【0001】
【産業上の利用分野】
本発明は磁性化粧板及びその製造方法に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
【特許文献1】特開平9−1743号公報
これまで壁面、テーブルなどの表面に接着する熱硬化性樹脂化粧板として、例えばメラミン樹脂化粧板が知られている。この化粧板の大部分は合板やパーティクルボードなどの木質系の躯体や基材に接着されており金属面への接着はスチールデスクなど極特異な例を除きほとんどなかった。
【0003】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
これは金属製の柱や金属製の壁面への施工は、金属製躯体は木質系のものに比べ多孔質でないため接着剤が浸みこまず接着剤が固化するまで時間がかかり、化粧板のズレが起こるため、微妙なズレを修正しながら位置合わせを必要とする施工方法はかなりの熟練度を要し、施工費用がかさむためであった。
【0004】
かような問題を解消する方法としてマジックテープ(登録商標)を用いる方法があるが、雄雌のテープの接合が強すぎて微妙なズレを修正しながら位置合わせすることができないため脱着を繰り返して施工しなければならず、施工面積が大きくなればなるほど難しくなり、以外と簡単に思える方法であるにもかかわらず、かえって熟練度を要するものとなっていた。
またマジックテープ(登録商標)は厚みが5〜8mmもあり接着剤と併用する場合には、空隙部分にマジックテープ(登録商標)の厚みの分だけ下地に接着剤を塗布しなければならず、接着剤の使用量が膨大なものになっていた。
【0005】
本発明はかかる状況に鑑み検討されたもので、化粧板を金属製躯体に接合する際、微妙なズレを修正しながら位置合わせができ、素人でも施工できる化粧板を提供するものであり、裏面が磁性化された化粧板を得ることを目的とする。
【0006】
ここで、本発明に近い従来技術として特開平9−1743号公報があり、基体の表面に化粧層を設け、基体の裏面に鉄粉層を設けて、化粧層に磁石が吸着可能になるようにして、メモ、貼り紙などを保持できる化粧板が開示されている。
しかしながら、本発明のように、化粧板そのものの裏面を着磁したものではない。
【0007】
【課題を解決するための手段】
すなわち、請求項1記載の発明は、下から順に、樹脂含浸コア紙(2)に強磁性粉末を樹脂中に分散した磁性樹脂を塗布した磁性コア紙(7)或いはコア紙に強磁性粉末を樹脂中に分散した磁性樹脂を含浸した磁性樹脂含浸コア紙(7´)、金属シート(5)、樹脂含浸コア紙(2)、樹脂含浸化粧紙(1)を積層し、熱圧成形後に着磁処理してなることを特徴とする磁性化粧板(10)である。
また、請求項2記載の発明は、該強磁性粉末がフェライト粉末或いは希土類粉末であることを特徴とする請求項1記載の磁性化粧板(10)である。
更に、請求項3記載の発明は、下から、樹脂含浸コア紙(2)に強磁性粉末を樹脂中に分散した磁性樹脂を塗布した磁性コア紙(7)或いはコア紙に強磁性粉末を樹脂中に分散した磁性樹脂を含浸した磁性樹脂含浸コア紙(7´)、金属シート(5)、樹脂含浸コア紙(2)、樹脂含浸化粧紙(1)を順次積層し、熱圧成形後に着磁処理することを特徴とする磁性化粧板(10)の製造である。
更にまた、請求項4記載の発明は、該強磁性粉末がフェライト粉末或いは希土類粉末であることを特徴とする請求項3記載の磁性化粧板(10)の製造方法である。
【0008】
以下、本発明を図面に基づいて詳細に説明する。
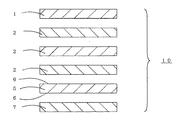
図1は本発明の磁性化粧板(10)の分解構成断面図である。下から順に、樹脂含浸コア紙に磁性樹脂を塗布した磁性コア(7)、両面にプライマー(6)を塗布した金属シート(5)、熱硬化性樹脂含浸コア紙(2)、樹脂含浸化粧紙(1)より構成されている。尚、図示はしないが、化粧紙の色、柄を保護し耐摩耗性を向上させる目的で、樹脂含浸化粧紙(1)の上に樹脂含浸表面紙を積層してもよい。
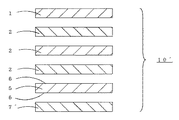
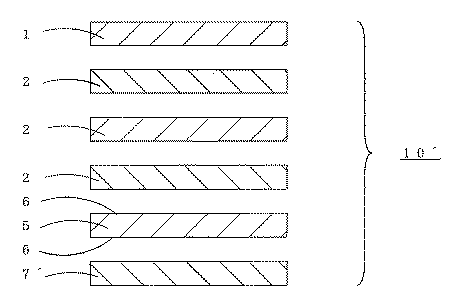
図2は、樹脂含浸コア紙に磁性樹脂を塗布した磁性コア(7)に代えて、コア紙に強磁性粉末を樹脂中に分散した磁性樹脂を含浸した磁性樹脂含浸コア紙(7´)を用いた磁性化粧板(10´)の分解構成断面図である。
【0009】
