JP2005292418A - Semiconductive member for image formation - Google Patents
Semiconductive member for image formation Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2005292418A JP2005292418A JP2004106398A JP2004106398A JP2005292418A JP 2005292418 A JP2005292418 A JP 2005292418A JP 2004106398 A JP2004106398 A JP 2004106398A JP 2004106398 A JP2004106398 A JP 2004106398A JP 2005292418 A JP2005292418 A JP 2005292418A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- weight
- outermost layer
- compound
- parts
- fluororesin
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Landscapes
- Electrophotography Configuration And Component (AREA)
- Electrostatic Charge, Transfer And Separation In Electrography (AREA)
- Compositions Of Macromolecular Compounds (AREA)
- Polyurethanes Or Polyureas (AREA)
Abstract
【課題】 画像形成装置の接触帯電手段において、紙粉・トナー等の付着を抑制し、内部、或いは内部及び最外層膜からのブリードを防止することにより、感光体汚染を防止し、導電性を損なわず、画像劣化もなく、すべり性向上、耐磨耗性付与し、耐久性にも優れた、帯電部材、転写部材等の電子写真方式の画像形成用半導電性部材を提供する。
【解決手段】 電子写真方式画像形成装置の接触帯電手段に使用する該帯電手段の最外層を構成する材料に、少なくとも架橋フッ素樹脂及び板状構造を有する無機充填剤及び導電性粒子を含有すること画像形成用半導電性部材を特徴とする。PROBLEM TO BE SOLVED: To prevent adhesion of paper powder, toner, etc. in a contact charging means of an image forming apparatus and prevent bleeding from the inside or the inner and outermost layer films, thereby preventing photoconductor contamination and conductivity. Disclosed is an electrophotographic image-forming semiconductive member such as a charging member or a transfer member that is not damaged, has no image deterioration, has improved slipperiness, imparts abrasion resistance, and has excellent durability.
SOLUTION: The material constituting the outermost layer of the charging means used for the contact charging means of the electrophotographic image forming apparatus contains at least a crosslinked fluororesin, an inorganic filler having a plate-like structure, and conductive particles. It features a semiconductive member for image formation.
Description
本発明は、複写機、レーザプリンター、ファクシミリ、これらの複合OA機器等における電子写真方式画像形成装置に使用する材料に関し、特に汚染防止、耐久性改善が可能な画像形成用帯電部材に用いられる最外層材料に関する。 The present invention relates to a material used for an electrophotographic image forming apparatus in a copying machine, a laser printer, a facsimile, a composite OA apparatus thereof, and the like, and particularly used for an image forming charging member capable of preventing contamination and improving durability. It relates to the outer layer material.
従来、複写機やプリンタにおいて、帯電ローラ、転写ローラ等の半導電性ローラは、感光体に接して回転するように設けられており、それぞれ機能を奏するようになっている。例えば、帯電ローラにおいては、静電潜像の形成される感光体に対する帯電方式のローラ帯電部材として用いられており、感光体表面に、電圧印加した帯電ローラを押し当て、接触させ、感光体と帯電ローラとが相互に回転するようにし、感光体表面を帯電せしめるものである。このように帯電ローラや転写ローラ等は、感光体に接し、回転するもので、その帯電のために適度な導電性を有していることが要求されている。 2. Description of the Related Art Conventionally, in a copying machine or a printer, semiconductive rollers such as a charging roller and a transfer roller are provided so as to rotate in contact with a photoreceptor, and each has a function. For example, the charging roller is used as a charging roller charging member for a photosensitive member on which an electrostatic latent image is formed. The charging roller is pressed against and brought into contact with the surface of the photosensitive member. The charging roller rotates relative to each other to charge the surface of the photoreceptor. As described above, the charging roller, the transfer roller, and the like are in contact with the photoreceptor and rotate, and are required to have appropriate conductivity for charging.
近年、複写機やプリンタ等は、高速・高寿命化、高画質化、省エネルギー化の要求が高まっている。例えば、省エネルギー化では、低温定着方式が採用され、トナーの低融点化が行われており、また、高画質化においては、重合等によるトナーの粒径を小さくしたり、球形にすることも行なわれている。 In recent years, copying machines, printers, and the like have been increasingly demanded for high speed, long life, high image quality, and energy saving. For example, in order to save energy, a low-temperature fixing method is adopted to lower the melting point of the toner, and in order to improve the image quality, the toner particle size is reduced by polymerization or made spherical. It is.
しかしながら、これら省エネルギー化や高画質化を行うためのトナーの低融点化や粒径の微細化・球形化は、帯電ローラや転写ローラ等の半導電性ローラにトナーの付着を引き起し易く、このような半導電性ローラにトナーが付着したり、固着したりすると、画質劣化が問題となってくる。つまり、通紙枚数の増大によって、トナーの付着による帯電ローラ等の半導電性ローラの全体としての抵抗が上昇し、またトナーの不均一付着による部分的な抵抗変化が引き起こされ、画質の劣化が生じることとなる。 However, lowering the melting point of the toner and making the particle size finer and spherical for energy saving and higher image quality are likely to cause toner adhesion to a semiconductive roller such as a charging roller or transfer roller, When toner adheres to or adheres to such a semiconductive roller, image quality deterioration becomes a problem. In other words, the increase in the number of sheets to pass increases the overall resistance of the semiconductive roller such as a charging roller due to toner adhesion, and causes a partial resistance change due to non-uniform adhesion of toner, resulting in deterioration of image quality. Will occur.
このような画質劣化防止には、トナーが帯電ローラ等の半導電性ローラ表面に付着しないようにすればよいが、例えば、従来のN−メトキシメチル化ナイロン等の親水性樹脂で最外層が形成されているローラは、高温・高湿下で抵抗変動やトナーのローラ表面への付着防止には有効ではなかった。 In order to prevent such image quality deterioration, it is only necessary to prevent the toner from adhering to the surface of the semiconductive roller such as a charging roller. For example, the outermost layer is formed of a conventional hydrophilic resin such as N-methoxymethylated nylon. The roller used is not effective in preventing resistance fluctuation and toner adhesion to the roller surface under high temperature and high humidity.
従来、帯電ローラなどに用いられる導電性ローラとしては、導電性芯金に導電性弾性体層を設け、この導電性弾性体層上にさらに抵抗調整層を設けた構造のものが知られている(例えば特許文献1〜4参照)。 Conventionally, as a conductive roller used for a charging roller or the like, a roller having a structure in which a conductive elastic body layer is provided on a conductive metal core and a resistance adjustment layer is further provided on the conductive elastic body layer is known. (For example, refer patent documents 1-4).
すなわち、かかる構造の導電性ローラは、一般的には、導電性粒子を混入したシリコーンゴム、エチレンプロピレンゴム、ニトリルゴム、ウレタンゴムなどの合成ゴムの弾性材料からなっている。 That is, the conductive roller having such a structure is generally made of an elastic material of synthetic rubber such as silicone rubber, ethylene propylene rubber, nitrile rubber, urethane rubber mixed with conductive particles.
上記半導電性ローラでは、弾性材料に種々のプロセスオイルや軟化剤などの液剤を添加して硬度を下げていたため、半導電性ローラの表面にウレタンやナイロンなどを初めとする種々の樹脂による保護層を設けて、ブリードの発生、感光体汚染の防止をしていた。 In the above-mentioned semiconductive roller, liquids such as various process oils and softeners are added to the elastic material to reduce the hardness. Therefore, the surface of the semiconductive roller is protected with various resins such as urethane and nylon. A layer was provided to prevent bleeding and photoconductor contamination.
しかしながら、例えば、これら半導電性ローラを高温・高湿下に長時間放置すると、樹脂成分が加水分解して潜像担持体に固着することがあったり、塗膜にあるピンホールなどから上記ゴム中成分が滲み出し、ブリードして感光体汚染をするなど、これらの耐環境特性は必ずしも満足されるものではなかった。 However, for example, if these semiconductive rollers are left for a long time under high temperature and high humidity, the resin component may be hydrolyzed and fixed to the latent image carrier, or the above rubber may be removed from pinholes in the coating film. These environmental resistance characteristics are not always satisfied, for example, the middle component oozes out and bleeds to contaminate the photoreceptor.
更に詳しく説明すると、このような構造の導電性ローラを帯電ローラとして用いた場合、帯電不良等による画像の不具合および感光体の汚染を防止するために、中間層および最外層を設けなければならないという問題があり、この結果、多層構造となり、コスト高となる。また、導電性弾性層の電気特性を混入された導電性粉末同士の接触により得ているので、電気的特性の不均一性による帯電むらが生じやすいという問題もでる。 More specifically, when a conductive roller having such a structure is used as a charging roller, an intermediate layer and an outermost layer must be provided in order to prevent image defects and contamination of the photoreceptor due to charging failure and the like. There is a problem, which results in a multi-layer structure and high costs. In addition, since the electrical characteristics of the conductive elastic layer are obtained by contact between the mixed conductive powders, there is a problem that uneven charging easily occurs due to non-uniformity of electrical characteristics.
一方、このような問題点を解決する導電性ローラとして、導電性芯金表面に、導電性粒子が分散されていない電気的中抵抗物質からなる弾性層を有し、この弾性層上に、前記物質より非粘着性の高い非粘着性物質からなる表面層を有する構造のものが知られている(例えば特許文献5、6参照)。 On the other hand, as a conductive roller that solves such problems, the surface of the conductive core bar has an elastic layer made of an electrically intermediate resistance material in which conductive particles are not dispersed. The thing of the structure which has the surface layer which consists of a non-adhesive substance whose non-adhesiveness is higher than a substance is known (for example, refer patent document 5, 6).
ここで、電気的中抵抗物質としては、エピクロルヒドリン−エチレンオキサイド−アリルグリシジルエーテル三元共重合体、またはエピクロルヒドリン−エチレンオキサイド二元共重合体の単独またはこれらの混合系のエピクロルヒドリンゴム(1×107〜1×1010Ω・cm)が挙げられており、非粘着性物質としては、フルオロオレフィンと水酸基含有ビニルエーテルを構成成分とした含フッ素共重合体をイソシアネートで架橋させて得られる含フッ素架橋共重合体が挙げられている。しかし、これらフッ素樹脂化合物のみでは紙粉やトナーのフィルミング付着防止及びブリード等による感光体汚染防止に効果が十分ではなかった。 Here, as an electrical resistance substance, epichlorohydrin-ethylene oxide-allyl glycidyl ether terpolymer, epichlorohydrin-ethylene oxide binary copolymer alone or a mixture thereof epichlorohydrin rubber (1 × 10 7) is used. ~1 × 10 10 Ω · cm) has been mentioned, non as the adhesive material, a fluorine-containing crosslinked copolymer obtained fluorine-containing copolymer was a component of fluoroolefin and hydroxyl group-containing vinyl ether is crosslinked with an isocyanate Polymers are mentioned. However, these fluororesin compounds alone are not sufficient in preventing the filming adhesion of paper dust and toner and preventing the photoreceptor from being contaminated by bleeding.
紙粉・トナー等の付着防止として、シリコーンオイルを添加することも提案されているが、紙粉・トナー等の付着防止には効果があるが、該シリコーンオイルが、反応性基を持つシリコーンオイルではない場合、シリコーンオイル自身が感光体を汚染する。また反応性基を持つシリコーンオイルの場合は塗膜内で反応することにより、そのもの自身がブリードすることなく感光体汚染性は低下し、良好であるが、単独では半導電性部材からの低分子化合物のブリード防止には効果が低いものであった(例えば特許文献7〜10参照)。 Although it has been proposed to add silicone oil as an anti-adhesion agent for paper dust / toner, etc., it is effective for preventing the adhering of paper dust / toner etc., but the silicone oil has a reactive group. If not, the silicone oil itself will contaminate the photoreceptor. In the case of a silicone oil having a reactive group, it reacts within the coating film, and the contamination of the photoreceptor is reduced without causing bleeding itself. The effect of preventing the bleeding of the compound was low (see, for example, Patent Documents 7 to 10).
上記のもの以外にも、基材がウレタンで疎水性ポリオール(フッ素ポリオール)とイソシアネートとの硬化で構成されているローラ(例えば特許文献11参照)が、フッ素樹脂ブリード防止層を設け、イソシアネート架橋剤でそれを硬化した半導電性ローラ(例えば特許文献12参照)が、非粘着性物質としてイソシアネート架橋剤で架橋したフッ素架橋共重合体を使用した導電性ローラ(例えば特許文献13参照)が、フッ素変性アクリレート系樹脂とフッ素オレフィン系樹脂とOH基を有する非(フッ素変性)アクリレート系樹脂とを、OH基と反応する化合物(ポリイソシアネート化合物)で架橋した半導電性ローラ(例えば特許文献14参照)が、さらに、Mg(1-X)AlX(OH)2(CO3)(X/2)・mH2Oで表されるハイドロタルサイト類化合物を含有する帯電部材(例えば特許文献15参照)が、それぞれ提案されている。 In addition to the above, a roller (for example, see Patent Document 11) in which the base material is urethane and is formed by curing a hydrophobic polyol (fluorine polyol) and isocyanate is provided with a fluororesin bleed prevention layer, and an isocyanate crosslinking agent A semiconductive roller (for example, see Patent Document 12) cured with a conductive roller (for example, see Patent Document 13) using a fluorine-crosslinked copolymer crosslinked with an isocyanate cross-linking agent as a non-adhesive substance. A semiconductive roller obtained by crosslinking a modified acrylate resin, a fluorine olefin resin, and a non- (fluorine modified) acrylate resin having an OH group with a compound (polyisocyanate compound) that reacts with an OH group (see, for example, Patent Document 14) Is further represented by Mg (1-X) Al X (OH) 2 (CO 3 ) (X / 2) · mH 2 O A charging member containing a lucite compound (see, for example, Patent Document 15) has been proposed.
また、フッ素ポリオールとポリイソシアネートとの高分子化合物を主体とする樹脂からなる表面層を設けた帯電部材(例えば特許文献16参照)が、さらに、ポリエステルポリオール又はアクリルポリオールをイソシアネートで硬化させた皮膜を設けた帯電部材及び転写部材(例えば特許文献17参照)が、それぞれ提案されている。 In addition, a charging member (see, for example, Patent Document 16) provided with a surface layer made of a resin mainly composed of a polymer compound of fluorine polyol and polyisocyanate is further provided with a film obtained by curing polyester polyol or acrylic polyol with isocyanate. Provided charging members and transfer members (see, for example, Patent Document 17) have been proposed.
しかしながら、これらの上記した半導電性弾性層に使用し、従来のフッ素樹脂化合物による紙粉・トナー付着防止及びシリコーンオイルによる離型性付与として最外層に使用されている半導電性部材からのブリードを防止する材料等では、半導電性部材表面へのブリード防止、感光体汚染を防止することは未だ十分ではなかった。
本発明は、上述した実情を考慮してなされたもので、半導電性弾性層の最外層に紙粉・トナーなどが付着するのを抑制し、更に内部からのブリードを防止することによって、感光体汚染を防止し、導電性を損なわず、それらによる画質劣化の問題の解消を図り、更にすべり性向上、耐磨耗性付与し、半導電性部材の耐久性を向上させた画像形成用半導電性部材を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in consideration of the above-described circumstances, and suppresses the adhesion of paper dust, toner, etc. to the outermost layer of the semiconductive elastic layer, and further prevents bleeding from the inside, thereby Image-forming semi-conductors that prevent body contamination, eliminate conductivity problems, eliminate image quality degradation problems, improve slipperiness and wear resistance, and improve the durability of semiconductive members. An object is to provide a conductive member.
