JP2006040059A - Object information acquiring device, object authentication devices, and control method thereof - Google Patents
Object information acquiring device, object authentication devices, and control method thereof Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2006040059A JP2006040059A JP2004220683A JP2004220683A JP2006040059A JP 2006040059 A JP2006040059 A JP 2006040059A JP 2004220683 A JP2004220683 A JP 2004220683A JP 2004220683 A JP2004220683 A JP 2004220683A JP 2006040059 A JP2006040059 A JP 2006040059A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- unit
- reading
- imaging
- range
- information
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
- Collating Specific Patterns (AREA)
- Image Input (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は無線周波数識別(RFID:Radio Frequency Identification)技術を用いた対象物情報取得装置、対象物認証装置、及びそれらの制御方法に関する。 The present invention relates to an object information acquisition apparatus, an object authentication apparatus, and a control method thereof using radio frequency identification (RFID) technology.
無線周波数識別(RFID)技術は、RFIDタグ(又はICタグ、ICカードなど)が保持する識別子などのデータを外部から電磁波を用いて非接触で読み取ることにより、そのタグを識別する技術である。そのタグに書き込み可能なメモリを備えたり、センサを組み合わせたりすることにより、様々な応用分野が考えられる。RFIDタグは、タグに電源(電池)を搭載するかしないかにより、能動型(電源付き)タグと受動型(電源なし)タグに大別される。 The radio frequency identification (RFID) technology is a technology for identifying a tag by reading data such as an identifier held by an RFID tag (or an IC tag, an IC card, etc.) from the outside using an electromagnetic wave in a non-contact manner. Various application fields can be considered by providing a memory writable to the tag or combining sensors. RFID tags are broadly classified into active (with power supply) tags and passive (without power supply) tags depending on whether or not a power supply (battery) is mounted on the tag.
外部装置から供給される電磁波によって動作する受動型のRFIDタグは、小型化技術の進展に伴い、近年その応用分野を急速に拡大しつつある。よく知られた例として、非接触ICカード型の定期券やエントランスカード等がある。 In recent years, passive RFID tags that operate using electromagnetic waves supplied from external devices have been rapidly expanding their application fields with the progress of miniaturization technology. Well-known examples include contactless IC card-type commuter passes and entrance cards.
また、シールに内蔵されたRFIDタグを物品に貼り付け、物品の配置場所或いは部屋の出入り口付近に設置されたRFID読取装置によって自動的にRFIDタグの存在及び記憶された情報を検出し、物品の無断持ち出しや盗難を防ぐために使用することができる。更に、バーコードに代わる次世代の物品識別技術として、サプライチェーンマネジメントの全ての段階(生産、流通、販売)で効率的な物品管理に役立てようという構想が示されている。 Also, the RFID tag built in the seal is affixed to the article, and the presence of the RFID tag and the stored information are automatically detected by the RFID reader installed near the place where the article is placed or the entrance of the room. Can be used to prevent unauthorized removal and theft. Furthermore, as a next-generation article identification technology that replaces barcodes, a concept is proposed that will be used for efficient article management at all stages of supply chain management (production, distribution, and sales).
上述の受動型のRFIDタグの多くは、送信電力が弱いためにRFID読取装置の近く(数cm〜数10cm程度)でしか読み取ることができないが、能動型のRFIDタグは送信電力を高めることにより比較的離れた場所(〜数m程度)から読み取ることが可能である。 Many of the passive RFID tags described above can be read only near the RFID reader (several centimeters to several tens of centimeters) because the transmission power is weak. However, active RFID tags can increase the transmission power. It is possible to read from a relatively distant place (about several meters).
このように、RFIDタグを全ての対象物に取り付ける(貼り付ける、組み込む、埋め込む)ことができれば、RFID読取装置を用いて簡単に対象物を識別することが可能となる。 As described above, if the RFID tag can be attached (attached, incorporated, embedded) to all the objects, the object can be easily identified using the RFID reader.
しかしながら、RFIDタグと対象物とは本来別物であるため、RFIDタグを故意に対象物から取り外して(剥がして、取り出して)単独で使用することができる。特に、人が携行する非接触ICカード(身分証明カードやエントランスカードの類)は極めて容易に他人が使用することができる。また、何らかの事故によってRFIDタグが対象物から外れてしまうこともあり得る。 However, since the RFID tag and the target object are originally different, the RFID tag can be intentionally removed from the target object (peeled and removed) and used alone. In particular, a non-contact IC card carried by a person (such as an identification card or an entrance card) can be used very easily by another person. In addition, the RFID tag may be detached from the object due to some accident.
更に、RFID読取装置が常に100%確実にRFIDタグを読み取れるとは限らない。例えば、タグと読取装置の位置関係(距離や向き)によって、その読み取り精度が変化してしまったり、複数のRFIDタグが重なっていたり、RFIDタグの周囲に金属などの導電体がある場合などは、読み取り精度が大きく低下することが多い。 Further, the RFID reader cannot always read the RFID tag with 100% certainty. For example, depending on the positional relationship (distance and orientation) between the tag and the reader, the reading accuracy may change, multiple RFID tags may overlap, or there may be a conductor such as metal around the RFID tag. Often, the reading accuracy is greatly reduced.
従って、RFIDタグだけを用いて対象物の識別や認証を行ったとしても、高い信頼性が得られるものではない。 Therefore, even if the object is identified and authenticated using only the RFID tag, high reliability cannot be obtained.
このような問題を解決するために、例えば特許文献1ではカメラとRFレシーバ(RFID読取装置)を組み合わせた画像認証システムを提案している。カメラ撮影と同時に、RFIDの読み取りを行い、撮影した画像データと読み取った識別子とを一体化して複合データを生成することにより、画像データと識別子とが同時に取得されることを保証している。これにより、ユーザは画像データを見ることで所定の対象物が存在することを確認でき、その画像データと同時に読み取られた識別子が対象物に取り付けられていた正当なものであることを確認できる、と主張している。
しかしながら、特許文献1記載の画像認証システムでは、RFIDタグ付きの対象物がシステムの近くに複数存在する場合について十分配慮がなされていない。例えば、複数の対象物A,B,C,…が互いに近くに置いてある場合、特許文献1記載のカメラを用いて撮影された画像には複数の対象物が映ってしまう可能性がある。 However, in the image authentication system described in Patent Document 1, sufficient consideration is not given to the case where there are a plurality of objects with RFID tags near the system. For example, when a plurality of objects A, B, C,... Are placed close to each other, there is a possibility that a plurality of objects are reflected in an image photographed using the camera described in Patent Document 1.
