JP2007187260A - Resin pulley - Google Patents
Resin pulley Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2007187260A JP2007187260A JP2006006346A JP2006006346A JP2007187260A JP 2007187260 A JP2007187260 A JP 2007187260A JP 2006006346 A JP2006006346 A JP 2006006346A JP 2006006346 A JP2006006346 A JP 2006006346A JP 2007187260 A JP2007187260 A JP 2007187260A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- resin
- polyamide
- pulley
- glass fiber
- rolling bearing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Abstract
Description
本発明は、樹脂製プーリに関し、より詳しくは自動車に搭載される補機類の駆動用ベルトやその他のベルトのテンショナ用、或いはアイドラプーリ等として使用される樹脂製プーリに関する。 The present invention relates to a resin pulley, and more particularly to a resin pulley used as a driving belt for auxiliary equipment mounted on an automobile, a tensioner for other belts, an idler pulley, or the like.
従来、自動車の補機類を駆動するベルトの案内用プーリとして、転がり軸受の外周に樹脂を一体成形してなる樹脂製プーリが採用されている。樹脂製プーリにおいては、ベルトを案内する外径部の成形精度、ベルト張力に耐える強度特性、連続負荷使用による耐熱性及び耐塩化カルシウム性等が要求されている。 2. Description of the Related Art Conventionally, resin pulleys formed by integrally molding resin on the outer periphery of a rolling bearing have been adopted as guide pulleys for belts that drive automobile auxiliary machinery. Resin pulleys are required to have molding accuracy of the outer diameter portion that guides the belt, strength characteristics that can withstand belt tension, heat resistance by using a continuous load, resistance to calcium chloride, and the like.
そこで、このような成形精度、強度、耐熱性及び耐塩化カルシウム性を向上させる樹脂材料として、ガラス繊維を15〜40重量%程度充填した強化ナイロン66、強化ナイロン610、強化ナイロン612、或いはポリフェニレンサルファイドとミネラルの複合材料や、ガラス繊維を43重量%含有した6ナイロン、66ナイロン、11ナイロン、12ナイロン等のポリアミド樹脂を使用した樹脂製プーリが提案されている。このような樹脂材料に含有されるガラス繊維は、直径10〜13μmの断面円形のものが使用されている(例えば、特許文献1、2参照。)。
Therefore, as such a resin material for improving molding accuracy, strength, heat resistance and calcium chloride resistance, reinforced nylon 66, reinforced nylon 610, reinforced nylon 612, or polyphenylene sulfide filled with about 15 to 40% by weight of glass fiber. And mineral composite materials, and resin pulleys using polyamide resins such as 6 nylon, 66 nylon, 11 nylon, and 12 nylon containing 43% by weight of glass fiber have been proposed. The glass fiber contained in such a resin material has a circular cross section with a diameter of 10 to 13 μm (see, for example,
しかしながら、上記の断面円形のガラス繊維で強化したポリアミド系材料等は、耐熱性、耐疲労性に優れるものの、成形品外径部の成形精度が悪く、十分満足のいくものではなかった。特に、外径部の真円度(樹脂部の外径円周表面の凹凸量)が大きかったり、外径部表面に存在する凹凸が大きい等の不具合が生じ、それによってベルトを回転させた時に発生する音のレベルが大きくなり、使用上問題があった。 However, the polyamide-based material reinforced with the glass fiber having the circular cross section is excellent in heat resistance and fatigue resistance, but the molding accuracy of the outer diameter portion of the molded product is poor and is not sufficiently satisfactory. In particular, when the roundness of the outer diameter part (the amount of unevenness on the outer diameter circumferential surface of the resin part) is large or the unevenness existing on the outer diameter part surface is large, when the belt is rotated as a result There was a problem in use because the level of generated sound increased.