本発明は、上記の問題点を解決するために鋭意検討した結果、画像形成用半導電性部材において、最外層に少なくとも架橋フッ素樹脂及び板状構造を有する無機充填剤及び導電性粒子を含有させることで、ブリードを防止することによって、感光体汚染を防止し、導電性を損なわずに、画質劣化の問題の解消を図り、すべり性向上、耐磨耗性付与し、半導電性部材の耐久性を向上させた電子写真方式の画像形成用半導電性部材が得られることを見出し、本発明に至った。 As a result of intensive studies to solve the above problems, the present invention includes an inorganic filler having at least a crosslinked fluororesin and a plate-like structure and conductive particles in the outermost layer in the semiconductive member for image formation. By preventing bleeding, photoconductor contamination is prevented, and the problem of image quality deterioration is solved without impairing conductivity, improving slipperiness and providing wear resistance, and durability of semiconductive members. The present inventors have found that an electrophotographic semiconductive member for image formation having improved properties can be obtained, and have led to the present invention.
上記の課題を解決するために、請求項1に記載の発明は、電子写真方式画像形成装置に使用する部材の最外層を構成する材料に、少なくとも架橋フッ素樹脂及び板状構造を有する無機充填剤及び導電性粒子を含有する画像形成用半導電性部材を特徴とする。 In order to solve the above problems, the invention according to claim 1 is an inorganic filler having at least a cross-linked fluororesin and a plate-like structure as a material constituting the outermost layer of a member used in an electrophotographic image forming apparatus. And an image-forming semiconductive member containing conductive particles.
また、請求項2に記載の発明は、前記最外層に使用する構成材料が、少なくとも架橋フッ素樹脂及び板状構造を有する無機充填剤及び導電性粒子とシリコーン化合物を含有する画像形成用半導電性部材を特徴とする。 According to a second aspect of the present invention, the constituent material used for the outermost layer contains at least a crosslinked fluororesin, an inorganic filler having a plate-like structure, conductive particles, and a silicone compound. Features a member.
また、請求項3に記載の発明は、前記最外層に使用する構成材料が、少なくとも架橋フッ素樹脂及び板状構造を有する無機充填剤及び導電性粒子とフッ素化シリコーン化合物を含有する画像形成用半導電性部材を特徴とする。 According to a third aspect of the present invention, in the image forming half, the constituent material used for the outermost layer contains at least a crosslinked fluororesin, an inorganic filler having a plate-like structure, conductive particles, and a fluorinated silicone compound. Features a conductive member.
また、請求項4に記載の発明は、前記最外層に使用する構成材料が、少なくとも架橋フッ素樹脂及び板状構造を有する無機充填剤及び導電性粒子と反応性基を有するシリコーン化合物を含有する画像形成用半導電性部材を特徴とする。 According to a fourth aspect of the present invention, there is provided an image in which the constituent material used for the outermost layer contains at least a crosslinked fluororesin, an inorganic filler having a plate-like structure, and a silicone compound having a conductive particle and a reactive group. Features a forming semiconductive member.
また、請求項5に記載の発明は、前記最外層に使用する構成材料が、少なくとも架橋フッ素樹脂及び板状構造を有する無機充填剤及び導電性粒子と反応性基を有するフッ素化シリコーン化合物を含有する画像形成用半導電性部材を特徴とする。 Further, in the invention described in claim 5, the constituent material used for the outermost layer contains at least a crosslinked fluororesin, an inorganic filler having a plate-like structure, and a fluorinated silicone compound having a conductive particle and a reactive group. The image forming semiconductive member is characterized.
また、請求項6に記載の発明は、前記最外層に使用する構成材料が、さらに少なくともポリオール化合物及びイソシアネート化合物を含有する請求項2から5のいずれか1項に記載の画像形成用半導電性部材を特徴とする。 Further, in the invention described in claim 6, the constituent material used for the outermost layer further contains at least a polyol compound and an isocyanate compound, and the semiconductivity for image formation according to any one of claims 2 to 5. Features a member.
また、請求項7に記載の発明は、前記最外層に使用する構成材料が、さらに少なくともフッ素ポリオール化合物及びイソシアネート化合物を含有する請求項2から5のいずれか1項に記載の半導電性部材を特徴とする。 The invention according to claim 7 is the semiconductive member according to any one of claims 2 to 5, wherein the constituent material used for the outermost layer further contains at least a fluorine polyol compound and an isocyanate compound. Features.
また、請求項8に記載の発明は、前記最外層に使用する構成材料が、さらに少なくともフッ素ポリオール化合物及びアクリル樹脂及びイソシアネート化合物を含有する請求項2から5のいずれか1項に記載の画像形成用半導電性部材を特徴とする。 The invention according to claim 8 is the image formation according to any one of claims 2 to 5, wherein the constituent material used for the outermost layer further contains at least a fluorine polyol compound, an acrylic resin, and an isocyanate compound. Features a semi-conductive member.
また、請求項9に記載の発明は、前記最外層に使用する構成材料が、さらに少なくともフッ素ポリオール化合物及びアクリルポリオール化合物及びイソシアネート化合物を含有する請求項2から5のいずれか1項に記載の画像形成用半導電性部材を特徴とする。 The invention according to claim 9 is the image according to any one of claims 2 to 5, wherein the constituent material used for the outermost layer further contains at least a fluorine polyol compound, an acrylic polyol compound, and an isocyanate compound. Features a forming semiconductive member.
本発明によれば、画像形成用半導電性部材において、最外層に架橋フッ素樹脂及び板状構造を有する無機充填剤及び導電性粒子を少なくとも含有することにより、内部からのブリードを防止し、感光体汚染を防止することができ、導電性を損なわずに、画質劣化の問題の解消を図り、すべり性向上、耐磨耗性付与し、半導電性部材の耐久性を向上させることが可能となる。 According to the present invention, in the semiconductive member for image formation, the outermost layer contains at least a cross-linked fluororesin, an inorganic filler having a plate-like structure, and conductive particles, thereby preventing bleeding from the inside and photosensitivity. It is possible to prevent body contamination, eliminate the problem of image quality deterioration without impairing conductivity, improve slipperiness, impart wear resistance, and improve the durability of semiconductive members Become.
また、画像形成用半導電性部材において、最外層に架橋フッ素樹脂及び板状構造を有する無機充填剤及び導電性粒子と、さらにシリコーン化合物を少なくとも含有することにより、特に最外層に紙粉・トナーなどが付着するのを抑制し、しかも内部からのブリードを防止することによって、感光体汚染を防止し、導電性画質劣化の問題の解消、すべり性向上、耐磨耗性付与、耐久性向上を実現することが可能となる。 Further, in the semiconductive member for image formation, the outermost layer contains at least a crosslinked fluororesin, an inorganic filler having a plate-like structure and conductive particles, and at least a silicone compound. In addition, it prevents contamination of the photoconductor by preventing bleed from inside, eliminating the problem of deterioration of conductive image quality, improving slipperiness, imparting wear resistance, and improving durability. It can be realized.
さらに、画像形成用半導電性部材において、最外層に架橋フッ素樹脂及び板状構造を有する無機充填剤及び導電性粒子とフッ素化シリコーン化合物を少なくとも含有することにより、また、最外層に架橋フッ素樹脂、板状構造無機充填剤及び導電性粒子と反応性基を有するシリコーン化合物を含有すること、また、最外層に架橋フッ素樹脂及び板状構造無機充填剤及び導電性粒子と反応性基を有するフッ素化シリコーン化合物を少なくとも含有するによって、特に最外層に紙粉・トナーなどが付着するのを抑制する効果を向上させることができ、更に内部からのブリードを防止する、感光体汚染を防止し、導電性を損なわずに、画質劣化の問題の解消を図り、すべり性向上、耐磨耗性付与し、半導電性部材の耐久性を向上させることができる。 Further, in the semiconductive member for image formation, the outermost layer contains at least a cross-linked fluororesin and an inorganic filler having a plate-like structure and conductive particles and a fluorinated silicone compound, and the outermost layer has a cross-linked fluororesin. A plate-like inorganic filler and a conductive compound and a silicone compound having a reactive group; and a cross-linked fluororesin and a plate-like inorganic filler and a conductive particle and a fluorine having a reactive group in the outermost layer. By containing at least a fluorinated silicone compound, the effect of suppressing the adhesion of paper dust, toner, etc. to the outermost layer can be improved, and further, bleeding from the inside can be prevented, photoconductor contamination can be prevented, and conductivity can be prevented. It is possible to solve the problem of image quality degradation without impairing the properties, improve the slipperiness, impart wear resistance, and improve the durability of the semiconductive member.
またさらに、請求項2〜5の画像形成用半導電性部材において、最外層に、さらにポリオール化合物及びイソシアネート化合物を少なくとも含有すること、さらにフッ素ポリオール化合物及びイソシアネート化合物を少なくとも含有することにより、最外層に紙粉・トナーなどが付着するのを抑制し、離型性を更に向上し、内部及び最外層塗膜からのブリードを防止することによって、感光体汚染を防止し、またローラ構造などの場合に最外層塗膜の追従性を向上させ、導電性を損なわずに、画質劣化の問題の解消を図り、すべり性向上、耐磨耗性付与し、半導電性部材の耐久性を向上させることができる。 Furthermore, in the semiconductive member for image formation according to any one of claims 2 to 5, the outermost layer further contains at least a polyol compound and an isocyanate compound, and further contains at least a fluorine polyol compound and an isocyanate compound. In the case of a roller structure, etc., by suppressing the adhesion of paper dust and toner to the surface, further improving the releasability, and preventing bleeding from the inner and outermost coating films. To improve the followability of the outermost layer coating film, eliminate the problem of image quality degradation without impairing the conductivity, improve the slipperiness, impart wear resistance, and improve the durability of the semiconductive member Can do.
前記請求項2〜5の画像形成用半導電性部材において、最外層に、さらにフッ素ポリオール化合物及びアクリル樹脂及びイソシアネート化合物を少なくとも含有すること、最外層に、さらにフッ素ポリオール化合物及びアクリルポリオール化合物を少なくとも含有することにより、特に最外層に紙粉・トナーなどが付着するのを抑制する効果を向上させることができ、離型性が更に向上し、更に内部及び最外層塗膜からのブリードを防止することによって、感光体汚染を防止できる。またローラ構造などの場合に最外層塗膜の追従性を向上させ、より導電性部材への密着性も向上し、最外層塗膜剥がれがなく、導電性を損なわずに、画質劣化の問題の解消を図り、すべり性向上、耐磨耗性付与し、半導電性部材の耐久性を向上させることができる。 6. The semiconductive member for image formation according to claim 2, wherein the outermost layer further contains at least a fluorine polyol compound, an acrylic resin and an isocyanate compound, and the outermost layer further contains at least a fluorine polyol compound and an acrylic polyol compound. By containing it, the effect of suppressing the adhesion of paper dust, toner, etc. to the outermost layer in particular can be improved, the releasability is further improved, and further bleeding from the inner and outermost layer coating is prevented. As a result, photoconductor contamination can be prevented. Also, in the case of a roller structure etc., the followability of the outermost layer coating film is improved, the adhesion to the conductive member is further improved, the outermost layer coating film is not peeled off, the conductivity is not impaired, and the image quality deterioration problem is Elimination can be achieved, slipperiness improvement and abrasion resistance can be imparted, and durability of the semiconductive member can be improved.
以下、本発明について具体的に詳しく説明する。
本発明の画像形成用半導電性部材は、最外層が架橋フッ素樹脂及び板状構造を有する無機充填剤及び導電性粒子を少なくとも含有する樹脂層から構成されており、該最外層には、これらの成分の他に、各用途に応じて、或いは必要に応じて、離型性付与のためにシリコーン化合物、更にはフッ素化シリコーン化合物、反応性基を有するシリコーン化合物、反応性基を有するフッ素化シリコーン化合物等や塗膜性向上、離型性付与等のために、さらにポリオール化合物及びイソシアネート化合物、フッ素ポリオール化合物及びイソシアネート化合物、アクリル樹脂、アクリルポリオール化合物等を種々含有しても良い。
Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail.
In the image-forming semiconductive member of the present invention, the outermost layer is composed of a crosslinked fluororesin, a resin layer containing at least an inorganic filler having a plate-like structure and conductive particles, and the outermost layer includes these In addition to these components, a silicone compound, further a fluorinated silicone compound, a silicone compound having a reactive group, and a fluorination having a reactive group for imparting releasability depending on each application or as required. In order to improve the silicone compound and the like, improve coating properties, impart releasability, and the like, it may further contain various polyol compounds and isocyanate compounds, fluorine polyol compounds and isocyanate compounds, acrylic resins, acrylic polyol compounds, and the like.
他にもレベリング剤、酸化防止剤、難燃剤、沈降防止剤、消泡剤、腐食防止剤、希釈用溶媒、増粘剤、チクソトロピー性付与剤、構造粘性付与剤等などの各種添加剤を含有しても良い。 In addition, various additives such as leveling agents, antioxidants, flame retardants, anti-settling agents, antifoaming agents, corrosion inhibitors, solvents for dilution, thickeners, thixotropic agents, structural viscosity agents, etc. You may do it.
本発明に使用される架橋フッ素樹脂は、無酸素の不活性ガス化雰囲気中でその融点より若干高い温度に保った状態で所定量の放射線を照射して架橋処理を行うようにして製造したものであり、耐摩耗性,耐クリープ性,耐放射線性等の諸特性に優れた架橋フッ素樹脂である。特に粉体架橋フッ素樹脂は特開2000−186155号公報、特開2000−186157号公報、特開2002−317055号公報、特開2002−317056号公報等の製造方法に準拠した方法より得られた架橋フッ素樹脂を使用した。なお、これら架橋フッ素樹脂の一般的な製造方法は特開平6−116423号公報及び特開平7−118423号公報に開示されており、その他のフッ素樹脂(テトラフルオロエチレン・ヘキサフルオロプロピレン共重合体(FEP)、テトラフルオロエチレン・パーフルオロアルキルビニルエーテル共重合体(PFA))については特開平11−49867号公報に開示されている。 The cross-linked fluororesin used in the present invention is produced by performing a cross-linking treatment by irradiating a predetermined amount of radiation while maintaining a temperature slightly higher than its melting point in an oxygen-free inert gasification atmosphere. It is a cross-linked fluororesin excellent in various properties such as wear resistance, creep resistance, and radiation resistance. In particular, the powder-crosslinked fluororesin was obtained by a method based on a production method such as JP 2000-186155 A, JP 2000-186157 A, JP 2002-317055 A, or JP 2002-317056 A. A cross-linked fluororesin was used. In addition, the general manufacturing method of these bridge | crosslinking fluororesins is disclosed by Unexamined-Japanese-Patent No. 6-116423 and Unexamined-Japanese-Patent No. 7-118423, and other fluororesins (tetrafluoroethylene-hexafluoropropylene copolymer ( FEP) and tetrafluoroethylene / perfluoroalkyl vinyl ether copolymer (PFA)) are disclosed in JP-A-11-49867.
フッ素樹脂の結晶融点以上の温度で、酸素不存在下において1kGy以上の電離性放射線を照射することにより、高強度で耐放射線性や耐熱性に優れた改質フッ素樹脂(架橋フッ素樹脂)を得ることができる。 By irradiation with ionizing radiation of 1 kGy or more in the absence of oxygen at a temperature equal to or higher than the crystal melting point of the fluororesin, a modified fluororesin (cross-linked fluororesin) having high strength and excellent radiation resistance and heat resistance is obtained. be able to.
PTFEの結晶融点以上の温度において放射線を照射すると架橋反応が起きる機構は次の様なものである。まず放射線の照射により分子鎖の切断およびフッ素原子の脱離が起きる。融点以上の温度であるため分子鎖はある程度自由に動けるようになり、分子鎖の切断により生成した分子鎖末端ラジカルとフッ素原子の脱離により生成したアルキル型ラジカルが反応する機会が与えられる。そしてこの反応により架橋が生じる。 The mechanism by which the crosslinking reaction occurs when irradiated with radiation at a temperature above the crystalline melting point of PTFE is as follows. First, molecular chains are broken and fluorine atoms are desorbed by irradiation with radiation. Since the temperature is higher than the melting point, the molecular chain can move freely to some extent, and an opportunity is given to react the molecular chain terminal radical generated by the molecular chain breakage and the alkyl radical generated by the elimination of the fluorine atom. This reaction causes crosslinking.