また、特許文献1記載のRFレシーバ(RFID読取装置)を用いて対象物のRFIDタグを読み取ると、複数の対象物A,B,C,…に取り付けられた複数の識別子ID_A,ID_B,ID_C,…を読み取ってしまう可能性が高い。 Further, when an RFID tag of an object is read using an RF receiver (RFID reader) described in Patent Document 1, a plurality of identifiers ID_A, ID_B, ID_C, attached to a plurality of objects A, B, C,. There is a high possibility of reading.
更に、特許文献1には、RFレシーバのアンテナとして指向性アンテナを用いることも記述されているが、この指向性アンテナの指向範囲(RFIDタグを読み取り可能な範囲)を制御できるわけではないため、RFレシーバの後方に置かれたRFIDタグを読み取る心配はないものの、RFレシーバの前方に置かれた複数のRFIDタグは全て読み出してしまう可能性が高い。 Further, Patent Document 1 also describes the use of a directional antenna as an RF receiver antenna, but the directional range of this directional antenna (a range in which an RFID tag can be read) cannot be controlled. Although there is no worry of reading the RFID tag placed behind the RF receiver, there is a high possibility that all of the plurality of RFID tags placed in front of the RF receiver will be read out.
即ち、特許文献1記載のシステムを利用した場合、複数の対象物A,B,C,…を含む画像と、複数の識別子ID_A,ID_B,ID_C,…を同時に読み出してしまうことになり、画像に映ったどの対象物がどの識別子に対応しているかを知ることはできない。更に、画像に映った対象物がm個(mは1以上)であるのに対して、読み取った識別子はn個(nはm以上)になることもあり得るため、複数の対象物の画像と複数の識別子との対応付けは一層困難になる。 That is, when the system described in Patent Document 1 is used, an image including a plurality of objects A, B, C,... And a plurality of identifiers ID_A, ID_B, ID_C,. It is impossible to know which object that is reflected corresponds to which identifier. Furthermore, although there are m objects (m is 1 or more) reflected in the image, the read identifier may be n (n is m or more). It becomes more difficult to associate a plurality of identifiers with each other.
本発明は、上述のような問題点に鑑みてなされたものであり、ある対象物を撮影する際に対象物に取り付けられたRFIDタグの読み取りを行う場合に、撮影パラメータとRFID読取パラメータとを互いに連動制御することにより、撮影範囲とRFID読取範囲を一致させることを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above-described problems. When an RFID tag attached to an object is read when an object is imaged, an imaging parameter and an RFID reading parameter are set. An object is to match the photographing range and the RFID reading range by performing interlock control.
また、撮影画像に映っている対象物の数又は読み取った識別子の数が1つになるように撮影パラメータとRFID読取パラメータとを互いに連動制御することにより、常に1つの対象物に対してのみ撮影とRFIDタグの読み取りを行うことを目的とする。 In addition, the shooting parameters and the RFID reading parameters are linked and controlled so that the number of objects reflected in the captured image or the number of read identifiers is one, so that only one object is always captured and RFIDd. The purpose is to read tags.
更に、読み取った識別子の一部又は全部があらかじめ決められた識別子と一致する場合のみ画像データと識別子からなる複合データを記憶することにより、所定の対象物だけを見つけ出し、発見時刻や場所を合わせて記憶することにより、対象物の追跡や管理に役立てることを目的とする。 Further, only when a part or all of the read identifiers matches a predetermined identifier, the composite data composed of the image data and the identifier is stored, so that only a predetermined object is found, and the discovery time and location are matched. It is intended to be useful for tracking and managing objects by memorizing them.
本発明は、対象物を撮影するための撮影手段と、前記対象物に貼り付けられたRFタグから情報を読み取る読取手段とを有する対象物情報取得装置であって、前記撮影手段により対象物を撮影する際の撮影範囲と、前記読取手段によりRFタグの情報を読み取る際の読取範囲とを一致させるべく、前記撮影手段の撮影パラメータと前記読取手段の読取パラメータとを制御する制御手段と、撮影された対象物の画像データと読み取られた情報とを組み合わせた複合データを生成する生成手段とを有することを特徴とする。 The present invention is an object information acquisition apparatus having an imaging means for imaging an object and a reading means for reading information from an RF tag attached to the object, wherein the object is captured by the imaging means. Control means for controlling the photographing parameters of the photographing means and the reading parameters of the reading means so as to make the photographing range for photographing coincide with the reading range for reading the information of the RF tag by the reading means; And generating means for generating composite data combining the read image data of the object and the read information.
また、本発明は、対象物を撮影するための撮影手段と、前記対象物に貼り付けられたRFタグから識別子を読み取る読取手段とを有する対象物認証装置であって、あらかじめ複数の対象物に対して画像特徴量と固有の識別子を組み合わせた複合データを記憶する記憶手段と、前記撮影手段により対象物を撮影する際の撮影範囲と、前記読取手段によりRFタグの識別子を読み取る際の読取範囲とを一致させるべく、前記撮影手段の撮影パラメータと前記読取手段の読取パラメータとを制御する制御手段と、撮影された画像データから画像特徴量を抽出する抽出手段と、前記抽出された画像特徴量と読み取られた識別子とを組み合わせた複合データを前記記憶手段に記憶されている複合データと比較することにより対象物を認証する認証手段とを有することを特徴とする。 In addition, the present invention is an object authentication apparatus having an imaging unit for imaging an object and a reading unit that reads an identifier from an RF tag attached to the object. On the other hand, storage means for storing composite data in which an image feature amount and a unique identifier are combined, an imaging range when the object is imaged by the imaging means, and a reading range when the identifier of the RF tag is read by the reading means In order to match the image capturing parameter of the image capturing unit and the reading parameter of the reading unit, an extracting unit for extracting an image feature amount from captured image data, and the extracted image feature amount Authentication means for authenticating the object by comparing composite data combining the read identifier with the composite data stored in the storage means; Characterized in that it has.
