JP2005298219A - Glass sheet having low reflection film for automobile - Google Patents
Glass sheet having low reflection film for automobile Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2005298219A JP2005298219A JP2002012560A JP2002012560A JP2005298219A JP 2005298219 A JP2005298219 A JP 2005298219A JP 2002012560 A JP2002012560 A JP 2002012560A JP 2002012560 A JP2002012560 A JP 2002012560A JP 2005298219 A JP2005298219 A JP 2005298219A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- glass plate
- film
- low
- automobiles
- reflection film
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 219
- 238000002834 transmittance Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 36
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 34
- 239000005340 laminated glass Substances 0.000 claims description 20
- 229910004298 SiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 16
- 229910010413 TiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 13
- 229910000906 Bronze Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 12
- 239000010974 bronze Substances 0.000 claims description 12
- KUNSUQLRTQLHQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N copper tin Chemical compound [Cu].[Sn] KUNSUQLRTQLHQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- 239000010419 fine particle Substances 0.000 claims description 10
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 10
- 239000005361 soda-lime glass Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 229920001169 thermoplastic Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000004416 thermosoftening plastic Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 abstract description 10
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 163
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 58
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 24
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 22
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 20
- UQSXHKLRYXJYBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron oxide Chemical compound [Fe]=O UQSXHKLRYXJYBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 18
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 16
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 15
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 13
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 11
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 10
- 238000003980 solgel method Methods 0.000 description 10
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 description 9
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 8
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 8
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 description 7
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 6
- 150000003377 silicon compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 6
- LIVNPJMFVYWSIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon monoxide Chemical compound [Si-]#[O+] LIVNPJMFVYWSIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 229920002037 poly(vinyl butyral) polymer Polymers 0.000 description 5
- -1 titanium alkoxide Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 4
- OGIDPMRJRNCKJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N titanium oxide Inorganic materials [Ti]=O OGIDPMRJRNCKJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oxalic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(O)=O MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 150000004703 alkoxides Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000013522 chelant Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000006103 coloring component Substances 0.000 description 3
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- MTHSVFCYNBDYFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethylene glycol Chemical compound OCCOCCO MTHSVFCYNBDYFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 3
- QSHDDOUJBYECFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N mercury Chemical compound [Hg] QSHDDOUJBYECFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229910052753 mercury Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000003960 organic solvent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229960005235 piperonyl butoxide Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000002310 reflectometry Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000005336 safety glass Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000004576 sand Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 150000003609 titanium compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- KBPLFHHGFOOTCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-Octanol Chemical compound CCCCCCCCO KBPLFHHGFOOTCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- SVTBMSDMJJWYQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylpentane-2,4-diol Chemical compound CC(O)CC(C)(C)O SVTBMSDMJJWYQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonia Chemical compound N QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron Chemical compound [B] ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-M Chloride anion Chemical compound [Cl-] VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorane Chemical compound F KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Butanol Chemical compound CCCCO LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphoric acid Chemical compound OP(O)(O)=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfur Chemical compound [S] NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UCKMPCXJQFINFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulphide Chemical compound [S-2] UCKMPCXJQFINFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titan oxide Chemical compound O=[Ti]=O GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Trifluoroacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(F)(F)F DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052796 boron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000003054 catalyst Substances 0.000 description 2
- SWXVUIWOUIDPGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N diacetone alcohol Chemical compound CC(=O)CC(C)(C)O SWXVUIWOUIDPGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- ZSIAUFGUXNUGDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexan-1-ol Chemical compound CCCCCCO ZSIAUFGUXNUGDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011229 interlayer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000001678 irradiating effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 2
- BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N methanoic acid Natural products OC=O BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000035699 permeability Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000004014 plasticizer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 2
- HUAUNKAZQWMVFY-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium;oxocalcium;hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[Na+].[Ca]=O HUAUNKAZQWMVFY-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007858 starting material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000011593 sulfur Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052717 sulfur Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- VXUYXOFXAQZZMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N titanium(IV) isopropoxide Chemical compound CC(C)O[Ti](OC(C)C)(OC(C)C)OC(C)C VXUYXOFXAQZZMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WKYKXNFEMCNSKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-methoxypropan-1-olate titanium(4+) Chemical compound COC([O-])CC.[Ti+4].COC([O-])CC.COC([O-])CC.COC([O-])CC WKYKXNFEMCNSKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XNWFRZJHXBZDAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-METHOXYETHANOL Chemical compound COCCO XNWFRZJHXBZDAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LCZVSXRMYJUNFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[2-(2-hydroxypropoxy)propoxy]propan-1-ol Chemical compound CC(O)COC(C)COC(C)CO LCZVSXRMYJUNFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VTYZTWSUUXQSPZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]ethanol;propan-2-ol;titanium Chemical compound [Ti].CC(C)O.CC(C)O.OCCN(CCO)CCO.OCCN(CCO)CCO VTYZTWSUUXQSPZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IZKAZYONCIKJID-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-butoxyethanol;2-ethoxyethanol Chemical compound CCOCCO.CCCCOCCO IZKAZYONCIKJID-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SVONRAPFKPVNKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-ethoxyethyl acetate Chemical compound CCOCCOC(C)=O SVONRAPFKPVNKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KTXWGMUMDPYXNN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-ethylhexan-1-olate;titanium(4+) Chemical compound [Ti+4].CCCCC(CC)C[O-].CCCCC(CC)C[O-].CCCCC(CC)C[O-].CCCCC(CC)C[O-] KTXWGMUMDPYXNN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QUVMSYUGOKEMPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylpropan-1-olate;titanium(4+) Chemical compound [Ti+4].CC(C)C[O-].CC(C)C[O-].CC(C)C[O-].CC(C)C[O-] QUVMSYUGOKEMPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SDTMFDGELKWGFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylpropan-2-olate Chemical compound CC(C)(C)[O-] SDTMFDGELKWGFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OSWFIVFLDKOXQC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(3-methoxyphenyl)aniline Chemical compound COC1=CC=CC(C=2C=CC(N)=CC=2)=C1 OSWFIVFLDKOXQC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MBMLMWLHJBBADN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ferrous sulfide Chemical compound [Fe]=S MBMLMWLHJBBADN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GRYLNZFGIOXLOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nitric acid Chemical compound O[N+]([O-])=O GRYLNZFGIOXLOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Sulfate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sulfate Chemical compound [O-]S([O-])(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- BOTDANWDWHJENH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetraethyl orthosilicate Chemical compound CCO[Si](OCC)(OCC)OCC