また、樹脂製プーリは、悪路走行時にベルトとの間に砂塵が入り込むと、外径部表面に摩耗が発生して上述の凹凸が大きくなったり、更に摩耗が進行してプーリの外径が小さくなると、ベルトが外れてしまう虞があった。このような摩耗は、プーリ表面に存在する充填材以外の部分から摩耗が進行し、外径部表面の面荒れが起きることで始まると推定される。 Also, if the resin pulley has sand dust in between it and the belt when traveling on rough roads, the outer surface of the outer diameter part will be worn and the unevenness will increase, or the wear will progress and the outer diameter of the pulley will increase. If it becomes smaller, there is a possibility that the belt may come off. Such wear is presumed to start when the wear progresses from a portion other than the filler present on the pulley surface and the surface of the outer diameter portion becomes rough.
本発明は、このような状況に着目してなされたものであって、外径部の成形精度の高精度化と耐摩耗性向上を併せて達成した樹脂製プーリを提供することを目的とする。 This invention is made paying attention to such a situation, and it aims at providing the resin-made pulley which achieved the high precision of the shaping | molding precision of an outer-diameter part, and the wear-resistant improvement collectively. .
上記目的を達成するために、本発明は、転がり軸受と、該転がり軸受の周囲に前記転がり軸受と一体に形成された樹脂部とを備えた樹脂製プーリにおいて、前記樹脂部が、異形断面のガラス繊維を20〜60重量%含有するポリアミド樹脂組成物からなることを特徴とする樹脂製プーリを提供する。 To achieve the above object, the present invention provides a resin pulley comprising a rolling bearing and a resin portion integrally formed with the rolling bearing around the rolling bearing, wherein the resin portion has an irregular cross section. A resin pulley comprising a polyamide resin composition containing 20 to 60% by weight of glass fiber is provided.
本発明の樹脂製プーリは、補強材に異形断面を有するガラス繊維を用いたことで、従来の円形断面のガラス繊維を用いた場合に比べて機械的強度が高く、耐摩耗性が向上し、更に外径円筒部の表面がより平滑となりベルト駆動時の音圧レベルが低くなる。 The resin pulley of the present invention uses a glass fiber having an irregular cross section as a reinforcing material, so that the mechanical strength is higher than when a conventional glass fiber having a circular cross section is used, and the wear resistance is improved. Furthermore, the surface of the outer diameter cylindrical portion becomes smoother and the sound pressure level when the belt is driven is lowered.
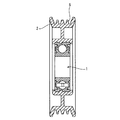
以下、本発明の実施形態について、図を参照して詳細に説明する。尚、図1は本発明にかかる樹脂製プーリの一実施形態を示す正面図であり、図2は図1のA−A線断面図である。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. FIG. 1 is a front view showing an embodiment of a resin pulley according to the present invention, and FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view taken along line AA of FIG.
図1及び図2において、樹脂製プーリは、転がり軸受1と、転がり軸受1の周囲に転がり軸受1と一体的に形成された樹脂部2とから構成されている。樹脂部2は、転がり軸受1の外輪に固着された内径円筒部3と、ベルト案内面4を有する外径円筒部5と、外径円筒部5と内径円筒部3との間に形成された円板部6とを有し、更に、該円板部6には多数のリブ7が放射状に形成されている。また、内径円筒部3には所定ピッチ円で等間隔に多数のゲート8が形成されており、これらゲート8に溶融樹脂が流し込まれ、射出成形により樹脂製プーリの製造がなされる。
1 and 2, the resin pulley includes a rolling bearing 1 and a
転がり軸受1は、図2に示すように、外輪外周部に樹脂部2の脱着を防止する凹溝9を有する接触ゴムシール付きの深溝玉軸受である。接触ゴムシール10のゴム材質としては、ニトリルゴム、水素添加ニトリルゴム、アクリルゴム等を原料とし、それに各種充填材を配合したものを用いることができる。また、転がり軸受1中に充填されているグリースとしては、使用温度を考慮して、ポリαオレフィン油、アルキルジフェニルエーテル油等を基油とし、ジウレア等を増ちょう剤とし、添加剤として酸化防止剤、摩耗防止剤等を更に加えたものが主に使用されている。