例示すると、まず出発フッ素樹脂に電離性放射線を照射する。それによって分子鎖が切断されるのであれば、空気中、酸素中、真空中、あるいは不活性ガス中のいずれであっても照射雰囲気は特に問わない。また放射線はガンマ線、電子線、X線、中性子線、高エネルギーイオンなどいずれであっても構わず、目的とする量の照射が実施されればよい。放射線の照射量は0.1kGy〜1000kGy程度が望ましい。0.1kGy未満では分子鎖の切断効果が最終的な樹脂特性の変化として反映され難く、1000kGyを超えて照射を行っても樹脂特性はほとんど変化しなくなる。この照射工程における雰囲気の温度は特に問わず、あらゆる温度領域において分子鎖の切断は達成され得る。しかし、照射する際の雰囲気の温度が高温であるほど分子鎖の切断は促進される。一方、液体窒素温度付近の低温度では分子鎖の運動が制限され、その結果、切断が抑制される。これらのことと取り扱いの用意さを考慮すると、室温からフッ素樹脂の融点以下の範囲の温度が好ましい。 For example, ionizing radiation is first irradiated to the starting fluororesin. The irradiation atmosphere is not particularly limited as long as the molecular chain is thereby cut off, whether in air, oxygen, vacuum, or inert gas. The radiation may be any of gamma rays, electron beams, X-rays, neutron rays, high-energy ions, etc., and it is sufficient that irradiation with a target amount is performed. The radiation dose is preferably about 0.1 kGy to 1000 kGy. If it is less than 0.1 kGy, the molecular chain scission effect is hardly reflected as the final change in the resin properties, and the resin properties hardly change even when irradiation is carried out in excess of 1000 kGy. The temperature of the atmosphere in this irradiation step is not particularly limited, and molecular chain scission can be achieved in any temperature range. However, the higher the temperature of the atmosphere at the time of irradiation, the more the molecular chain breakage is promoted. On the other hand, the movement of the molecular chain is limited at a low temperature near the liquid nitrogen temperature, and as a result, the cleavage is suppressed. Considering these and the preparation for handling, a temperature in the range from room temperature to the melting point of the fluororesin is preferable.
次いで真空中あるいは不活性ガスの導入により酸素による酸化が抑制された雰囲気中でフッ素樹脂に融点以上の温度において電離性放射線を照射して架橋させる。このときの放射線の照射量は1kGy〜10MGyが望ましい。分子鎖の切断の場合と同様に1kGy未満の照射量による架橋では架橋後の樹脂特性に著しい変化をあたえることができず、10MGyを超えて照射を行っても樹脂特性はほとんど変化しなくなる。酸素による酸化が抑制された雰囲気中で照射を行なう理由は、酸素が存在すると放射線の照射によって生成した反応活性点が酸素と優先的に反応して架橋反応を阻害するのを防ぐためである。また融点以上の雰囲気温度において照射を行なう理由は、フッ素樹脂を融点以上の温度において保持することにより分子鎖の運動を活性化させ、分子鎖中に生成した反応活性点どうしが反応する機会を高めて架橋構造を形成させるためである。 Next, the fluororesin is cross-linked by irradiation with ionizing radiation at a temperature equal to or higher than the melting point in a vacuum or in an atmosphere in which oxidation by oxygen is suppressed by introducing an inert gas. The radiation dose at this time is preferably 1 kGy to 10 MGy. As in the case of molecular chain scission, cross-linking with an irradiation dose of less than 1 kGy cannot give a significant change in the resin properties after cross-linking, and the resin properties hardly change even when irradiation exceeds 10 MGy. The reason why irradiation is performed in an atmosphere in which oxidation by oxygen is suppressed is to prevent reaction active sites generated by radiation irradiation from preferentially reacting with oxygen and inhibiting the crosslinking reaction when oxygen is present. The reason for irradiating at an atmospheric temperature above the melting point is to activate the movement of the molecular chain by holding the fluororesin at a temperature above the melting point, and to increase the chance that the reaction active points generated in the molecular chain react. This is to form a crosslinked structure.
出発フッ素樹脂の素性についての制約はなく、既存のフッ素樹脂をそのまま利用することが可能である。本発明によれば、既存フッ素樹脂を利用しながらも、分子鎖の切断に要する放射線の量と、架橋に要する放射線の量を変化させることにより、得られる架橋フッ素樹脂の特性を幅広く変化させることが可能となる。
例えば、フッ素樹脂としてはテトラフルオロエチレン・ヘキサフルオロプロピレン共重合体(FEP)、テトラフルオロエチレン・パーフルオロアルキルビニルエーテル共重合体(PFA)、エチレン・テトラフルオロエチレン系共重合体(ETFE及びPVdF)等からのフッ素系樹脂の選択、2種類以上の樹脂の混合、分子量の異なる同一樹脂の混合なども挙げられる。
There is no restriction on the identity of the starting fluororesin, and the existing fluororesin can be used as it is. According to the present invention, the properties of the obtained cross-linked fluororesin can be widely changed by changing the amount of radiation required for molecular chain scission and the amount of radiation required for cross-linking while using the existing fluororesin. Is possible.
Examples of fluororesins include tetrafluoroethylene / hexafluoropropylene copolymer (FEP), tetrafluoroethylene / perfluoroalkyl vinyl ether copolymer (PFA), and ethylene / tetrafluoroethylene copolymer (ETFE and PVdF). The selection of fluorine-based resins from the above, the mixing of two or more types of resins, the mixing of the same resins having different molecular weights, etc.
本発明において、架橋フッ素樹脂を用いることにより、上記作用効果が奏される理由は定かではないが、上記架橋フッ素樹脂の架橋構造から来る特性であるすべり性、低摩擦性が向上し、紙やクリーニングブレード等による表面の磨耗を抑制し、画像形成用半導電性部材の耐久性を向上させるものと考えられる。 In the present invention, by using a cross-linked fluororesin, the reason why the above-described effect is achieved is not clear, but the slipperiness and low friction properties, which are the characteristics resulting from the cross-linked structure of the cross-linked fluororesin, are improved. It is considered that the surface abrasion due to a cleaning blade or the like is suppressed and the durability of the image-forming semiconductive member is improved.
なお、上記の架橋フッ素樹脂の添加量は最外層材料に対して0.1〜30重量%の範囲が好ましく、最外層材料とのマッチング、放電条件等などに応じて変化させる。該添加量が30重量%を超えると最外層の成膜性や塗膜強度の低下等を生じることがある。更に好ましくは、1〜10重量%である。 The addition amount of the above-mentioned crosslinked fluororesin is preferably in the range of 0.1 to 30% by weight with respect to the outermost layer material, and is changed according to matching with the outermost layer material, discharge conditions, and the like. If the amount added exceeds 30% by weight, the film formability of the outermost layer, the strength of the coating film, etc. may be lowered. More preferably, it is 1 to 10% by weight.
次に本発明に使用される板状構造を有する無機充填剤は、一般に形状が板状のものである。ここで本発明でいう板状とは、相対する2面(卓面)が、特に発達した構造のものを言う。 Next, the inorganic filler having a plate-like structure used in the present invention generally has a plate-like shape. Here, the plate shape referred to in the present invention refers to a structure in which two opposing surfaces (table surfaces) are particularly developed.
本発明で使用される板状構造の無機充填剤としては、特にフィラーとして汎用のタルク、天然マイカ、合成マイカ、セリサイト、ガラスフレーク、天然ハイドロタルサイト、合成タルサイト、水酸化マグネシウム、板状水酸化アルミニウム、板状酸化鉄、板状炭酸カルシウム、黒鉛、BN等々が挙げられるが、これらに限定されるものではない。なお、水酸化マグネシウム、水酸化アルミニウム、タルサイトなどは難燃効果も付与でき、好ましい。なお、平均粒径は0.01〜5μmが好ましく、更に好適には0.1〜1μmである。0.01μm未満ではブリード防止効果が抑制され、5μmを超えると表面粗さからくる画像品質に問題が出る。 As an inorganic filler having a plate-like structure used in the present invention, general-purpose talc, natural mica, synthetic mica, sericite, glass flake, natural hydrotalcite, synthetic talcite, magnesium hydroxide, plate-like are used as fillers. Examples thereof include, but are not limited to, aluminum hydroxide, plate-like iron oxide, plate-like calcium carbonate, graphite, and BN. Magnesium hydroxide, aluminum hydroxide, talcite and the like are preferable because they can impart a flame-retardant effect. The average particle size is preferably from 0.01 to 5 μm, more preferably from 0.1 to 1 μm. If it is less than 0.01 μm, the bleed prevention effect is suppressed, and if it exceeds 5 μm, there is a problem in image quality due to surface roughness.
本発明において、板状構造を有する無機充填剤を用いることによって、上記作用効果が奏される理由は定かではないが、板状構造であることによって、充填剤同士が重なり合って、バリア機能の発揮あるいは層間にブリード成分の吸着等によって、半導電性ゴム層からの低分子物質がブリードされるのを抑制するものと考えられる。また、クレー、珪藻土、シリカ等の充填剤を添加しても良い。 In the present invention, by using an inorganic filler having a plate-like structure, the reason why the above-mentioned effects are achieved is not clear, but by having a plate-like structure, the fillers overlap each other and exhibit a barrier function. Or it is thought that it suppresses that the low molecular substance from a semiconductive rubber layer is bleed | bleeded by adsorption | suction etc. of a bleed component between layers. Moreover, you may add fillers, such as clay, diatomaceous earth, and silica.
なお、上記の無機充填剤の添加量は最外層材料に対して0.1〜30重量%の範囲が好ましく、最外層材料とのマッチング、放電条件等などに応じて変化させる。該添加量が0.1重量%未満ではブリード抑制効果が低く、30重量%を超えると最外層の成膜性や塗膜強度の低下等を生じることがある。更に好ましくは、1〜10重量%である。 The addition amount of the inorganic filler is preferably in the range of 0.1 to 30% by weight with respect to the outermost layer material, and is changed according to matching with the outermost layer material, discharge conditions, and the like. If the added amount is less than 0.1% by weight, the bleed suppressing effect is low, and if it exceeds 30% by weight, the film formability of the outermost layer, the coating strength may be lowered, and the like may occur. More preferably, it is 1 to 10% by weight.
本発明に使用される導電性粒子としては、好ましくは平均粒径0.01〜5μmの無機または有機の電子伝導性粒子が用いられる。該導電性粒子としては、カーボンブラック、グラファイト、フッ化カーボンや、アルミニウム、銅、ニッケル、ステンレス鋼等の各種導電性金属または合金、さらに酸化錫、酸化インジウム、酸化チタン、酸化亜鉛、酸化錫−酸化アンチモン複合酸化物、酸化錫−酸化インジウム複合酸化物等の各種導電性金属酸化物、さらには絶縁物質の表面を導電化処理したものなどの1種または2種以上の微粉末を用いることができる。
これらの導電性粒子は1種用いてもよく、2種以上を組み合わせて用いてもよい。
As the conductive particles used in the present invention, inorganic or organic electron conductive particles having an average particle diameter of 0.01 to 5 μm are preferably used. Examples of the conductive particles include carbon black, graphite, carbon fluoride, various conductive metals or alloys such as aluminum, copper, nickel, stainless steel, tin oxide, indium oxide, titanium oxide, zinc oxide, tin oxide It is possible to use one or more fine powders such as various conductive metal oxides such as antimony oxide composite oxide and tin oxide-indium oxide composite oxide, and further, the surface of an insulating material subjected to conductive treatment. it can.
These conductive particles may be used alone or in combination of two or more.
また、これらの導電性粒子の添加量としては特に制限はなく、各種状況に応じ、最外層の全量に対し、通常0.01〜40重量%、好ましくは5〜20重量%の割合で添加される。カーボンブラック等の導電性粒子を添加することにより、所定の抵抗値に制御することができる。この表面層の抵抗は、体積抵抗率で1×103〜1×1012Ω・cmであることが好ましく、更に好ましくは1×105〜1×1010Ω・cmである。 Moreover, there is no restriction | limiting in particular as addition amount of these electroconductive particle, According to various situations, it is 0.01-40 weight% normally with respect to the total amount of outermost layer, Preferably it is added in the ratio of 5-20 weight%. The By adding conductive particles such as carbon black, the resistance can be controlled to a predetermined value. The surface layer preferably has a volume resistivity of 1 × 10 3 to 1 × 10 12 Ω · cm, more preferably 1 × 10 5 to 1 × 10 10 Ω · cm.
本発明において、架橋フッ素樹脂及び板状構造を有する無機充填剤と導電性粒子の使用割合は、特に制限はなく、各種状況、例えば目的とする体積抵抗率等に応じて定められる。 In the present invention, the use ratio of the crosslinked fluororesin and the inorganic filler having a plate-like structure and the conductive particles is not particularly limited, and is determined according to various situations, for example, target volume resistivity.
本発明において、半導電性部材の最外層は、上記の架橋フッ素樹脂及び板状構造を有する無機充填剤及び導電性粒子を少なくとも含有する樹脂層から構成され、本発明に用いられる最外層を構成する樹脂としては、熱可塑性樹脂及び熱硬化性樹脂のいずれも用いることができる。 In the present invention, the outermost layer of the semiconductive member is composed of the above-mentioned crosslinked fluororesin and a resin layer containing at least an inorganic filler having a plate-like structure and conductive particles, and constitutes the outermost layer used in the present invention. As the resin to be used, any of a thermoplastic resin and a thermosetting resin can be used.
熱可塑樹脂としては熱可塑性アクリル樹脂、熱可塑性ウレタン樹脂や熱可塑性フッ素樹脂などが挙げられる。熱硬化樹脂としてはポリエステル樹脂、アミノ樹脂、エポキシ樹脂、熱硬化性ポリウレタン樹脂、熱硬化性アクリル樹脂や各々のフッ素変性樹脂などが挙げられる。 Examples of the thermoplastic resin include thermoplastic acrylic resins, thermoplastic urethane resins, and thermoplastic fluororesins. Examples of the thermosetting resin include polyester resins, amino resins, epoxy resins, thermosetting polyurethane resins, thermosetting acrylic resins, and respective fluorine-modified resins.
これらの中で、該樹脂としては、例えば、塗膜性を良好とするポリオール化合物とイソシアネート化合物からなるものが好ましい。例えばポリオール化合物としては、ポリエステルポリオール、ポリエーテルポリオール、ポリカーボネートポリオール、アクリルポリオール、フッ素ポリオールおよびこれらの共重合ポリオール等を挙げることができる。 In these, as this resin, what consists of a polyol compound and an isocyanate compound which make a coating film property favorable is preferable, for example. For example, examples of the polyol compound include polyester polyol, polyether polyol, polycarbonate polyol, acrylic polyol, fluorine polyol, and copolymerized polyols thereof.
また、例えば、ポリエステルポリオールとしては、二塩基酸や、そのエステル、酸ハライド、酸無水物等の反応性酸誘導体とグリコール、アミノアルコール等の単独または混合物との縮合反応により得られるポリエステルポリオール、ポリエステルアミドポリオールが挙げられる。 Further, for example, as polyester polyols, polyester polyols and polyesters obtained by condensation reaction of dibasic acids or reactive acid derivatives such as esters, acid halides, and acid anhydrides with glycols or amino alcohols alone or in mixtures. Amide polyols are mentioned.
また、ポリカーボネートポリオールとしては、一般には多価アルコールとエチレンカーボネート、ジメチルカーボネート、ジエチルカーボネート、ジフェニルカーボネート等との脱アルコール反応などにより得られるものが挙げられる。
またポリエーテルポリオールとしては、エチレンオキサイド、プロピレンオキサイド、テトラヒドロフラン等を開環重合させて得られるポリエチレングリコール、ポリプロピレングリコール、ポリテトラメチレンエーテルグリコール等、およびこれらのコポリマーが挙げられる。
Examples of the polycarbonate polyol include those obtained by a dealcoholization reaction between a polyhydric alcohol and ethylene carbonate, dimethyl carbonate, diethyl carbonate, diphenyl carbonate or the like.