BOTDANWDWHJENH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OXMKQIVTFWEMRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N [B+3].CCCC[O-].CCCC[O-].CCCC[O-] Chemical compound [B+3].CCCC[O-].CCCC[O-].CCCC[O-] OXMKQIVTFWEMRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002250 absorbent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002745 absorbent Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003377 acid catalyst Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002378 acidificating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910000147 aluminium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- JPUHCPXFQIXLMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium triethoxide Chemical compound CCO[Al](OCC)OCC JPUHCPXFQIXLMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910021529 ammonia Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000003373 anti-fouling effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000006121 base glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001639 boron compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- FPCJKVGGYOAWIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N butan-1-ol;titanium Chemical compound [Ti].CCCCO.CCCCO.CCCCO.CCCCO FPCJKVGGYOAWIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MTKOCRSQUPLVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N butan-1-olate;titanium(2+) Chemical compound CCCCO[Ti]OCCCC MTKOCRSQUPLVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003638 chemical reducing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005229 chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- IFMWVBVPVXRZHE-UHFFFAOYSA-M chlorotitanium(3+);propan-2-olate Chemical compound [Cl-].[Ti+4].CC(C)[O-].CC(C)[O-].CC(C)[O-] IFMWVBVPVXRZHE-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000010941 cobalt Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910017052 cobalt Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- GUTLYIVDDKVIGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N cobalt atom Chemical compound [Co] GUTLYIVDDKVIGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004040 coloring Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005336 cracking Methods 0.000 description 1
- XXJWXESWEXIICW-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethylene glycol monoethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCCOCCO XXJWXESWEXIICW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940075557 diethylene glycol monoethyl ether Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000003618 dip coating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004090 dissolution Methods 0.000 description 1
- UHSDHNXHBQDMMH-UHFFFAOYSA-L ethanolate;titanium(4+);dichloride Chemical compound CCO[Ti](Cl)(Cl)OCC UHSDHNXHBQDMMH-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 125000001495 ethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 230000005284 excitation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010304 firing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000006260 foam Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019253 formic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000007756 gravure coating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940051250 hexylene glycol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229910000358 iron sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- BAUYGSIQEAFULO-UHFFFAOYSA-L iron(2+) sulfate (anhydrous) Chemical compound [Fe+2].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O BAUYGSIQEAFULO-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 230000031700 light absorption Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000005499 meniscus Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910001507 metal halide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000005309 metal halides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- ZEIWWVGGEOHESL-UHFFFAOYSA-N methanol;titanium Chemical compound [Ti].OC.OC.OC.OC ZEIWWVGGEOHESL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CRNJBCMSTRNIOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N methanolate silicon(4+) Chemical compound [Si+4].[O-]C.[O-]C.[O-]C.[O-]C CRNJBCMSTRNIOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910017604 nitric acid Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- KQJBQMSCFSJABN-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecan-1-olate;titanium(4+) Chemical compound [Ti+4].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC[O-].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC[O-].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC[O-].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC[O-] KQJBQMSCFSJABN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000006408 oxalic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000007800 oxidant agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- HVAMZGADVCBITI-UHFFFAOYSA-M pent-4-enoate Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)CCC=C HVAMZGADVCBITI-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000011148 porous material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007639 printing Methods 0.000 description 1
- HKJYVRJHDIPMQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N propan-1-olate;titanium(4+) Chemical compound CCCO[Ti](OCCC)(OCCC)OCCC HKJYVRJHDIPMQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KVIKMJYUMZPZFU-UHFFFAOYSA-N propan-2-ol;titanium Chemical compound [Ti].CC(C)O.CC(C)O KVIKMJYUMZPZFU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007650 screen-printing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000005368 silicate glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002893 slag Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052938 sodium sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000011152 sodium sulphate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000004528 spin coating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004544 sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003381 stabilizer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002562 thickening agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- JMXKSZRRTHPKDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N titanium ethoxide Chemical compound [Ti+4].CC[O-].CC[O-].CC[O-].CC[O-] JMXKSZRRTHPKDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005341 toughened glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- WOZZOSDBXABUFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N tri(butan-2-yloxy)alumane Chemical compound [Al+3].CCC(C)[O-].CCC(C)[O-].CCC(C)[O-] WOZZOSDBXABUFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MYWQGROTKMBNKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N tributoxyalumane Chemical compound [Al+3].CCCC[O-].CCCC[O-].CCCC[O-] MYWQGROTKMBNKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YNJBWRMUSHSURL-UHFFFAOYSA-N trichloroacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(Cl)(Cl)Cl YNJBWRMUSHSURL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AJSTXXYNEIHPMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N triethyl borate Chemical compound CCOB(OCC)OCC AJSTXXYNEIHPMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UAEJRRZPRZCUBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N trimethoxyalumane Chemical compound [Al+3].[O-]C.[O-]C.[O-]C UAEJRRZPRZCUBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WRECIMRULFAWHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N trimethyl borate Chemical compound COB(OC)OC WRECIMRULFAWHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OBROYCQXICMORW-UHFFFAOYSA-N tripropoxyalumane Chemical compound [Al+3].CCC[O-].CCC[O-].CCC[O-] OBROYCQXICMORW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LTEHWCSSIHAVOQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N tripropyl borate Chemical compound CCCOB(OCCC)OCCC LTEHWCSSIHAVOQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZMCWFMOZBTXGKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N tritert-butyl borate Chemical compound CC(C)(C)OB(OC(C)(C)C)OC(C)(C)C ZMCWFMOZBTXGKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C03—GLASS; MINERAL OR SLAG WOOL
- C03C—CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF GLASSES, GLAZES OR VITREOUS ENAMELS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF GLASS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF FIBRES OR FILAMENTS MADE FROM GLASS, MINERALS OR SLAGS; JOINING GLASS TO GLASS OR OTHER MATERIALS
- C03C17/00—Surface treatment of glass, not in the form of fibres or filaments, by coating
- C03C17/34—Surface treatment of glass, not in the form of fibres or filaments, by coating with at least two coatings having different compositions
- C03C17/3411—Surface treatment of glass, not in the form of fibres or filaments, by coating with at least two coatings having different compositions with at least two coatings of inorganic materials
- C03C17/3417—Surface treatment of glass, not in the form of fibres or filaments, by coating with at least two coatings having different compositions with at least two coatings of inorganic materials all coatings being oxide coatings
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B17/00—Layered products essentially comprising sheet glass, or glass, slag, or like fibres
- B32B17/06—Layered products essentially comprising sheet glass, or glass, slag, or like fibres comprising glass as the main or only constituent of a layer, next to another layer of a specific material
- B32B17/10—Layered products essentially comprising sheet glass, or glass, slag, or like fibres comprising glass as the main or only constituent of a layer, next to another layer of a specific material of synthetic resin
- B32B17/10005—Layered products essentially comprising sheet glass, or glass, slag, or like fibres comprising glass as the main or only constituent of a layer, next to another layer of a specific material of synthetic resin laminated safety glass or glazing
- B32B17/10009—Layered products essentially comprising sheet glass, or glass, slag, or like fibres comprising glass as the main or only constituent of a layer, next to another layer of a specific material of synthetic resin laminated safety glass or glazing characterized by the number, the constitution or treatment of glass sheets