本発明によれば、撮影対象物以外のRFIDタグの読み取りを防止することができる。 According to the present invention, reading of RFID tags other than the object to be photographed can be prevented.
以下、図面を参照しながら発明を実施するための最良の形態について詳細に説明する。尚、実施例では、無線周波数識別(RFID:Radio Frequency Identification)技術を用いた受動型のRFIDタグを対象物に貼り付け、RFID読取機能を有する外部装置がそのRFIDタグの情報を読み取り、対象物の認証を行う場合について説明する。 The best mode for carrying out the invention will be described below in detail with reference to the drawings. In the embodiment, a passive RFID tag using a radio frequency identification (RFID) technology is attached to an object, and an external device having an RFID reading function reads the information of the RFID tag. A case where authentication is performed will be described.
実施例1では、外部装置として、対象物をカメラ機能により撮影すると同時に、対象物に貼り付けられたRFIDタグの情報(識別子)をRFID読取機能により読み取る対象物情報取得装置を例に説明する。 In the first embodiment, as an external apparatus, an object information acquisition apparatus will be described as an example in which an object is photographed by a camera function and at the same time information (identifier) of an RFID tag attached to the object is read by an RFID reading function.
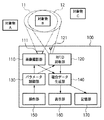
図1は、実施例1における対象物情報取得装置の構成の一例を示すブロック図である。図1に示すように、対象物情報取得装置100には、画像撮影部110、RFID読取部120、パラメータ制御部130、複合データ生成部140、操作部150、表示部160、記憶部170の各構成要素が含まれる。以下、各構成要素の詳細を順に説明する。
FIG. 1 is a block diagram illustrating an example of the configuration of the object information acquisition apparatus according to the first embodiment. As shown in FIG. 1, the object
画像撮影部110は所定のズーム機構111を備えており、ズーム倍率又は視野角及び焦点距離(フォーカス)を制御可能である。また好ましくは、画像撮影部110は不図示のパン・チルト機構を備えており、左右及び上下方向に撮影の向きを変えることができるように構成されている。
The
RFID読取部120は特定の方向にあるRFIDタグとのみ無線通信するための指向性アンテナ121を備えており、その指向性アンテナ121から発する電波の広がる範囲(以下、アンテナの指向範囲と呼ぶ)と電波の到達距離に影響するアンテナの出力レベル(電磁波の放射強度又は受信感度)とを制御可能である。
The
パラメータ制御部130は、操作部150から入力されたユーザからの指示に応じて、画像撮影部110の撮影パラメータ及びRFID読取部120のRFID読取パラメータを同時に連動して制御する。この連動制御の方法は図3及び図4を用いて更に後述する。尚、ユーザからの指示は必ずしも必要ではなく、あらかじめ制御規則を決めておくことにより、パラメータ制御部130が自動的にパラメータの連動制御を行うことができる。
The
複合データ生成部140は、画像撮影部110から撮影された画像データを受け取り、RFID読取部120から読み取ったRFIDタグの識別子を受け取る。その後、あらかじめ決められた方法で画像データと識別子とを組み合わせ、複合データを生成する。この生成の際に、暗号化やデータ圧縮など複合データに所定の変換を施しても良い。
The composite
表示部160は複合データ生成部140から画像データ及び識別子を受け取り、これらのデータをそれぞれデータに適した方法でユーザに表示する。
The
即ち、画像データはビットマップ表示し、識別子は文字表示するか又はあらかじめ決められた対応表を用いてアイコンやグラフなどに変換してビットマップ表示する。 That is, the image data is displayed as a bitmap, and the identifier is displayed as a character or converted into an icon or graph using a predetermined correspondence table and displayed as a bitmap.
尚、対象物情報取得装置100が自動制御又は遠隔制御される場合は、操作部150と同様に表示部160が含まれない構成もあり得る。
In addition, when the object
記憶部170は、複合データ生成部140から受け取った複合データを記憶媒体に記憶する。記憶媒体としては、RAM、フラッシュROM、ハードディスク、メモリカード、USBメモリ、磁気テープ、光ディスク、磁気ディスク、各種DVDディスクなど、様々な媒体を用いることができる。
The
図2は、アンテナの特性を制御可能な指向性アンテナ121の構成例を示す図である。図2に示すように、指向性アンテナ121は、多数のパッチアンテナ123をアレイ状に配置したパッチアレイアンテナ122で構成されている。パッチアンテナ123は小さな四角形で示されており、横16×縦16の合計256個配置されているが、この素子数はある程度任意に増減することができ、アンテナの特性に影響を及ぼす。
FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a configuration example of the
尚、パッチアレイアンテナ122に限らず、アレイアンテナでは、一般的に、素子数を増やせば増やすほど鋭い指向性を実現できる。また、素子サイズ及び素子の配置間隔は、アンテナで送受信する電波の搬送周波数によって最適値が決まる。
Note that not only the
本実施例におけるパッチアレイアンテナ122では、アンテナの中心から一定の範囲内にある素子にのみ給電できるように、各素子と給電線の間には不図示の電気的スイッチが存在する。尚、電気的スイッチは、トランジスタやMEMS(Micro Electro-Mecanical System)スイッチなどで実現できる。そして、給電範囲124は、給電された素子だけを囲む範囲を示している。
In the
図3は、撮影パラメータの一部である撮影のズーム倍率と、RFID読取パラメータの一部であるアンテナの給電範囲との対応関係の具体例を示す図である。撮影のズーム倍率を変えた時の撮影範囲は、撮影した画像を人間が見るか或いは画像処理によって自動計測することができる。また、アンテナのX,Y方向の給電範囲を変えた時の電波の指向性の鋭さ(指向範囲)は、電波暗室において多数の地点で受信電波強度を計測することにより計算することができる。 FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating a specific example of a correspondence relationship between the zooming magnification of shooting, which is a part of the shooting parameters, and the feeding range of the antenna, which is a part of the RFID reading parameter. The shooting range when the zoom magnification of shooting is changed can be automatically measured by a person viewing the shot image or by image processing. Further, the sharpness of the directivity (directivity range) of the radio wave when the feeding range in the X and Y directions of the antenna is changed can be calculated by measuring the received radio wave intensity at many points in the anechoic chamber.