As shown in FIG. 2, the rolling
樹脂部2は、樹脂材料に補強材として異形断面を有するガラス繊維を配合した樹脂組成物からなる。樹脂材料としては、耐疲労性に優れるポリアミド6、ポリアミド66、ポリアミド46等のポリアミド樹脂をベース樹脂とすることが好ましい。また、ベース樹脂の分子量は、射出成形性を考慮すると、数平均分子量で13000〜30000、更に耐疲労性、高成形精度を考慮すると、好ましくは、数平均分子量で18000〜25000の範囲である。数平均分子量が13000未満の場合には、分子量が低すぎて、耐疲労性が低く、実用性がない。一方、数平均分子量が30000を越える場合には耐疲労性は向上するものの、プーリに必要な衝撃強度等の機械的強度を達成するために異形断面を有するガラス繊維を規定量含有させると、成形時の溶融粘度が高くなり、射出成形により高精度でプーリを製造することが難しくなる。
The
また、吸水性を低下させて、耐塩化カルシウム性を向上させるためには、これらベース樹脂に、低吸水の他のポリアミド樹脂や酸無水物で変性されたポリオリフィン樹脂等の樹脂を組み合わせたり、耐衝撃性を改善するエチレンプロピレン非共役ジエンゴム(EPDM)等のゴム状物質を組み合わせてもよい。 In addition, in order to reduce the water absorption and improve the calcium chloride resistance, these base resins may be combined with other polyamide resins with low water absorption or polyolefin resins modified with acid anhydrides, You may combine rubber-like substances, such as ethylene propylene nonconjugated diene rubber (EPDM) which improves impact property.
低吸水のポリアミド樹脂の具体例としては、ポリアミド12、ポリアミド11、ポリアミド612、ポリアミド610、ポリアミド6I6T、ポリアミドMXD6、変性ポリアミド12、変性ポリアミド6T等を使用することができる。これら低吸水性ポリアミド樹脂の混入量は、ポリアミド6、ポリアミド66、ポリアミド46等の高吸水性ポリアミド樹脂50〜90重量%に対して、10〜50重量%である。上記の低吸水性ポリアミド樹脂の中では、変性ポリアミド12は、非晶性であることから高吸水性ポリアミド樹脂との相溶性が高く、混合によって機械的強度が低下することがないため、特に好ましい。また、これら低吸水性ポリアミド樹脂は、2種類以上を混合して用いてもよく、その場合にも変性ポリアミド12と他の低吸水性ポリアミド樹脂とを組み合わせると、変性ポリアミド12が相溶化剤として機能し、混合によって機械的強度が低下することがなくなり、好ましい。
Specific examples of the low water-absorbing polyamide resin may include polyamide 12,
異形断面を有するガラス繊維は、その断面形状が円形でなければよく、例えばまゆ形、楕円、長円等の断面形状を有するガラス繊維を用いることができる。好ましくは、異形比(長径部と短径部との比率)が1.5〜5であるガラス繊維であり、2〜4であるガラス繊維がより好ましい。異形比が1.5未満では機械的強度の向上等の効果が少なく、異形比が5を越えると扁平すぎて安定して製造するのが難しくなる。また、短径部は5〜12μmであることが好ましい。短径部が5μm未満では細すぎて製造時に破断、破損するため、低コストで安定した品質を保つのが難しく、実用性が低い。一方、短径部が12μmを越える場合は、異形比を考慮すると繊維が太すぎ、樹脂中での分散性に劣るようになり、強度ムラが発生するおそれがある。 The glass fiber having an irregular cross section need not be circular in cross section, and for example, a glass fiber having a cross section such as an eyebrow shape, an ellipse, or an ellipse can be used. Preferably, it is a glass fiber having a deformed ratio (ratio of the major axis part to the minor axis part) of 1.5 to 5, and more preferably a glass fiber of 2 to 4. If the profile ratio is less than 1.5, the effect of improving the mechanical strength is small, and if the profile ratio exceeds 5, it is too flat and it is difficult to produce stably. Moreover, it is preferable that a short diameter part is 5-12 micrometers. If the short diameter part is less than 5 μm, it is too thin and breaks or breaks during production. Therefore, it is difficult to maintain a stable quality at low cost, and the practicality is low. On the other hand, when the minor axis part exceeds 12 μm, the fiber is too thick considering the profile ratio, and the dispersibility in the resin becomes inferior, which may cause unevenness in strength.
