JP2006207343A - Floor material - Google Patents
Floor material Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2006207343A JP2006207343A JP2005024233A JP2005024233A JP2006207343A JP 2006207343 A JP2006207343 A JP 2006207343A JP 2005024233 A JP2005024233 A JP 2005024233A JP 2005024233 A JP2005024233 A JP 2005024233A JP 2006207343 A JP2006207343 A JP 2006207343A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- layer
- resin
- flooring
- decorative
- impregnated
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Abstract
Description
本発明は、木質系基材と、この木質系基材に装飾層を設けた床材に関し、さらに詳しくは、耐擦傷性や耐汚染性、特に耐キャスター性や耐落下衝撃性に優れた床材に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a wood base material and a floor material provided with a decorative layer on the wood base material, and more particularly, a floor having excellent scratch resistance and contamination resistance, particularly caster resistance and drop impact resistance. It relates to materials.
従来から、木質系基材に化粧シートを貼着した床材が知られている。前記化粧シートとしては、床材として求められる表面物性、すなわち、耐擦傷性や耐汚染性を確保する意味から、通常は表面に硬化型樹脂からなる表面保護層が設けられている。また、床材に用いられる前記木質系基材としては、通常はラワン材を用いた合板が用いられているが、このような合板からなる床材はキャスター付き家具のキャスター部、あるいは、椅子や机等の脚部先端部に荷重が掛かった場合に、その表面に傷が付いたり、あるいは、凹んだりし易いという問題や合板表面の凹凸がそのまま化粧シート表面に現出して意匠性を損ない易いという問題があった(たとえば、特許文献1参照)。 Conventionally, flooring materials in which a decorative sheet is attached to a wooden base material are known. As the decorative sheet, a surface protective layer made of a curable resin is usually provided on the surface in order to ensure surface physical properties required for a flooring material, that is, scratch resistance and stain resistance. In addition, as the wooden base material used for flooring, a plywood using Lauan material is usually used, but the flooring made of such a plywood is a caster part of furniture with casters, or a chair or When a load is applied to the tip of a leg of a desk or the like, the surface is easily scratched or dented, and the unevenness of the plywood surface appears on the surface of the decorative sheet as it is, and the design is likely to be impaired. (For example, refer to Patent Document 1).
そこで、木質系基材として前記化粧シートを貼着する側の前記合板の面に中密度繊維板、いわゆるMDFを積層した複合材を用いた床材が採用されるようになり、上記した合板からなる木質系基材を用いた床材の問題を解決することができたが、このような中密度繊維板を用いた複合基材からなる床材は合板単体からなる床材に比べて、それだけコストが高い上に、中密度繊維板は水を吸収して膨らみ、床面に波打ちが生じ易いために、水が床に飛散し易い台所等の床には使い辛いという問題があった。
そこで本発明は、上記問題に鑑みてなされたものであって、その目的の第1は、水の影響を受け難く、耐擦傷性や耐汚染性等の表面物性に優れることは言うに及ばず、特に、キャスター等に荷重が掛かった場合においても、すなわち耐キャスター性においても表面に傷や凹みが付き難く、耐落下衝撃性においても優れる床材を提供することである。また、本発明の目的の第2は、凹凸の少ない平滑性に優れた外観を有する床材を提供することである。 Therefore, the present invention has been made in view of the above problems, and it is needless to say that the first object of the present invention is hardly affected by water and is excellent in surface physical properties such as scratch resistance and contamination resistance. In particular, even when a load is applied to a caster or the like, that is, to provide a flooring material that is less likely to have scratches or dents on the surface in terms of caster resistance and that is excellent in drop impact resistance. A second object of the present invention is to provide a flooring material having an appearance with few irregularities and excellent smoothness.
本発明者は、上記課題を達成するために、請求項1記載の本発明は、合板の一方の面に樹脂含浸材硬化層を積層した複合材の前記樹脂含浸材硬化層面に接着剤層と装飾層が順に積層されると共に前記装飾層の表層に電離放射線硬化型樹脂からなる表面保護層が設けられた床材において、前記樹脂含浸材硬化層が30g/m2以上の坪量からなるガラスペーパーに熱硬化型樹脂を含浸させた樹脂含浸材を前記合板の一方の面に熱圧着して一体成形された層であることを特徴とするものである。 In order to achieve the above object, the inventor of the present invention is characterized in that the present invention according to claim 1 includes an adhesive layer on the resin impregnated cured layer surface of a composite material in which a resin impregnated cured layer is laminated on one surface of a plywood. In a flooring in which decoration layers are sequentially laminated and a surface protective layer made of an ionizing radiation curable resin is provided on the surface of the decoration layer, the resin-impregnated material cured layer has a basis weight of 30 g / m 2 or more. It is a layer integrally formed by thermocompression bonding a resin impregnated material obtained by impregnating paper with a thermosetting resin to one surface of the plywood.
また、請求項2記載の本発明は、請求項1記載の床材において、前記樹脂含浸材硬化層が複層からなることを特徴とするものである。
The present invention according to
また、請求項3記載の本発明は、請求項1、2のいずれかに記載の床材において、前記装飾層が合成樹脂製シート基材からなる化粧シートであることを特徴とするものである。
Further, the present invention according to
また、請求項4記載の本発明は、請求項3記載の床材において、前記合成樹脂製シート基材がオレフィン系熱可塑性樹脂からなることを特徴とするものである。 According to a fourth aspect of the present invention, in the flooring according to the third aspect, the synthetic resin sheet base material is made of an olefinic thermoplastic resin.
また、請求項5記載の本発明は、請求項3、4のいずれかに記載の床材において、前記表面保護層が前記合成樹脂製シート基材にアクリル樹脂とウレタン樹脂の共重合体とイソシアネートとから形成されたプライマー層を介して形成されていることを特徴とするものである。
Further, the present invention according to
また、請求項6記載の本発明は、請求項3記載の床材において、前記装飾層が前記合成樹脂製シート基材からなる化粧シートの前記接着剤層側の面にバッカー材を積層したものであることを特徴とするものである。
Further, the present invention according to
また、請求項7記載の本発明は、請求項1、2のいずれかに記載の床材において、前記装飾層が紙系シート基材からなる化粧シートであることを特徴とするものである。
The present invention according to
また、請求項8記載の本発明は、請求項1〜7のいずれかに記載の床材において、前記表面保護層が微粒子を含有した層であることを特徴とするものである。
The invention according to
また、請求項9記載の本発明は、請求項1、2のいずれかに記載の床材において、前記装飾層が突板であることを特徴とするものである。
The present invention according to claim 9 is characterized in that, in the flooring according to any one of
また、請求項10記載の本発明は、請求項1〜9のいずれかに記載の床材において、前記合板の他方の面に樹脂含浸材硬化層を積層すると共に、該樹脂含浸材硬化層が硬化型樹脂を含浸させた樹脂含浸材を前記合板の他方の面に熱圧着して一体成形された層であることを特徴とするものである。このように構成することにより、加工時や時間経過に伴う複合材しいては床材の反りや捩れを防止することができる。 The present invention according to claim 10 is the flooring according to any one of claims 1 to 9, wherein the resin impregnated cured layer is laminated on the other surface of the plywood, The resin impregnated material impregnated with a curable resin is a layer integrally formed by thermocompression bonding to the other surface of the plywood. By configuring in this way, it is possible to prevent warping or twisting of the flooring material of the composite material during processing or over time.
本発明の床材は、樹脂含浸材硬化層を坪量が30g/m2以上のガラスペーパーに熱硬化型樹脂を含浸させた樹脂含浸材により形成したことにより、前記樹脂含浸材硬化層に硬さを付与することができ、耐キャスター性等においても、表面に傷や凹みが付き難く、耐落下衝撃性においても優れた効果を奏すると共に凹凸の少ない平滑性に優れた外観を有するという効果を奏し、また、装飾層の表層に電離放射線硬化型樹脂からなる表面保護層を設けたことにより、耐擦傷性や耐汚染性に優れた効果を奏するものである。 In the flooring of the present invention, the resin impregnated cured layer is formed of a resin impregnated material obtained by impregnating a glass paper having a basis weight of 30 g / m 2 or more with a thermosetting resin. In terms of caster resistance, etc., the surface is less likely to be scratched or dented, has excellent effects in terms of drop impact resistance, and has an excellent appearance with less unevenness and smoothness. In addition, by providing a surface protective layer made of an ionizing radiation curable resin on the surface of the decorative layer, an effect excellent in scratch resistance and contamination resistance is exhibited.
上記の本発明について、図面等を用いて以下に詳しく説明する。
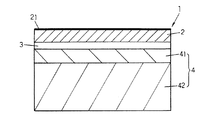
図1は本発明にかかる床材の基本的な層構成を図解的に示す図、図2は本発明の床材を構成する表層に表面保護層を備えた装飾層の第1実施形態を図解的に示す層構成図、図3は本発明の床材を構成する表層に表面保護層を備えた装飾層の第2実施形態を図解的に示す層構成図、図4は本発明の床材を構成する表層に表面保護層を備えた装飾層の第3実施形態を図解的に示す層構成図、図5は本発明の床材を構成する表層に表面保護層を備えた装飾層の第4実施形態を図解的に示す層構成図であり、図中の1は床材、2,2’は装飾層、3,3’,3”は接着剤層、4は複合材、5,5’,5”はプライマー層、6は凹凸模様、7はワイピングインキ、8は絵柄印刷層、8’はベタ柄印刷層、9はバッカー材、21は表面保護層、22は合成樹脂製透明シート、22’は合成樹脂製シート、23は紙系シート、41は樹脂含浸紙硬化層、42は合板、αは微粒子をそれぞれ示す。
The present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the drawings.