磁性コア紙(7)は、化粧板用のクラフト紙、不織布などのコア紙に熱硬化性樹脂を主成分とする樹脂液を含浸した樹脂含浸コア紙(2)に、熱硬化性樹脂を主成分とする樹脂液に強磁性粉末を配合したものを、リバースコート、グラビアコート、バーコート、カーテンフローコート、ナイフコートなどのコーティング方法により塗布したものである。
また、磁性樹脂含浸コア紙(7´)は、化粧板用のクラフト紙、不織布などのコア紙に熱硬化性樹脂を主成分とする樹脂液に強磁性粉末を配合した磁性樹脂を公知の手段により、含浸し、乾燥したものである。
【0010】
使用される熱硬化性樹脂としては、化粧板用に供される熱硬化性樹脂、例えば、アミノーホルムアルデヒド樹脂、フェノール樹脂、不飽和ポリエステル樹脂、ジアリルフタレート樹脂などが挙げられる。中でも、耐熱性、強度などの諸物性に優れるアミノーホルムアルデヒド樹脂或いはフェノール樹脂を選択するのが好ましく、アミノ−ホルムアルデヒド樹脂としてはアミノ化合物、例えばメラミン、尿素、ベンゾグアナミン、アセトグアナミンなどとホルムアルデヒドを反応させた初期縮合物のほか、メチルアルコール、エチルアルコールなどの低級アルコ−ルによるエ−テル化、パラトルエンスルホンアミドなどの可塑化を促す反応性変性剤で変性されたものが適用できる。
【0011】
フェノール樹脂は、フェノール類とアルデヒド類とをフェノール性水酸基1モルに対してアルデヒド類を1〜1.3モルの割合で塩基性触媒下にて反応させて得られるもので、フェノール類としては、フェノール、クレゾール、キシレノール、オクチルフェノール、フェニルフェノール、ビスフェノールA、ビスフェノールS、ビスフェノールFなどが挙げられ、アルデヒド類としては、ホルムアルデヒド、パラホルムアルデヒド、グリオキザール、トリオキザールなどが挙げられる。
更に、必要に応じてパラスルフォンアミド、桐油、燐酸エステル類、グリコール類などの可塑化を促す変性剤で変性されたものも適用でき、塩基性触媒としては、ナトリウム、カリウムなどのアルカリ金属、及びマグネシウム、カルシウムなどのアルカリ土類金属の酸化物や水酸化物、及びトリエチルアミン、トリエタノールアミンなどのアミン類、アンモニアが挙げられる。
【0012】
不飽和ポリエステル樹脂は、不飽和二塩基酸及び/又はその酸無水物などと、必要に応じて用いられるその他の飽和酸及び/又はその酸無水物とを含む酸成分と、多価アルコールとを窒素やアルゴンなどの不活性ガス雰囲気下で160〜230℃程度、好ましくは210〜230℃で常法に従い脱水縮合反応させた不飽和ポリエステルに、モノマー、重合開始剤などを配合したものが挙げられる。
不飽和二塩基酸及びその酸無水物としては、マレイン酸、フマル酸、イタコン酸、無水マレイン酸などが挙げられ、必要に応じて用いられるその他の飽和酸及び/又はその酸無水物としては、無水フタル酸、フタル酸、イソフタル酸、テレフタル酸、テトラヒドロ無水フタル酸、ヘキサヒドロ無水フタル酸、ヘキサヒドロフタル酸、テトラヒドロ無水フタル酸、テトラヒドロフタル酸、アジピン酸、セバチン酸などの飽和二塩基酸などが挙げられる。
多価アルコールとしては、エチレングリコール、ジエチレングリコール、プロピレングリコール、ジプロピレングリコール、1,3―ブタンジオール、1,4―ブタンジオール、2,3―ブタンジオール、1,5―ペンタジオール、1,6―ヘキサンジオール、トリエチレングリコール、ネオペンチルグリコールなどの二価アルコール、グリセリン、トリメチロールプロパンなどの三価アルコール、ペンタエリスリトールなどの四価アルコールなどが挙げられる。
【0013】
本発明で用いる強磁性粉末とは、磁性体中に磁気モーメントを有する磁性原子の原子磁気モーメント配列から、磁性体内部で磁化をひとりでに作り上げる性質を示すものをいい、具体的には、フェライト粉末、希土類粉末、アルニコ粉末などが挙げられるが、磁性化粧板(10、10´)の面積が大きくなればなるほど、また、厚みが厚くなればなるほど重くなるため高磁力が必要とされ、磁性層の膜厚を薄膜化した際に、十分な磁力による吸着力を得るため、アルニコ粉末に比べ磁束密度の大きいフェライト粉末や希土類粉末がとりわけ好ましい。これらの強磁性粉末はシラン系カップリング剤、チタネート系カップリング剤などで表面処理が施されてもよい。
【0014】
アルニコ粉末は、アルミニウム、ニッケル、コバルト、鉄などを主成分とし、鋳造後、燃焼されたものを粉砕したものである。
【0015】
フェライト粉末は、高純度の鉄酸化物粉末に、コバルト、マンガン、ニッケル、亜鉛、バリウム、ストロンチウムなどの二価の陽イオン金属の酸化物を微量添加して、混合、仮焼成したものを粉砕して、1μ程度のきわめて細かな微粒子にしたものである。
【0016】
希土類粉末は、スカンジウム、イットリウム、ランタン、セリウム、プラセオジウム、ネオジウム、プロメチウム、サマリウム、ユーロビウム、ガドリウム、テレビウム、ジスプロジウム、ホルミウム、エルビウム、ツリウム、イッテルビウム、ルテチウムなどの希土類金属を磁性材料に混ぜ合わせたものである。とりわけ、サマリウム−コバルト系、サマリウム−鉄−窒素系、ネオジウム−鉄−ボロン系、セリウム−コバルト系、イットリウム−コバルト系などが好ましい。
【0017】
強磁性粉末の大きさはりん片状の場合、厚みは1〜50μm、幅は50〜500μm、また、球状の場合、平均粒径は0.1〜40μmが好ましく、この範囲であれば熱硬化性樹脂を主成分とする樹脂液に均一に分散でき、磁気特性も適切なものとなる。小さすぎると、磁気特性が低下しやすく、大きすぎると、強磁性粉末の配向性が悪くなる。粉末化は、ジェットミルやボールミルなどで行われる。
また、強磁性粉末の配合割合は樹脂100重量部に対して20〜70重量部が好ましく、配合割合は多ければ多いほど磁気特性が向上するが上限を超えると接着力が劣りやすくなり、下限に満たないと磁束密度が少なすぎ磁気的性質が低下しやすくなる。
樹脂含浸コア紙(2)に塗布する強磁性粉末の量は1000〜5000g/m2とするのが好ましく、塗布量が下限に満たないと、着磁した後の磁力が弱く、上限を超えると、強磁性粉末の付着ムラが生じ、コストアップになる。
【0018】
磁性コア紙(7)の上には、軟鉄、Ti、Fe、Ni、Co、珪素鋼、パーマロイ(Ni35〜80%Ni−Fe合金)、フェライト系ステンレス(SUS430)、マルテンサイト系ステンレス(SUS410)などの金属のシートが配され、この金属シート(5)の両面にはプライマー(6)が塗布されている。特に、金属は、軟鉄、Fe、Ni、Co、珪素鋼、パーマロイ、フェライト系ステンレス、マルテンサイト系ステンレスなどの高透磁率、具体的には透磁率が5以上の軟磁性体が磁力を製品の化粧表面方向の磁力を遮り、磁力を増幅させるという面から好適である。硬磁性体であると着磁され製品の化粧表面方向の磁力が透過しやすくなる。厚みは50μ〜2mm程度であれば、磁力が確保でき、箔状のものや板状のものが利用でき、取り扱い性を考慮して適宜選択すればよい。
金属シート(5)は前処理が施されていてもよく、前処理としては、たとえば酸洗、薬剤脱脂、アルカリ脱脂などの清浄処理、サンドブラスト処理、バフ研磨処理、ワイヤーブラシ処理、バレル処理、スチールウール研磨処理などの機械的処理、電解エッチング処理などの活性化処理、クロメート系処理、リン酸塩系処理、リン酸亜鉛系処理などの化成処理が挙げらる。
【0019】
プライマー(6)としては、シリコーン樹脂系のプライマー(6)、不飽和ポリエステル樹脂系のプライマー(6)、メラミン樹脂系のプライマー(6)、ウレタン樹脂系のプライマー(6)、エポキシ樹脂系のプライマー(6)などが挙げられ、コア紙に含浸される樹脂の種類、金属の種類により適宜選択すればよく、ナチュラルロールコート、リバースロールコート、カーテンフローコート、スプレーコート等の通常の方法で塗布することができ、塗膜厚は1〜10μm、好ましくは2〜5μmであることが好ましい。また、必要に応じて、ストロンチウムクロメートなどの防錆顔料、その他のクロム酸化合物を含ませてもよい。
【0020】
樹脂含浸化粧紙(1)は、化粧板用の化粧紙にジアリルフタレート樹脂、アミノーホルムアルデヒド樹脂、不飽和ポリエステル樹脂などの熱硬化性樹脂を主成分をする樹脂液を含浸したものであり、必要に応じて用いる樹脂含浸表面紙は、化粧紙を保護するために用い、化粧板用の表面紙に同様の樹脂液を含浸したものが用いられる。アミノ−ホルムアルデヒド樹脂が好適で、中でも耐熱性に優れるメラミン−ホルムアルデヒド樹脂が好ましい。
【0021】
これらの磁性化粧板(10、10´)を構成する材料を積層した後の熱圧成形は、平板プレス、連続プレスなど通常公知のプレス機で行えばよく、磁場配向方法としては、用いる磁性体粉末の有する磁化保磁力(iHc)以上の磁力を有する永久磁石あるいは電磁石(ソレノイドコイル)を用いて行えばよく、配向処理後は着磁処理が施される。着磁処理は、例えば電磁石、着磁ヨーク、着磁コイルなど公知の方法が適用でき、着磁電源装置としては、着磁エネルギーをコンデンサーに充電し、そのエネルギーを瞬時に放電させるコンデンサー型着磁電源装置を用いればよい。
与える磁界の強さ(H)は、磁石の磁化保磁力(iHc)の2〜3倍以上が必要で、磁界が低いと飽和着磁ができず、磁石の特性を有効に利用できない。飽和着磁に必要な磁界は、アルニコで2000〜8000(Oe)、フェライトで8000〜14000(Oe)、希土類で12000〜32000(Oe)であればよい。
【0022】
以下、本発明について実施例、比較例を挙げてより詳細に説明する。
【実施例】
実施例1
樹脂含浸化粧紙
坪量100g/m2の無地柄の化粧紙に,メラミン−ホルムアルデヒド樹脂を主成分とする樹脂液を、式1に示す含浸率が100%となるように含浸してメラミン樹脂含浸化粧紙を得た。
【式1】
樹脂含浸コア紙
坪量198g/m2のクラフト紙にフェノール樹脂を主成分とする樹脂液を、式1に示す含浸率が50%となるように含浸してフェノール樹脂含浸コア紙を得た。
磁性コア紙
りん片状で厚みが10〜25μm、幅が200〜350μmのネオジウム−鉄−ボロン系の強磁性粉末をフェノール樹脂を主成分とする樹脂液に分散し、フェノール樹脂含浸コア紙の片面にバーコート法により、強磁性粉末量が2000g/m2となるように塗布して、磁性コア紙(7)を得た。
金属シート
厚み200μ、透磁率8のフェライト系ステンレス(SUS430)シートの両面にシリコーン系プライマー(6)(東レ・ダウコーニング(株)製 商品名
プライマー(6)D)を塗布量が10g/m2となるように塗布した。
磁性化粧板の製造
下から順に、磁性コア紙(7)を1枚、強磁性粉末を塗布した面がSUSシートに向き合うように積層し、次いで、フェノール樹脂含浸コア紙を4枚、メラミン樹脂含浸化粧紙を1枚積層した後、平板プレス機にて、温度130℃、圧力50kg/m2、時間80分で熱圧成形した。しかる後、積層方向に磁場配向した後、ヨークを用いて、ピッチ間隔3mmで、1000V、1000μFの条件で着磁処理して実施例1の磁性化粧板(10)を得た。
【0023】
実施例2
実施例1において、りん片状で厚みが10〜25μm、幅が200〜350μmのネオジウム−鉄−ボロン系の強磁性粉末に代えて、平均粒径1.10μmのストロンチウムフェライトを用いた以外は同様に実施して実施例2の磁性化粧板を得た。
【0024】
実施例3
実施例1において、磁性コア紙(7)に代えて、りん片状で厚みが10〜25μm、幅が200〜350μmのネオジウム−鉄−ボロン系の強磁性粉末をフェノール樹脂を主成分とする樹脂液に分散し、クラフト紙に式1で示される含浸率が60%となるように含浸した磁性樹脂含浸コア紙(7´)を用いた以外は同様に実施して実施例3の磁性化粧板(10´)を得た。
【0025】
比較例1
実施例1において、りん片状で厚みが10〜25μm、幅が200〜350μmのネオジウム−鉄−ボロン系の強磁性粉末の塗布量が800kg/m2となるように塗布した以外は同様に実施して比較例1の化粧板を得た。
【0026】
比較例2
実施例1において、りん片状で厚みが10〜25μm、幅が200〜350μmのネオジウム−鉄−ボロン系の強磁性粉末の塗布量が6000g/m2となるように塗布した以外は同様に実施して比較例2の化粧板を得たが、強磁性粉末の付着ムラが生じた。
【0027】
評価結果を表1に示す。
【表1】
【0028】
【発明の効果】
本発明によれば、化粧板を金属製躯体に接合するにあたり、裏面に磁性層を設けた化粧板を用いるので、施工する際微妙なズレを修正しながら行うことができ、熟練度を必要としない。
また、化粧層の柄、色に飽きた場合や、取り替えを必要とするときは容易に交換することができる。
更に、永久固定が必要な場合は接着剤、両面テープなどと併用してもよい。
加えて、磁性コア紙と樹脂含浸コア紙との間に金属シートを介しているので、化粧表面方向への磁力は遮られ、通常使用する範囲においては支障がない。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】磁性化粧板10の分解構成断面図。
【図2】磁性化粧板10´の分解構成断面図。
【符号の説明】
1 樹脂含浸化粧紙
2 樹脂含浸コア紙
5 金属シート
6 プライマー
7 磁性コア紙
7´磁性樹脂含浸コア紙
8 強磁性粉末塗布面
10 磁性化粧板
10´磁性化粧板[0001]
[Industrial applications]
The present invention relates to a magnetic decorative plate and a method for producing the same.
[0002]
[Prior art]
[Patent Document 1] Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 9-1743 Until now, for example, a melamine resin decorative plate has been known as a thermosetting resin decorative plate adhered to a surface of a wall surface, a table or the like. Most of the decorative boards are adhered to wood-based skeletons and base materials such as plywood and particle boards, and hardly adhered to metal surfaces except for extremely specific cases such as steel desks.
[0003]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
This is because when applying to metal pillars or metal wall surfaces, the metal body is not as porous as wood-based ones, so it takes time for the adhesive to infiltrate and the adhesive to solidify, causing a gap in the decorative board. Therefore, a construction method that requires alignment while correcting a delicate misalignment requires considerable skill and increases construction costs.
[0004]
As a method for solving such a problem, there is a method using a magic tape (registered trademark). However, since the bonding of the male and female tapes is too strong to correct the delicate misalignment, it is not possible to perform positioning while repeating attachment and detachment. It had to be constructed, and the larger the construction area, the more difficult it was, and in spite of the seemingly simple method, it required skill.
In addition, when the magic tape (registered trademark) has a thickness of 5 to 8 mm and is used together with an adhesive, the adhesive must be applied to the base by an amount corresponding to the thickness of the magic tape (registered trademark) in the gap portion. The amount of adhesive used was enormous.
[0005]
The present invention has been studied in view of such circumstances, and when joining a decorative board to a metal frame, it is possible to adjust the position while correcting subtle deviations, and to provide a decorative board that can be installed even by amateurs. It is an object of the present invention to obtain a magnetized decorative board.
[0006]
Here, as a conventional technique close to the present invention, there is Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 9-1743, in which a decorative layer is provided on the surface of the base, and an iron powder layer is provided on the back of the base so that the magnet can be attracted to the decorative layer. A decorative board capable of holding a memo, a sticker, and the like is disclosed.
However, unlike the present invention, the rear surface of the decorative plate itself is not magnetized.
[0007]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
That is, the invention according to claim 1 provides, in order from the bottom, a magnetic core paper (7) in which a magnetic resin in which a ferromagnetic powder is dispersed in a resin is applied to a resin-impregnated core paper (2) or the ferromagnetic powder is applied to the core paper. A magnetic resin-impregnated core paper (7 ') impregnated with a magnetic resin dispersed in a resin, a metal sheet (5), a resin-impregnated core paper (2), and a resin-impregnated decorative paper (1) are laminated, and are put on after hot pressing. A magnetic decorative plate (10) characterized by being subjected to a magnetic treatment.
The invention according to claim 2 is the magnetic decorative plate (10) according to claim 1, wherein the ferromagnetic powder is a ferrite powder or a rare earth powder.
Furthermore, the invention according to claim 3 is a magnetic core paper (7) obtained by applying a magnetic resin in which a ferromagnetic powder is dispersed in a resin to a resin-impregnated core paper (2), or the ferromagnetic powder is applied to the core paper from the bottom. A magnetic resin-impregnated core paper (7 ') impregnated with a magnetic resin dispersed therein, a metal sheet (5), a resin-impregnated core paper (2), and a resin-impregnated decorative paper (1) are laminated in this order, and are put on after hot pressing. It is a process for producing a magnetic decorative plate (10), which is subjected to a magnetic treatment.
Furthermore, the invention according to claim 4 is the method for producing a magnetic decorative plate (10) according to claim 3, wherein the ferromagnetic powder is a ferrite powder or a rare earth powder.
[0008]
Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
FIG. 1 is an exploded configuration sectional view of a magnetic decorative plate (10) of the present invention. From the bottom, in order from the bottom, a magnetic core (7) in which a magnetic resin is applied to a resin-impregnated core paper, a metal sheet (5) in which primers (6) are applied to both surfaces, a thermosetting resin-impregnated core paper (2), and a resin-impregnated decorative paper It is composed of (1). Although not shown, a resin-impregnated surface paper may be laminated on the resin-impregnated decorative paper (1) for the purpose of protecting the color and pattern of the decorative paper and improving wear resistance.
FIG. 2 shows a magnetic paper impregnated core paper (7 ′) obtained by impregnating a magnetic resin in which a ferromagnetic powder is dispersed in a resin instead of a magnetic core (7) obtained by applying a magnetic resin to a resin impregnated core paper. It is a decomposition | disassembly structure sectional drawing of the magnetic decorative board (10 ') used.
[0009]
The magnetic core paper (7) is mainly made of resin-impregnated core paper (2) obtained by impregnating core paper such as kraft paper for decorative board or nonwoven fabric with a resin liquid containing a thermosetting resin as a main component. A resin solution containing a ferromagnetic powder mixed with a resin solution is applied by a coating method such as reverse coating, gravure coating, bar coating, curtain flow coating, or knife coating.
The magnetic resin-impregnated core paper (7 ') is made by mixing a magnetic resin obtained by mixing a ferromagnetic powder with a resin liquid containing a thermosetting resin as a main component in a core paper such as kraft paper for a decorative board or a nonwoven fabric. Impregnated and dried.
[0010]
Examples of the thermosetting resin used include thermosetting resins used for decorative boards, for example, amino-formaldehyde resin, phenol resin, unsaturated polyester resin, diallyl phthalate resin and the like. Among them, it is preferable to select an amino-formaldehyde resin or a phenol resin which is excellent in various physical properties such as heat resistance and strength. In addition to the initial condensate, those modified with a reactive modifier which promotes etherification with a lower alcohol such as methyl alcohol or ethyl alcohol or plasticization such as paratoluenesulfonamide can be used.
[0011]
Phenol resin is obtained by reacting phenols and aldehydes with aldehydes at a ratio of 1 to 1.3 mol per mol of phenolic hydroxyl group under a basic catalyst, and as phenols, Examples include phenol, cresol, xylenol, octylphenol, phenylphenol, bisphenol A, bisphenol S, bisphenol F, and aldehydes include formaldehyde, paraformaldehyde, glyoxal, and trioxal.
Further, if necessary, parasulfonamide, tung oil, phosphates, those modified with a modifier that promotes plasticization such as glycols can also be applied.As the basic catalyst, sodium, alkali metals such as potassium, and Oxides and hydroxides of alkaline earth metals such as magnesium and calcium; amines such as triethylamine and triethanolamine; and ammonia.
[0012]
The unsaturated polyester resin comprises an unsaturated dibasic acid and / or an acid anhydride thereof, and an acid component containing another saturated acid and / or an acid anhydride thereof used as necessary, and a polyhydric alcohol. An unsaturated polyester obtained by dehydration-condensation reaction at about 160 to 230 ° C., preferably 210 to 230 ° C. in an ordinary gas atmosphere under an inert gas atmosphere such as nitrogen or argon, and a mixture of a monomer, a polymerization initiator, and the like. .
Examples of unsaturated dibasic acids and anhydrides thereof include maleic acid, fumaric acid, itaconic acid, and maleic anhydride, and other saturated acids and / or acid anhydrides used as needed include: Saturated dibasic acids such as phthalic anhydride, phthalic acid, isophthalic acid, terephthalic acid, tetrahydrophthalic anhydride, hexahydrophthalic anhydride, hexahydrophthalic acid, tetrahydrophthalic anhydride, tetrahydrophthalic acid, adipic acid, sebacic acid, etc. No.
Polyhydric alcohols include ethylene glycol, diethylene glycol, propylene glycol, dipropylene glycol, 1,3-butanediol, 1,4-butanediol, 2,3-butanediol, 1,5-pentadiol, and 1,6- Examples include dihydric alcohols such as hexanediol, triethylene glycol and neopentyl glycol, trihydric alcohols such as glycerin and trimethylolpropane, and tetrahydric alcohols such as pentaerythritol.
[0013]
The ferromagnetic powder used in the present invention refers to a material exhibiting a property of making magnetization by itself inside a magnetic material from an atomic magnetic moment arrangement of magnetic atoms having a magnetic moment in a magnetic material, specifically, ferrite powder, Rare earth powders, alnico powders, and the like can be cited. The larger the area of the magnetic decorative plate (10, 10 ') and the thicker the thickness, the heavier the magnet. In order to obtain a sufficient magnetic attraction force when the thickness is reduced, ferrite powder or rare earth powder having a higher magnetic flux density than alnico powder is particularly preferable. These ferromagnetic powders may be subjected to a surface treatment with a silane coupling agent, a titanate coupling agent, or the like.
[0014]
Alnico powder contains aluminum, nickel, cobalt, iron, or the like as a main component, and is obtained by pulverizing a burned material after casting.
[0015]
Ferrite powder is obtained by adding a small amount of divalent cation metal oxide such as cobalt, manganese, nickel, zinc, barium, strontium, etc. to high-purity iron oxide powder, pulverizing the mixture and calcining it. And very fine particles of about 1 μm.
[0016]
Rare earth powder is a mixture of rare earth metals such as scandium, yttrium, lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, eurobium, gadolinium, televisionium, disprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, and lutetium mixed with a magnetic material. It is. In particular, samarium-cobalt, samarium-iron-nitrogen, neodymium-iron-boron, cerium-cobalt, yttrium-cobalt and the like are preferable.
[0017]
When the size of the ferromagnetic powder is scaly, the thickness is 1 to 50 μm, the width is 50 to 500 μm, and when it is spherical, the average particle size is preferably 0.1 to 40 μm. It can be uniformly dispersed in a resin liquid containing a conductive resin as a main component, and the magnetic properties are also appropriate. If it is too small, the magnetic properties tend to deteriorate, and if it is too large, the orientation of the ferromagnetic powder deteriorates. Powdering is performed by a jet mill, a ball mill, or the like.
Further, the compounding ratio of the ferromagnetic powder is preferably 20 to 70 parts by weight with respect to 100 parts by weight of the resin. As the compounding ratio increases, the magnetic properties improve, but when the ratio exceeds the upper limit, the adhesive strength tends to deteriorate. If not, the magnetic flux density is too low, and the magnetic properties tend to deteriorate.
The amount of the ferromagnetic powder applied to the resin-impregnated core paper (2) is preferably 1000 to 5000 g / m 2. If the amount of application is less than the lower limit, the magnetic force after magnetization is weak, and if it exceeds the upper limit, As a result, non-uniform adhesion of the ferromagnetic powder occurs, which increases the cost.
[0018]
On the magnetic core paper (7), soft iron, Ti, Fe, Ni, Co, silicon steel, permalloy (Ni 35-80% Ni-Fe alloy), ferritic stainless steel (SUS430), martensitic stainless steel (SUS410) A metal sheet such as a metal sheet is disposed, and a primer (6) is applied to both sides of the metal sheet (5). In particular, the metal is a soft magnetic material having a high magnetic permeability such as soft iron, Fe, Ni, Co, silicon steel, permalloy, ferritic stainless steel, martensitic stainless steel, etc. It is preferable from the viewpoint of blocking the magnetic force in the direction of the makeup surface and amplifying the magnetic force. If it is a hard magnetic material, it will be magnetized and the magnetic force in the direction of the cosmetic surface of the product will easily pass through. When the thickness is about 50 μm to 2 mm, a magnetic force can be secured, a foil-like or plate-like thing can be used, and it may be appropriately selected in consideration of handleability.
The metal sheet (5) may have been subjected to a pretreatment, such as a cleaning treatment such as pickling, chemical degreasing, or alkali degreasing, sandblasting, buffing, wire brushing, barrel treatment, or steel. Examples include mechanical treatment such as wool polishing treatment, activation treatment such as electrolytic etching treatment, and chemical conversion treatment such as chromate treatment, phosphate treatment, and zinc phosphate treatment.
[0019]
As the primer (6), a silicone resin primer (6), an unsaturated polyester resin primer (6), a melamine resin primer (6), a urethane resin primer (6), an epoxy resin primer (6) and the like, which may be appropriately selected depending on the type of resin and the type of metal impregnated in the core paper, and are applied by a normal method such as a natural roll coat, a reverse roll coat, a curtain flow coat, or a spray coat. Preferably, the coating thickness is 1 to 10 μm, preferably 2 to 5 μm. If necessary, a rust-preventive pigment such as strontium chromate and other chromic acid compounds may be contained.
[0020]
The resin-impregnated decorative paper (1) is obtained by impregnating a decorative paper for decorative board with a resin liquid mainly containing a thermosetting resin such as diallyl phthalate resin, amino-formaldehyde resin and unsaturated polyester resin. The resin-impregnated surface paper used in accordance with (1) is used to protect decorative paper, and is obtained by impregnating a surface paper for decorative board with the same resin liquid. Amino-formaldehyde resins are preferred, and melamine-formaldehyde resins having excellent heat resistance are preferred.
[0021]
The hot-press forming after laminating the materials constituting these magnetic decorative plates (10, 10 ') may be performed by a commonly known press such as a flat plate press, a continuous press, and the like. This may be performed using a permanent magnet or an electromagnet (solenoid coil) having a magnetic coercive force (iHc) of the powder or more, and a magnetizing process is performed after the orientation process. Known methods such as an electromagnet, a magnetized yoke, and a magnetized coil can be used for the magnetizing process.As a magnetized power supply device, a capacitor-type magnetized device that charges a capacitor with magnetizing energy and discharges the energy instantaneously. A power supply device may be used.
The strength (H) of the applied magnetic field needs to be two to three times or more the magnetization coercive force (iHc) of the magnet. If the magnetic field is low, saturation magnetization cannot be performed, and the characteristics of the magnet cannot be used effectively. The magnetic field required for saturation magnetization may be 2000 to 8000 (Oe) for alnico, 8000 to 14000 (Oe) for ferrite, and 12000 to 32000 (Oe) for rare earth.
[0022]
Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail with reference to Examples and Comparative Examples.
【Example】
Example 1
Resin-impregnated decorative paper A plain pattern decorative paper having a basis weight of 100 g / m 2 is impregnated with a resin solution containing a melamine-formaldehyde resin as a main component so that the impregnation rate shown in Formula 1 becomes 100%, and the melamine resin is impregnated. I got decorative paper.
(Equation 1)
Resin-impregnated core paper Kraft paper having a basis weight of 198 g / m 2 was impregnated with a resin solution containing a phenol resin as a main component so that the impregnation rate shown in Formula 1 was 50%, to obtain a phenol resin-impregnated core paper.
One side of a phenolic resin-impregnated core paper in which flaky neodymium-iron-boron-based ferromagnetic powder having a thickness of 10 to 25 μm and a width of 200 to 350 μm is dispersed in a resin solution containing a phenol resin as a main component. The resultant was applied by a bar coating method so that the amount of ferromagnetic powder became 2000 g / m 2 to obtain a magnetic core paper (7).
A ferrite-based stainless steel (SUS430) sheet having a metal sheet thickness of 200 μm and a magnetic permeability of 8 is coated with a silicone primer (6) (trade name: Primer (6) D, manufactured by Dow Corning Toray Co., Ltd.) on both sides at an application amount of 10 g / m 2. It applied so that it might become.
In order from the production of the magnetic decorative board, one magnetic core paper (7) is laminated so that the surface coated with the ferromagnetic powder faces the SUS sheet, and then four phenol resin impregnated core papers and melamine resin impregnated. After laminating one piece of decorative paper, it was hot-pressed with a flat plate press at a temperature of 130 ° C., a pressure of 50 kg / m 2 and a time of 80 minutes. Thereafter, after the magnetic field was oriented in the laminating direction, the magnetic decorative plate (10) of Example 1 was obtained by performing a magnetizing treatment using a yoke at a pitch of 3 mm under the conditions of 1000 V and 1000 μF.
[0023]
Example 2
Example 1 is the same as Example 1 except that strontium ferrite having an average particle size of 1.10 μm was used instead of the neodymium-iron-boron-based ferromagnetic powder having a scale shape of 10 to 25 μm and a width of 200 to 350 μm. The magnetic decorative plate of Example 2 was obtained.
[0024]
Example 3
In Example 1, instead of the magnetic core paper (7), a scaly, neodymium-iron-boron-based ferromagnetic powder having a thickness of 10 to 25 μm and a width of 200 to 350 μm is a resin mainly composed of a phenol resin. The magnetic decorative board of Example 3 was prepared in the same manner except that the magnetic resin-impregnated core paper (7 ') dispersed in a liquid and impregnated in kraft paper so that the impregnation represented by Formula 1 was 60% was used. (10 ′) was obtained.
[0025]
Comparative Example 1
Example 1 was carried out in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the coating amount of the neodymium-iron-boron-based ferromagnetic powder having a scale shape of 10 to 25 µm and a width of 200 to 350 µm was 800 kg / m 2. Thus, a decorative plate of Comparative Example 1 was obtained.
[0026]
Comparative Example 2
Example 1 was carried out in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the coating amount of the neodymium-iron-boron-based ferromagnetic powder having a scale shape of 10 to 25 µm and a width of 200 to 350 µm was 6000 g / m 2. Thus, the decorative plate of Comparative Example 2 was obtained, but uneven adhesion of the ferromagnetic powder occurred.
[0027]
Table 1 shows the evaluation results.
[Table 1]
[0028]
【The invention's effect】
According to the present invention, in joining the decorative plate to the metal frame, the decorative plate provided with the magnetic layer on the back surface is used, so that it can be performed while correcting a delicate misalignment at the time of construction, and requires skill. do not do.
In addition, when the pattern or color of the decorative layer becomes tired or when replacement is required, it can be easily replaced.
Further, when permanent fixing is required, it may be used together with an adhesive, a double-sided tape, or the like.
In addition, since the metal sheet is interposed between the magnetic core paper and the resin-impregnated core paper, the magnetic force in the direction of the decorative surface is blocked, and there is no problem in the range of normal use.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is an exploded configuration sectional view of a magnetic decorative plate 10. FIG.
FIG. 2 is an exploded cross-sectional view of a magnetic decorative plate 10 ′.
[Explanation of symbols]
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1 Resin impregnated decorative paper 2 Resin impregnated core paper 5 Metal sheet 6 Primer 7 Magnetic core paper 7 'Magnetic resin impregnated core paper 8 Ferromagnetic powder coated surface 10 Magnetic decorative board 10' Magnetic decorative board