。また、短径部は5〜12μmであることが好ましい。短径部が5μm未満では細すぎて製造時に破断、破損するため、低コストで安定した品質を保つのが難しく、実用性が低い。一方、短径部が12μmを越える場合は、異形比を考慮すると繊維が太すぎ、樹脂中での分散性に劣るようになり、樹脂部に強度ムラが発生するおそれがある。 A glass fiber having an irregular cross section is a glass fiber having a non-circular cross section. Examples of the cross-sectional shape include eyebrows, ellipses, and ellipses. Preferably, it is a glass fiber having a deformed ratio (ratio of the major axis part to the minor axis part) of 1.5 to 5, and more preferably a glass fiber of 2 to 4. If the profile ratio is less than 1.5, the effect of improving the mechanical strength is small, and if the profile ratio exceeds 5, it is too flat and it is difficult to produce stably. Moreover, it is preferable that a short diameter part is 5-12 micrometers. If the short diameter part is less than 5 μm, it is too thin and breaks or breaks during production. Therefore, it is difficult to maintain a stable quality at low cost, and the practicality is low. On the other hand, when the minor axis exceeds 12 μm, the fiber is too thick in consideration of the deformed ratio, resulting in poor dispersibility in the resin, and unevenness in strength may occur in the resin part.
異形断面を有するガラス繊維の含有量は、樹脂組成物全量の10〜40質量%であり、好ましくは25〜30質量%である。含有率が10質量%未満では補強効果が少なく、40質量%を越える場合は、射出成形に適した流動性が得られなくなるとともに、靭性が低下して成形時の金型からの無理抜き時やころ挿入時に破損するおそれがあり、好ましくない。 Content of the glass fiber which has an irregular cross section is 10-40 mass% of the resin composition whole quantity, Preferably it is 25-30 mass%. When the content is less than 10% by mass, the reinforcing effect is small. When the content exceeds 40% by mass, fluidity suitable for injection molding cannot be obtained, and toughness is reduced and forced removal from the mold at the time of molding or There is a risk of damage when the roller is inserted, which is not preferable.
本発明で用いる異形断面を有するガラス繊維は、従来の円形断面のガラス繊維に比べて折れ難く、樹脂と混練し、射出成形した時に円形断面のガラス繊維に比べて長い状態で樹脂中に分散する。そのため、同一含有量で比較すると、円形断面のガラス繊維に比べて、機械的強度を高める効果に優れる。また、異形断面を有するガラス繊維は、成形時に保持器表面と平行に面をなすように配向するため、面で荷重を受けることができ、耐荷重性に優れるようになる。更に、径方向にも若干の補強効果が現われ、機械的強度がより高まるとともに、寸法変化の差異が小さくなるためヒケが発生し難くなる。 The glass fiber having a modified cross section used in the present invention is less likely to break than a conventional glass fiber having a circular cross section, and is dispersed in the resin in a longer state than the glass fiber having a circular cross section when kneaded with a resin and injection molded. . Therefore, when compared with the same content, the effect of increasing the mechanical strength is superior to that of glass fibers having a circular cross section. Further, since the glass fiber having an irregular cross section is oriented so as to form a plane parallel to the cage surface at the time of molding, it can receive a load on the plane and has excellent load resistance. Furthermore, a slight reinforcing effect appears in the radial direction, the mechanical strength is further increased, and the difference in dimensional change is reduced, so that sink marks are less likely to occur.
また、異形断面を有するガラス繊維は、上記した樹脂との接着性を考慮して、片末端にエポキシ基やアミノ基等を有するシランカプッリング剤、あるいはエポキシ系、ウレタン系、アクリル系等のサイジング剤で表面処理したものを用いることが好ましい。シランカップシング剤やサイジング剤は、樹脂の種類に応じて選択され、例えば、エポキシ基やアミノ基等を有するシランカップリング剤は、エポキシ基やアミノ基が樹脂のアミド結合に作用して補強効果を向上させる。 In addition, the glass fiber having an irregular cross section is a silane coupling agent having an epoxy group, an amino group or the like at one end, or an epoxy type, urethane type, acrylic type or the like in consideration of adhesiveness with the above-described resin. It is preferable to use a surface-treated product. Silane coupling agents and sizing agents are selected according to the type of resin. For example, silane coupling agents having an epoxy group, amino group, or the like have a reinforcing effect because the epoxy group or amino group acts on the amide bond of the resin. To improve.