このように、それぞれの範囲をあらかじめ計測しておくことにより、撮影範囲及び電波の指向範囲がほぼ一致するような撮影のズーム倍率とアンテナの給電範囲との対応関係を複数選び出すことができるので、図3に例示したような対応関係が得られる。 In this way, by measuring each range in advance, it is possible to select a plurality of correspondences between the shooting zoom magnification and the feeding range of the antenna so that the shooting range and the directivity range of the radio wave substantially match, The correspondence as illustrated in FIG. 3 is obtained.
尚、アンテナのX,Y方向の給電範囲の各欄に示した数値は、図2に示したX,Y座標に対応しており、パッチアンテナ123の配置間隔を「1」とした場合の数値である。
Note that the numerical values shown in each column of the feeding range of the antenna in the X and Y directions correspond to the X and Y coordinates shown in FIG. 2, and the numerical values when the arrangement interval of the
図4は、撮影パラメータの一部である撮影の焦点距離(F値)と、RFID読取パラメータの一部であるアンテナの出力レベルとの対応関係の具体例を示す図である。アンテナの出力レベルを変えた時の電波到達距離は、電波暗室においてアンテナの指向範囲内の多数の地点で受信電波強度を計測することにより計算することができる。 FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating a specific example of a correspondence relationship between the focal length (F value) of imaging, which is a part of imaging parameters, and the output level of an antenna, which is a part of RFID reading parameters. The radio wave arrival distance when the output level of the antenna is changed can be calculated by measuring the received radio wave intensity at many points within the antenna directivity range in the anechoic chamber.
従って、撮影の焦点距離(F値)とアンテナの電波到達距離とが一致するように、アンテナの出力レベルを選ぶことにより、図4に例示したような対応関係が得られる。 Therefore, by selecting the output level of the antenna so that the focal length (F value) of photographing matches the radio wave arrival distance of the antenna, the correspondence relationship illustrated in FIG. 4 can be obtained.
尚、図3及び図4に示した各欄の数値は一例であり、対象物情報取得装置100の部品構成、構造並びに製造方法などによって異なるため、装置の種類毎に個別に計測を行い、計測結果に基づいてそれぞれ異なる対応関係を作成することが好ましい。
Note that the numerical values in each column shown in FIG. 3 and FIG. 4 are examples, and differ depending on the component configuration, structure, manufacturing method, and the like of the object
以上の構成において、画像撮影部110が画像を撮影する撮影範囲11とRFID読取部120がRFIDタグを読み取るRFID読取範囲12とがほぼ同じ範囲になるように、パラメータ制御部130が画像撮影部110とRFID読取部120とを連動制御することにより、撮影範囲11及びRFID読取範囲12内に1つの対象物Bだけを含むようにすることができる。
In the above configuration, the
ここで、対象物情報取得装置100にて所望の対象物を撮影すると同時に、その対象物に貼り付けられたRFIDタグの識別子を読み取る際に、パラメータ制御部130が実行する制御について説明する。尚、所望の対象物として図1に示す対象物Bを撮影する場合を例に説明する。
Here, the control executed by the
図5は、実施例1におけるパラメータ制御部130の制御手順を示すフローチャートである。まず、ステップS501において、パラメータ制御部130は対象物Bを撮影するように画像撮影部110に指示する。これにより、画像撮影部110は撮影範囲が対象物Bの撮影範囲11となるように、ズーム機構111のズーム倍率及び焦点距離を調整し、対象物Bだけを撮影する。
FIG. 5 is a flowchart illustrating a control procedure of the
次に、ステップS502において、パラメータ制御部130は、画像撮影部110からズーム倍率及び焦点距離を撮影パラメータとして入力し、その撮影パラメータに基づいて、撮影範囲11とRFID読取範囲12とがほぼ同じ範囲になるように、RFID読取部120の読取パラメータを決定する。
Next, in step S502, the
具体的には、撮影のズーム倍率が1.5であれば、図3に示すズーム倍率とアンテナの給電範囲との対応関係からX方向及びY方向の給電範囲を±5以内(図2に示す給電範囲124)と決定し、撮影の焦点距離が4.3であれば、図4に示す焦点距離とアンテナの出力レベルとの対応関係から出力レベルを90%と決定する。 Specifically, if the shooting zoom magnification is 1.5, the power supply ranges in the X and Y directions are within ± 5 based on the correspondence between the zoom magnification shown in FIG. 3 and the power supply range of the antenna (shown in FIG. 2). If the focal length of imaging is 4.3, the output level is determined to be 90% from the correspondence between the focal length and the antenna output level shown in FIG.
次に、ステップS503において、RFID読取部120に決定した給電範囲及び出力レベルを指示する。これにより、RFID読取部120がその給電範囲及び出力レベルに従って指向性アンテナ121を制御し、RFID読取範囲12内の対象物Bに貼り付けられたRFIDタグの識別子を読み取る。
In step S503, the
このようにして、複合データ生成部140には対象物Bだけを撮影した画像データ及び対象物Bに取り付けられたRFIDタグから読み出された識別子が入力され、複合データ生成部140が画像データ及び識別子から複合データを生成し、表示部160に表示又は記憶部170に記憶することができる。
In this way, the composite
即ち、複合データ生成部140は対象物が1つしか映っていないとき及び識別子が1つのときのみ複合データを生成することにより、複合データの利用価値を向上させることができる。尚、複数の対象物が映っている場合は、再度撮影をやり直すように制御することも可能である。
That is, the composite
また、複合データ生成部140が不図示の識別子判定部により読み取った識別子の一部又は全部があらかじめ決められた識別子と一致するか否かを判定し、一致すると判定した場合のみ画像データと識別子からなる複合データを記憶部170に記憶することにより、所定の対象物だけを見つけ出すことができる。
Further, it is determined whether or not a part or all of the identifiers read by the identifier determination unit (not shown) by the composite
更に、所定の識別子の発見時刻や発見場所を複合データと合わせて記憶部170に記憶することにより、対象物の追跡や保管場所の管理に役立てることができる。
Further, by storing the discovery time and discovery location of a predetermined identifier in the
ここで、所定の識別子の発見時刻は、不図示のシステムタイマーを利用することにより取得するものとする。また、所定の識別子の発見場所は、対象物情報取得装置の設置場所をあらかじめユーザが操作部150から入力して記憶部170に記憶させておくか、或いはGPS(Global Positioning System)などの位置計測システムを利用することにより取得するものとする。
Here, the discovery time of the predetermined identifier is acquired by using a system timer (not shown). In addition, the location where the predetermined identifier is found is that the installation location of the object information acquisition apparatus is previously input by the user from the
次に、図面を参照しながら本発明に係る実施例2について詳細に説明する。実施例2では、外部装置として、対象物をカメラ機能により撮影すると同時に、対象物に貼り付けられたRFIDタグの情報(識別子)をRFID読取機能により読み取り対象物を認証する対象物認証装置を例に説明する。 Next, Embodiment 2 according to the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. In the second embodiment, as an external device, an object authentication device that captures an object by a camera function and simultaneously reads information (identifier) of an RFID tag attached to the object by an RFID reading function and authenticates the object. Explained.