Examples of the polyether polyol include polyethylene glycol, polypropylene glycol, polytetramethylene ether glycol and the like obtained by ring-opening polymerization of ethylene oxide, propylene oxide, tetrahydrofuran and the like, and copolymers thereof.
さらにフッ素ポリオールとは、イソシアネートと反応する基(水酸基)を1つ以上持ったフッ素樹脂である。例示すれば、テトラフルオロエチレン−パーフルオロアルキルビニルエーテル共重合体、テトラフルオロエチレン−ヘキサフルオロプロピレン−パーフルオロアルキルビニルエーテル共重合体の水酸基変性樹脂などの水酸基含有のフッ素樹脂等が挙げられる。具体的には、水酸基を有するFEVE(フルオロエチレン単位とビニルエーテル単位)交互共重合体が挙げられる。 Further, the fluoropolyol is a fluororesin having one or more groups (hydroxyl groups) that react with isocyanate. For example, a hydroxyl-containing fluororesin such as a tetrafluoroethylene-perfluoroalkyl vinyl ether copolymer, a hydroxyl-modified resin of tetrafluoroethylene-hexafluoropropylene-perfluoroalkyl vinyl ether copolymer, and the like can be given. Specifically, a FEVE (fluoroethylene unit and vinyl ether unit) alternating copolymer having a hydroxyl group can be mentioned.
またアクリルポリオールとは、水酸基を持つアクリルモノマーとアクリル酸エステルとの共重合体等のアクリル樹脂である。水酸基は該アクリル樹脂主鎖に無秩序に配置されている。水酸基含有比は種々共重合比で制御することができる。例えば、AA/HPA/MMA/BMA/BAや、AA/HPMA/MMA/BMA/BA(AAはアクリル酸、HPAはヒドロキシプロピルアクリレート、HPMAはヒドロキシプロピルメタクリレート、MMAはメチルメタクリレート、BMAはブチルメタクリレート、BAはブチルアクリレートを指す。)が挙げられる。 The acrylic polyol is an acrylic resin such as a copolymer of an acrylic monomer having a hydroxyl group and an acrylic ester. The hydroxyl groups are randomly arranged in the main chain of the acrylic resin. The hydroxyl group content ratio can be controlled by various copolymerization ratios. For example, AA / HPA / MMA / BMA / BA, AA / HPMA / MMA / BMA / BA (AA is acrylic acid, HPA is hydroxypropyl acrylate, HPMA is hydroxypropyl methacrylate, MMA is methyl methacrylate, BMA is butyl methacrylate, BA refers to butyl acrylate).
さらにまたこれらの共重合ポリオールとしては、前記ポリエステルポリオールやポリカーボネートポリオール、ポリエーテルポリオールを共重合成分としたポリエステルポリカーボネートポリオールやポリエステルポリエーテルポリオール等が挙げられる。 Furthermore, examples of these copolymer polyols include polyester polycarbonate polyols, polyester polyether polyols, and the like using the above-described polyester polyols, polycarbonate polyols, and polyether polyols as copolymerization components.
架橋剤として添加されるイソシアネート化合物は、分子中に2個以上のイソシアネート基をもつ化合物であり、一般にポリウレタンの製造原料として用いられるイソシアネートと同様のものを用いることができる。 The isocyanate compound added as a crosslinking agent is a compound having two or more isocyanate groups in the molecule, and the same isocyanate as that generally used as a raw material for producing polyurethane can be used.
具体的には、トリレンジイソシアネート(TDI)、ジフェニルメタンジイソシアネート(MDI)、ナフタレンジイソシアネート(NDI)、トリジンジイソシアネート(TODI)、ヘキサメチレンジイソシアネート(HDI)、イソホロンジイソシアネート(IPDI)、フェニレンジイソシアネート、キシリレンジイソシアネート(XDI)、テトラメチルキシリレンジイソシアネート(TMXDI)、シクロヘキサンジイソシアネート、リジンエステルトリイソシアネート、ウンデカントリイソシアネート、ヘキサメチレントリイソシアネート、トリフェニルメタントリイソシアネート、及びこれらイソシアネート化合物の重合体、誘導体、変性体、水素添加体等が挙げられる。 Specifically, tolylene diisocyanate (TDI), diphenylmethane diisocyanate (MDI), naphthalene diisocyanate (NDI), tolidine diisocyanate (TODI), hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI), isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI), phenylene diisocyanate, xylylene diisocyanate ( XDI), tetramethylxylylene diisocyanate (TMXDI), cyclohexane diisocyanate, lysine ester triisocyanate, undecane triisocyanate, hexamethylene triisocyanate, triphenylmethane triisocyanate, and polymers, derivatives, modified products, hydrogenated products of these isocyanate compounds Examples include the body.
これらの中では、特に、ヘキサメチレンジイソシアネート、イソホロンジイソシアネート等の脂肪族または脂肪環族イソシアネート及びこれらの重合体、誘導体、変性体が耐オゾン性や耐熱性などから好適である。 Of these, aliphatic or alicyclic isocyanates such as hexamethylene diisocyanate and isophorone diisocyanate, and polymers, derivatives and modified products thereof are particularly preferred from the viewpoint of ozone resistance and heat resistance.
また、ウレタン形成反応に際して使用される助剤としては、グリコール類、ヘキサントリオール、トリメチロールプロパン、アミン類等の鎖延長剤あるいは架橋剤などを挙げることができる。なお、上記ポリオールとイソシアネート化合物のNCO/OHモル比は、1.0/1.0〜1.8/1.0が好適である。 Examples of the auxiliary agent used in the urethane forming reaction include chain extenders such as glycols, hexanetriol, trimethylolpropane, amines, and crosslinking agents. The NCO / OH molar ratio between the polyol and the isocyanate compound is preferably 1.0 / 1.0 to 1.8 / 1.0.
また、離型性を与える未架橋フッ素系樹脂を含有させることもできる。該フッ素系樹脂としてはポリテトラフルオロエチレン、テトラフルオロエチレン−パーフルオロアルキルビニルエーテル共重合体、テトラフルオロエチレン−ヘキサフルオロプロピレン−パーフルオロアルキルビニルエーテル共重合体、テトラフルオロエチレン−エチレン共重合体、ポリクロロトリフルオロエチレン、クロロトリフルオロエチレン−エチレン共重合体、テトラフルオロエチレン−ビニリデンフルオライド共重合体、ポリビニリデンフルオライド及びポリビニルフルオライド等が挙げられる。 In addition, an uncrosslinked fluororesin that imparts releasability can also be contained. Examples of the fluororesin include polytetrafluoroethylene, tetrafluoroethylene-perfluoroalkyl vinyl ether copolymer, tetrafluoroethylene-hexafluoropropylene-perfluoroalkyl vinyl ether copolymer, tetrafluoroethylene-ethylene copolymer, polychloroethylene. Examples thereof include trifluoroethylene, chlorotrifluoroethylene-ethylene copolymer, tetrafluoroethylene-vinylidene fluoride copolymer, polyvinylidene fluoride, and polyvinyl fluoride.
特にテトラフルオロエチレン−パーフルオロアルキルビニルエーテル共重合体、テトラフルオロエチレン−ヘキサフルオロプロピレン−パーフルオロアルキルビニルエーテル共重合体の水酸基変性樹脂などの水酸基含有のフッ素樹脂をフッ素ポリオール化合物としてイソシアネート化合物と反応させることにより、良好な塗膜を与え、好適である。これらの樹脂は、一種用いてもよいし、二種以上を組み合わせて用いてもよい。 Reacting a hydroxyl group-containing fluororesin such as a tetrafluoroethylene-perfluoroalkyl vinyl ether copolymer or a hydroxyl-modified resin of tetrafluoroethylene-hexafluoropropylene-perfluoroalkyl vinyl ether copolymer with an isocyanate compound as a fluoropolyol compound Gives a good coating film, which is preferable. These resins may be used alone or in combination of two or more.
上記フッ素ポリオール化合物とイソシアネート化合物との反応塗膜は、ビニルエーテル単位の側鎖の官能基、例えば、アルキル基、アルキレン基の種類を変えること、イソシアネート化合物に高分子量のポリイソシアネート化合物を使用することなどにより、塗膜の伸び、摩擦係数を任意に調整することができる。特に伸び、膜硬度を調整した場合には最外層の可撓性を向上させることができ、それによって屈曲性に優れた部材を得ることができる。その際、伸びが50%未満では亀裂が入ってブリード防止効果がなくなることがあるため、50%以上の伸びに調整するのが好ましい。 The reaction coating film of the above-mentioned fluorine polyol compound and isocyanate compound is to change the functional group of the side chain of the vinyl ether unit, for example, the type of alkyl group or alkylene group, to use a high molecular weight polyisocyanate compound as the isocyanate compound, etc. Thus, the elongation of the coating film and the friction coefficient can be arbitrarily adjusted. In particular, when the elongation and film hardness are adjusted, the flexibility of the outermost layer can be improved, whereby a member having excellent flexibility can be obtained. At that time, if the elongation is less than 50%, cracking may occur and the bleed prevention effect may be lost. Therefore, the elongation is preferably adjusted to 50% or more.
これらフッ素ポリオール化合物とイソシアネート化合物との反応樹脂を用いると、帯電部材の表面汚染を避けることができる。具体例としては、カンペ(登録商標)フロンHD(関西ペイント社製)、ルミフロン(登録商標)シリーズ(旭硝子社製)、ゼッフル(登録商標)シリーズ(ダイキン社製)等のフッ素ポリオール化合物と、ヘキサメチレンジイソシアネートのトリメチロールプロパン付加物、トリレンジイソシアネートのトリメチロールプロパン付加物等のポリオール付加ポリイソシアネート化合物や、さらにメラミン樹脂等のアミノ樹脂とを反応させた架橋構造の最外層塗膜が挙げられる。 When a reaction resin of these fluorine polyol compound and isocyanate compound is used, surface contamination of the charging member can be avoided. Specific examples include fluorine polyol compounds such as Campe (registered trademark) Freon HD (manufactured by Kansai Paint), Lumiflon (registered trademark) series (manufactured by Asahi Glass Co., Ltd.), Zaffle (registered trademark) series (manufactured by Daikin), hexa Examples thereof include an outermost coating film having a crosslinked structure obtained by reacting a polyol-added polyisocyanate compound such as a trimethylolpropane adduct of methylene diisocyanate and a trimethylolpropane adduct of tolylene diisocyanate and an amino resin such as a melamine resin.
また、本発明において、必要に応じ、上記樹脂に他樹脂を添加することができる。他樹脂としては、例えば、前記したアクリル樹脂、ポリウレタン樹脂、ナイロン樹脂、シリコーン樹脂、ポリエステル樹脂、エポキシ樹脂、セルロース、メラミン樹脂などが挙げられるが、分散性向上、導電性ゴム部への塗膜接着性向上、静電的な紙粉・トナー防汚性の観点より、アクリル樹脂が好適である。これらは必要に応じて単独で、組み合わせて添加してもよい。ここでアクリル樹脂を用いる場合、前記したアクリルポリオールを使用し、ポリオール成分として前記イソシアネートを反応させてもよい。 Moreover, in this invention, other resin can be added to the said resin as needed. Other resins include, for example, the acrylic resin, polyurethane resin, nylon resin, silicone resin, polyester resin, epoxy resin, cellulose, melamine resin, etc., but improved dispersibility, adhesion of the coating film to the conductive rubber part Acrylic resin is preferred from the viewpoint of improving the performance and electrostatic paper dust / toner antifouling property. These may be added alone or in combination as necessary. When using an acrylic resin here, the above-mentioned acrylic polyol may be used and the said isocyanate may be made to react as a polyol component.
上記塗膜において、離型性が不十分な場合もあり、シリコーン化合物、更にはフッ素化シリコーン化合物、塗膜により強固に離型性成分を固定化する反応性基を有するシリコーン化合物、反応性基を有するフッ素化シリコーン化合物等を添加することが好ましく、これら化合物を添加することにより、より紙粉・トナー付着に対する離型性を向上させることができる。 In the coating film, the releasability may be insufficient. Silicone compound, further fluorinated silicone compound, silicone compound having a reactive group for firmly fixing the releasable component by the coating film, reactive group It is preferable to add a fluorinated silicone compound or the like having the above, and by adding these compounds, it is possible to further improve the releasability against paper dust and toner adhesion.
本発明に使用されるシリコーン化合物、更にはフッ素化シリコーン化合物、反応性基を有するシリコーン化合物、反応性基を有するフッ素化シリコーン化合物の例としては、特に限定はなく、例えばポリエーテル変性シリコーンオイル、高級脂肪酸エステル変性シリコーンオイル、メチルスチリル変性シリコーンオイル、アルキル変性シリコーンオイル、高級アルコキシ変性シリコーンオイルが好ましい。相溶性が良好で、充填剤による保持性が高いという点から、ポリエーテル変性シリコーンオイル、高級脂肪酸エステル変性シリコーンオイルが特に好ましい。 Examples of the silicone compound used in the present invention, further a fluorinated silicone compound, a silicone compound having a reactive group, and a fluorinated silicone compound having a reactive group are not particularly limited. For example, polyether-modified silicone oil, Higher fatty acid ester-modified silicone oils, methylstyryl-modified silicone oils, alkyl-modified silicone oils, and higher alkoxy-modified silicone oils are preferred. Polyether-modified silicone oils and higher fatty acid ester-modified silicone oils are particularly preferred from the viewpoints of good compatibility and high retention by fillers.
同様にフッ素化シリコーン化合物としては、一般にフロオロシリコーンオイルと言われる化合物、例えば、3,3,3−トリフロロプロピルメチルシロキサン、3,3,3−トリフロロプロピルメチルシロキサン−ジメチルシロキサンコポリマー、ビス(トリデカフロロオクチル)テトラメチルシロキサンや、フルオロシリコーングリースなどが挙げられるが、これらに限定されるものではない。なお、これらは塗膜溶液のレベリングにも寄与する効果もあり、塗膜の平滑性向上となる。 Similarly, fluorinated silicone compounds include compounds generally referred to as fluorosilicone oils such as 3,3,3-trifluoropropylmethylsiloxane, 3,3,3-trifluoropropylmethylsiloxane-dimethylsiloxane copolymer, bis (Tridecafluorooctyl) tetramethylsiloxane, fluorosilicone grease, and the like are exemplified, but the invention is not limited to these. In addition, these also have the effect which contributes to the leveling of a coating-film solution, and it becomes the smoothness improvement of a coating film.
これらシリコーン化合物及びフッ素化シリコーン化合物の分子量は、400〜50000の範囲のものが好ましく、特に好ましくは1000〜20000の範囲である。配合割合は、溶媒を含まない塗膜成分100重量部に対して0.4重量部以下の範囲に設定することが好ましく、特に好ましくは0.01〜0.2重量部の範囲である。0重量部であると、離型性に対して十分な効果を発揮できず、0.4重量部を超えるとブリード等の汚染原因になる可能性がある。 The molecular weight of these silicone compounds and fluorinated silicone compounds is preferably in the range of 400-50000, particularly preferably in the range of 1000-20000. The blending ratio is preferably set in the range of 0.4 parts by weight or less, particularly preferably in the range of 0.01 to 0.2 parts by weight with respect to 100 parts by weight of the coating film component not containing the solvent. If it is 0 part by weight, a sufficient effect on the releasability cannot be exhibited, and if it exceeds 0.4 part by weight, it may cause contamination such as bleeding.
特に塗膜に離型性成分を固定する目的で、反応性基を有するシリコーン化合物、反応性基を有するフッ素化シリコーン化合物が、より耐ブリード性にも効果があり、好ましい。 In particular, a silicone compound having a reactive group and a fluorinated silicone compound having a reactive group are more preferable for the purpose of fixing a release component to the coating film because they are more effective in bleeding resistance.