FIG. 1 is a diagram schematically showing a basic layer structure of a flooring according to the present invention, and FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a first embodiment of a decorative layer having a surface protective layer on the surface layer constituting the flooring of the present invention. FIG. 3 is a layer configuration diagram schematically showing a second embodiment of a decorative layer having a surface protective layer on the surface layer constituting the floor material of the present invention, and FIG. 4 is a floor material of the present invention. Fig. 5 is a layer configuration diagram schematically showing a third embodiment of a decorative layer provided with a surface protective layer on the surface layer constituting Fig. 5, and Fig. 5 shows a decorative layer provided with a surface protective layer on the surface layer constituting the flooring of the present invention. 4 is a layer configuration diagram schematically showing an embodiment, in which 1 is a flooring, 2, 2 'is a decorative layer, 3, 3', 3 "are adhesive layers, 4 is a composite material, 5, 5 ', 5' is a primer layer, 6 is an uneven pattern, 7 is a wiping ink, 8 is a pattern printing layer, 8 'is a solid printing layer, 9 is a backer material, 21 is a surface protective layer, 22 is a synthetic resin A transparent sheet, 22 'is a synthetic resin sheet, 23 is a paper-based sheet, 41 is a resin-impregnated paper cured layer, 42 is a plywood, and α is a fine particle.
図1は本発明にかかる床材の基本的な層構成を図解的に示す図であって、床材1は合板42上に樹脂含浸材硬化層41が積層された複合材4の前記樹脂含浸材硬化層41上に接着剤層3を介して電離放射線硬化型樹脂からなる表面保護層21を有する装飾層2が設けられたものである。また、前記樹脂含浸材硬化層41は、前記合板42の表面凹凸が床材1とした際に表層に現出するのを防止すると共に、床材1とした際に耐落下衝撃性や耐キャスター性を向上させるために設けるものである。前記合板42としては、たとえば、ラワン材や松材からなる合板を挙げることができ、繊維方向が異なる単板を一層毎に複数層、たとえば、3層、5層、7層を配置したものであって、表層の繊維方向が合板の長手方向と平行に構成されたもの、あるいは、表層の繊維方向が合板の長手方向と直交する方向に構成されたものの、いずれであってもよいものである。また、図示はしないが、前記合板42の側端部には雌実、雄実からなる実部が設けられ、床材1同士の前記雌実、前記雄実を嵌合させて床材1が床下地上に敷設される。
FIG. 1 is a diagram schematically showing a basic layer structure of a flooring according to the present invention. The flooring 1 is the resin impregnation of a composite material 4 in which a cured resin impregnating
前記樹脂含浸材硬化層41としては、熱硬化型樹脂をガラスペーパーに含浸させた樹脂含浸材を用いて、前記樹脂含浸材を前記合板42上に載置して熱圧成形することにより前記合板42と一体化した複合材4を得ることができる。この熱圧成形条件としては、使用する熱硬化型樹脂により異なるが、たとえば、温度130〜160℃、圧力7〜13kg/cm2、加圧時間20〜120秒程度である。熱硬化型樹脂としては、たとえば、不飽和ポリエステル樹脂、1液ないし2液硬化型ポリウレタン樹脂、エポキシ樹脂、アミノアルキッド樹脂、フェノール樹脂、尿素樹脂、ジアリルフタレート樹脂、メラミン樹脂、グアナミン樹脂、メラミン−尿素共縮合樹脂、珪素樹脂、ポリシロキサン樹脂等を例示することができ、これらの1種ないし2種以上を混合して用いることができる。また、熱硬化型樹脂を含浸させる基材としての坪量が30g/m2以上のガラスペーパーとしては、Eガラス繊維が好ましく、しかも50%以上含有しているものである。残分としてはパルプ繊維等の抄紙に適合性がある繊維であればよいものであり、坪量としては大きいほど好ましいものであるが、より好ましくは50g/m2以上であり、コストや作業性を勘案すると60g/m2以下である。坪量が30g/m2未満の場合は耐落下衝撃性において十分に満足できる効果が得られない。また、ガラス繊維は6〜20μmの太さで、長さが5〜30mmのカット繊維を主成分とするガラス繊維からなるものが適当であり、太さが6μm未満の場合は、耐落下衝撃性において、ガラスペーパーを用いた効果が望めず、20μm超の場合は、耐落下衝撃性において、一層の向上効果が望めず、コストを勘案すると用いない方がよい。カット繊維の長さは抄紙性を考慮すると5〜30mmが適当である。上記した太さや長さのカット繊維を主成分とするガラス繊維からなる坪量が30g/m2以上、好ましくは50g/m2以上のガラスペーパーを用いることにより、耐落下衝撃性に優れると共に表面平滑性に優れた床材とすることができるものであり、ガラスペーパーに代えて、たとえば、太さが100μm以上のガラスクロス(ガラス織布)を用いた場合は、織目が表面に現出するために意匠性において好ましくなく、繊維太さや坪量が上記した範囲のガラスペーパーが好ましいものである。また、ガラスペーパーに硬化型樹脂を含浸させる方法としては、液状化した熱硬化型樹脂を浸漬法やロールコート法、グラビアコート法等の周知の両面ないし片面塗布により含浸させると共に乾燥させればよいものである。熱硬化型樹脂のウエット状態の塗布量としては、概ね50〜300g/m2、好ましくは70〜250g/m2である。また、ガラスペーパーは必要に応じてシランカップリング剤やチタンカップリング剤等の周知の易接着処理剤で処理してもよいものである。
As the resin impregnated material cured
また、前記樹脂含浸材硬化層41は、必要に応じて、無機充填剤を含んだものであってもよいのであって、無機充填剤としては、たとえば、粉末状の酸化アルミニウム、炭化珪素、二酸化珪素、チタン酸カルシウム、チタン酸バリウム、マグネシウムパイロボレート、酸化亜鉛、窒化珪素、酸化ジルコニウム、酸化クロム、酸化鉄、窒化硼素、ダイヤモンド、金剛砂等を例示することができる。
Further, the resin impregnated cured
なお、図示はしないが、前記樹脂含浸材硬化層41を合板42の両面に設けた構成からなる複合材としてもよいものであって、このように構成した複合材は前記複合材4と比べて加工時の反りや捩れ、あるいは、時間経過に伴う複合材しいては床材の反りや捩れを防止することができる。なお、前記合板42の他方の面、すなわち、前記装飾層2を設ける面と反対側の面に設ける前記樹脂含浸材硬化層41は、加工時の反りや捩れ、あるいは、床材とした際の反りや捩れの点から、前記装飾層2側に設ける前記樹脂含浸材硬化層41と同じ材料で形成するのが好ましいが、前記合板42への水分の浸入や前記合板42からの水分の放出を防止できればよいという観点であれば、含浸させる基材としてはガラスペーパーに限ることはなく、たとえば、薄葉紙、クラフト紙、チタン紙等の紙基材や綿布、あるいは、各種素材からなる織布や不織布等の布基材を挙げることができ、その坪量としては概ね30〜120g/m2が適当であり、基材に含浸させる熱硬化型樹脂としては上記したものと同じ樹脂を用いることができる。
Although not shown in the drawing, a composite material having a structure in which the resin impregnated cured
次に、後述する電離放射線硬化型樹脂からなる表面保護層21を備えた装飾層2と前記複合材4の前記樹脂含浸材硬化層41とを積層する前記接着剤層3について説明する。前記接着剤層3としては、ポリオール成分とイソシアネート成分からなる2液硬化型ポリウレタン系接着剤を用いて周知のドライラミネーション法で形成すればよい。前記ポリオール成分としては、ポリエステルポリオール、ポリエステルポリウレタンポリオール、ポリエーテルポリオール、ポリエーテルポリウレタンポリオール等を挙げることができ、イソシアネート成分としては、TDI、MDI、HDI、PIDI、XDI等のジイソシアネートおよびこれらを出発原料とする変性体を挙げることができるが、塗布量や作業性および作業環境を考慮すると、湿気硬化型ホットメルト接着剤が好ましい。
Next, the said
湿気硬化型ホットメルト接着剤は、分子末端にイソシアネート基を有するプレポリマーを必須成分とする組成物である。前記プレポリマーは、通常は分子両末端にイソシアネート基をそれぞれ1個以上有するポリイソシアネートプレポリマーであり、常温で固体の熱可塑性樹脂の状態にあるものである。イソシアネート基同士が空気中の水分により反応して鎖延長反応を起こし、分子鎖中に尿素結合を有する反応物を生じ、この尿素結合にさらに分子末端のイソシアネート基が反応し、ビューレット結合を起こして分岐し、架橋反応を起こす。分子末端にイソシアネート基を有するプレポリマーの分子鎖の骨格構造は任意であるが、具体的には、ウレタン結合を有するポリウレタン骨格、エステル結合を有するポリエステル骨格、ポリブタジエン骨格等である。これらの1種ないし2種以上の骨格構造を適宜採用することにより、接着剤物性を調整することができる。なお、分子鎖中にウレタン結合がある場合は、このウレタン結合とも末端イソシアネート基が反応して、アロファネート結合を生じ、このアロファネート結合によっても架橋反応を起こす。 The moisture-curing hot melt adhesive is a composition containing a prepolymer having an isocyanate group at a molecular terminal as an essential component. The prepolymer is usually a polyisocyanate prepolymer having one or more isocyanate groups at both molecular ends, and is in the state of a thermoplastic resin that is solid at room temperature. Isocyanate groups react with each other by moisture in the air to cause chain extension reaction, resulting in a reaction product having a urea bond in the molecular chain, and the isocyanate group at the end of the molecule reacts with this urea bond, causing a burette bond. Branches and causes a crosslinking reaction. The skeleton structure of the molecular chain of the prepolymer having an isocyanate group at the molecular terminal is arbitrary, and specific examples include a polyurethane skeleton having a urethane bond, a polyester skeleton having an ester bond, and a polybutadiene skeleton. Adhesive properties can be adjusted by appropriately employing one or more skeleton structures. In addition, when there is a urethane bond in the molecular chain, the terminal isocyanate group reacts with this urethane bond to produce an allophanate bond, and this allophanate bond also causes a crosslinking reaction.