図6は、実施例2における対象物認証装置の構成の一例を示すブロック図である。尚、図6において、図1と同じ構成要素には同一の符号を付し、その説明は省略する。ここでは、図1と異なる構成要素について説明する。 FIG. 6 is a block diagram illustrating an example of the configuration of the object authentication device according to the second embodiment. In FIG. 6, the same components as those in FIG. 1 are denoted by the same reference numerals, and the description thereof is omitted. Here, components different from those in FIG. 1 will be described.
図6に示すように、実施例2の対象物認証装置200では、画像特徴量抽出部210、複合データ記憶部220及び認証部230が新たに加わっている。
As shown in FIG. 6, in the
画像特徴量抽出部210は画像撮影部110から撮影した画像データを受け取った後、あらかじめ決められた画像処理アルゴリズムを用いて、映っている物の形状や色彩などの画像特徴量を自動的に抽出する。
After receiving the image data taken from the
複合データ生成部140は画像特徴量抽出部210から抽出した画像特徴量を受け取り、RFID読取部120から読み取ったRFIDタグの識別子を受け取る。その後、あらかじめ決められた方法で画像特徴量と識別子とを組み合わせ、複合データを生成する。
The composite
複合データ記憶部220には、あらかじめ様々な対象物から得られた画像特徴量と識別子からなる複合データのリストを記憶しておく。
The composite
つまり、様々な対象物一つ一つに対してあらかじめ画像撮影を行い、画像特徴量を抽出し、同時にRFIDタグから識別子を読み取り、抽出した画像特徴量と読み取った識別子とを組み合わせることにより複合データを作成しておき、そのリストを記憶しておくものである。 In other words, composite data is obtained by capturing images in advance for each of various objects, extracting image feature amounts, simultaneously reading identifiers from RFID tags, and combining the extracted image feature amounts and the read identifiers. Is created and the list is stored.
認証部230は、複合データ生成部140から受け取った複合データを複合データ記憶部220に記憶された複合データのリストと照合することにより、対象物の認証を行う。この認証は、識別子の照合と画像特徴量の照合の2段階で行われるため、従来のRFID技術を用いた識別子だけの認証やバイオメトリクス技術を用いた顔画像又は指紋画像だけの認証と比べて格段に信頼性が増す。
The
以上の構成において、画像撮影部110が画像を撮影する撮影範囲11とRFID読取部120がRFIDタグを読み取るRFID読取範囲12とがほぼ同じ範囲になるように、パラメータ制御部130が画像撮影部110とRFID読取部120とを連動制御する。画像特徴量抽出部210が画像撮影部110から撮影した画像データを受け取った後、あらかじめ決められた画像処理アルゴリズムを用いて、映っている物の形状や色彩などの画像特徴量を自動的に抽出し、複合データ生成部140が画像特徴量抽出部210からの画像特徴量と、RFID読取部120からのRFIDタグの識別子とをあらかじめ決められた方法で組み合わせて複合データを生成する。そして、認証部230が複合データ生成部140から受け取った複合データを複合データ記憶部220に記憶された複合データのリストと照合することにより、対象物の認証を行い、認証結果(認証成功又は認証失敗)は表示部160に表示される。
In the above configuration, the
これにより、複合データ生成部140は対象物が1つしか映っていないとき及び識別子が1つのときのみ複合データを生成し、認証部230が対象物の認識を行うことにより、複合データの利用価値を向上させることができる。
As a result, the composite
尚、本発明は複数の機器(例えば、ホストコンピュータ,インターフェース機器,リーダ,プリンタなど)から構成されるシステムに適用しても、1つの機器からなる装置(例えば、複写機,ファクシミリ装置など)に適用しても良い。 Even if the present invention is applied to a system composed of a plurality of devices (for example, a host computer, an interface device, a reader, a printer, etc.), it is applied to an apparatus (for example, a copier, a facsimile machine, etc.) composed of a single device. It may be applied.
また、本発明の目的は前述した実施形態の機能を実現するソフトウェアのプログラムコードを記録した記録媒体を、システム或いは装置に供給し、そのシステム或いは装置のコンピュータ(CPU若しくはMPU)が記録媒体に格納されたプログラムコードを読出し実行することによっても、達成されることは言うまでもない。 Another object of the present invention is to supply a recording medium in which a program code of software realizing the functions of the above-described embodiments is recorded to a system or apparatus, and the computer (CPU or MPU) of the system or apparatus stores it in the recording medium. Needless to say, this can also be achieved by reading and executing the programmed program code.
この場合、記録媒体から読出されたプログラムコード自体が前述した実施形態の機能を実現することになり、そのプログラムコードを記憶した記録媒体は本発明を構成することになる。 In this case, the program code itself read from the recording medium realizes the functions of the above-described embodiment, and the recording medium storing the program code constitutes the present invention.