反応性基を有するシリコーン化合物は、イソシアネート架橋剤や塗膜材料との硬化反応を適宜選択でき、多量配合も可能となり、離型性向上に有効である。上記反応性基としては、アミノ基、水酸基、カルボキシル基、エポキシ基、アクリル基などが挙げられる。 The silicone compound having a reactive group can appropriately select a curing reaction with an isocyanate cross-linking agent or a coating material, and can be incorporated in a large amount, which is effective for improving the releasability. Examples of the reactive group include an amino group, a hydroxyl group, a carboxyl group, an epoxy group, and an acrylic group.
具体的には、カルビノール変性シリコーンオイル、アミノ変性シリコーンオイル、カルボキシル変性シリコーンオイル、メルカプト変性シリコーンオイル、エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル、メタクリロキシ変性シリコーンオイル、フェノール変性シリコーンオイルが等好ましい。また、これら反応性シリコーン化合物の変性形態としては、側鎖型、両末端型、片末端型、側鎖両末端型が好ましい。 Specifically, carbinol-modified silicone oil, amino-modified silicone oil, carboxyl-modified silicone oil, mercapto-modified silicone oil, epoxy-modified silicone oil, methacryloxy-modified silicone oil, phenol-modified silicone oil and the like are preferable. Moreover, as a modified | denatured form of these reactive silicone compounds, a side chain type, a both terminal type, a single terminal type, and a side chain both terminal type are preferable.
同様に反応性基を有するフッ素化シリコーン化合物としては、ビニル末端基、シラノ−ル末端基等のフッ素化シリコーン化合物が挙げられ、具体的にはビニル末端トリフロロプロピルメチルシロキサンージメチルシロキサンコポリマー、シラノール末端ポリトリフロロトリフロロプロピルメチルシロキサン等が挙げられる。この反応性基を有するフッ素化シリコーン化合物は上記反応性シリコーン化合物と同様に離型性を高めるとともに、フッ素基による汚れの付着防止とブリード防止効果を更に向上させることが出来る。 Similarly, examples of the fluorinated silicone compound having a reactive group include fluorinated silicone compounds such as vinyl end groups and silanol end groups. Specifically, vinyl-terminated trifluoropropylmethylsiloxane-dimethylsiloxane copolymer, silanol Examples include terminal polytrifluorotrifluoropropylmethylsiloxane. The fluorinated silicone compound having a reactive group can improve the releasability as well as the reactive silicone compound, and can further improve the effect of preventing the adhesion of dirt and bleeding by the fluorine group.
これら反応性基を持つシリコーン化合物は、樹脂との相溶性があり、塗膜に均一に分散し、これらは塗膜溶液のレベリングにも寄与する効果もあり、塗膜の平滑性向上となる。特に、アミノ基、水酸基、カルボキシル基を持ったシリコーン化合物は、イソシアネート化合物との硬化反応により、最外層塗膜に固定出来る。また、エポキシ基を持ったシリコーン化合物は、上記フッ素樹脂の活性水素と反応し、固定化される。これにより、最外層の離型性向上・摩擦力の低下が起こり、更に、これらは導電性ゴム成分中の低分子物質のブリードも防ぎ、バリア効果も供することができ、より感光体汚染、更には紙粉・トナー付着を低減させることができる。更にまた、シリコーン化合物の多量含有が可能となり、より離型性向上となる。 These silicone compounds having a reactive group are compatible with the resin and are uniformly dispersed in the coating film, which also contributes to the leveling of the coating film solution and improves the smoothness of the coating film. In particular, a silicone compound having an amino group, a hydroxyl group, or a carboxyl group can be fixed to the outermost layer coating film by a curing reaction with an isocyanate compound. The silicone compound having an epoxy group reacts with the active hydrogen of the fluororesin and is immobilized. As a result, the releasability of the outermost layer is improved and the frictional force is reduced, and furthermore, they can prevent bleeding of low-molecular substances in the conductive rubber component, and can also provide a barrier effect, and more contamination of the photoreceptor, Can reduce paper dust and toner adhesion. Furthermore, a large amount of the silicone compound can be contained, and the releasability is further improved.
上記反応性基を有するシリコーン化合物及び反応性基を有するフッ素化シリコーン化合物は、分子量が400〜50000の範囲に設定されたものが好ましく、特に好ましくは1000〜20000の範囲である。 As for the silicone compound which has the said reactive group, and the fluorinated silicone compound which has a reactive group, what was set to the range of the molecular weight of 400-50000 is preferable, Most preferably, it is the range of 1000-20000.
また、上記反応性基を有するシリコーン化合物及び反応性基を有するフッ素化シリコーン化合物の配合割合は、溶媒を含まない塗膜成分100重量部に対して0.4重量部以下の範囲に設定することが好ましく、特に好ましくは0.01〜0.2重量部の範囲である。0重量部であると、離型性に対して十分な効果を発揮できず、0.4重量部を超えるとブリード等の汚染原因になる可能性がある。これらシリコーン化合物等を塗膜材料に添加すると、高離型性を付与することが出来、有用である。 The blending ratio of the silicone compound having a reactive group and the fluorinated silicone compound having a reactive group should be set in a range of 0.4 parts by weight or less with respect to 100 parts by weight of a coating film component not containing a solvent. Is particularly preferable, and the range is 0.01 to 0.2 parts by weight. If it is 0 part by weight, a sufficient effect on the releasability cannot be exhibited, and if it exceeds 0.4 part by weight, it may cause contamination such as bleeding. When these silicone compounds and the like are added to the coating material, high release properties can be imparted, which is useful.
なお、この最外層の厚さは、特に制限されないが、通常50μm以下、特に1〜30μmとすることが好ましく、50μmを越えると硬くなって、最外層の柔軟性が損なわれてしまうことがあり、あまり好ましくはない。 The thickness of the outermost layer is not particularly limited, but is usually 50 μm or less, preferably 1 to 30 μm, and if it exceeds 50 μm, it becomes hard and the flexibility of the outermost layer may be impaired. , Not very preferable.
また、これらの化合物を溶解し最外層形成用の塗膜塗料とする場合に用いられる有機溶媒としては、非プロトン系極性溶媒を用いるのが好ましく、特に、酢酸ブチル、シクロヘキサノン、トルエン、キシレン、ジメチルホルムアミド等溶媒を添加することが出来る。 In addition, it is preferable to use an aprotic polar solvent as an organic solvent used when dissolving these compounds to form a coating film for forming the outermost layer, and in particular, butyl acetate, cyclohexanone, toluene, xylene, dimethyl. A solvent such as formamide can be added.
また、最外層の形成方法としては、特に制限されるものではないが、層を形成する各成分を含む塗料を調整し、このコーティング液の塗布方法は、特に制限するものではなく、従来公知のディッピング法、スプレーコーティング法、ロールコート法等が挙げられる。 In addition, the outermost layer forming method is not particularly limited, but a coating material containing each component forming the layer is prepared, and the coating liquid application method is not particularly limited, and is conventionally known. Examples include a dipping method, a spray coating method, and a roll coating method.
本発明の半導電性部材が帯電ローラの場合の適当な抵抗は、良好な画像を得るためには、体積抵抗率が1×102〜1×1012Ω・cmであることが好ましく、特に1×105〜1×1010Ω・cmであることが好ましい。また、このようにして作製された最外層に凹凸があると、トナーが詰まってしまい画像不良の原因となるため、最外層はできるだけ平滑な方が好ましい。このように作製した半導電性部材を使用した帯電ローラは印字抜け、ムラ、カブリのない画像を安定的に得ることができ、温・湿度に対する耐環境性に優れる。 An appropriate resistance when the semiconductive member of the present invention is a charging roller is preferably a volume resistivity of 1 × 10 2 to 1 × 10 12 Ω · cm in order to obtain a good image. It is preferably 1 × 10 5 to 1 × 10 10 Ω · cm. Further, if the outermost layer produced in this way has irregularities, the toner is clogged and causes image defects. Therefore, the outermost layer is preferably as smooth as possible. The charging roller using the semiconductive member thus produced can stably obtain an image free from printing omission, unevenness, and fogging, and is excellent in environmental resistance against temperature and humidity.
なお、本発明の帯半導電性部材は、例えば、帯電ローラとして接触帯電方式に用いられるものであり、被帯電体に接触するものであれば、特にその形状が限定されるものではない。他の形態としては、プレート状、ブロック状などの各種形状のものが適用可能である。 The band semiconductive member of the present invention is used in, for example, a contact charging system as a charging roller, and the shape is not particularly limited as long as it is in contact with an object to be charged. As other forms, various shapes such as a plate shape and a block shape are applicable.
帯電ローラの場合には、これらの内側に金属あるいはプラスチック製のシャフトを設けてもよい。また、本発明の半導電性部材が帯電ローラの場合の構造は、弾性層と少なくとも1層の塗膜層とから成り、弾性層としては弾性体が、塗膜層としては樹脂層が用いられる。金属あるいはプラスチック製のシャフトと、このシャフトの外周に形成された弾性層と、上記弾性層の表面に形成された、導電剤を添加した樹脂から構成される最外層とから成る帯電ローラを例示することができる。 In the case of a charging roller, a metal or plastic shaft may be provided inside these rollers. In addition, the structure in the case where the semiconductive member of the present invention is a charging roller includes an elastic layer and at least one coating layer, and an elastic body is used as the elastic layer and a resin layer is used as the coating layer. . Illustrated is a charging roller comprising a shaft made of metal or plastic, an elastic layer formed on the outer periphery of the shaft, and an outermost layer formed of a resin added with a conductive agent formed on the surface of the elastic layer. be able to.
本発明の半導電部材において用いられる弾性層としては、特に限定されるものではないが、従来から弾性層として用いられているゴム、樹脂、発泡体で形成することができる。具体的には、ポリウレタン、シリコーンゴム、ブタジエンゴム、イソプレンゴム、クロロプレンゴム、スチレン−ブタジエンゴム、エチレン−プロピレンゴム、ノルボルネンゴム、スチレン−ブタジエン−スチレンゴム、エピクロルヒドリン系ゴム、フッ素ゴム、アクリルゴム等を基材ゴムとするゴム組成物が挙げられ、これらのゴム材料を2種以上ブレンドしてもよい。 Although it does not specifically limit as an elastic layer used in the semiconductive member of this invention, It can form with the rubber | gum, resin, and foam which were conventionally used as an elastic layer. Specifically, polyurethane, silicone rubber, butadiene rubber, isoprene rubber, chloroprene rubber, styrene-butadiene rubber, ethylene-propylene rubber, norbornene rubber, styrene-butadiene-styrene rubber, epichlorohydrin rubber, fluorine rubber, acrylic rubber, etc. The rubber composition used as the base rubber may be mentioned, and two or more of these rubber materials may be blended.
この弾性層に、イオン導電剤や電子導電剤などの導電剤を添加し、所定の導電性を付与することができる。また、イオン導電剤の例としては、テトラエチルアンモニウム、テトラブチルアンモニウム、ラウリルトリメチルアンモニウム、ドデシルトリメチルアンモニウム、ステアリルトリメチルアンモニウム、オクタデシルトリメチルアンモニウム、ヘキサデシルトリメチルアンモニウム、ベンジルトリメチルアンモニウム、変性脂肪族ジメチルエチルアンモニウムなどの過塩素酸塩、塩素酸塩、塩酸塩、臭素酸塩、ヨウ素酸塩、ホウフッ化水素酸塩、硫酸塩、アルキル硫酸塩、カルボン酸塩、スルホン酸塩、PF6塩、BF4塩などのようなアンモニウム塩、あるいは、リチウム、ナトリウム、カルシウム、マグネシウムなどのアルカリ金属またはアルカリ土類金属の過塩素酸塩、塩素酸塩、塩酸塩、臭素酸塩、ヨウ素酸塩、ホウフッ化水素酸塩、トリフルオロメチル硫酸塩、スルホン酸塩、PF6塩、BF4塩などが挙げられる。 A conductive agent such as an ionic conductive agent or an electronic conductive agent can be added to the elastic layer to impart predetermined conductivity. Examples of ionic conductive agents include tetraethylammonium, tetrabutylammonium, lauryltrimethylammonium, dodecyltrimethylammonium, stearyltrimethylammonium, octadecyltrimethylammonium, hexadecyltrimethylammonium, benzyltrimethylammonium, and modified aliphatic dimethylethylammonium. Such as perchlorate, chlorate, hydrochloride, bromate, iodate, borofluoride, sulfate, alkyl sulfate, carboxylate, sulfonate, PF6 salt, BF4 salt etc. Ammonium salt or perchlorate, chlorate, hydrochloride, bromate, iodate, borofluoride of alkali metal or alkaline earth metal such as lithium, sodium, calcium, magnesium Trifluoromethyl sulfate, sulfonate, PF6 @ salts, and the like BF4 salt.
更に、電子導電剤の例としては、カーボンブラック、グラファイト、アルミニウム、銅、ニッケル、ステンレス鋼等の各種導電性金属または合金、酸化錫、酸化インジウム、酸化チタン、酸化亜鉛、酸化錫−酸化アンチモン複合酸化物、酸化錫−酸化インジウム複合酸化物等の各種導電性金属酸化物、絶縁物質の表面を導電化処理したものなどの1種または2種以上の微粉末を用いることができる。 Furthermore, examples of the electronic conductive agent include various conductive metals or alloys such as carbon black, graphite, aluminum, copper, nickel, stainless steel, tin oxide, indium oxide, titanium oxide, zinc oxide, tin oxide-antimony oxide composite. One kind or two or more kinds of fine powders such as oxides, various conductive metal oxides such as tin oxide-indium oxide composite oxide, and the like obtained by subjecting the surface of an insulating material to a conductive treatment can be used.
また、これらの導電剤の添加量としては特に制限はなく、各種状況に応じて適宜選択される。イオン導電剤の場合には、ゴム100重量部に対して、通常0.01〜5重量部、好ましくは0.05〜2重量部である。また、電子導電剤の場合には、通常0.5〜50重量部、好ましくは1〜40重量部である。これらの処方により、弾性層の体積抵抗率を1×103〜1×1010Ω・cm、特に、1×104〜1×108Ω・cmに調整することが好ましい。なお、この導電性弾性層には、必要に応じ、充填材、架橋剤、発泡剤等、ゴム用添加剤を添加することもできる。 Moreover, there is no restriction | limiting in particular as addition amount of these electrically conductive agents, According to various situations, it selects suitably. In the case of an ionic conductive agent, the amount is usually 0.01 to 5 parts by weight, preferably 0.05 to 2 parts by weight with respect to 100 parts by weight of rubber. Moreover, in the case of an electronic conductive agent, it is 0.5-50 weight part normally, Preferably it is 1-40 weight part. By these prescriptions, it is preferable to adjust the volume resistivity of the elastic layer to 1 × 10 3 to 1 × 10 10 Ω · cm, particularly 1 × 10 4 to 1 × 10 8 Ω · cm. In addition, rubber additives such as a filler, a crosslinking agent, and a foaming agent can be added to the conductive elastic layer as necessary.
また、本発明の半導電性部材使用の帯電装置としては、例えば、被帯電体である感光ドラムに、本発明の半導電性部材の帯電部材である帯電ローラを接触させつつ従動回転させるとともに、電圧印可手段により、感光ドラムと帯電ローラとの間に、直流電圧、あるいは直流電圧に交流電圧を重畳した電圧を印可して上記感光ドラムを帯電させるように構成した帯電装置を例示することができる。なお、本発明の半導電性部材使用の帯電装置は、これに限るものではなく、被帯電体や帯電部材の形態、あるいは電圧印可手段による電圧印可方式などは適宜変更してもよい。 Further, as the charging device using the semiconductive member of the present invention, for example, the charging roller which is the charging member of the semiconductive member of the present invention is driven to rotate while being in contact with the photosensitive drum which is the charged body, A charging device configured to charge the photosensitive drum by applying a DC voltage or a voltage obtained by superimposing an AC voltage on the DC voltage between the photosensitive drum and the charging roller by the voltage applying means can be exemplified. . The charging device using the semiconductive member of the present invention is not limited to this, and the form of the member to be charged and the charging member, the voltage applying method by the voltage applying means, or the like may be appropriately changed.