ポリイソシアネートプレポリマーの具体例としては、たとえば、ポリオールに過剰のイソシアネートを反応させた分子末端にイソシアネート基を有し、かつ、分子鎖中にウレタン結合を有するポリウレタン骨格の、ウレタンプレポリマーがある。また、特開昭64−14287号公報に開示されているような、ポリイソシアネートにポリエステルポリオールとポリブタジエン骨格を有するポリオールとを任意の順序で加えて付加反応させて得られたポリエステル骨格とポリブタジエン骨格とがウレタン結合により結合された構造を有し、かつ、分子末端にイソシアネート基を有する結晶性ウレタンプレポリマー、あるいは、特開平2−305882号公報に開示されているような、ポリカーボネート系ポリオールとポリイソシアネートを反応させて得られる分子中に2個以上のイソシアネート基を有するポリカーボネート系ウレタンプレポリマー、ポリエステル系ポリオールとポリイソシアネートを反応させて得られる分子中に2個以上のイソシアネート基を有するポリエステル系ウレタンプレポリマー等が挙げられる。 Specific examples of the polyisocyanate prepolymer include a urethane prepolymer having a polyurethane skeleton having an isocyanate group at a molecular terminal obtained by reacting an excess isocyanate with a polyol and having a urethane bond in the molecular chain. Further, as disclosed in JP-A No. 64-14287, a polyester skeleton and a polybutadiene skeleton obtained by adding a polyester polyol and a polyol having a polybutadiene skeleton to polyisocyanate in an arbitrary order and performing an addition reaction A crystalline urethane prepolymer having a structure in which is bonded by a urethane bond and having an isocyanate group at the molecular end, or a polycarbonate-based polyol and a polyisocyanate as disclosed in JP-A-2-305882 A polycarbonate urethane prepolymer having two or more isocyanate groups in the molecule obtained by reacting the polyester, and a polyester urethane having two or more isocyanate groups in the molecule obtained by reacting the polyester polyol and polyisocyanate. Emissions prepolymers, and the like.
また、湿気硬化型ホットメルト接着剤としては、上記した各種ポリイソシアネートプレポリマーの他に、各種物性を調節するために、上記した必須反応成分に、必要に応じて、熱可塑性樹脂、粘着付与剤、可塑剤、充填剤等の各種副材料を添加することもできる。これらの副材料としては、たとえば、エチレン−酢酸ビニル共重合体、低分子量ポリエチレン、変性ポリオレフィン、アタクチックポリプロピレン、線状ポリエステル、エチレン−エチルアクリレート(EAA)、エチレン−メタクリレート(EMA)、2−ヒドロキシエチルメタクリレート(HEMA)等の熱可塑性樹脂、テルペン−フェノール樹脂、アビエチン酸ロジンエステル等の粘着付与剤、炭酸カルシウム、硫酸バリウム、シリカ、アルミナ等の微粉末からなる充填剤(体質顔料)、着色顔料、硬化触媒、水分除去剤、貯蔵安定剤、老化防止剤等である。 In addition to the above-mentioned various polyisocyanate prepolymers, the moisture-curable hot-melt adhesive includes, as necessary, the above-described essential reaction components, thermoplastic resins, and tackifiers. Various sub-materials such as plasticizers and fillers can also be added. Examples of these secondary materials include ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer, low molecular weight polyethylene, modified polyolefin, atactic polypropylene, linear polyester, ethylene-ethyl acrylate (EAA), ethylene-methacrylate (EMA), 2-hydroxy. Thermoplastic resins such as ethyl methacrylate (HEMA), terpene-phenol resins, tackifiers such as rosin ester of abietic acid, fillers (external pigments) composed of fine powders such as calcium carbonate, barium sulfate, silica, and alumina, coloring pigments , Curing catalyst, moisture remover, storage stabilizer, anti-aging agent and the like.
上記した湿気硬化型ホットメルト接着剤の塗布量は、固形分として概ね20〜90g/m2、好ましくは40〜60g/m2である。接着剤の塗布面は、前記装飾層2の前記表面保護層21の反対面であってもよいし、前記樹脂含浸材硬化層41面であってもよいものである。
The coating amount of moisture-curable hot-melt adhesives described above are generally 20~90g / m 2 as solids, preferably 40 to 60 g / m 2. The adhesive application surface may be the surface opposite to the surface
次に、電離放射線硬化型樹脂からなる表面保護層21を有する装飾層2について説明する。図2は本発明の床材を構成する表層に表面保護層を備えた装飾層の第1実施形態を図解的に示す層構成図であって、装飾層2は合成樹脂製シート基材としての合成樹脂製透明シート22の一方の面にエンボス加工を施して凹凸模様6を設け、その上からワイピング処理を施して前記凹凸模様6の凹部内にワイピングインキ7を充填した後に、表出面全面にプライマー層5を設けると共に前記合成樹脂製透明シート22の他方の面にプライマー層5’を介して絵柄印刷層8、ベタ柄印刷層8’を順に印刷形成した合成樹脂製シート基材からなる化粧シートであって、該化粧シートの前記プライマー層5上に電離放射線硬化型樹脂からなる表面保護層21を形成したものである。この装飾層2は該装飾層2の前記ベタ柄印刷層82と前記複合材4の前記樹脂含浸材硬化層41とが前記接着剤層3を介して貼合される。
Next, the
図3は本発明の床材を構成する表層に表面保護層を備えた装飾層の第2実施形態を図解的に示す層構成図であって、装飾層2は合成樹脂製シート基材としての合成樹脂製シート22’の少なくとも一方の面にプライマー層5”を設け、該プライマー層5”上にベタ柄印刷層8’、絵柄印刷層8を順に印刷形成し、さらに前記絵柄印刷層8側の面全面に前記接着剤層3で説明した、ポリオール成分とイソシアネート成分からなる2液硬化型ポリウレタン系接着剤で形成した接着剤層3’を介して合成樹脂製透明シート22が周知のドライラミネーション法で貼合され、該合成樹脂製透明シート22の表面にエンボス加工を施して凹凸模様6を設け、その後、図2に示したと同様に、凹凸模様6の上からワイピング処理を施して前記凹凸模様6の凹部内にワイピングインキ7を充填し、さらに表面にプライマー層5を設けた合成樹脂製シート基材からなる化粧シートであって、該化粧シートの前記プライマー層5上に電離放射線硬化型樹脂からなる表面保護層21を形成したものである。この装飾層2は該装飾層2の前記合成樹脂製シート22’と前記複合材4の前記樹脂含浸材硬化層41とが前記接着剤層3を介して貼合される。前記合成樹脂製シート22’は、一般的には着色シートが用いられるが、無着色シートであってもよい。なお、図2、3に示した装飾層2は、エンボス加工とワイピング処理した実施態様を示したが、本発明に供する装飾層2はこれに限るものではなく、表面平滑性に優れた鏡面仕上げの装飾層であってもよいものである。
FIG. 3 is a layer configuration diagram schematically showing a second embodiment of a decorative layer having a surface protective layer on the surface layer constituting the flooring of the present invention. The
図4は本発明の床材を構成する表層に表面保護層を備えた装飾層の第3実施形態を図解的に示す層構成図であって、装飾層2は紙系シート基材としての紙系シート23の一方の面にベタ柄印刷層8’、絵柄印刷層8を順に印刷形成した紙系シート基材からなる化粧シートであって、前記絵柄印刷層8側の面全面に微粒子αを含有した電離放射線硬化型樹脂からなる表面保護層21を形成したものである。この装飾層2は該装飾層2の前記紙系シート23と前記複合材4の前記樹脂含浸材硬化層41とが前記接着剤層3を介して貼合される。
FIG. 4 is a layer configuration diagram schematically showing a third embodiment of a decorative layer provided with a surface protective layer on the surface layer constituting the flooring of the present invention, wherein the