このプログラムコードを供給するための記録媒体としては、例えばフロッピー(登録商標)ディスク,ハードディスク,光ディスク,光磁気ディスク,CD−ROM,CD−R,磁気テープ,不揮発性のメモリカード,ROMなどを用いることができる。 As a recording medium for supplying the program code, for example, a floppy (registered trademark) disk, a hard disk, an optical disk, a magneto-optical disk, a CD-ROM, a CD-R, a magnetic tape, a nonvolatile memory card, a ROM, or the like is used. be able to.
また、コンピュータが読出したプログラムコードを実行することにより、前述した実施形態の機能が実現されるだけでなく、そのプログラムコードの指示に基づき、コンピュータ上で稼働しているOS(オペレーティングシステム)などが実際の処理の一部又は全部を行い、その処理によって前述した実施形態の機能が実現される場合も含まれることは言うまでもない。 Further, by executing the program code read by the computer, not only the functions of the above-described embodiments are realized, but also an OS (operating system) operating on the computer based on the instruction of the program code. It goes without saying that a case where the function of the above-described embodiment is realized by performing part or all of the actual processing and the processing is included.
更に、記録媒体から読出されたプログラムコードが、コンピュータに挿入された機能拡張ボードやコンピュータに接続された機能拡張ユニットに備わるメモリに書込まれた後、そのプログラムコードの指示に基づき、その機能拡張ボードや機能拡張ユニットに備わるCPUなどが実際の処理の一部又は全部を行い、その処理によって前述した実施形態の機能が実現される場合も含まれることは言うまでもない。 Further, after the program code read from the recording medium is written in a memory provided in a function expansion board inserted into the computer or a function expansion unit connected to the computer, the function expansion is performed based on the instruction of the program code. It goes without saying that the CPU or the like provided in the board or the function expansion unit performs part or all of the actual processing and the functions of the above-described embodiments are realized by the processing.
11 撮影範囲
12 RFID読取範囲
100 対象物情報取得装置
110 画像撮影部
111 ズーム機構
120 RFID読取部
121 指向性アンテナ
122 パッチアレイアンテナ
123 パッチアンテナ(1素子)
124 給電範囲
130 パラメータ制御部
140 複合データ生成部
150 操作部
160 表示部
170 記憶部
200 対象物認証装置
210 画像特徴量抽出部
220 複合データ記憶部
230 認証部
DESCRIPTION OF
124
Claims (15)
前記撮影手段により対象物を撮影する際の撮影範囲と、前記読取手段によりRFタグの情報を読み取る際の読取範囲とを一致させるべく、前記撮影手段の撮影パラメータと前記読取手段の読取パラメータとを制御する制御手段と、
撮影された対象物の画像データと読み取られた情報とを組み合わせた複合データを生成する生成手段とを有することを特徴とする対象物情報取得装置。 An object information acquisition apparatus having an imaging unit for imaging an object and a reading unit that reads information from an RF tag attached to the object,
An imaging parameter of the imaging unit and a reading parameter of the reading unit are set so that the imaging range when the object is imaged by the imaging unit and the reading range when the information of the RF tag is read by the reading unit are matched. Control means for controlling;
An object information acquisition apparatus comprising: generation means for generating composite data combining image data of a photographed object and the read information.
前記読取パラメータとして前記指向性アンテナの指向範囲を制御可能であり、前記撮影パラメータとして視野角又はズーム率を制御可能であり、
前記制御手段は、前記視野角又はズーム率と連動して前記指向性アンテナの指向範囲を制御することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の対象物情報取得装置。 The reading means has a directional antenna capable of receiving with high sensitivity electromagnetic waves coming from a direction within a certain angular range (directing range) centered on the line-of-sight direction of the photographing means,
The directivity range of the directional antenna can be controlled as the reading parameter, and the viewing angle or the zoom rate can be controlled as the imaging parameter.
The target information acquisition apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the control unit controls a directivity range of the directional antenna in conjunction with the viewing angle or the zoom rate.
前記制御部は、焦点距離と連動してアンテナ出力を制御することを特徴とする請求項2に記載の対象物情報取得装置。 The focal length can be controlled as the shooting parameter, and the antenna output of the directional antenna can be controlled as the reading parameter.
The target information acquisition apparatus according to claim 2, wherein the control unit controls the antenna output in conjunction with a focal length.
前記判定手段により映っている対象物の数が1つであると判定されたときに、前記複合データを生成することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の対象物情報取得装置。 The generating unit includes a determining unit that performs image processing on the image data of the photographed object to determine whether the number of objects reflected therein is one or not.
2. The object information acquisition apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the composite data is generated when it is determined that the number of objects reflected by the determination unit is one.
前記判定手段により前記対象物からの情報であると判定されたときに、前記複合データを生成することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の対象物情報取得装置。 The generation unit includes a determination unit that determines whether the read information is information from the object;
The object information acquisition apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the composite data is generated when the determination unit determines that the information is information from the object.
前記読み取られた情報が、あらかじめ決められた情報と一致する場合、前記複合データを生成することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の対象物情報取得装置。 Determination means for determining whether or not the read information matches predetermined information;
The object information acquisition apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the composite data is generated when the read information matches predetermined information.
あらかじめ複数の対象物に対して画像特徴量と固有の識別子を組み合わせた複合データを記憶する記憶手段と、
前記撮影手段により対象物を撮影する際の撮影範囲と、前記読取手段によりRFタグの識別子を読み取る際の読取範囲とを一致させるべく、前記撮影手段の撮影パラメータと前記読取手段の読取パラメータとを制御する制御手段と、
撮影された画像データから画像特徴量を抽出する抽出手段と、
前記抽出された画像特徴量と読み取られた識別子とを組み合わせた複合データを前記記憶手段に記憶されている複合データと比較することにより対象物を認証する認証手段とを有することを特徴とする対象物認証装置。 An object authentication apparatus having an imaging unit for imaging an object and a reading unit that reads an identifier from an RF tag attached to the object,
Storage means for storing composite data combining image features and unique identifiers for a plurality of objects in advance;
An imaging parameter of the imaging unit and a reading parameter of the reading unit are set so that the imaging range when the object is imaged by the imaging unit and the reading range when the identifier of the RF tag is read by the reading unit are matched. Control means for controlling;
Extraction means for extracting image feature values from the captured image data;
And an authentication unit that authenticates the object by comparing composite data obtained by combining the extracted image feature quantity and the read identifier with the composite data stored in the storage unit. Product authentication device.