尚、異形断面を有するガラス繊維は、得られる樹脂製保持器において、300〜900μmの繊維長を有することが好ましく、350〜600μmの繊維長であることがより好ましい。繊維長が300μm未満では、補強効果及び寸法安定効果が少なく、好ましくない。一方、樹脂との混練、射出成形を行う過程で900μmを越えるような長い繊維状態を維持するのは困難であり、繊維長の上限は製造工程に由来して設定した値である。このような繊維長とするには、混練条件や成形条件を調整すればよい。 The glass fiber having an irregular cross section preferably has a fiber length of 300 to 900 μm, more preferably 350 to 600 μm, in the obtained resin cage. If the fiber length is less than 300 μm, the reinforcing effect and the dimensional stability effect are small, which is not preferable. On the other hand, it is difficult to maintain a long fiber state exceeding 900 μm in the process of kneading with resin and injection molding, and the upper limit of the fiber length is a value set from the manufacturing process. In order to obtain such a fiber length, kneading conditions and molding conditions may be adjusted.
また、異形断面を有するガラス繊維の一部を、炭素繊維等の他の繊維状補強材、あるいはチタン酸カリウムウィスカー等のウィスカー状補強材で代替してもよい。 A part of the glass fiber having an irregular cross section may be replaced with another fibrous reinforcing material such as carbon fiber or a whisker-like reinforcing material such as potassium titanate whisker.
更に、樹脂組成物には着色剤等を添加してもよく、耐熱性が十分ではない樹脂を用いる場合には、成形時及び使用時の熱による劣化を防止するためにヨウ化物系熱安定化剤やアミン系酸化防止剤を、それぞれ単独あるいは併用して添加することが好ましい。また、耐衝撃性を改善するために、エチレンプロピレン非共役ジエンゴム(EPDM)等のゴム状物質を配合してもよい。 Furthermore, a colorant or the like may be added to the resin composition. When a resin having insufficient heat resistance is used, iodide-based heat stabilization is performed to prevent deterioration due to heat during molding and use. It is preferable to add an agent or an amine-based antioxidant alone or in combination. In order to improve the impact resistance, a rubber-like substance such as ethylene propylene non-conjugated diene rubber (EPDM) may be blended.
尚、上記の樹脂、異形断面を有するガラス繊維及びその他の配合物を用いて樹脂製保持器を製造する方法としては、生産性から、射出成形が好ましい。 In addition, from the viewpoint of productivity, injection molding is preferred as a method for producing a resin cage using the above-mentioned resin, glass fiber having a modified cross section and other blends.
以下に実施例及び比較例を挙げて本発明を更に説明するが、本発明はこれにより何ら制限されるものではない。 Examples The present invention will be further described below with reference to examples and comparative examples, but the present invention is not limited thereby.
(実施例1〜3、比較例1)
表1に示す如く、合成樹脂及びガラス繊維を用いて樹脂組成物を調製した。尚、樹脂に用いたPA66は宇部興産(株)製「UBEナイロン2020U(銅系熱安定剤含有)」であり、PA46はDJEP社製「Stanyl TW341(銅系熱安定剤含有)」であり、L−PPSはポリプラスチック(株)製「フォートロン0220A9」である。また、タフ化剤は住友化学(株)製「ボンドファーストE(エチレン−グリシジルメタクリレート(GMA)共重合体、GMA含有量12%)」である。一方、ガラス繊維については、何れもアミノ系シランカップリング剤処理品であり、実施例では長円断面ガラス繊維(日東紡績(株)製「CSG3PA-820」、異形比4、短径7μm、ウレタン系サイジング剤処理)、比較例1では平均直径約13μmの円形断面ガラス繊維を用いた。
(Examples 1 to 3, Comparative Example 1)
As shown in Table 1, a resin composition was prepared using a synthetic resin and glass fiber. In addition, PA66 used for the resin is “UBE nylon 2020U (containing copper heat stabilizer)” manufactured by Ube Industries, Ltd., and PA46 is “Stanyl TW341 (containing copper heat stabilizer)” manufactured by DJEP, L-PPS is “Fortron 0220A9” manufactured by Polyplastics Co., Ltd. The toughening agent is “Bond First E (ethylene-glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) copolymer, GMA content 12%)” manufactured by Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd. On the other hand, the glass fibers are all treated with an amino-based silane coupling agent. In the examples, glass fibers with an oblong cross section (“CSG3PA-820” manufactured by Nitto Boseki Co., Ltd., deformed ratio 4, short diameter 7 μm, urethane) System sizing agent treatment) In Comparative Example 1, circular cross-section glass fibers having an average diameter of about 13 μm were used.