次に、前記装飾層2を構成する諸材料について説明する。まず、前記合成樹脂製透明シート22および前記合成樹脂製シート22’としては、加工適性に優れ、燃焼時に有害なガスを発生しないことなどから、飽和ポリエステル樹脂や低密度ポリエチレン(線状低密度ポリエチレンを含む)、中密度ポリエチレン、高密度ポリエチレン、ホモポリプロピレン、エチレンαオレフィン共重合体、ポリメチルペンテン、ポリブテン、エチレン−プロピレン共重合体、プロピレン−ブテン共重合体、エチレン−酢酸ビニル共重合体、エチレン−酢酸ビニル共重合体ケン化物、あるいは、これらの混合物等のオレフィン系熱可塑性樹脂を挙げることができるが、比較的安価であることを考慮すると前記オレフィン系熱可塑性樹脂が好ましい。前記合成樹脂製透明シート22および前記合成樹脂製シート22’は未延伸の状態、あるいは、一軸ないし二軸方向に延伸した状態のいずれの状態であってもよいものであって、厚さとしては概ね60〜300μm程度である。また、これらのシートは必要に応じて必要な面にコロナ放電処理、プラズマ処理、オゾン処理等の周知の易接着処理を施してもよいものである。
Next, various materials constituting the
また、前記紙系シート23としては、薄葉紙、クラフト紙、チタン紙、リンター紙、板紙、石膏ボード紙、上質紙、コート紙、アート紙、硫酸紙、グラシン紙、パーチメント紙、パラフィン紙、和紙等を挙げることができるし、ガラス繊維、石綿、チタン酸カリウム繊維、アルミナ繊維、シリカ繊維、炭素繊維等の無機質繊維、ポリエステル、ビニロン等の有機樹脂等を用いた織布ないし不織布等を挙げることができるが、織布は織目が表面に現出するために意匠性から用いない方がよい。
Examples of the paper-based
また、前記絵柄印刷層8および前記ベタ柄印刷層8’としては、グラビア印刷法、オフセット印刷法、シルクスクリーン印刷法等の周知の印刷法でインキを用いて形成することができる。前記絵柄印刷層8としては、たとえば、木目模様、石目模様、布目模様、皮紋模様、幾何学模様、文字、記号、線画、各種抽象模様柄であり、前記ベタ柄印刷層8’としては隠蔽性を有する着色インキでベタ印刷したものである。図2〜4においては、前記絵柄印刷層8と前記ベタ柄印刷層8’の両印刷層を設けた構成を示したが、いずれか一方の構成であってもよいものである。
The
また、前記絵柄印刷層8および前記ベタ柄印刷層8’を形成するインキとしては、ビヒクルとして塩素化ポリエチレン、塩素化ポリプロピレン等の塩素化ポリオレフィン、ポリエステル、イソシアネートとポリオールとからなるポリウレタン、ポリアクリル、ポリ酢酸ビニル、ポリ塩化ビニル、塩化ビニル−酢酸ビニル共重合体、セルロース系樹脂、ポリアミド樹脂等を1種ないし2種以上混合して用い、これに顔料、溶剤、各種補助剤等を加えてインキ化したものを用いることができ、環境問題を考慮すると、ポリエステル、イソシアネートとポリオールからなるポリウレタン、ポリアクリル、ポリ酢酸ビニル、セルロース系樹脂、ポリアミド系樹脂等の1種ないし2種以上混合した非塩素系のビヒクルが適当であり、より好ましくはポリエステル、イソシアネートとポリオールからなるポリウレタン、ポリアクリル、ポリアミド系樹脂等の1種ないし2種以上混合したものである。また、前記ワイピングインキ7についても、上記したインキを用いればよいものである。
Examples of the ink for forming the
次に、前記表面保護層21を形成する電離放射線硬化型樹脂について説明する。電離放射線硬化型樹脂としては、分子中に、(メタ)アクリロイル基、(メタ)アクリロイルオキシ基等のラジカル重合性不飽和基、またはエポキシ基等のカチオン重合性官能基を有する単量体、プレポリマーまたはポリマーからなる。これら単量体、プレポリマーまたはポリマーは、単体で用いるか、あるいは、複数種混合して用いる。なお、本明細書で(メタ)アクリレートとは、アクリレートないしメタアクリレートの意味で用いる。また、電離放射線とは、電磁波ないし荷電粒子線のうち分子を重合あるいは架橋し得るエネルギー量子を有するものを意味し、通常は紫外線ないし電子線である。
Next, the ionizing radiation curable resin for forming the surface
ラジカル重合性不飽和基を有するプレポリマーとしては、ポリエステル(メタ)アクリレート、ウレタン(メタ)アクリレート、エポキシ(メタ)アクリレート、メラミン(メタ)アクリレート、トリアジン(メタ)アクリレート、ポリビニルピロリドン等が挙げられる。このプレポリマーは、通常、分子量が10000程度以下のものが用いられる。分子量が10000を超えると硬化した樹脂層の耐擦傷性、耐摩耗性、耐薬品性、耐熱性等の表面物性が不足する。上記のアクリレートとメタアクリレートとは共用し得るが、電離放射線での架橋硬化速度という点ではアクリレートの方が速いため、高速度、短時間で能率よく硬化させるという目的ではアクリレートの方が有利である。 Examples of the prepolymer having a radical polymerizable unsaturated group include polyester (meth) acrylate, urethane (meth) acrylate, epoxy (meth) acrylate, melamine (meth) acrylate, triazine (meth) acrylate, and polyvinylpyrrolidone. This prepolymer usually has a molecular weight of about 10,000 or less. When the molecular weight exceeds 10,000, the cured resin layer has insufficient surface properties such as scratch resistance, abrasion resistance, chemical resistance, and heat resistance. The acrylate and methacrylate can be used in common, but the acrylate is more advantageous for the purpose of curing efficiently at a high speed and in a short time because the acrylate is faster in terms of the crosslinking curing rate with ionizing radiation. .
カチオン重合性官能基を有するプレポリマーとしては、ビスフェノール型エポキシ樹脂、ノボラック型エポキシ樹脂、脂環型エポキシ樹脂等のエポキシ系樹脂、脂肪族系ビニルエーテル、芳香族系ビニルエーテル、ウレタン系ビニルエーテル、エステル系ビニルエーテル等のビニルエーテル系樹脂、環状エーテル化合物、スピロ化合物等のプレポリマーが挙げられる。 Examples of the prepolymer having a cationically polymerizable functional group include epoxy resins such as bisphenol type epoxy resins, novolac type epoxy resins, and alicyclic epoxy resins, aliphatic vinyl ethers, aromatic vinyl ethers, urethane vinyl ethers, and ester vinyl ethers. And prepolymers such as vinyl ether resins, cyclic ether compounds, and spiro compounds.
ラジカル重合性不飽和基を有する単量体の例としては、(メタ)アクリレート化合物の単官能単量体として、メチル(メタ)アクリレート、エチル(メタ)アクリレート、ブチル(メタ)アクリレート、メトキシエチル(メタ)アクリレート、メトキシブチル(メタ)アクリレート、ブトキシエチル(メタ)アクリレート、2エチルヘキシル(メタ)アクリレート、N,N−ジメチルアミノメチル(メタ)アクリレート、N,N−ジメチルアミノエチル(メタ)アクリレート、N,N−ジエチルアミノエチル(メタ)アクリレート、N,N−ジエチルアミノプロピル(メタ)アクリレート、N,N−ジベンジルアミノエチル(メタ)アクリレート、ラウリル(メタ)アクリレート、イソボニル(メタ)アクリレート、エチルカルビトール(メタ)アクリレート、フェノキシエチル(メタ)アクリレート、フェノキシポリエチレングリコール(メタ)アクリレート、テトラヒドロフルフリル(メタ)アクリレート、メトキシプロピレングリコール(メタ)アクリレート、2−(メタ)アクリロイルオキシエチル−2−ヒドロキシプロピルフタレート、2−(メタ)アクリロイルオキシプロピルハイドロゲンテレフタレート等が挙げられる。 Examples of monomers having a radically polymerizable unsaturated group include (meth) acrylate compound monofunctional monomers such as methyl (meth) acrylate, ethyl (meth) acrylate, butyl (meth) acrylate, methoxyethyl ( (Meth) acrylate, methoxybutyl (meth) acrylate, butoxyethyl (meth) acrylate, 2-ethylhexyl (meth) acrylate, N, N-dimethylaminomethyl (meth) acrylate, N, N-dimethylaminoethyl (meth) acrylate, N , N-diethylaminoethyl (meth) acrylate, N, N-diethylaminopropyl (meth) acrylate, N, N-dibenzylaminoethyl (meth) acrylate, lauryl (meth) acrylate, isobornyl (meth) acrylate, ethyl carbitol ( Me ) Acrylate, phenoxyethyl (meth) acrylate, phenoxypolyethylene glycol (meth) acrylate, tetrahydrofurfuryl (meth) acrylate, methoxypropylene glycol (meth) acrylate, 2- (meth) acryloyloxyethyl-2-hydroxypropyl phthalate, 2 -(Meth) acryloyloxypropyl hydrogen terephthalate and the like.