前記読取パラメータとして前記指向性アンテナの指向範囲を制御可能であり、前記撮影パラメータとして視野角又はズーム率を制御可能であり、
前記制御手段は、前記視野角又はズーム率と連動して前記指向性アンテナの指向範囲を制御することを特徴とする請求項9に記載の対象物認証装置。 The reading means has a directional antenna capable of receiving with high sensitivity electromagnetic waves coming from a direction within a certain angular range (directing range) centered on the line-of-sight direction of the photographing means,
The directivity range of the directional antenna can be controlled as the reading parameter, and the viewing angle or the zoom rate can be controlled as the imaging parameter.
The object authentication apparatus according to claim 9, wherein the control unit controls a directivity range of the directional antenna in conjunction with the viewing angle or the zoom rate.
前記制御部は、焦点距離と連動してアンテナ出力を制御することを特徴とする請求項9に記載の対象物認証装置。 The focal length can be controlled as the shooting parameter, and the antenna output of the directional antenna can be controlled as the reading parameter.
The object authentication apparatus according to claim 9, wherein the control unit controls an antenna output in conjunction with a focal length.
前記判定手段により映っている対象物の数が1つであると判定されたときに、対象物を認証することを特徴とする請求項9に記載の対象物認証装置。 The authentication unit includes a determination unit that determines whether or not the number of objects reflected in the image data of the photographed object is one by performing image processing on the image data;
The object authentication apparatus according to claim 9, wherein the object is authenticated when it is determined that the number of objects reflected by the determination unit is one.
前記判定手段により前記対象物からの識別子であると判定されたときに、対象物を認証することを特徴とする請求項9に記載の対象物認証装置。 The authentication unit includes a determination unit that determines whether the read identifier is an identifier from the object,
The object authentication apparatus according to claim 9, wherein the object is authenticated when the determination unit determines that the identifier is an identifier from the object.
前記撮影手段により対象物を撮影する際の撮影範囲と、前記読取手段によりRFタグの情報を読み取る際の読取範囲とを一致させるべく、前記撮影手段の撮影パラメータと前記読取手段の読取パラメータとを制御する制御工程と、
撮影された対象物の画像データと読み取られた情報とを組み合わせた複合データを生成する生成工程とを有することを特徴とする対象物情報取得装置の制御方法。 A method for controlling an object information acquisition apparatus, comprising: an imaging unit for imaging an object; and a reading unit that reads information from an RF tag attached to the object,
An imaging parameter of the imaging unit and a reading parameter of the reading unit are set so that the imaging range when the object is imaged by the imaging unit and the reading range when the information of the RF tag is read by the reading unit are matched. A control process to control;
A control method for an object information acquiring apparatus, comprising: a generation step of generating composite data combining image data of a photographed object and read information.
前記撮影手段により対象物を撮影する際の撮影範囲と、前記読取手段によりRFタグの識別子を読み取る際の読取範囲とを一致させるべく、前記撮影手段の撮影パラメータと前記読取手段の読取パラメータとを制御する制御工程と、
撮影された画像データから画像特徴量を抽出する抽出工程と、
前記抽出された画像特徴量と読み取られた識別子とを組み合わせた複合データを前記記憶手段に記憶されている複合データと比較することにより対象物を認証する認証工程とを有することを特徴とする対象物認証装置の制御方法。 An image capturing means for capturing an object, a reading means for reading an identifier from an RF tag attached to the object, and composite data combining image feature amounts and unique identifiers for a plurality of objects in advance. A method for controlling an object authentication device having storage means for storing,
An imaging parameter of the imaging unit and a reading parameter of the reading unit are set so that the imaging range when the object is imaged by the imaging unit and the reading range when the identifier of the RF tag is read by the reading unit are matched. A control process to control;
An extraction step of extracting image feature values from the captured image data;
And an authentication step of authenticating the object by comparing composite data obtained by combining the extracted image feature quantity and the read identifier with composite data stored in the storage means. Control method for object authentication device.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004220683A JP2006040059A (en) | 2004-07-28 | 2004-07-28 | Object information acquiring device, object authentication devices, and control method thereof |
| US11/190,624 US7362219B2 (en) | 2004-07-28 | 2005-07-26 | Information acquisition apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004220683A JP2006040059A (en) | 2004-07-28 | 2004-07-28 | Object information acquiring device, object authentication devices, and control method thereof |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006040059A true JP2006040059A (en) | 2006-02-09 |
| JP2006040059A5 JP2006040059A5 (en) | 2007-09-13 |
Family
ID=35904972
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004220683A Pending JP2006040059A (en) | 2004-07-28 | 2004-07-28 | Object information acquiring device, object authentication devices, and control method thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2006040059A (en) |
Cited By (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007213298A (en) * | 2006-02-09 | 2007-08-23 | Sato Corp | RFID printer |
| JP2008090796A (en) * | 2006-10-05 | 2008-04-17 | Denso Wave Inc | Reader/writer |
| JP2009187250A (en) * | 2008-02-06 | 2009-08-20 | Brother Ind Ltd | Wireless tag search device |
| US7812727B2 (en) | 2007-07-31 | 2010-10-12 | Fujitsu Limited | Wireless tag determination method, wireless tag determination system, reader control device, and storage medium |
| JP2012079101A (en) * | 2010-10-01 | 2012-04-19 | Nippon Signal Co Ltd:The | Authentication system |
| US8614753B2 (en) | 2007-07-02 | 2013-12-24 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Method and apparatus for generating image file having object information |
| JP2014142721A (en) * | 2013-01-22 | 2014-08-07 | Toshiba Tec Corp | Wireless tag communication device and program |
| KR20150103048A (en) * | 2013-01-02 | 2015-09-09 | 더 보잉 컴파니 | Active rfid tag with passive interrogator |
| CN111382588A (en) * | 2018-12-25 | 2020-07-07 | 欧姆龙株式会社 | Tag communication system, portable terminal, and computer-readable storage medium |
| JP2021012557A (en) * | 2019-07-08 | 2021-02-04 | 株式会社デンソーウェーブ | Authentication system |
| JP7348979B1 (en) | 2022-03-22 | 2023-09-21 | ソフトバンク株式会社 | Communication device, program, and control method |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000261751A (en) * | 1998-12-17 | 2000-09-22 | Internatl Business Mach Corp <Ibm> | System and method for image recognition |