- B32B17/10036—Layered products essentially comprising sheet glass, or glass, slag, or like fibres comprising glass as the main or only constituent of a layer, next to another layer of a specific material of synthetic resin laminated safety glass or glazing characterized by the number, the constitution or treatment of glass sheets comprising two outer glass sheets
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B17/00—Layered products essentially comprising sheet glass, or glass, slag, or like fibres
- B32B17/06—Layered products essentially comprising sheet glass, or glass, slag, or like fibres comprising glass as the main or only constituent of a layer, next to another layer of a specific material
- B32B17/10—Layered products essentially comprising sheet glass, or glass, slag, or like fibres comprising glass as the main or only constituent of a layer, next to another layer of a specific material of synthetic resin
- B32B17/10005—Layered products essentially comprising sheet glass, or glass, slag, or like fibres comprising glass as the main or only constituent of a layer, next to another layer of a specific material of synthetic resin laminated safety glass or glazing
- B32B17/10165—Functional features of the laminated safety glass or glazing
- B32B17/10174—Coatings of a metallic or dielectric material on a constituent layer of glass or polymer
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C03—GLASS; MINERAL OR SLAG WOOL
- C03C—CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF GLASSES, GLAZES OR VITREOUS ENAMELS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF GLASS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF FIBRES OR FILAMENTS MADE FROM GLASS, MINERALS OR SLAGS; JOINING GLASS TO GLASS OR OTHER MATERIALS
- C03C3/00—Glass compositions
- C03C3/04—Glass compositions containing silica
- C03C3/076—Glass compositions containing silica with 40% to 90% silica, by weight
- C03C3/083—Glass compositions containing silica with 40% to 90% silica, by weight containing aluminium oxide or an iron compound
- C03C3/085—Glass compositions containing silica with 40% to 90% silica, by weight containing aluminium oxide or an iron compound containing an oxide of a divalent metal
- C03C3/087—Glass compositions containing silica with 40% to 90% silica, by weight containing aluminium oxide or an iron compound containing an oxide of a divalent metal containing calcium oxide, e.g. common sheet or container glass
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C03—GLASS; MINERAL OR SLAG WOOL
- C03C—CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF GLASSES, GLAZES OR VITREOUS ENAMELS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF GLASS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF FIBRES OR FILAMENTS MADE FROM GLASS, MINERALS OR SLAGS; JOINING GLASS TO GLASS OR OTHER MATERIALS
- C03C4/00—Compositions for glass with special properties
- C03C4/02—Compositions for glass with special properties for coloured glass
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C03—GLASS; MINERAL OR SLAG WOOL
- C03C—CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF GLASSES, GLAZES OR VITREOUS ENAMELS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF GLASS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF FIBRES OR FILAMENTS MADE FROM GLASS, MINERALS OR SLAGS; JOINING GLASS TO GLASS OR OTHER MATERIALS
- C03C4/00—Compositions for glass with special properties
- C03C4/08—Compositions for glass with special properties for glass selectively absorbing radiation of specified wave lengths
- C03C4/082—Compositions for glass with special properties for glass selectively absorbing radiation of specified wave lengths for infrared absorbing glass
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C03—GLASS; MINERAL OR SLAG WOOL
- C03C—CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF GLASSES, GLAZES OR VITREOUS ENAMELS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF GLASS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF FIBRES OR FILAMENTS MADE FROM GLASS, MINERALS OR SLAGS; JOINING GLASS TO GLASS OR OTHER MATERIALS
- C03C4/00—Compositions for glass with special properties
- C03C4/08—Compositions for glass with special properties for glass selectively absorbing radiation of specified wave lengths
- C03C4/085—Compositions for glass with special properties for glass selectively absorbing radiation of specified wave lengths for ultraviolet absorbing glass
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Geochemistry & Mineralogy (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Joining Of Glass To Other Materials (AREA)
- Surface Treatment Of Glass (AREA)
Abstract
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板に関し、特に自動車のウインドシールド合わせガラスに好適な自動車低反射膜付きガラス板に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
例えば、自動車のウインドシールドガラスでは、ダッシュボードの写り込みなどを防ぐために、低反射膜付きガラス板が求められている。このようなガラス板として、本出願人は特開2000−256042にて、「自動車用低反射ガラス物品」を提案している。
【0003】
すなわち、「透明ガラス基体の少なくとも片側表面に、ガラス面側から数えて第1層の膜の屈折率(n1)が1.65〜2.20で、かつ膜厚が110〜150nmである薄膜層であり、次いで該第1層薄膜上に、第2層として屈折率(n2)が1.37〜1.49でかつ膜厚が81〜100nmであるシリカを主成分とする薄膜層を被覆積層してなり、可視光を膜面側から12度および60度の入射角でそれぞれ入射したときの反射光がそれぞれ22%以下および10%以下の刺激純度を有する自動車用低反射ガラス物品」である。
【0004】
ところで自動車用ガラス板では、冷房負荷の低減などのために、赤外線の遮蔽能も求められている。例えば、特開2001−151539では、Fe2O3換算した全鉄0.3〜1%含有するソーダライムシリカガラスからなるガラス板を、赤外線熱遮蔽微粒子を含む中間膜で合わせた合わせガラスが提案されている。
【0005】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
上述した特開2000−256042では、ガラス基板としては、透明ガラスであれば無着色あるいは着色のどちらでもよいことが示されている。着色ガラスとして具体的には、グリーン、ブロンズ、グレーあるいは高性能UVカットグリーンガラス、高性能UVカットブロンズガラス等が挙げられ、特に自動車用としてはグリーン色系、なかでも熱線・紫外線吸収性能を得やすいものであればより好ましい、としている。
【0006】
しかしながら、実施例で用いられているガラス基板は、無着色ソーダライム珪酸塩ガラス板のみであって、着色ガラスを基板とした場合における低反射膜の作用効果は十分に示されていない。
【0007】
また、上述した特開2001−151539では、実施例において可視光線透過率が70%以上に限定されている。このことから明らかなように、自動車用安全ガラスの規格を満足させるために、ガラスの組み合わせや中間膜に分散させる微粒子の量に制約を受けていることがわかる。また、低反射機能については言及されていない。
【0008】
そこで本発明は、自動車用ガラスにおける規格である可視光線透過率70%以上を実現した上で、優れた低反射性と優れた日射遮蔽性能を実現した自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板の提供を目的とする。
【0009】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明は、透明体上に設けられた低反射膜が光の反射を抑えることによって、結果的に透明体の透過光線量を増加させる効果を利用している。すなわち、可視光線透過率が少なくとも68%であるガラス板を用いれば、少なくとも70%の可視光線透過率が確保され、さらに日射透過率は低反射膜未形成であるガラス板の日射透過率をほぼ維持することができ、優れた低反射性を有する自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板を得ることができる。
【0010】
すなわち本発明は、請求項1に記載の発明として、
自動車用ガラス板であって、車内面側の主表面に2層式低反射膜が設けられている自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板において、
前記ガラス板のみの可視光線透過率は少なくとも68%であり、低反射膜付きガラス板としての可視光線透過率が、少なくとも70%であることを特徴とする自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板である。
【0011】
請求項2に記載の発明として、
請求項1に記載の自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板において、
前記低反射膜は、ガラス側から数えて第1層が、屈折率(n1)=1.68〜2.3でかつ膜厚(d1)=100〜140nmであり、該第1層上に積層される第2層が、屈折率(n2)=1.4〜1.5でかつ膜厚(d2)=80〜110nmである2層式低反射膜である自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板である。
【0012】
請求項3に記載の発明として、
請求項2に記載の自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板において、
前記低反射膜の第1層が屈折率(n1)=1.70〜1.95で、かつ第2層が屈折率(n2)=1.40〜1.47である自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板である。
【0013】
請求項4に記載の発明として、
請求項1〜3いずれか1項に記載の自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板において、
前記ガラス板は、グリーン系、ブロンズ系、グレー系、UVカットグリーン系、またはUVカットブロンズ系の単一ガラス板である自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板である。
【0014】
請求項5に記載の発明として、
請求項4に記載の自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板において、
前記ガラス板は、グリーン系またはUVカットグリーン系ガラスであって、
前記ガラスは、質量百分率表示でFe2O3換算した全鉄0.3〜1%を含有するソーダライムシリカガラスからなる自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板である。
【0015】
請求項6に記載の発明として、
請求項1〜3いずれか1項に記載の自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板において、
前記ガラス板は、少なくとも2枚の単一ガラス板が熱可塑性中間膜を介して接着された合わせガラスである自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板である。
【0016】
請求項7に記載の発明として、
請求項6に記載の自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板において、
前記合わせガラスの中間膜は、0.2μm以下の粒径よりなるITO微粒子を、中間膜に対して0.01〜0.8質量%の割合で含んでいる自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板である。
【0017】
請求項8に記載の発明として、
請求項6または7に記載の自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板において、
前記ガラス板は、クリア系、グリーン系、ブロンズ系、グレー系、UVカットグリーン系、およびUVカットブロンズ系ガラス板のうち、同種または異種のガラス板を組み合わせてなる合わせガラス板である自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板(ただし、クリア系ガラス板同士を組み合わせた合わせガラス板を除く)である。
【0018】
請求項9に記載の発明として、
請求項1〜8いずれか1項に記載の自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板において、
前記低反射膜は、膜面側から可視光線がそれぞれ入射角12度および60度で入射したときの可視光反射率が、それぞれ4.8%以下および11.0%以下の可視光線反射率を有している自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板である。
【0019】
請求項10に記載の発明として、
請求項1〜9いずれか1項に記載の自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板において、
前記低反射膜は、膜面側から可視光線がそれぞれ入射角12度および60度で入射したときの可視光反射率が、当該ガラス板であって前記低反射膜未形成のガラス面におけるそれぞれ12度および60度の入射角での可視光反射率よりも、それぞれ少なくとも2.4%および少なくとも3.5%小さい可視光反射率を有している自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板である。
【0020】
請求項11に記載の発明として、
請求項1〜10いずれか1項に記載の自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板において、
前記低反射膜の第1層は、SiO2およびTiO2を含有して、あるいは実質的にTiO2のみからなる自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板である。
【0021】
請求項12に記載の発明として、
請求項1〜11いずれか1項に記載の自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板において、
前記第1層はモル比でTi:Si=35:65〜100:0であり、第2層はSiO2を含有する自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板である。
【0022】
請求項13に記載の発明として、
請求項1〜12いずれか1項に記載の自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板において、
前記低反射膜の第2層は、実質的にSiO2のみからなる自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板である。
【0023】
請求項14に記載の発明として、
請求項1〜13いずれか1項に記載の自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板において、
前記低反射膜は、膜面側から可視光線が入射角12度および60度でそれぞれ入射したときの可視光が、それぞれ22%以下および10%以下の刺激純度を有している自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板である。
【0024】
(低反射膜)
まず、本発明による自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板を構成する低反射膜について述べる。2層式低反射膜の第1層(高屈折率膜)は、屈折率(n1)=1.68〜2.3でかつ膜厚(d1)=100〜140nmとすることが好ましい。
【0025】
第1層の屈折率(n1)が1.68未満であると、高入射角から低入射角にわたる入射光に対して十分な反射光強度の低減効果が得られない。
【0026】
第1層の屈折率(n1)が2.3よりも大きくなると、特定波長の反射率は下げられるものの、可視域全体でみると着色や反射が強くなって、可視光透過率が70%以下となり、所望の反射低減効果が得られないためである。第1層の屈折率(n1)の好ましい範囲は、1.70から1.95である。
【0027】
また第1層膜の厚み(d1)が100nmより小さいと、高入射角度における反射率が大きくなる。他方、第1層膜の厚み(d1)が140nmより大きくなると、低入射角度における反射率が大きくなる。
【0028】
この第1層は、SiO2およびTiO2を主成分として、あるいは実質的にTiO2のみ、含有することが好ましい。屈折率が比較的高いTiO2(屈折率=2.3程度)と、屈折率が比較的低いSiO2(屈折率=1.45程度)とを種々組み合わせて混合することで、第1層の屈折率(n1)を1.7〜2.3の範囲に自由にコントロールすることができる。なお屈折率=2.3の場合、この第1層は実質的にTiO2のみから構成されることになる。
【0029】