また、ラジカル重合性不飽和基を有する多官能単量体として、エチレングリコールジ(メタ)アクリレート、ジエチレングリコールジ(メタ)アクリレート、トリエチレングリコールジ(メタ)アクリレート、プロピレングリコールジ(メタ)アクリレート、ジプロピレングリコール(メタ)アクリレート、ネオペンチルグリコールジ(メタ)アクリレート、1,6−ヘキサンジオールジ(メタ)アクリレート、1,9−ノナンジオールジ(メタ)アクリレート、テトラエチレングリコールジ(メタ)アクリレート、トリプロピレングリコールジ(メタ)アクリレート、ビスフェノール−A−ジ(メタ)アクリレート、トリメチロールプロパントリ(メタ)アクリレート、トリメチロールプロパンエチレンオキサイドトリ(メタ)アクリレート、ペンタエリスリトールトリ(メタ)アクリレート、ペンタエリスリトールテトラ(メタ)アクリレート、ジペンタエリスリトールペンタ(メタ)アクリレート、ジペンタエリスリトールヘキサ(メタ)アクリレート、グリセリンポリエチレンオキサイドトリ(メタ)アクリレート、トリス(メタ)アクリロイルオキシエチルフォスフェート等が挙げられる。 In addition, as a polyfunctional monomer having a radical polymerizable unsaturated group, ethylene glycol di (meth) acrylate, diethylene glycol di (meth) acrylate, triethylene glycol di (meth) acrylate, propylene glycol di (meth) acrylate, di Propylene glycol (meth) acrylate, neopentyl glycol di (meth) acrylate, 1,6-hexanediol di (meth) acrylate, 1,9-nonanediol di (meth) acrylate, tetraethylene glycol di (meth) acrylate, tri Propylene glycol di (meth) acrylate, bisphenol-A-di (meth) acrylate, trimethylolpropane tri (meth) acrylate, trimethylolpropane ethylene oxide tri (meth) acrylate , Pentaerythritol tri (meth) acrylate, pentaerythritol tetra (meth) acrylate, dipentaerythritol penta (meth) acrylate, dipentaerythritol hexa (meth) acrylate, glycerin polyethylene oxide tri (meth) acrylate, tris (meth) acryloyloxy Examples thereof include ethyl phosphate.
カチオン重合性官能基を有する単量体は、上記カチオン重合性官能基を有するプレポリマーの単量体を用いることができる。 As the monomer having a cationic polymerizable functional group, a prepolymer monomer having the cationic polymerizable functional group can be used.
上記した電離放射線硬化型樹脂を、紫外線を照射することにより硬化させる場合には、増感剤として光重合開始剤を添加する。ラジカル重合性不飽和基を有する樹脂系の場合の光重合開始剤は、アセトフェノン類、ベンゾフェノン類、チオキサントン類、ベンゾイン、ベンゾイン、ベンゾインメチルエーテル、ミヒラーベンゾイルベンゾエート、ミヒラーケトン、ジフェニルサルファイド、ジベンジルジサルファイド、ジエチルオキサイト、トリフェニルビイミダゾール、イソプロピル−N,N−ジメチルアミノベンゾエート等を単独ないし混合して用いることができる。また、カチオン重合性官能基を有する樹脂系の場合は、芳香族ジアゾニウム塩、芳香族スルホニウム塩、メタロセン化合物、ベンゾインスルホン酸エステル、フリールオキシキソニウムジアリルヨードシル塩等を単独ないし混合物として用いることができる。なお、これら光重合開始剤の添加量は、一般に、電離放射線硬化型樹脂100重量部に対して、0.1〜10重量部程度である。前記表面保護層21の形成方法としては、前記した電離放射線硬化型樹脂を溶液化し、グラビアコート法やロールコート法等の周知の塗布方法で前記合成樹脂製透明シート22あるいは前記紙系基材23の所定の面に塗布することにより形成することができる。塗布量としては、固形分として概ね5〜200g/m2が適当であり、好ましくは15〜30g/m2である。
When the above-mentioned ionizing radiation curable resin is cured by irradiating with ultraviolet rays, a photopolymerization initiator is added as a sensitizer. In the case of a resin system having a radical polymerizable unsaturated group, photoinitiators include acetophenones, benzophenones, thioxanthones, benzoin, benzoin, benzoin methyl ether, Michler benzoylbenzoate, Michler ketone, diphenyl sulfide, dibenzyl disulfide , Diethyl oxide, triphenylbiimidazole, isopropyl-N, N-dimethylaminobenzoate and the like can be used alone or in combination. In the case of a resin system having a cationically polymerizable functional group, an aromatic diazonium salt, an aromatic sulfonium salt, a metallocene compound, a benzoin sulfonic acid ester, a freeroxyxonium diallyl iodosyl salt, etc. should be used alone or as a mixture. Can do. In addition, generally the addition amount of these photoinitiators is about 0.1-10 weight part with respect to 100 weight part of ionizing radiation curable resins. As the method for forming the surface
次に、電離放射線硬化型樹脂からなる前記表面保護層21に、一層の耐擦傷性や耐摩耗性を付与する場合には、酸化アルミニウム、炭化珪素、二酸化珪素、チタン酸カルシウム、チタン酸バリウム、マグネシウムパイロボレート、酸化亜鉛、窒化珪素、酸化ジルコニウム、酸化クロム、酸化鉄、窒化硼素、ダイヤモンド、金剛砂、黒鉛等の無機粒子、あるいは、架橋アクリル等の合成樹脂からなるビーズなどの有機粒子等の微粒子α(図4参照)を加えることにより達成することができる。前記微粒子α(図4参照)は微粒子表面に突起や角のあるものでもよいが、突起や角のない真球状、楕円上、あるいは、これらに近い形状が加工適性の点から、また、靴底等を摩耗させない点等から好ましい。前記微粒子αの平均粒子径としては、前記表面保護層21の塗膜厚さにより選択して用いる必要があるが、基本的には前記微粒子αが前記表面保護層21から一部表出するように選択すべきであり、通常、平均粒径としては5〜100μm程度のものである。また、前記微粒子αの電離放射線硬化型樹脂100重量部に対する割合は1〜50重量部、好ましくは5〜20重量部である。なお、実施例においては、前記微粒子αを図4に示した第3実施形態の装飾層2の表面保護層21にのみ含有させたものを示したが、図2、3の第1実施形態、第2実施形態の装飾層2の前記表面保護層21に含有させてもよいものである。
Next, when the surface
次に、前記プライマー層5、5’、5”について説明する。前記プライマー層5は前記合成樹脂製透明シート22と前記表面保護層21との接着強度を向上させる目的で設けるものであり、前記プライマー層5’は前記合成樹脂製透明シート22と前記絵柄印刷層8ならびに前記ベタ柄印刷層8’との接着強度を向上させる目的で設けるものであり、前記プライマー層5”は前記合成樹脂製シート22’と前記ベタ柄印刷層8’との接着強度を向上させる目的で設けるものである。以下、前記プライマー層5、5’、5”を総称してプライマー層と呼称する。このプライマー層としては、(i)アクリル樹脂とウレタン樹脂との共重合体と、(ii)イソシアネートとからなる樹脂で形成されたものである。すなわち、(i)のアクリル樹脂とウレタン樹脂との共重合体は、末端に水酸基を有するアクリル重合体成分(成分A)、両末端に水酸基を有するポリエステルポリオール成分(成分B)、ジイソシアネート成分(成分C)を配合して反応させてプレポリマーとなし、該プレポリマーにさらにジアミンなどの鎖延長剤(成分D)を添加して鎖延長することで得られるものである。この反応によりポリエステルウレタンが形成されると共にアクリル重合体成分が分子中に導入され、末端に水酸基を有するアクリル−ポリエステルウレタン共重合体が形成される。このアクリル−ポリエステルウレタン共重合体の末端の水酸基を(ii)のイソシアネートと反応させて硬化させたものが前記プライマー層である。
Next, the primer layers 5, 5 ′, 5 ″ will be described. The
前記成分Aは、末端に水酸基を有する直鎖状のアクリル酸エステル重合体が用いられる。具体的には、末端に水酸基を有する直鎖状のポリメチルメタクリレート(PMMA)が耐候性(特に光劣化に対する特性)に優れ、ウレタンと共重合させて相溶化するのが容易である点から好ましい。前記成分Aは、共重合体においてアクリル樹脂成分となるものであり、分子量5000〜7000(重量平均分子量)のものが耐候性、接着性が特に良好であるために好ましく用いられる。また、前記成分Aは、両末端に水酸基を有するもののみを用いてもよいが、片末端に共役二重結合が残っているものを上記の両末端に水酸基を有するものと混合して用いてもよいものである。共役二重結合が残っているアクリル重合体を混合することにより、前記プライマー層と接する層、たとえば、前記表面保護層21の電離放射線硬化型樹脂とアクリル重合体の共役二重結合が反応するために電離放射線硬化型樹脂との間の接着性を向上させることができる。
As the component A, a linear acrylate polymer having a hydroxyl group at the terminal is used. Specifically, linear polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) having a hydroxyl group at the terminal is preferable because it is excellent in weather resistance (particularly the property against photodegradation) and can be easily copolymerized with urethane. . The component A is an acrylic resin component in the copolymer, and those having a molecular weight of 5000 to 7000 (weight average molecular weight) are preferably used because of particularly good weather resistance and adhesiveness. In addition, the component A may be used only having a hydroxyl group at both ends, but a mixture having a conjugated double bond at one end is mixed with the above-mentioned one having a hydroxyl group at both ends. Is also good. By mixing the acrylic polymer in which the conjugated double bond remains, the conjugated double bond of the layer contacting the primer layer, for example, the ionizing radiation curable resin of the surface
前記成分Bは、ジイソシアネートと反応してポリエステルウレタンを形成し、共重合体においてウレタン樹脂成分を構成するものである。前記成分Bは、両末端に水酸基を有するポリエステルジオールが用いられる。このポリエステルジオールとしては、芳香族ないしスピロ環骨格を有するジオール化合物とラクトン化合物ないしその誘導体、またはエポキシ化合物との付加反応生成物、二塩基酸とジオールとの縮合生成物、および、環状エステル化合物から誘導されるポリエステル化合物等を挙げることができる。上記ジオールとしては、エチレングリコール、プロピレングリコール、ジエチレングリコール、ブタンジオール、ヘキサンジオール、メチルペンテンジオール等の短鎖ジオール、1,4−シクロヘキサンジメタノール等の脂環族短鎖ジオール等を挙げることができる。また、上記二塩基酸としては、アジピン酸、フタル酸、イソフタル酸、テレフタル酸等を挙げることができる。ポリエステルポリオールとして好ましいのは、酸成分としてアジピン酸ないしアジピン酸とテレフタル酸の混合物、特にアジピン酸が好ましく、ジオール成分として3−メチルペンタンジオールおよび1,4−シクロヘキサンジメタノールを用いたアジペート系ポリエステルである。 Component B reacts with diisocyanate to form polyester urethane and constitutes a urethane resin component in the copolymer. The component B is a polyester diol having hydroxyl groups at both ends. Examples of the polyester diol include an addition reaction product of a diol compound having an aromatic or spiro ring skeleton and a lactone compound or a derivative thereof, or an epoxy compound, a condensation product of a dibasic acid and a diol, and a cyclic ester compound. Examples thereof include a derived polyester compound. Examples of the diol include short-chain diols such as ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, diethylene glycol, butanediol, hexanediol, and methylpentenediol, and alicyclic short-chain diols such as 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol. Examples of the dibasic acid include adipic acid, phthalic acid, isophthalic acid, terephthalic acid, and the like. Preferred as the polyester polyol is adipate-based polyester using adipic acid or a mixture of adipic acid and terephthalic acid as the acid component, particularly preferably adipic acid, and 3-methylpentanediol and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol as the diol component. is there.