| JP2001338295A (en) * | 2000-05-26 | 2001-12-07 | Wens Network Kk | Identity authenticating system based on biological information |
| JP2001338296A (en) * | 2000-03-22 | 2001-12-07 | Toshiba Corp | Face image recognition device and traffic control device |
| JP2004120304A (en) * | 2002-09-26 | 2004-04-15 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | Information recorder |
| JP2004175509A (en) * | 2002-11-27 | 2004-06-24 | Nec Corp | Article location management device |
-
2004
- 2004-07-28 JP JP2004220683A patent/JP2006040059A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000261751A (en) * | 1998-12-17 | 2000-09-22 | Internatl Business Mach Corp <Ibm> | System and method for image recognition |
| JP2001338296A (en) * | 2000-03-22 | 2001-12-07 | Toshiba Corp | Face image recognition device and traffic control device |
| JP2001338295A (en) * | 2000-05-26 | 2001-12-07 | Wens Network Kk | Identity authenticating system based on biological information |
| JP2004120304A (en) * | 2002-09-26 | 2004-04-15 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | Information recorder |
| JP2004175509A (en) * | 2002-11-27 | 2004-06-24 | Nec Corp | Article location management device |
Cited By (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007213298A (en) * | 2006-02-09 | 2007-08-23 | Sato Corp | RFID printer |
| JP2008090796A (en) * | 2006-10-05 | 2008-04-17 | Denso Wave Inc | Reader/writer |
| KR101485458B1 (en) * | 2007-07-02 | 2015-01-26 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method For Creating Image File Including Information of Individual And Apparatus Thereof |
| US8614753B2 (en) | 2007-07-02 | 2013-12-24 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Method and apparatus for generating image file having object information |
| US7812727B2 (en) | 2007-07-31 | 2010-10-12 | Fujitsu Limited | Wireless tag determination method, wireless tag determination system, reader control device, and storage medium |
| JP2009187250A (en) * | 2008-02-06 | 2009-08-20 | Brother Ind Ltd | Wireless tag search device |
| JP2012079101A (en) * | 2010-10-01 | 2012-04-19 | Nippon Signal Co Ltd:The | Authentication system |
| KR20150103048A (en) * | 2013-01-02 | 2015-09-09 | 더 보잉 컴파니 | Active rfid tag with passive interrogator |
| JP2016505980A (en) * | 2013-01-02 | 2016-02-25 | ザ・ボーイング・カンパニーTheBoeing Company | Passive RFID Assisted Active RFID Tag |
| KR102083210B1 (en) | 2013-01-02 | 2020-03-02 | 더 보잉 컴파니 | Active rfid tag with passive interrogator |
| JP2014142721A (en) * | 2013-01-22 | 2014-08-07 | Toshiba Tec Corp | Wireless tag communication device and program |
| CN111382588A (en) * | 2018-12-25 | 2020-07-07 | 欧姆龙株式会社 | Tag communication system, portable terminal, and computer-readable storage medium |
| CN111382588B (en) * | 2018-12-25 | 2024-07-30 | 欧姆龙株式会社 | Tag communication system, portable terminal, and computer-readable storage medium |
| JP2021012557A (en) * | 2019-07-08 | 2021-02-04 | 株式会社デンソーウェーブ | Authentication system |
| JP7259601B2 (en) | 2019-07-08 | 2023-04-18 | 株式会社デンソーウェーブ | Authentication system |
| US12026976B2 (en) | 2019-07-08 | 2024-07-02 | Denso Wave Incorporated | Authentication system and authentication method |
| JP7348979B1 (en) | 2022-03-22 | 2023-09-21 | ソフトバンク株式会社 | Communication device, program, and control method |
| JP2023140202A (en) * | 2022-03-22 | 2023-10-04 | ソフトバンク株式会社 | Communication device, program, and control method |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7362219B2 (en) | Information acquisition apparatus | |
| CN104794419B (en) | The information-reading method of portable terminal device and portable terminal device | |
| US20150199890A1 (en) | Systems and methods for rfid-based retail management | |
| WO2010035525A1 (en) | Goods management system | |
| US20110156907A1 (en) | Apparatus for communicating with rfid tag and system for article management | |
| JP2006040059A (en) | Object information acquiring device, object authentication devices, and control method thereof | |
| US9888451B2 (en) | Method of dynamically associating an accessory ID with a portable memory device and displaying confirmation of the association | |
| US20150243063A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for displaying biometric information | |
| US10943155B2 (en) | System of recognizing identity of object and method of automatically recognizing identity of object | |
| JP2007193566A (en) | Rfid system | |
| JP4706914B2 (en) | Goods management system | |
| JP2006040035A (en) | Information acquisition device, distinguishing method for distinguishing position of photographic target object inside photographic image, and target object specification method for specifying photographic target object inside photographic image | |
| KR20100102285A (en) | Locating system and method using cctv and radio frequency identification technology | |
| US20190278927A1 (en) | Electronic document display control system | |
| JP6794242B2 (en) | Wireless communication device and ticket gate | |
| US7940632B2 (en) | Recording medium, data use limitating method, and program | |
| JP2017046324A (en) | User terminal, object recognition server, notification method and user terminal program | |
| EP4044064B1 (en) | Radio frequency identification terminal and use method therefor | |
| JP2004342007A (en) | Article retrieval system | |
| JP4314168B2 (en) | IC tag system | |
| JP7325297B2 (en) | Wireless tag position detection system | |
| JP6720699B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus, information processing system, authentication method and program | |
| CN110390217B (en) | Tag communication apparatus, control method thereof, and computer-readable storage medium | |
| KR20200060994A (en) | Method for monitoring material location using low-power infrared beacon and speed camera and system using the same | |
| JP5673208B2 (en) | Mobile terminal and program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070727 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070727 |
|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20070727 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20100720 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100730 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20101122 |