そして、樹脂組成物から引張試験用及びそり量測定(ISO D−1規格)用の各試験片を作製し、引張強度及びそり量を測定した。また、樹脂組成物を射出成形して、ATやMT等で使用される自動車駆動用円錐ころ軸受とほぼ同サイズのHR30305C(d25、D62、T18.25、B17、C14)の保持器を作製し、外観観察を行った。それぞれの結果を表1に示す。 And each test piece for tensile tests and warpage amount measurement (ISO D-1 standard) was produced from the resin composition, and the tensile strength and warpage amount were measured. In addition, a resin composition is injection molded to produce a cage of HR30305C (d25, D62, T18.25, B17, C14) that is approximately the same size as a tapered roller bearing for driving an automobile used in AT, MT, etc. The appearance was observed. The results are shown in Table 1.
表1に示すように、異形断面を有するガラス繊維を配合することで、円形断面を有するガラス繊維を配合した場合と比べても機械的強度が向上する。また、そり量も少なく、幅狭の小径の保持器であっても表面にヒケの発生がなく、高精度で成形でき、しかも射出成形が可能であり生産性にも優れる。 As shown in Table 1, the mechanical strength is improved by blending glass fibers having an irregular cross section as compared with the case of blending glass fibers having a circular cross section. In addition, the amount of warpage is small, and even a narrow, small-diameter cage is free from sink marks on the surface, can be molded with high accuracy, can be injection molded, and is excellent in productivity.
1 内輪軌道
2 内輪
3 外輪軌道
4 外輪
5 円錐ころ
6 保持器
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1
Claims (1)
前記保持器が、異形断面を有するガラス繊維を10〜40質量%の割合で含有する合成樹脂組成物からなることを特徴とする自動車駆動用円錐ころ軸受。 In a tapered roller bearing for driving an automobile comprising at least an inner ring, an outer ring, a cage and a roller,
A tapered roller bearing for driving an automobile, wherein the cage is made of a synthetic resin composition containing glass fibers having an irregular cross section at a ratio of 10 to 40% by mass.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007005566A JP2008169970A (en) | 2007-01-15 | 2007-01-15 | Tapered roller bearings for driving automobiles |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007005566A JP2008169970A (en) | 2007-01-15 | 2007-01-15 | Tapered roller bearings for driving automobiles |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2008169970A true JP2008169970A (en) | 2008-07-24 |
| JP2008169970A5 JP2008169970A5 (en) | 2009-12-17 |
Family
ID=39698247
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007005566A Withdrawn JP2008169970A (en) | 2007-01-15 | 2007-01-15 | Tapered roller bearings for driving automobiles |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2008169970A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016165547A (en) * | 2012-05-24 | 2016-09-15 | サンスター スイス エスエー | Manufacturing method of interdental cleaning implement and interdental cleaning implement |
-
2007
- 2007-01-15 JP JP2007005566A patent/JP2008169970A/en not_active Withdrawn
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016165547A (en) * | 2012-05-24 | 2016-09-15 | サンスター スイス エスエー | Manufacturing method of interdental cleaning implement and interdental cleaning implement |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN107107410B (en) | Retainer for rolling bearing and rolling bearing | |
| US20140206487A1 (en) | Toothed belt | |
| JP4003035B2 (en) | Rolling bearing | |
| JP4946498B2 (en) | Resin pulley | |
| WO2022071172A1 (en) | Rolling bearing | |
| WO2013031249A1 (en) | Thrust bearing | |
| JP5358871B2 (en) | Cylinder roller bearing cage, cylindrical roller bearing | |
| US5590225A (en) | Plastic holder for bearing | |
| JP2008169970A (en) | Tapered roller bearings for driving automobiles | |
| JP2008202781A (en) | Rolling bearing | |
| JP2013167295A (en) | Rolling bearing | |
| JP2008138835A (en) | Alternator bearing | |
| JP2001317554A (en) | Cage for rolling bearing | |
| JP2007177843A (en) | Rolling bearing | |
| JP2008256166A (en) | Thrust needle roller bearing | |
| JP6697235B2 (en) | Rolling bearing | |
| JP2010053971A (en) | Retainer for rolling bearing, method of manufacturing the same, and the rolling bearing | |
| JP2007303601A (en) | Rolling bearings for hybrid vehicles | |
| JP2002130295A (en) | Method of manufacturing plastic cage for rolling bearing and rolling bearing provided with the cage | |
| JP2007170430A (en) | Rolling bearings for hybrid vehicles | |
| JP2007024187A (en) | Plastic cage for rolling bearings | |
| JPH11336765A (en) | Plastic cage for rolling bearings | |
| JP2019052706A (en) | Cage for conical roller bearing and conical roller bearing | |
| JP2010209927A (en) | Rolling bearing | |
| JP2007057011A (en) | Rolling bearing |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20091028 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20091028 |
|
| A761 | Written withdrawal of application |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A761 Effective date: 20100526 |