前記プライマー層において、前記成分Bと前記成分Cとが反応して形成されるウレタン樹脂成分は、前記プライマー層に柔軟性を与え、前記合成樹脂製透明シート22あるいは前記合成樹脂製シート22’との接着性に寄与する。また、アクリル重合体からなるアクリル樹脂成分は、前記プライマー層において耐候性および耐ブロッキング性に寄与する。ウレタン樹脂において、前記成分Bの分子量は前記プライマー層に柔軟性を十分に発揮可能なウレタン樹脂が得られる範囲であればよく、アジピン酸ないしアジピン酸とテレフタル酸の混合物と、3−メチルペンタンジオールおよび1,4−シクロヘキサンジメタノールからなるポリエステルジオールの場合、500〜5000(重量平均分子量)が好ましい。
In the primer layer, the urethane resin component formed by the reaction of the component B and the component C gives the primer layer flexibility, and the synthetic resin
前記成分Cは、1分子中に2個のイソシアネート基を有する脂肪族ないし脂環族のジイソシアネート化合物が用いられる。このジイソシアネートとしては、たとえば、テトラ目チレンジイソシアネート、2,2,4(2,4,4)−1,6−ヘキサメチレンジイソシアネート、イソホロンジイソシアネート、4,4’−ジシクロヘキシルメタンジイソシアネート、1,4’−シクロヘキシルジイソシアネート等を挙げることができる。ジイソシアネート成分としては、イソホロンジイソシアネートが物性およびコストが優れる点で好ましい。上記の成分A〜Cを反応させる場合のアクリル重合体、ポリエステルポリオールおよび後述する鎖延長剤の合計の水酸基(アミノ基の場合もある)と、イソシアネート基の当量比はイソシアネート基が過剰となるようにする。 As the component C, an aliphatic or alicyclic diisocyanate compound having two isocyanate groups in one molecule is used. As this diisocyanate, for example, tetra-ethylene diisocyanate, 2,2,4 (2,4,4) -1,6-hexamethylene diisocyanate, isophorone diisocyanate, 4,4′-dicyclohexylmethane diisocyanate, 1,4′- Examples thereof include cyclohexyl diisocyanate. As the diisocyanate component, isophorone diisocyanate is preferable in terms of excellent physical properties and cost. When the above-mentioned components A to C are reacted, the equivalent ratio of the total hydroxyl group (may be an amino group) of the acrylic polymer, polyester polyol and chain extender described below and the isocyanate group is such that the isocyanate group becomes excessive. To.
上記の三成分A、B、Cを60〜120℃で2〜10時間程度反応させると、ジイソシアネートのイソシアネート基がポリエステルポリオール末端の水酸基と反応してポリエステルウレタン樹脂成分が形成されると共にアクリル重合体末端の水酸基にジイソシアネートが付加した化合物も混在し、過剰のイソシアネート基および水酸基が残存した状態のプレポリマーが形成される。このプレポリマーに鎖延長剤として、たとえば、イソホロンジアミン、ヘキサメチレンジアミン等のジアミンを加えてイソシアネート基を前記鎖延長剤と反応させ、鎖延長することでアクリル重合体成分がポリエステルウレタンの分子中に導入され、末端に水酸基を有する(i)のアクリル−ポリエステルウレタン共重合体を得ることができる。 When the above three components A, B and C are reacted at 60 to 120 ° C. for about 2 to 10 hours, the isocyanate group of the diisocyanate reacts with the hydroxyl group at the end of the polyester polyol to form a polyester urethane resin component and an acrylic polymer. A compound in which a diisocyanate is added to a terminal hydroxyl group is also mixed, and a prepolymer is formed in a state where excess isocyanate groups and hydroxyl groups remain. As a chain extender, for example, a diamine such as isophorone diamine or hexamethylene diamine is added to this prepolymer, the isocyanate group is reacted with the chain extender, and the chain is extended so that the acrylic polymer component is contained in the polyester urethane molecule. The (i) acrylic-polyester urethane copolymer introduced and having a hydroxyl group at the terminal can be obtained.
(i)のアクリル−ポリエステルウレタン共重合体に、(ii)のイソシアネートを加えると共に、塗布法、乾燥後の塗布量を考慮して必要な粘度に調節した塗布液となし、グラビアコート法、ロールコート法等の周知の塗布法で塗布することにより前記プライマー層を形成することができる。プライマー層の乾燥後の塗布量としては、1〜20g/m2であり、好ましくは1〜5g/m2である。また、このプライマー層は、必要に応じてシリカ粉末などの充填剤、光安定剤、着色剤等の添加剤を添加した層としてもよいものである。また、(ii)のイソシアネートとしては、(i)のアクリル−ポリエステルウレタン共重合体の水酸基と反応して架橋硬化させることが可能なものであればよく、たとえば、2価以上の脂肪族ないし芳香族イソシアネートが使用でき、特に熱変色防止、耐候性の点から脂肪族イソシアネートが望ましい。具体的には、トリレンジイソシアネート、キシリレンジイソシアネート、4,4’−ジシクロヘキシルメタンジイソシアネート、ヘキサメチレンジイソシアネート、リジンジイソシアネートの単量体、または、これらの2量体、3量体などの多量体、あるいは、これらのイソシアネートをポリオールに付加した誘導体(アダクト体)のようなポリイソシアネートなどを挙げることができる。なお、図2、図3の装飾層2においては、プライマー層(図2、3上、符号5、5’、5”で示した層)を設けた構成のものを示したが、これは、床材としての高レベルの要求に応える仕様であり、床材としての要求レベルが低い場合にはこれらプライマー層(図2、3上、符号5、5’、5”で示した層)は必ず設けなければならないものでもないし、また、図4において、前記紙系シート23と前記ベタ柄印刷層8’との間、あるいは、前記ベタ柄印刷層8’および前記絵柄印刷層8と前記表面保護層21との間に上記したプライマー層を設けて接着強度を向上させるなり、あるいは、前記ベタ柄印刷層8’および前記絵柄印刷層8の表面保護をするなりして高レベルの要求に応える仕様としてもよいものである。
Addition of isocyanate of (ii) to acrylic-polyester urethane copolymer of (i), coating method, coating solution adjusted to necessary viscosity in consideration of coating amount after drying, gravure coating method, roll The primer layer can be formed by coating by a known coating method such as a coating method. The coating amount after drying of the primer layer is from 1 to 20 g / m 2, preferably from 1 to 5 g / m 2. The primer layer may be a layer to which an additive such as a filler such as silica powder, a light stabilizer, or a colorant is added as necessary. The isocyanate of (ii) is not limited as long as it can be crosslinked and cured by reacting with the hydroxyl group of the acrylic-polyester urethane copolymer of (i). An aliphatic isocyanate can be used, and an aliphatic isocyanate is particularly desirable from the viewpoint of thermal discoloration prevention and weather resistance. Specifically, tolylene diisocyanate, xylylene diisocyanate, 4,4′-dicyclohexylmethane diisocyanate, hexamethylene diisocyanate, lysine diisocyanate monomer, or a multimer such as dimer or trimer thereof, or And polyisocyanates such as derivatives (adducts) obtained by adding these isocyanates to polyols. In addition, in the
また、前記凹凸模様6は加熱プレスやヘアライン加工などにより形成することができ、その模様としては、たとえば、導管溝、石板表面凹凸、布表面テクスチュア、梨地、砂目、ヘアライン、万線条溝、鏡面等である。
Moreover, the said uneven |
また、図5は本発明の床材を構成する表層に表面保護層を備えた装飾層の第4実施形態を図解的に示す層構成図であって、装飾層2’は図3に示した第2実施形態の装飾層2の前記合成樹脂製シート22’の面に、先に説明した前記接着剤層3と同じ樹脂からなる接着剤層3”を介してバッカー材9を積層したものであって、これ以外は図3に示した第2実施形態と同じである。この場合は、図示はしないが、図1に示した前記装飾層2に代えて前記装飾層2’を用いて、前記装飾層2’の前記バッカー材9と前記複合材4の前記樹脂含浸材硬化層41とが前記接着剤層3を介して貼合されて床材1となる。前記バッカー材9としては、昨今の環境問題を考慮してハロゲン元素を分子構造中に含まない樹脂が適当であり、たとえば、ポリプロピレン、エチレン−ビニルアルコール共重合体、ポリメチレン、ポリメチルペンテン、ポリエチレンテレフタレート、ポリブチレンテレフタレート、ポリカーボネート、ポリアリレート、ポリエチレンナフタレート−イソフタレート共重合体、ポリイミド、ポリスチレン、ポリアミド、ABS等の樹脂からなるシート、あるいは、結晶性ポリエチレンテレフタレートシート(いわゆるC−PET)や非晶性ポリエチレンテレフタレートシート(いわゆるA−PET)、あるいは、耐熱性の高いポリアルキレンテレフタレートシート〔いわゆる、イーストマンケミカルカンパニー製PET−G(商品名)〕などを例示することができ、厚さとしては概ね200〜500μmが適当である。これらのシートは単層であってもよいし、複層であってもよいし、また、用いる樹脂は単独であってもよいし、混合物であってもよい。また、前記バッカー材9は必要な面に、必要に応じてコロナ放電処理、オゾン処理、プラズマ処理等の易接着処理を施すことができる。なお、図示はしないが、前記バッカー材9を図2に示した第1実施形態の装飾層2の裏面(表面保護層21の反対面)に適用してもよいものである。
FIG. 5 is a layer configuration diagram schematically showing a fourth embodiment of the decorative layer having a surface protective layer on the surface layer constituting the flooring of the present invention, and the