異形断面を有するガラス繊維の含有量は、樹脂組成物全量の20〜60質量%であり、好ましくは25〜50質量%である。含有量が20質量%未満では補強効果が少なく、60質量%を越える場合は、射出成形に適した流動性が得られないばかりでなく、外径円筒部5や断面部に存在するリブ7を精度良く成形するのが難しくなる。
Content of the glass fiber which has an irregular cross section is 20-60 mass% of the resin composition whole quantity, Preferably it is 25-50 mass%. When the content is less than 20% by mass, the reinforcing effect is small. When the content exceeds 60% by mass, not only fluidity suitable for injection molding can be obtained, but also the outer diameter
本発明で用いる異形断面を有するガラス繊維は、従来の円形断面のガラス繊維に比べて折れ難く、ベース樹脂と混練し、射出成形した時に円形断面のガラス繊維に比べて長い状態で樹脂中に分散する。そのため、同一含有量で比較すると、円形断面のガラス繊維に比べて、引張強さや衝撃強さ等の機械的強度を高める効果に優れる。また、異形断面を有するガラス繊維は、成形時に外径円筒部5の外表面と平行に面をなすように配向するため、ベルトとの摺動による摩耗も少なくなる。更に、繊維の長さ方向の補強効果に加えて短径部方向にも若干の補強効果が現われるため、プーリ全体に満遍なく補強効果が発現し、吸水による寸法変化を抑える効果も高まり、外径円筒部5の真円度が高くなり、表面の凹凸も小さくなる。
The glass fiber having an irregular cross section used in the present invention is less likely to break than a conventional glass fiber having a circular cross section, and is dispersed in the resin in a longer state than the glass fiber having a circular cross section when kneaded with a base resin and injection molded. To do. Therefore, when compared with the same content, the effect of increasing mechanical strength such as tensile strength and impact strength is superior to that of glass fibers having a circular cross section. In addition, since the glass fiber having an irregular cross section is oriented so as to be parallel to the outer surface of the outer diameter
また、異形断面を有するガラス繊維は、ベース樹脂との接着性を考慮して、片末端にエポキシ基やアミノ基等を有するシランカプッリング剤、あるいはエポキシ系、ウレタン系、アクリル系等のサイジング剤で表面処理したものを用いることが好ましい。シランカップシング剤やサイジング剤は、ベース樹脂の種類に応じて選択され、例えば、エポキシ基やアミノ基等を有するシランカップリング剤は、エポキシ基やアミノ基がポリアミド樹脂のアミド結合に作用して補強効果を向上させる。 In addition, the glass fiber having an irregular cross-section is a silane coupling agent having an epoxy group or an amino group at one end, or a sizing agent such as an epoxy type, a urethane type, or an acrylic type in consideration of adhesiveness with the base resin. It is preferable to use a surface-treated product. Silane coupling agents and sizing agents are selected according to the type of base resin. For example, silane coupling agents having an epoxy group or amino group have an epoxy group or amino group acting on the amide bond of the polyamide resin. Improve the reinforcement effect.
尚、異形断面を有するガラス繊維は、得られる樹脂製プーリにおいて、300〜900μmの繊維長を有することが好ましく、350〜600μmの繊維長であることがより好ましい。繊維長が300μm未満では、補強効果及び寸法安定効果が少なく、好ましくない。一方、ベース樹脂との混練、射出成形を行う過程で900μmを越えるような長い繊維状態を維持するのは困難であり、繊維長の上限は製造工程に由来して設定した値である。このような繊維長とするには、混練条件や成形条件を調整すればよい。 In addition, it is preferable that the glass fiber which has a deformed cross section has a fiber length of 300-900 micrometers in the resin pulley obtained, and it is more preferable that it is a fiber length of 350-600 micrometers. If the fiber length is less than 300 μm, the reinforcing effect and the dimensional stability effect are small, which is not preferable. On the other hand, it is difficult to maintain a long fiber state exceeding 900 μm in the process of kneading with the base resin and injection molding, and the upper limit of the fiber length is a value set from the manufacturing process. In order to obtain such a fiber length, kneading conditions and molding conditions may be adjusted.