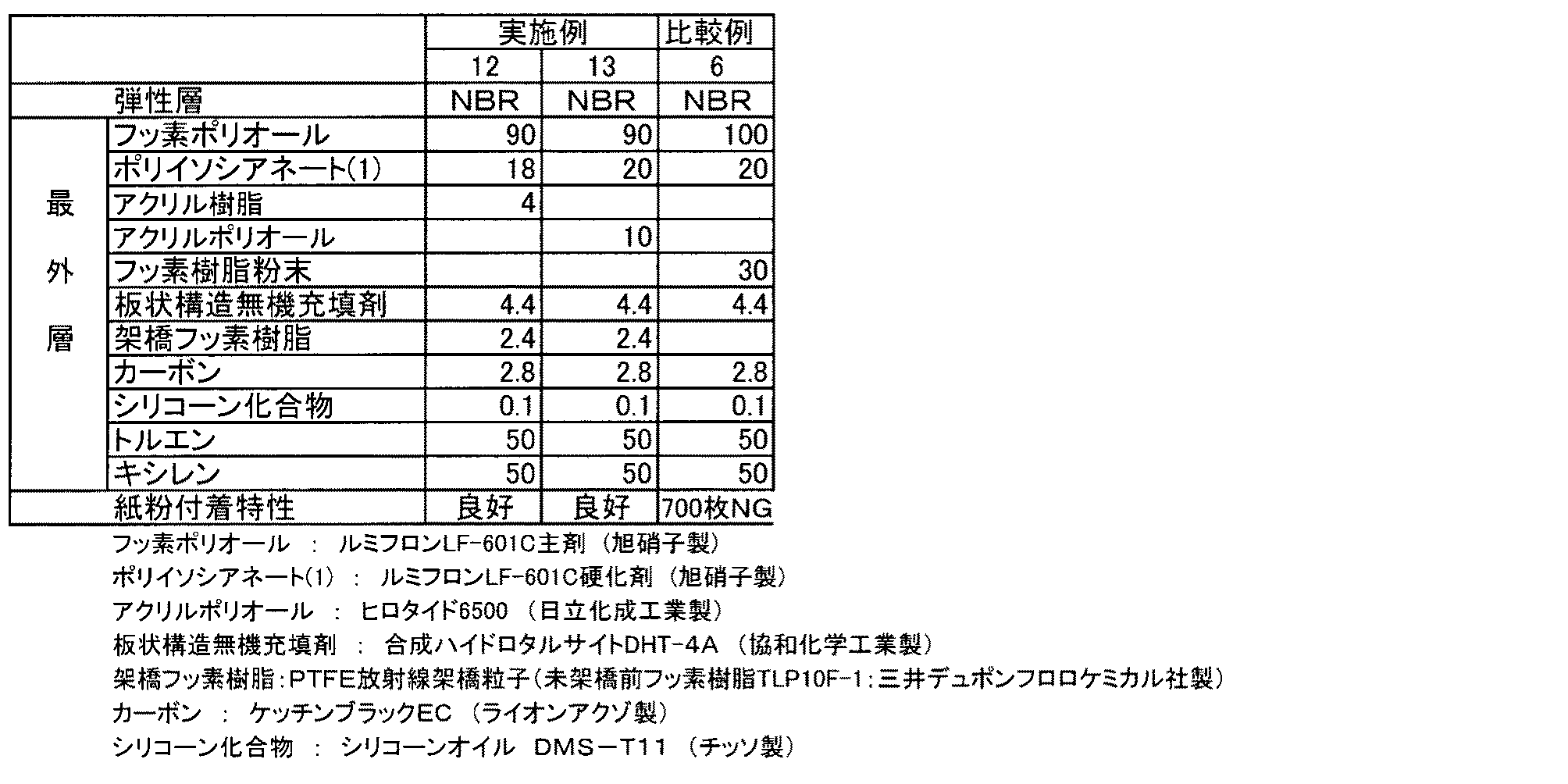
以下に、実施例、比較例を示し、本発明を具体的に説明するが、本発明はこれらに限定されるものではない。 Hereinafter, the present invention will be specifically described with reference to Examples and Comparative Examples, but the present invention is not limited to these.
先ず、下記組成の半導電性部材表面処理液を調整した。
ポリフッ化ビニリデン−テトラフルオロエチレン−ヘキサフルオロプロピレン三元共重合体/アクリル樹脂(ポリメチルメタクリレート)混合組成物(ノバフッソ(登録商標)PF250:大日本色材工業製) 100重量部
導電性粒子:酸化チタン(MT-150A:テイカ(株)製) 4.9重量部
板状構造無機充填剤:合成ハイドロタルサイト(DHT−4A(登録商標):協和化学工業製) 0.14重量部
架橋フッ素樹脂:PTFE放射線架橋粒子(未架橋前フッ素樹脂TLP10F-1:三井デュポンフロロケミカル社製) 0.20重量部
次いで、8Φの芯金上に3mm肉厚の三元系エピクロルヒドリンゴム(GECO)弾性層(体積抵抗率R:2.5×107Ω・cm、LogR:7.4)を設けたローラ上に上記調整液を硬化後の膜厚が5μmとなるように、スプレー塗工し、実施例1の半導電性部材(ローラ抵抗R′:1.1×106Ω、LogR′:6.0)を作製した。
この半導電性部材を帯電ローラとしてリコーimagio感光体トナーキットMに搭載し60℃−30%RH環境下に10日間放置した。しかる後、リコーimagio感光体トナーキットMをリコーImagio MF−1530に搭載し画像を出力させ、半導電性部材が接触していたOPC部分に異常が認められないか否かの評価試験を行なった。
First, a semiconductive member surface treatment solution having the following composition was prepared.
Polyvinylidene fluoride-tetrafluoroethylene-hexafluoropropylene terpolymer / acrylic resin (polymethylmethacrylate) mixed composition (Novafusso (registered trademark) PF250: manufactured by Dainippon Color Industries) 100 parts by weight Conductive particles: oxidation Titanium (MT-150A: manufactured by Teika Co., Ltd.) 4.9 parts by weight Plate-like inorganic filler: Synthetic hydrotalcite (DHT-4A (registered trademark): manufactured by Kyowa Chemical Industry) 0.14 parts by weight Cross-linked fluororesin : PTFE radiation crosslinked particles (uncrosslinked fluororesin TLP10F-1: manufactured by Mitsui DuPont Fluorochemical Co., Ltd.) 0.20 parts by weight Next, a 3 mm thick ternary epichlorohydrin rubber (GECO) elastic layer (GECO) elastic layer (8 Φ core metal) The film thickness after curing the adjustment liquid on a roller provided with a volume resistivity R: 2.5 × 10 7 Ω · cm, Log R: 7.4) is 5 μm. The semiconductive member of Example 1 (roller resistance R ′: 1.1 × 10 6 Ω, Log R ′: 6.0) was produced by spray coating.
This semiconductive member was mounted as a charging roller in the Ricoh imagio photoconductor toner kit M, and left in an environment of 60 ° C.-30% RH for 10 days. Thereafter, the Ricoh imageio photoconductor toner kit M was mounted on the Ricoh Imageo MF-1530, an image was output, and an evaluation test was performed to determine whether there was any abnormality in the OPC portion where the semiconductive member was in contact.
実施例1において、三元系エピクロルヒドリンゴム(GECO)弾性層に代えて、カーボンで抵抗調整されたNBR弾性層(体積抵抗率R:4.0×106Ω・cm、LogR:6.6)を設けた以外は、実施例1と全く同様にして実施例2の半導電性部材(ローラ抵抗R′:1.8×105Ω、LogR′:5.2)を作製し、実施例1と同様の評価試験を行なった。 In Example 1, instead of the ternary epichlorohydrin rubber (GECO) elastic layer, an NBR elastic layer whose volume is adjusted with carbon (volume resistivity R: 4.0 × 10 6 Ω · cm, Log R: 6.6) The semiconductive member of Example 2 (roller resistance R ′: 1.8 × 10 5 Ω, Log R ′: 5.2) was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that The same evaluation test was conducted.
[比較例1]
下記組成の半導電性部材表面処理液を調整した。
ポリフッ化ビニリデン−テトラフルオロエチレン−ヘキサフルオロプロピレン三元共重合体/アクリル樹脂混合組成物(ノバフッソ(登録商標)PF250:大日本色材工業製) 100重量部
導電性粒子:酸化チタン(MT-150A:テイカ(株)製) 4.9重量部
次いで、8Φの芯金上に3mm肉厚の三元系エピクロルヒドリンゴム(GECO)弾性層を設けたローラ上に上記調整液を硬化後の膜厚が5μmとなるように、スプレー塗工し、比較例1の半導電性部材を作製し、実施例1と同様の評価試験を行なった。
[Comparative Example 1]
A semiconductive member surface treatment solution having the following composition was prepared.
Polyvinylidene fluoride-tetrafluoroethylene-hexafluoropropylene terpolymer / acrylic resin mixed composition (Novafusso (registered trademark) PF250: manufactured by Dainippon Color Materials Co., Ltd.) 100 parts by weight Conductive particles: Titanium oxide (MT-150A 4.9 parts by weight Next, the film thickness after curing the above adjustment liquid on a roller provided with a 3 mm thick ternary epichlorohydrin rubber (GECO) elastic layer on an 8Φ cored bar. The semiconductive member of Comparative Example 1 was prepared by spray coating so that the thickness was 5 μm, and the same evaluation test as in Example 1 was performed.
[比較例2]
比較例1において、三元系エピクロルヒドリンゴム(GECO)弾性層に代えて、実施例2で用いたものと同様のカーボンで抵抗調整されたNBR弾性層を用いた以外は、比較例1と全く同様にして比較例2の半導電性部材を作製し、実施例1と同様の評価試験を行なった。
[Comparative Example 2]
In Comparative Example 1, in place of the ternary epichlorohydrin rubber (GECO) elastic layer, the same as in Comparative Example 1 except that an NBR elastic layer having a resistance adjusted with carbon similar to that used in Example 2 was used. Thus, the semiconductive member of Comparative Example 2 was produced, and the same evaluation test as in Example 1 was performed.
[比較例3]
実施例1において、表面層を設けない以外は、実施例1と同様の、芯金上に三元系エピクロルヒドリンゴム(GECO)弾性層のみを設けた比較例3の半導電性部材を作製し、実施例1と同様の評価試験を行なった。
[Comparative Example 3]
In Example 1, except that the surface layer is not provided, a semiconductive member of Comparative Example 3 in which only the ternary epichlorohydrin rubber (GECO) elastic layer is provided on the cored bar is prepared as in Example 1, The same evaluation test as in Example 1 was performed.
[比較例4]
実施例2において、表面層を設けない以外は、実施例2と同様の、芯金上にカーボンで抵抗調整されたNBR弾性層のみを設けた比較例4の半導電性部材を作製し、実施例1と同様の評価試験を行なった。
実施例1、2及び比較例1、2、3、4で得られた半導電性部材の評価試験結果を表1に示す。なお表1中の使用割合は重量部である。
[Comparative Example 4]
In Example 2, a semiconductive member of Comparative Example 4 having only an NBR elastic layer whose resistance was adjusted with carbon on a cored bar was prepared, except that a surface layer was not provided. The same evaluation test as in Example 1 was performed.
Table 1 shows the evaluation test results of the semiconductive members obtained in Examples 1 and 2 and Comparative Examples 1, 2, 3, and 4. In Table 1, the use ratio is parts by weight.
下記組成の半導電性部材表面処理液を調整した。
ポリフッ化ビニリデン−テトラフルオロエチレン−ヘキサフルオロプロピレン三元共重合体/アクリル樹脂混合組成物(ノバフッソ(登録商標)PF250:大日本色材工業製) 100重量部
導電性粒子:酸化チタン(MT−150A:テイカ(株)製) 4.9重量部
板状構造無機充填剤:合成ハイドロタルサイト(DHT−4A(登録商標):協和化学工業製) 0.14重量部
架橋フッ素樹脂:PTFE放射線架橋粒子(未架橋前フッ素樹脂TLP10F-1:三井デュポンフロロケミカル社製) 0.20重量部
シリコーン化合物:シリコーンオイル(DMS-T11:チッソ(株)製)
0.0032重量部
次いで、8Φの芯金上に3mm肉厚の三元系エピクロルヒドリンゴム(GECO)弾性層を設けたローラ上に上記調整液を硬化後の膜厚が5μmとなるように、スプレー塗工し、実施例3の半導電性部材を作製した。
この半導電性部材を帯電ローラとしてリコーImagio Neo 270に搭載し、5%チャート(A4)で6万枚コピーを取った後、帯電ローラ両端部、中央部3箇所の汚れをテープで剥離し、濃度計(X−Rite 508:X−Rite Inc.社製)にて測定した夫々のテープの汚れ濃度を、帯電ローラの汚れ特性値とした。
A semiconductive member surface treatment solution having the following composition was prepared.
Polyvinylidene fluoride-tetrafluoroethylene-hexafluoropropylene terpolymer / acrylic resin mixed composition (Novafusso (registered trademark) PF250: manufactured by Dainippon Color Materials Co., Ltd.) 100 parts by weight Conductive particles: Titanium oxide (MT-150A) 4.9 parts by weight Plate-like inorganic filler: Synthetic hydrotalcite (DHT-4A (registered trademark): manufactured by Kyowa Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.) 0.14 parts by weight Crosslinked fluororesin: PTFE radiation crosslinked particles (Uncrosslinked fluororesin TLP10F-1: manufactured by Mitsui DuPont Fluorochemical Co., Ltd.) 0.20 parts by weight Silicone compound: Silicone oil (DMS-T11: manufactured by Chisso Corporation)
0.0032 parts by weight Next, spray the adjustment liquid on a roller provided with a 3 mm thick ternary epichlorohydrin rubber (GECO) elastic layer on an 8Φ core so that the film thickness after curing is 5 μm. The semiconductive member of Example 3 was produced by coating.
This semiconductive member is mounted on a Ricoh Imagio Neo 270 as a charging roller, and after taking 60,000 copies with a 5% chart (A4), the dirt on both ends of the charging roller and the central portion are peeled off with tape, The dirt density of each tape measured with a densitometer (X-Rite 508: manufactured by X-Rite Inc.) was taken as the dirt characteristic value of the charging roller.
[比較例5]
表面処理液の組成を下記組成とした以外は実施例3と全く同様してに比較例5の半導電性部材を作製し、実施例3と同様の耐汚れ特性の評価を行なった。
ポリフッ化ビニリデン−テトラフルオロエチレン−ヘキサフルオロプロピレン三元共重合体/アクリル樹脂混合組成物(ノバフッソ(登録商標)PF250:大日本色材工業製) 100重量部
導電性粒子:酸化チタン(MT−150A:テイカ(株)製) 4.9重量部
滑剤:脂肪酸アマイド(カワスリップVL:川研ファインケミカル)
1.2重量部
[Comparative Example 5]
A semiconductive member of Comparative Example 5 was prepared in exactly the same manner as in Example 3 except that the composition of the surface treatment liquid was changed to the following composition, and the same antifouling property as in Example 3 was evaluated.