第1層を、SiO2およびTiO2を主成分として、あるいは実質的にTiO2のみから構成すると、耐久性に優れた膜とすることができる。またその他の成分として、屈折率(n1)=1.68〜2.3を満足する範囲で、ZrO2(屈折率=1.95程度)、CeO2、Bi2O3等を、それら合計で10質量%以下の量を添加してもよい。
【0030】
さらに低反射膜の第2層(低屈折率膜)を、屈折率(n2)=1.4〜1.5でかつ膜厚(d2)=80〜110nmとしている。
【0031】
第2層の屈折率(n2)が小さいほど、反射低減効果が大きくなる。しかし、屈折率(n2)が1.4以下である光学薄膜では、膜の密度が小さくなったり、表面の凹凸形状が大きくなったりする。このため、耐摩耗性、耐薬品性、防汚性、耐候性などが悪くなり、耐久性を兼ね備えた光学薄膜は、実現が困難である。
【0032】
また第2層の屈折率(n2)が1.5を超えると、所望の反射低減効果が得られない。好ましい第2層の屈折率(n2)は、1.40〜1.47である。
【0033】
第2膜の厚み(d2)が80nm未満であると、反射光の強度を十分に減ずることができなくなる。第2膜の厚み(d2)が100nmを越えると、低入射角度の反射率が大きくなる。
【0034】
第2層は、実質的にSiO2からなることが好ましい。第2層を実質的にSiO2からなる膜は、化学的安定性、熱的安定性、機械的強度に優れているので、好適である。
【0035】
また、SiO2膜の屈折率は製法にも依存するが、約1.45である。そこでさらに低い屈折率の膜が必要な場合は、SiO2膜の表面に微小な凹凸形状を形成したり、SiO2膜の内部を独立泡状または貫通気孔状の多孔質として、見掛けの屈折率を下げてもよい。また、低屈折率を有する無機微粒子を膜中に入れて、屈折率を下げてもよい。
【0036】
第2層としては、SiO2膜とすることが好ましいが、第2層の屈折率(n2)が1.5以下を満足する範囲で、SiO2以外にB2O3、Al2O3等の酸化物を、合計で15モル%以下含有していても差し支えない。
【0037】
本発明における低反射膜の第1層および第2層を形成する方法としては、ゾル−ゲル法や、スパッタ法、CVD法で形成することが可能である。このうち、コストの面からゾル−ゲル法が望ましい。
【0038】
本発明の低反射膜を構成する第1層および第2層を、ゾル−ゲル法にて形成すると、成膜性がよい上に、均質な膜が得やく、かつ高耐久性を有するので、好適である。
【0039】
(ゾル−ゲル法)
ゾル−ゲル法による塗布溶液のコーティング方法については、スピンコート法、ディップコート法、メニスカスコート法、フローコート法、ロールコート法、グラビアコート法、フレキソ印刷法、スクリーン印刷法など挙げることができる。
【0040】
例えば、本発明における低反射膜の第1層をゾル−ゲル法により形成する場合、すなわち酸化チタン(TiO2)および酸化珪素(SiO2)を含有する光学薄膜として形成する場合、そのコーティング液組成物は、チタン化合物、珪素化合物および溶媒からなり、チタン化合物と珪素化合物を有機溶媒に混合することにより得ることができる。
【0041】
また例えば、本発明における低反射膜の第2層をゾル−ゲル法により形成する場合、すなわち酸化珪素を含有する光学薄膜として形成する場合、そのコーティング液組成物は、珪素化合物および溶媒からなり、珪素化合物を有機溶媒に混合することにより得ることができる。
【0042】
ゾル−ゲル法にて形成する第1層は、モル比でTiO2:SiO2=35:65〜100:0とし、同じく第2層は、SiO2のみからなることが好ましい。
【0043】
上述した各成分の組み合わせのなかでもでも、TiO2およびSiO2は、それらのアルコキシドが安定であるので、好適である。
【0044】
第1層に含有される酸化チタンの出発原料であるチタン化合物としては、チタンアルコキシド、チタンアルコキシド塩化物、チタンキレート化物などが用いられる。チタンアルコキシドとしては、チタンメトキシド、チタンエトキシド、チタンn-プロポキシド、チタンイソプロポキシド、チタンn-ブトキシド、チタンイソブトキシド、チタンメトキシプロポキシド、チタンステアリルオキシド、チタン2-エチルヘキシオキシドなどが例示できる。
【0045】
チタンアルコキシド塩化物としては、チタンクロリドトリイソプロポキシド、チタンジクロリドジエトキシドなどが挙げられる。チタンキレート化物としては、チタントリイソプロポキサシド(2,4-ペンタンジオネート)、チタンジイソプロポキシド(ビス-2,4-ペンタンジオネート)、チタンアリルアセテートトリイソプロポキシド、チタンビス(トリエタノールアミン)ジイソプロポキシド、チタンジ-n-ブトキシド(ビス-2,4-ペンタンジオネート)などが用いられる。
【0046】
第1層および第2層に含有される酸化珪素の出発原料である珪素化合物としては、シリコンアルコキシドをアルコールなどの溶媒に混ぜ、酸性や塩基性の触媒で加水分解、重合を進めたものが用いられる。シリコンアルコキシドとしては、シリコンメトキシド、シリコンエトキシドあるいはそれらのオリゴマー体が用いられる。
【0047】
第2層形成用のコーティング液組成物として、珪素化合物の他に含有させるホウ素化合物としては、ボロンメトキシド、ボロンエトキシド、ボロンn-プロポキシド、ボロンi-プロポキシド、ボロンn-ブトキシド、ボロンs-ブトキシド、ボロンt-ブトキシドおよびこれらのキレート化合物が用いられる。
【0048】
また第2層形成用のコーティング液組成物として添加されるアルミニウム化合物としては、アルミニウムメトキシド、アルミニウムエトキシド、アルミニウムn-プロポキシド、アルミニウムi-プロポキシド、アルミニウムn-ブトキシド、アルミニウムs-ブトキシド、アルミニウムt-ブトキシドおよびこれらのキレート化合物が用いられる。
【0049】
キレート化合物としては、アルミニウム(ジ-s-ブトキシド)エチルアセトアセトネート、アルミニウム(s-ブトキシド)ビスエチルアセトアセトネート、アルミニウム(ジi-プロポキシド)エチルアセトアセトネートなどが好便に用いられる。
【0050】
第1層および第2層形成用のコーティング液組成物に含まれる酸触媒としては塩酸、硫酸、硝酸、塩化水素酸、酢酸、しゅう酸、トリクロロ酢酸、トリフルオロ酢酸、リン酸、フッ酸、蟻酸などが用いられる。塩基性触媒としてはアンモニア、アミン類が用いられる。
【0051】
さらに、第1層および第2層形成用コーティング液組成物に用いられる有機溶媒は、コーティング方法に依存するが、メタノール、エタノール、イソプロパノール、ブタノール、ヘキサノール、オクタノール、2-メトキシエタノール、2-エトキシエタノール、2-ブトキシエタノール、セロソルブアセテート、ジエチレングリコールモノエチルエーテル、へキシレングリコール、ジエチレングリコール、トリプロピレングリコール、ジアセトンアルコールなどが挙げられる。
【0052】
コーティング液組成物としては、上述した溶媒を単独で、またはコーティング液の粘度、表面張力などを調節するために、複数の溶媒を組み合わせて用いても構わない。また安定化剤、レベリング剤、増粘剤などを必要に応じて、少量加えても構わない。溶媒の使用量は、最終的に得られる高屈折率膜および低屈折率膜の膜厚や、採用するコーティング方法にも依存する。通常の場合、溶媒は、全固形分が1〜20%の範囲内に入るように、使用されるとよい。
【0053】
上記コーティング液組成物を前記塗布方法で塗布したあと、乾燥または/および250℃以上の温度で加熱焼成して、次の塗布液を塗布する工程を繰り返すことにより、低反射膜付きガラス板を得ることができる。
【0054】
このようにして得られた低反射膜は、透明性、耐環境性、耐擦傷性などの特性に優れている。またこのような構成とすると、層を重ねても、第1層と第2層の緻密化の過程における膜剥離やクラックの生成を抑制することができる。この膜剥離やクラックは、熱収縮率の違いにより生じると考えられる。
【0055】
上記の250℃以上の加熱による乾燥/焼成を用いる製造方法に代えて、次に述べる光照射方法を用いることもできる。すなわち、上記コーティング液組成物を前記コーティング方法でコートしたあと、可視光線よりも波長の短い電磁波をコーティング膜に照射する工程を行い、引き続いて次のコーティング液をコートする工程を行うという、コート−乾燥工程を繰り返す方法である。
【0056】
可視光線より短い波長を有する電磁波としては、γ線、X線、紫外線があるが、大面積を有する基体への照射を考慮した装置上の実用性の点から紫外線照射が好ましい。紫外光源としてはエキシマランプ、低圧水銀ランプ、高圧水銀ランプ、メタルハライドランプなどが用いられる。
【0057】
365nmを主波長とし254nm、303nmの波長の光を効率よく発光する高圧水銀ランプを用いて、10mW/cm2以上、好ましくは50mW/cm2以上、さらに好ましくは100mW/cm2以上の照射強度で、コーティング膜に照射することが望ましい。
【0058】
このような紫外線光源を用いて、100mJ/cm2以上、好ましくは500mJ/cm2以上、さらに好ましくは1000mJ/cm2以上の照射エネルギーを、上述のコーティング液組成物がコートされた面に照射するとよい。このことにより、低温で透明性、耐環境性、耐擦傷性などの特性に優れ、クラックの生じにくい積層構造の低反射膜を得ることができる。
【0059】
また紫外線を照射しながら、熱による乾燥および/または焼成を同時に行ってもよい。紫外線照射による乾燥方法と、好ましくは250℃以下の温度での熱乾燥による乾燥工程を同時に用いてもよい。このように紫外線照射を利用することにより、乾燥工程の高速化がなされ、生産性を飛躍的に向上させることができる。
【0060】
(ガラス板の組成)
さらに本発明では、ガラス板のみの可視光線透過率が、少なくとも68%であるガラス板を用いる。すなわち例えば、着色されたガラス板としては、グリーン系、ブロンズ系、グレー系あるいは高性能UVカットグリーンガラス、高性能UVカットブロンズガラス等が好ましい。特に、自動車用窓材ではグリーン色系、なかでも熱線・紫外線吸収性能を得やすいものであれば、より好ましい。
【0061】
このような着色ガラス板に用いられる着色成分としては、鉄、コバルト、ニッケルなどが挙げられる。
【0062】
なかでも、鉄を着色成分として含有するソーダライムシリカガラスは、ソーダライムシリカ系の母ガラスに質量百分率表示で、Fe2O3換算した全鉄0.3〜1%を含有するソーダライムシリカガラスであることが好ましい。
【0063】
さらに、近赤外線領域の波長の光の吸収は、全鉄のうちの2価の鉄による吸収が支配的である。したがって、Fe2O3換算したFeO(2価の鉄)と、Fe2O3換算した全鉄の比が0.20〜0.40であることがさらに好ましい。
【0064】
上記特性を有するガラス板としては、実質的に質量百分率表示で、以下の組成からなるソーダライムシリカガラスを用いることが好ましい。
【0065】
質量%で表示して、
SiO2:65〜80%、
Al2O3:0〜5%、
MgO:0〜10%、
CaO:5〜15%、
MgO+CaO:5〜15%、
Na2O:10〜18%、
K2O:0〜5%、
Na2O+K2O:10〜20%、
B2O3:0〜5%、
からなる母ガラス組成と、
着色成分として、
Fe2O3に換算した全酸化鉄(T−Fe2O3):0.3〜1.0%、
CeO2:0〜2.0%、
TiO2:0〜1.0%、
からなる紫外線赤外線吸収ガラスである。
【0066】
また、前記紫外線赤外線吸収ガラスにおける母ガラス組成に、SO3:0.07〜0.30%を含むことが好ましい。
【0067】
前記紫外線赤外線吸収ガラスにおいて、酸化鉄は、ガラス中ではFe2O3とFeOの状態で存在する。Fe2O3は、CeO2,TiO2と共に、紫外線吸収能を高める成分であり、FeOは熱線吸収能を高める成分である。
【0068】
この場合、全酸化鉄量(T-Fe2O3)が、0.3〜1.0%の範囲にある場合には、所望の全太陽光エネルギー吸収能を得るためには、FeO/T-Fe2O3の比は、0.20〜0.40の範囲にあることが好ましい。この場合のFeOの量としては、通常Fe2O3に換算した数値が用いられる。
【0069】
また、上記の組成範囲のガラスに、着色剤としてCoO、NiO、MnO、V2O5、MoO3等、また還元剤としてSnO2を、1種類または2種類以上の合計量で0〜1%の範囲で、本発明が目的とする緑色系の色調を損なわない範囲で添加してもよい。特にCoOは青色の色調を与えるので、Fe2O3、CeO2、TiO2の量増によりガラスの色調が黄色味を帯びるのを抑制するのに有効であり、その好ましい範囲は3〜20ppmである。
【0070】
SO3は、原料に加えられたボウ硝(硫酸ナトリウム)などのイオウ含有原料中のイオウ分が、酸化物としてガラス中に残留したものである。この紫外線赤外線吸収ガラスにおいて、SO3の量が非常に重要な役割を果たす。
【0071】
この紫外線赤外線吸収ガラスでは、酸化剤であるFe2O3、CeO2を比較的多量に含有しながら、還元度を通常より高くする必要がある。上述のように、ケイ砂未溶解の塊(いわゆるスカム)や、シリカ分の多いリーム(いわゆるシリカリッチリーム)を生じ易い。このような現象を防ぐには、ケイ砂の溶解を促進するために、ガラス中のSO3含有量を0.07%より大きくすることが必要である。このためには、バッチに添加するボウ硝の量を、通常の量より多くする、例えばケイ砂1000kg(1トン)当たりの量を20kg程度、あるいはそれ以上に上げることや、硫酸鉄などの他の硫酸塩を原料として加えることにより可能である。
【0072】
しかしながら、このようにガラス中のSO3含有量を上げることは、一方ではリボイルによる泡の生成、特にスターラー撹拌によるリボイルという別の問題を引き起こす。このようなリボイル現象は、SO3含有量が高くなるほど起こり易い。このリボイル現象による歩留まり低下を防ぐには、ガラス中のSO3含有量は0.30%より小さくするのが望ましい。
【0073】
また、所望のガラスの還元度を達成しながら、スカム,シリカリッチリームの生成を防ぐと同時に、リボイルによる泡生成を防ぐため、ガラス中のSO3含有を上記のような望ましい範囲に調整するためには、原料としてサルファイドイオン含有物(例えば硫化鉄のような硫化物や高炉スラグ、例えばカルマイト社製カルマイト、川鉄鉱業製リバーマイトなど)を使用することが望ましい。
【0074】
ガラス板のみの可視光線透過率の上限は、本発明において特に限定されない。ただし、可視光線透過率が75%以下のガラス板の場合、低反射膜による可視光線透過率の増加が効果的であるので、好ましい。
【0075】
またガラス板は、着色されたガラス板のみならず、ガラス板の可視光線透過率が少なくとも68%であれば、例えば熱線反射膜付きガラス板であってよい。
【0076】
さらに強化ガラス板であっても、未強化ガラス板であってもよい。また形状的には、平板であっても、曲げガラスでもよい。
【0077】
またさらに単板ガラスのみならず、合わせガラス板であってもよいし、複層ガラスであってもよい。
【0078】
なお上述した着色されたガラス板の説明は、ガラス板が単板である場合である。例えば、合わせガラスで構成される場合は、少なくとも1枚の単一ガラス板が、上述した透明でかつ着色されたガラス板であればよく、他の単一ガラス板はクリア板でもよい。要するに、ガラス板のみの可視光線透過率が、少なくとも68%であればよい。
【0079】
本発明におけるガラス板とは、1.5〜6.5mの厚み(合わせガラスまたは複層ガラスの場合は、各ガラス板の外側面の距離を厚みとする)を有することが好ましい。
【0080】
【発明の実施の形態】
本発明による自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板を、実施例および参考例を用いて詳細に説明する。
【0081】
(実施例1)
実施例1による自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板は、以下の構成よりなる。
・構成:UVG2.1mm/中間膜/UVG2.1mm/低反射膜
なおUVG2.1mmは、UVカットグリーンガラス板で、厚みが2.1mmであることを表している。
【0082】
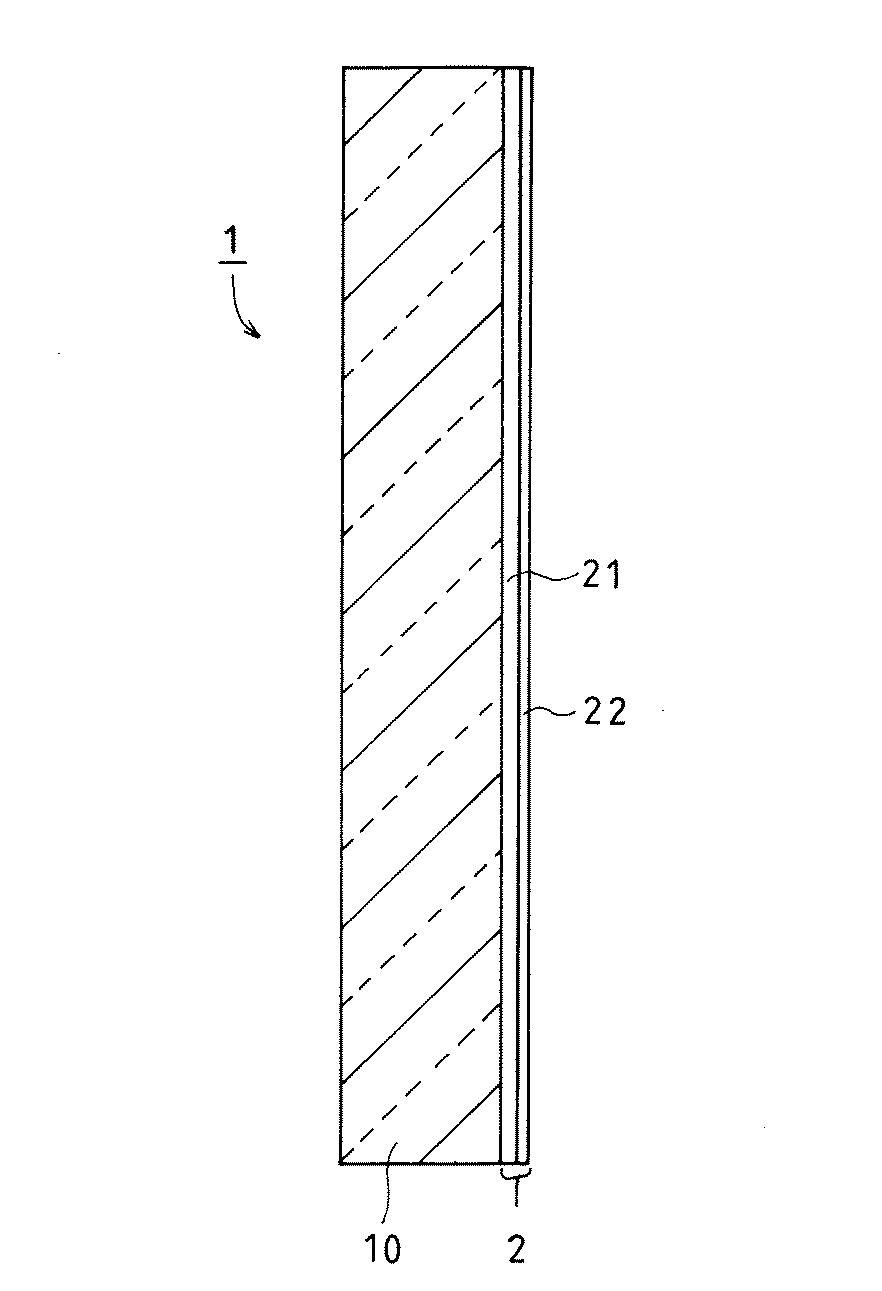
実施例1の自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板の断面構造を、模式的に図1に示した。自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板1は、車外側単一ガラス板11と車内側単一ガラス板12を、中間膜13(PVB膜)を介して接着した合わせガラスの車内側表面に、低反射膜2(21,22)を形成したものである。
【0083】
またガラス基板2の車内側となる面に、低反射膜を以下のようにして形成した。まず第1層である高屈折率膜は、TiO2とSiO2からなる。ゾル−ゲル法にて形成した。膜厚は130nmとし、屈折率は1.75であった。
【0084】
さらに、第2層である低屈折率膜はSiO2からなり、ゾル−ゲル法にて形成した。膜厚は90nmとし、屈折率は1.45であった。
【0085】
上記ガラス基板1,2を、通常の中間膜(PVB膜)を用いて、公知の合わせ工程を経て、合わせガラスを作製した。
【0086】
なお実施例1を始め、以下の実施例および比較例におけるガラスサンプルの光学特性を表1に示した。なお実施例1は、サンプル6のガラス基板に低反射膜を形成した例である。
【0087】
【表1】
クリア:無着色ガラス板、GRN:グリーンガラス板、UVG:UVカットグリーンガラス板、ノーマル:通常のPVB膜、
【0088】
また、上述したグリーンガラス板とUVカットグリーンガラスの具体的組成を、質量%表示で表2に示した。
【0089】
【表2】
【0090】
実施例1により得られた自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板の光学特性を表3に示す。また併せて、他の実施例の光学特性も示す。
【0091】
【表3】
【0092】
実施例1によれば、可視光線透過率は74%であり、低反射膜によってサンプル6と比較して、約2%可視光線透過率の増加を示している。また可視光線反射率は、12度で3%、60度で約4%の低減効果を示した。さらに日射透過率は、参考例1の無着色ガラス板の合わせガラスと比較して、約35%の低減効果を示した。このことから、この実施例1は、優れた低反射性能と日射遮蔽性能を両立していることがわかった。
【0093】
(実施例2)
実施例2による自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板は、以下の構成よりなる。
・構成:UVG2.1mm/ITO分散中間膜/UVG2.1mm/低反射膜
【0094】
実施例2においては、中間膜にITO微粒子を0.1wt%の割合で分散させている。これは、まず可塑剤(3GH:積水化学工業(株)製)に、粒子径が0.2μm以下のITO微粒子を、固形分が約10%になるように分散し、分散液を調合した。ポリビニルブチラール(PVB)樹脂100部に対して、上記分散液を1部、さらに可塑剤(3GH)を39部(いずれも質量部)添加して、中間膜を成形した。
【0095】
実施例1において、通常の中間膜に代えて、ITO微粒子を分散した中間膜を用いた以外は、同様の工程で合わせガラスを作製した。その光学特性を表3に示した。
【0096】
実施例2によれば、可視光線透過率は、71.2%と自動車用安全ガラスとしての規格を満足している。また日射透過率は、実施例1と比較してさらに5%ほど低減していた。このことから、この実施例2は、優れた低反射性能と日射遮蔽性能を両立していることがわかった。
【0097】
(実施例3)
実施例3による自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板は、以下の構成よりなる。
・構成:UVG2.3mm/中間膜/UVG2.3mm/低反射膜
【0098】
実施例3は、実施例1において、ガラス基板の板厚が異なるだけで、その他は同様の工程で合わせガラスを作製した自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板である。その光学特性を表3に示した。なお実施例3は、サンプル8のガラス基板に低反射膜を形成した例である。
【0099】
実施例3によれば、基本となるサンプル8では可視光線透過率は69%であるのに対し、低反射膜を形成したことによって可視光線透過率は増加し、自動車用安全ガラスの規格を満足するようになった。また、可視光線反射率及び日射透過率も、実施例1と比較してさらに低減していた。このことから、この実施例3は、優れた低反射性能と日射遮蔽性能を両立していることがわかった。
【0100】
(実施例4)
実施例4による自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板は、以下の構成よりなる。
・構成:GRN2.1mm/中間膜/GRN2.1mm/低反射膜
【0101】
実施例4は、実施例1において、ガラス基板の種類が異なり、グリーンガラス板としている。その他は、実施例1と同様の構成、および同様の工程で合わせガラスを作製した。その光学特性を表3に示した。なお実施例4は、サンプル4のガラス基板に低反射膜を形成した例である。
【0102】
実施例4によれば、参考例1と比較して、可視光線反射率及び日射透過率は低減していた。この実施例4は、実施例1〜3には劣るものの、優れた低反射性能と日射遮蔽性能を両立していることがわかった。
【0103】
(実施例5)
実施例5による自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板は、以下の構成よりなる。
・構成:UVG6.0(単板)/低反射膜
【0104】
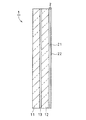
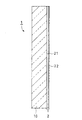
実施例2の自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板の断面構造を、模式的に図2に示した。自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板1は、単一ガラス板10の車内側表面に、低反射膜2(21,22)を形成したものである。
【0105】
この実施例5は、単板のUVカットグリーンガラス板(6mm厚、サンプル9)に、本発明に適用される低反射膜を形成した例である。
【0106】
実施例5によれば、実施例3と同様に、基本となるサンプル9では可視光線透過率は69.5%であるのに対し、低反射膜を形成したの効果により、可視光線透過率は71.5%まで増加した。また、可視光線反射率及び日射透過率も低減しており、低反射性能と日射遮蔽性能を両立していることがわかった。
【0107】
(比較例1)
比較例1による自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板は、以下の構成よりなる。
・構成:クリア2.1mm/中間膜/クリア2.1mm/低反射膜
【0108】
比較例1は、実施例1において、ガラス基板が異なるだけで、その他は同様の工程で合わせガラスを作製した自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板である。その光学特性を表3に示した。なお比較例1は、サンプル2のガラス基板に低反射膜を形成した例である。
【0109】
比較例1によれば、サンプル2に低反射膜を形成することにより、可視光線反射率の低減効果を示した。しかし、斜め入射による反射低減機能が、角度:12度/60度=5.0%/11.8%と、十分な性能ではなかった。また、日射透過率は、77%と非常に高かった。
【0110】
【発明の効果】
以上詳細に説明したように、本発明による自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板では、可視光域に吸収のあるガラス板に低反射膜を施している。このため、優れた低反射性能と、自動車用ガラス板としての可視光線透過率を両立することができる。
【0111】
さらに、本発明による自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板を構成するガラス板を、熱線吸収ガラスとすると、低反射性能と日射遮蔽性能を両立することができる。
【0112】
また本発明による自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板では、その表面に低反射膜を形成しているので、ガラス板表面での反射損失を抑えることができる。その結果、ガラス板としての透過率を向上させることができるので、ガラス基板での日射の吸収能をより大きくすることが可能となる。
【0113】
具体的には、可視光線透過率がわずかに70%以下のガラス板であっても、本発明によれば、自動車用ガラス板として採用可能である。その結果、より優れた日射遮蔽性が得られる。
【0114】
またさらに、熱線吸収剤として有効なITO微粒子を分散した中間膜を用いる場合であっても、上述したのと同じく、ガラス板としての透過率を向上させることができるので、高吸収ガラス板を採用することができる。その結果、高価であるITO微粒子の分散量が少なくしても、優れた日射遮蔽性能を得ることが可能である。このことは、コストダウンに大きく寄与する。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明による自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板の断面構造を説明する図である。
【図2】本発明の別形態による自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板の断面構造を説明する図である。
【符号の説明】
1:自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板
10:単一ガラス板
11:車外側単一ガラス板
12:車内側単一ガラス板
13:中間膜
2:低反射膜
21:低反射膜の第1層(高屈折率膜)
22:低反射膜の第2層(低屈折率膜)[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a glass plate with a low-reflection film for automobiles, and more particularly to a glass plate with a low-reflection automobile film suitable for windshield laminated glass for automobiles.
[0002]
[Prior art]
For example, in a windshield glass of an automobile, a glass plate with a low reflection film is required to prevent the reflection of a dashboard. As such a glass plate, the present applicant has proposed a “low reflection glass article for automobiles” in Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 2000-256042.
[0003]
That is, “a thin film layer having a refractive index (n1) of the first layer of 1.65 to 2.20 and a film thickness of 110 to 150 nm counted from the glass surface side on at least one surface of the transparent glass substrate. Then, a thin film layer mainly composed of silica having a refractive index (n2) of 1.37 to 1.49 and a film thickness of 81 to 100 nm is coated and laminated on the first layer thin film. And a low reflection glass article for automobiles in which the reflected light when the visible light is incident at an incident angle of 12 degrees and 60 degrees from the film surface side has an excitation purity of 22% or less and 10% or less, respectively. .
[0004]
By the way, in the glass plate for motor vehicles, the infrared shielding ability is also calculated | required for the reduction of the cooling load etc. For example, in Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 2001-151539, Fe 2 O Three A laminated glass in which a glass plate made of soda lime silica glass containing 0.3 to 1% of all iron converted is combined with an intermediate film containing infrared heat shielding fine particles has been proposed.
[0005]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
JP-A 2000-256042 described above shows that the glass substrate may be either non-colored or colored as long as it is transparent glass. Specific examples of colored glass include green, bronze, gray or high-performance UV-cut green glass, high-performance UV-cut bronze glass, etc. Especially for automobiles, green color, especially heat ray / ultraviolet absorption performance is obtained. It is more preferable if it is easy.
[0006]
However, the glass substrate used in the examples is only a non-colored soda lime silicate glass plate, and the effect of the low reflection film when the colored glass is used as the substrate is not sufficiently shown.
[0007]
Moreover, in the above-mentioned Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2001-151539, the visible light transmittance is limited to 70% or more in the embodiment. As is apparent from this, in order to satisfy the standards for automotive safety glass, it is understood that there are restrictions on the combination of glass and the amount of fine particles dispersed in the intermediate film. Further, no mention is made of the low reflection function.
[0008]
Accordingly, the present invention provides a glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles that achieves a visible light transmittance of 70% or more, which is a standard for glass for automobiles, and realizes excellent low reflectivity and excellent solar shading performance. Objective.
[0009]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The present invention utilizes the effect of increasing the amount of transmitted light of the transparent body as a result of the low reflection film provided on the transparent body suppressing light reflection. That is, if a glass plate having a visible light transmittance of at least 68% is used, a visible light transmittance of at least 70% is ensured, and the solar transmittance is approximately the same as that of the glass plate having no low reflection film formed thereon. A glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles that can be maintained and has excellent low reflectivity can be obtained.
[0010]
That is, the present invention is the invention according to claim 1,
In a glass plate for automobiles, and a glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles provided with a two-layer low reflection film on the main surface on the inner surface side of the car,
A glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles, wherein the visible light transmittance of only the glass plate is at least 68%, and the visible light transmittance as a glass plate with a low reflection film is at least 70%. .
[0011]
As invention of
In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to claim 1,
The low reflection film has a refractive index (n 1 ) = 1.68-2.3 and the film thickness (d 1 ) = 100 to 140 nm, and the second layer stacked on the first layer has a refractive index (n 2 ) = 1.4 to 1.5 and film thickness (d 2 ) = A glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles, which is a two-layer low reflection film having a thickness of 80 to 110 nm.
[0012]
As invention of Claim 3,
In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to
The first layer of the low reflection film has a refractive index (n 1 ) = 1.70-1.95 and the second layer has a refractive index (n 2 ) = 1.40 to 1.47.
[0013]
As invention of Claim 4,
In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
The glass plate is a glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles, which is a single glass plate of green, bronze, gray, UV cut green, or UV cut bronze.
[0014]
As invention of Claim 5,
In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to claim 4,
The glass plate is green or UV cut green glass,
The glass is Fe in mass percentage. 2 O Three It is a glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles made of soda lime silica glass containing 0.3 to 1% of all iron converted.
[0015]
As invention of Claim 6,
In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
The glass plate is a glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles, which is a laminated glass in which at least two single glass plates are bonded via a thermoplastic intermediate film.
[0016]
As invention of Claim 7,
In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to claim 6,
The interlayer film of the laminated glass is a glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles containing ITO fine particles having a particle diameter of 0.2 μm or less at a ratio of 0.01 to 0.8% by mass with respect to the intermediate film. is there.
[0017]
As invention of Claim 8,
In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to claim 6 or 7,
The glass plate is a laminated glass plate made of a combination of the same or different glass plates among clear, green, bronze, gray, UV cut green, and UV cut bronze glass plates. It is a glass plate with a reflective film (however, excluding a laminated glass plate obtained by combining clear glass plates).
[0018]
As invention of Claim 9,
In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to any one of claims 1 to 8,
The low reflection film has a visible light reflectance of 4.8% or less and 11.0% or less when visible light is incident at an incident angle of 12 degrees and 60 degrees, respectively, from the film surface side. It is a glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles.
[0019]
As an invention according to
In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to any one of claims 1 to 9,
The low reflection film has a visible light reflectance of 12 when the visible light is incident at an incident angle of 12 degrees and 60 degrees from the film surface side, respectively, on the glass surface where the low reflection film is not formed. It is a glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles having a visible light reflectance of at least 2.4% and at least 3.5% smaller than the visible light reflectance at an incident angle of 60 degrees and 60 degrees, respectively.
[0020]
As invention of
In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to any one of claims 1 to 10,
The first layer of the low reflection film is made of SiO. 2 And TiO 2 Or substantially TiO 2 It is a glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles consisting of only the above.
[0021]
As invention of
In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to any one of claims 1 to 11,
The first layer has a molar ratio of Ti: Si = 35: 65 to 100: 0, and the second layer is SiO. 2 Is a glass plate with a low-reflection film for automobiles.
[0022]
As invention of
In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to any one of claims 1 to 12,
The second layer of the low reflection film is substantially made of SiO. 2 It is a glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles consisting of only the above.
[0023]
As invention of Claim 14,
In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to any one of claims 1 to 13,
The low-reflection film has a low-reflection for automobiles in which visible light has a stimulus purity of 22% or less and 10% or less, respectively, when visible light is incident at an incident angle of 12 degrees and 60 degrees from the film surface side. It is a glass plate with a film.