また、異形断面を有するガラス繊維の一部を、炭素繊維等の他の繊維状補強材、あるいはチタン酸カリウムウィスカー等のウィスカー状補強材で代替してもよい。 A part of the glass fiber having an irregular cross section may be replaced with another fibrous reinforcing material such as carbon fiber or a whisker-like reinforcing material such as potassium titanate whisker.
樹脂組成物には、更に着色剤等を添加してもよい。また、放熱性を向上させるために、熱伝導率が10W/m・K以上の高熱伝導性充填材、具体的には、アルミナ、マグネシア、窒化アルミニウム、炭化珪素、ベリリア、グラファイト等を更に添加してもよい。更に、外径円筒部5の凹凸を更に減少させたり、外径円筒部5の耐摩耗性を更に向上させるために、粒子状充填材、具体的には、炭酸カルシウム、クレー、タルク、シリカ、ウォラストナイト等を添加してもよい。粒子状充填材としては、上記説明した高熱伝導性充填材も粒子状であれば、同様の効果を有する。また、成形時及び使用時の熱による劣化を防止するために、樹脂材料にヨウ化物系熱安定剤やアミン系酸化防止剤を、それぞれ単独あるいは併用して添加することが好ましい。
A colorant or the like may be further added to the resin composition. In order to improve heat dissipation, a high thermal conductive filler having a thermal conductivity of 10 W / m · K or more, specifically, alumina, magnesia, aluminum nitride, silicon carbide, beryllia, graphite, etc. are further added. May be. Furthermore, in order to further reduce the unevenness of the outer diameter
以下に、本発明の実施例について説明するが、本発明はこれにより何ら制限されるものではない。 Examples of the present invention will be described below, but the present invention is not limited thereto.
(実施例1)
ポリアミド66(宇部興産(株)製「UBEナイロン2026U」、数平均分子量26000、ヨウ化銅系添加剤含有)70質量%、断面長円形のガラス繊維(日東紡績(株)製「CSG 3PA−820」、異形比4、短径部7μm、ウレタン系サイジング剤処理)30質量%の樹脂組成物を、外輪外周部に凹溝を有する接触ゴムシール付き深溝玉軸受(6203DDL18)をコアにして、軸受の外輪と金型との間に形成される空間部にインサート成形(射出成形)を行い、樹脂製プーリを得た。
Example 1
Polyamide 66 ("UBE Nylon 2026U" manufactured by Ube Industries, Ltd., number average molecular weight 26000, containing copper iodide-based additive) 70% by mass, oblong glass fiber ("CSG 3PA-820" manufactured by Nittobo Co., Ltd.) ”, Profile ratio 4,
(実施例2)
ベース樹脂としてポリアミド46(DJEP製「Stanyl TW341」、銅系熱安定剤含有)を用いた以外は、実施例1と同様にして樹脂製プーリを得た。
(Example 2)
A resin pulley was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that polyamide 46 ("Stanyl TW341" manufactured by DJEP, containing a copper heat stabilizer) was used as the base resin.
(実施例3)
ベース樹脂として、ポリアミド66(宇部興産(株)製「UBEナイロン2026U」、数平均分子量26000、ヨウ化銅系添加剤含有)とポリアミド612(ダイセルデフザ(株)製「ベスタミドDX9301」との1:1混合物を用いた以外は、実施例1と同様にして樹脂製プーリを得た。
(Example 3)
As a base resin, 1: 1 of polyamide 66 (“UBE nylon 2026U” manufactured by Ube Industries, Ltd., number average molecular weight 26000, containing copper iodide-based additive) and polyamide 612 (“Vestamide DX9301” manufactured by Daicel Defusa Co., Ltd.) A resin pulley was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the mixture was used.
(比較例1)
ガラス繊維含有ポリアミド66(宇部興産(株)製「UBEナイロン2020GU6」、数平均分子量20000、ヨウ化銅系添加剤含有、直径13μmのシランカップリング剤処理したガラス繊維を30質量%含有)を、外輪外周部に凹溝を有する接触ゴムシール付き深溝玉軸受(6203DDL18)をコアにして、軸受の外輪と金型との間に形成される空間部にインサート成形(射出成形)を行い、樹脂製プーリを得た。
(Comparative Example 1)
Glass fiber-containing polyamide 66 (“UBE nylon 2020GU6” manufactured by Ube Industries, Ltd., containing a number average molecular weight of 20,000, containing a copper iodide-based additive, containing 30% by mass of glass fiber treated with a silane coupling agent having a diameter of 13 μm), A deep groove ball bearing (6203DDL18) with a contact rubber seal having a groove on the outer ring outer peripheral part is used as a core, and insert molding (injection molding) is performed in a space formed between the outer ring of the bearing and a mold, and a resin pulley Got.
[外径円筒部成形精度評価]
実施例1〜3及び比較例1の各樹脂製プーリについて、外径円筒部の中間高さでの凹凸量を測定した。測定結果を表1に示す。
[Outside cylindrical part forming accuracy evaluation]
About each resin pulley of Examples 1-3 and Comparative Example 1, the unevenness | corrugation amount in the intermediate height of an outer diameter cylindrical part was measured. The measurement results are shown in Table 1.
[外径円筒部耐摩耗性評価]
図3は本耐摩耗性試験で使用した耐摩耗性試験機42の構成を示す。耐摩耗性試験機42は、駆動モータ(図示せず)に繋がった駆動輪44と従動輪46とを備える。駆動輪44と従動輪46にはベルト48が架け渡されて連結されている。そして、駆動輪44と従動輪46間には、試験対象となる樹脂製プーリ11がベルト案内面31をベルト48と接触させながら取り付け可能としている。尚、この樹脂製プーリ11の転がり軸受には、下向きに980Nの荷重が掛けられており、この荷重によって樹脂製プーリ11のベルト案内面31がベルト48に押し付けられている。そして、駆動輪44が回転するとベルト48を介して従動輪46が回転駆動され、ベルト48に押し付けられたベルト案内面31が回転される。また、耐摩耗性試験機42において、恒温槽50中の雰囲気は120℃に維持されており、更にこの雰囲気中には、関東ローム粉JIS#8が空間容積で0.02%の条件を満足するようにファンによって漂わせてある。この恒温槽50中の雰囲気は、自動車の補機類に使用される樹脂製プーリが悪路走行中にあることを再現したものである。
[Abrasion resistance evaluation of outer cylindrical part]
FIG. 3 shows the configuration of the
そして、実施例1〜3及び比較例1の各樹脂製プーリを耐摩耗性試験機42に取り付け、8000min−1で回転させた。100時間回転させた後、耐摩耗性試験機42を停止させて、樹脂製プーリを室温まで冷却し、樹脂製プーリ11のベルト案内面31の半径方向摩耗量を、基準位置(軸方向中央部)で測定した。摩耗量を表1に併せて示す。
Then, each of the resin pulleys of Examples 1 to 3 and Comparative Example 1 was attached to the
表1から明らかなように、異形断面を有するガラス繊維を用いることにより、異方性の低下と外径円筒部5の表面と平行にガラス繊維が配向することにより、外径部凹凸量の低下、耐摩耗性の向上が図られることがわかった。
As is clear from Table 1, by using glass fibers having a modified cross section, the decrease in anisotropy and the amount of irregularities in the outer diameter portion are reduced due to the orientation of the glass fibers parallel to the surface of the outer diameter
尚、本実施形態では、前述した実施形態に限定されるものではなく、適宜変更、改良等が可能である。上記実施形態では、外周円筒部がフラット形状の樹脂製プーリについて説明してきたが、図4に示すような外周円筒部5がVリブ状の樹脂製プーリや、転がり軸受と別体で成形される構成の樹脂製プーリについても適用可能である。
In addition, in this embodiment, it is not limited to embodiment mentioned above, A change, improvement, etc. are possible suitably. In the above embodiment, the outer peripheral cylindrical portion has been described with respect to a flat resin pulley, but the outer peripheral
1 転がり軸受
2 樹脂部
3 内径円筒部
4 ベルト案内面
5 外径円筒部
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (1)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006006346A JP2007187260A (en) | 2006-01-13 | 2006-01-13 | Resin pulley |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006006346A JP2007187260A (en) | 2006-01-13 | 2006-01-13 | Resin pulley |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2007187260A true JP2007187260A (en) | 2007-07-26 |
| JP2007187260A5 JP2007187260A5 (en) | 2009-01-15 |
Family
ID=38342564
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006006346A Pending JP2007187260A (en) | 2006-01-13 | 2006-01-13 | Resin pulley |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2007187260A (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105840786A (en) * | 2016-06-06 | 2016-08-10 | 吉林大学 | Unsupported automatic tension sprocket wheel |
| US9635971B2 (en) | 2010-12-22 | 2017-05-02 | Nestec S.A. | System of a container for storing and dispensing a product and a machine for dosing the product |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH02173047A (en) * | 1988-12-26 | 1990-07-04 | Polyplastics Co | Fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin composition |
| JP2004340256A (en) * | 2003-05-15 | 2004-12-02 | Nsk Ltd | Resin-made pulley |
-
2006
- 2006-01-13 JP JP2006006346A patent/JP2007187260A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH02173047A (en) * | 1988-12-26 | 1990-07-04 | Polyplastics Co | Fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin composition |
| JP2004340256A (en) * | 2003-05-15 | 2004-12-02 | Nsk Ltd | Resin-made pulley |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9635971B2 (en) | 2010-12-22 | 2017-05-02 | Nestec S.A. | System of a container for storing and dispensing a product and a machine for dosing the product |
| CN105840786A (en) * | 2016-06-06 | 2016-08-10 | 吉林大学 | Unsupported automatic tension sprocket wheel |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4946498B2 (en) | Resin pulley | |
| JP2007070592A (en) | Rubber composition, method for producing rubber composition, and friction drive belt | |
| JP4171899B2 (en) | Resin pulley | |
| EP1394442B1 (en) | Resin pulley | |
| CN104011432A (en) | Sliding Element For Use In An Engine Or Chain Transmission Apparatus | |
| JP2007187260A (en) | Resin pulley | |
| JP2015010225A (en) | Resin composition and seal member | |
| JP4389624B2 (en) | Synthetic resin pulley | |
| JP2007107614A (en) | Cage for rolling bearing | |
| JP2007002968A (en) | Resin pulley | |
| JP4352508B2 (en) | Resin pulley | |
| JP2007192386A (en) | Pulley device | |
| JP4572844B2 (en) | Resin pulley | |
| US20070272781A1 (en) | Resin pulley | |
| JP2005076859A (en) | Pulley made of resin, and its manufacturing method | |
| JP2016161010A (en) | Resin pulley | |
| CN1203129C (en) | Polyether aromatic ketone resin composition and film and sheet | |
| JP2007177843A (en) | Rolling bearing | |
| JP2009222110A (en) | Resin pulley | |
| JP4375081B2 (en) | Resin pulley | |
| JP6616920B1 (en) | Toothed pulley | |
| JP2008157440A (en) | High load transmission belt | |
| JP2004262615A (en) | Guide shoe of elevator | |
| KR101776410B1 (en) | A resin composition for timing chain guide | |
| JP2006145044A (en) | Resin pulley |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20071128 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20081120 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20081120 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100824 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20100826 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100930 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20101102 |