Polyvinylidene fluoride-tetrafluoroethylene-hexafluoropropylene terpolymer / acrylic resin mixed composition (Novafusso (registered trademark) PF250: manufactured by Dainippon Color Material Industries) 100 parts by weight Conductive particles: Titanium oxide (MT-150A) 4.9 parts by weight Lubricant: Fatty acid amide (Kawaslip VL: Kawaken Fine Chemical)
1.2 parts by weight
表面処理液の組成を下記組成とした以外は実施例3と全く同様にして実施例4の半導電性部材を作製し、実施例3と同様の耐汚れ特性の評価を行なった。
ポリフッ化ビニリデン−テトラフルオロエチレン−ヘキサフルオロプロピレン三元共重合体/アクリル樹脂混合組成物(ノバフッソ(登録商標)PF250:大日本色材工業製) 100重量部
導電性粒子:酸化チタン(MT-150A:テイカ(株)製) 4.9重量部
板状構造無機充填剤:合成ハイドロタルサイト(DHT-4A(登録商標):協和化学工業製) 0.14重量部
架橋フッ素樹脂:PTFE放射線架橋粒子(未架橋前フッ素樹脂TLP10F-1:三井デュポンフロロケミカル社製) 0.20重量部
シリコーン化合物:フッ素化シリコーン化合物(FMS−121:チッソ(株)製) 0.0032重量部
A semiconductive member of Example 4 was produced in the same manner as in Example 3 except that the composition of the surface treatment liquid was changed to the following composition, and the same anti-smudge property as in Example 3 was evaluated.
Polyvinylidene fluoride-tetrafluoroethylene-hexafluoropropylene terpolymer / acrylic resin mixture composition (Novafusso (registered trademark) PF250: manufactured by Dainippon Color Industries) 100 parts by weight Conductive particles: Titanium oxide (MT-150A) 4.9 parts by weight Plate-like inorganic filler: Synthetic hydrotalcite (DHT-4A (registered trademark): manufactured by Kyowa Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.) 0.14 parts by weight Crosslinked fluororesin: PTFE radiation crosslinked particles (Uncrosslinked fluororesin TLP10F-1: manufactured by Mitsui DuPont Fluorochemical Co., Ltd.) 0.20 parts by weight Silicone compound: fluorinated silicone compound (FMS-121: manufactured by Chisso Corporation) 0.0032 parts by weight
表面処理液の組成を下記組成とした以外は、実施例3と全く同様にして実施例5の半導電性部材を作製し、実施例3と同様の耐汚れ特性の評価を行なった。
ポリフッ化ビニリデン−テトラフルオロエチレン−ヘキサフルオロプロピレン三元共重合体/アクリル樹脂混合組成物(ノバフッソ(登録商標)PF250:大日本色材工業製) 100重量部
導電性粒子:酸化チタン(MT-150A:テイカ(株)製) 4.9重量部
板状構造無機充填剤:合成ハイドロタルサイト(DHT−4A(登録商標):協和化学工業製) 0.14重量部
架橋フッ素樹脂:PTFE放射線架橋粒子(未架橋前フッ素樹脂TLP10F-1:三井デュポンフロロケミカル社製) 0.20重量部
シリコーン化合物:シラノール末端シリコーン(DMS−S15:チッソ(株)製) 0.0032重量部
A semiconductive member of Example 5 was produced in the same manner as in Example 3 except that the composition of the surface treatment liquid was changed to the following composition, and the same antifouling property as in Example 3 was evaluated.
Polyvinylidene fluoride-tetrafluoroethylene-hexafluoropropylene terpolymer / acrylic resin mixture composition (Novafusso (registered trademark) PF250: manufactured by Dainippon Color Industries) 100 parts by weight Conductive particles: Titanium oxide (MT-150A) 4.9 parts by weight Plate-like inorganic filler: Synthetic hydrotalcite (DHT-4A (registered trademark): manufactured by Kyowa Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.) 0.14 parts by weight Crosslinked fluororesin: PTFE radiation crosslinked particles (Uncrosslinked fluororesin TLP10F-1: manufactured by Mitsui DuPont Fluorochemical Co., Ltd.) 0.20 parts by weight Silicone compound: Silanol-terminated silicone (DMS-S15: manufactured by Chisso Corporation) 0.0032 parts by weight
実施例5のシリコーン化合物をシラノール末端ポリトリフロロプロピルメチルシロキサン(FMS−9921:チッソ(株)製)に代え、同一重量部加えた以外は、実施例5と全く同様にして実施例6の半導電性部材を作製し、実施例3と同様の耐汚れ特性の評価を行なった。 The silicone compound of Example 5 was replaced with silanol-terminated polytrifluoropropylmethylsiloxane (FMS-9921: manufactured by Chisso Corp.), and the same weight part was added. A conductive member was prepared, and the same antifouling property as in Example 3 was evaluated.
実施例6において、架橋フッ素樹脂:PTFE放射線架橋粒子(未架橋前フッ素樹脂TLP10F-1:三井デュポンフロロケミカル社製)0.20重量部に代え、PTFE放射線架橋粒子(未架橋前フッ素樹脂MP1300:三井デュポンフロロケミカル社製)を同一重量部加えた以外は、実施例5と全く同様にして実施例7の半導電性部材を作製し、実施例3と同様の耐汚れ特性の評価を行なった。 In Example 6, instead of 0.20 parts by weight of crosslinked fluororesin: PTFE radiation crosslinked particles (uncrosslinked fluororesin TLP10F-1: manufactured by Mitsui DuPont Fluorochemical Co., Ltd.), PTFE radiation crosslinked particles (uncrosslinked fluororesin MP1300: A semiconductive member of Example 7 was prepared in the same manner as in Example 5 except that the same part by weight of Mitsui DuPont Fluoro Chemical Co.) was added, and the same antifouling property as in Example 3 was evaluated. .
表面処理液の組成を下記組成とした以外は実施例3と全く同様にして実施例8の半導電性部材を作製し、実施例3と同様の耐汚れ特性の評価を行なった。
ポリエステルポリオール(ユーラック(登録商標)C-230U:広野化学製)
100重量部
ポリイソシアネート(ユーラック(登録商標)PU−614:広野化学製) 33重量部
カーボン(ケッチェンブラック(登録商標)EC:ライオンアクゾ製)
2.8重量部
板状構造無機充填剤:合成ハイドロタルサイト(DHT−4A(登録商標):協和化学工業製) 4.4重量部
架橋フッ素樹脂:PTFE放射線架橋粒子(未架橋前フッ素樹脂TLP10F-1:三井デュポンフロロケミカル社製) 2.4重量部
シリコーン化合物:シラノール末端シリコーンDMS−S15:チッソ(株)製) 0.1重量部
トルエン 50重量部
キシレン 50重量部
A semiconductive member of Example 8 was produced in the same manner as in Example 3 except that the composition of the surface treatment liquid was changed to the following composition, and the same antifouling property as in Example 3 was evaluated.
Polyester polyol (Yurak (registered trademark) C-230U: manufactured by Hirono Chemical)
100 parts by weight Polyisocyanate (Yurak (registered trademark) PU-614: manufactured by Hirono Chemical) 33 parts by weight Carbon (Ketjen Black (registered trademark) EC: manufactured by Lion Akzo)
2.8 parts by weight Plate-like structure inorganic filler: Synthetic hydrotalcite (DHT-4A (registered trademark): manufactured by Kyowa Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.) 4.4 parts by weight Cross-linked fluororesin: PTFE radiation cross-linked particles (uncrosslinked pre-fluorinated resin TLP10F -1: Mitsui DuPont Fluorochemical Co., Ltd.) 2.4 parts by weight Silicone compound: Silanol-terminated silicone DMS-S15: manufactured by Chisso Corporation 0.1 part by weight Toluene 50 parts by weight Xylene 50 parts by weight
表面処理液の組成を下記組成とした以外は実施例3と全く同様にして実施例9の半導電性部材を作製し、実施例3と同様の耐汚れ特性の評価を行なった。
ポリエステルポリオール(ユーラック(登録商標)C−230U:広野化学製) 100重量部
ポリイソシアネート(ユーラック(登録商標)PU−614:広野化学製) 33重量部
カーボン(ケッチェンブラック(商標)EC:ライオンアクゾ製) 2.8重量部
板状構造無機充填剤:合成ハイドロタルサイト(DHT−4A(登録商標):協和化学工業製) 4.4重量部
架橋フッ素樹脂:PTFE放射線架橋粒子(未架橋前フッ素樹脂TLP10F-1:三井デュポンフロロケミカル社製) 2.4重量部
シリコーン化合物:シラノール末端ポリトリフロロプロピルメチルシロキサン(FMS−9921:チッソ(株)製) 0.1重量部
トルエン 50重量部
キシレン 50重量部
A semiconductive member of Example 9 was produced in exactly the same manner as in Example 3 except that the composition of the surface treatment liquid was changed to the following composition, and the stain resistance characteristics were evaluated in the same manner as in Example 3.
Polyester polyol (Eurach (registered trademark) C-230U: manufactured by Hirono Chemical Co., Ltd.) 100 parts by weight Polyisocyanate (Eurac (registered trademark) PU-614: manufactured by Hirono Chemical Co., Ltd.) 33 parts by weight Carbon (Ketjen Black (registered trademark) EC: Lion Akzo) 2.8 parts by weight Plate-like structure inorganic filler: Synthetic hydrotalcite (DHT-4A (registered trademark): manufactured by Kyowa Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.) 4.4 parts by weight Cross-linked fluororesin: PTFE radiation cross-linked particles (fluorine before uncross-linking) Resin TLP10F-1: manufactured by Mitsui DuPont Fluorochemical Co., Ltd.) 2.4 parts by weight Silicone compound: Silanol-terminated polytrifluoropropylmethylsiloxane (FMS-9921: manufactured by Chisso Corporation) 0.1 part by weight Toluene 50 parts by weight Xylene 50 Parts by weight
表面処理液の組成を下記組成とした以外は実施例3と全く同様に実施例10の半導電性部材を作製し、実施例3と同様の耐汚れ特性の評価を行なった。
フッ素ポリオール(ルミフロン(登録商標)LF−601C主剤:旭硝子製) 100重量部
ポリイソシアネート(ルミフロン(商標)LF-601C硬化剤:旭硝子製)
20重量部
カーボン(ケッチェンブラック(登録商標)EC:ライオンアクゾ製)
2.8重量部
板状構造無機充填剤:合成ハイドロタルサイト(DHT−4A(登録商標):協和化学工業製) 4.4重量部
架橋フッ素樹脂:PTFE放射線架橋粒子(未架橋前フッ素樹脂TLP10F-1:三井デュポンフロロケミカル社製) 2.4重量部
シリコーン化合物:シラノール末端シリコーン(DMS-S15:チッソ(株)製) 0.1重量部
トルエン 50重量部
キシレン 50重量部
A semiconductive member of Example 10 was produced in the same manner as in Example 3 except that the composition of the surface treatment liquid was changed to the following composition, and the same antifouling property as in Example 3 was evaluated.
Fluoropolyol (Lumiflon (registered trademark) LF-601C main agent: manufactured by Asahi Glass) 100 parts by weight Polyisocyanate (Lumiflon (TM) LF-601C curing agent: manufactured by Asahi Glass)
20 parts by weight carbon (Ketjen Black (registered trademark) EC: manufactured by Lion Akzo)
2.8 parts by weight Plate-like structure inorganic filler: Synthetic hydrotalcite (DHT-4A (registered trademark): manufactured by Kyowa Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.) 4.4 parts by weight Cross-linked fluororesin: PTFE radiation cross-linked particles (uncrosslinked pre-fluorinated resin TLP10F -1: Mitsui DuPont Fluoro Chemical Co., Ltd.) 2.4 parts by weight Silicone compound: Silanol-terminated silicone (DMS-S15: manufactured by Chisso Corporation) 0.1 part by weight Toluene 50 parts by weight Xylene 50 parts by weight
表面処理液の組成を下記組成とした以外は実施例3と全く同様にして実施例11の半導電性部材を作製し、実施例3と同様の耐汚れ特性の評価を行なった。
フッ素ポリオール(ルミフロン(登録商標)LF-601C主剤:旭硝子製) 100重量部
ポリイソシアネート(ミフロン(登録商標)LF-601C硬化剤:旭硝子製)
20重量部
カーボン(ケッチェンブラック(商標)EC:ライオンアクゾ製) 2.8重量部
板状構造無機充填剤:合成ハイドロタルサイト(DHT−4A(登録商標):協和化学工業製) 4.4重量部
架橋フッ素樹脂:PTFE放射線架橋粒子(未架橋前フッ素樹脂TLP10F-1:三井デュポンフロロケミカル社製) 2.4重量部
シリコーン化合物:シラノール末端ポリフロロプロピルメチルシロキサン(FMS−9921:チッソ製) 0.1重量部
トルエン 50重量部
キシレン 50重量部
A semiconductive member of Example 11 was produced in the same manner as in Example 3 except that the composition of the surface treatment liquid was changed to the following composition, and the stain resistance characteristics were evaluated in the same manner as in Example 3.
Fluoropolyol (Lumiflon (registered trademark) LF-601C main agent: manufactured by Asahi Glass) 100 parts by weight Polyisocyanate (Miflon (registered trademark) LF-601C curing agent: manufactured by Asahi Glass)
20 parts by weight Carbon (Ketjen Black (trademark) EC: manufactured by Lion Akzo) 2.8 parts by weight Plate-like structure inorganic filler: Synthetic hydrotalcite (DHT-4A (registered trademark): manufactured by Kyowa Chemical Industry) 4.4 Weight parts Cross-linked fluororesin: PTFE radiation cross-linked particles (uncrosslinked fluororesin TLP10F-1: manufactured by Mitsui DuPont Fluorochemical Co., Ltd.) 2.4 parts by weight Silicone compound: Silanol-terminated polyfluoropropylmethylsiloxane (FMS-9921: manufactured by Chisso) 0.1 parts by weight Toluene 50 parts by weight Xylene 50 parts by weight
実施例3、4、5、6、7及び比較例5で得られた各ローラの6万枚コピー後の帯電ローラ汚れ評価結果を表2に示す。
また、実施例8、9、10、11で得られた半導電性部材(帯電ローラ)は表層処理液メイン樹脂と反応性シリコーン化合物の組合せがローラ汚れに及ぼす影響を調べたものである。実施例7、8、9、10の各ローラの6万枚コピー後の帯電ローラ汚れ評価結果を表2に示す。
なお、表2中の原材料の使用割合は、重量部で示す。
また、表2中の評価は下記に示すものである。
ローラ汚れ濃度 平均:ローラ中央、両端部 3点の汚れ濃度平均値
ローラ汚れ濃度 標準偏差:ローラ中央、両端部 3点の汚れ濃度偏差
Table 2 shows the results of charging roller contamination evaluation after 60,000 copies of each roller obtained in Examples 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 and Comparative Example 5.
Further, the semiconductive members (charging rollers) obtained in Examples 8, 9, 10, and 11 were examined for the influence of the combination of the surface treatment liquid main resin and the reactive silicone compound on the roller dirt. Table 2 shows the result of charging roller contamination evaluation after 60,000 copies of each of the rollers of Examples 7, 8, 9, and 10.
In addition, the usage-amount of the raw material in Table 2 is shown by a weight part.
The evaluation in Table 2 is shown below.
Roller dirt density average: Average dirt density at the center of the roller, 3 points on both ends Roller dirt density standard deviation: Roller dirt density, deviation of the dirt density at 3 points on the center of the roller
また実施例8〜11に使用されている表面処理液のメイン樹脂は何れもポリオール化合物及びイソシアネート化合物を有するものである。実施例3〜7と実施例8〜11のローラ汚れ濃度は、全くシリコーン化合物を添加していない比較例5に比較し明らかに低いと言える。
また実施例8〜11に使用されている表面処理液のメイン樹脂は何れもポリオール化合物及びイソシアネート化合物を有するものである。実施例3〜7と実施例8〜11のローラ汚れ濃度を比較すると、実施例8〜11の各ローラの汚れが実施例3〜7のそれより低い事は明白である。従って、少なくとも、反応性を有するシリコーン化合物を表面処理液に使用する場合、処理液中にポリオール化合物及びイソシアネート化合物を含有させる事でシリコーン化合物の効果をより引き出す事が出来ると言える。請求項6及び7の発明はこの結果に基づくものである。
さらに、実施例11のローラ汚れ濃度が他のローラに汚れ濃度に比較し最も低く、他の実施例ローラ汚れ濃度との差は統計的に有意と言える。尚、実施例11の表面処理液には反応基を有するフッ素化シリコーン化合物とフッ素ポリオール化合物及びイソシアネート化合物が含まれている。
In addition, the main resin of the surface treatment liquid used in Examples 8 to 11 has a polyol compound and an isocyanate compound. It can be said that the roller dirt density of Examples 3 to 7 and Examples 8 to 11 is clearly lower than that of Comparative Example 5 in which no silicone compound is added.