[0024]
(Low reflective film)
First, the low reflection film constituting the glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles according to the present invention will be described. The first layer (high refractive index film) of the two-layer low reflection film has a refractive index (n 1 ) = 1.68-2.3 and the film thickness (d 1 ) = 100 to 140 nm is preferable.
[0025]
Refractive index of the first layer (n 1 ) Is less than 1.68, a sufficient effect of reducing the intensity of reflected light cannot be obtained for incident light ranging from a high incident angle to a low incident angle.
[0026]
Refractive index of the first layer (n 1 ) Is greater than 2.3, the reflectance at a specific wavelength is lowered, but coloring and reflection become stronger in the entire visible range, and the visible light transmittance is 70% or less, and a desired reflection reduction effect is achieved. This is because it cannot be obtained. Refractive index of the first layer (n 1 ) Is preferably 1.70 to 1.95.
[0027]
The thickness of the first layer film (d 1 ) Is smaller than 100 nm, the reflectivity at a high incident angle increases. On the other hand, the thickness of the first layer film (d 1 ) Becomes larger than 140 nm, the reflectance at a low incident angle increases.
[0028]
This first layer is SiO 2 And TiO 2 As a main component or substantially TiO 2 It is preferable to contain only. TiO with relatively high refractive index 2 (Refractive index = about 2.3) and SiO having a relatively low refractive index 2 (Refractive index = 1.45 or so) in various combinations and mixing, the refractive index of the first layer (n 1 ) Can be freely controlled within the range of 1.7 to 2.3. When the refractive index is 2.3, the first layer is substantially TiO. 2 It will consist of only.
[0029]
The first layer is SiO 2 And TiO 2 As a main component or substantially TiO 2 When it consists only of, it can be set as the film | membrane excellent in durability. As other components, the refractive index (n 1 ) = 1.68 to 2.3, ZrO 2 (Refractive index = 1.95 or so), CeO 2 , Bi 2 O Three Etc. may be added in an amount of 10 mass% or less in total.
[0030]
Furthermore, the second layer (low refractive index film) of the low reflection film is changed to a refractive index (n 2 ) = 1.4 to 1.5 and film thickness (d 2 ) = 80 to 110 nm.
[0031]
Refractive index of the second layer (n 2 ) Is smaller, the reflection reduction effect is greater. However, the refractive index (n 2 ) Is 1.4 or less, the density of the film is reduced or the uneven shape of the surface is increased. For this reason, wear resistance, chemical resistance, antifouling properties, weather resistance, etc. are deteriorated, and an optical thin film having durability is difficult to realize.
[0032]
The refractive index of the second layer (n 2 ) Exceeding 1.5, the desired reflection reduction effect cannot be obtained. Preferred refractive index of the second layer (n 2 ) Is 1.40 to 1.47.
[0033]
Second film thickness (d 2 ) Less than 80 nm, the intensity of the reflected light cannot be reduced sufficiently. Second film thickness (d 2 ) Exceeds 100 nm, the reflectance at a low incident angle increases.
[0034]
The second layer is substantially SiO 2 Preferably it consists of. The second layer is substantially SiO 2 A film made of is preferable because it is excellent in chemical stability, thermal stability, and mechanical strength.
[0035]
In addition, SiO 2 The refractive index of the film is about 1.45, although it depends on the manufacturing method. Therefore, when a film having a lower refractive index is required, SiO 2 Form minute uneven shapes on the surface of the film, 2 The apparent refractive index may be lowered by making the inside of the film porous such as a closed bubble or a through-pore. Further, the refractive index may be lowered by putting inorganic fine particles having a low refractive index in the film.
[0036]
As the second layer, SiO 2 Although it is preferable to use a film, the refractive index of the second layer (n 2 ) Within a range satisfying 1.5 or less, SiO 2 Besides B 2 O Three , Al 2 O Three The oxides such as the above may be contained in a total amount of 15 mol% or less.
[0037]
As a method for forming the first layer and the second layer of the low reflection film in the present invention, it can be formed by a sol-gel method, a sputtering method, or a CVD method. Among these, the sol-gel method is desirable from the viewpoint of cost.
[0038]
When the first layer and the second layer constituting the low reflection film of the present invention are formed by a sol-gel method, the film formability is good, and a homogeneous film is easily obtained and has high durability. Is preferred.
[0039]
(Sol-gel method)
Examples of the coating method of the coating solution by the sol-gel method include spin coating, dip coating, meniscus coating, flow coating, roll coating, gravure coating, flexographic printing, and screen printing.
[0040]
For example, when the first layer of the low reflection film in the present invention is formed by a sol-gel method, that is, titanium oxide (
[0041]
For example, when the second layer of the low reflection film in the present invention is formed by a sol-gel method, that is, when it is formed as an optical thin film containing silicon oxide, the coating liquid composition is composed of a silicon compound and a solvent, It can be obtained by mixing a silicon compound with an organic solvent.
[0042]
The first layer formed by the sol-gel method has a molar ratio of TiO. 2 : SiO 2 = 35: 65 to 100: 0, and the second layer is made of SiO. 2 It is preferable that it consists only of.
[0043]
Among the combinations of the components described above, TiO 2 And SiO 2 Are preferred because their alkoxides are stable.
[0044]
As the titanium compound that is a starting material of titanium oxide contained in the first layer, titanium alkoxide, titanium alkoxide chloride, titanium chelate, and the like are used. Titanium alkoxides include titanium methoxide, titanium ethoxide, titanium n-propoxide, titanium isopropoxide, titanium n-butoxide, titanium isobutoxide, titanium methoxypropoxide, titanium stearyl oxide, titanium 2-ethylhexoxide, etc. Can be illustrated.
[0045]
Examples of the titanium alkoxide chloride include titanium chloride triisopropoxide and titanium dichloride diethoxide. Titanium chelate products include titanium triisopropoxaside (2,4-pentanedionate), titanium diisopropoxide (bis-2,4-pentanedionate), titanium allyl acetate triisopropoxide, titanium bis (tri Ethanolamine) diisopropoxide, titanium di-n-butoxide (bis-2,4-pentandionate) and the like are used.
[0046]
As a silicon compound that is a starting material of silicon oxide contained in the first layer and the second layer, a silicon alkoxide mixed with a solvent such as alcohol and then hydrolyzed and polymerized with an acidic or basic catalyst is used. It is done. As the silicon alkoxide, silicon methoxide, silicon ethoxide, or oligomers thereof are used.
[0047]
As the coating liquid composition for forming the second layer, the boron compound to be contained in addition to the silicon compound is boron methoxide, boron ethoxide, boron n-propoxide, boron i-propoxide, boron n-butoxide, boron. s-Butoxide, boron t-butoxide and their chelating compounds are used.
[0048]
Examples of the aluminum compound added as the coating liquid composition for forming the second layer include aluminum methoxide, aluminum ethoxide, aluminum n-propoxide, aluminum i-propoxide, aluminum n-butoxide, aluminum s-butoxide, Aluminum t-butoxide and these chelating compounds are used.
[0049]
As the chelate compound, aluminum (di-s-butoxide) ethyl acetoacetonate, aluminum (s-butoxide) bisethyl acetoacetonate, aluminum (di-propoxide) ethyl acetoacetonate and the like are conveniently used.
[0050]
Acid catalysts contained in the coating liquid composition for forming the first layer and the second layer include hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, acetic acid, oxalic acid, trichloroacetic acid, trifluoroacetic acid, phosphoric acid, hydrofluoric acid, formic acid Etc. are used. As the basic catalyst, ammonia and amines are used.
[0051]
Furthermore, although the organic solvent used for the coating liquid composition for forming the first layer and the second layer depends on the coating method, methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, butanol, hexanol, octanol, 2-methoxyethanol, 2-ethoxyethanol 2-butoxyethanol, cellosolve acetate, diethylene glycol monoethyl ether, hexylene glycol, diethylene glycol, tripropylene glycol, diacetone alcohol and the like.
[0052]
As the coating liquid composition, the above-described solvents may be used alone or in combination with a plurality of solvents in order to adjust the viscosity, surface tension and the like of the coating liquid. Moreover, you may add a stabilizer, a leveling agent, a thickener, etc. as needed. The amount of the solvent used depends on the film thickness of the finally obtained high refractive index film and low refractive index film and the coating method to be employed. In the usual case, the solvent may be used so that the total solid content falls within the range of 1-20%.
[0053]
After the coating liquid composition is applied by the above application method, it is dried or / and heated and fired at a temperature of 250 ° C. or higher to repeat the step of applying the next application liquid to obtain a glass plate with a low reflection film. be able to.
[0054]
The thus obtained low reflection film is excellent in properties such as transparency, environmental resistance and scratch resistance. Further, with such a configuration, even if the layers are stacked, it is possible to suppress film peeling and generation of cracks in the process of densifying the first layer and the second layer. This film peeling or cracking is considered to be caused by a difference in heat shrinkage rate.
[0055]
Instead of the manufacturing method using drying / firing by heating at 250 ° C. or higher, the light irradiation method described below can be used. That is, after coating the coating liquid composition by the coating method, a step of irradiating the coating film with electromagnetic waves having a wavelength shorter than that of visible light is performed, followed by a step of coating the next coating liquid. This is a method of repeating the drying step.
[0056]
The electromagnetic wave having a wavelength shorter than visible light includes γ-rays, X-rays, and ultraviolet rays. However, ultraviolet irradiation is preferable from the viewpoint of practicality on an apparatus in consideration of irradiation to a substrate having a large area. As the ultraviolet light source, an excimer lamp, a low-pressure mercury lamp, a high-pressure mercury lamp, a metal halide lamp, or the like is used.
[0057]
Using a high-pressure mercury lamp that emits light at wavelengths of 254 nm and 303 nm with a dominant wavelength of 365 nm, 10 mW / cm 2 Or more, preferably 50 mW / cm 2 Or more, more preferably 100 mW / cm 2 It is desirable to irradiate the coating film with the above irradiation intensity.
[0058]
Using such an ultraviolet light source, 100 mJ / cm 2 Or more, preferably 500 mJ / cm 2 Or more, more preferably 1000 mJ / cm 2 The above irradiation energy may be applied to the surface coated with the above-described coating liquid composition. As a result, it is possible to obtain a low reflection film having a laminated structure that is excellent in properties such as transparency, environmental resistance, and scratch resistance at low temperatures and is less prone to cracks.
[0059]
Moreover, you may dry and / or bake with heat simultaneously, irradiating with an ultraviolet-ray. You may use simultaneously the drying method by the ultraviolet irradiation, and the drying process by the heat drying at the temperature of preferably 250 degrees C or less. By using ultraviolet irradiation in this way, the drying process is speeded up, and productivity can be dramatically improved.
[0060]
(Composition of glass plate)
Furthermore, in this invention, the glass plate whose visible light transmittance | permeability only of a glass plate is at least 68% is used. That is, for example, as the colored glass plate, green, bronze, gray, high performance UV cut green glass, high performance UV cut bronze glass, or the like is preferable. In particular, it is more preferable if the window material for automobiles is green-colored, and in particular, can easily obtain heat ray / ultraviolet absorption performance.
[0061]
Examples of the coloring component used for such a colored glass plate include iron, cobalt, nickel and the like.
[0062]
Among them, soda lime silica glass containing iron as a coloring component is a mass percentage display on a soda lime silica base glass, Fe 2 O Three It is preferable that it is soda-lime silica glass containing 0.3 to 1% of total iron converted.
[0063]
Furthermore, absorption of light having a wavelength in the near infrared region is dominated by divalent iron out of total iron. Therefore, Fe 2 O Three Converted FeO (divalent iron) and Fe 2 O Three It is more preferable that the converted ratio of total iron is 0.20 to 0.40.
[0064]
As the glass plate having the above characteristics, it is preferable to use soda lime silica glass having substantially the following mass percentage and having the following composition.
[0065]
Display in mass%,
SiO 2 : 65-80%
Al 2 O Three : 0 to 5%
MgO: 0 to 10%,
CaO: 5 to 15%,
MgO + CaO: 5 to 15%,
Na 2 O: 10 to 18%
K 2 O: 0 to 5%
Na 2 O + K 2 O: 10 to 20%,
B 2 O Three : 0 to 5%
A mother glass composition comprising:
As a coloring component,
Fe 2 O Three Total iron oxide converted into T (Fe 2 O Three ): 0.3-1.0%,
CeO 2 : 0 to 2.0%,
TiO 2 : 0 to 1.0%,
It is an ultraviolet and infrared ray absorbing glass made of
[0066]
In addition, in the mother glass composition in the ultraviolet and infrared absorbing glass, SO Three : It is preferable to contain 0.07 to 0.30%.
[0067]
In the ultraviolet and infrared absorbing glass, iron oxide is Fe in the glass. 2 O Three And FeO. Fe 2 O Three Is CeO 2 , TiO 2 At the same time, it is a component that enhances the ability to absorb ultraviolet rays, and FeO is a component that enhances the ability to absorb heat rays.
[0068]
In this case, the total iron oxide content (T-Fe 2 O Three ) Is in the range of 0.3-1.0%, in order to obtain the desired total solar energy absorption capacity, FeO / T-Fe 2 O Three The ratio is preferably in the range of 0.20 to 0.40. In this case, the amount of FeO is usually Fe. 2 O Three The numerical value converted into is used.
[0069]
In addition, the glass having the above composition range has CoO, NiO, MnO, V as colorants. 2 O Five , MoO Three And SnO as a reducing agent 2 May be added within a range of 0 to 1% in a total amount of one kind or two or more kinds within a range not impairing the green color tone intended by the present invention. In particular, since CoO gives a blue color tone, FeO 2 O Three , CeO 2 TiO 2 It is effective to suppress the color tone of the glass from becoming yellowish due to the increase in the amount, and the preferred range is 3 to 20 ppm.
[0070]
SO Three In this case, the sulfur content in the sulfur-containing raw material such as bow glass (sodium sulfate) added to the raw material remains in the glass as an oxide. In this ultraviolet and infrared absorbing glass, SO Three The amount of plays a very important role.
[0071]
In this ultraviolet and infrared absorbing glass, the oxidizing agent Fe 2 O Three , CeO 2 It is necessary to make the degree of reduction higher than usual while containing a relatively large amount. As described above, silica sand undissolved lump (so-called scum) and silica-rich ream (so-called silica rich ream) are likely to occur. In order to prevent such a phenomenon, SO in the glass is promoted in order to promote dissolution of silica sand. Three It is necessary to make the content larger than 0.07%. For this purpose, the amount of bow glass added to the batch is increased from the usual amount, for example, the amount per 1000 kg (1 ton) of silica sand is increased to about 20 kg or more, iron sulfate, etc. It is possible to add as a raw material sulfate.
[0072]
However, the SO in the glass is thus Three Increasing the content, on the other hand, causes another problem of foam formation by reboil, especially reboil by stirrer stirring. Such reboil phenomenon is Three The higher the content, the more likely it is. In order to prevent the yield reduction due to the reboil phenomenon, SO in the glass Three The content is desirably smaller than 0.30%.
[0073]
In addition, in order to prevent the formation of scum and silica-rich reams, while at the same time achieving the desired degree of reduction of the glass, at the same time to prevent the formation of bubbles due to reboil, Three In order to adjust the content to the desired range as described above, a sulfide ion-containing material (for example, a sulfide such as iron sulfide or a blast furnace slag such as calumite manufactured by Calmite or Rivertite manufactured by Kawatetsu Mining Co., Ltd.) is used. Is desirable.
[0074]
The upper limit of the visible light transmittance of only the glass plate is not particularly limited in the present invention. However, in the case of a glass plate having a visible light transmittance of 75% or less, an increase in visible light transmittance by a low reflection film is effective, which is preferable.
[0075]
Further, the glass plate may be not only a colored glass plate but also a glass plate with a heat ray reflective film, for example, as long as the visible light transmittance of the glass plate is at least 68%.
[0076]
Further, it may be a tempered glass plate or an untempered glass plate. In terms of shape, it may be a flat plate or bent glass.
[0077]
Furthermore, it may be a laminated glass plate as well as a single glass plate, and may be a multi-layer glass.
[0078]
In addition, description of the colored glass plate mentioned above is a case where a glass plate is a single plate. For example, in the case of being composed of laminated glass, at least one single glass plate may be the transparent and colored glass plate described above, and the other single glass plate may be a clear plate. In short, the visible light transmittance of only the glass plate may be at least 68%.
[0079]
The glass plate in the present invention preferably has a thickness of 1.5 to 6.5 m (in the case of laminated glass or multilayer glass, the distance between the outer surfaces of the glass plates is the thickness).
[0080]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles according to the present invention will be described in detail with reference to Examples and Reference Examples.
[0081]
(Example 1)
The glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles according to Example 1 has the following configuration.
Configuration: UVG 2.1 mm / intermediate film / UVG 2.1 mm / low reflection film
UVG 2.1 mm is a UV cut green glass plate and represents a thickness of 2.1 mm.
[0082]
The cross-sectional structure of the glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles of Example 1 is schematically shown in FIG. The glass plate 1 with a low reflection film for automobiles has a low reflection on the vehicle inner surface of laminated glass in which the vehicle outer
[0083]
In addition, a low reflection film was formed on the surface of the
[0084]
Further, the low refractive index film as the second layer is made of SiO. 2 And was formed by a sol-gel method. The film thickness was 90 nm and the refractive index was 1.45.
[0085]
A laminated glass was produced from the
[0086]
The optical characteristics of the glass samples in Example 1 and the following Examples and Comparative Examples are shown in Table 1. Example 1 is an example in which a low-reflection film is formed on the glass substrate of Sample 6.
[0087]
[Table 1]
Clear: uncolored glass plate, GRN: green glass plate, UVG: UV cut green glass plate, normal: normal PVB film,
[0088]
Further, specific compositions of the above-described green glass plate and UV cut green glass are shown in Table 2 in terms of mass%.
[0089]
[Table 2]
[0090]
Table 3 shows the optical characteristics of the glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles obtained in Example 1. In addition, the optical characteristics of other examples are also shown.
[0091]
[Table 3]
[0092]
According to Example 1, the visible light transmittance is 74%, and the low reflection film shows an increase in visible light transmittance of about 2% compared to Sample 6. Further, the visible light reflectance was reduced by 3% at 12 degrees and about 4% at 60 degrees. Further, the solar transmittance was reduced by about 35% compared with the laminated glass of the uncolored glass plate of Reference Example 1. From this, it was found that Example 1 has both excellent low reflection performance and solar shading performance.
[0093]
(Example 2)
The glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles according to Example 2 has the following configuration.
Configuration: UVG 2.1 mm / ITO dispersed interlayer film / UVG 2.1 mm / low reflection film
[0094]
In Example 2, ITO fine particles are dispersed in the intermediate film at a rate of 0.1 wt%. First, ITO fine particles having a particle diameter of 0.2 μm or less were dispersed in a plasticizer (3GH: manufactured by Sekisui Chemical Co., Ltd.) so that the solid content was about 10%, and a dispersion was prepared. An intermediate film was formed by adding 1 part of the dispersion and 39 parts (all parts by mass) of a plasticizer (3GH) to 100 parts of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) resin.
[0095]
In Example 1, a laminated glass was produced in the same process except that an intermediate film in which ITO fine particles were dispersed was used instead of the normal intermediate film. The optical characteristics are shown in Table 3.
[0096]
According to Example 2, the visible light transmittance is 71.2%, which satisfies the standard for automobile safety glass. Further, the solar radiation transmittance was further reduced by about 5% as compared with Example 1. From this, it was found that Example 2 has both excellent low reflection performance and solar shading performance.
[0097]
(Example 3)
The glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles according to Example 3 has the following configuration.
Configuration: UVG 2.3 mm / intermediate film / UVG 2.3 mm / low reflection film
[0098]
Example 3 is a glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles in which laminated glass was produced in the same process as Example 1 except that the thickness of the glass substrate was different. The optical characteristics are shown in Table 3. Example 3 is an example in which a low reflection film is formed on the glass substrate of Sample 8.
[0099]
According to Example 3, the visible light transmittance of the basic sample 8 is 69%, whereas the visible light transmittance increases due to the formation of the low-reflection film, and satisfies the standard of safety glass for automobiles. It was way. Further, the visible light reflectance and the solar radiation transmittance were further reduced as compared with Example 1. From this, it was found that Example 3 has both excellent low reflection performance and solar shading performance.
[0100]
Example 4
The glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles according to Example 4 has the following configuration.
Configuration: GRN 2.1 mm / intermediate film / GRN 2.1 mm / low reflection film
[0101]
Example 4 differs from Example 1 in the type of glass substrate, and is a green glass plate. Others produced the laminated glass by the structure similar to Example 1, and the same process. The optical characteristics are shown in Table 3. Example 4 is an example in which a low-reflection film is formed on the glass substrate of Sample 4.
[0102]
According to Example 4, compared with Reference Example 1, the visible light reflectance and the solar radiation transmittance were reduced. Although this Example 4 was inferior to Examples 1-3, it turned out that the outstanding low reflection performance and solar radiation shielding performance are compatible.
[0103]
(Example 5)
The glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles according to Example 5 has the following configuration.
Configuration: UVG 6.0 (single plate) / low reflection film
[0104]
The cross-sectional structure of the glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles of Example 2 is schematically shown in FIG. The glass plate 1 with a low reflection film for automobiles is obtained by forming a low reflection film 2 (21, 22) on the inner surface of a
[0105]
Example 5 is an example in which a low-reflection film applied to the present invention is formed on a single-plate UV-cut green glass plate (thickness 6 mm, sample 9).
[0106]
According to Example 5, as in Example 3, the basic sample 9 has a visible light transmittance of 69.5%, but the visible light transmittance is Increased to 71.5%. Moreover, the visible light reflectance and the solar radiation transmittance were also reduced, and it was found that both low reflection performance and solar radiation shielding performance were achieved.
[0107]
(Comparative Example 1)
The glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles according to Comparative Example 1 has the following configuration.
・ Configuration: Clear 2.1mm / Intermediate film / Clear 2.1mm / Low reflective film
[0108]
Comparative Example 1 is a glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles in which laminated glass was produced in the same process except that the glass substrate was different from Example 1. The optical characteristics are shown in Table 3. Comparative Example 1 is an example in which a low reflection film is formed on the glass substrate of
[0109]
According to Comparative Example 1, the effect of reducing the visible light reflectance was shown by forming a low reflection film on
[0110]
【The invention's effect】
As described above in detail, in the glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles according to the present invention, the low reflection film is applied to the glass plate having absorption in the visible light region. For this reason, the outstanding low reflection performance and the visible light transmittance | permeability as a glass plate for motor vehicles can be made compatible.
[0111]
Furthermore, when the glass plate which comprises the glass plate with the low reflection film for motor vehicles by this invention is made into heat ray absorption glass, low reflection performance and solar radiation shielding performance can be made compatible.
[0112]
Moreover, in the glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles according to the present invention, since the low reflection film is formed on the surface thereof, reflection loss on the surface of the glass plate can be suppressed. As a result, since the transmittance as a glass plate can be improved, it is possible to further increase the ability to absorb solar radiation on the glass substrate.
[0113]
Specifically, even a glass plate having a visible light transmittance of only 70% or less can be employed as an automotive glass plate according to the present invention. As a result, better solar shading can be obtained.
[0114]
Furthermore, even when using an intermediate film in which ITO fine particles that are effective as a heat ray absorbent are dispersed, the transmittance as a glass plate can be improved as described above, so a high absorption glass plate is adopted. can do. As a result, it is possible to obtain excellent solar shading performance even if the amount of dispersion of expensive ITO fine particles is small. This greatly contributes to cost reduction.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating a cross-sectional structure of a glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles according to the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a cross-sectional structure of a glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles according to another embodiment of the present invention.
[Explanation of symbols]
1: Automotive glass plate with low reflection film
10: Single glass plate
11: Single outside glass plate
12: Single glass plate inside the car
13: Intermediate film
2: Low reflection film
21: First layer of a low reflection film (high refractive index film)
22: Second layer of low reflection film (low refractive index film)
Claims (14)
前記ガラス板のみの可視光線透過率は少なくとも68%であり、低反射膜付きガラス板としての可視光線透過率が、少なくとも70%であることを特徴とする自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板。In a glass plate for automobiles, and a glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles provided with a two-layer low reflection film on the main surface on the inner surface side of the car,
The glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles, wherein the visible light transmittance of only the glass plate is at least 68%, and the visible light transmittance as a glass plate with a low reflection film is at least 70%.
前記低反射膜は、ガラス側から数えて第1層が、屈折率(n1)=1.68〜2.3でかつ膜厚(d1)=100〜140nmであり、該第1層上に積層される第2層が、屈折率(n2)=1.4〜1.5でかつ膜厚(d2)=80〜110nmである2層式低反射膜である自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板。In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to claim 1,
The low reflection film has a first layer counting from the glass side and having a refractive index (n 1 ) = 1.68 to 2.3 and a film thickness (d 1 ) = 100 to 140 nm. The low-reflection film for automobiles is a two-layer low-reflection film having a refractive index (n 2 ) = 1.4 to 1.5 and a film thickness (d 2 ) = 80 to 110 nm. Glass plate with.
前記低反射膜の第1層が屈折率(n1)=1.70〜1.95で、かつ第2層が屈折率(n2)=1.40〜1.47である自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板。In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to claim 2,
Low reflection for automobiles, wherein the first layer of the low reflection film has a refractive index (n 1 ) = 1.70 to 1.95, and the second layer has a refractive index (n 2 ) = 1.40 to 1.47. Glass plate with film.
前記ガラス板は、グリーン系、ブロンズ系、グレー系、UVカットグリーン系、またはUVカットブロンズ系の単一ガラス板である自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板。In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
The glass plate is a glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles, which is a single glass plate of green, bronze, gray, UV cut green, or UV cut bronze.
前記ガラス板は、グリーン系またはUVカットグリーン系ガラスであって、
前記ガラスは、質量百分率表示でFe2O3換算した全鉄0.3〜1%を含有するソーダライムシリカガラスからなる自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板。In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to claim 4,
The glass plate is green or UV cut green glass,
The glass, automotive low reflection film-coated glass plate made of soda lime silica glass containing 0.3 to 1% total iron Fe 2 O 3 in terms represented by mass percentage.
前記ガラス板は、少なくとも2枚の単一ガラス板が熱可塑性中間膜を介して接着された合わせガラスである自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板。In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
The glass plate is a glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles, which is a laminated glass in which at least two single glass plates are bonded via a thermoplastic intermediate film.
前記合わせガラスの中間膜は、0.2μm以下の粒径よりなるITO微粒子を、中間膜に対して0.01〜0.8質量%の割合で含んでいる自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板。In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to claim 6,
The laminated glass intermediate film is a glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles, which contains ITO fine particles having a particle diameter of 0.2 μm or less at a ratio of 0.01 to 0.8 mass% with respect to the intermediate film.
前記ガラス板は、クリア系、グリーン系、ブロンズ系、グレー系、UVカットグリーン系、およびUVカットブロンズ系ガラス板のうち、同種または異種のガいラス板を組み合わせてなる合わせガラス板である自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板(ただし、クリア系ガラス板同士を組み合わせた合わせガラス板を除く)。In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to claim 6 or 7,
The glass plate is a laminated glass plate formed by combining the same type or different types of glass plates among the clear, green, bronze, gray, UV cut green, and UV cut bronze glass plates. Glass plate with low reflective film for use (excluding laminated glass plates made by combining clear glass plates).
前記低反射膜は、膜面側から可視光線がそれぞれ入射角12度および60度で入射したときの可視光反射率が、それぞれ4.8%以下および11.0%以下の可視光線反射率を有している自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板である。In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to any one of claims 1 to 8,
The low reflection film has a visible light reflectance of 4.8% or less and 11.0% or less when visible light is incident at an incident angle of 12 degrees and 60 degrees, respectively, from the film surface side. It is a glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles.
前記低反射膜は、膜面側から可視光線がそれぞれ入射角12度および60度で入射したときの可視光反射率が、当該ガラス板であって前記低反射膜未形成のガラス面におけるそれぞれ12度および60度の入射角での可視光反射率よりも、それぞれ少なくとも2.4%および少なくとも3.5%小さい可視光反射率を有している自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板。In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to any one of claims 1 to 9,
The low reflection film has a visible light reflectance of 12 when the visible light is incident at an incident angle of 12 degrees and 60 degrees from the film surface side, respectively, on the glass surface where the low reflection film is not formed. A glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles having a visible light reflectance of at least 2.4% and at least 3.5% smaller than the visible light reflectance at an incident angle of 60 degrees and 60 degrees, respectively.
前記低反射膜の第1層は、SiO2およびTiO2を含有して、あるいは実質的にTiO2のみからなる自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板。In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to any one of claims 1 to 10,
The first layer of the low-reflection film is a glass plate with a low-reflection film for automobiles containing SiO 2 and TiO 2 or consisting essentially of TiO 2 .
前記第1層はモル比でTi:Si=35:65〜100:0であり、第2層はSiO2を含有する自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板である。In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to any one of claims 1 to 11,
The first layer has a molar ratio of Ti: Si = 35: 65 to 100: 0, and the second layer is a glass plate with a low reflection film for automobiles containing SiO 2 .
前記低反射膜の第2層は、実質的にSiO2のみからなる自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板。In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to any one of claims 1 to 12,
The second layer of the low-reflection film is a glass plate with a low-reflection film for automobiles substantially composed of only SiO 2 .
前記低反射膜は、膜面側から可視光線が入射角12度および60度でそれぞれ入射したときの可視光が、それぞれ22%以下および10%以下の刺激純度を有している自動車用低反射膜付きガラス板。In the glass plate with a low reflective film for automobiles according to any one of claims 1 to 13,
The low-reflection film has a low-reflection for automobiles in which visible light has a stimulus purity of 22% or less and 10% or less, respectively, when visible light is incident at an incident angle of 12 degrees and 60 degrees from the film surface side. Glass plate with film.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002012560A JP2005298219A (en) | 2002-01-22 | 2002-01-22 | Glass sheet having low reflection film for automobile |
| PCT/JP2003/000512 WO2003062165A1 (en) | 2002-01-22 | 2003-01-22 | Glass sheet with low reflection coating |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002012560A JP2005298219A (en) | 2002-01-22 | 2002-01-22 | Glass sheet having low reflection film for automobile |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005298219A true JP2005298219A (en) | 2005-10-27 |
Family
ID=27606050
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002012560A Pending JP2005298219A (en) | 2002-01-22 | 2002-01-22 | Glass sheet having low reflection film for automobile |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2005298219A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2003062165A1 (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014062733A (en) * | 2006-10-16 | 2014-04-10 | Eurokera Snc | Glass-ceramic plate and method for manufacturing the same |
| WO2019194292A1 (en) * | 2018-04-05 | 2019-10-10 | Agc株式会社 | Laminated glass |
| WO2020017495A1 (en) * | 2018-07-17 | 2020-01-23 | Agc株式会社 | Optical member |
| JP2025520787A (en) * | 2022-06-30 | 2025-07-03 | フーイャォ グラス インダストリー グループ カンパニー リミテッド | Laminated Window Glass |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107099776B (en) * | 2017-04-21 | 2019-11-08 | 咸宁南玻节能玻璃有限公司 | A high-definition neutral color low-emissivity coated glass and its preparation method |
| CN114349359B (en) * | 2021-12-27 | 2023-06-09 | 盐城牧东光电科技有限公司 | A low-reflection and high-transparency cover plate and its manufacturing process |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2748743B1 (en) * | 1996-05-14 | 1998-06-19 | Saint Gobain Vitrage | GLASS WITH ANTI-REFLECTIVE COATING |
| FR2787440B1 (en) * | 1998-12-21 | 2001-12-07 | Saint Gobain Vitrage | TRANSPARENT SUBSTRATE HAVING AN ANTI-REFLECTIVE COATING |
| JP3678043B2 (en) * | 1999-03-10 | 2005-08-03 | 日本板硝子株式会社 | Low reflection glass articles for automobiles |
| EP1136457A4 (en) * | 1999-09-14 | 2002-10-23 | Asahi Glass Co Ltd | LAMINATE GLASS |
-
2002
- 2002-01-22 JP JP2002012560A patent/JP2005298219A/en active Pending
-
2003
- 2003-01-22 WO PCT/JP2003/000512 patent/WO2003062165A1/en not_active Ceased
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014062733A (en) * | 2006-10-16 | 2014-04-10 | Eurokera Snc | Glass-ceramic plate and method for manufacturing the same |
| WO2019194292A1 (en) * | 2018-04-05 | 2019-10-10 | Agc株式会社 | Laminated glass |
| JPWO2019194292A1 (en) * | 2018-04-05 | 2021-05-13 | Agc株式会社 | Laminated glass |
| JP7222393B2 (en) | 2018-04-05 | 2023-02-15 | Agc株式会社 | laminated glass |
| WO2020017495A1 (en) * | 2018-07-17 | 2020-01-23 | Agc株式会社 | Optical member |
| JPWO2020017495A1 (en) * | 2018-07-17 | 2021-08-19 | Agc株式会社 | Optical member |
| JP7298073B2 (en) | 2018-07-17 | 2023-06-27 | Agc株式会社 | Optical member |
| JP2025520787A (en) * | 2022-06-30 | 2025-07-03 | フーイャォ グラス インダストリー グループ カンパニー リミテッド | Laminated Window Glass |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2003062165A1 (en) | 2003-07-31 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN103260870B (en) | Items with low reflective coating | |
| WO1999025660A1 (en) | Ultraviolet/infrared absorbing glass, ultraviolet/infrared absorbing glass sheet, ultraviolet/infrared absorbing glass sheet coated with colored film, and window glass for vehicles | |
| WO2015041257A1 (en) | Tempered glass plate with low reflective coating and production method therfor | |
| JP7748350B2 (en) | Glass laminate | |
| US5976678A (en) | Colored film-covered glass articles | |
| WO1999033759A1 (en) | Ultraviolet/infrared absorbent glass, ultraviolet/infrared absorbent glass plate, ultraviolet/infrared absorbent glass plate coated with colored film, and window glass for vehicle | |
| KR20250012053A (en) | Decorative enamel for automotive glass and related methods | |
| JP2008037668A (en) | Laminated glass for windows | |
| EP0890556B1 (en) | Thin film for optics, composition for the formation thereof, and ultraviolet-absorbing and heat-reflecting glass made by using the same | |
| JP2005298219A (en) | Glass sheet having low reflection film for automobile | |
| EP0823405B1 (en) | Glass article covered with colored film | |
| JP3678043B2 (en) | Low reflection glass articles for automobiles | |
| JP2000143288A (en) | Colored film coated glass article | |
| JP2004338985A (en) | Substrate with heat ray shielding film, and its production method | |
| JPH10236847A (en) | Optical thin film, its forming composition and ultraviolet-absorbing and heat ray-reflecting glass using the composition | |
| KR20250123769A (en) | Laminated glazing for illuminated vehicles and vehicles equipped therewith | |
| JP2000335940A (en) | Low-reflecting glass article | |
| JP2000280738A (en) | Automobile low-reflective colored film-coated windshield window | |
| JP2001206736A (en) | Method for manufacturing colored film-coated glass article and colored film-coated glass article | |
| JPH11228176A (en) | High visible light transmitting ultraviolet absorbing glass and ultraviolet absorbing colored glass plate | |
| JP2015074583A (en) | Coating glass plate with mark and method for producing the same | |
| JP4023206B2 (en) | Bent glass plate for vehicles with optical equipment | |
| JPWO2004046057A1 (en) | Thermal shielding plate, method for producing the same, and liquid composition used therefor | |
| JP2895746B2 (en) | Reflection reduction glass | |
| JP2024113661A (en) | Glass Laminate |