なお、今までは、表層に表面保護層21を設けた装飾層2、2’ということで説明してきたが、本発明の床材はこれに限ることはなく、たとえば、図2、3、5における前記プライマー層5および/ないし前記表面保護層21を形成する前の装飾層2、2’を前記複合材4に積層した後に前記プライマー層5および/ないし前記表面保護層21を設けるように構成してもよいし、また、図4における前記表面保護層21を形成する前の装飾層2を前記複合材4に積層した後に前記表面保護層21を設けるように構成してもよいものである。また、図示はしないが、図2〜5に示した装飾層2、2’に代えて、厚さが0.15〜0.7mm、好ましくは0.15〜0.3mmのカシ、ナラ、セン、ブナ、ケヤキ、カシ等の突板を用いてもよいものである。この場合は、当然のことながら、表面保護層21は複合材4に突板を積層した後に設けるものである。また、図示はしないが、図2〜5に示した装飾層2、2’に代えて、ポリプロピレンフィルムの一方の面に上記した突板を貼合して後に前記ポリプロピレンフィルム側からエンボス加工を施し、その後に前記ポリプロピレンフィルム面に電離放射線硬化型樹脂からなる表面保護層を設けた積層材を用いてもよいものである。なお、突板を用いる仕様にあっては、突板の裏面(合板側となる面)に干割れ防止や加工性を考慮して紙や不織布を貼合してもよいものである。
Heretofore, the description has been made with the
次に、本発明について、以下に実施例を挙げてさらに詳しく説明する。 Next, the present invention will be described in more detail with reference to the following examples.
[第1の複合材の作製]
坪量60g/m2のガラスペーパー〔王子製紙製:GHN−00−060(GC)L(商品名)〕を、含浸樹脂(不飽和ポリエステル樹脂/ジアリルフタレート樹脂=80/20)100重量部に対して3種混合溶媒(アセトン/ブタノール/ペンタノール)67重量部を配合した含浸樹脂溶液に浸漬してウエット状態で242g/m2の樹脂を含浸させた樹脂含浸材(含浸樹脂を固形分として22g/m2含浸させた樹脂含浸材)を作製した。次に、11.7mm厚さに調節されたラワン合板(5ply)の一方の面に上記で作製した樹脂含浸材を載置して、熱圧プレス(条件:145℃、8kg/cm2、1分)して樹脂含浸材硬化層を一方の面に有する第1の複合材を作製した。
[Production of first composite material]
Glass paper having a basis weight of 60 g / m 2 [manufactured by Oji Paper Co., Ltd .: GHN-00-060 (GC) L (trade name)] was added to 100 parts by weight of impregnating resin (unsaturated polyester resin / diallyl phthalate resin = 80/20). In contrast, a resin impregnated material impregnated with 242 g / m 2 of resin in a wet state by dipping in an impregnated resin solution containing 67 parts by weight of a mixed solvent of three types (acetone / butanol / pentanol) A resin-impregnated material impregnated with 22 g / m 2 ) was prepared. Next, the resin impregnated material prepared above was placed on one surface of a lauan plywood (5ply) adjusted to a thickness of 11.7 mm, and hot pressing (conditions: 145 ° C., 8 kg / cm 2 , 1 And a first composite material having a resin impregnated cured layer on one side was prepared.
[第2の複合材の作製]
ガラスペーパーの坪量を50g/m2〔王子製紙製:GHN−00−050(GC)L(商品名)〕とした以外は、第1の複合材と同様にして第2の複合材を作製した。
[Production of second composite material]
A second composite material is produced in the same manner as the first composite material, except that the basis weight of the glass paper is 50 g / m 2 [Oji Paper: GHN-00-050 (GC) L (trade name)]. did.
[第3の複合材の作製]
ガラスペーパーの坪量を30g/m2〔王子製紙製:GHN−00−030(GC)L(商品名)〕とした以外は、第1の複合材と同様にして第3の複合材を作製した。
[Production of third composite material]
A third composite material was produced in the same manner as the first composite material, except that the basis weight of the glass paper was 30 g / m 2 [Oji Paper Co., Ltd .: GHN-00-030 (GC) L (trade name)]. did.
[第4の複合材の作製]
ガラスペーパーに代えて坪量60g/m2のクラフト紙を用いた以外は第1の複合材と同様にして第4の複合材を作製した。
[Fabrication of fourth composite material]
A fourth composite material was produced in the same manner as the first composite material except that kraft paper having a basis weight of 60 g / m 2 was used instead of glass paper.
[第5の複合材の作製]
ガラスペーパーに代えて坪量60g/m2のポリエステル不織布を用いた以外は第1の複合材と同様にして第5の複合材を作製した。
[Fifth composite material production]
A fifth composite material was produced in the same manner as the first composite material except that a polyester nonwoven fabric having a basis weight of 60 g / m 2 was used instead of the glass paper.
[第1実施形態の表面保護層を備えた装飾層(第1実施形態の化粧シート)の作製]
両面にコロナ放電処理を施した120μm厚さのポリプロピレンフィルム〔三菱化学エムケーブイ(株)製:150AG3(商品名)〕の一方の面(裏面)にアクリル−ウレタン樹脂(アクリルポリオール100重量部にヘキサメチレンジイソシアネート5重量部を添加した樹脂)溶液をグラビア印刷法で固形分が2g/m2となるように塗布して印刷用プライマー層を形成し、該印刷用プライマー層上にアクリル−ウレタン樹脂(アクリルポリオール100重量部にヘキサメチレンジイソシアネート5重量部を添加した樹脂)からなる印刷インキを用いてグラビア印刷法で木目模様の絵柄印刷層とベタ柄印刷層を形成した。その後、前記ポリプロピレンフィルムの他方の面(表面)に前記木目模様の絵柄印刷層の導管部に対応するようにエンボス版で凹部を設け、該凹部内にアクリル−ウレタン樹脂(アクリルポリオール100重量部にヘキサメチレンジイソシアネート5重量部を添加した樹脂)からなるセピア色のワイピングインキを充填して乾燥させると共に、その上にアクリル−ウレタン樹脂(アクリルポリオール100重量部にヘキサメチレンジイソシアネート5重量部を添加した樹脂)溶液をグラビア印刷法で固形分が2g/m2となるように塗布して表面保護層用プライマー層を形成し、その後に、該表面保護層用プライマー層上に電離放射線硬化型樹脂〔大日精化工業(株)製:EBF−04(商品名)〕をロールコート法で塗布・乾燥して後に電子線(175KeV、5Mrad)を照射して固形分が20g/m2の表面保護層を形成した第1実施形態の表面保護層を備えた装飾層(第1実施形態の化粧シート)を作製した。
[Preparation of a decorative layer (a decorative sheet of the first embodiment) provided with the surface protective layer of the first embodiment]
An acrylic-urethane resin (hexamethylene on 100 parts by weight of acrylic polyol) on one side (back side) of a 120 μm-thick polypropylene film (manufactured by Mitsubishi Chemical MKV Co., Ltd .: 150AG3 (trade name)) subjected to corona discharge treatment on both sides A resin containing 5 parts by weight of diisocyanate) is applied by gravure printing so that the solid content is 2 g / m 2 to form a printing primer layer, and an acrylic-urethane resin (acrylic) is formed on the printing primer layer. Using a printing ink made of a resin in which 5 parts by weight of hexamethylene diisocyanate was added to 100 parts by weight of polyol, a woodgrain pattern printing layer and a solid pattern printing layer were formed by gravure printing. Thereafter, a concave portion is provided with an embossed plate on the other surface (front surface) of the polypropylene film so as to correspond to the conduit portion of the wood grain pattern printed layer, and an acrylic-urethane resin (acrylic polyol 100 parts by weight) is formed in the concave portion. A sepia-colored wiping ink comprising 5 parts by weight of hexamethylene diisocyanate) is filled and dried, and an acrylic-urethane resin (a resin in which 5 parts by weight of hexamethylene diisocyanate is added to 100 parts by weight of acrylic polyol). ) The solution is applied by gravure printing so that the solid content is 2 g / m 2 to form a primer layer for the surface protective layer, and then ionizing radiation curable resin [large Nissei Kagaku Kogyo Co., Ltd .: EBF-04 (trade name)] was applied and dried by a roll coating method, and then Line (175KeV, 5Mrad) solids by irradiating it to prepare a decorative layer having a surface protective layer of the first embodiment to form a surface protective layer of 20 g / m 2 (decorative sheet of the first embodiment).
上記で作製した第1の複合材の前記樹脂含浸材硬化剤層面に湿気硬化型ホットメルト接着剤〔日立化成工業(株)製:ハイボンYR010−8L(商品名)〕をロールコート法で44g/m2塗布すると共に上記で作製した第1実施形態の化粧シートを表面保護層21が表出するように積層して本発明の床材を得た。
A moisture curable hot melt adhesive [manufactured by Hitachi Chemical Co., Ltd .: Hibon YR010-8L (trade name)] is applied to the surface of the resin impregnated material curing agent layer of the first composite material prepared above by a roll coating method. The flooring of the present invention was obtained by applying m 2 and laminating the decorative sheet of the first embodiment produced above so that the surface
第1の複合材に代えて第2の複合材を用いた以外は実施例1と同様にして本発明の床材を得た。 A flooring of the present invention was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the second composite material was used instead of the first composite material.
第1の複合材に代えて第3の複合材を用いた以外は実施例1と同様にして本発明の床材を得た。 A flooring of the present invention was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the third composite material was used instead of the first composite material.
[比較例1]
第1の複合材に代えて第4の複合材を用いた以外は実施例1と同様にして比較例とする床材を得た。
[Comparative Example 1]
A flooring as a comparative example was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the fourth composite material was used instead of the first composite material.
[比較例2]
第1の複合材に代えて第5の複合材を用いた以外は実施例1と同様にして比較例とする床材を得た。
[Comparative Example 2]
A flooring as a comparative example was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the fifth composite material was used instead of the first composite material.
上記で作製した実施例1〜3、および、比較例1、2の床材について、耐落下衝撃性を下記する評価方法で評価し、その結果を表1に示した。なお、耐落下衝撃性の評価方法としては、化粧シート側からデュポン式衝撃試験(重り:500g、落下高さ:300mm、打ち径R:6.3mm)を行い、その時の床材の凹み深さ(単位:μm)を測定した。凹み深さが小さい程、耐落下衝撃性に優れる。参考としてその際に用いたラワン合板についても耐落下衝撃性を評価した。 With respect to the floor materials of Examples 1 to 3 and Comparative Examples 1 and 2 prepared above, the drop impact resistance was evaluated by the evaluation method described below, and the results are shown in Table 1. In addition, as an evaluation method of the drop impact resistance, a DuPont impact test (weight: 500 g, drop height: 300 mm, striking diameter R: 6.3 mm) is performed from the decorative sheet side, and the depth of the floor material dent at that time (Unit: μm) was measured. The smaller the dent depth, the better the drop impact resistance. For reference, the drop impact resistance of the lauan plywood used at that time was also evaluated.
表1からも明らかなように、実施例1〜3の床材は、比較例1、2の床材に比べて耐落下衝撃性において優れ、特に実施例1、2の床材は比較例1、2の床材に比べて格段に優れた耐落下衝撃性を有するものとすることができた。なお、耐キャスター性については耐落下衝撃性と同様な傾向の結果となるので、評価は省略した。 As is clear from Table 1, the flooring materials of Examples 1 to 3 are superior in drop impact resistance compared to the flooring materials of Comparative Examples 1 and 2, and the flooring materials of Examples 1 and 2 are particularly Comparative Example 1. It was possible to have a drop impact resistance that was significantly superior to that of No. 2 flooring. The caster resistance was a result of the same tendency as the drop impact resistance, so evaluation was omitted.
1 床材
2,2’ 装飾層
3,3’,3” 接着剤層
4 複合材
5,5’,5” プライマー層
6 凹凸模様
7 ワイピングインキ
8 絵柄印刷層
8’ ベタ柄印刷層
9 バッカー材
21 表面保護層
22 合成樹脂製透明シート
22’ 合成樹脂製シート
23 紙系シート
41 樹脂含浸紙硬化層
42 合板
α 微粒子
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1
Claims (10)
A resin impregnated cured layer was laminated on the other side of the plywood, and the resin impregnated cured layer impregnated with a curable resin was thermocompression-bonded to the other side of the plywood and integrally molded. It is a layer, The flooring in any one of Claims 1-9 characterized by the above-mentioned.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005024233A JP2006207343A (en) | 2005-01-31 | 2005-01-31 | Floor material |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005024233A JP2006207343A (en) | 2005-01-31 | 2005-01-31 | Floor material |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006207343A true JP2006207343A (en) | 2006-08-10 |
Family
ID=36964492
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005024233A Withdrawn JP2006207343A (en) | 2005-01-31 | 2005-01-31 | Floor material |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2006207343A (en) |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008081972A (en) * | 2006-09-26 | 2008-04-10 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | Flooring |
| JP2008081969A (en) * | 2006-09-26 | 2008-04-10 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | Flooring |
| JP2008088741A (en) * | 2006-10-03 | 2008-04-17 | Sumitomo Forestry Co Ltd | Flooring and manufacturing method therefor |
| JP2012041747A (en) * | 2010-08-19 | 2012-03-01 | Panasonic Electric Works Co Ltd | Composite floor material |
| CN102926521A (en) * | 2012-10-26 | 2013-02-13 | 银海木业(江苏)有限公司 | LV flow coating series laminate floor and painting process |
| JP2014043770A (en) * | 2013-11-25 | 2014-03-13 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | Flooring material |
| CN107514121A (en) * | 2017-08-16 | 2017-12-26 | 芜湖通全科技有限公司 | A kind of novel floor |
-
2005
- 2005-01-31 JP JP2005024233A patent/JP2006207343A/en not_active Withdrawn
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008081972A (en) * | 2006-09-26 | 2008-04-10 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | Flooring |
| JP2008081969A (en) * | 2006-09-26 | 2008-04-10 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | Flooring |
| JP2008088741A (en) * | 2006-10-03 | 2008-04-17 | Sumitomo Forestry Co Ltd | Flooring and manufacturing method therefor |
| JP2012041747A (en) * | 2010-08-19 | 2012-03-01 | Panasonic Electric Works Co Ltd | Composite floor material |
| CN102926521A (en) * | 2012-10-26 | 2013-02-13 | 银海木业(江苏)有限公司 | LV flow coating series laminate floor and painting process |
| JP2014043770A (en) * | 2013-11-25 | 2014-03-13 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | Flooring material |
| CN107514121A (en) * | 2017-08-16 | 2017-12-26 | 芜湖通全科技有限公司 | A kind of novel floor |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4985736B2 (en) | Cosmetic material | |
| JP4569720B2 (en) | Cosmetics for flooring | |
| JP2006212903A (en) | Surface layer-modified plywood made of needle-leaved tree, its manufacturing method and floor material using the surface layer-modified plywood | |
| JP2006207343A (en) | Floor material | |
| JP4605844B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of decorative material for flooring | |
| JP4797692B2 (en) | Flooring | |
| JP2006207346A (en) | Floor material | |
| JP2008082119A (en) | Flooring | |
| JP3642994B2 (en) | Decorative material for flooring and method for producing the same | |
| JP2007077763A (en) | Flooring | |
| JP2006097321A (en) | Decoration material for floor | |
| JP2006046053A (en) | Floor material | |
| JP2006225935A (en) | Compound substrate and flooring material using the same | |
| JP5634656B2 (en) | Flooring | |
| JP4170989B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of decorative material for flooring | |
| JP2007077726A (en) | Flooring | |
| JP2009074255A (en) | Floor material | |
| JP5519095B2 (en) | Flooring | |
| JP5011635B2 (en) | Cosmetic material | |
| JP4815652B2 (en) | Cosmetic material | |
| KR20090091188A (en) | Decorative sheet and decorative plate using the decorative sheet | |
| JP5879872B2 (en) | Floor decorative material | |
| JP2008240423A (en) | Floor material | |
| JP5664743B2 (en) | Flooring | |
| JP2007239445A (en) | Flooring |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A300 | Withdrawal of application because of no request for examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A300 Effective date: 20080401 |