In addition, the main resin of the surface treatment liquid used in Examples 8 to 11 has a polyol compound and an isocyanate compound. Comparing the roller dirt density of Examples 3-7 and Examples 8-11, it is clear that the dirt of each roller of Examples 8-11 is lower than that of Examples 3-7. Therefore, at least when a reactive silicone compound is used in the surface treatment liquid, it can be said that the effect of the silicone compound can be further extracted by including a polyol compound and an isocyanate compound in the treatment liquid. The inventions of claims 6 and 7 are based on this result.
Further, the roller dirt density of Example 11 is the lowest compared to the dirt density of the other rollers, and the difference from the other Examples of roller dirt density is statistically significant. The surface treatment liquid of Example 11 contains a fluorinated silicone compound having a reactive group, a fluorine polyol compound, and an isocyanate compound.
下記組成の半導電性部材表面処理液を調整した。
フッ素ポリオール(ルミフロン(登録商標)LF-601C主剤:旭硝子製)
90重量部
ポリイソシアネート(ルミフロン(商標)LF-601C硬化剤:旭硝子製)
18重量部
アクリル樹脂(ポリメチルメタクリレート) 4重量部
カーボン(ケッチェンブラック(商標)EC:ライオンアクゾ製) 2.8重量部
板状構造無機充填剤:合成ハイドロタルサイト(DHT−4A(登録商標):協和化学工業製) 4.4重量部
架橋フッ素樹脂:PTFE放射線架橋粒子(未架橋前フッ素樹脂TLP10F-1:三井デュポンフロロケミカル社製) 2.4重量部
シリコーン化合物:シリコーンオイル(DMS−T11:チッソ)0.1重量部
トルエン 50重量部
キシレン 50重量部
次いで、18Φの芯金上に6mm肉厚の実施例2で用いたものと同様のカーボンで抵抗調整されたNBR弾性層を設けたローラ上に上記調整液を硬化後の膜厚が15μmとなるように、スプレー塗工し、実施例12の半導電性部材を作製した。
この半導電性部材を2次転写ローラとしてリコーImagio Color2800に搭載し紙粉付着特性を評価した。
A semiconductive member surface treatment solution having the following composition was prepared.
Fluoropolyol (Lumiflon (registered trademark) LF-601C main agent: Asahi Glass)
90 parts by weight polyisocyanate (Lumiflon (trademark) LF-601C curing agent: manufactured by Asahi Glass)
18 parts by weight Acrylic resin (polymethyl methacrylate) 4 parts by weight Carbon (Ketjen Black (trademark) EC: manufactured by Lion Akzo) 2.8 parts by weight Plate-like inorganic filler: Synthetic hydrotalcite (DHT-4A (registered trademark) ): Kyowa Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.) 4.4 parts by weight Cross-linked fluororesin: PTFE radiation cross-linked particles (uncrosslinked fluororesin TLP10F-1: Mitsui DuPont Fluoro Chemical Co., Ltd.) 2.4 parts by weight Silicone compound: Silicone oil (DMS- T11: Chisso) 0.1 parts by weight Toluene 50 parts by weight Xylene 50 parts by weight Next, an NBR elastic layer having a resistance adjusted with carbon similar to that used in Example 2 having a thickness of 6 mm is provided on a 18 Φ cored bar. The semiconducting member of Example 12 was prepared by spray coating the adjusted liquid on the roller so that the film thickness after curing was 15 μm. .
This semiconductive member was mounted on a Ricoh Imagio Color 2800 as a secondary transfer roller, and the paper dust adhesion characteristics were evaluated.
尚、紙粉付着特性は以下の方法で測定した。
紙粉付着特性評価法
i. 任意の原稿をImagio Color 2800原稿台にセットする。
ii. AR Color・100g(A3版)を給紙トレイにセットし、1000枚コピーを取る。
iii. クリーニング性評価(注1)
iv. クリーニング性OKの場合はiに戻り、再度i 、ii、iii をクリーニング性がNGに成る迄繰り返す。クリーニング性NGの場合はここ迄コピーを取ったAR Color(A3版)の総コピー枚数をカウントし紙粉付着特性とする。
※注1 クリーニング性評価
1、2本のソリッドバンドパターンを有するA3版チャートを原稿台にセットする。
2、A3版トレイにA4転写紙を横にセットし、単色で10枚コピーを取る。
3、次いで単色で1枚コピーをとり、クリーニング性評価サンプルとする。
4、クリーニング性は上記3項の評価サンプル裏面のソリッドパター対応部が トナー汚れ無 : クリーニング性 OK
トナー汚れ有 : クリーニング性 NG
と評価する。
The paper dust adhesion characteristics were measured by the following method.
Paper dust adhesion evaluation method i. Arbitrary documents are set on the Image Color 2800 document table.
ii. Place AR Color 100g (A3 version) in the paper feed tray and take 1000 copies.
iii. Evaluation of cleaning performance (Note 1)
iv. If the cleaning property is OK, the process returns to i, and i, ii, and iii are repeated again until the cleaning property becomes NG. In the case of cleaning ability NG, the total number of copies of AR Color (A3 version) that has been copied so far is counted to obtain paper dust adhesion characteristics.
* Note 1: Evaluation of cleaning performance Set A3 size chart with 1 or 2 solid band patterns on the platen.
2. Set A4 transfer paper horizontally on the A3 plate tray, and make 10 copies in a single color.
3. Next, make a single color copy and use it as a cleaning property evaluation sample.
4. The cleaning property is that the solid pattern corresponding part on the back of the evaluation sample in the above item 3 is not contaminated with toner: Cleaning property OK
Toner smudged: Cleanability NG
And evaluate.
表面処理液の組成を下記組成とした以外は実施例12と全く同様にして実施例13の半導電性部材を作製し、実施例12と同様の紙粉付着特性の評価を行なった。
フッ素ポリオール(ルミフロン(登録商標)LF-601C主剤:旭硝子製) 90重量部
ポリイソシアネート(ルミフロン(商標)LF-601C硬化剤:旭硝子製)
20重量部
アクリルポリオール(ヒタロイド(登録商標)6500:日立化成工業製) 10重量部
カーボン(ケッチェンブラック(登録商標)EC:ライオンアクゾ製)
2.8重量部
板状構造無機充填剤:合成ハイドロタルサイト(DHT−4A(登録商標):協和化学工業製) 4.4重量部
架橋フッ素樹脂:PTFE放射線架橋粒子(未架橋前フッ素樹脂TLP10F-1:三井デュポンフロロケミカル社製) 2.4重量部
シリコーン化合物:シリコーンオイル(DMS−T11:チッソ製)
0.1重量部
トルエン 50重量部
キシレン 50重量部
A semiconductive member of Example 13 was prepared in exactly the same manner as in Example 12 except that the composition of the surface treatment liquid was changed to the following composition, and the paper dust adhesion characteristics as in Example 12 were evaluated.
Fluoropolyol (Lumiflon (registered trademark) LF-601C main agent: manufactured by Asahi Glass) 90 parts by weight Polyisocyanate (Lumiflon (TM) LF-601C curing agent: manufactured by Asahi Glass)
20 parts by weight Acrylic polyol (Hitaroid (registered trademark) 6500: manufactured by Hitachi Chemical Co., Ltd.) 10 parts by weight Carbon (Ketjen Black (registered trademark) EC: manufactured by Lion Akzo)
2.8 parts by weight Plate-like structure inorganic filler: Synthetic hydrotalcite (DHT-4A (registered trademark): manufactured by Kyowa Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.) 4.4 parts by weight Cross-linked fluororesin: PTFE radiation cross-linked particles (uncrosslinked pre-fluorinated resin TLP10F -1: Mitsui DuPont Fluoro Chemical Co., Ltd.) 2.4 parts by weight Silicone compound: Silicone oil (DMS-T11: manufactured by Chisso)
0.1 parts by weight Toluene 50 parts by weight Xylene 50 parts by weight
[比較例6]
表面処理液の組成を下記組成とした以外は実施例12と全く同様にして比較例6の半導電性部材を作製し、実施例12と同様の紙粉付着特性の評価を行なった。
フッ素ポリオール(ルミフロン(登録商標)LF-601C主剤:旭硝子製) 100重量部
ポリイソシアネート(ルミフロン(商標)LF-601C硬化剤:旭硝子製)
20重量部
フッ素樹脂粉末(MP102 :三井デュポンフロロケミカル社製) 30重量部
カーボン(ケッチェンブラック(商標)EC:ライオンアクゾ製) 2.8重量部
シリコーン化合物:シリコーンオイル(DMS−T11:チッソ)0.1重量部
トルエン 50重量部
キシレン 50重量部
[Comparative Example 6]
A semiconductive member of Comparative Example 6 was prepared in exactly the same manner as in Example 12 except that the composition of the surface treatment liquid was changed to the following composition, and the paper dust adhesion characteristics as in Example 12 were evaluated.
Fluoropolyol (Lumiflon (registered trademark) LF-601C main agent: manufactured by Asahi Glass) 100 parts by weight Polyisocyanate (Lumiflon (trademark) LF-601C curing agent: manufactured by Asahi Glass)
20 parts by weight Fluororesin powder (MP102: manufactured by Mitsui DuPont Fluorochemical Co., Ltd.) 30 parts by weight Carbon (Ketjen Black (trademark) EC: manufactured by Lion Akzo) 2.8 parts by weight Silicone compound: Silicone oil (DMS-T11: Chisso) 0.1 parts by weight Toluene 50 parts by weight Xylene 50 parts by weight
実施例12、実施例13及び比較例6で得られた2次転写ローラの紙粉付着特
性評価結果を表3に示す。
なお、表3中の原材料の使用割合は重量部で示す。
また、表3中の紙粉付着特性の“良好”は50K枚評価で汚れ未発生の場合を
示す。
Table 3 shows the evaluation results of the paper dust adhesion characteristics of the secondary transfer rollers obtained in Example 12, Example 13, and Comparative Example 6.
In addition, the usage-amount of the raw material in Table 3 is shown by a weight part.
Also, “good” of the paper dust adhesion characteristics in Table 3 indicates the case where no dirt is generated in the evaluation of 50K sheets.
Claims (9)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004106398A JP4383943B2 (en) | 2004-03-31 | 2004-03-31 | Semiconductive member for image formation |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004106398A JP4383943B2 (en) | 2004-03-31 | 2004-03-31 | Semiconductive member for image formation |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005292418A true JP2005292418A (en) | 2005-10-20 |
| JP4383943B2 JP4383943B2 (en) | 2009-12-16 |
Family
ID=35325411
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004106398A Expired - Fee Related JP4383943B2 (en) | 2004-03-31 | 2004-03-31 | Semiconductive member for image formation |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4383943B2 (en) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007138034A (en) * | 2005-11-18 | 2007-06-07 | Canon Inc | Conductive elastic member for electrophotographic apparatus |
| JP2007225998A (en) * | 2006-02-24 | 2007-09-06 | Canon Inc | Charging member |
| JP2007232926A (en) * | 2006-02-28 | 2007-09-13 | Canon Inc | Process cartridge and electrophotographic apparatus |
| JP2007232876A (en) * | 2006-02-28 | 2007-09-13 | Canon Inc | Charging member, process cartridge, and electrophotographic apparatus |
| WO2010050372A1 (en) * | 2008-10-27 | 2010-05-06 | キヤノン株式会社 | Electrificating member, method for manufacturing the electrificating member, process cartridge, and electrophotographic device |
| JP2010191259A (en) * | 2009-02-19 | 2010-09-02 | Canon Inc | Charging member, process cartridge, and electrophotographic device |
-
2004
- 2004-03-31 JP JP2004106398A patent/JP4383943B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007138034A (en) * | 2005-11-18 | 2007-06-07 | Canon Inc | Conductive elastic member for electrophotographic apparatus |
| JP2007225998A (en) * | 2006-02-24 | 2007-09-06 | Canon Inc | Charging member |
| JP2007232926A (en) * | 2006-02-28 | 2007-09-13 | Canon Inc | Process cartridge and electrophotographic apparatus |
| JP2007232876A (en) * | 2006-02-28 | 2007-09-13 | Canon Inc | Charging member, process cartridge, and electrophotographic apparatus |
| WO2010050372A1 (en) * | 2008-10-27 | 2010-05-06 | キヤノン株式会社 | Electrificating member, method for manufacturing the electrificating member, process cartridge, and electrophotographic device |
| CN102197343A (en) * | 2008-10-27 | 2011-09-21 | 佳能株式会社 | Electrificating member, method for manufacturing the electrificating member, process cartridge, and electrophotographic device |
| EP2352067A4 (en) * | 2008-10-27 | 2012-09-26 | Canon Kk | ELECTRIFICATION ELEMENT, METHOD FOR PRODUCING THE ELECTRIFICATION ELEMENT, PROCESS CARTRIDGE AND ELECTRO-PHOTOGRAPHIC DEVICE |
| CN102197343B (en) * | 2008-10-27 | 2015-02-25 | 佳能株式会社 | Charging member, method for manufacturing the charging member, process cartridge, and electrophotographic device |
| US8980423B2 (en) | 2008-10-27 | 2015-03-17 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Charging member, process for its production, process cartridge |
| JP2010191259A (en) * | 2009-02-19 | 2010-09-02 | Canon Inc | Charging member, process cartridge, and electrophotographic device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP4383943B2 (en) | 2009-12-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9360789B1 (en) | Member for electrophotography, process cartridge and image forming apparatus | |
| US8923732B2 (en) | Charging member, manufacturing method therefor, and electrophotographic apparatus | |
| US9372429B2 (en) | Charging member, manufacturing method for charging member, electrophotographic apparatus, and process cartridge | |
| JP2019095672A (en) | Process cartridge and electrophotographic image formation device | |
| CN109923481B (en) | Charging member for electrophotographic apparatus and method for producing the charging member for electrophotographic apparatus | |
| JP2008129481A (en) | Semiconductive member for image formation, image forming apparatus, image forming method, and process cartridge | |
| US10768557B2 (en) | Intermediary transfer belt and image forming apparatus | |
| JP6451295B2 (en) | Conductive elastic belt, conductive elastic belt unit, image forming apparatus | |
| JP4383943B2 (en) | Semiconductive member for image formation | |
| JP7319907B2 (en) | Conductive roll for electrophotographic equipment | |
| JP4762574B2 (en) | Semiconductive member for image processing apparatus | |
| JP5591082B2 (en) | Charging roller and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP4220315B2 (en) | Semiconductive member for image formation | |
| JP6909623B2 (en) | Development roll for electrophotographic equipment | |
| JP2007155769A (en) | Conductive rubber roller | |
| JP2007114373A (en) | Cleaning device, process cartridge, and image forming apparatus | |
| JP2005292454A (en) | Semiconductive member for image formation and image forming apparatus using the member | |
| JP3901380B2 (en) | Charging member and charging device | |
| WO2022176820A1 (en) | Charging roll for electrophotographic equipment | |
| CN110036348B (en) | Charge rollers for electrophotographic equipment | |
| JP2017181687A (en) | Charging member, charging device, process cartridge, and image forming apparatus | |
| JP7710979B2 (en) | Charging roll for electrophotographic equipment and method for producing the charging roll for electrophotographic equipment | |
| US10060028B2 (en) | Charging member, manufacturing method therefor, a process cartridge, and electrophotographic apparatus | |
| JP2004245933A (en) | Electrifying roller and electrifying device using the same | |
| JP2019032463A (en) | Intermediate transfer belt and image forming apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20061129 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20090907 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20090915 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20090924 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121002 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131002 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |